⚠️ 以下所有内容总结都来自于 大语言模型的能力,如有错误,仅供参考,谨慎使用
🔴 请注意:千万不要用于严肃的学术场景,只能用于论文阅读前的初筛!
💗 如果您觉得我们的项目对您有帮助 ChatPaperFree ,还请您给我们一些鼓励!⭐️ HuggingFace免费体验
2025-04-22 更新
Does Reinforcement Learning Really Incentivize Reasoning Capacity in LLMs Beyond the Base Model?
Authors:Yang Yue, Zhiqi Chen, Rui Lu, Andrew Zhao, Zhaokai Wang, Yang Yue, Shiji Song, Gao Huang
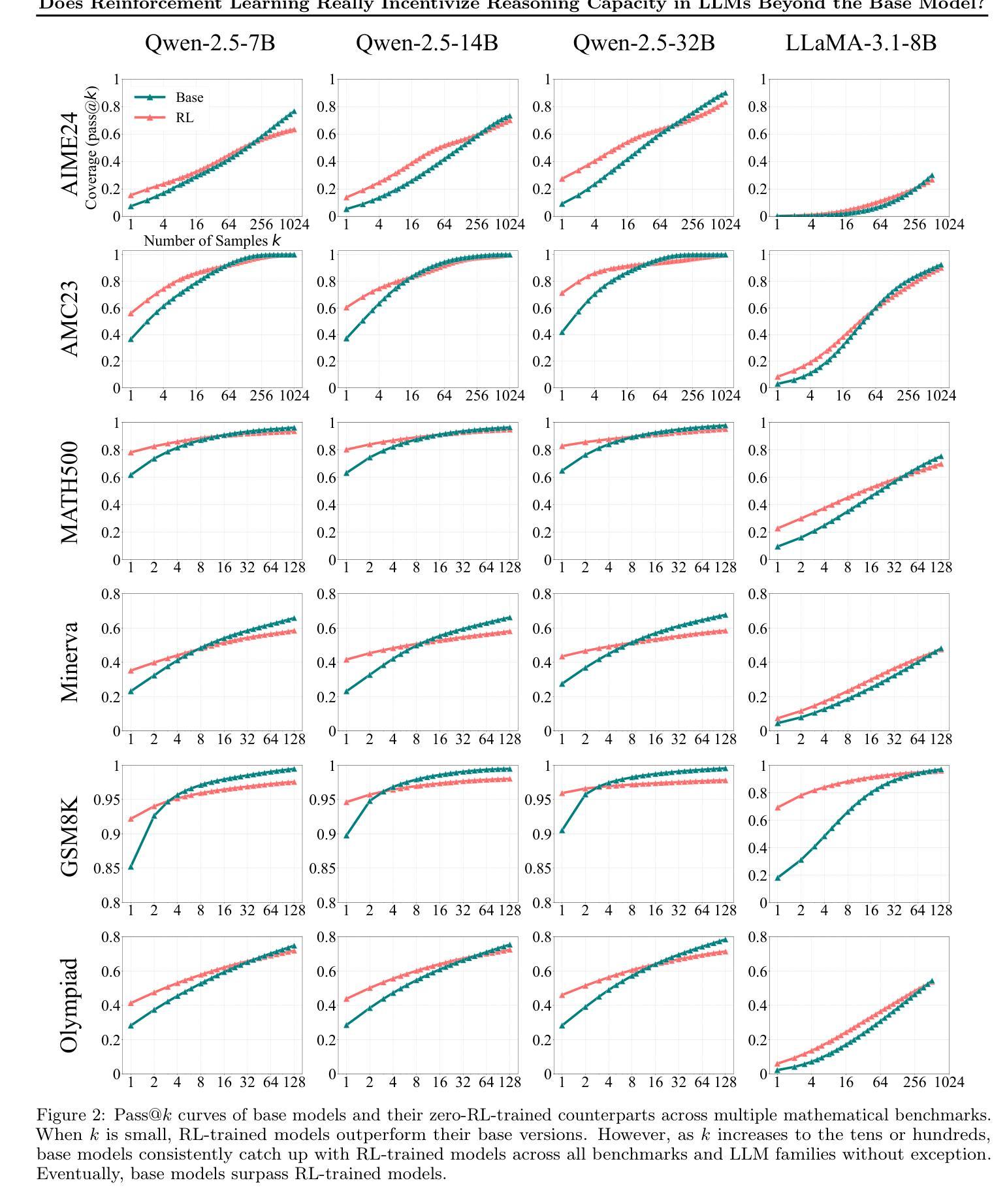
Reinforcement Learning with Verifiable Rewards (RLVR) has recently demonstrated notable success in enhancing the reasoning capabilities of LLMs, particularly in mathematics and programming tasks. It is widely believed that RLVR enables LLMs to continuously self-improve, thus acquiring novel reasoning abilities that exceed corresponding base models’ capacity. In this study, however, we critically re-examines this assumption by measuring the pass@\textit{k} metric with large values of \textit{k} to explore the reasoning capability boundary of the models across a wide range of model families and benchmarks. Surprisingly, the RL does \emph{not}, in fact, elicit fundamentally new reasoning patterns. While RL-trained models outperform their base models at smaller values of $k$ (\eg, $k$=1), base models can achieve a comparable or even higher pass@$k$ score compared to their RL counterparts at large $k$ values. The reasoning paths generated by RL-trained models are already included in the base models’ sampling distribution, suggesting that most reasoning abilities manifested in RL-trained models are already obtained by base models. Further analysis shows that RL training boosts the performance by biasing the model’s output distribution toward paths that are more likely to yield rewards, therefore sampling correct responses more efficiently. But this also results in a narrower reasoning capability boundary compared to base models. Similar results are observed in visual reasoning tasks trained with RLVR. Moreover, we find that distillation can genuinely introduce new knowledge into the model, different from RLVR. These findings underscore a critical limitation of RLVR in advancing LLM reasoning abilities which requires us to fundamentally rethink the impact of RL training in reasoning LLMs and the need of a better paradigm. Project Page: https://limit-of-RLVR.github.io
强化学习与可验证奖励(RLVR)最近在增强大型语言模型的推理能力方面取得了显著的成功,特别是在数学和编程任务中。人们普遍认为,RLVR使大型语言模型能够持续自我改进,从而获得超过相应基础模型容量的新型推理能力。然而,本研究通过测量pass@\emph{k}指标,并设置较大的\emph{k}值来重新评估这一假设,以探索模型跨多个模型家族和基准测试集的推理能力边界。令人惊讶的是,RL并没有引发根本性的新推理模式。尽管在较小的k值(例如k=1)下,RL训练的模型优于基础模型,但在较大的k值下,基础模型甚至可以取得与RL训练模型相当的甚至更高的pass@k分数。RL训练模型产生的推理路径已包含在基础模型的采样分布中,这表明RL训练模型中展现的大多数推理能力已被基础模型所获得。进一步的分析表明,RL训练通过使模型输出分布偏向于更可能产生奖励的路径,从而提高性能,从而更有效地抽取正确响应。但这与基础模型相比,也导致了较窄的推理能力边界。在RLVR训练的视觉推理任务中也观察到类似的结果。此外,我们发现蒸馏法可以真正地将新知识引入模型中,这与RLVR不同。这些发现突出了RLVR在推进大型语言模型推理能力方面的关键局限性,这要求我们从根本上重新思考RL训练在推理大型语言模型中的作用以及是否需要更好的范式。项目页面:https://limit-of-RLVR.github.io
论文及项目相关链接
PDF 24 pages, 19 figures
Summary
强化学习通过奖励验证(RLVR)在提升大型语言模型(LLM)的推理能力方面取得了显著的成功,特别是在数学和编程任务中。然而,本研究通过测量pass@\textit{k}指标对大模型进行批判性考察,发现在宽泛的模型家族和基准测试中,强化学习并不激发新的推理模式。在较大的k值下,基础模型的性能可与强化学习模型相当甚至更高。强化学习训练使模型输出分布偏向于更易产生奖励的路径,从而提高性能,但这也导致与基础模型相比,其推理能力边界较窄。类似的结果也出现在使用RLVR训练的视觉推理任务中。此外,研究发现蒸馏可以真正地为模型引入新知识,与RLVR不同。这些发现突显了RLVR在提升LLM推理能力方面的关键局限性,需要我们对强化学习在LLM推理中的影响进行根本性的重新思考,并需要更好的范式。
Key Takeaways
- 强化学习通过奖励验证(RLVR)增强了LLM在数学和编程任务中的推理能力。
- 通过测量pass@\textit{k}指标发现,在较大的k值下,基础模型的性能可与强化学习模型相当或更高。
- 强化学习训练使模型输出偏向于更容易产生奖励的路径,从而提高性能。
- 强化学习并不激发新的推理模式,其展现的推理路径已包含在基础模型的采样分布中。
- 强化学习训练会导致模型推理能力边界较窄,相较于基础模型。
- 在视觉推理任务中,使用RLVR训练也出现了类似的结果。
点此查看论文截图

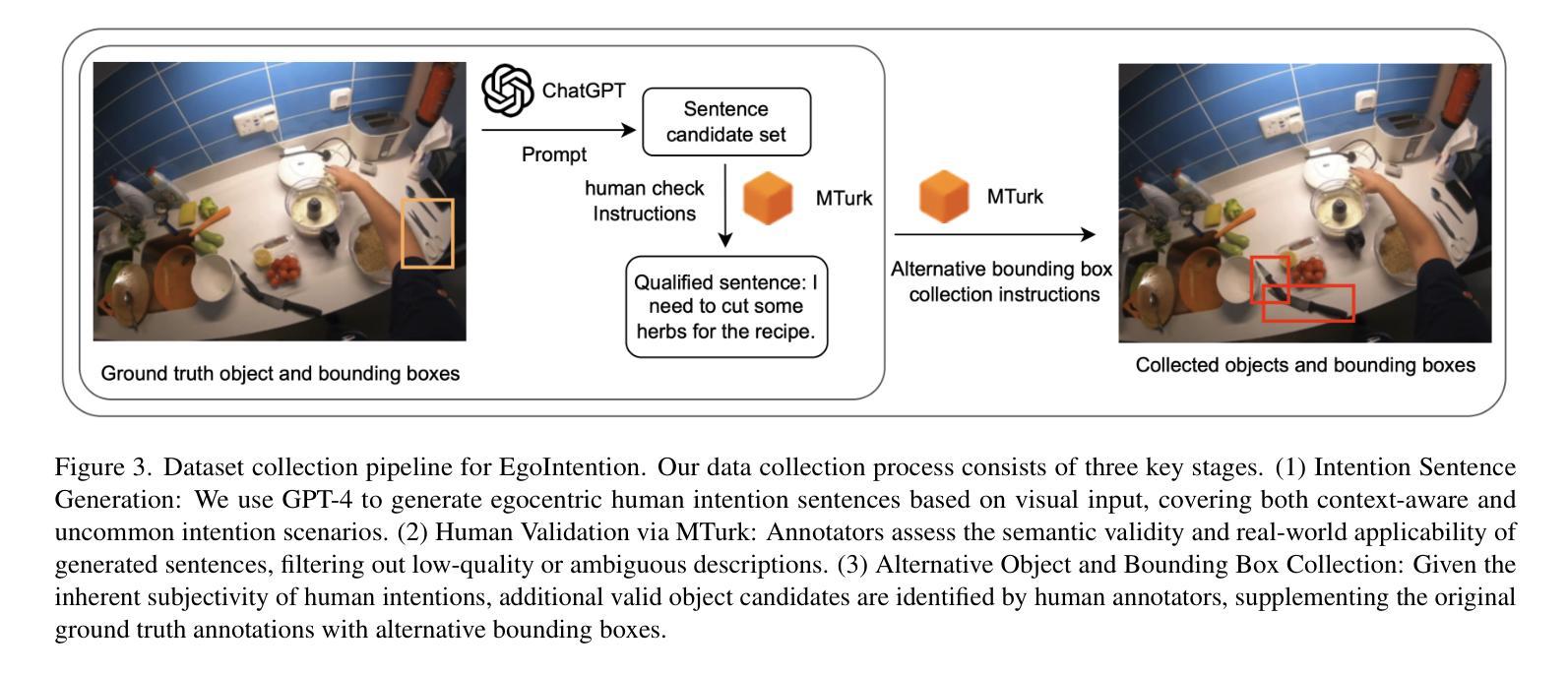
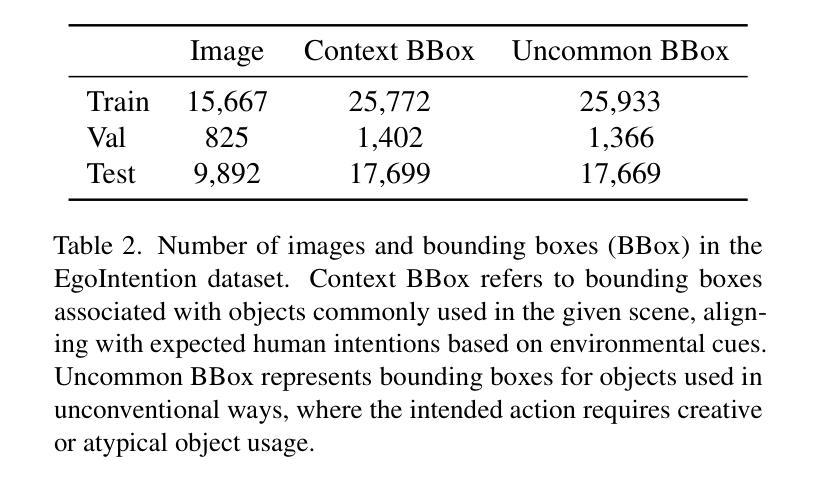
Visual Intention Grounding for Egocentric Assistants
Authors:Pengzhan Sun, Junbin Xiao, Tze Ho Elden Tse, Yicong Li, Arjun Akula, Angela Yao
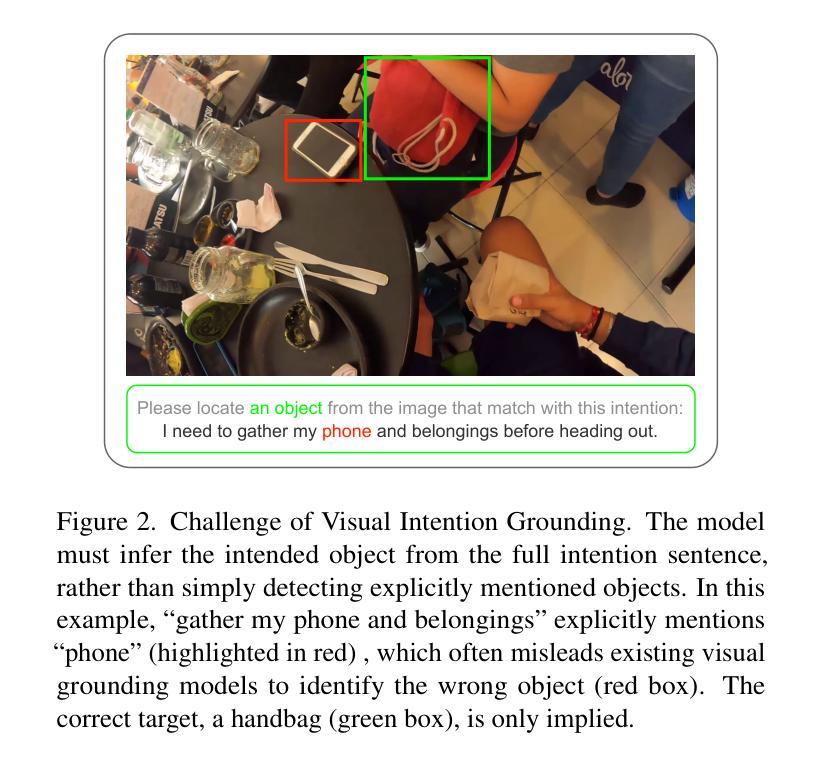
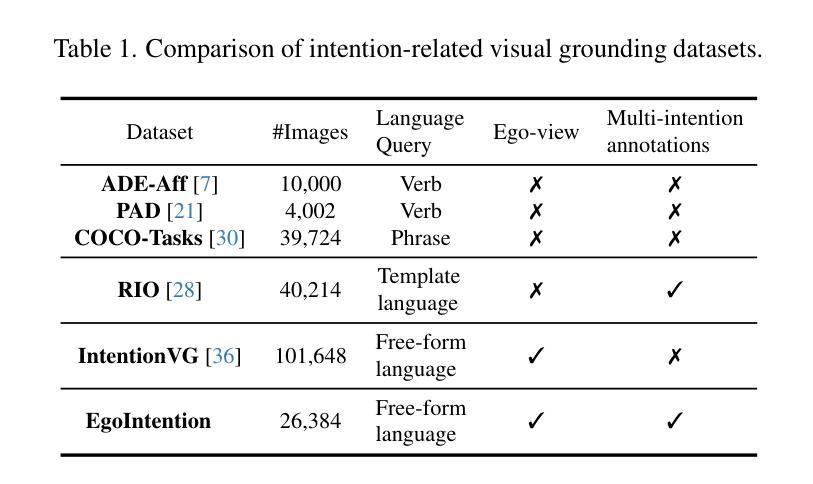
Visual grounding associates textual descriptions with objects in an image. Conventional methods target third-person image inputs and named object queries. In applications such as AI assistants, the perspective shifts – inputs are egocentric, and objects may be referred to implicitly through needs and intentions. To bridge this gap, we introduce EgoIntention, the first dataset for egocentric visual intention grounding. EgoIntention challenges multimodal LLMs to 1) understand and ignore unintended contextual objects and 2) reason about uncommon object functionalities. Benchmark results show that current models misidentify context objects and lack affordance understanding in egocentric views. We also propose Reason-to-Ground (RoG) instruction tuning; it enables hybrid training with normal descriptions and egocentric intentions with a chained intention reasoning and object grounding mechanism. RoG significantly outperforms naive finetuning and hybrid training on EgoIntention, while maintaining or slightly improving naive description grounding. This advancement enables unified visual grounding for egocentric and exocentric visual inputs while handling explicit object queries and implicit human intentions.
视觉定位是将文本描述与图像中的物体关联起来。传统的方法主要针对第三人称图像输入和命名物体查询。在人工智能助手等应用中,视角会发生变化——输入是自我中心的,物体可能通过需求和意图被隐含地提及。为了弥补这一差距,我们引入了EgoIntention,这是第一个针对自我中心视觉意图定位的数据集。EgoIntention挑战了跨模态大型语言模型,使其能够理解和忽略非上下文中的物体,并对不寻常物体的功能进行推理。基准测试结果表明,当前模型会错误识别上下文中的物体,在自我中心视角中缺乏功能理解。我们还提出了Reason-to-Ground(RoG)指令微调方法;它通过混合正常描述和自我中心意图的混合训练,以及链式意图推理和物体定位机制,实现了显著的效果。在EgoIntention数据集上,RoG相较于简单微调模型和混合训练模型具有显著优势,同时在简单的描述定位上能够保持或稍微提高性能。这一进展使统一处理自我中心和外部中心的视觉输入,以及处理显性物体查询和隐性人类意图成为可能。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
视觉定位是将文本描述与图像中的物体相关联。传统方法主要针对第三人称图像输入和命名物体查询。在人工智能助手等应用中,视角会发生变化——输入是以自我为中心的,物体可能通过需求和意图隐含地指代。为了弥补这一差距,我们推出了EgoIntention,这是首个针对以自我为中心的可视意图定位的数据集。EgoIntention挑战了跨模态大型语言模型,以理解和忽略无意中的上下文物体以及推理不寻常的物体功能。基准测试结果显示,当前模型在识别上下文物体方面存在缺陷,在以自我为中心的观点中缺乏承担理解的能力。我们还提出了Reason-to-Ground(RoG)指令调整;它通过混合正常描述和以自我为中心的意图进行混合训练,并带有连锁意图推理和物体定位机制。RoG在EgoIntention上的表现显著优于简单的微调器和混合训练,同时在描述定位方面保持或略有改进。这一进展使得统一以自我为中心和以外部为中心的可视输入的定位成为可能,同时处理明确的物体查询和隐含的人类意图。
Key Takeaways
- 视觉定位结合了文本描述和图像中的物体。
- 传统方法主要集中在第三人称图像输入和命名物体查询上。
- 在如AI助手等应用中,视角转变为以自我为中心,物体通过需求和意图隐含指代。
- EgoIntention数据集解决了以自我为中心的可视意图定位的挑战。
- 当前模型在识别上下文物体和理解以自我为中心的视角中的物体功能方面存在缺陷。
- Reason-to-Ground(RoG)指令调整通过混合训练提高了模型的性能。
点此查看论文截图


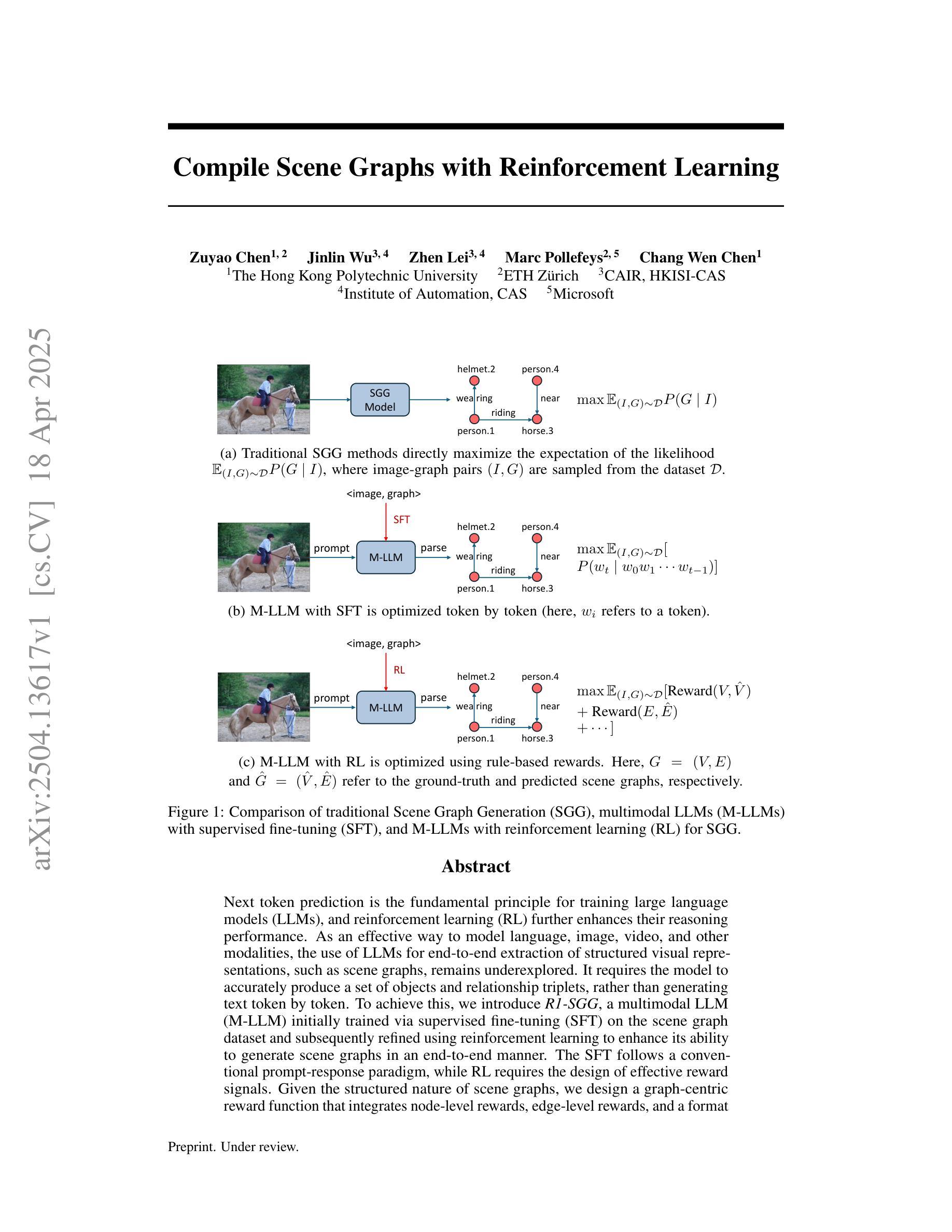
Compile Scene Graphs with Reinforcement Learning
Authors:Zuyao Chen, Jinlin Wu, Zhen Lei, Marc Pollefeys, Chang Wen Chen
Next token prediction is the fundamental principle for training large language models (LLMs), and reinforcement learning (RL) further enhances their reasoning performance. As an effective way to model language, image, video, and other modalities, the use of LLMs for end-to-end extraction of structured visual representations, such as scene graphs, remains underexplored. It requires the model to accurately produce a set of objects and relationship triplets, rather than generating text token by token. To achieve this, we introduce R1-SGG, a multimodal LLM (M-LLM) initially trained via supervised fine-tuning (SFT) on the scene graph dataset and subsequently refined using reinforcement learning to enhance its ability to generate scene graphs in an end-to-end manner. The SFT follows a conventional prompt-response paradigm, while RL requires the design of effective reward signals. Given the structured nature of scene graphs, we design a graph-centric reward function that integrates node-level rewards, edge-level rewards, and a format consistency reward. Our experiments demonstrate that rule-based RL substantially enhances model performance in the SGG task, achieving a zero failure rate–unlike supervised fine-tuning (SFT), which struggles to generalize effectively. Our code is available at https://github.com/gpt4vision/R1-SGG.
接下来令牌预测是训练大型语言模型(LLM)的基本原则,强化学习(RL)进一步增强了其推理性能。作为对语言、图像、视频等多种模式进行有效建模的一种手段,使用大型语言模型进行端到端的结构化视觉表示提取(如场景图)仍然缺乏研究。这需要模型准确生成一组对象和关系三元组,而不是逐个生成文本令牌。为了实现这一点,我们引入了R1-SGG,这是一个多模态大型语言模型(M-LLM),最初通过场景图数据集上的监督微调(SFT)进行训练,随后使用强化学习进行精炼,以提高其端到端生成场景图的能力。SFT遵循传统的提示-响应范式,而RL需要设计有效的奖励信号。考虑到场景图的结构性特点,我们设计了一个以图形为中心的奖励函数,它结合了节点级奖励、边缘级奖励和格式一致性奖励。我们的实验表明,基于规则的RL在很大程度上提高了SGG任务中的模型性能,实现了零失败率——这与在有效推广方面表现挣扎的监督微调(SFT)形成鲜明对比。我们的代码可以在https://github.com/gpt4vision/R1-SGG找到。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
大型语言模型(LLM)采用下一代令牌预测原则进行训练,强化学习(RL)进一步提高其推理性能。尽管LLM在端到端提取结构化视觉表示(如场景图)方面有着广泛的应用前景,但相关研究仍然不足。本研究引入R1-SGG,一种多模态LLM(M-LLM),采用场景图数据集进行基于监督微调(SFT)的初步训练,然后使用强化学习进一步优化,旨在提高其生成场景图的能力。结合节点级别和边缘级别的奖励以及格式一致性奖励,设计了一个以图形为中心的奖励函数。实验表明,基于规则的RL在SGG任务中显著提高模型性能,达到零故障率。代码可在GitHub上获取。
Key Takeaways
- 大型语言模型(LLM)基于下一代令牌预测原则进行训练。
- 强化学习(RL)增强LLM的推理性能。
- LLMs在端到端提取结构化视觉表示(如场景图)方面的应用尚待探索。
- R1-SGG是一种多模态LLM,旨在提高生成场景图的能力。
- R1-SGG通过监督微调(SFT)初步训练,并使用强化学习进一步优化。
- 设计了一个以图形为中心的奖励函数,包括节点级别、边缘级别和格式一致性奖励。
点此查看论文截图
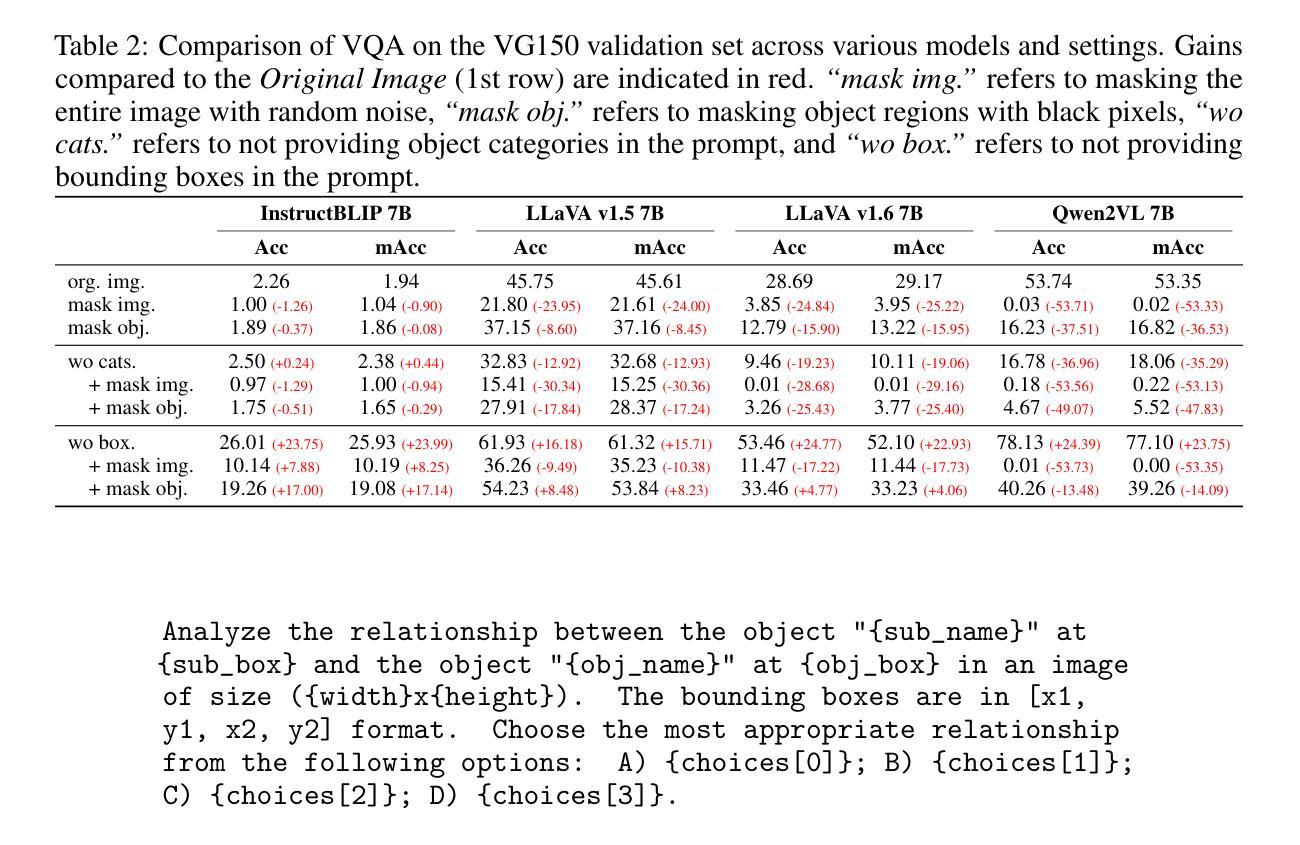
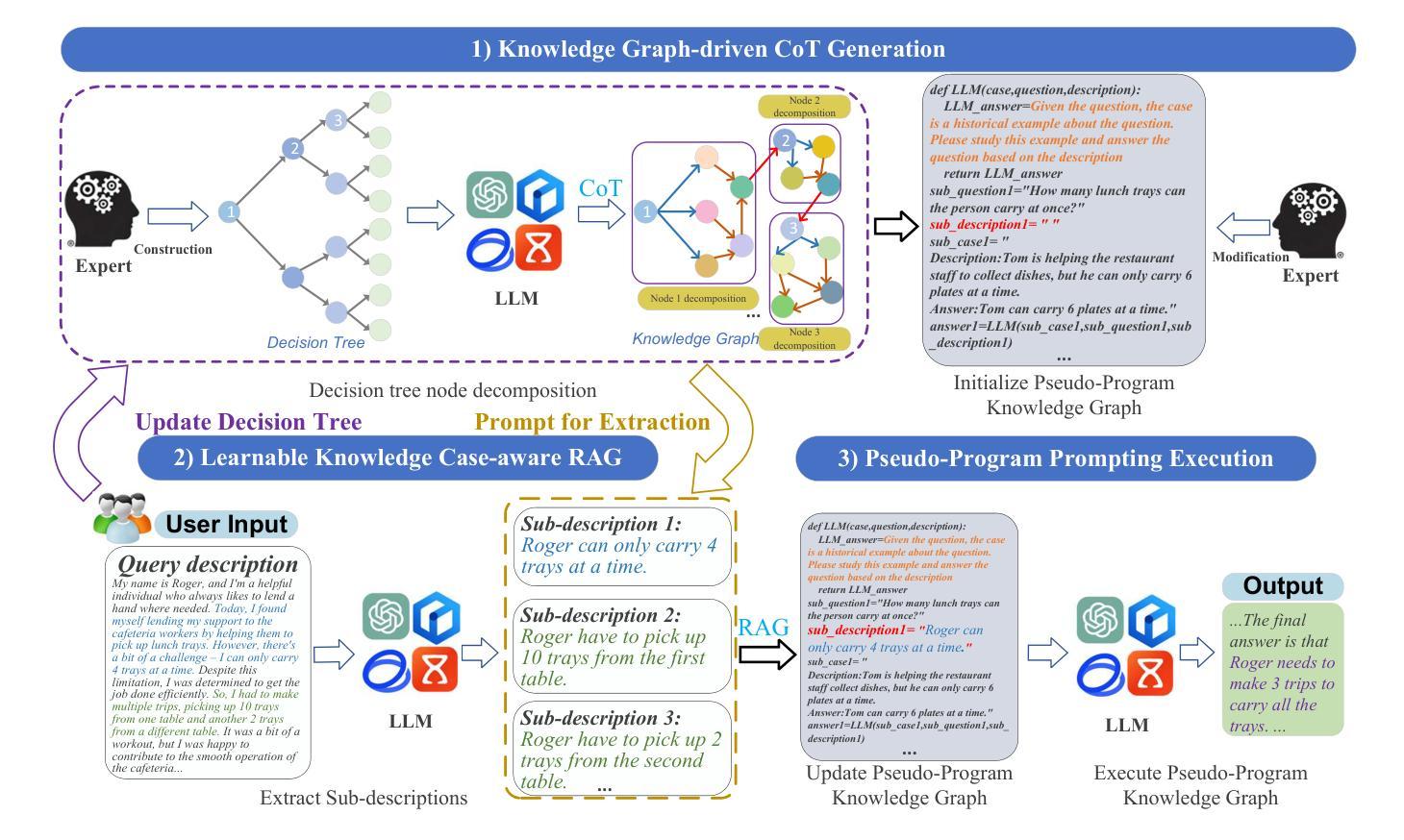
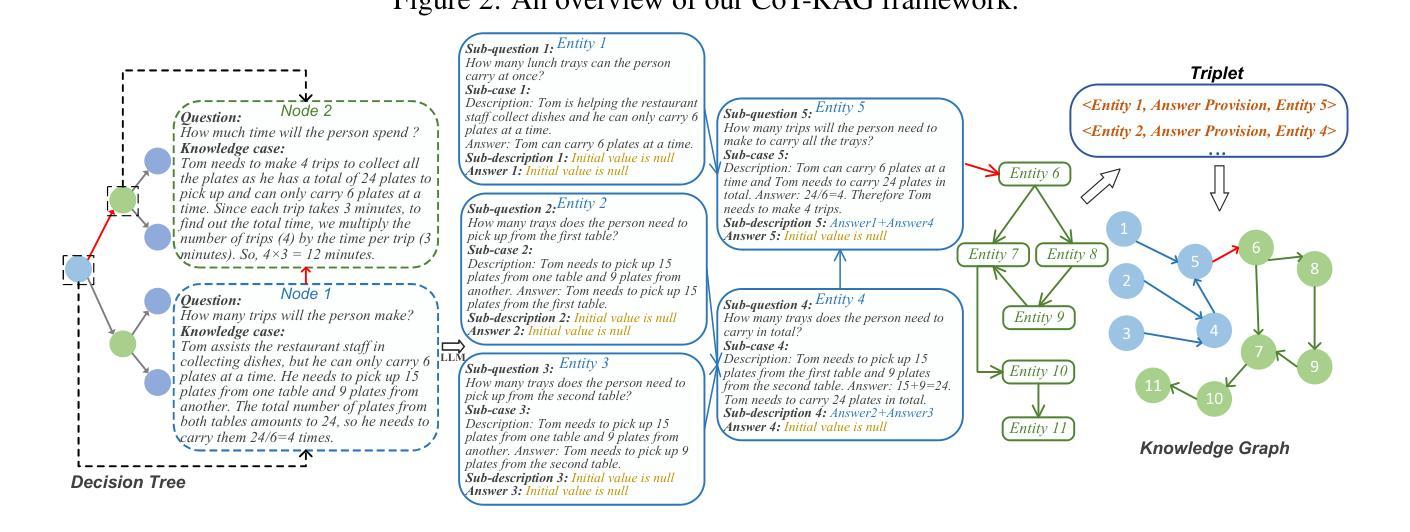
CoT-RAG: Integrating Chain of Thought and Retrieval-Augmented Generation to Enhance Reasoning in Large Language Models
Authors:Feiyang Li, Peng Fang, Zhan Shi, Arijit Khan, Fang Wang, Dan Feng, Weihao Wang, Xin Zhang, Yongjian Cui
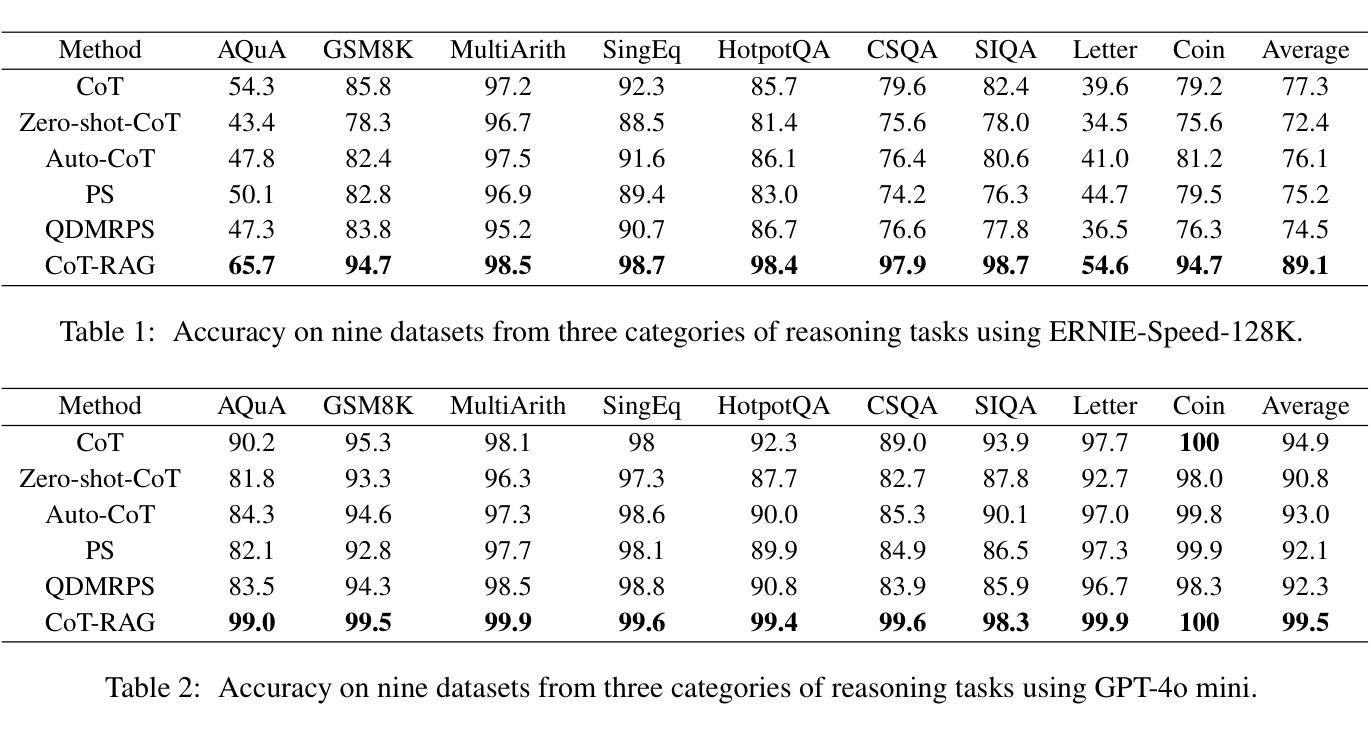
While chain-of-thought (CoT) reasoning improves the performance of large language models (LLMs) in complex tasks, it still has two main challenges: the low reliability of relying solely on LLMs to generate reasoning chains and the interference of natural language reasoning chains on the inference logic of LLMs. To address these issues, we propose CoT-RAG, a novel reasoning framework with three key designs: (i) Knowledge Graph-driven CoT Generation, featuring knowledge graphs to modulate reasoning chain generation of LLMs, thereby enhancing reasoning credibility; (ii) Learnable Knowledge Case-aware RAG, which incorporates retrieval-augmented generation (RAG) into knowledge graphs to retrieve relevant sub-cases and sub-descriptions, providing LLMs with learnable information; (iii) Pseudo-Program Prompting Execution, which encourages LLMs to execute reasoning tasks in pseudo-programs with greater logical rigor. We conduct a comprehensive evaluation on nine public datasets, covering three reasoning problems. Compared with the-state-of-the-art methods, CoT-RAG exhibits a significant accuracy improvement, ranging from 4.0% to 23.0%. Furthermore, testing on four domain-specific datasets, CoT-RAG shows remarkable accuracy and efficient execution, highlighting its strong practical applicability and scalability.
虽然链式思维(CoT)推理在复杂任务中提高了大型语言模型(LLM)的性能,但它仍然面临两个主要挑战:仅依赖LLM生成推理链的低可靠性以及自然语言推理链对LLM推理逻辑的影响。为了解决这些问题,我们提出了CoT-RAG这一新型推理框架,它包含三个关键设计:(i)知识图谱驱动的CoT生成,利用知识图谱来调节LLM的推理链生成,从而提高推理的可信度;(ii)可学习的知识案例感知RAG,将检索增强生成(RAG)纳入知识图谱,以检索相关的子案例和子描述,为LLM提供可学习的信息;(iii)伪程序提示执行,鼓励LLM在伪程序中执行推理任务,提高逻辑严谨性。我们在九个公开数据集上进行了全面评估,涵盖三种推理问题。与最先进的方法相比,CoT-RAG在准确率上有了显著的提高,范围在4.0%到23.0%之间。此外,在四个领域特定的数据集上进行测试,CoT-RAG显示出卓越的准确性和高效的执行力,突显了其强大的实用性、适用性和可扩展性。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary:
链式思维(CoT)推理虽能提高大型语言模型(LLM)在复杂任务中的表现,但仍面临两大挑战。为解决这些问题,提出CoT-RAG这一新型推理框架,包括知识图谱驱动CoT生成、可学习知识案例感知RAG和伪程序提示执行三个关键设计。在九个公共数据集上的全面评估表明,与现有先进方法相比,CoT-RAG的准确率显著提高,范围在4.0%到23.0%之间。在四个领域特定数据集上的测试进一步凸显了其强大的实用性、可扩展性和高效执行。
Key Takeaways:
- 链式思维(CoT)推理在大型语言模型(LLM)中虽有优势,但仍存在可靠性低和干扰推理链生成的问题。
- 提出CoT-RAG新型推理框架,包括知识图谱驱动CoT生成、可学习知识案例感知RAG和伪程序提示执行三大关键设计。
- 知识图谱用于调制LLM的推理链生成,提高推理可信度。
- 检索增强生成(RAG)技术被纳入知识图谱中,可检索相关子案例和子描述,为LLM提供可学习信息。
- CoT-RAG采用伪程序提示执行,鼓励LLM在伪程序中执行推理任务,提高逻辑严谨性。
- 在九个公共数据集上的评估显示,CoT-RAG相比最先进的方法准确率显著提高。
点此查看论文截图

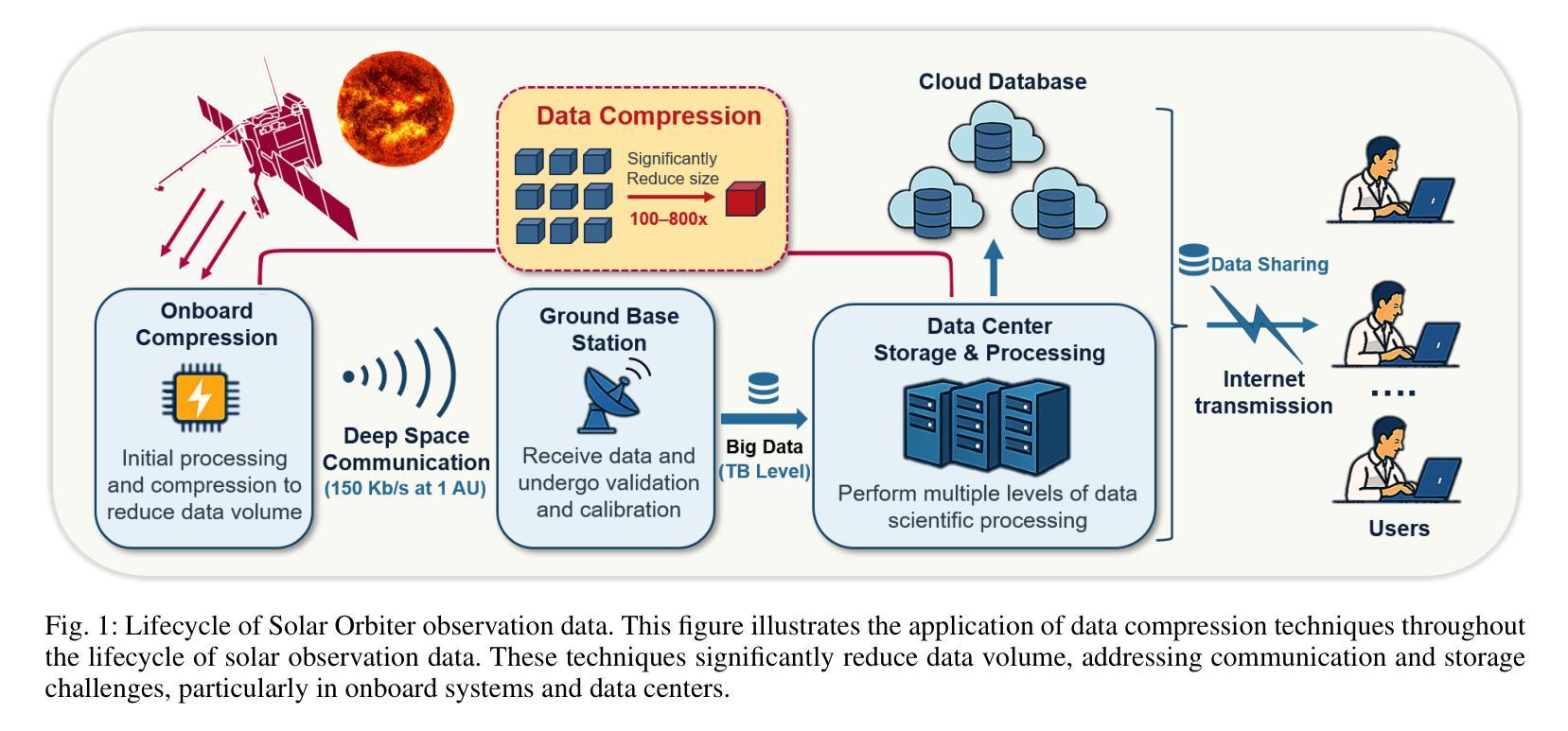
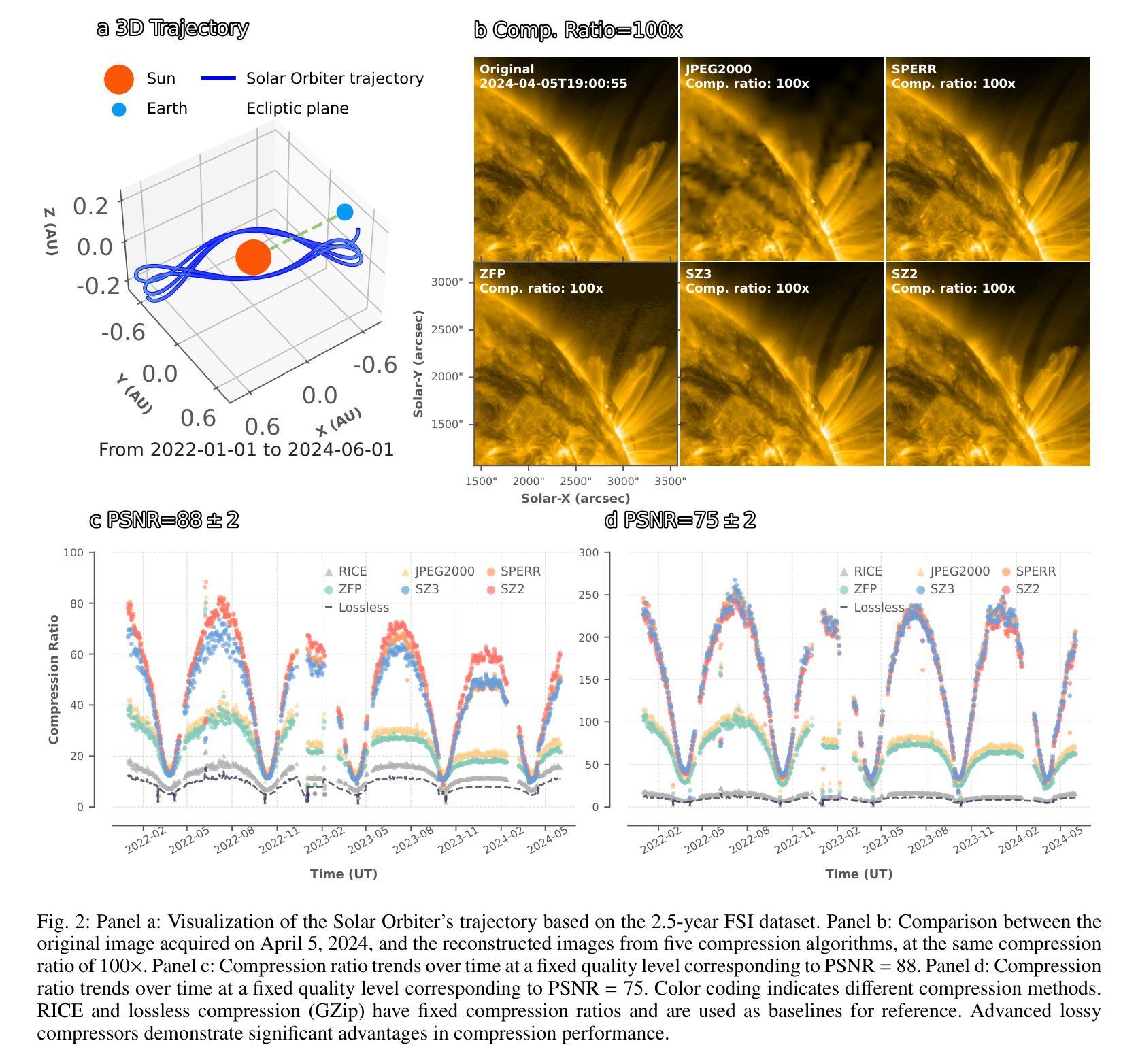
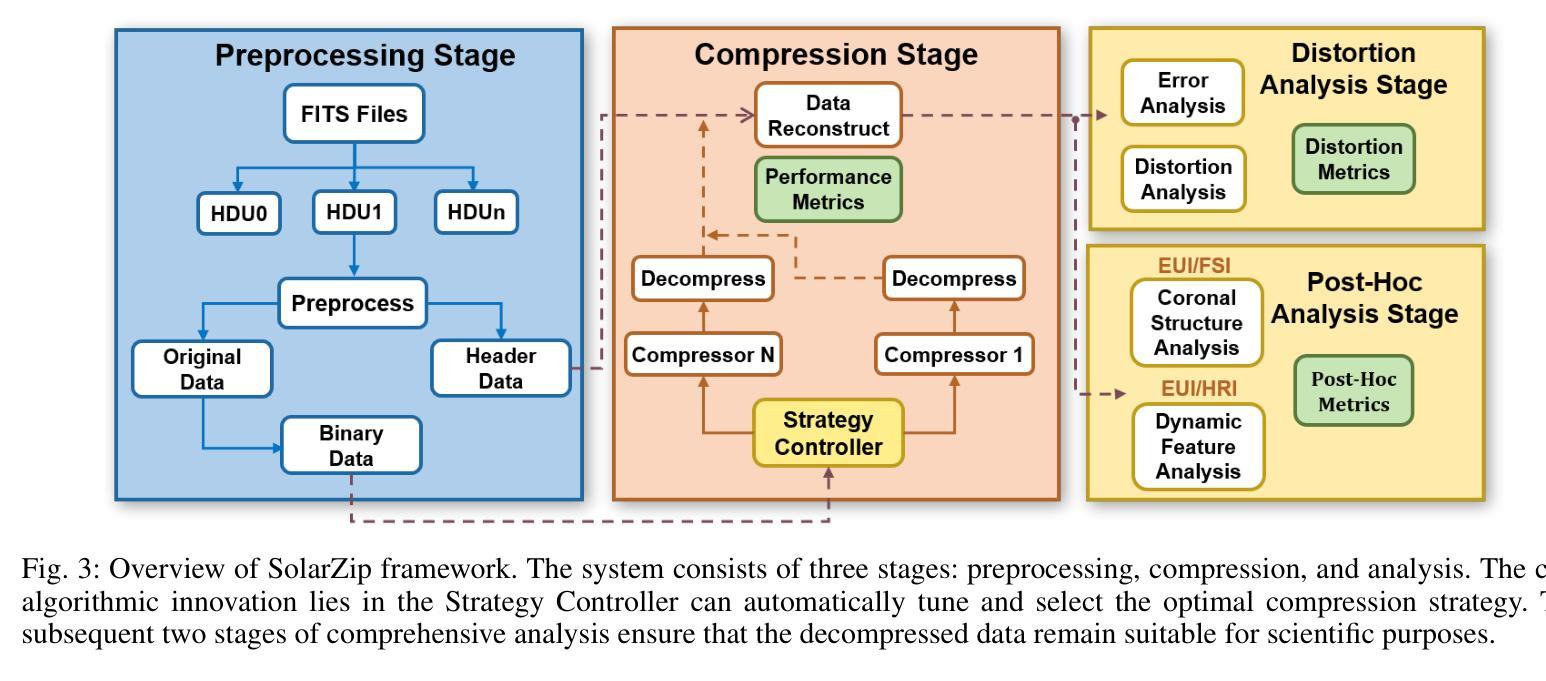
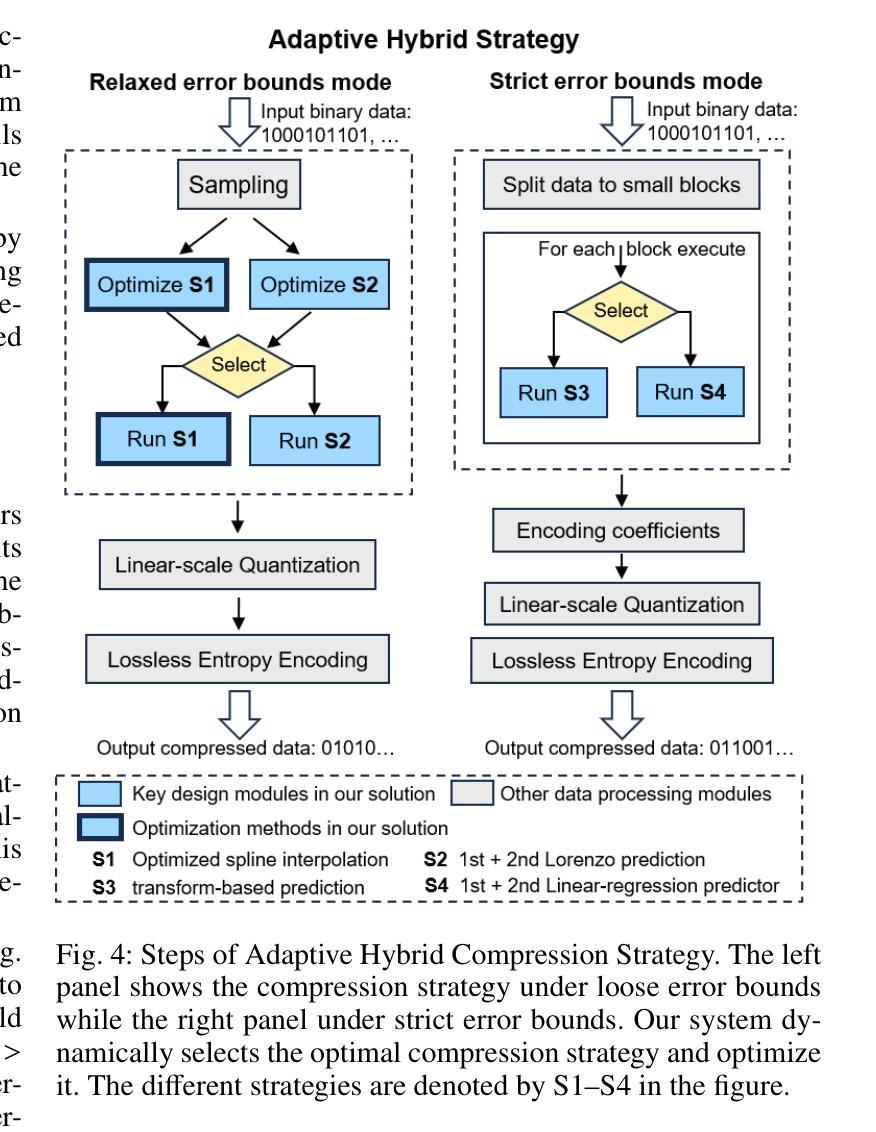
SolarZip: An Efficient and Adaptive Compression Framework for solar EUV imaging data
Authors:Zedong Liu, Song Tan, Alexander Warmuth, Frédéric Schuller, Yun Hong, Wenjing Huang, Yida Gu, Bojing Zhu, Guangming Tan, Dingwen Tao
Context: With the advancement of solar physics research, next-generation solar space missions and ground-based telescopes face significant challenges in efficiently transmitting and/or storing large-scale observational data. Aims: We develop an efficient compression and evaluation framework for solar EUV data, specifically optimized for Solar Orbiter Extreme Ultraviolet Imager (EUI) data, significantly reducing data volume while preserving scientific usability. Methods: We systematically evaluated four error-bounded lossy compressors across two EUI datasets. However, the existing methods cannot perfectly handle the EUI datasets (with continuously changing distance and significant resolution differences). Motivated by this, we develop an adaptive hybrid compression strategy with optimized interpolation predictors. Moreover, we designed a two-stage evaluation framework integrating distortion analysis with downstream scientific workflows, ensuring that observational analysis is not affected at high compression ratios. Results: Our framework SolarZip achieved up to 800x reduction for Full Sun Imager (FSI) data and 500x for High Resolution Imager (HRI$_{\text{EUV}}$) data. It significantly outperformed both traditional and advanced algorithms, achieving 3-50x higher compression ratios than traditional algorithms, surpassing the second-best algorithm by up to 30%. Simulation experiments verified that SolarZip can reduce data transmission time by up to 270x while ensuring the preservation of scientific usability. Conclusions: The SolarZip framework significantly enhances solar observational data compression efficiency while preserving scientific usability by dynamically selecting optimal compression methods based on observational scenarios and user requirements. This provides a promising data management solution for deep space missions like Solar Orbiter.
背景:随着太阳物理学研究的进步,下一代太阳空间任务和地面望远镜在有效地传输和/或存储大规模观测数据方面面临重大挑战。目标:我们为太阳轨道器极紫外成像仪(EUI)数据开发了一个高效压缩和评估框架,该框架能在减少数据量的同时保持数据的科学可用性。方法:我们系统地评估了四个误差有界的有损压缩机,跨越两个EUI数据集。然而,现有方法无法完美处理EUI数据集(具有连续变化的距离和显著的分辨率差异)。受此启发,我们开发了一种带有优化插值预测器的自适应混合压缩策略。此外,我们设计了一个两阶段的评估框架,将失真分析与下游科学工作流程相结合,确保在高压缩比下观测分析不受影响。结果:我们的SolarZip框架实现了对全日成像仪(FSI)数据高达800倍的压缩比,而对高分辨率成像仪(HRI$_{EUV}$)数据则实现了高达500倍的压缩比。与传统的先进算法相比,它大大优于这些算法,实现了高达传统算法3至50倍的高压缩比,并超过了第二好的算法高达30%。模拟实验证实,SolarZip能在确保科学可用性的前提下,将数据传输时间缩短高达270倍。结论:SolarZip框架通过根据观测场景和用户要求动态选择最佳压缩方法,在保持科学可用性的同时大大提高了太阳观测数据的压缩效率。这为深空任务如太阳能轨道器提供了有前景的数据管理解决方案。
论文及项目相关链接
摘要
随着太阳物理学研究的进展,下一代太空任务和地面望远镜在传输和存储大规模观测数据时面临巨大挑战。本文开发了一种针对太阳轨道器极紫外成像仪(EUI)数据的压缩与评估框架,能够在减少数据量的同时保持科学可用性。通过对四种误差限制有损压缩器的系统评估,提出了一种自适应混合压缩策略,并设计了包含失真分析和下游科学工作流程的两阶段评估框架。结果显示,SolarZip框架对全日成像仪(FSI)数据的压缩比达到800倍,对高分辨率极紫外成像仪(HRI)数据的压缩比为500倍。与传统的先进算法相比,SolarZip框架压缩效率更高,且能保持科学可用性。此外,SolarZip能减少数据传输时间高达270倍。结论:SolarZip框架通过动态选择最佳压缩方法,提高了太阳观测数据的压缩效率并保持了科学可用性,为深空任务如Solar Orbiter提供了有前景的数据管理解决方案。
关键见解
- SolarZip框架旨在优化下一代太阳观测数据的压缩效率,特别是在处理太阳轨道器极紫外成像仪(EUI)数据时效果显著。
- SolarZip框架通过开发自适应混合压缩策略,优化了插值预测器,提高了数据压缩比。
- SolarZip框架通过两阶段评估框架确保了压缩数据的质量和科学可用性,包括失真分析和下游科学工作流程的集成。
- SolarZip实现了高达800倍的FSI数据压缩比和500倍的HRI数据压缩比,显著优于传统和先进算法。
- SolarZip框架在保证科学质量的前提下,能有效减少数据传输时间,最高可达270倍。
- SolarZip框架提供了一个有前途的数据管理解决方案,适用于需要高效处理大规模观测数据的深空任务,如Solar Orbiter。
点此查看论文截图

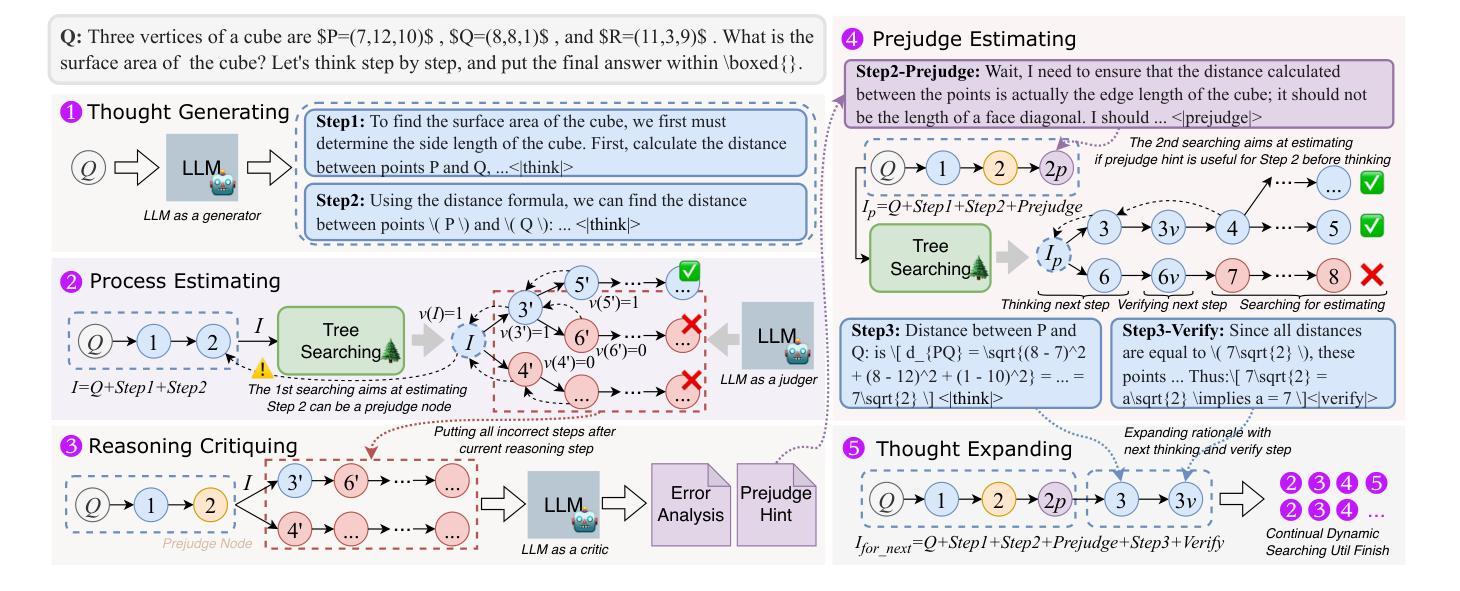
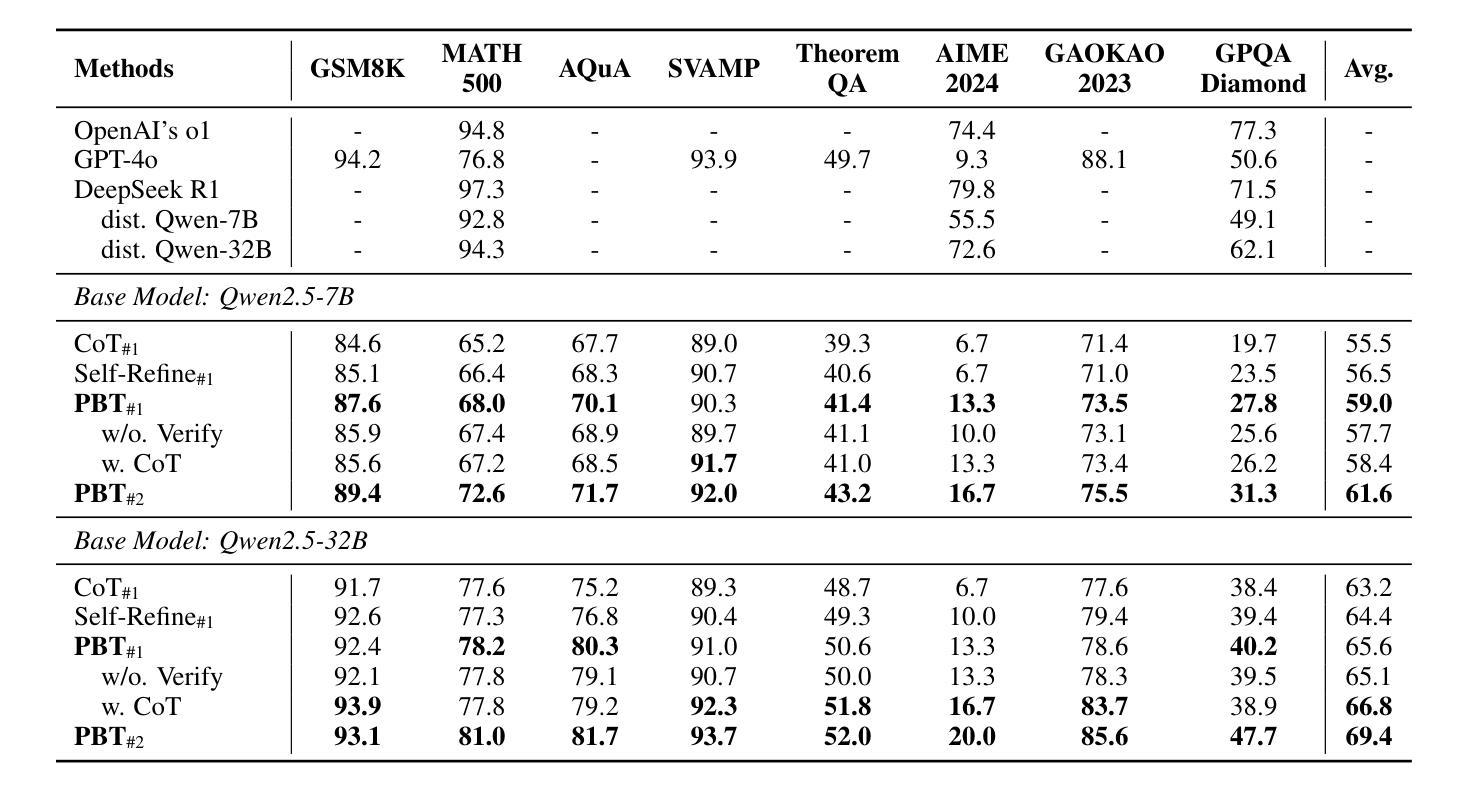
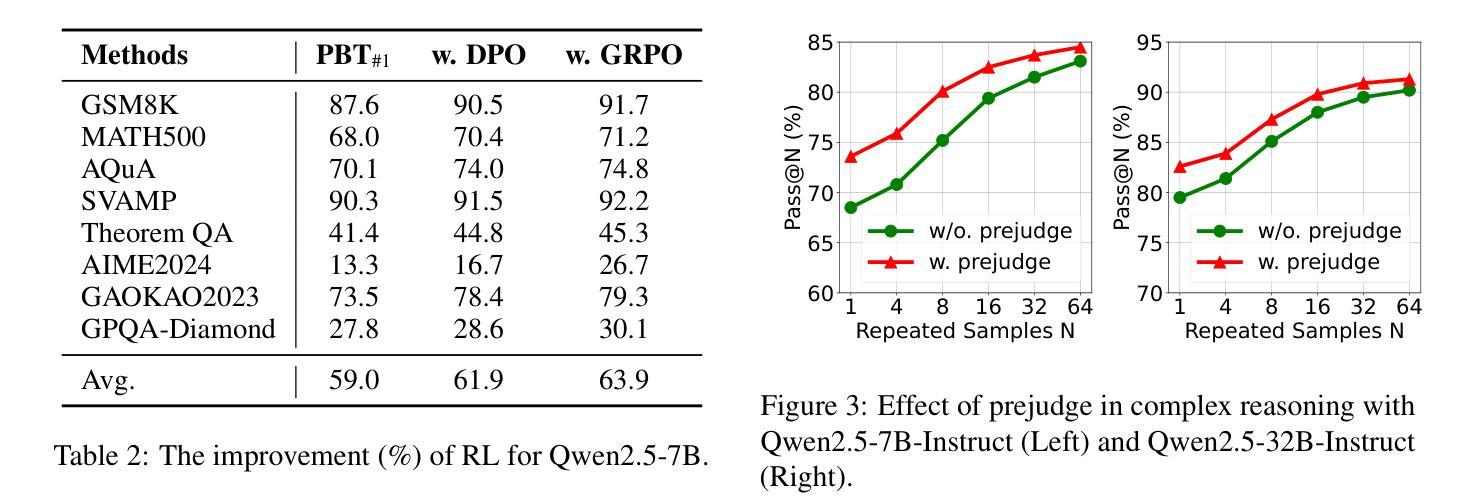
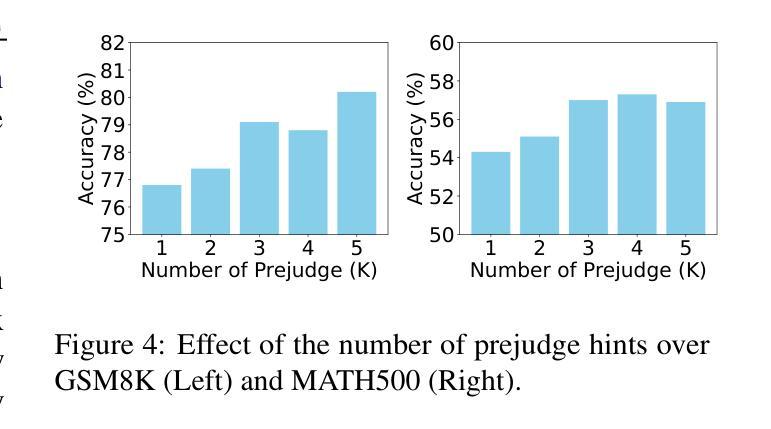
Prejudge-Before-Think: Enhancing Large Language Models at Test-Time by Process Prejudge Reasoning
Authors:Jianing Wang, Jin Jiang, Yang Liu, Mengdi Zhang, Xunliang Cai
In this paper, we introduce a new \emph{process prejudge} strategy in LLM reasoning to demonstrate that bootstrapping with process prejudge allows the LLM to adaptively anticipate the errors encountered when advancing the subsequent reasoning steps, similar to people sometimes pausing to think about what mistakes may occur and how to avoid them, rather than relying solely on trial and error. Specifically, we define a prejudge node in the rationale, which represents a reasoning step, with at least one step that follows the prejudge node that has no paths toward the correct answer. To synthesize the prejudge reasoning process, we present an automated reasoning framework with a dynamic tree-searching strategy. This framework requires only one LLM to perform answer judging, response critiquing, prejudge generation, and thought completion. Furthermore, we develop a two-phase training mechanism with supervised fine-tuning (SFT) and reinforcement learning (RL) to further enhance the reasoning capabilities of LLMs. Experimental results from competition-level complex reasoning demonstrate that our method can teach the model to prejudge before thinking and significantly enhance the reasoning ability of LLMs. Code and data is released at https://github.com/wjn1996/Prejudge-Before-Think.
本文介绍了一种新的大型语言模型(LLM)推理中的“过程预判”策略,以展示通过过程预判进行引导,可以使LLM自适应地预测在推进后续推理步骤时遇到的错误,类似于人们有时会停下来思考可能出现的错误以及如何避免错误,而不是仅仅依赖试错。具体来说,我们在理由中定义了一个预判节点,代表一个推理步骤,至少有一个步骤跟随预判节点,该节点没有通向正确答案的路径。为了综合预判推理过程,我们提出了一个动态树搜索策略的自动化推理框架。该框架只需要一个LLM来完成答案判断、响应评价、预判生成和思维完善。此外,我们开发了一种两阶段训练机制,采用有监督微调(SFT)和强化学习(RL),以进一步提高LLM的推理能力。来自竞赛级复杂推理的实验结果表明,我们的方法能够教会模型在思考之前进行预判,并显著提高LLM的推理能力。相关代码和数据已发布在https://github.com/wjn1996/Prejudge-Before-Think。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
本论文提出了一种新的预判断过程策略,用于LLM推理。通过引入预判断节点,模型能够在推理过程中预测可能出现的错误,并自适应地调整后续推理步骤,从而提高推理能力。实验结果表明,该方法能显著提高LLM的推理能力。
Key Takeaways
- 引入预判断过程策略,使LLM在推理过程中能够预测并适应可能出现的错误。
- 定义预判断节点为包含至少一个后续步骤的节点,这些步骤不包含通向正确答案的路径。
- 提出自动化推理框架,采用动态树搜索策略进行预判断推理过程。
- 仅需要一个LLM来完成答案判断、响应评价、预判断生成和思维补全。
- 采用两阶段训练机制,包括监督微调(SFT)和强化学习(RL),进一步增强LLM的推理能力。
- 实验结果表明,预判断过程能够提高LLM在竞赛级复杂推理任务中的表现。
点此查看论文截图

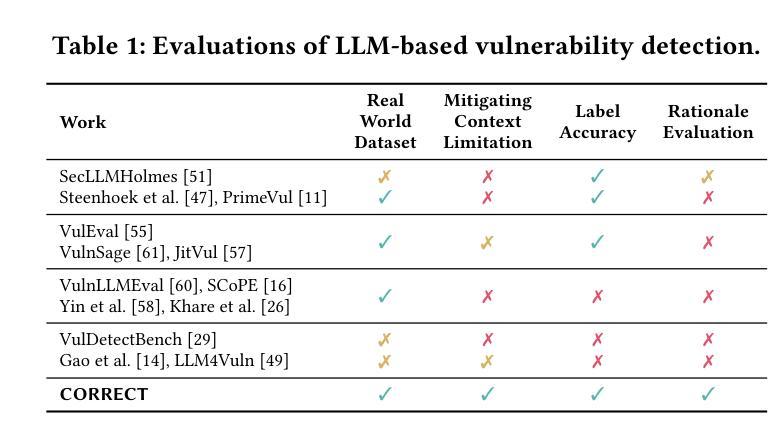
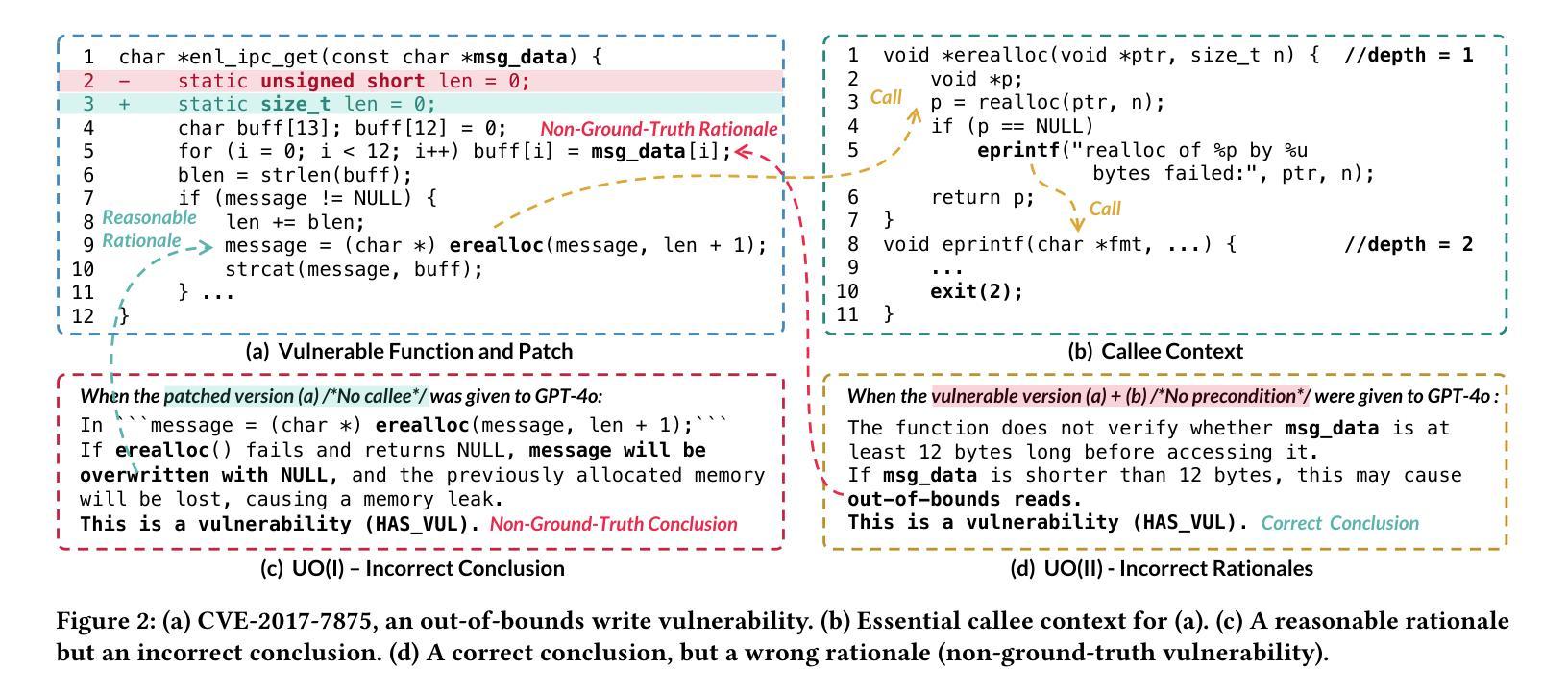
Everything You Wanted to Know About LLM-based Vulnerability Detection But Were Afraid to Ask
Authors:Yue Li, Xiao Li, Hao Wu, Minghui Xu, Yue Zhang, Xiuzhen Cheng, Fengyuan Xu, Sheng Zhong
Large Language Models are a promising tool for automated vulnerability detection, thanks to their success in code generation and repair. However, despite widespread adoption, a critical question remains: Are LLMs truly effective at detecting real-world vulnerabilities? Current evaluations, which often assess models on isolated functions or files, ignore the broader execution and data-flow context essential for understanding vulnerabilities. This oversight leads to two types of misleading outcomes: incorrect conclusions and flawed rationales, collectively undermining the reliability of prior assessments. Therefore, in this paper, we challenge three widely held community beliefs: that LLMs are (i) unreliable, (ii) insensitive to code patches, and (iii) performance-plateaued across model scales. We argue that these beliefs are artifacts of context-deprived evaluations. To address this, we propose CORRECT (Context-Rich Reasoning Evaluation of Code with Trust), a new evaluation framework that systematically incorporates contextual information into LLM-based vulnerability detection. We construct a context-rich dataset of 2,000 vulnerable-patched program pairs spanning 99 CWEs and evaluate 13 LLMs across four model families. Our framework elicits both binary predictions and natural-language rationales, which are further validated using LLM-as-a-judge techniques. Our findings overturn existing misconceptions. When provided with sufficient context, SOTA LLMs achieve significantly improved performance (e.g., 0.7 F1-score on key CWEs), with 0.8 precision. We show that most false positives stem from reasoning errors rather than misclassification, and that while model and test-time scaling improve performance, they introduce diminishing returns and trade-offs in recall. Finally, we uncover new flaws in current LLM-based detection systems, such as limited generalization and overthinking biases.
大型语言模型(LLMs)在自动漏洞检测方面展现出巨大的潜力,其在代码生成和修复方面的成功功不可没。然而,尽管其广泛应用,仍有一个关键问题悬而未决:LLMs在检测现实世界中的漏洞时是否真正有效?现有的评估通常只在孤立的函数或文件上评估模型,忽略了理解漏洞所必需的更广泛的执行和数据流上下文。这种监督导致了两种误导性的结果:错误的结论和缺陷理由,共同削弱了先前评估的可靠性。因此,本文中,我们挑战了社区中三个普遍存在的观点:(i)LLMs不可靠,(ii)对代码补丁不敏感,(iii)模型规模扩大性能停滞不前。我们认为这些观点都是缺乏上下文评估所产生的结果。为了解决这一问题,我们提出了CORRECT(基于信任的丰富上下文推理评估代码),这是一个新的评估框架,系统地结合上下文信息到基于LLM的漏洞检测中。我们构建了一个包含2000个脆弱补丁程序对的丰富上下文数据集,涵盖了99个CWE,评估了四个家族中的13个LLM。我们的框架引发了二元预测和自然语言理由,并进一步使用LLM-as-a-judge技术进行验证。我们的研究结果表明,在提供足够上下文的情况下,最新LLM的性能显著提高(例如在关键CWE上达到0.7的F1分数),精确度为0.8。我们发现大多数误报源于推理错误而非误分类,并且虽然模型和测试时的缩放可以提高性能,但它们会带来回报递减和召回率方面的权衡。最后,我们发现了当前基于LLM的检测系统中的新漏洞,例如有限的泛化能力和过度思考偏见。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
大型语言模型在自动化漏洞检测方面展现出潜力,尤其在代码生成和修复方面。然而,关于其是否能有效检测真实世界漏洞的问题仍存在疑问。当前评估模型的方法常常局限于对孤立函数或文件的评估,忽略了执行和数据流上下文的重要性,这导致评估结果存在误导性。为解决这一问题,本文提出了一个新的评估框架CORRECT,该框架系统地结合上下文信息进行基于大型语言模型的漏洞检测。通过构建包含2000个漏洞修复程序对的丰富上下文数据集,并对四个模型家族的13个大型语言模型进行评估,发现当提供足够的上下文时,当前顶尖的大型语言模型性能显著提升。
Key Takeaways
- 大型语言模型在自动化漏洞检测方面具有潜力。
- 当前漏洞检测评估方法忽略了执行和数据流上下文的重要性。
- 新的评估框架CORRECT结合上下文信息进行大型语言模型漏洞检测。
- 提供足够上下文时,顶尖大型语言模型性能显著提升。
- 大型语言模型的误报主要源于推理错误而非误分类。
- 模型和测试时的扩展虽然能提高性能,但存在回报递减和召回率权衡的问题。
点此查看论文截图

Chain-of-Thought Textual Reasoning for Few-shot Temporal Action Localization
Authors:Hongwei Ji, Wulian Yun, Mengshi Qi, Huadong Ma
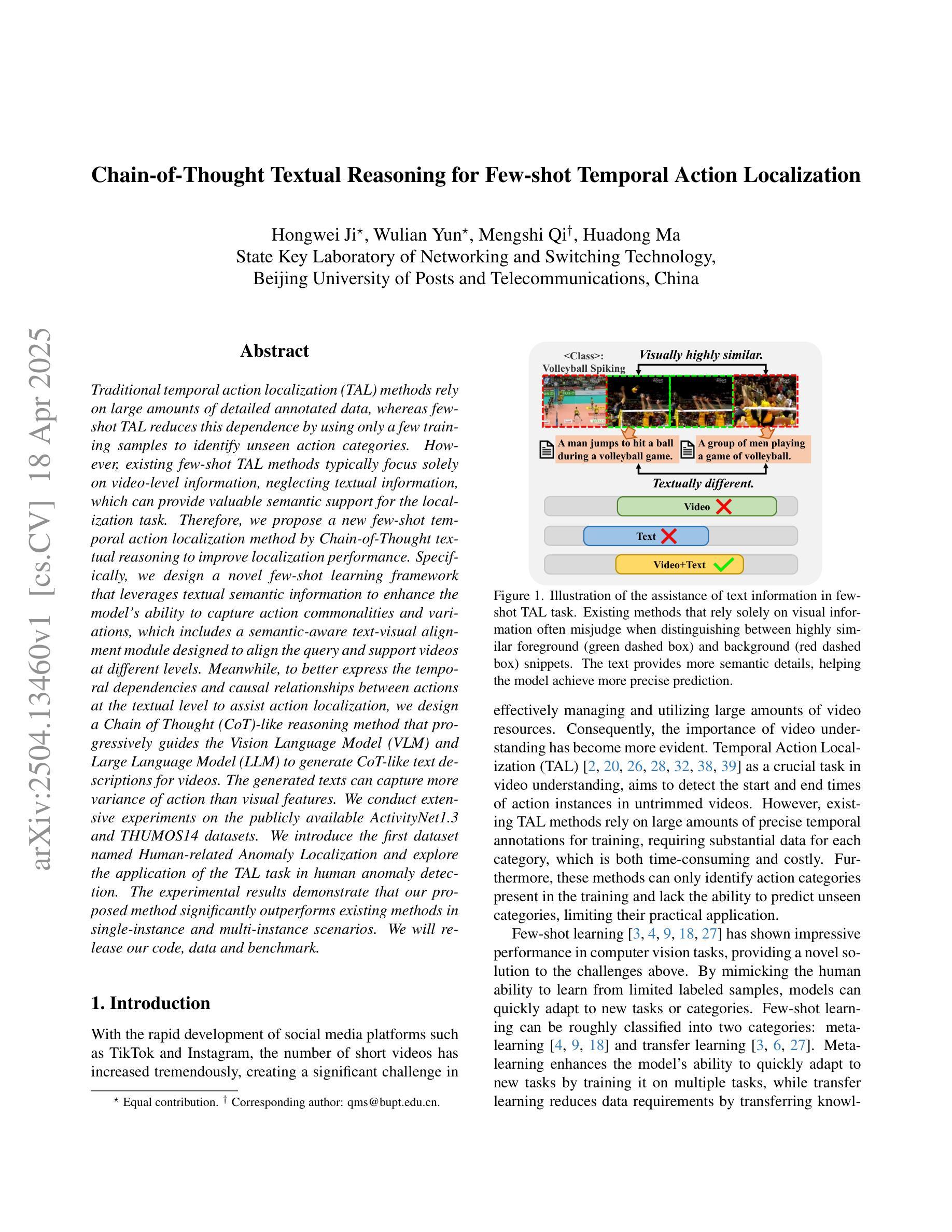
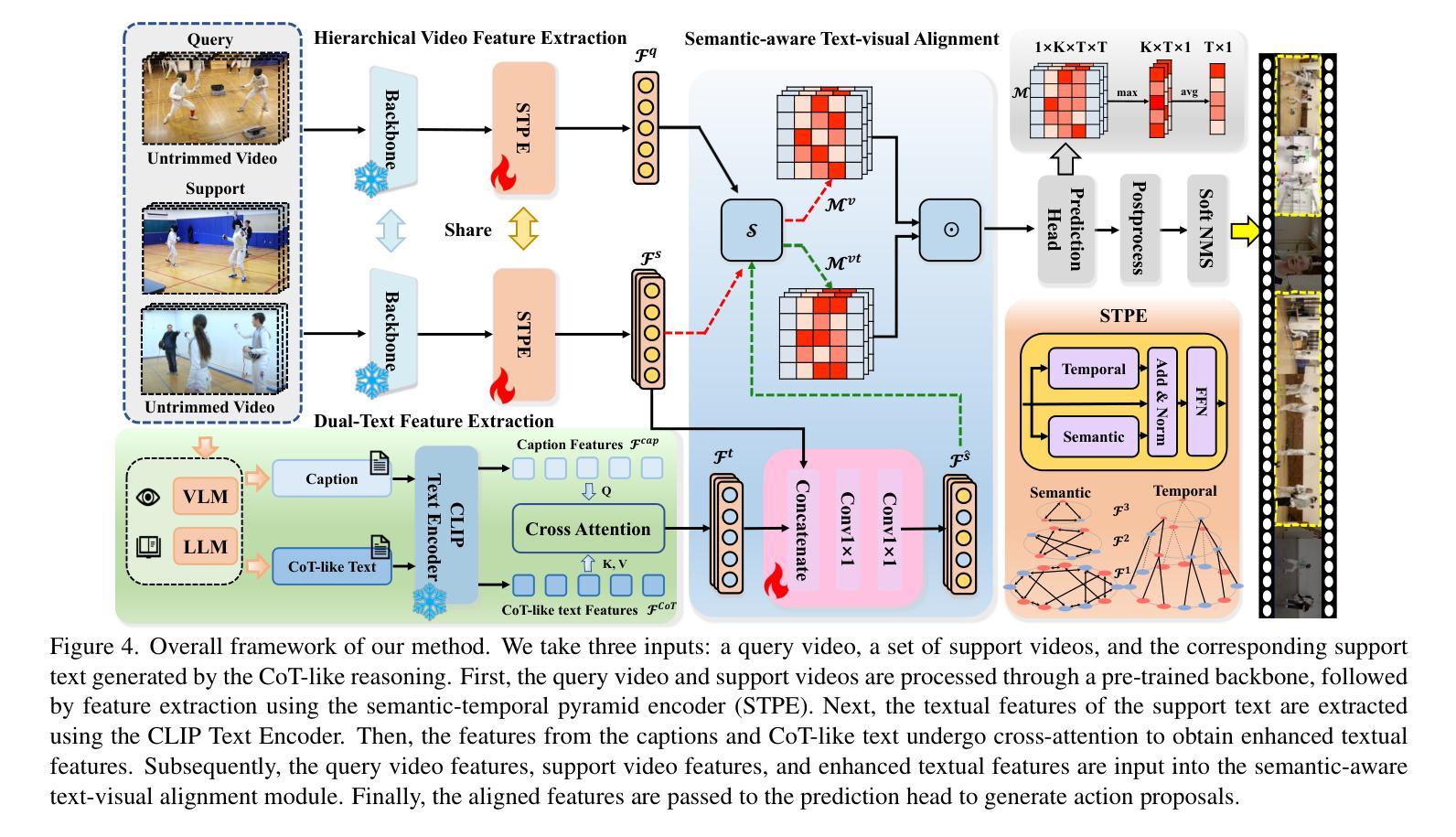
Traditional temporal action localization (TAL) methods rely on large amounts of detailed annotated data, whereas few-shot TAL reduces this dependence by using only a few training samples to identify unseen action categories. However, existing few-shot TAL methods typically focus solely on video-level information, neglecting textual information, which can provide valuable semantic support for the localization task. Therefore, we propose a new few-shot temporal action localization method by Chain-of-Thought textual reasoning to improve localization performance. Specifically, we design a novel few-shot learning framework that leverages textual semantic information to enhance the model’s ability to capture action commonalities and variations, which includes a semantic-aware text-visual alignment module designed to align the query and support videos at different levels. Meanwhile, to better express the temporal dependencies and causal relationships between actions at the textual level to assist action localization, we design a Chain of Thought (CoT)-like reasoning method that progressively guides the Vision Language Model (VLM) and Large Language Model (LLM) to generate CoT-like text descriptions for videos. The generated texts can capture more variance of action than visual features. We conduct extensive experiments on the publicly available ActivityNet1.3 and THUMOS14 datasets. We introduce the first dataset named Human-related Anomaly Localization and explore the application of the TAL task in human anomaly detection. The experimental results demonstrate that our proposed method significantly outperforms existing methods in single-instance and multi-instance scenarios. We will release our code, data and benchmark.
传统的时间动作定位(TAL)方法依赖于大量的详细标注数据,而少样本TAL则通过仅使用少量的训练样本来识别未见过的动作类别,减少了这种依赖。然而,现有的少样本TAL方法通常只关注视频层面的信息,忽视了文本信息,这可以为定位任务提供有价值的语义支持。因此,我们提出了一种新的基于思维链文本推理的少样本时间动作定位方法,以提高定位性能。具体来说,我们设计了一种新颖的少样本学习框架,利用文本语义信息来提高模型捕捉动作共性和变化的能力,其中包括一个语义感知的文本-视觉对齐模块,旨在在不同层次上对齐查询和支持视频。同时,为了更好地表达文本层面上动作的时空依赖和因果关系,帮助动作定位,我们设计了一种类似思维链(CoT)的推理方法,逐步引导视觉语言模型(VLM)和大型语言模型(LLM)为视频生成类似思维链的文本描述。生成的文本可以捕捉比视觉特征更多的动作变化。我们在公开可用的ActivityNet1.3和THUMOS14数据集上进行了大量实验。我们引入了名为Human-related Anomaly Localization的第一个数据集,并探索了TAL任务在人类异常检测中的应用。实验结果表明,我们提出的方法在单实例和多实例场景中均显著优于现有方法。我们将发布我们的代码、数据和基准测试。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
本文提出一种基于Chain-of-Thought文本推理的新的少样本时序动作定位方法。通过设计新的少样本学习框架和语义感知文本视觉对齐模块,该方法利用文本语义信息提高模型捕捉动作共性和变化的能力。同时,通过设计Chain of Thought(CoT)推理方法,协助在文本层面上表达动作间的时序依赖和因果关系,以辅助动作定位。实验结果表明,该方法在ActivityNet1.3和THUMOS14数据集上显著优于现有方法,并在人类异常检测的应用中表现优异。
Key Takeaways
- 提出了基于Chain-of-Thought文本推理的少样本时序动作定位方法。
- 设计了新的少样本学习框架,利用文本语义信息提高模型性能。
- 引入语义感知文本视觉对齐模块,对齐查询和支撑视频的不同层次。
- 通过Chain of Thought(CoT)推理方法,在文本层面上表达动作间的时序依赖和因果关系。
- 生成的文本描述能捕捉比视觉特征更多的动作变化。
- 在ActivityNet1.3和THUMOS14数据集上进行了广泛实验,并显著优于现有方法。
点此查看论文截图

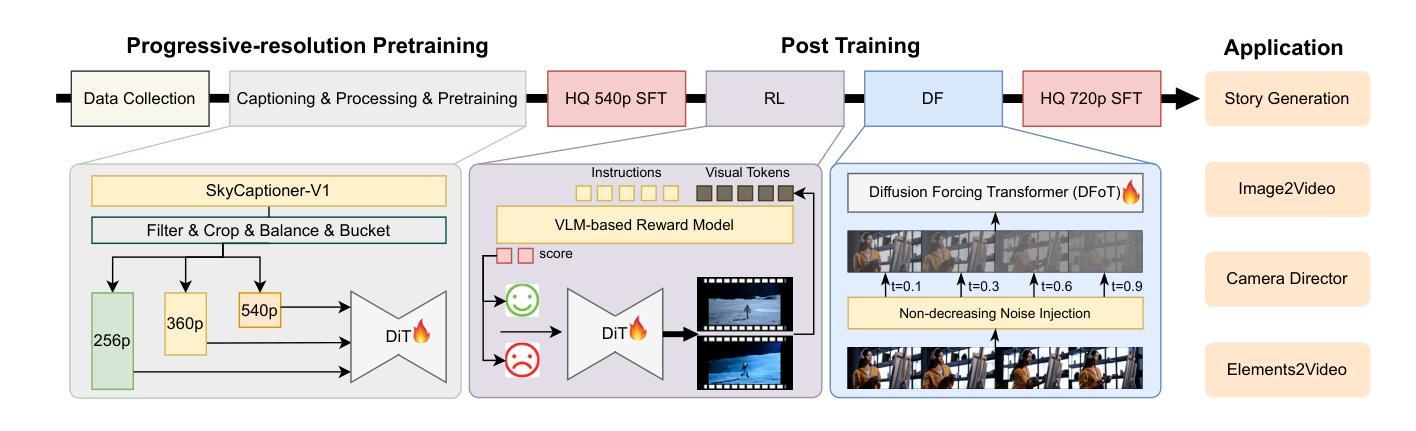
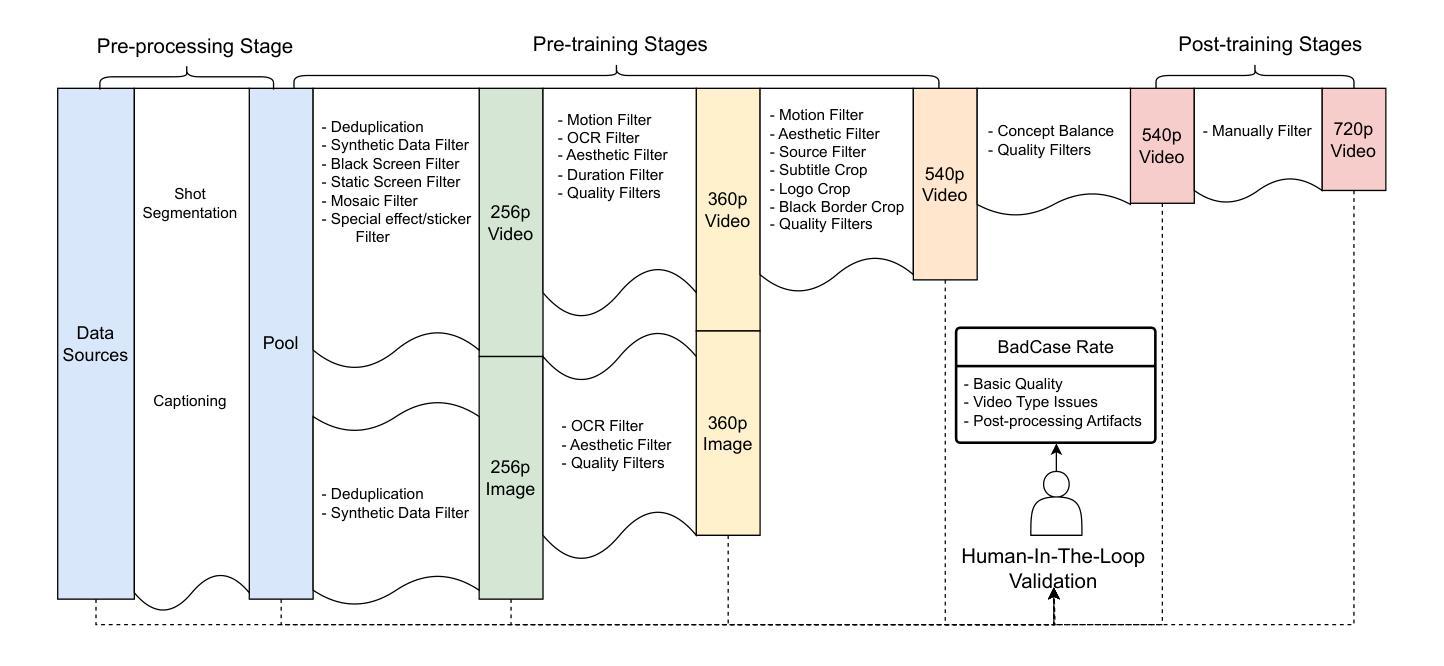
SkyReels-V2: Infinite-length Film Generative Model
Authors:Guibin Chen, Dixuan Lin, Jiangping Yang, Chunze Lin, Juncheng Zhu, Mingyuan Fan, Hao Zhang, Sheng Chen, Zheng Chen, Chengchen Ma, Weiming Xiong, Wei Wang, Nuo Pang, Kang Kang, Zhiheng Xu, Yuzhe Jin, Yupeng Liang, Yubing Song, Peng Zhao, Boyuan Xu, Di Qiu, Debang Li, Zhengcong Fei, Yang Li, Yahui Zhou
Recent advances in video generation have been driven by diffusion models and autoregressive frameworks, yet critical challenges persist in harmonizing prompt adherence, visual quality, motion dynamics, and duration: compromises in motion dynamics to enhance temporal visual quality, constrained video duration (5-10 seconds) to prioritize resolution, and inadequate shot-aware generation stemming from general-purpose MLLMs’ inability to interpret cinematic grammar, such as shot composition, actor expressions, and camera motions. These intertwined limitations hinder realistic long-form synthesis and professional film-style generation. To address these limitations, we propose SkyReels-V2, an Infinite-length Film Generative Model, that synergizes Multi-modal Large Language Model (MLLM), Multi-stage Pretraining, Reinforcement Learning, and Diffusion Forcing Framework. Firstly, we design a comprehensive structural representation of video that combines the general descriptions by the Multi-modal LLM and the detailed shot language by sub-expert models. Aided with human annotation, we then train a unified Video Captioner, named SkyCaptioner-V1, to efficiently label the video data. Secondly, we establish progressive-resolution pretraining for the fundamental video generation, followed by a four-stage post-training enhancement: Initial concept-balanced Supervised Fine-Tuning (SFT) improves baseline quality; Motion-specific Reinforcement Learning (RL) training with human-annotated and synthetic distortion data addresses dynamic artifacts; Our diffusion forcing framework with non-decreasing noise schedules enables long-video synthesis in an efficient search space; Final high-quality SFT refines visual fidelity. All the code and models are available at https://github.com/SkyworkAI/SkyReels-V2.
最近视频生成的进展得益于扩散模型和自回归框架的推动,但仍存在关于提示遵循、视觉质量、运动动态和时长的协调方面的关键挑战:为了增强时间视觉质量而妥协运动动态,受限制的视频时长(5-10秒)以优先考虑分辨率,以及由于通用多模态大型语言模型(MLLM)无法解释电影语法(如镜头构图、演员表情和相机运动)而导致的拍摄意识生成不足。这些交织的限制阻碍了现实的长形式合成和专业电影风格的生成。为了解决这些局限性,我们提出了SkyReels-V2,一种无限长电影生成模型,它协同多模态大型语言模型(MLLM)、多阶段预训练、强化学习和扩散强制框架。首先,我们设计了一种全面的视频结构表示,它结合了多模态LLM的一般描述和子专家模型的详细镜头语言。借助人工标注,我们随后训练了一个统一的视频字幕器,名为SkyCaptioner-V1,以有效地标注视频数据。其次,我们为基本的视频生成建立了渐进式分辨率预训练,然后是四阶段的后训练增强:初始概念平衡的监督微调(SFT)提高了基线质量;使用人工注释和合成失真数据的特定运动强化学习(RL)训练解决了动态伪影问题;我们的扩散强制框架与不断增长的噪声时间表相结合,能够在有效的搜索空间中进行长视频合成;最后的高质量SFT改进了视觉保真度。所有代码和模型均可在https://github.com/SkyworkAI/SkyReels-V2找到。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF 31 pages,10 figures
Summary
最近视频生成领域的进展主要得益于扩散模型和自回归框架,但仍面临提示遵循、视觉质量、运动动力和时长等方面的挑战。为解决这些限制,我们提出了SkyReels-V2,一种无限长电影生成模型,融合了多模态大型语言模型(MLLM)、多阶段预训练、强化学习和扩散强制框架。通过设计全面的视频结构表示、训练统一视频标注器、建立渐进式分辨率预训练以及四个阶段的后期训练增强等措施来应对挑战。
Key Takeaways
- 视频生成领域虽有所进展,但仍面临提示遵循、视觉质量、运动动力和时长等方面的挑战。
- SkyReels-V2模型旨在解决这些限制,通过融合MLLM、多阶段预训练、强化学习和扩散强制框架来提升视频生成质量。
- 全面的视频结构表示结合了多模态LLM的一般描述和子专家模型的详细镜头语言。
- 使用人类注释训练了统一视频标注器SkyCaptioner-V1,以高效标注视频数据。
- 建立了渐进式分辨率预训练,为后续的视频生成奠定基础。
- 四个阶段的后期训练增强措施,包括初始概念平衡的监督微调、针对运动动力的强化学习训练、扩散强制框架以及最终的高质量监督微调。
点此查看论文截图



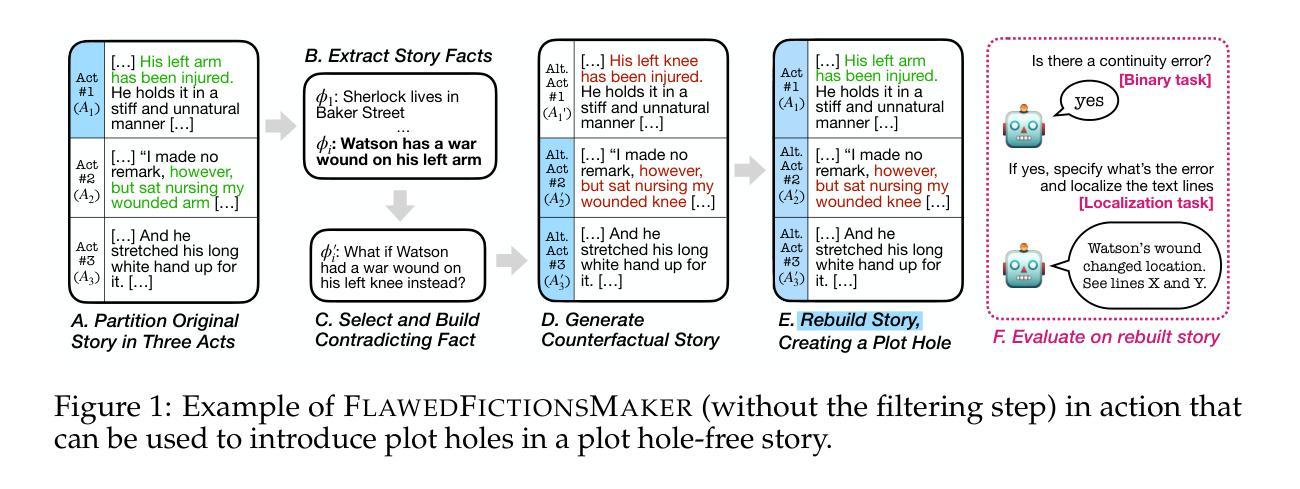
Finding Flawed Fictions: Evaluating Complex Reasoning in Language Models via Plot Hole Detection
Authors:Kabir Ahuja, Melanie Sclar, Yulia Tsvetkov
Stories are a fundamental aspect of human experience. Engaging deeply with stories and spotting plot holes – inconsistencies in a storyline that break the internal logic or rules of a story’s world – requires nuanced reasoning skills, including tracking entities and events and their interplay, abstract thinking, pragmatic narrative understanding, commonsense and social reasoning, and theory of mind. As Large Language Models (LLMs) increasingly generate, interpret, and modify text, rigorously assessing their narrative consistency and deeper language understanding becomes critical. However, existing benchmarks focus mainly on surface-level comprehension. In this work, we propose plot hole detection in stories as a proxy to evaluate language understanding and reasoning in LLMs. We introduce FlawedFictionsMaker, a novel algorithm to controllably and carefully synthesize plot holes in human-written stories. Using this algorithm, we construct a benchmark to evaluate LLMs’ plot hole detection abilities in stories – FlawedFictions – , which is robust to contamination, with human filtering ensuring high quality. We find that state-of-the-art LLMs struggle in accurately solving FlawedFictions regardless of the reasoning effort allowed, with performance significantly degrading as story length increases. Finally, we show that LLM-based story summarization and story generation are prone to introducing plot holes, with more than 50% and 100% increases in plot hole detection rates with respect to human-written originals.
故事是人类经验的基本组成部分。深入参与故事和发现情节漏洞——故事情节中的不一致之处破坏了其内部逻辑或故事世界的规则——需要微妙的推理技能,包括追踪实体和事件及其相互作用、抽象思维、实用叙事理解、常识和社会推理以及心智理论。随着大型语言模型(LLM)越来越多地生成、解释和修改文本,严格评估其叙事一致性以及更深层次的语言理解能力变得至关重要。然而,现有的基准测试主要关注于表层理解。在这项工作中,我们提出将情节漏洞检测作为评估LLM的语言理解和推理能力的代理。我们介绍了FlawedFictionsMaker这一新型算法,该算法能够可控且仔细地合成人类写作故事中的情节漏洞。使用该算法,我们构建了一个基准测试来评估LLM的情节漏洞检测能力——FlawedFictions,该测试稳健且不易受到污染的影响,并通过人工过滤确保高质量。我们发现,即使允许先进的LLM进行推理努力,它们在解决FlawedFictions方面的表现仍然不佳,并且随着故事长度的增加,性能会显著下降。最后,我们证明了基于LLM的故事摘要和故事生成容易引入情节漏洞,与人类原始作品的情节漏洞检测率相比,其漏洞检测率分别增加了50%和100%以上。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF Preprint
Summary:
本文关注故事中的情节漏洞检测,认为这是评估大型语言模型深层次语言理解和推理能力的重要标准。文章提出了一种新算法FlawedFictionsMaker,用于合成带有情节漏洞的故事,并构建了一个基准测试FlawedFictions,以评估语言模型检测故事中的情节漏洞的能力。实验发现,即使是最先进的大型语言模型,在面临FlawedFictions挑战时也难以准确解决问题,随着故事长度的增加,性能会显著下降。此外,基于大型语言模型的故事摘要和故事生成也容易产生情节漏洞。
Key Takeaways:
- 故事中的情节漏洞检测是评估大型语言模型深层次语言理解和推理能力的重要标准。
- FlawedFictionsMaker算法能够合成带有情节漏洞的故事。
- FlawedFictions基准测试用于评估语言模型检测故事中的情节漏洞的能力。
- 先进的大型语言模型在FlawedFictions挑战方面表现不佳,随着故事长度的增加,性能下降。
- 基于大型语言模型的故事摘要生成易产生情节漏洞。
- 大型语言模型在故事生成中也容易引入情节漏洞。
点此查看论文截图

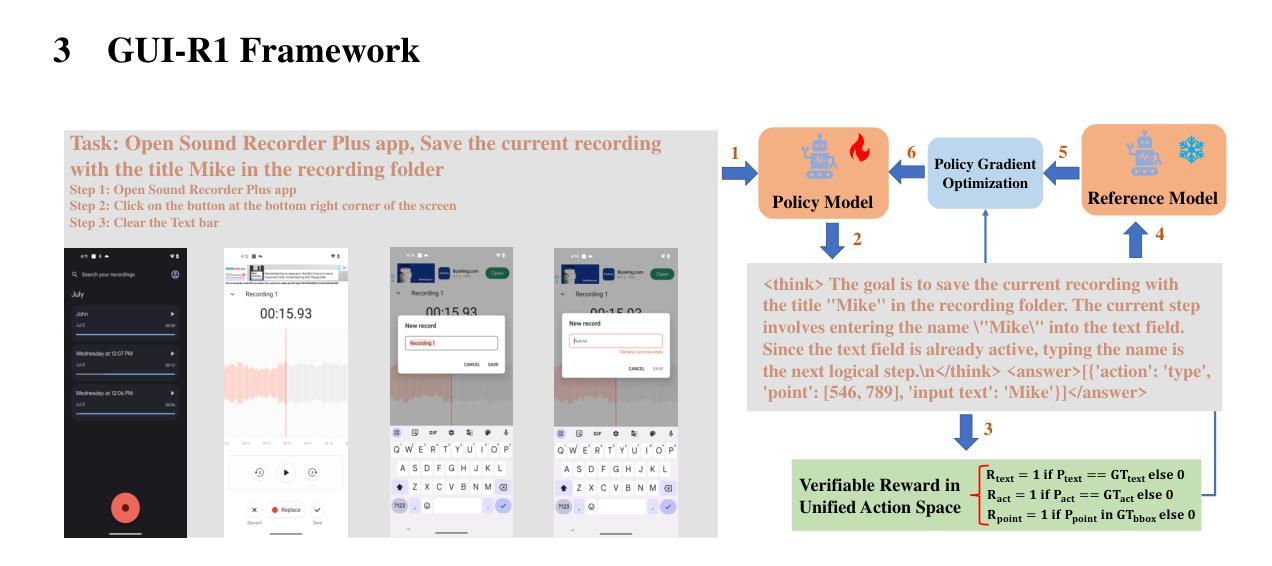
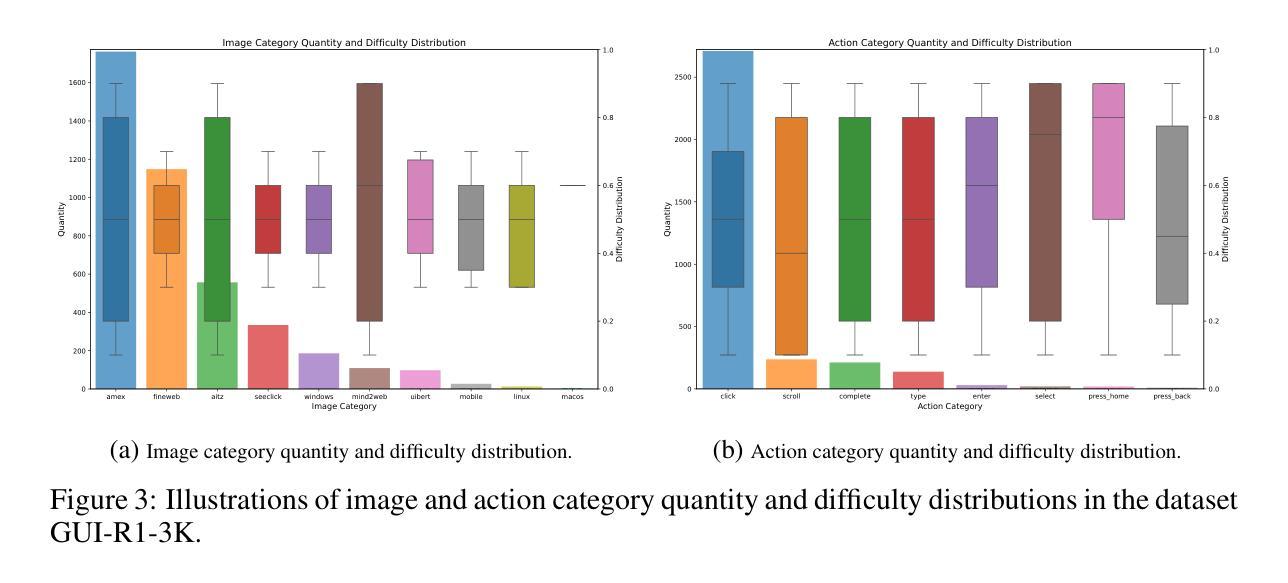
GUI-R1 : A Generalist R1-Style Vision-Language Action Model For GUI Agents
Authors:Run Luo, Lu Wang, Wanwei He, Xiaobo Xia
Existing efforts in building Graphical User Interface (GUI) agents largely rely on the training paradigm of supervised fine-tuning on Large Vision-Language Models (LVLMs). However, this approach not only demands extensive amounts of training data but also struggles to effectively understand GUI screenshots and generalize to unseen interfaces. The issue significantly limits its application in real-world scenarios, especially for high-level tasks. Inspired by Reinforcement Fine-Tuning (RFT) in large reasoning models (e.g., DeepSeek-R1), which efficiently enhances the problem-solving capabilities of large language models in real-world settings, we propose \name, the first reinforcement learning framework designed to enhance the GUI capabilities of LVLMs in high-level real-world task scenarios, through unified action space rule modeling. By leveraging a small amount of carefully curated high-quality data across multiple platforms (including Windows, Linux, MacOS, Android, and Web) and employing policy optimization algorithms such as Group Relative Policy Optimization (GRPO) to update the model, \name achieves superior performance using only 0.02% of the data (3K vs. 13M) compared to previous state-of-the-art methods like OS-Atlas across eight benchmarks spanning three different platforms (mobile, desktop, and web). These results demonstrate the immense potential of reinforcement learning based on unified action space rule modeling in improving the execution capabilities of LVLMs for real-world GUI agent tasks.
现有的图形用户界面(GUI)代理构建工作主要依赖于在大视觉语言模型(LVLMs)上进行的有监督微调训练范式。然而,这种方法不仅需求大量的训练数据,而且在理解GUI截图和泛化到未见过的界面方面也存在困难。这一问题极大地限制了其在现实场景中的应用,尤其是高级任务。受大型推理模型中的强化微调(RFT)的启发(例如DeepSeek-R1),强化学习能够提升大型语言模型在现实环境中的问题解决能力。因此,我们提出名为“名称”的强化学习框架,它是首个旨在通过统一动作空间规则建模增强LVLMs在现实高级任务场景中的GUI能力。通过利用跨多个平台(包括Windows、Linux、MacOS、Android和Web)的少量精心挑选的高质量数据,并采用如集团相对策略优化(GRPO)等策略优化算法来更新模型,“名称”仅使用0.02%的数据(3K对1.3M)就实现了在跨越三个不同平台(移动、桌面和网页)的八个基准测试中的卓越性能,超越了之前的先进方法,如OS-Atlas。这些结果证明了基于统一动作空间规则建模的强化学习在提升LVLMs执行现实GUI代理任务的能力方面具有巨大潜力。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
基于大型视觉语言模型(LVLMs)的图形用户界面(GUI)代理构建工作大多依赖于监督精细调整的训练模式。然而,这种方法不仅需求大量的训练数据,而且在理解GUI截图和泛化到未见过的界面上存在困难。本文受大型推理模型中的强化精细调整(RFT)的启发,提出了一个强化学习框架——名为\name,旨在通过统一动作空间规则建模,提高LVLMs在真实世界高级任务场景中的GUI能力。通过使用跨多个平台的小量精心挑选的高质量数据,并采用群体相对策略优化(GRPO)等策略优化算法来更新模型,\name在仅使用0.02%(3K vs 13M)数据的情况下,在涵盖三个不同平台(移动、桌面和网页)的八个基准测试中实现了优于OS-Atlas等现有先进方法的性能。这显示了基于统一动作空间规则建模的强化学习在提升LVLMs执行真实世界GUI代理任务方面的巨大潜力。
Key Takeaways
- GUI代理的构建主要依赖于大型视觉语言模型的监督精细调整训练模式,但需要大量数据和面临理解和泛化难题。
- 强化学习框架\name被提出,用于通过统一动作空间规则建模提高LVLMs在真实世界高级任务场景中的GUI能力。
- \name使用跨平台高质量小量数据进行训练,通过策略优化算法如GRPO更新模型。
点此查看论文截图
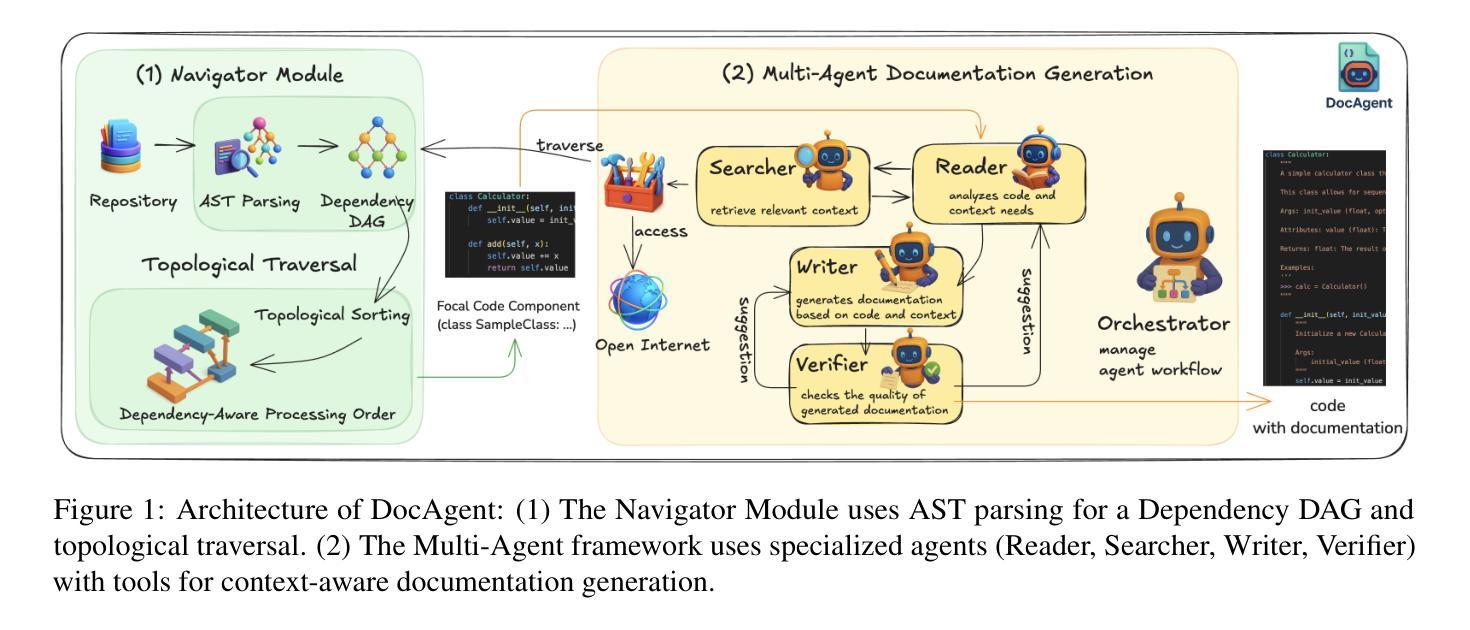
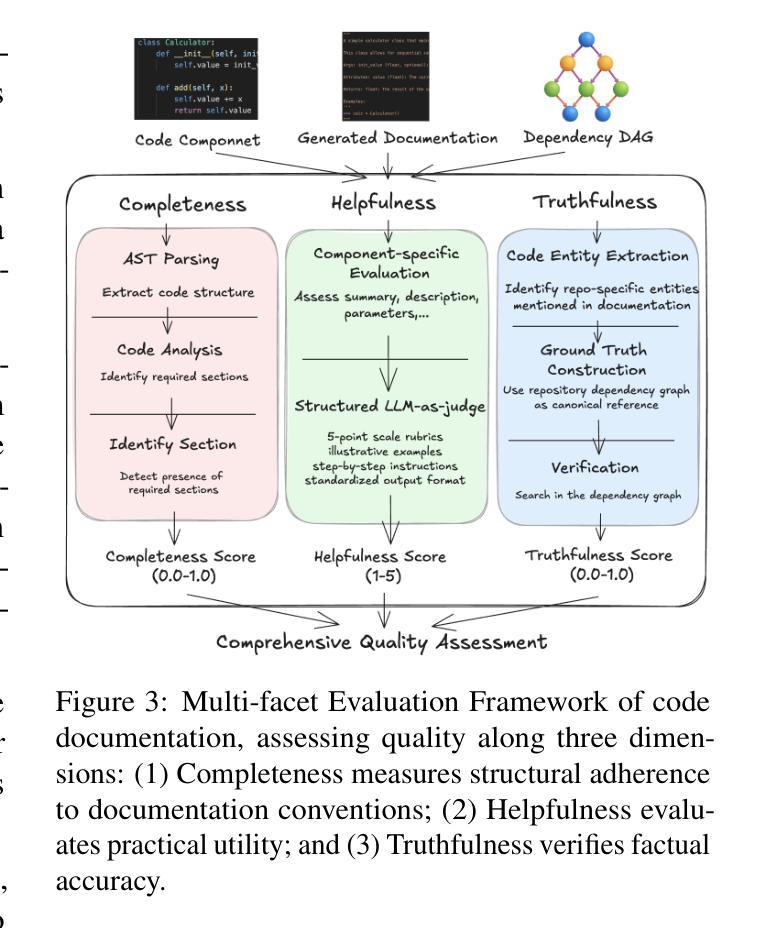
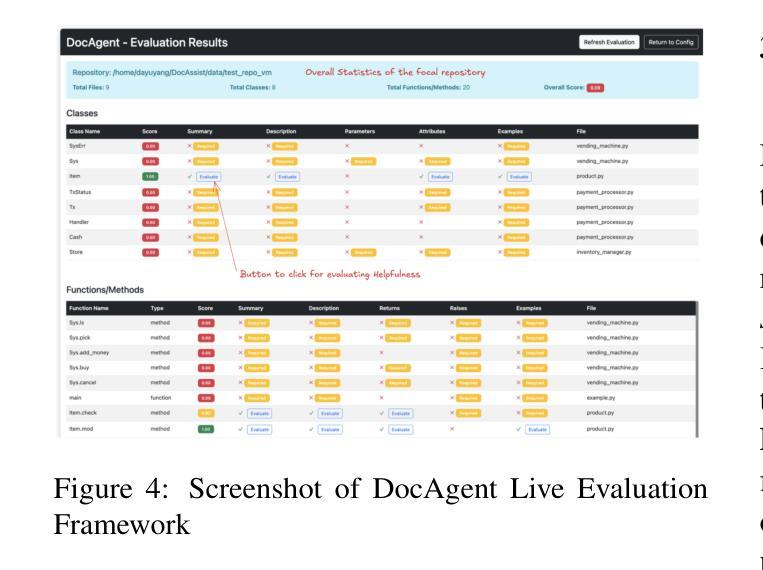
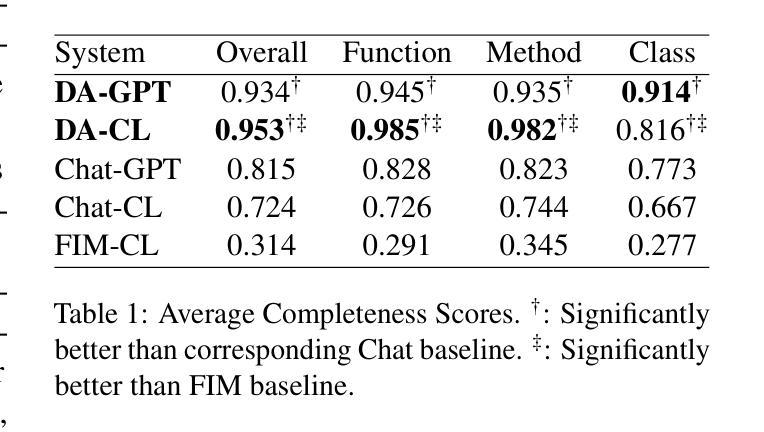
DocAgent: A Multi-Agent System for Automated Code Documentation Generation
Authors:Dayu Yang, Antoine Simoulin, Xin Qian, Xiaoyi Liu, Yuwei Cao, Zhaopu Teng, Grey Yang
High-quality code documentation is crucial for software development especially in the era of AI. However, generating it automatically using Large Language Models (LLMs) remains challenging, as existing approaches often produce incomplete, unhelpful, or factually incorrect outputs. We introduce DocAgent, a novel multi-agent collaborative system using topological code processing for incremental context building. Specialized agents (Reader, Searcher, Writer, Verifier, Orchestrator) then collaboratively generate documentation. We also propose a multi-faceted evaluation framework assessing Completeness, Helpfulness, and Truthfulness. Comprehensive experiments show DocAgent significantly outperforms baselines consistently. Our ablation study confirms the vital role of the topological processing order. DocAgent offers a robust approach for reliable code documentation generation in complex and proprietary repositories.
高质量的代码文档对软件开发至关重要,特别是在人工智能时代。然而,使用大型语言模型(LLM)自动生成文档仍然具有挑战性,因为现有方法通常会产生不完整、无帮助或事实错误的输出。我们引入了DocAgent,这是一个使用拓扑代码处理进行增量上下文构建的新型多智能体协作系统。专门的智能体(阅读器、搜索器、编写器、验证器、协调器)协同生成文档。我们还提出了一个多方面的评估框架,评估文档的完整性、帮助性和真实性。综合实验表明,DocAgent持续且显著优于基线。我们的消融研究证实了拓扑处理顺序的重要作用。DocAgent为复杂和专有存储库中的可靠代码文档生成提供了稳健的方法。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF Public Repo: https://github.com/facebookresearch/DocAgent
Summary
本文强调高质量代码文档在软件开发中的重要性,特别是在人工智能时代。然而,使用大型语言模型(LLMs)自动生成文档仍然具有挑战性,因为现有方法往往产生不完整、无帮助或事实错误的输出。为此,本文介绍了DocAgent,一种利用拓扑代码处理的多智能体协作系统,用于增量构建上下文。通过专门的智能体(阅读器、搜索器、编写器、验证器、协调器)协同生成文档。同时,提出了一种多维评估框架,评估文档的完整性、帮助性和真实性。实验表明,DocAgent在复杂和专有存储库中显著优于基线方法。
Key Takeaways
- 高质量代码文档在软件开发中的重要性。
- 使用大型语言模型自动生成代码文档的现有挑战:不完整、无帮助或事实错误的输出。
- DocAgent系统介绍:利用拓扑代码处理和多智能体协作生成文档。
- DocAgent系统中的智能体角色:阅读器、搜索器、编写器、验证器和协调器。
- 多维评估框架:评估文档的完整性、帮助性和真实性。
- DocAgent在复杂和专有存储库中的性能显著优于基线方法。
点此查看论文截图


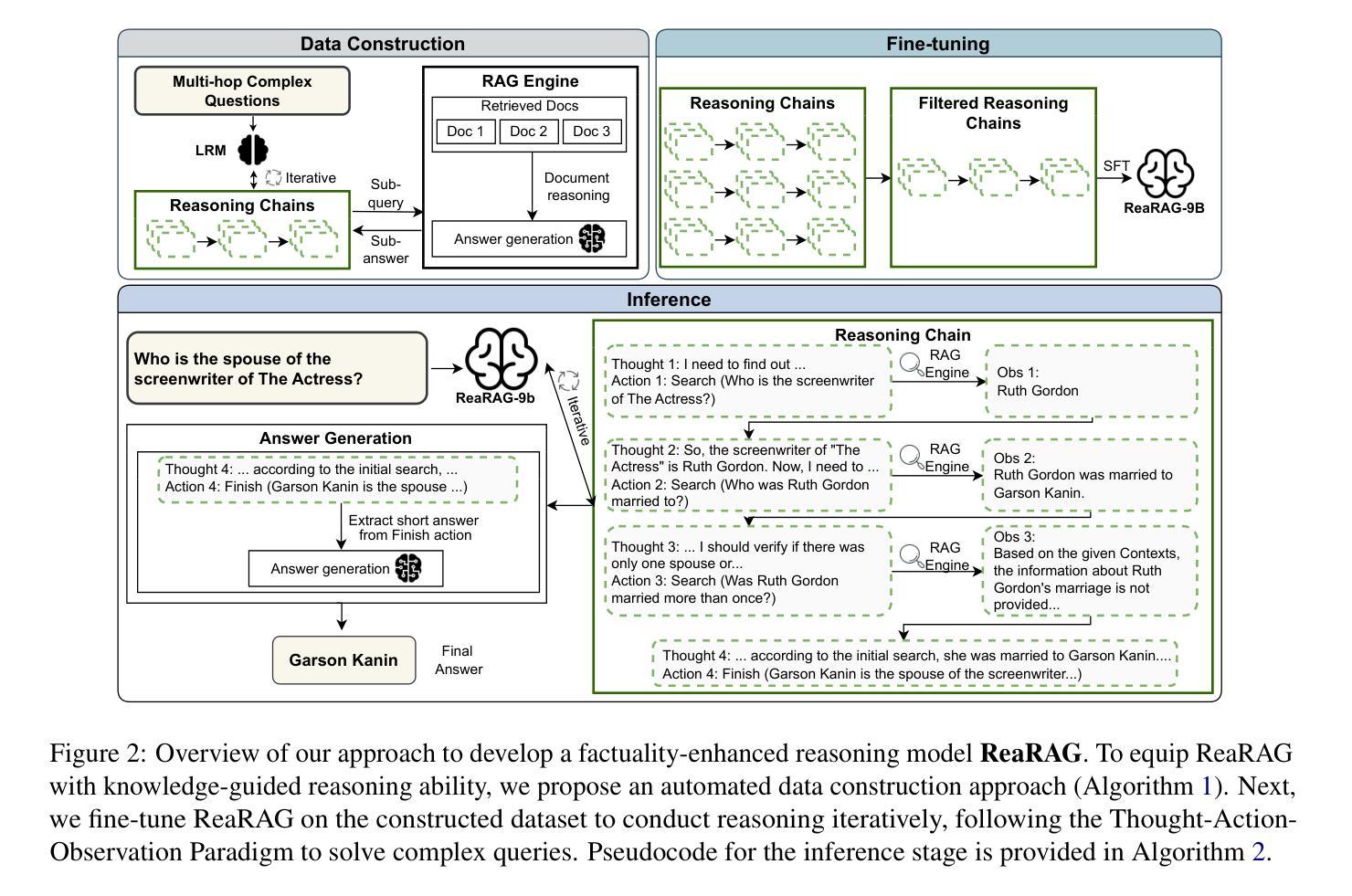
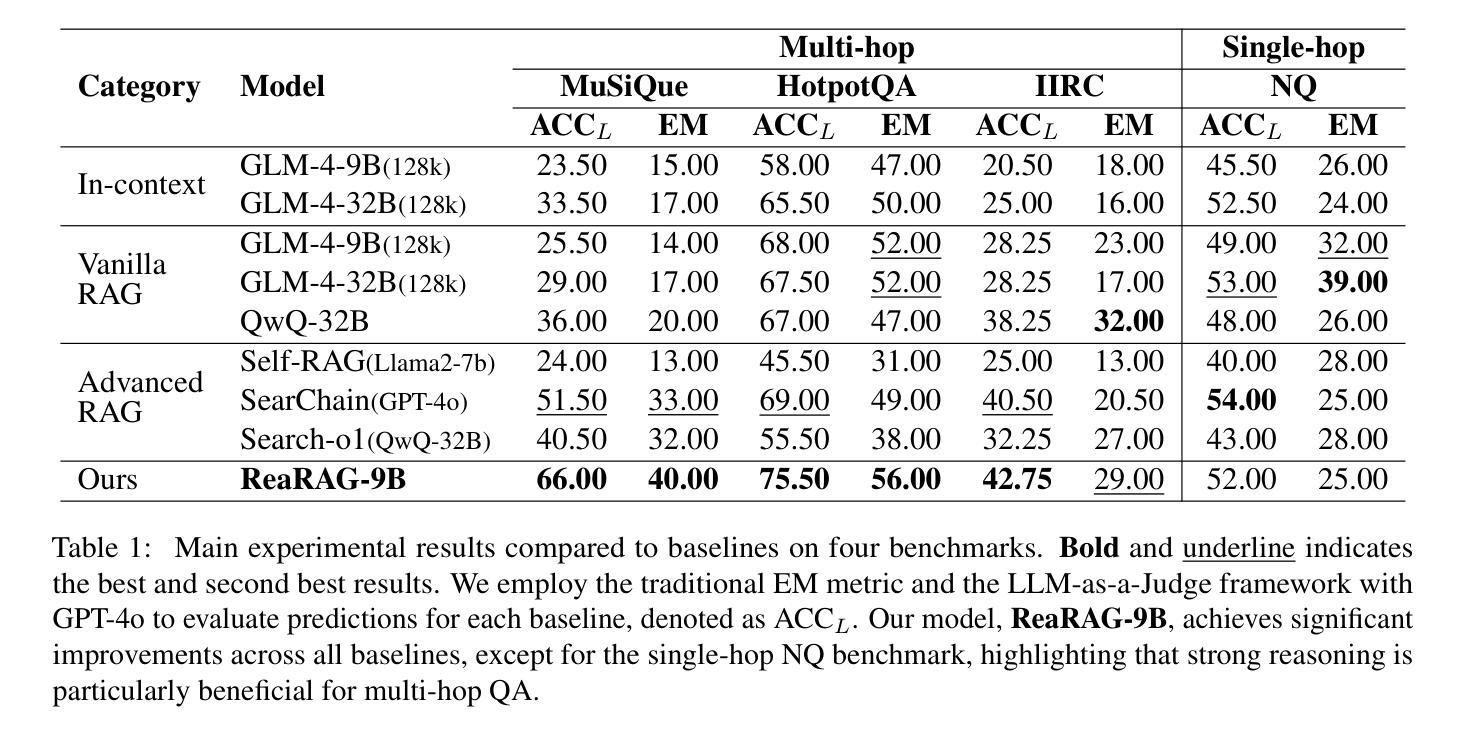
ReaRAG: Knowledge-guided Reasoning Enhances Factuality of Large Reasoning Models with Iterative Retrieval Augmented Generation
Authors:Zhicheng Lee, Shulin Cao, Jinxin Liu, Jiajie Zhang, Weichuan Liu, Xiaoyin Che, Lei Hou, Juanzi Li
Large Reasoning Models (LRMs) exhibit remarkable reasoning abilities but rely primarily on parametric knowledge, limiting factual accuracy. While recent works equip reinforcement learning (RL)-based LRMs with retrieval capabilities, they suffer from overthinking and lack robustness in reasoning, reducing their effectiveness in question answering (QA) tasks. To address this, we propose ReaRAG, a factuality-enhanced reasoning model that explores diverse queries without excessive iterations. Our solution includes a novel data construction framework with an upper bound on the reasoning chain length. Specifically, we first leverage an LRM to generate deliberate thinking, then select an action from a predefined action space (Search and Finish). For Search action, a query is executed against the RAG engine, where the result is returned as observation to guide reasoning steps later. This process iterates until a Finish action is chosen. Benefiting from ReaRAG’s strong reasoning capabilities, our approach outperforms existing baselines on multi-hop QA. Further analysis highlights its strong reflective ability to recognize errors and refine its reasoning trajectory. Our study enhances LRMs’ factuality while effectively integrating robust reasoning for Retrieval-Augmented Generation (RAG).
大型推理模型(LRMs)展现出显著的推理能力,但主要依赖于参数知识,这限制了事实准确性。虽然最近的工作为基于强化学习(RL)的LRMs配备了检索能力,但它们在推理时过于深思熟虑,缺乏稳健性,降低了在问答(QA)任务中的有效性。为了解决这一问题,我们提出了ReaRAG,这是一种增强事实性的推理模型,它可以在不进行过多次迭代的情况下探索各种查询。我们的解决方案包括一个具有推理链长度上限的新型数据构建框架。具体来说,我们首先利用LRM进行深思熟虑的生成,然后从预定的动作空间(搜索和完成)中选择一个动作。对于搜索动作,会对RAG引擎执行一个查询,返回的结果将作为观察结果来指导后续的推理步骤。这个过程将一直迭代,直到选择一个完成动作。ReaRAG的强推理能力使其在多跳问答任务上的表现优于现有基线。进一步的分析突显了其强大的反思能力,能够识别错误并优化其推理轨迹。我们的研究提高了LRMs的事实性,同时有效地将稳健推理整合到增强检索生成(RAG)中。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
大型推理模型展现出卓越的推理能力,但主要依赖参数知识,限制了事实准确性。本研究提出一种增强事实性的推理模型ReaRAG,通过构建新型数据框架并限制推理链长度,解决现有模型过度思考、缺乏稳健性的问题。ReaRAG利用LRM进行深思熟虑,从预定义动作空间(搜索与完成)中选择动作。搜索动作通过RAG引擎执行查询并返回结果指导后续推理步骤。本研究增强了LRM的事实性,并有效集成了稳健推理,提高了多跳问答任务上的性能。
Key Takeaways
- 大型推理模型主要依赖参数知识,限制了事实准确性。
- ReaRAG模型旨在解决现有模型过度思考、缺乏稳健性的问题。
- ReaRAG通过构建新型数据框架,并结合预定义动作空间实现增强事实性的推理。
- ReaRAG利用LRM进行深思熟虑,并通过搜索动作与RAG引擎交互获取结果。
- ReaRAG模型在多跳问答任务上表现出优越性能。
- 进一步分析显示,ReaRAG具有强大的反思能力,能够识别错误并优化推理轨迹。
点此查看论文截图