⚠️ 以下所有内容总结都来自于 大语言模型的能力,如有错误,仅供参考,谨慎使用
🔴 请注意:千万不要用于严肃的学术场景,只能用于论文阅读前的初筛!
💗 如果您觉得我们的项目对您有帮助 ChatPaperFree ,还请您给我们一些鼓励!⭐️ HuggingFace免费体验
2025-04-19 更新
EmoVoice: LLM-based Emotional Text-To-Speech Model with Freestyle Text Prompting
Authors:Guanrou Yang, Chen Yang, Qian Chen, Ziyang Ma, Wenxi Chen, Wen Wang, Tianrui Wang, Yifan Yang, Zhikang Niu, Wenrui Liu, Fan Yu, Zhihao Du, Zhifu Gao, ShiLiang Zhang, Xie Chen
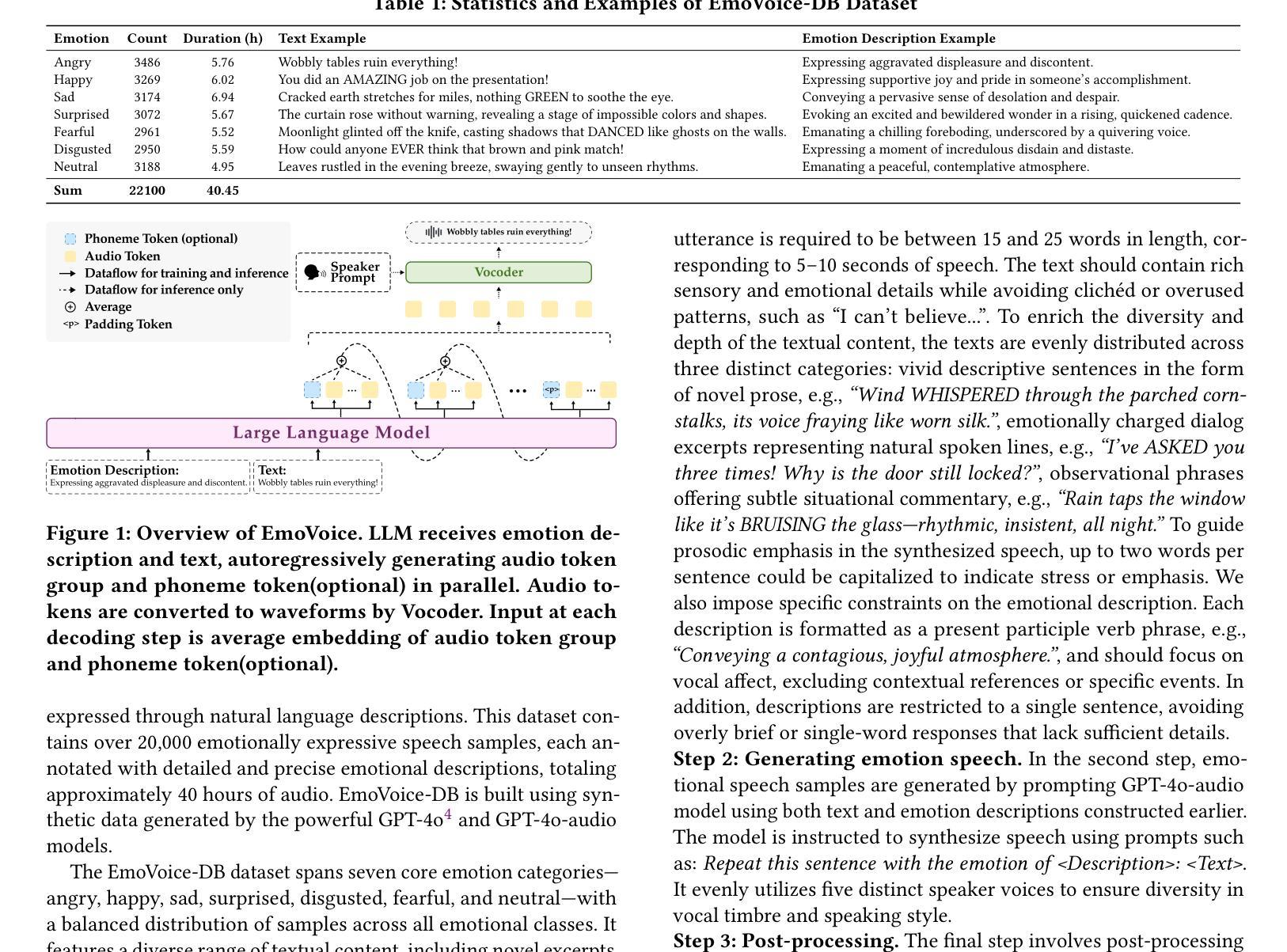
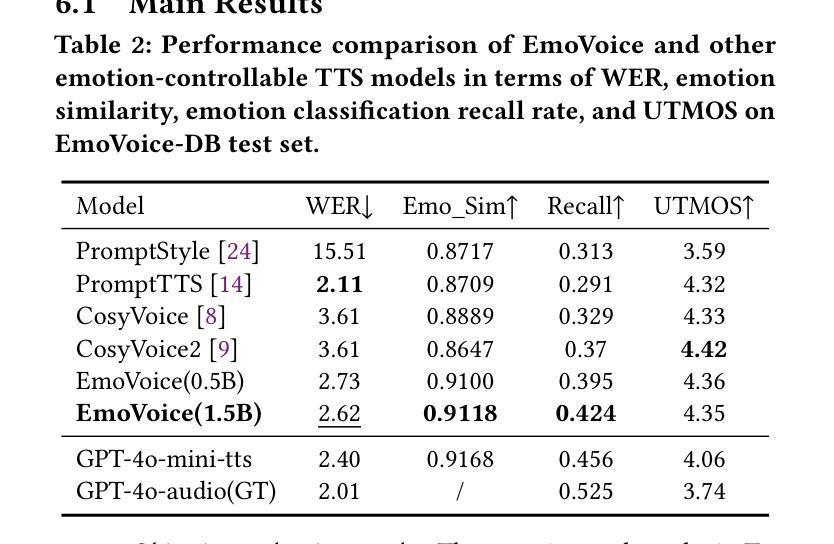
Human speech goes beyond the mere transfer of information; it is a profound exchange of emotions and a connection between individuals. While Text-to-Speech (TTS) models have made huge progress, they still face challenges in controlling the emotional expression in the generated speech. In this work, we propose EmoVoice, a novel emotion-controllable TTS model that exploits large language models (LLMs) to enable fine-grained freestyle natural language emotion control, and a phoneme boost variant design that makes the model output phoneme tokens and audio tokens in parallel to enhance content consistency, inspired by chain-of-thought (CoT) and modality-of-thought (CoM) techniques. Besides, we introduce EmoVoice-DB, a high-quality 40-hour English emotion dataset featuring expressive speech and fine-grained emotion labels with natural language descriptions. EmoVoice achieves state-of-the-art performance on the English EmoVoice-DB test set using only synthetic training data, and on the Chinese Secap test set using our in-house data. We further investigate the reliability of existing emotion evaluation metrics and their alignment with human perceptual preferences, and explore using SOTA multimodal LLMs GPT-4o-audio and Gemini to assess emotional speech. Demo samples are available at https://anonymous.4open.science/r/EmoVoice-DF55. Dataset, code, and checkpoints will be released.
人类言语不仅仅是为了传递信息,更是一种深刻的情感交流和个人之间的联系。尽管文本转语音(TTS)模型已经取得了巨大的进步,但在控制生成语音的情感表达方面仍面临挑战。在这项工作中,我们提出了EmoVoice,一种新型的情感可控TTS模型,它利用大型语言模型(LLM)实现细粒度的自由式自然语言情感控制,并设计了一种音素增强变体,使模型能够并行输出音素标记和音频标记,以增强内容的一致性,这得益于思维链(CoT)和模态思维(CoM)技术。此外,我们还介绍了EmoVoice-DB,一个高质量40小时英语情感数据集,以表现性言语和精细情绪标签的自然语言描述为特色。EmoVoice仅使用合成训练数据,在英语EmoVoice-DB测试集上达到了最新技术水平,在我们内部数据使用的中文Secap测试集上也取得了良好效果。我们进一步研究了现有情感评估指标的可靠性及其与人类感知偏好的一致性,并探讨了使用最先进的多媒体LLMs GPT-4o-audio和Gemini来评估情感语音。演示样品可在链接处找到。数据集、代码和检查点将随后发布。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
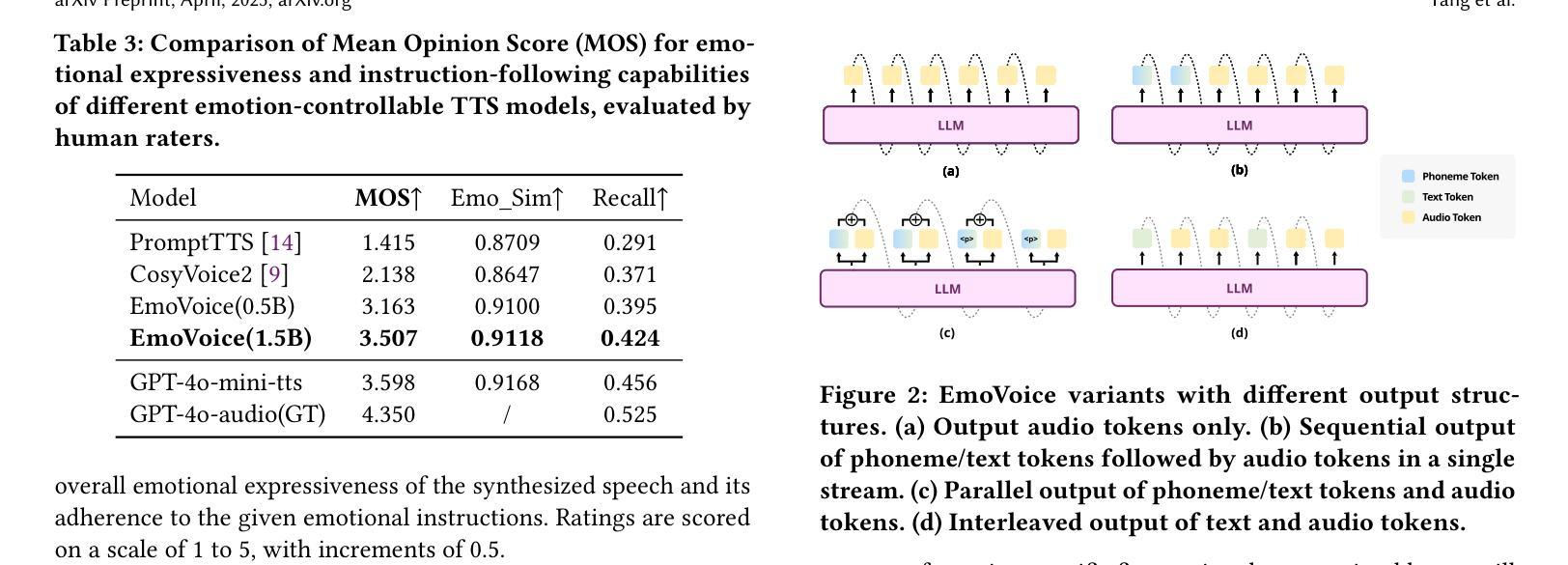
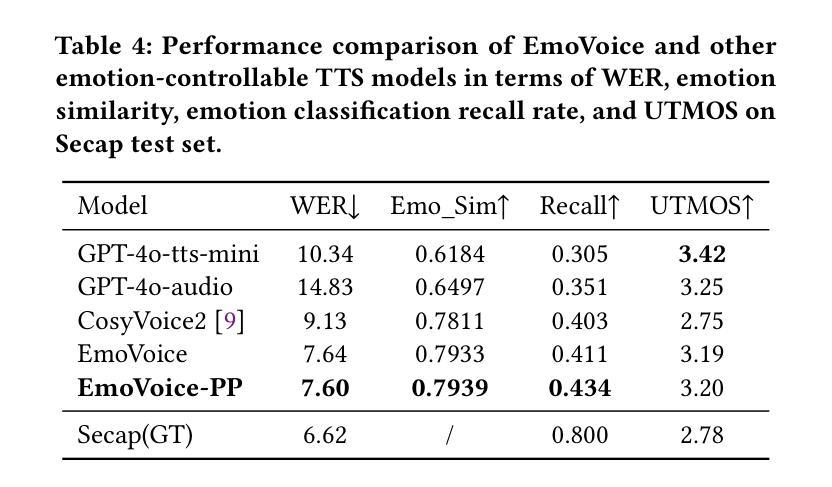
该研究提出了一种名为EmoVoice的新型情感可控的TTS模型。该模型利用大型语言模型进行精细的自由式自然语言情感控制,并采用并行输出语音标记和音频标记的变体设计增强内容一致性。此外,该研究还引入了高质量的情感数据集EmoVoice-DB,并对现有情感评估指标的可靠性及其与人类感知偏好的一致性进行了调查。
Key Takeaways
- EmoVoice是一个情感可控的TTS模型,利用大型语言模型实现精细的自由式自然语言情感控制。
- EmoVoice采用并行输出语音标记和音频标记的变体设计,以增强内容一致性。
- 引入高质量的情感数据集EmoVoice-DB,用于训练和评估TTS模型的性能。
- EmoVoice在英文情感数据集EmoVoice-DB测试集上的表现达到最新水平,且在中英文Secap测试集上使用内部数据也有良好表现。
- 研究对现有情感评估指标的可靠性进行了调查,并探讨了它们与人类感知偏好的一致性。
- 研究利用最先进的GPT-4o-audio和Gemini等多媒体大型语言模型来评估情感语音。
点此查看论文截图

GOAT-TTS: LLM-based Text-To-Speech Generation Optimized via A Dual-Branch Architecture
Authors:Yaodong Song, Hongjie Chen, Jie Lian, Yuxin Zhang, Guangmin Xia, Zehan Li, Genliang Zhao, Jian Kang, Yongxiang Li, Jie Li
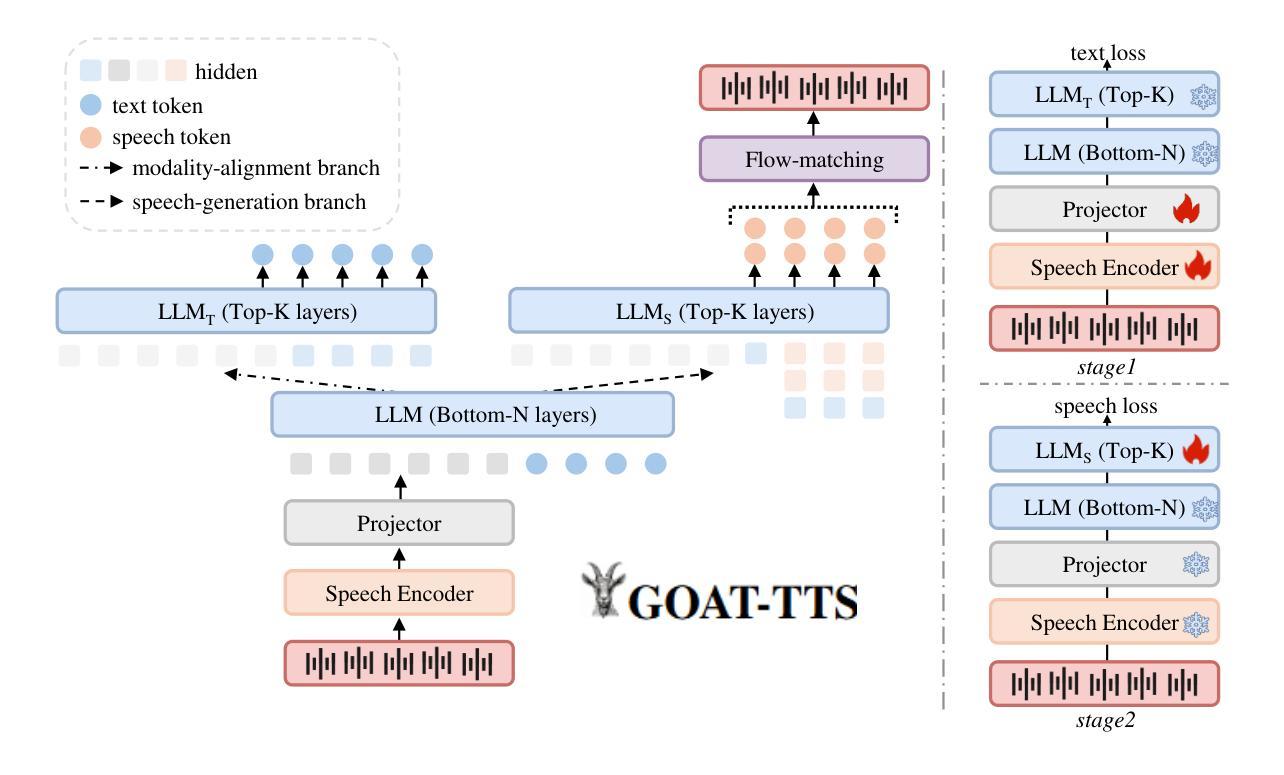
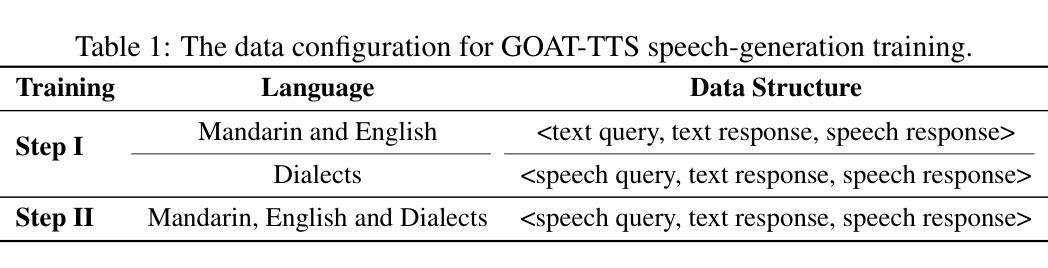
While large language models (LLMs) have revolutionized text-to-speech (TTS) synthesis through discrete tokenization paradigms, current architectures exhibit fundamental tensions between three critical dimensions: 1) irreversible loss of acoustic characteristics caused by quantization of speech prompts; 2) stringent dependence on precisely aligned prompt speech-text pairs that limit real-world deployment; and 3) catastrophic forgetting of the LLM’s native text comprehension during optimization for speech token generation. To address these challenges, we propose an LLM-based text-to-speech Generation approach Optimized via a novel dual-branch ArchiTecture (GOAT-TTS). Our framework introduces two key innovations: (1) The modality-alignment branch combines a speech encoder and projector to capture continuous acoustic embeddings, enabling bidirectional correlation between paralinguistic features (language, timbre, emotion) and semantic text representations without transcript dependency; (2) The speech-generation branch employs modular fine-tuning on top-k layers of an LLM for speech token prediction while freezing the bottom-k layers to preserve foundational linguistic knowledge. Moreover, multi-token prediction is introduced to support real-time streaming TTS synthesis. Experimental results demonstrate that our GOAT-TTS achieves performance comparable to state-of-the-art TTS models while validating the efficacy of synthesized dialect speech data.
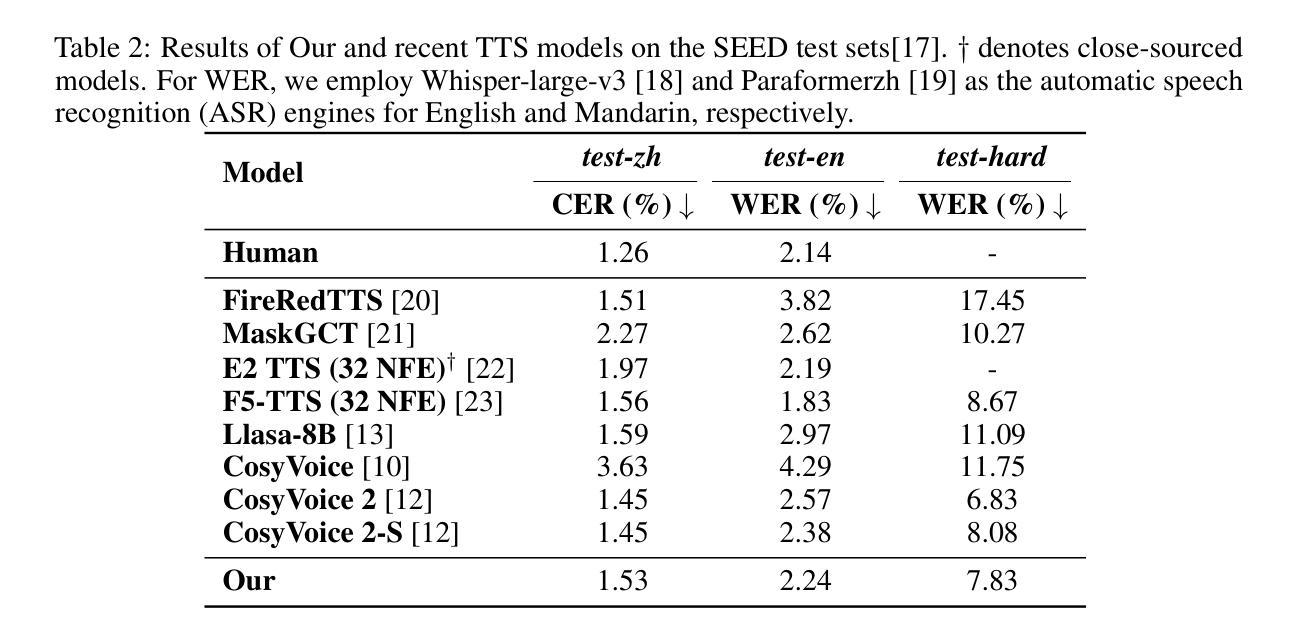
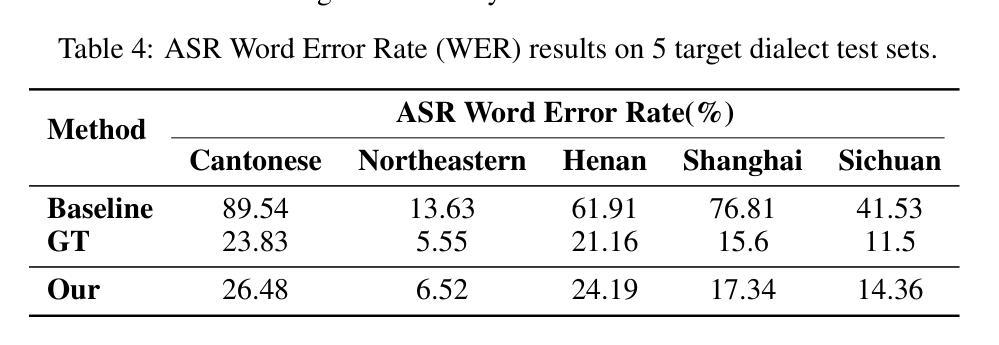
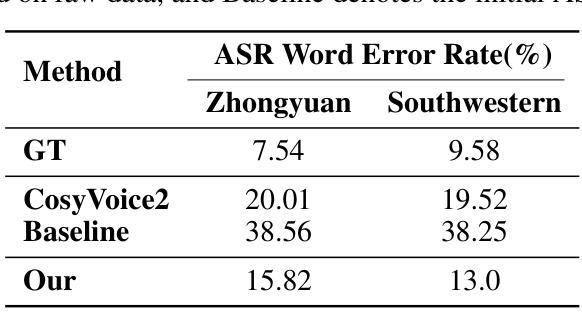
虽然大型语言模型(LLM)通过离散标记化范式彻底改变了文本到语音(TTS)的合成,但当前的架构在三个关键维度之间表现出根本性的矛盾:1)由于语音提示的量化而导致的不可逆的声学特征损失;2)严格依赖于精确对齐的语音文本对,这限制了其在现实世界中的部署;3)在优化语音标记生成过程中,LLM对原生文本理解能力的灾难性遗忘。为了应对这些挑战,我们提出了一种基于LLM的文本到语音生成方法,通过一种新的双分支架构(GOAT-TTS)进行优化。我们的框架引入了两项关键创新:1)模态对齐分支结合了语音编码器和投影仪,以捕获连续的声学嵌入,实现在无字幕依赖的情况下,副语言特征(语言、音色、情感)与语义文本表示之间的双向关联;2)语音生成分支采用模块化微调,对LLM的前k层进行语音标记预测,同时冻结底部k层以保持基础语言知识。此外,引入了多标记预测,以支持实时流式TTS合成。实验结果表明,我们的GOAT-TTS模型性能与最先进的TTS模型相当,同时验证了合成方言语音数据的有效性。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
基于大型语言模型(LLM)的文本到语音(TTS)合成方法已经取得了显著进展。然而,当前架构在三个关键维度上存在根本性缺陷:量化语音提示导致的不可逆声学特征损失、对精确对齐的语音文本对的严格依赖以及优化语音令牌生成时LLM对原生文本理解的灾难性遗忘。为解决这些挑战,我们提出了通过新型双分支架构(GOAT-TTS)优化的LLM文本到语音生成方法。该方法包括两个关键创新点:模态对齐分支和语音生成分支。
Key Takeaways
- 大型语言模型在文本到语音合成中实现了显著进展,但仍面临声学特征损失、对齐精确性问题以及文本理解能力遗忘的挑战。
- GOAT-TTS通过双分支架构解决了上述问题,包括模态对齐分支和语音生成分支的创新设计。
- 模态对齐分支结合了语音编码器和投影器,捕捉连续声学嵌入,实现了跨语言特征(语言、音色、情感)与语义文本表示之间的双向关联,无需依赖转录。
- 语音生成分支采用模块化微调LLM的前k层进行语音令牌预测,同时冻结底层k层以保留基础语言知识。引入多令牌预测支持实时流式TTS合成。
点此查看论文截图

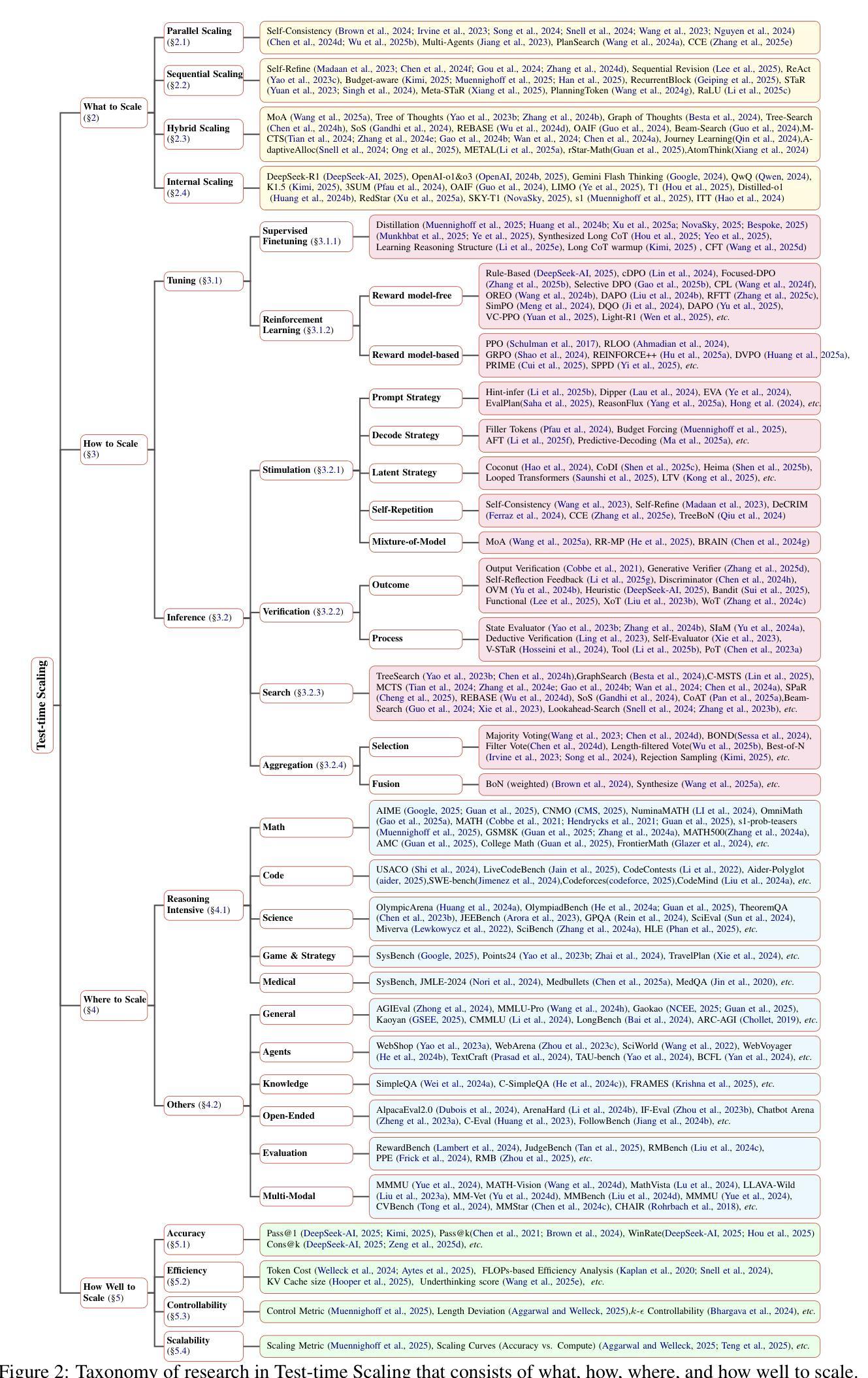
What, How, Where, and How Well? A Survey on Test-Time Scaling in Large Language Models
Authors:Qiyuan Zhang, Fuyuan Lyu, Zexu Sun, Lei Wang, Weixu Zhang, Zhihan Guo, Yufei Wang, Niklas Muennighoff, Irwin King, Xue Liu, Chen Ma
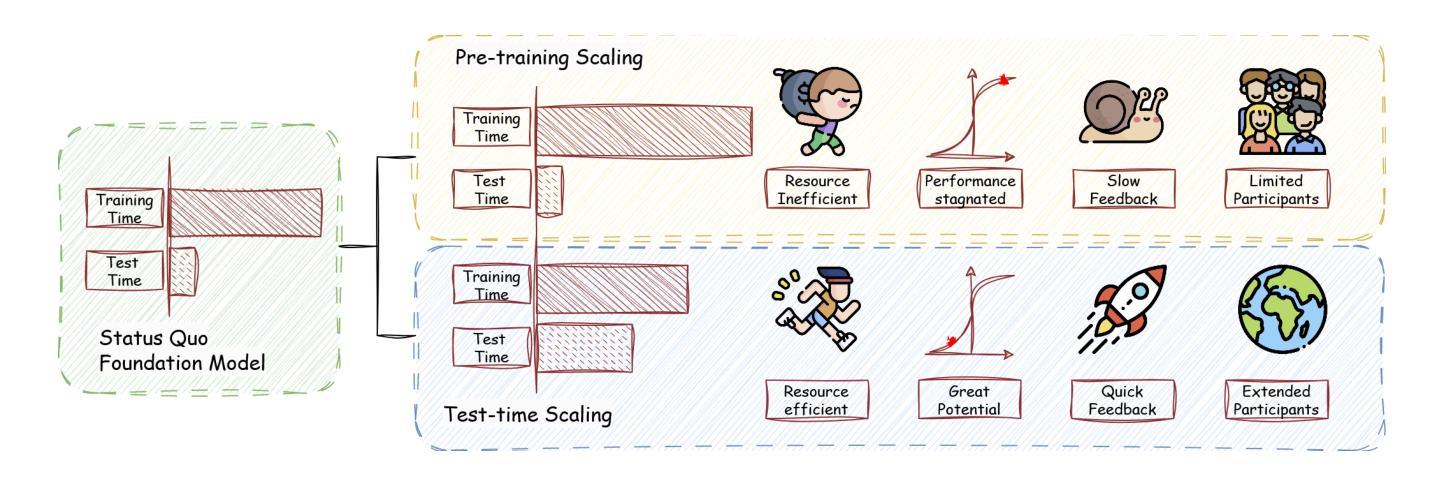
As enthusiasm for scaling computation (data and parameters) in the pretraining era gradually diminished, test-time scaling (TTS), also referred to as ``test-time computing’’ has emerged as a prominent research focus. Recent studies demonstrate that TTS can further elicit the problem-solving capabilities of large language models (LLMs), enabling significant breakthroughs not only in specialized reasoning tasks, such as mathematics and coding, but also in general tasks like open-ended Q&A. However, despite the explosion of recent efforts in this area, there remains an urgent need for a comprehensive survey offering a systemic understanding. To fill this gap, we propose a unified, multidimensional framework structured along four core dimensions of TTS research: what to scale, how to scale, where to scale, and how well to scale. Building upon this taxonomy, we conduct an extensive review of methods, application scenarios, and assessment aspects, and present an organized decomposition that highlights the unique functional roles of individual techniques within the broader TTS landscape. From this analysis, we distill the major developmental trajectories of TTS to date and offer hands-on guidelines for practical deployment. Furthermore, we identify several open challenges and offer insights into promising future directions, including further scaling, clarifying the functional essence of techniques, generalizing to more tasks, and more attributions. Our repository is available on https://github.com/testtimescaling/testtimescaling.github.io/
随着预训练时代扩大计算规模(数据和参数)的热情逐渐消退,测试时扩展(Test-Time Scaling,简称TTS),也称为“测试时计算”,已成为一个突出的研究焦点。最近的研究表明,TTS可以进一步激发大型语言模型(LLM)的问题解决能力,不仅在数学和编程等专项推理任务上取得重大突破,而且在开放问答等一般任务上也有突破。然而,尽管最近这个领域的努力如火如荼,但仍迫切需要一个全面的调查以提供系统理解。为了填补这一空白,我们提出了一个统一的、多维度的框架,该框架沿着TTS研究的四个核心维度构建:扩展什么、如何扩展、在哪里扩展以及如何评估扩展效果。基于这种分类,我们对方法、应用场景和评估方面进行了广泛的回顾,并提出了有条理的分解,突出了个人技术在更广泛的TTS景观中的独特功能角色。通过这一分析,我们总结了TTS至今的主要发展轨迹,并为实际部署提供了实用指南。此外,我们还确定了几个开放挑战,并对未来有前景的方向提供了见解,包括进一步扩展、澄清技术的功能本质、推广到更多任务以及更多归因。我们的仓库可在https://github.com/testtimescaling/testtimescaling.github.io/访问。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF v2: Creating the GitHub repository, Citing some missed works, Incorporating two new domains (agentic and evaluation) in where to scale, Incorporating one direction (thoughtology research) in challenge and future work
Summary
随着预训练时代对计算规模(数据和参数)的热情逐渐消退,测试时缩放(TTS)技术受到广泛关注。近期研究表明,TTS可进一步激发大型语言模型(LLM)的问题解决能力,不仅在数学和编码等专项推理任务中表现突出,在开放问答等通用任务中也有显著成效。然而,尽管相关研究如火如荼,仍缺乏对该技术的系统性综述。为此,本文提出一个多维度框架,从TTS的核心四个维度(即缩放内容、缩放方式、缩放场景和评估方式)出发进行全面梳理和分析。通过深入研究方法和应用情境,对TTS的独特功能角色进行有条理地解构。本文总结了TTS的主要发展轨迹,为实际应用提供了实用指南,并指出了几个开放挑战和未来发展方向。
Key Takeaways
- 测试时缩放(TTS)技术成为当前研究焦点,可进一步提升大型语言模型(LLM)的问题解决能力。
- TTS在专项推理任务和通用任务中都表现出显著成效。
- 目前缺乏关于TTS技术的系统性综述,本文旨在填补这一空白。
- 本文提出多维度框架,从缩放内容、方式、场景和评估方式四个核心维度对TTS进行全面分析。
- TTS的独特功能角色被有条理地解构,对方法和应用情境进行了深入研究。
- 本文总结了TTS的主要发展轨迹,为实际应用提供了指南。
- 指出TTS面临的开放挑战和未来发展方向,包括进一步缩放、明确技术功能本质、任务通用化和更多归因研究。
点此查看论文截图

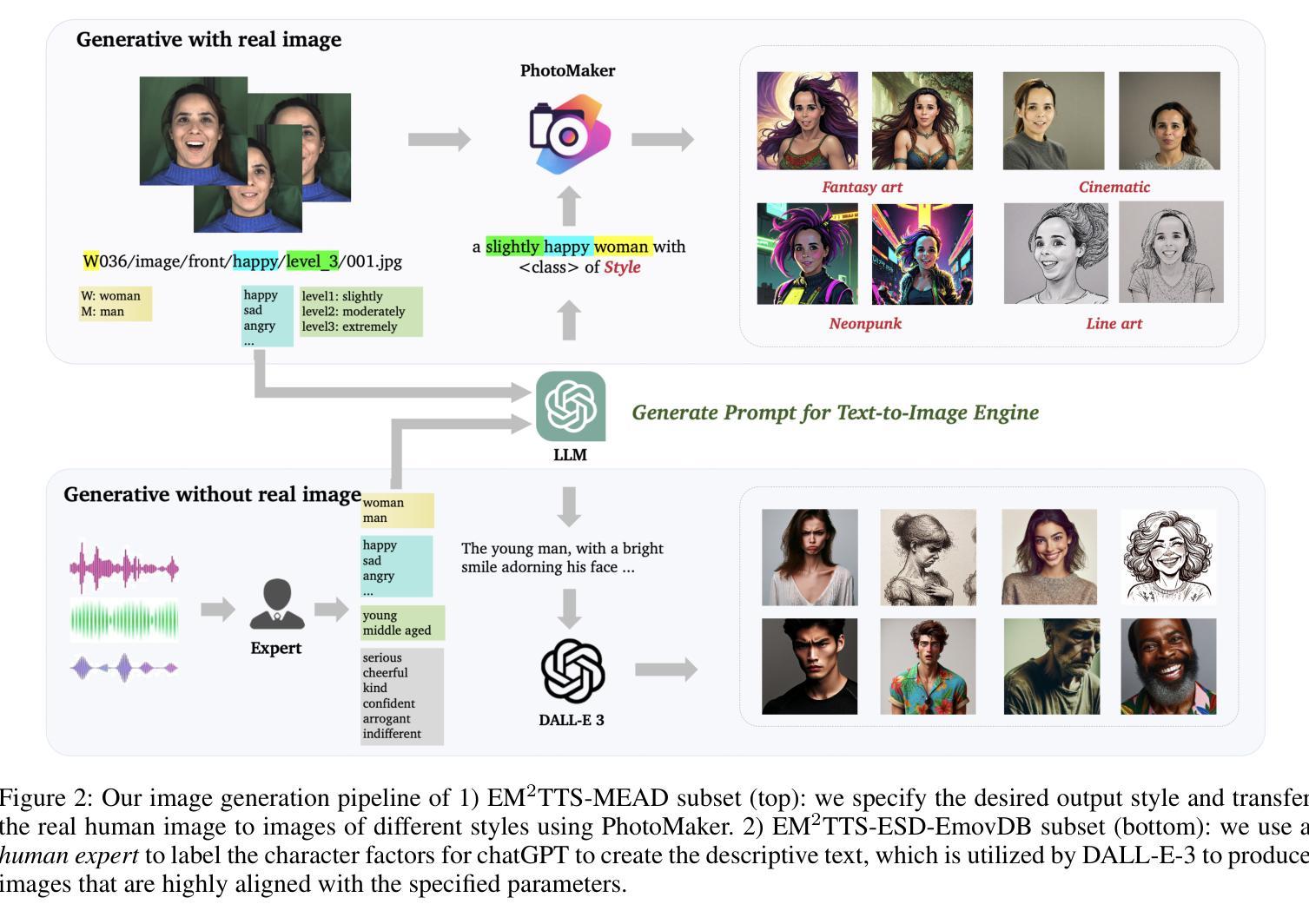
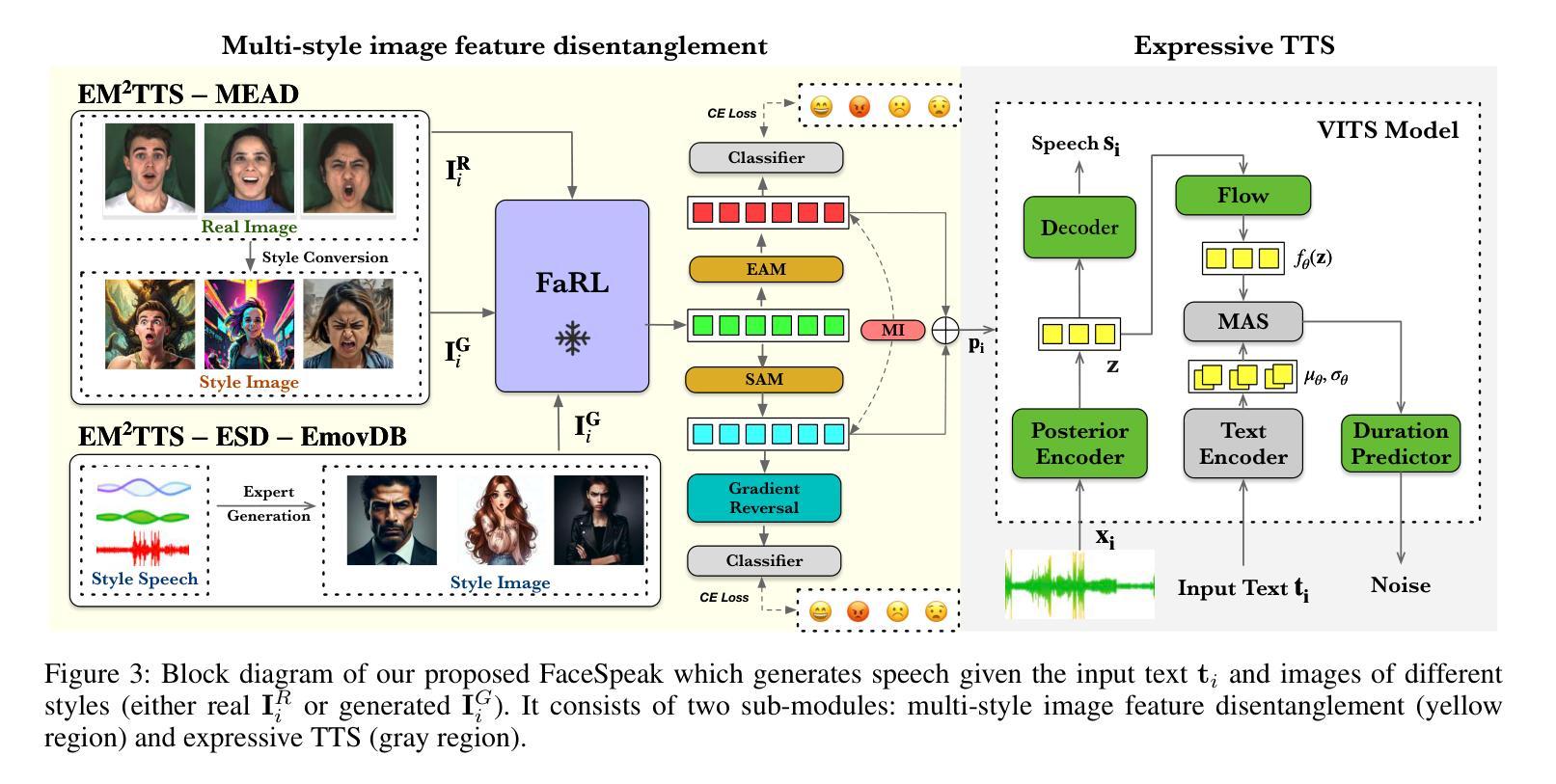
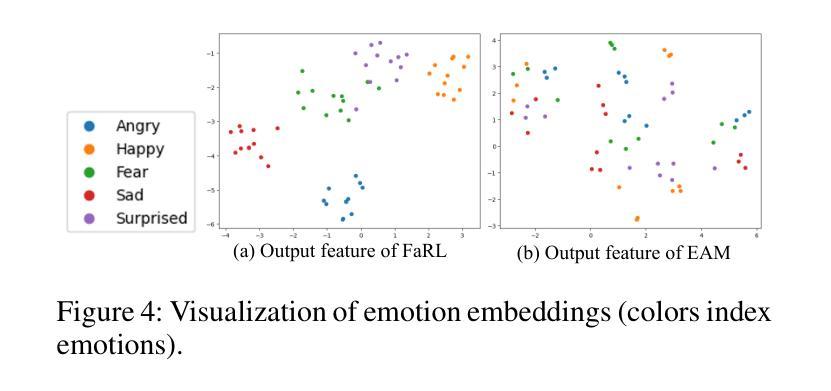
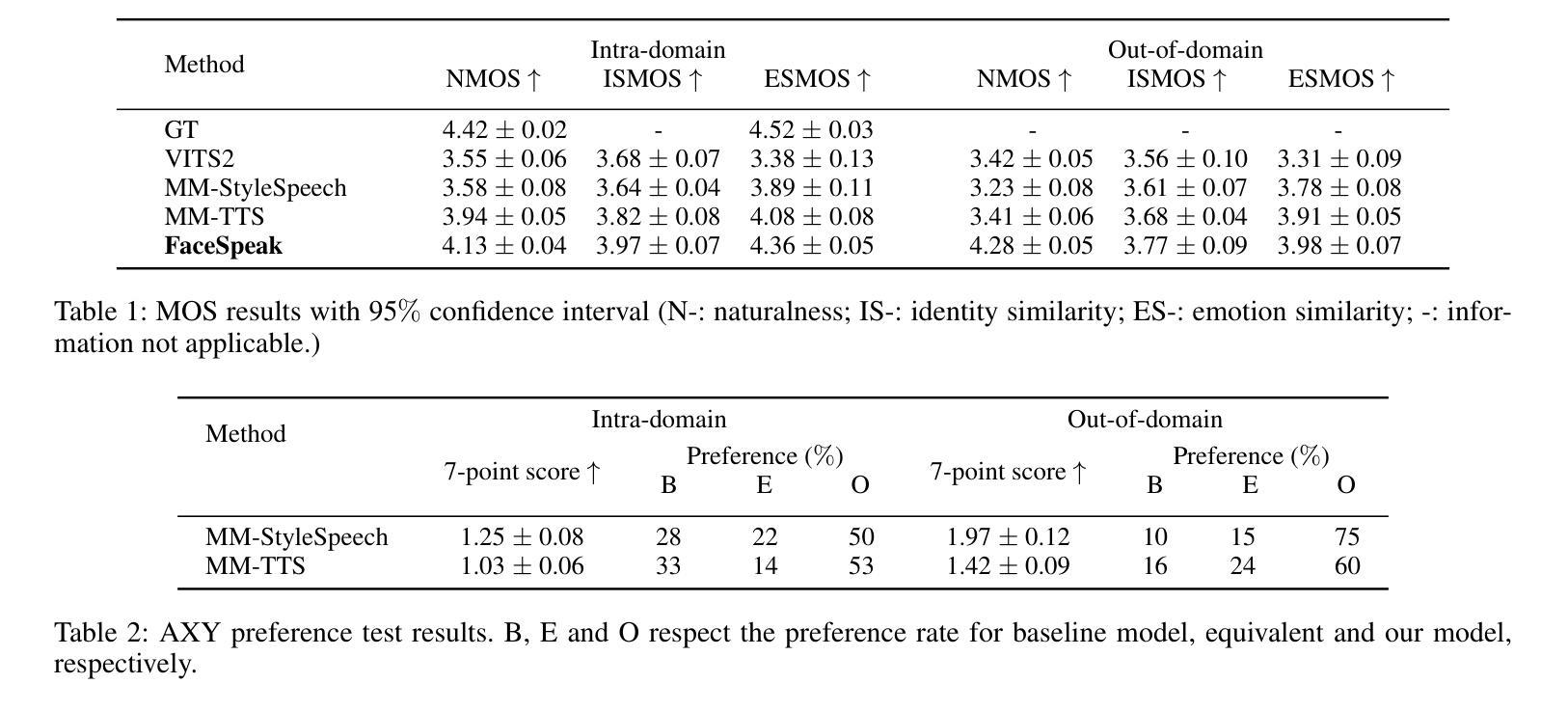
FaceSpeak: Expressive and High-Quality Speech Synthesis from Human Portraits of Different Styles
Authors:Tian-Hao Zhang, Jiawei Zhang, Jun Wang, Xinyuan Qian, Xu-Cheng Yin
Humans can perceive speakers’ characteristics (e.g., identity, gender, personality and emotion) by their appearance, which are generally aligned to their voice style. Recently, vision-driven Text-to-speech (TTS) scholars grounded their investigations on real-person faces, thereby restricting effective speech synthesis from applying to vast potential usage scenarios with diverse characters and image styles. To solve this issue, we introduce a novel FaceSpeak approach. It extracts salient identity characteristics and emotional representations from a wide variety of image styles. Meanwhile, it mitigates the extraneous information (e.g., background, clothing, and hair color, etc.), resulting in synthesized speech closely aligned with a character’s persona. Furthermore, to overcome the scarcity of multi-modal TTS data, we have devised an innovative dataset, namely Expressive Multi-Modal TTS, which is diligently curated and annotated to facilitate research in this domain. The experimental results demonstrate our proposed FaceSpeak can generate portrait-aligned voice with satisfactory naturalness and quality.
人类可以通过观察说话者的外貌来感知他们的特征(如身份、性别、个性和情感),这些特征通常与他们的语音风格相符。近期,面向视觉的文本转语音(TTS)学者将他们的研究重点放在真实人脸图像上,从而限制了有效语音合成在具有多样角色和图像风格的大量潜在应用场景中的应用。为了解决这个问题,我们引入了一种新型FaceSpeak方法。它从各种图像风格中提取显著的身份特征和情感表示。同时,它减轻了额外信息(如背景、服装和发色等)的影响,从而合成与角色个性紧密对齐的语音。此外,为了克服多模态TTS数据的稀缺问题,我们创建了一个创新的数据集,即表达性多模态TTS,该数据集经过精心策划和标注,以促进该领域的研究。实验结果表明,我们提出的FaceSpeak可以生成与肖像对齐的、具有令人满意的自然度和质量的语音。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF Accepted by AAAI 2025
Summary
人类可以通过外观感知说话者的特征(如身份、性别、个性和情感),这些特征通常与他们的语音风格相符。近期,视觉驱动的文本转语音(TTS)学者将研究重点放在真实人物面部,限制了有效语音合成在具有多样角色和图像风格的大量潜在应用场景中的应用。为解决此问题,我们引入了全新的FaceSpeak方法。它能从各种图像风格中提取重要的身份特征和情感表示。同时,它减轻了额外信息(如背景、服装和发色等)的影响,从而合成与角色个性紧密对齐的语音。此外,为了克服多模式TTS数据的稀缺性,我们精心创建了一个创新数据集,名为表达多模式TTS数据集,该数据集经过精心策划和标注,以促进该领域的研究。实验结果表明,我们提出的FaceSpeak能够生成与肖像相符的自然流畅且质量高的语音。
Key Takeaways
- 人类通过外观感知说话者特征,与语音风格相符。
- 当前视觉驱动的TTS研究侧重于真实人脸,限制了语音合成的应用场景多样性。
- FaceSpeak方法能从多种图像风格中提取身份和情绪特征。
- FaceSpeak能够减轻背景、服装和发色等额外信息的影响,合成与角色个性对齐的语音。
- 提出了一个创新的多模式TTS数据集,名为表达多模式TTS数据集,用于促进该领域研究。
- 该数据集经过精心策划和标注。
点此查看论文截图