⚠️ 以下所有内容总结都来自于 大语言模型的能力,如有错误,仅供参考,谨慎使用
🔴 请注意:千万不要用于严肃的学术场景,只能用于论文阅读前的初筛!
💗 如果您觉得我们的项目对您有帮助 ChatPaperFree ,还请您给我们一些鼓励!⭐️ HuggingFace免费体验
2025-04-23 更新
Exploring Modality Guidance to Enhance VFM-based Feature Fusion for UDA in 3D Semantic Segmentation
Authors:Johannes Spoecklberger, Wei Lin, Pedro Hermosilla, Sivan Doveh, Horst Possegger, M. Jehanzeb Mirza
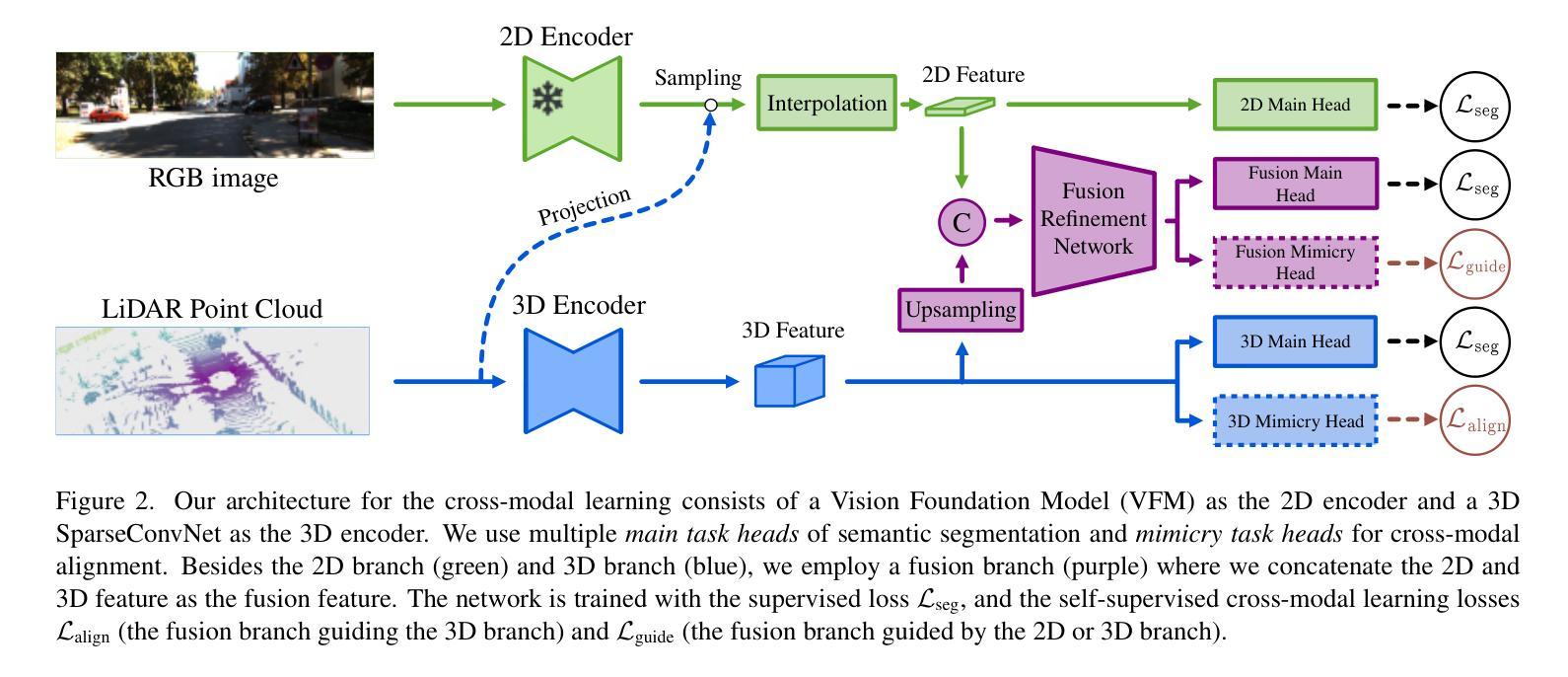
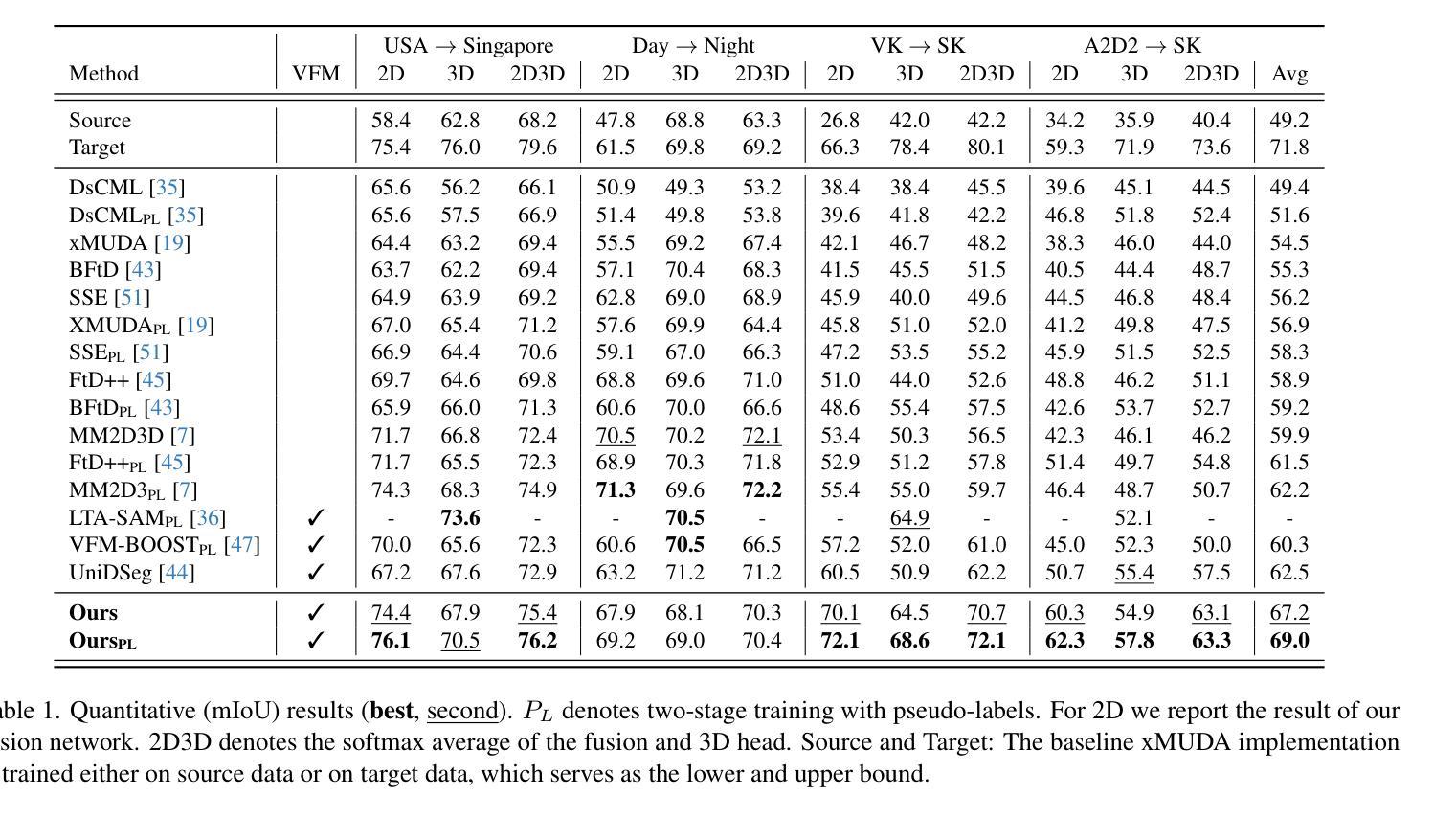
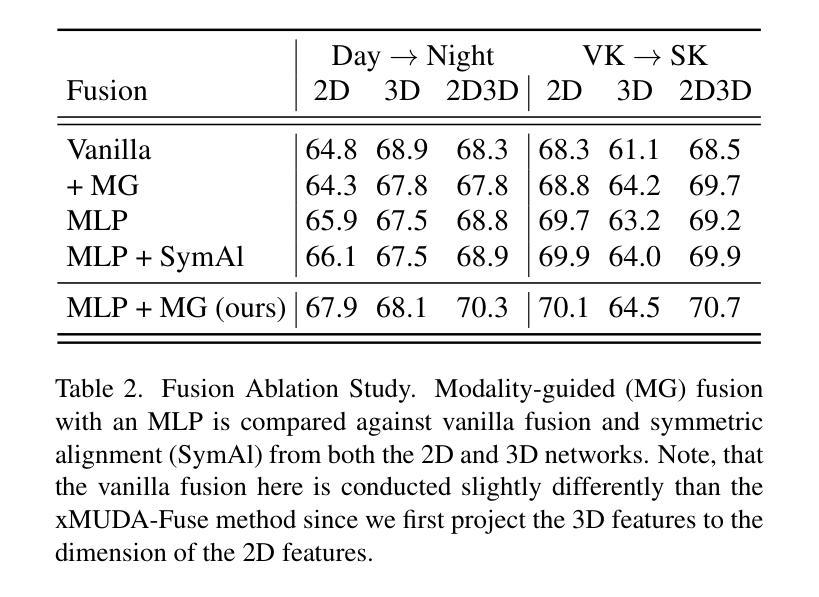
Vision Foundation Models (VFMs) have become a de facto choice for many downstream vision tasks, like image classification, image segmentation, and object localization. However, they can also provide significant utility for downstream 3D tasks that can leverage the cross-modal information (e.g., from paired image data). In our work, we further explore the utility of VFMs for adapting from a labeled source to unlabeled target data for the task of LiDAR-based 3D semantic segmentation. Our method consumes paired 2D-3D (image and point cloud) data and relies on the robust (cross-domain) features from a VFM to train a 3D backbone on a mix of labeled source and unlabeled target data. At the heart of our method lies a fusion network that is guided by both the image and point cloud streams, with their relative contributions adjusted based on the target domain. We extensively compare our proposed methodology with different state-of-the-art methods in several settings and achieve strong performance gains. For example, achieving an average improvement of 6.5 mIoU (over all tasks), when compared with the previous state-of-the-art.
视觉基础模型(VFMs)已成为众多下游视觉任务(如图像分类、图像分割和对象定位)的实际选择。然而,它们也可以为下游的3D任务提供巨大的效用,这些任务可以利用跨模态信息(例如来自配对图像数据)。在我们的工作中,我们进一步探索了VFM在激光雷达基于的3D语义分割任务中的自适应能力,即从标记的源数据到未标记的目标数据。我们的方法使用配对2D-3D(图像和点云)数据,并依赖于VFM的稳健(跨域)特征来训练混合的标记源数据和未标记目标数据的3D主干网络。我们方法的核心是一个融合网络,它受到图像和点云流的指导,根据目标域调整其相对贡献。我们在不同的设置下与不同的最新方法进行了广泛的比较,并实现了显著的性能提升。例如,与之前的最新技术相比,在所有任务上的平均提高了6.5 mIoU。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
本文探讨了Vision Foundation Models(VFMs)在LiDAR基于的3D语义分割任务中的应用。通过使用配对2D-3D数据和VFM的跨域特征,研究了一种适应从有标签源数据到无标签目标数据的方法。方法的核心是一个由图像和点云流引导的融合网络,根据目标域调整它们的相对贡献。该方法在不同设置下与不同先进方法进行了广泛比较,取得了显著的性能提升,例如与先前最先进的相比,平均提高了6.5 mIoU。
Key Takeaways
- Vision Foundation Models (VFMs) 可用于多种下游视觉任务,包括LiDAR基于的3D语义分割。
- VFMs在跨模态信息方面具有显著效用,特别是在配对图像数据中。
- 研究了一种利用VFMs从有标签源数据适应到无标签目标数据的方法,涉及混合数据训练。
- 方法的核心是一个融合网络,由图像和点云流共同引导,并根据目标域调整贡献。
- 该方法实现了对多种先进方法的广泛比较,并在不同设置下表现出优越性能。
- 与先前的技术相比,该方法在平均交并比(mIoU)方面取得了显著改进,提高了6.5 mIoU。
点此查看论文截图

Segment Any Crack: Deep Semantic Segmentation Adaptation for Crack Detection
Authors:Ghodsiyeh Rostami, Po-Han Chen, Mahdi S. Hosseini
Image-based crack detection algorithms are increasingly in demand in infrastructure monitoring, as early detection of cracks is of paramount importance for timely maintenance planning. While deep learning has significantly advanced crack detection algorithms, existing models often require extensive labeled datasets and high computational costs for fine-tuning, limiting their adaptability across diverse conditions. This study introduces an efficient selective fine-tuning strategy, focusing on tuning normalization components, to enhance the adaptability of segmentation models for crack detection. The proposed method is applied to the Segment Anything Model (SAM) and five well-established segmentation models. Experimental results demonstrate that selective fine-tuning of only normalization parameters outperforms full fine-tuning and other common fine-tuning techniques in both performance and computational efficiency, while improving generalization. The proposed approach yields a SAM-based model, Segment Any Crack (SAC), achieving a 61.22% F1-score and 44.13% IoU on the OmniCrack30k benchmark dataset, along with the highest performance across three zero-shot datasets and the lowest standard deviation. The results highlight the effectiveness of the adaptation approach in improving segmentation accuracy while significantly reducing computational overhead.
基于图像的裂缝检测算法在基础设施监测中的需求日益增加,因为早期裂缝检测对于及时维护规划至关重要。虽然深度学习已经显著推动了裂缝检测算法的发展,但现有模型通常需要大量标记数据集和较高的计算成本来进行微调,这限制了它们在各种条件下的适应性。本研究引入了一种高效的选择性微调策略,专注于调整归一化组件,以提高裂缝检测中分割模型的适应性。所提出的方法应用于“任何物体分割模型”(SAM)和五种成熟的分割模型。实验结果表明,仅对归一化参数进行选择性微调在性能和计算效率上优于全面微调和其他常见的微调技术,同时提高了泛化能力。所提出的方法产生了一种基于SAM的模型——任何裂缝分割(SAC),在OmniCrack30k基准数据集上实现了61.22%的F1分数和44.13%的IoU,同时在三个零样本数据集上性能最高,标准偏差最低。结果突出了适应方法的改进在分割精度方面的有效性,同时显著降低了计算开销。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
图像裂缝检测算法在基础设施监测中需求日益增长,早期裂缝检测对及时维护规划至关重要。本研究提出了一种高效的选择性微调策略,通过优化归一化组件增强分割模型在裂缝检测中的适应性。实验结果表明,仅对归一化参数进行选择性微调在性能和计算效率上优于全面微调和其他常见微调技术,同时提高了模型的泛化能力。基于Segment Anything Model(SAM)的SAC模型在OmniCrack30k基准数据集上取得了最高的性能表现。
Key Takeaways
- 图像裂缝检测算法的重要性在于早期检测裂缝对基础设施维护的及时性。
- 现有的深度学习方法对裂缝检测算法进行了显著改进,但仍面临标签数据集需求量大和计算成本高的挑战。
- 研究提出了一种高效的选择性微调策略,专注于归一化组件的调优,以提高分割模型在裂缝检测中的适应性。
- 实验证明,仅对归一化参数进行选择性微调能提高模型的性能和泛化能力,同时降低计算成本。
- 基于Segment Anything Model(SAM)的SAC模型在多个基准数据集上取得了显著的性能表现。尤其是在OmniCrack30k数据集上达到了较高的F1分数和IoU值。
点此查看论文截图

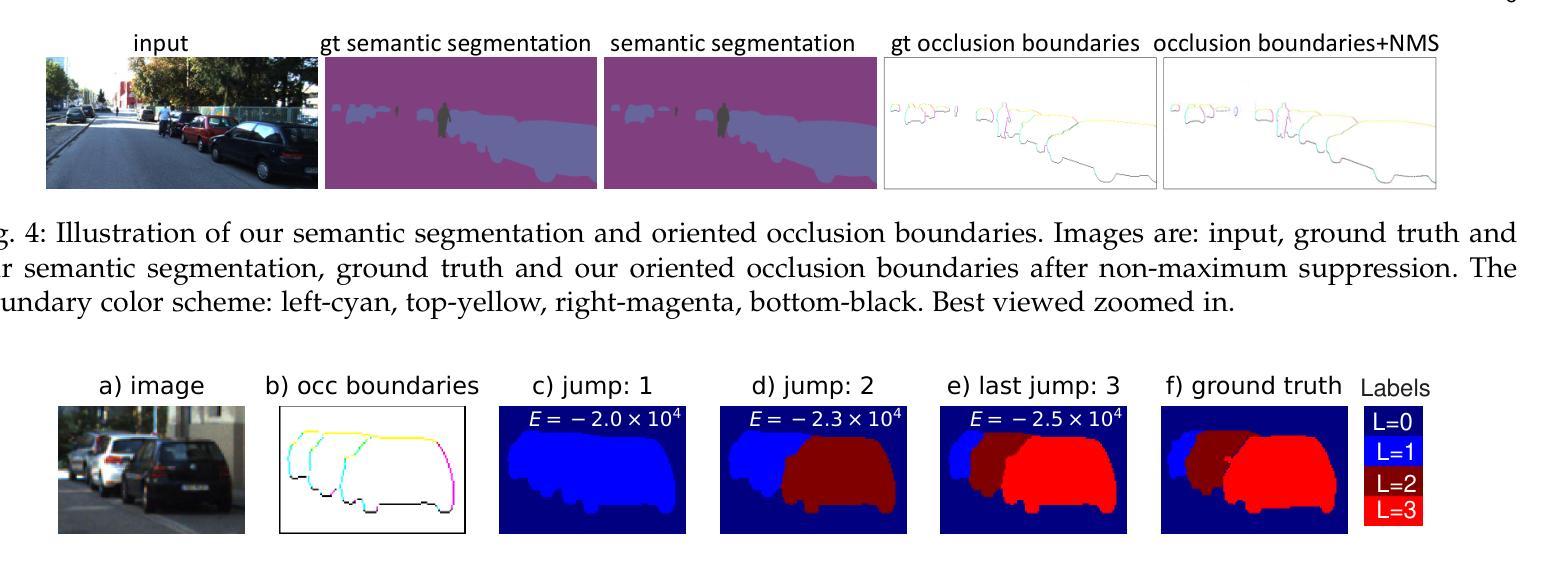
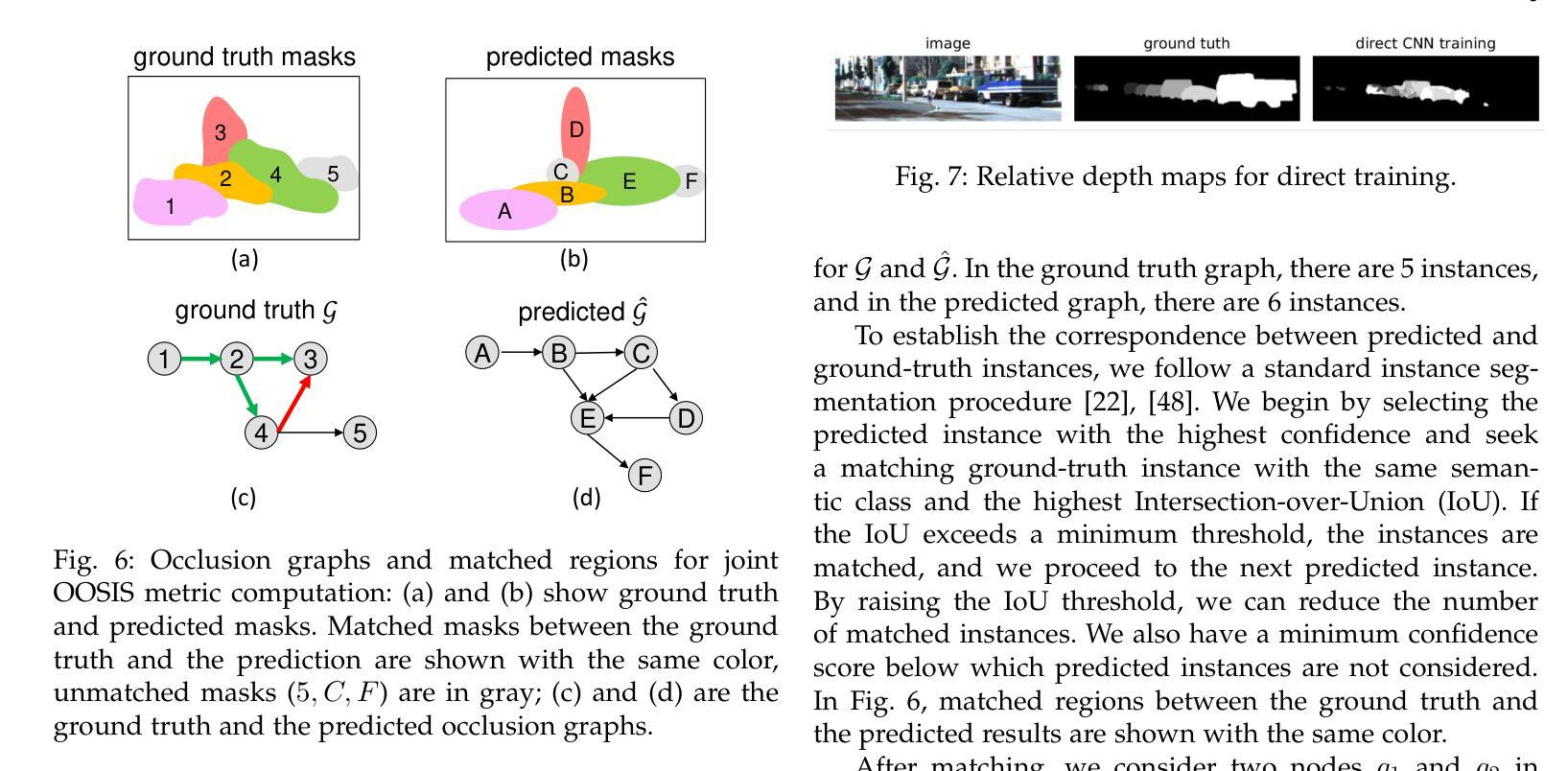
Occlusion-Ordered Semantic Instance Segmentation
Authors:Soroosh Baselizadeh, Cheuk-To Yu, Olga Veksler, Yuri Boykov
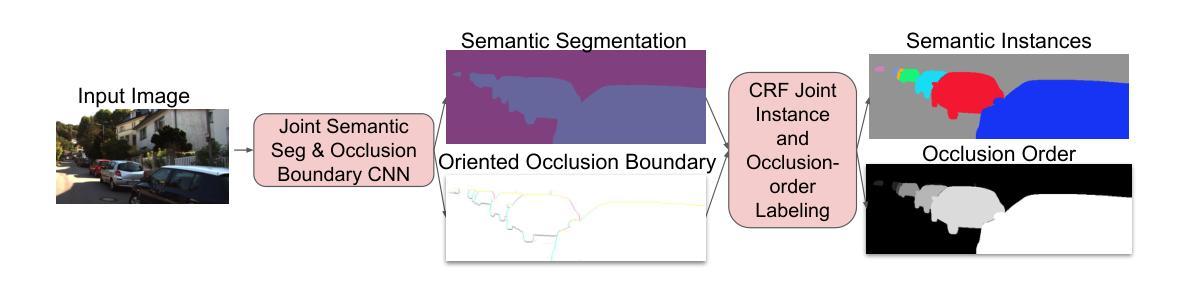
Standard semantic instance segmentation provides useful, but inherently 2D information from a single image. To enable 3D analysis, one usually integrates absolute monocular depth estimation with instance segmentation. However, monocular depth is a difficult task. Instead, we leverage a simpler single-image task, occlusion-based relative depth ordering, providing coarser but useful 3D information. We show that relative depth ordering works more reliably from occlusions than from absolute depth. We propose to solve the joint task of relative depth ordering and segmentation of instances based on occlusions. We call this task Occlusion-Ordered Semantic Instance Segmentation (OOSIS). We develop an approach to OOSIS that extracts instances and their occlusion order simultaneously from oriented occlusion boundaries and semantic segmentation. Unlike popular detect-and-segment framework for instance segmentation, combining occlusion ordering with instance segmentation allows a simple and clean formulation of OOSIS as a labeling problem. As a part of our solution for OOSIS, we develop a novel oriented occlusion boundaries approach that significantly outperforms prior work. We also develop a new joint OOSIS metric based both on instance mask accuracy and correctness of their occlusion order. We achieve better performance than strong baselines on KINS and COCOA datasets.
标准语义实例分割提供了来自单幅图像的二维信息,虽然有用,但本质上是二维的。为了进行三维分析,通常需要将单眼绝对深度估计与实例分割相结合。然而,单眼深度是一项艰巨的任务。相反,我们利用更简单的单图像任务——基于遮挡的相对深度排序,提供粗略但有用的三维信息。我们表明,相对深度排序从遮挡物中比从绝对深度中更可靠地工作。我们提出解决基于遮挡的相对深度排序和实例分割的联合任务。我们将此任务称为遮挡有序语义实例分割(OOSIS)。我们开发了一种面向OOSIS的方法,可以同时从定向遮挡边界和语义分割中提取实例及其遮挡顺序。与流行的用于实例分割的检测和分割框架不同,将遮挡排序与实例分割相结合可以简单明了地将OOSIS表述为标签问题。作为我们对OOSIS解决方案的一部分,我们开发了一种新型的定向遮挡边界方法,该方法显著优于先前的工作。我们还开发了一种新的联合OOSIS指标,该指标既基于实例掩模的准确性,也基于遮挡顺序的正确性。我们在KINS和COCOA数据集上实现了优于强大基准线的性能。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
本文介绍了基于遮挡排序的语义实例分割(OOSIS)任务,该任务结合了相对深度排序和实例分割。文章指出,通过利用单图像中的遮挡信息,可以提取出实例及其遮挡顺序,形成一种更简单的3D分析方法。与流行的检测和分割框架不同,OOSIS能够将实例分割和遮挡排序相结合,简化为一个标签问题。同时,提出了一种新型的定向遮挡边界方法,在性能指标上优于先前的工作。
Key Takeaways
- OOSIS任务结合了相对深度排序和实例分割,提供了一种更简单的3D分析方法。
- 通过利用单图像中的遮挡信息,可以提取出实例及其遮挡顺序。
- 与流行的检测和分割框架不同,OOSIS将实例分割和遮挡排序结合,简化为标签问题。
- 提出了一种新型的定向遮挡边界方法,显著提高了性能。
- 开发了针对OOSIS的新联合度量标准,结合实例掩膜准确性和遮挡顺序的正确性。
- 在KINS和COCOA数据集上,相较于强大的基线模型,取得了更好的性能表现。
点此查看论文截图

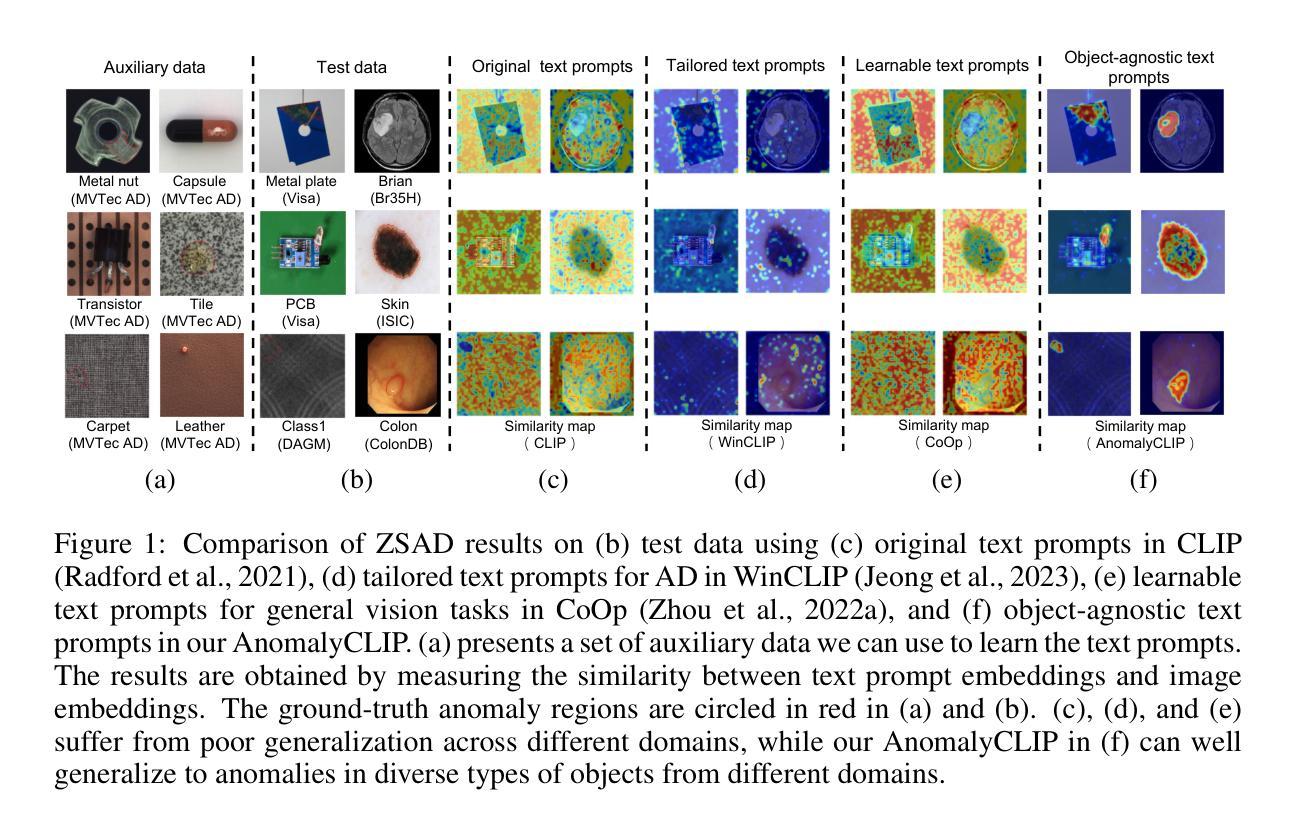
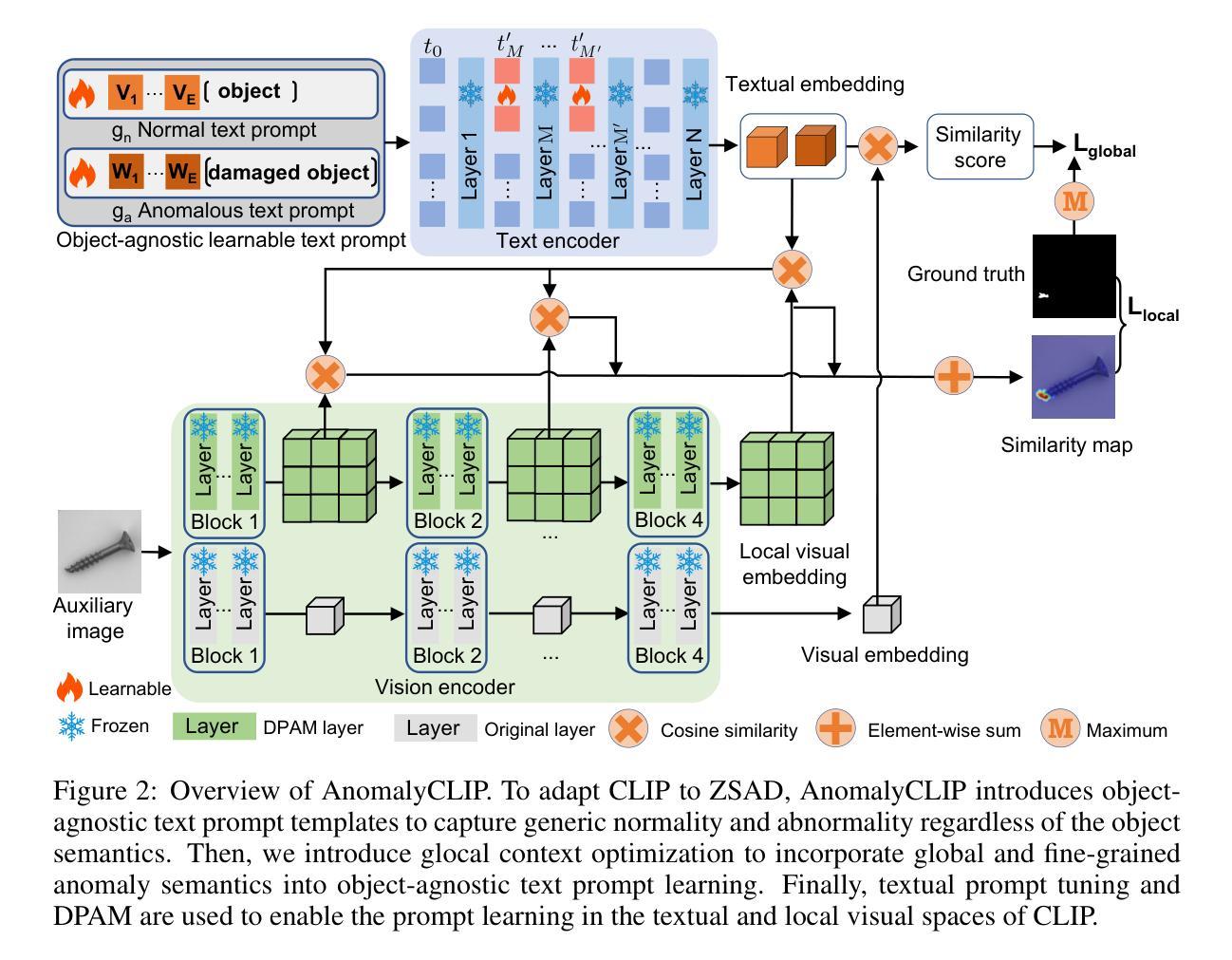
AnomalyCLIP: Object-agnostic Prompt Learning for Zero-shot Anomaly Detection
Authors:Qihang Zhou, Guansong Pang, Yu Tian, Shibo He, Jiming Chen
Zero-shot anomaly detection (ZSAD) requires detection models trained using auxiliary data to detect anomalies without any training sample in a target dataset. It is a crucial task when training data is not accessible due to various concerns, eg, data privacy, yet it is challenging since the models need to generalize to anomalies across different domains where the appearance of foreground objects, abnormal regions, and background features, such as defects/tumors on different products/organs, can vary significantly. Recently large pre-trained vision-language models (VLMs), such as CLIP, have demonstrated strong zero-shot recognition ability in various vision tasks, including anomaly detection. However, their ZSAD performance is weak since the VLMs focus more on modeling the class semantics of the foreground objects rather than the abnormality/normality in the images. In this paper we introduce a novel approach, namely AnomalyCLIP, to adapt CLIP for accurate ZSAD across different domains. The key insight of AnomalyCLIP is to learn object-agnostic text prompts that capture generic normality and abnormality in an image regardless of its foreground objects. This allows our model to focus on the abnormal image regions rather than the object semantics, enabling generalized normality and abnormality recognition on diverse types of objects. Large-scale experiments on 17 real-world anomaly detection datasets show that AnomalyCLIP achieves superior zero-shot performance of detecting and segmenting anomalies in datasets of highly diverse class semantics from various defect inspection and medical imaging domains. Code will be made available at https://github.com/zqhang/AnomalyCLIP.
零样本异常检测(ZSAD)要求使用辅助数据训练的检测模型能够在目标数据集中无需任何训练样本进行异常检测。当由于各种原因无法访问训练数据时,这是一项至关重要的任务,例如数据隐私。然而,由于模型需要泛化到不同领域的异常,前景对象、异常区域和背景特征(如不同产品/器官上的缺陷/肿瘤)的出现可能变化很大,因此这具有挑战性。最近的大型预训练视觉语言模型(VLMs),如CLIP,在各种视觉任务中表现出了强大的零样本识别能力,包括异常检测。然而,它们的ZSAD性能较弱,因为VLMs更侧重于对前景对象的类别语义进行建模,而不是图像中的异常/正常性。在本文中,我们介绍了一种新方法,名为AnomalyCLIP,用于适应CLIP,以实现不同领域的准确ZSAD。AnomalyCLIP的关键洞察力是学习独立于对象的文本提示,以捕获图像中的通用正常性和异常性,而无论其前景对象如何。这使得我们的模型能够关注异常图像区域,而不是对象语义,从而实现对各种对象类型的通用正常性和异常性识别。在17个真实世界的异常检测数据集上进行的大规模实验表明,AnomalyCLIP在具有高度多样化类别语义的数据集(来自各种缺陷检测和医学影像领域)中实现了出色的零样本检测和分割异常的性能。代码将在https://github.com/zqhang/AnomalyCLIP上提供。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF Accepted by ICLR 2024
摘要
本研究解决了零样本异常检测(ZSAD)的难题,利用大型预训练视觉语言模型(VLMs)如CLIP进行异常检测。针对CLIP在ZSAD中的性能不足,本研究提出了一种名为AnomalyCLIP的新方法,通过学习对象无关的文本提示,实现对图像中通用正常和异常的捕捉,使模型关注异常图像区域而非对象语义,在多种类型的对象上实现通用的正常和异常识别。在17个真实世界的异常检测数据集上的大规模实验表明,AnomalyCLIP在高度多样的类别语义和不同缺陷检测和医学影像领域的异常检测和分割上取得了出色的零样本性能。
关键见解
- 零样本异常检测(ZSAD)是在无法访问训练数据的情况下检测异常的关键任务,因为数据隐私等问题。
- 大型预训练视觉语言模型(VLMs)如CLIP在异常检测中具有零样本识别的能力。
- CLIP在ZSAD中的性能因关注对象语义而非图像中的正常/异常而受限。
- AnomalyCLIP通过适应CLIP进行准确的跨域ZSAD。
- AnomalyCLIP的关键在于学习对象无关的文本提示,捕捉图像中的通用正常和异常。
- AnomalyCLIP使模型关注异常图像区域,实现多样化的正常和异常识别。
点此查看论文截图