⚠️ 以下所有内容总结都来自于 大语言模型的能力,如有错误,仅供参考,谨慎使用
🔴 请注意:千万不要用于严肃的学术场景,只能用于论文阅读前的初筛!
💗 如果您觉得我们的项目对您有帮助 ChatPaperFree ,还请您给我们一些鼓励!⭐️ HuggingFace免费体验
2025-04-22 更新
Collective Learning Mechanism based Optimal Transport Generative Adversarial Network for Non-parallel Voice Conversion
Authors:Sandipan Dhar, Md. Tousin Akhter, Nanda Dulal Jana, Swagatam Das
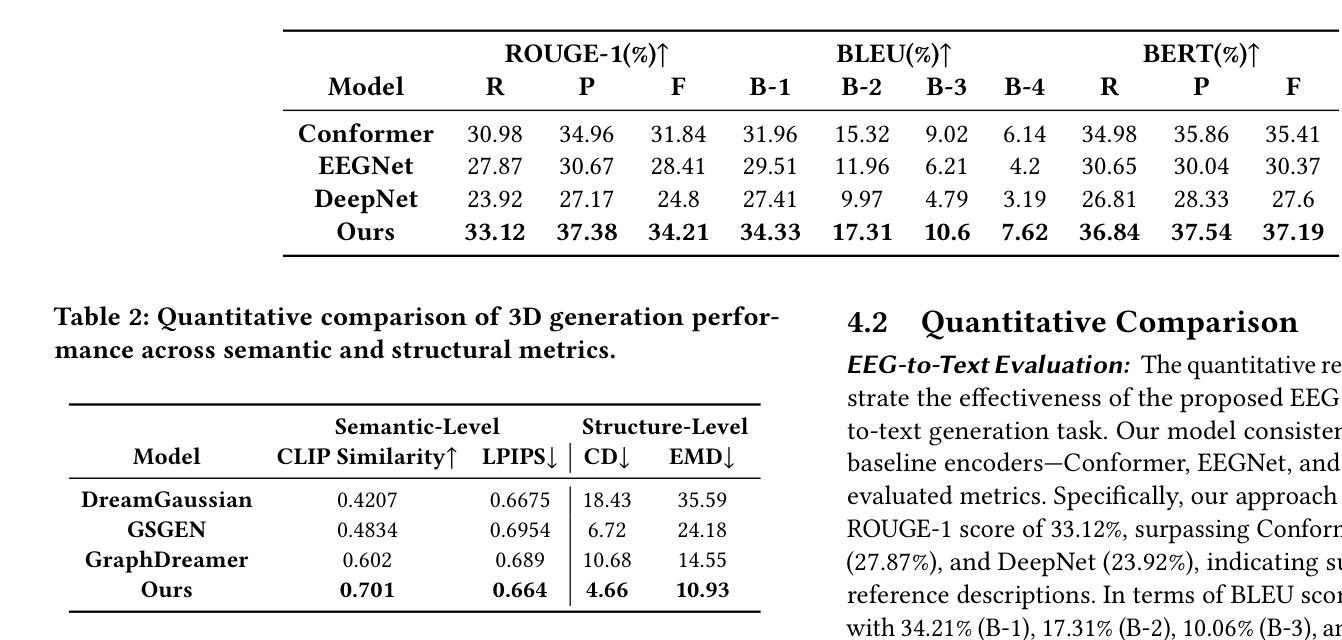
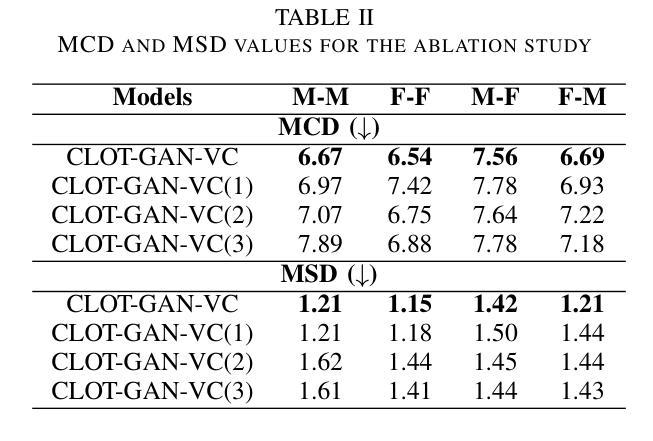
After demonstrating significant success in image synthesis, Generative Adversarial Network (GAN) models have likewise made significant progress in the field of speech synthesis, leveraging their capacity to adapt the precise distribution of target data through adversarial learning processes. Notably, in the realm of State-Of-The-Art (SOTA) GAN-based Voice Conversion (VC) models, there exists a substantial disparity in naturalness between real and GAN-generated speech samples. Furthermore, while many GAN models currently operate on a single generator discriminator learning approach, optimizing target data distribution is more effectively achievable through a single generator multi-discriminator learning scheme. Hence, this study introduces a novel GAN model named Collective Learning Mechanism-based Optimal Transport GAN (CLOT-GAN) model, incorporating multiple discriminators, including the Deep Convolutional Neural Network (DCNN) model, Vision Transformer (ViT), and conformer. The objective of integrating various discriminators lies in their ability to comprehend the formant distribution of mel-spectrograms, facilitated by a collective learning mechanism. Simultaneously, the inclusion of Optimal Transport (OT) loss aims to precisely bridge the gap between the source and target data distribution, employing the principles of OT theory. The experimental validation on VCC 2018, VCTK, and CMU-Arctic datasets confirms that the CLOT-GAN-VC model outperforms existing VC models in objective and subjective assessments.
生成对抗网络(GAN)模型在图像合成领域取得巨大成功后,其在语音合成领域也取得了显著进展,利用对抗学习过程来适应目标数据的精确分布。特别是在基于GAN的语音转换(VC)模型的最新技术中,真实和GAN生成的语音样本之间的自然度存在很大差异。此外,虽然许多GAN模型目前采用单一生成器判别器学习方法,但通过单一生成器多判别器学习方案可以更有效地优化目标数据分布。因此,本研究引入了一种新型的GAN模型,称为基于集体学习机制的优化传输GAN(CLOT-GAN)模型,该模型结合了多个判别器,包括深度卷积神经网络(DCNN)模型、视觉转换器(ViT)和转换器。集成各种判别器的目的在于它们能够借助集体学习机制理解梅尔频谱图的音域分布。同时,引入最优传输(OT)损失旨在利用最优传输理论的原则,精确弥合源数据分布与目标数据分布之间的差距。在VCC 2018、VCTK和CMU-Arctic数据集上的实验验证表明,CLOT-GAN-VC模型在客观和主观评估中均优于现有VC模型。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF 7 pages, 2 figures, 3 tables
Summary
生成对抗网络(GAN)在语音合成领域取得显著进展,通过对抗学习过程适应目标数据的精确分布。当前先进GAN模型在真实与生成语音样本的自然度上存在差异。研究引入了一种新型集体学习机制基础上的最优传输GAN(CLOT-GAN)模型,通过单生成器多鉴别器学习方案更高效地优化目标数据分布。采用深度卷积神经网络(DCNN)、视觉Transformer(ViT)和Conformer等多种鉴别器,旨在理解梅尔频谱的共振峰分布。实验验证表明,CLOT-GAN模型在客观和主观评估上均优于现有语音转换模型。
Key Takeaways
- GAN模型在语音合成领域取得显著进展,通过对抗学习过程适应目标数据的精确分布。
- 当前先进GAN模型在真实与生成语音样本的自然度上仍存在差距。
- CLOT-GAN模型采用单生成器多鉴别器学习方案,旨在优化目标数据分布。
- CLOT-GAN模型集成了DCNN、ViT和Conformer等多种鉴别器,以理解梅尔频谱的共振峰分布。
- CLOT-GAN模型采用集体学习机制,有助于提升模型性能。
- CLOT-GAN模型引入最优传输(OT)损失,旨在缩小源和目标数据分布之间的差距。
点此查看论文截图

Fighting Fires from Space: Leveraging Vision Transformers for Enhanced Wildfire Detection and Characterization
Authors:Aman Agarwal, James Gearon, Raksha Rank, Etienne Chenevert
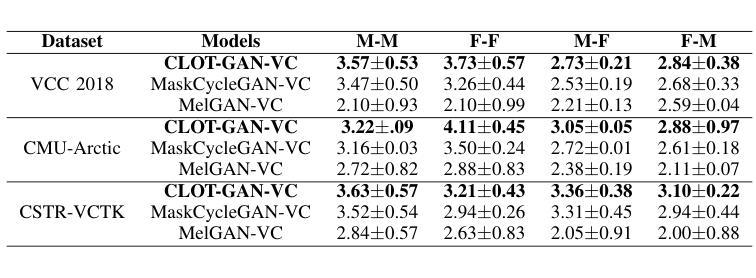
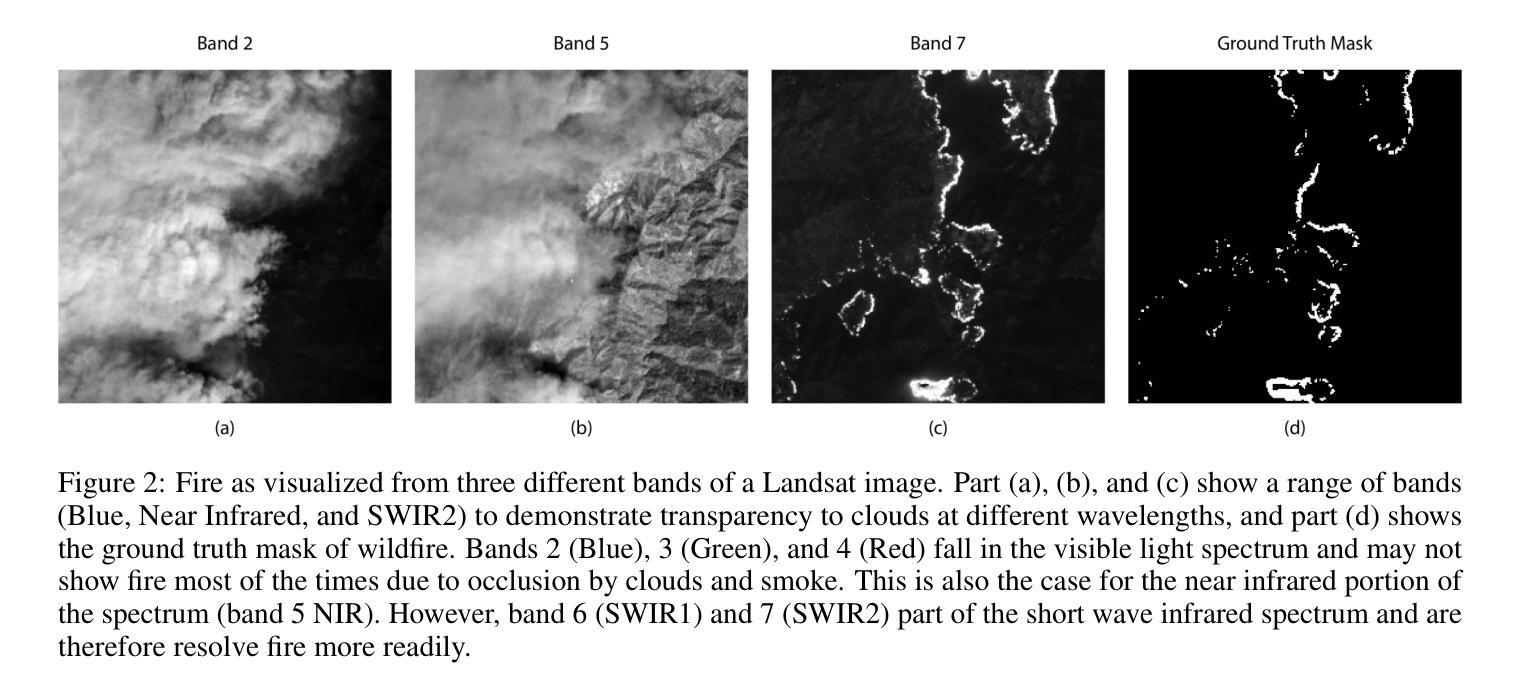
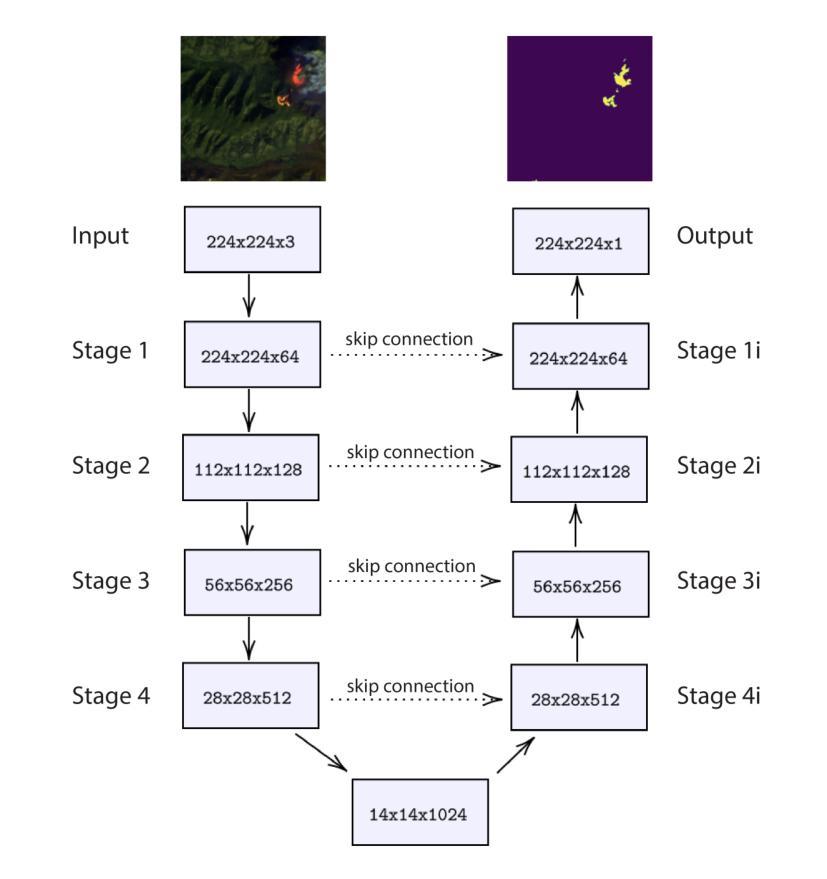
Wildfires are increasing in intensity, frequency, and duration across large parts of the world as a result of anthropogenic climate change. Modern hazard detection and response systems that deal with wildfires are under-equipped for sustained wildfire seasons. Recent work has proved automated wildfire detection using Convolutional Neural Networks (CNNs) trained on satellite imagery are capable of high-accuracy results. However, CNNs are computationally expensive to train and only incorporate local image context. Recently, Vision Transformers (ViTs) have gained popularity for their efficient training and their ability to include both local and global contextual information. In this work, we show that ViT can outperform well-trained and specialized CNNs to detect wildfires on a previously published dataset of LandSat-8 imagery. One of our ViTs outperforms the baseline CNN comparison by 0.92%. However, we find our own implementation of CNN-based UNet to perform best in every category, showing their sustained utility in image tasks. Overall, ViTs are comparably capable in detecting wildfires as CNNs, though well-tuned CNNs are still the best technique for detecting wildfire with our UNet providing an IoU of 93.58%, better than the baseline UNet by some 4.58%.
随着人为气候变化的影响,全球许多地区的野火在强度、频率和持续时间上都不断加剧。现代应对野火的危险检测和响应系统尚不具备应对持续野火季节的能力。近期的研究证明,利用卷积神经网络(CNN)在卫星图像上进行训练的自动化野火检测技术可以实现较高的准确性。然而,CNN的训练计算成本较高,且仅涉及局部图像上下文信息。最近,视觉变压器(ViT)因其高效的训练能力和同时包含局部和全局上下文信息的能力而受到欢迎。在这项工作中,我们展示了ViT在Landsat-8图像发布的数据集上检测野火时,可以表现得比训练良好的专业CNN更好。我们的一个ViT比基线CNN高出0.92%。然而,我们发现我们自己的基于CNN的UNet实现表现最好,在各类别中都表现出其持续的图像任务实用性。总体而言,ViT在检测野火方面与CNN相当有能力,但经过良好调整的CNN仍然是我们检测野火的最佳技术,我们的UNet达到了93.58%的IoU,比基线UNet高出约4.58%。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
野火随着人为造成的气候变化在强度、频率和持续时间上都不断加剧。现代应对野火的危险检测和响应系统尚不足以应对持续性的野火季节。最新研究证明,使用卫星图像训练的卷积神经网络(CNN)在自动化野火检测方面可达到高准确率。然而,CNN的训练计算量大且仅涉及局部图像上下文信息。最近,视觉转换器(ViT)因其高效的训练能力和同时包含局部和全局上下文信息的能力而受到关注。本研究表明,ViT在检测野火方面可以超越训练良好的专业CNN,在先前发布的LandSat-8图像数据集上表现优异。然而,我们发现自己的CNN-based UNet实现表现最佳,在各类别中都表现出其持续的实用性。总体而言,ViT在检测野火方面具备与CNN相当的能力,但在我们的数据集中使用精细调整的CNN仍是最佳技术,其中UNet的IoU达到93.58%,比基线UNet高出4.58%。
Key Takeaways
- 人为气候变化导致全球野火强度、频率和持续时间增加。
- 现代危险检测和响应系统在应对持续野火季节方面尚显不足。
- 卷积神经网络(CNN)在自动化野火检测方面具有较高的准确率,但存在计算量大和仅涉及局部图像上下文信息的局限性。
- 视觉转换器(ViT)因其高效的训练能力和包含局部及全局上下文信息的能力而受到关注。
- 在特定数据集上,ViT在野火检测方面的性能可超越CNN。
- UNet实现的CNN表现最佳,在各种类别中均表现出持续的实用性。
点此查看论文截图

Decoding Vision Transformers: the Diffusion Steering Lens
Authors:Ryota Takatsuki, Sonia Joseph, Ippei Fujisawa, Ryota Kanai
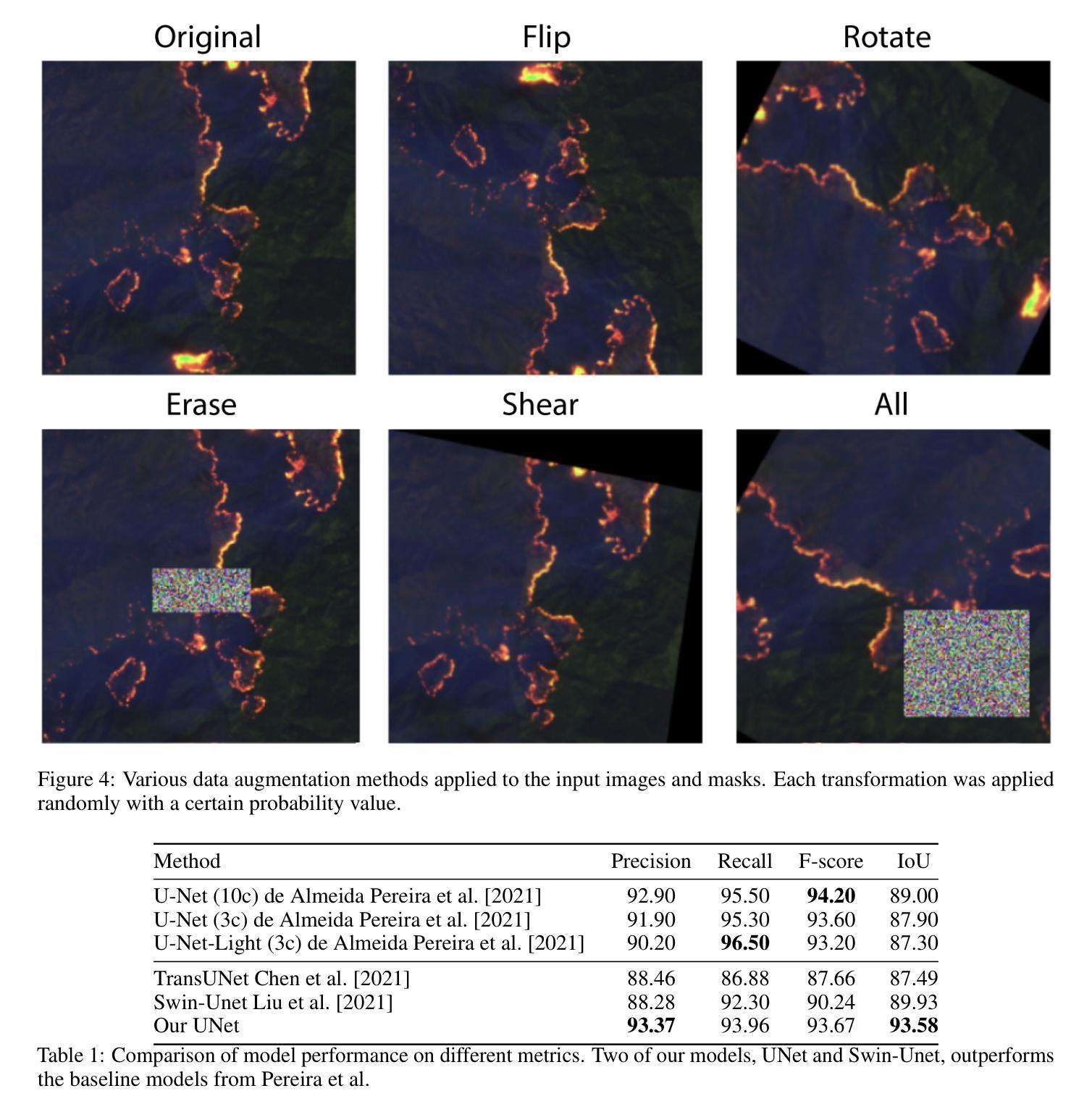
Logit Lens is a widely adopted method for mechanistic interpretability of transformer-based language models, enabling the analysis of how internal representations evolve across layers by projecting them into the output vocabulary space. Although applying Logit Lens to Vision Transformers (ViTs) is technically straightforward, its direct use faces limitations in capturing the richness of visual representations. Building on the work of Toker et al. (2024)~\cite{Toker2024-ve}, who introduced Diffusion Lens to visualize intermediate representations in the text encoders of text-to-image diffusion models, we demonstrate that while Diffusion Lens can effectively visualize residual stream representations in image encoders, it fails to capture the direct contributions of individual submodules. To overcome this limitation, we propose \textbf{Diffusion Steering Lens} (DSL), a novel, training-free approach that steers submodule outputs and patches subsequent indirect contributions. We validate our method through interventional studies, showing that DSL provides an intuitive and reliable interpretation of the internal processing in ViTs.
Logit Lens是广泛应用于基于转换器的语言模型机械解释性的方法,通过将内部表示投影到输出词汇空间来分析它们在各层如何演变。虽然将Logit Lens应用于视觉转换器(ViTs)在技术上很直观,但其直接使用在捕捉视觉表示的丰富性方面存在局限性。在Toker等人(2024)的工作基础上~\cite{Toker2024-ve},他们介绍了Diffusion Lens,用于可视化文本到图像扩散模型的文本编码器中的中间表示,我们证明虽然Diffusion Lens可以有效地可视化图像编码器中的残差流表示,但它无法捕捉单个子模块的直接贡献。为了克服这一局限性,我们提出了扩散转向镜头(DSL),这是一种新型、无需训练的方法,可以引导子模块输出并修补随后的间接贡献。我们通过干预研究验证了我们的方法,表明DSL为ViTs的内部处理提供了直观和可靠的解释。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF 12 pages, 17 figures. Accepted to the CVPR 2025 Workshop on Mechanistic Interpretability for Vision (MIV)
摘要
Logit Lens作为一种广泛应用于基于Transformer的语言模型的机械解释性方法,通过将内部表示投影到输出词汇空间来研究内部表示如何在各层中演变。尽管将Logit Lens应用于Vision Transformers(ViTs)在技术上很直观,但其直接使用在捕捉视觉表示的丰富性方面存在局限性。本研究借鉴Toker等人(2024)的工作,他们引入了Diffusion Lens来可视化文本编码器中的中间表示,并证明Diffusion Lens可以有效地可视化图像编码器中的残差流表示,但它无法捕捉各个子模块的直接影响。为了克服这一局限性,我们提出了无训练阶段的**Diffusion Steering Lens (DSL)**方法,通过干预子模块输出和补丁间接贡献来引导视线。我们通过干预研究验证了该方法,表明DSL为ViTs的内部处理提供了直观且可靠的解释。
关键见解
- Logit Lens虽然广泛应用于基于Transformer的语言模型的解释性,但在捕捉Vision Transformers(ViTs)的视觉表示丰富性方面存在局限性。
- Diffusion Lens能有效可视化图像编码器中的残差流表示,但无法捕捉子模块的直接影响。
- DSL方法借鉴了Diffusion Lens的思想并进行了改进,提出了一种无训练阶段的解读机制来捕捉ViTs内部的动态。
- DSL能够直观并可靠地解释Vision Transformers的内部处理过程。
- DSL通过干预子模块输出和补丁间接贡献来引导视线,从而更有效地揭示模型内部的工作机制。
- 研究通过干预研究验证了DSL的有效性。
点此查看论文截图


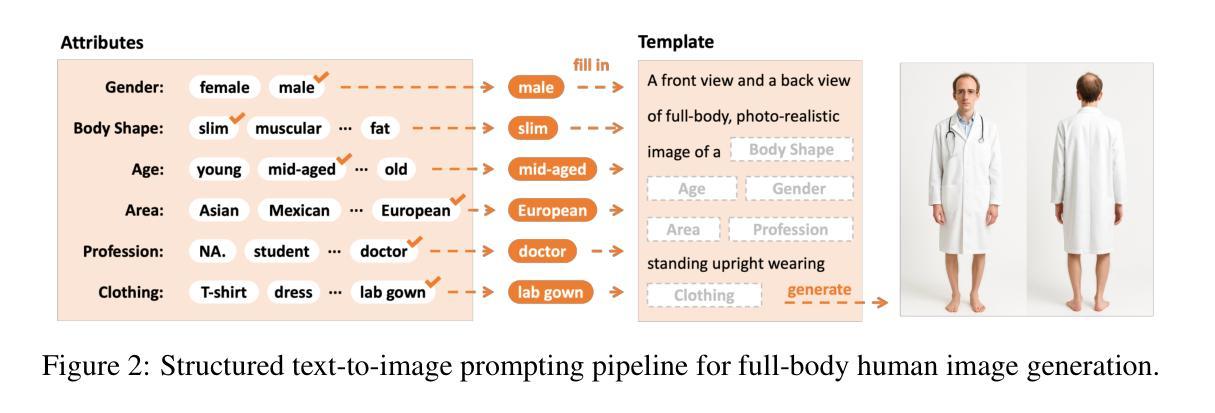
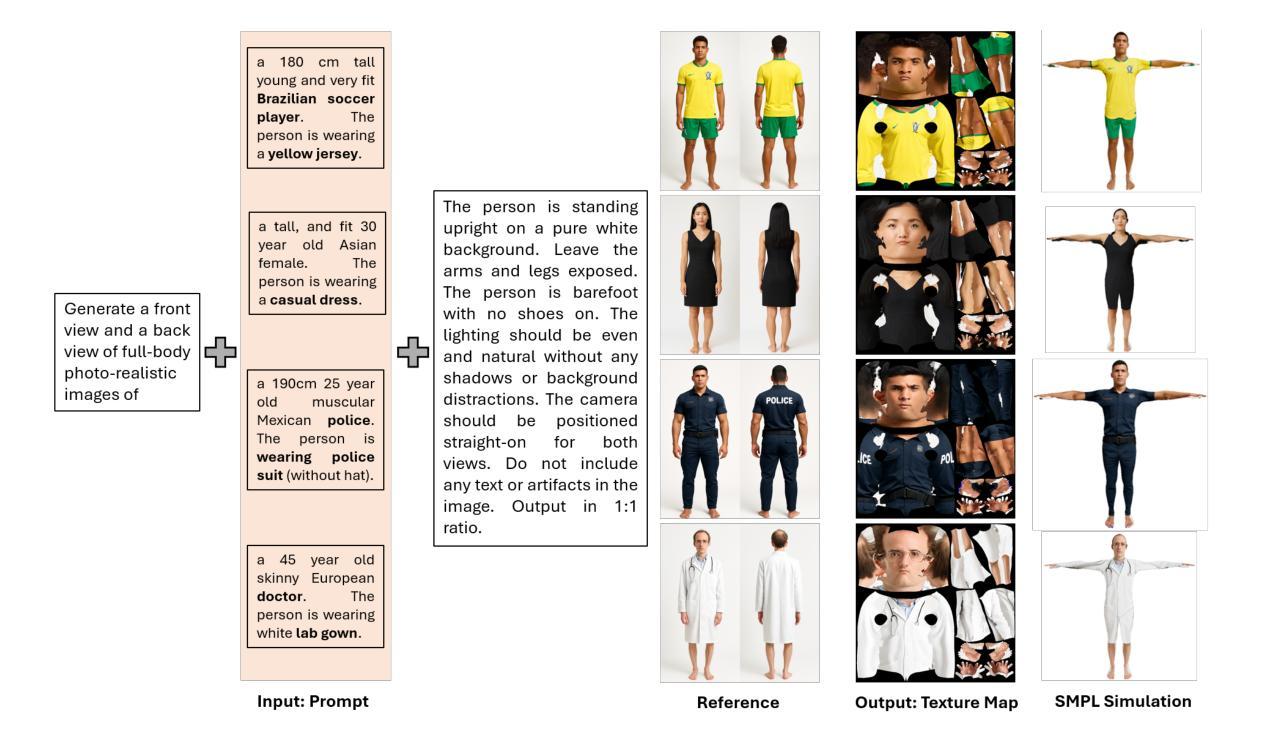
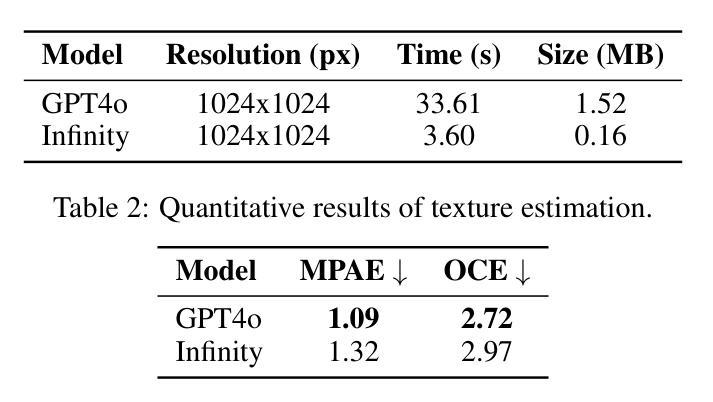
SMPL-GPTexture: Dual-View 3D Human Texture Estimation using Text-to-Image Generation Models
Authors:Mingxiao Tu, Shuchang Ye, Hoijoon Jung, Jinman Kim
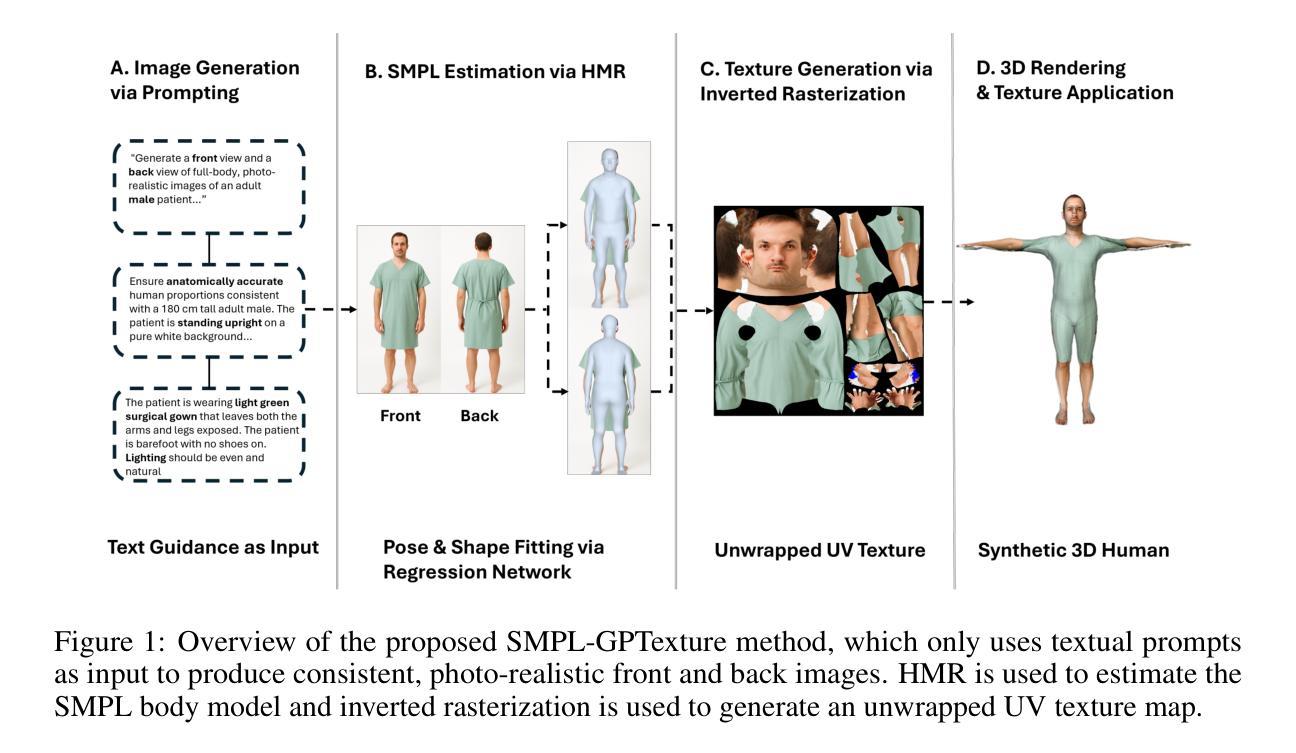
Generating high-quality, photorealistic textures for 3D human avatars remains a fundamental yet challenging task in computer vision and multimedia field. However, real paired front and back images of human subjects are rarely available with privacy, ethical and cost of acquisition, which restricts scalability of the data. Additionally, learning priors from image inputs using deep generative models, such as GANs or diffusion models, to infer unseen regions such as the human back often leads to artifacts, structural inconsistencies, or loss of fine-grained detail. To address these issues, we present SMPL-GPTexture (skinned multi-person linear model - general purpose Texture), a novel pipeline that takes natural language prompts as input and leverages a state-of-the-art text-to-image generation model to produce paired high-resolution front and back images of a human subject as the starting point for texture estimation. Using the generated paired dual-view images, we first employ a human mesh recovery model to obtain a robust 2D-to-3D SMPL alignment between image pixels and the 3D model’s UV coordinates for each views. Second, we use an inverted rasterization technique that explicitly projects the observed colour from the input images into the UV space, thereby producing accurate, complete texture maps. Finally, we apply a diffusion-based inpainting module to fill in the missing regions, and the fusion mechanism then combines these results into a unified full texture map. Extensive experiments shows that our SMPL-GPTexture can generate high resolution texture aligned with user’s prompts.
在计算机视觉和多媒体领域,为3D人类角色生成高质量、逼真的纹理仍然是一个基本且具有挑战性的任务。然而,由于隐私、伦理和采集成本等问题,人类主题的真实配对正面和背面图像很少可用,这限制了数据的可扩展性。此外,使用深度生成模型(如GAN或扩散模型)从图像输入中学习先验知识,以推断未见区域(如人体背面),通常会导致伪影、结构不一致或丢失细节。为了解决这些问题,我们提出了SMPL-GPTexture(带有皮肤的多人物线性模型-通用纹理),这是一种新颖的流程,它以自然语言提示作为输入,并利用最先进的文本到图像生成模型来生成配对的高分辨率正面和背面图像作为纹理估计的起点。使用生成的配对双视图图像,我们首先采用人体网格恢复模型,在图像像素和每个视图的3D模型的UV坐标之间获得稳健的2D到3D SMPL对齐。其次,我们使用反向光栅化技术显式地将观察到的颜色从输入图像投影到UV空间中,从而生成准确且完整的纹理映射。最后,我们应用基于扩散的填充模块来填充缺失区域,然后融合机制将这些结果组合成统一的完整纹理图。大量实验表明,我们的SMPL-GPTexture可以根据用户的提示生成高分辨率纹理。
论文及项目相关链接
摘要
本文提出一种基于自然语言提示的SMPL-GPTexture新流程,用于生成高质量、逼真的三维人类角色纹理。利用先进的文本转图像生成模型,产生配对的、高分辨率的前侧和后背人体图像作为纹理估计的起点。借助生成的双视图图像,采用人体网格恢复模型获得图像像素与三维模型UV坐标之间的稳健对齐。接着使用逆向渲染技术将观察到的颜色从输入图像投影到UV空间,生成准确完整的纹理映射。最后通过基于扩散的补全模块填充缺失区域,融合机制将这些结果合并成统一的完整纹理映射图。实验表明,SMPL-GPTexture可根据用户提示生成与之一致的高分辨率纹理。
关键见解
- 论文涉及计算机视觉和多媒体领域,关注于为3D人类角色生成高质量、逼真的纹理的挑战。
- 真实配对的前侧和后背人体图像因隐私、伦理和采集成本而难以获得,限制了数据规模。
- 使用深度生成模型(如GANs或扩散模型)从图像中学习先验来推断未观察到的区域(如人体背部)可能导致伪影、结构不一致或细节丢失。
- 提出的SMPL-GPTexture流程采用自然语言提示作为输入,并利用先进的文本转图像生成模型来产生配对的双视图图像。
- 利用生成的双视图图像进行稳健的二维到三维模型对齐。
- 通过逆向渲染技术生成纹理映射图,并明确地将观察到的颜色从输入图像投影到UV空间。
- 采用基于扩散的补全模块填充缺失区域,并通过融合机制生成统一的完整纹理映射图。实验证明该方法的有效性。
点此查看论文截图

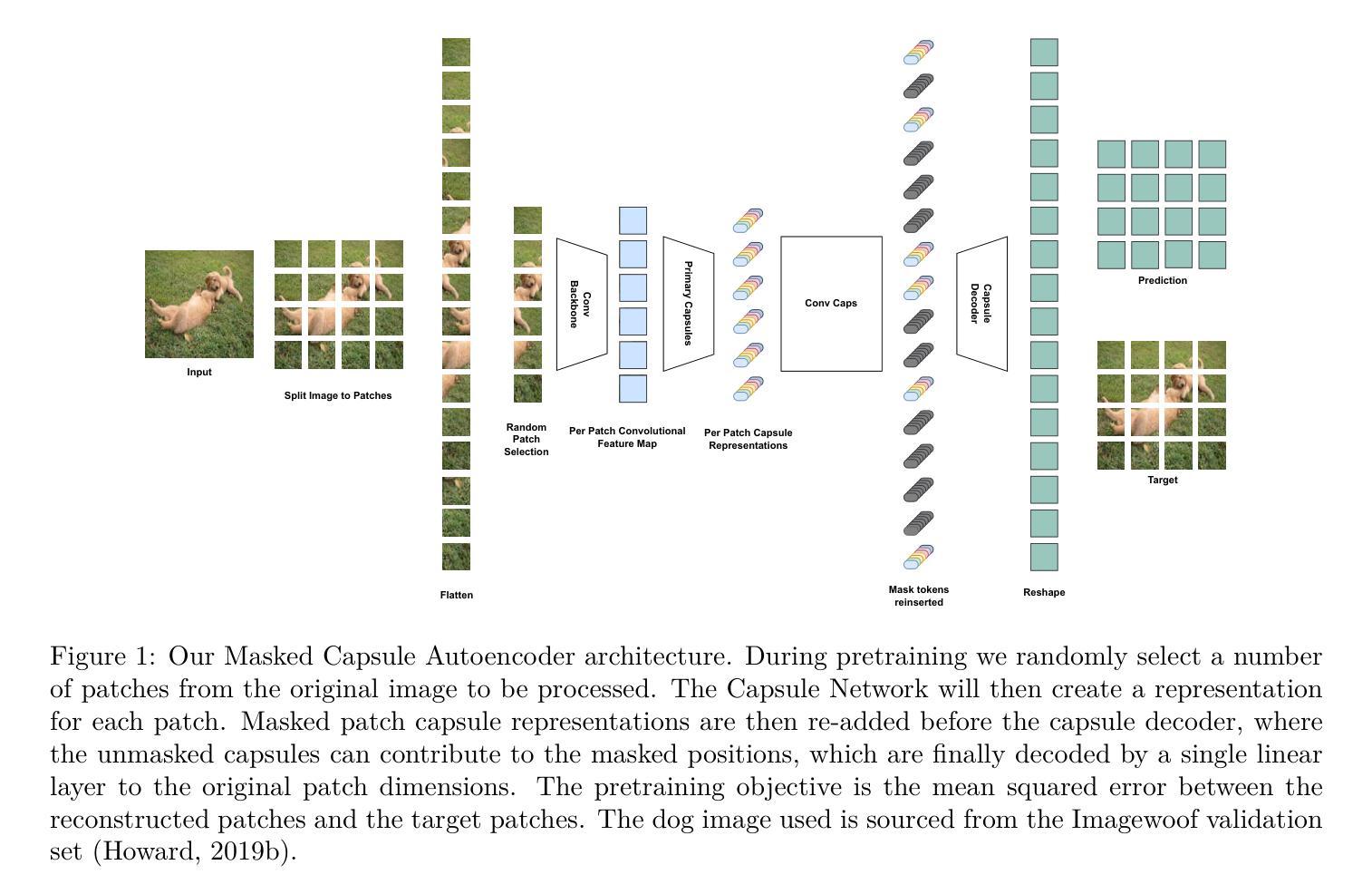
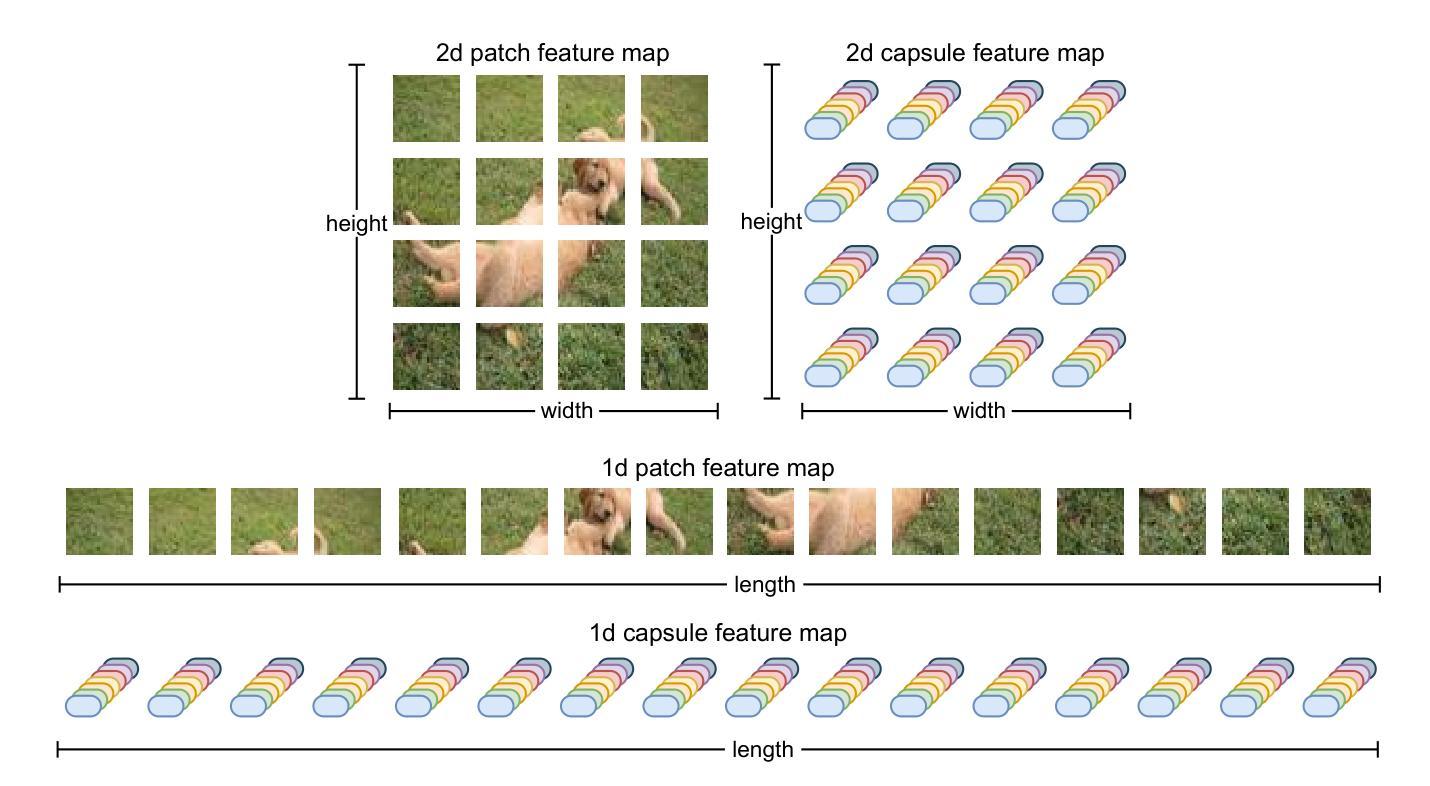
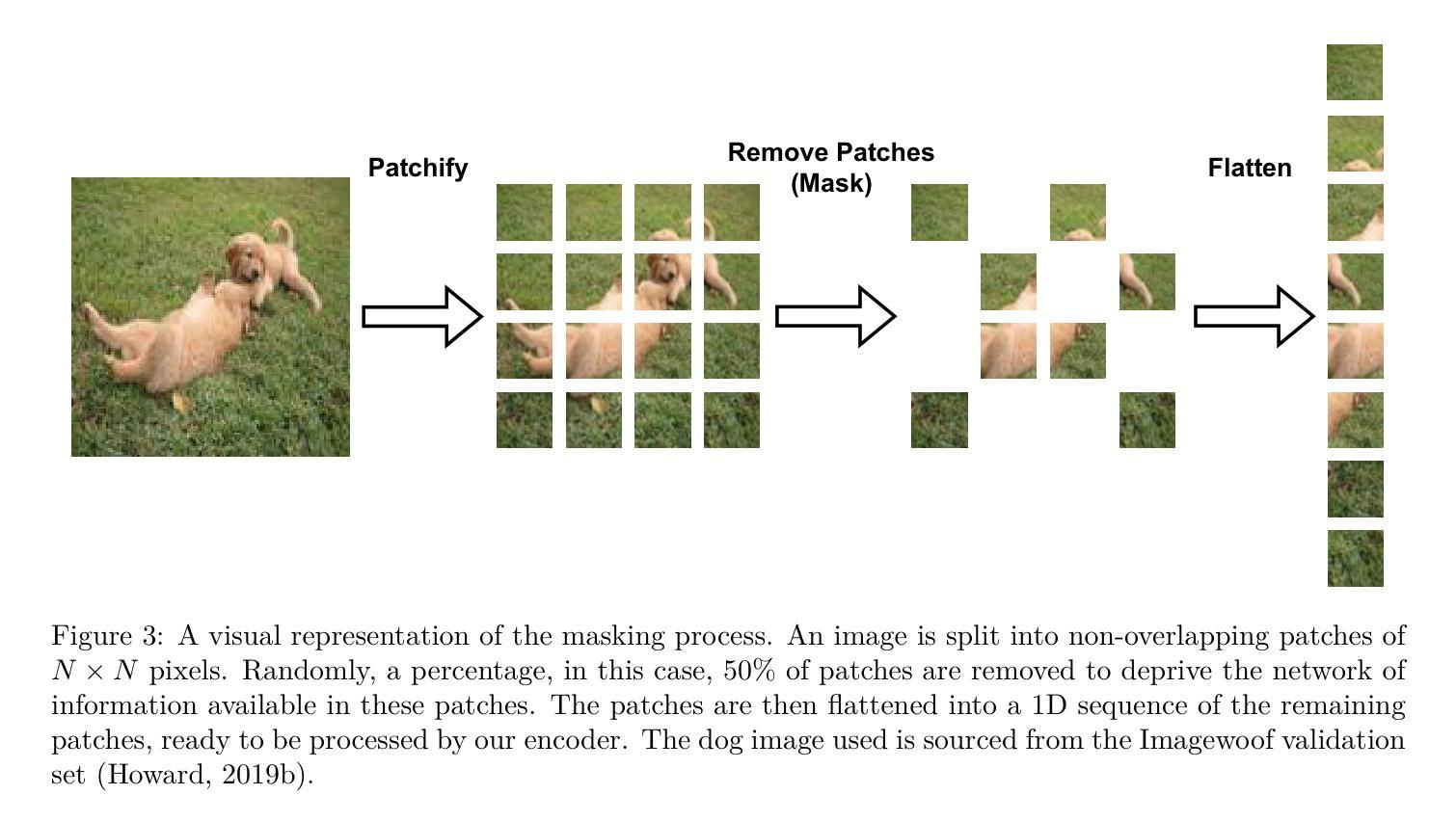
Masked Capsule Autoencoders
Authors:Miles Everett, Mingjun Zhong, Georgios Leontidis
We propose Masked Capsule Autoencoders (MCAE), the first Capsule Network that utilises pretraining in a modern self-supervised paradigm, specifically the masked image modelling framework. Capsule Networks have emerged as a powerful alternative to Convolutional Neural Networks (CNNs). They have shown favourable properties when compared to Vision Transformers (ViT), but have struggled to effectively learn when presented with more complex data. This has led to Capsule Network models that do not scale to modern tasks. Our proposed MCAE model alleviates this issue by reformulating the Capsule Network to use masked image modelling as a pretraining stage before finetuning in a supervised manner. Across several experiments and ablations studies we demonstrate that similarly to CNNs and ViTs, Capsule Networks can also benefit from self-supervised pretraining, paving the way for further advancements in this neural network domain. For instance, by pretraining on the Imagenette dataset-consisting of 10 classes of Imagenet-sized images-we achieve state-of-the-art results for Capsule Networks, demonstrating a 9% improvement compared to our baseline model. Thus, we propose that Capsule Networks benefit from and should be trained within a masked image modelling framework, using a novel capsule decoder, to enhance a Capsule Network’s performance on realistically sized images.
我们提出了Masked Capsule Autoencoders(MCAE),这是第一个在现代自我监督范式中利用预训练的Capsule网络,特别是遮挡图像建模框架。Capsule网络已被视为卷积神经网络(CNN)的有力替代。与视觉转换器(ViT)相比,它们显示出有利的特性,但在面对更复杂的数据时,有效学习的能力受到限制。这导致Capsule网络模型无法适应现代任务。我们提出的MCAE模型通过重新制定Capsule网络,使用遮挡图像建模作为预训练阶段,然后在监督方式下进行微调,从而缓解了这个问题。通过多次实验和消减研究,我们证明与CNN和ViT类似,Capsule网络也可以从自我监督的预训练中受益,为神经网络领域的进一步发展铺平了道路。例如,通过在Imagenette数据集上进行预训练,该数据集包含ImageNet大小图像的10个类别,我们实现了Capsule网络的最先进结果,与我们的基线模型相比,展示了9%的改进。因此,我们提出Capsule网络受益于并在遮挡图像建模框架内进行了训练,使用一个新型的胶囊解码器,以提高Capsule网络在现实大小图像上的性能。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF 15 pages, 7 figures, 5 tables - accepted at TMLR
Summary
Masked Capsule Autoencoders(MCAE)是一种利用现代自监督学习范式的预训练胶囊网络。胶囊网络是卷积神经网络(CNN)的有力替代,但与视觉转换器(ViT)相比,它们在处理复杂数据时显示出优势。MCAE模型通过采用掩码图像建模作为预训练阶段,再监督微调,解决了胶囊网络难以有效处理复杂数据的问题。实验和消融研究表明,与CNN和ViT类似,胶囊网络也可以从自监督预训练中受益。通过在Imagenette数据集上进行预训练,我们的模型实现了胶囊网络的最先进结果,相比基线模型提高了9%。因此,我们提议胶囊网络的训练和增强应在掩码图像建模框架内进行,使用新型胶囊解码器,以提高胶囊网络在现实尺寸图像上的性能。
Key Takeaways
- Masked Capsule Autoencoders (MCAE) 是首个结合现代自监督学习范式的胶囊网络。
- 胶囊网络是卷积神经网络(CNN)的替代方案,尤其适合处理复杂数据。
- MCAE模型通过掩码图像建模作为预训练阶段,提升了胶囊网络处理复杂数据的能力。
- 实验和消融研究表明,胶囊网络也能从自监督预训练中受益。
- 在Imagenette数据集上预训练的MCAE模型实现了胶囊网络的最优性能,相比基线模型提高了9%。
- 提议在掩码图像建模框架内训练和增强胶囊网络。
点此查看论文截图