⚠️ 以下所有内容总结都来自于 大语言模型的能力,如有错误,仅供参考,谨慎使用
🔴 请注意:千万不要用于严肃的学术场景,只能用于论文阅读前的初筛!
💗 如果您觉得我们的项目对您有帮助 ChatPaperFree ,还请您给我们一些鼓励!⭐️ HuggingFace免费体验
2025-04-22 更新
Decoding Vision Transformers: the Diffusion Steering Lens
Authors:Ryota Takatsuki, Sonia Joseph, Ippei Fujisawa, Ryota Kanai
Logit Lens is a widely adopted method for mechanistic interpretability of transformer-based language models, enabling the analysis of how internal representations evolve across layers by projecting them into the output vocabulary space. Although applying Logit Lens to Vision Transformers (ViTs) is technically straightforward, its direct use faces limitations in capturing the richness of visual representations. Building on the work of Toker et al. (2024)~\cite{Toker2024-ve}, who introduced Diffusion Lens to visualize intermediate representations in the text encoders of text-to-image diffusion models, we demonstrate that while Diffusion Lens can effectively visualize residual stream representations in image encoders, it fails to capture the direct contributions of individual submodules. To overcome this limitation, we propose \textbf{Diffusion Steering Lens} (DSL), a novel, training-free approach that steers submodule outputs and patches subsequent indirect contributions. We validate our method through interventional studies, showing that DSL provides an intuitive and reliable interpretation of the internal processing in ViTs.
Logit Lens是广泛应用于基于转换器的语言模型的机械解释性的方法,它通过投影到输出词汇空间来分析内部表示如何在各层中演变。虽然将Logit Lens应用于视觉转换器(ViTs)在技术上很直接,但其直接使用在捕捉视觉表示的丰富性方面存在局限性。基于Toker等人(2024)的工作,他们引入了Diffusion Lens来可视化文本到图像扩散模型的文本编码器的中间表示,我们证明虽然Diffusion Lens可以有效地可视化图像编码器的剩余流表示,但它无法捕捉单个子模块的直接贡献。为了克服这一局限性,我们提出了Diffusion Steering Lens(DSL),这是一种新型的无训练方法,用于引导子模块输出并修补随后的间接贡献。我们通过干预研究验证了我们的方法,表明DSL为ViTs的内部处理提供了直观可靠的解释。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF 12 pages, 17 figures. Accepted to the CVPR 2025 Workshop on Mechanistic Interpretability for Vision (MIV)
Summary
基于Logit Lens方法的广泛应用,尽管其应用于Vision Transformers(ViTs)在技术上较为直接,但在捕捉视觉表示的丰富性方面存在局限性。针对这一问题,本文提出一种名为Diffusion Steering Lens(DSL)的新型无训练方法,通过干预研究验证了其在直观可靠地解释ViTs内部处理方面的有效性。该方法通过控制子模块输出并调整间接贡献,有效地克服了现有方法的局限。
Key Takeaways
- Logit Lens是一种广泛应用于基于转换器的语言模型的机械解释方法,用于分析内部表示如何在不同层中演化并投影到输出词汇空间。
- 虽然Logit Lens在Vision Transformers (ViTs)中的应用在技术上较为直接,但在捕捉视觉表示的丰富性方面存在局限性。
- Diffusion Lens虽然可以有效地可视化文本编码器中的中间表示,但在捕捉图像编码器的剩余流表示方面存在不足。
- DSL(Diffusion Steering Lens)是一种新型的无训练方法,旨在克服现有方法的局限性,通过控制子模块输出和调整间接贡献来可视化ViTs的内部处理。
- DSL通过干预研究验证了其在直观可靠地解释ViTs内部处理方面的有效性。
- DSL提供了一个有效的工具来深入了解Vision Transformers的工作机制,有助于进一步改进和优化这些模型。
点此查看论文截图


ESPLoRA: Enhanced Spatial Precision with Low-Rank Adaption in Text-to-Image Diffusion Models for High-Definition Synthesis
Authors:Andrea Rigo, Luca Stornaiuolo, Mauro Martino, Bruno Lepri, Nicu Sebe
Diffusion models have revolutionized text-to-image (T2I) synthesis, producing high-quality, photorealistic images. However, they still struggle to properly render the spatial relationships described in text prompts. To address the lack of spatial information in T2I generations, existing methods typically use external network conditioning and predefined layouts, resulting in higher computational costs and reduced flexibility. Our approach builds upon a curated dataset of spatially explicit prompts, meticulously extracted and synthesized from LAION-400M to ensure precise alignment between textual descriptions and spatial layouts. Alongside this dataset, we present ESPLoRA, a flexible fine-tuning framework based on Low-Rank Adaptation, specifically designed to enhance spatial consistency in generative models without increasing generation time or compromising the quality of the outputs. In addition to ESPLoRA, we propose refined evaluation metrics grounded in geometric constraints, capturing 3D spatial relations such as \textit{in front of} or \textit{behind}. These metrics also expose spatial biases in T2I models which, even when not fully mitigated, can be strategically exploited by our TORE algorithm to further improve the spatial consistency of generated images. Our method outperforms the current state-of-the-art framework, CoMPaSS, by 13.33% on established spatial consistency benchmarks.
扩散模型已经彻底改变了文本到图像(T2I)的合成方式,生成了高质量、逼真的图像。然而,它们在正确呈现文本提示中描述的空间关系方面仍存在困难。为了解决T2I生成中空间信息缺失的问题,现有方法通常使用外部网络条件和预定义布局,导致计算成本较高且灵活性降低。我们的方法建立在精心挑选的空间明确提示数据集上,这些数据集是从LAION-400M中提取和合成的,以确保文本描述和空间布局之间的精确对齐。除此之外,我们推出了ESPLoRA,这是一个基于低秩适应的灵活微调框架,专门设计用于提高生成模型的空间一致性,而不会增加生成时间或牺牲输出质量。除了ESPLoRA,我们还提出了基于几何约束的精炼评估指标,捕捉3D空间关系,如“在……前面”或“在……后面”。这些指标还暴露了T2I模型中的空间偏见,即使无法完全缓解,也可以被我们的TORE算法策略性利用,以进一步提高生成图像的空间一致性。我们的方法在建立的空间一致性基准测试上,比当前最先进的框架CoMPaSS高出13.33%。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
文本到图像合成领域,扩散模型已经实现了革命性的进展,生成了高质量逼真的图像。然而,现有模型在渲染文本提示中的空间关系方面仍存在困难。针对这一问题,本文提出了一种基于LAION-400M数据集的空间明确提示的精细数据集,并引入了ESPLoRA框架,通过低秩自适应技术提高生成模型的空间一致性,无需增加生成时间并保障输出质量。此外,本文还提出了基于几何约束的评估指标和TORE算法进一步改善生成图像的空间一致性。本文方法在空间一致性基准测试中较当前先进框架CoMPaSS高出13.33%。
Key Takeaways
- 扩散模型在文本到图像合成领域取得显著进展,生成高质量图像。
- 现有模型在渲染文本中的空间关系时存在困难。
- 本文提出基于LAION-400M数据集的空间明确提示的精细数据集,确保文本描述与空间布局之间的精确对齐。
- 引入ESPLoRA框架,通过低秩自适应技术提高生成模型的空间一致性。
- 提出基于几何约束的评估指标,以捕捉图像中的三维空间关系。
- 本文方法较当前先进框架在空间一致性方面有所提升。
点此查看论文截图

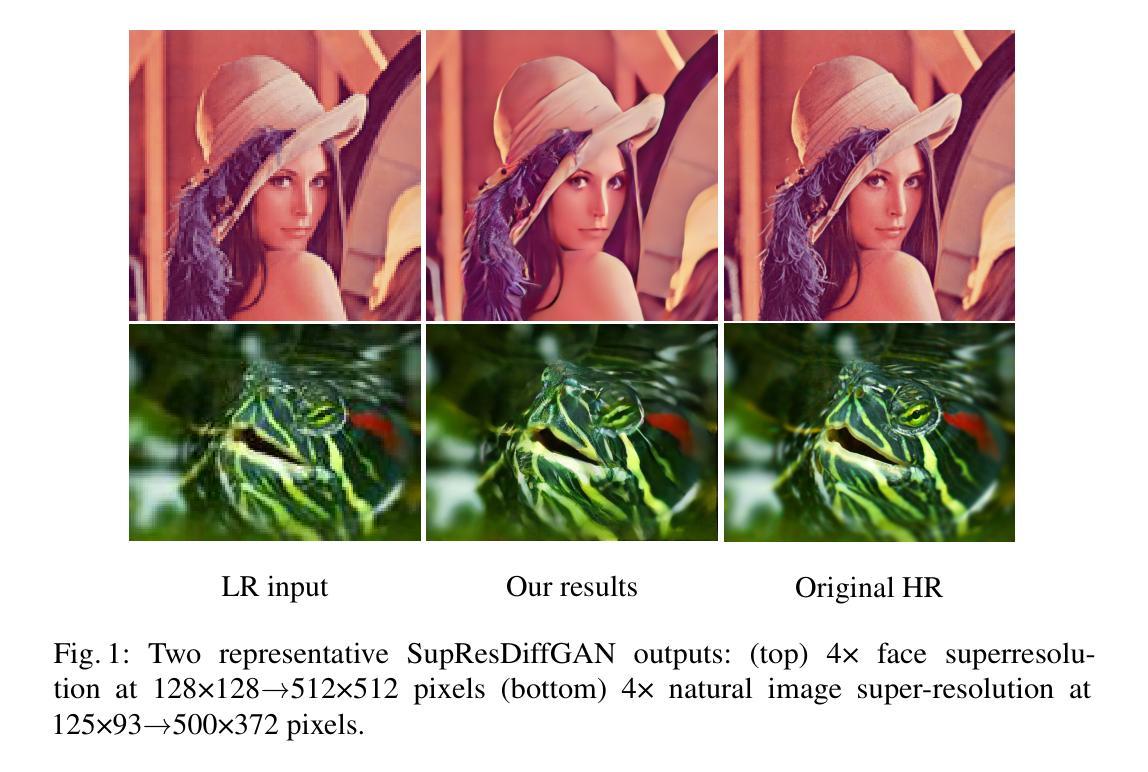
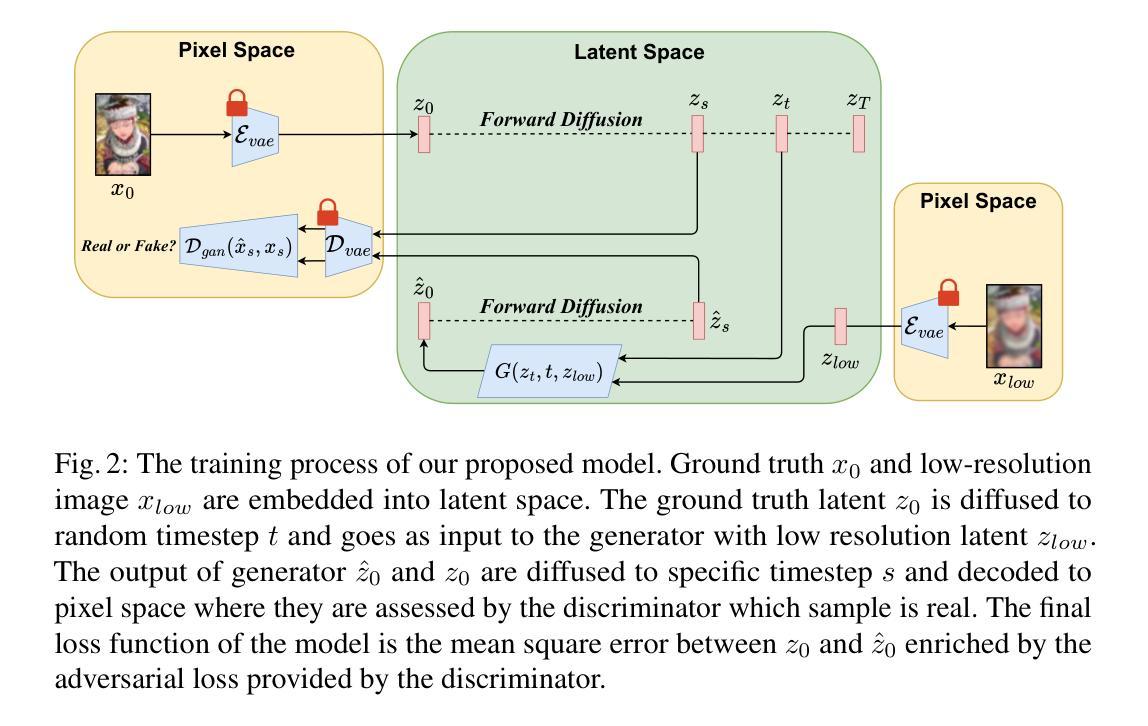
SupResDiffGAN a new approach for the Super-Resolution task
Authors:Dawid Kopeć, Wojciech Kozłowski, Maciej Wizerkaniuk, Dawid Krutul, Jan Kocoń, Maciej Zięba
In this work, we present SupResDiffGAN, a novel hybrid architecture that combines the strengths of Generative Adversarial Networks (GANs) and diffusion models for super-resolution tasks. By leveraging latent space representations and reducing the number of diffusion steps, SupResDiffGAN achieves significantly faster inference times than other diffusion-based super-resolution models while maintaining competitive perceptual quality. To prevent discriminator overfitting, we propose adaptive noise corruption, ensuring a stable balance between the generator and the discriminator during training. Extensive experiments on benchmark datasets show that our approach outperforms traditional diffusion models such as SR3 and I$^2$SB in efficiency and image quality. This work bridges the performance gap between diffusion- and GAN-based methods, laying the foundation for real-time applications of diffusion models in high-resolution image generation.
在这项工作中,我们提出了SupResDiffGAN,这是一种新型混合架构,结合了生成对抗网络(GANs)和扩散模型的优点,用于超分辨率任务。通过利用潜在空间表示和减少扩散步骤的数量,SupResDiffGAN实现了比其他基于扩散的超分辨率模型更快的推理时间,同时保持了有竞争力的感知质量。为了防止判别器过度拟合,我们提出了自适应噪声腐蚀,确保在训练过程中生成器和判别器之间的稳定平衡。在基准数据集上的广泛实验表明,我们的方法在效率和图像质量方面优于传统的扩散模型,如SR3和I$^2$SB。这项工作缩小了扩散模型和基于GAN的方法之间的性能差距,为扩散模型在实时高分辨率图像生成中的应用奠定了基础。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF 25th International Conference on Computational Science
Summary
本文介绍了SupResDiffGAN,这是一种结合了生成对抗网络(GANs)和扩散模型优势的新型混合架构,用于超分辨率任务。通过利用潜在空间表示和减少扩散步骤的数量,SupResDiffGAN实现了比其他基于扩散的超分辨率模型更快的推理时间,同时保持了有竞争力的感知质量。为防止判别器过拟合,提出了自适应噪声腐蚀方法,确保生成器和判别器在训练过程中的稳定平衡。在基准数据集上的广泛实验表明,我们的方法在提高效率和图像质量方面优于传统的扩散模型,如SR3和I$^2$SB。这项工作缩小了扩散模型和基于GAN的方法之间的性能差距,为扩散模型在实时高分辨率图像生成中的应用奠定了基础。
Key Takeaways
- SupResDiffGAN结合了GANs和扩散模型的优点,用于超分辨率任务。
- 通过利用潜在空间表示和减少扩散步骤,实现了快速推理。
- 自适应噪声腐蚀方法确保生成器和判别器的稳定平衡,防止判别器过拟合。
- 在基准数据集上的实验表明,SupResDiffGAN在效率和图像质量方面优于传统扩散模型。
- 该工作提高了扩散模型在实时高分辨率图像生成中的性能。
- SupResDiffGAN的出现缩小了扩散模型和基于GAN的方法之间的性能差距。
点此查看论文截图


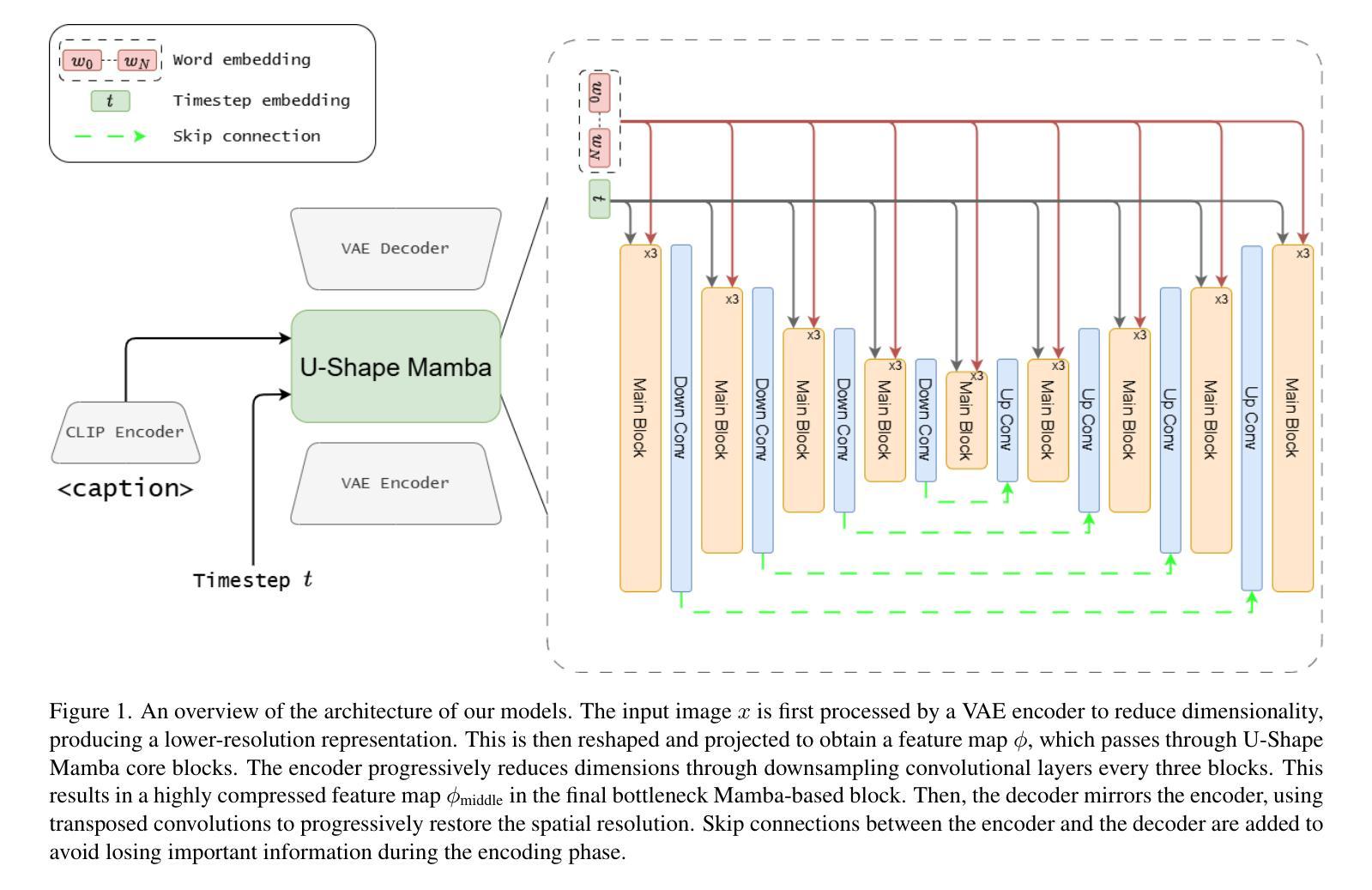
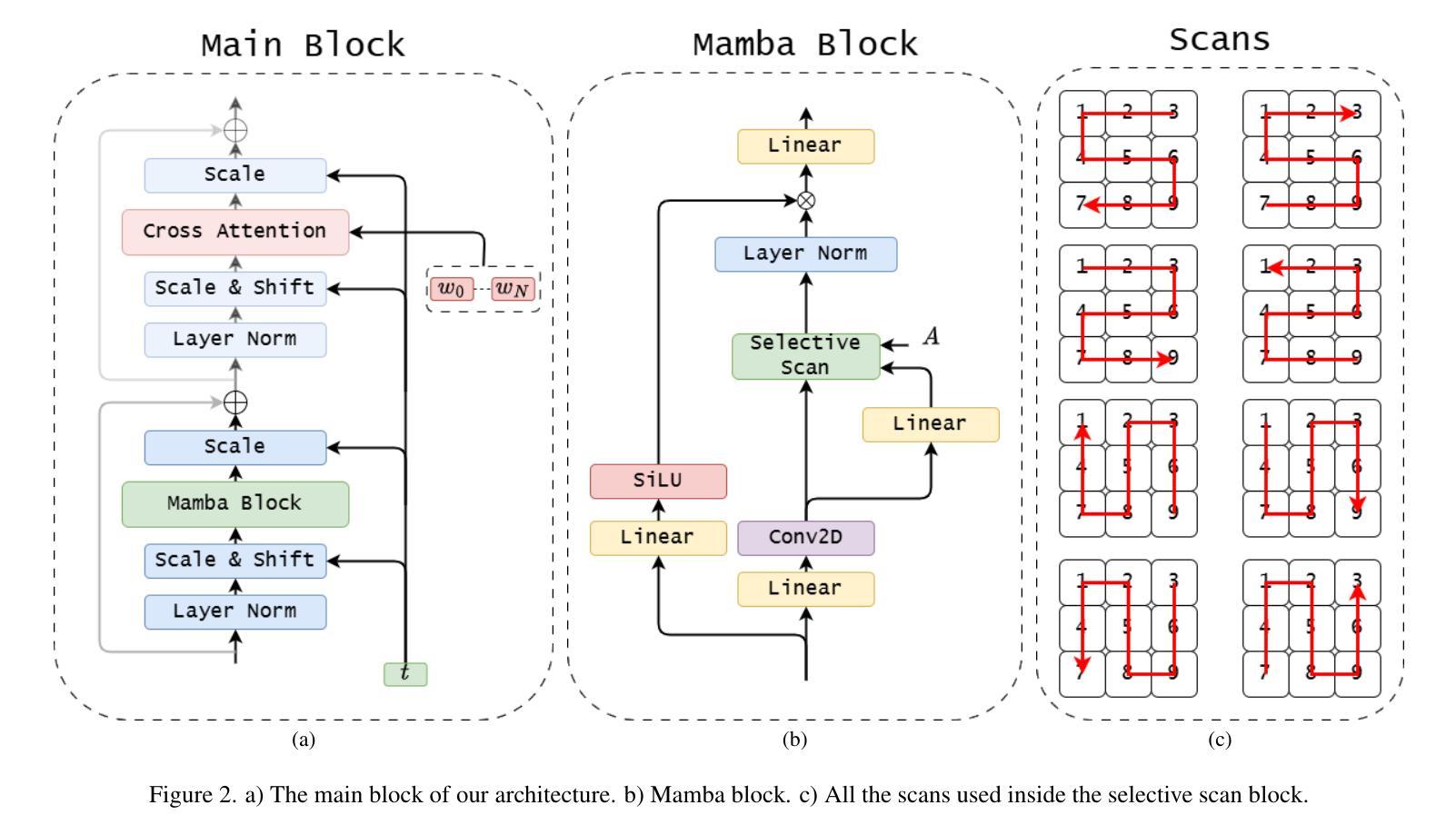
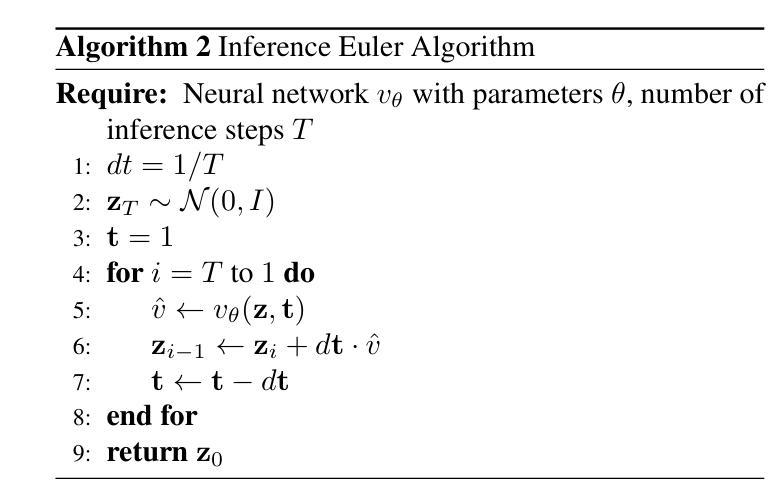
U-Shape Mamba: State Space Model for faster diffusion
Authors:Alex Ergasti, Filippo Botti, Tomaso Fontanini, Claudio Ferrari, Massimo Bertozzi, Andrea Prati
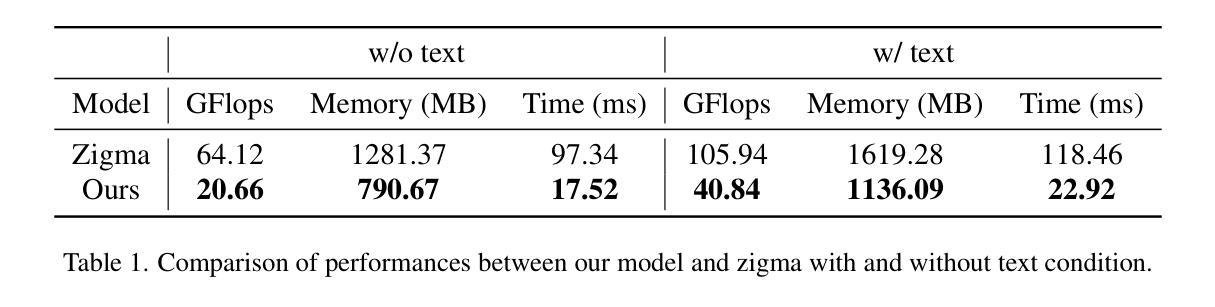
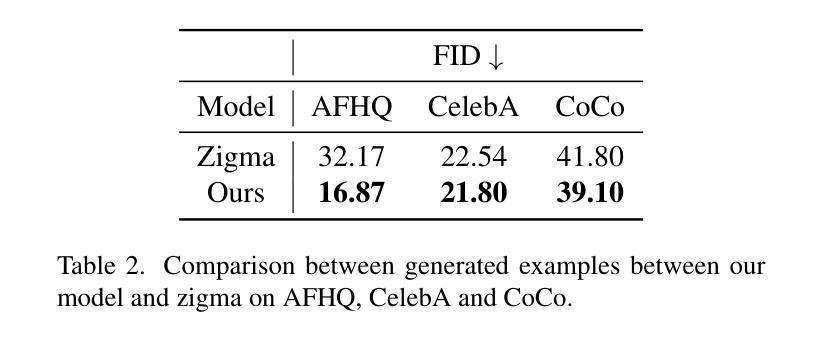
Diffusion models have become the most popular approach for high-quality image generation, but their high computational cost still remains a significant challenge. To address this problem, we propose U-Shape Mamba (USM), a novel diffusion model that leverages Mamba-based layers within a U-Net-like hierarchical structure. By progressively reducing sequence length in the encoder and restoring it in the decoder through Mamba blocks, USM significantly lowers computational overhead while maintaining strong generative capabilities. Experimental results against Zigma, which is currently the most efficient Mamba-based diffusion model, demonstrate that USM achieves one-third the GFlops, requires less memory and is faster, while outperforming Zigma in image quality. Frechet Inception Distance (FID) is improved by 15.3, 0.84 and 2.7 points on AFHQ, CelebAHQ and COCO datasets, respectively. These findings highlight USM as a highly efficient and scalable solution for diffusion-based generative models, making high-quality image synthesis more accessible to the research community while reducing computational costs.
扩散模型已成为高质量图像生成的最流行方法,但其高计算成本仍然是一个巨大的挑战。为了解决这个问题,我们提出了U形Mamba(USM),这是一种新型的扩散模型,它利用Mamba基础的层在一个类似U-Net的层次结构中。通过逐步减少编码器中的序列长度并在解码器中通过Mamba块进行恢复,USM在保持强大的生成能力的同时,大大降低了计算开销。与当前最有效的基于Mamba的扩散模型Zigma相比,实验结果表明,USM实现了三分之一倍的GFlops,需要的内存更少且速度更快,同时在图像质量上优于Zigma。在AFHQ、CelebAHQ和COCO数据集上,Frechet Inception Distance(FID)分别提高了15.3、0.84和2.7点。这些发现突出了USM作为基于扩散的生成模型的高效且可扩展的解决方案,使高质量图像合成更容易为研究领域所接触,同时降低了计算成本。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF Accepeted at CVPR 2025 eLVM workshop
Summary
本文提出了一种新型的扩散模型U-Shape Mamba(USM),它利用基于Mamba的层次结构来降低计算成本并维持强大的生成能力。实验结果表明,相较于当前最高效的Mamba扩散模型Zigma,USM的计算量减少了三分之一,内存需求更低,速度更快,并且在图像质量上优于Zigma。在AFHQ、CelebAHQ和COCO数据集上,Frechet Inception Distance(FID)分别提高了15.3、0.84和2.7点。这使得高效且可扩展的扩散生成模型成为可能,使高质量图像合成更加易于研究人员使用,同时降低了计算成本。
Key Takeaways
- U-Shape Mamba(USM)是一种新型的扩散模型,结合了Mamba和U-Net的技术特点。
- USM通过渐进地减少编码器中的序列长度并恢复解码器中的序列长度来显著降低计算成本。
- USM相较于现有的Mamba扩散模型Zigma,在计算效率、内存使用和速度方面都有显著提升。
- USM在图像质量上优于Zigma,并在AFHQ、CelebAHQ和COCO数据集上的FID得分有所提高。
- USM提供了一个高度有效的框架,适用于扩散基础的生成模型。
- USM降低了高质量图像合成的计算成本,更易于研究人员使用。
点此查看论文截图


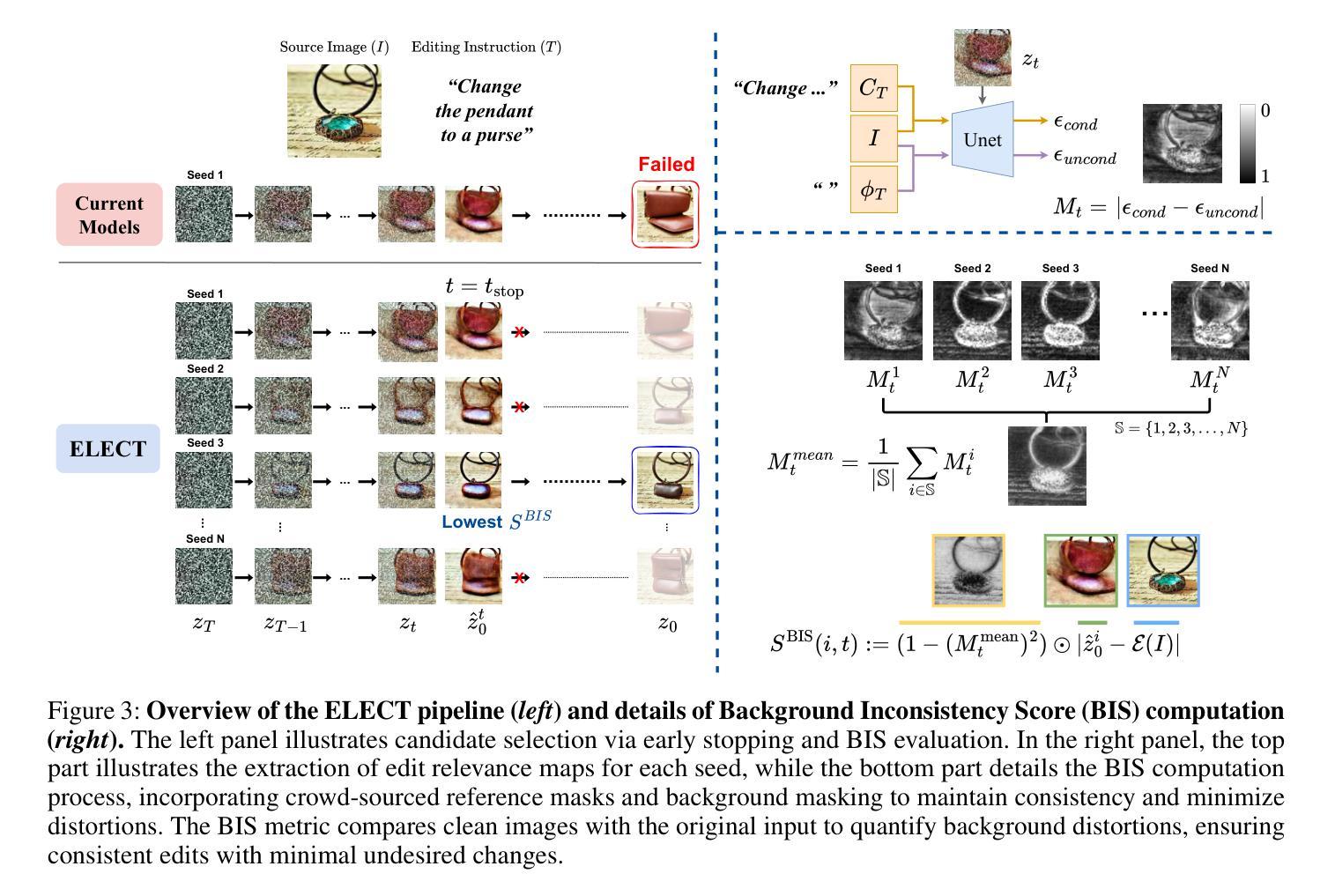
Early Timestep Zero-Shot Candidate Selection for Instruction-Guided Image Editing
Authors:Joowon Kim, Ziseok Lee, Donghyeon Cho, Sanghyun Jo, Yeonsung Jung, Kyungsu Kim, Eunho Yang
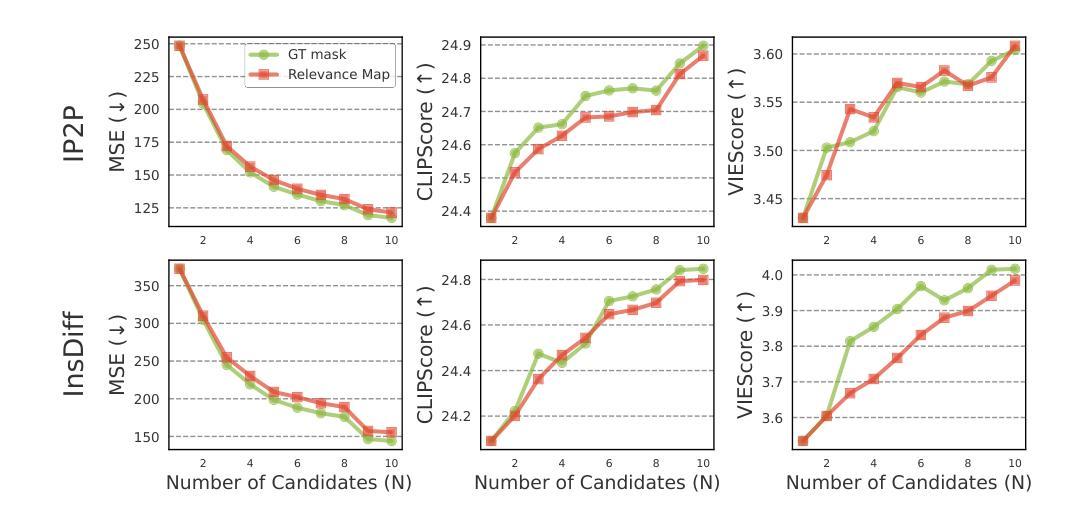
Despite recent advances in diffusion models, achieving reliable image generation and editing remains challenging due to the inherent diversity induced by stochastic noise in the sampling process. Instruction-guided image editing with diffusion models offers user-friendly capabilities, yet editing failures, such as background distortion, frequently occur. Users often resort to trial and error, adjusting seeds or prompts to achieve satisfactory results, which is inefficient. While seed selection methods exist for Text-to-Image (T2I) generation, they depend on external verifiers, limiting applicability, and evaluating multiple seeds increases computational complexity. To address this, we first establish a multiple-seed-based image editing baseline using background consistency scores, achieving Best-of-N performance without supervision. Building on this, we introduce ELECT (Early-timestep Latent Evaluation for Candidate Selection), a zero-shot framework that selects reliable seeds by estimating background mismatches at early diffusion timesteps, identifying the seed that retains the background while modifying only the foreground. ELECT ranks seed candidates by a background inconsistency score, filtering unsuitable samples early based on background consistency while preserving editability. Beyond standalone seed selection, ELECT integrates into instruction-guided editing pipelines and extends to Multimodal Large-Language Models (MLLMs) for joint seed and prompt selection, further improving results when seed selection alone is insufficient. Experiments show that ELECT reduces computational costs (by 41 percent on average and up to 61 percent) while improving background consistency and instruction adherence, achieving around 40 percent success rates in previously failed cases - without any external supervision or training.
尽管扩散模型近期取得了进展,但由于采样过程中随机噪声引起的固有多样性,实现可靠的图像生成和编辑仍然具有挑战性。带有扩散模型的指令导向图像编辑提供了用户友好的功能,但编辑失败(例如背景失真)的情况仍然经常发生。用户经常需要反复试验,调整种子或提示才能获得满意的结果,这很不高效。虽然针对文本到图像(T2I)生成的种子选择方法已经存在,但它们依赖于外部验证器,限制了其适用性,并且评估多个种子会增加计算复杂性。为了解决这一问题,我们首先建立了一个基于多种子的图像编辑基线,使用背景一致性分数,无需监督即可实现最佳N性能。在此基础上,我们引入了ELECT(用于候选种子选择的早期时间步长潜在评估),这是一个零样本框架,通过估计早期扩散时间步长中的背景不匹配来选择可靠的种子,识别出保留背景而只修改前景的种子。ELECT通过背景不一致性分数对种子候选进行排名,基于早期背景一致性过滤掉不合适的样本,同时保留可编辑性。除了单独的种子选择外,ELECT还可以集成到指令导向的编辑管道中,并扩展到多模态大型语言模型(MLLMs)进行联合种子和提示选择,在仅依靠种子选择不足以提高结果时进一步改进结果。实验表明,ELECT在降低计算成本(平均降低了41%,最高可达61%)的同时,提高了背景一致性和指令遵循性,在未接受外部监督或培训的情况下,在未成功案例中实现了约40%的成功率。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
本文介绍了在扩散模型领域面临的挑战和问题,特别是在图像生成和编辑过程中由于随机噪声引起的多样性问题。文章提出了一种基于多种种子的图像编辑方法和ELECT框架,能够在无需外部监督的情况下选择可靠的种子,并在早期扩散阶段通过估计背景不一致性来选择保留背景而只修改前景的种子。ELECT不仅提高了背景一致性和指令遵循性,还降低了计算成本,使得图像编辑更加高效。
Key Takeaways
- 扩散模型在图像生成和编辑中仍存在挑战,特别是由于采样过程中的随机噪声引起的多样性问题。
- 指令引导的图像编辑具有用户友好的能力,但编辑失败(如背景失真)经常发生。
- 现有种子选择方法依赖于外部验证器,限制了其应用,而评估多个种子增加了计算复杂性。
- 建立了基于多种子的图像编辑基线,使用背景一致性分数实现最佳N性能,无需监督。
- 引入ELECT框架,通过估计早期扩散阶段背景不匹配来选择可靠种子,选择保留背景同时只修改前景的种子。
- ELECT通过背景不一致性分数对种子候选进行排名,早期过滤不适合的样本,同时保持可编辑性。
点此查看论文截图



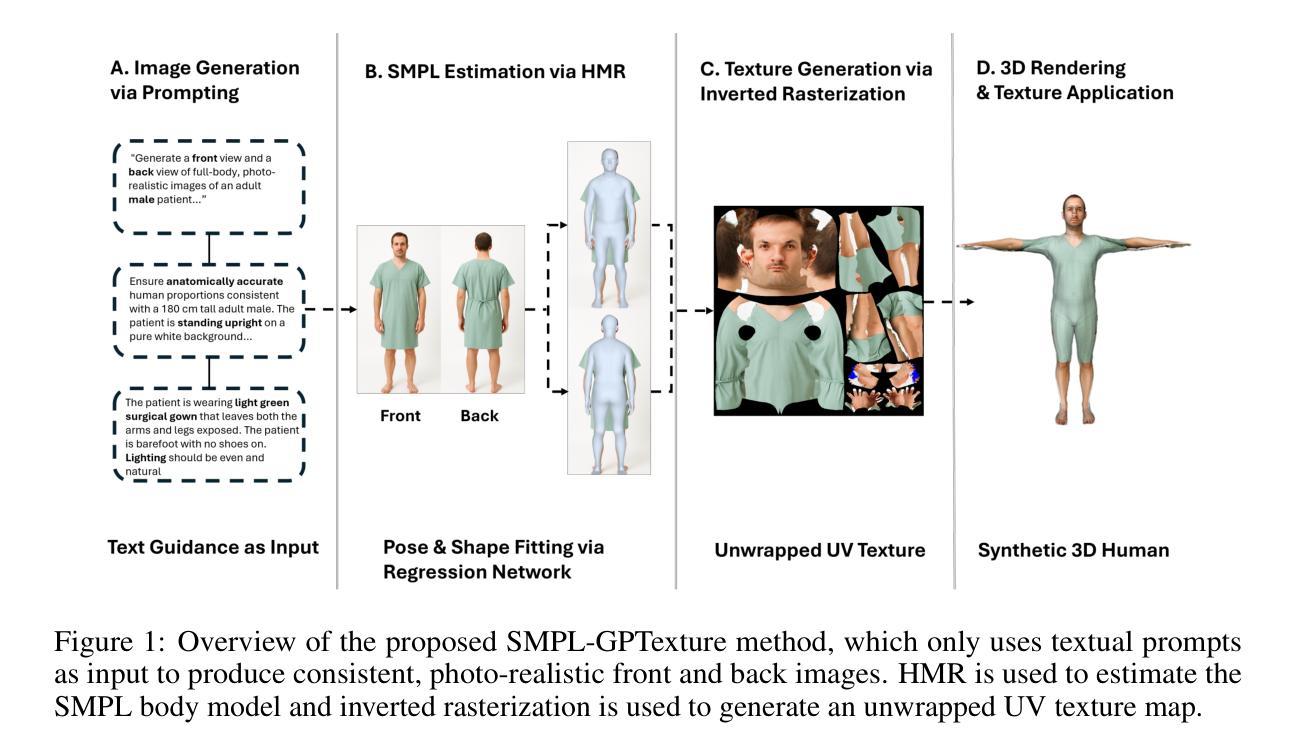
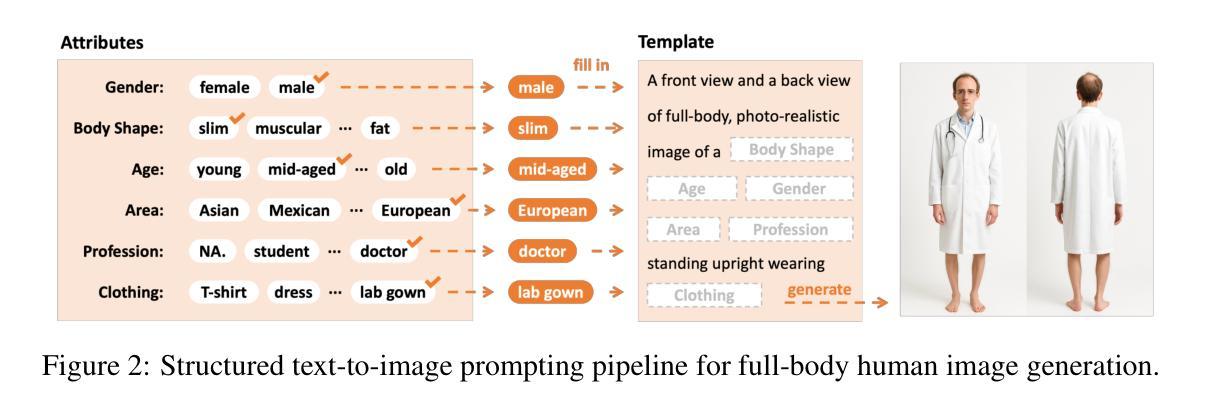
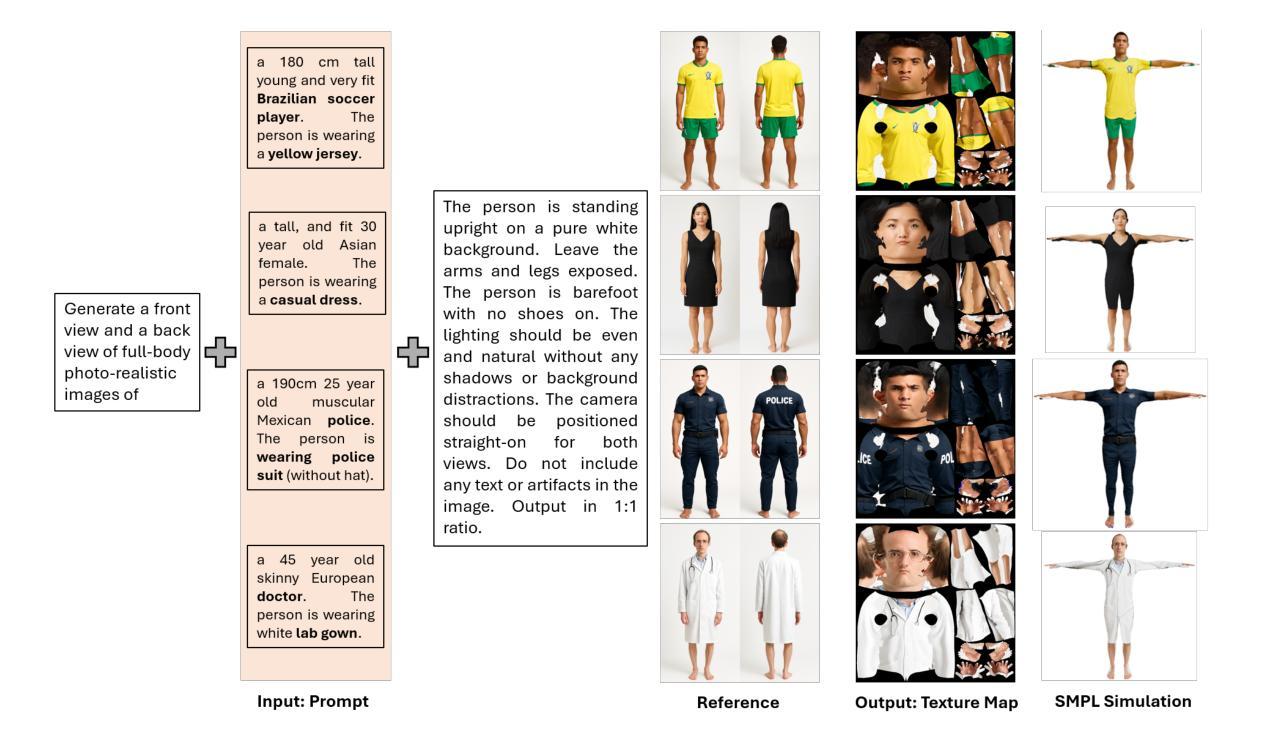
SMPL-GPTexture: Dual-View 3D Human Texture Estimation using Text-to-Image Generation Models
Authors:Mingxiao Tu, Shuchang Ye, Hoijoon Jung, Jinman Kim
Generating high-quality, photorealistic textures for 3D human avatars remains a fundamental yet challenging task in computer vision and multimedia field. However, real paired front and back images of human subjects are rarely available with privacy, ethical and cost of acquisition, which restricts scalability of the data. Additionally, learning priors from image inputs using deep generative models, such as GANs or diffusion models, to infer unseen regions such as the human back often leads to artifacts, structural inconsistencies, or loss of fine-grained detail. To address these issues, we present SMPL-GPTexture (skinned multi-person linear model - general purpose Texture), a novel pipeline that takes natural language prompts as input and leverages a state-of-the-art text-to-image generation model to produce paired high-resolution front and back images of a human subject as the starting point for texture estimation. Using the generated paired dual-view images, we first employ a human mesh recovery model to obtain a robust 2D-to-3D SMPL alignment between image pixels and the 3D model’s UV coordinates for each views. Second, we use an inverted rasterization technique that explicitly projects the observed colour from the input images into the UV space, thereby producing accurate, complete texture maps. Finally, we apply a diffusion-based inpainting module to fill in the missing regions, and the fusion mechanism then combines these results into a unified full texture map. Extensive experiments shows that our SMPL-GPTexture can generate high resolution texture aligned with user’s prompts.
生成高质量、逼真的3D人类角色纹理仍是计算机视觉和多媒体领域的一项基本且具有挑战性的任务。然而,由于隐私、伦理和采集成本等原因,实际的人像前后图像很难获得,这限制了数据的可扩展性。此外,使用深度生成模型(如GAN或扩散模型)从图像输入中学习先验知识,以推断未见区域(如人的背部),通常会导致伪影、结构不一致或细节丢失。为了解决这些问题,我们提出了SMPL-GPTexture(皮肤多人线性模型-通用纹理),这是一种新型管道,它以自然语言提示为输入,利用最先进的文本到图像生成模型,生成配对的高分辨率人像前后图像,作为纹理估计的起点。使用生成的配对双视图图像,我们首先采用人体网格恢复模型,获得图像像素和每个视图的3D模型的UV坐标之间的稳健的2D-to-3D SMPL对齐。其次,我们使用反向光栅化技术,将观察到的颜色从输入图像显式投影到UV空间,从而生成准确、完整的纹理映射。最后,我们应用基于扩散的填充模块来填充缺失区域,然后融合机制将这些结果组合成统一的完整纹理映射。大量实验表明,我们的SMPL-GPTexture可以生成与用户提示对齐的高分辨率纹理。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
本文介绍了一种名为SMPL-GPTexture的新流程,用于生成高质量的人像纹理。该流程采用自然语言提示作为输入,利用先进的文本到图像生成模型产生配对的高分辨率前后图像。通过对生成图像的2D到3D SMPL对齐,以及将观察到的颜色从输入图像投影到UV空间的反转渲染技术,最终生成准确完整的纹理映射。该流程解决了现实世界图像配对困难及深生成模型在推断未可见区域时产生的伪像问题。
Key Takeaways
- SMPL-GPTexture利用自然语言提示作为输入,生成高质量的人像纹理。
- 采用先进的文本到图像生成模型产生配对的高分辨率前后图像。
- 通过2D-to-3D SMPL对齐,实现图像像素与3D模型的UV坐标对应。
- 采用反转渲染技术将观察到的颜色从输入图像投影到UV空间,生成准确完整的纹理映射。
- 流程解决了现实世界图像配对困难的问题。
- 解决深生成模型在推断未可见区域(如人背)时产生的伪像、结构不一致或细节丢失问题。
点此查看论文截图

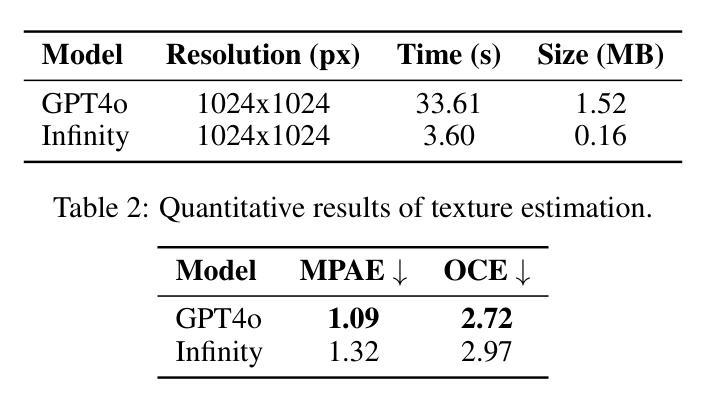
WaterFlow: Learning Fast & Robust Watermarks using Stable Diffusion
Authors:Vinay Shukla, Prachee Sharma, Ryan Rossi, Sungchul Kim, Tong Yu, Aditya Grover
The ability to embed watermarks in images is a fundamental problem of interest for computer vision, and is exacerbated by the rapid rise of generated imagery in recent times. Current state-of-the-art techniques suffer from computational and statistical challenges such as the slow execution speed for practical deployments. In addition, other works trade off fast watermarking speeds but suffer greatly in their robustness or perceptual quality. In this work, we propose WaterFlow (WF), a fast and extremely robust approach for high fidelity visual watermarking based on a learned latent-dependent watermark. Our approach utilizes a pretrained latent diffusion model to encode an arbitrary image into a latent space and produces a learned watermark that is then planted into the Fourier Domain of the latent. The transformation is specified via invertible flow layers that enhance the expressivity of the latent space of the pre-trained model to better preserve image quality while permitting robust and tractable detection. Most notably, WaterFlow demonstrates state-of-the-art performance on general robustness and is the first method capable of effectively defending against difficult combination attacks. We validate our findings on three widely used real and generated datasets: MS-COCO, DiffusionDB, and WikiArt.
将图片嵌入水印是计算机视觉领域的一个基础且重要的问题,近年来随着生成图像技术的快速发展,这一问题变得愈发严重。当前最先进的技术面临着计算和统计方面的挑战,如在实际部署中的执行速度较慢。此外,其他方法虽然水印速度快,但在鲁棒性或感知质量方面存在很大缺陷。在这项工作中,我们提出了WaterFlow(WF),这是一种基于学习到的潜在依赖水印的快速且极其鲁棒的高保真视觉水印方法。我们的方法利用预训练的潜在扩散模型将任意图像编码到潜在空间,并产生学习的水印,然后将其植入到潜在空间的傅立叶域。通过可逆流层指定转换,增强了预训练模型的潜在空间的表现力,可以更好地保持图像质量,同时实现鲁棒和可追踪的检测。值得一提的是,WaterFlow在一般鲁棒性方面达到了最新技术水平,并且是第一种能够有效防范复杂组合攻击的方法。我们在三个广泛使用的真实和生成数据集MS-COCO、DiffusionDB和WikiArt上验证了我们的发现。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
本文介绍了一种基于预训练扩散模型的快速且高度鲁棒的高保真视觉水印嵌入方法WaterFlow。它通过利用扩散模型将任意图像编码到潜在空间,并在潜在空间的傅立叶域中植入学习到的水印来实现高效水印嵌入。此方法使用可逆流层进行转换,提高了预训练模型的潜在空间表达能力,从而更好地保持了图像质量并实现了鲁棒和可追踪的检测。WaterFlow在一般鲁棒性方面表现出卓越的性能,并且是首个能够有效防御复杂组合攻击的方法。在MS-COCO、DiffusionDB和WikiArt三个广泛使用的真实和生成数据集上的验证结果证明了其有效性。
Key Takeaways
- WaterFlow是一种基于预训练扩散模型的快速且高度鲁棒的高保真视觉水印嵌入方法。
- WaterFlow利用扩散模型将图像编码到潜在空间,并在潜在空间的傅立叶域中植入学习到的水印。
- WaterFlow使用可逆流层进行转换,提高了预训练模型的潜在空间表达能力。
- WaterFlow能够很好地保持图像质量,同时实现鲁棒和可追踪的检测。
- WaterFlow在一般鲁棒性方面表现出卓越的性能,并能够有效防御复杂组合攻击。
- WaterFlow在MS-COCO、DiffusionDB和WikiArt三个数据集上的验证结果证明了其有效性。
点此查看论文截图

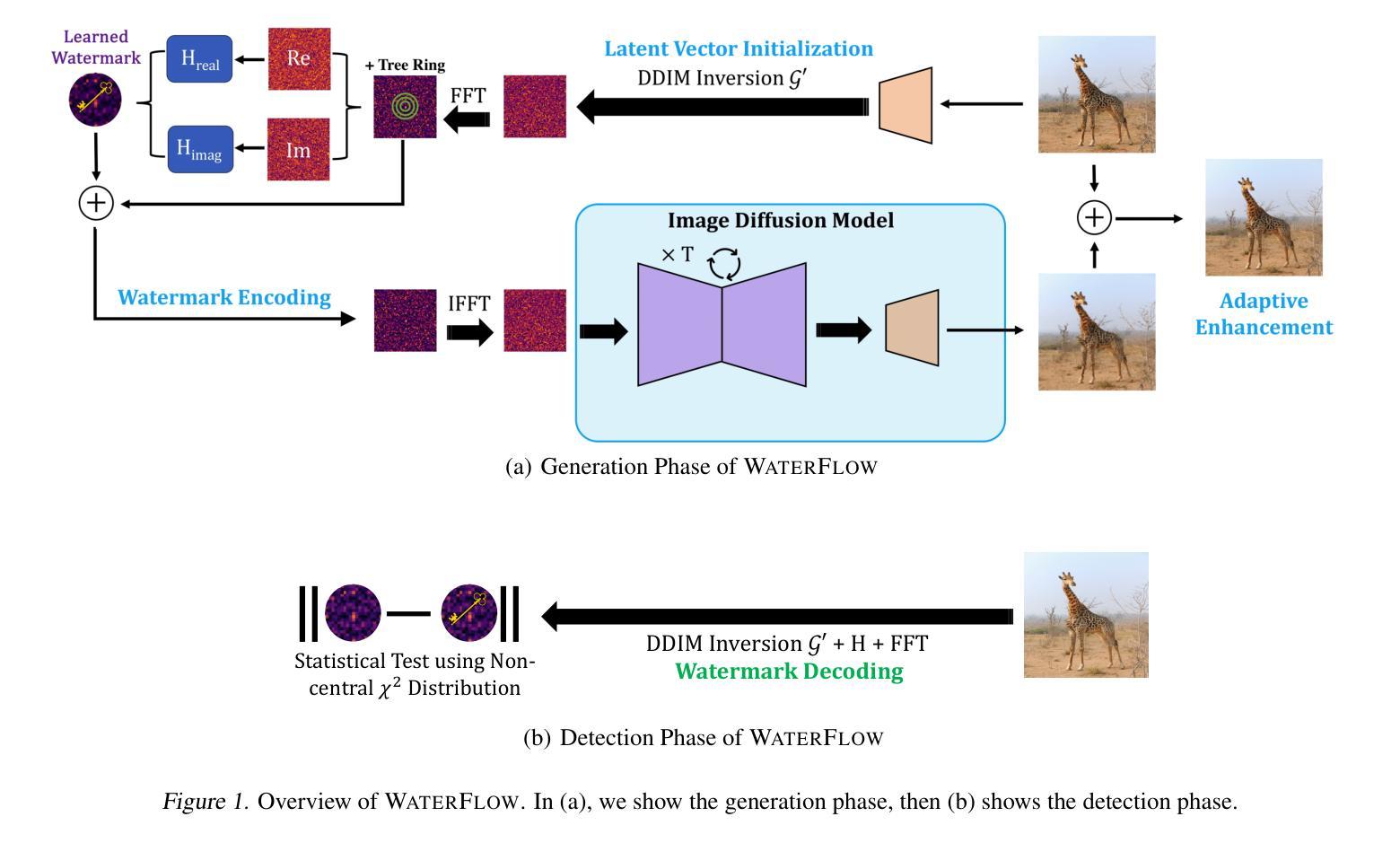
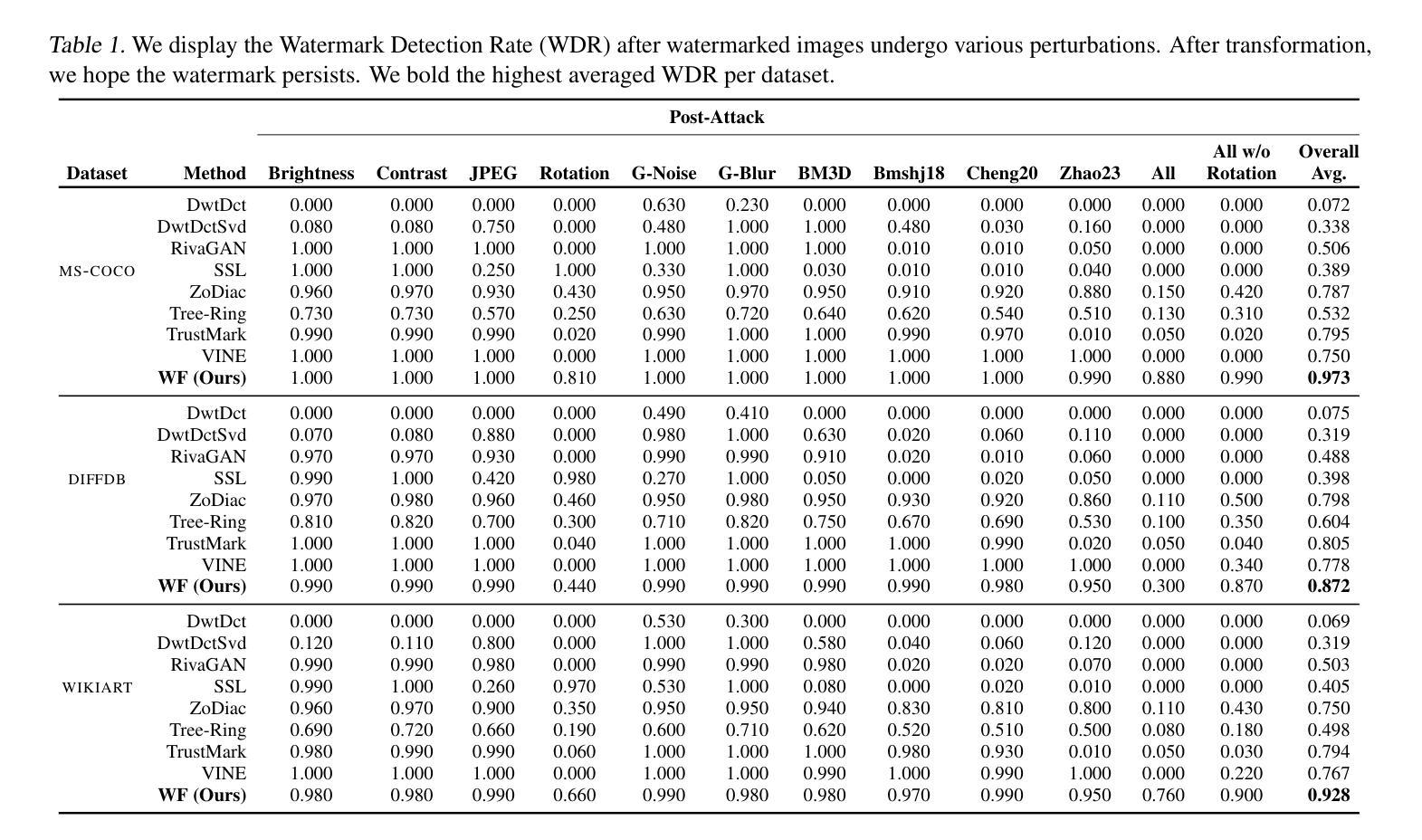
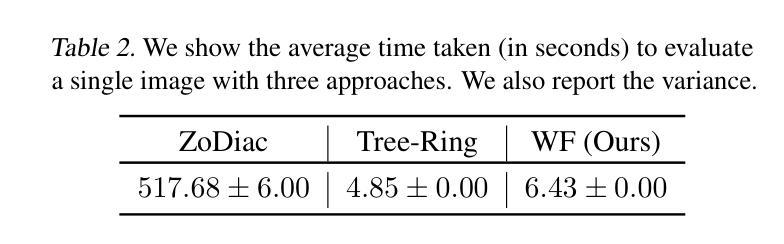
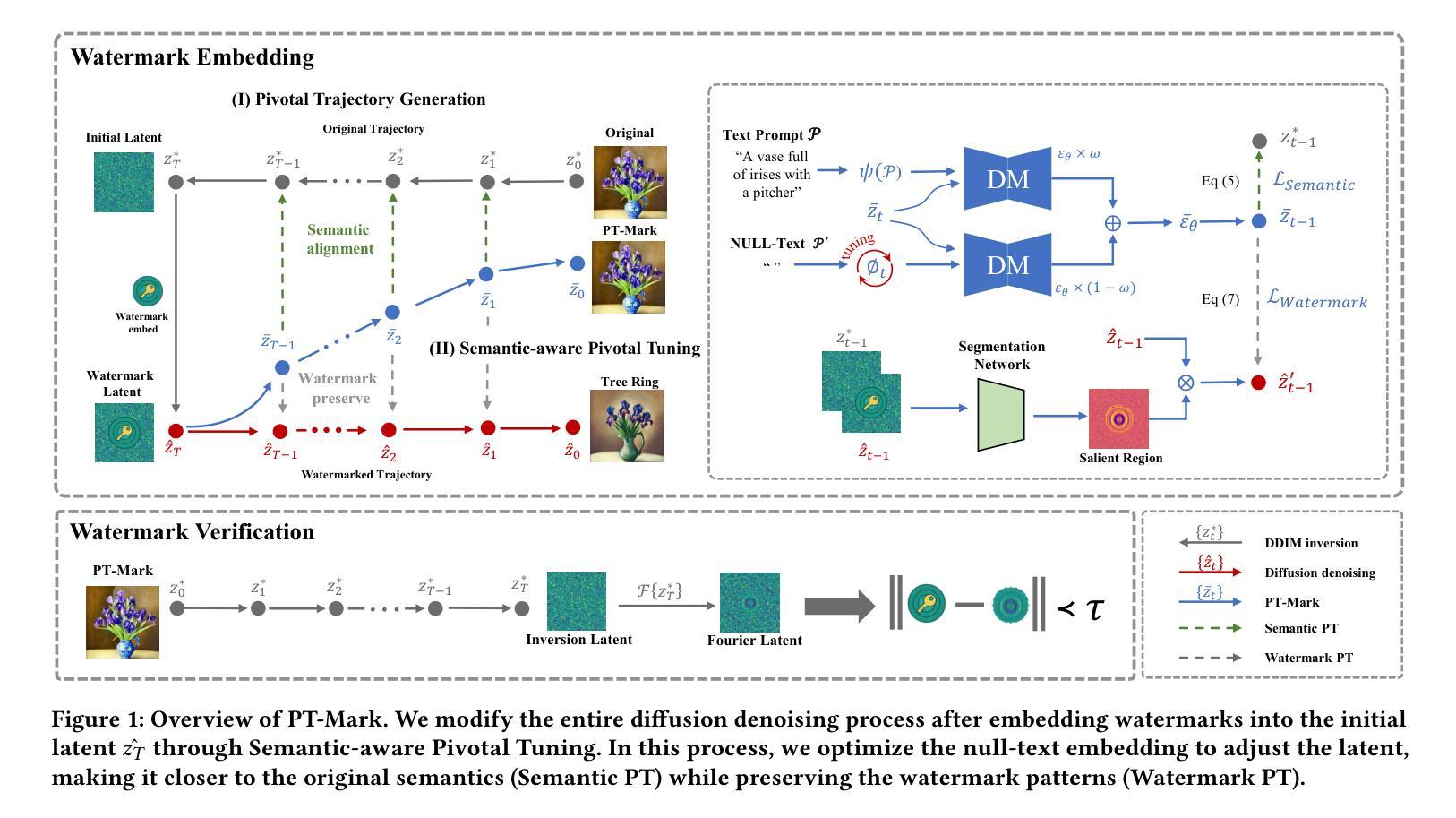
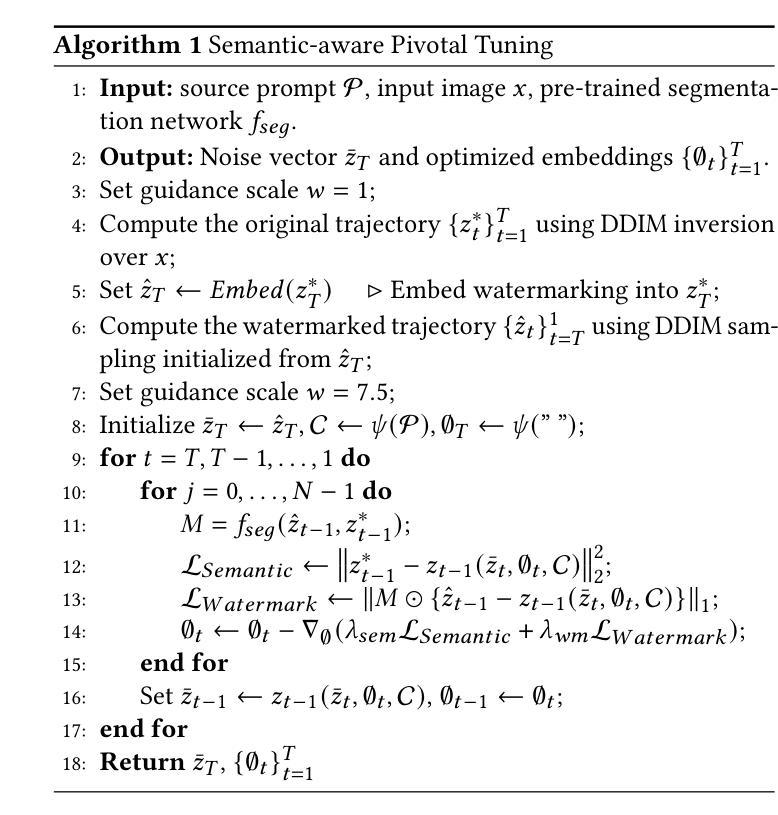
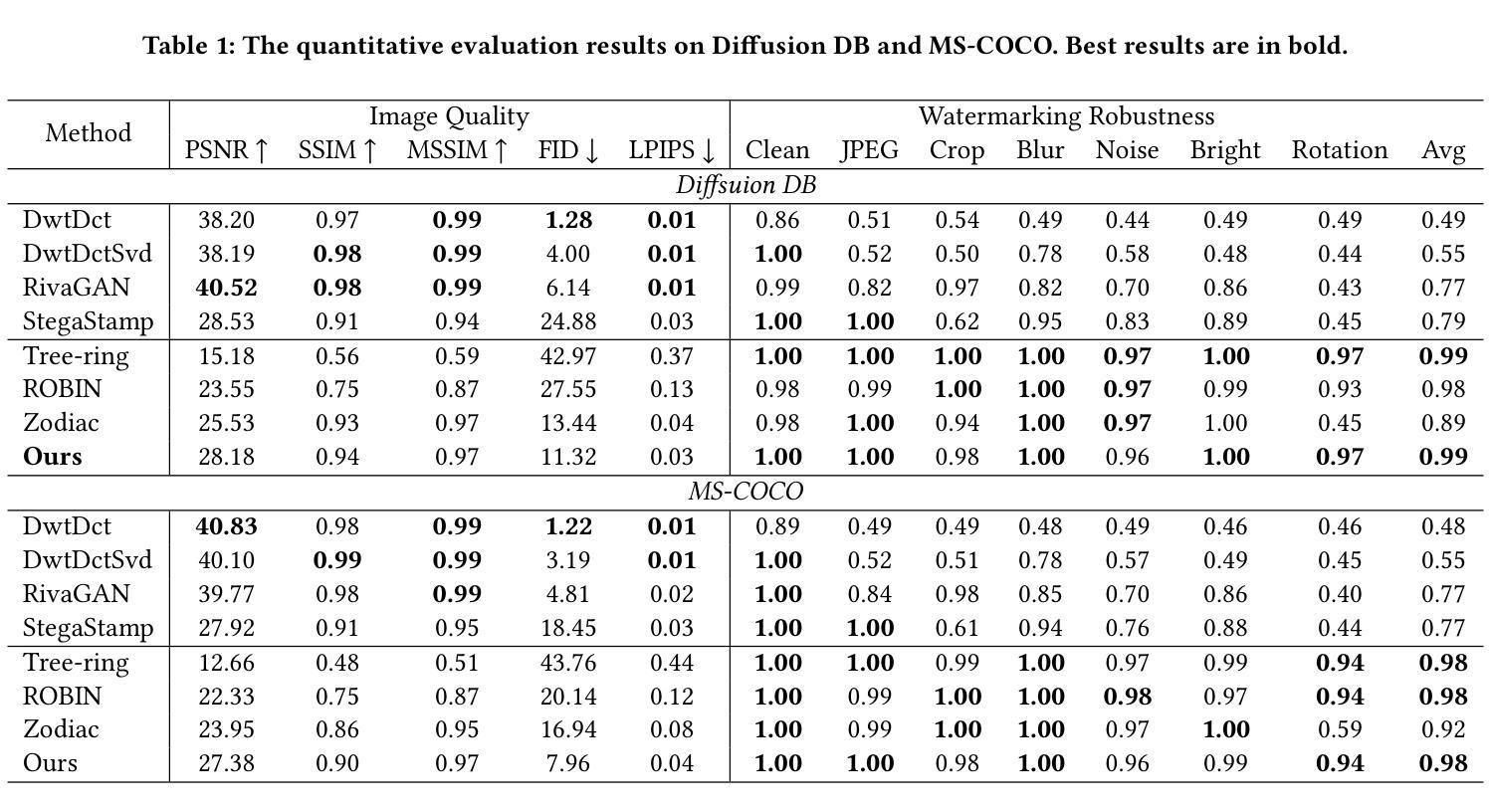
PT-Mark: Invisible Watermarking for Text-to-image Diffusion Models via Semantic-aware Pivotal Tuning
Authors:Yaopeng Wang, Huiyu Xu, Zhibo Wang, Jiacheng Du, Zhichao Li, Yiming Li, Qiu Wang, Kui Ren
Watermarking for diffusion images has drawn considerable attention due to the widespread use of text-to-image diffusion models and the increasing need for their copyright protection. Recently, advanced watermarking techniques, such as Tree Ring, integrate watermarks by embedding traceable patterns (e.g., Rings) into the latent distribution during the diffusion process. Such methods disrupt the original semantics of the generated images due to the inevitable distribution shift caused by the watermarks, thereby limiting their practicality, particularly in digital art creation. In this work, we present Semantic-aware Pivotal Tuning Watermarks (PT-Mark), a novel invisible watermarking method that preserves both the semantics of diffusion images and the traceability of the watermark. PT-Mark preserves the original semantics of the watermarked image by gradually aligning the generation trajectory with the original (pivotal) trajectory while maintaining the traceable watermarks during whole diffusion denoising process. To achieve this, we first compute the salient regions of the watermark at each diffusion denoising step as a spatial prior to identify areas that can be aligned without disrupting the watermark pattern. Guided by the region, we then introduce an additional pivotal tuning branch that optimizes the text embedding to align the semantics while preserving the watermarks. Extensive evaluations demonstrate that PT-Mark can preserve the original semantics of the diffusion images while integrating robust watermarks. It achieves a 10% improvement in the performance of semantic preservation (i.e., SSIM, PSNR, and LPIPS) compared to state-of-the-art watermarking methods, while also showing comparable robustness against real-world perturbations and four times greater efficiency.
针对扩散图像的水印技术已引起广泛关注,这主要是由于文本到图像扩散模型的广泛应用和对版权保护的不断增长的需求。最近,先进的水印技术,如Tree Ring,通过在扩散过程中将可追踪的模式(例如圆环)嵌入潜在分布来集成水印。这些方法由于水印导致的不可避免的分发偏移,破坏了生成图像的原语义,从而限制了它们的实用性,特别是在数字艺术创作中。在这项工作中,我们提出了语义感知的枢轴调整水印(PT-Mark),这是一种新的不可见水印方法,既能保留扩散图像语义,又能追踪水印。PT-Mark通过在整个扩散去噪过程中逐渐调整生成轨迹与原始(枢轴)轨迹的对齐,同时保持可追踪的水印,从而保留了水印图像的原始语义。为了实现这一点,我们首先计算每个扩散去噪步骤中水印的显著区域作为空间先验,以识别可以在不破坏水印模式的情况下对齐的区域。在该区域的指导下,然后我们引入了一个额外的枢轴调整分支,以优化文本嵌入,在对齐语义的同时保留水印。广泛评估表明,PT-Mark能够在集成稳健水印的同时保留扩散图像的原始语义。与最先进的水印技术相比,它在语义保留性能(即SSIM、PSNR和LPIPS)方面实现了10%的改进,同时显示出对现实世界扰动的相当稳健性,并且效率提高了四倍。
论文及项目相关链接
摘要
文本介绍了扩散图像水印技术的新进展。由于文本到图像扩散模型广泛应用及其版权保护需求增加,水印技术受到关注。最新方法如Tree Ring通过在扩散过程中嵌入可追踪模式(如圆环)进行水印集成,但会破坏生成图像的原语义。本文提出一种新型不可见水印技术——语义感知关键调整水印(PT-Mark),该技术既保留扩散图像语义又具备水印可追踪性。PT-Mark通过逐步调整生成轨迹与原始(关键)轨迹对齐,同时在整个扩散去噪过程中保持可追踪水印,保护水印图像的原语义。为达成此目标,首先在每个扩散去噪步骤计算水印的显著区域作为空间先验,以识别可对齐区域而不干扰水印图案。受该区域引导,引入额外关键调整分支优化文本嵌入,在对齐语义的同时保留水印。评估显示,PT-Mark在集成稳健水印的同时,保留扩散图像的原语义,较先进水印方法在语义保留性能上提升10%,同时展现对现实世界扰动的稳健性并提高效率四倍。
关键见解
- 水印技术对于保护文本到图像扩散模型的版权至关重要。
- 最新方法如Tree Ring虽然能够集成水印,但会破坏生成图像的原语义。
- PT-Mark是一种新型不可见水印技术,旨在解决现有技术破坏图像原语义的问题。
- PT-Mark通过逐步对齐生成轨迹与原始轨迹,同时保持整个扩散去噪过程中的水印可追踪性,保护图像的原语义。
- PT-Mark引入空间先验和关键调整分支来实现语义保留和水印的集成。
- 评估显示PT-Mark在语义保留、稳健性和效率方面较先进方法有所提升。
点此查看论文截图

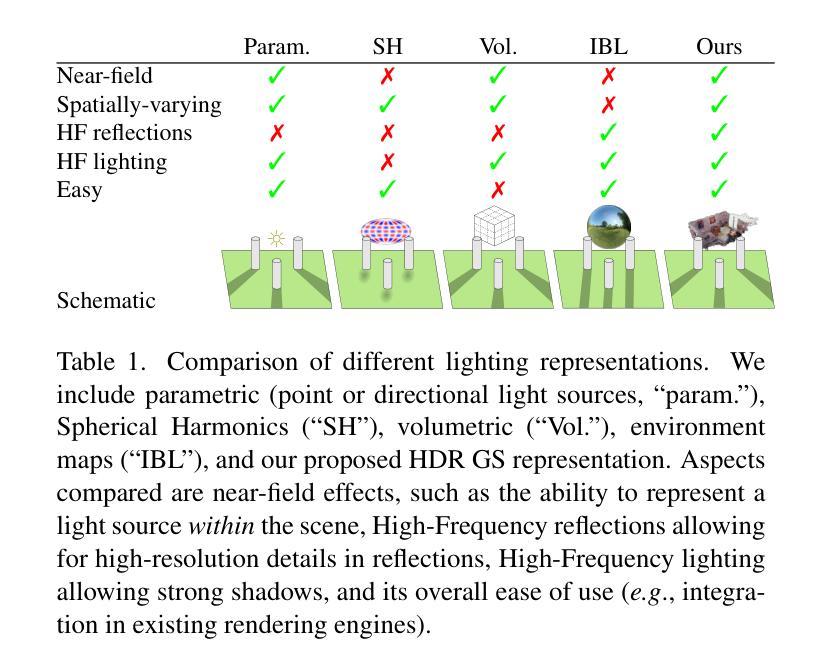
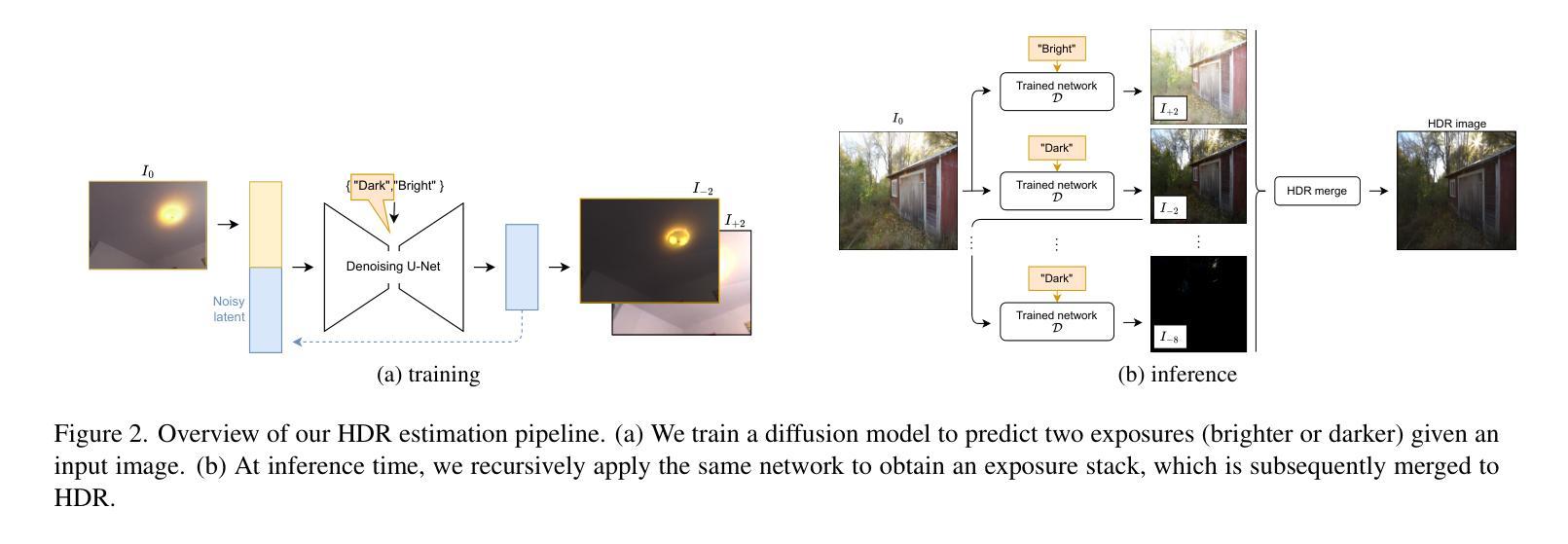
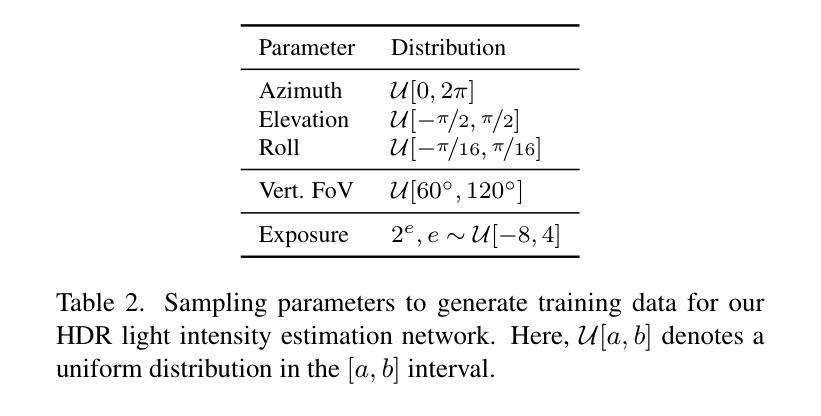
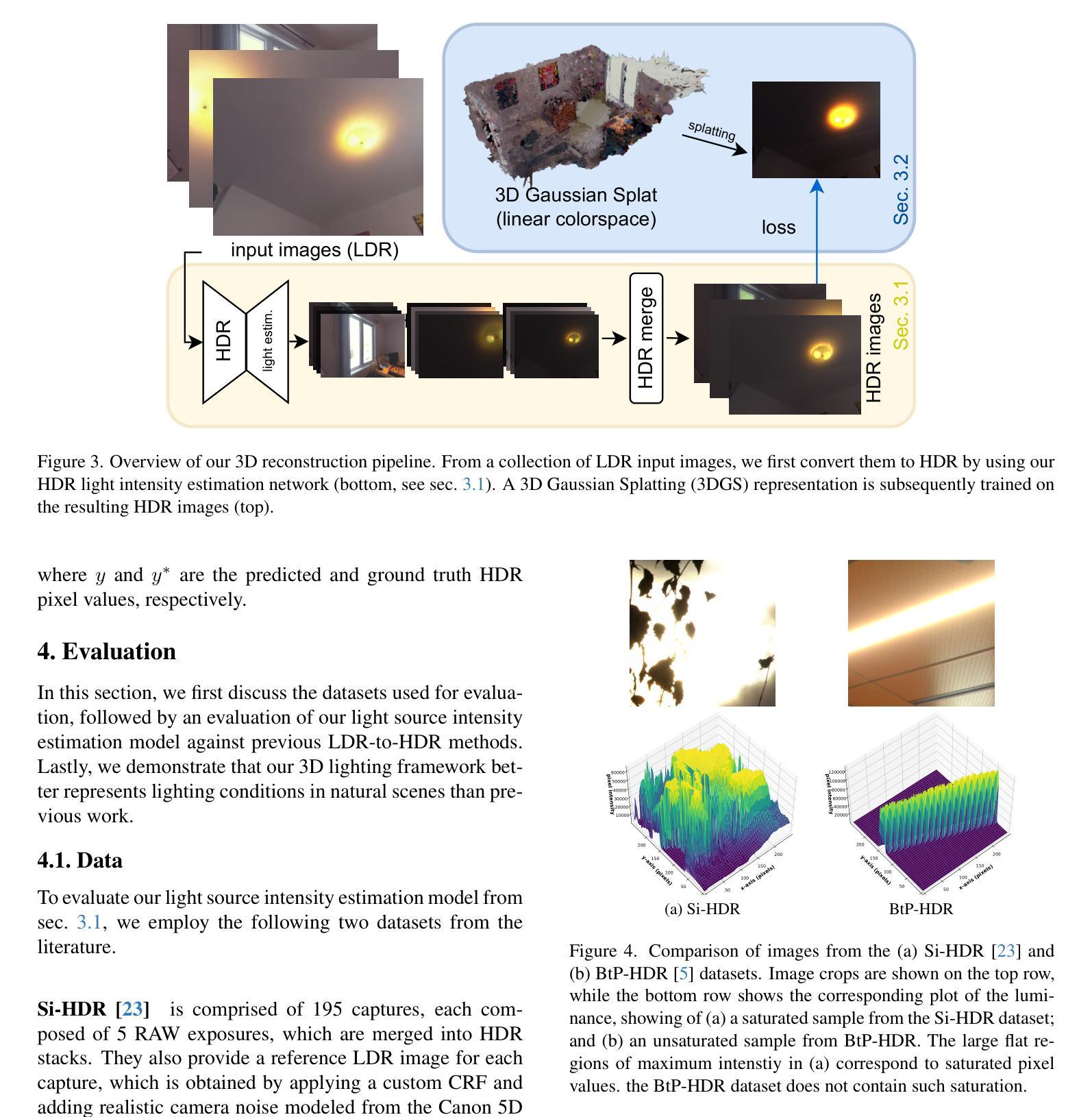
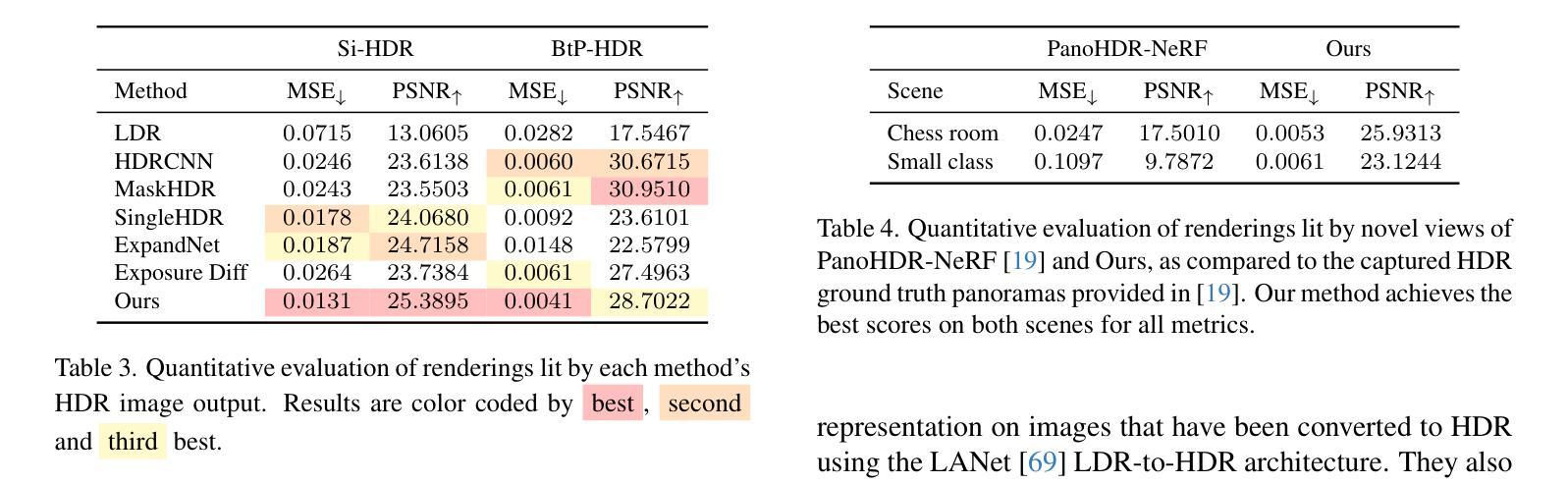
GaSLight: Gaussian Splats for Spatially-Varying Lighting in HDR
Authors:Christophe Bolduc, Yannick Hold-Geoffroy, Zhixin Shu, Jean-François Lalonde
We present GaSLight, a method that generates spatially-varying lighting from regular images. Our method proposes using HDR Gaussian Splats as light source representation, marking the first time regular images can serve as light sources in a 3D renderer. Our two-stage process first enhances the dynamic range of images plausibly and accurately by leveraging the priors embedded in diffusion models. Next, we employ Gaussian Splats to model 3D lighting, achieving spatially variant lighting. Our approach yields state-of-the-art results on HDR estimations and their applications in illuminating virtual objects and scenes. To facilitate the benchmarking of images as light sources, we introduce a novel dataset of calibrated and unsaturated HDR to evaluate images as light sources. We assess our method using a combination of this novel dataset and an existing dataset from the literature. Project page: https://lvsn.github.io/gaslight/
我们提出了GaSLight方法,该方法可以从常规图像生成空间变化的光照。我们的方法建议使用HDR高斯Splats作为光源表示,这是首次将常规图像作为3D渲染器的光源。我们的两阶段过程首先利用扩散模型中的先验知识,以合理且准确的方式增强图像的动态范围。接下来,我们使用高斯Splats对3D照明进行建模,以实现空间变化的光照。我们的方法在HDR估计及其应用于照明虚拟对象和场景方面产生了最先进的成果。为了对图像作为光源进行基准测试,我们引入了一个新型的校准和不饱和HDR数据集来评估图像作为光源。我们使用这个新型数据集和文献中的现有数据集来评估我们的方法。项目页面:https://lvsn.github.io/gaslight/
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
我们提出了GaSLight方法,该方法可以从常规图像生成空间变化照明。我们的方法使用HDR高斯Splats作为光源表示,这是首次在3D渲染中使用常规图像作为光源。我们的两步过程首先利用扩散模型中的先验知识,以合理且准确的方式增强图像的动态范围。接下来,我们使用高斯Splats对3D照明进行建模,实现空间变化照明。我们的方法在HDR估计及其用于照亮虚拟对象和场景方面的应用方面达到了最新水平。为了方便将图像作为光源进行基准测试,我们引入了一个新型校准和不饱和HDR数据集来评估图像作为光源。我们使用这个新数据集和现有文献数据集来评估我们的方法。
Key Takeaways
- GaSLight方法能够从常规图像生成空间变化照明。
- HDR高斯Splats首次被用作光源表示,用于3D渲染中的常规图像。
- 该方法分为两个阶段:第一阶段增强图像动态范围,第二阶段使用高斯Splats进行3D照明建模,实现空间变化照明。
- 方法在HDR估计方面达到最新水平,并成功应用于照亮虚拟对象和场景。
- 为了评估图像作为光源的效果,引入了一个新型校准和不饱和HDR数据集。
- 该方法结合了新型数据集和现有数据集进行评估。
点此查看论文截图

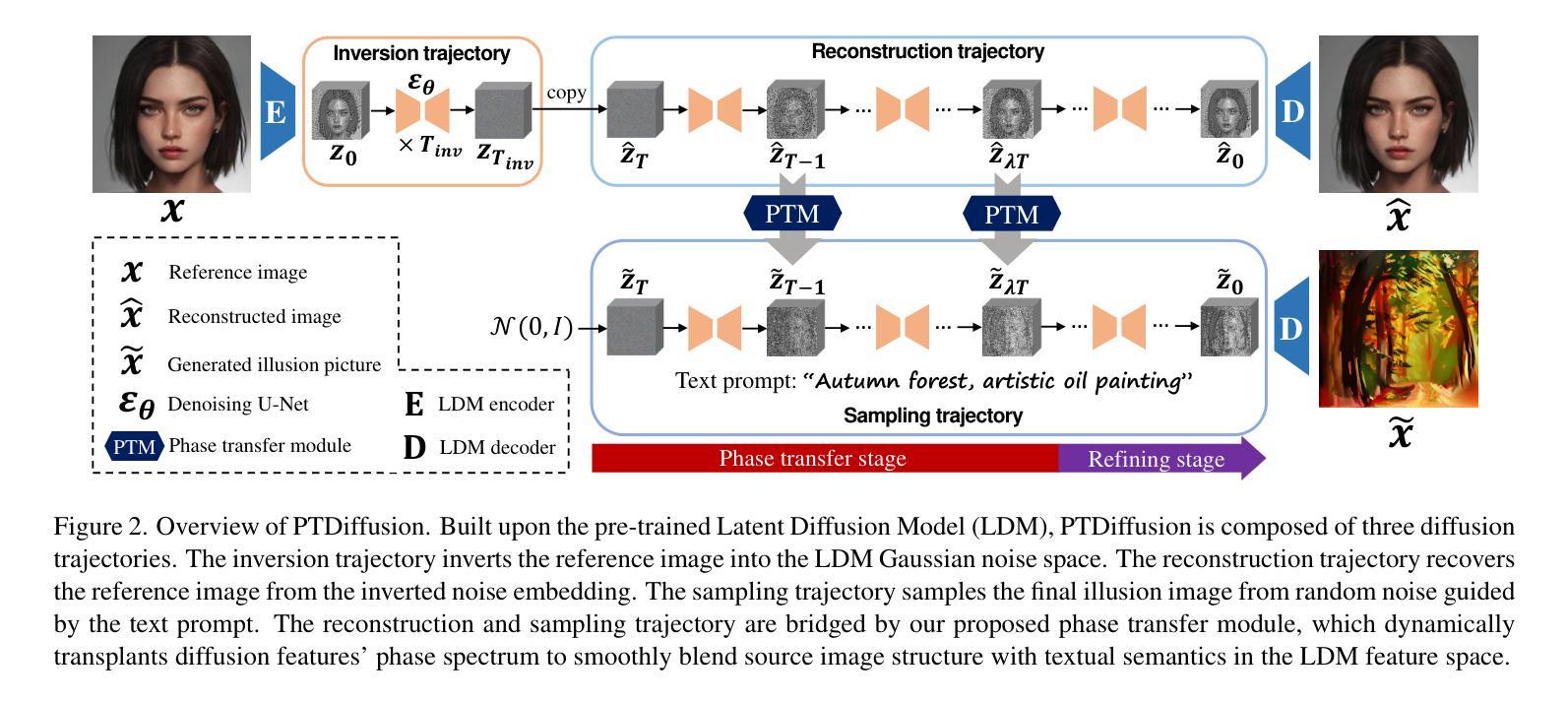
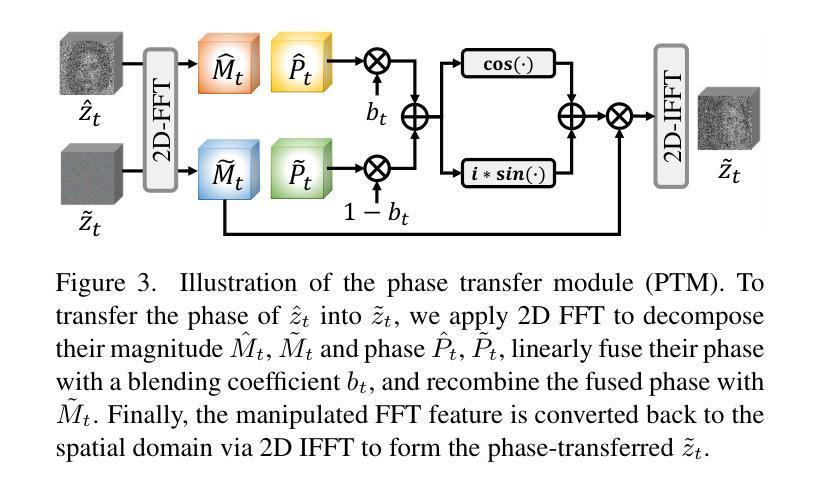
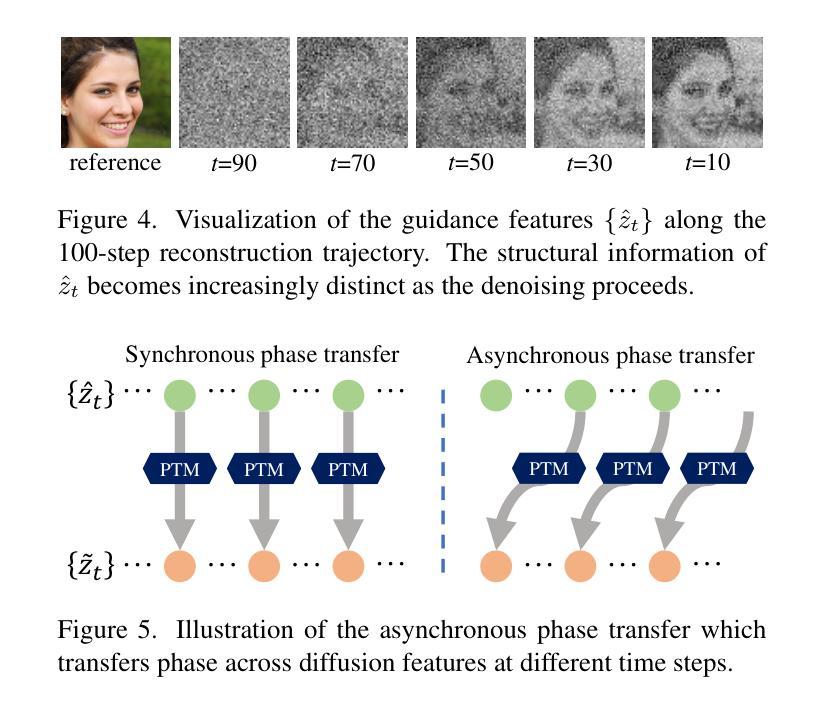
PTDiffusion: Free Lunch for Generating Optical Illusion Hidden Pictures with Phase-Transferred Diffusion Model
Authors:Xiang Gao, Shuai Yang, Jiaying Liu
Optical illusion hidden picture is an interesting visual perceptual phenomenon where an image is cleverly integrated into another picture in a way that is not immediately obvious to the viewer. Established on the off-the-shelf text-to-image (T2I) diffusion model, we propose a novel training-free text-guided image-to-image (I2I) translation framework dubbed as \textbf{P}hase-\textbf{T}ransferred \textbf{Diffusion} Model (PTDiffusion) for hidden art syntheses. PTDiffusion harmoniously embeds an input reference image into arbitrary scenes described by the text prompts, producing illusion images exhibiting hidden visual cues of the reference image. At the heart of our method is a plug-and-play phase transfer mechanism that dynamically and progressively transplants diffusion features’ phase spectrum from the denoising process to reconstruct the reference image into the one to sample the generated illusion image, realizing deep fusion of the reference structural information and the textual semantic information in the diffusion model latent space. Furthermore, we propose asynchronous phase transfer to enable flexible control to the degree of hidden content discernability. Our method bypasses any model training and fine-tuning process, all while substantially outperforming related text-guided I2I methods in image generation quality, text fidelity, visual discernibility, and contextual naturalness for illusion picture synthesis, as demonstrated by extensive qualitative and quantitative experiments. Our project is publically available at \href{https://xianggao1102.github.io/PTDiffusion_webpage/}{this web page}.
光学错觉隐藏图像是一种有趣的视觉感知现象,图像巧妙地融入另一幅图片中,使观众无法立即识别。我们基于现成的文本到图像(T2I)扩散模型,提出了一种无需训练、文本引导的图像到图像(I2I)转换框架,名为“阶段转移扩散模型”(PTDiffusion),用于合成隐藏艺术。PTDiffusion和谐地将输入参考图像嵌入由文本提示描述的任意场景中,生成显示参考图像隐藏视觉线索的错觉图像。我们的方法核心是一个即插即用的相位转移机制,它动态且渐进地移植扩散特征在降噪过程中的相位谱,重建将参考图像采样到生成的错觉图像中,实现在扩散模型潜在空间中参考结构信息和文本语义信息的深度融合。此外,我们提出了异步相位转移,以实现灵活控制隐藏内容可辨识度的程度。我们的方法绕过了任何模型训练和微调过程,同时在图像生成质量、文本忠实度、视觉辨识度和上下文自然度方面大大优于相关的文本引导I2I方法,为错觉图像合成提供了广泛的质量和数量实验证明。我们的项目已在以下网页公开:[https://xianggao110
论文及项目相关链接
PDF Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPR 2025)
Summary
本文介绍了一种基于现成的文本到图像(T2I)扩散模型的新型训练免文本引导图像到图像(I2I)转换框架——PTDiffusion(相位转移扩散模型),用于合成隐藏艺术图像。该模型能够将输入参考图像嵌入到文本描述的场景中,生成带有参考图像隐藏视觉线索的错觉图像。其核心机制是即插即用的相位转移机制,该机制动态地逐步转移去噪过程中的扩散特征的相位谱,实现在扩散模型潜在空间中的参考结构信息和文本语义信息的深度融合。此外,还提出了异步相位转移,以实现灵活控制隐藏内容的可辨识程度。该方法无需任何模型训练和微调过程,在图像生成质量、文本忠实度、视觉可辨识度和上下文自然度等方面均大大优于相关文本引导的I2I方法,为错觉图像合成提供了新的方向。
Key Takeaways
- 利用文本到图像的扩散模型开发了一种新型的文本引导图像到图像转换框架PTDiffusion。
- PTDiffusion能够在文本描述的场景中嵌入参考图像,生成带有隐藏视觉线索的错觉图像。
- PTDiffusion的核心机制是相位转移机制,该机制实现了在扩散模型潜在空间中的参考结构信息和文本语义信息的深度融合。
- 提出了异步相位转移,以实现对隐藏内容可辨识度的灵活控制。
- 该方法无需任何模型训练和微调过程。
- PTDiffusion在图像生成质量、文本忠实度、视觉可辨识度和上下文自然度等方面显著优于其他相关方法。
点此查看论文截图


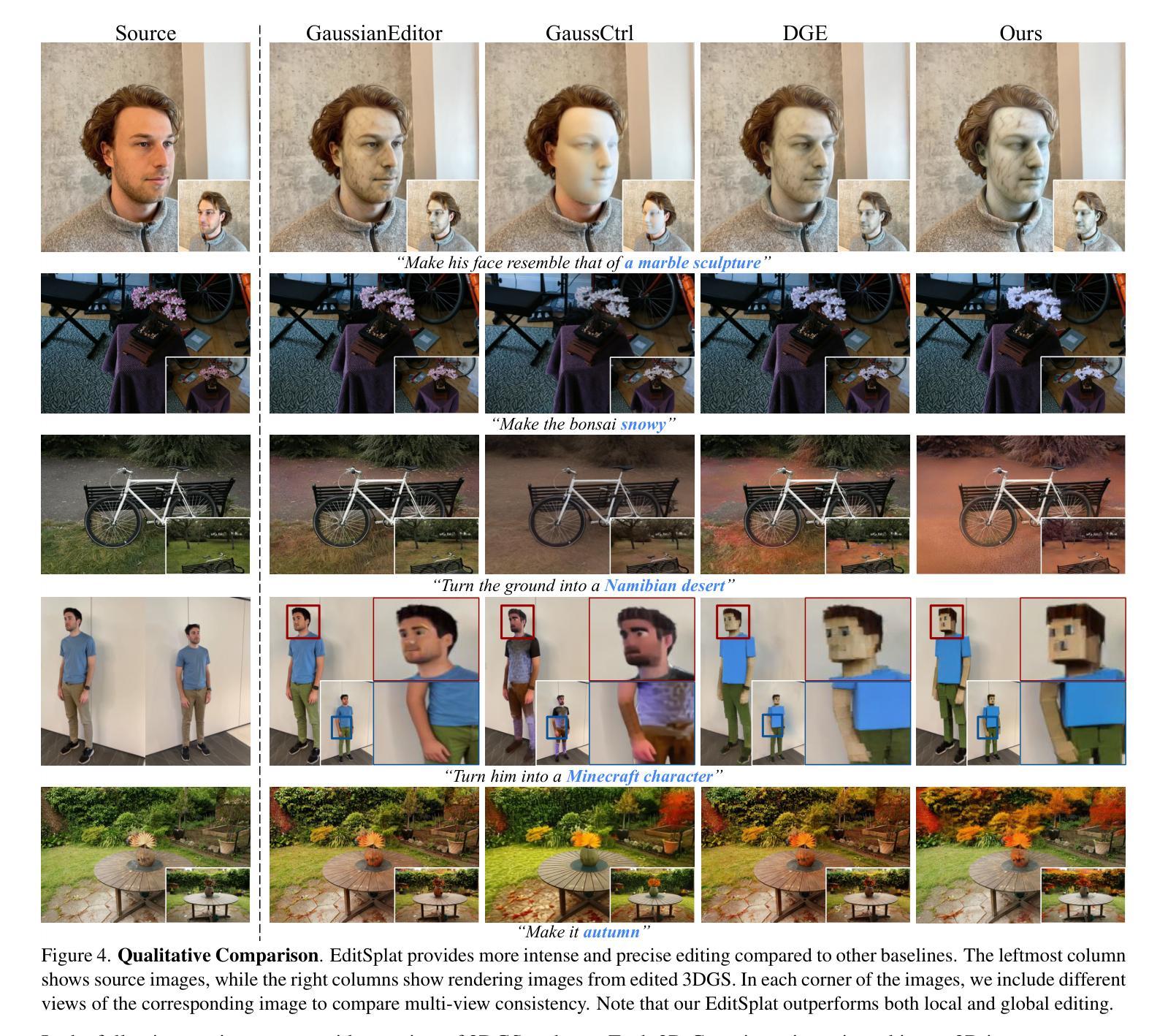
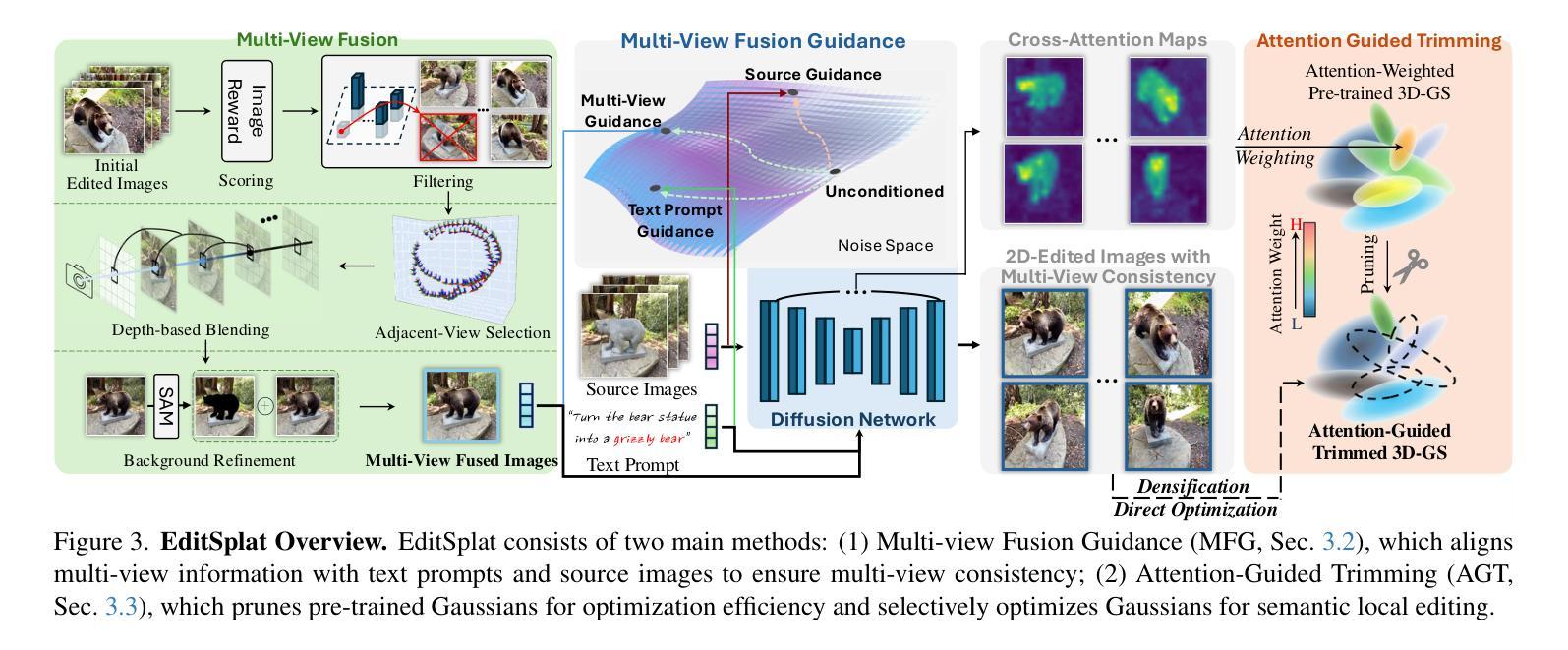
EditSplat: Multi-View Fusion and Attention-Guided Optimization for View-Consistent 3D Scene Editing with 3D Gaussian Splatting
Authors:Dong In Lee, Hyeongcheol Park, Jiyoung Seo, Eunbyung Park, Hyunje Park, Ha Dam Baek, Sangheon Shin, Sangmin Kim, Sangpil Kim
Recent advancements in 3D editing have highlighted the potential of text-driven methods in real-time, user-friendly AR/VR applications. However, current methods rely on 2D diffusion models without adequately considering multi-view information, resulting in multi-view inconsistency. While 3D Gaussian Splatting (3DGS) significantly improves rendering quality and speed, its 3D editing process encounters difficulties with inefficient optimization, as pre-trained Gaussians retain excessive source information, hindering optimization. To address these limitations, we propose EditSplat, a novel text-driven 3D scene editing framework that integrates Multi-view Fusion Guidance (MFG) and Attention-Guided Trimming (AGT). Our MFG ensures multi-view consistency by incorporating essential multi-view information into the diffusion process, leveraging classifier-free guidance from the text-to-image diffusion model and the geometric structure inherent to 3DGS. Additionally, our AGT utilizes the explicit representation of 3DGS to selectively prune and optimize 3D Gaussians, enhancing optimization efficiency and enabling precise, semantically rich local editing. Through extensive qualitative and quantitative evaluations, EditSplat achieves state-of-the-art performance, establishing a new benchmark for text-driven 3D scene editing.
最近的3D编辑技术进展突出了文本驱动方法在实时、用户友好的AR/VR应用中的潜力。然而,当前的方法依赖于二维扩散模型,而没有充分考虑到多视角信息,导致多视角不一致。虽然三维高斯平铺(3DGS)技术显著提高了渲染质量和速度,但其三维编辑过程在优化方面遇到了困难,因为预训练的高斯保留了过多的源信息,阻碍了优化。为了解决这些局限性,我们提出了EditSplat,这是一种新型的文本驱动三维场景编辑框架,它集成了多视角融合指导(MFG)和注意力引导修剪(AGT)。我们的MFG通过融入扩散过程中的关键多视角信息,利用文本到图像的扩散模型的非分类器指导以及3DGS所固有的几何结构,确保多视角的一致性。此外,我们的AGT利用3DGS的显式表示进行有选择性地修剪和优化三维高斯,提高优化效率,实现精确且语义丰富的局部编辑。通过广泛的质量和数量评估,EditSplat达到了最先进的性能,为文本驱动的三维场景编辑建立了新的基准。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
本文介绍了文本驱动的3D场景编辑框架EditSplat,该框架集成了多视角融合引导(MFG)和注意力引导修剪(AGT)。EditSplat解决了现有方法在实时编辑过程中的多视角不一致和优化效率低下的问题,提高了渲染质量和速度。通过引入MFG和AGT,EditSplat实现了多视角一致性,并提高了优化效率,为精确、语义丰富的局部编辑提供了可能。经过定性和定量评估,EditSplat达到了业界领先水平,为文本驱动的3D场景编辑树立了新的基准。
Key Takeaways
以下是文本的关键要点:
- 当前3D编辑方法存在多视角不一致的问题。
- 现有方法主要依赖二维扩散模型,忽略了多视角信息的重要性。
- EditSplat框架集成了多视角融合引导(MFG)和注意力引导修剪(AGT),解决了上述问题。
- MFG通过引入文本到图像的扩散模型的分类器自由引导以及3D几何结构,确保多视角一致性。
- AGT利用显式的3DGS表示选择性地修剪和优化三维高斯分布,提高了优化效率和精确性。
- EditSplat框架实现了精确、语义丰富的局部编辑,并达到了业界领先水平。
点此查看论文截图



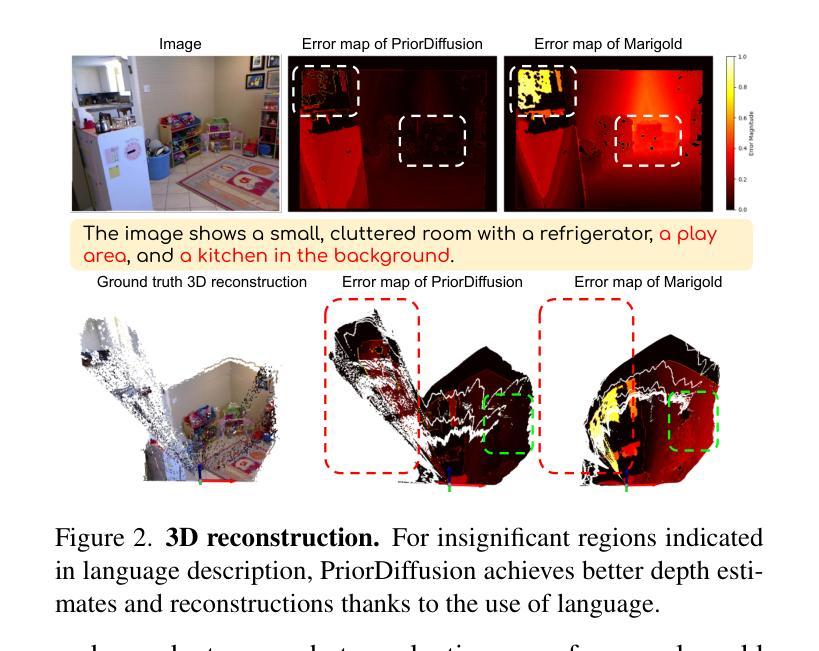
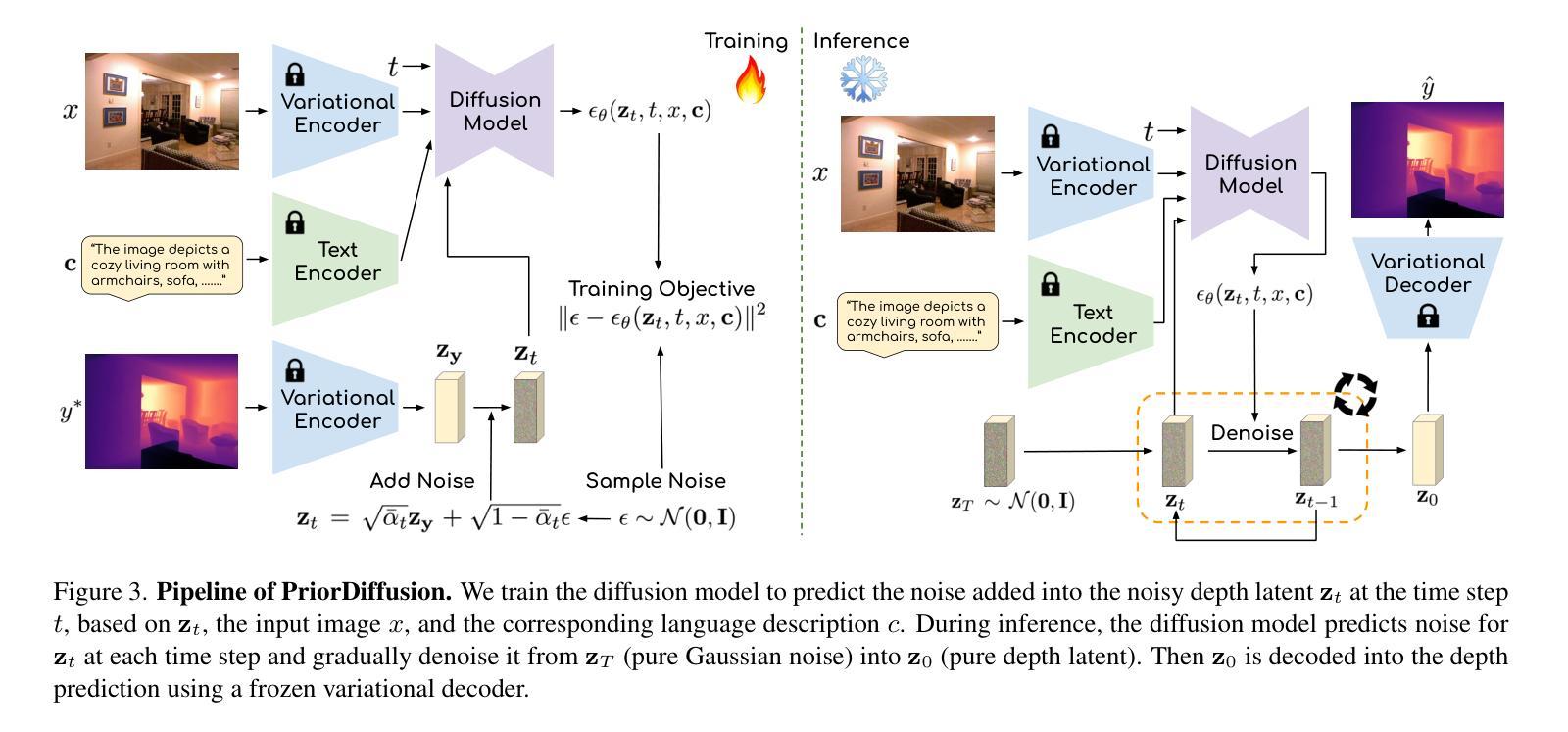
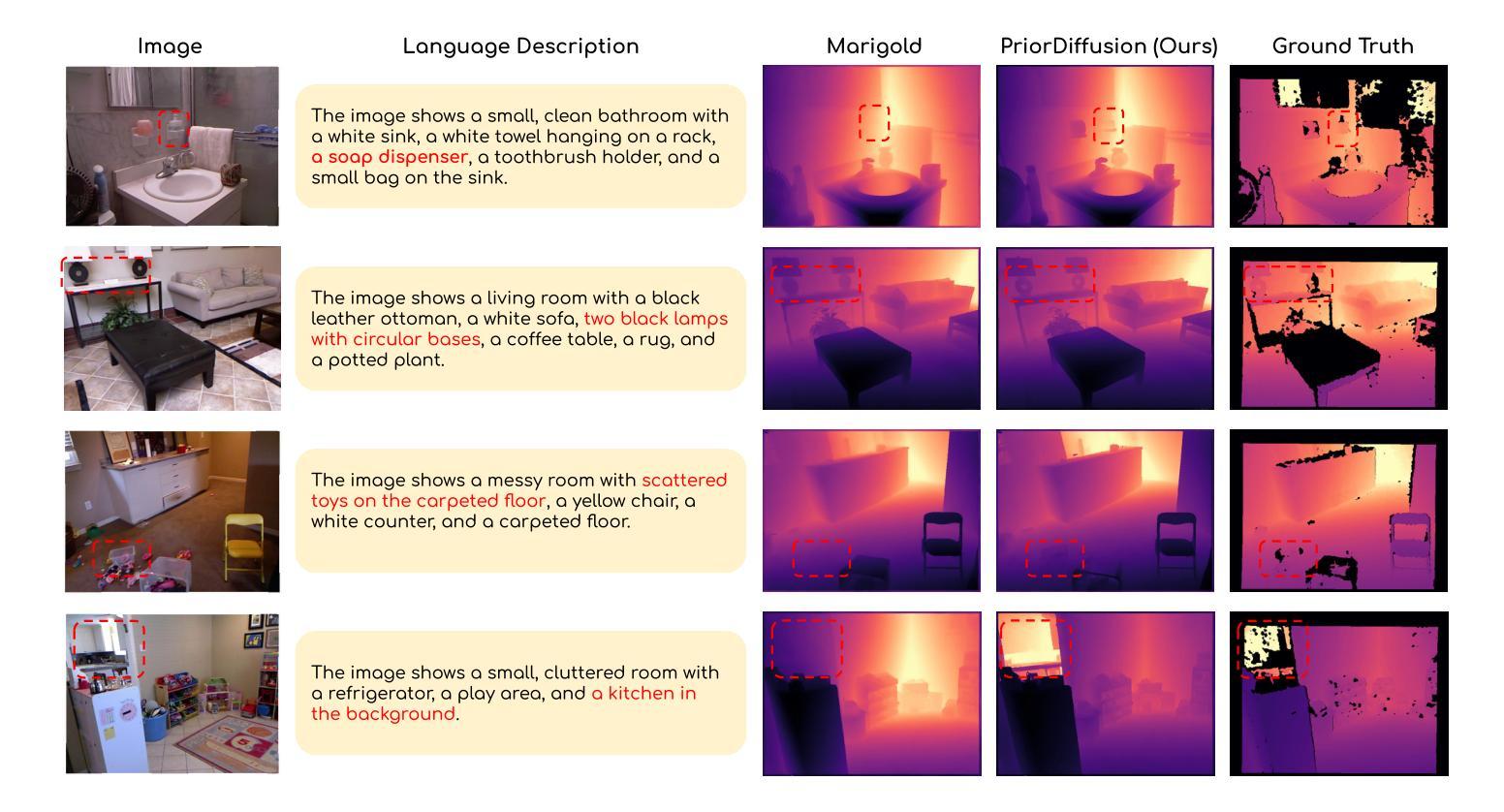
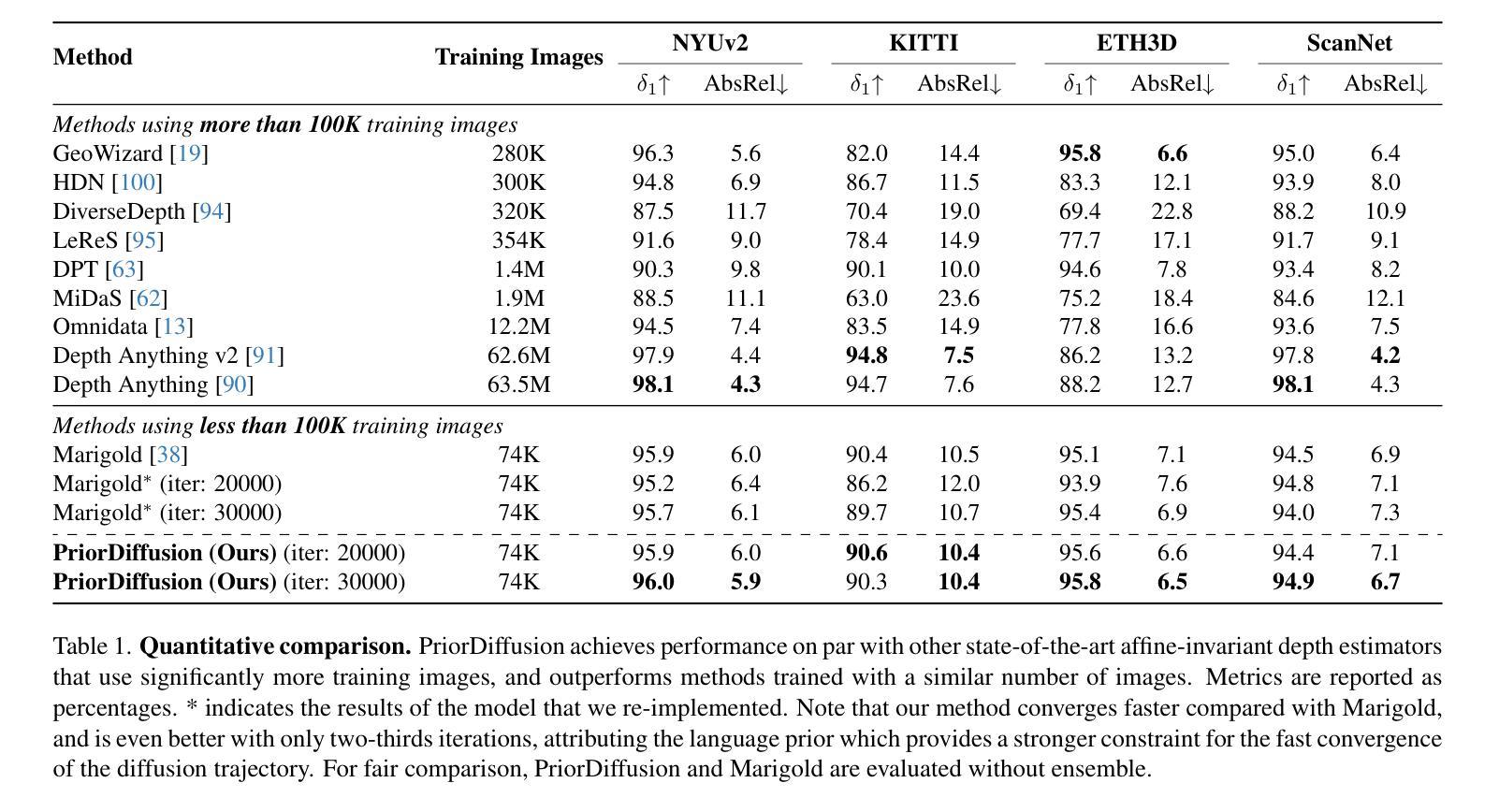
PriorDiffusion: Leverage Language Prior in Diffusion Models for Monocular Depth Estimation
Authors:Ziyao Zeng, Jingcheng Ni, Daniel Wang, Patrick Rim, Younjoon Chung, Fengyu Yang, Byung-Woo Hong, Alex Wong
Traditional monocular depth estimation suffers from inherent ambiguity and visual nuisance. We argue that language prior can enhance monocular depth estimation by leveraging the inductive bias learned during the text-to-image pre-training of diffusion models. The ability of these models to generate images that align with text indicates that they have learned the spatial relationships, size, and shape of specified objects, which can be applied to improve depth estimation. Thus, we propose PriorDiffusion, using a pre-trained text-to-image diffusion model that takes both images and corresponding text descriptions to infer affine-invariant depth through a denoising process. We also show that language prior enhances the model’s perception of specific regions of images that users care about and describe. Simultaneously, language prior acts as a constraint to accelerate the convergence of both training and the inference diffusion trajectory. By training on HyperSim and Virtual KITTI, we achieve faster training convergence, fewer inference diffusion steps, and state-of-the-art zero-shot performance across NYUv2, KITTI, ETH3D, and ScanNet. Code will be released upon acceptance.
传统单目深度估计存在固有的模糊性和视觉干扰问题。我们认为,通过利用扩散模型在文本到图像预训练过程中学到的归纳偏见,语言先验可以增强单目深度估计。这些模型能够生成与文本相符的图像,表明它们已经学会了指定对象的空间关系、大小和形状,这可以用于改进深度估计。因此,我们提出了PriorDiffusion,它使用预训练的文本到图像扩散模型,该模型通过去噪过程推断仿射不变深度,该过程既涉及图像又涉及相应的文本描述。我们还表明,语言先验提高了模型对用户关心和描述的图像特定区域的感知能力。同时,语言先验作为约束,加速了训练和推理扩散轨迹的收敛。通过在HyperSim和Virtual KITTI上进行训练,我们实现了更快的训练收敛速度、更少的推理扩散步骤,以及在NYUv2、KITTI、ETH3D和ScanNet上的最先进的零样本性能。代码将在接受后发布。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
本文提出利用文本先验信息增强单目深度估计的方法,借助扩散模型的文本到图像预训练中的归纳偏置。扩散模型在生成与文本对应的图像时,已学习物体空间关系、大小和形状,可应用于深度估计。因此,本文提出PriorDiffusion,使用预训练的文本到图像扩散模型,结合图像和相应文本描述,通过去噪过程推断仿射不变深度。同时,文本先验信息提高了模型对用户关注图像特定区域的感知能力,并作为约束加速训练和推理扩散轨迹的收敛。在HyperSim和Virtual KITTI数据集上训练,实现更快的训练收敛速度、更少的推理扩散步骤,以及在NYUv2、KITTI、ETH3D和ScanNet上的零样本性能达到领先水平。
Key Takeaways
- 文本先验信息可增强单目深度估计,利用扩散模型的归纳偏置。
- 扩散模型在生成图像时已学习空间关系、大小和形状,可应用于深度估计。
- 提出PriorDiffusion方法,结合图像和文本描述,通过去噪过程推断深度。
- 文本先验信息提高模型对图像特定区域的感知能力。
- 文本先验信息作为约束,加速训练和推理扩散轨迹的收敛。
- 在多个数据集上实现快速训练收敛和零样本性能领先水平。
点此查看论文截图


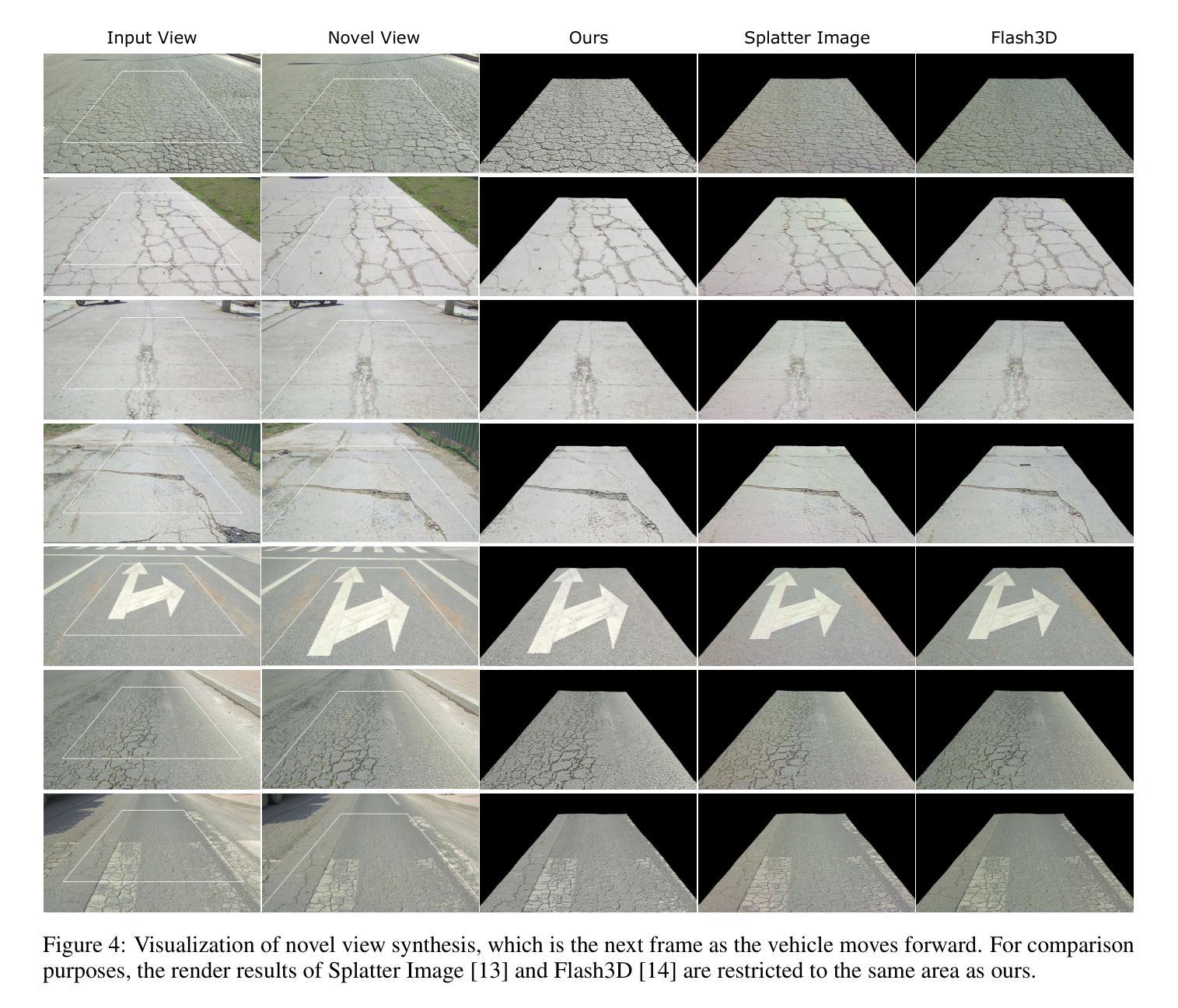
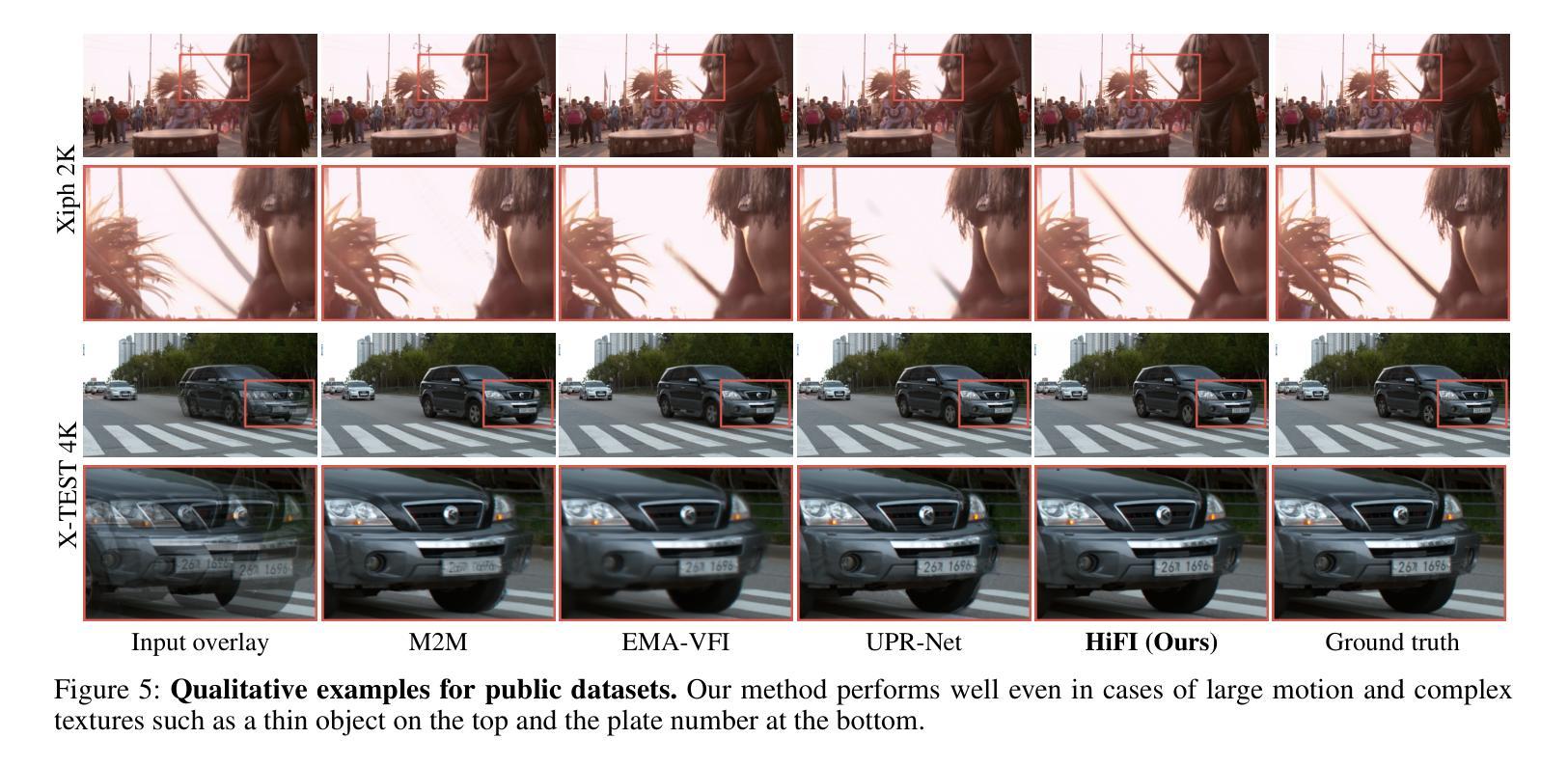
High-Resolution Frame Interpolation with Patch-based Cascaded Diffusion
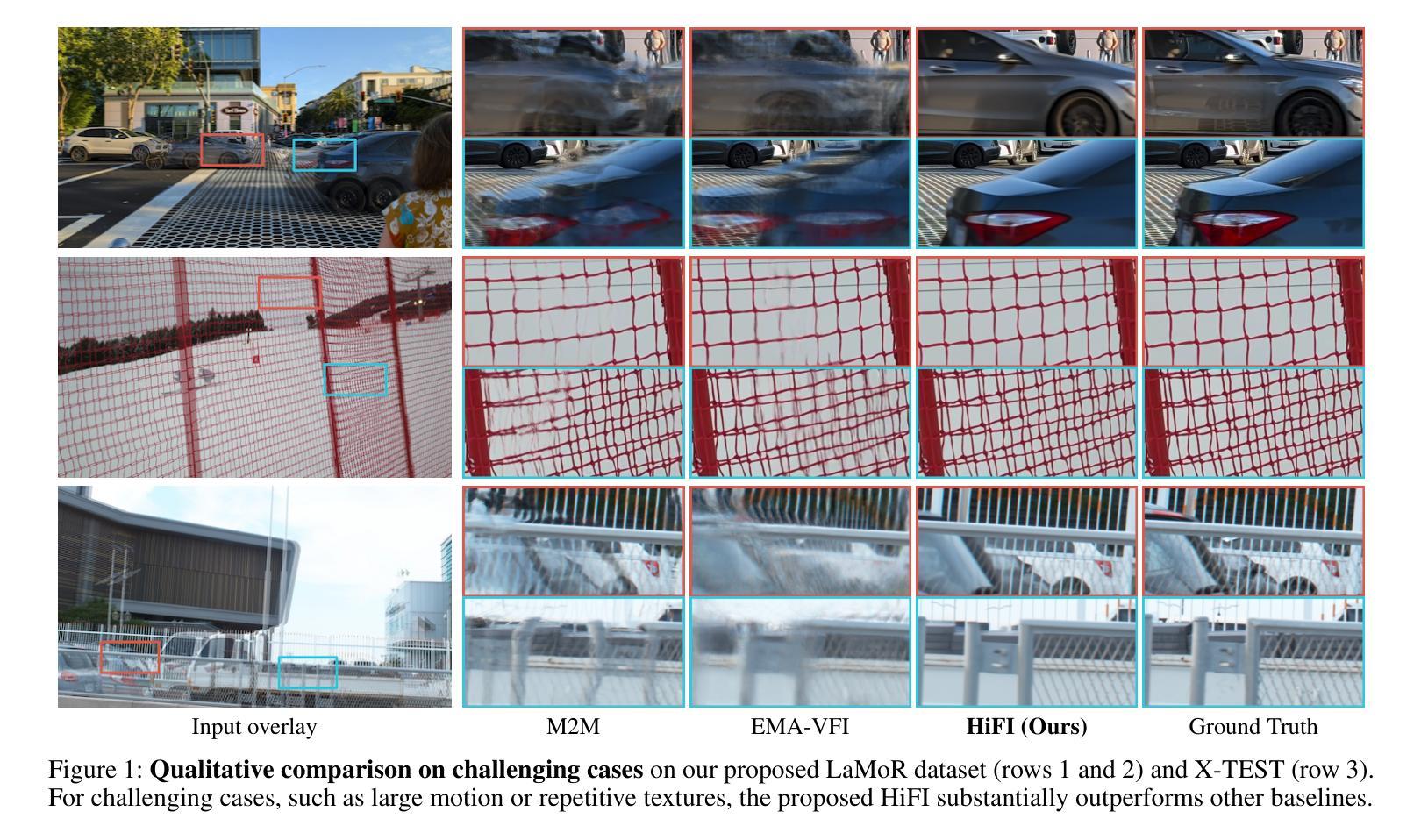
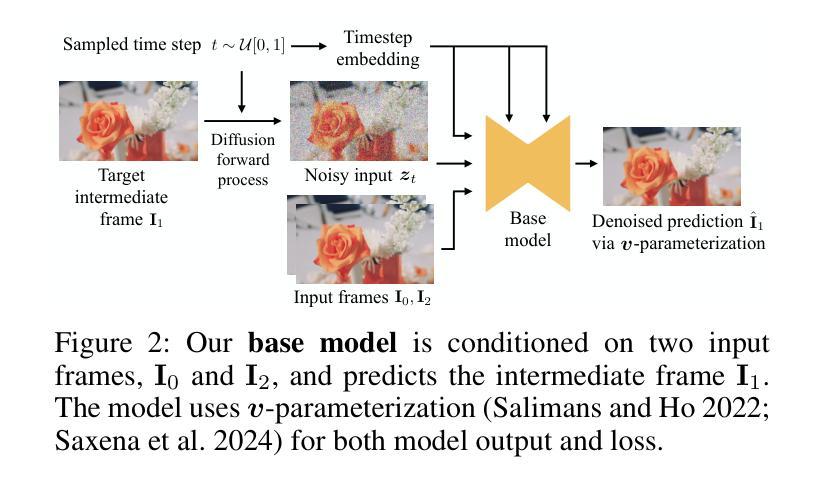
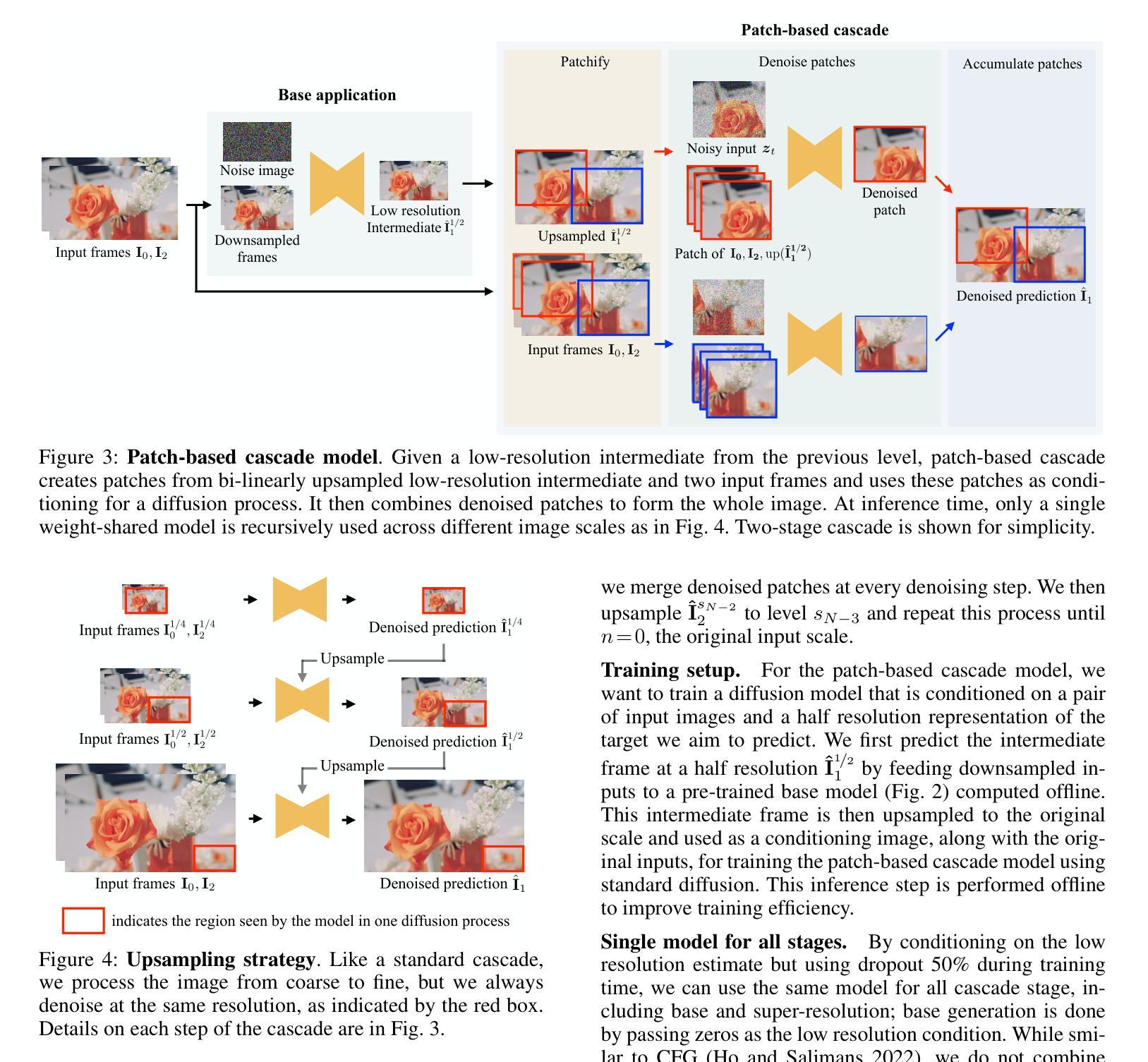
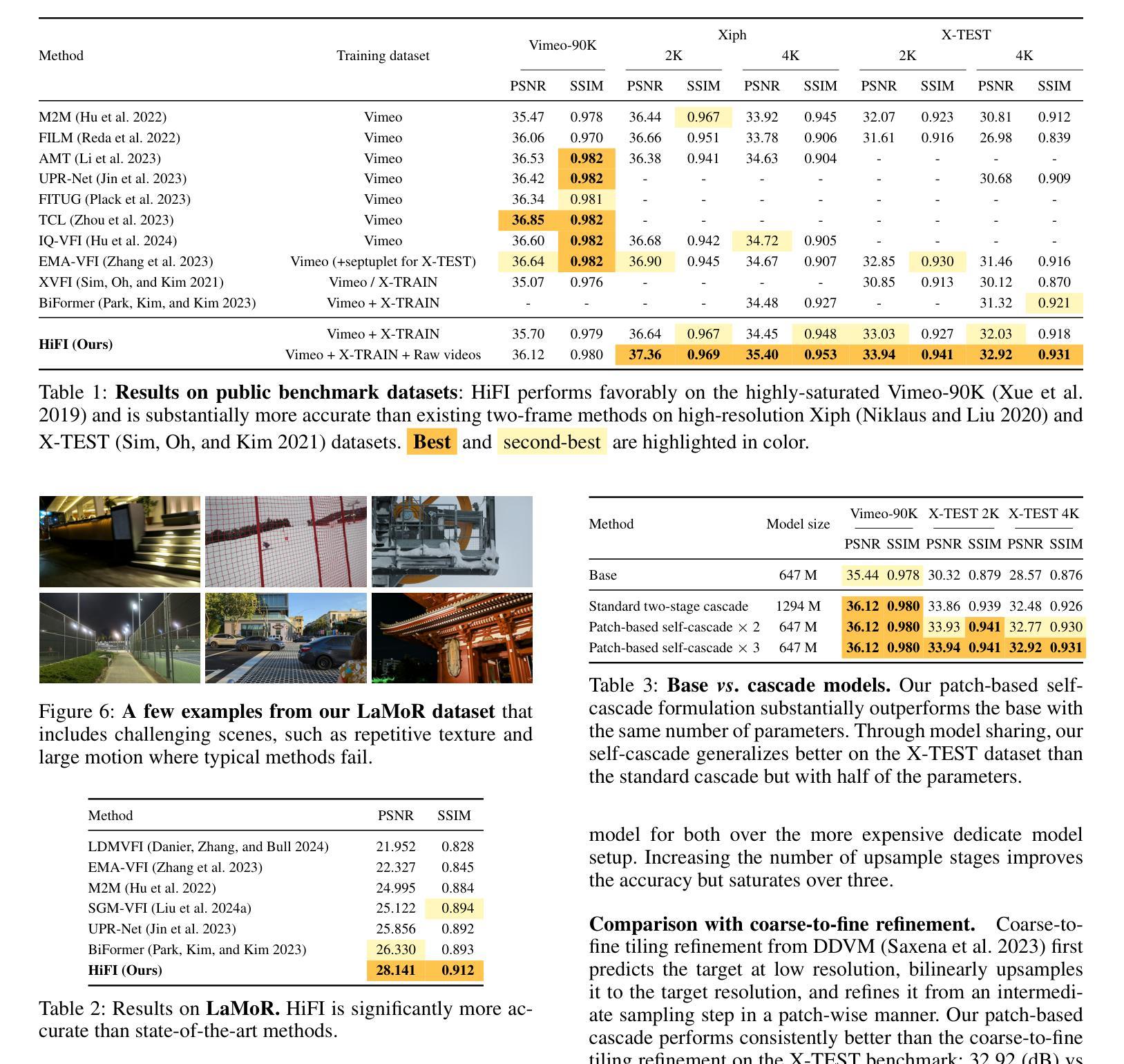
Authors:Junhwa Hur, Charles Herrmann, Saurabh Saxena, Janne Kontkanen, Wei-Sheng Lai, Yichang Shih, Michael Rubinstein, David J. Fleet, Deqing Sun
Despite the recent progress, existing frame interpolation methods still struggle with processing extremely high resolution input and handling challenging cases such as repetitive textures, thin objects, and large motion. To address these issues, we introduce a patch-based cascaded pixel diffusion model for high resolution frame interpolation, HIFI, that excels in these scenarios while achieving competitive performance on standard benchmarks. Cascades, which generate a series of images from low to high resolution, can help significantly with large or complex motion that require both global context for a coarse solution and detailed context for high resolution output. However, contrary to prior work on cascaded diffusion models which perform diffusion on increasingly large resolutions, we use a single model that always performs diffusion at the same resolution and upsamples by processing patches of the inputs and the prior solution. At inference time, this drastically reduces memory usage and allows a single model, solving both frame interpolation (base model’s task) and spatial up-sampling, saving training cost as well. HIFI excels at high-resolution images and complex repeated textures that require global context, achieving comparable or state-of-the-art performance on various benchmarks (Vimeo, Xiph, X-Test, and SEPE-8K). We further introduce a new dataset, LaMoR, that focuses on particularly challenging cases, and HIFI significantly outperforms other baselines. Please visit our project page for video results: https://hifi-diffusion.github.io
尽管近期有所进展,现有的帧插值方法在处理极高分辨率输入以及面对重复纹理、细薄物体和大动作等复杂情况时仍面临挑战。为了解决这些问题,我们引入了一种基于补丁的级联像素扩散模型,用于高分辨率帧插值(HIFI),该模型在这些场景中表现出色,同时在标准基准测试中实现了具有竞争力的性能。级联生成从低到高的分辨率图像系列,有助于处理需要全局上下文进行粗略解决方案和详细上下文以生成高分辨率输出的大动作或复杂动作。然而,与先前关于级联扩散模型的工作不同,这些工作在越来越高的分辨率上执行扩散,我们使用一个始终在同一分辨率上执行扩散的单一模型,并通过处理输入和先前解决方案的补丁来进行上采样。在推理时间,这大大降低了内存使用,并允许一个单一模型同时解决帧插值(基础模型的任务)和空间上采样,从而节省了训练成本。HIFI在高分辨率图像和复杂重复纹理方面表现出色,这些图像需要全局上下文,在各种基准测试(Vimeo、Xiph、X-Test和SEPE-8K)上达到了相当或最先进的性能。我们还引入了一个新的数据集LaMoR,该数据集专注于特别具有挑战性的情况,HIFI显著优于其他基线模型。有关视频结果的详细信息,请访问我们的项目页面:https://hifi-diffusion.github.io。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF Project page: https://hifi-diffusion.github.io/
Summary
基于现有的帧插值方法在处理极高分辨率输入时面临的挑战,如重复纹理、薄对象和大运动等问题,我们提出了一种基于补丁的级联像素扩散模型——HIFI。它通过级联生成一系列图像,从低分辨率到高分辨率,在处理大或复杂的运动时表现出卓越性能。不同于先前的级联扩散模型,HIFI始终在相同分辨率下进行扩散,并通过处理输入和先前解决方案的补丁来进行上采样。在推断时,这大大降低了内存使用,并允许一个单一模型同时解决帧插值(基础模型的任务)和空间上采样,降低了训练成本。HIFI在高分辨率图像和复杂重复纹理上表现出卓越性能,在各种基准测试(如Vimeo、Xiph、X-Test和SEPE-8K)上达到或超越现有最佳水平。我们还引入了一个新数据集LaMoR,专注于特别具有挑战性的案例,HIFI在此数据集上的表现显著优于其他基线方法。
Key Takeaways
- 现有帧插值方法在处理高分辨输入时存在挑战,如重复纹理、薄对象和大运动。
- 引入的HIFI模型采用基于补丁的级联像素扩散方法,针对这些挑战场景表现出卓越性能。
- HIFI通过级联生成低分辨率到高分辨率的图像,处理大或复杂的运动。
- 与其他级联扩散模型不同,HIFI在相同分辨率下进行扩散,并通过处理补丁进行上采样,降低内存使用并降低训练成本。
- HIFI在高分辨率图像和复杂重复纹理上表现优秀,在各种基准测试上达到或超越最佳水平。
- HIFI在新引入的LaMoR数据集上显著优于其他基线方法。
点此查看论文截图


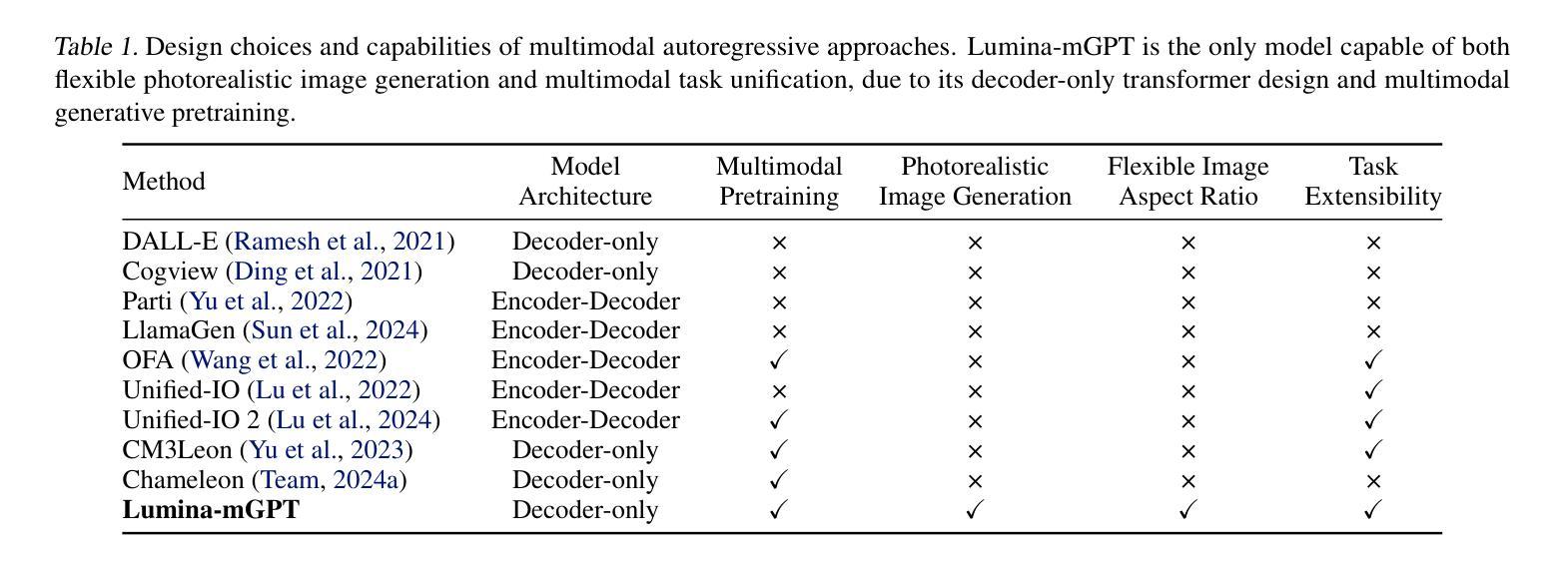
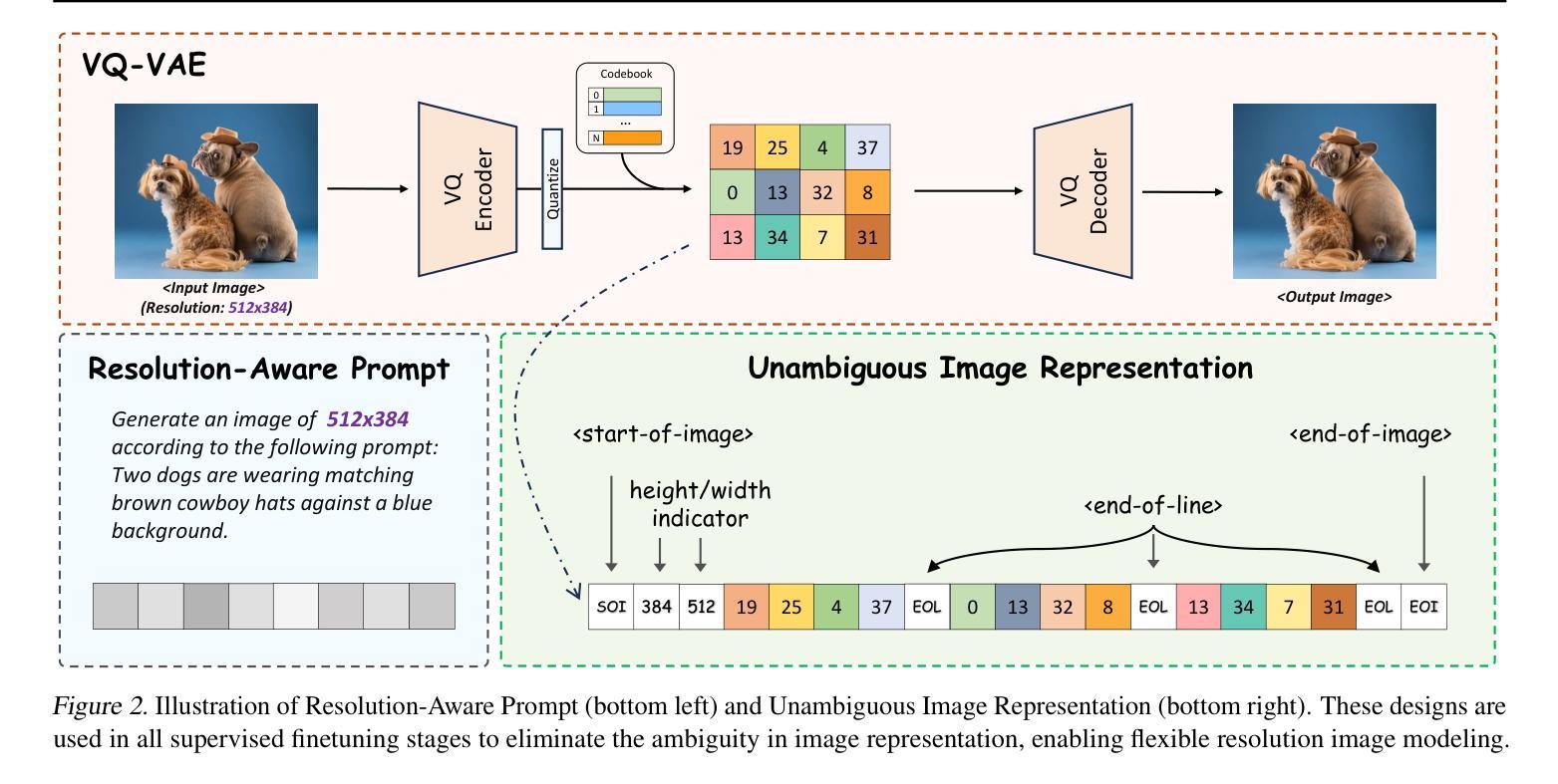
Lumina-mGPT: Illuminate Flexible Photorealistic Text-to-Image Generation with Multimodal Generative Pretraining
Authors:Dongyang Liu, Shitian Zhao, Le Zhuo, Weifeng Lin, Yu Qiao, Hongsheng Li, Peng Gao
We present Lumina-mGPT, a family of multimodal autoregressive models capable of various vision and language tasks, particularly excelling in generating flexible photorealistic images from text descriptions. By initializing from multimodal Generative PreTraining (mGPT), we demonstrate that decoder-only Autoregressive (AR) model can achieve image generation performance comparable to modern diffusion models with high efficiency through Flexible Progressive Supervised Fine-tuning (FP-SFT). Equipped with our proposed Unambiguous image Representation (UniRep), Lumina-mGPT can flexibly generate high-quality images of varying aspect ratios. Building on the strong image generation capabilities, we further explore Ominiponent Supervised Fine-tuning (Omni-SFT), an initial attempt to elevate Lumina-mGPT into a unified multi-modal generalist. The resulting model demonstrates versatile multimodal capabilities, including visual generation tasks like text-to-image/multiview generation and controllable generation, visual recognition tasks like segmentation and depth estimation, and vision-language tasks like multi-turn visual question answering, showing the rosy potential of the technical direction. Codes and checkpoints are available at https://github.com/Alpha-VLLM/Lumina-mGPT.
我们推出了Lumina-mGPT,这是一系列多模态自回归模型,能够执行各种视觉和语言任务,特别是在根据文本描述生成灵活的光栅图像方面表现出色。通过采用多模态生成预训练(mGPT)进行初始化,我们证明只使用解码器的自回归(AR)模型可以通过灵活的渐进式监督微调(FP-SFT)实现与现代扩散模型相当的高效图像生成性能。配备我们提出的明确图像表示(UniRep),Lumina-mGPT可以灵活地生成各种纵横比的高质量图像。在强大的图像生成能力基础上,我们进一步探索了全能监督微调(Omni-SFT),这是首次尝试将Lumina-mGPT提升为统一的多模态全能模型。结果证明该模型具有多种多模态功能,包括视觉生成任务(如文本到图像/多视图生成和可控生成)、视觉识别任务(如分割和深度估计)以及视觉语言任务(如多轮视觉问答),展示了技术方向的广阔潜力。相关代码和检查点已发布在https://github.com/Alpha-VLLM/Lumina-mGPT。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF Code available at: https://github.com/Alpha-VLLM/Lumina-mGPT
Summary
Lumina-mGPT是一个多模态自回归模型家族,擅长根据文本描述生成灵活逼真的图像。通过多模态生成预训练(mGPT)初始化,证明解码器仅自回归(AR)模型通过灵活渐进监督微调(FP-SFT)即可实现与现代扩散模型相当的高效率图像生成性能。配备提出的明确图像表示(UniRep),Lumina-mGPT可灵活生成各种纵横比的高质量图像。在强大的图像生成能力基础上,进一步探索了万能监督微调(Omni-SFT),初步尝试将Lumina-mGPT提升为统一的多模态通用模型。该模型展示多功能多模态能力,包括文本到图像/多视图生成、可控生成、视觉识别任务如分割和深度估计,以及视觉语言任务如多轮视觉问答等。代码和检查点可通过https://github.com/Alpha-VLLM/Lumina-mGPT获取。
Key Takeaways
- Lumina-mGPT是一个多模态自回归模型,擅长文本驱动的图像生成,具有灵活性和高质量。
- 通过多模态生成预训练(mGPT)初始化,该模型实现了高效的图像生成性能。
- Lumina-mGPT配备了明确图像表示(UniRep),能够生成不同纵横比的高质量图像。
- 模型通过灵活渐进监督微调(FP-SFT)进行优化,提高了性能。
- 模型展示了多功能多模态能力,包括文本到图像生成、视觉识别任务和视觉语言任务等。
- Omni-SFT是一种尝试将Lumina-mGPT提升为统一多模态通用模型的初步探索。
点此查看论文截图



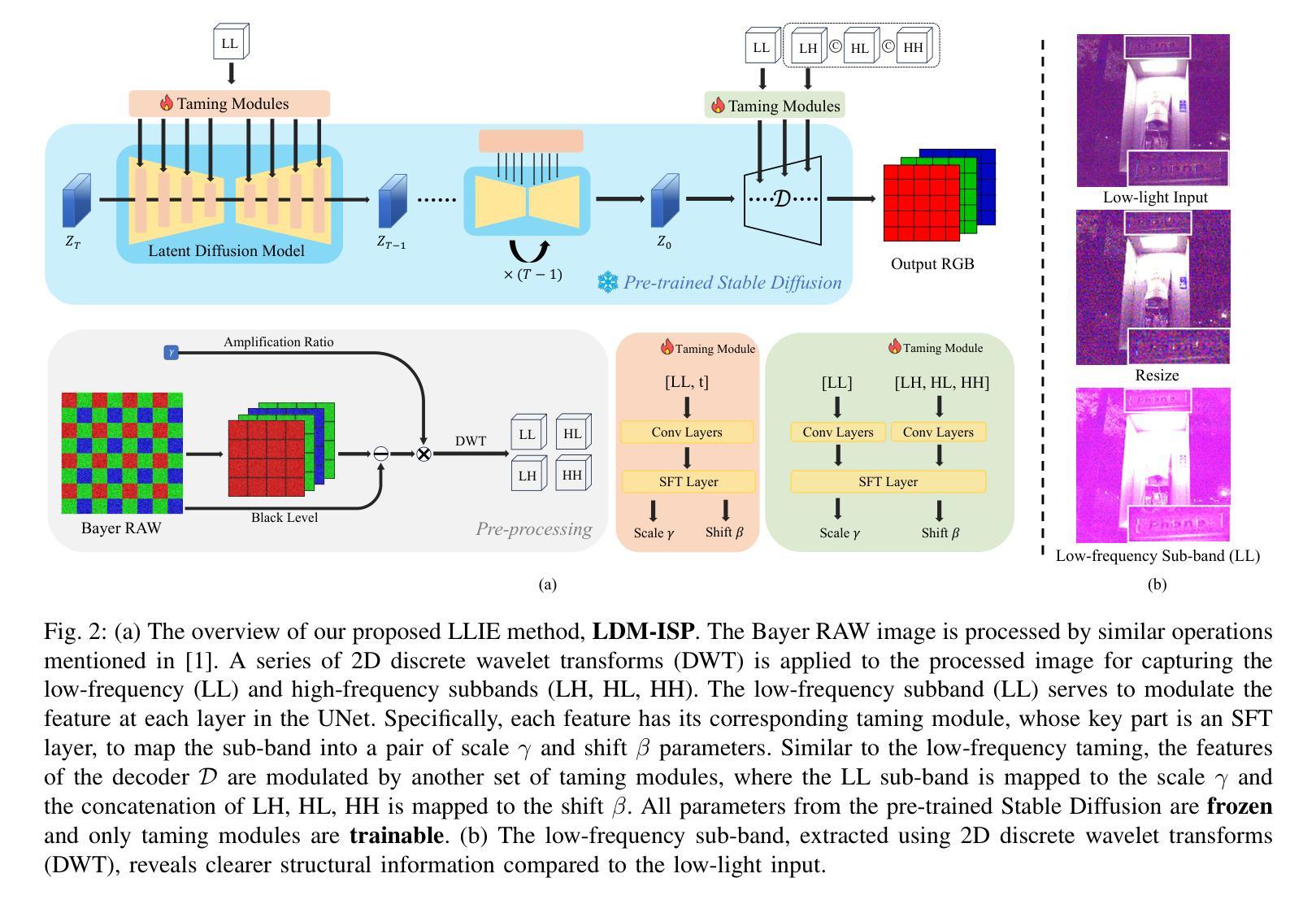
LDM-ISP: Enhancing Neural ISP for Low Light with Latent Diffusion Models
Authors:Qiang Wen, Zhefan Rao, Yazhou Xing, Qifeng Chen
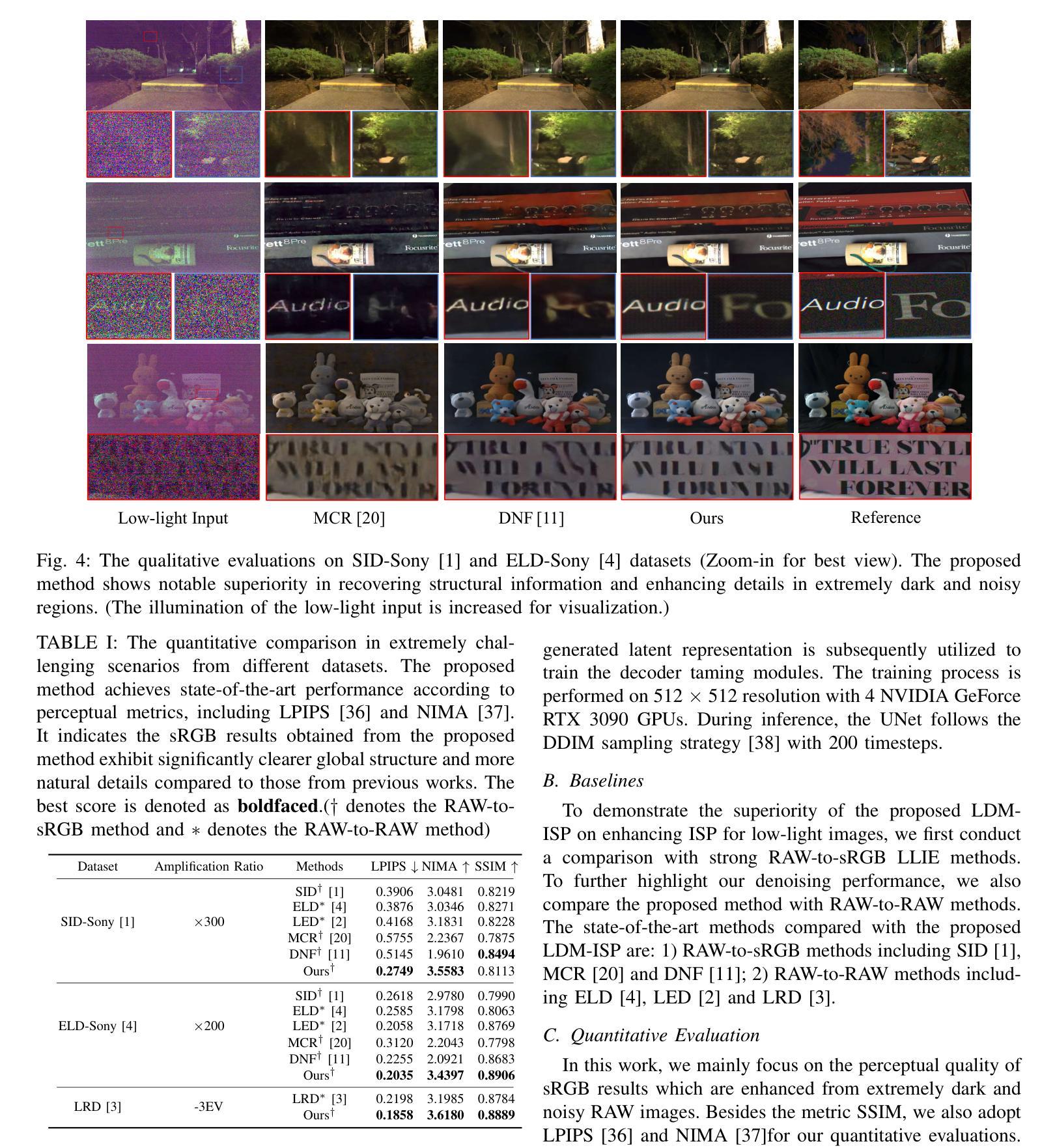
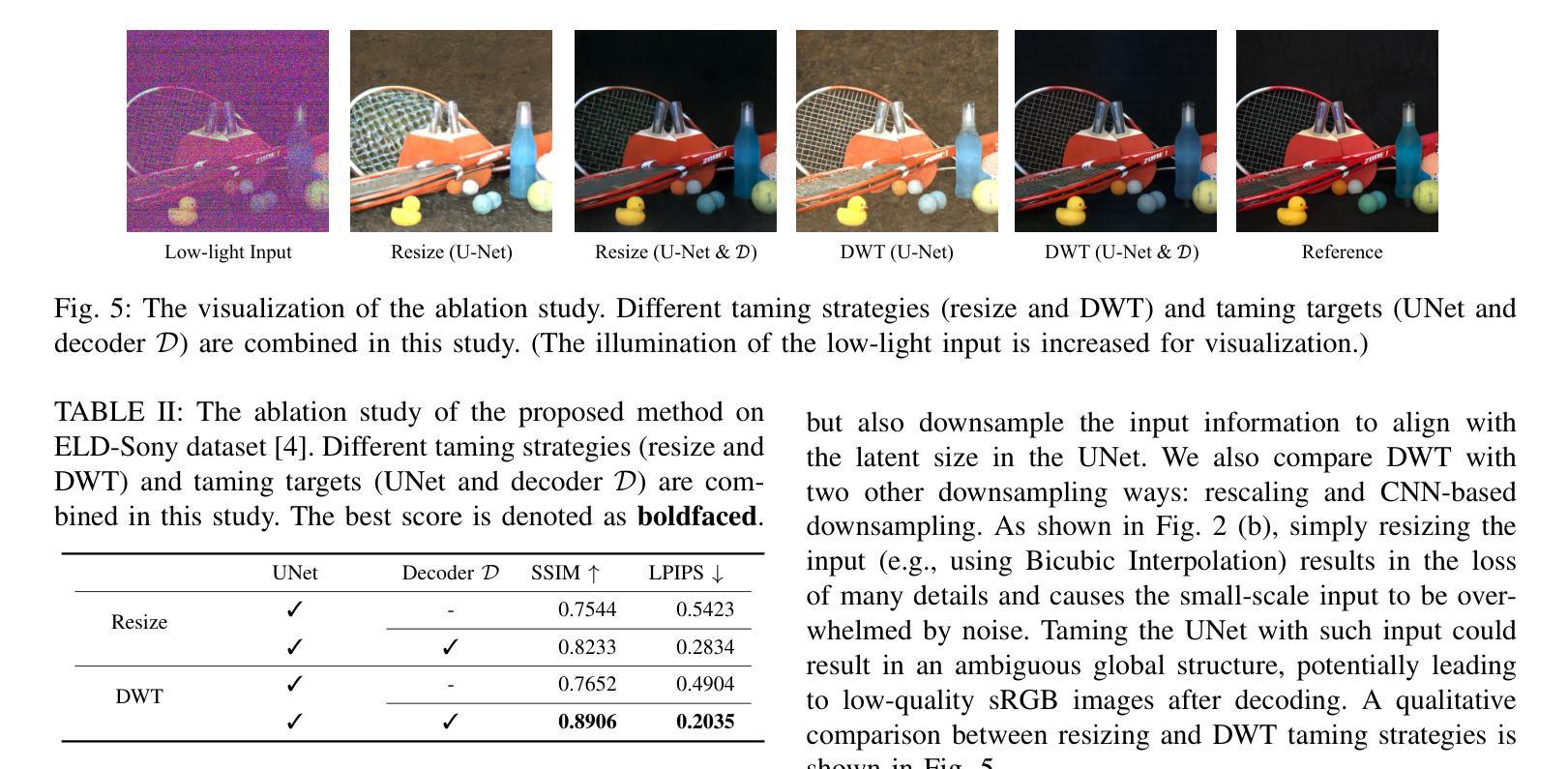
Enhancing a low-light noisy RAW image into a well-exposed and clean sRGB image is a significant challenge for modern digital cameras. Prior approaches have difficulties in recovering fine-grained details and true colors of the scene under extremely low-light environments due to near-to-zero SNR. Meanwhile, diffusion models have shown significant progress towards general domain image generation. In this paper, we propose to leverage the pre-trained latent diffusion model to perform the neural ISP for enhancing extremely low-light images. Specifically, to tailor the pre-trained latent diffusion model to operate on the RAW domain, we train a set of lightweight taming modules to inject the RAW information into the diffusion denoising process via modulating the intermediate features of UNet. We further observe different roles of UNet denoising and decoder reconstruction in the latent diffusion model, which inspires us to decompose the low-light image enhancement task into latent-space low-frequency content generation and decoding-phase high-frequency detail maintenance. Through extensive experiments on representative datasets, we demonstrate our simple design not only achieves state-of-the-art performance in quantitative evaluations but also shows significant superiority in visual comparisons over strong baselines, which highlight the effectiveness of powerful generative priors for neural ISP under extremely low-light environments. The project page is available at https://csqiangwen.github.io/projects/ldm-isp/
将低光环境下的噪声RAW图像增强为曝光良好、清晰的sRGB图像,对于现代数码相机来说是一个巨大的挑战。由于信噪比接近零,先前的方法在极端低光环境下恢复场景的细微细节和真实颜色方面存在困难。同时,扩散模型在通用域图像生成方面取得了显著进展。在本文中,我们提出利用预训练的潜在扩散模型来进行神经网络ISP,以提升低光图像。具体来说,为了调整预训练的潜在扩散模型在RAW域上运行,我们训练了一系列轻量级驯服模块,通过将RAW信息注入扩散去噪过程,调制UNet的中间特征。我们进一步观察到UNet去噪和解码器重建在潜在扩散模型中的不同作用,这激励我们将低光图像增强任务分解为潜在空间的低频内容生成和解码阶段的高频细节维护。通过在代表性数据集上进行大量实验,我们证明了我们的简单设计不仅在定量评估中达到了最新性能,而且在视觉比较方面显著优于强大的基准模型,这突出了强大生成先验在极端低光环境下的神经网络ISP的有效性。项目页面可在https://csqiangwen.github.io/projects/ldm-isp/找到。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
利用预训练潜伏扩散模型,通过神经网络ISP增强低光图像。训练轻量级驯服模块将RAW信息注入扩散去噪过程,分解低光图像增强任务为潜伏空间低频内容生成和解码阶段高频细节维护,实现先进性能并显著优于基准线。
Key Takeaways
- 利用预训练潜伏扩散模型进行神经网络ISP,以应对低光环境下的图像增强挑战。
- 训练轻量级驯服模块,将RAW信息注入扩散去噪过程。
- 分解低光图像增强任务为潜伏空间低频内容生成和解码阶段高频细节维护。
- UNet去噪和解码器重建在潜伏扩散模型中扮演不同角色。
- 提出的简单设计在代表性数据集上进行广泛实验,实现先进性能。
- 该方法在定量评估中表现优异,并在视觉比较中显著优于其他方法。
点此查看论文截图

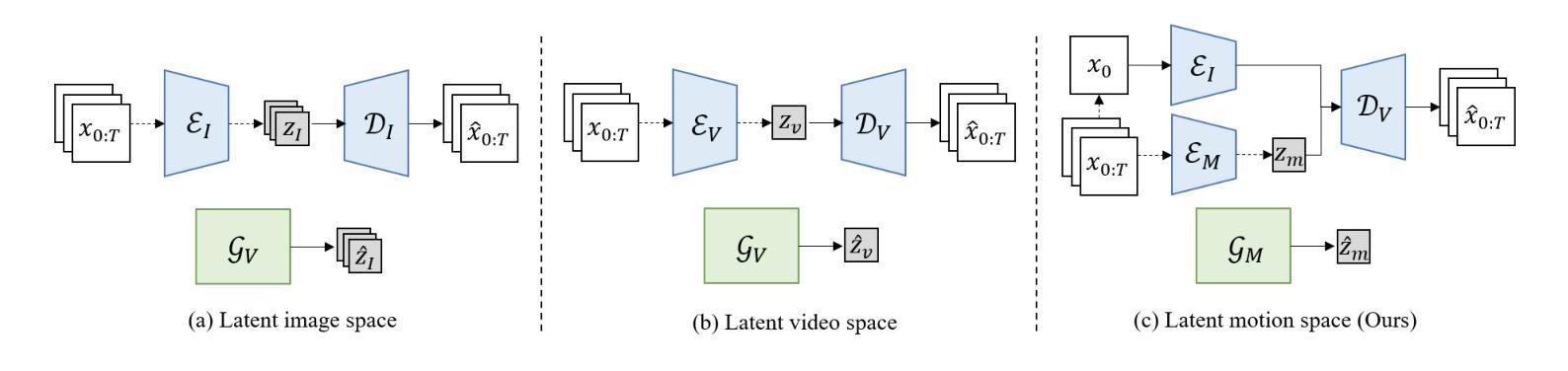
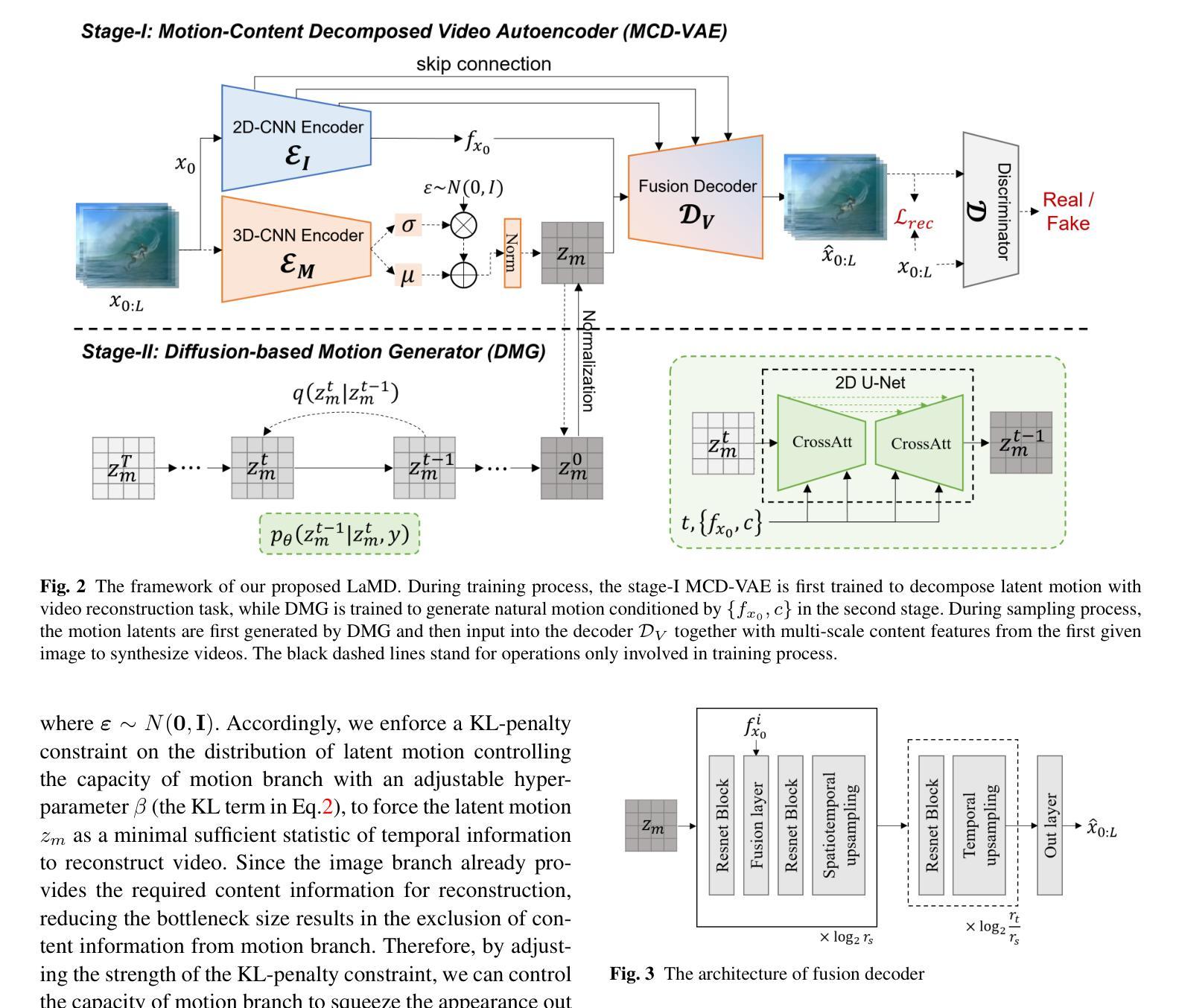
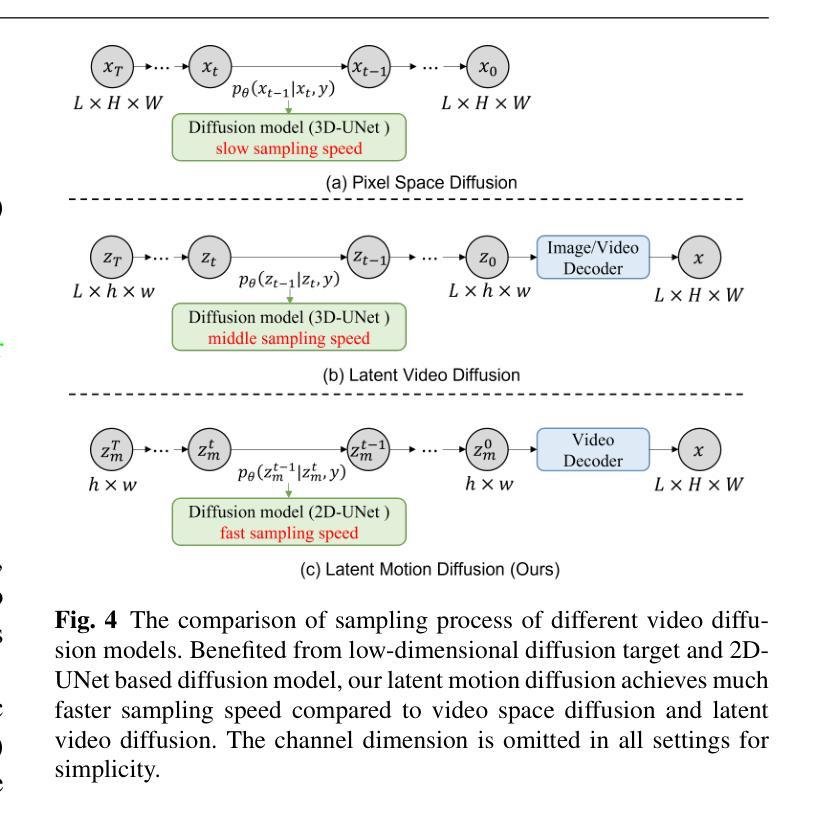
LaMD: Latent Motion Diffusion for Image-Conditional Video Generation
Authors:Yaosi Hu, Zhenzhong Chen, Chong Luo
The video generation field has witnessed rapid improvements with the introduction of recent diffusion models. While these models have successfully enhanced appearance quality, they still face challenges in generating coherent and natural movements while efficiently sampling videos. In this paper, we propose to condense video generation into a problem of motion generation, to improve the expressiveness of motion and make video generation more manageable. This can be achieved by breaking down the video generation process into latent motion generation and video reconstruction. Specifically, we present a latent motion diffusion (LaMD) framework, which consists of a motion-decomposed video autoencoder and a diffusion-based motion generator, to implement this idea. Through careful design, the motion-decomposed video autoencoder can compress patterns in movement into a concise latent motion representation. Consequently, the diffusion-based motion generator is able to efficiently generate realistic motion on a continuous latent space under multi-modal conditions, at a cost that is similar to that of image diffusion models. Results show that LaMD generates high-quality videos on various benchmark datasets, including BAIR, Landscape, NATOPS, MUG and CATER-GEN, that encompass a variety of stochastic dynamics and highly controllable movements on multiple image-conditional video generation tasks, while significantly decreases sampling time.
视频生成领域最近引入了扩散模型,该领域已经看到了迅速的改进。虽然这些模型在提升外观质量方面取得了成功,但它们仍然面临着在有效采样视频的同时生成连贯且自然动作的挑战。在本文中,我们提出将视频生成简化为动作生成问题,以提高动作的表达能力并使视频生成更加易于管理。这可以通过将视频生成过程分解为潜在动作生成和视频重建来实现。具体来说,我们提出了一个潜在动作扩散(LaMD)框架,该框架由动作分解视频自编码器和基于扩散的动作生成器组成,以实现这个想法。通过精心设计,动作分解视频自编码器可以将运动模式压缩成简洁的潜在动作表示。因此,基于扩散的动作生成器能够在连续潜在空间下在多模态条件下高效生成逼真的动作,其成本类似于图像扩散模型。结果表明,LaMD在各种基准数据集上生成了高质量的视频,包括BAIR、Landscape、NATOPS、MUG和CATER-GEN,涵盖了多种随机动态和高度可控的动作在多个图像条件视频生成任务中,同时显著减少了采样时间。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF accepted by IJCV
摘要
最新扩散模型在视频生成领域取得了快速进展,成功提高了视频外观质量。然而,这些模型在生成连贯、自然动作以及高效采样视频方面仍面临挑战。本文提出将视频生成简化为动作生成问题,以提高动作的表达性和视频生成的易管理性。通过分解为潜在动作生成和视频重建两个步骤来实现。具体来说,我们提出了潜在动作扩散(LaMD)框架,包括运动分解视频自编码器和基于扩散的运动生成器。运动分解视频自编码器能够压缩运动模式成简洁的潜在运动表示,而基于扩散的运动生成器则能在多模态条件下在连续的潜在空间高效生成真实动作,成本类似于图像扩散模型。实验结果表明,LaMD在各种基准数据集上生成了高质量的视频,涵盖多种随机动态和高度可控的动作,显著减少了采样时间。
关键见解
- 扩散模型在视频生成领域取得显著进展,但仍面临生成连贯自然动作和高效采样视频的挑战。
- 提出将视频生成简化为动作生成问题,以提高动作表达性和视频生成的易管理性。
- 引入潜在动作扩散(LaMD)框架,包括运动分解视频自编码器和基于扩散的运动生成器。
- 运动分解视频自编码器能压缩运动模式到简洁的潜在运动表示。
- 基于扩散的运动生成器能在多模态条件下高效生成真实动作。
- LaMD框架能在各种基准数据集上生成高质量的视频,涵盖多种随机动态和高度可控的动作。
- LaMD框架显著减少了采样时间。
点此查看论文截图