⚠️ 以下所有内容总结都来自于 大语言模型的能力,如有错误,仅供参考,谨慎使用
🔴 请注意:千万不要用于严肃的学术场景,只能用于论文阅读前的初筛!
💗 如果您觉得我们的项目对您有帮助 ChatPaperFree ,还请您给我们一些鼓励!⭐️ HuggingFace免费体验
2025-04-22 更新
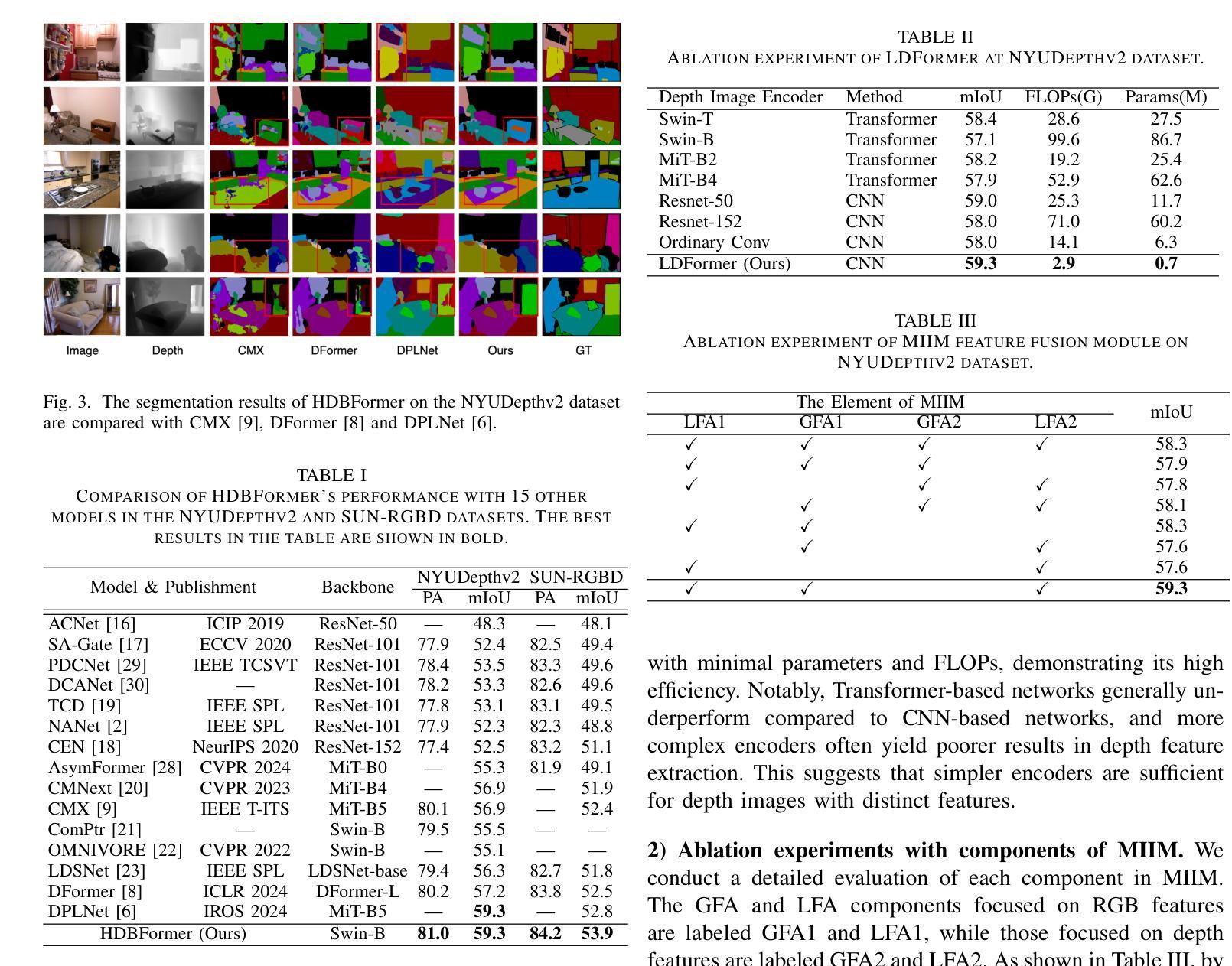
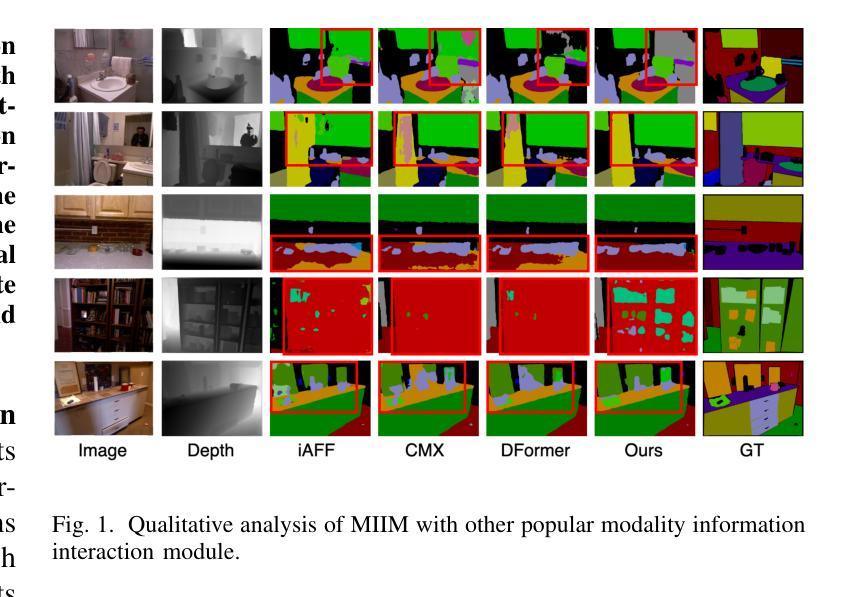
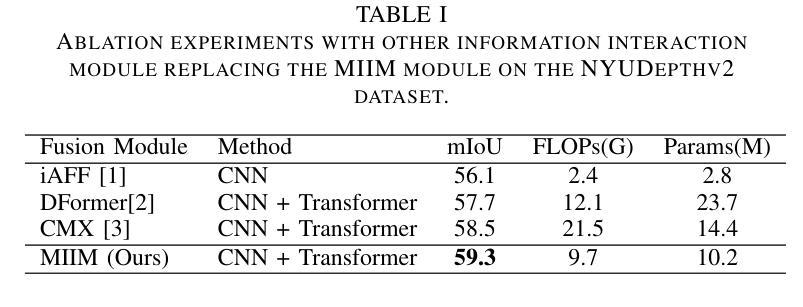
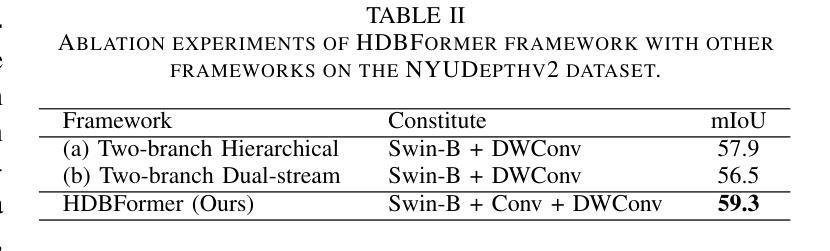
HDBFormer: Efficient RGB-D Semantic Segmentation with A Heterogeneous Dual-Branch Framework
Authors:Shuobin Wei, Zhuang Zhou, Zhengan Lu, Zizhao Yuan, Binghua Su
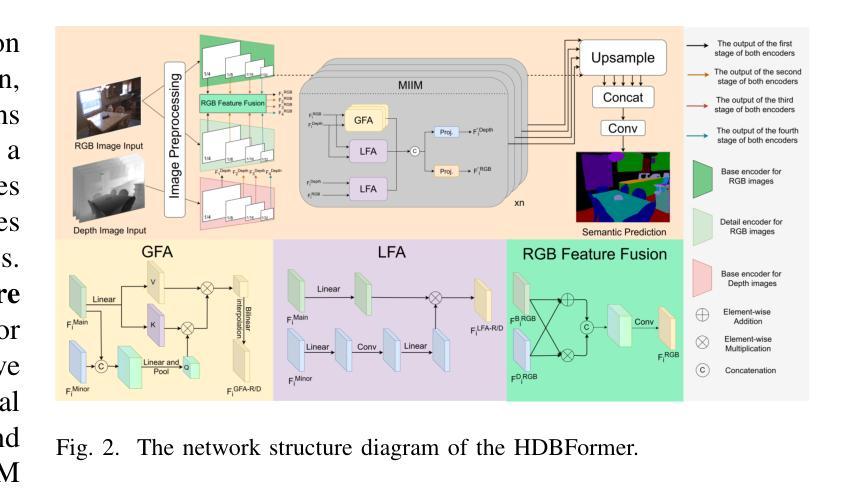
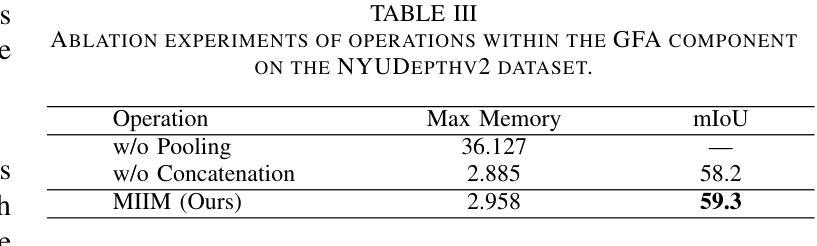
In RGB-D semantic segmentation for indoor scenes, a key challenge is effectively integrating the rich color information from RGB images with the spatial distance information from depth images. However, most existing methods overlook the inherent differences in how RGB and depth images express information. Properly distinguishing the processing of RGB and depth images is essential to fully exploiting their unique and significant characteristics. To address this, we propose a novel heterogeneous dual-branch framework called HDBFormer, specifically designed to handle these modality differences. For RGB images, which contain rich detail, we employ both a basic and detail encoder to extract local and global features. For the simpler depth images, we propose LDFormer, a lightweight hierarchical encoder that efficiently extracts depth features with fewer parameters. Additionally, we introduce the Modality Information Interaction Module (MIIM), which combines transformers with large kernel convolutions to interact global and local information across modalities efficiently. Extensive experiments show that HDBFormer achieves state-of-the-art performance on the NYUDepthv2 and SUN-RGBD datasets. The code is available at: https://github.com/Weishuobin/HDBFormer.
在室内场景的RGB-D语义分割中,一个关键挑战是如何有效地整合RGB图像中的丰富色彩信息与深度图像中的空间距离信息。然而,大多数现有方法忽视了RGB和深度图像在表达信息上的内在差异。正确区分RGB和深度图像的处理对于充分利用它们的独特和显著特征至关重要。为了解决这一问题,我们提出了一种新型异构双分支框架,名为HDBFormer,专门设计用于处理这些模态差异。对于包含丰富细节的RGB图像,我们采用基础编码器和细节编码器来提取局部和全局特征。对于更简单的深度图像,我们提出了LDFormer,这是一种轻量级的分层编码器,能够高效地提取深度特征并且参数更少。此外,我们还引入了模态信息交互模块(MIIM),它将变压器与具有大内核的卷积相结合,以有效地跨模态交互全局和局部信息。大量实验表明,HDBFormer在NYUDepthv2和SUN-RGBD数据集上达到了最先进的性能。代码可用在:https://github.com/Weishuobin/HDBFormer。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF 6 pages, 4 figures, published to IEEE Signal Processing Letter
Summary
本文提出一种针对室内场景RGB-D语义分割的新颖异质双分支框架HDBFormer。该框架区分处理RGB图像和深度图像,分别设计编码器和特征提取模块。实验结果显示,HDBFormer在NYUDepthv2和SUN-RGBD数据集上取得了最佳性能。
Key Takeaways
- RGB-D语义分割面临的关键挑战是整合RGB图像的色彩信息和深度图像的空间距离信息。
- 现有方法忽略了RGB和深度图像表达信息时的内在差异。
- HDBFormer框架被设计来处理不同模态的数据,对RGB图像采用基础与细节编码器提取局部与全局特征,对深度图像采用轻量级分层编码器。
- 引入Modality Information Interaction Module(MIIM),结合变压器和大内核卷积,有效交互跨模态的全局和局部信息。
- HDBFormer在NYUDepthv2和SUN-RGBD数据集上实现了最佳性能。
- 框架的代码已公开可用。
点此查看论文截图

SAR Object Detection with Self-Supervised Pretraining and Curriculum-Aware Sampling
Authors:Yasin Almalioglu, Andrzej Kucik, Geoffrey French, Dafni Antotsiou, Alexander Adam, Cedric Archambeau
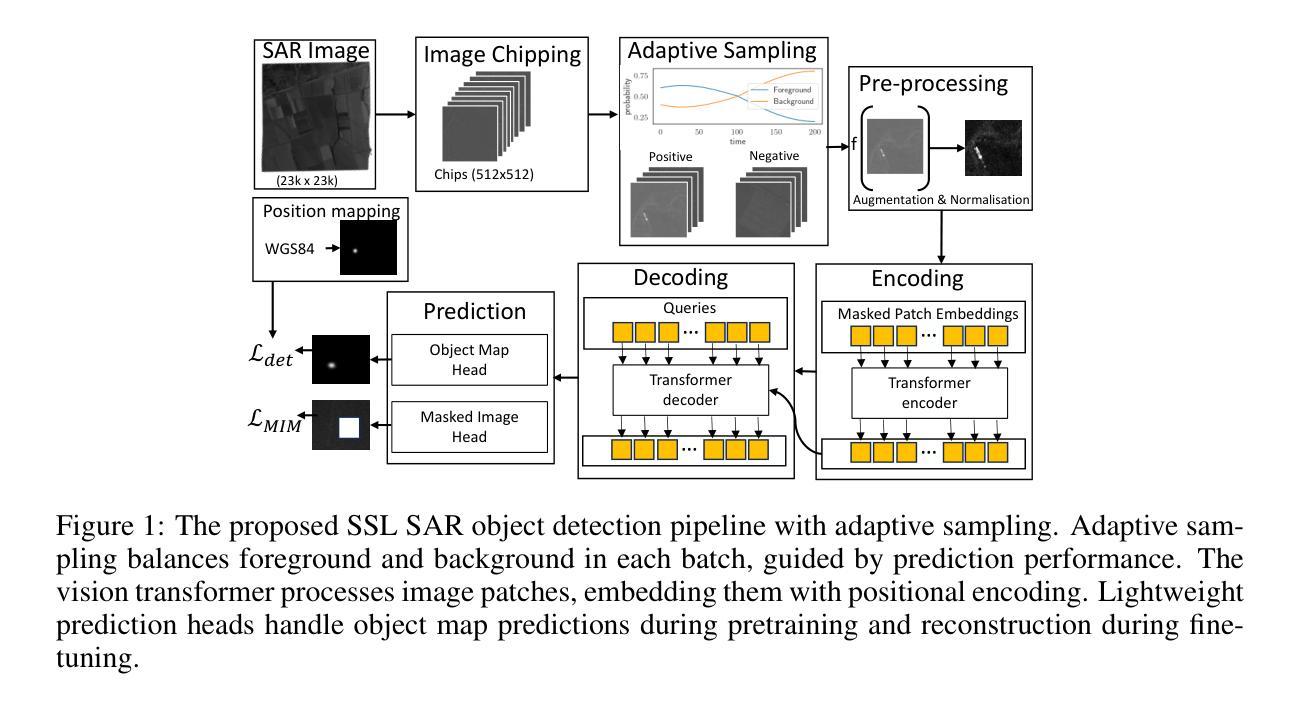
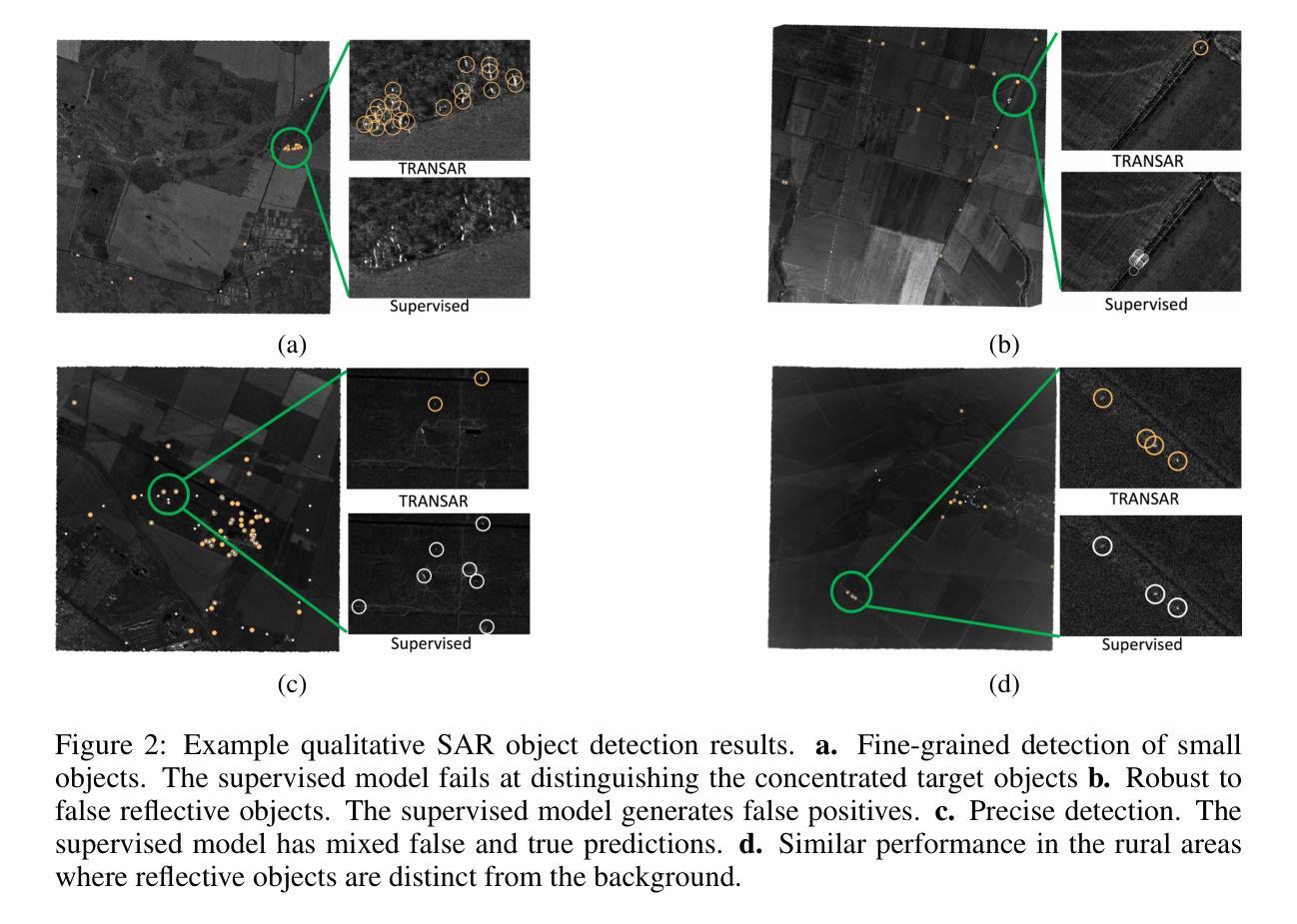
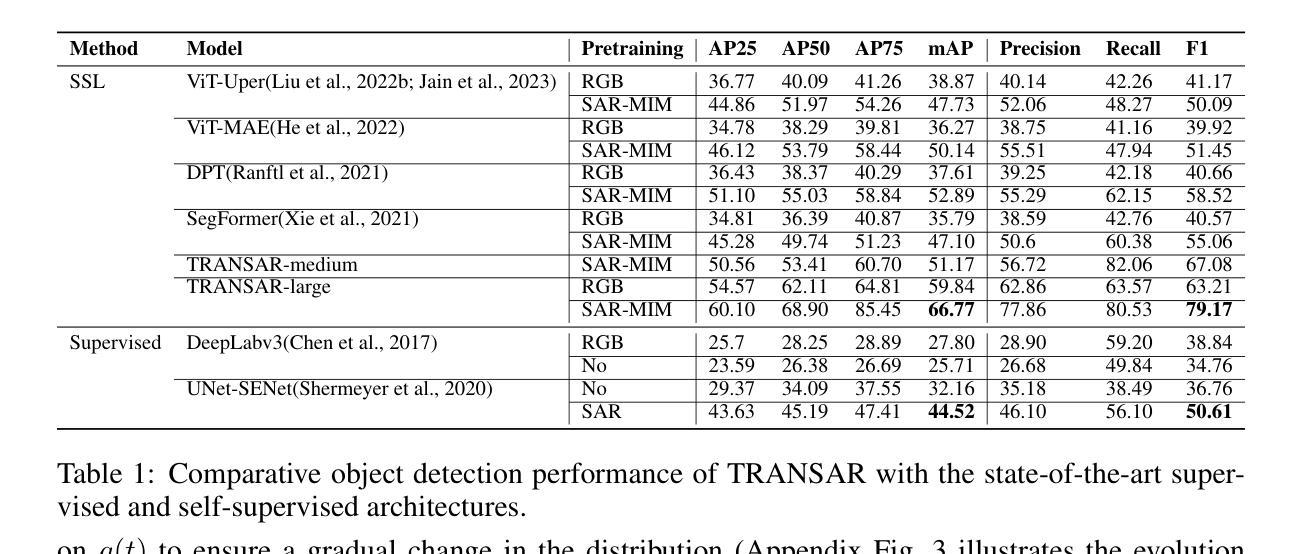
Object detection in satellite-borne Synthetic Aperture Radar (SAR) imagery holds immense potential in tasks such as urban monitoring and disaster response. However, the inherent complexities of SAR data and the scarcity of annotations present significant challenges in the advancement of object detection in this domain. Notably, the detection of small objects in satellite-borne SAR images poses a particularly intricate problem, because of the technology’s relatively low spatial resolution and inherent noise. Furthermore, the lack of large labelled SAR datasets hinders the development of supervised deep learning-based object detection models. In this paper, we introduce TRANSAR, a novel self-supervised end-to-end vision transformer-based SAR object detection model that incorporates masked image pre-training on an unlabeled SAR image dataset that spans more than $25,700$ km\textsuperscript{2} ground area. Unlike traditional object detection formulation, our approach capitalises on auxiliary binary semantic segmentation, designed to segregate objects of interest during the post-tuning, especially the smaller ones, from the background. In addition, to address the innate class imbalance due to the disproportion of the object to the image size, we introduce an adaptive sampling scheduler that dynamically adjusts the target class distribution during training based on curriculum learning and model feedback. This approach allows us to outperform conventional supervised architecture such as DeepLabv3 or UNet, and state-of-the-art self-supervised learning-based arhitectures such as DPT, SegFormer or UperNet, as shown by extensive evaluations on benchmark SAR datasets.
卫星遥感合成孔径雷达(SAR)图像中的目标检测在城市监测和灾害响应等任务中具有巨大潜力。然而,SAR数据固有的复杂性和标注的稀缺性给该领域目标检测的进步带来了重大挑战。特别是卫星SAR图像中小目标的检测是一个特别复杂的问题,因为该技术的空间分辨率相对较低和固有的噪声干扰。此外,缺乏大规模的标注SAR数据集阻碍了基于深度学习的监督式目标检测模型的发展。在本文中,我们介绍了TRANSAR,这是一种新型的基于自我监督的端到端视觉Transformer的SAR目标检测模型。该模型在超过$ 25,700 $平方公里的地面区域的未标记SAR图像数据集上进行了遮挡图像预训练。与传统的目标检测公式不同,我们的方法利用辅助二元语义分割来辅助设计分割感兴趣的物体对象在调准过程中特别的较小目标将其从背景中区分出来。此外为了解决目标相对于图像尺寸的天生的类别不平衡问题,我们引入了自适应采样调度器能够根据课程学习和模型反馈动态调整训练期间的目标类别分布。该方法允许我们在基准SAR数据集上进行了广泛评估表现出色超过了传统的监督架构如DeepLabv3或UNet以及最先进的基于自我监督学习的架构如DPT、SegFormer或UperNet。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF Accepted to ICLR 2025 ML4RS https://ml-for-rs.github.io/iclr2025/
Summary
本文介绍了基于SAR卫星图像的物体检测技术在城市监测和灾害响应等领域的应用潜力。针对SAR数据本身的复杂性和标注数据的稀缺性所带来的挑战,提出了一种名为TRANSAR的新型自监督端到端视觉Transformer模型。该模型通过在未标记的SAR图像数据集上进行掩码图像预训练,并结合辅助二进制语义分割来检测小物体。此外,还引入了一种自适应采样调度器来解决固有的类别不平衡问题。通过对比基准SAR数据集上的评估结果,证明了该方法优于传统的监督架构以及最新的自监督学习架构。
Key Takeaways
- SAR物体检测技术在城市监测和灾害响应等领域具有巨大潜力。
- TRANSAR模型是一种基于自监督学习的SAR物体检测模型,采用视觉Transformer技术。
- TRANSAR模型在未标记的SAR图像数据集上进行掩码图像预训练,并借助辅助二进制语义分割检测小物体。
- 自适应采样调度器解决了类别不平衡问题。
- 对比基准SAR数据集上的评估结果,该方法相较于传统和最新自监督架构具有优越性。
点此查看论文截图

Beneath the Surface: The Role of Underwater Image Enhancement in Object Detection
Authors:Ali Awad, Ashraf Saleem, Sidike Paheding, Evan Lucas, Serein Al-Ratrout, Timothy C. Havens
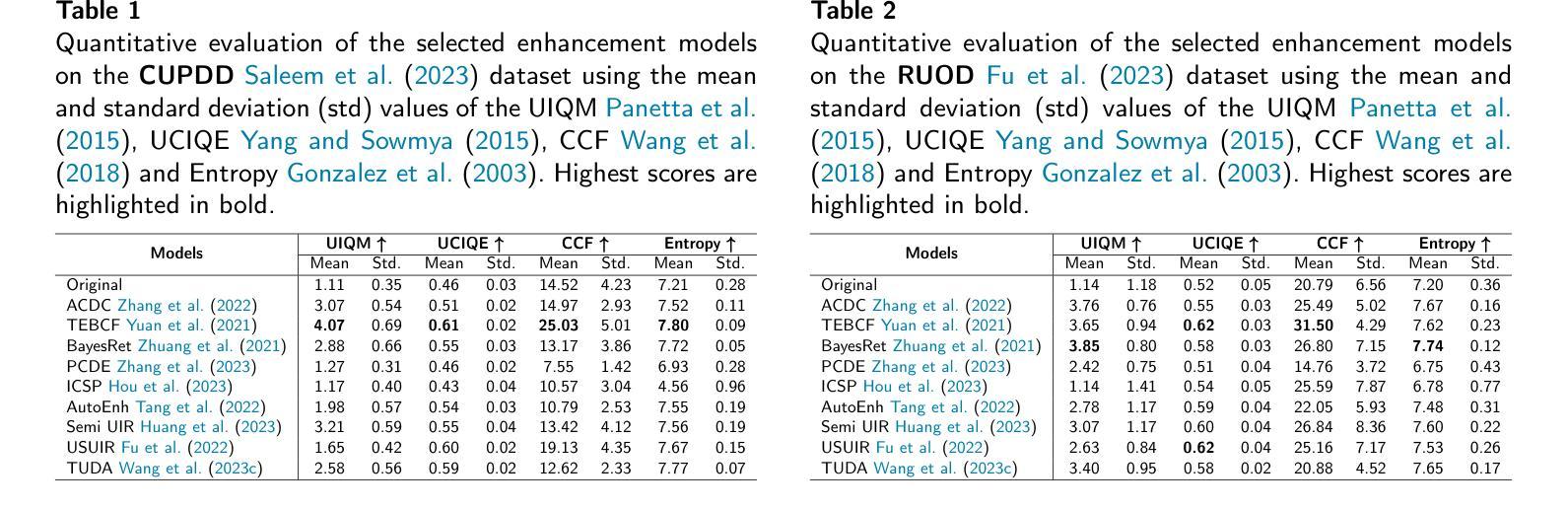
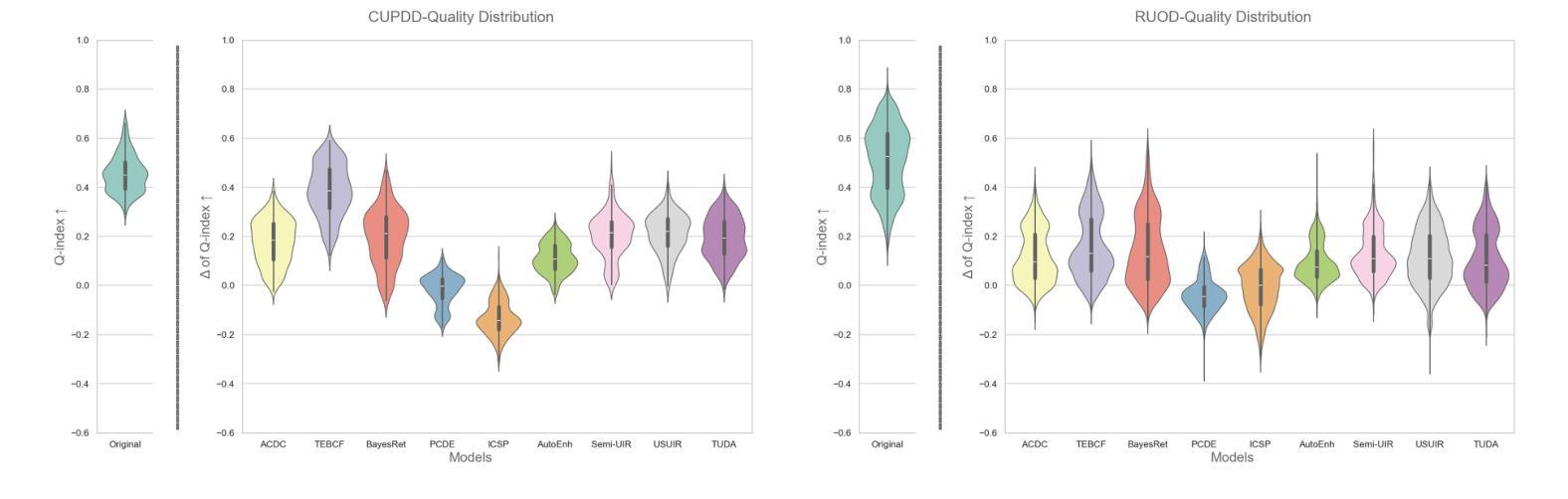
Underwater imagery often suffers from severe degradation resulting in low visual quality and reduced object detection performance. This work aims to evaluate state-of-the-art image enhancement models, investigate their effects on underwater object detection, and explore their potential to improve detection performance. To this end, we apply nine recent underwater image enhancement models, covering physical, non-physical and learning-based categories, to two recent underwater image datasets. Following this, we conduct joint qualitative and quantitative analyses on the original and enhanced images, revealing the discrepancy between the two analyses, and analyzing changes in the quality distribution of the images after enhancement. We then train three recent object detection models on the original datasets, selecting the best-performing detector for further analysis. This detector is subsequently re-trained on the enhanced datasets to evaluate changes in detection performance, highlighting the adverse effect of enhancement on detection performance at the dataset level. Next, we perform a correlation study to examine the relationship between various enhancement metrics and the mean Average Precision (mAP). Finally, we conduct an image-level analysis that reveals images of improved detection performance after enhancement. The findings of this study demonstrate the potential of image enhancement to improve detection performance and provide valuable insights for researchers to further explore the effects of enhancement on detection at the individual image level, rather than at the dataset level. This could enable the selective application of enhancement for improved detection. The data generated, code developed, and supplementary materials are publicly available at: https://github.com/RSSL-MTU/Enhancement-Detection-Analysis.
水下图像往往遭受严重退化,导致视觉质量低下和对象检测性能下降。这项工作旨在评估最先进的图像增强模型,研究它们对水下对象检测的影响,并探索它们提高检测性能的潜力。为此,我们应用九个最近的水下图像增强模型(包括物理类、非物理类和基于学习类),对两个最近的水下图像数据集进行处理。接下来,我们对原始图像和增强后的图像进行定性和定量分析,揭示两种分析之间的差异,并分析增强后图像质量分布的变化。然后我们在原始数据集上训练三个最近的物体检测模型,选取性能最佳的检测器进行进一步分析。该检测器随后在增强数据集上进行再训练,以评估检测性能的变化,突出增强在数据集层面上的不利影响。接下来,我们进行相关性研究,以检查各种增强指标与平均精度(mAP)之间的关系。最后,我们进行了图像层面的分析,揭示了增强后检测性能有所提高的图像。这项研究的结果表明图像增强在提高检测性能方面潜力巨大,并为研究人员进一步探索增强对个体图像层面检测的影响提供了宝贵见解,而不是数据集层面。这可以实现选择性应用增强技术以改善检测效果。生成的数据、开发的代码和补充材料可公开访问:https://github.com/RSSL-MTU/Enhancement-Detection-Analysis。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
本文旨在评估先进的图像增强模型对水下目标检测的影响及其改善检测性能的潜力。研究采用了多种水下图像增强模型,对原始和改进的图像进行了定性和定量分析,并重新训练了目标检测模型以评估性能变化。研究发现,图像增强具有改善检测性能的潜力,但增强效果在不同图像间的差异较大。该分析为研究人员在个体图像层面进一步探索增强对检测的影响提供了有价值的见解。
Key Takeaways
- 本文评估了多种水下图像增强模型对目标检测的影响。
- 通过定性和定量分析,研究了增强模型对图像质量分布的影响。
- 重新训练目标检测模型,评估增强数据集对检测性能的改变。
- 发现增强模型在某些情况下可能对检测性能产生负面影响。
- 强调了进行个体图像层面的增强与检测分析的重要性。
点此查看论文截图