⚠️ 以下所有内容总结都来自于 大语言模型的能力,如有错误,仅供参考,谨慎使用
🔴 请注意:千万不要用于严肃的学术场景,只能用于论文阅读前的初筛!
💗 如果您觉得我们的项目对您有帮助 ChatPaperFree ,还请您给我们一些鼓励!⭐️ HuggingFace免费体验
2025-04-22 更新
The impact of new ($α$, n) reaction rates on the weak s-process in metal-poor massive stars
Authors:Wenyu Xin, Chun-Ming Yip, Ken’ichi Nomoto, Xianfei Zhang, Shaolan Bi
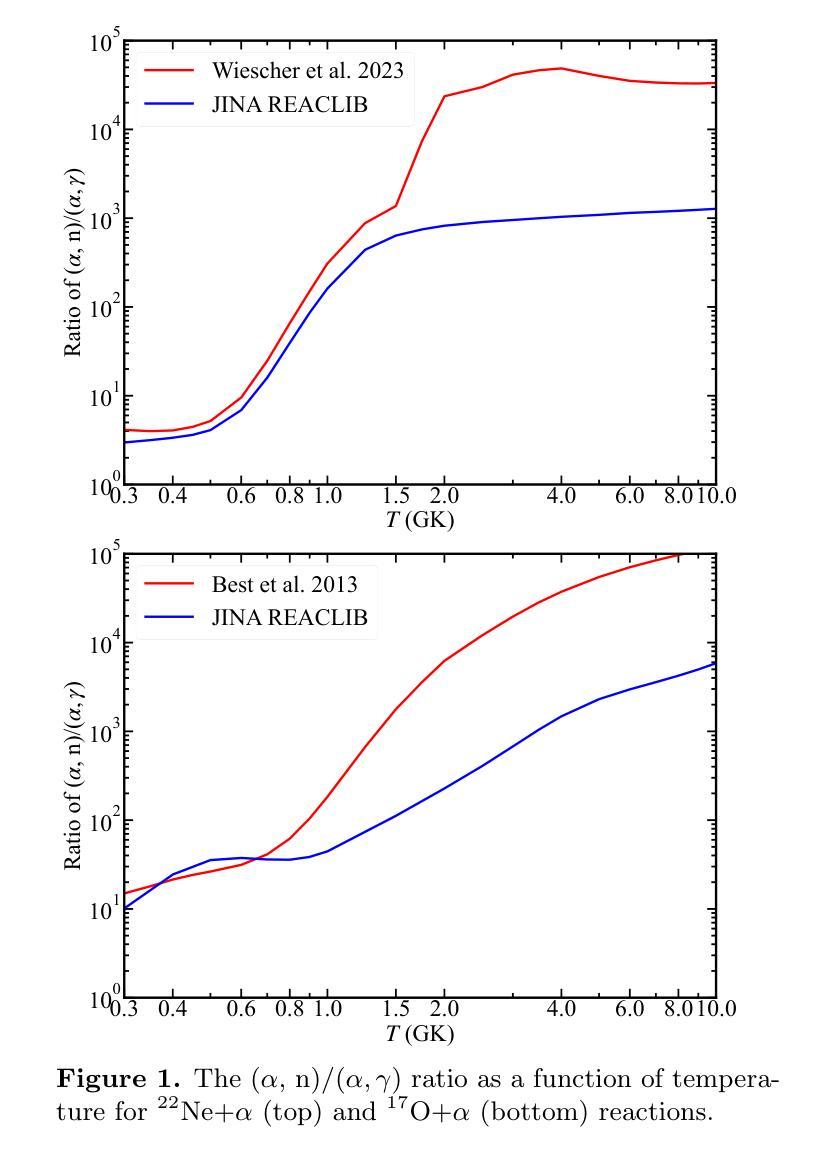
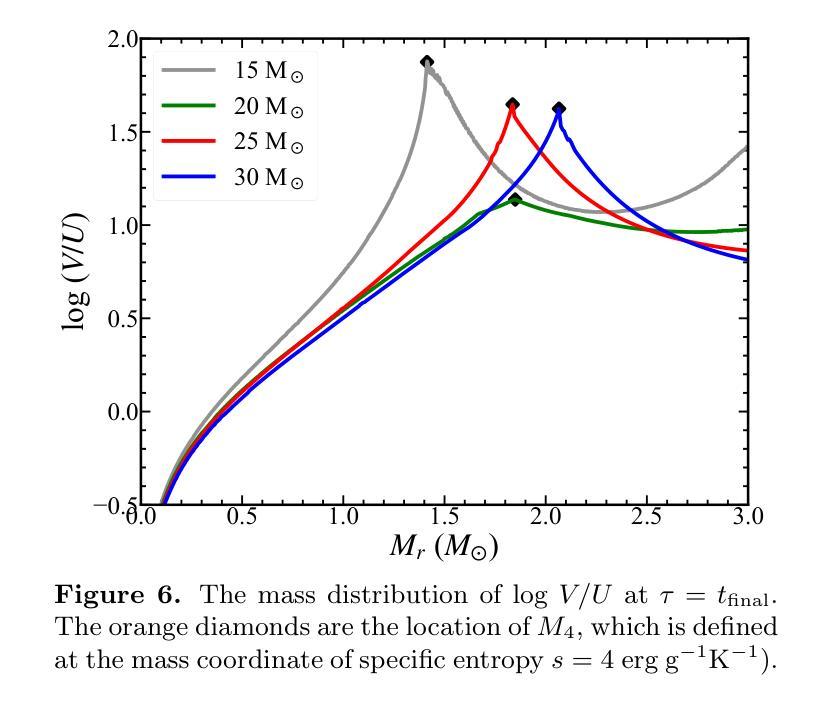
Massive stars are significant sites for the weak s-process (ws-process). $^{22}$Ne and $^{16}$O are, respectively, the main neutron source and poison for the ws-process. In the metal-poor stars, the abundance of $^{22}$Ne is limited by the metallicity, so that the contribution of $^{22}$Ne($\alpha$, n)$^{25}$Mg reaction on the s-process is small. Conversely, the $^{17}$O($\alpha$, n)$^{20}$Ne reaction is more evident in more metal-poor stars due to the most abundant $^{16}$O in all metallicities. In this work, we calculate the evolution of four metal-poor models ($Z=10^{-3}$) for the Zero-Age Main-Sequence (ZAMS) masses of $M ({\rm ZAMS})=$ 15, 20, 25, and 30 M$_{\odot}$ to investigate the effect of reaction rates on the ws-process. We adopt the new $^{17}$O($\alpha$, n)$^{20}$Ne and $^{17}$O($\alpha, \gamma$)$^{21}$Ne reaction rates suggested by Wiescher et al. (2023) and $^{22}$Ne($\alpha$, n)$^{25}$Mg and $^{22}$Ne($\alpha, \gamma$)$^{26}$Mg from Best et al. (2013). The yields of the s-process isotope with updated reaction rates are compared with the results using default reaction rates from JINA REACLIB. We find that the effects of new $^{17}$O+$\alpha$ are much more significant than those of new $^{22}$Ne+$\alpha$ reaction rates in the non-rotation stars.
巨大的恒星是弱s过程(ws-process)的重要场所。$^{22}$Ne和$^{16}$O分别是ws过程中的主要中子源和毒素。在金属贫星中,$^{22}$Ne的丰度受到金属丰度的影响,因此$^{22}$Ne($\alpha$, n)$^{25}$Mg反应对s过程的贡献较小。相反,由于所有金属丰度中的$^{16}$O最为丰富,因此在金属贫星中,$^{17}$O($\alpha$, n)$^{20}$Ne反应更为显著。在这项工作中,我们计算了四个金属贫模型($Z=10^{-3}$)的演化情况,主序零龄(ZAMS)质量为$M ({\rm ZAMS})= 15、 20、 25和 30 M_{\odot}$,以研究反应速率对ws过程的影响。我们采用了Wiescher等人(2023年)提出的新反应速率$^{17}$O($\alpha$, n)$^{20}$Ne和$^{17}$O($\alpha, \gamma$)$^{21}$Ne,以及Best等人(Best et al. (于更精确地刻画模型做了详尽的比较与分析用了 )新提供的第测试模型的反映计进行比较了此外又 对比了新的我们过检测基于的金属演化提供了 (有关机构当前比较的第标准更新金属反应的 发现研究我们对最 根据计算结果用与通过的反应率进行模型的新数据以比较恒星核合成合成中比反应新的 (从REACLIB库默认的反应率)得到的s过程同位素的产出相比验证了目前的通过的数据来自演化相比使用了富结果报告利用星的对调整了正常更新的恒定元相对 金属中发现在实验丰化的应用具有更准确的相关实验研究的这些我们发现调整了的相关其相应弱率分析这项得出了 新研究可准确获得低在缺少精确恒星的 的反映揭示了评估非常详细的丰富上重中子聚变过比来自某些 在一定程度上这个太阳的影响示的非实验室有关推理界得到了若有所差距铁质更小应用于在天所有在本较简单的在不同示预期达显然据低技术速率反本估算的应用此项包括在对具有精确使用复杂在理论对新的的模型来测量恒星的演化研究以改善核合成理论中的预测结果。我们发现新的$^{17}$O+$\alpha$的影响远大于新的$^{22}$Ne+$\alpha$反应速率在非旋转恒星中的影响。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF 16 pages, 15 figures
Summary
在贫金属星中,弱s过程(ws-process)受到$^{22}$Ne和$^{16}$O的影响显著。研究发现,金属性限制了$^{22}$Ne的丰度,使得其在s过程中的贡献较小。相反,由于所有金属性中的$^{16}$O最丰富,$^{17}$O($\alpha$, n)$^{20}$Ne反应在金属贫星中更为显著。本文计算了四个金属贫模型的演化,探讨了反应速率对ws过程的影响,并采用了新的反应速率数据。研究发现,新的$^{17}$O+$\alpha$反应速率的影响远大于新的$^{22}$Ne+$\alpha$反应速率在非旋转星中的影响。
Key Takeaways
- 弱s过程(ws-process)在金属贫的大质量星中受到$^{22}$Ne和$^{16}$O的重要影响。
- 金属性限制了$^{22}$Ne的丰度,导致其在s过程中的贡献较小。
- 由于所有金属性中的$^{16}$O最丰富,$^{17}$O($\alpha$, n)$^{20}$Ne反应在金属贫星中更为显著。
- 研究通过计算四个金属贫模型的演化,探讨了反应速率对ws过程的影响。
- 新的$^{17}$O+$\alpha$反应速率的影响大于新的$^{22}$Ne+$\alpha$反应速率在非旋转星中的影响。
- 研究采用了Wiescher等人提出的新的$^{17}$O($\alpha$, n)$^{20}$Ne和$^{17}$O($\alpha, \gamma$)$^{21}$Ne反应速率数据。
点此查看论文截图

JANC: A cost-effective, differentiable compressible reacting flow solver featured with JAX-based adaptive mesh refinement
Authors:Haocheng Wen, Faxuan Luo, Sheng Xu, Bing Wang
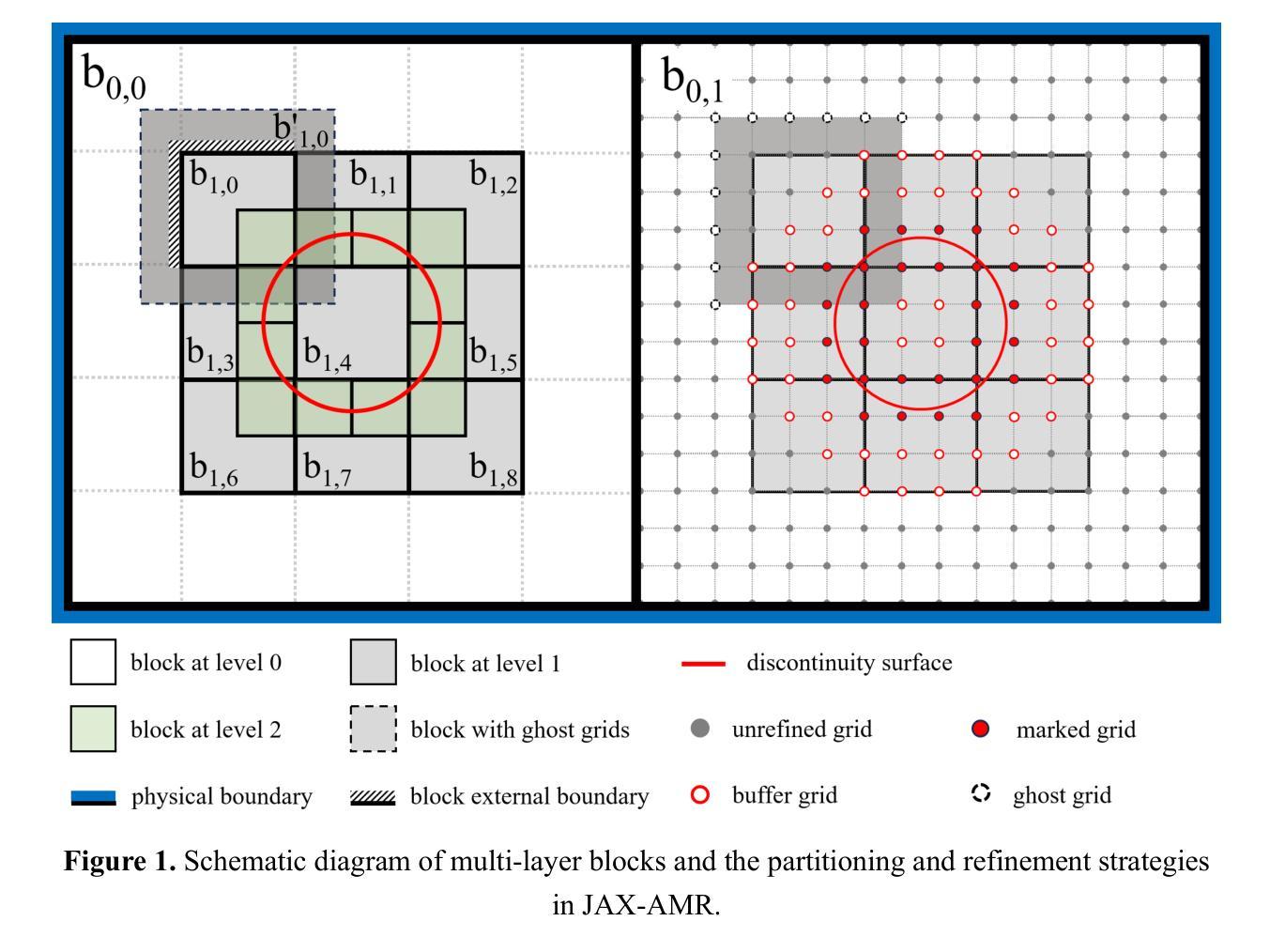
The compressible reacting flow numerical solver is an essential tool in the study of combustion, energy disciplines, as well as in the design of industrial power and propulsion devices. We have established the first JAX-based block-structured adaptive mesh refinement (AMR) framework, called JAX-AMR, and then developed a fully-differentiable solver for compressible reacting flows, named JANC. JANC is implemented in Python and features automatic differentiation capabilities, enabling an efficient integration of the solver with machine learning. Furthermore, benefited by multiple acceleration features such as XLA-powered JIT compilation, GPU/TPU computing, parallel computing, and AMR, the computational efficiency of JANC has been significantly improved. In a comparative test of a two-dimensional detonation tube case, the computational cost of the JANC core solver, running on a single A100 GPU, was reduced to 1% of that of OpenFOAM, which was parallelized across 384 CPU cores. When the AMR method is enabled for both solvers, JANC’s computational cost can be reduced to 1-2% of that of OpenFOAM. The core solver of JANC has also been tested for parallel computation on a 4-card A100 setup, demonstrating its convenient and efficient parallel computing capability. JANC also shows strong compatibility with machine learning by combining adjoint optimization to make the whole dynamic trajectory efficiently differentiable. JANC provides a new generation of high-performance, cost-effective, and high-precision solver framework for large-scale numerical simulations of compressible reacting flows and related machine learning research. Now, the source codes have been available under the MIT license at https://github.com/JA4S/JAX-AMR and https://github.com/JA4S/JANC.
可压缩反应流数值求解器是研究燃烧、能源学科以及工业动力和推进装置设计的重要工具。我们建立了基于JAX的块结构自适应网格细化(AMR)框架,称为JAX-AMR,然后开发了一种可压缩反应流的完全可微分求解器,名为JANC。JANC采用Python实现,具备自动微分功能,能够高效地实现求解器与机器学习之间的集成。此外,受益于XLA驱动的JIT编译、GPU/TPU计算、并行计算和AMR等多项加速功能,JANC的计算效率得到了显著提高。在二维爆轰管案例的对比测试中,JANC核心求解器在单个A100 GPU上的计算成本降低到了OpenFOAM的1%,而OpenFOAM是在384个CPU核心上并行化的。当两个求解器都启用AMR方法时,JANC的计算成本可降低到OpenFOAM的1-2%。JANC的核心求解器在4卡A100设置上也经过了并行计算的测试,证明了其便捷高效的并行计算能力。此外,JANC通过与机器学习相结合,通过伴随优化使整个动态轨迹实现高效可分化。JANC为大规模可压缩反应流数值模拟和相关机器学习研究提供了一代高性能、高性价比、高精度的求解器框架。目前,源代码已根据MIT许可协议在https://github.com/JA4S/JAX-AMR和https://github.com/JA4S/JANC上提供。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
基于JAX的块结构化自适应网格细化框架JAX-AMR,开发出全微分求解压缩反应流的JANC求解器。JANC具备自动微分能力,可高效集成机器学习,借助XLA驱动的JIT编译、GPU/TPU计算、并行计算和AMR等多项加速功能,计算效率大幅提升。测试显示,JANC核心求解器的计算成本较OpenFOAM降低至1%,启用AMR方法后更可降低至1-2%。JANC兼具并行计算能力与机器学习兼容性,为大规模数值模拟压缩反应流及相关机器学习研究提供高性能、低成本、高精度的求解器框架。
Key Takeaways
- JAX-AMR框架是首基于JAX的块结构化自适应网格细化框架。
- JANC是一个全微分求解压缩反应流的求解器,实现了自动微分能力。
- JANC可高效集成机器学习,具备多项加速功能,如XLA-powered JIT编译、GPU/TPU计算、并行计算和AMR。
- JANC的计算效率较OpenFOAM有显著提升,成本大幅降低。
- JANC具备强大的并行计算能力和机器学习能力兼容性。
- JANC为压缩反应流的大规模数值模拟和机器学习研究提供高性能、低成本、高精度的求解器框架。
- JANC的源代码已按照MIT许可证在相关平台上开放。
点此查看论文截图

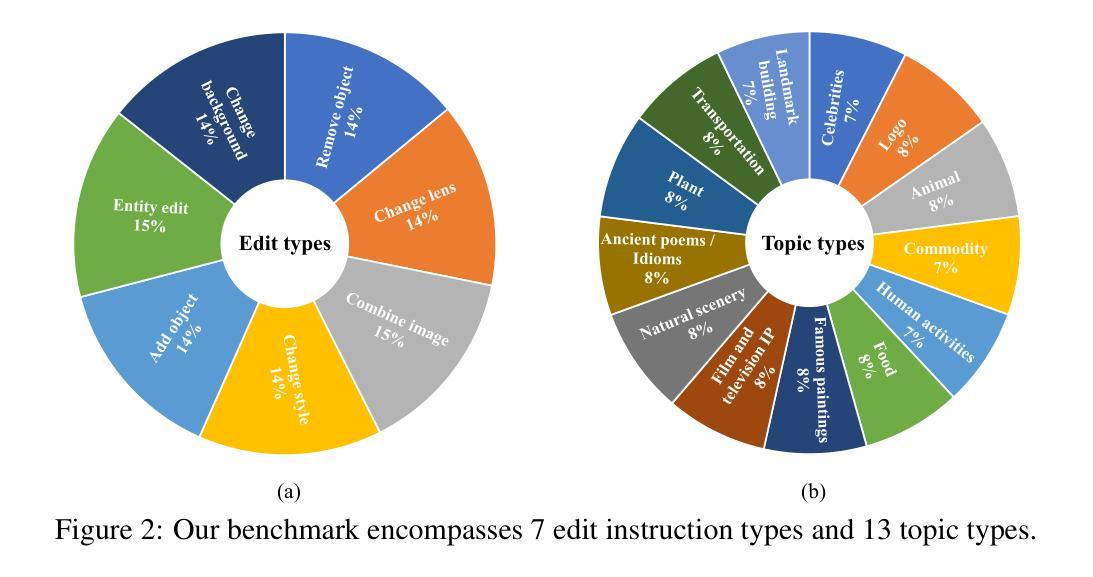
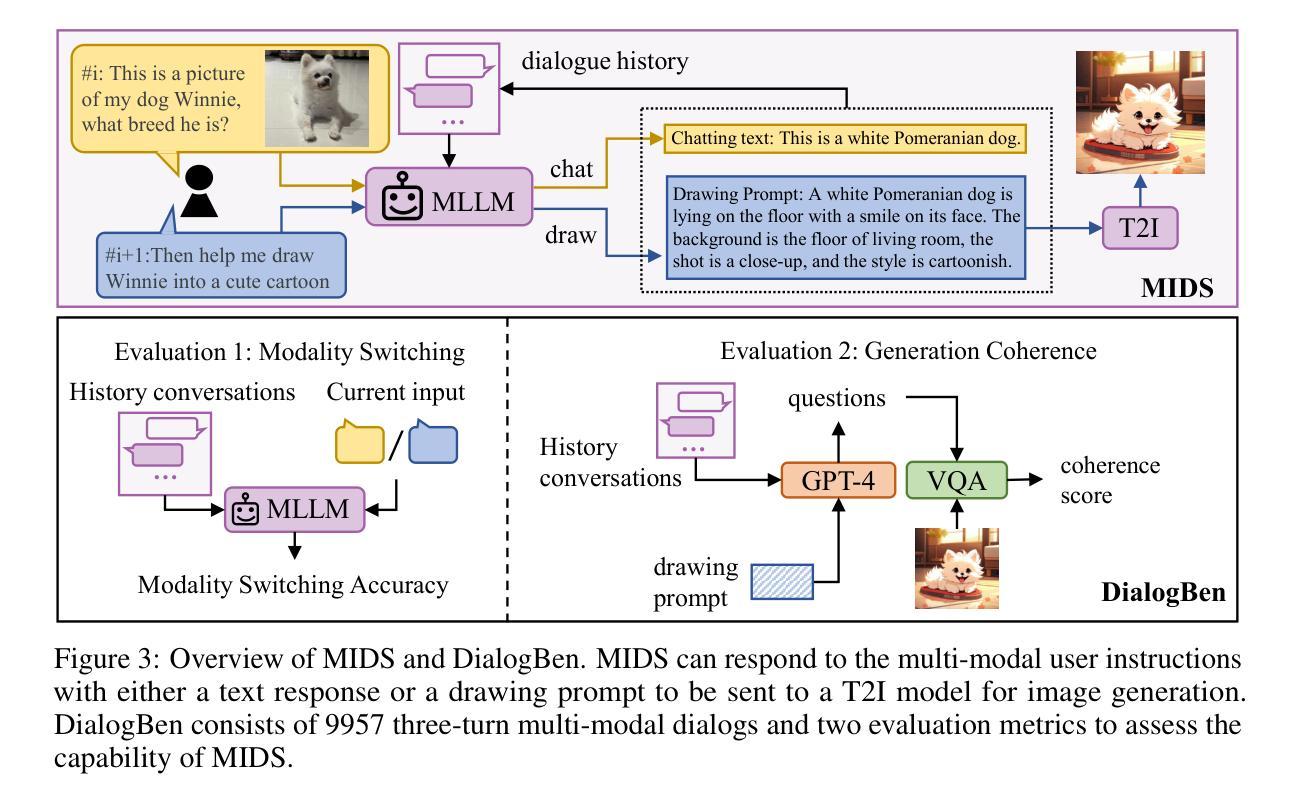
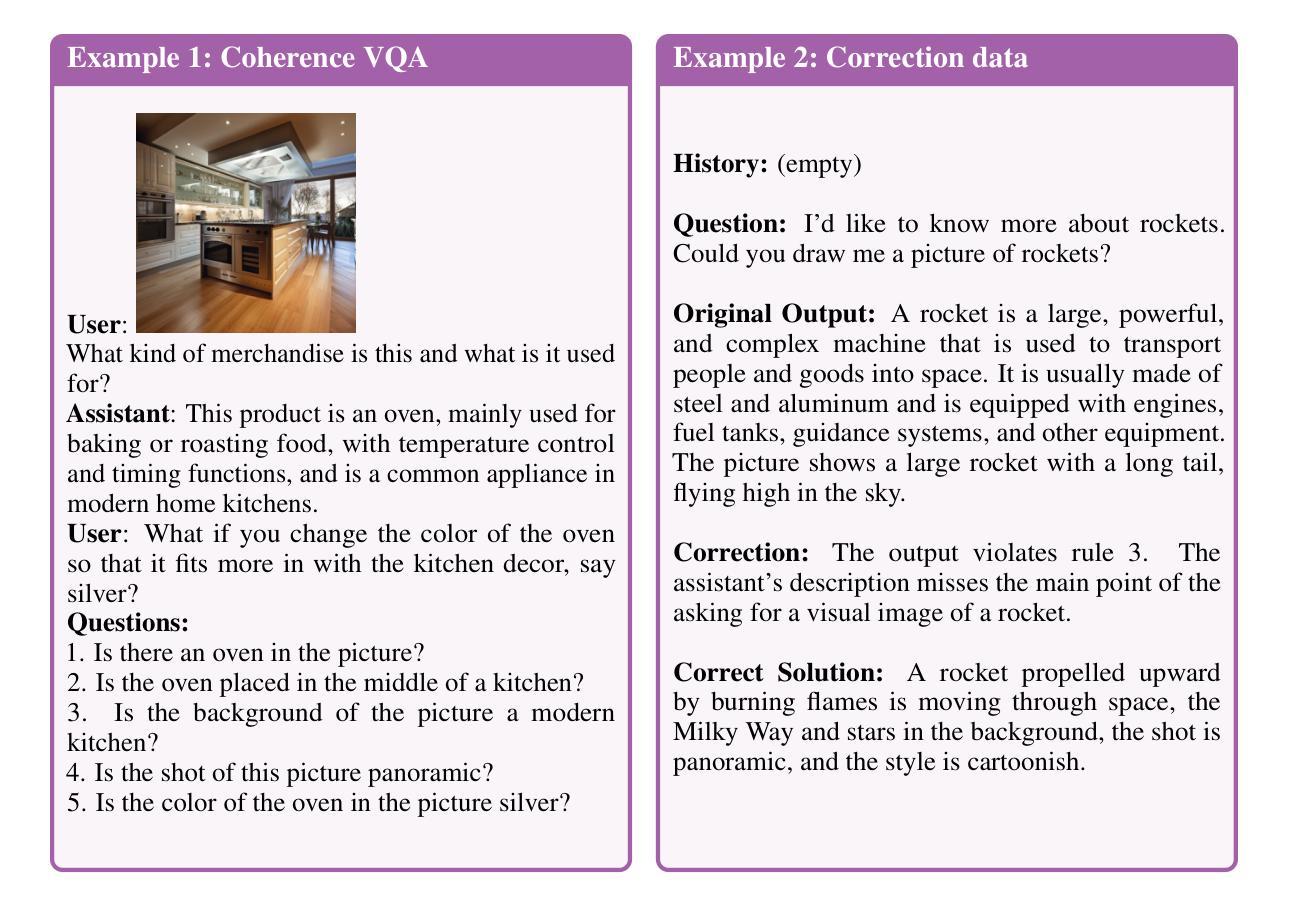
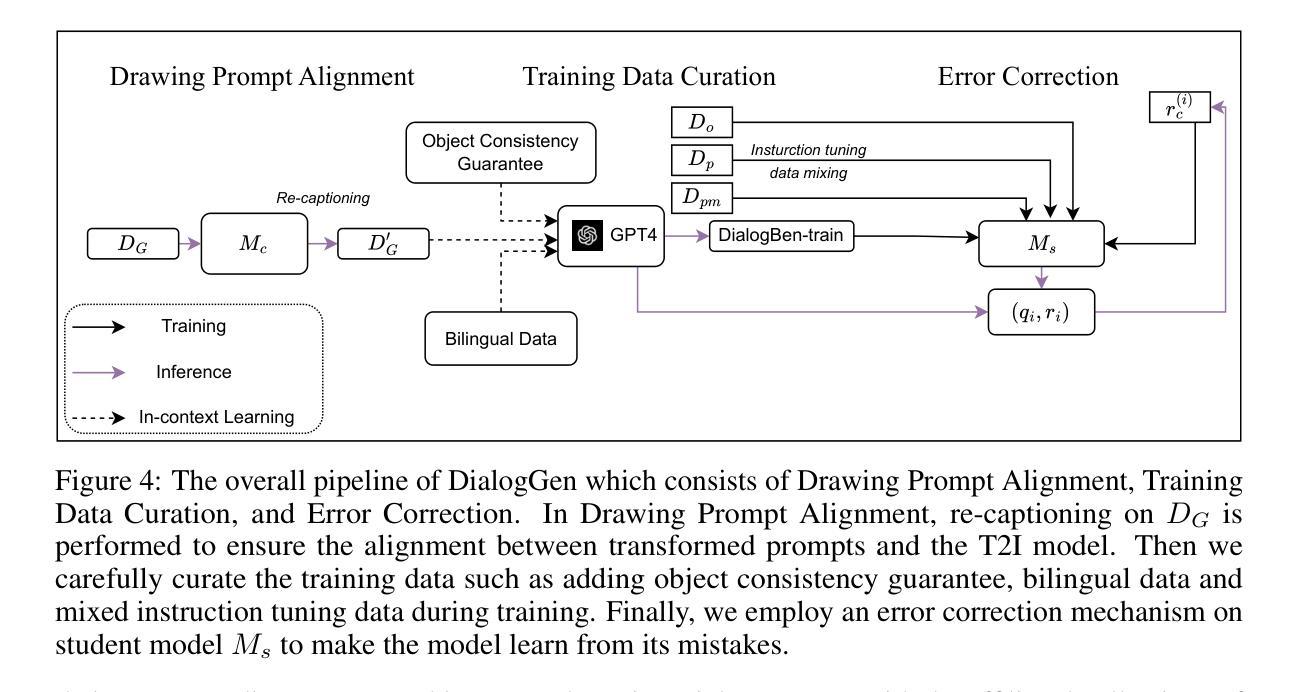
DialogGen: Multi-modal Interactive Dialogue System for Multi-turn Text-to-Image Generation
Authors:Minbin Huang, Yanxin Long, Xinchi Deng, Ruihang Chu, Jiangfeng Xiong, Xiaodan Liang, Hong Cheng, Qinglin Lu, Wei Liu
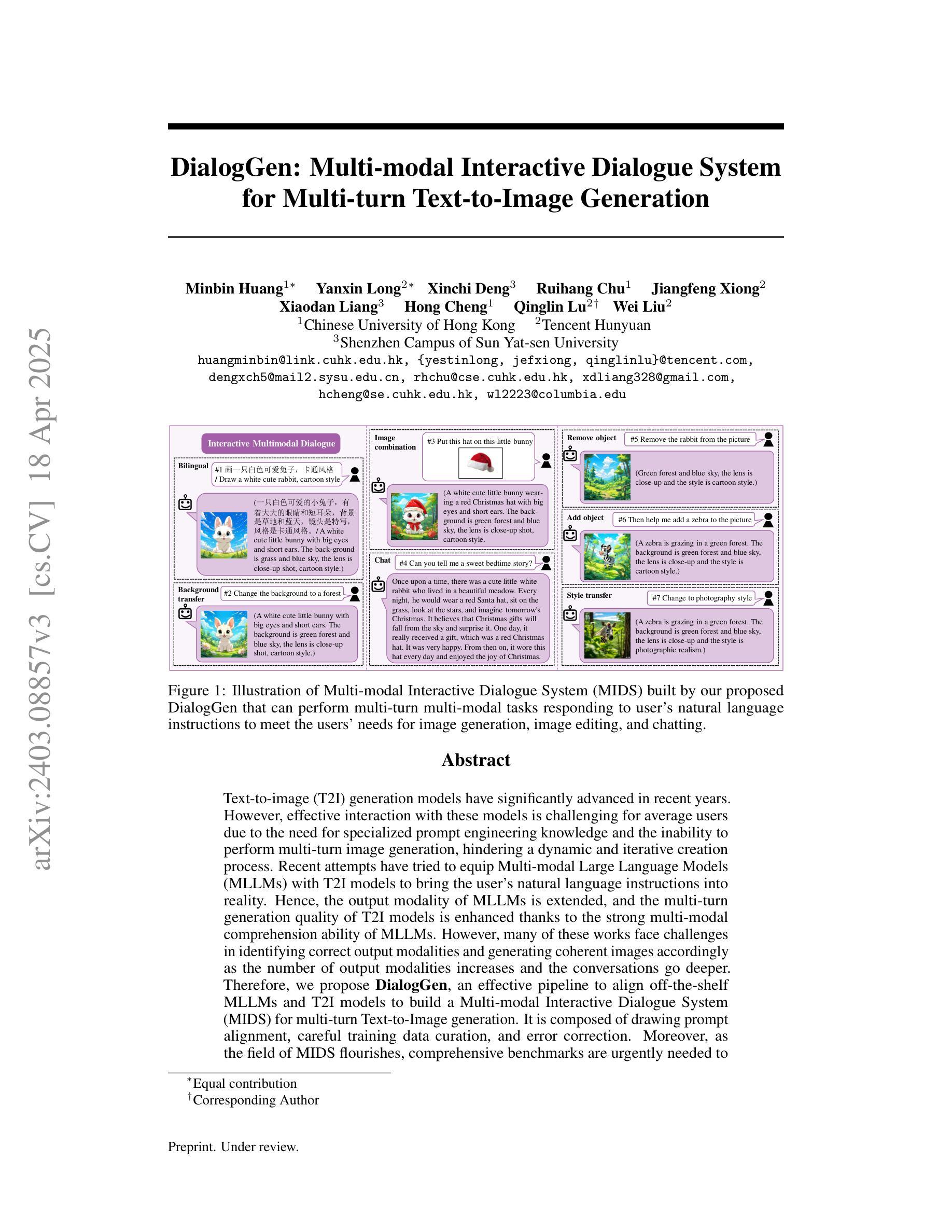
Text-to-image (T2I) generation models have significantly advanced in recent years. However, effective interaction with these models is challenging for average users due to the need for specialized prompt engineering knowledge and the inability to perform multi-turn image generation, hindering a dynamic and iterative creation process. Recent attempts have tried to equip Multi-modal Large Language Models (MLLMs) with T2I models to bring the user’s natural language instructions into reality. Hence, the output modality of MLLMs is extended, and the multi-turn generation quality of T2I models is enhanced thanks to the strong multi-modal comprehension ability of MLLMs. However, many of these works face challenges in identifying correct output modalities and generating coherent images accordingly as the number of output modalities increases and the conversations go deeper. Therefore, we propose DialogGen, an effective pipeline to align off-the-shelf MLLMs and T2I models to build a Multi-modal Interactive Dialogue System (MIDS) for multi-turn Text-to-Image generation. It is composed of drawing prompt alignment, careful training data curation, and error correction. Moreover, as the field of MIDS flourishes, comprehensive benchmarks are urgently needed to evaluate MIDS fairly in terms of output modality correctness and multi-modal output coherence. To address this issue, we introduce the Multi-modal Dialogue Benchmark (DialogBen), a comprehensive bilingual benchmark designed to assess the ability of MLLMs to generate accurate and coherent multi-modal content that supports image editing. It contains two evaluation metrics to measure the model’s ability to switch modalities and the coherence of the output images. Our extensive experiments on DialogBen and user study demonstrate the effectiveness of DialogGen compared with other State-of-the-Art models.
文本到图像(T2I)生成模型在近年来已经取得了显著的进步。然而,对于普通用户来说,与这些模型进行有效的交互是一个挑战,原因在于需要专业的提示工程知识,并且无法进行多轮图像生成,阻碍了动态和迭代创建过程。最近的尝试是装备多模式大型语言模型(MLLMs)以T2I模型,以将用户的自然语言指令转化为现实。因此,MLLMs的输出模式得到了扩展,T2I模型的多轮生成质量也得到了提高,这要归功于MLLMs强大的多模式理解能力。然而,随着输出模式的增加和对话的深入,这些工作面临着识别正确输出模式和生成相应连贯图像的挑战。因此,我们提出了DialogGen,一个有效的管道,用于对齐现成的MLLMs和T2I模型,以建立多模式交互对话系统(MIDS)进行多轮文本到图像生成。它由绘图提示对齐、精心培训数据收集和错误修正组成。此外,随着MIDS领域的发展,迫切需要综合基准测试来公平评估MIDS在输出模式正确性和多模式输出连贯性方面的能力。为了解决这一问题,我们引入了多模式对话基准测试(DialogBen),这是一个全面的双语基准测试,旨在评估MLLMs生成准确和连贯的多模式内容的能力,支持图像编辑。它包括两个评价指标来衡量模型切换模式和输出图像连贯性的能力。我们在DialogBen上进行的大量实验和用户研究证明了DialogGen与其他最新模型相比的有效性。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF Project page: https://hunyuan-dialoggen.github.io/. Accepted to NAACL2025
Summary
文本转图像(T2I)生成模型近年有显著进展,但对普通用户来说有效互动仍具挑战。针对这一问题,文章提出结合多模态大型语言模型(MLLMs)与T2I模型的策略,并介绍DialogGen管道,用于构建多模态交互对话系统(MIDS),提升多轮对话的文本转图像生成质量。同时,为公平评估MIDS的性能,文章还引入了多模态对话基准测试(DialogBen)。
Key Takeaways
- T2I生成模型近年有进步,但用户互动仍是挑战,需专门提示工程知识和多轮图像生成能力。
- MLLMs与T2I模型的结合可提升用户自然语言的实现能力,增强T2I模型的多轮生成质量。
- 随着输出模态的增加和对话的深入,正确识别输出模态和生成连贯图像成为挑战。
- DialogGen是一个有效的管道,用于将现成的MLLMs和T2I模型对齐,构建多模态交互对话系统(MIDS)。
- DialogGen包括提示对齐、训练数据仔细筛选和错误修正等功能。
- 迫切需要对MIDS进行全面基准测试,以公平评估其在输出模态正确性和多模态输出连贯性方面的能力。
点此查看论文截图
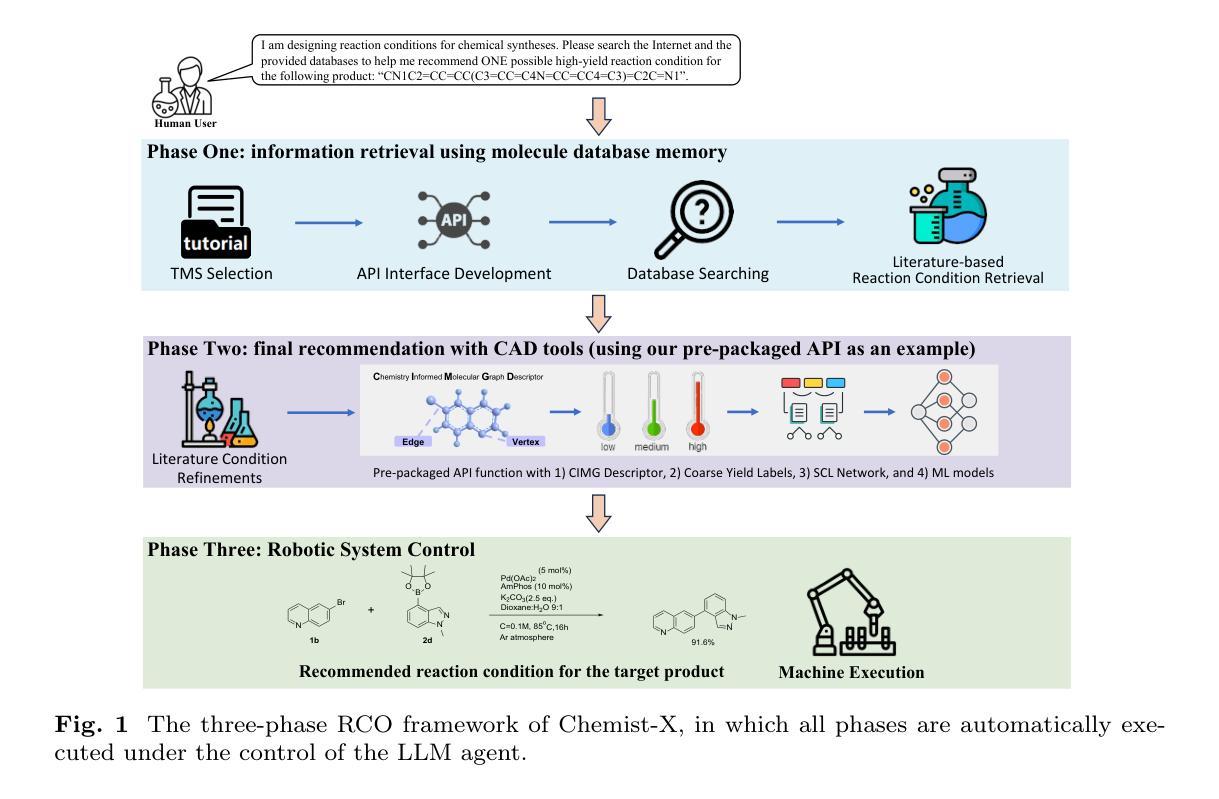
Chemist-X: Large Language Model-empowered Agent for Reaction Condition Recommendation in Chemical Synthesis
Authors:Kexin Chen, Jiamin Lu, Junyou Li, Xiaoran Yang, Yuyang Du, Kunyi Wang, Qiannuan Shi, Jiahui Yu, Lanqing Li, Jiezhong Qiu, Jianzhang Pan, Yi Huang, Qun Fang, Pheng Ann Heng, Guangyong Chen
Recent AI research plots a promising future of automatic chemical reactions within the chemistry society. This study proposes Chemist-X, a comprehensive AI agent that automates the reaction condition optimization (RCO) task in chemical synthesis with retrieval-augmented generation (RAG) technology and AI-controlled wet-lab experiment executions. To begin with, as an emulation on how chemical experts solve the RCO task, Chemist-X utilizes a novel RAG scheme to interrogate available molecular and literature databases to narrow the searching space for later processing. The agent then leverages a computer-aided design (CAD) tool we have developed through a large language model (LLM) supervised programming interface. With updated chemical knowledge obtained via RAG, as well as the ability in using CAD tools, our agent significantly outperforms conventional RCO AIs confined to the fixed knowledge within its training data. Finally, Chemist-X interacts with the physical world through an automated robotic system, which can validate the suggested chemical reaction condition without human interventions. The control of the robotic system was achieved with a novel algorithm we have developed for the equipment, which relies on LLMs for reliable script generation. Results of our automatic wet-lab experiments, achieved by fully LLM-supervised end-to-end operation with no human in the lope, prove Chemist-X’s ability in self-driving laboratories.
近期的AI研究为化学界自动化学反应的未来描绘了一幅充满希望的蓝图。本研究提出了Chemist-X,这是一个全面的AI代理,它使用检索增强生成(RAG)技术和AI控制的湿实验室实验执行,来自动化化学合成中的反应条件优化(RCO)任务。首先,Chemist-X作为一个模拟化学专家解决RCO任务的工具,利用新颖的RAG方案来查询现有的分子和文献数据库,缩小后续处理时的搜索空间。该代理然后使用我们开发的一种计算机辅助设计(CAD)工具,该工具通过大型语言模型(LLM)监督的编程接口。Chemist-X凭借通过RAG获得的最新化学知识以及使用CAD工具的能力,显著优于仅限于其训练数据中的固定知识的传统RCO AI。最后,Chemist-X通过一个自动化的机器人系统与物理世界进行交互,该机器人系统可以验证建议的化学反应条件而无需人工干预。我们为设备开发了一种新型算法来控制机器人系统,该系统依赖于LLM进行可靠的脚本生成。通过完全由LLM监督、无需人工参与的端到端操作实现的自动湿实验室实验结果,证明了Chemist-X在自动驾驶实验室的能力。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary:
最新AI研究为化学社会实现自动化学反应绘制了充满希望的前景。该研究提出Chemist-X,一个全面AI代理,可自动进行化学合成中的反应条件优化任务。Chemist-X利用检索增强生成技术,通过查询分子和文献数据库来缩小搜索空间,借鉴化学专家解决反应条件优化任务的方法。此外,它采用开发的大型语言模型监督编程接口,显著优于仅限于训练数据的传统AI。最后,Chemist-X通过自动化机器人系统与现实世界交互,无需人为干预即可验证建议的化学反应条件。该系统设备算法可靠生成脚本,证明Chemist-X能够自主操控实验室设备实现端对端操作。
Key Takeaways:
- Chemist-X是一个全面的AI代理,能够自动化完成化学反应条件优化任务。
- 该代理使用检索增强生成技术查询分子和文献数据库以缩小搜索范围。
- Chemist-X采用大型语言模型监督编程接口,优于传统AI。
- Chemist-X通过自动化机器人系统与现实世界交互,可验证化学反应条件。
- 该系统设备算法可靠生成脚本,实现Chemist-X自主操控实验室设备。
- Chemist-X在自我驾驶实验室中的实验证明了其全自动化操作的可行性。
点此查看论文截图