⚠️ 以下所有内容总结都来自于 大语言模型的能力,如有错误,仅供参考,谨慎使用
🔴 请注意:千万不要用于严肃的学术场景,只能用于论文阅读前的初筛!
💗 如果您觉得我们的项目对您有帮助 ChatPaperFree ,还请您给我们一些鼓励!⭐️ HuggingFace免费体验
2025-04-22 更新
Towards Accurate and Interpretable Neuroblastoma Diagnosis via Contrastive Multi-scale Pathological Image Analysis
Authors:Zhu Zhu, Shuo Jiang, Jingyuan Zheng, Yawen Li, Yifei Chen, Manli Zhao, Weizhong Gu, Feiwei Qin, Jinhu Wang, Gang Yu
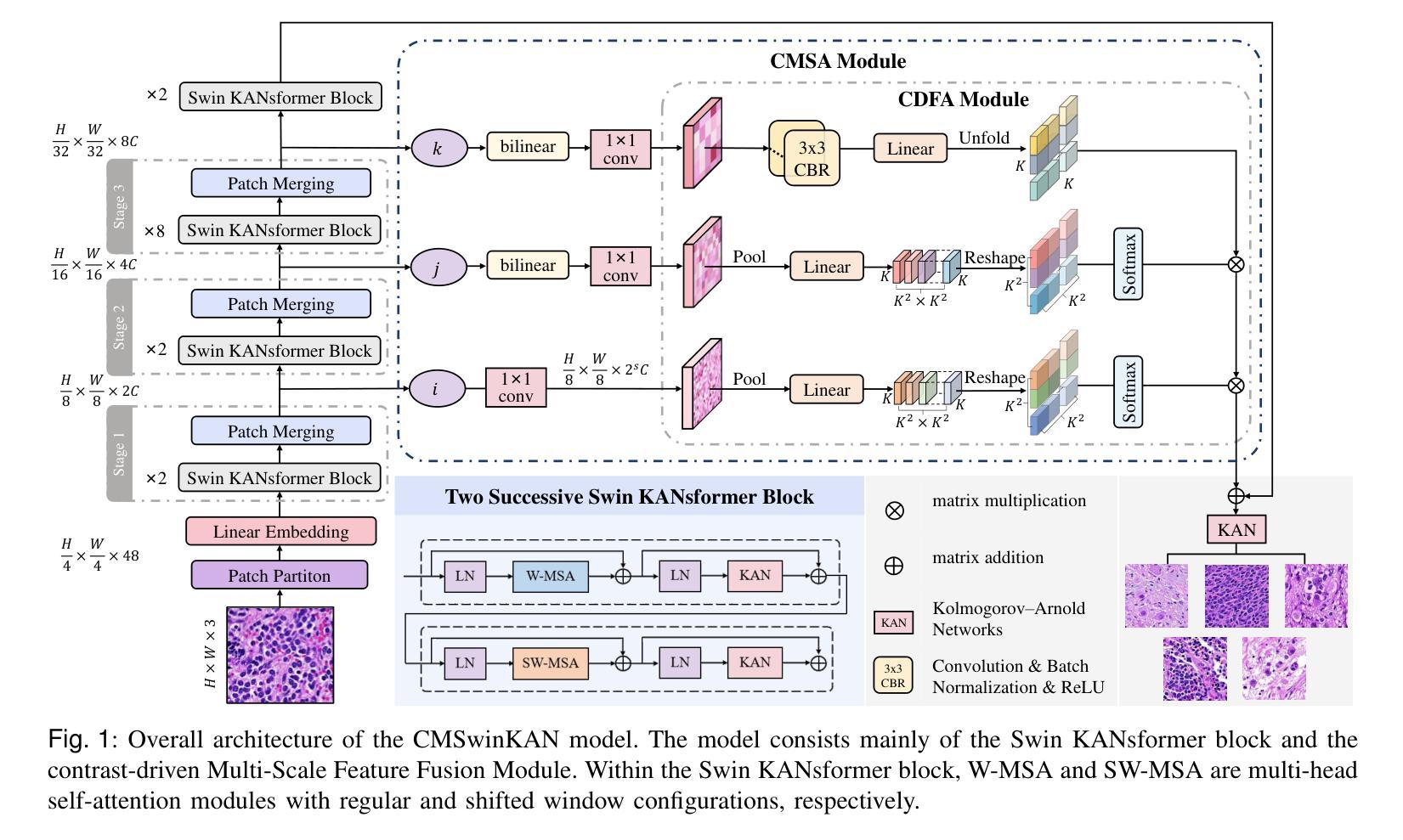
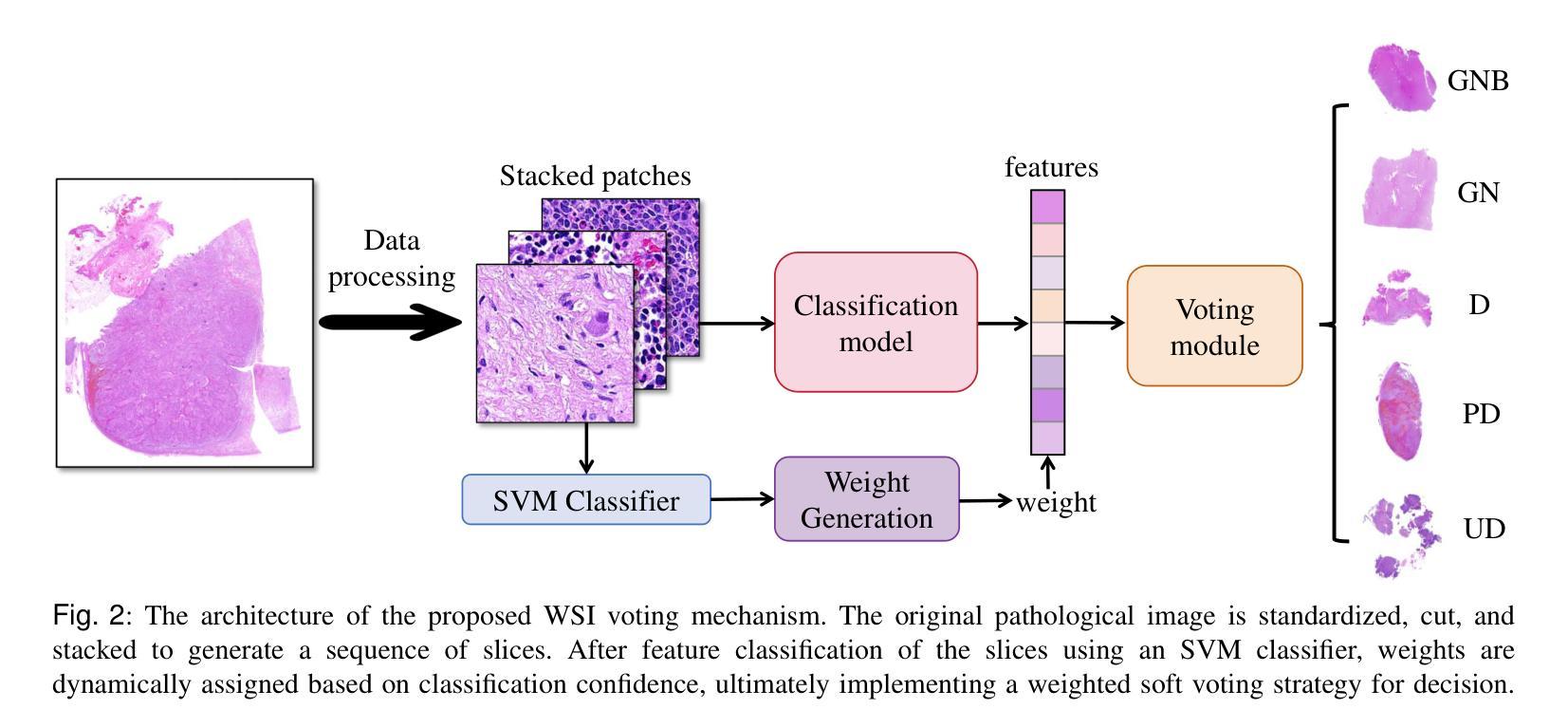
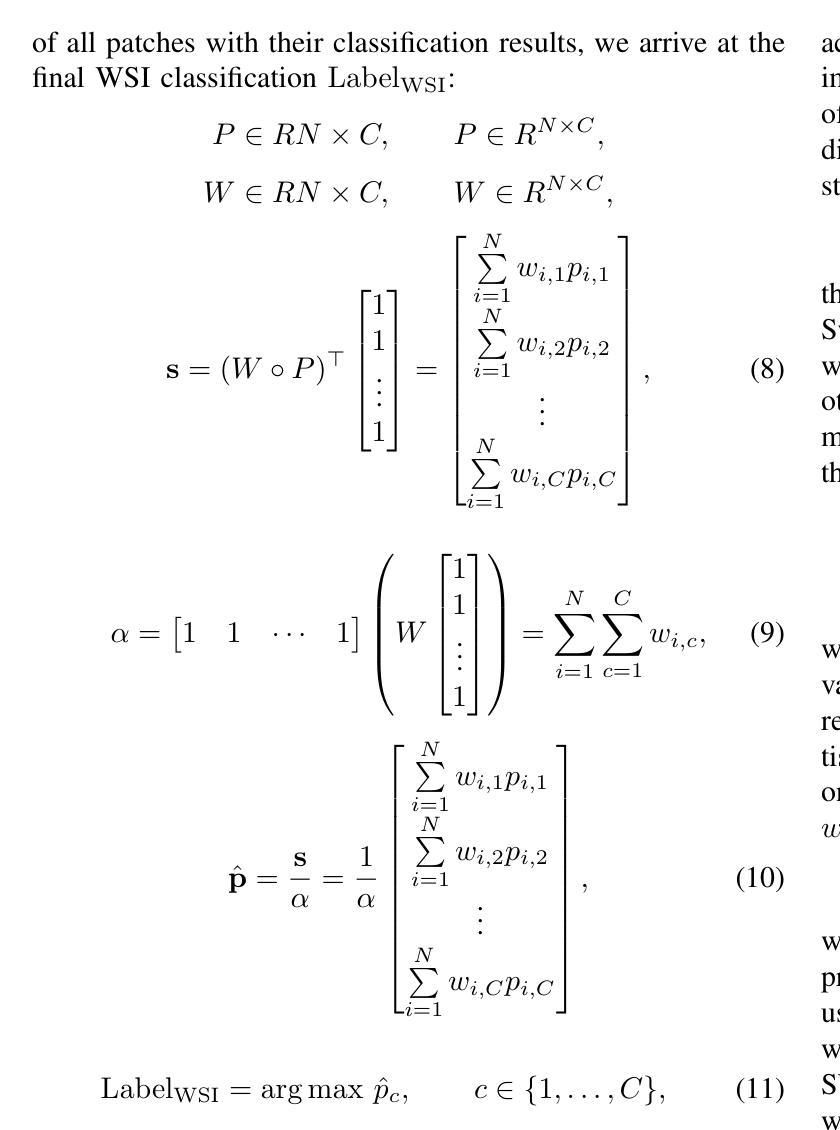
Neuroblastoma, adrenal-derived, is among the most common pediatric solid malignancies, characterized by significant clinical heterogeneity. Timely and accurate pathological diagnosis from hematoxylin and eosin-stained whole slide images is critical for patient prognosis. However, current diagnostic practices primarily rely on subjective manual examination by pathologists, leading to inconsistent accuracy. Existing automated whole slide image classification methods encounter challenges such as poor interpretability, limited feature extraction capabilities, and high computational costs, restricting their practical clinical deployment. To overcome these limitations, we propose CMSwinKAN, a contrastive-learning-based multi-scale feature fusion model tailored for pathological image classification, which enhances the Swin Transformer architecture by integrating a Kernel Activation Network within its multilayer perceptron and classification head modules, significantly improving both interpretability and accuracy. By fusing multi-scale features and leveraging contrastive learning strategies, CMSwinKAN mimics clinicians’ comprehensive approach, effectively capturing global and local tissue characteristics. Additionally, we introduce a heuristic soft voting mechanism guided by clinical insights to seamlessly bridge patch-level predictions to whole slide image-level classifications. We validate CMSwinKAN on the PpNTs dataset, which was collaboratively established with our partner hospital and the publicly accessible BreakHis dataset. Results demonstrate that CMSwinKAN performs better than existing state-of-the-art pathology-specific models pre-trained on large datasets. Our source code is available at https://github.com/JSLiam94/CMSwinKAN.
神经母细胞瘤肾上腺来源是儿童最常见的实体恶性肿瘤之一,具有显著的临床异质性。从苏木精和伊红染色的全切片图像进行及时准确的病理诊断对患者的预后至关重要。然而,当前的诊断实践主要依赖于病理医师的主观手动检查,导致准确性不一致。现有的全自动切片图像分类方法面临可解释性差、特征提取能力有限以及计算成本高的挑战,限制了其在临床实践中的部署。为了克服这些局限性,我们提出了CMSwinKAN,这是一种基于对比学习的多尺度特征融合模型,专门用于病理图像分类。它通过集成内核激活网络增强了Swin Transformer架构的多层感知器和分类头模块,显著提高了可解释性和准确性。通过融合多尺度特征和利用对比学习策略,CMSwinKAN模仿了临床医生全面的方法,有效地捕捉了全局和局部组织特征。此外,我们引入了一种受临床见解启发式的软投票机制,无缝地连接了补丁级别的预测到全切片图像级别的分类。我们在与合作医院共同建立的PpNTs数据集和可公开访问的BreakHis数据集上验证了CMSwinKAN。结果表明,CMSwinKAN的性能优于在大型数据集上预训练的现有最先进的病理学专用模型。我们的源代码可在https://github.com/JSLiam94/CMSwinKAN上找到。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF 14pages, 8 figures
Summary
本文介绍了一种基于对比学习的多尺度特征融合模型CMSwinKAN,用于神经母细胞瘤等肾上腺衍生肿瘤的病理图像分类。该模型通过整合核激活网络,增强了Swin Transformer架构的可解释性和准确性。通过多尺度特征融合和对比学习策略,CMSwinKAN有效捕捉全局和局部组织特征,模仿医生的综合诊断方法。在PpNTs和BreakHis数据集上的验证结果显示,CMSwinKAN表现优于现有的病理学特定模型。
Key Takeaways
- 神经母细胞瘤是常见的儿童实体恶性肿瘤,具有显著的临床异质性,及时准确的病理诊断对预后至关重要。
- 当前诊断方法主要依赖病理医师的主观手动检查,存在准确性不一致的问题。
- CMSwinKAN模型结合对比学习与多尺度特征融合,提高了病理图像分类的准确性和可解释性。
- CMSwinKAN通过整合核激活网络,增强Swin Transformer架构的性能。
- 模型能捕捉全局和局部组织特征,模仿医生的综合诊断方法。
- 在PpNTs和BreakHis数据集上的验证结果显示CMSwinKAN优于现有模型。
点此查看论文截图

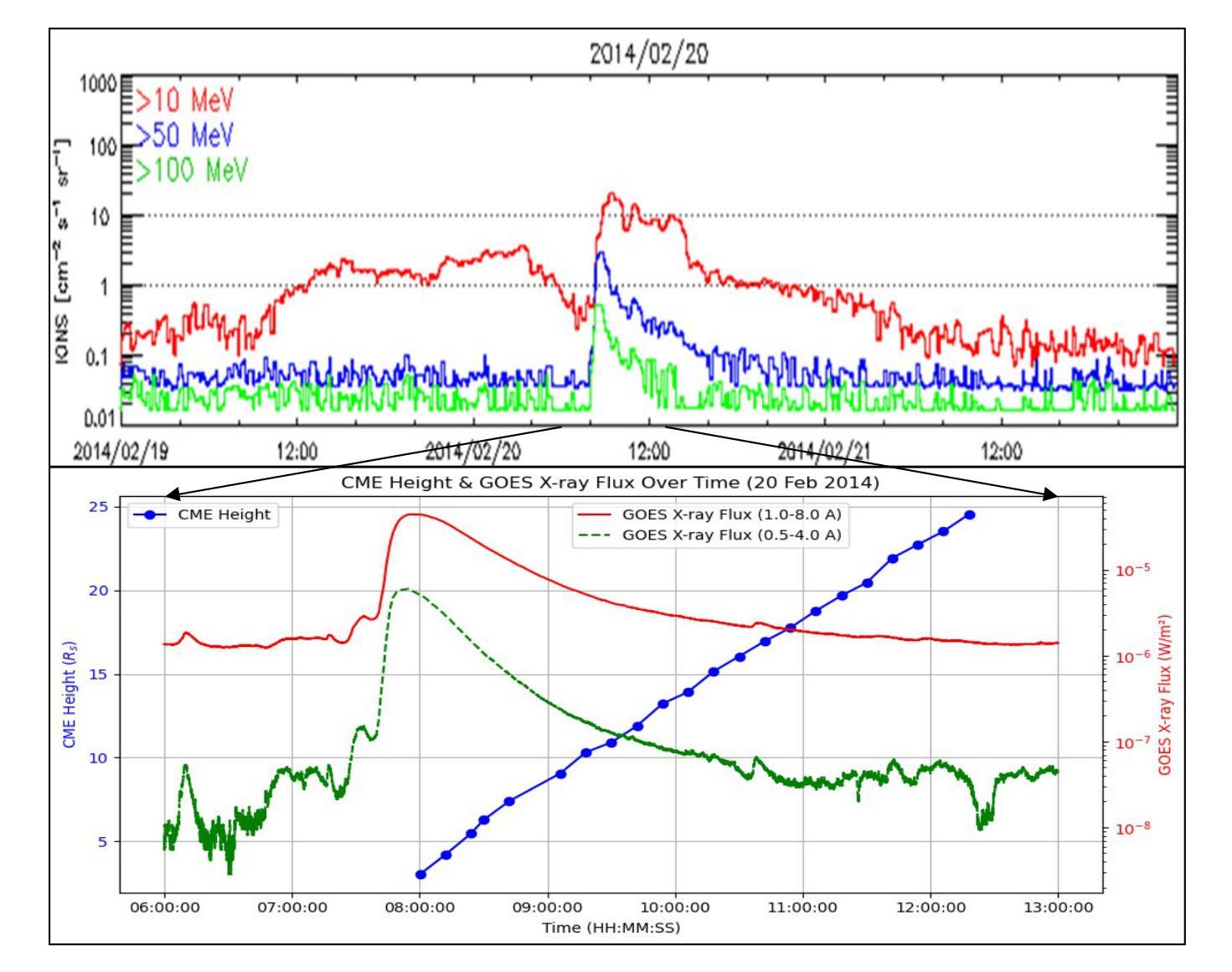
Study of Solar Energetic Particles: their Source Regions, Flares and CMEs during Solar Cycles 23-24
Authors:Raj Kumar, Ramesh Chandra, Bimal Pande, Seema Pande
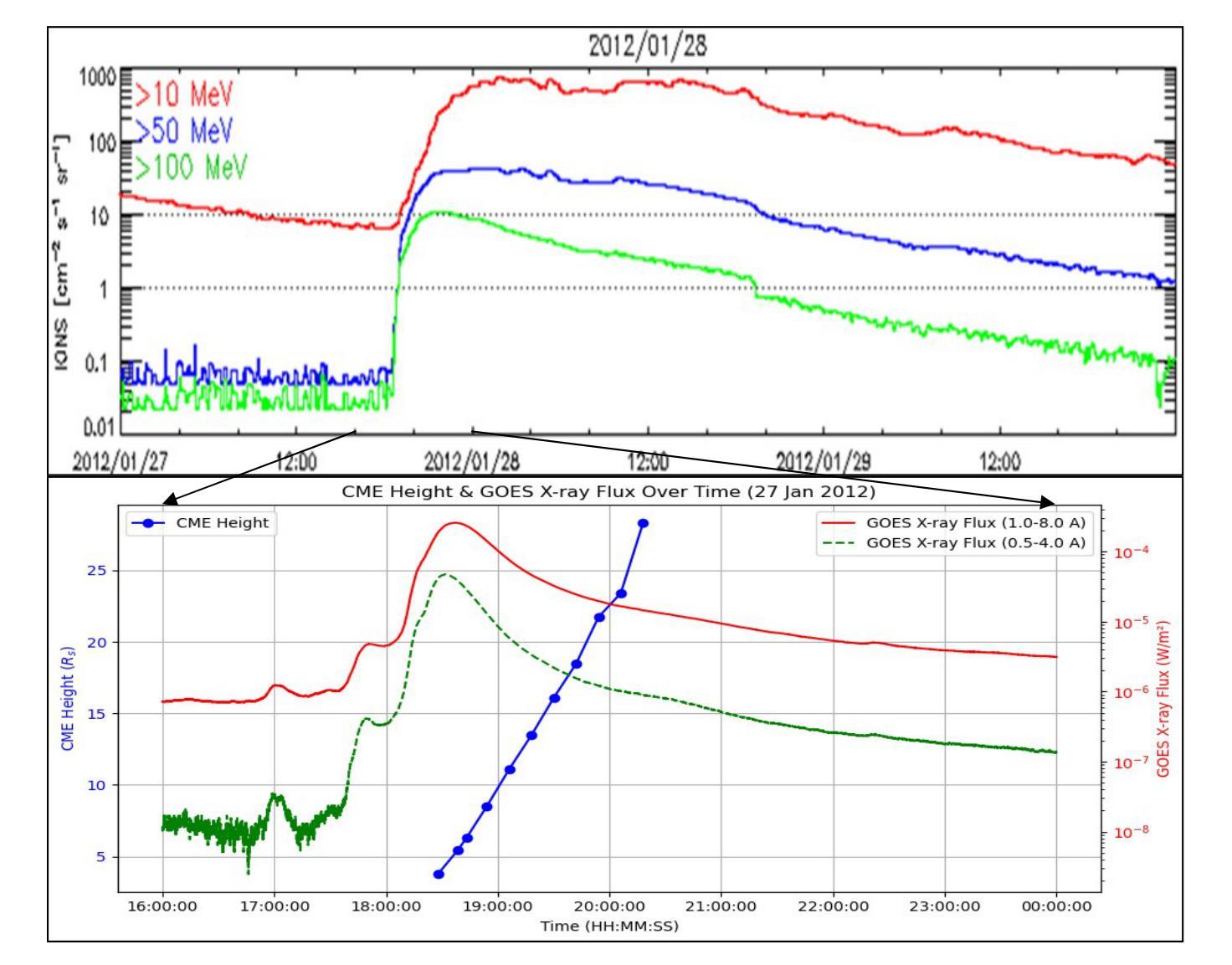
In this work, we examine the association between solar active regions and 152 solar flares, coronal mass ejections, and solar energetic particle (SEP) events over solar cycles 23-24 (1997-2017). The CDAW center’s GOES data in the energy channel >10 MeV (Major SEPs; solar proton events) with flux >= 10 pfu was used for our investigation. For the associated activities, we have analyzed the data from space born satellites namely: SOHO/LASCO and SDO/AIA. We found a moderate correlation (55 %) between SXR flux and sunspot area i.e., active regions with larger sunspot areas generally generate larger flares. We found that most of the SEPs are originated from the magnetically complex active regions i.e., hale class beta-gamma-delta and beta. Very few events were associated with unipolar active regions. Stronger GOES X-ray is linked to more impulsive events, as evidenced by the negative correlation (-0.40) between X-ray flux and SEP duration. In the active region beta-gamma-delta, the highest average SEP intensity (2051 pfu) was detected. In the data set used, only 10 % SEPs are found impulsive in nature, while the remaining 90 % are gradual in nature. All the impulsive events had SEP intensity less than 100 pfu and most of the CMEs associated with these events were decelerated CMEs. We discovered that the majority of faster CMEs are linked to the most complex magnetic active regions. This indicates that high speed CMEs are produced by magnetically complex active regions. We discovered that 58 SEP events in our data set are linked to accelerated CMEs, while 82 are linked to decelerated CMEs. The highest average CME width is found corresponding to magnetically most complex active regions beta-delta, gamma-delta, alpha-gamma-delta and beta-gamma-delta, which shows that large CMEs are the consequences of magnetically complex active regions.
在这项工作中,我们研究了太阳活动区域与太阳周期中的太阳耀斑(solar flare)、日冕物质抛射(coronal mass ejection)以及太阳高能粒子(SEP)事件之间的关联关系,涵盖了太阳周期的第23和第24周期(即太阳活动高年,从1997年至2017年)。我们使用了CDAW中心的GOES数据对大于10MeV的质子能量进行研究,并针对其质量选择辐射通量大于等于每平方微米十亿电子伏(pfu)的数据进行分析。对于相关的活动数据,我们分析了太空探测器(如SOHO/LASCO和SDO/AIA)提供的数据。我们发现太阳软X射线辐射通量与太阳黑子面积之间存在中度相关性(即百分之五十五),活跃区域的太阳黑子面积越大通常引发的大型爆发越明显。大多数太阳高能粒子来自磁场复杂的活跃区域,如beta-gamma-delta型和beta型,非常少的部分来源于单极活动区。此外还发现强劲的GOES射线是与更多的突发事件紧密联系的证据表现在这两者间的负相关性(负零点四),这代表着强烈的X射线射流会导致高能粒子持续时间减少。在beta-gamma-delta型的活跃区域中检测到了最高的平均SEP强度(每平方微米两千零五十一电子伏)。在所使用的数据集中,仅有百分之十的SEP是突发性的,其余百分之九十是逐渐发展的。所有突发性事件的SEP强度均低于每平方微米一百电子伏,并且与这些事件相关的日冕物质抛射大多数是减速抛射。我们发现大多数高速日冕物质抛射与最复杂的磁场活跃区域相关联。这表明高速的日冕物质抛射是由磁场复杂的活跃区域引起的。我们发现数据集中有百分之五十八的SEP事件与加速日冕物质抛射相关,而有百分之八十二则与减速日冕物质抛射有关。对应于最复杂的活跃区域如beta-delta型、gamma-delta型以及alpha-gamma-delta型和beta-gamma-delta型时平均日冕物质抛射宽度最高,这表明大规模的日冕物质抛射是磁场复杂活跃区域的结果。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF 26 pages, 09 figures (accepted for publication in Indian Journal of Physics)
摘要
本文研究了第23至第24个太阳周期(即过去自一九九七年起的二十年)中太阳活动区域与太阳耀斑爆发、日冕物质喷射以及高能太阳粒子事件的关联。利用CDAW中心的GOES数据进行分析,主要关注了能量通道大于或等于十MeV的SEP事件。结合SOHO/LASCO和SDO/AIA等太空卫星的数据,研究发现太阳X射线流量与太阳黑子面积之间存在中度相关性(约百分之五十五),表明较大太阳黑子区域的活跃区域通常产生更大的耀斑。此外,大多数SEP事件源自复杂的磁活跃区域,如β-γ-δ和β类Hale区域。很少有事件与单极活跃区域相关。还发现强烈的GOES X射线与更突发性事件有关,表现为X射线流量与SEP持续时间之间的负相关性(-零点四)。在β-γ-δ活跃区域检测到最高的平均SEP强度(两千零五十一pfu)。数据集中仅有百分之十的SEP属于突发性事件,其余百分之九十则为渐进性事件。所有突发性事件的SEP强度均低于一百pfu,并且大多数与之相关的CME都是减速的CME。研究还发现,大多数高速CME与最复杂的磁活跃区域有关,表明高速CME是由复杂的磁活跃区域产生的。数据集中有百分之五十八的SEP事件与加速的CME相关,而百分之八十二与减速的CME相关。最大的CME宽度通常出现在最复杂的磁活跃区域,如β-δ、γ-δ和α-γ-δ以及β-γ-δ区域。这表明大型CME是复杂磁活跃区域的结果。总结而言,本研究探讨了太阳活动区域的磁场复杂性与高能太阳粒子事件之间的关联性及其背后的物理机制。
关键见解
- 太阳活动区域与太阳耀斑爆发、日冕物质喷射及高能太阳粒子事件之间存在显著关联。
- 太阳X射线流量与太阳黑子面积之间存在中度相关性,暗示大耀斑更可能出现在较大太阳黑子区域的活跃区域。
- 大部分高能太阳粒子事件源自复杂的磁活跃区域,如β-γ-δ类区域。单极活跃区域与之相关的事件很少。
- 强烈的GOES X射线流量与更突发性的事件有关,表现为X射线流量与SEP持续时间之间的负相关性。
- 数据集中仅有小部分SEP事件为突发性,大部分属于渐进性事件。与突发性事件相关的CME大多是减速的。
- 高速CME多与最复杂的磁活跃区域有关。这表明高速CME的产生与复杂的磁活跃区域密切相关。
点此查看论文截图

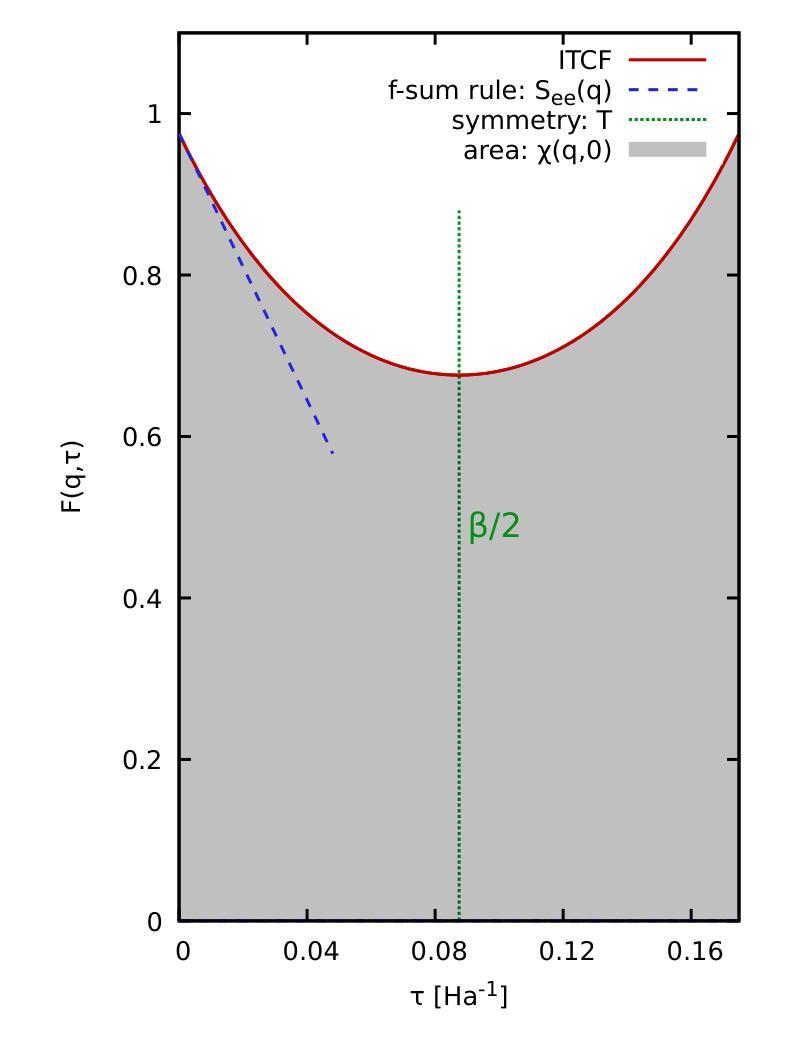
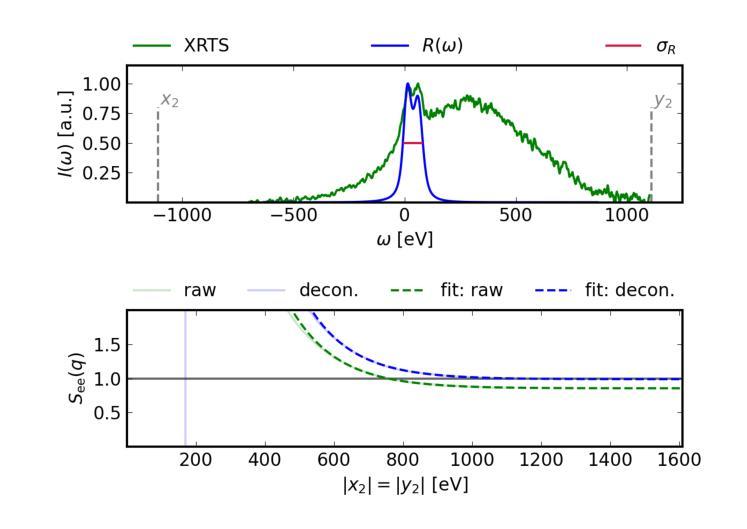
Static linear density response from X-ray Thomson scattering measurements: a case study of warm dense beryllium
Authors:Sebastian Schwalbe, Hannah Bellenbaum, Tilo Döppner, Maximilian Böhme, Thomas Gawne, Dominik Kraus, Michael J. MacDonald, Zhandos Moldabekov, Panagiotis Tolias, Jan Vorberger, Tobias Dornheim
Linear response theory is ubiquitous throughout physics and plays a central role in the theoretical description of warm dense matter – an extreme state that occurs within compact astrophysical objects and that is traversed on the compression path of a fuel capsule in inertial confinement fusion applications. Here we show how one can relate the static linear density response function to X-ray Thomson scattering (XRTS) measurements, which opens up new possibilities for the diagnostics of extreme states of matter, and for the rigorous assessment and verification of theoretical models and approximations. As a practical example, we consider an XRTS data set of warm dense beryllium taken at the National Ignition Facility [T.D"oppner \emph{et al.}, \textit{Nature} \textbf{618}, 270-275 (2023)]. The comparison with state-of-the-art \emph{ab initio} path integral Monte Carlo (PIMC) simulations [T.Dornheim \emph{et al.}, \textit{Nature Commun.}~(in print), arXiv:2402.19113] gives us a best estimate of the mass density of $\rho=18\pm6,$g/cc, which is consistent with previous PIMC and density functional theory based studies, but rules out the original estimate of $\rho=34\pm4,$g/cc based on a Chihara model fit.
线性响应理论在物理学中无处不在,并在描述热密物质的理论中起到核心作用。这是一种极端状态,出现在致密的天体物理对象中,也出现在惯性约束聚变应用的燃料胶囊压缩路径上。在这里,我们展示了如何将静态线性密度响应函数与X射线汤姆森散射(XRTS)测量相关联,这为极端物质状态的诊断、理论模型和近似的严格评估和验证提供了新的可能性。作为一个实际例子,我们考虑了在国家点火设施(T. Doppner等人,《自然》杂志,第618期,270-275页(2023年))获取的温热致密铍的XRTS数据集。与最新的从头开始路径积分蒙特卡洛(PIMC)模拟(Dornheim等人,《自然通讯》(印刷中),arXiv:2402.19113)的比较,为我们提供了最佳质量密度估计值ρ=18±6 g/cc。这与之前的PIMC和基于密度泛函理论的研究相一致,但排除了基于Chihara模型拟合的原始估计值ρ=34±4 g/cc。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
线性响应理论在物理学中普遍存在,对于描述热密物质的理论起到了核心作用。本文通过展示静态线性密度响应函数与X射线汤姆森散射测量的关系,为极端物质状态的诊断和理论模型与近似的严格评估验证提供了新的可能性。对比实验数据与最先进的从头计算路径积分蒙特卡洛模拟,得到最佳估计质量密度。
Key Takeaways
- 线性响应理论在描述热密物质中起到核心作用,特别是在物理和天体物理学领域。
- X射线汤姆森散射测量与静态线性密度响应函数的关系可用于极端物质状态的诊断。
- 通过对比实验数据与最新的从头计算路径积分蒙特卡洛模拟,可以对理论模型进行验证和评估。
- 文中以热密铍为例,给出了基于最新模拟的最佳估计质量密度。
- 这一估计与之前的PIMC和密度泛函理论研究一致,排除了基于Chihara模型拟合的原始估计。
- 该研究为惯性约束聚变应用中燃料胶囊的压缩路径提供了新视角。
点此查看论文截图

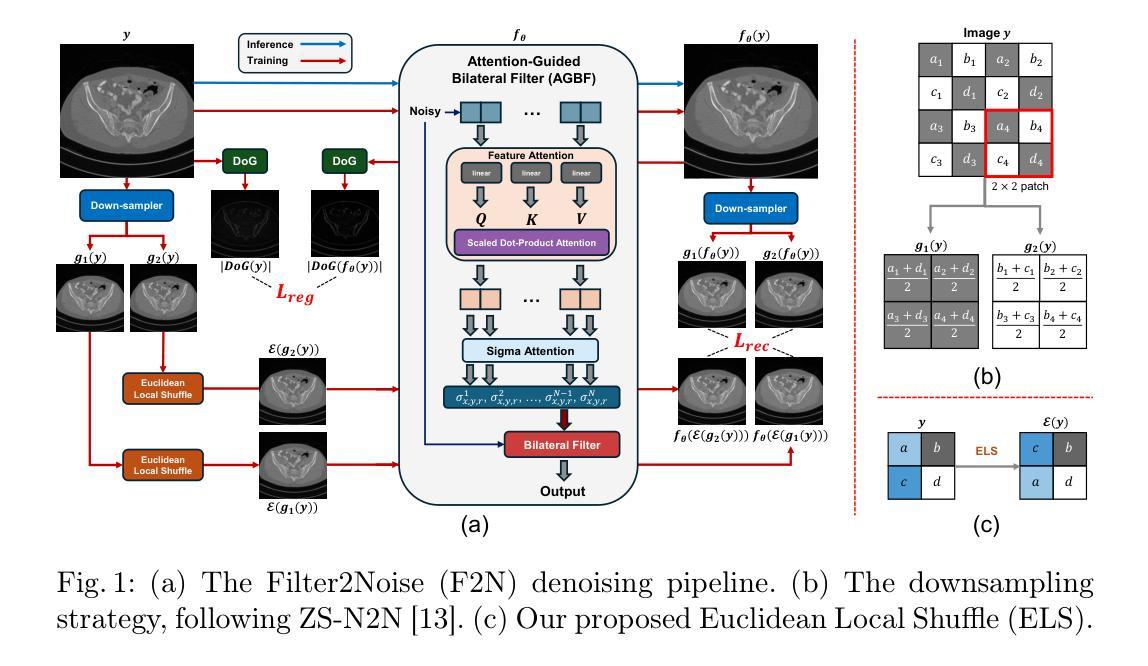
Filter2Noise: Interpretable Self-Supervised Single-Image Denoising for Low-Dose CT with Attention-Guided Bilateral Filtering
Authors:Yipeng Sun, Linda-Sophie Schneider, Mingxuan Gu, Siyuan Mei, Chengze Ye, Fabian Wagner, Siming Bayer, Andreas Maier
Effective denoising is crucial in low-dose CT to enhance subtle structures and low-contrast lesions while preventing diagnostic errors. Supervised methods struggle with limited paired datasets, and self-supervised approaches often require multiple noisy images and rely on deep networks like U-Net, offering little insight into the denoising mechanism. To address these challenges, we propose an interpretable self-supervised single-image denoising framework – Filter2Noise (F2N). Our approach introduces an Attention-Guided Bilateral Filter that adapted to each noisy input through a lightweight module that predicts spatially varying filter parameters, which can be visualized and adjusted post-training for user-controlled denoising in specific regions of interest. To enable single-image training, we introduce a novel downsampling shuffle strategy with a new self-supervised loss function that extends the concept of Noise2Noise to a single image and addresses spatially correlated noise. On the Mayo Clinic 2016 low-dose CT dataset, F2N outperforms the leading self-supervised single-image method (ZS-N2N) by 4.59 dB PSNR while improving transparency, user control, and parametric efficiency. These features provide key advantages for medical applications that require precise and interpretable noise reduction. Our code is demonstrated at https://github.com/sypsyp97/Filter2Noise.git .
在低剂量计算机断层扫描(CT)中,有效的去噪对于增强细微结构和低对比度病变至关重要,同时防止诊断错误。监督方法受限于配对数据集,而自监督方法通常需要多个噪声图像,并依赖于U-Net等深度网络,对去噪机制提供很少的洞察。为了解决这些挑战,我们提出了一种可解释的自监督单图像去噪框架——Filter2Noise(F2N)。我们的方法引入了一个注意力引导双边滤波器,该滤波器可通过轻量级模块预测空间变化的滤波器参数,以适应每个噪声输入。这些参数可以在训练后进行可视化和调整,以实现用户控制的特定感兴趣区域的去噪。为了实现单图像训练,我们引入了一种新的下采样洗牌策略,以及一种新的自监督损失函数,它将Noise2Noise的概念扩展到单图像并解决空间相关噪声问题。在梅奥诊所2016年低剂量CT数据集上,F2N在PSNR方面比领先的自监督单图像方法(ZS-N2N)高出4.59 dB,同时提高了透明度、用户控制力和参数效率。这些特点对于要求精确和可解释降噪的医学应用提供了关键优势。我们的代码演示在https://github.com/sypsyp97/Filter2Noise.git。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF preprint
Summary
本文提出了一种名为Filter2Noise(F2N)的可解释性自监督单图像去噪框架。它通过引入注意力引导双边滤波器,自适应于每个噪声输入,并通过轻量级模块预测空间变化的滤波器参数,实现用户可在训练后针对特定感兴趣区域进行可视化并调整去噪效果。此外,采用了一种新的下采样洗牌策略,配合自监督损失函数,将Noise2Noise的概念扩展到单图像上,并解决空间相关噪声问题。在Mayo Clinic 2016低剂量CT数据集上,F2N表现出优于现有自监督单图像方法(ZS-N2N)的优异性能,提高了峰值信噪比(PSNR)4.59 dB,同时提高了透明度、用户控制和参数效率。这对于需要精确和可解释性降噪的医学应用具有重要意义。
Key Takeaways
- 有效去噪在低剂量CT中至关重要,能提高细微结构和低对比度病变的识别度,防止诊断错误。
- 监督方法受限于配对数据集,自监督方法则需要多噪声图像并依赖深度网络(如U-Net),对于去噪机制提供较少见解。
- 提出的Filter2Noise(F2N)框架是一种可解释的自监督单图像去噪方法。
- F2N通过注意力引导双边滤波器自适应于每个噪声输入,并引入轻量级模块以预测空间变化的滤波器参数,实现用户可控的特定区域去噪。
- F2N采用新的下采样洗牌策略和自监督损失函数,扩展Noise2Noise概念至单图像,解决空间相关噪声问题。
- 在Mayo Clinic 2016低剂量CT数据集上,F2N相比现有自监督单图像方法提高了4.59 dB PSNR,同时增强透明度、用户控制和参数效率。
点此查看论文截图

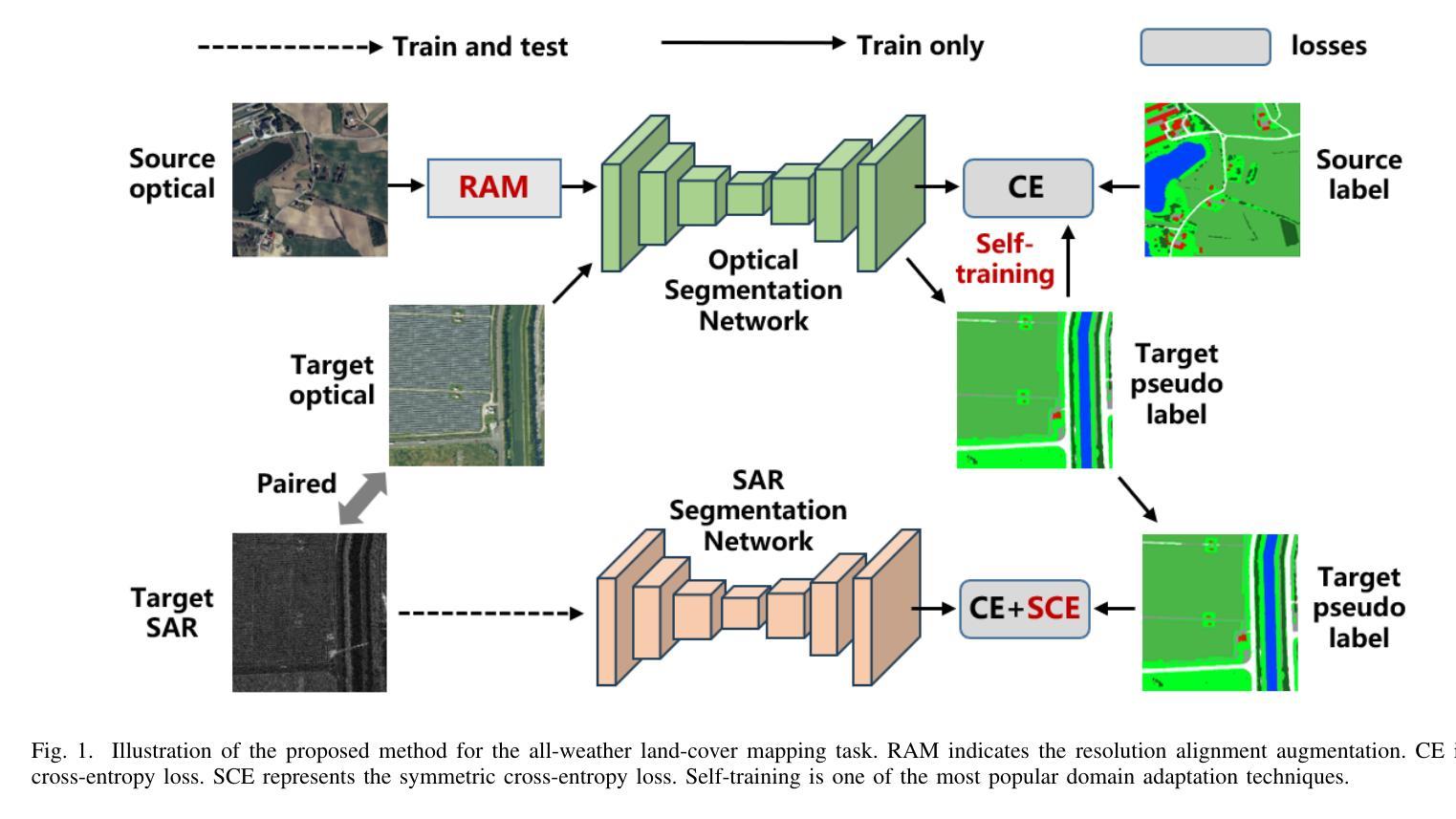
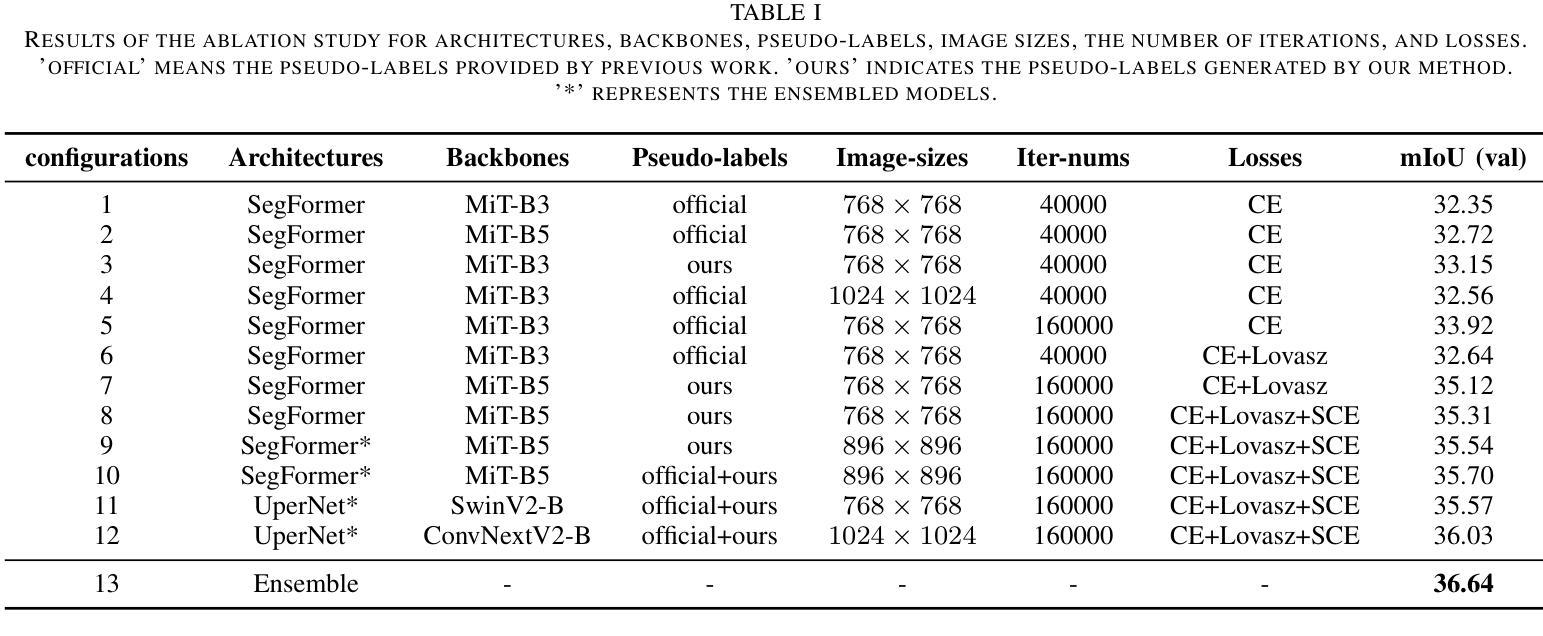
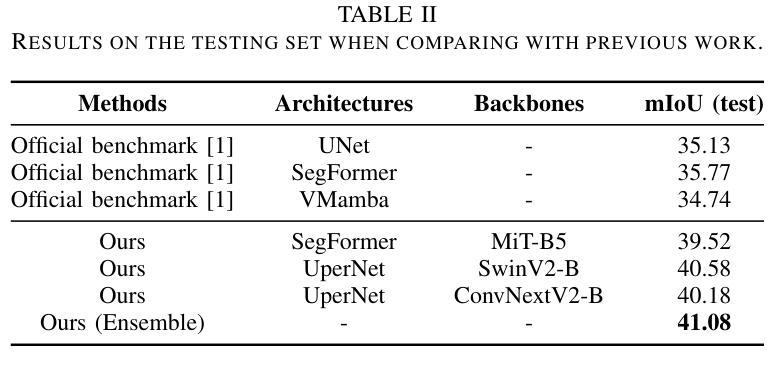
Learning from Noisy Pseudo-labels for All-Weather Land Cover Mapping
Authors:Wang Liu, Zhiyu Wang, Xin Guo, Puhong Duan, Xudong Kang, Shutao Li
Semantic segmentation of SAR images has garnered significant attention in remote sensing due to the immunity of SAR sensors to cloudy weather and light conditions. Nevertheless, SAR imagery lacks detailed information and is plagued by significant speckle noise, rendering the annotation or segmentation of SAR images a formidable task. Recent efforts have resorted to annotating paired optical-SAR images to generate pseudo-labels through the utilization of an optical image segmentation network. However, these pseudo-labels are laden with noise, leading to suboptimal performance in SAR image segmentation. In this study, we introduce a more precise method for generating pseudo-labels by incorporating semi-supervised learning alongside a novel image resolution alignment augmentation. Furthermore, we introduce a symmetric cross-entropy loss to mitigate the impact of noisy pseudo-labels. Additionally, a bag of training and testing tricks is utilized to generate better land-cover mapping results. Our experiments on the GRSS data fusion contest indicate the effectiveness of the proposed method, which achieves first place. The code is available at https://github.com/StuLiu/DFC2025Track1.git.
SAR图像的语义分割在遥感领域受到了广泛关注,因为SAR传感器不受天气和光照条件的影响。然而,SAR图像缺乏详细信息,并且受到斑点噪声的困扰,这使得SAR图像的标注或分割成为一项艰巨的任务。近期的研究尝试对配对的光学SAR图像进行标注,以利用光学图像分割网络生成伪标签。然而,这些伪标签充满了噪声,导致SAR图像分割性能不佳。本研究介绍了一种更精确的方法生成伪标签,该方法结合了半监督学习以及一种新型图像分辨率对齐增强技术。此外,我们还引入了对称交叉熵损失来减轻噪声伪标签的影响。同时,我们还采用了一系列训练和测试技巧来生成更好的土地覆盖映射结果。我们在GRSS数据融合竞赛上的实验证明了所提方法的有效性,该方法取得了第一名。代码可在https://github.com/StuLiu/DFC2025Track1.git获取。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
SAR图像语义分割因其不受天气和光照条件影响的特性而受到遥感领域的关注。但SAR图像缺乏详细信息且易受斑点噪声影响,使得SAR图像的标注或分割成为一项艰巨的任务。本研究通过结合半监督学习和新颖的图像分辨率对齐增强方法,提出了一种更精确的生成伪标签的方法。此外,引入对称交叉熵损失以减轻噪声伪标签的影响,并使用一系列训练和测试技巧来生成更好的土地覆盖映射结果。在GRSS数据融合竞赛上的实验验证了所提方法的有效性,该方法取得了第一名,代码已公开。
Key Takeaways
- SAR图像语义分割在遥感领域具有重要性,因为它不受天气和光照条件的限制。
- SAR图像缺乏详细信息和易受斑点噪声影响,使得标注和分割变得困难。
- 本研究提出了一种结合半监督学习和图像分辨率对齐增强方法生成更精确伪标签的方法。
- 引入对称交叉��熵损失以减轻噪声伪标签对分割性能的影响。
- 使用一系列训练和测试技巧来提高土地覆盖映射结果的准确性。
- 在GRSS数据融合竞赛上进行的实验验证了所提出方法的有效性,并取得了第一名的好成绩。
点此查看论文截图

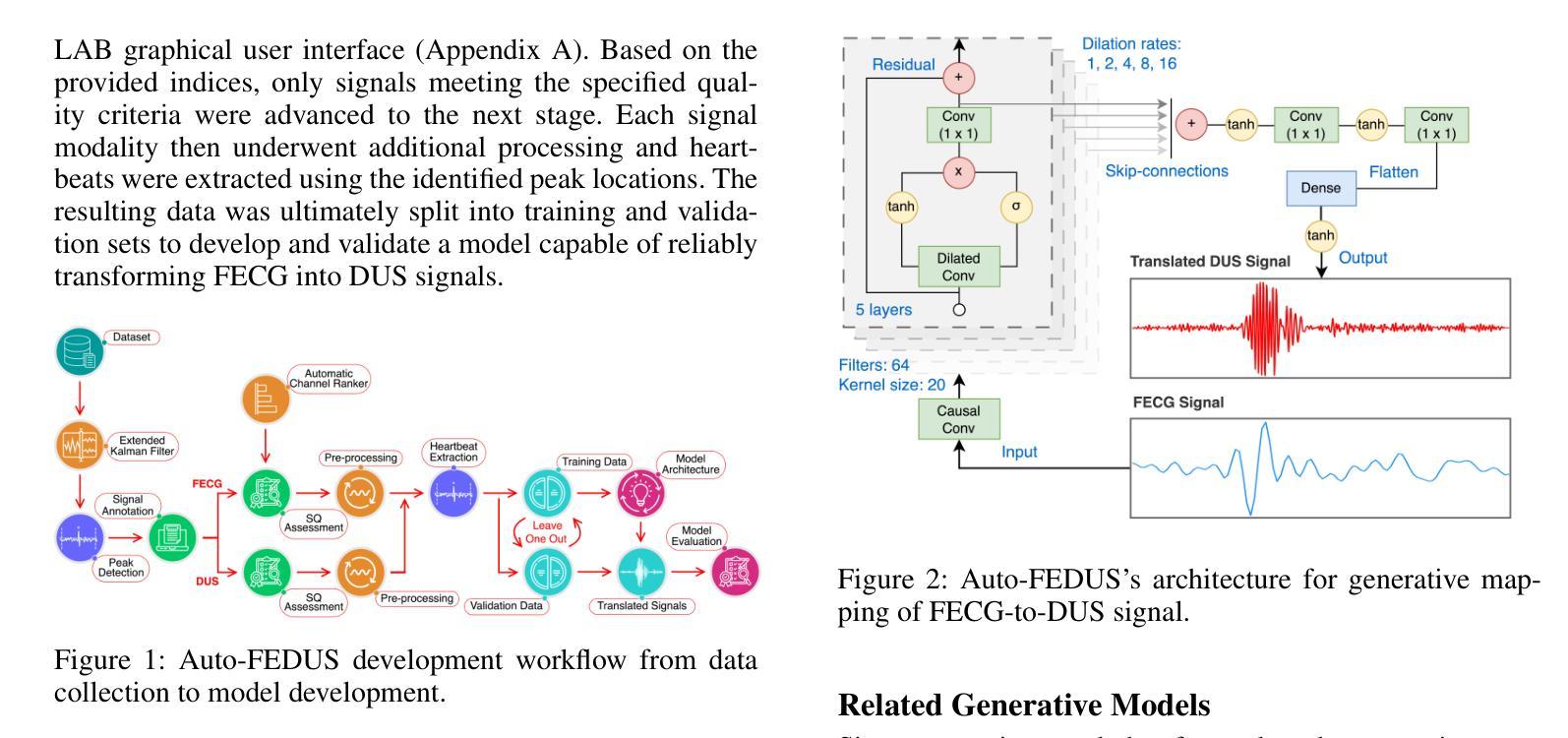
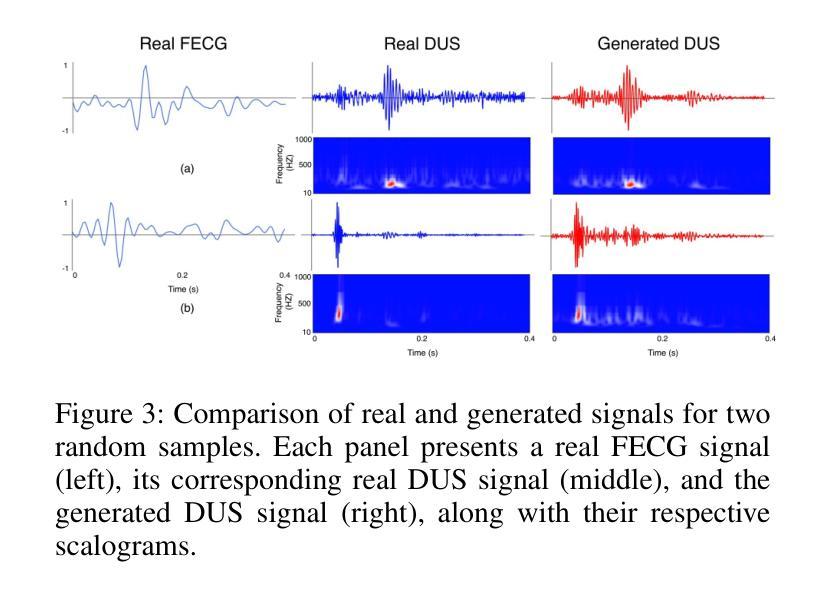
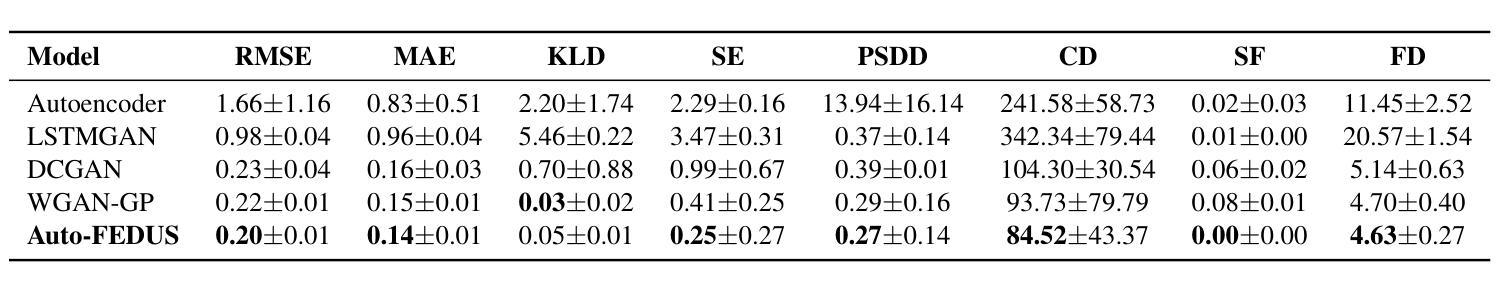
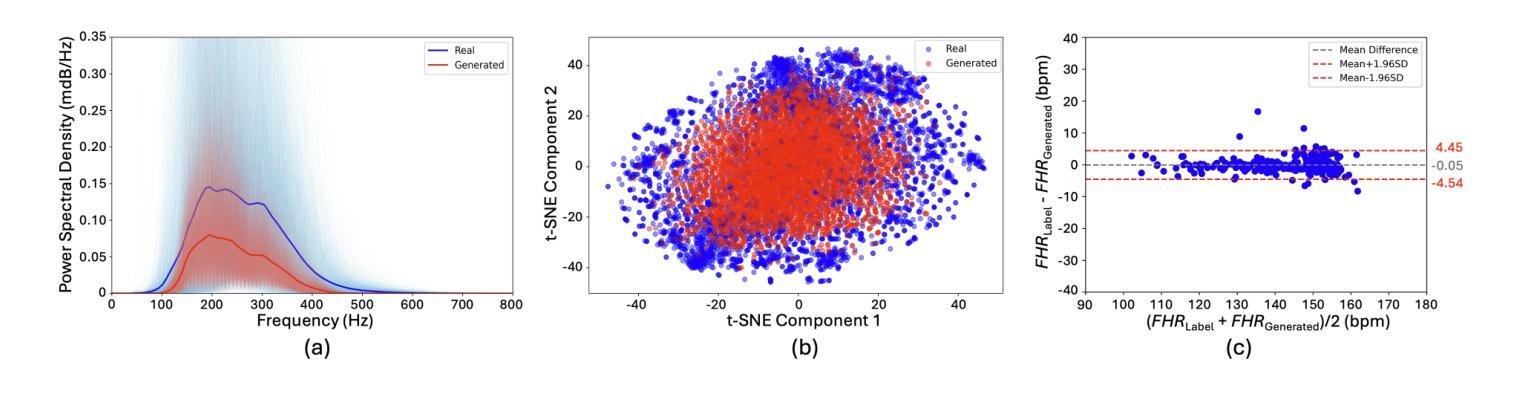
Auto-FEDUS: Autoregressive Generative Modeling of Doppler Ultrasound Signals from Fetal Electrocardiograms
Authors:Alireza Rafiei, Gari D. Clifford, Nasim Katebi
Fetal health monitoring through one-dimensional Doppler ultrasound (DUS) signals offers a cost-effective and accessible approach that is increasingly gaining interest. Despite its potential, the development of machine learning based techniques to assess the health condition of mothers and fetuses using DUS signals remains limited. This scarcity is primarily due to the lack of extensive DUS datasets with a reliable reference for interpretation and data imbalance across different gestational ages. In response, we introduce a novel autoregressive generative model designed to map fetal electrocardiogram (FECG) signals to corresponding DUS waveforms (Auto-FEDUS). By leveraging a neural temporal network based on dilated causal convolutions that operate directly on the waveform level, the model effectively captures both short and long-range dependencies within the signals, preserving the integrity of generated data. Cross-subject experiments demonstrate that Auto-FEDUS outperforms conventional generative architectures across both time and frequency domain evaluations, producing DUS signals that closely resemble the morphology of their real counterparts. The realism of these synthesized signals was further gauged using a quality assessment model, which classified all as good quality, and a heart rate estimation model, which produced comparable results for generated and real data, with a Bland-Altman limit of 4.5 beats per minute. This advancement offers a promising solution for mitigating limited data availability and enhancing the training of DUS-based fetal models, making them more effective and generalizable.
通过一维多普勒超声(DUS)信号进行胎儿健康监测是一种成本效益高且易于实施的方法,越来越受到关注。尽管其潜力巨大,但利用机器学习方法评估母亲和胎儿健康状况的DUS信号技术仍相对有限。这种缺乏主要是由于缺乏大量可靠的DUS数据集进行解读以及不同孕期数据存在不平衡的问题。为应对这一挑战,我们引入了一种新型的autoregressive生成模型(Auto-FEDUS),旨在将胎儿心电图(FECG)信号映射到相应的DUS波形上。该模型利用基于膨胀因果卷积的神经网络时序网络直接在波形层面进行操作,有效捕捉信号中的短期和长期依赖关系,保持生成数据的完整性。跨主体实验表明,在时间域和频域评估中,Auto-FEDUS均优于传统生成架构,产生的DUS信号形态与真实信号非常相似。这些合成信号的逼真性进一步通过质量评估模型进行了衡量,所有信号均被分类为高质量信号;同时,心率估计模型对生成数据和真实数据产生的结果相当,Bland-Altman限值为每分钟4.5次心跳。这一进展为解决数据有限的问题提供了一个有前景的解决方案,并有望增强基于DUS的胎儿模型的训练效果,使其更具有效性和泛化能力。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF AAAI 2025 Workshop on Large Language Models and Generative AI for Health
Summary
该文本介绍了一种通过一维多普勒超声(DUS)信号进行胎儿健康监测的方法,该方法具有成本效益高、易于获取的特点,越来越受到关注。然而,由于缺乏大量的DUS数据集和可靠的解释参考以及不同孕期数据的失衡,使用机器学习方法评估母婴健康状况的技术发展受到限制。为此,研究团队提出了一种新型的自动回归生成模型Auto-FEDUS,用于将胎儿心电图(FECG)信号映射到相应的DUS波形上。该模型利用基于扩张因果卷积的神经网络时间网络直接在波形级别进行操作,可以有效地捕捉信号中的短期和长期依赖性,保持生成数据的完整性。研究表明,Auto-FEDUS在时间域和频域评估方面都优于传统生成架构,生成的DUS信号与实际信号的形态非常相似。该研究的进展为解决数据有限性问题提供了一个有前途的解决方案,并有助于提高基于DUS的胎儿模型的有效性和通用性。
Key Takeaways
- 一维多普勒超声(DUS)信号用于胎儿健康监测是一种经济、方便的方法,备受关注。
- 基于机器学习的DUS技术评估母婴健康状况仍处于起步阶段。
- 缺乏大规模的DUS数据集以及可靠的数据解释和不平衡的孕期数据限制了技术发展。
- 引入新型自动回归生成模型Auto-FEDUS,将胎儿心电图(FECG)信号映射到DUS波形上。
- Auto-FEDUS利用神经网络时间网络捕捉信号中的短期和长期依赖性。
- Auto-FEDUS生成的DUS信号与实际信号的形态相似,通过质量评估模型和心率估计模型验证其真实性。
点此查看论文截图

Efficient Brain Tumor Segmentation Using a Dual-Decoder 3D U-Net with Attention Gates (DDUNet)
Authors:Mohammad Mahdi Danesh Pajouh
Cancer remains one of the leading causes of mortality worldwide, and among its many forms, brain tumors are particularly notorious due to their aggressive nature and the critical challenges involved in early diagnosis. Recent advances in artificial intelligence have shown great promise in assisting medical professionals with precise tumor segmentation, a key step in timely diagnosis and treatment planning. However, many state-of-the-art segmentation methods require extensive computational resources and prolonged training times, limiting their practical application in resource-constrained settings. In this work, we present a novel dual-decoder U-Net architecture enhanced with attention-gated skip connections, designed specifically for brain tumor segmentation from MRI scans. Our approach balances efficiency and accuracy by achieving competitive segmentation performance while significantly reducing training demands. Evaluated on the BraTS 2020 dataset, the proposed model achieved Dice scores of 85.06% for Whole Tumor (WT), 80.61% for Tumor Core (TC), and 71.26% for Enhancing Tumor (ET) in only 50 epochs, surpassing several commonly used U-Net variants. Our model demonstrates that high-quality brain tumor segmentation is attainable even under limited computational resources, thereby offering a viable solution for researchers and clinicians operating with modest hardware. This resource-efficient model has the potential to improve early detection and diagnosis of brain tumors, ultimately contributing to better patient outcomes
癌症仍然是全球主要的死亡原因之一,而在其多种形态中,脑肿瘤因其侵袭性以及早期诊断的艰巨挑战而特别恶名昭彰。人工智能领域的最新进展在协助医疗专业人士进行精确的肿瘤分割方面显示出巨大的潜力,这是及时诊断和治疗计划的关键步骤。然而,许多最先进的分割方法需要大量的计算资源和长时间的训练,这在资源受限的环境中限制了它们的实际应用。在这项工作中,我们提出了一种新型的双解码器U-Net架构,该架构增强了注意力门控跳跃连接,专门用于从MRI扫描中分割脑肿瘤。我们的方法通过实现竞争性的分割性能同时显著提高训练效率来平衡效率和准确性。在BraTS 2020数据集上评估,所提出模型在50个周期内实现了整体肿瘤(WT)的Dice得分为85.06%,肿瘤核心(TC)的得分为80.61%,增强肿瘤(ET)的得分为71.26%,超过了常用的一些U-Net变体。我们的模型证明了即使在有限的计算资源下也能实现高质量的脑肿瘤分割,从而为使用适度硬件的研究人员和临床医生提供了切实可行的解决方案。这种资源高效型的模型有潜力改善脑肿瘤的早期检测和诊断,最终为患者带来更好的治疗效果。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
人工智能在脑肿瘤分割上展现出巨大潜力,有助医学专业人士进行精确肿瘤分割,但现有方法计算资源需求大、训练时间长。本研究提出一种新型双解码器U-Net架构,结合注意力门控跳过连接,专为从MRI扫描中分割脑肿瘤而设计。该模型在BraTS 2020数据集上表现优越,显著减少训练需求,平衡了效率和准确性,为有限资源下研究者与临床医生提供可行解决方案。
Key Takeaways
- 癌症仍是全球主要死亡原因之一,脑肿瘤因其侵袭性和早期诊断的挑战性而备受关注。
- 人工智能在脑肿瘤分割方面展现出巨大潜力,有助于医学专业人士进行精确诊断。
- 现有分割方法计算资源需求大、训练时间长,限制了其在资源有限环境下的应用。
- 本研究提出了一种新型双解码器U-Net架构,结合注意力门控跳过连接,专为脑肿瘤分割设计。
- 该模型在BraTS 2020数据集上表现优越,取得了较高的分割准确性。
- 模型在仅50个周期(epochs)内达到了高Dice得分,对整体肿瘤、肿瘤核心和增强肿瘤的分割准确率分别达到了85.06%、80.61%和71.26%。
点此查看论文截图

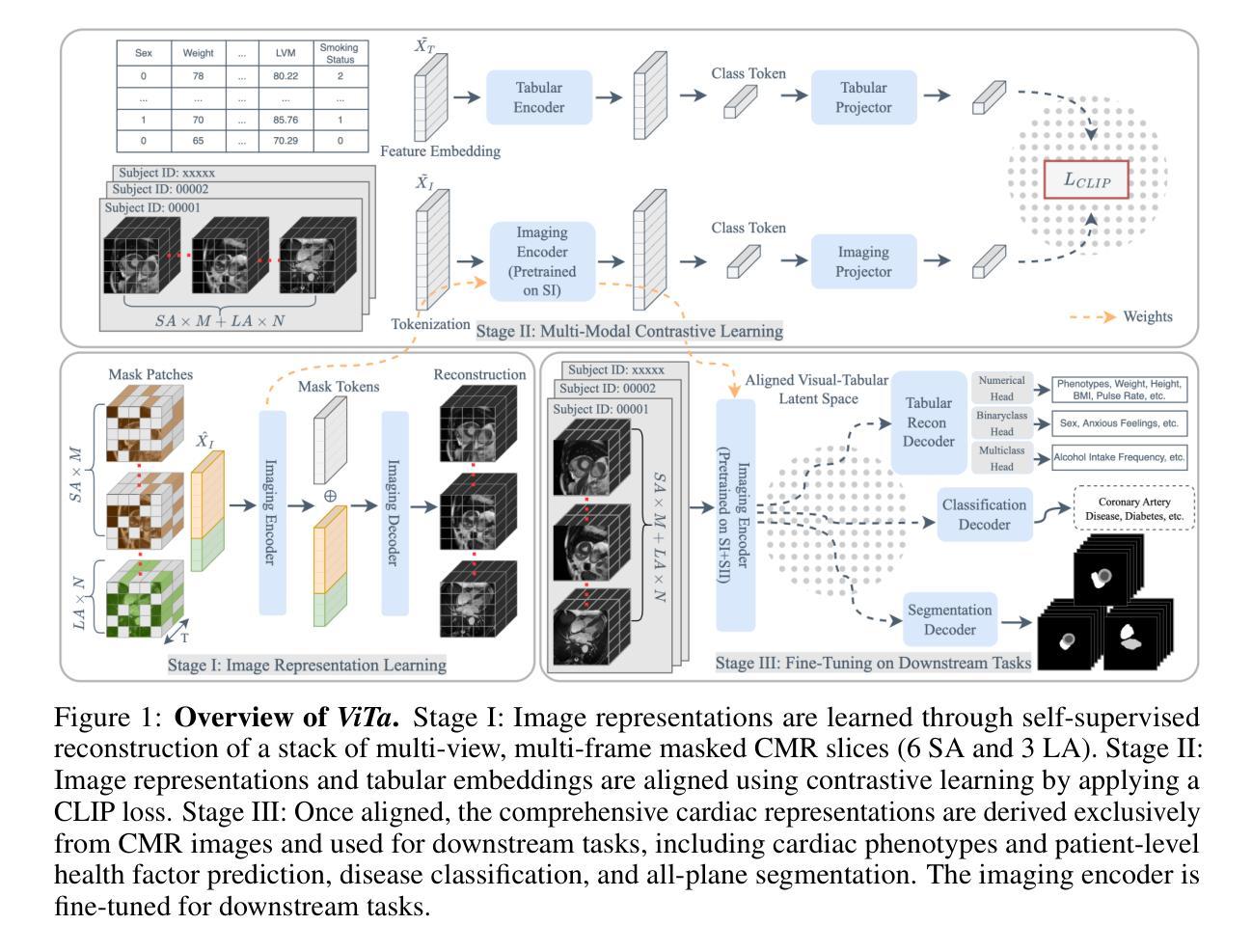
Towards Cardiac MRI Foundation Models: Comprehensive Visual-Tabular Representations for Whole-Heart Assessment and Beyond
Authors:Yundi Zhang, Paul Hager, Che Liu, Suprosanna Shit, Chen Chen, Daniel Rueckert, Jiazhen Pan
Cardiac magnetic resonance imaging is the gold standard for non-invasive cardiac assessment, offering rich spatio-temporal views of the cardiac anatomy and physiology. Patient-level health factors, such as demographics, metabolic, and lifestyle, are known to substantially influence cardiovascular health and disease risk, yet remain uncaptured by CMR alone. To holistically understand cardiac health and to enable the best possible interpretation of an individual’s disease risk, CMR and patient-level factors must be jointly exploited within an integrated framework. Recent multi-modal approaches have begun to bridge this gap, yet they often rely on limited spatio-temporal data and focus on isolated clinical tasks, thereby hindering the development of a comprehensive representation for cardiac health evaluation. To overcome these limitations, we introduce ViTa, a step toward foundation models that delivers a comprehensive representation of the heart and a precise interpretation of individual disease risk. Leveraging data from 42,000 UK Biobank participants, ViTa integrates 3D+T cine stacks from short-axis and long-axis views, enabling a complete capture of the cardiac cycle. These imaging data are then fused with detailed tabular patient-level factors, enabling context-aware insights. This multi-modal paradigm supports a wide spectrum of downstream tasks, including cardiac phenotype and physiological feature prediction, segmentation, and classification of cardiac and metabolic diseases within a single unified framework. By learning a shared latent representation that bridges rich imaging features and patient context, ViTa moves beyond traditional, task-specific models toward a universal, patient-specific understanding of cardiac health, highlighting its potential to advance clinical utility and scalability in cardiac analysis.
心脏磁共振成像(Cardiac magnetic resonance imaging,简称CMR)是非侵入性心脏评估的金标准,能够丰富地展现心脏解剖和生理的时空视图。已知患者层面的健康因素,如人口统计学特征、新陈代谢和生活方式,会对心血管健康和疾病风险产生重大影响,但仅靠CMR无法获取这些信息。为了全面了解心脏健康并能够对个人的疾病风险进行最佳解读,必须在综合框架内共同利用CMR和患者层面的因素。最近的多模态方法已经开始弥合这一差距,但它们往往依赖于有限的时空数据,并专注于孤立的临床任务,从而阻碍了心脏健康评估的综合表现的发展。为了克服这些局限性,我们引入了ViTa,这是朝着基础模型迈出的一步,它提供了心脏的全面表征和对个体疾病风险的精确解读。ViTa利用来自42,000名英国生物银行参与者的数据,融合了短轴和长轴的3D+T电影堆栈,能够完整捕捉心脏周期。然后,这些成像数据与详细的表格患者层面因素相结合,提供情境感知的见解。这种多模态范式支持广泛的下游任务,包括心脏表型预测、生理特征预测、分割以及单一统一框架内的代谢疾病分类等。通过学习与丰富的成像特征和患者上下文相关的共享潜在表征,ViTa超越了传统的任务特定模型,朝着具有患者特异性的心脏健康通用理解的方向发展,这突显了其在心脏分析的临床实用性和可扩展性方面的潜力。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
心脏磁共振成像在非侵入性心脏评估中是金标准,但无法获取患者级别的健康因素(如人口统计、代谢和生活方式等)。为了全面了解心脏健康和解释个体疾病风险,必须联合利用心脏磁共振成像和患者级别因素。ViTa模型通过整合心脏磁共振成像数据和患者级别因素,实现了心脏的全面表示和个体疾病风险的精确解释。该模型支持广泛的下游任务,包括心脏表型预测、生理特征预测、分割和心脏代谢疾病的分类等。
Key Takeaways
- 心脏磁共振成像在非侵入性心脏评估中具有重要地位,但缺乏对患者级别因素的捕捉。
- 患者级别的健康因素,如人口统计、代谢和生活方式,对心血管健康有重要影响。
- ViTa模型整合了心脏磁共振成像数据和患者级别因素,为心脏健康提供了全面的表示。
- ViTa模型利用多维时空数据支持广泛的下游任务,包括心脏表型和生理特征预测等。
- 该模型实现了从传统的任务特定模型向通用患者特定理解心脏的转化。
- ViTa模型的潜力在于提高心脏分析的临床实用性和可扩展性。
点此查看论文截图

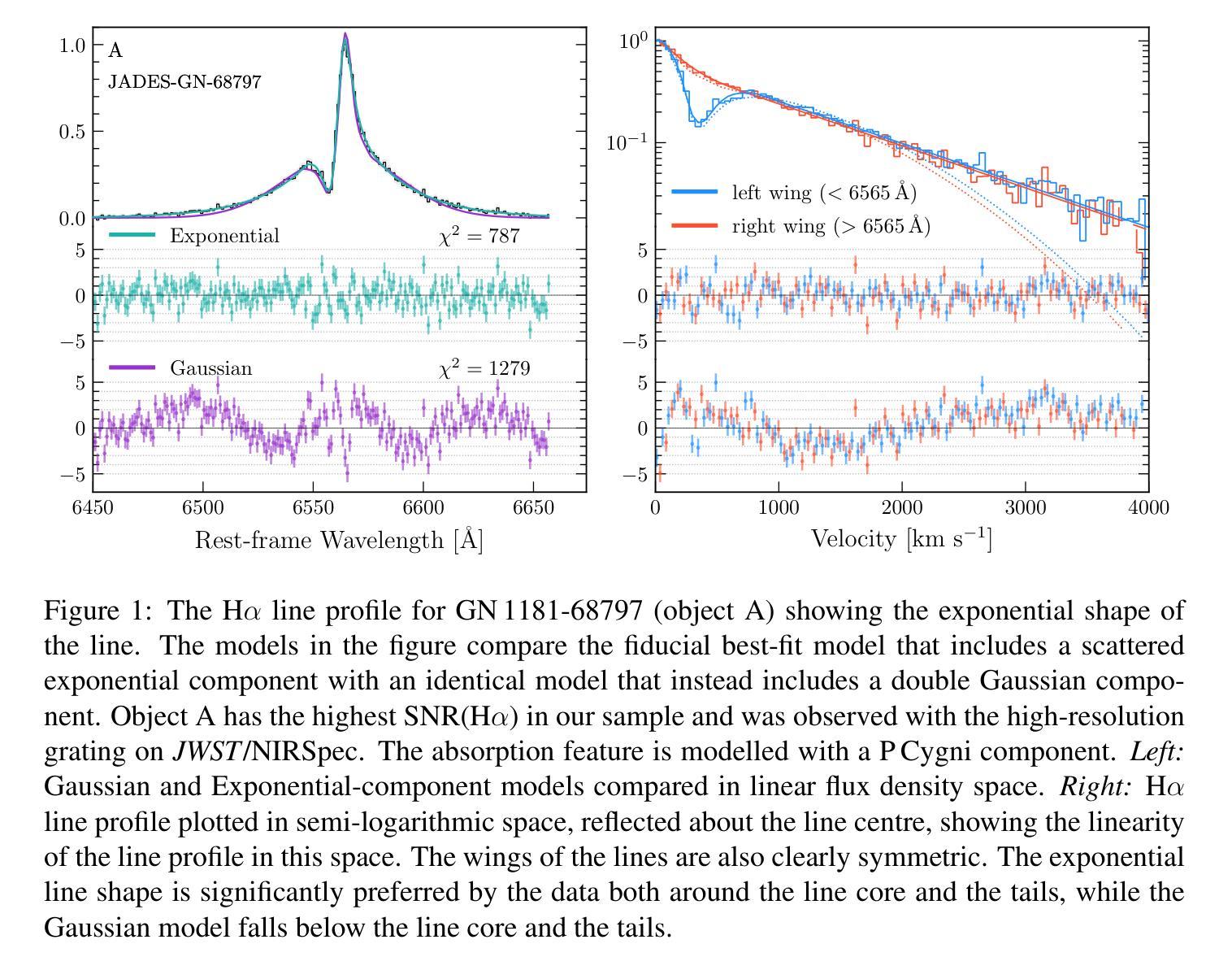
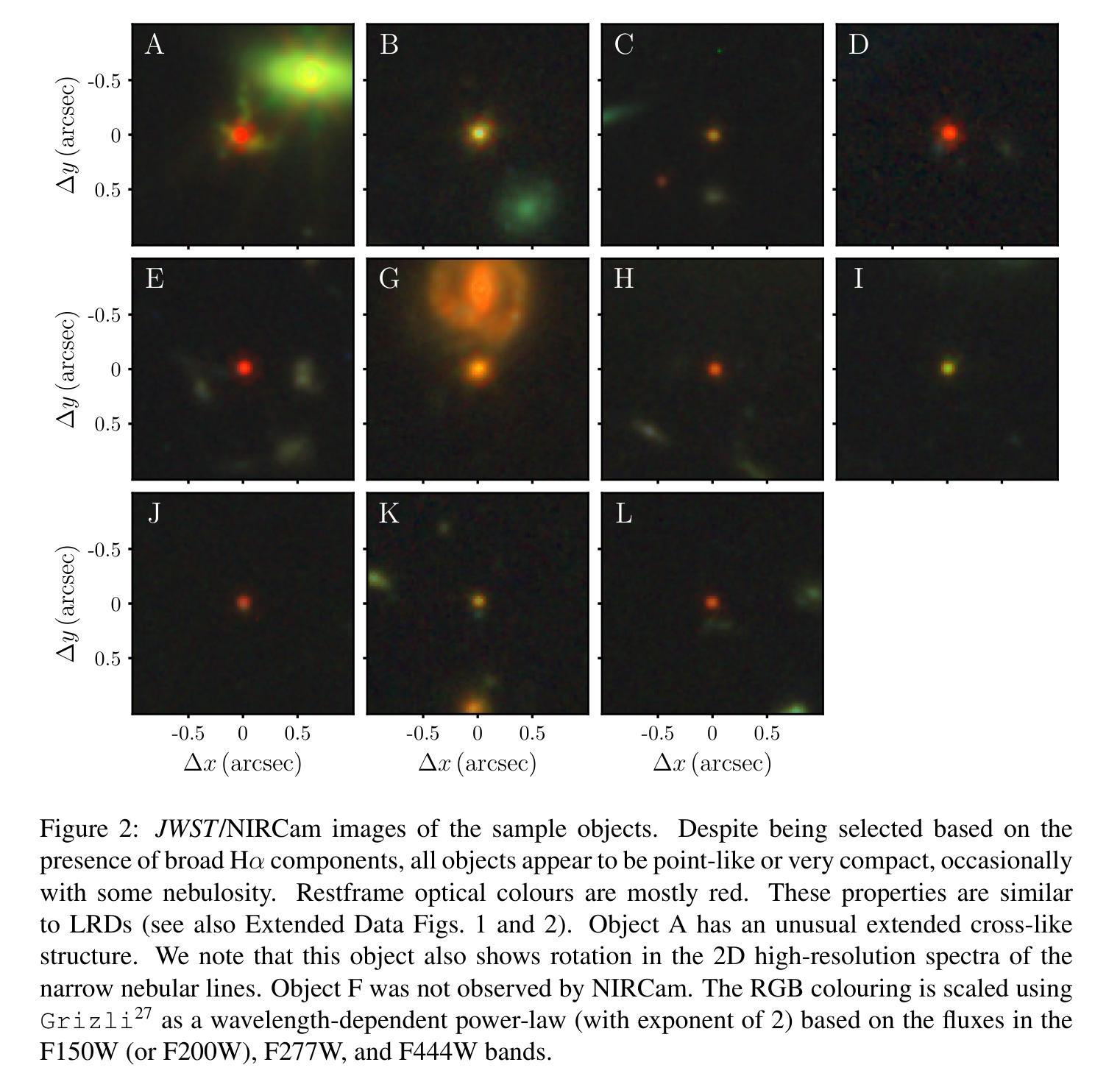
JWST’s little red dots: an emerging population of young, low-mass AGN cocooned in dense ionized gas
Authors:V. Rusakov, D. Watson, G. P. Nikopoulos, G. Brammer, R. Gottumukkala, T. Harvey, K. E. Heintz, R. D. Nielsen, S. A. Sim, A. Sneppen, A. P. Vijayan, N. Adams, D. Austin, C. J. Conselice, C. M. Goolsby, S. Toft, J. Witstok
JWST has uncovered large numbers of compact galaxies at high redshift with broad hydrogen/helium lines. These include the enigmatic population known as “little red dots” (LRDs). Their nature is debated, but they are thought to be powered by supermassive black holes (SMBHs) or intense star formation. They exhibit unusual properties for SMBHs, such as black holes that are overmassive for their host galaxies and extremely weak X-ray and radio emission. Using the highest-quality JWST spectra, we show here that the lines are broadened by electron scattering with a narrow intrinsic line core. The data require high electron column densities and compact sizes (light days), which, when coupled with their high luminosities can only be explained by SMBH accretion. The narrow intrinsic cores of the lines imply upper limits on the black hole masses of $10^{5-7}$ $M_{\odot}$, two orders of magnitude lower than previous estimates. These are among the lowest mass SMBHs known at high redshift and suggest that this is a population of young, rapidly growing SMBHs. They are enshrouded in a dense cocoon of ionized gas, probably related to their youth, from which they are accreting close to the Eddington limit. Reprocessed nebular emission from the dense cocoon dominates the optical spectrum, explaining most LRD spectral characteristics and helping to suppress radio and X-ray emission.
JWST揭示了大量高红移的紧凑星系,具有广泛的氢/氦线。其中包括被称为“小红点”(LRDs)的神秘群体。它们的本质尚存争议,但据认为是由超大质量黑洞(SMBHs)或强烈的恒星形成所驱动的。它们展现出SMBHs的不寻常特性,例如宿主星系的超大质量黑洞和极其微弱的X射线和无线电辐射。我们在这里使用高质量的JWST光谱显示,这些线通过电子散射而展宽,具有狭窄的内在线芯。数据需要高电子柱密度和紧凑大小(光日),当与它们的高光度相结合时,只能由SMBH吸积来解释。线条的狭窄内在核心暗示黑洞质量的上限为$10^{5-7}$ $M_{\odot}$,比先前的估计低两个数量级。这些是在高红移处已知的最低质量SMBHs,表明这是一群年轻且快速生长的SMBHs。它们被密集的离子化气体斗篷所包围,可能与它们的年轻有关,它们正在接近爱丁顿极限进行吸积。来自密集斗篷的再加工星云发射物主导了光学光谱,解释了大多数LRD光谱特征并有助于抑制无线电和X射线辐射。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF 46 pages, 25 figures, 4 tables, submitted to Nature. Updated spectroscopic data ID convention
Summary
JWST发现大量高红移处的紧凑星系,具有宽阔的氢/氦线,包括被称为“小红点”(LRDs)的神秘群体。它们可能由超大质量黑洞(SMBHs)或强烈的恒星形成所驱动,展现出SMBHs的不寻常特性,如相对于宿主星系过于巨大的黑洞,以及极弱的X射线和无线电辐射。利用JWST最高质量的光谱数据,显示这些线路是由电子散射所加宽,具有狭窄的内在线芯。数据需要高电子柱密度和紧凑大小(光日),当与它们的高光度相结合时,只能由SMBH吸积来解释。狭窄的内在线芯对黑洞质量设定了上限,为$10^{5-7}$ $M_{\odot}$,比之前估计低两个数量级。它们是在高红移处已知质量最低的SMBHs之一,表明这是一群年轻的、快速生长的SMBHs。它们被密集的离子化气体包围,可能与它们的年轻有关,正在接近爱丁顿极限进行吸积。重新加工的星云发射从密集的包层中主导了光学光谱,解释了大多数LRD光谱特征,并有助于抑制无线电和X射线辐射。
Key Takeaways
- JWST在高红移处发现了大量紧凑星系,其中含有“小红点”(LRDs)等神秘群体。
- LRDs可能由超大质量黑洞(SMBHs)或强烈的恒星形成所驱动。
- SMBHs展现出不同于常规的特性,如相对宿主星系过于巨大和弱X射线、无线电辐射。
- 高质量的JWST光谱数据显示,线路因电子散射而加宽,具有狭窄的内在线芯。
- 需要高电子柱密度和紧凑大小来解释数据,这暗示了SMBH吸积的可能性。
- 狭窄的内在线芯表明黑洞质量上限较低,说明这些SMBHs可能年轻且正在迅速增长。
点此查看论文截图

A Survey on Self-supervised Contrastive Learning for Multimodal Text-Image Analysis
Authors:Asifullah Khan, Laiba Asmatullah, Anza Malik, Shahzaib Khan, Hamna Asif
Self-supervised learning is a machine learning approach that generates implicit labels by learning underlined patterns and extracting discriminative features from unlabeled data without manual labelling. Contrastive learning introduces the concept of “positive” and “negative” samples, where positive pairs (e.g., variation of the same image/object) are brought together in the embedding space, and negative pairs (e.g., views from different images/objects) are pushed farther away. This methodology has shown significant improvements in image understanding and image text analysis without much reliance on labeled data. In this paper, we comprehensively discuss the terminologies, recent developments and applications of contrastive learning with respect to text-image models. Specifically, we provide an overview of the approaches of contrastive learning in text-image models in recent years. Secondly, we categorize the approaches based on different model structures. Thirdly, we further introduce and discuss the latest advances of the techniques used in the process such as pretext tasks for both images and text, architectural structures, and key trends. Lastly, we discuss the recent state-of-art applications of self-supervised contrastive learning Text-Image based models.
自监督学习是一种机器学习的方法,它通过学习潜在的模式并从无标签数据中提取辨别特征,从而生成隐式标签,而无需手动标注。对比学习引入了“正样本”和“负样本”的概念,其中正样本对(例如,同一图像/对象的变体)被聚集在嵌入空间中,而负样本对(例如,来自不同图像/对象的视图)则被推开。这种方法在图像理解和图像文本分析方面取得了显著的改进,而且不需要大量依赖标注数据。在本文中,我们全面讨论了与文本-图像模型相关的对比学习的术语、最新发展以及应用。具体地,我们概述了近年来文本-图像模型中对比学习的方法。其次,我们根据不同的模型结构对方法进行了分类。此外,我们还介绍了讨论了在过程中使用的最新技术的进展,例如图像和文本的预训练任务、架构结构和关键趋势。最后,我们讨论了基于文本-图像模型的自监督对比学习的最新前沿应用。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
自监督学习通过从非标记数据中学习潜在模式和提取判别特征,生成隐式标签,无需人工标注。对比学习引入了“正样本”和“负样本”的概念,将正样本对拉近嵌入空间,将负样本对推开。此方法在图像理解和文本分析方面显著提高了效果,对标注数据的依赖较小。本文综述了文本图像模型的对比学习术语、最新发展及应用,按模型结构分类,并介绍了最新的技术进展和应用趋势。
Key Takeaways
- 自监督学习是通过学习潜在模式和提取非标记数据的判别特征来生成隐式标签。
- 对比学习在自监督学习中引入正样本和负样本概念,用于拉近或推开样本对在嵌入空间中的距离。
- 对比学习方法在图像理解和文本分析方面显示出显著的效果提升。
- 论文全面讨论了文本图像模型的对比学习术语和最新发展。
- 论文按模型结构分类了对比学习的方法。
- 论文介绍了最新的技术进展,包括图像和文本的预训练任务、架构结构和关键趋势。
点此查看论文截图

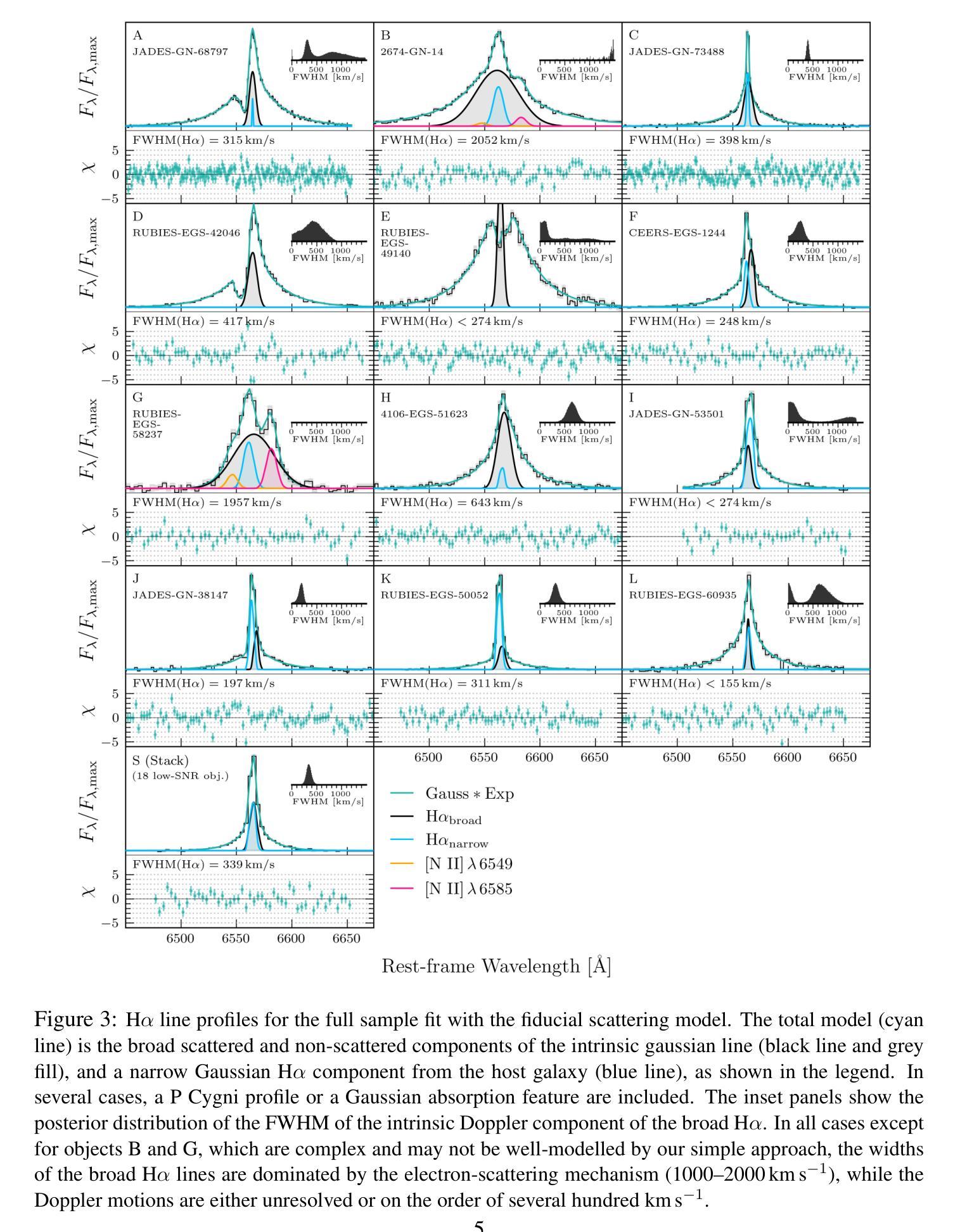
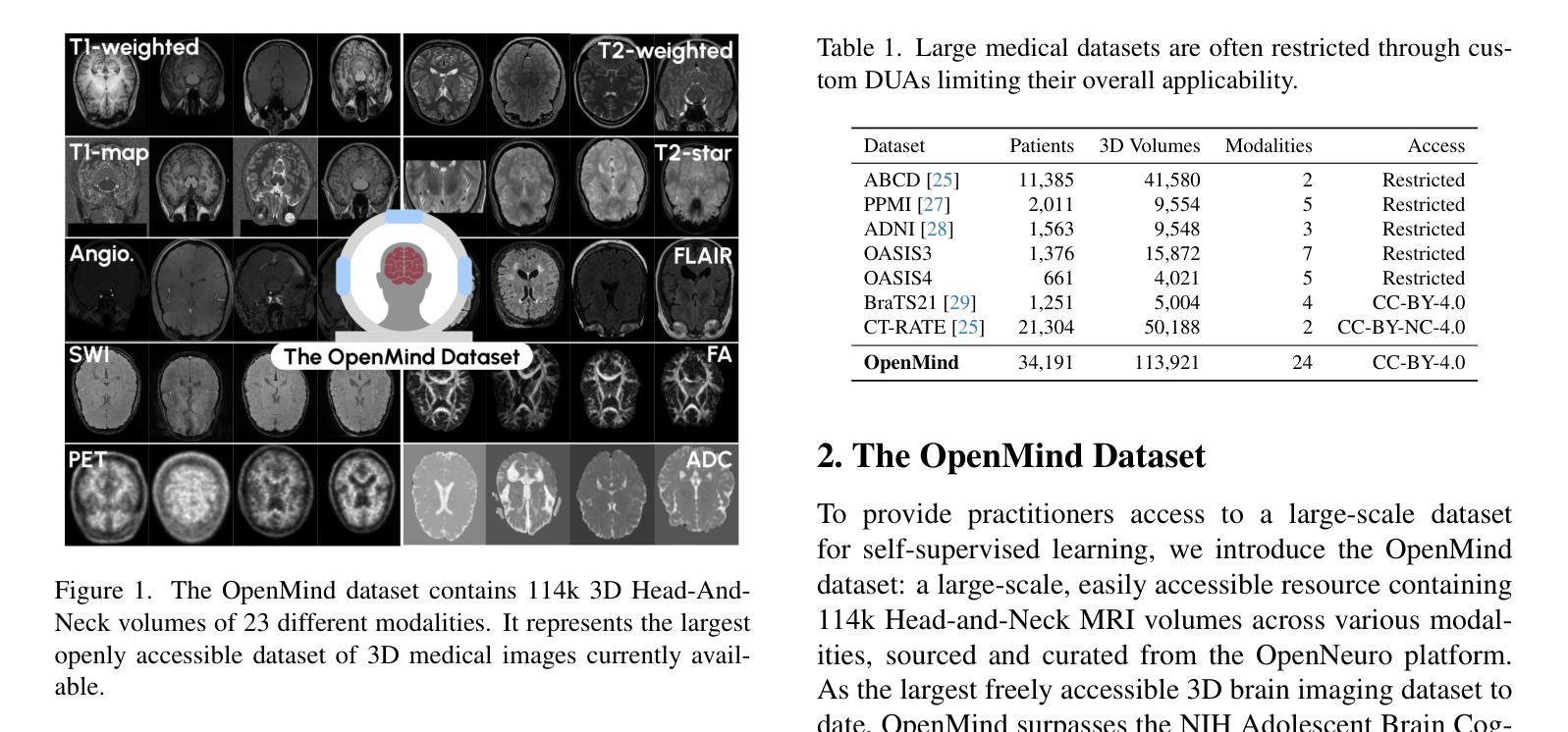
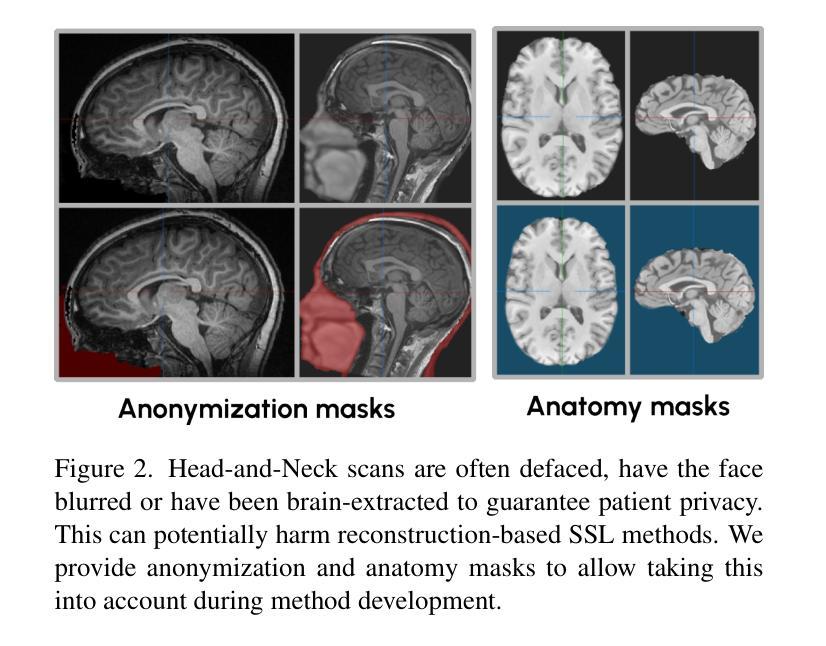
An OpenMind for 3D medical vision self-supervised learning
Authors:Tassilo Wald, Constantin Ulrich, Jonathan Suprijadi, Sebastian Ziegler, Michal Nohel, Robin Peretzke, Gregor Köhler, Klaus H. Maier-Hein
The field of self-supervised learning (SSL) for 3D medical images lacks consistency and standardization. While many methods have been developed, it is impossible to identify the current state-of-the-art, due to i) varying and small pretraining datasets, ii) varying architectures, and iii) being evaluated on differing downstream datasets. In this paper, we bring clarity to this field and lay the foundation for further method advancements through three key contributions: We a) publish the largest publicly available pre-training dataset comprising 114k 3D brain MRI volumes, enabling all practitioners to pre-train on a large-scale dataset. We b) benchmark existing 3D self-supervised learning methods on this dataset for a state-of-the-art CNN and Transformer architecture, clarifying the state of 3D SSL pre-training. Among many findings, we show that pre-trained methods can exceed a strong from-scratch nnU-Net ResEnc-L baseline. Lastly, we c) publish the code of our pre-training and fine-tuning frameworks and provide the pre-trained models created during the benchmarking process to facilitate rapid adoption and reproduction.
自监督学习(SSL)在3D医学图像领域缺乏一致性和标准化。虽然已开发了许多方法,但由于i)预训练数据集各不相同且规模较小,ii)架构各异,以及iii)在不同的下游数据集上进行评估,因此无法确定当前的最先进方法。在本文中,我们通过三个主要贡献使该领域清晰化,并为进一步的方法发展奠定基础:我们a)发布了最大的公开预训练数据集,包含114k个3D大脑MRI体积,使所有从业者都可以在大规模数据集上进行预训练。我们b)在此数据集上对现有的3D自监督学习方法进行基准测试,针对最先进的人工神经网络(CNN)和Transformer架构,明确了3D SSL预训练的状态。我们发现了许多结果,其中表明预训练方法超过了从头开始的nnU-Net ResEnc-L基线。最后,我们c)发布我们的预训练和微调框架的代码,并提供在基准测试过程中创建的预训练模型,以促进快速采用和复现。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF Pre-Print; Dataset, Benchmark and Codebase available through https://github.com/MIC-DKFZ/nnssl
Summary
本文介绍了针对3D医学图像的自监督学习(SSL)领域缺乏一致性和标准化的问题。文章通过三个关键贡献来澄清该领域并为进一步的方法发展奠定基础:发布最大的公开预训练数据集,包含11.4万3D脑部MRI体积,使所有实践者都可以在大规模数据集上进行预训练;在此数据集上对现有3D自监督学习方法进行基准测试,以澄清3D SSL预训练的当前状态;最后,发布预训练和微调框架的代码,并提供在基准测试过程中创建的预训练模型,以促进快速采用和复制。
Key Takeaways
- 3D医学图像自监督学习(SSL)领域缺乏一致性和标准化。
- 文章发布了包含大量数据的最大公开预训练数据集。
- 对现有3D自监督学习方法进行了基准测试,发现预训练的方法可以超越从头开始的nnU-Net ResEnc-L基线。
- 文章提供了预训练和微调框架的代码以及预训练模型,方便其他研究者使用。
- 文章强调了不同预训练数据集、架构以及下游数据集对评估自监督学习方法的影响。
- 文章通过对比不同架构(CNN和Transformer)在基准测试中的表现,为未来的研究提供了方向。
点此查看论文截图

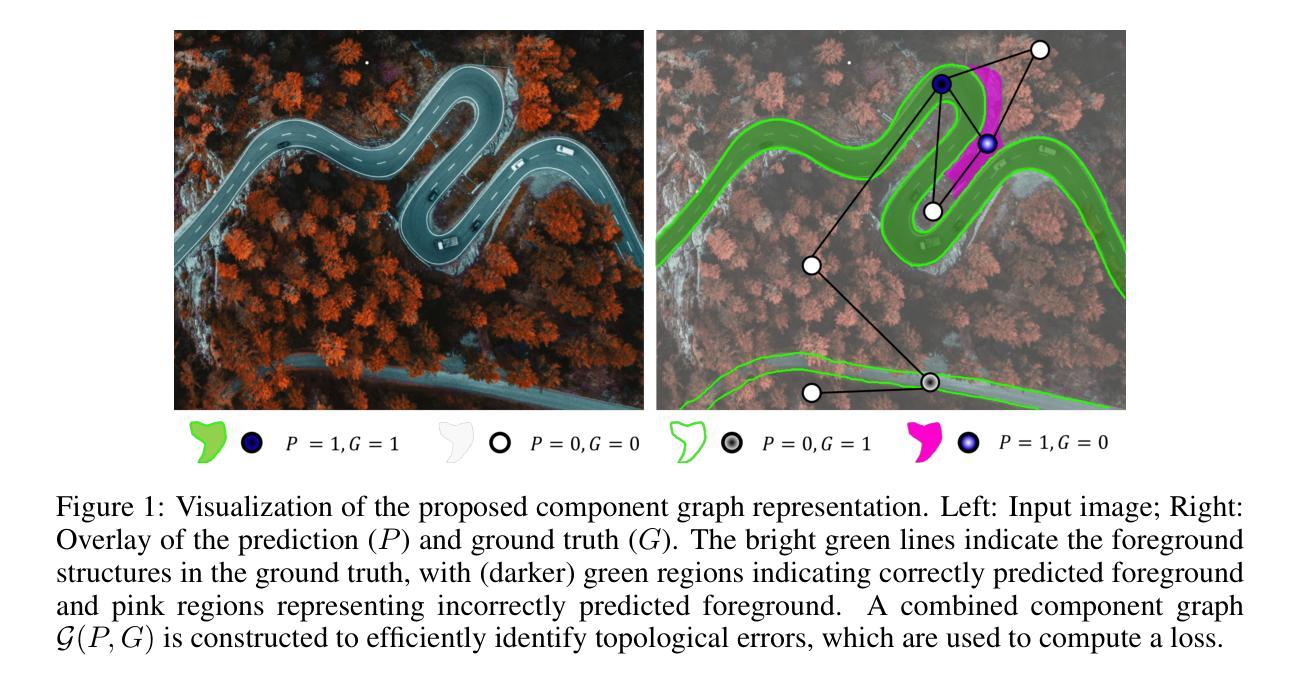
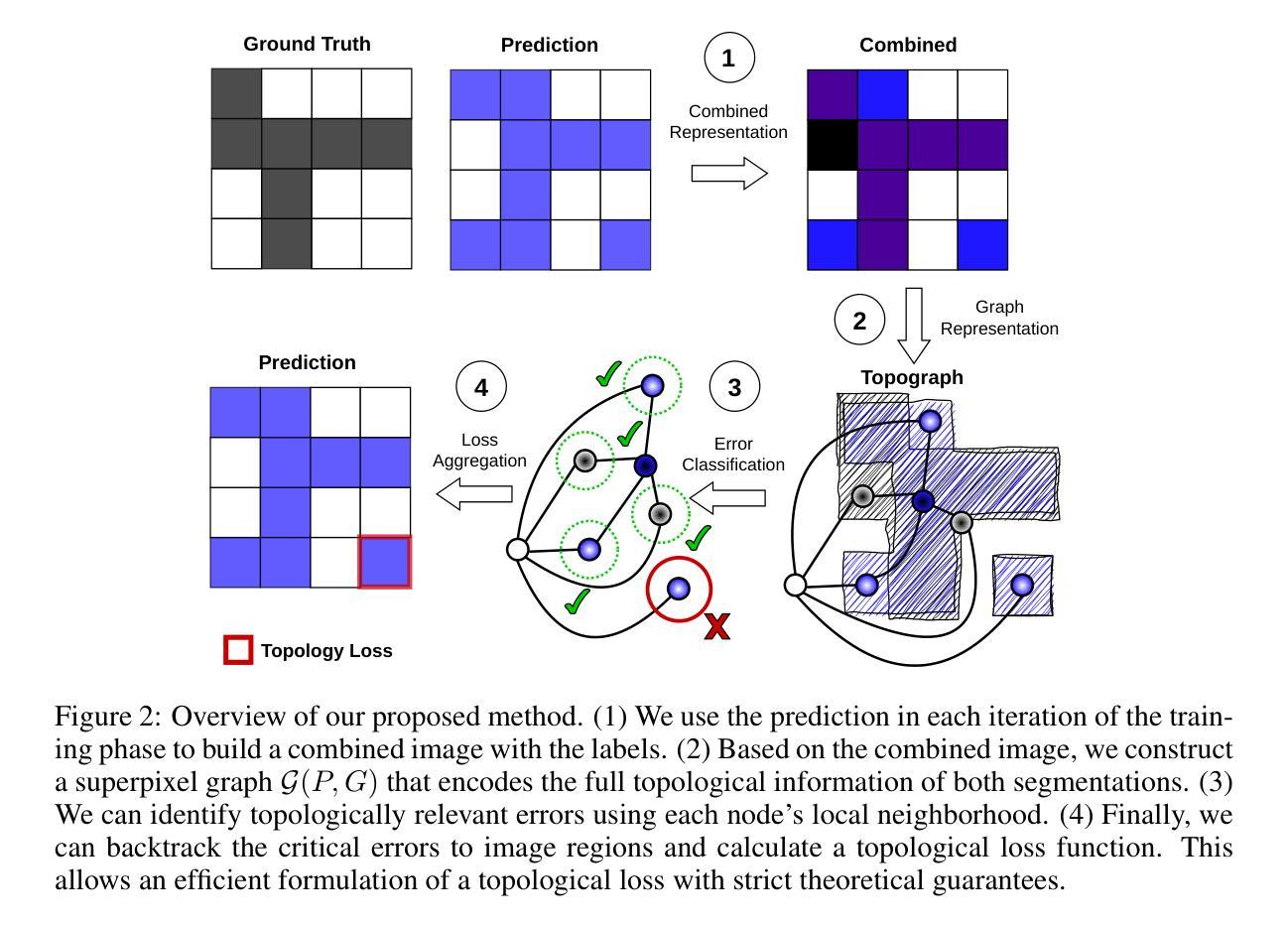
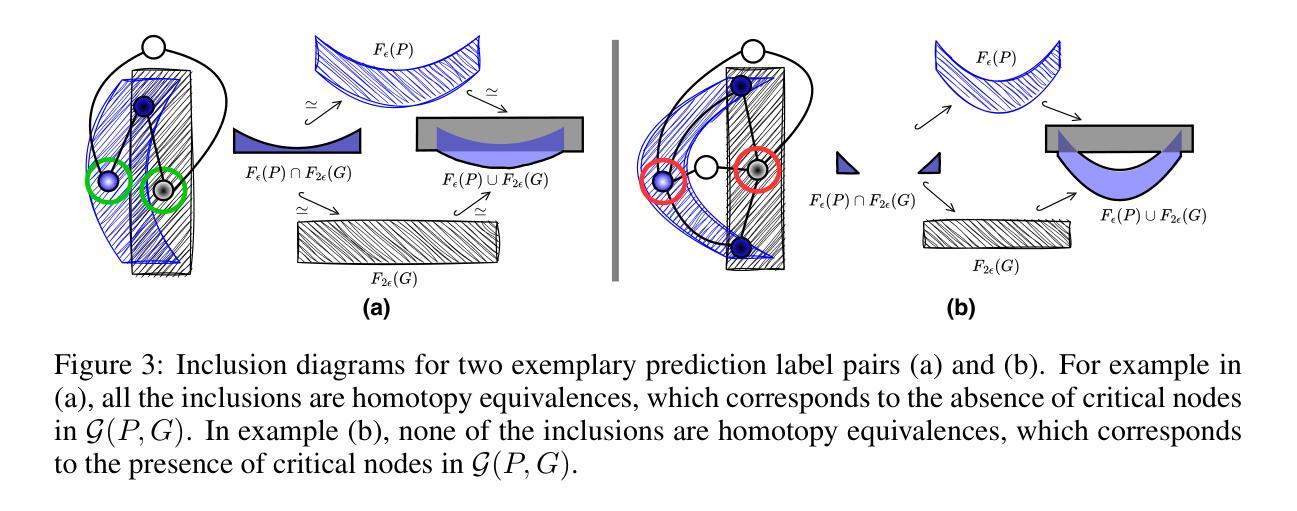
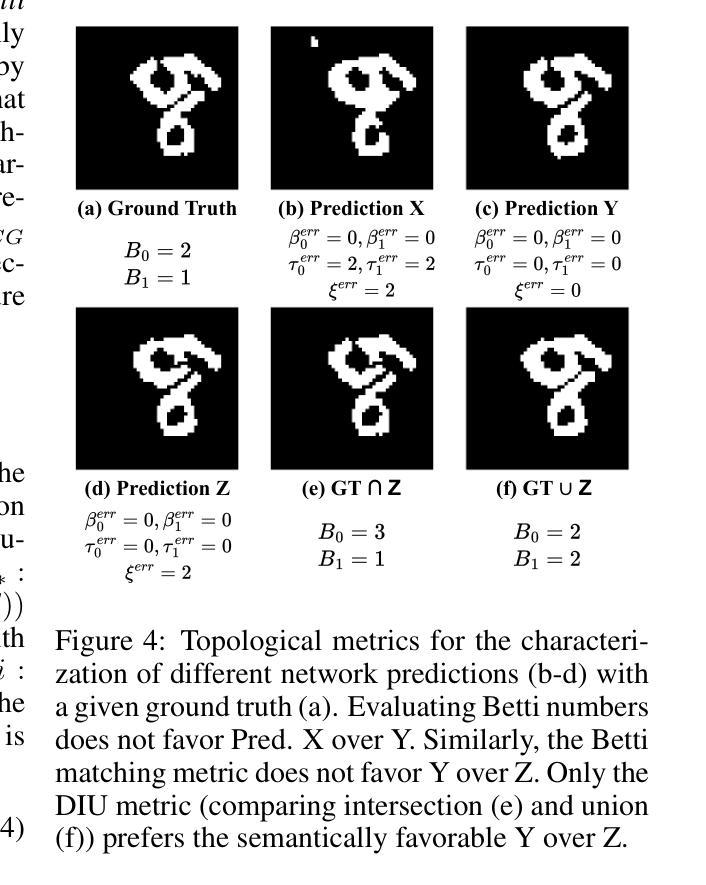
Topograph: An efficient Graph-Based Framework for Strictly Topology Preserving Image Segmentation
Authors:Laurin Lux, Alexander H. Berger, Alexander Weers, Nico Stucki, Daniel Rueckert, Ulrich Bauer, Johannes C. Paetzold
Topological correctness plays a critical role in many image segmentation tasks, yet most networks are trained using pixel-wise loss functions, such as Dice, neglecting topological accuracy. Existing topology-aware methods often lack robust topological guarantees, are limited to specific use cases, or impose high computational costs. In this work, we propose a novel, graph-based framework for topologically accurate image segmentation that is both computationally efficient and generally applicable. Our method constructs a component graph that fully encodes the topological information of both the prediction and ground truth, allowing us to efficiently identify topologically critical regions and aggregate a loss based on local neighborhood information. Furthermore, we introduce a strict topological metric capturing the homotopy equivalence between the union and intersection of prediction-label pairs. We formally prove the topological guarantees of our approach and empirically validate its effectiveness on binary and multi-class datasets. Our loss demonstrates state-of-the-art performance with up to fivefold faster loss computation compared to persistent homology methods.
拓扑正确性在许多图像分割任务中起着至关重要的作用,然而,大多数网络都是使用像素级损失函数(如Dice系数)进行训练的,忽视了拓扑准确性。现有的拓扑感知方法往往缺乏稳健的拓扑保证,仅限于特定用例,或计算成本高昂。在这项工作中,我们提出了一种新型的图论基础框架,用于拓扑准确的图像分割,既计算高效又通用性强。我们的方法构建了一个组件图,该图完全编码了预测和真实标签的拓扑信息,使我们能够高效地识别出拓扑关键区域,并根据局部邻域信息聚合损失。此外,我们引入了一种严格的拓扑度量标准,捕获预测标签对联合与交集之间的同胚等价性。我们正式证明了我们的方法的拓扑保证,并在二进制和多类别数据集上进行了实证验证。我们的损失函数表现出最佳性能,与持久同构方法相比,损失计算速度提高了五倍。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
本文提出一种基于图的新型拓扑精确图像分割框架,该框架能够利用拓扑信息进行高效计算并且具有广泛的应用性。通过构建组件图来全面编码预测和真实值的拓扑信息,该方法能够迅速识别出拓扑关键区域并根据局部邻域信息聚合损失。此外,引入了一种严格的拓扑度量标准,捕获预测标签对并集和交集之间的同胚等价性。该方法在二分类和多分类数据集上均表现出优异性能,且相较于持久同源性方法,损失计算速度提高了五倍。
Key Takeaways
- 拓扑正确性在图像分割任务中起关键作用,但大多数网络使用像素级损失函数进行训练,忽略了拓扑准确性。
- 现有拓扑感知方法常常缺乏稳健的拓扑保证,仅限于特定用例,或计算成本高昂。
- 本文提出了一种新型的图基框架,用于拓扑准确的图像分割,该框架既计算高效又通用性强。
- 通过构建组件图,该方法能够全面编码预测和真实值的拓扑信息。
- 引入了一种严格的拓扑度量标准,用于捕获预测标签对的拓扑等价性。
- 该方法具有形式化的拓扑保证,并在二分类和多分类数据集上进行了实证验证。
点此查看论文截图

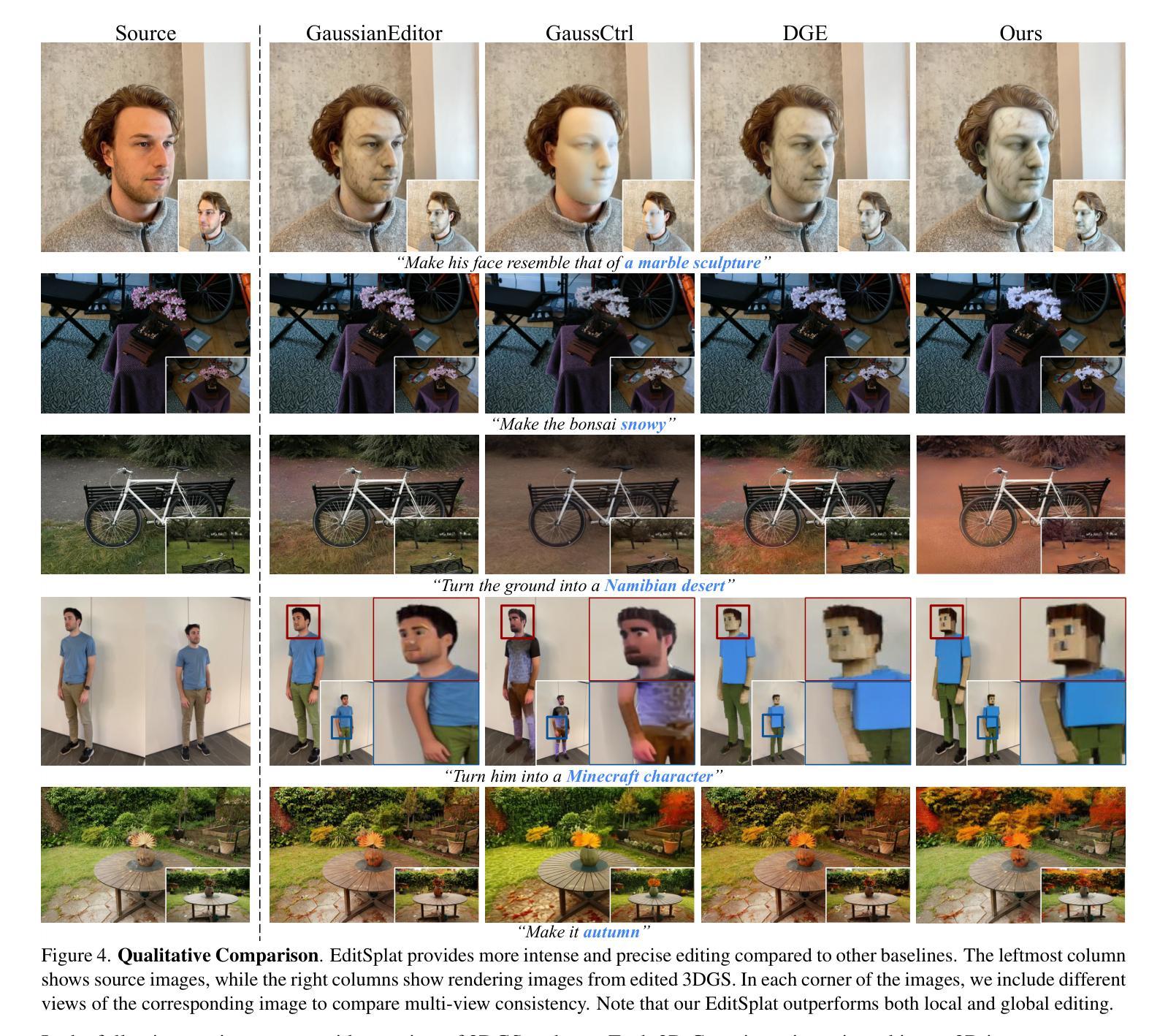
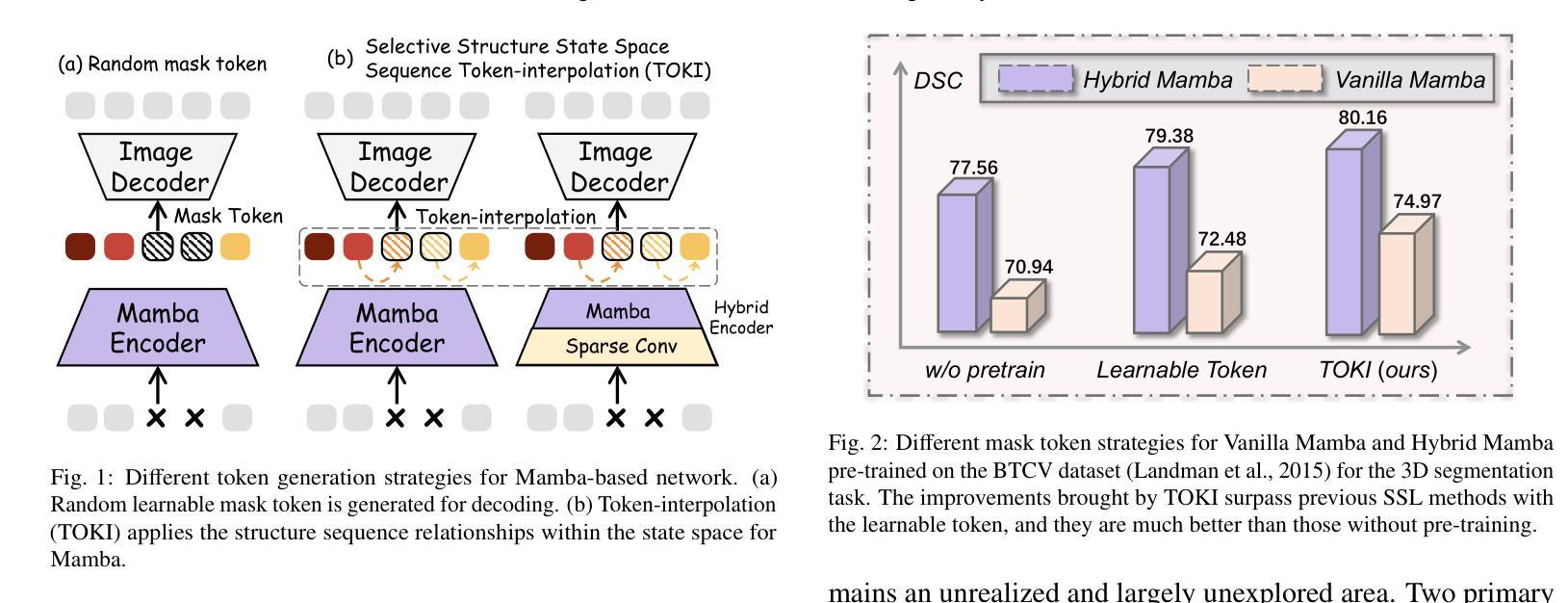
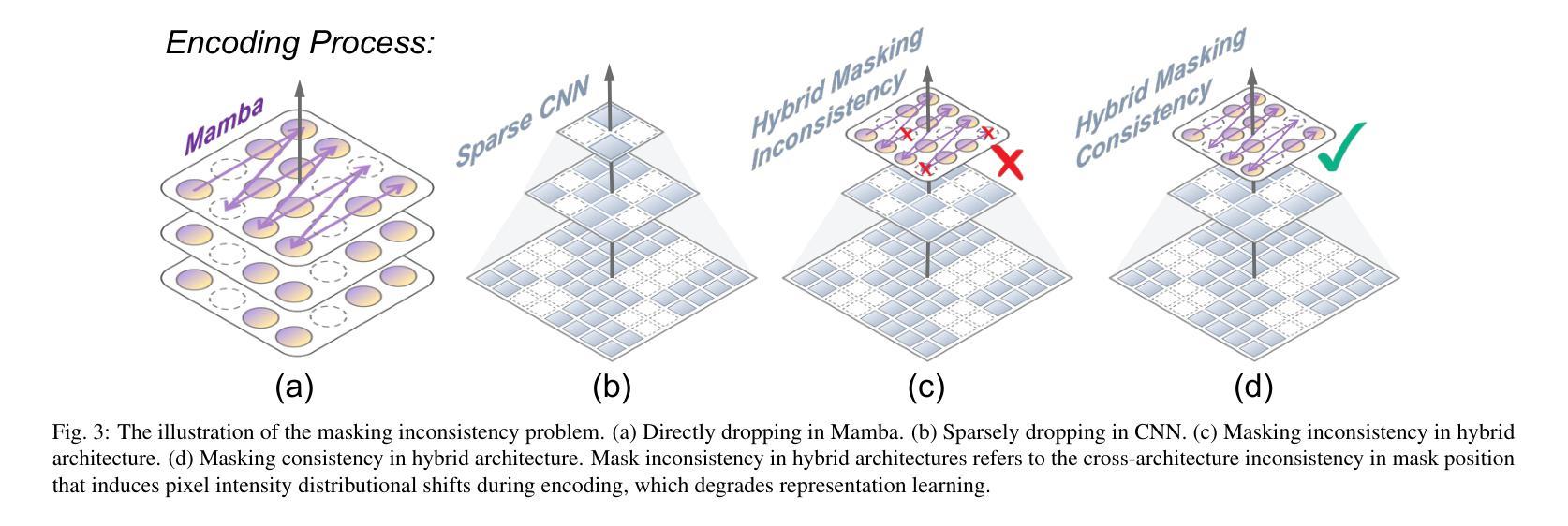
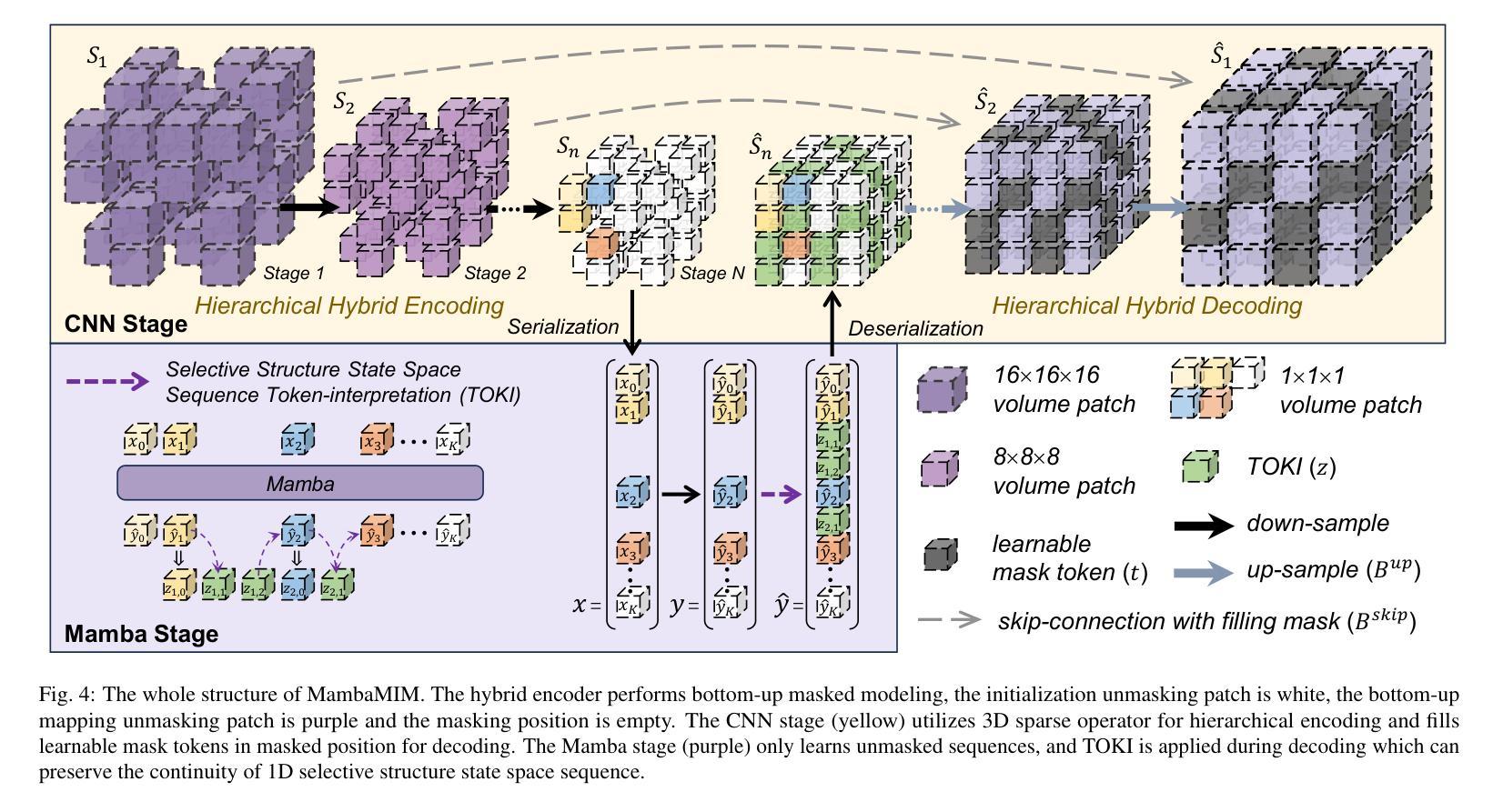
MambaMIM: Pre-training Mamba with State Space Token Interpolation and its Application to Medical Image Segmentation
Authors:Fenghe Tang, Bingkun Nian, Yingtai Li, Zihang Jiang, Jie Yang, Wei Liu, S. Kevin Zhou
Recently, the state space model Mamba has demonstrated efficient long-sequence modeling capabilities, particularly for addressing long-sequence visual tasks in 3D medical imaging. However, existing generative self-supervised learning methods have not yet fully unleashed Mamba’s potential for handling long-range dependencies because they overlook the inherent causal properties of state space sequences in masked modeling. To address this challenge, we propose a general-purpose pre-training framework called MambaMIM, a masked image modeling method based on a novel TOKen-Interpolation strategy (TOKI) for the selective structure state space sequence, which learns causal relationships of state space within the masked sequence. Further, MambaMIM introduces a bottom-up 3D hybrid masking strategy to maintain a masking consistency across different architectures and can be used on any single or hybrid Mamba architecture to enhance its multi-scale and long-range representation capability. We pre-train MambaMIM on a large-scale dataset of 6.8K CT scans and evaluate its performance across eight public medical segmentation benchmarks. Extensive downstream experiments reveal the feasibility and advancement of using Mamba for medical image pre-training. In particular, when we apply the MambaMIM to a customized architecture that hybridizes MedNeXt and Vision Mamba, we consistently obtain the state-of-the-art segmentation performance. The code is available at: https://github.com/FengheTan9/MambaMIM.
最近,状态空间模型Mamba在长时间序列建模方面表现出了高效的性能,特别是在处理三维医学影像中的长时间序列视觉任务方面。然而,现有的生成式自监督学习方法尚未充分发挥Mamba在处理长距离依赖关系方面的潜力,因为它们忽略了状态空间序列在掩模建模中的固有因果特性。为了解决这一挑战,我们提出了一种通用的预训练框架,称为MambaMIM。这是一种基于新型TOKEN插值策略(TOKI)的掩模图像建模方法,用于选择性结构状态空间序列,学习掩模序列中状态空间的因果关系。此外,MambaMIM引入了一种自下而上的三维混合掩模策略,以在不同架构之间保持掩模的一致性,并且可以在任何单一或混合Mamba架构上使用,以增强其多尺度和长距离表示能力。我们在包含六千八百个CT扫描的大规模数据集上预训练了MambaMIM,并在八个公共医学分割基准上评估了其性能。大量的下游实验验证了使用Mamba进行医学图像预训练的可行性和先进性。特别是当我们将MambaMIM应用于混合MedNeXt和视觉Mamba的定制架构时,我们始终获得最先进的分割性能。代码可从以下网站获取:https://github.com/FengheTan9/MambaMIM。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF Accepted by Medical Image Analysis. Code: https://github.com/FengheTan9/MambaMIM
摘要
Mamba模型具有高效的序列建模能力,特别是处理长期序列视觉任务在3D医学影像方面表现优异。但现有的生成式自监督学习方法未能充分发挥Mamba在处理长期依赖关系方面的潜力,因为它们忽视了状态空间序列的内在因果特性在遮掩建模中的作用。为此,我们提出了一种通用的预训练框架MambaMIM,这是一种基于新型Token插值策略(TOKI)的遮掩图像建模方法,用于选择性结构状态空间序列,学习遮掩序列中状态空间的因果关系。此外,MambaMIM引入了一种自下而上的3D混合遮掩策略,以保持不同架构之间的遮掩一致性,可应用于任何单一或混合Mamba架构,以增强其多尺度和长期表示能力。我们在包含大型CT扫描数据集上预训练了MambaMIM,并在八个公共医学分割基准上评估了其性能。下游实验表明使用Mamba进行医学图像预训练的可行性和先进性。特别是将MambaMIM应用于混合MedNeXt和Vision Mamba的定制架构时,我们获得了领先的分割性能。相关代码已发布在:https://github.com/FengheTan9/MambaMIM。
**关键见解**
1. Mamba模型在处理和解决长期序列视觉任务方面表现出强大的能力,特别是在医学成像领域。
2. 现有的生成式自监督学习方法未充分利用Mamba模型的长期依赖处理潜力,原因是忽视了其状态空间序列的因果特性。
3. 提出了一种新的预训练框架MambaMIM,结合了遮掩图像建模和一种新型的Token插值策略(TOKI)。这有助于学习状态空间序列中的因果关系。
4. MambaMIM引入了混合遮掩策略,以提高模型在多尺度和长期表示方面的能力,同时适用于多种架构。
5. 在大规模医学图像数据集上进行了预训练实验,验证了MambaMIM的有效性。
6. 在多个公共医学分割基准测试中,MambaMIM展现了卓越的性能。特别是当与其他架构结合时,其表现尤为突出。
点此查看论文截图