⚠️ 以下所有内容总结都来自于 大语言模型的能力,如有错误,仅供参考,谨慎使用
🔴 请注意:千万不要用于严肃的学术场景,只能用于论文阅读前的初筛!
💗 如果您觉得我们的项目对您有帮助 ChatPaperFree ,还请您给我们一些鼓励!⭐️ HuggingFace免费体验
2025-04-23 更新
OPO: Making Decision-Focused Data Acquisition Decisions
Authors:Egon Peršak, Miguel F. Anjos
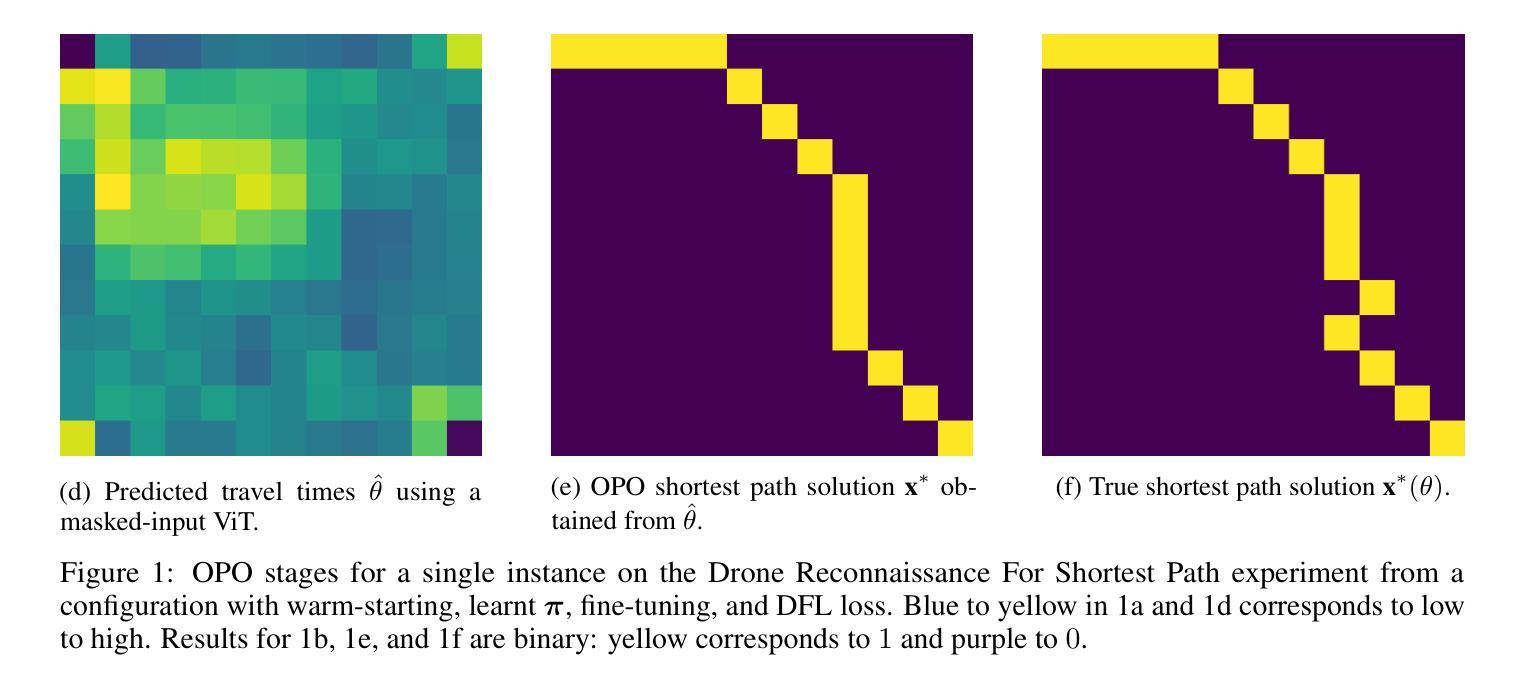
We propose a model for making data acquisition decisions for variables in contextual stochastic optimisation problems. Data acquisition decisions are typically treated as separate and fixed. We explore problem settings in which the acquisition of contextual variables is costly and consequently constrained. The data acquisition problem is often solved heuristically for proxy objectives such as coverage. The more intuitive objective is the downstream decision quality as a result of data acquisition decisions. The whole pipeline can be characterised as an optimise-then-predict-then-optimise (OPO) problem. Analogously, much recent research has focused on how to integrate prediction and optimisation (PO) in the form of decision-focused learning. We propose leveraging differentiable optimisation to extend the integration to data acquisition. We solve the data acquisition problem with well-defined constraints by learning a surrogate linear objective function. We demonstrate an application of this model on a shortest path problem for which we first have to set a drone reconnaissance strategy to capture image segments serving as inputs to a model that predicts travel costs. We ablate the problem with a number of training modalities and demonstrate that the differentiable optimisation approach outperforms random search strategies.
我们提出一种用于解决上下文随机优化问题中的变量数据采集决策模型。通常,数据采集决策被视为独立且固定的。我们探索了在获取上下文变量成本高昂从而受到限制的情境设置。数据获取问题通常通过启发式方法解决,以覆盖等代理目标为主。更直观的目标是数据获取决策所导致的下游决策质量。整个流程可以特征化为一个先优化再预测再优化(OPO)问题。类似地,最近的研究主要集中在如何将预测和优化(PO)以决策聚焦学习的形式结合起来。我们提出利用可微优化来将数据采集扩展到预测和优化集成中。我们通过学习一个替代的线性目标函数来解决具有明确约束的数据采集问题。我们在最短路径问题上展示了该模型的一个应用,为此我们必须首先设置无人机侦察策略以捕获图像片段,将其作为预测旅行成本的模型的输入。我们通过多种训练模式来剥离这个问题,并证明可微优化方法优于随机搜索策略。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
本文提出一种用于解决上下文随机优化问题中的变量数据获取决策模型。针对数据获取成本高昂且受限的问题设置,文章探索了一种利用可微优化来扩展数据获取中预测与优化集成的方法。通过解决具有明确约束的数据获取问题,学习代理线性目标函数。在无人机侦察策略的最短路径问题上进行了应用演示。
Key Takeaways
- 文章提出了一种针对上下文随机优化问题中变量数据获取决策的新型模型。
- 数据获取决策通常被视为独立且固定的,但文章强调其优化重要性。
- 当下游决策质量作为数据获取决策更直观的目标时,数据获取问题常被启发式地解决为代理目标如覆盖问题。
- 文章提出利用可微优化来扩展预测与优化(PO)在数据获取中的集成。
- 通过解决具有明确约束的数据获取问题,学习代理线性目标函数是本文的关键方法。
- 文章在一个无人机侦察策略的最短路径问题上展示了该模型的应用实例。
点此查看论文截图

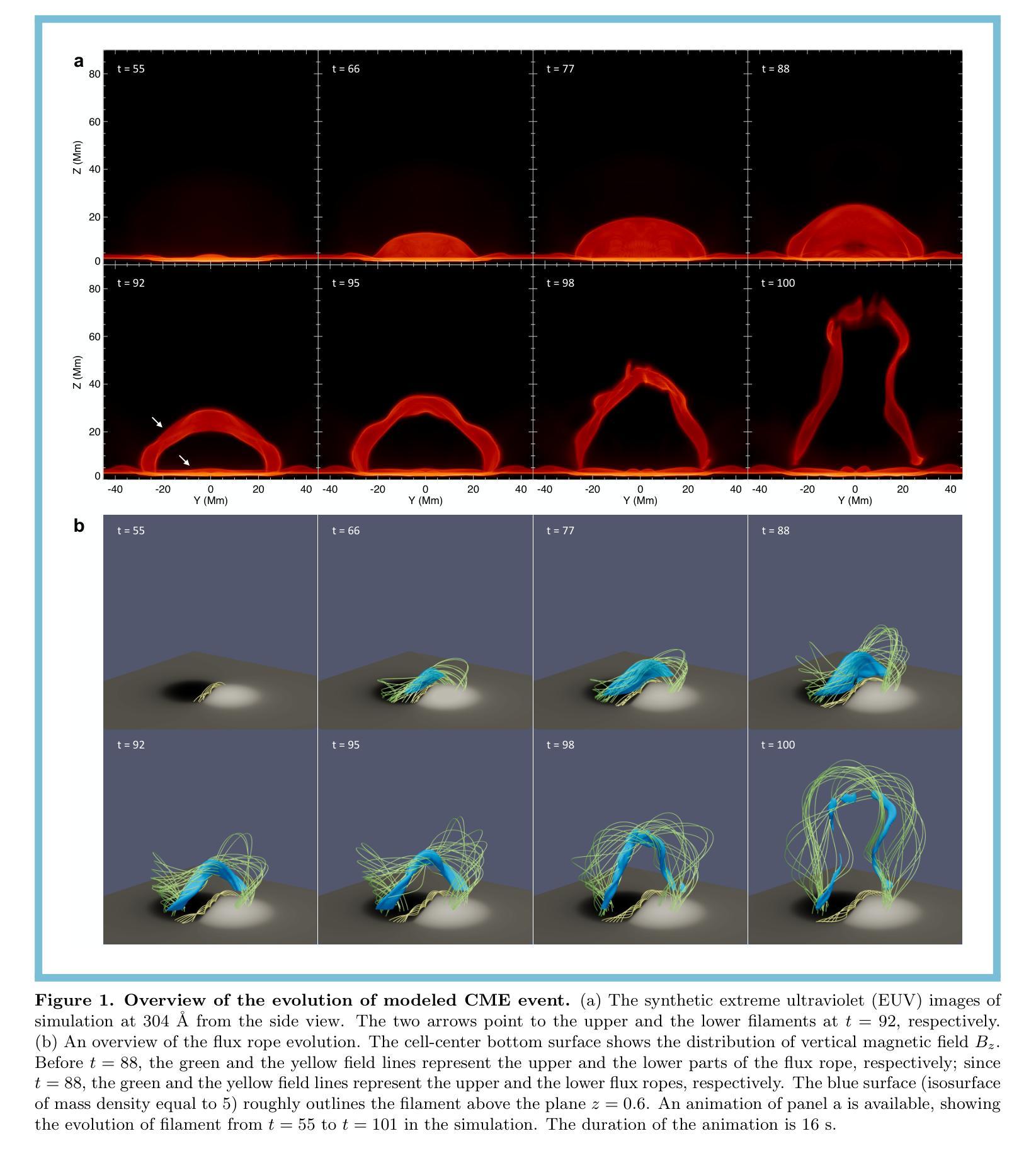
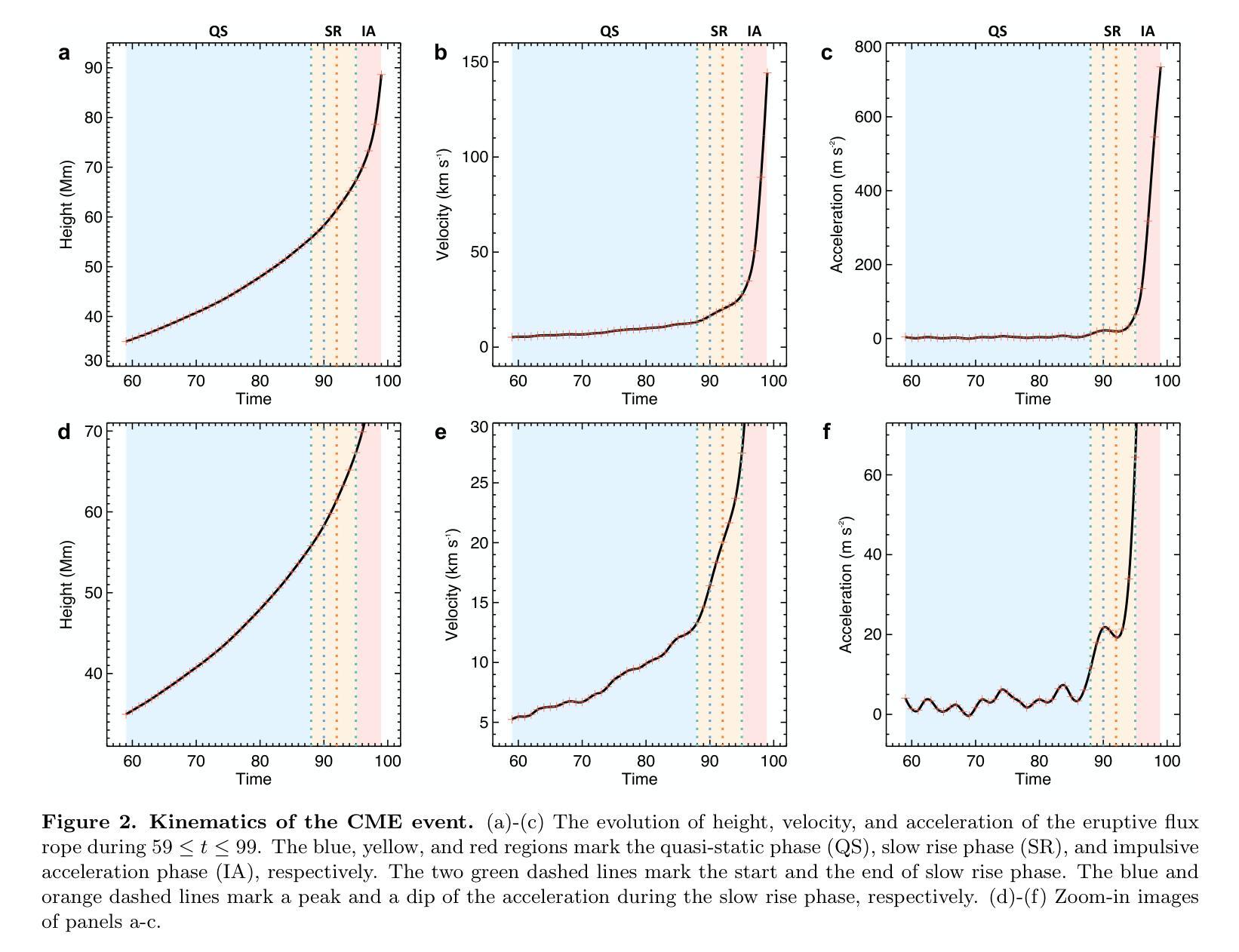
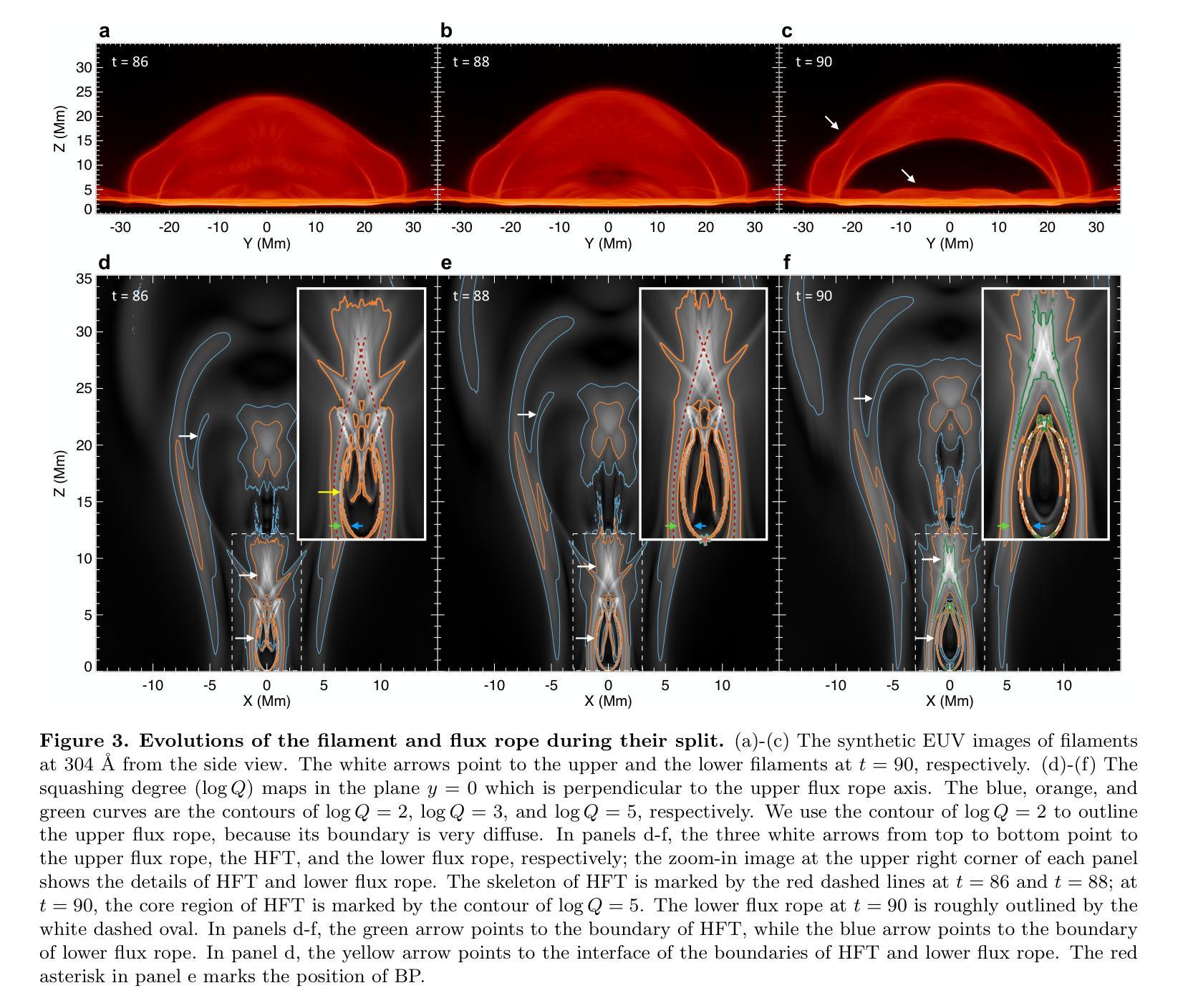
Initiation Route of Coronal Mass Ejections: II. The Role of Filament Mass
Authors:Chen Xing, Xin Cheng, Guillaume Aulanier, Mingde Ding
The thorough understanding on the initiation of coronal mass ejections (CMEs), which is manifested as a slow rise of pre-eruptive structures before the impulsive ejection in kinematics, is the key for forecasting the solar eruptions. In our previous work, we showed that the slow rise of a hot flux rope with coronal mass density is caused by the moderate magnetic reconnection occurring in the hyperbolic flux tube (HFT) combined with the torus instability. However, it remains unclear how the initiation process varies when a filament is present in the pre-eruptive flux rope. In this work, we reveal the complete initiation route of a CME containing filament mass with a state-of-the-art full-magnetohydrodynamics simulation. The comprehensive analyses show that the filament mass has an important impact on the CME initiation through triggering and driving the slow rise of flux rope with its drainage, besides the contributions of HFT reconnection and torus instability. Finally, in combination with our previous work, we propose that the enhanced drainage of filament mass and various features related to the HFT reconnection, such as, the split of pre-eruptive structure and the pre-flare loops and X-ray emissions, can serve as the precursors of CME initiation in observations.
对日冕物质抛射(CMEs)起始过程的理解,表现为动力学中的爆发前结构缓慢上升,是预测太阳爆发的关键。在我们之前的工作中,我们展示了热磁通绳与日冕物质密度的缓慢上升是由双曲磁通管(HFT)中发生的适度磁重联与托卡马克不稳定共同作用引起的。然而,当前仍存在疑问:当预爆发磁通绳中存在日珥时,起始过程如何变化。在这项工作中,我们通过最先进的全磁流体动力学模拟揭示了包含日珥质量的CME的完整起始途径。综合分析表明,除了HFT重联和托卡马克不稳定性的贡献外,日珥质量通过触发和驱动磁通绳的缓慢上升对其排水过程有重要影响。最后,结合我们之前的工作,我们提出增强的日珥质量排水以及与HFT重联相关的各种特征,如预爆发结构的分裂、预耀斑环和X射线发射,可以作为观测中CME起始的预兆。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF 19 pages, 6 figures; accepted for publication in ApJ
Summary
在全面理解日冕物质喷射(CMEs)的启动机制方面,关键在于理解动力学中的缓慢上升阶段预喷结构前的表现。过去的研究表明,热磁通绳的缓慢上升是由于双曲通量管中的中度磁重联和环面不稳定性的共同作用所致。然而,当前工作中揭示了在预喷磁通绳中存在细丝物质时,启动过程的完整性变化。全面分析表明,除了双曲通量管重联和环面不稳定性的贡献外,细丝物质的排水对CME启动有重要影响,并能驱动磁通绳的缓慢上升。结合先前的工作,我们提出增强的细丝物质排水以及与双曲通量管重联相关的各种特征(如预喷结构的分裂和预耀斑环以及X射线发射)可以作为观测中CME启动的前兆。
Key Takeaways
- 理解日冕物质喷射(CMEs)启动机制的关键在于预喷结构前的缓慢上升阶段。
- 过去的研究已经确定了热磁通绳缓慢上升的原因是由双曲通量管中的磁重联和环面不稳定性共同作用所致。
- 当前工作揭示了当预喷磁通绳中存在细丝物质时,CME启动过程的完整性变化。
- 细丝物质的排水对CME启动有重要影响,能驱动磁通绳的缓慢上升。
- 全面分析表明,除了双曲通量管重联和环面不稳定性的贡献外,细丝物质在CME启动过程中起到触发作用。
- 增强细丝物质排水是观测中CME启动的一个重要前兆。
点此查看论文截图

Unveiling Fine Structure and Energy-driven Transition of Photoelectron Kikuchi Diffraction
Authors:Trung-Phuc Vo, Olena Tkach, Aki Pulkkinen, Didier Sebilleau, Aimo Winkelmann, Olena Fedchenko, Yaryna Lytvynenko, Dmitry Vasilyev, Hans-Joachim Elmers, Gerd Schonhense, Jan Minar
The intricate fine structure of Kikuchi diffraction plays a vital role in probing phase transformations and strain distributions in functional materials, particularly in electron microscopy. Beyond these applications, it also proves essential in photoemission spectroscopy (PES) at high photon energies, aiding in the disentanglement of complex angle-resolved PES data and enabling emitter-site-specific studies. However, the detection and analysis of these rich faint structures in photoelectron diffraction (PED), especially in the hard X-ray regime, remain highly challenging, with only a limited number of simulations successfully reproducing these patterns. The strong energy dependence of Kikuchi patterns further complicates their interpretation, necessitating advanced theoretical approaches. To enhance structural analysis, we present a comprehensive theoretical study of fine diffraction patterns and their evolution with energy by simulating core-level emissions from Ge(100) and Si(100). Using multiple-scattering theory and the fully relativistic one-step photoemission model, we simulate faint pattern networks for various core levels across different kinetic energies (106 eV - 4174 eV), avoiding cluster size convergence issues inherent in cluster-based methods. Broadening in patterns is discussed via the inelastic scattering treatment. For the first time, circular dichroism has been observed and successfully reproduced in the angular distribution of Si (100) 1s, revealing detailed features and asymmetries up to 31%. Notably, we successfully replicate experimental bulk and more “surface-sensitivity” diffraction features, further validating the robustness of our simulations. The results show remarkable agreement with the experimental data obtained using circularly polarized radiations, demonstrating the potential of this methodology for advancing high-energy PES investigations.
赤穗图像的精细结构在探测功能材料的相变和应变分布,特别是在电子显微镜学中起着至关重要的作用。除了这些应用之外,它在高能光子光谱的光发射光谱(PES)中也证明是不可或缺的,有助于解决复杂的角度解析PES数据,并能够实现发射器特定部位的研究。然而,在光电子衍射(PED)中检测和解析这些丰富的微弱结构,特别是在硬X射线领域,仍然是非常具有挑战性的任务,只有有限的模拟成功地复制了这些模式。赤穗图案的强能量依赖性进一步复杂了它们的解释,需要高级理论方法。为了增强结构分析,我们对精细衍射图案及其随能量的演变进行了全面的理论研究,通过模拟Ge(100)和Si(100)的核心水平发射。我们利用多重散射理论和完全相对论的一步光发射模型,模拟了不同核心能级在不同动能(106电子伏特至4174电子伏特)下的微弱图案网络,避免了集群大小收敛问题。图案的展宽通过非弹性散射处理进行了讨论。首次观察到圆二色性并在硅(100)的角分布中成功复制出来,揭示了高达31%的详细特征和不对称性。值得注意的是,我们成功地复制了实验中的整体和更“表面敏感”的衍射特征,进一步验证了模拟的稳定性。与利用圆偏振辐射获得的实验数据相比,结果表现出显著的一致性,证明了这种方法在高能PES研究中的潜力。
论文及项目相关链接
摘要
本文探讨了Kikuchi衍射精细结构在功能材料相变和应变分布研究中的重要性,特别是在电子显微镜中的应用。此外,它还在高能光子光谱学中的光发射光谱学(PES)中发挥着关键作用,有助于解开复杂的角度解析PES数据,并支持进行发射器位点的专项研究。然而,在光电子衍射(PED)中检测和解析这些丰富的微弱结构,特别是在硬X射线领域,仍然存在巨大的挑战。仅有有限的模拟成功复制了这些模式。Kikuchi图案的强烈能量依赖性进一步增加了其解释的复杂性,需要高级理论方法。为了增强结构分析,我们对精细衍射图案及其随能量的演变进行了全面的理论研究,通过对Ge(100)和Si(100)的核心水平发射进行模拟。利用多重散射理论和完全相对论的一阶光发射模型,我们模拟了不同动能范围(106 eV - 4174 eV)内各种核心层次的微弱图案网络,避免了集群大小收敛问题。通过非弹性散射处理讨论了图案的展宽。首次观察到硅(100)1s的圆二色性,并在其角度分布中成功复制,揭示了高达31%的特征和不对称性。我们成功地复制了实验中的大体和更“表面敏感性”的衍射特征,进一步验证了模拟的稳健性。该研究结果与实验数据表现出显著的一致性,特别是在使用圆偏振辐射的情况下,证明了该方法在高能PES研究中的潜力。
关键见解
- Kikuchi衍射的精细结构在探索功能材料的相变和应变分布中起关键作用,特别是在电子显微镜学中。
- 在高能光子光谱学中,Kikuchi衍射也助于解开复杂的光发射光谱(PES)数据并支持特定研究。
- 在硬X射线领域检测和解析光电子衍射(PED)中的微弱结构具有挑战性。
- 只有有限的模拟成功复制了这些图案网络的不同动能范围内的各种核心层次。
- 利用多重散射理论和完全相对论的一阶光发射模型成功模拟了精细衍射图案及其随能量的演变。
- 第一次观察到硅(Si)中的圆二色性现象并成功模拟,揭示了其角度分布的特征和不对称性。
点此查看论文截图

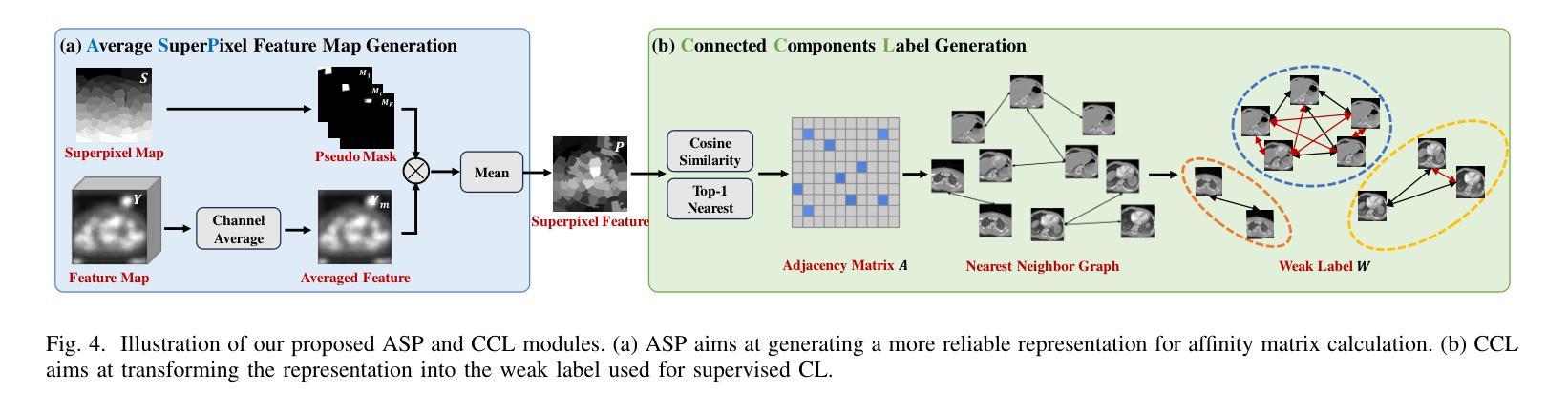
SuperCL: Superpixel Guided Contrastive Learning for Medical Image Segmentation Pre-training
Authors:Shuang Zeng, Lei Zhu, Xinliang Zhang, Hangzhou He, Yanye Lu
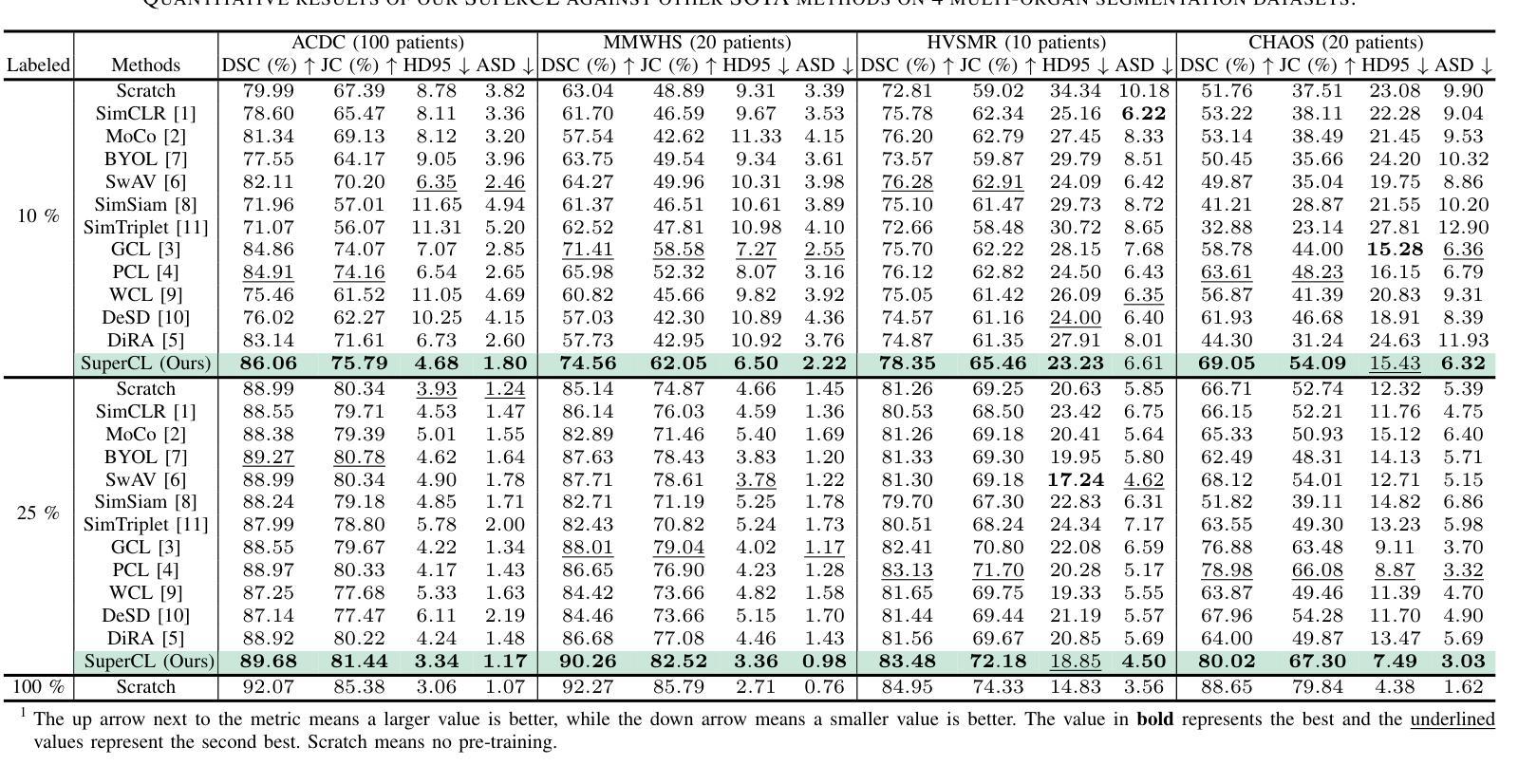
Medical image segmentation is a critical yet challenging task, primarily due to the difficulty of obtaining extensive datasets of high-quality, expert-annotated images. Contrastive learning presents a potential but still problematic solution to this issue. Because most existing methods focus on extracting instance-level or pixel-to-pixel representation, which ignores the characteristics between intra-image similar pixel groups. Moreover, when considering contrastive pairs generation, most SOTA methods mainly rely on manually setting thresholds, which requires a large number of gradient experiments and lacks efficiency and generalization. To address these issues, we propose a novel contrastive learning approach named SuperCL for medical image segmentation pre-training. Specifically, our SuperCL exploits the structural prior and pixel correlation of images by introducing two novel contrastive pairs generation strategies: Intra-image Local Contrastive Pairs (ILCP) Generation and Inter-image Global Contrastive Pairs (IGCP) Generation. Considering superpixel cluster aligns well with the concept of contrastive pairs generation, we utilize the superpixel map to generate pseudo masks for both ILCP and IGCP to guide supervised contrastive learning. Moreover, we also propose two modules named Average SuperPixel Feature Map Generation (ASP) and Connected Components Label Generation (CCL) to better exploit the prior structural information for IGCP. Finally, experiments on 8 medical image datasets indicate our SuperCL outperforms existing 12 methods. i.e. Our SuperCL achieves a superior performance with more precise predictions from visualization figures and 3.15%, 5.44%, 7.89% DSC higher than the previous best results on MMWHS, CHAOS, Spleen with 10% annotations. Our code will be released after acceptance.
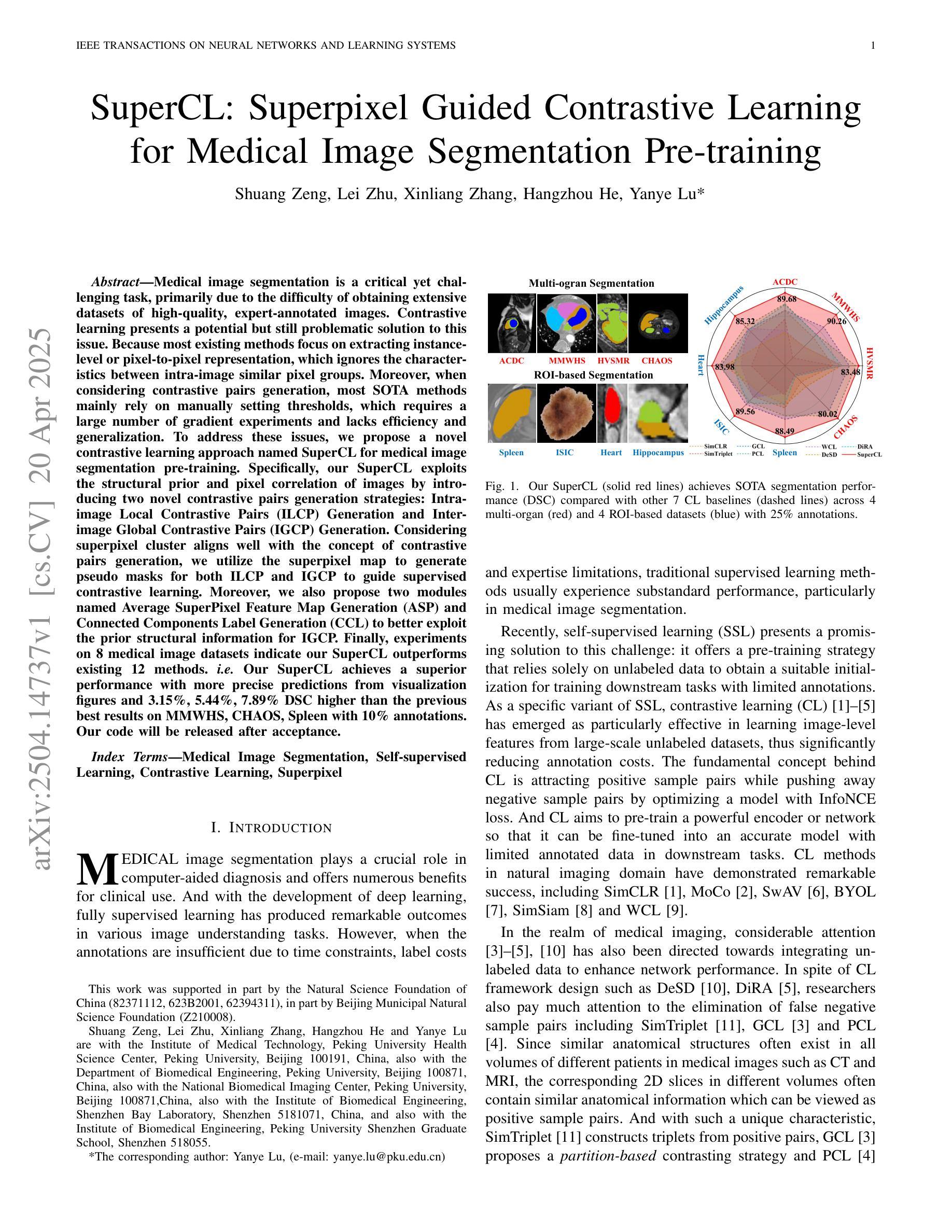
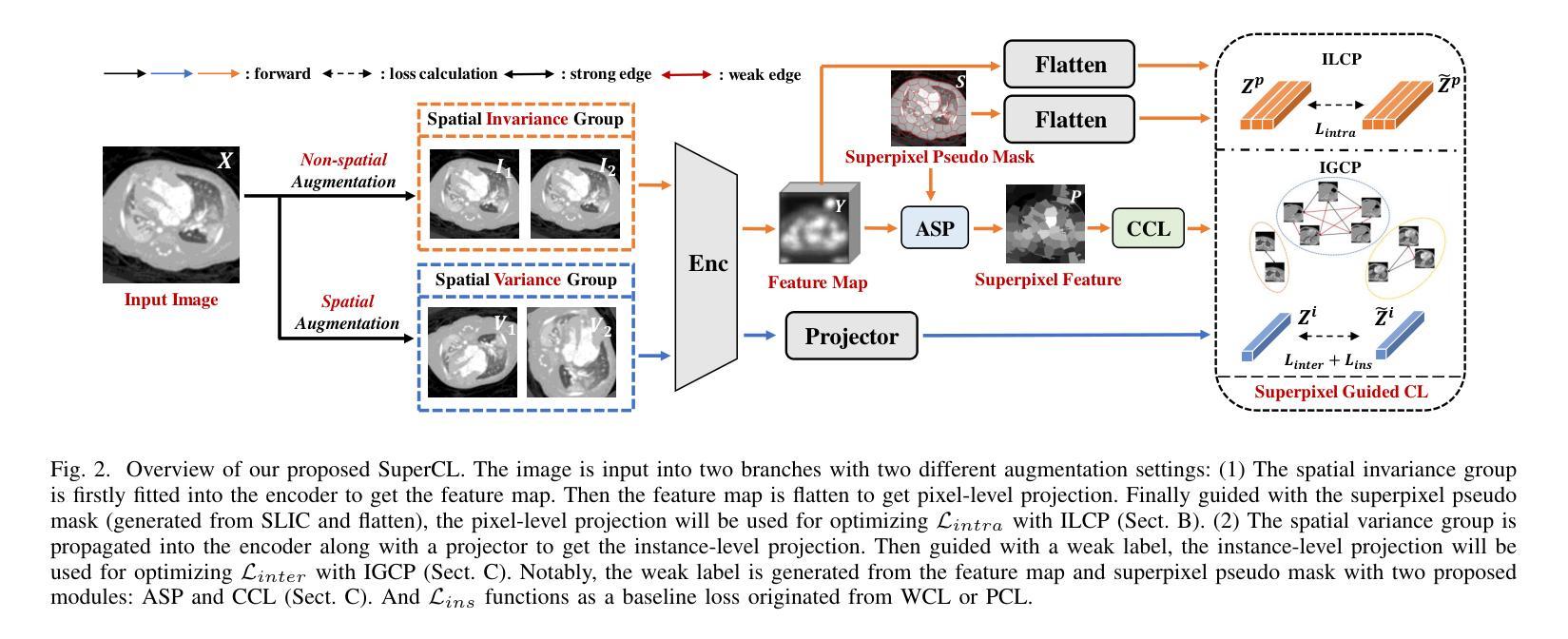
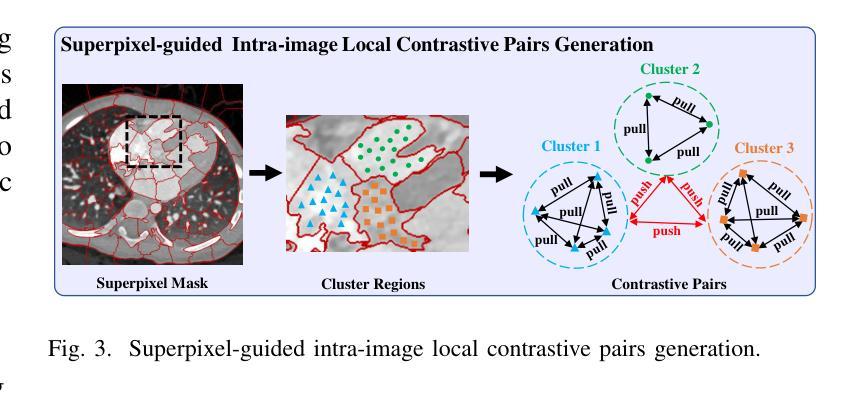
医学图像分割是一项至关重要但具有挑战性的任务,主要是由于获得大量高质量、专家注释的图像数据集十分困难。对比学习为解决这一问题提供了潜在但仍有问题的解决方案。因为大多数现有方法专注于提取实例级或像素对像素的表示,这忽略了图像内相似像素组之间的特征。此外,在对比对生成时,大多数最先进的方法主要依赖于人工设置阈值,这需要大量的梯度实验,缺乏效率和泛化能力。为了解决这些问题,我们提出了一种名为SuperCL的新型对比学习方法,用于医学图像分割的预训练。具体来说,我们的SuperCL通过引入两种新型的对比对生成策略,利用图像的结构先验和像素相关性:图像内局部对比对(ILCP)生成和图像间全局对比对(IGCP)生成。考虑到超像素聚类与对比对生成的概念相吻合,我们利用超像素图生成ILCP和IGCP的伪掩码,以指导有监督的对比学习。此外,我们还提出了名为平均超像素特征图生成(ASP)和连通组件标签生成(CCL)的两个模块,以更好地利用IGCP的先验结构信息。最后,在8个医学图像数据集上的实验表明,我们的SuperCL优于现有的12种方法。即,我们的SuperCL在可视化图上实现了更精确的预测,并且在MMWHS、CHAOS、Spleen数据集上分别提高了3.15%、5.44%、7.89%的DSC分数超越之前最好的结果。代码将在接受后发布。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
医学图像分割是一项重要而具有挑战性的任务,主要因为获取高质量、专家标注的庞大数据集很困难。对比学习为解决这一问题提供了潜在方案,但现有方法忽视了图像内相似像素群之间的特性,且在生成对比对时多依赖人工设定阈值,效率低下且缺乏通用性。本研究提出一种名为SuperCL的新型对比学习方法,用于医学图像分割预训练。该方法利用图像的结构先验和像素相关性,引入两种新型对比对生成策略:ILCP(图像内局部对比对生成)和IGCP(图像间全局对比对生成)。同时,结合超像素地图生成伪掩膜来指导监督对比学习。在8个医学图像数据集上的实验表明,SuperCL相较于其他12种方法表现更优,预测更精确,并在MMWHS、CHAOS和脾脏数据集上分别提高了3.15%、5.44%、7.89%的DSC得分。
Key Takeaways
- 医学图像分割面临获取高质量、专家标注的大规模数据集困难的问题。
- 对比学习是解决这一问题的潜在方案,但现有方法存在局限性。
- 提出一种新型对比学习方法SuperCL,用于医学图像分割预训练。
- SuperCL利用图像的结构先验和像素相关性,引入ILCP和IGCP两种新型对比对生成策略。
- 结合超像素地图生成伪掩膜来指导监督对比学习。
- 在多个医学图像数据集上的实验表明,SuperCL表现优于其他方法。
点此查看论文截图
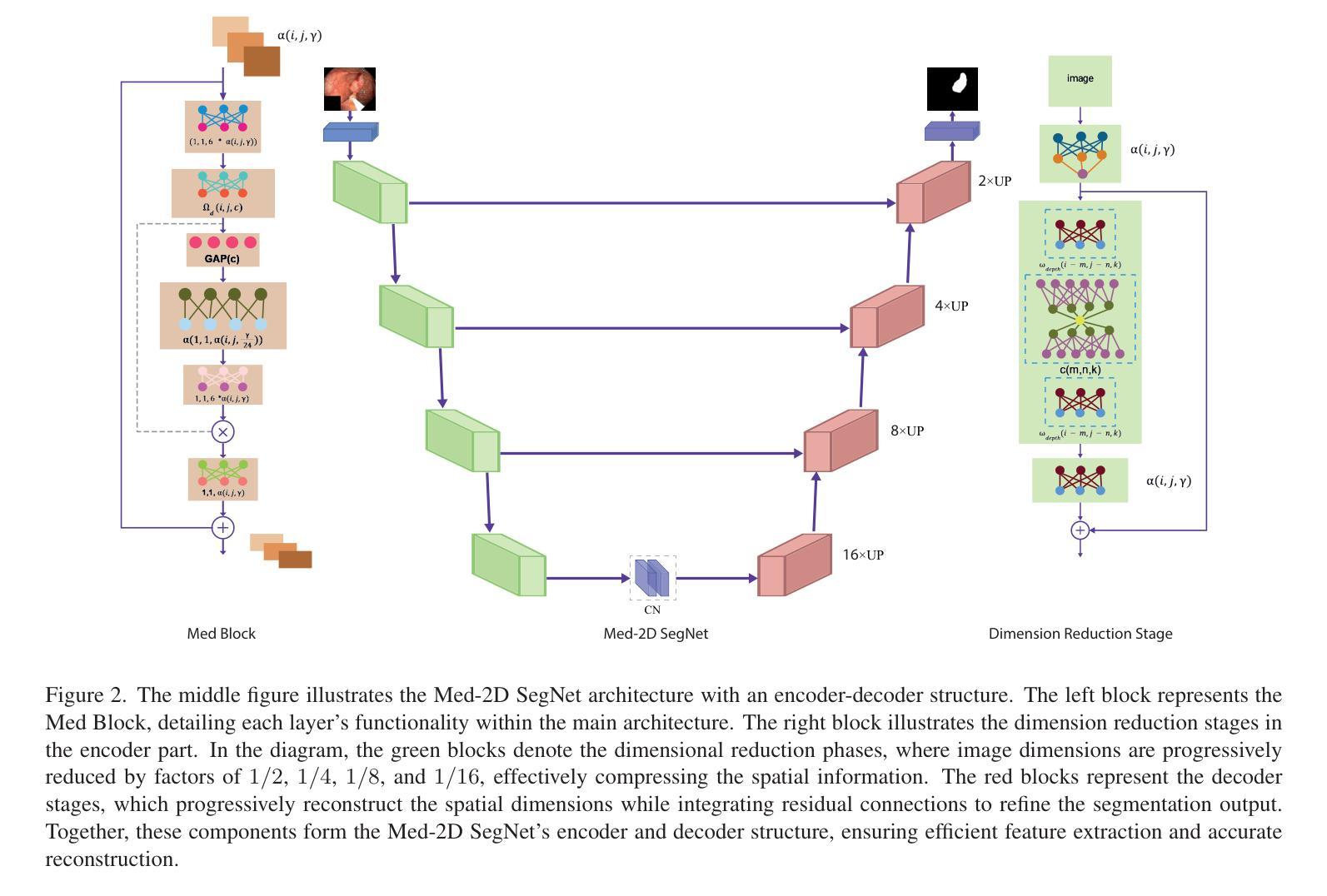
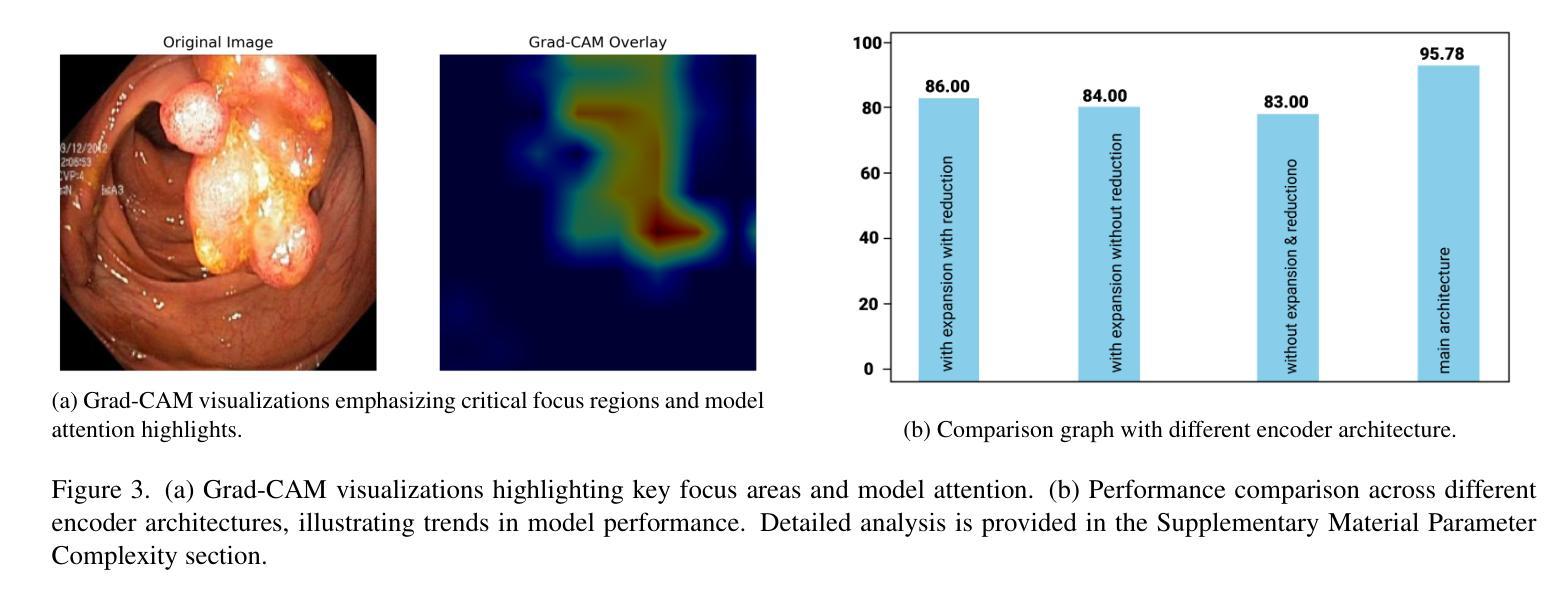
Med-2D SegNet: A Light Weight Deep Neural Network for Medical 2D Image Segmentation
Authors:Md. Sanaullah Chowdhury, Salauddin Tapu, Noyon Kumar Sarkar, Ferdous Bin Ali, Lameya Sabrin
Accurate and efficient medical image segmentation is crucial for advancing clinical diagnostics and surgical planning, yet remains a complex challenge due to the variability in anatomical structures and the demand for low-complexity models. In this paper, we introduced Med-2D SegNet, a novel and highly efficient segmentation architecture that delivers outstanding accuracy while maintaining a minimal computational footprint. Med-2D SegNet achieves state-of-the-art performance across multiple benchmark datasets, including KVASIR-SEG, PH2, EndoVis, and GLAS, with an average Dice similarity coefficient (DSC) of 89.77% across 20 diverse datasets. Central to its success is the compact Med Block, a specialized encoder design that incorporates dimension expansion and parameter reduction, enabling precise feature extraction while keeping model parameters to a low count of just 2.07 million. Med-2D SegNet excels in cross-dataset generalization, particularly in polyp segmentation, where it was trained on KVASIR-SEG and showed strong performance on unseen datasets, demonstrating its robustness in zero-shot learning scenarios, even though we acknowledge that further improvements are possible. With top-tier performance in both binary and multi-class segmentation, Med-2D SegNet redefines the balance between accuracy and efficiency, setting a new benchmark for medical image analysis. This work paves the way for developing accessible, high-performance diagnostic tools suitable for clinical environments and resource-constrained settings, making it a step forward in the democratization of advanced medical technology.
准确高效的医学图像分割对于推动临床诊断和手术计划至关重要,但由于解剖结构的可变性和对低复杂度模型的需求,它仍然是一个复杂的挑战。在本文中,我们介绍了Med-2D SegNet,这是一种新型高效的分割架构,能够在保持出色准确性的同时,保持较低的计算开销。Med-2D SegNet在多个基准数据集上实现了最先进的性能,包括KVASIR-SEG、PH2、EndoVis和GLAS,在20个不同数据集的平均Dice相似系数(DSC)为89.77%。其成功的核心是紧凑的Med Block,这是一种专用的编码器设计,结合了维度扩展和参数减少,能够在精确提取特征的同时,将模型参数保持在一个较低的数量,仅有207万。Med-2D SegNet在跨数据集泛化方面表现出色,特别是在息肉分割方面,它在KVASIR-SEG数据集上进行训练,在未见过的数据集上表现出强大的性能,证明了其在零样本学习场景中的稳健性,尽管我们承认还可以进行进一步的改进。无论在二元分割和多类分割方面,Med-2D SegNet都重新定义了准确性与效率之间的平衡,为医学图像分析设定了新的基准。这项工作为开发适合临床环境和资源受限环境的高性能诊断工具铺平了道路,是先进医疗技术民主化的又一进步。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
本文介绍了一种新型高效的医学图像分割架构Med-2D SegNet,该架构在多个基准数据集上实现了卓越的性能,平均Dice相似系数(DSC)为89.77%。其核心在于紧凑的Med Block,能够实现精确的特征提取并保持模型参数的低计数。Med-2D SegNet擅长跨数据集泛化,特别是在息肉分割中表现突出。该架构重新定义了准确性和效率之间的平衡,为医学图像分析设定了新的基准,为临床环境和资源受限的环境开发高性能诊断工具铺平了道路。
Key Takeaways
- Med-2D SegNet是一种高效医学图像分割架构,具备出色的性能。
- 它在多个基准数据集上实现了平均Dice相似系数(DSC)为89.77%的高准确率。
- Med Block是架构的核心,能够实现精确的特征提取并保持模型参数的低计数。
- Med-2D SegNet擅长跨数据集泛化,特别是在息肉分割等任务中表现优异。
- 该架构具备优异的二进制和多类分割性能。
- Med-2D SegNet为医学图像分析设定了新的性能基准,并朝着开发高性能诊断工具的目标迈进了一步。
点此查看论文截图

OmniV-Med: Scaling Medical Vision-Language Model for Universal Visual Understanding
Authors:Songtao Jiang, Yuan Wang, Sibo Song, Yan Zhang, Zijie Meng, Bohan Lei, Jian Wu, Jimeng Sun, Zuozhu Liu
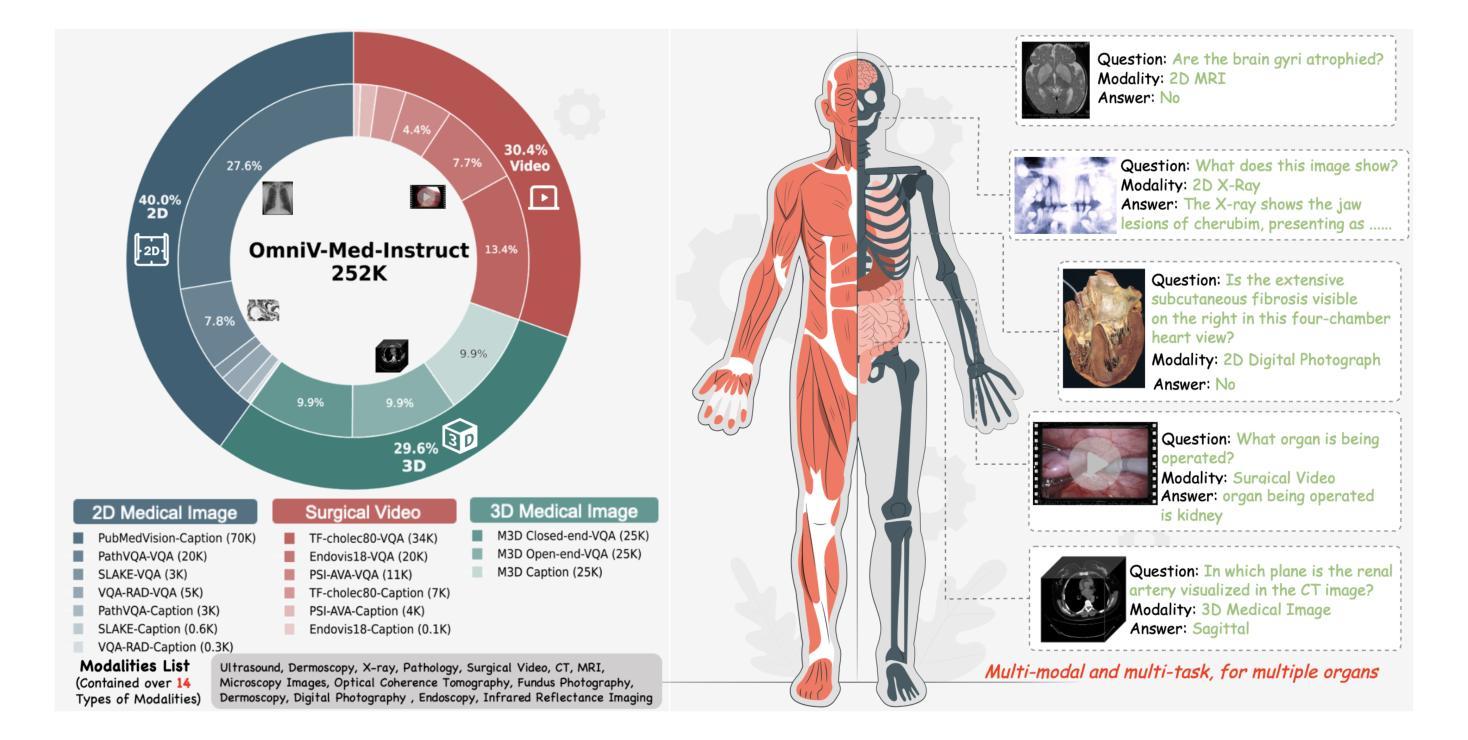
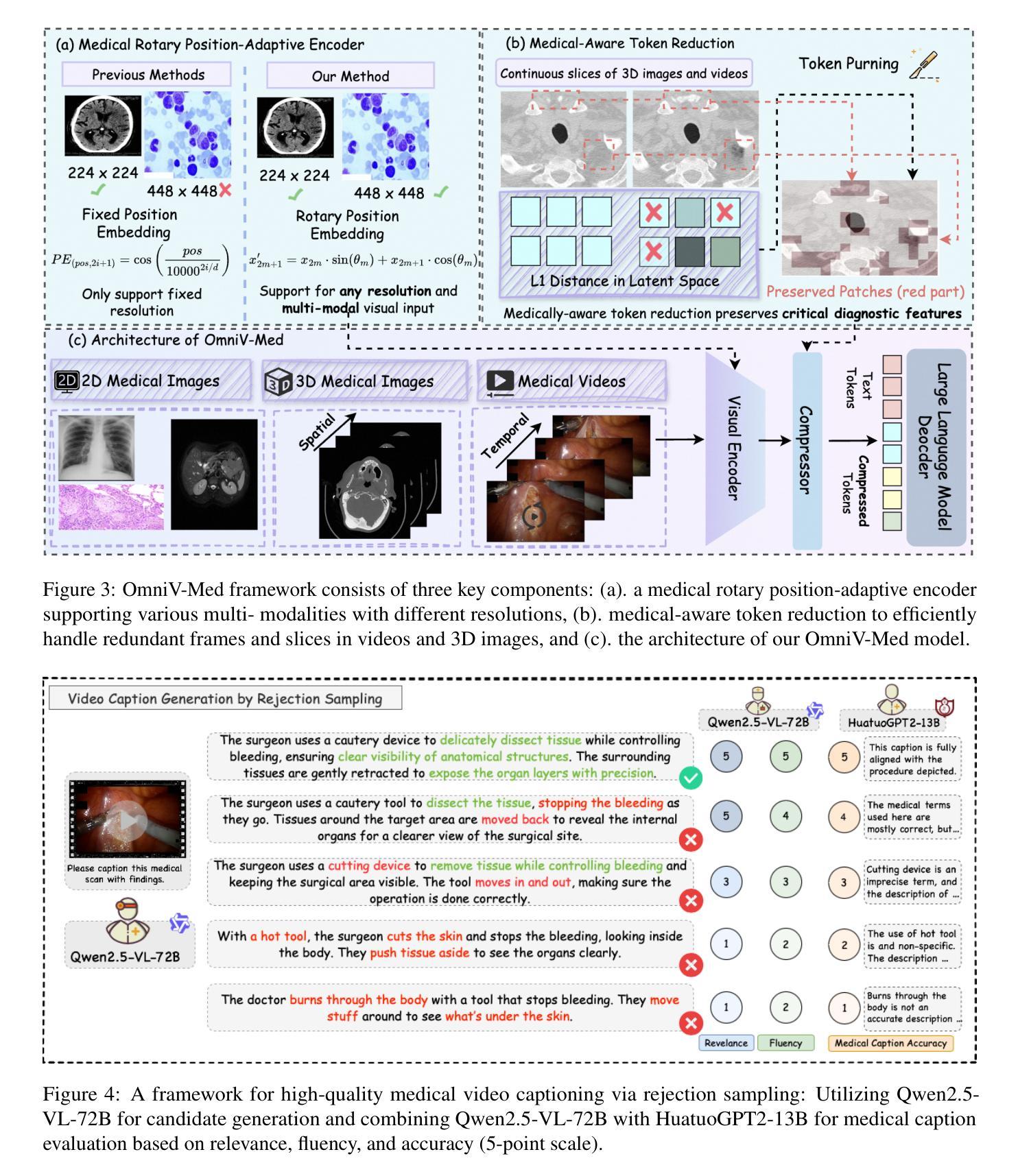
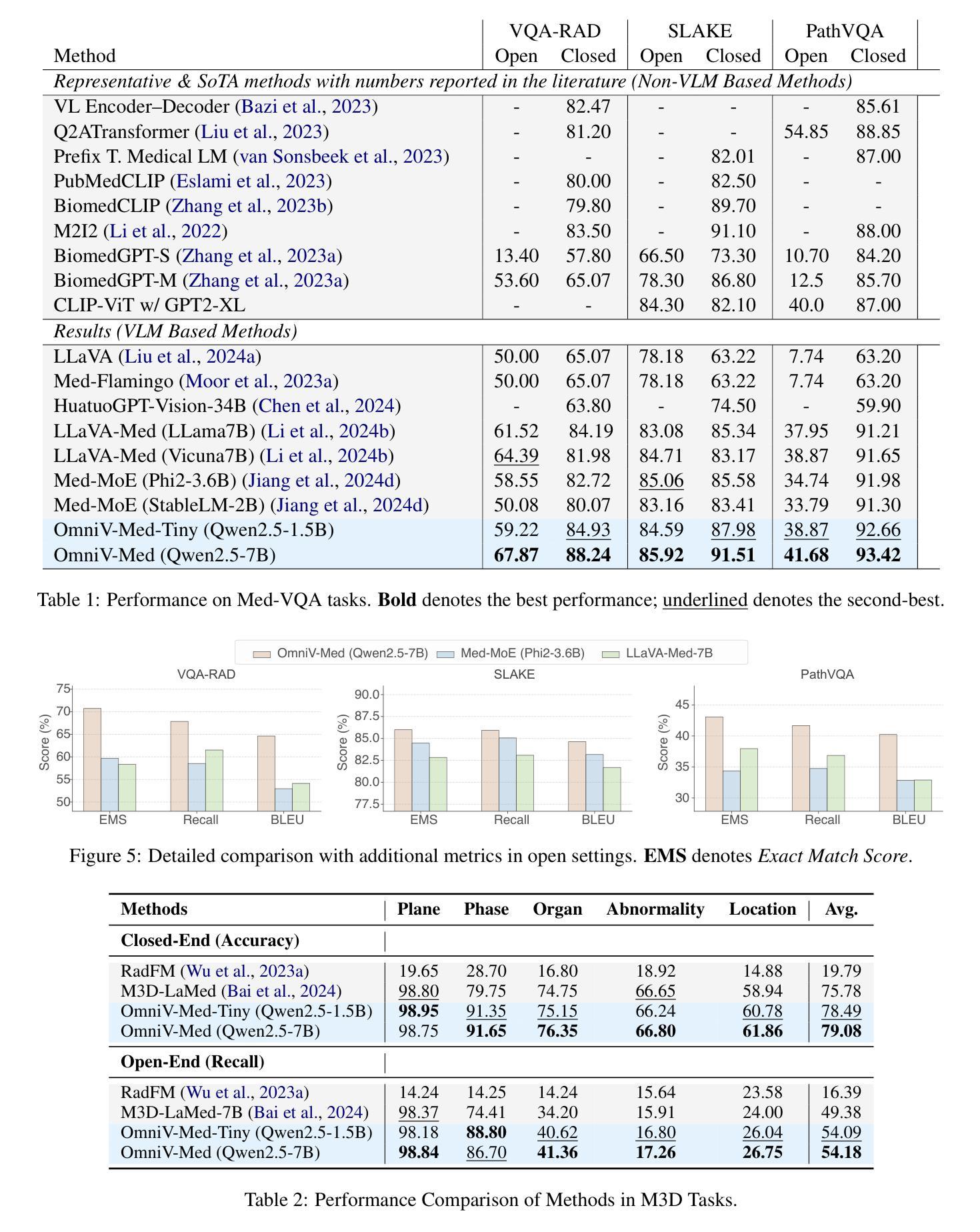
The practical deployment of medical vision-language models (Med-VLMs) necessitates seamless integration of textual data with diverse visual modalities, including 2D/3D images and videos, yet existing models typically employ separate encoders for different modalities. To address this limitation, we present OmniV-Med, a unified framework for multimodal medical understanding. Our technical contributions are threefold: First, we construct OmniV-Med-Instruct, a comprehensive multimodal medical dataset containing 252K instructional samples spanning 14 medical image modalities and 11 clinical tasks. Second, we devise a rotary position-adaptive encoder that processes multi-resolution 2D/3D images and videos within a unified architecture, diverging from conventional modality-specific encoders. Third, we introduce a medical-aware token pruning mechanism that exploits spatial-temporal redundancy in volumetric data (e.g., consecutive CT slices) and medical videos, effectively reducing 60% of visual tokens without performance degradation. Empirical evaluations demonstrate that OmniV-Med-7B achieves state-of-the-art performance on 7 benchmarks spanning 2D/3D medical imaging and video understanding tasks. Notably, our lightweight variant (OmniV-Med-1.5B) attains comparable performance while requiring only 8 RTX3090 GPUs for training and supporting efficient long-video inference. Data, code and model will be released.
医疗视觉语言模型(Med-VLMs)的实际部署需要无缝集成文本数据与包括二维/三维图像和视频在内的多种视觉模式。然而,现有模型通常针对不同模式使用单独的编码器。针对这一局限性,我们提出了OmniV-Med,这是一个用于多模式医疗理解的统一框架。我们的技术贡献有三点:首先,我们构建了OmniV-Med-Instruct,这是一个包含252K指令样本的综合多模式医疗数据集,涵盖14种医疗图像模式和11种临床任务。其次,我们设计了一种旋转位置自适应编码器,能够在统一架构中处理多分辨率的二维/三维图像和视频,与传统的模式特定编码器不同。第三,我们引入了一种医学感知令牌修剪机制,该机制利用体积数据(例如连续的CT切片)和医疗视频中的时空冗余,有效地减少了60%的视觉令牌,而不会对性能产生负面影响。经验评估表明,OmniV-Med-7B在涵盖二维/三维医学成像和视频理解任务的7个基准测试上达到了最先进的性能。值得注意的是,我们的轻量级变体(OmniV-Med-1.5B)在性能上与之相当,同时仅需要8个RTX3090 GPU进行训练,并支持高效的长视频推理。数据、代码和模型将公开发布。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
本文介绍了一个名为OmniV-Med的统一框架,用于多模态医学理解。该框架实现了文本数据与多种视觉模态(包括二维/三维图像和视频)的无缝集成。其主要贡献包括构建多模态医学数据集OmniV-Med-Instruct,设计旋转位置适应性编码器以及引入医学感知令牌修剪机制。该框架在二维/三维医学成像和视频理解任务上实现了最佳性能,并且提供了轻量级变体以支持高效的长视频推理。
Key Takeaways
- OmniV-Med框架实现了多模态医学数据的统一处理,包括二维/三维图像和视频。
- 构建了一个全面的多模态医学数据集OmniV-Med-Instruct,包含252K教学样本。
- 提出了旋转位置适应性编码器,能在统一架构中处理多分辨率的二维/三维图像和视频。
- 引入了医学感知令牌修剪机制,利用体积数据和医学视频的时空冗余性,有效减少视觉令牌数量。
- OmniV-Med框架在多个基准测试中实现了最佳性能,涵盖了二维/三维医学成像和视频理解任务。
- 提供了轻量级变体OmniV-Med-1.5B,可在8个RTX3090 GPU上进行训练,并支持高效的长视频推理。
点此查看论文截图

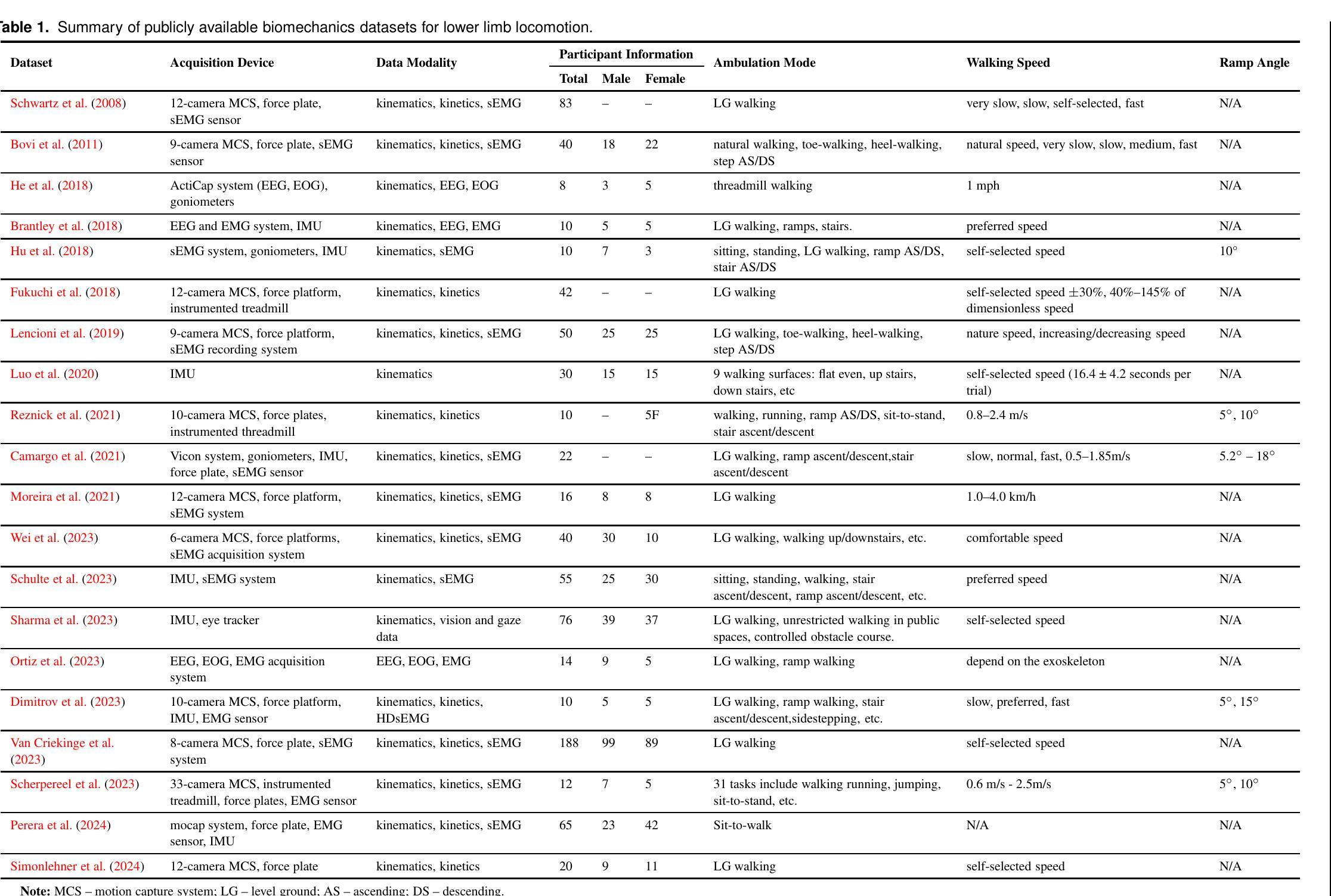
K2MUSE: A human lower limb multimodal dataset under diverse conditions for facilitating rehabilitation robotics
Authors:Jiwei Li, Bi Zhang, Xiaowei Tan, Wanxin Chen, Zhaoyuan Liu, Juanjuan Zhang, Weiguang Huo, Jian Huang, Lianqing Liu, Xingang Zhao
The natural interaction and control performance of lower limb rehabilitation robots are closely linked to biomechanical information from various human locomotion activities. Multidimensional human motion data significantly deepen the understanding of the complex mechanisms governing neuromuscular alterations, thereby facilitating the development and application of rehabilitation robots in multifaceted real-world environments. However, currently available lower limb datasets are inadequate for supplying the essential multimodal data and large-scale gait samples necessary for effective data-driven approaches, and they neglect the significant effects of acquisition interference in real applications.To fill this gap, we present the K2MUSE dataset, which includes a comprehensive collection of multimodal data, comprising kinematic, kinetic, amplitude-mode ultrasound (AUS), and surface electromyography (sEMG) measurements. The proposed dataset includes lower limb multimodal data from 30 able-bodied participants walking under different inclines (0$^\circ$, $\pm$5$^\circ$, and $\pm$10$^\circ$), various speeds (0.5 m/s, 1.0 m/s, and 1.5 m/s), and different nonideal acquisition conditions (muscle fatigue, electrode shifts, and inter-day differences). The kinematic and ground reaction force data were collected via a Vicon motion capture system and an instrumented treadmill with embedded force plates, whereas the sEMG and AUS data were synchronously recorded for thirteen muscles on the bilateral lower limbs. This dataset offers a new resource for designing control frameworks for rehabilitation robots and conducting biomechanical analyses of lower limb locomotion. The dataset is available at https://k2muse.github.io/.
下文详细阐述了下肢康复机器人的自然交互与控制性能与各种人类运动活动的生物力学信息之间的紧密联系。多维度的运动数据极大地加深了我们对神经肌肉改变控制的复杂机制的理解,从而促进了康复机器人在多方面的真实世界环境中的开发和应用。然而,当前可用的下肢数据集不足以提供必要的多模式数据和大规模的步态样本,无法满足有效的数据驱动方法的需求,而且它们忽视了真实应用中采集干扰的显著影响。为了填补这一空白,我们推出了K2MUSE数据集,其中包括全面的多模式数据集合,包括运动学、动力学、振幅模式超声(AUS)和表面肌电图(sEMG)测量值。所提出的数据集包括来自30名身体健全者在不同的倾斜度(0°, ±5°, 和±10°)、各种速度(0.5 m/s, 1.0 m/s, 和 1.5 m/s)和不同非理想采集条件(肌肉疲劳、电极移位和日间差异)下的下肢多模式数据。运动学和地面反应力数据是通过Vicon动作捕捉系统和配备力板的仪器化跑步机收集的,而sEMG和AUS数据则同步记录了双腿的十三块肌肉。该数据集为设计康复机器人的控制框架和进行下肢运动生物力学分析提供了新的资源。数据集可在https://k2muse.github.io/获取。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF 23 pages, 13 figures,4 tables
Summary
本文介绍了K2MUSE数据集,该数据集包含多种模式的数据,包括运动学、动力学、振幅模式超声波(AUS)和表面肌电图(sEMG)测量值。数据集包含30名身体健全者在不同坡度、速度和非理想采集条件下的下肢多模式数据。该数据集为康复机器人的控制框架设计和下肢运动生物力学分析提供了新的资源。
Key Takeaways
- K2MUSE数据集包含多种模式的数据,如运动学、动力学、AUS和sEMG测量值,用于深入分析下肢康复机制。
- 数据集包含来自30名身体健全者的下肢多模式数据,涵盖了不同的行走条件,如坡度、速度和肌肉状态。
- 数据集考虑了非理想采集条件,如肌肉疲劳、电极移位和日间差异,增加了数据的实用性。
- K2MUSE数据集有助于为康复机器人设计控制框架,并进行下肢运动的生物力学分析。
- 数据集可通过https://k2muse.github.io/访问。
- 该数据集的重要性在于填补了现有下肢数据集在提供必要多模式数据和大规模步态样本方面的不足。
点此查看论文截图


LGD: Leveraging Generative Descriptions for Zero-Shot Referring Image Segmentation
Authors:Jiachen Li, Qing Xie, Xiaohan Yu, Hongyun Wang, Jinyu Xu, Yongjian Liu, Yongsheng Gao
Zero-shot referring image segmentation aims to locate and segment the target region based on a referring expression, with the primary challenge of aligning and matching semantics across visual and textual modalities without training. Previous works address this challenge by utilizing Vision-Language Models and mask proposal networks for region-text matching. However, this paradigm may lead to incorrect target localization due to the inherent ambiguity and diversity of free-form referring expressions. To alleviate this issue, we present LGD (Leveraging Generative Descriptions), a framework that utilizes the advanced language generation capabilities of Multi-Modal Large Language Models to enhance region-text matching performance in Vision-Language Models. Specifically, we first design two kinds of prompts, the attribute prompt and the surrounding prompt, to guide the Multi-Modal Large Language Models in generating descriptions related to the crucial attributes of the referent object and the details of surrounding objects, referred to as attribute description and surrounding description, respectively. Secondly, three visual-text matching scores are introduced to evaluate the similarity between instance-level visual features and textual features, which determines the mask most associated with the referring expression. The proposed method achieves new state-of-the-art performance on three public datasets RefCOCO, RefCOCO+ and RefCOCOg, with maximum improvements of 9.97% in oIoU and 11.29% in mIoU compared to previous methods.
零样本指代图像分割旨在基于指代表达式定位并分割目标区域,其主要挑战在于在没有训练的情况下实现视觉和文本模态之间的语义对齐和匹配。之前的工作通过利用视觉语言模型和掩膜提案网络进行区域文本匹配来解决这一挑战。然而,这种范式可能导致由于自由形式的指代表达式固有的模糊性和多样性而导致目标定位错误。为了缓解这个问题,我们提出了LGD(利用生成描述),一个利用多模态大型语言模型的先进语言生成能力来提高视觉语言模型中区域文本匹配性能的框架。具体来说,我们首先设计两种提示,属性提示和周围提示,来引导多模态大型语言模型生成与指代对象的关键属性和周围对象的细节相关的描述,分别称为属性描述和周围描述。其次,引入了三种视觉文本匹配分数,以评估实例级视觉特征与文本特征之间的相似性,从而确定与指代表达式最相关的掩膜。所提出的方法在RefCOCO、RefCOCO+和RefCOCOg三个公共数据集上实现了最新性能,与以前的方法相比,在IoU和mIoU方面分别提高了最高9.97%和11.29%。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
本文提出一种利用多模态大型语言模型的生成描述能力,增强视觉语言模型在零样本图像分割中的区域文本匹配性能的方法。通过设计属性提示和环绕提示,生成与指代对象的关键属性和周围对象相关的描述,引入三种视觉文本匹配评分,提高指代表达式与实例级视觉特征的相似性评估准确性。该方法在三个公共数据集上取得了最新性能。
Key Takeaways
- 零样本图像分割旨在根据引用表达式定位并分割目标区域,主要挑战是在视觉和文本模态之间实现语义对齐和匹配,而无需训练。
- 现有方法通过利用视觉语言模型和掩膜提案网络进行区域文本匹配来解决这一挑战。
- 现有方法可能因自由形式的引用表达式固有的模糊性和多样性而导致目标定位错误。
- LGD(利用生成描述)框架通过利用多模态大型语言模型的先进语言生成能力来增强区域文本匹配性能。
- LGD设计了属性提示和环绕提示,以生成与指代对象的关键属性和周围对象相关的描述,称为属性描述和环绕描述。
- 引入三种视觉文本匹配评分,以评估实例级视觉特征与文本特征之间的相似性,从而确定与引用表达式最相关的掩膜。
点此查看论文截图


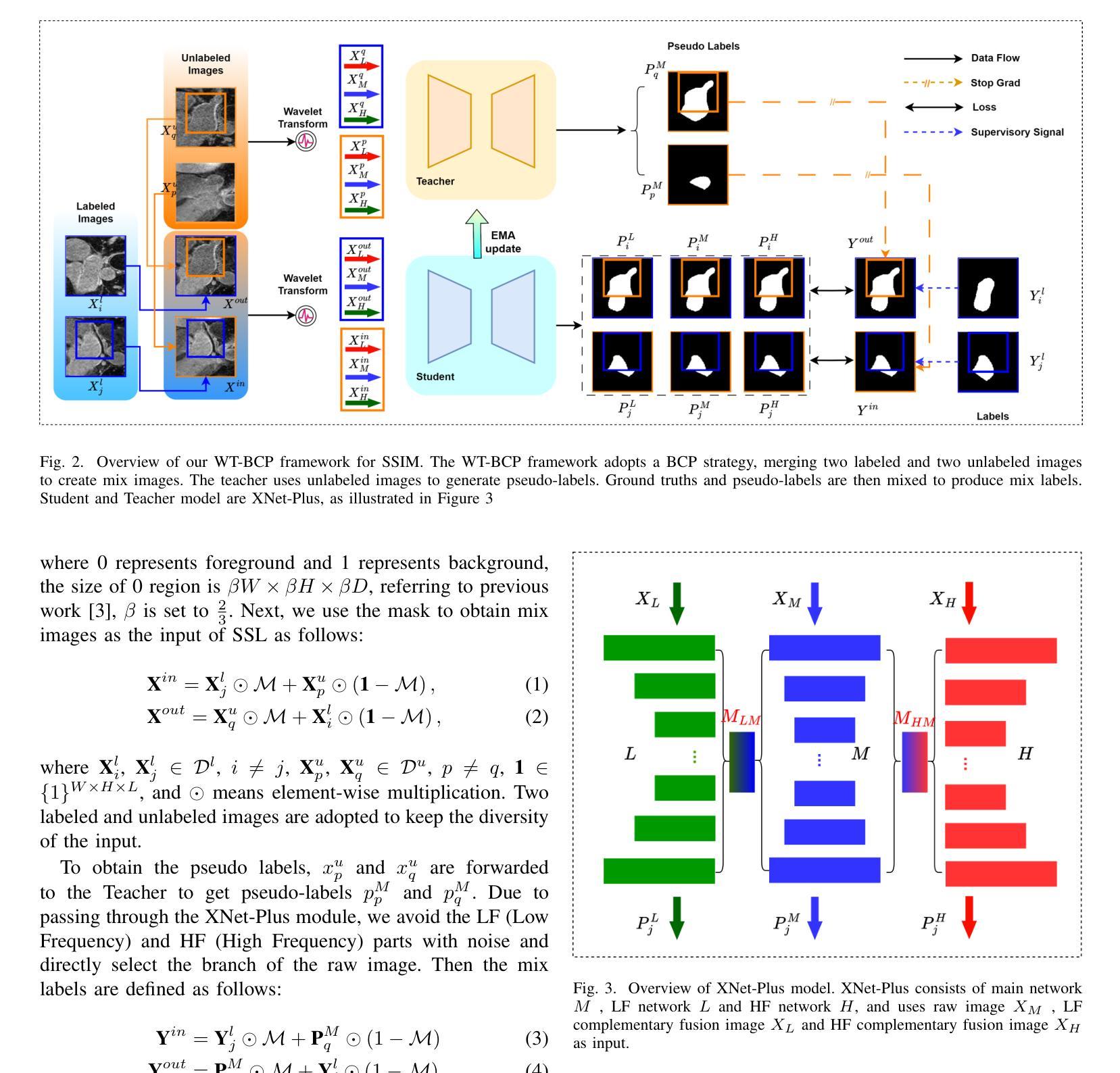
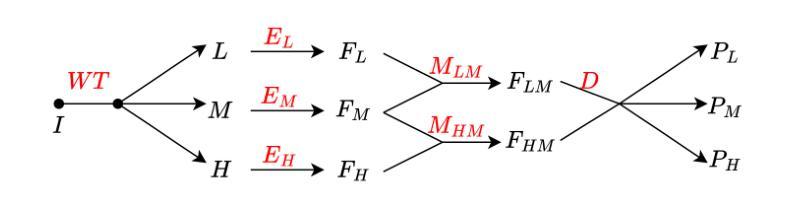
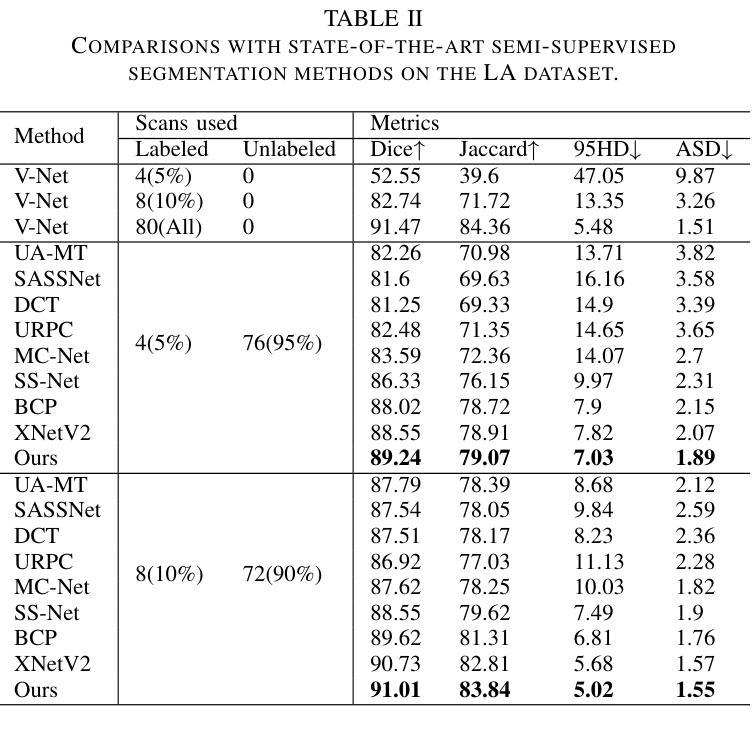
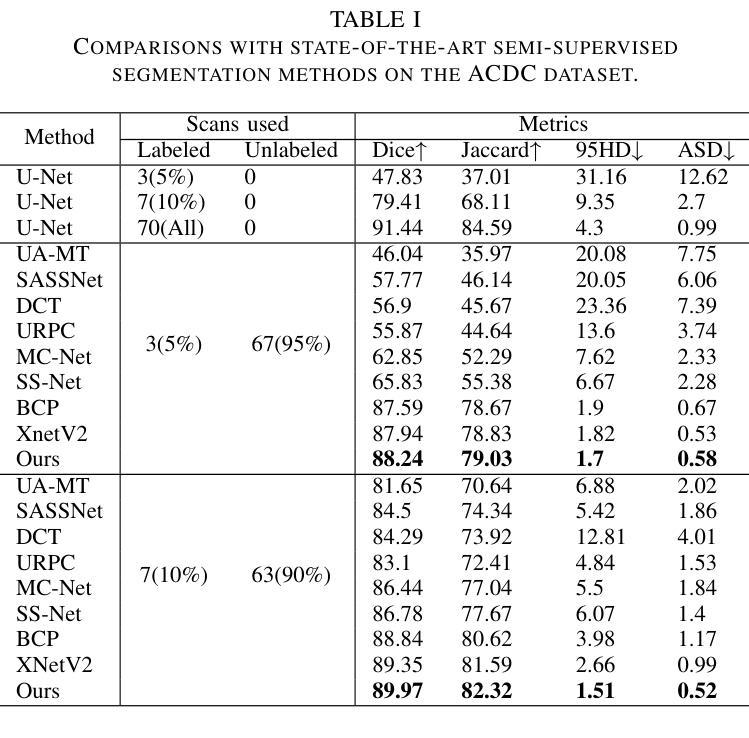
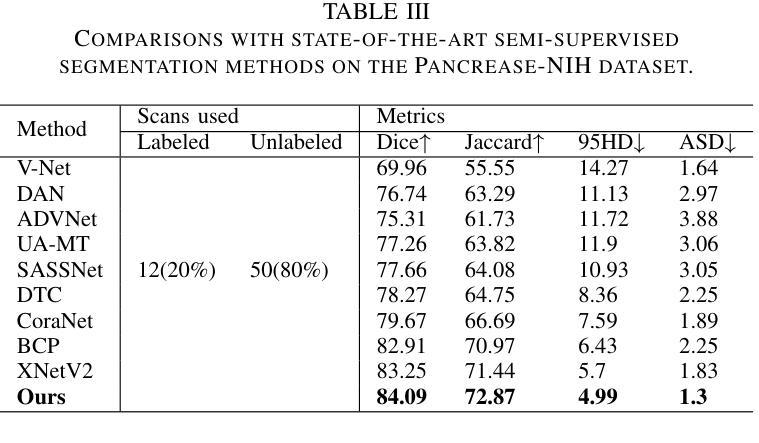
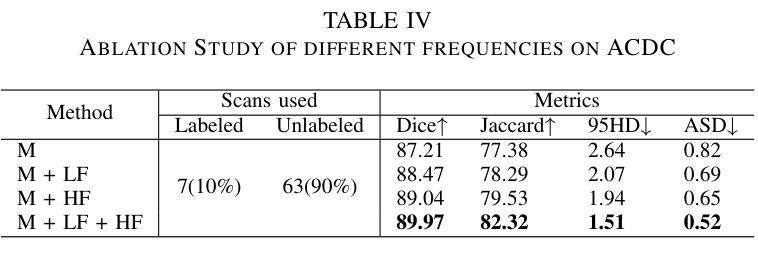
WT-BCP: Wavelet Transform based Bidirectional Copy-Paste for Semi-Supervised Medical Image Segmentation
Authors:Mingya Zhang, Liang Wang, Limei Gu, Tingsheng Ling, Xianping Tao
Semi-supervised medical image segmentation (SSMIS) shows promise in reducing reliance on scarce labeled medical data. However, SSMIS field confronts challenges such as distribution mismatches between labeled and unlabeled data, artificial perturbations causing training biases, and inadequate use of raw image information, especially low-frequency (LF) and high-frequency (HF) components.To address these challenges, we propose a Wavelet Transform based Bidirectional Copy-Paste SSMIS framework, named WT-BCP, which improves upon the Mean Teacher approach. Our method enhances unlabeled data understanding by copying random crops between labeled and unlabeled images and employs WT to extract LF and HF details.We propose a multi-input and multi-output model named XNet-Plus, to receive the fused information after WT. Moreover, consistency training among multiple outputs helps to mitigate learning biases introduced by artificial perturbations. During consistency training, the mixed images resulting from WT are fed into both models, with the student model’s output being supervised by pseudo-labels and ground-truth. Extensive experiments conducted on 2D and 3D datasets confirm the effectiveness of our model.Code: https://github.com/simzhangbest/WT-BCP.
半监督医学图像分割(SSMIS)在减少对稀缺标记医学数据的依赖方面显示出巨大的潜力。然而,SSMIS领域面临着诸多挑战,如标记和无标记数据分布不匹配、人为扰动导致训练偏见以及未充分利用原始图像信息,特别是低频(LF)和高频(HF)成分。为了应对这些挑战,我们提出了一种基于小波变换的双向复制粘贴SSMIS框架,名为WT-BCP,该框架改进了Mean Teacher方法。我们的方法通过在有标签和无标签图像之间复制随机裁剪部分来提高对无标签数据的理解,并利用WT提取LF和HF细节。我们提出了一种名为XNet-Plus的多输入多输出模型,以接收WT融合后的信息。此外,多个输出之间的一致性训练有助于减轻人为扰动引入的学习偏见。在一致性训练过程中,通过WT生成的混合图像被输入到两个模型中,学生模型的输出受到伪标签和真实标签的监督。在二维和三维数据集上进行的广泛实验证实了我们的模型的有效性。代码地址:https://github.com/simzhangbest/WT-BCP。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF 6 pages
Summary
医学图像半监督分割(SSMIS)面临挑战,如数据分布不匹配、训练偏见以及低频(LF)和高频(HF)成分的使用不足等。为此,提出基于小波变换的双向复制粘贴SSMIS框架WT-BCP,改进Mean Teacher方法,提高未标记数据理解,通过WT提取LF和HF细节。同时引入多输入多输出模型XNet-Plus和一致性训练策略来缓解学习偏见。代码开源。
Key Takeaways
- SSMIS技术在减少依赖稀缺标记医学数据方面展现潜力。
- 目前SSMIS面临挑战包括数据分布不匹配、训练偏见以及低频高频成分使用不足等。
- WT-BCP框架通过小波变换改善未标记数据理解。
- WT-BCP采用基于Mean Teacher方法的改进。
- XNet-Plus模型用于接收小波变换后的融合信息。
- 一致性训练策略有助于缓解由人工扰动引入的学习偏见。
点此查看论文截图

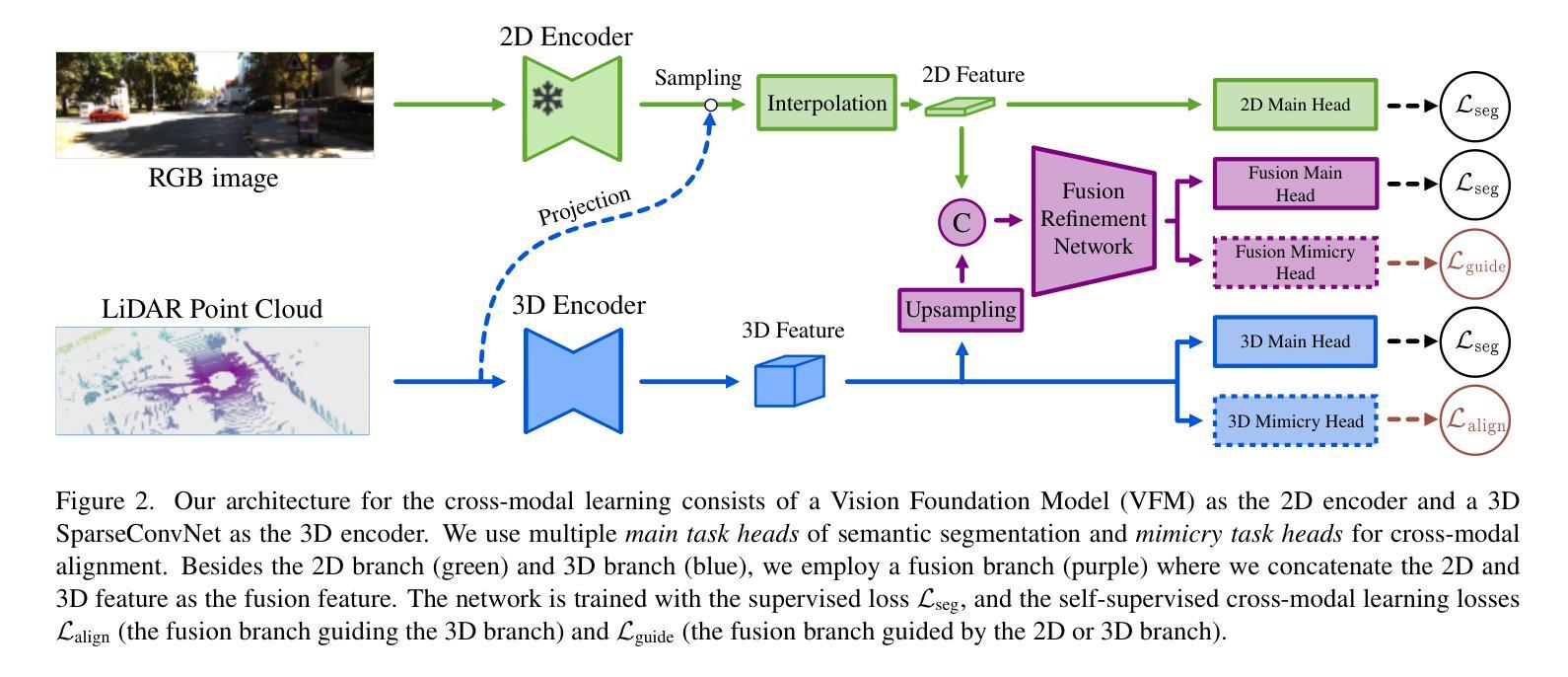
Exploring Modality Guidance to Enhance VFM-based Feature Fusion for UDA in 3D Semantic Segmentation
Authors:Johannes Spoecklberger, Wei Lin, Pedro Hermosilla, Sivan Doveh, Horst Possegger, M. Jehanzeb Mirza
Vision Foundation Models (VFMs) have become a de facto choice for many downstream vision tasks, like image classification, image segmentation, and object localization. However, they can also provide significant utility for downstream 3D tasks that can leverage the cross-modal information (e.g., from paired image data). In our work, we further explore the utility of VFMs for adapting from a labeled source to unlabeled target data for the task of LiDAR-based 3D semantic segmentation. Our method consumes paired 2D-3D (image and point cloud) data and relies on the robust (cross-domain) features from a VFM to train a 3D backbone on a mix of labeled source and unlabeled target data. At the heart of our method lies a fusion network that is guided by both the image and point cloud streams, with their relative contributions adjusted based on the target domain. We extensively compare our proposed methodology with different state-of-the-art methods in several settings and achieve strong performance gains. For example, achieving an average improvement of 6.5 mIoU (over all tasks), when compared with the previous state-of-the-art.
视觉基础模型(VFMs)已成为许多下游视觉任务(如图像分类、图像分割和对象定位)的实际选择。然而,它们也可以为下游的3D任务提供重要效用,这些任务可以利用跨模态信息(例如,来自配对图像数据)。在我们的工作中,我们进一步探索了VFM在激光雷达基于的3D语义分割任务中的用途,该任务从标记源数据适应到无标记目标数据。我们的方法使用配对2D-3D(图像和点云)数据,并依赖于VFM的稳健(跨域)特征,在标记源数据和无标记目标数据的混合上训练一个3D主干。我们方法的核心是一个融合网络,该网络由图像和点云流共同引导,并根据目标域调整它们的相对贡献。我们在不同的设置下与不同的最先进方法进行了广泛的比较,并实现了强大的性能提升。例如,与以前的最先进方法相比,在所有任务上的平均提高了6.5 mIoU。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
本文探讨了Vision Foundation Models(VFMs)在LiDAR基于的3D语义分割任务中的适用性。研究利用配对2D-3D数据进行跨域特征提取,通过VFM训练3D骨干网,并借助融合网络结合图像和点云流,实现源到目标域的适应。该研究在不同设置下与其他先进方法进行比较,取得了显著的性能提升,例如在所有任务上平均提高了6.5 mIoU。
Key Takeaways
- Vision Foundation Models (VFMs) 可以为下游的3D任务提供显著效用,特别是在利用跨模态信息的情况下。
- 研究探索了VFM在LiDAR-based 3D语义分割任务中的适应性问题,从标签源数据适应到无标签目标数据。
- 研究利用配对2D-3D数据(图像和点云)进行训练,并依赖VFM的稳健跨域特征。
- 融合网络是该方法的核心,它结合了图像和点云流,并根据目标域调整其相对贡献。
- 与其他先进方法相比,该方法在多个设置下实现了显著的性能提升。
- 该研究在所有任务上实现了平均6.5 mIoU的提升,这显示了其方法的优越性。
点此查看论文截图

Association between nutritional factors, inflammatory biomarkers and cancer types: an analysis of NHANES data using machine learning
Authors:Yuqing Liu, Meng Zhao, Guanlan Hu, Yuchen Zhang
Background. Diet and inflammation are critical factors influencing cancer risk. However, the combined impact of nutritional status and inflammatory biomarkers on cancer status and type, using machine learning (ML), remains underexplored. Objectives. This study investigates the association between nutritional factors, inflammatory biomarkers, and cancer status, and whether these relationships differ across cancer types using National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey (NHANES) data. Methods. We analyzed 24 macro- and micronutrients, C-reactive protein (CRP), and the advanced lung cancer inflammation index (ALI) in 26,409 NHANES participants (2,120 with cancer). Multivariable logistic regression assessed associations with cancer prevalence. We also examined whether these features differed across the five most common cancer types. To evaluate predictive value, we applied three ML models - Logistic Regression, Random Forest, and XGBoost - on the full feature set. Results. The cohort’s mean age was 49.1 years; 34.7% were obese. Comorbidities such as anemia and liver conditions, along with nutritional factors like protein and several vitamins, were key predictors of cancer status. Among the models, Random Forest performed best, achieving an accuracy of 0.72. Conclusions. Higher-quality nutritional intake and lower levels of inflammation may offer protective effects against cancer. These findings highlight the potential of combining nutritional and inflammatory markers with ML to inform cancer prevention strategies.
背景。饮食和炎症是影响癌症风险的关键因素。然而,使用机器学习(ML)结合营养状况和炎症生物标志物对癌症状况和类型的影响的研究仍然不足。目标。本研究旨在探讨营养因素、炎症生物标志物与癌症状况之间的关联,并研究这些关系在不同癌症类型中是否有所不同,同时使用国家健康和营养检查调查(NHANES)数据进行分析。方法。我们分析了NHANES的26409名参与者(其中2120名患有癌症)的24种宏量和微量元素、C反应蛋白(CRP)和高级肺癌炎症指数(ALI)。多元逻辑回归用于评估与癌症发病率的关系。我们还检查了这些特征是否在五种最常见的癌症类型中存在差异。为了评估预测价值,我们在整个特征集上应用了三种机器学习模型,包括逻辑回归、随机森林和XGBoost。结果。该队列的平均年龄为49.1岁,其中34.7%为肥胖人群。贫血和肝脏疾病等伴随疾病,以及蛋白质和各种维生素等营养因素,是癌症状况的主要预测因素。在模型中,随机森林表现最佳,准确率为0.72。结论。高质量的营养摄入和较低的炎症水平可能对预防癌症具有保护作用。这些发现强调了结合营养和炎症标志物与机器学习来为癌症预防策略提供信息的潜力。
论文及项目相关链接
摘要
医学研究表明饮食与炎症是癌症风险的重要影响因素。本研究使用全国健康和营养普查数据,调查营养因素、炎症标志物与癌症状态之间的关联,并探索这些关系在不同癌症类型中是否有差异。分析显示,贫血和肝脏疾病等并发疾病以及蛋白质和维生素等营养因素都是癌症状况的关键预测因子。机器学习模型(随机森林模型)的预测准确性最高,达到0.72。研究指出优质营养摄入和较低的炎症水平可能对预防癌症有保护作用。结合营养和炎症标志物与机器学习有助于制定癌症预防策略。
关键要点
- 饮食与炎症是癌症风险的关键因素。
- 本研究利用全国健康和营养普查数据,探讨了营养因素、炎症标志物与癌症状态的关系。
- 并发疾病如贫血和肝脏疾病以及营养因素如蛋白质和多种维生素,都是预测癌症的关键因素。
- 机器学习模型(随机森林模型)显示出最高的预测准确性。
- 优质营养摄入和较低的炎症水平可能有助于预防癌症。
点此查看论文截图

Stochastic momentum ADMM for nonconvex and nonsmooth optimization with application to PnP algorithm
Authors:Kangkang Deng, Shuchang Zhang, Boyu Wang, Jiachen Jin, Juan Zhou, Hongxia Wang
This paper proposes SMADMM, a single-loop Stochastic Momentum Alternating Direction Method of Multipliers for solving a class of nonconvex and nonsmooth composite optimization problems. SMADMM achieves the optimal oracle complexity of $\mathcal{O}(\epsilon^{-3/2})$ in the online setting. Unlike previous stochastic ADMM algorithms that require large mini-batches or a double-loop structure, SMADMM uses only $\mathcal{O}(1)$ stochastic gradient evaluations per iteration and avoids costly restarts. To further improve practicality, we incorporate dynamic step sizes and penalty parameters, proving that SMADMM maintains its optimal complexity without the need for large initial batches. We also develop PnP-SMADMM by integrating plug-and-play priors, and establish its theoretical convergence under mild assumptions. Extensive experiments on classification, CT image reconstruction, and phase retrieval tasks demonstrate that our approach outperforms existing stochastic ADMM methods both in accuracy and efficiency, validating our theoretical results.
本文提出了SMADMM,这是一种单环随机动量交替方向法(Stochastic Momentum Alternating Direction Method of Multipliers),用于解决一类非凸非光滑复合优化问题。SMADMM在在线设置下达到了最优的$\mathcal{O}(\epsilon^{-3/2})$的Oracle复杂性。不同于之前需要大批量微批处理或双重循环结构的随机ADMM算法,SMADMM每次迭代只使用$\mathcal{O}(1)$个随机梯度评估,避免了昂贵的重新启动。为了进一步提高实用性,我们引入了动态步长和惩罚参数,证明了SMADMM在不需要大量初始批次的情况下,仍能维持其最优复杂性。我们还通过集成即插即用先验(plug-and-play priors)开发了PnP-SMADMM,并在温和假设下建立了其理论收敛性。在分类、CT图像重建和相位检索任务上的大量实验表明,我们的方法在准确性和效率上均优于现有的随机ADMM方法,验证了我们的理论结果。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF 27 Pages
Summary
本文提出了一种名为SMADMM的单循环随机动量交替方向法,用于解决一类非凸和非光滑复合优化问题。SMADMM在线环境中实现了最优的$\mathcal{O}(\epsilon^{-3/2})$复杂度。与需要大型迷你批次或双重循环结构的先前随机ADMM算法不同,SMADMM每次迭代仅使用$\mathcal{O}(1)$随机梯度评估,避免了昂贵的重新启动。通过融入动态步长和惩罚参数,我们证明SMADMM在不需要大型初始批次的情况下也能保持其最优复杂度。此外,我们开发了PnP-SMADMM,通过整合即插即用先验,并在温和的假设下建立了其理论收敛性。在分类、CT图像重建和相位检索任务上的广泛实验表明,我们的方法在准确性和效率上都优于现有的随机ADMM方法,验证了我们的理论结果。
Key Takeaways
- SMADMM是一种用于解决非凸和非光滑复合优化问题的单循环随机动量交替方向法。
- SMADMM实现了在线环境中的最优$\mathcal{O}(\epsilon^{-3/2})$复杂度。
- 与其他随机ADMM算法不同,SMADMM每次迭代仅使用$\mathcal{O}(1)$随机梯度评估,避免了重启成本。
- SMADMM通过融入动态步长和惩罚参数,在不需要大型初始批次的情况下也能保持最优复杂度。
- 开发了PnP-SMADMM,结合了即插即用先验,增强了实用性。
- PnP-SMADMM在分类、CT图像重建和相位检索等任务上表现优异,理论和实际表现均优于现有随机ADMM方法。
点此查看论文截图

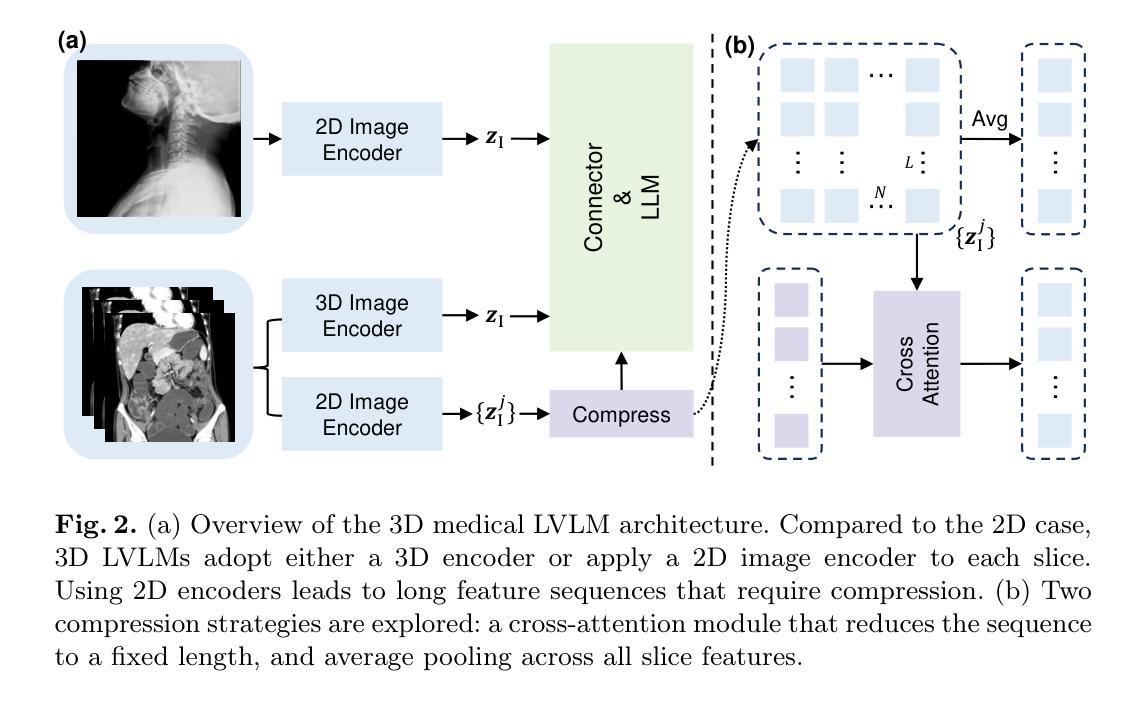
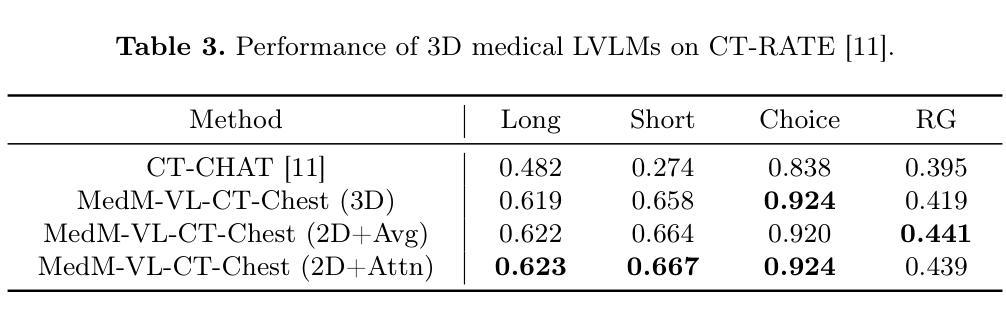
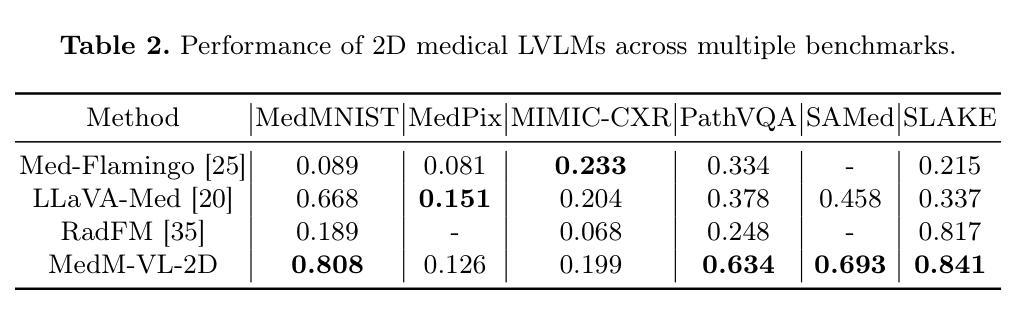
MedM-VL: What Makes a Good Medical LVLM?
Authors:Yiming Shi, Shaoshuai Yang, Xun Zhu, Haoyu Wang, Miao Li, Ji Wu
Medical image analysis is essential in modern healthcare. Deep learning has redirected research focus toward complex medical multimodal tasks, including report generation and visual question answering. Traditional task-specific models often fall short in handling these challenges. Large vision-language models (LVLMs) offer new solutions for solving such tasks. In this study, we build on the popular LLaVA framework to systematically explore model architectures and training strategies for both 2D and 3D medical LVLMs. We present extensive empirical findings and practical guidance. To support reproducibility and future research, we release a modular codebase, MedM-VL, and two pre-trained models: MedM-VL-2D for 2D medical image analysis and MedM-VL-CT-Chest for 3D CT-based applications. The code and models are available at: https://github.com/MSIIP/MedM-VL
现代医学中,医学图像分析扮演着至关重要的角色。深度学习将研究焦点转向了复杂的医学多模态任务,包括报告生成和视觉问答。传统的针对特定任务的模型在处理这些挑战时往往力不从心。大型视觉语言模型(LVLMs)为解决此类任务提供了新的解决方案。在这项研究中,我们以流行的LLaVA框架为基础,系统地探索了用于二维和三维医学LVLMs的模型架构和训练策略。我们提供了丰富的实证结果和实践指导。为了支持可复制性和未来的研究,我们发布了一个模块化代码库MedM-VL和两个预训练模型:用于二维医学图像分析的MedM-VL-2D和用于基于三维CT应用的MedM-VL-CT-Chest。代码和模型可在https://github.com/MSIIP/MedM-VL获取。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
本文介绍了医学图像分析在现代医疗中的重要性,深度学习在解决复杂医学多模态任务(如报告生成和视觉问答)方面的应用。传统的任务特定模型在处理这些挑战时常常不足。大型视觉语言模型(LVLMs)为解决这些任务提供了新的解决方案。本研究基于流行的LLaVA框架,系统地探索了二维和三维医学LVLM的模型架构和训练策略,并提供丰富的实证研究和实用指导。为支持复现和未来研究,我们发布了模块化代码库MedM-VL和两个预训练模型:用于二维医学图像分析的MedM-VL-2D和用于三维CT应用的MedM-VL-CT-Chest。
Key Takeaways
- 医学图像分析在现代医疗中的重要性。
- 深度学习在解决复杂医学多模态任务中的应用。
- 传统任务特定模型在处理多模态任务时的局限性。
- 大型视觉语言模型(LVLMs)为解决医学多模态任务提供新方案。
- 基于LLaVA框架探索了二维和三维医学LVLM的模型架构和训练策略。
- 提供了丰富的实证研究和实用指导。
点此查看论文截图

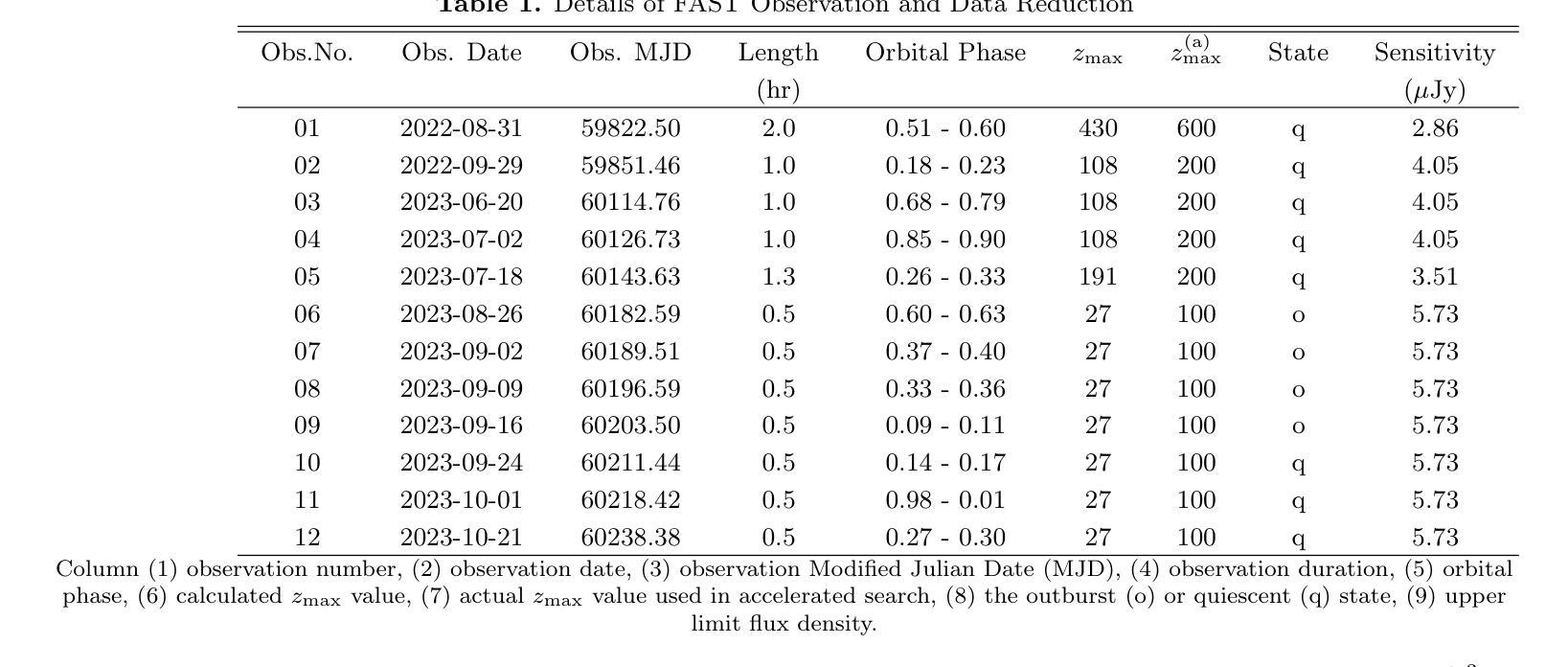
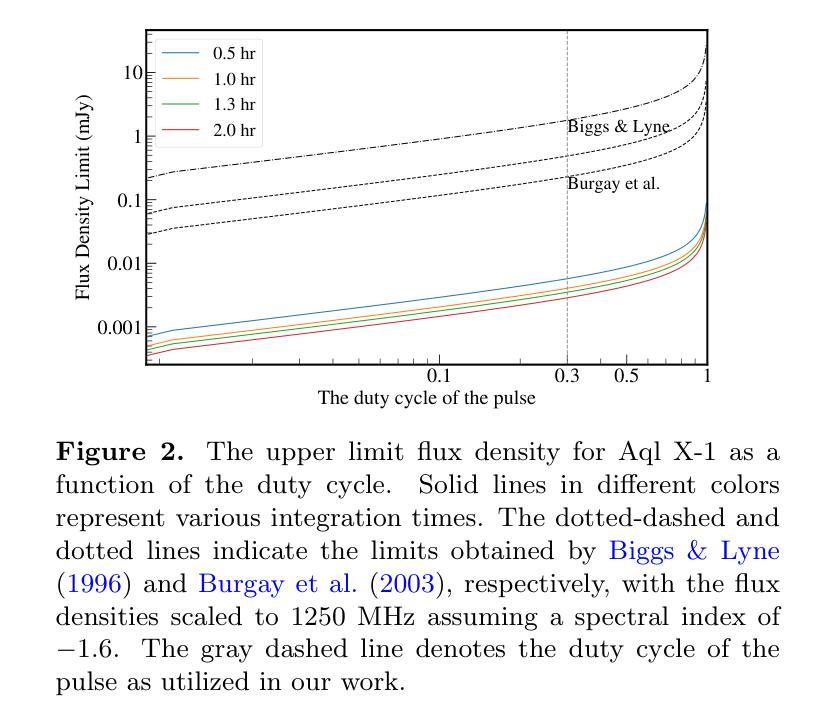
Radio pulse search from Aql X-1
Authors:Long Peng, Zhaosheng Li, Yuanyue Pan, Shanshan Weng, Wengming Yan, Na Wang, Bojun Wang, Shuangqiang Wang
We present 12 observations of the accreting millisecond X-ray pulsar Aql X-1, taken from August 2022 to October 2023 using the Five-hundred-meter Aperture Spherical Radio Telescope at 1250 MHz. These observations covered both the quiescence and X-ray outburst states, as determined by analyzing the X-ray data from the Neutron Star Interior Composition Explorer and the Monitor of All-sky X-ray Image. Periodicity and single-pulse searches were conducted for each observation, but no pulsed signals were detected. The obtained upper limit flux densities are in the range of 2.86-5.73 uJy, which provide the lowest limits to date. We discuss several mechanisms that may prevent detection, suggesting that Aql X-1 may be in the radio-ejection state during quiescence, where the radio pulsed emissions are absorbed by the matter surrounding the system.
我们展示了使用口径为五百米球面射电望远镜在1250兆赫下从2022年8月到2023年10月对增亮型毫秒X射线脉冲星Aql X-1进行的12次观测结果。这些观测涵盖了静止期和X射线爆发状态,这是通过分析来自中子星内部结构探测器和全天空X射线图像监测器的X射线数据来确定的。我们对每次观测进行了周期性和单脉冲搜索,但没有检测到脉冲信号。所获得的流量密度上限范围为2.86-5.73微焦耳/平方分米,这是迄今为止的最低限度。我们讨论了可能阻止探测的几种机制,并提出Aql X-1可能在静止期处于射电喷射状态,射电脉冲发射被系统周围的物质吸收。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF 8 pages, 2 figures, submitted to ApJ on December 10, 2024; accepted for publication on March 4, 2025; published on April 3, 2025
Summary
利用500米口径球面望远镜在1250兆赫的频率下,我们对渐增型毫秒X射线脉冲星Aql X-1进行了为期一年半的观察。分析结果涵盖其静止和X射线爆发状态,但未检测到脉冲信号。获得的上限流量密度范围在2.86-5.73微焦耳之间,为目前最低值。讨论了可能阻碍检测的几个机制,推测Aql X-1在静止期可能处于无线电喷射状态,无线电脉冲发射被系统周围的物质吸收。
Key Takeaways
- 使用500米口径球面望远镜进行了Aql X-1的观察。
- 观察频率是1250兆赫,时间从2022年8月到2023年10月。
- 分析了Aql X-1的静止和X射线爆发状态。
- 未检测到脉冲信号。
- 获得的上限流量密度范围在2.86-5.73微焦耳之间,为目前最低值。
- 讨论了可能阻碍检测的几个机制。
点此查看论文截图


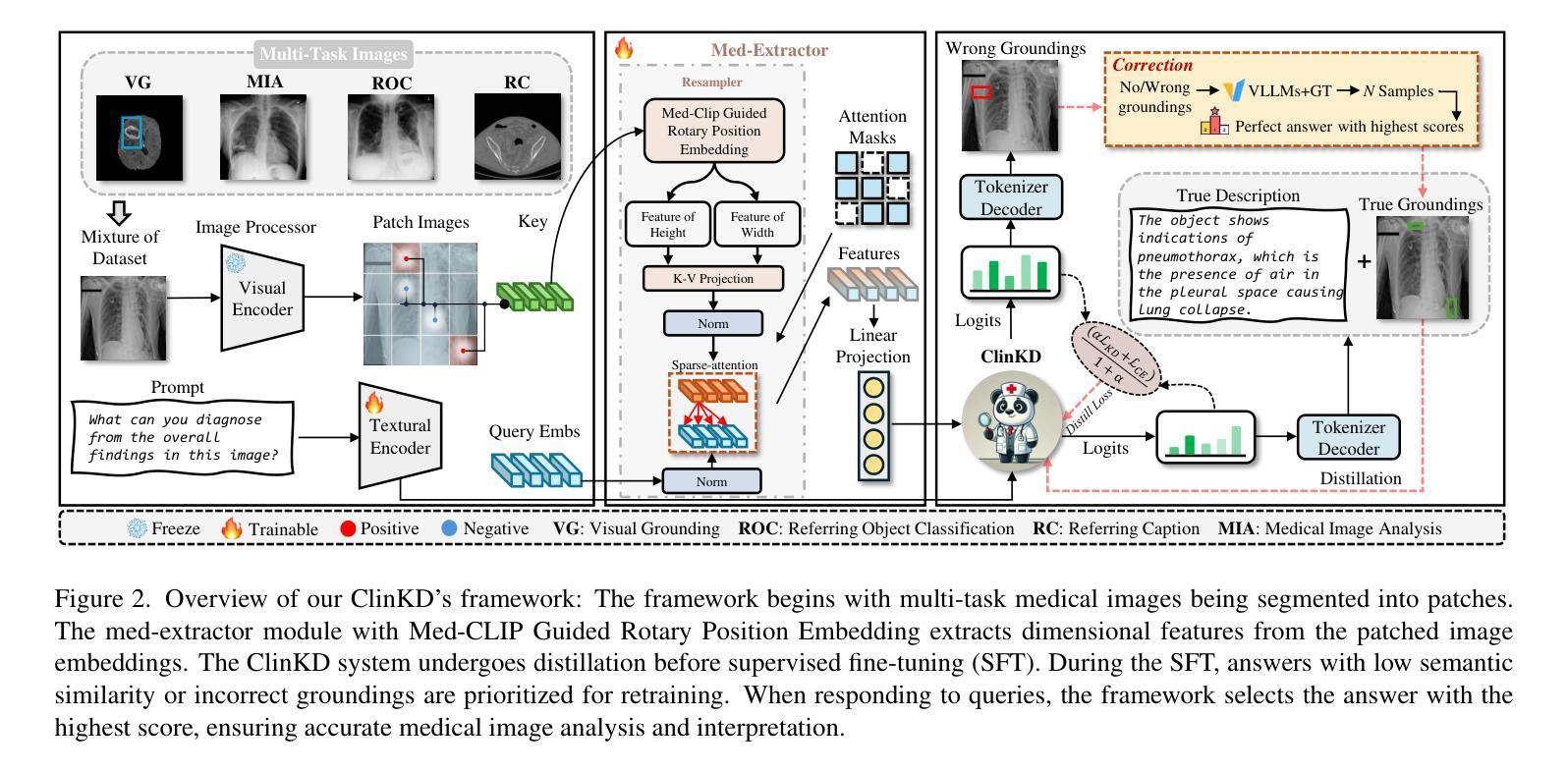
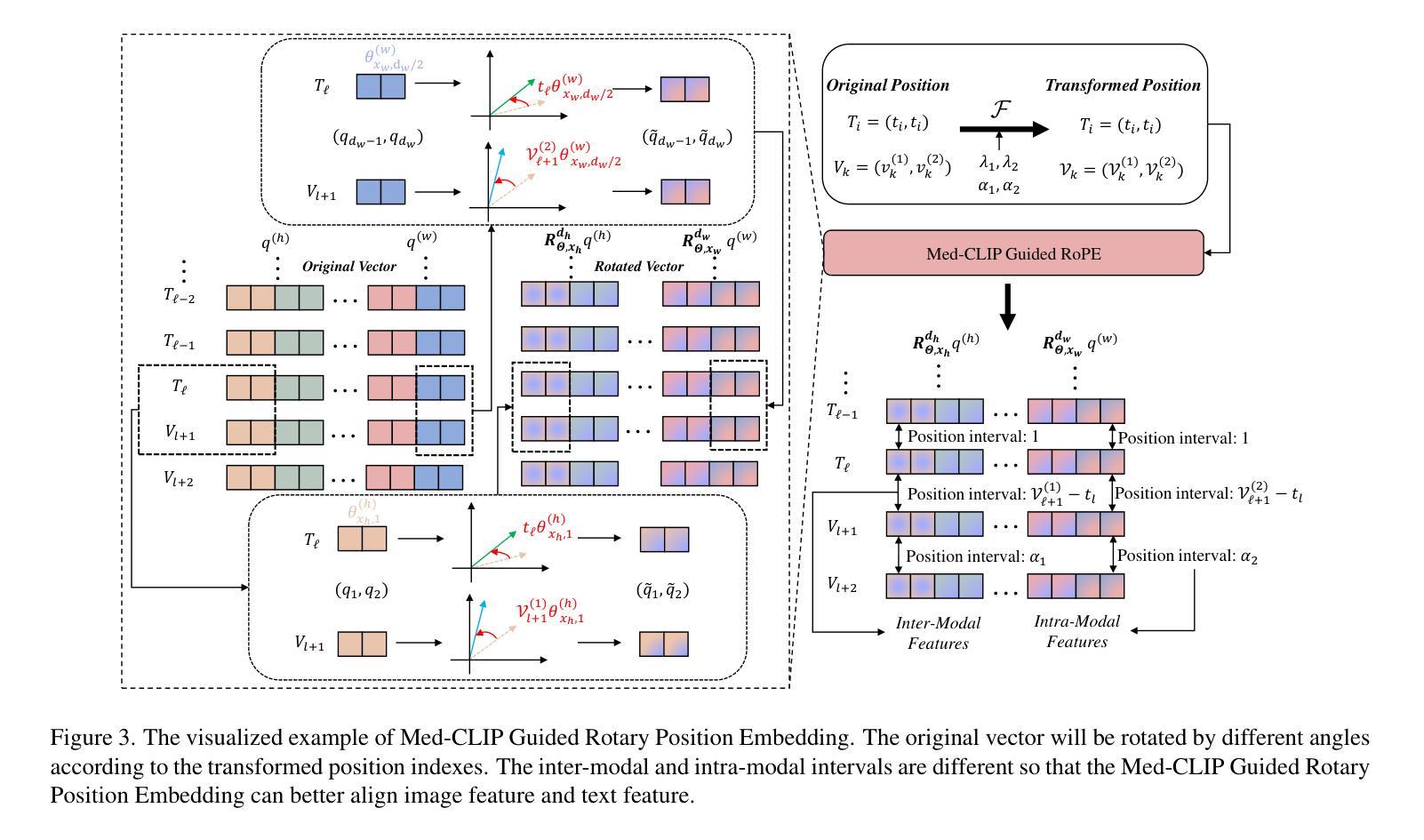
ClinKD: Cross-Modal Clinical Knowledge Distiller For Multi-Task Medical Images
Authors:Hongyu Ge, Longkun Hao, Zihui Xu, Zhenxin Lin, Bin Li, Shoujun Zhou, Hongjin Zhao, Yihang Liu
Medical Visual Question Answering (Med-VQA) represents a critical and challenging subtask within the general VQA domain. Despite significant advancements in general Visual Question Answering (VQA), multimodal large language models (MLLMs) still exhibit substantial limitations when handling multi-task VQA scenarios. These limitations manifest through erroneous spatial localization and misinterpretation of medical images, which primarily arise from two fundamental issues: inadequate image-text alignment and insufficient medical knowledge in general-purpose MLLMs for specialized medical applications. To address these issues, we introduce the Cross-Modal Clinical Knowledge Distiller (ClinKD), an innovative framework designed to enhance image-text alignment and establish more effective medical knowledge adaptation mechanisms, which enables MLLMs to adapt to medical knowledge. Our extensive experimental evaluations demonstrate that the ClinKD achieves state-of-the-art performance on the Med-GRIT-270k dataset, a challenging medical benchmark containing fine-grained multi-task QA pairs. The results indicate that our approach not only significantly improves image-text alignment but also effectively enables MLLMs to adapt to the medical knowledge. The source code for ClinKD is available at: https://github.com/overloadedHenry/ClinKD.
医疗视觉问答(Med-VQA)是通用VQA领域中的一个重要且具有挑战性的子任务。尽管通用视觉问答(VQA)领域取得了重大进展,但在处理多任务VQA场景时,多模态大型语言模型(MLLMs)仍然表现出明显的局限性。这些局限性表现为医疗图像的空间定位错误和误解,主要源于两个基本问题:图像文本对齐不足以及通用MLLMs在专用医疗应用中医学知识的不足。为了解决这些问题,我们引入了跨模态临床知识蒸馏器(ClinKD),这是一个创新框架,旨在增强图像文本对齐并建立更有效的医学知识适应机制,使MLLMs能够适应医学知识。我们的广泛实验评估表明,ClinKD在Med-GRIT-270k数据集上达到了最新技术水平,这是一个包含精细粒度多任务问答对的具有挑战性的医疗基准测试。结果表明,我们的方法不仅显著改善了图像文本对齐,而且有效地使MLLMs适应了医学知识。ClinKD的源代码可在以下网址找到:https://github.com/overloadedHenry/ClinKD。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
本文介绍了医疗视觉问答(Med-VQA)的重要性及其所面临的挑战。针对多任务视觉问答场景中的多模态大型语言模型(MLLMs)存在的空间定位错误和对医疗图像误解的问题,提出了跨模态临床知识蒸馏器(ClinKD)框架。ClinKD通过增强图像文本对齐和建立有效的医学知识适应机制,提高了MLLMs在医疗知识方面的适应能力。在Med-GRIT-270k数据集上的实验评估表明,ClinKD取得了最先进的性能。
Key Takeaways
- Med-VQA是VQA领域中的一个重要且具挑战性的子任务。
- MLLMs在处理多任务VQA场景时存在空间定位错误和医疗图像误解的问题。
- 这些问题主要源于图像文本对齐不足和通用MLLMs在专门医疗应用中的医学知识不足。
- 跨模态临床知识蒸馏器(ClinKD)框架旨在增强图像文本对齐并建立有效的医学知识适应机制。
- ClinKD能显著提高MLLMs对医疗知识的适应能力。
- 在Med-GRIT-270k数据集上,ClinKD取得了最先进的性能。
点此查看论文截图

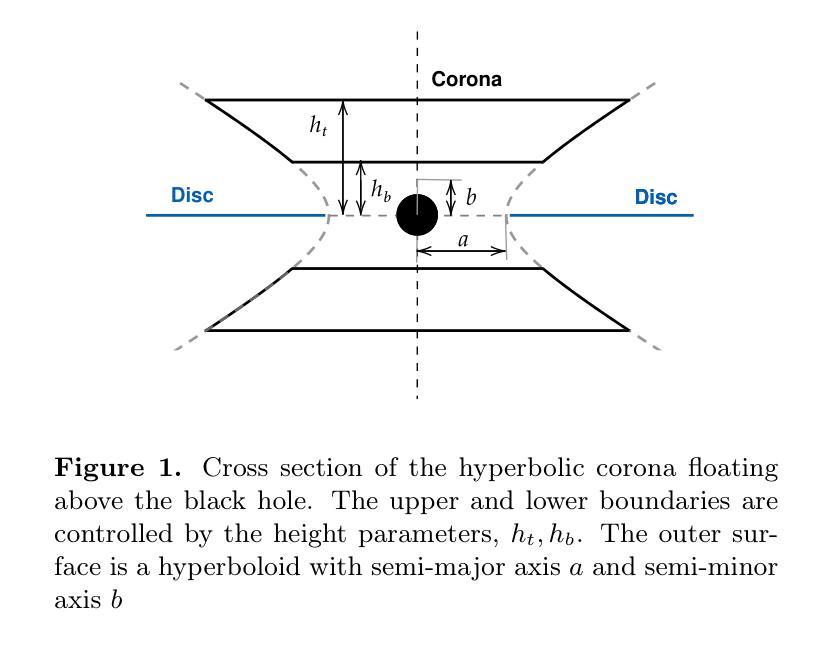
Modeling fast X-ray variability around an accreting black hole
Authors:Yejing Zhan, Bei You, Adam Ingram, Wenkang Jiang, Fayin Wang
X-ray inter-band time lags are observed during the outbursts of black hole X-ray binaries (BHXRBs). Timing analysis of fast variability in low Fourier frequency bands shows that high-energy photons lag behind low-energy photons, a phenomenon referred to as hard lag. Conversely, in high Fourier frequency bands, low-energy photons lag behind high-energy photons, known as soft lag. This frequency-dependent lag spectrum suggests that the lags arise from different physical processes. Notably, a trend has been observed wherein the lags shift towards shorter timescales during the rising hard state, indicating an evolution in the inner accretion flow. In this study, we simulate these inter-band lags by conducting Monte Carlo simulations of the rapid variability within the geometry of a jet base corona. We consider both inward propagating accretion rate fluctuations and reverberation (light crossing) delays in our simulations. We successfully reproduce both low-frequency hard lags and high-frequency soft lags in a self-consistent manner. We replicate the observed evolution of the frequency-dependent lag spectra by varying the geometrical scale of the corona and the viscous frequency of the disc. Finally, we discuss the potential of a spherical corona and emphasize that polarization observations from the Imaging X-ray Polarimetry Explorer (IXPE) and the enhanced X-ray Timing and Polarimetry mission (eXTP) will be crucial for distinguishing the corona’s geometry in future studies.
在黑洞X射线双星(BHXRBs)的爆发期间,观察到X射线波段之间的时间延迟。低傅里叶频带快速变化的定时分析表明,高能光子落后于低能光子,这种现象被称为硬滞后。相反,在高傅里叶频带中,低能光子落后于高能光子,称为软滞后。这种与频率相关的滞后光谱表明滞后是由不同的物理过程引起的。值得注意的是,已经观察到一种趋势,即滞后时间向更短的时间尺度转变,这在增强的硬态中尤为明显,表明内积盘在发生变化。在这项研究中,我们通过模拟喷流基冕几何结构内的快速变化来进行蒙特卡罗模拟,以模拟这些波段间的滞后现象。我们在模拟中考虑了向内传播的吸积率波动和回声(光速穿越)延迟。我们成功地以一致的方式再现了低频硬滞后和高频软滞后。通过改变冕的几何尺度和盘的粘性频率,我们复制了观察到的频率相关滞后光谱的演变。最后,我们讨论了球形冕的潜力,并强调成像X射线偏振仪(IXPE)和增强的X射线定时和偏振任务(eXTP)的偏振观测对于未来研究中区分冕的几何形状将是至关重要的。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF 17 pages, 9 figures, accepted by ApJ
Summary
本文研究了黑洞X射线双星(BHXRBs)爆发期间的X射线波段间时间延迟现象。通过蒙特卡洛模拟,成功模拟了低频硬滞后和高频软滞后的产生机制,揭示了延迟是由于冠层几何结构变化引起的向内传播的吸积率波动和回声延迟。此外,文章还讨论了球形冠层的可能性,并强调了未来研究中极化观测对于区分冠层几何结构的重要性。
Key Takeaways
- BHXRBs爆发期间存在X射线波段间时间延迟现象。
- 高能光子在低频带的时间滞后于低能光子,产生硬滞后现象。
- 低能光子在高频带的时间滞后于高能光子,产生软滞后现象。
- 时间滞后现象在不同频率下的表现揭示出不同的物理过程。
- 蒙特卡洛模拟成功模拟了这种波段间的时间滞后现象,与观察结果相符。
- 延迟现象的变化与冠层几何结构和吸积盘的粘性频率有关。
点此查看论文截图

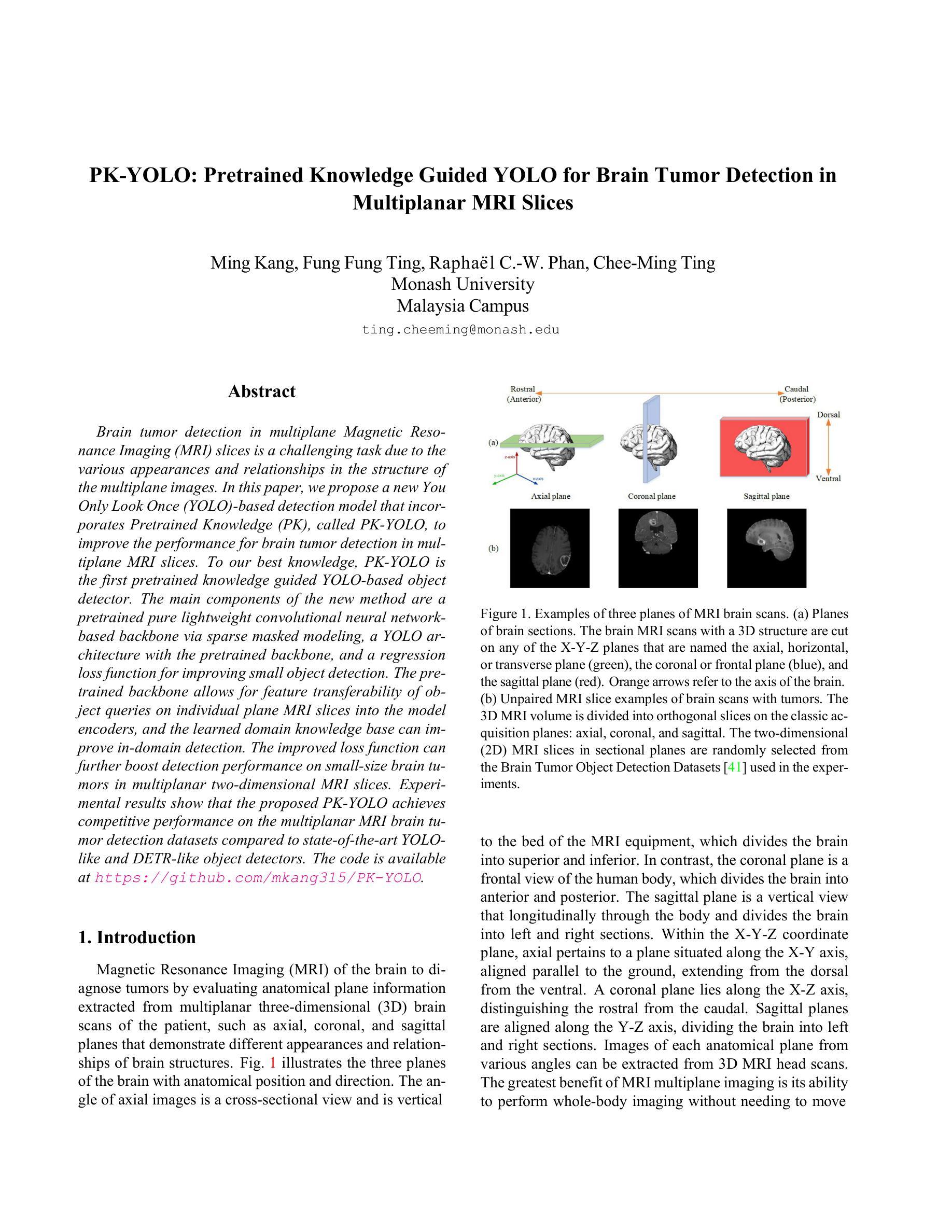
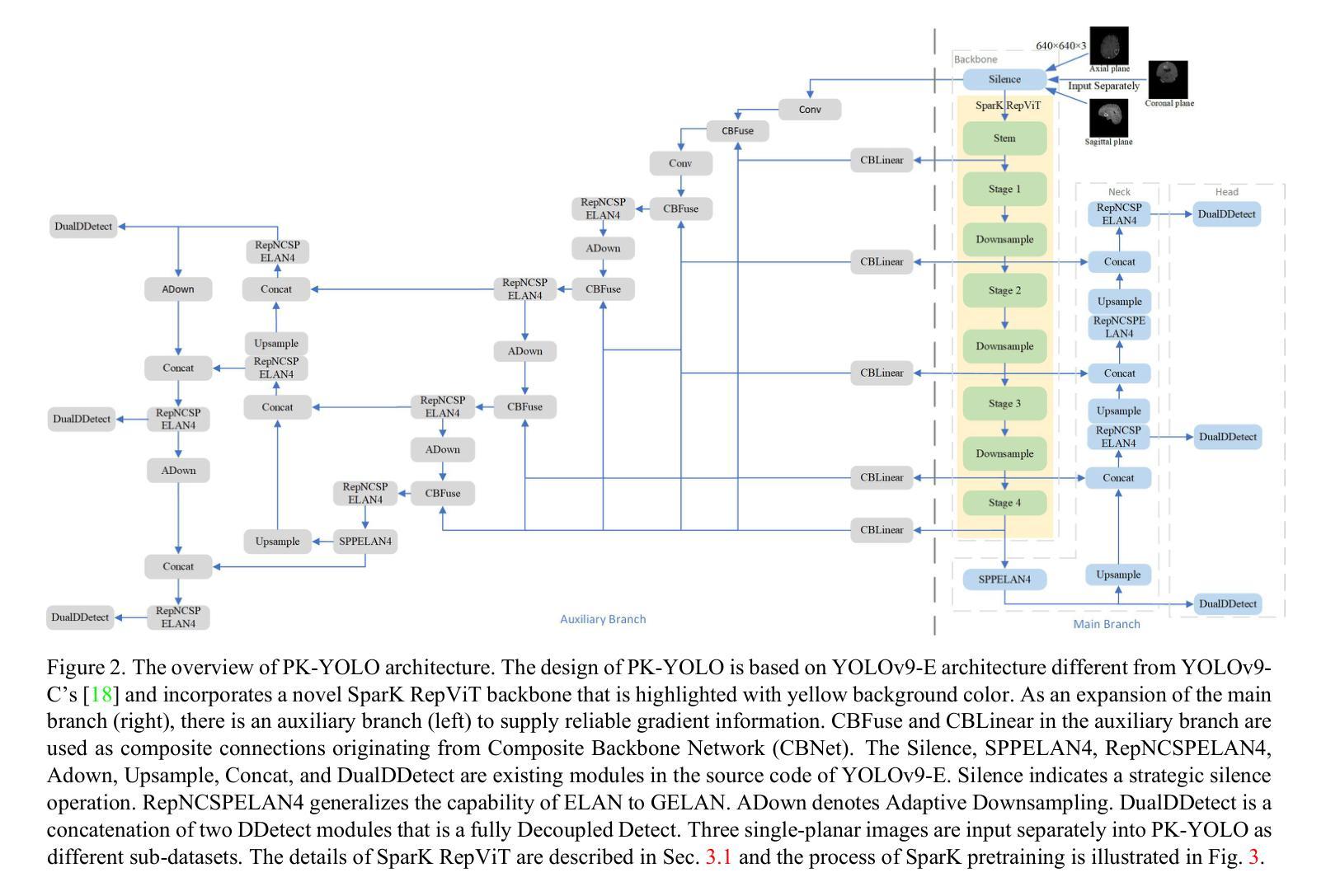
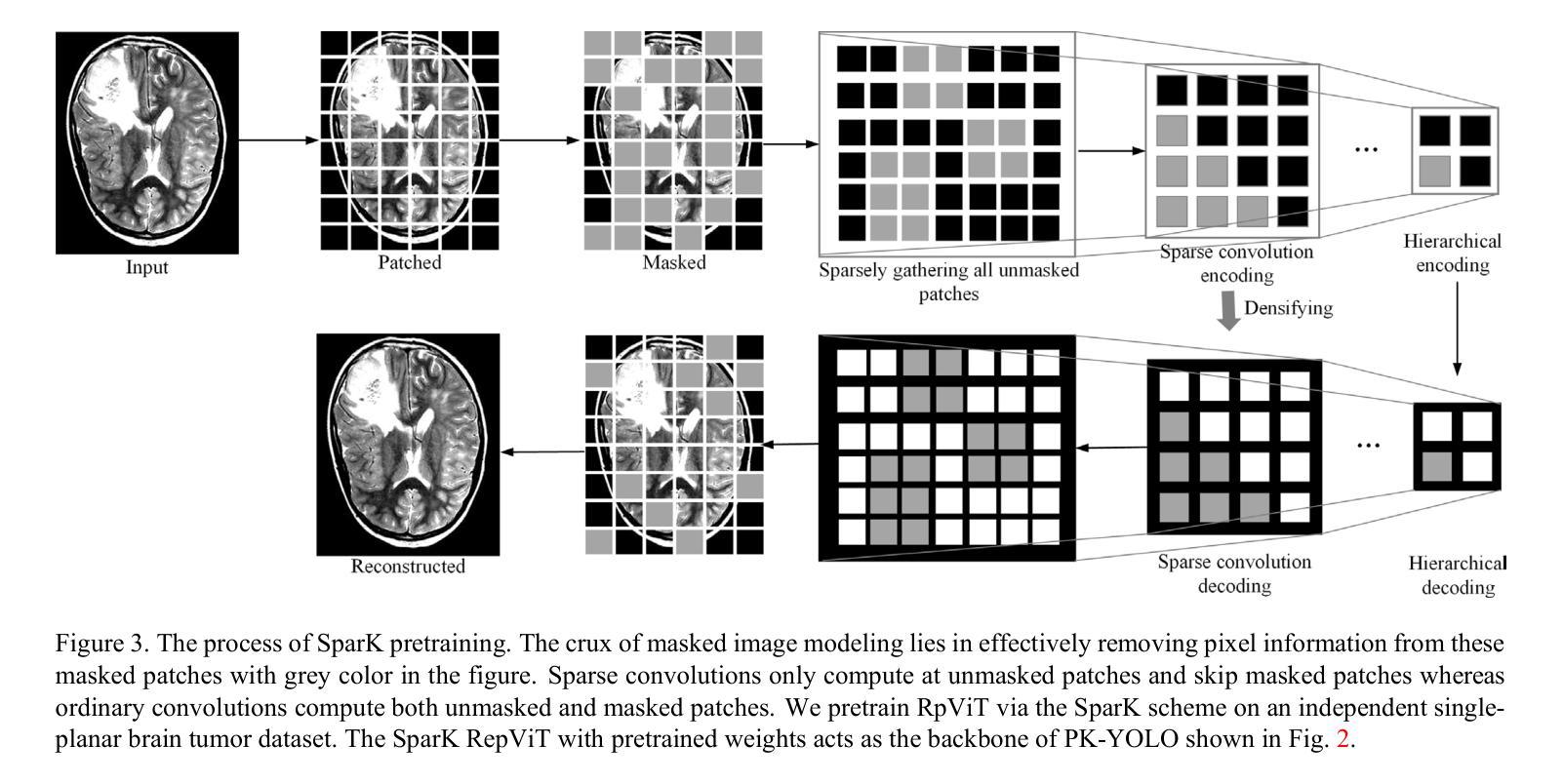
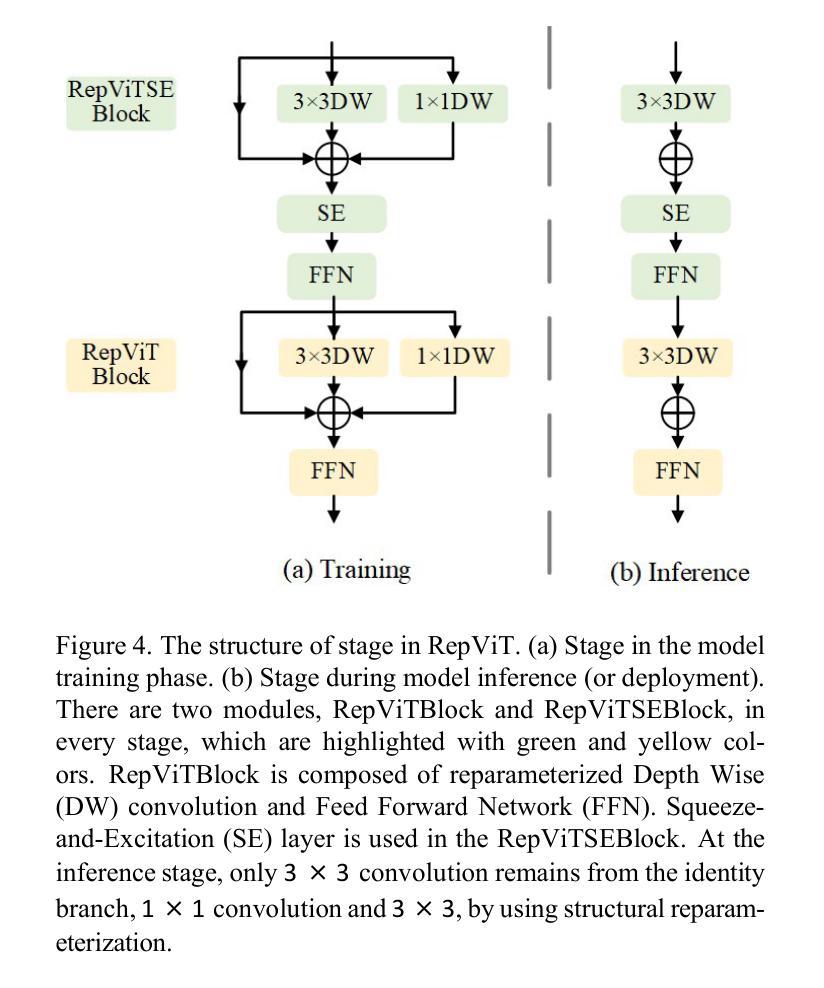
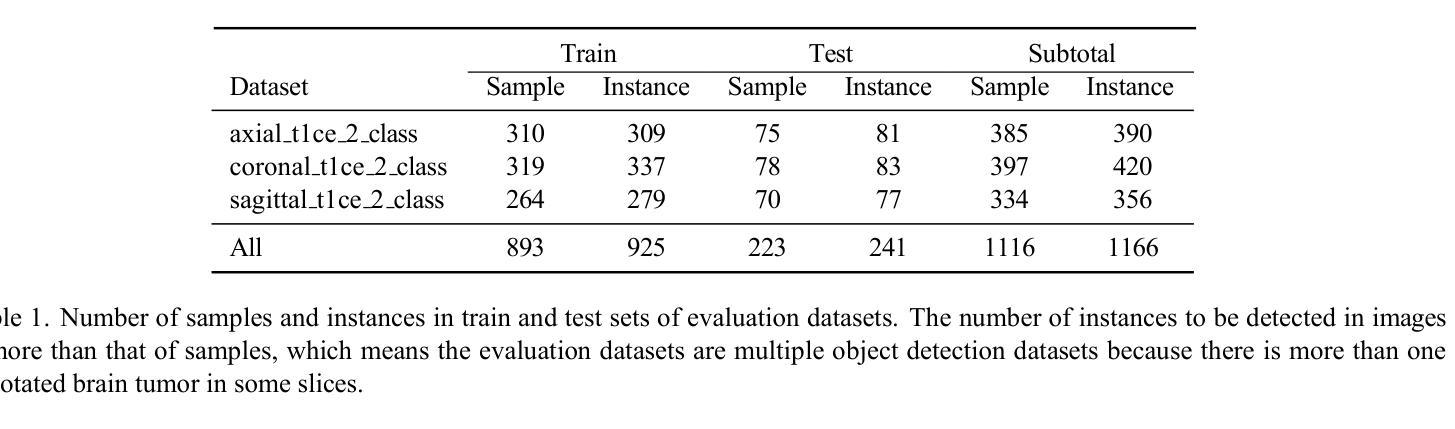
PK-YOLO: Pretrained Knowledge Guided YOLO for Brain Tumor Detection in Multiplanar MRI Slices
Authors:Ming Kang, Fung Fung Ting, Raphaël C. -W. Phan, Chee-Ming Ting
Brain tumor detection in multiplane Magnetic Resonance Imaging (MRI) slices is a challenging task due to the various appearances and relationships in the structure of the multiplane images. In this paper, we propose a new You Only Look Once (YOLO)-based detection model that incorporates Pretrained Knowledge (PK), called PK-YOLO, to improve the performance for brain tumor detection in multiplane MRI slices. To our best knowledge, PK-YOLO is the first pretrained knowledge guided YOLO-based object detector. The main components of the new method are a pretrained pure lightweight convolutional neural network-based backbone via sparse masked modeling, a YOLO architecture with the pretrained backbone, and a regression loss function for improving small object detection. The pretrained backbone allows for feature transferability of object queries on individual plane MRI slices into the model encoders, and the learned domain knowledge base can improve in-domain detection. The improved loss function can further boost detection performance on small-size brain tumors in multiplanar two-dimensional MRI slices. Experimental results show that the proposed PK-YOLO achieves competitive performance on the multiplanar MRI brain tumor detection datasets compared to state-of-the-art YOLO-like and DETR-like object detectors. The code is available at https://github.com/mkang315/PK-YOLO.
在多平面磁共振成像(MRI)切片中检测脑肿瘤是一项具有挑战性的任务,由于多平面图像的结构中的不同外观和关系。在本文中,我们提出了一种新的基于You Only Look Once(YOLO)的检测模型,该模型结合了预训练知识(PK),称为PK-YOLO,以提高在多平面MRI切片中检测脑肿瘤的性能。据我们所知,PK-YOLO是第一个基于预训练知识的YOLO目标检测器。新方法的 主要组件包括通过稀疏掩模建模的预训练纯轻量化卷积神经网络主干、带有预训练主干的YOLO架构,以及用于改进小目标检测的回归损失函数。预训练的主干允许将单个平面MRI切片上的目标查询的特征可迁移性转移到模型编码器,并且学习到的领域知识库可以提高领域内的检测性能。改进的损失函数可以进一步提高在多平面二维MRI切片中小尺寸脑肿瘤的检测性能。实验结果表明,与最先进的类似YOLO和DETR的目标检测器相比,所提出的PK-YOLO在多平面MRI脑肿瘤检测数据集上实现了具有竞争力的性能。代码可在https://github.com/mkang315/PK-YOLO上找到。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF References updated; for example, papers in NeurIPS 2024 proceedings appeared on 6 Feb 2025 and AAAI 2025 one on 11 Apr 2025
Summary
基于多平面磁共振成像(MRI)的脑肿瘤检测因图像结构的多样性和复杂性而具有挑战性。本研究提出一种新型的基于You Only Look Once(YOLO)的检测模型,结合预训练知识(PK),称为PK-YOLO,以提高在多平面MRI切片中检测脑肿瘤的性能。PK-YOLO是首个基于预训练知识的YOLO目标检测器。该方法主要包括通过稀疏掩模建模的预训练轻量级卷积神经网络主干、带有预训练主干的YOLO架构,以及用于改进小目标检测的回归损失函数。预训练的主干允许将单个平面MRI切片上的目标查询的特征转移到模型编码器,而学习到的领域知识库可以提高领域内的检测性能。改进的损失函数可以进一步提高在多平面二维MRI切片中检测小尺寸脑肿瘤的性能。实验结果表明,与最新的YOLO和DETR类似的目标检测器相比,所提出的PK-YOLO在多平面MRI脑肿瘤检测数据集上表现出竞争力。
Key Takeaways
- PK-YOLO是一个结合预训练知识的YOLO目标检测模型,适用于多平面MRI切片中的脑肿瘤检测。
- 该模型采用预训练的轻量级卷积神经网络主干,通过稀疏掩模建模增强特征提取能力。
- YOLO架构结合预训练主干,能有效处理MRI切片中的复杂图像结构。
- 回归损失函数的改进提高了对小尺寸脑肿瘤的检测性能。
- 预训练的主干能够实现特征的可转移性,提高检测效果。
- PK-YOLO在多平面MRI脑肿瘤检测数据集上的表现具有竞争力。
点此查看论文截图
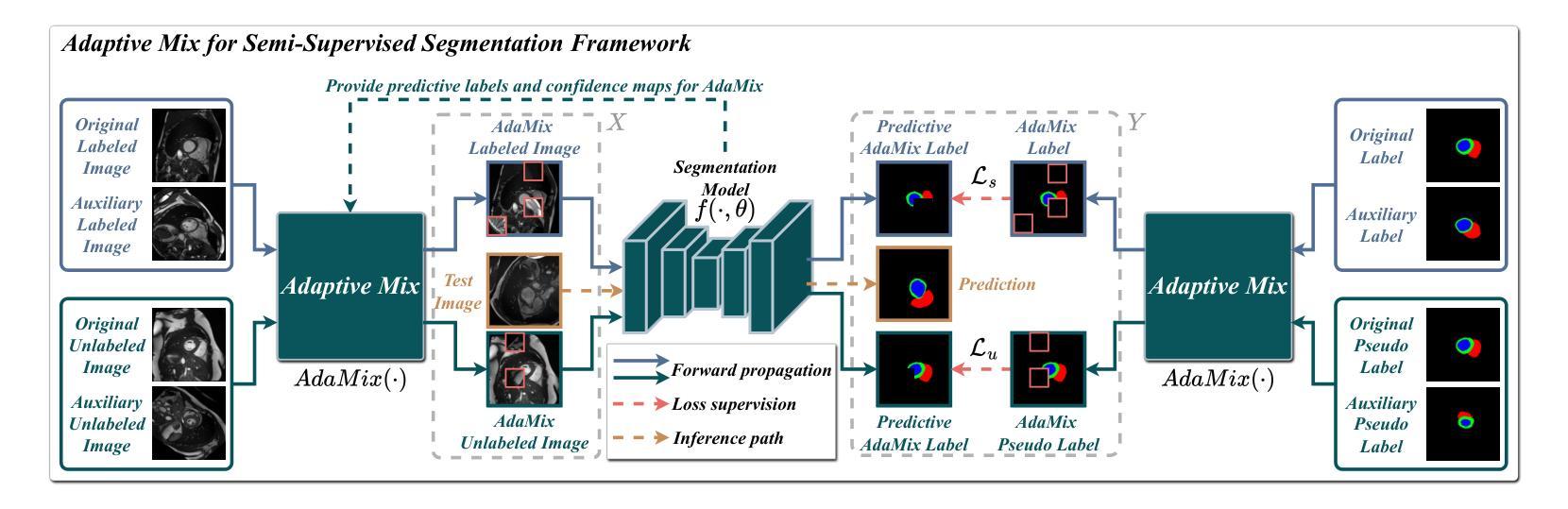
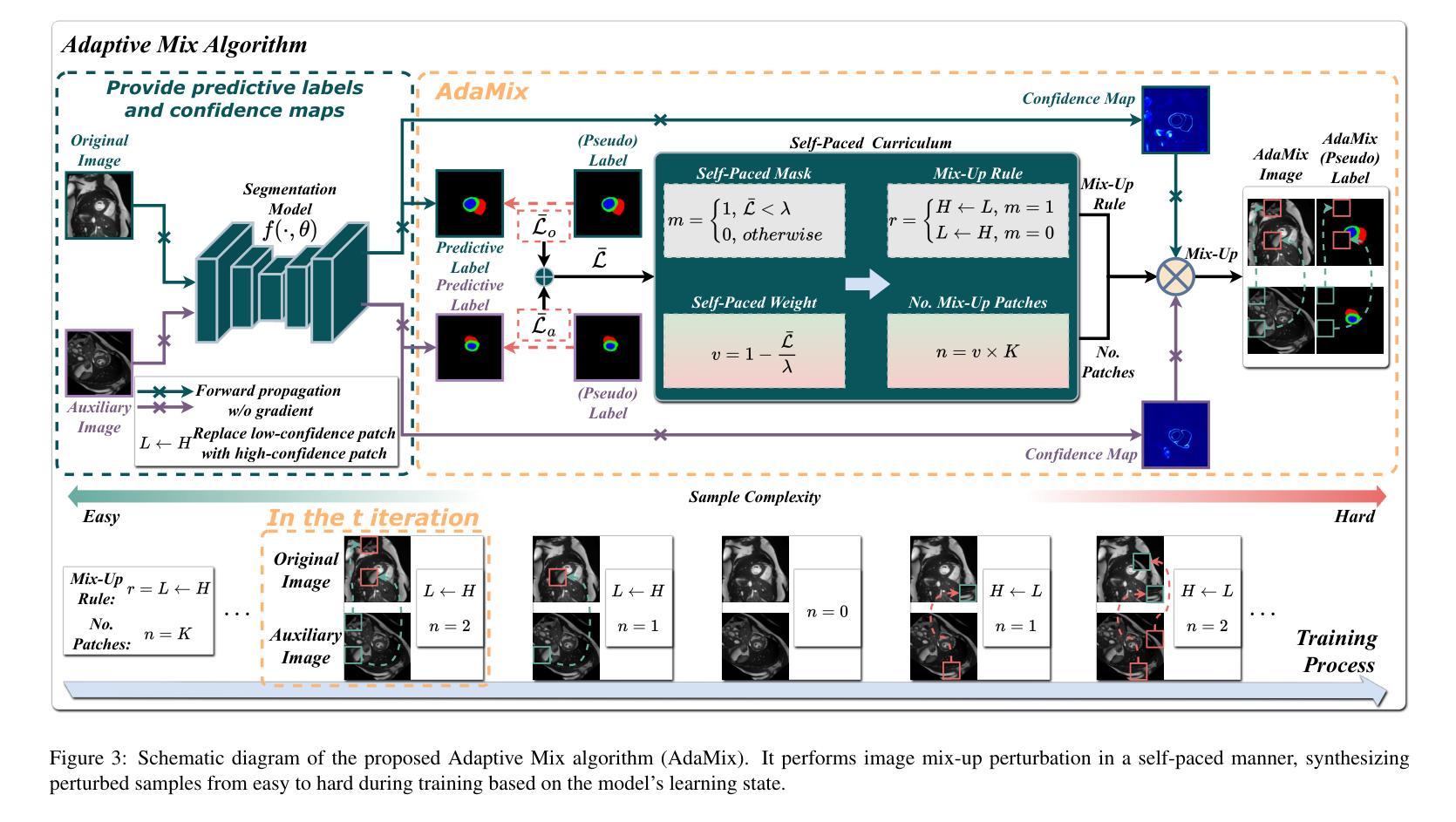
Adaptive Mix for Semi-Supervised Medical Image Segmentation
Authors:Zhiqiang Shen, Peng Cao, Junming Su, Jinzhu Yang, Osmar R. Zaiane
Mix-up is a key technique for consistency regularization-based semi-supervised learning methods, blending two or more images to generate strong-perturbed samples for strong-weak pseudo supervision. Existing mix-up operations are performed either randomly or with predefined fixed rules, such as replacing low-confidence patches with high-confidence ones. The former lacks control over the perturbation degree, leading to overfitting on randomly perturbed samples, while the latter tends to generate images with trivial perturbations, both of which limit the effectiveness of consistency regularization. This paper aims to answer the following question: How can image mix-up perturbation be adaptively performed during training? To this end, we propose an Adaptive Mix algorithm (AdaMix) for image mix-up in a self-paced learning manner. Given that, in general, a model’s performance gradually improves during training, AdaMix is equipped with a self-paced curriculum that, in the initial training stage, provides relatively simple perturbed samples and then gradually increases the difficulty of perturbed images by adaptively controlling the perturbation degree based on the model’s learning state estimated by a self-paced regularize. We develop three frameworks with our AdaMix, i.e., AdaMix-ST, AdaMix-MT, and AdaMix-CT, for semi-supervised medical image segmentation. Extensive experiments on three public datasets show that the proposed frameworks can achieve superior performance. For example, compared with the state-of-the-art, AdaMix-CT achieves relative improvements of 2.62% in Dice similarity coefficient and 48.25% in average surface distance on the ACDC dataset with 10% labeled data. The results demonstrate that mix-up operations with dynamically adjusted perturbation strength based on the segmentation model’s state can significantly enhance the effectiveness of consistency regularization.
混合是半监督学习方法中的一种关键技术,它结合了两种或多种图像来生成强烈干扰的样本以进行强弱伪监督。现有的混合操作是随机或按预定的固定规则执行,例如用高置信度的补丁替换低置信度的补丁。前者缺乏对干扰程度的控制,导致随机干扰样本的过度拟合,而后者倾向于生成具有轻微干扰的图像。两者都限制了一致性正则化的有效性。本文旨在回答以下问题:如何在训练过程中自适应地执行图像混合干扰?为此,我们提出了一种自适应混合算法(AdaMix)用于以自我安排的学习方式进行图像混合。鉴于模型的性能通常在训练过程中逐渐提高,AdaMix配备了一种自我安排课程,在初始训练阶段提供相对简单的干扰样本,然后通过自适应控制干扰程度来逐渐增加干扰图像的难度。干扰程度的控制基于模型的学习状态,由自我安排的正则化进行估算。我们开发了三种使用AdaMix的框架,即AdaMix-ST、AdaMix-MT和AdaMix-CT,用于半监督医学图像分割。在三个公共数据集上的大量实验表明,所提出的框架可以取得卓越的性能。例如,与最先进的方法相比,AdaMix-CT在只有10%标记数据的ACDC数据集上,在Dice相似系数上实现了相对提高2.62%,在平均表面距离上实现了相对提高48.25%。结果表明,基于分割模型状态的动态调整混合操作的干扰强度可以显着提高一致性正则化的有效性。
论文及项目相关链接
摘要
医学图像半监督学习中的自适应混合算法研究。针对现有混合操作的局限性,本文提出一种自适应混合算法(AdaMix),能够根据模型的学习状态自适应调整扰动程度。开发三个针对医学图像分割的半监督学习框架,并在三个公共数据集上进行实验验证,显示出优越性能。
关键见解
- 介绍了医学图像半监督学习中混合技术的重要性。
- 分析现有混合操作的局限性,包括随机操作导致的过度拟合和固定规则产生的轻微扰动。
- 提出自适应混合算法(AdaMix),能够根据模型的学习状态动态调整扰动强度。
- AdaMix配备自我进度的课程,在训练初期提供简单的扰动样本,然后逐渐增加扰动图像的难度。
- 开发三个基于AdaMix的框架,用于医学图像分割的半监督学习。
- 在三个公共数据集上的实验表明,所提出的框架性能优于其他方法。
点此查看论文截图



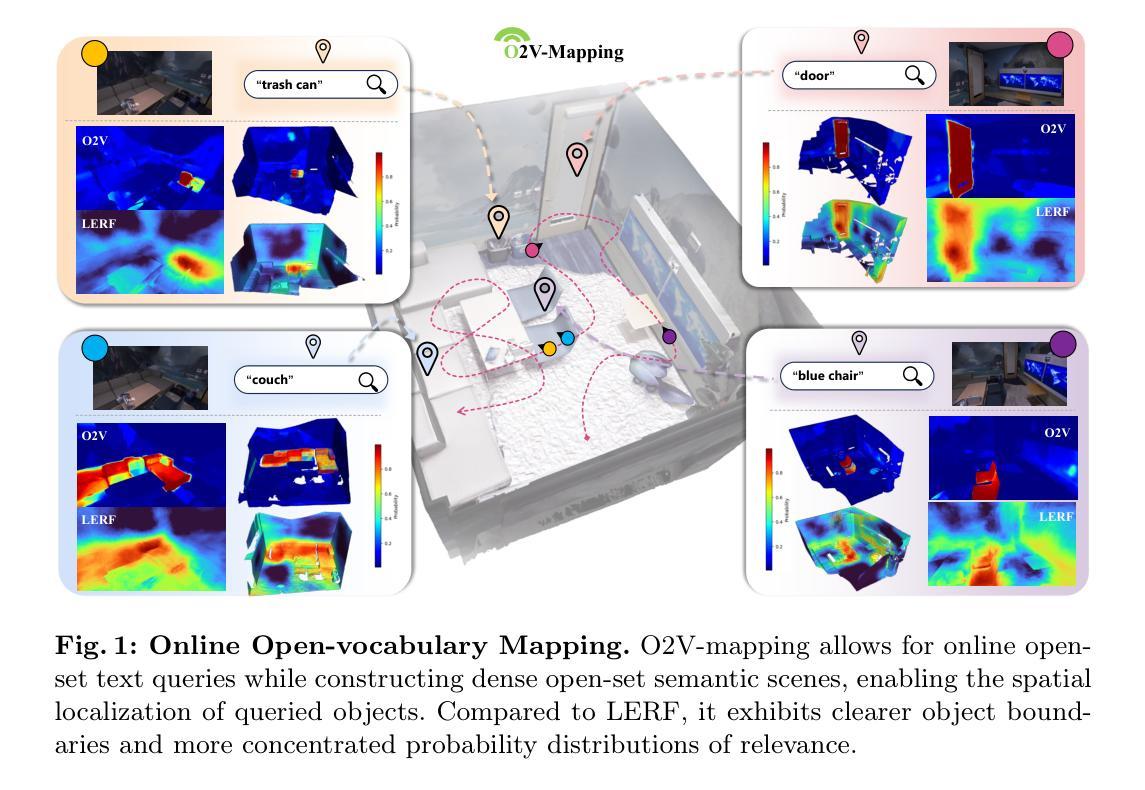
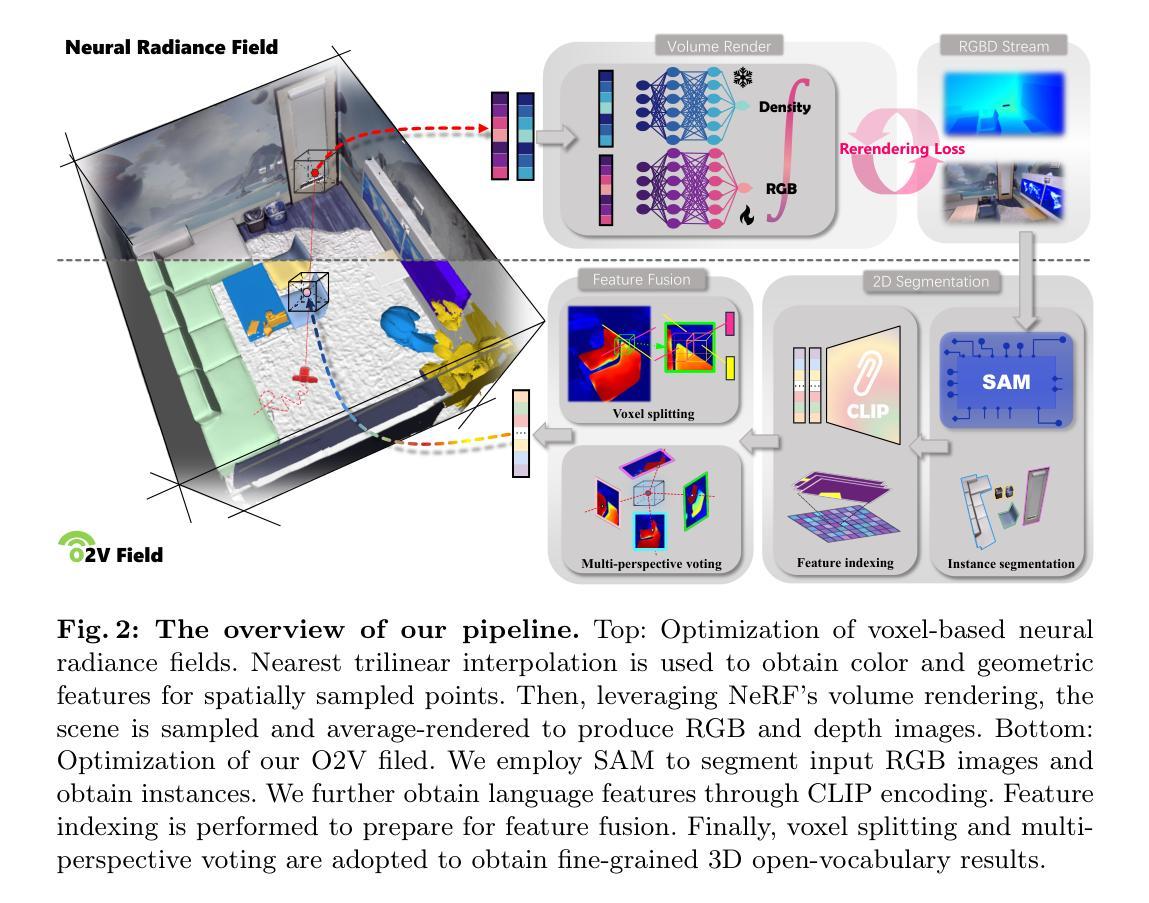
O2V-Mapping: Online Open-Vocabulary Mapping with Neural Implicit Representation
Authors:Muer Tie, Julong Wei, Zhengjun Wang, Ke Wu, Shansuai Yuan, Kaizhao Zhang, Jie Jia, Jieru Zhao, Zhongxue Gan, Wenchao Ding
Online construction of open-ended language scenes is crucial for robotic applications, where open-vocabulary interactive scene understanding is required. Recently, neural implicit representation has provided a promising direction for online interactive mapping. However, implementing open-vocabulary scene understanding capability into online neural implicit mapping still faces three challenges: lack of local scene updating ability, blurry spatial hierarchical semantic segmentation and difficulty in maintaining multi-view consistency. To this end, we proposed O2V-mapping, which utilizes voxel-based language and geometric features to create an open-vocabulary field, thus allowing for local updates during online training process. Additionally, we leverage a foundational model for image segmentation to extract language features on object-level entities, achieving clear segmentation boundaries and hierarchical semantic features. For the purpose of preserving consistency in 3D object properties across different viewpoints, we propose a spatial adaptive voxel adjustment mechanism and a multi-view weight selection method. Extensive experiments on open-vocabulary object localization and semantic segmentation demonstrate that O2V-mapping achieves online construction of language scenes while enhancing accuracy, outperforming the previous SOTA method.
在线构建开放式语言场景对机器人应用至关重要,这些应用需要开放式词汇交互场景理解。最近,神经隐式表示方法为在线交互式映射提供了有前途的方向。然而,将开放式词汇场景理解能力融入在线神经隐式映射仍然面临三个挑战:缺乏局部场景更新能力、空间层次语义分割模糊以及维持多视角一致性困难。为此,我们提出了O2V-mapping,它利用基于体素的语言和几何特征来创建开放式词汇场,从而允许在线训练过程中的局部更新。此外,我们利用图像分割的基础模型来提取对象级实体的语言特征,实现清晰的分割边界和层次语义特征。为了保持不同视角下3D对象属性的一致性,我们提出了一种空间自适应体素调整机制和一种多视角权重选择方法。在开放式词汇对象定位和语义分割方面的广泛实验表明,O2V-mapping实现了语言场景的在线构建,提高了准确性,超越了之前的最优方法。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF ECCV2024
Summary
在线构建开放词汇语言场景对机器人应用至关重要,其中要求开放词汇互动场景理解。近期,神经隐式表示法为在线互动映射提供了有前景的方向,但在实现开放词汇场景理解能力到在线神经隐式映射仍面临三个挑战:缺乏局部场景更新能力、空间层次语义分割模糊以及多视角一致性维护困难。为此,我们提出了O2V-mapping,利用基于体素的语言和几何特征创建开放词汇场,允许在线训练过程中的局部更新。此外,我们采用图像分割基础模型提取对象级别的语言特征,实现清晰的分割边界和层次语义特征。为了保持不同视角下物体属性的一致性,我们提出了空间自适应体素调整机制和一种多视角权重选择方法。在开放词汇对象定位和语义分割方面的广泛实验表明,O2V-mapping可实现语言场景的在线构建,提高了准确性,超过了以前的最优方法。
Key Takeaways
- 在线构建开放词汇语言场景对机器人应用至关重要。
- 神经隐式表示法为在线互动映射提供了有前景的方向。
- 实现开放词汇场景理解能力到在线神经隐式映射面临三大挑战。
- O2V-mapping利用基于体素的语言和几何特征创建开放词汇场,支持局部更新。
- 采用图像分割基础模型实现清晰分割边界和层次语义特征。
- 提出空间自适应体素调整机制以维护多视角一致性。
点此查看论文截图

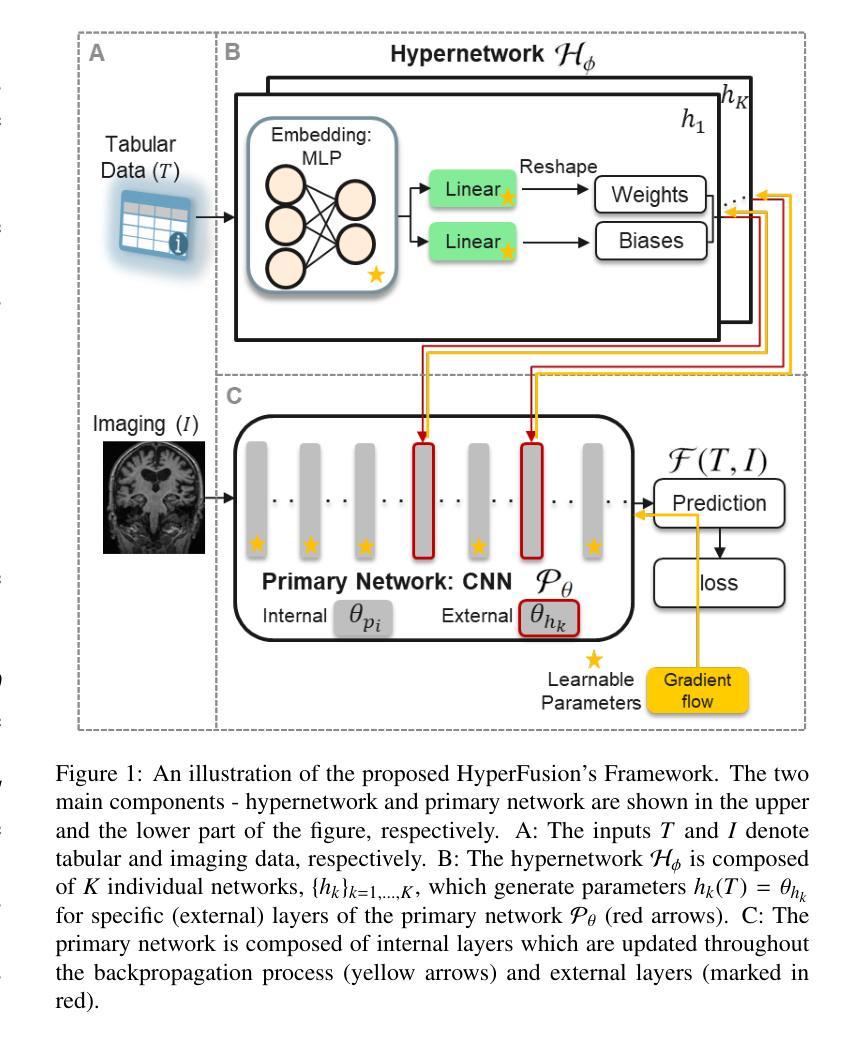
HyperFusion: A Hypernetwork Approach to Multimodal Integration of Tabular and Medical Imaging Data for Predictive Modeling
Authors:Daniel Duenias, Brennan Nichyporuk, Tal Arbel, Tammy Riklin Raviv
The integration of diverse clinical modalities such as medical imaging and the tabular data extracted from patients’ Electronic Health Records (EHRs) is a crucial aspect of modern healthcare. Integrative analysis of multiple sources can provide a comprehensive understanding of the clinical condition of a patient, improving diagnosis and treatment decision. Deep Neural Networks (DNNs) consistently demonstrate outstanding performance in a wide range of multimodal tasks in the medical domain. However, the complex endeavor of effectively merging medical imaging with clinical, demographic and genetic information represented as numerical tabular data remains a highly active and ongoing research pursuit. We present a novel framework based on hypernetworks to fuse clinical imaging and tabular data by conditioning the image processing on the EHR’s values and measurements. This approach aims to leverage the complementary information present in these modalities to enhance the accuracy of various medical applications. We demonstrate the strength and generality of our method on two different brain Magnetic Resonance Imaging (MRI) analysis tasks, namely, brain age prediction conditioned by subject’s sex and multi-class Alzheimer’s Disease (AD) classification conditioned by tabular data. We show that our framework outperforms both single-modality models and state-of-the-art MRI tabular data fusion methods. A link to our code can be found at https://github.com/daniel4725/HyperFusion
将医学成像与从患者电子健康记录(EHRs)中提取的表格数据等多样临床模式的整合是现代医疗保健的一个重要方面。多源整合分析可以全面理解患者的临床状况,提高诊断和治疗决策。深度神经网络(DNNs)在医疗领域的多模式任务中表现出卓越的性能。然而,有效地将医学成像与临床、人口统计学和遗传信息合并的复杂工作,表现为数值表格数据的形式,仍是活跃且持续的研究追求。我们提出了一种基于超网络的新型框架,通过以电子健康记录中的值和测量为条件,融合临床成像和表格数据。该方法旨在利用这些模式中存在的补充信息,提高各种医疗应用的准确性。我们在两个不同的脑部磁共振成像(MRI)分析任务上展示了我们的方法的优势和通用性,即根据受试者性别进行脑龄预测,以及根据表格数据进行的多类阿尔茨海默病(AD)分类。我们展示我们的框架超越了单模式模型和最先进的MRI表格数据融合方法。我们的代码链接为:https://github.com/daniel4725/HyperFusion
论文及项目相关链接
PDF 20 pages, 11 figures
Summary
医学成像与电子健康记录(EHRs)表格数据的融合是现代医疗的关键。深度学习网络(DNNs)在此领域的多模式任务中表现出卓越性能。本研究提出一种基于超网络的新框架,通过条件图像处理将临床成像与表格数据融合,利用这两种模式的互补信息提高医疗应用的准确性。该框架在脑磁共振成像(MRI)分析任务中表现出优异性能。
Key Takeaways
- 医学成像与电子健康记录(EHRs)表格数据的融合对现代医疗至关重要。
- 深度学习网络(DNNs)在多模式任务中表现卓越。
- 提出基于超网络的新框架,融合医学成像与表格数据。
- 该框架通过条件图像处理,旨在利用两种模式的互补信息。
- 框架在脑磁共振成像(MRI)分析任务中表现出优异性能,如脑龄预测和阿尔茨海默病分类。
- 新框架优于单模式模型和先进的MRI表格数据融合方法。
点此查看论文截图