⚠️ 以下所有内容总结都来自于 大语言模型的能力,如有错误,仅供参考,谨慎使用
🔴 请注意:千万不要用于严肃的学术场景,只能用于论文阅读前的初筛!
💗 如果您觉得我们的项目对您有帮助 ChatPaperFree ,还请您给我们一些鼓励!⭐️ HuggingFace免费体验
2025-04-22 更新
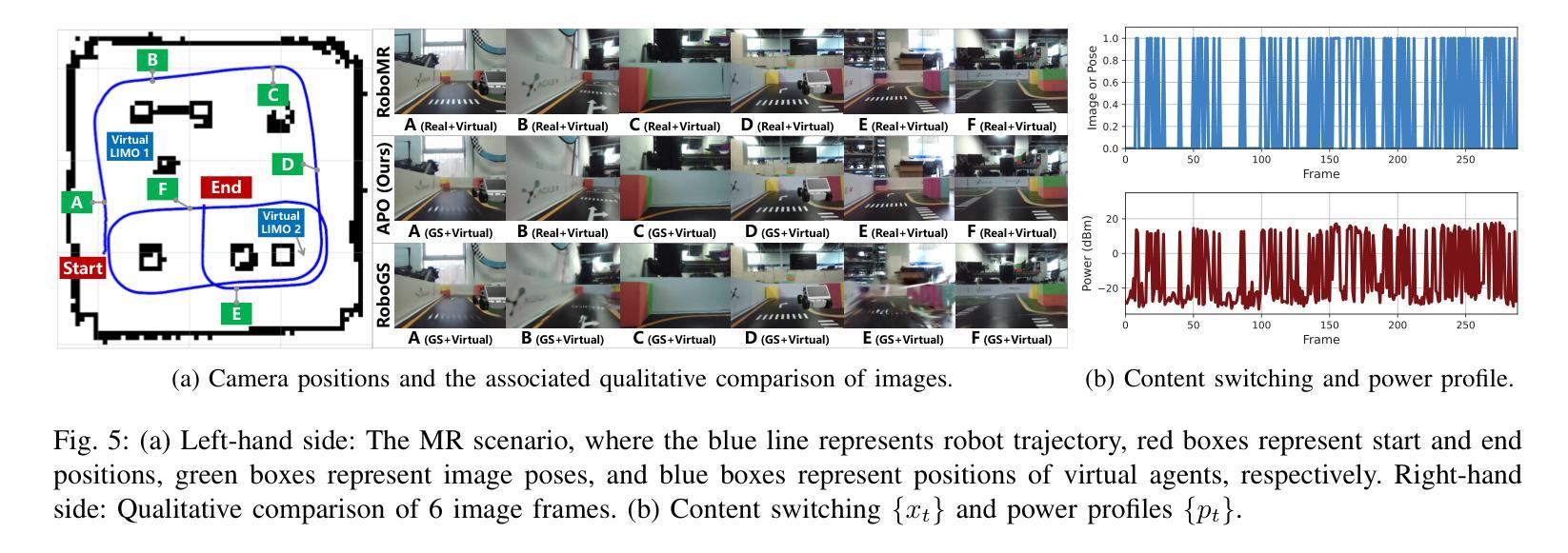
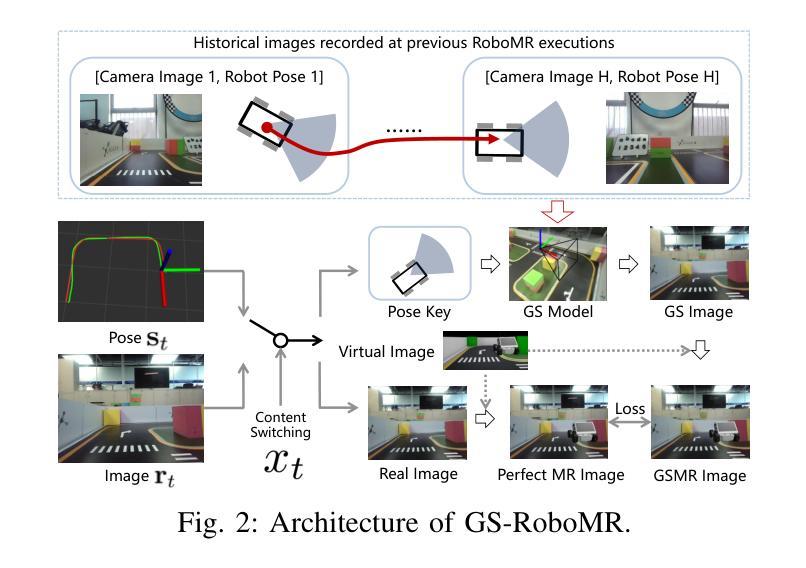
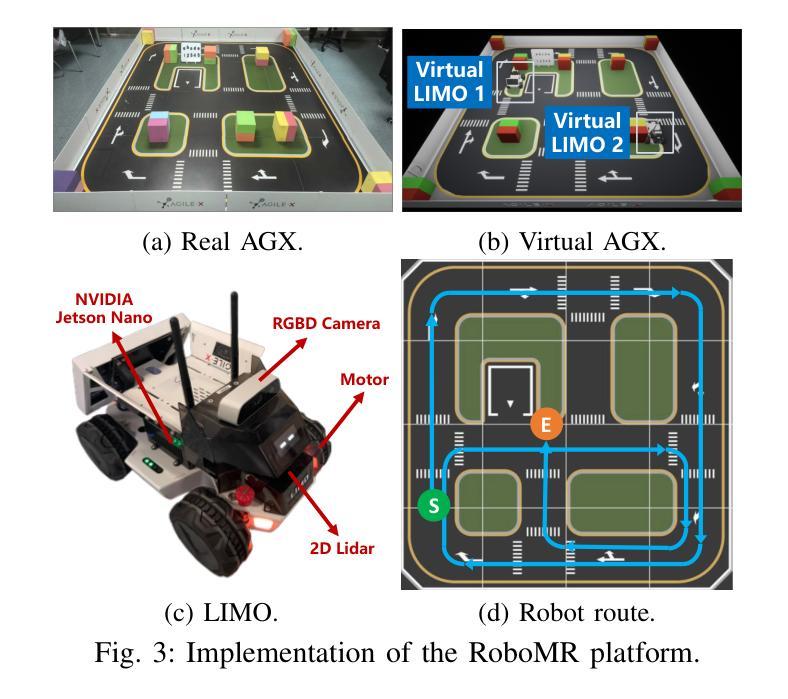
Green Robotic Mixed Reality with Gaussian Splatting
Authors:Chenxuan Liu, He Li, Zongze Li, Shuai Wang, Wei Xu, Kejiang Ye, Derrick Wing Kwan Ng, Chengzhong Xu
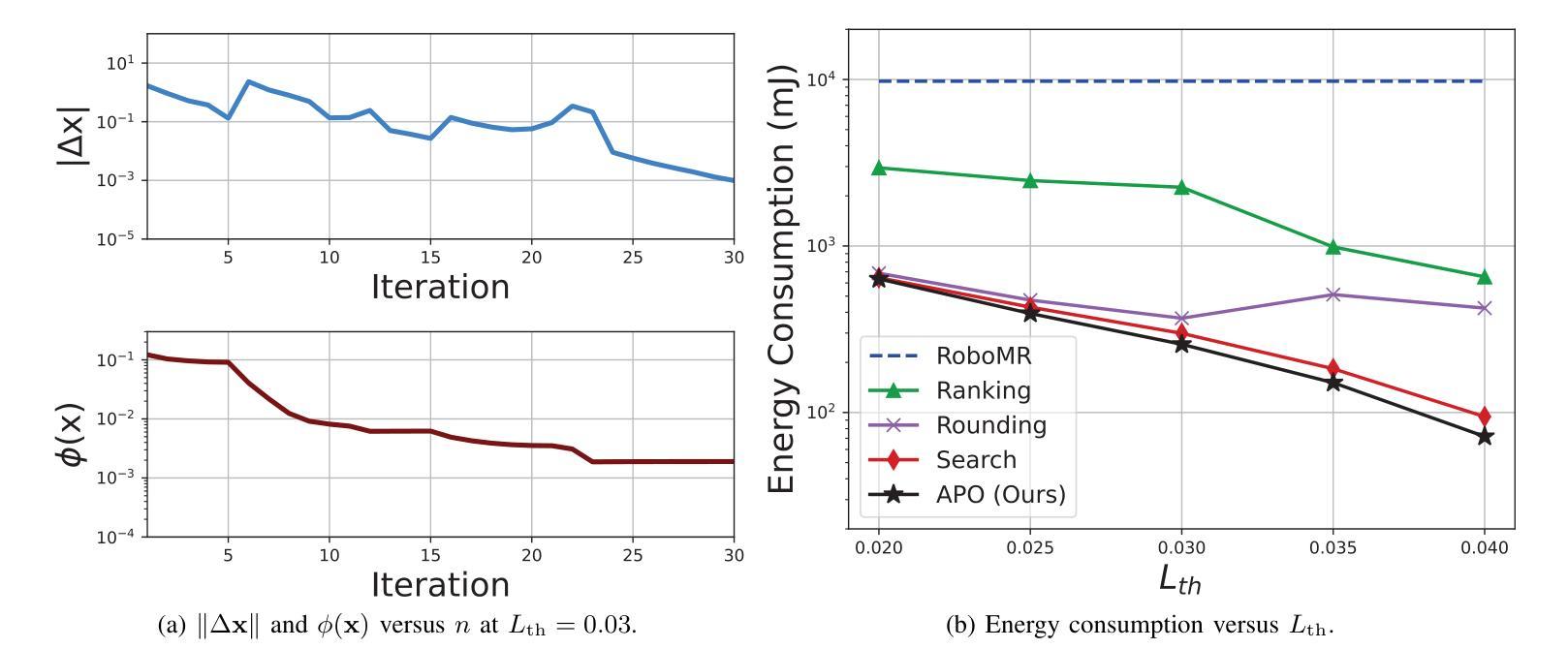
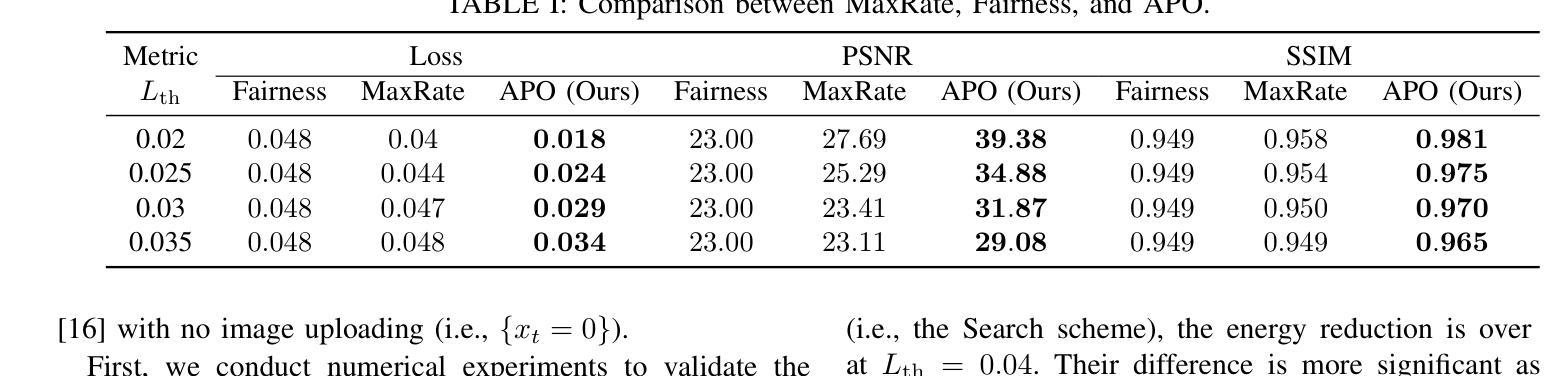
Realizing green communication in robotic mixed reality (RoboMR) systems presents a challenge, due to the necessity of uploading high-resolution images at high frequencies through wireless channels. This paper proposes Gaussian splatting (GS) RoboMR (GSRMR), which achieves a lower energy consumption and makes a concrete step towards green RoboMR. The crux to GSRMR is to build a GS model which enables the simulator to opportunistically render a photo-realistic view from the robot’s pose, thereby reducing the need for excessive image uploads. Since the GS model may involve discrepancies compared to the actual environments, a GS cross-layer optimization (GSCLO) framework is further proposed, which jointly optimizes content switching (i.e., deciding whether to upload image or not) and power allocation across different frames. The GSCLO problem is solved by an accelerated penalty optimization (APO) algorithm. Experiments demonstrate that the proposed GSRMR reduces the communication energy by over 10x compared with RoboMR. Furthermore, the proposed GSRMR with APO outperforms extensive baseline schemes, in terms of peak signal-to-noise ratio (PSNR) and structural similarity index measure (SSIM).
在机器人混合现实(RoboMR)系统中实现绿色通信是一个挑战,因为需要通过无线信道以高频率上传高分辨率图像。本文提出了高斯飞溅(GS)RoboMR(GSRMR),它降低了能耗,是朝着绿色RoboMR迈出的具体一步。GSRMR的关键是建立GS模型,使模拟器能够根据机器人的姿态随机呈现逼真的视图,从而减少过多的图像上传需求。由于GS模型可能与实际环境存在偏差,因此进一步提出了GS跨层优化(GSCLO)框架,该框架联合优化内容切换(即决定是否上传图像)和不同帧之间的功率分配。GSCLO问题通过加速惩罚优化(APO)算法解决。实验表明,与RoboMR相比,所提出的GSRMR将通信能耗降低了超过10倍。此外,与广泛的基线方案相比,带有APO的GSRMR在峰值信噪比(PSNR)和结构相似性指数度量(SSIM)方面表现出更好的性能。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF 6 pages, 5 figures, accepted by IEEE INFOCOM 2025 Workshop on Networked Robotics and Communication Systems
Summary
本文提出一种基于高斯涂抹技术(GS)的机器人混合现实(RoboMR)系统(GSRMR),通过构建GS模型降低高解析度图像的高频上传需求,实现绿色通信。为优化GS模型与实体环境差异,进一步提出GS跨层优化(GSCLO)框架,通过内容切换与功率分配联合优化,采用加速惩罚优化(APO)算法解决GSCLO问题。实验证明,GSRMR系统较传统RoboMR系统能减少超过10倍的通信能耗,并在峰值信噪比(PSNR)和结构相似性指数度量(SSIM)方面优于其他基线方案。
Key Takeaways
- 高频上传高解析度图像是RoboMR系统实现绿色通信的挑战。
- GSRMR通过构建GS模型降低图像上传需求,实现绿色通信。
- GSRMR技术能显著减少通信能耗,较传统RoboMR系统减少超过10倍。
- 为优化GS模型与实体环境的差异,提出GS跨层优化(GSCLO)框架。
- GSCLO框架通过联合优化内容切换和功率分配来解决问题。
- 采用加速惩罚优化(APO)算法解决GSCLO问题。
点此查看论文截图


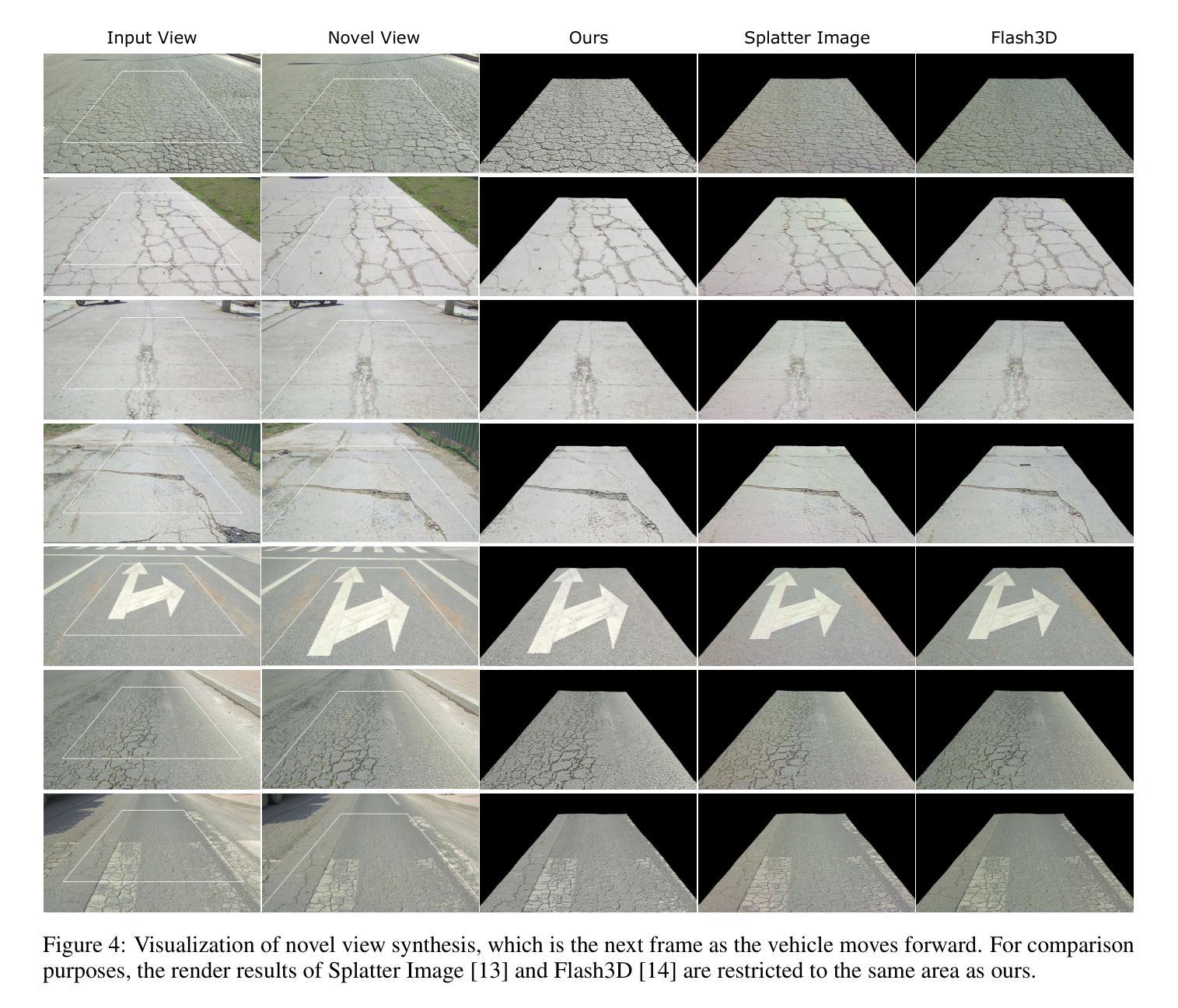
BEV-GS: Feed-forward Gaussian Splatting in Bird’s-Eye-View for Road Reconstruction
Authors:Wenhua Wu, Tong Zhao, Chensheng Peng, Lei Yang, Yintao Wei, Zhe Liu, Hesheng Wang
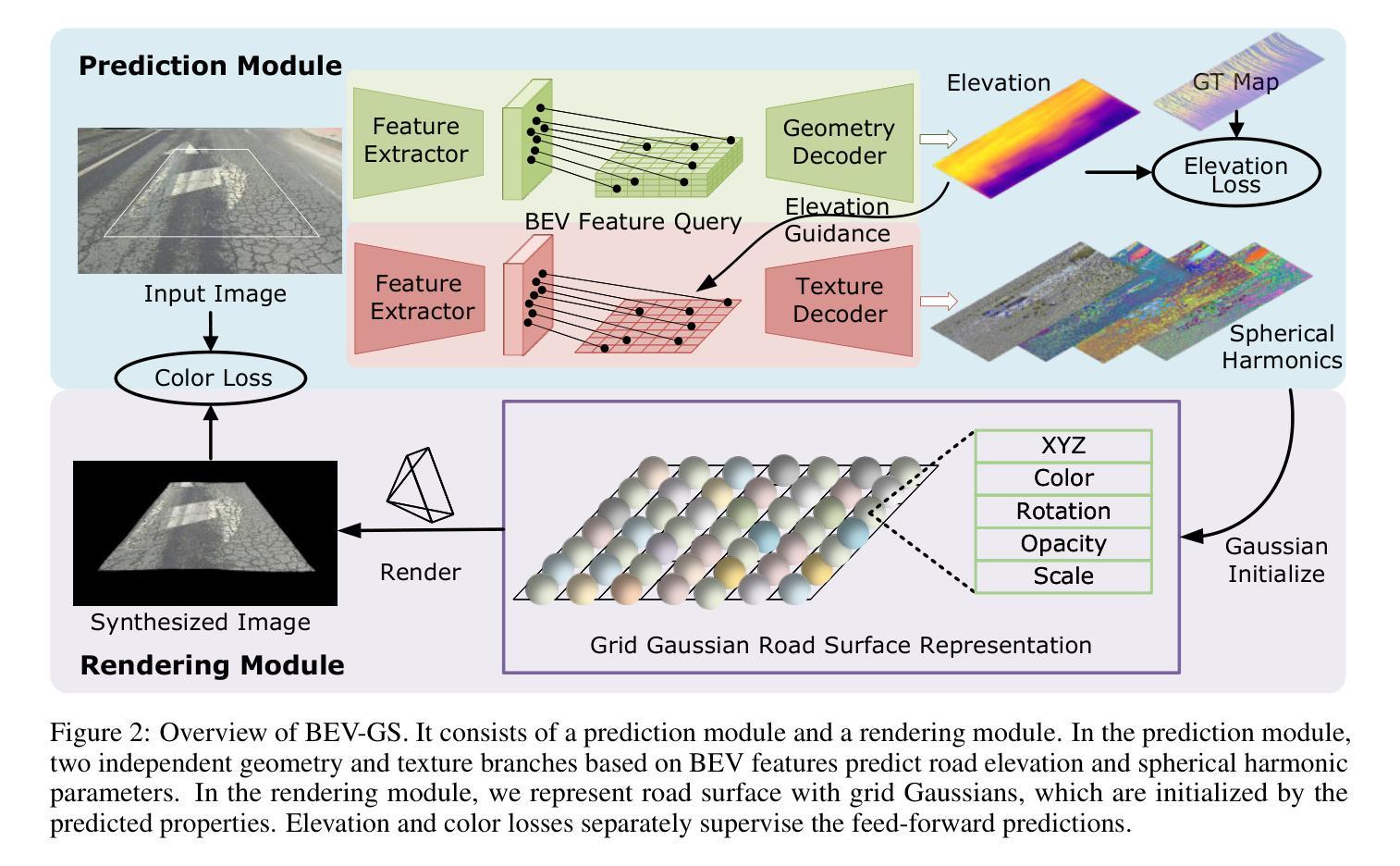
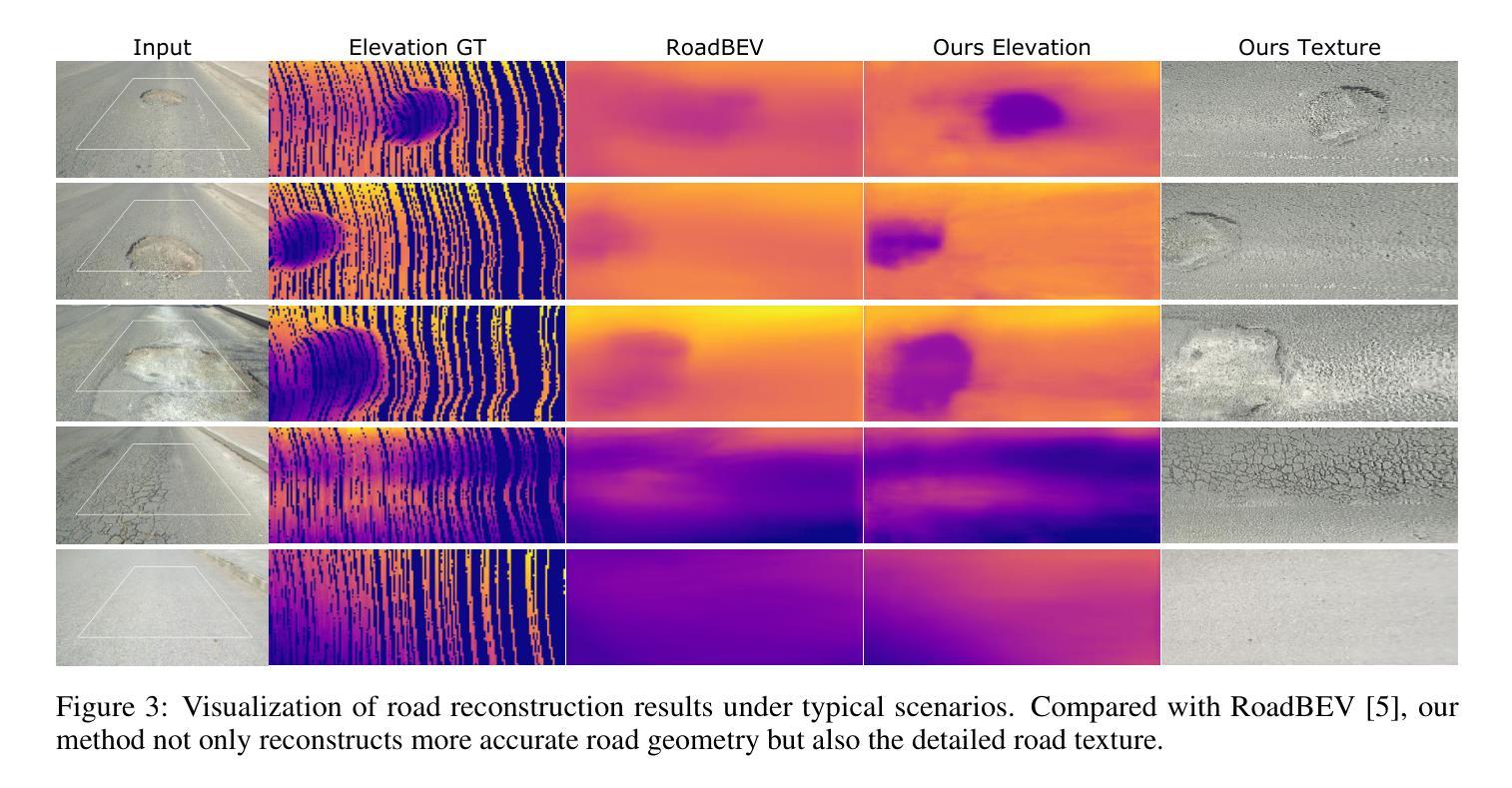
Road surface is the sole contact medium for wheels or robot feet. Reconstructing road surface is crucial for unmanned vehicles and mobile robots. Recent studies on Neural Radiance Fields (NeRF) and Gaussian Splatting (GS) have achieved remarkable results in scene reconstruction. However, they typically rely on multi-view image inputs and require prolonged optimization times. In this paper, we propose BEV-GS, a real-time single-frame road surface reconstruction method based on feed-forward Gaussian splatting. BEV-GS consists of a prediction module and a rendering module. The prediction module introduces separate geometry and texture networks following Bird’s-Eye-View paradigm. Geometric and texture parameters are directly estimated from a single frame, avoiding per-scene optimization. In the rendering module, we utilize grid Gaussian for road surface representation and novel view synthesis, which better aligns with road surface characteristics. Our method achieves state-of-the-art performance on the real-world dataset RSRD. The road elevation error reduces to 1.73 cm, and the PSNR of novel view synthesis reaches 28.36 dB. The prediction and rendering FPS is 26, and 2061, respectively, enabling high-accuracy and real-time applications. The code will be available at: \href{https://github.com/cat-wwh/BEV-GS}{\texttt{https://github.com/cat-wwh/BEV-GS}}
路面是车轮或机器人脚部的唯一接触媒介。对于无人驾驶汽车和移动机器人来说,重建路面至关重要。最近关于神经辐射场(NeRF)和高斯贴图(GS)的研究在场景重建方面取得了显著成果。然而,它们通常依赖于多视角图像输入,并且需要长时间的优化。在本文中,我们提出了基于前馈高斯贴图的实时单帧路面重建方法BEV-GS。BEV-GS由预测模块和渲染模块组成。预测模块引入了遵循鸟瞰图范式的单独几何和纹理网络。几何和纹理参数直接从单帧图像中估计,避免了针对每个场景的优化。在渲染模块中,我们利用网格高斯进行路面表示和新视角合成,这与路面特性更加吻合。我们的方法在真实世界数据集RSRD上达到了最新性能。路面高程误差降低到1.73厘米,新视角合成的峰值信噪比达到28.36分贝。预测和渲染的FPS分别为26和2061,可实现高精度和实时应用。代码将在以下网址提供:https://github.com/cat-wwh/BEV-GS。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
本文提出了一种基于前馈高斯映射(Gaussian Splatting)的实时单帧路面重建方法,称为BEV-GS。该方法包括预测模块和渲染模块,预测模块采用鸟瞰图范式,引入单独的几何和纹理网络,直接从单帧图像估计几何和纹理参数,避免了逐场景的优化。渲染模块使用网格高斯进行路面表示和新颖视图合成。该方法在真实世界数据集RSRD上实现了最先进的性能,路面高程误差降低到1.73厘米,新颖视图合成的峰值信噪比达到28.36分贝,预测和渲染的帧数分别为每秒26帧和每秒2061帧,可实现高精度和实时应用。
Key Takeaways
- 提出了基于前馈高斯映射(Gaussian Splatting)的实时单帧路面重建方法BEV-GS。
- BEV-GS包含预测模块和渲染模块,预测模块采用鸟瞰图范式,直接从单帧图像估计几何和纹理参数。
- 渲染模块使用网格高斯进行路面表示和新颖视图合成,与路面特性更相符。
- 在真实世界数据集RSRD上实现了最先进的性能,路面高程误差降低到1.73厘米,PSNR达到28.36分贝。
- BEV-GS具有高的预测和渲染速度,分别为每秒26帧和每秒2061帧,适用于实时应用。
点此查看论文截图


EDGS: Eliminating Densification for Efficient Convergence of 3DGS
Authors:Dmytro Kotovenko, Olga Grebenkova, Björn Ommer
3D Gaussian Splatting reconstructs scenes by starting from a sparse Structure-from-Motion initialization and iteratively refining under-reconstructed regions. This process is inherently slow, as it requires multiple densification steps where Gaussians are repeatedly split and adjusted, following a lengthy optimization path. Moreover, this incremental approach often leads to suboptimal renderings, particularly in high-frequency regions where detail is critical. We propose a fundamentally different approach: we eliminate densification process with a one-step approximation of scene geometry using triangulated pixels from dense image correspondences. This dense initialization allows us to estimate rough geometry of the scene while preserving rich details from input RGB images, providing each Gaussian with well-informed colors, scales, and positions. As a result, we dramatically shorten the optimization path and remove the need for densification. Unlike traditional methods that rely on sparse keypoints, our dense initialization ensures uniform detail across the scene, even in high-frequency regions where 3DGS and other methods struggle. Moreover, since all splats are initialized in parallel at the start of optimization, we eliminate the need to wait for densification to adjust new Gaussians. Our method not only outperforms speed-optimized models in training efficiency but also achieves higher rendering quality than state-of-the-art approaches, all while using only half the splats of standard 3DGS. It is fully compatible with other 3DGS acceleration techniques, making it a versatile and efficient solution that can be integrated with existing approaches.
3D高斯摊铺(3DGS)从稀疏的运动结构初始化开始重建场景,并通过迭代优化细化未重建区域。这个过程本质上是缓慢的,因为它需要进行多次稠密化步骤,高斯函数需要反复分割和调整,沿着漫长的优化路径进行。此外,这种增量方法往往导致次优渲染,特别是在高频区域,细节至关重要。我们提出了一种根本不同的方法:通过密集图像对应关系的三角化像素进行场景几何的一阶近似,从而消除稠密化过程。这种密集初始化允许我们估计场景的粗略几何形状,同时保留输入RGB图像的丰富细节,为每个高斯提供颜色、尺度和位置的准确信息。因此,我们大大缩短了优化路径,并消除了对稠密化的需求。与传统的依赖于稀疏关键点的方法不同,我们的密集初始化确保了场景中的均匀细节,即使在3DGS和其他方法表现困难的高频区域也是如此。此外,由于所有摊铺都在优化开始时并行初始化,我们不需要等待稠密化来调整新的高斯函数。我们的方法不仅在训练效率上超越了经过速度优化的模型,而且达到了比最新技术更高的渲染质量,同时使用的摊铺数量只有标准3DGS的一半。它与其他3DGS加速技术完全兼容,是一种通用且高效的解决方案,可以与现有方法集成。
论文及项目相关链接
摘要
本研究提出一种新型的基于像素稠密的初始化场景的几何方法。传统的场景重建通过稀疏SfM初始化和多次高斯分割优化来完成,速度慢且在高频区域细节渲染不足。我们的方法使用稠密图像对应的三角形像素直接完成场景几何的初步估计,实现场景的快速、全面且高质量重建。在单次操作中对场景的粗糙几何进行初始化的同时保留丰富细节,极大地简化了优化过程,避免反复迭代的必要步骤,避免了精细密度处理的繁琐过程。与传统的稀疏关键点依赖方法相比,我们的稠密初始化保证了场景的统一细节渲染效果,尤其在需要精细处理的高频区域展现了其优越性。此研究打破了现有的方法局限性,将各高斯的色彩、尺寸和位置得到更好预测。实验结果证明我们的方法在训练效率和渲染质量上都超过了现有的模型,并使用半数的标准的溅波次数达到更佳的效果,显示出极大的兼容性可与现有高效的重建方法进行整合融合以生成更高的精度重建。总结言之,此论文展现了一种新颖的建模重建思路与方法并适用于现代实际应用中的场景重建问题。
关键见解
- 提出一种基于稠密像素初始化场景的几何方法,避免了传统方法中多次迭代的密集化过程。
- 通过稠密图像对应的三角形像素估计场景的初步几何形态,快速准确地实现场景的重建,保持高频区域的丰富细节。
点此查看论文截图


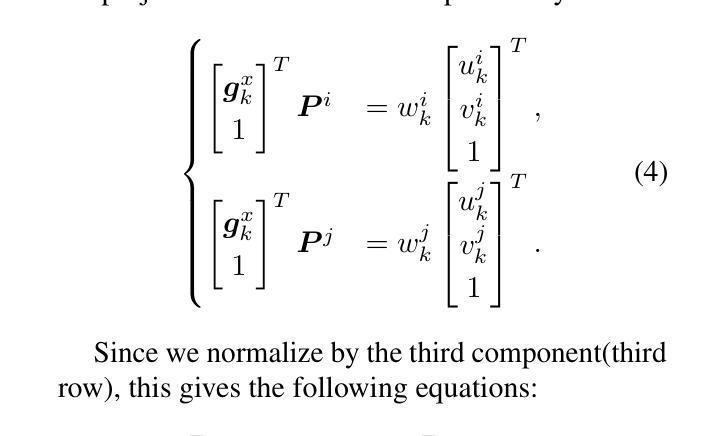
ODHSR: Online Dense 3D Reconstruction of Humans and Scenes from Monocular Videos
Authors:Zetong Zhang, Manuel Kaufmann, Lixin Xue, Jie Song, Martin R. Oswald
Creating a photorealistic scene and human reconstruction from a single monocular in-the-wild video figures prominently in the perception of a human-centric 3D world. Recent neural rendering advances have enabled holistic human-scene reconstruction but require pre-calibrated camera and human poses, and days of training time. In this work, we introduce a novel unified framework that simultaneously performs camera tracking, human pose estimation and human-scene reconstruction in an online fashion. 3D Gaussian Splatting is utilized to learn Gaussian primitives for humans and scenes efficiently, and reconstruction-based camera tracking and human pose estimation modules are designed to enable holistic understanding and effective disentanglement of pose and appearance. Specifically, we design a human deformation module to reconstruct the details and enhance generalizability to out-of-distribution poses faithfully. Aiming to learn the spatial correlation between human and scene accurately, we introduce occlusion-aware human silhouette rendering and monocular geometric priors, which further improve reconstruction quality. Experiments on the EMDB and NeuMan datasets demonstrate superior or on-par performance with existing methods in camera tracking, human pose estimation, novel view synthesis and runtime. Our project page is at https://eth-ait.github.io/ODHSR.
创建真实场景和从单一的单眼视频重构人物对于人类为中心的三维世界的感知尤为突出。最近的神经渲染进展已经实现了全景式的人景重建,但需要预先校准的相机和人体姿势,以及长时间的训练时间。在这项工作中,我们引入了一种新型统一框架,它以在线方式同时执行相机跟踪、人体姿态估计和人与场景的重建。三维高斯混合映射被用于有效地学习人类和场景的Gaussian基元,而基于重建的相机跟踪和人体姿态估计模块的设计,旨在实现对姿势和外观的全面理解和有效分离。具体来说,我们设计了一个人体变形模块来重建细节,并增强对分布外姿势的泛化能力。为了准确学习人与场景之间的空间相关性,我们引入了遮挡感知的人形轮廓渲染和单眼几何先验,这进一步提高了重建质量。在EMDB和NeuMan数据集上的实验表明,在相机跟踪、人体姿态估计、新视角合成和运行时等方面,我们的性能优于或相当于现有方法。我们的项目页面是https://eth-ait.github.io/ODHSR。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF Accepted at CVPR 2025
Summary
该文介绍了一个统一框架,能在线同时进行摄像机追踪、人体姿态估计和人机场景重建。利用3D高斯拼贴学习高斯原始人体和场景,设计重建的相机追踪和人体姿态估计模块,实现整体理解和有效的姿态与外观分离。通过设计人体变形模块来重建细节,提高泛化能力,以准确学习人与场景的空间关联。引入遮挡感知的人体轮廓渲染和单目几何先验,进一步提高重建质量。
Key Takeaways
- 提出了一个统一框架,实现摄像机追踪、人体姿态估计和人机场景重建。
- 利用3D高斯拼贴学习高斯原始人体和场景。
- 设计了基于重建的相机追踪和人体姿态估计模块,实现整体理解和姿态与外观的有效分离。
- 通过设计人体变形模块来重建细节,提高模型的泛化能力。
- 准确学习人与场景的空间关联。
- 引入遮挡感知的人体轮廓渲染来提高重建质量。
点此查看论文截图

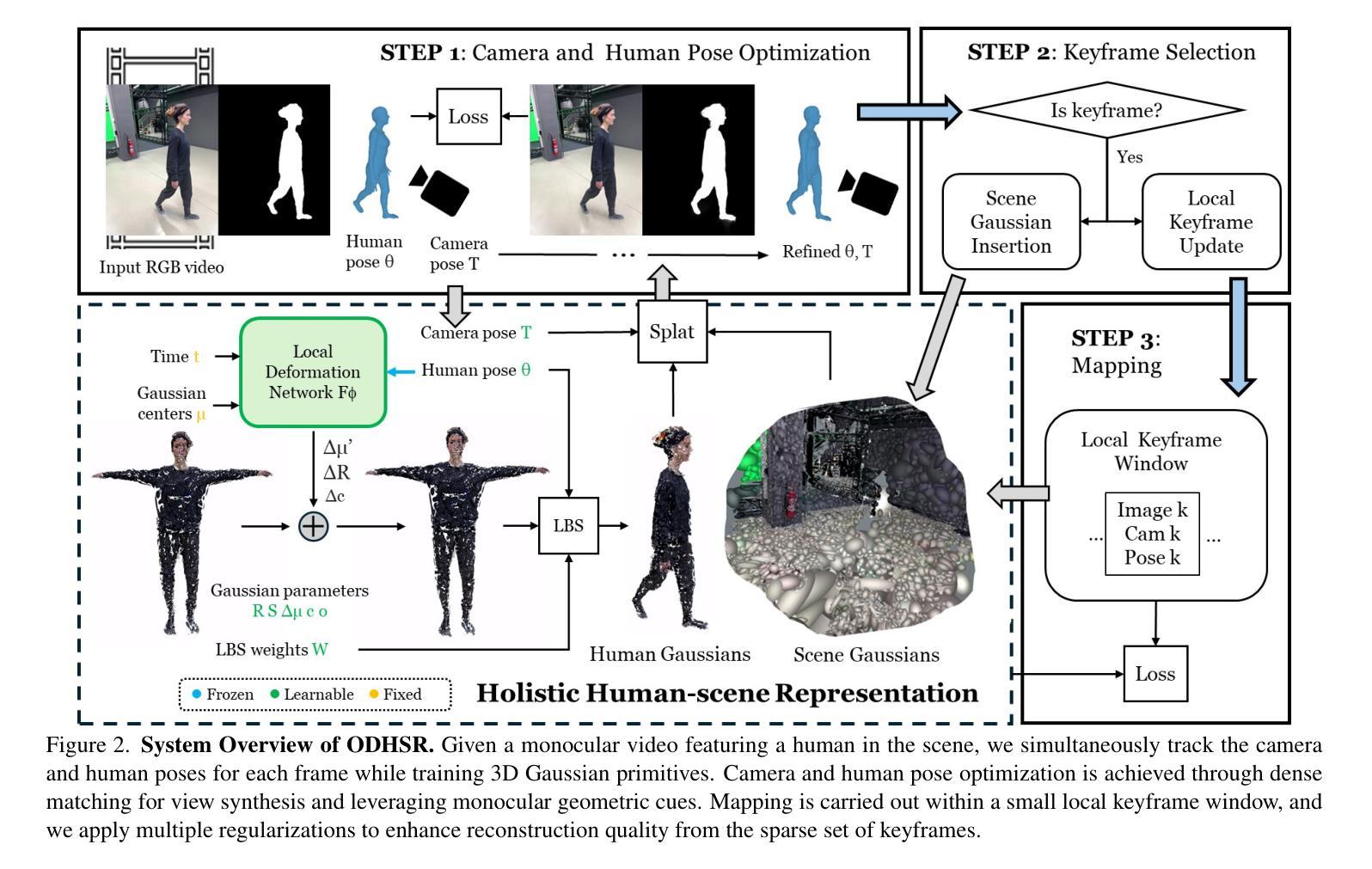
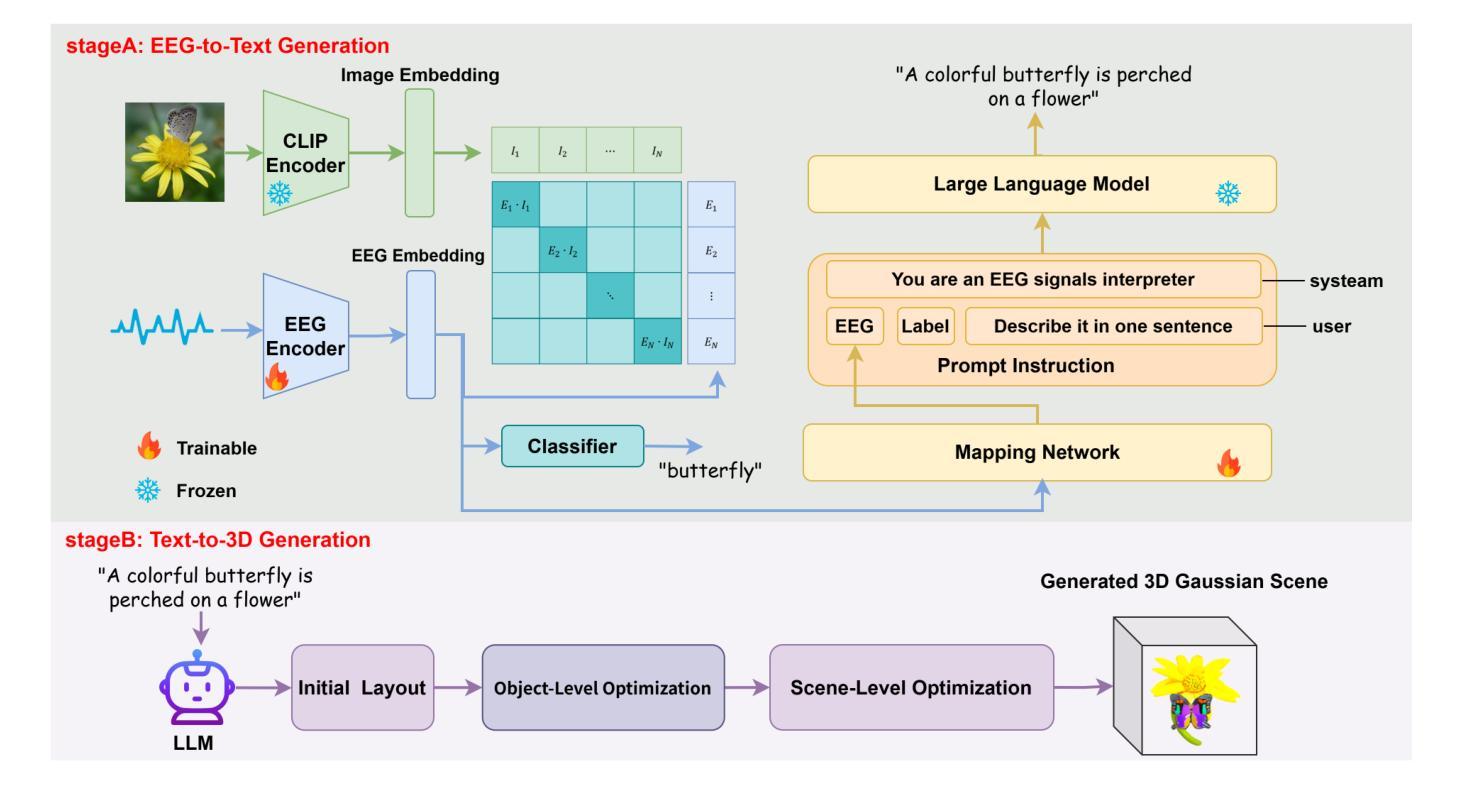
Mind2Matter: Creating 3D Models from EEG Signals
Authors:Xia Deng, Shen Chen, Jiale Zhou, Lei Li
The reconstruction of 3D objects from brain signals has gained significant attention in brain-computer interface (BCI) research. Current research predominantly utilizes functional magnetic resonance imaging (fMRI) for 3D reconstruction tasks due to its excellent spatial resolution. Nevertheless, the clinical utility of fMRI is limited by its prohibitive costs and inability to support real-time operations. In comparison, electroencephalography (EEG) presents distinct advantages as an affordable, non-invasive, and mobile solution for real-time brain-computer interaction systems. While recent advances in deep learning have enabled remarkable progress in image generation from neural data, decoding EEG signals into structured 3D representations remains largely unexplored. In this paper, we propose a novel framework that translates EEG recordings into 3D object reconstructions by leveraging neural decoding techniques and generative models. Our approach involves training an EEG encoder to extract spatiotemporal visual features, fine-tuning a large language model to interpret these features into descriptive multimodal outputs, and leveraging generative 3D Gaussians with layout-guided control to synthesize the final 3D structures. Experiments demonstrate that our model captures salient geometric and semantic features, paving the way for applications in brain-computer interfaces (BCIs), virtual reality, and neuroprosthetics. Our code is available in https://github.com/sddwwww/Mind2Matter.
从脑电波信号重建三维物体在脑机接口(BCI)研究中受到广泛关注。目前的研究主要利用功能磁共振成像(fMRI)进行三维重建任务,因其具有出色的空间分辨率。然而,fMRI的临床应用受限于其高昂的成本和无法支持实时操作。相比之下,脑电图(EEG)作为经济实惠、非侵入式和移动式的实时脑机交互系统解决方案,具有明显优势。虽然深度学习领域的最新进展在神经网络数据生成图像方面取得了显著进展,但将脑电图信号解码为结构化三维表示仍被大大忽视。在本文中,我们提出了一种新型框架,该框架利用神经解码技术和生成模型将脑电图记录转化为三维物体重建。我们的方法包括训练EEG编码器以提取时空视觉特征,微调大型语言模型以将这些特征解释为描述性多模式输出,并利用带有布局指导控制的生成三维高斯来合成最终的三维结构。实验表明,我们的模型能够捕捉显著的几何和语义特征,为脑机接口(BCI)、虚拟现实和神经仿生器件的应用铺平道路。我们的代码可在链接中找到。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
本文提出一种基于脑电图(EEG)记录的神经网络解码技术和生成模型的新框架,用于将EEG信号解码为三维物体重建。该框架包括训练EEG编码器提取时空视觉特征,微调大型语言模型以解释这些特征并生成多模态输出,并利用布局指导控制的生成三维高斯模型合成最终的三维结构。实验表明,该模型能够捕捉重要的几何和语义特征,为脑机接口、虚拟现实和神经仿生等领域的应用开辟了道路。
Key Takeaways
- 重建三维物体从脑信号在脑机接口(BCI)研究中受到关注。
- 当前研究主要利用功能磁共振成像(fMRI)进行三维重建任务,但其高昂成本和无法支持实时操作限制了临床应用。
- 与之相比,脑电图(EEG)作为一种经济、无创、可移动解决方案,在实时脑机交互系统中具有明显优势。
- 深度学习在图像生成方面具有显著进展,但将EEG信号解码为结构化三维表示仍然未被充分探索。
- 本文提出了一种新框架,该框架结合神经网络解码技术和生成模型,能将EEG记录转化为三维物体重建。
- 该框架包括训练EEG编码器、微调大型语言模型和利用生成三维高斯模型进行合成。
点此查看论文截图

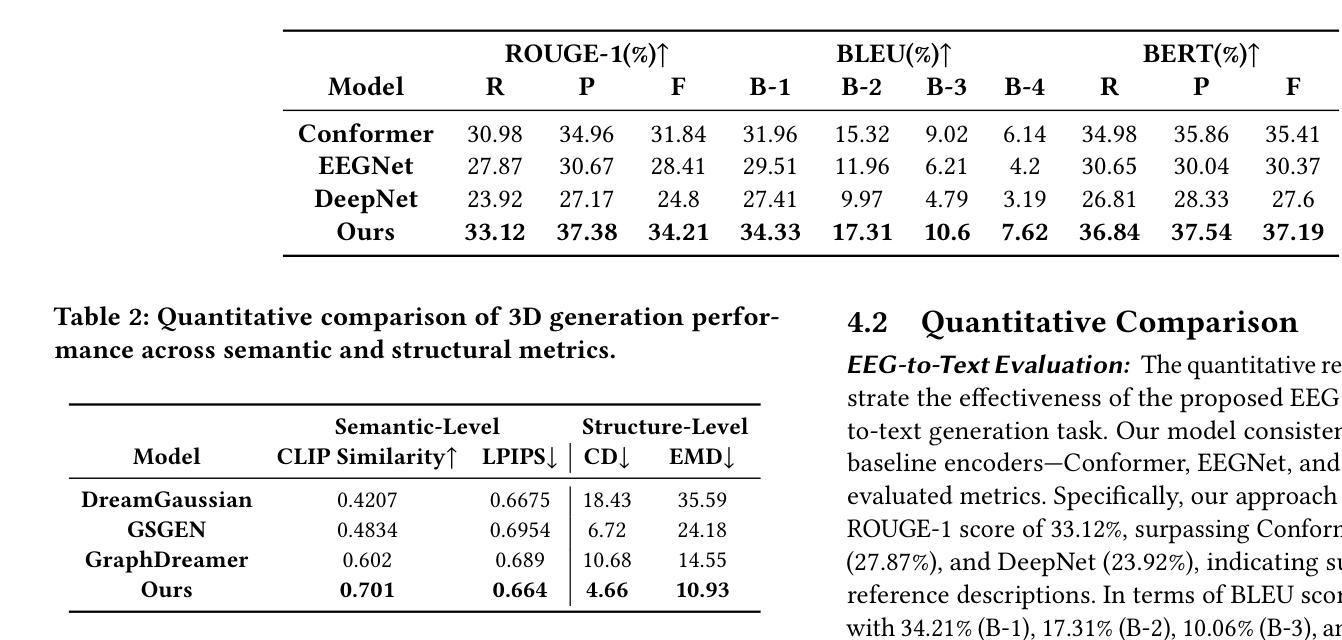
GaSLight: Gaussian Splats for Spatially-Varying Lighting in HDR
Authors:Christophe Bolduc, Yannick Hold-Geoffroy, Zhixin Shu, Jean-François Lalonde
We present GaSLight, a method that generates spatially-varying lighting from regular images. Our method proposes using HDR Gaussian Splats as light source representation, marking the first time regular images can serve as light sources in a 3D renderer. Our two-stage process first enhances the dynamic range of images plausibly and accurately by leveraging the priors embedded in diffusion models. Next, we employ Gaussian Splats to model 3D lighting, achieving spatially variant lighting. Our approach yields state-of-the-art results on HDR estimations and their applications in illuminating virtual objects and scenes. To facilitate the benchmarking of images as light sources, we introduce a novel dataset of calibrated and unsaturated HDR to evaluate images as light sources. We assess our method using a combination of this novel dataset and an existing dataset from the literature. Project page: https://lvsn.github.io/gaslight/
我们提出了GaSLight方法,该方法可以从常规图像生成空间变化的光照。我们的方法建议使用HDR高斯斑点作为光源表示,这标志着常规图像首次可以作为三维渲染器的光源。我们的两阶段过程首先利用扩散模型中嵌入的先验知识来增强图像的可信度和准确性,从而扩展图像的动态范围。接下来,我们使用高斯斑点对三维照明进行建模,实现空间变化的光照。我们的方法在HDR估计及其应用于照明虚拟对象和场景方面产生了最先进的成果。为了促进将图像作为基准光源的评估,我们引入了一个全新的校准和不饱和HDR数据集来评估图像作为光源。我们使用这个新数据集和文献中的现有数据集来评估我们的方法。项目页面:https://lvsn.github.io/gaslight/
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
本文介绍了名为GaSLight的方法,该方法能够从常规图像生成空间变化的照明效果。该方法采用HDR高斯Splats作为光源表示,首次实现了常规图像在三维渲染器中的作为光源应用。通过利用扩散模型中的先验知识,首先增强图像的动态范围。然后,使用高斯Splats进行三维照明建模,实现空间变化照明效果。该方法在HDR估算及其虚拟对象和场景的照明应用中取得了最新结果。为了将图像作为光源进行基准测试,我们引入了一个新型的校准不饱和HDR数据集。
Key Takeaways
- GaSLight方法能够从常规图像生成空间变化的照明效果。
- HDR高斯Splats被用作光源表示,实现了常规图像在三维渲染中的创新应用。
- 方法通过利用扩散模型中的先验知识,准确增强图像动态范围。
- 采用高斯Splats进行三维照明建模,达到空间变化照明。
- 方法在HDR估算方面取得了最新结果,并成功应用于虚拟对象和场景的照明。
- 为了评估图像作为光源的效果,引入了一个新型的校准不饱和HDR数据集。
点此查看论文截图

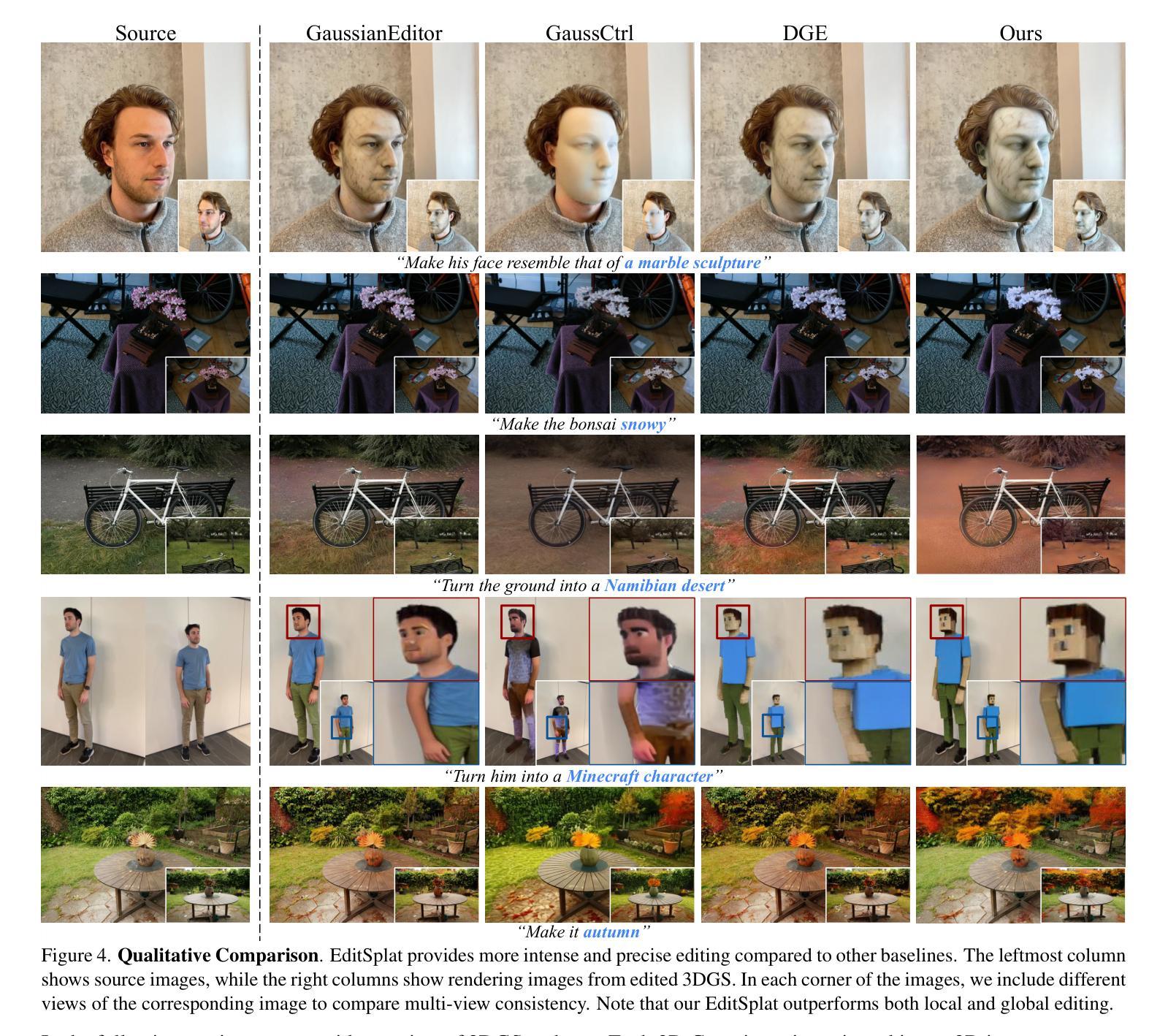
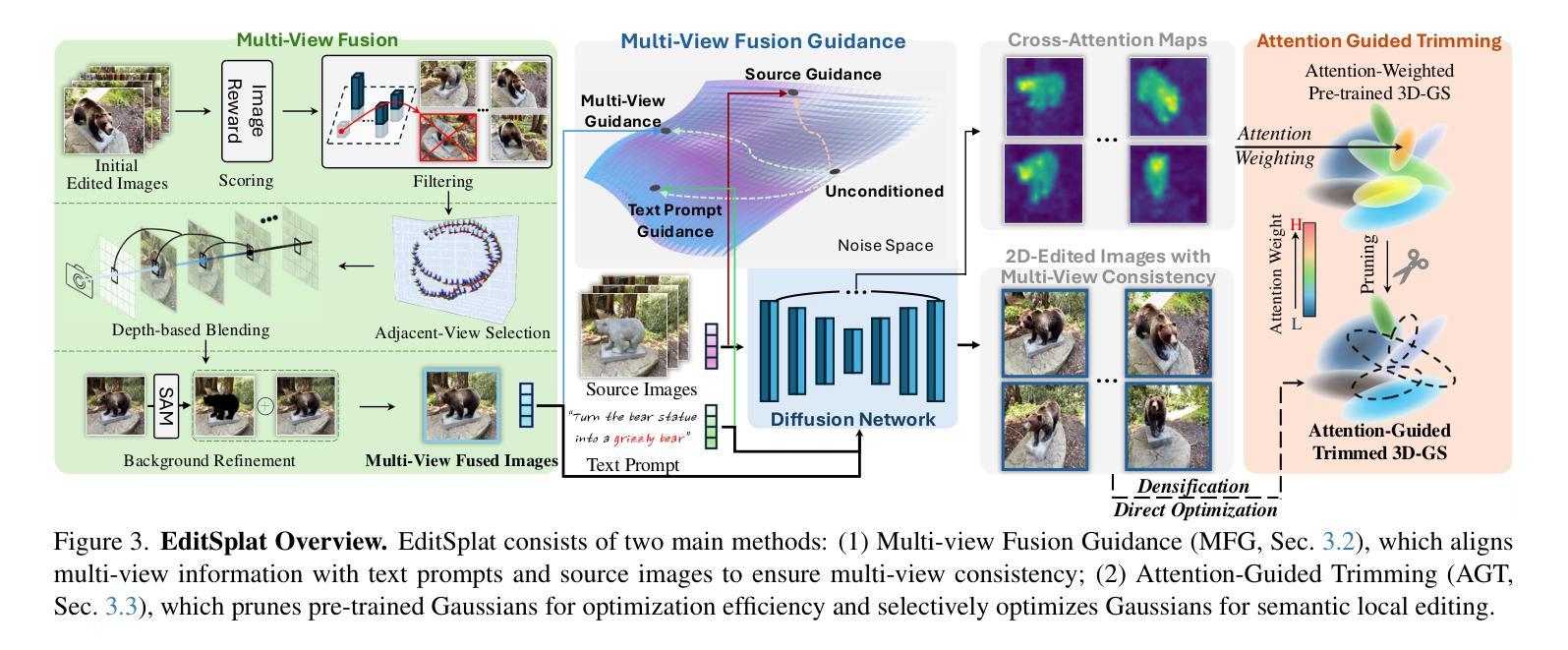
EditSplat: Multi-View Fusion and Attention-Guided Optimization for View-Consistent 3D Scene Editing with 3D Gaussian Splatting
Authors:Dong In Lee, Hyeongcheol Park, Jiyoung Seo, Eunbyung Park, Hyunje Park, Ha Dam Baek, Sangheon Shin, Sangmin Kim, Sangpil Kim
Recent advancements in 3D editing have highlighted the potential of text-driven methods in real-time, user-friendly AR/VR applications. However, current methods rely on 2D diffusion models without adequately considering multi-view information, resulting in multi-view inconsistency. While 3D Gaussian Splatting (3DGS) significantly improves rendering quality and speed, its 3D editing process encounters difficulties with inefficient optimization, as pre-trained Gaussians retain excessive source information, hindering optimization. To address these limitations, we propose EditSplat, a novel text-driven 3D scene editing framework that integrates Multi-view Fusion Guidance (MFG) and Attention-Guided Trimming (AGT). Our MFG ensures multi-view consistency by incorporating essential multi-view information into the diffusion process, leveraging classifier-free guidance from the text-to-image diffusion model and the geometric structure inherent to 3DGS. Additionally, our AGT utilizes the explicit representation of 3DGS to selectively prune and optimize 3D Gaussians, enhancing optimization efficiency and enabling precise, semantically rich local editing. Through extensive qualitative and quantitative evaluations, EditSplat achieves state-of-the-art performance, establishing a new benchmark for text-driven 3D scene editing.
近期三维编辑技术的进展凸显了文本驱动方法在实时、用户友好的AR/VR应用中的潜力。然而,当前的方法依赖于二维扩散模型,而没有充分考虑到多视角信息,导致多视角不一致。虽然三维高斯摊铺(3DGS)显著提高了渲染质量和速度,但其三维编辑过程在优化方面遇到了困难,因为预训练的高斯值保留了过多的源信息,阻碍了优化。为了解决这个问题,我们提出了EditSplat,这是一种新颖的文本驱动三维场景编辑框架,它融合了多视角融合指导(MFG)和注意力引导修剪(AGT)。我们的MFG通过融入扩散过程中的关键多视角信息,利用无分类器指导的文本到图像扩散模型和固有的三维几何结构,确保多视角的一致性。此外,我们的AGT利用三维高斯表示的显式表达来选择性修剪和优化三维高斯值,提高优化效率,实现精确且语义丰富的局部编辑。通过广泛的质量和数量评估,EditSplat达到了最先进的性能水平,为文本驱动的三维场景编辑建立了新的基准。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
本文主要介绍了基于文本的实时三维场景编辑技术的前沿进展。针对现有技术的不足,如多视角信息利用不足和预训练高斯模型优化效率低下等问题,提出了名为EditSplat的新型文本驱动三维场景编辑框架。该框架结合了多视角融合引导(MFG)和注意力引导修剪(AGT)两大技术,提高了渲染质量和速度,实现了多视角一致性,优化了编辑效率,并实现了精确、语义丰富的局部编辑。通过广泛的定性和定量评估,EditSplat达到了业界领先水平,为基于文本的实时三维场景编辑树立了新的标杆。
Key Takeaways
- 近期三维编辑技术的进步突显了文本驱动方法在实时AR/VR应用的潜力。
- 当前方法主要依赖二维扩散模型,缺乏多视角信息的考虑,导致多视角不一致性。
- 3D高斯贴图(3DGS)能提高渲染质量和速度,但其三维编辑过程面临优化效率低下的问题。
- EditSplat框架通过结合多视角融合引导(MFG)和注意力引导修剪(AGT)解决上述问题。
- MFG通过融入多视角信息到扩散过程中确保多视角一致性,利用文本到图像的扩散模型的分类器引导以及固有的三维几何结构。
- AGT利用3DGS的显式表示进行选择性修剪和优化三维高斯模型,提高优化效率并实现精确、语义丰富的局部编辑。
点此查看论文截图