⚠️ 以下所有内容总结都来自于 大语言模型的能力,如有错误,仅供参考,谨慎使用
🔴 请注意:千万不要用于严肃的学术场景,只能用于论文阅读前的初筛!
💗 如果您觉得我们的项目对您有帮助 ChatPaperFree ,还请您给我们一些鼓励!⭐️ HuggingFace免费体验
2025-04-23 更新
DSPO: Direct Semantic Preference Optimization for Real-World Image Super-Resolution
Authors:Miaomiao Cai, Simiao Li, Wei Li, Xudong Huang, Hanting Chen, Jie Hu, Yunhe Wang
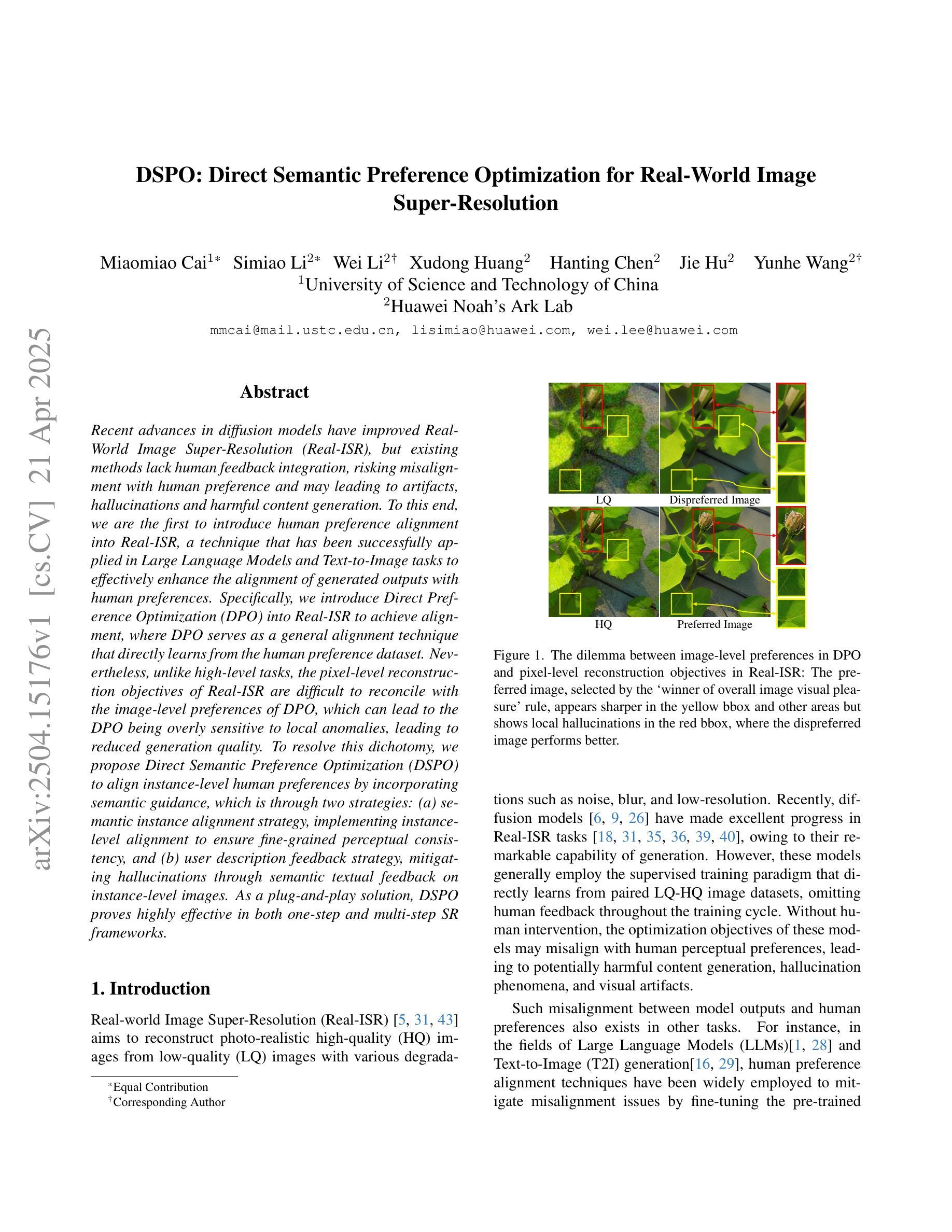
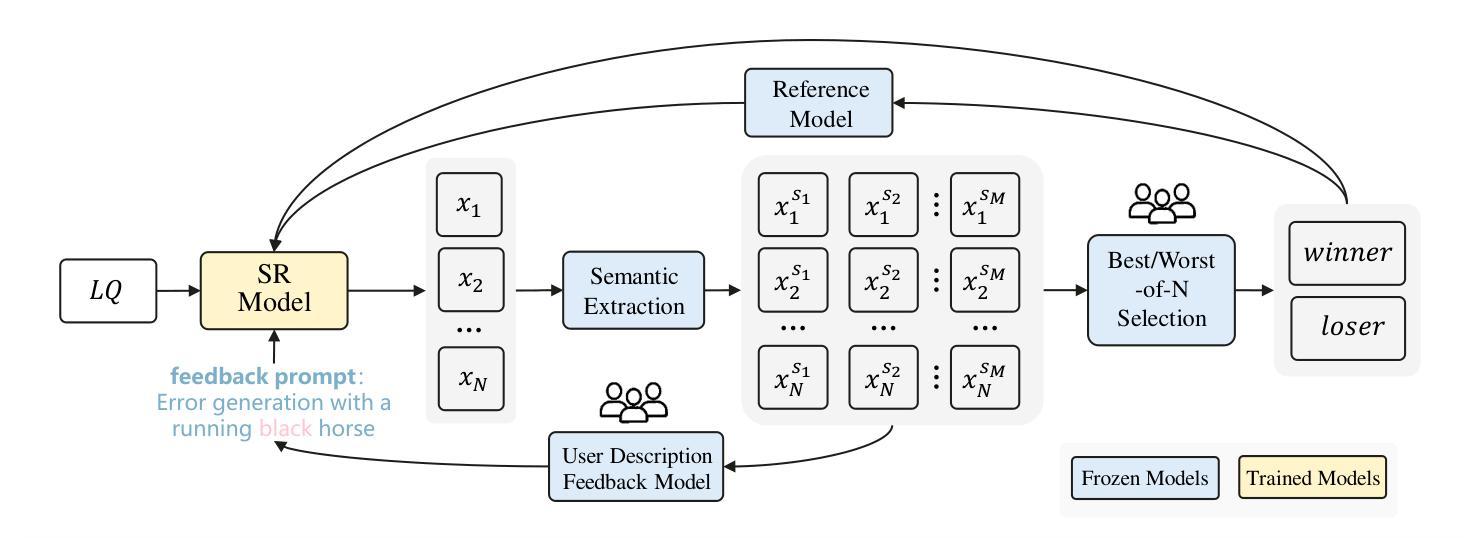
Recent advances in diffusion models have improved Real-World Image Super-Resolution (Real-ISR), but existing methods lack human feedback integration, risking misalignment with human preference and may leading to artifacts, hallucinations and harmful content generation. To this end, we are the first to introduce human preference alignment into Real-ISR, a technique that has been successfully applied in Large Language Models and Text-to-Image tasks to effectively enhance the alignment of generated outputs with human preferences. Specifically, we introduce Direct Preference Optimization (DPO) into Real-ISR to achieve alignment, where DPO serves as a general alignment technique that directly learns from the human preference dataset. Nevertheless, unlike high-level tasks, the pixel-level reconstruction objectives of Real-ISR are difficult to reconcile with the image-level preferences of DPO, which can lead to the DPO being overly sensitive to local anomalies, leading to reduced generation quality. To resolve this dichotomy, we propose Direct Semantic Preference Optimization (DSPO) to align instance-level human preferences by incorporating semantic guidance, which is through two strategies: (a) semantic instance alignment strategy, implementing instance-level alignment to ensure fine-grained perceptual consistency, and (b) user description feedback strategy, mitigating hallucinations through semantic textual feedback on instance-level images. As a plug-and-play solution, DSPO proves highly effective in both one-step and multi-step SR frameworks.
在扩散模型的最新进展中,真实世界图像超分辨率(Real-ISR)技术得到了提升。然而,现有方法缺乏人类反馈集成,存在与人类偏好不一致的风险,可能导致出现伪影、幻觉和有害内容生成。为此,我们首次将人类偏好对齐技术引入Real-ISR。该技术已成功应用于大型语言模型和文本到图像任务,旨在有效提高生成输出与人类偏好的对齐程度。具体来说,我们为Real-ISR引入了直接偏好优化(DPO)以实现对齐,其中DPO作为一种通用对齐技术,直接从人类偏好数据集中学习。然而,与高级任务不同,Real-ISR的像素级重建目标与DPO的图像级偏好难以协调,可能导致DPO对局部异常过于敏感,从而降低生成质量。为了解决这一矛盾,我们提出了直接语义偏好优化(DSPO),通过融入语义指导来对齐实例级人类偏好。这包括两个策略:(a)语义实例对齐策略,实现实例级对齐以确保精细的感知一致性;(b)用户描述反馈策略,通过实例级图像的语义文本反馈来缓解幻觉问题。作为一种即插即用解决方案,DSPO在单步和多步超分辨率框架中都证明了其高度有效性。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
本文介绍了在扩散模型中引入人类偏好对齐技术来解决真实世界图像超分辨率(Real-ISR)中的一些问题,如对齐人类偏好不足和可能产生伪像和有害内容等。为了解决这些不足,引入了直接偏好优化(DPO),并结合语义指导进行改进提出了直接语义偏好优化(DSPO)。通过语义实例对齐策略和实例级别的用户描述反馈策略实现细粒度的感知一致性并减少伪像。DSPO作为一种即插即用解决方案,在一步和多步SR框架中均表现出高度有效性。
Key Takeaways
- 扩散模型在Real-ISR中的最新进展面临与人类偏好对齐不足的问题,可能导致伪像和有害内容生成。
- 为解决此问题,首次将人类偏好对齐技术引入Real-ISR。
- 采用直接偏好优化(DPO)技术实现人类偏好对齐,但面临与Real-ISR像素级重建目标的不协调问题。
- 提出直接语义偏好优化(DSPO)来解决DPO的局限性,结合语义指导进行实例级别的人类偏好对齐。
- DSPO通过两个策略实现:语义实例对齐和用户描述反馈,确保细粒度的感知一致性并减少伪像。
点此查看论文截图
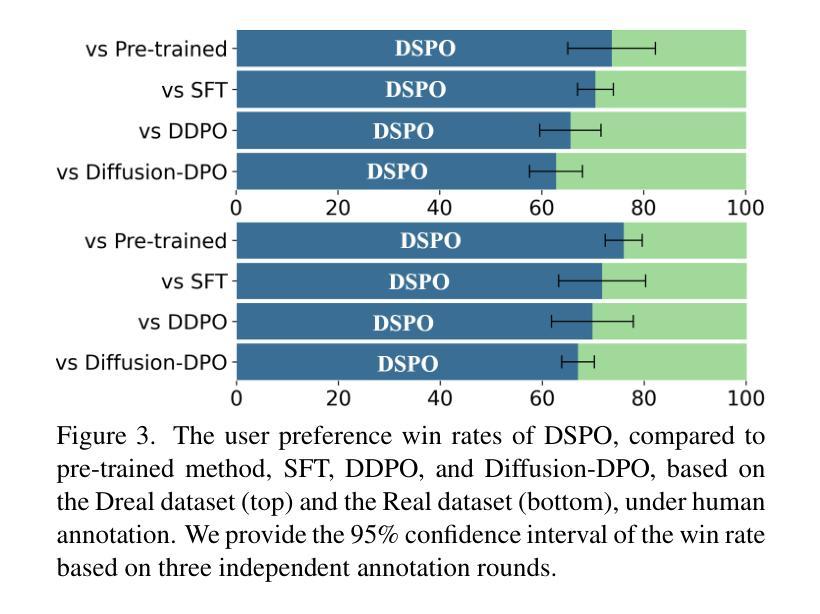
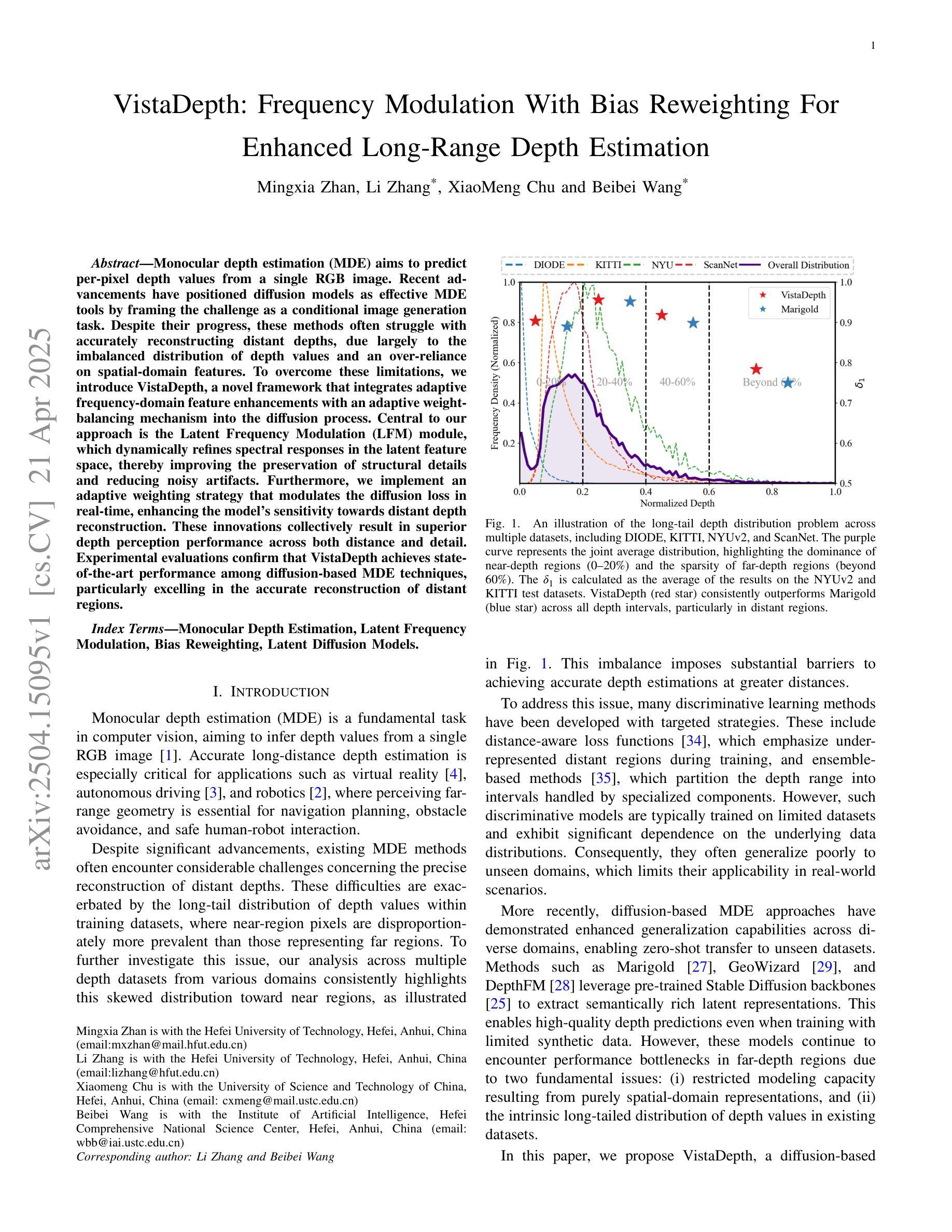
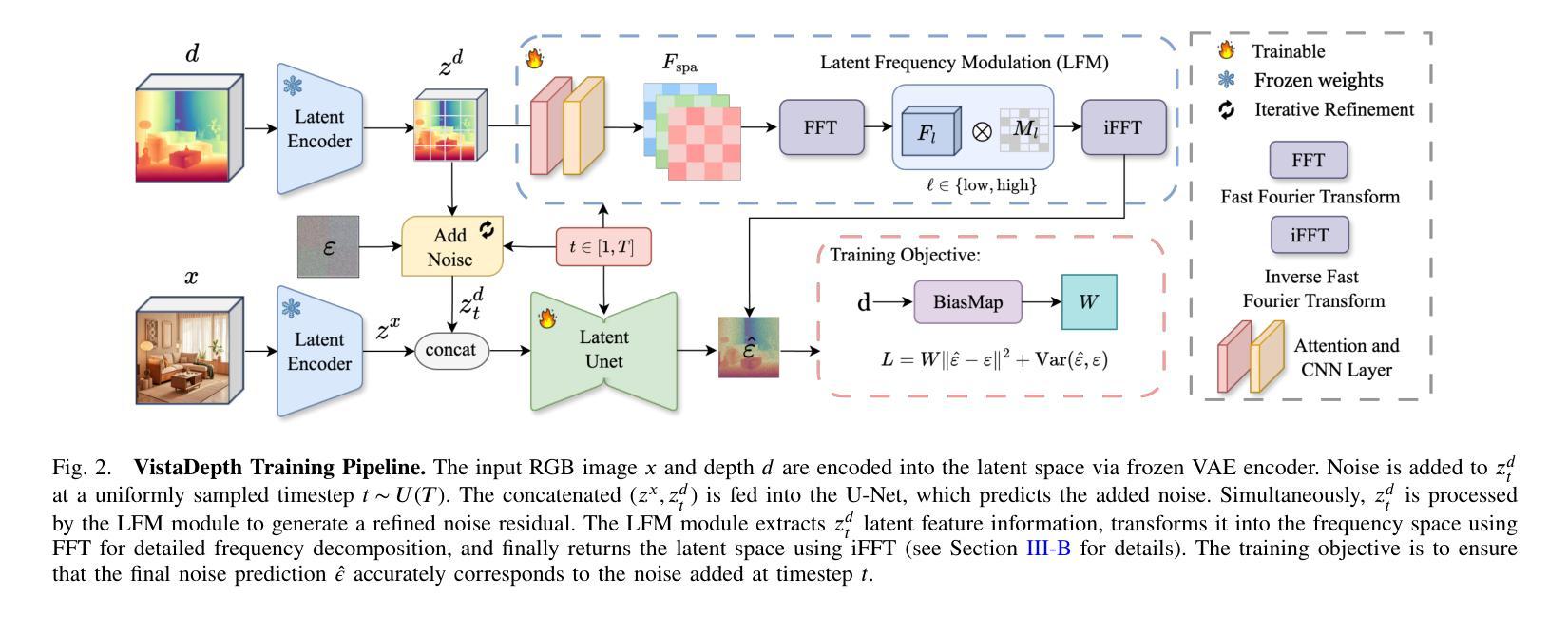
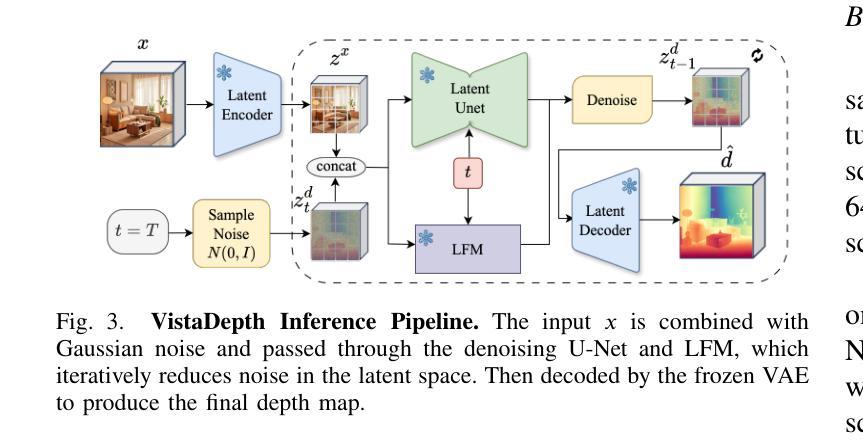
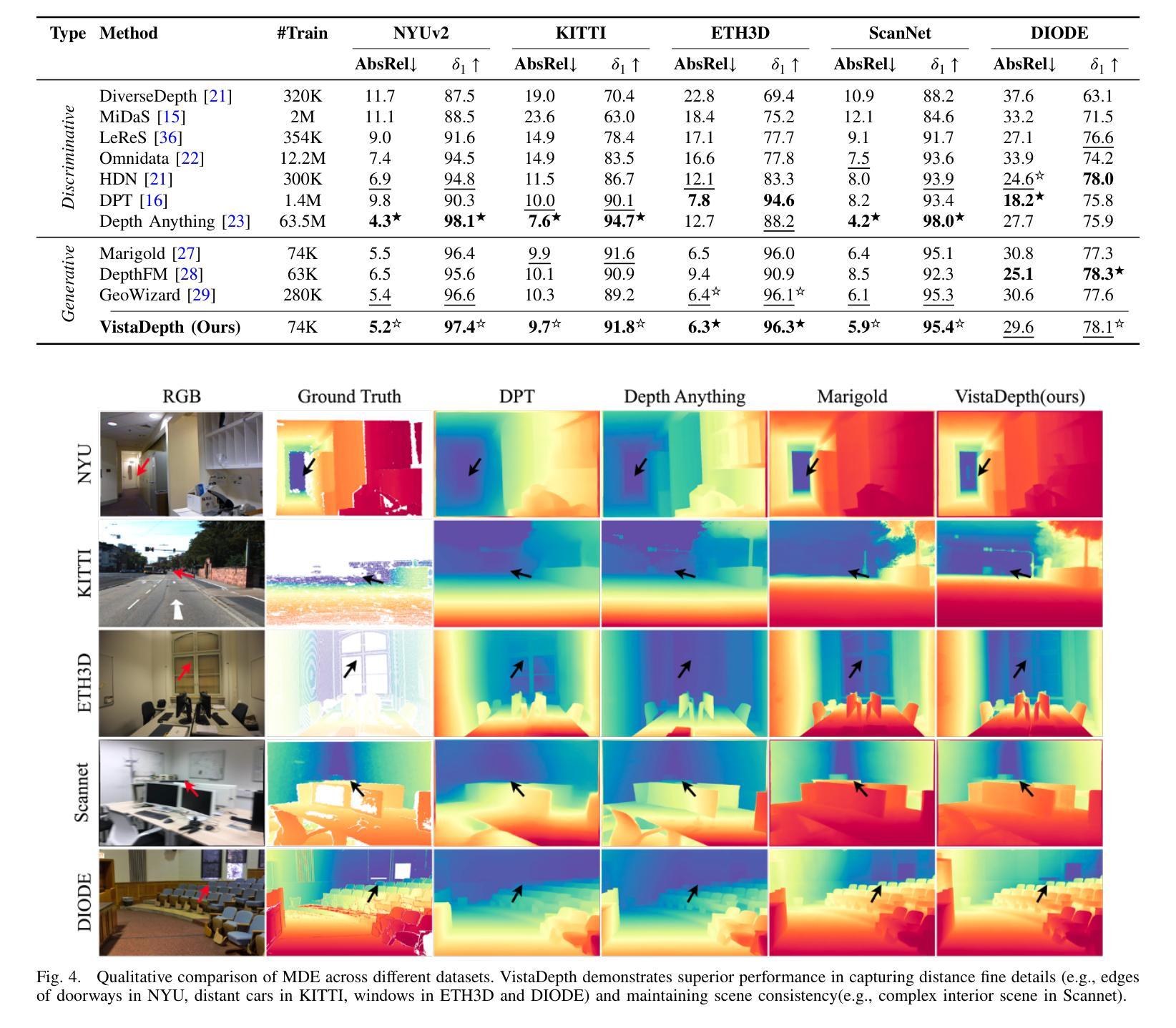
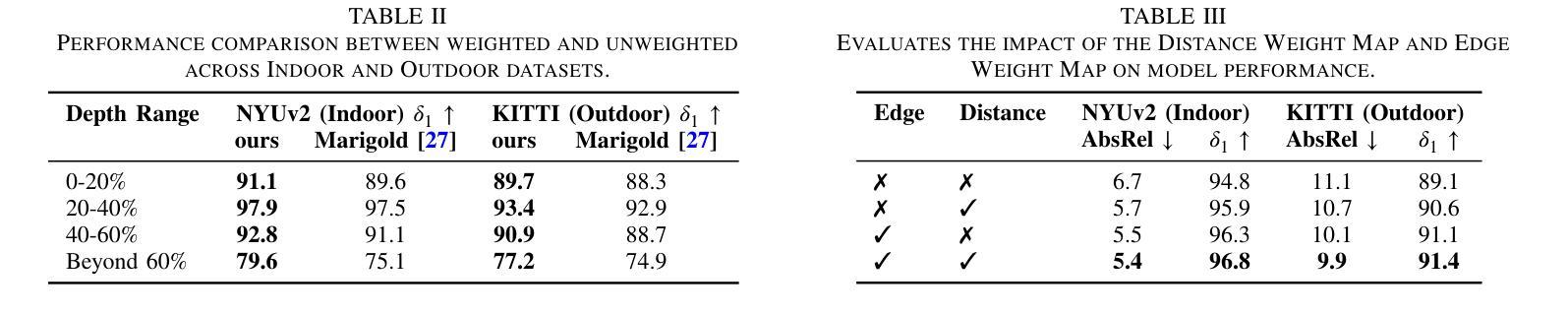
VistaDepth: Frequency Modulation With Bias Reweighting For Enhanced Long-Range Depth Estimation
Authors:Mingxia Zhan, Li Zhang, XiaoMeng Chu, Beibei Wang
Monocular depth estimation (MDE) aims to predict per-pixel depth values from a single RGB image. Recent advancements have positioned diffusion models as effective MDE tools by framing the challenge as a conditional image generation task. Despite their progress, these methods often struggle with accurately reconstructing distant depths, due largely to the imbalanced distribution of depth values and an over-reliance on spatial-domain features. To overcome these limitations, we introduce VistaDepth, a novel framework that integrates adaptive frequency-domain feature enhancements with an adaptive weight-balancing mechanism into the diffusion process. Central to our approach is the Latent Frequency Modulation (LFM) module, which dynamically refines spectral responses in the latent feature space, thereby improving the preservation of structural details and reducing noisy artifacts. Furthermore, we implement an adaptive weighting strategy that modulates the diffusion loss in real-time, enhancing the model’s sensitivity towards distant depth reconstruction. These innovations collectively result in superior depth perception performance across both distance and detail. Experimental evaluations confirm that VistaDepth achieves state-of-the-art performance among diffusion-based MDE techniques, particularly excelling in the accurate reconstruction of distant regions.
单眼深度估计(MDE)旨在从单一RGB图像预测每个像素的深度值。最近的进展将扩散模型定位为有效的MDE工具,将挑战视为条件图像生成任务。尽管有所进展,这些方法在准确重建远距离深度方面仍面临困难,这主要是由于深度值分布不平衡以及过于依赖空间域特征。为了克服这些限制,我们引入了VistaDepth,这是一个新型框架,将自适应频域特征增强和自适应权重平衡机制集成到扩散过程中。我们的方法的核心是潜在频率调制(LFM)模块,它动态地优化潜在特征空间中的光谱响应,从而提高结构细节的保留,减少噪声伪影。此外,我们实现了一种自适应加权策略,实时调整扩散损失,提高模型对远距离深度重建的敏感性。这些创新共同导致了在距离和细节方面的深度感知性能优越。实验评估证实,VistaDepth在基于扩散的MDE技术中达到最新水平,特别是在准确重建远距离区域方面表现出色。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF 8 pages, 6 figures, 4 tables
Summary
扩散模型在单目深度估计(MDE)领域展现出强大的潜力,通过将挑战转化为条件图像生成任务。然而,现有方法常常在重建远距离深度时存在不足。为此,本文提出了VistaDepth框架,集成了自适应频域特征增强和自适应权重平衡机制。该框架通过潜频率调制(LFM)模块动态优化频谱响应,提高了结构细节的保留并减少了噪声伪影。此外,实施自适应权重策略,实时调整扩散损失,提高对远距离深度重建的敏感度。这些创新使VistaDepth在距离和细节方面的深度感知性能均达到一流水平。
Key Takeaways
- 扩散模型在单目深度估计中展现出有效性。
- 现有方法面临重建远距离深度的挑战,主要由于深度值分布不平衡及过度依赖空间域特征。
- VistaDepth框架通过集成自适应频域特征增强和自适应权重平衡机制来克服这些挑战。
- Latent Frequency Modulation(LFM)模块动态优化频谱响应,提高结构细节保留并减少噪声伪影。
- 实施自适应权重策略,实时调整扩散损失,增强模型对远距离深度重建的敏感度。
- VistaDepth在深度感知性能上达到一流水平,特别是在准确重建远距离区域方面。
点此查看论文截图
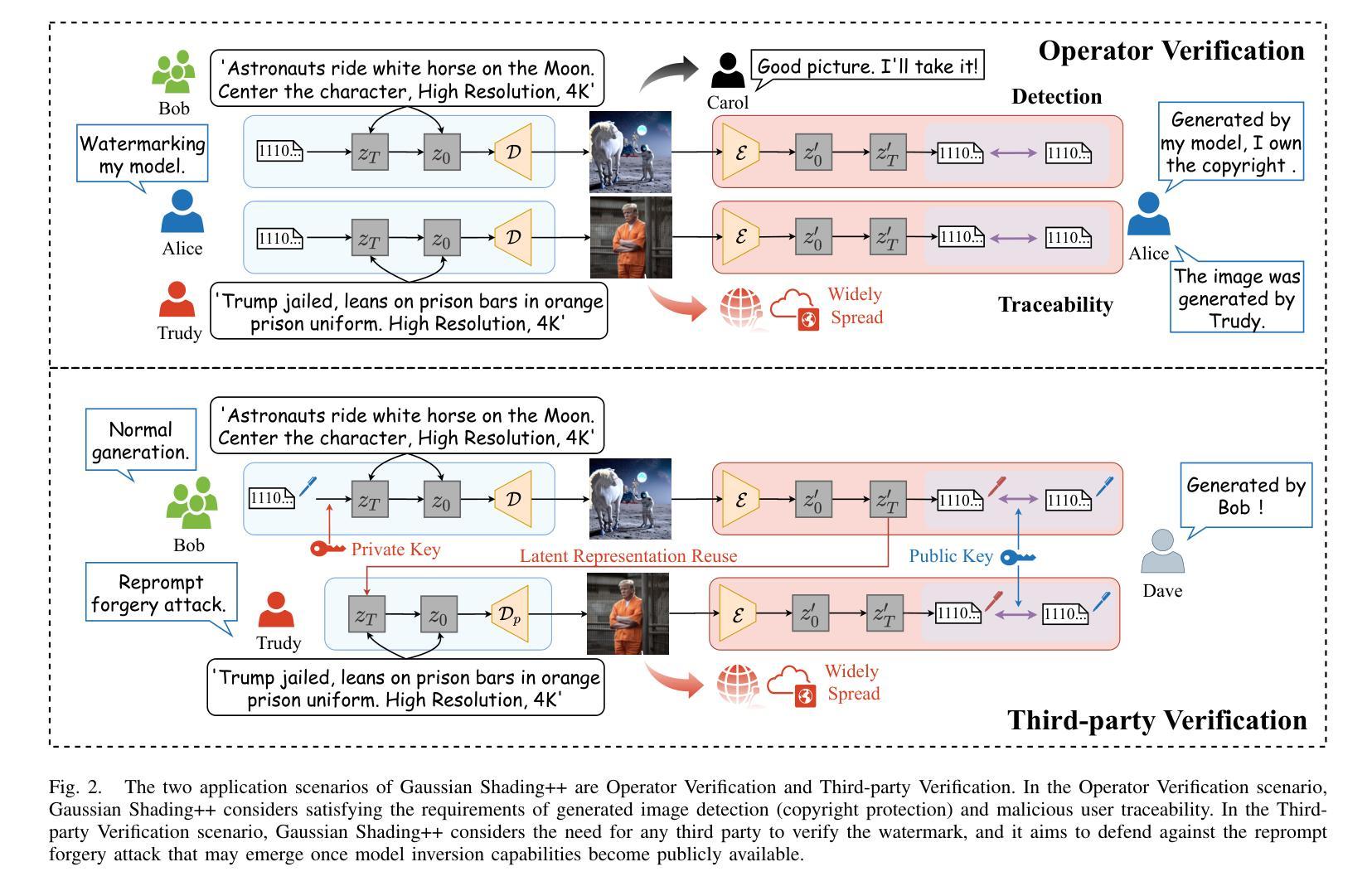
Gaussian Shading++: Rethinking the Realistic Deployment Challenge of Performance-Lossless Image Watermark for Diffusion Models
Authors:Zijin Yang, Xin Zhang, Kejiang Chen, Kai Zeng, Qiyi Yao, Han Fang, Weiming Zhang, Nenghai Yu
Ethical concerns surrounding copyright protection and inappropriate content generation pose challenges for the practical implementation of diffusion models. One effective solution involves watermarking the generated images. Existing methods primarily focus on ensuring that watermark embedding does not degrade the model performance. However, they often overlook critical challenges in real-world deployment scenarios, such as the complexity of watermark key management, user-defined generation parameters, and the difficulty of verification by arbitrary third parties. To address this issue, we propose Gaussian Shading++, a diffusion model watermarking method tailored for real-world deployment. We propose a double-channel design that leverages pseudorandom error-correcting codes to encode the random seed required for watermark pseudorandomization, achieving performance-lossless watermarking under a fixed watermark key and overcoming key management challenges. Additionally, we model the distortions introduced during generation and inversion as an additive white Gaussian noise channel and employ a novel soft decision decoding strategy during extraction, ensuring strong robustness even when generation parameters vary. To enable third-party verification, we incorporate public key signatures, which provide a certain level of resistance against forgery attacks even when model inversion capabilities are fully disclosed. Extensive experiments demonstrate that Gaussian Shading++ not only maintains performance losslessness but also outperforms existing methods in terms of robustness, making it a more practical solution for real-world deployment.
关于扩散模型的实用化,存在关于版权保护和不当内容生成的伦理问题所带来的挑战。一种有效的解决方案是在生成的图像上添加水印。现有方法主要关注确保水印嵌入不会降低模型性能。然而,他们往往忽视了真实部署场景中关键挑战,如水印密钥管理的复杂性、用户定义的生成参数以及第三方验证的困难。为了解决这一问题,我们提出了高斯阴影++(Gaussian Shading++),这是一种针对真实世界部署的扩散模型水印方法。我们提出了一种双通道设计,利用伪随机纠错编码对水印伪随机化所需的随机种子进行编码,在固定水印密钥下实现性能无损的水印,并解决密钥管理挑战。此外,我们将生成和反转过程中引入的失真建模为加性白色高斯噪声通道,并在提取过程中采用新型软决策解码策略,确保即使在生成参数变化时也具有强大的稳健性。为了实现第三方验证,我们引入了公钥签名,即使在模型反转能力完全公开的情况下,也能提供一定的抗伪造攻击能力。大量实验表明,高斯阴影++不仅保持了性能无损,而且在稳健性方面优于现有方法,使其成为真实世界部署的更实用解决方案。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF 18 pages, 8 figures
Summary
针对扩散模型实际应用中的版权保护与不当内容生成等伦理问题,提出一种名为Gaussian Shading++的模型水印方法。该方法采用双通道设计,利用伪随机纠错码编码水印随机种子,实现固定水印密钥下的性能无损水印,并克服密钥管理挑战。同时,对生成和反转过程中引入的失真进行建模,采用新颖的软决策解码策略,确保在生成参数变化时仍具有强大的稳健性。为了支持第三方验证,集成了公钥签名,即使模型反转能力完全公开,也能提供一定程度的防篡改攻击能力。实验表明,Gaussian Shading++不仅保持性能无损,而且在稳健性方面超越现有方法,成为更适用于实际部署的实用解决方案。
Key Takeaways
- 扩散模型实际应用面临版权保护与内容适当性挑战。
- 水印嵌入需确保不影响模型性能且适应现实部署的复杂性。
- Gaussian Shading++采用双通道设计及伪随机纠错码实现性能无损水印。
- 该方法克服密钥管理难题,并确保在生成参数变化时仍具有稳健性。
- 通过建模生成和反转过程中的失真,采用软决策解码策略增强稳健性。
- 集成公钥签名以支持第三方验证,增强防篡改能力。
点此查看论文截图
PIV-FlowDiffuser:Transfer-learning-based denoising diffusion models for PIV
Authors:Qianyu Zhu, Junjie Wang, Jeremiah Hu, Jia Ai, Yong Lee
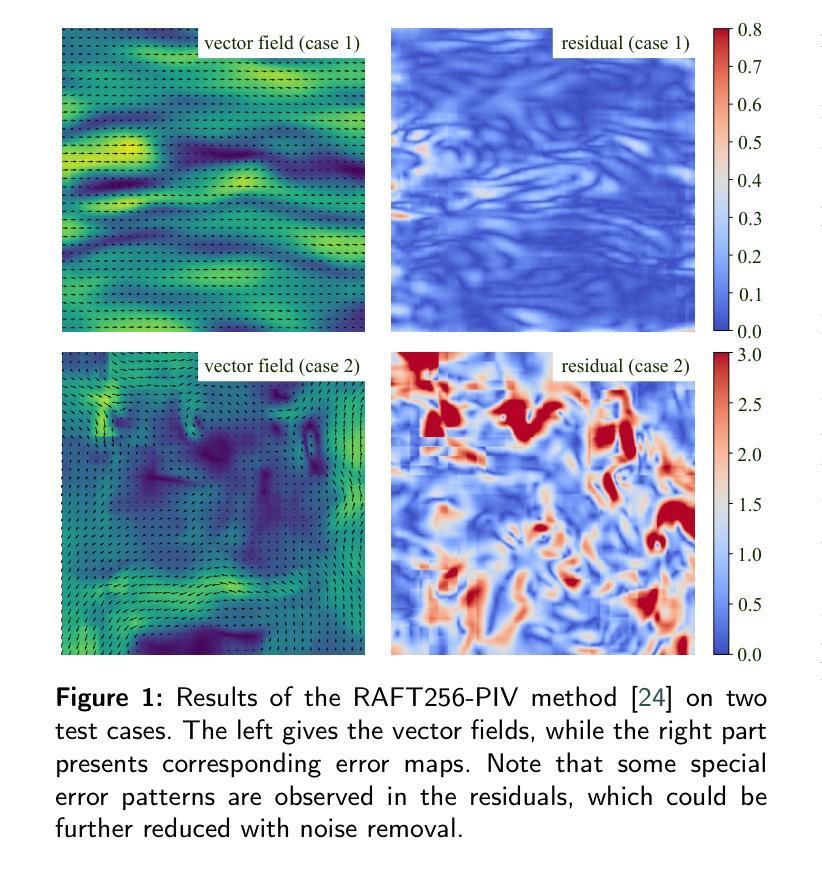
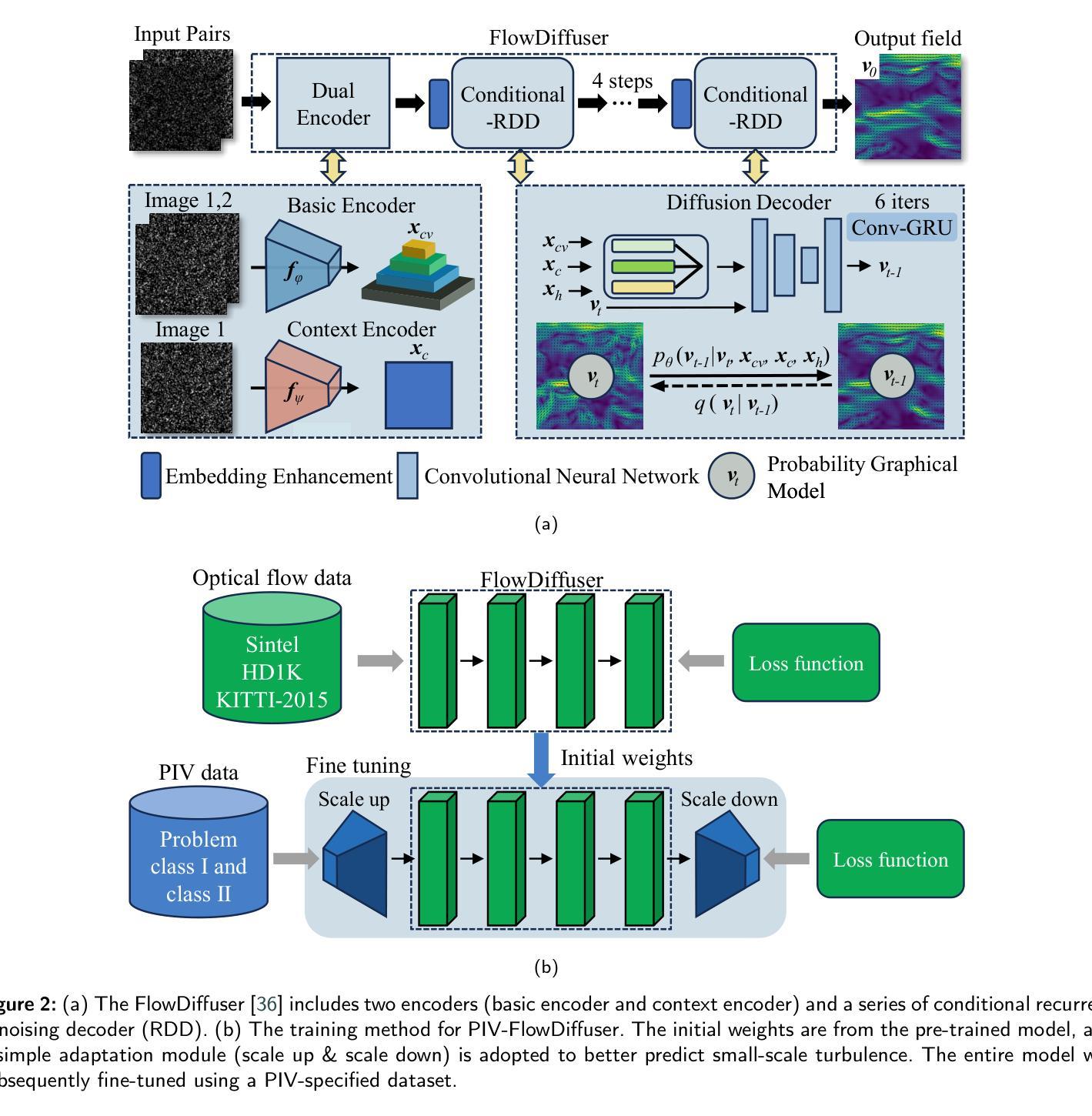
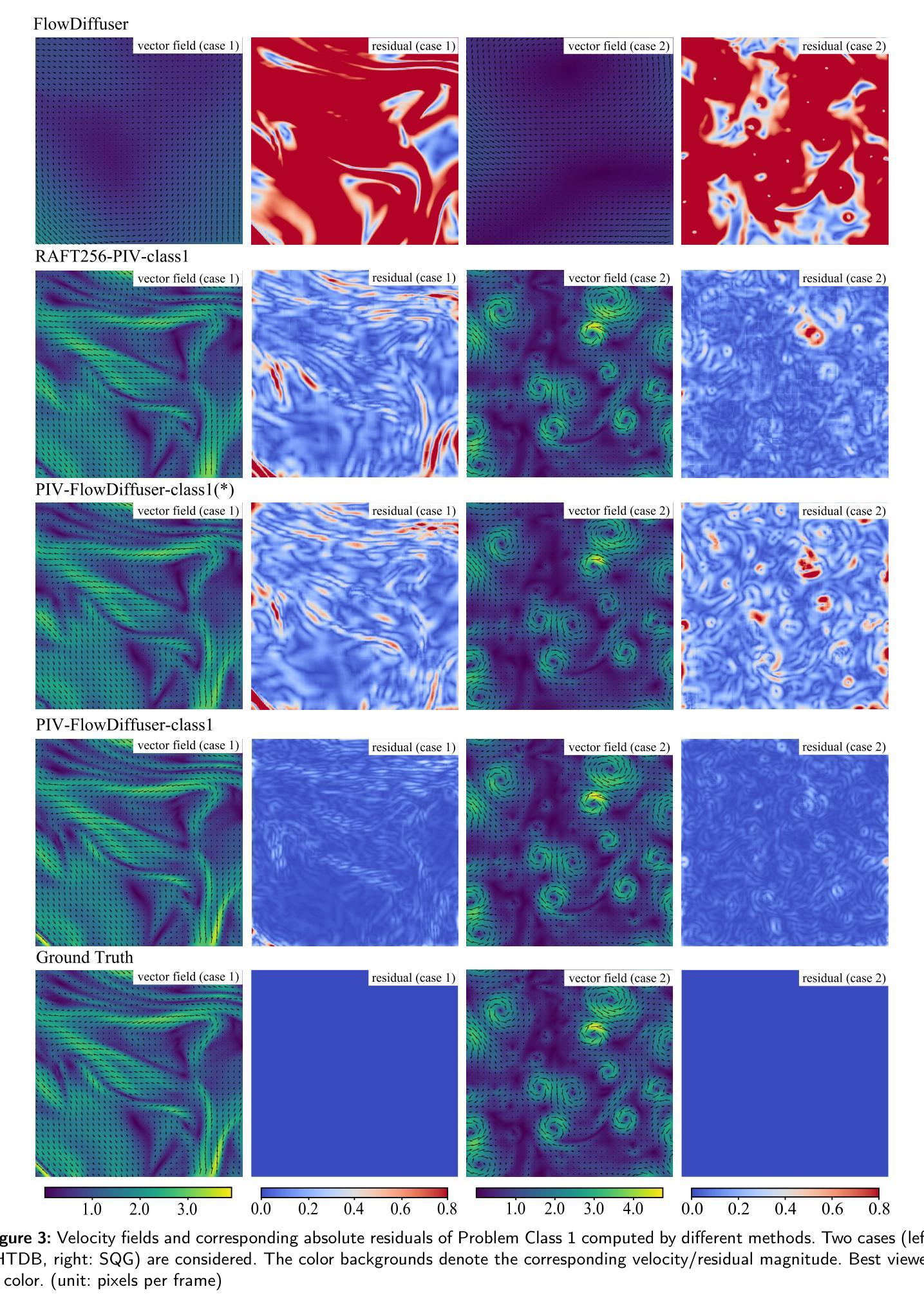
Deep learning algorithms have significantly reduced the computational time and improved the spatial resolution of particle image velocimetry(PIV). However, the models trained on synthetic datasets might have a degraded performance on practical particle images due to domain gaps. As a result, special residual patterns are often observed for the vector fields of deep learning-based estimators. To reduce the special noise step-by-step, we employ a denoising diffusion model(FlowDiffuser) for PIV analysis. And the data-hungry iterative denoising diffusion model is trained via a transfer learning strategy, resulting in our PIV-FlowDiffuser method. Specifically, (1) pre-training a FlowDiffuser model with multiple optical flow datasets of the computer vision community, such as Sintel, KITTI, etc; (2) fine-tuning the pre-trained model on synthetic PIV datasets. Note that the PIV images are upsampled by a factor of two to resolve the small-scale turbulent flow structures. The visualized results indicate that our PIV-FlowDiffuser effectively suppresses the noise patterns. Therefore, the denoising diffusion model reduces the average end-point error~($AEE$) by 59.4% over RAFT256-PIV baseline on the classic Cai’s dataset. Besides, PIV-FlowDiffuser exhibits enhanced generalization performance on unseen particle images due to transfer learning. Overall, this study highlights the transfer-learning-based denoising diffusion models for PIV. And a detailed implementation is recommended for interested readers in the repository https://github.com/Zhu-Qianyu/PIV-FlowDiffuser.
深度学习算法显著减少了粒子图像测速法(PIV)的计算时间并提高了其空间分辨率。然而,由于在特定领域存在的差距,那些在合成数据集上训练的模型在实际粒子图像上的性能可能会下降。因此,基于深度学习的估计器的矢量场通常会出现特殊的残余模式。为了逐步减少特殊噪声,我们为PIV分析采用了一种去噪扩散模型(FlowDiffuser)。数据渴求型的迭代去噪扩散模型通过迁移学习策略进行训练,从而形成了我们的PIV-FlowDiffuser方法。具体而言,(1)使用计算机视觉社区的多个光学流动数据集(如Sintel、KITTI等)对FlowDiffuser模型进行预训练;(2)在合成PIV数据集上对预训练模型进行微调。请注意,PIV图像被放大两倍以解决小尺度湍流结构的问题。可视化结果表明,我们的PIV-FlowDiffuser有效地抑制了噪声模式。因此,在经典的Cai数据集上,与RAFT256-PIV基线相比,去噪扩散模型将终点误差平均值(AEE)降低了59.4%。此外,由于迁移学习,PIV-FlowDiffuser在未见过的粒子图像上表现出增强的泛化性能。总体而言,该研究突出了基于迁移学习的去噪扩散模型在PIV中的应用。感兴趣的读者可以在https://github.com/Zhu-Qianyu/PIV-FlowDiffuser仓库中找到详细的实现方法。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
深度学习算法显著减少了粒子图像测速(PIV)的计算时间,提高了空间分辨率。但模型在实用粒子图像上因领域差距可能存在性能下降问题。为逐步减少特殊噪声,采用去噪扩散模型(FlowDiffuser)进行PIV分析。通过迁移学习策略训练数据渴求的迭代去噪扩散模型,形成PIV-FlowDiffuser方法。预训练FlowDiffuser模型于计算机视觉社区的多光流数据集,如Sintel、KITTI等,再对合成PIV数据集进行微调。PIV图像放大两倍以解析小尺度湍流结构。可视化结果表明,PIV-FlowDiffuser有效抑制了噪声模式。相较于RAFT256-PIV基准,PIV-FlowDiffuser将终点平均误差(AEE)降低了59.4%。此外,由于迁移学习,PIV-FlowDiffuser在未见过的粒子图像上展现出更好的泛化性能。
Key Takeaways
- 深度学习算法在粒子图像测速(PIV)中显著提高了计算效率和空间分辨率。
- 模型在实用粒子图像上的性能可能因领域差距而下降。
- 引入去噪扩散模型(FlowDiffuser)以减小特殊噪声。
- 采用迁移学习策略训练数据渴求的FlowDiffuser模型。
- 模型预训练基于计算机视觉社区的多光流数据集。
- PIV图像放大解析小尺度湍流结构。
点此查看论文截图

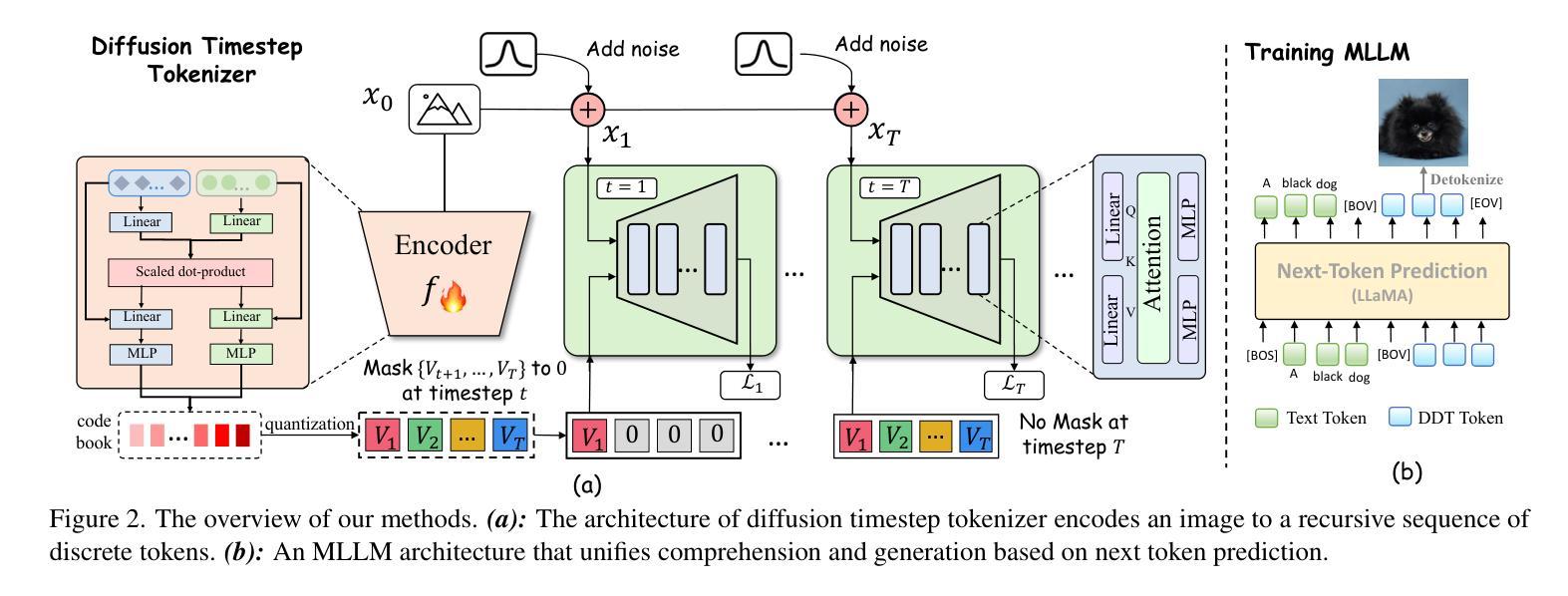
Generative Multimodal Pretraining with Discrete Diffusion Timestep Tokens
Authors:Kaihang Pan, Wang Lin, Zhongqi Yue, Tenglong Ao, Liyu Jia, Wei Zhao, Juncheng Li, Siliang Tang, Hanwang Zhang
Recent endeavors in Multimodal Large Language Models (MLLMs) aim to unify visual comprehension and generation by combining LLM and diffusion models, the state-of-the-art in each task, respectively. Existing approaches rely on spatial visual tokens, where image patches are encoded and arranged according to a spatial order (e.g., raster scan). However, we show that spatial tokens lack the recursive structure inherent to languages, hence form an impossible language for LLM to master. In this paper, we build a proper visual language by leveraging diffusion timesteps to learn discrete, recursive visual tokens. Our proposed tokens recursively compensate for the progressive attribute loss in noisy images as timesteps increase, enabling the diffusion model to reconstruct the original image at any timestep. This approach allows us to effectively integrate the strengths of LLMs in autoregressive reasoning and diffusion models in precise image generation, achieving seamless multimodal comprehension and generation within a unified framework. Extensive experiments show that we achieve superior performance for multimodal comprehension and generation simultaneously compared with other MLLMs. Project Page: https://DDT-LLaMA.github.io/.
最近的多模态大型语言模型(MLLMs)的努力旨在通过结合LLM和扩散模型(这两项任务中的最新技术)来统一视觉理解和生成。现有的方法依赖于空间视觉符号,其中图像补丁被编码并按空间顺序排列(例如,光栅扫描)。然而,我们表明空间符号缺乏语言固有的递归结构,因此对LLM来说形成了一种无法掌握的语言。在本文中,我们通过利用扩散时间步长来学习离散、递归的视觉符号,构建了一种适当的视觉语言。我们提出的符号随着时间步长的增加,递归地弥补了噪声图像中逐渐丧失的属性,使扩散模型能够在任何时间步长重建原始图像。这种方法使我们能够有效地整合LLM在自回归推理和扩散模型在精确图像生成方面的优势,在一个统一框架内实现无缝的多模态理解和生成。大量实验表明,我们在多模态理解和生成方面与其他MLLM相比取得了优越的性能。项目页面:https://DDT-LLaMA.github.io/。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF Accepted by CVPR 2025 (Oral)
Summary
多模态大型语言模型(MLLMs)最新尝试旨在通过结合LLM和扩散模型(每个任务的最新技术),统一视觉理解和生成。现有方法依赖于空间视觉符号,图像块按空间顺序编码和排列(例如,栅格扫描)。然而,研究表明空间符号缺乏语言固有的递归结构,因此形成了一种LLM无法掌握的不可能语言。本文利用扩散时间步长构建了一种适当的视觉语言,学习离散、递归的视觉符号。所提出的符号随着时间步长的增加,递归地弥补了噪声图像中逐渐丧失的属性,使扩散模型能够在任何时间步长重建原始图像。这种方法有效地结合了LLM在自动推理中的优势和扩散模型在精确图像生成中的优势,在一个统一框架内实现了无缝的多模态理解和生成。实验表明,与其他MLLM相比,我们在多模态理解和生成方面同时实现了卓越的性能。
Key Takeaways
- 多模态大型语言模型(MLLMs)结合了LLM和扩散模型,以统一视觉理解和生成。
- 现有方法使用空间视觉符号,但存在递归结构缺失的问题。
- 提出一种基于扩散时间步长的视觉语言,通过离散、递归的视觉符号解决现有问题。
- 符号设计能随时间步长递归补偿图像属性损失,实现在任何时间步长重建原始图像。
- 整合了LLM的自动推理优势和扩散模型的精确图像生成能力。
- 在统一框架内实现了无缝的多模态理解和生成。
- 实验显示,该方法在多模态理解和生成方面性能卓越。
点此查看论文截图
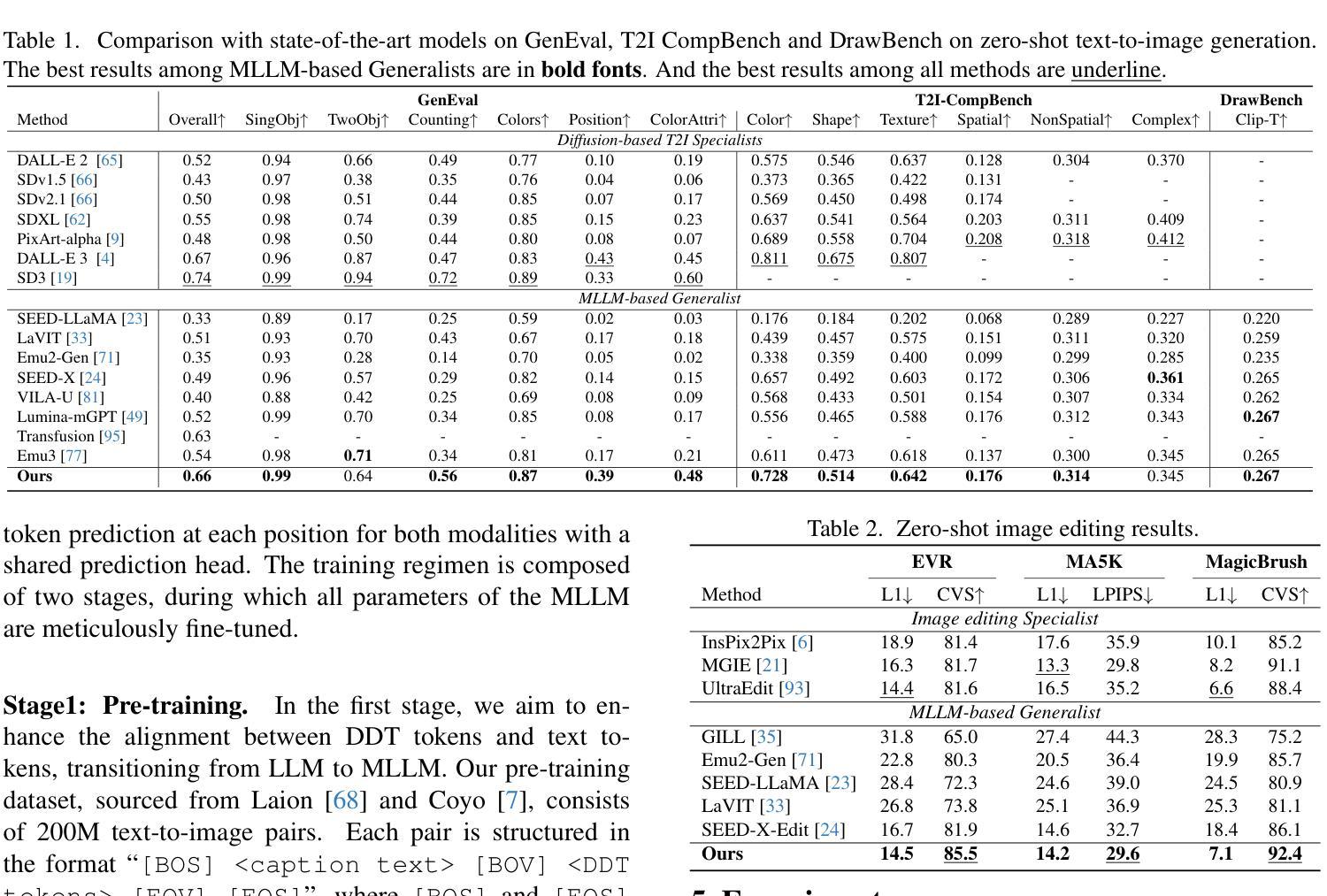


SUDO: Enhancing Text-to-Image Diffusion Models with Self-Supervised Direct Preference Optimization
Authors:Liang Peng, Boxi Wu, Haoran Cheng, Yibo Zhao, Xiaofei He
Previous text-to-image diffusion models typically employ supervised fine-tuning (SFT) to enhance pre-trained base models. However, this approach primarily minimizes the loss of mean squared error (MSE) at the pixel level, neglecting the need for global optimization at the image level, which is crucial for achieving high perceptual quality and structural coherence. In this paper, we introduce Self-sUpervised Direct preference Optimization (SUDO), a novel paradigm that optimizes both fine-grained details at the pixel level and global image quality. By integrating direct preference optimization into the model, SUDO generates preference image pairs in a self-supervised manner, enabling the model to prioritize global-level learning while complementing the pixel-level MSE loss. As an effective alternative to supervised fine-tuning, SUDO can be seamlessly applied to any text-to-image diffusion model. Importantly, it eliminates the need for costly data collection and annotation efforts typically associated with traditional direct preference optimization methods. Through extensive experiments on widely-used models, including Stable Diffusion 1.5 and XL, we demonstrate that SUDO significantly enhances both global and local image quality. The codes are provided at \href{https://github.com/SPengLiang/SUDO}{this link}.
之前的文本到图像扩散模型通常使用有监督微调(SFT)来提升预训练基础模型的性能。然而,这种方法主要最小化像素级别的均方误差(MSE)损失,忽视了图像级别全局优化的需求,这对于实现高感知质量和结构连贯性至关重要。在本文中,我们引入了自我监督直接偏好优化(SUDO),这是一种新的范式,能够优化像素级别的精细细节和全局图像质量。通过将直接偏好优化整合到模型中,SUDO能够以自我监督的方式生成偏好图像对,使模型能够优先学习全局级别的知识,同时补充像素级别的MSE损失。作为有监督微调的有效替代方案,SUDO可以无缝地应用于任何文本到图像扩散模型。重要的是,它消除了与传统直接偏好优化方法相关的昂贵的数据收集和注释工作。通过广泛使用的模型的大量实验,包括Stable Diffusion 1.5和XL,我们证明了SUDO显著提高了全局和局部图像质量。相关代码提供在这个链接:[https://github.com/SPengLiang/SUDO]。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
本文提出了一种新型的文本到图像扩散模型优化方法——Self-sUpervised Direct preference Optimization(SUDO)。SUDO不仅能优化像素级别的细节,还能提升图像全局质量。它通过自我监督的方式生成偏好图像对,使模型在全局层面学习,同时补充像素级的均方误差损失。SUDO可无缝应用于任何文本到图像的扩散模型,并显著提高了图像的全局和局部质量。
Key Takeaways
- 传统文本到图像扩散模型主要依赖监督微调(SFT)来优化预训练基础模型,但这种方法主要关注像素级的均方误差损失,忽视了全局优化的重要性。
- SUDO是一种新型优化范式,能同时优化像素级的细节和图像的全局质量。
- SUDO通过自我监督的方式生成偏好图像对,使模型在全局层面学习,提升了模型的性能。
- SUDO可无缝集成到任何文本到图像的扩散模型中,作为监督微调的替代方案。
- SUDO显著提高了图像的全局和局部质量,通过广泛使用的模型实验得到了验证。
- SUDO降低了对传统直接偏好优化方法所需的高昂数据采集和标注成本。
点此查看论文截图


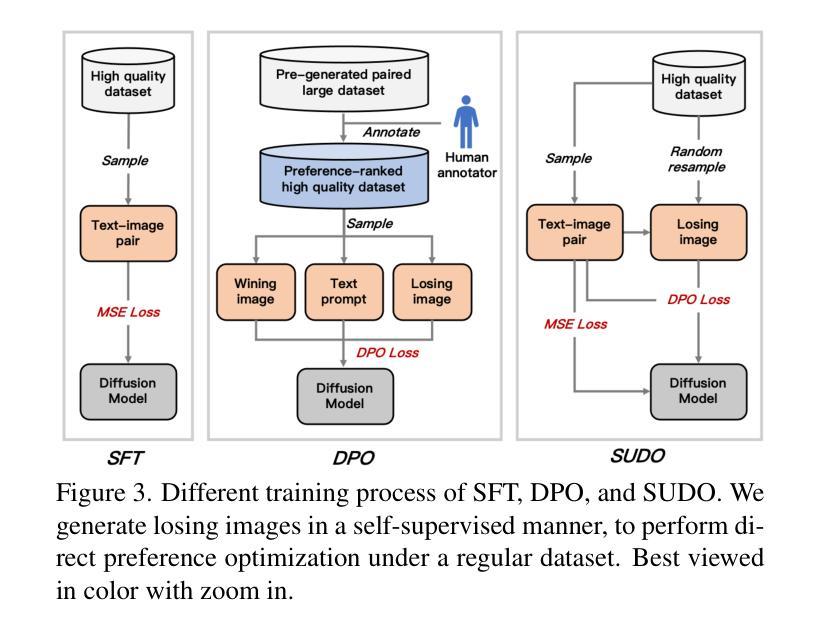

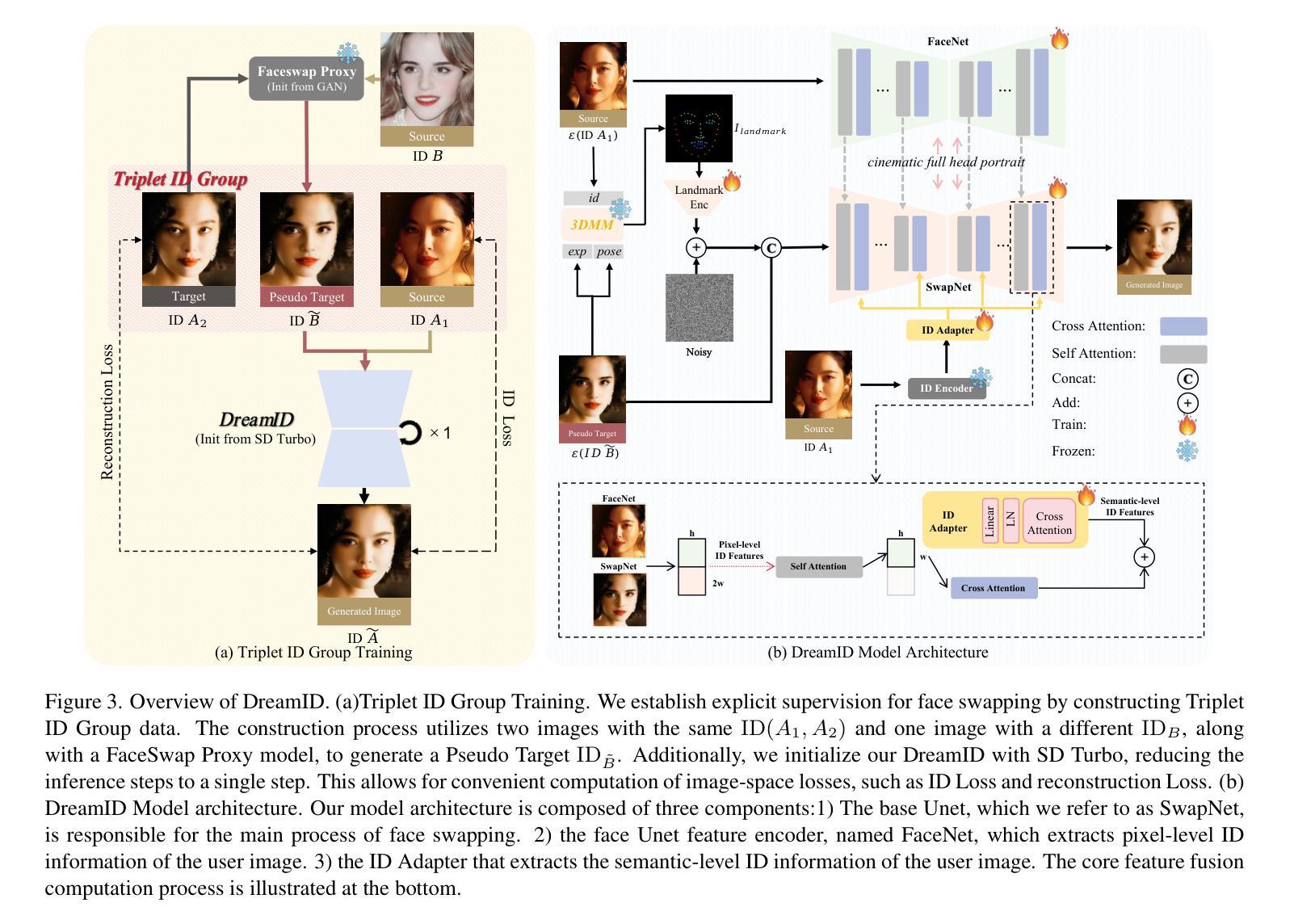
DreamID: High-Fidelity and Fast diffusion-based Face Swapping via Triplet ID Group Learning
Authors:Fulong Ye, Miao Hua, Pengze Zhang, Xinghui Li, Qichao Sun, Songtao Zhao, Qian He, Xinglong Wu
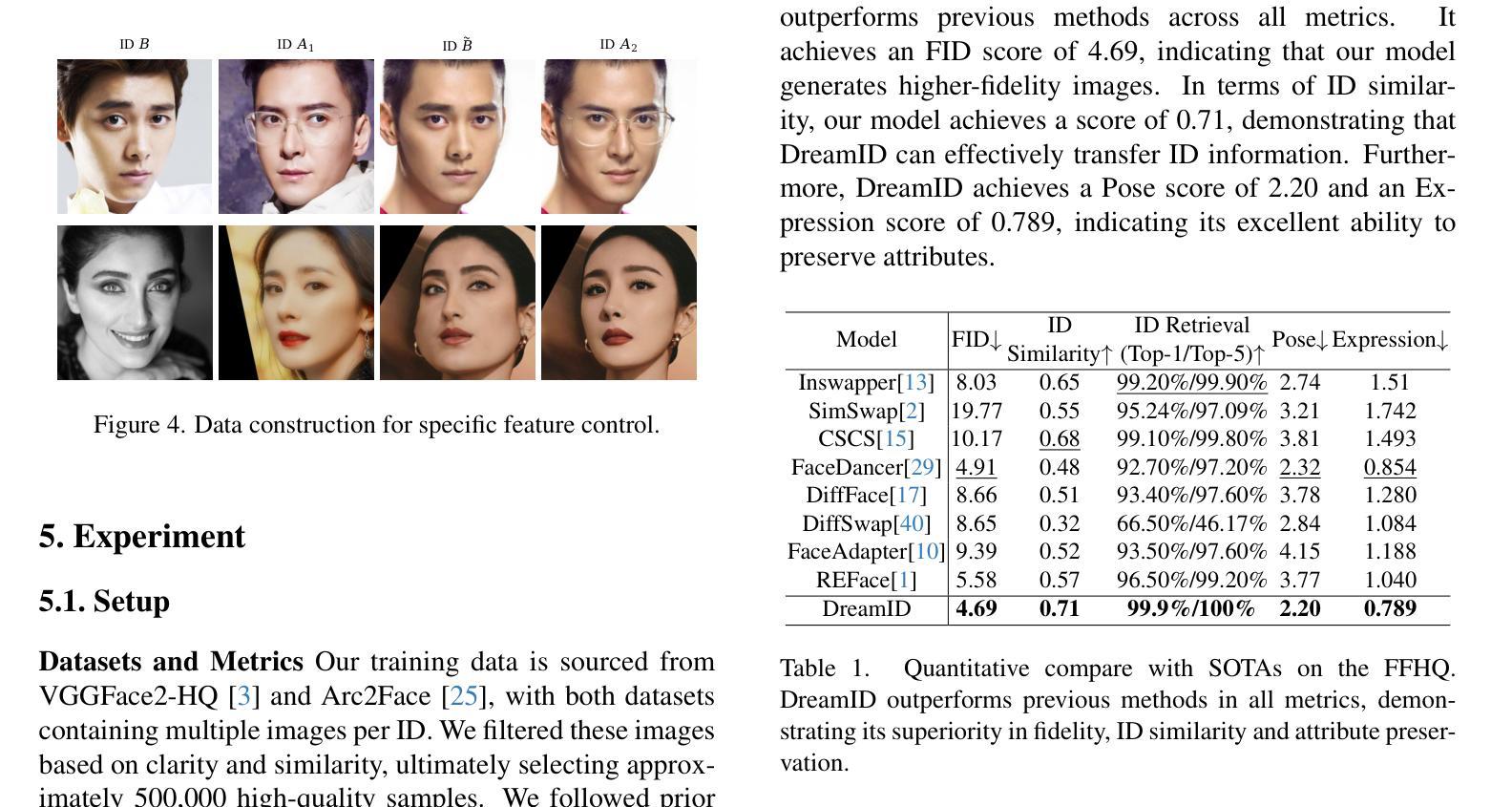
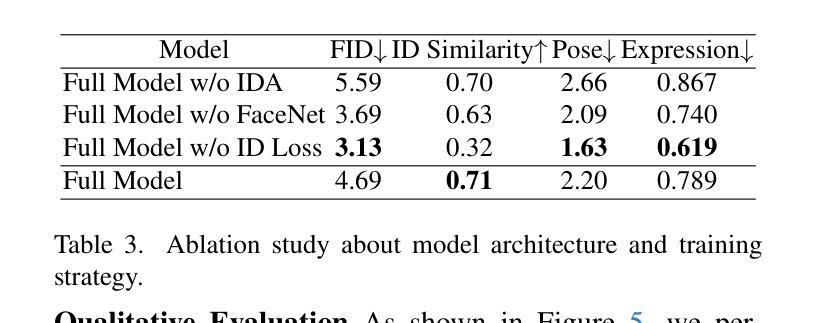
In this paper, we introduce DreamID, a diffusion-based face swapping model that achieves high levels of ID similarity, attribute preservation, image fidelity, and fast inference speed. Unlike the typical face swapping training process, which often relies on implicit supervision and struggles to achieve satisfactory results. DreamID establishes explicit supervision for face swapping by constructing Triplet ID Group data, significantly enhancing identity similarity and attribute preservation. The iterative nature of diffusion models poses challenges for utilizing efficient image-space loss functions, as performing time-consuming multi-step sampling to obtain the generated image during training is impractical. To address this issue, we leverage the accelerated diffusion model SD Turbo, reducing the inference steps to a single iteration, enabling efficient pixel-level end-to-end training with explicit Triplet ID Group supervision. Additionally, we propose an improved diffusion-based model architecture comprising SwapNet, FaceNet, and ID Adapter. This robust architecture fully unlocks the power of the Triplet ID Group explicit supervision. Finally, to further extend our method, we explicitly modify the Triplet ID Group data during training to fine-tune and preserve specific attributes, such as glasses and face shape. Extensive experiments demonstrate that DreamID outperforms state-of-the-art methods in terms of identity similarity, pose and expression preservation, and image fidelity. Overall, DreamID achieves high-quality face swapping results at 512*512 resolution in just 0.6 seconds and performs exceptionally well in challenging scenarios such as complex lighting, large angles, and occlusions.
在这篇论文中,我们介绍了DreamID,这是一款基于扩散技术的换脸模型,实现了高水平的身份相似性、属性保留、图像保真度和快速推理速度。与通常依赖隐式监督且难以达到满意结果的换脸训练过程不同,DreamID通过构建三元组ID组数据实现了换脸的显式监督,从而显著提高了身份相似性和属性保留。扩散模型的迭代性质给利用高效的图像空间损失函数带来了挑战,因为在训练期间通过耗时多步采样来获得生成图像是不切实际的。为了解决这个问题,我们利用了加速扩散模型SD Turbo,将推理步骤减少到单次迭代,能够在显式三元组ID组监督下进行高效的像素级端到端训练。此外,我们提出了一种改进的基于扩散的模型架构,包括SwapNet、FaceNet和ID适配器。这一稳健的架构充分释放了三元组ID组显式监督的威力。最后,为了进一步完善我们的方法,我们在训练过程中显式修改了三元组ID组数据,以微调并保留特定属性,如眼镜和脸型。大量实验表明,DreamID在身份相似性、姿势和表情保留以及图像保真度方面均优于最新技术。总体而言,DreamID在512*512分辨率下实现了高质量换脸,仅需0.6秒,且在复杂光照、大角度和遮挡等挑战场景下表现尤为出色。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
本文介绍了基于扩散模型的面部替换模型DreamID,它实现了高身份相似性、属性保留、图像保真度和快速推理速度。DreamID通过构建Triplet ID Group数据实现显式监督,显著提高身份相似性和属性保留。为解决扩散模型的迭代性质带来的挑战,采用加速扩散模型SD Turbo,将推理步骤减少到单次迭代,实现高效的像素级端到端训练。此外,提出改进的基于扩散的模型架构,包括SwapNet、FaceNet和ID适配器,充分利用Triplet ID Group的显式监督。最后,通过训练时显式修改Triplet ID Group数据,实现对特定属性(如眼镜和脸型)的精细调整和保留。DreamID在身份相似性、姿势和表情保留、图像保真度等方面表现出超越现有方法的效果,在复杂场景(如复杂光照、大角度遮挡)中表现尤为出色。
Key Takeaways
- DreamID是基于扩散模型的面部替换模型,实现了高身份相似性、属性保留、图像保真度和快速推理速度。
- DreamID通过构建Triplet ID Group数据实现显式监督,提高身份相似性和属性保留。
- 采用加速扩散模型SD Turbo,减少推理步骤,实现高效像素级端到端训练。
- 改进的基于扩散的模型架构包括SwapNet、FaceNet和ID适配器,充分利用显式监督。
- DreamID通过修改Triplet ID Group数据在训练过程中实现特定属性的精细调整和保留。
- DreamID在多个方面超越现有方法,如身份相似性、姿势和表情保留、图像保真度等。
点此查看论文截图

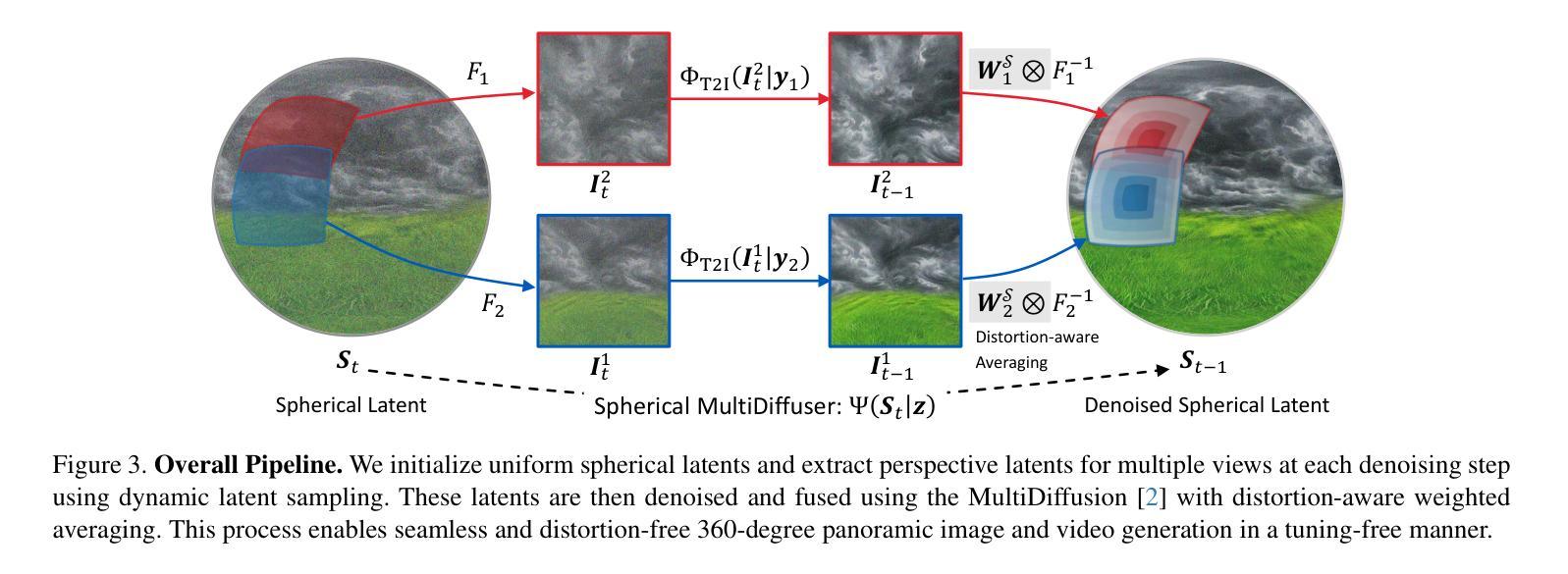
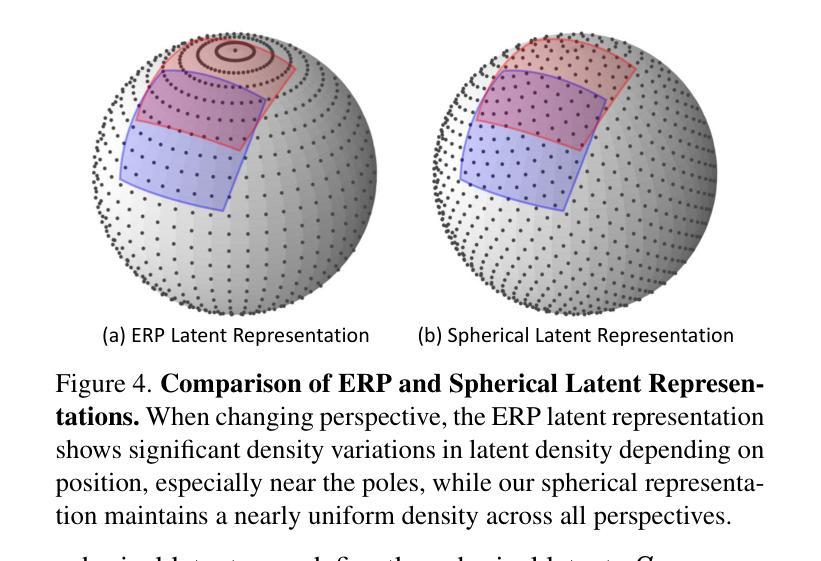
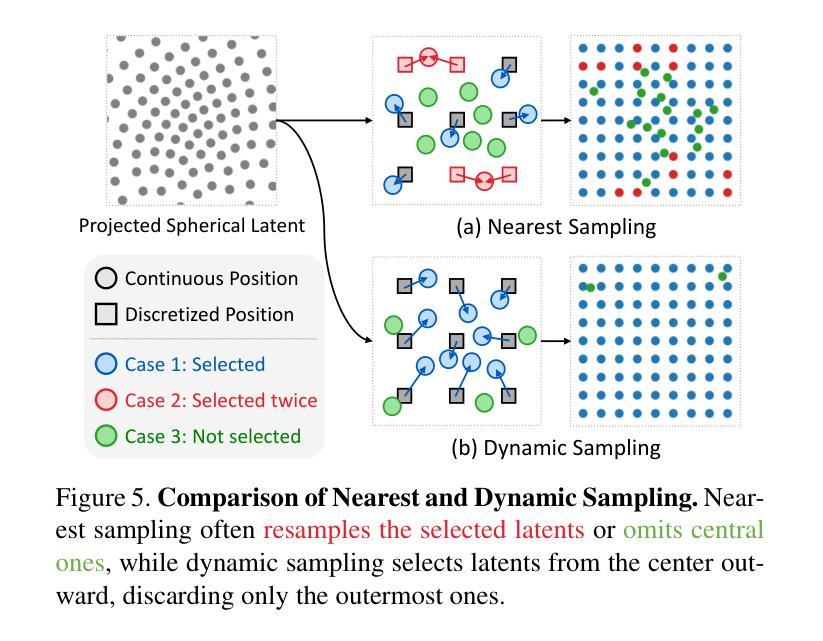
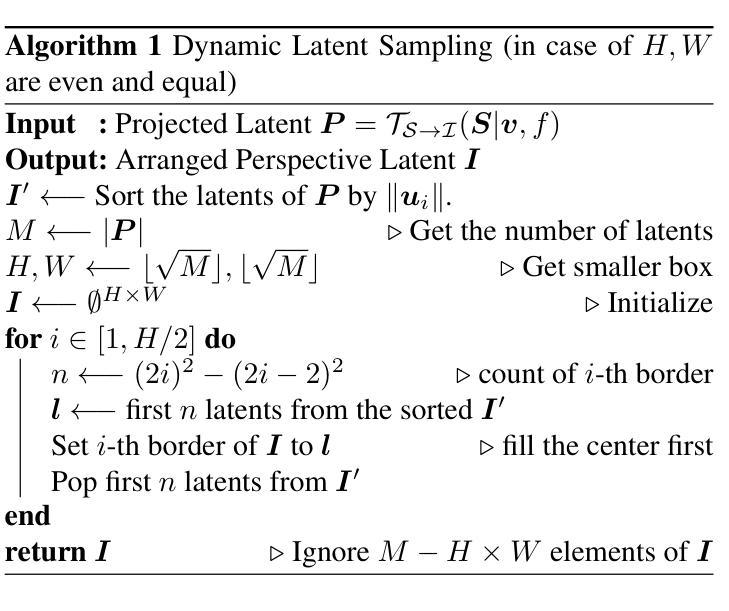
SphereDiff: Tuning-free Omnidirectional Panoramic Image and Video Generation via Spherical Latent Representation
Authors:Minho Park, Taewoong Kang, Jooyeol Yun, Sungwon Hwang, Jaegul Choo
The increasing demand for AR/VR applications has highlighted the need for high-quality 360-degree panoramic content. However, generating high-quality 360-degree panoramic images and videos remains a challenging task due to the severe distortions introduced by equirectangular projection (ERP). Existing approaches either fine-tune pretrained diffusion models on limited ERP datasets or attempt tuning-free methods that still rely on ERP latent representations, leading to discontinuities near the poles. In this paper, we introduce SphereDiff, a novel approach for seamless 360-degree panoramic image and video generation using state-of-the-art diffusion models without additional tuning. We define a spherical latent representation that ensures uniform distribution across all perspectives, mitigating the distortions inherent in ERP. We extend MultiDiffusion to spherical latent space and propose a spherical latent sampling method to enable direct use of pretrained diffusion models. Moreover, we introduce distortion-aware weighted averaging to further improve the generation quality in the projection process. Our method outperforms existing approaches in generating 360-degree panoramic content while maintaining high fidelity, making it a robust solution for immersive AR/VR applications. The code is available here. https://github.com/pmh9960/SphereDiff
随着AR/VR应用的日益增长,对高质量360度全景内容的需求也日益凸显。然而,由于等距投影(ERP)引入的严重失真,生成高质量360度全景图像和视频仍然是一项具有挑战性的任务。现有方法要么对预训练的扩散模型进行微调以适应有限的ERP数据集,要么尝试无需调整的方法,这些方法仍然依赖于ERP潜在表示,导致极地的附近出现不连续。在本文中,我们介绍了SphereDiff,这是一种利用最新扩散模型无缝生成360度全景图像和视频的新方法,无需额外调整。我们定义了一个球形潜在表示,确保所有角度的均匀分布,以缓解ERP固有的失真。我们将MultiDiffusion扩展到球形潜在空间,并提出一种球形潜在采样方法,以直接使用预训练的扩散模型。此外,我们还引入了失真感知加权平均,以进一步改进投影过程中的生成质量。我们的方法在生成360度全景内容时优于现有方法,同时保持了高保真度,成为沉浸式AR/VR应用的稳健解决方案。代码可在以下链接中找到:https://github.com/pmh9960/SphereDiff。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
在增强现实(AR)/虚拟现实(VR)应用需求不断增加的背景下,高质量的全景内容需求凸显。然而,生成高质量的全景图像和视频因等距投影(ERP)引起的严重扭曲而面临挑战。现有方法要么对预训练的扩散模型进行微调,要么尝试无调参方法,但都依赖于ERP潜在表示,导致极点附近出现不连续。本文提出SphereDiff,利用最新的扩散模型无缝生成全景图像和视频的新方法,无需额外调整。通过定义球形潜在表示,确保所有视角的均匀分布,减轻ERP固有的扭曲。扩展到球形潜在空间并提出球形潜在采样方法,直接使用预训练的扩散模型。此外,引入失真感知加权平均,进一步改进投影过程中的生成质量。该方法在生成全景内容方面优于现有方法,同时保持高保真,成为沉浸式AR/VR应用的稳健解决方案。
Key Takeaways
- AR/VR应用需求增加,需要高质量的全景内容。
- 生成高质量全景图像和视频面临等距投影(ERP)引起的严重扭曲的挑战。
- 现有方法依赖于ERP潜在表示,导致极点附近的不连续性。
- SphereDiff利用最新的扩散模型提出一种无缝生成全景图像和视频的方法,无需额外调整。
- 定义球形潜在表示,确保所有视角的均匀分布,减轻ERP的扭曲。
- 扩展到球形潜在空间,提出球形潜在采样方法,直接使用预训练的扩散模型。
- 引入失真感知加权平均,改进投影过程中的生成质量,使方法优于现有方法。
点此查看论文截图



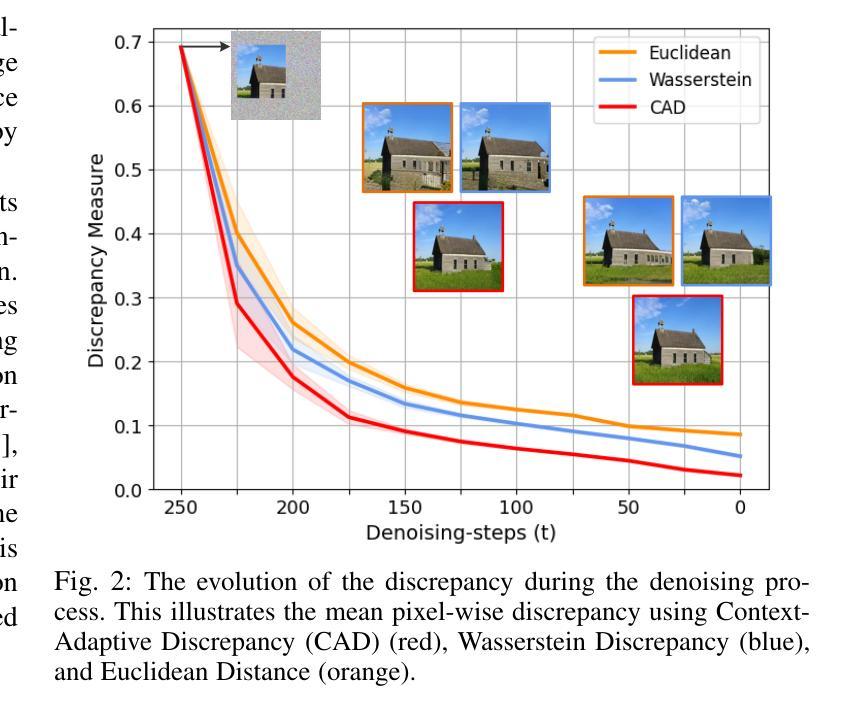
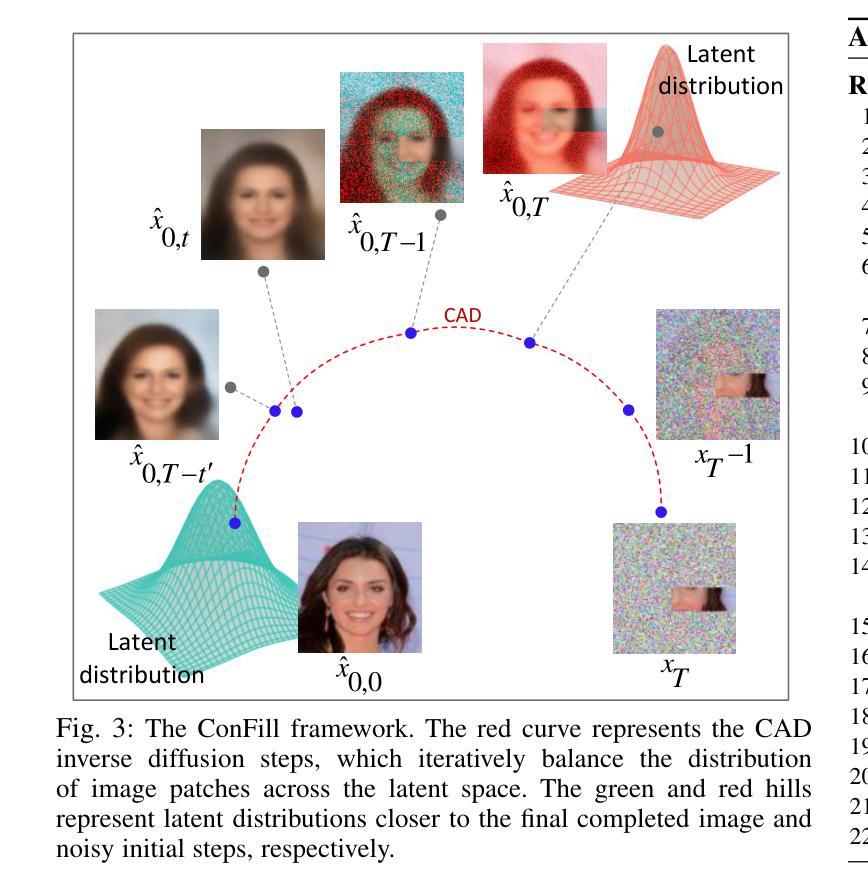
From Missing Pieces to Masterpieces: Image Completion with Context-Adaptive Diffusion
Authors:Pourya Shamsolmoali, Masoumeh Zareapoor, Huiyu Zhou, Michael Felsberg, Dacheng Tao, Xuelong Li
Image completion is a challenging task, particularly when ensuring that generated content seamlessly integrates with existing parts of an image. While recent diffusion models have shown promise, they often struggle with maintaining coherence between known and unknown (missing) regions. This issue arises from the lack of explicit spatial and semantic alignment during the diffusion process, resulting in content that does not smoothly integrate with the original image. Additionally, diffusion models typically rely on global learned distributions rather than localized features, leading to inconsistencies between the generated and existing image parts. In this work, we propose ConFill, a novel framework that introduces a Context-Adaptive Discrepancy (CAD) model to ensure that intermediate distributions of known and unknown regions are closely aligned throughout the diffusion process. By incorporating CAD, our model progressively reduces discrepancies between generated and original images at each diffusion step, leading to contextually aligned completion. Moreover, ConFill uses a new Dynamic Sampling mechanism that adaptively increases the sampling rate in regions with high reconstruction complexity. This approach enables precise adjustments, enhancing detail and integration in restored areas. Extensive experiments demonstrate that ConFill outperforms current methods, setting a new benchmark in image completion.
图像补全是一项具有挑战性的任务,特别是在确保生成的内容无缝集成到图像现有部分时。虽然最近的扩散模型显示出了一定的潜力,但它们通常难以在已知和未知(缺失)区域之间保持连贯性。这一问题源于扩散过程中缺乏明确的空间和语义对齐,导致内容无法平稳地融入原始图像。此外,扩散模型通常依赖于全局学习分布而非局部特征,导致生成图像部分与现有图像部分之间存在不一致。
在本工作中,我们提出了ConFill,一种新型框架,引入上下文自适应差异(CAD)模型,以确保已知和未知区域的中间分布在扩散过程中紧密对齐。通过结合CAD,我们的模型在每一步扩散中逐渐减少了生成图像和原始图像之间的差异,从而实现上下文对齐的补全。此外,ConFill使用一种新的动态采样机制,自适应地在高重建复杂度的区域增加采样率。这种方法能够实现精确调整,增强恢复区域的细节和集成度。大量实验表明,ConFill优于当前方法,在图像补全方面树立了新的基准。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF Accepted in TPAMI
Summary
本文提出一种名为ConFill的新框架,用于图像补全任务。该框架通过引入上下文自适应差异模型,确保已知和未知区域的中间分布在整个扩散过程中紧密对齐。此外,它还采用动态采样机制,在重建复杂度高的区域自适应增加采样率,以提高恢复区域的细节和集成度。实验表明,ConFill在图像补全任务上优于当前方法,树立了新的基准。
Key Takeaways
- ConFill框架被提出用于解决图像补全任务中的挑战,特别是确保生成内容与现有图像部分的无缝集成。
- 上下文自适应差异模型(CAD)被引入,以确保已知和未知区域的中间分布在扩散过程中的紧密对齐。
- ConFill通过采用动态采样机制,在重建复杂度高的区域自适应增加采样率,提高恢复区域的细节和集成度。
- 该框架通过减少生成图像和原始图像之间的差异,实现了上下文对齐的补全。
- 与现有方法相比,ConFill在图像补全任务上表现出卓越性能。
- ConFill的引入为图像补全任务树立了新的基准。
点此查看论文截图
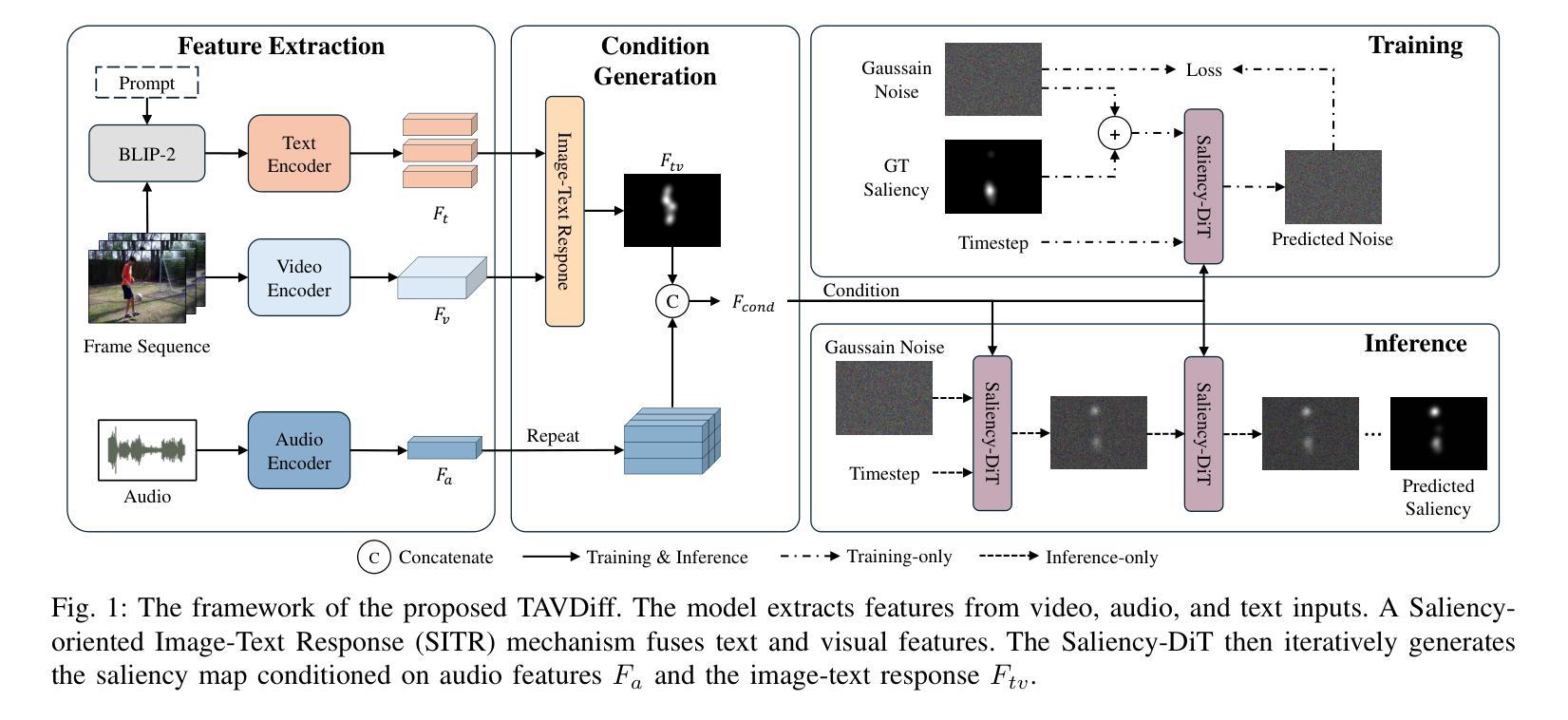
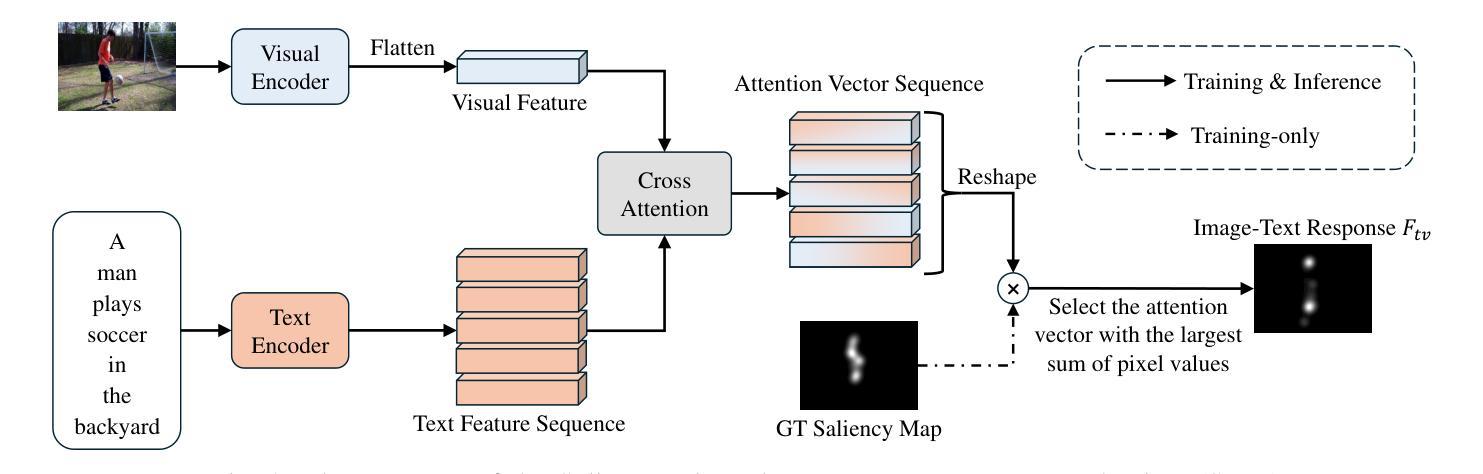
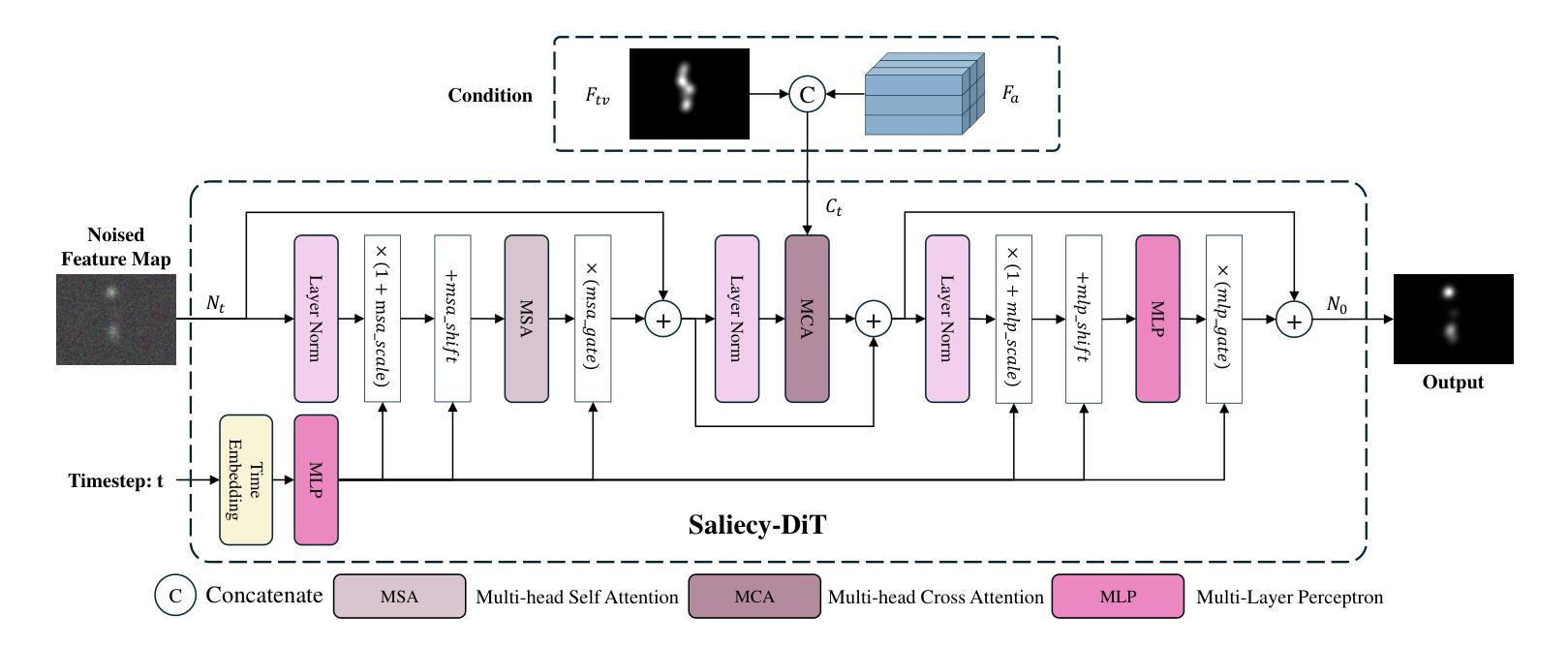
Text-Audio-Visual-conditioned Diffusion Model for Video Saliency Prediction
Authors:Li Yu, Xuanzhe Sun, Wei Zhou, Moncef Gabbouj
Video saliency prediction is crucial for downstream applications, such as video compression and human-computer interaction. With the flourishing of multimodal learning, researchers started to explore multimodal video saliency prediction, including audio-visual and text-visual approaches. Auditory cues guide the gaze of viewers to sound sources, while textual cues provide semantic guidance for understanding video content. Integrating these complementary cues can improve the accuracy of saliency prediction. Therefore, we attempt to simultaneously analyze visual, auditory, and textual modalities in this paper, and propose TAVDiff, a Text-Audio-Visual-conditioned Diffusion Model for video saliency prediction. TAVDiff treats video saliency prediction as an image generation task conditioned on textual, audio, and visual inputs, and predicts saliency maps through stepwise denoising. To effectively utilize text, a large multimodal model is used to generate textual descriptions for video frames and introduce a saliency-oriented image-text response (SITR) mechanism to generate image-text response maps. It is used as conditional information to guide the model to localize the visual regions that are semantically related to the textual description. Regarding the auditory modality, it is used as another conditional information for directing the model to focus on salient regions indicated by sounds. At the same time, since the diffusion transformer (DiT) directly concatenates the conditional information with the timestep, which may affect the estimation of the noise level. To achieve effective conditional guidance, we propose Saliency-DiT, which decouples the conditional information from the timestep. Experimental results show that TAVDiff outperforms existing methods, improving 1.03%, 2.35%, 2.71% and 0.33% on SIM, CC, NSS and AUC-J metrics, respectively.
视频显著性预测对于下游应用至关重要,例如视频压缩和人机交互。随着多模态学习的蓬勃发展,研究者开始探索多模态视频显著性预测,包括视听和文本视觉方法。听觉线索引导观众的目光指向声源,而文本线索为理解视频内容提供语义指导。整合这些互补线索可以提高显著性预测的准确性。因此,本文尝试同时分析视觉、听觉和文本模态,并提出TAVDiff,一种用于视频显著性预测的文-音-视觉条件扩散模型。TAVDiff将视频显著性预测视为一项受文本、音频和视觉输入影响的图像生成任务,并通过逐步去噪来预测显著性地图。为了有效利用文本,我们采用大型多模态模型来生成视频帧的文本描述,并引入面向显著性的图像文本响应(SITR)机制,以生成图像文本响应图。它作为条件信息,指导模型定位与文本描述语义相关的视觉区域。对于听觉模态,它作为另一种条件信息,指导模型关注声音指示的显著区域。同时,由于扩散变压器(DiT)直接将条件信息与时间步长连接起来,可能会影响噪声水平的估计。为了实现有效的条件指导,我们提出了Saliency-DiT,它将条件信息与时间步长解耦。实验结果表明,TAVDiff在SIM、CC、NSS和AUC-J指标上的表现优于现有方法,分别提高了1.03%、2.35%、2.71%和0.33%。
论文及项目相关链接
摘要
本文研究了视频显著性预测的多模态学习方法,包括音频视觉和文本视觉方法。通过整合视觉、听觉和文本线索,提出了一种名为TAVDiff的文本音频视觉扩散模型,用于视频显著性预测。TAVDiff将视频显著性预测视为基于文本、音频和视觉输入的图像生成任务,并通过逐步去噪预测显著性地图。实验结果表明,TAVDiff在SIM、CC、NSS和AUC-J指标上的性能分别提高了1.03%、2.35%、2.71%和0.33%,优于现有方法。
关键见解
- 视频显著性预测是视频压缩和人机交互等下游应用的关键。
- 多模态学习(包括音频视觉和文本视觉方法)在视频显著性预测中具有重要意义。
- 听觉和文本线索能提高显著性预测的精度。
- TAVDiff模型是一个基于文本、音频和视觉的扩散模型,用于视频显著性预测。
- TAVDiff将视频显著性预测视为基于多模态输入的图像生成任务。
- Saliency-DiT被提出以解决扩散变压器(DiT)在条件信息处理上的问题,实现更有效的条件引导。
- 实验结果表明,TAVDiff在多个评价指标上优于现有方法。
点此查看论文截图


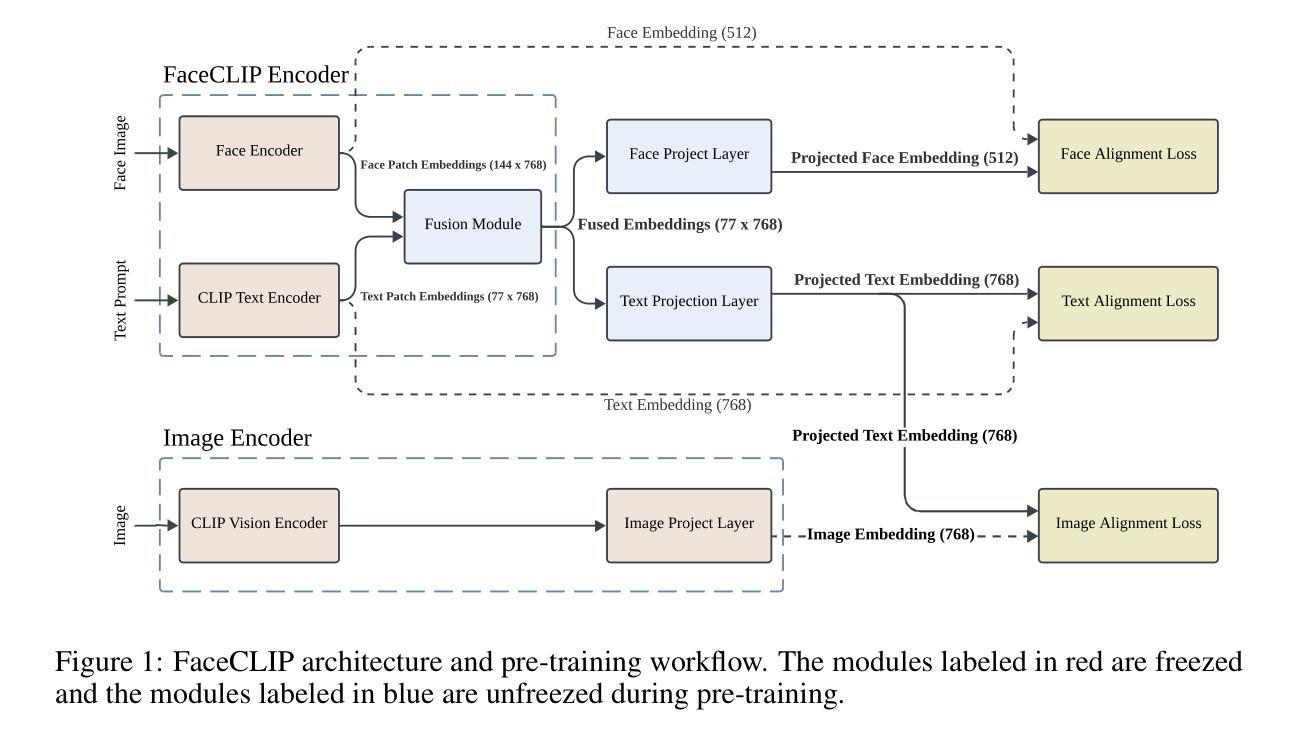
Learning Joint ID-Textual Representation for ID-Preserving Image Synthesis
Authors:Zichuan Liu, Liming Jiang, Qing Yan, Yumin Jia, Hao Kang, Xin Lu
We propose a novel framework for ID-preserving generation using a multi-modal encoding strategy rather than injecting identity features via adapters into pre-trained models. Our method treats identity and text as a unified conditioning input. To achieve this, we introduce FaceCLIP, a multi-modal encoder that learns a joint embedding space for both identity and textual semantics. Given a reference face and a text prompt, FaceCLIP produces a unified representation that encodes both identity and text, which conditions a base diffusion model to generate images that are identity-consistent and text-aligned. We also present a multi-modal alignment algorithm to train FaceCLIP, using a loss that aligns its joint representation with face, text, and image embedding spaces. We then build FaceCLIP-SDXL, an ID-preserving image synthesis pipeline by integrating FaceCLIP with Stable Diffusion XL (SDXL). Compared to prior methods, FaceCLIP-SDXL enables photorealistic portrait generation with better identity preservation and textual relevance. Extensive experiments demonstrate its quantitative and qualitative superiority.
我们提出了一种新的ID保留生成框架,采用多模态编码策略,而不是通过适配器向预训练模型注入身份特征。我们的方法将身份和文本视为统一的条件输入。为实现这一点,我们引入了FaceCLIP,这是一种多模态编码器,它学习身份和文本语义的联合嵌入空间。给定参考面部和文本提示,FaceCLIP生成一个统一表示,该表示对身份和文本进行编码,使基础扩散模型能够生成身份一致且文本对齐的图像。我们还提出了一种使用损失函数对齐其联合表示与面部、文本和图像嵌入空间的FaceCLIP多模态对齐算法进行训练。然后,我们将FaceCLIP与Stable Diffusion XL(SDXL)相结合,构建了FaceCLIP-SDXL这一ID保留图像合成管道。与之前的方法相比,FaceCLIP-SDXL能够实现具有更好身份保留和文本相关性的逼真肖像生成。大量实验证明了其在数量和质量上的优越性。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
本文提出了一种新的身份保留生成框架,采用多模态编码策略,而非通过适配器注入身份特征到预训练模型中。该方法将身份和文字视为统一的条件输入。为此,引入了FaceCLIP多模态编码器,学习身份和文本语义的联合嵌入空间。给定参考人脸和文字提示,FaceCLIP产生统一表征,编码身份和文本,以条件基础扩散模型生成一致身份和文本对齐的图像。还提出了多模态对齐算法来训练FaceCLIP,使用损失函数将其联合表征与人脸、文本和图像嵌入空间对齐。通过整合FaceCLIP与Stable Diffusion XL(SDXL),构建了FaceCLIP-SDXL身份保留图像合成管道。相比以往方法,FaceCLIP-SDXL能实现更逼真的肖像生成,具有更好的身份保留和文本相关性。
Key Takeaways
- 引入了一种新的ID保留生成框架,使用多模态编码策略。
- 提出了FaceCLIP多模态编码器,用于学习身份和文本语义的联合嵌入空间。
- FaceCLIP能生成统一表征,编码身份和文本,为扩散模型提供条件。
- 引入了多模态对齐算法来训练FaceCLIP。
- 构建了FaceCLIP-SDXL图像合成管道,整合了FaceCLIP与Stable Diffusion XL。
- FaceCLIP-SDXL能实现更逼真的肖像生成。
- 该方法在身份保留和文本相关性方面表现出优越性。
点此查看论文截图


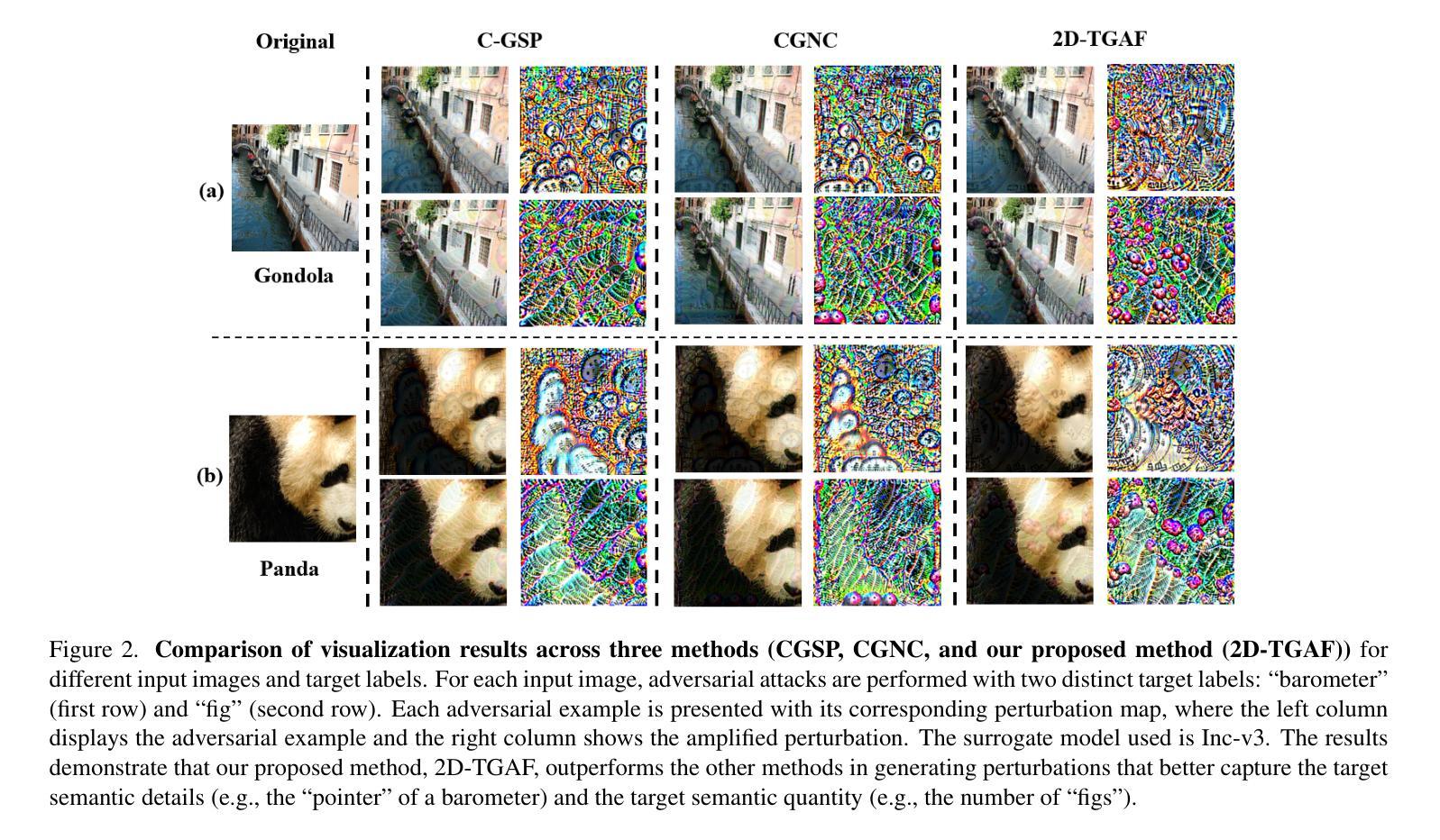
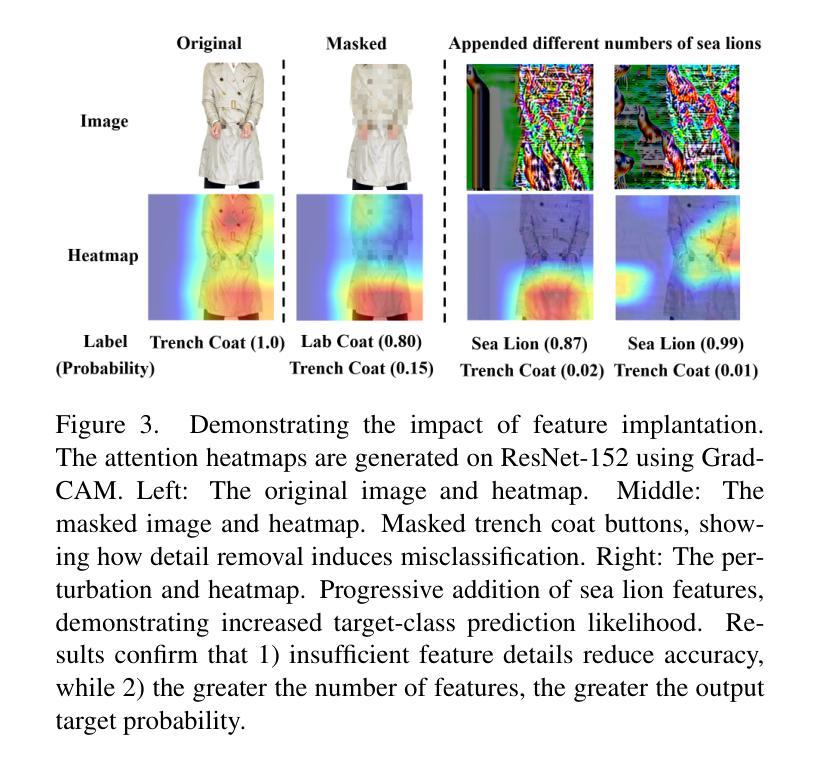
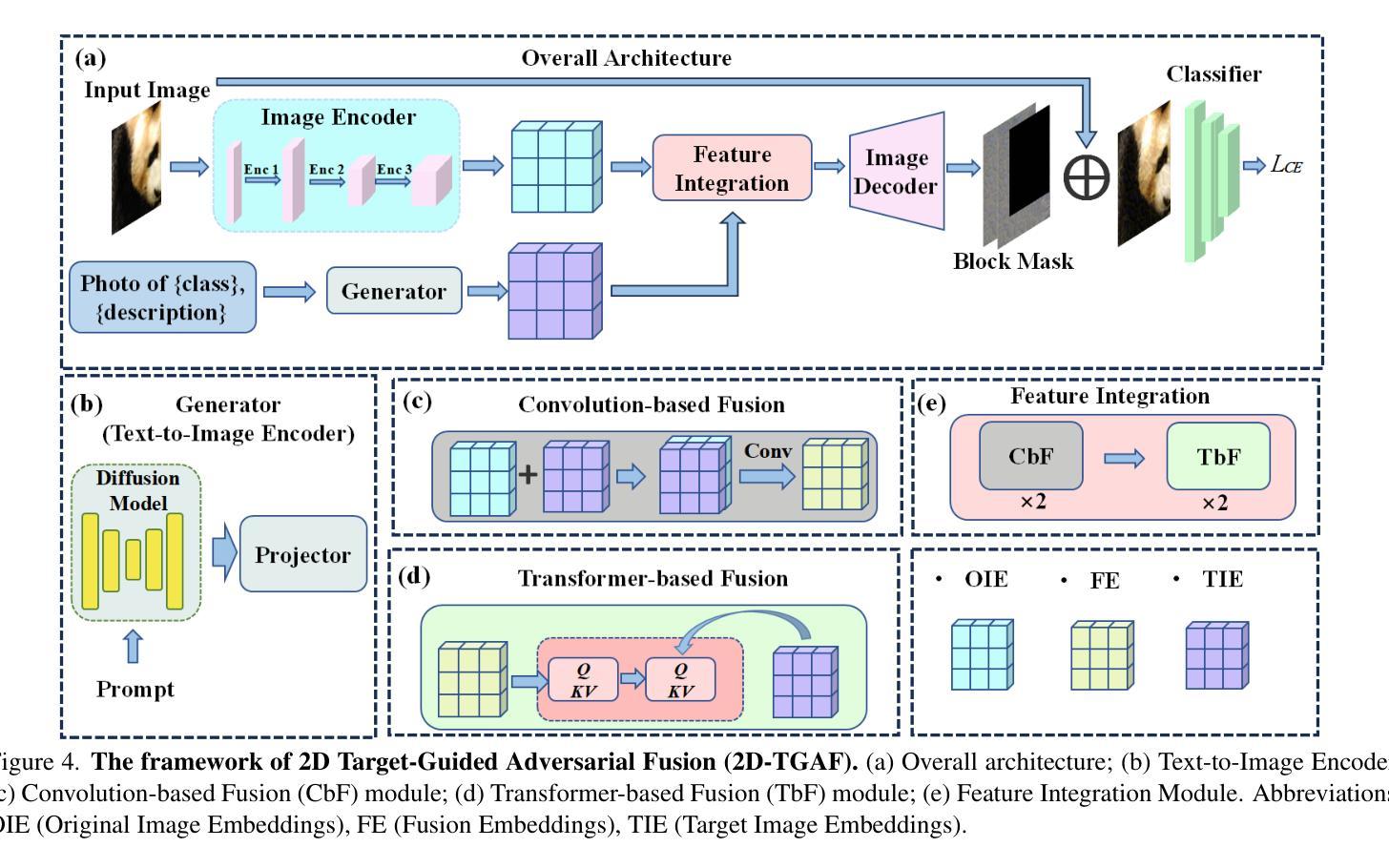
Rethinking Target Label Conditioning in Adversarial Attacks: A 2D Tensor-Guided Generative Approach
Authors:Hangyu Liu, Bo Peng, Pengxiang Ding, Donglin Wang
Compared to single-target adversarial attacks, multi-target attacks have garnered significant attention due to their ability to generate adversarial images for multiple target classes simultaneously. Existing generative approaches for multi-target attacks mainly analyze the effect of the use of target labels on noise generation from a theoretical perspective, lacking practical validation and comprehensive summarization. To address this gap, we first identify and validate that the semantic feature quality and quantity are critical factors affecting the transferability of targeted attacks: 1) Feature quality refers to the structural and detailed completeness of the implanted target features, as deficiencies may result in the loss of key discriminative information; 2) Feature quantity refers to the spatial sufficiency of the implanted target features, as inadequacy limits the victim model’s attention to this feature. Based on these findings, we propose the 2D Tensor-Guided Adversarial Fusion (2D-TGAF) framework, which leverages the powerful generative capabilities of diffusion models to encode target labels into two-dimensional semantic tensors for guiding adversarial noise generation. Additionally, we design a novel masking strategy tailored for the training process, ensuring that parts of the generated noise retain complete semantic information about the target class. Extensive experiments on the standard ImageNet dataset demonstrate that 2D-TGAF consistently surpasses state-of-the-art methods in attack success rates, both on normally trained models and across various defense mechanisms.
相较于单目标对抗攻击,多目标攻击因其能够同时为多个目标类别生成对抗样本而备受关注。现有的多目标攻击的生成方法主要从理论角度分析了目标标签的使用对噪声生成的影响,缺乏实际验证和全面的总结。为了填补这一空白,我们首先确定并验证了语义特征的质量和数量是影响目标攻击迁移性的关键因素:1)特征质量指的是植入的目标特征的结构和细节的完整性,因为缺陷可能会导致关键判别信息的丢失;2)特征数量指的是植入的目标特征的空间充足性,因为不足会限制目标模型对这个特征的关注。基于这些发现,我们提出了二维张量引导对抗融合(2D-TGAF)框架,该框架利用扩散模型的强大生成能力,将目标标签编码为二维语义张量,以指导对抗噪声生成。此外,我们还针对训练过程设计了一种新型掩码策略,确保生成的噪声部分保留有关目标类别的完整语义信息。在标准ImageNet数据集上的大量实验表明,无论是在正常训练的模型上还是在各种防御机制之间,2D-TGAF的攻击力始终超过现有最先进的方法。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF 12 pages, 4 figures
Summary
多目标攻击因其能够同时为多个目标类别生成对抗性图像而受到关注。现有生成式方法主要从理论角度分析了目标标签的使用对噪声生成的影响,缺乏实际验证和全面总结。研究发现语义特征的质量和数量是影响目标攻击可迁移性的关键因素。为此,提出了基于扩散模型的二维张量引导对抗融合框架(2D-TGAF),将目标标签编码为二维语义张量,引导对抗噪声生成。在ImageNet数据集上的实验表明,2D-TGAF在攻击成功率上超越了现有方法,无论是对正常训练的模型还是各种防御机制。
Key Takeaways
- 多目标攻击能同时为多个目标类别生成对抗性图像,受到广泛关注。
- 现有方法主要从理论角度研究目标标签对噪声生成的影响,缺乏实际验证和全面总结。
- 语义特征的质量和数量是影响目标攻击可迁移性的关键因素。
- 特征质量指植入目标特征的结构和细节完整性,不足会导致关键判别信息丢失。
- 特征数量指植入目标特征的空间充足性,不足会限制受害者模型的注意力。
- 提出的2D-TGAF框架利用扩散模型的强大生成能力,将目标标签编码为二维语义张量,指导对抗噪声生成。
点此查看论文截图


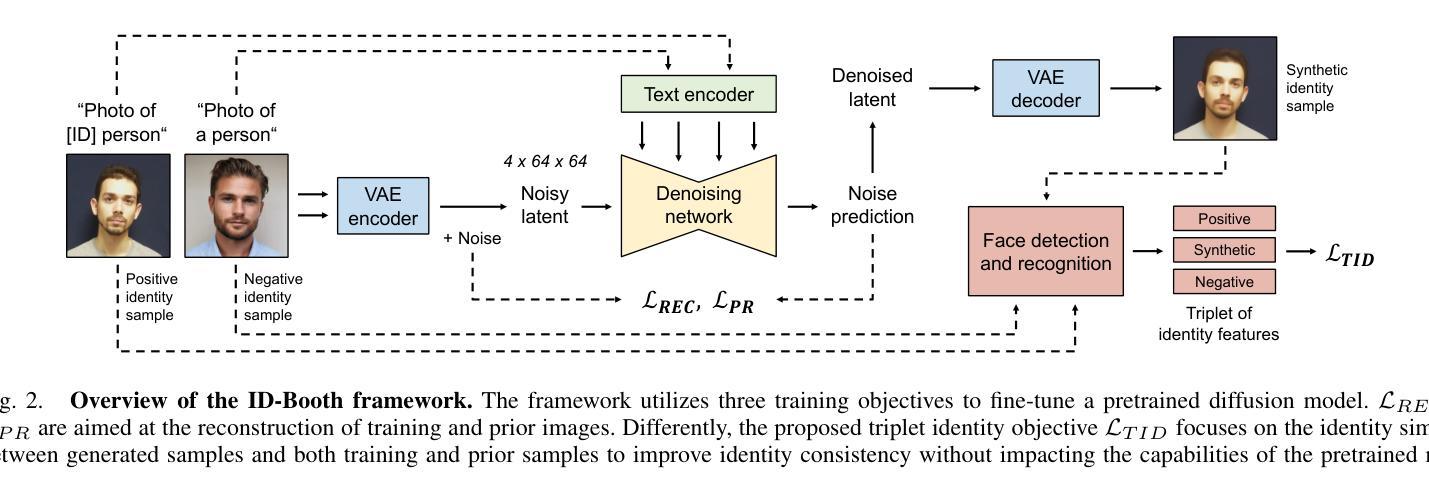
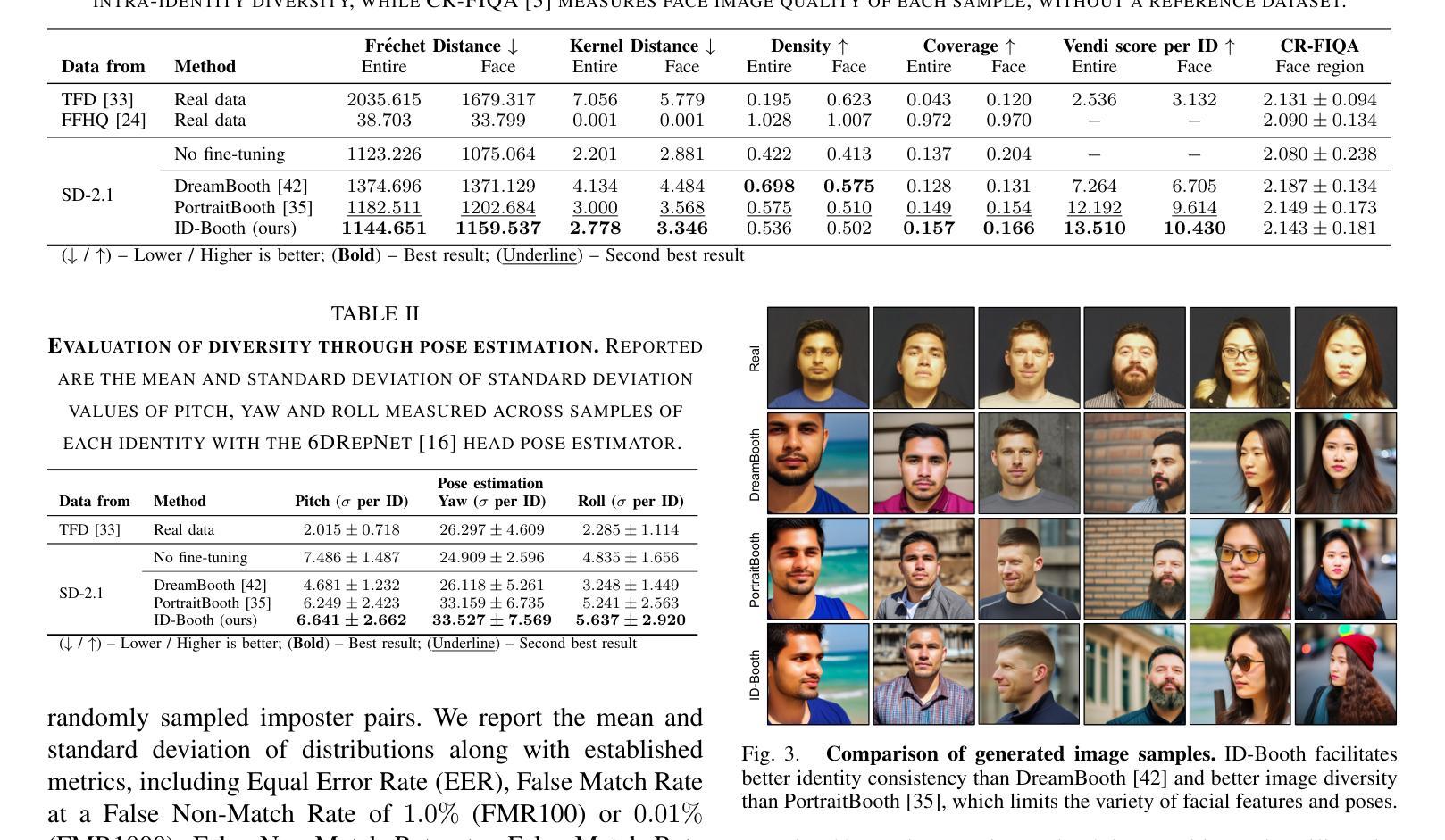
ID-Booth: Identity-consistent Face Generation with Diffusion Models
Authors:Darian Tomašević, Fadi Boutros, Chenhao Lin, Naser Damer, Vitomir Štruc, Peter Peer
Recent advances in generative modeling have enabled the generation of high-quality synthetic data that is applicable in a variety of domains, including face recognition. Here, state-of-the-art generative models typically rely on conditioning and fine-tuning of powerful pretrained diffusion models to facilitate the synthesis of realistic images of a desired identity. Yet, these models often do not consider the identity of subjects during training, leading to poor consistency between generated and intended identities. In contrast, methods that employ identity-based training objectives tend to overfit on various aspects of the identity, and in turn, lower the diversity of images that can be generated. To address these issues, we present in this paper a novel generative diffusion-based framework, called ID-Booth. ID-Booth consists of a denoising network responsible for data generation, a variational auto-encoder for mapping images to and from a lower-dimensional latent space and a text encoder that allows for prompt-based control over the generation procedure. The framework utilizes a novel triplet identity training objective and enables identity-consistent image generation while retaining the synthesis capabilities of pretrained diffusion models. Experiments with a state-of-the-art latent diffusion model and diverse prompts reveal that our method facilitates better intra-identity consistency and inter-identity separability than competing methods, while achieving higher image diversity. In turn, the produced data allows for effective augmentation of small-scale datasets and training of better-performing recognition models in a privacy-preserving manner. The source code for the ID-Booth framework is publicly available at https://github.com/dariant/ID-Booth.
最近生成建模技术的进步使得能够生成适用于各种领域的高质量合成数据,包括人脸识别。在这里,最先进的生成模型通常依赖于对功能强大的预训练扩散模型进行条件设定和微调,以促进所需身份的逼真图像合成。然而,这些模型在训练过程中往往不考虑主体的身份,导致生成图像与预期身份之间的一致性较差。相比之下,采用基于身份的训练目标的方法往往会在身份的各个方面过度拟合,从而降低了可以生成的图像多样性。为了解决这些问题,我们在本文中提出了一种新型的基于扩散的生成框架,称为ID-Booth。ID-Booth包括一个负责数据生成的降噪网络、一个用于将图像映射到低维潜在空间及其反向映射的变分自动编码器以及一个文本编码器,该编码器允许基于提示控制生成过程。该框架利用了一种新型的三重身份训练目标,能够在保持预训练扩散模型的合成能力的同时,实现身份一致的图像生成。利用最先进的潜在扩散模型和不同的提示进行的实验表明,我们的方法在身份内一致性和身份间可分离性方面优于其他方法,同时实现了较高的图像多样性。进而,生成的数据可以有效地增强小规模数据集,并以保护隐私的方式训练性能更好的识别模型。ID-Booth框架的源代码可在https://github.com/dariant/ID-Booth公开获取。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF IEEE International Conference on Automatic Face and Gesture Recognition (FG) 2025, 14 pages
摘要
本文介绍了一种基于扩散的新型生成模型ID-Booth,该模型解决了现有生成模型在人脸识别领域面临的身份一致性问题。ID-Booth通过使用去噪网络进行数据生成,通过变分自动编码器实现图像到低维潜在空间的映射和反映射,并利用文本编码器实现基于提示的控制生成过程。其采用新颖的三重身份训练目标,能够在保持预训练扩散模型的合成能力的同时,实现身份一致的图像生成。实验表明,与竞争方法相比,该方法在身份内一致性和身份间可分离性方面表现更佳,同时实现更高的图像多样性。因此,生成的数据可以有效地增强小规模数据集并训练性能更好的识别模型。
关键见解
- 最新生成模型技术已能够实现高质量合成数据的生成,适用于包括人脸识别在内的多个领域。
- 现有先进技术生成模型在身份一致性方面存在问题,训练时未考虑主体身份导致生成图像与预期身份不一致。
- 基于身份的训练目标方法虽然能提高身份一致性,但可能导致图像多样性降低。
- ID-Booth框架解决了上述问题,通过去噪网络、变分自动编码器和文本编码器实现更灵活的图像生成控制。
- ID-Booth采用新颖的三重身份训练目标,实现身份一致的图像生成同时保持较高的图像多样性。
- 实验表明,ID-Booth框架能提高图像生成的同一身份内一致性以及不同身份间的可分离性。
点此查看论文截图

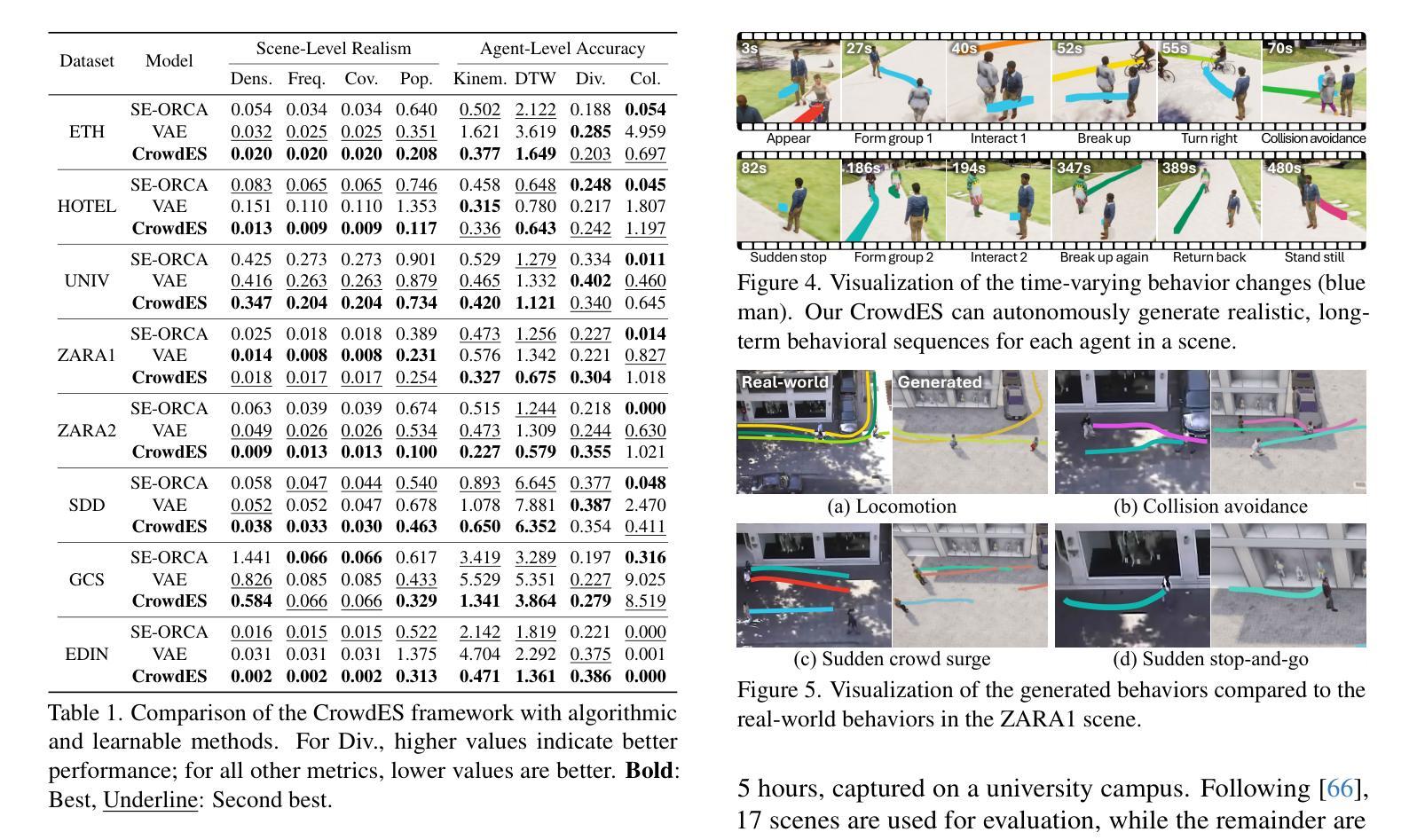
Continuous Locomotive Crowd Behavior Generation
Authors:Inhwan Bae, Junoh Lee, Hae-Gon Jeon
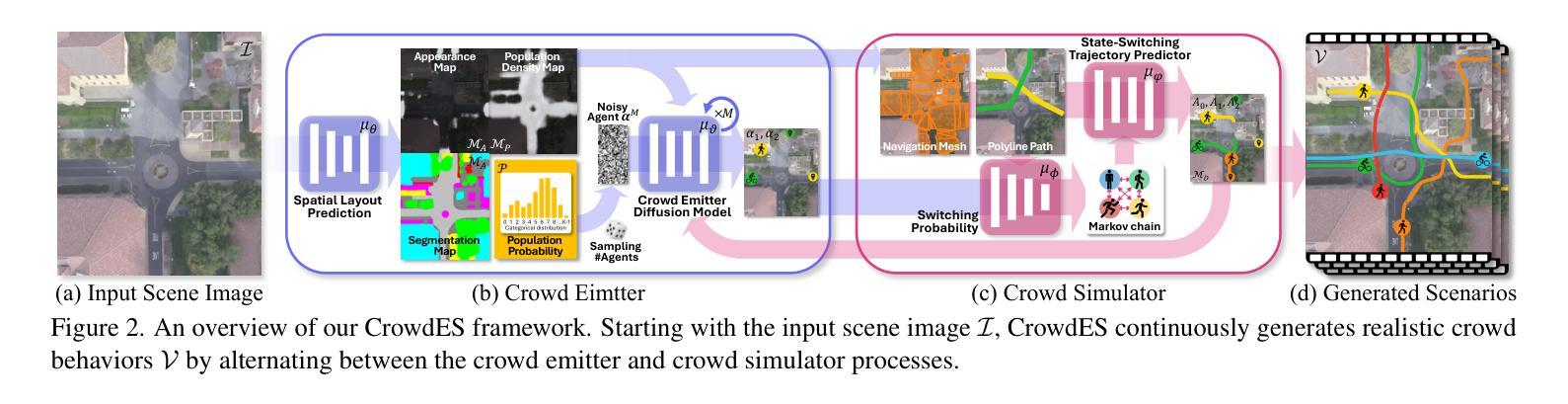
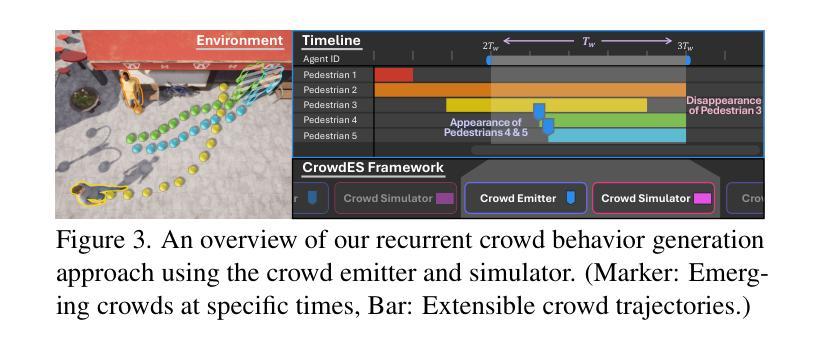
Modeling and reproducing crowd behaviors are important in various domains including psychology, robotics, transport engineering and virtual environments. Conventional methods have focused on synthesizing momentary scenes, which have difficulty in replicating the continuous nature of real-world crowds. In this paper, we introduce a novel method for automatically generating continuous, realistic crowd trajectories with heterogeneous behaviors and interactions among individuals. We first design a crowd emitter model. To do this, we obtain spatial layouts from single input images, including a segmentation map, appearance map, population density map and population probability, prior to crowd generation. The emitter then continually places individuals on the timeline by assigning independent behavior characteristics such as agents’ type, pace, and start/end positions using diffusion models. Next, our crowd simulator produces their long-term locomotions. To simulate diverse actions, it can augment their behaviors based on a Markov chain. As a result, our overall framework populates the scenes with heterogeneous crowd behaviors by alternating between the proposed emitter and simulator. Note that all the components in the proposed framework are user-controllable. Lastly, we propose a benchmark protocol to evaluate the realism and quality of the generated crowds in terms of the scene-level population dynamics and the individual-level trajectory accuracy. We demonstrate that our approach effectively models diverse crowd behavior patterns and generalizes well across different geographical environments. Code is publicly available at https://github.com/InhwanBae/CrowdES .
对人群行为的建模和再现是心理学、机器人技术、交通工程和虚拟环境等多个领域的重要课题。传统方法主要关注即时场景的合成,很难复制现实世界中人群的连续性。在本文中,我们介绍了一种自动生成连续、现实的人群轨迹的新方法,该方法具有不同的个体行为和个体间的交互。我们首先设计了一个人群发射器模型。为此,我们从单个输入图像中获取空间布局,包括分割图、外观图、人口密度图和人口概率,然后进行人群生成。发射器通过分配独立的行为特征(如代理的类型、速度、起始/结束位置)在时间上持续放置个体,使用扩散模型。接下来,我们的人群模拟器产生他们的长期运动。为了模拟各种动作,它可以根据马尔可夫链增强其行为。因此,通过交替使用所提出的发射器和模拟器,我们的整体框架能够在场景中填充具有不同行为的人群。请注意,该框架中的所有组件都是用户可控的。最后,我们提出了一个基准协议,以评估生成人群的现实性和质量,包括场景级的人口动态和个体级的轨迹精度。我们证明了我们的方法能够有效地模拟不同的人群行为模式,并在不同的地理环境中具有良好的通用性。代码公开在https://github.com/InhwanBae/CrowdES。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF Accepted at CVPR 2025. Project page: https://ihbae.com/publication/crowdes/
摘要
本文介绍了一种自动生成连续、真实人群轨迹的新方法,该方法能够模拟出人群中的不同行为和个体间的交互。通过设计人群发射器模型,从单一输入图像中获取空间布局,包括分割图、外观图、人口密度图和人口概率等,来生成人群。利用扩散模型为个体分配独立的行为特征,如类型、速度以及起始/终止位置,然后由人群模拟器产生长期运动。模拟器可以通过马尔可夫链增强各种行为。整个框架通过交替使用发射器和模拟器来模拟场景中的人群行为。所有组件都是用户可控的。此外,本文还提出了一个基准协议,以评估生成人群的真实感和质量,包括场景级别的人口动态和个体级别的轨迹精度。实验证明,该方法能够有效地模拟出多样的人群行为模式,并在不同的地理环境中具有良好的泛化能力。
关键见解
- 介绍了一种自动生成连续、真实人群轨迹的新方法,弥补了传统方法难以复制人群连续性的缺点。
- 通过设计人群发射器模型,从单一输入图像中获取空间布局,为生成人群提供基础。
- 利用扩散模型为个体分配独立的行为特征,实现行为的多样化。
- 采用了人群模拟器来产生长期运动,并通过马尔可夫链增强行为的多样性。
- 框架中的组件都是用户可控的,提供了高度的灵活性。
- 提出了一种基准协议来评估生成人群的真实感和质量,包括场景级别和个体级别的评估指标。
- 实验证明,该方法能够有效地模拟出多样的人群行为模式,并具有良好的泛化能力。
点此查看论文截图

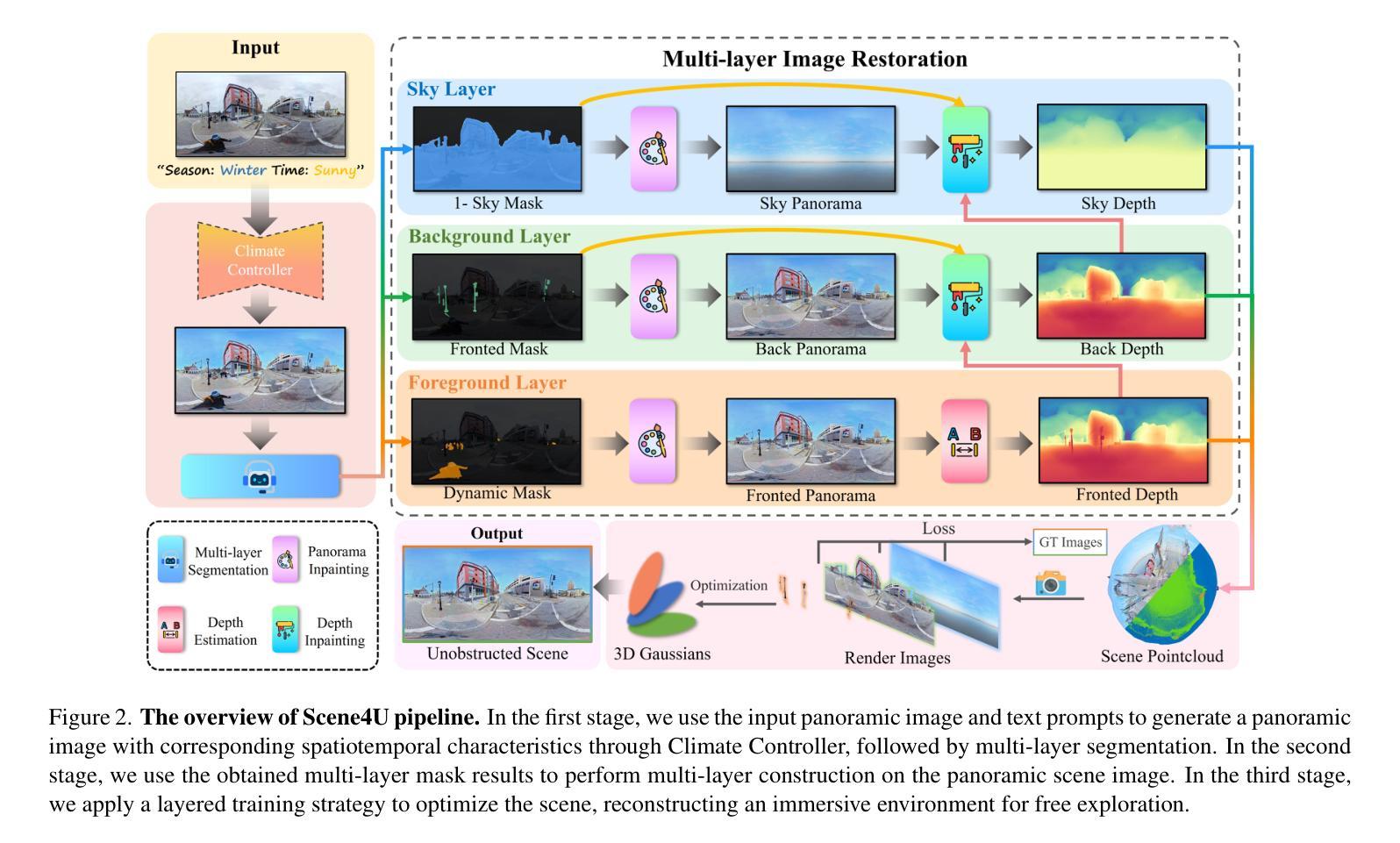
Scene4U: Hierarchical Layered 3D Scene Reconstruction from Single Panoramic Image for Your Immerse Exploration
Authors:Zilong Huang, Jun He, Junyan Ye, Lihan Jiang, Weijia Li, Yiping Chen, Ting Han
The reconstruction of immersive and realistic 3D scenes holds significant practical importance in various fields of computer vision and computer graphics. Typically, immersive and realistic scenes should be free from obstructions by dynamic objects, maintain global texture consistency, and allow for unrestricted exploration. The current mainstream methods for image-driven scene construction involves iteratively refining the initial image using a moving virtual camera to generate the scene. However, previous methods struggle with visual discontinuities due to global texture inconsistencies under varying camera poses, and they frequently exhibit scene voids caused by foreground-background occlusions. To this end, we propose a novel layered 3D scene reconstruction framework from panoramic image, named Scene4U. Specifically, Scene4U integrates an open-vocabulary segmentation model with a large language model to decompose a real panorama into multiple layers. Then, we employs a layered repair module based on diffusion model to restore occluded regions using visual cues and depth information, generating a hierarchical representation of the scene. The multi-layer panorama is then initialized as a 3D Gaussian Splatting representation, followed by layered optimization, which ultimately produces an immersive 3D scene with semantic and structural consistency that supports free exploration. Scene4U outperforms state-of-the-art method, improving by 24.24% in LPIPS and 24.40% in BRISQUE, while also achieving the fastest training speed. Additionally, to demonstrate the robustness of Scene4U and allow users to experience immersive scenes from various landmarks, we build WorldVista3D dataset for 3D scene reconstruction, which contains panoramic images of globally renowned sites. The implementation code and dataset will be released at https://github.com/LongHZ140516/Scene4U .
基于沉浸式与真实的三维场景重建在计算机视觉与计算机图形学领域的各个子领域中有着重大的实际应用价值。一般而言,沉浸式与真实场景应无动态物体的遮挡干扰,保持全局纹理的一致性,并允许无限制的探索。当前主流的图像驱动场景构建方法通过移动虚拟相机迭代优化初始图像以生成场景。然而,先前的方法在由于不同相机姿态下的全局纹理不一致导致的视觉断层方面遇到了困难,并且他们经常由于前景背景遮挡导致场景空洞。为此,我们提出了一种基于全景图像的新型分层三维场景重建框架,名为Scene4U。具体来说,Scene4U结合了开放词汇分割模型与大型语言模型,将真实全景图像分解为多个层次。然后,我们采用基于扩散模型的分层修复模块,利用视觉线索和深度信息恢复被遮挡区域,生成场景的层次表示。多层全景图像被初始化为三维高斯溅射表示,随后进行分层优化,最终生成具有语义和结构一致性的沉浸式三维场景,支持自由探索。Scene4U在LPIPS上提高了24.24%,在BRISQUE上提高了24.40%,同时达到了最快的训练速度。此外,为了证明Scene4U的稳健性并让用户能够体验来自不同地标的沉浸式场景,我们建立了用于三维场景重建的WorldVista3D数据集,其中包含全球知名景点的全景图像。实现代码和数据集将在https://github.com/LongHZ140516/Scene4U上发布。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF CVPR 2025, 11 pages, 7 figures
Summary
该文本介绍了全景图像驱动的三维场景重建的重要性和现有方法的局限性。提出了一种新型的分层三维场景重建框架Scene4U,利用全景图像进行场景重建,解决了传统方法在全球纹理不一致和前景背景遮挡导致的问题。该框架通过分解全景图像为多层,并利用扩散模型修复遮挡区域,生成具有语义和结构一致性的沉浸式三维场景。Scene4U性能优越,在LPIPS和BRISQUE指标上分别提高了24.24%和24.40%,同时训练速度最快。还构建了WorldVista3D数据集用于三维场景重建,包含全球知名地点的全景图像。
Key Takeaways
- 重建沉浸式且逼真的三维场景在计算机视觉和计算机图形学领域具有实际意义。
- 当前主流方法通过迭代优化初始图像生成场景,但面临全球纹理不一致和前景背景遮挡的问题。
- Scene4U框架利用全景图像进行分层场景重建,解决了上述问题。
- Scene4U采用开放式词汇分割模型与大型语言模型集成,并通过扩散模型修复遮挡区域。
- Scene4U生成具有语义和结构一致性的沉浸式三维场景,并支持自由探索。
- Scene4U性能优越,在LPIPS和BRISQUE指标上有显著改进。
点此查看论文截图



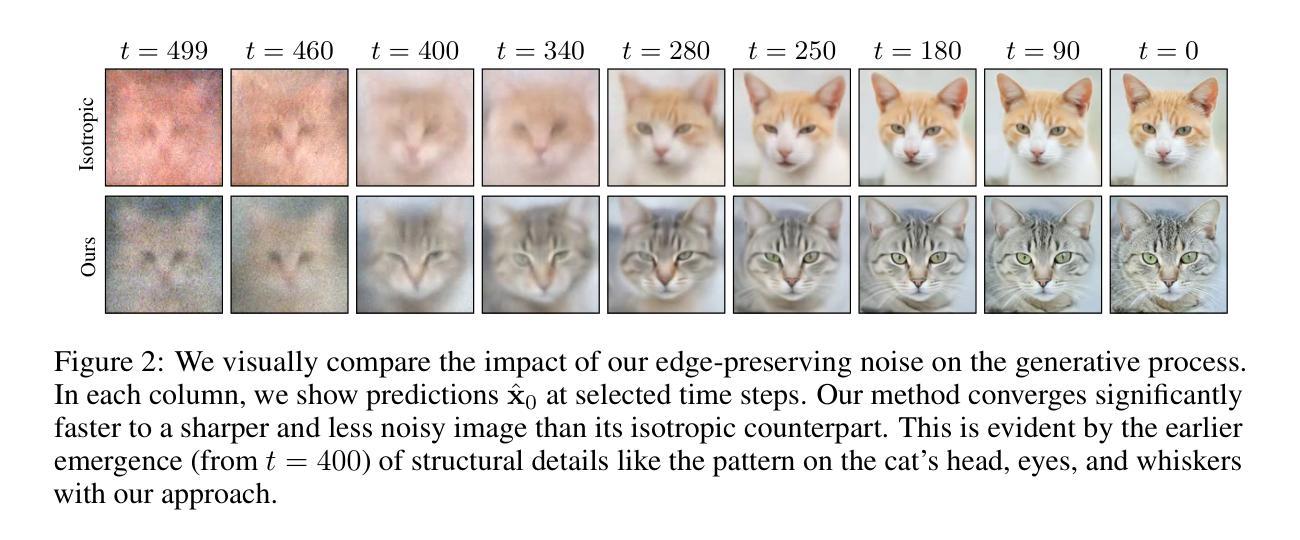
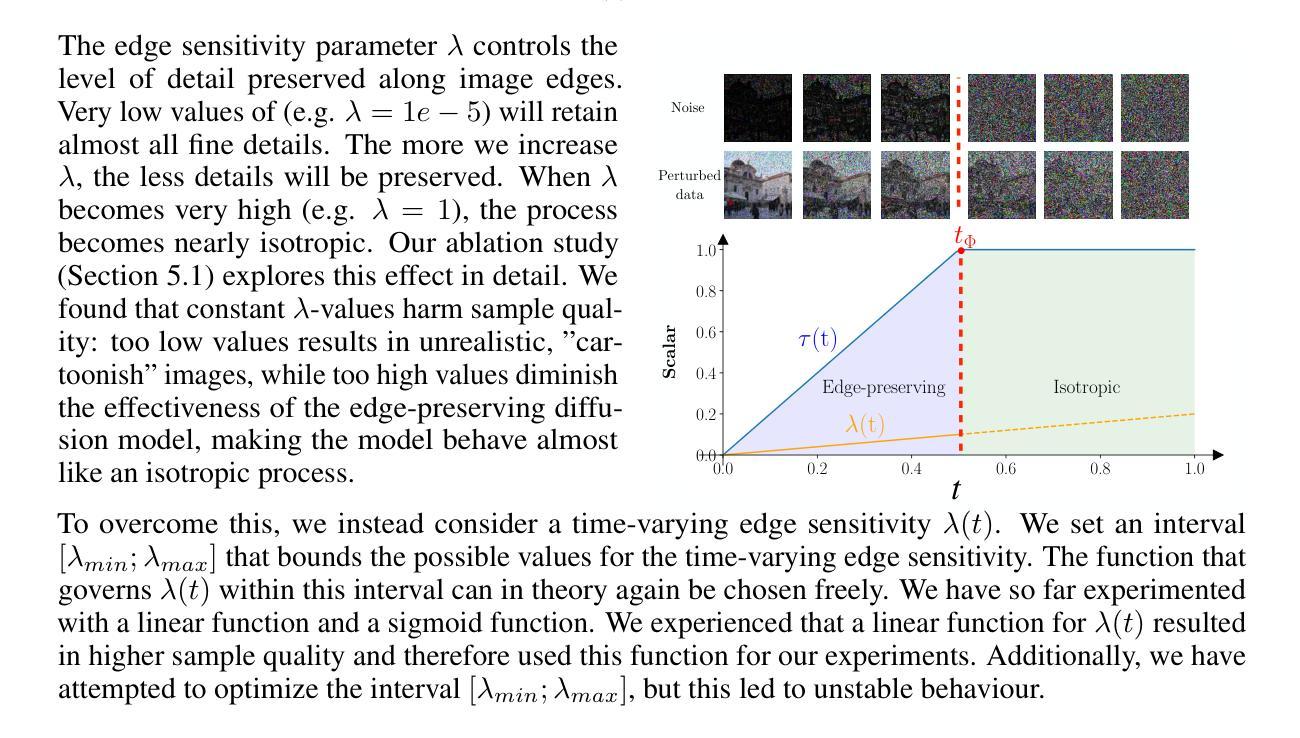
Edge-preserving noise for diffusion models
Authors:Jente Vandersanden, Sascha Holl, Xingchang Huang, Gurprit Singh
Classical generative diffusion models learn an isotropic Gaussian denoising process, treating all spatial regions uniformly, thus neglecting potentially valuable structural information in the data. Inspired by the long-established work on anisotropic diffusion in image processing, we present a novel edge-preserving diffusion model that generalizes over existing isotropic models by considering a hybrid noise scheme. In particular, we introduce an edge-aware noise scheduler that varies between edge-preserving and isotropic Gaussian noise. We show that our model’s generative process converges faster to results that more closely match the target distribution. We demonstrate its capability to better learn the low-to-mid frequencies within the dataset, which plays a crucial role in representing shapes and structural information. Our edge-preserving diffusion process consistently outperforms state-of-the-art baselines in unconditional image generation. It is also particularly more robust for generative tasks guided by a shape-based prior, such as stroke-to-image generation. We present qualitative and quantitative results (FID and CLIP score) showing consistent improvements of up to 30% for both tasks.
经典生成式扩散模型学习等向高斯去噪过程,对所有空间区域进行统一处理,从而忽略了数据中可能存在的有价值的结构信息。受图像处理中已久经建立的异向扩散工作的启发,我们提出了一种新的边缘保持扩散模型,它通过考虑混合噪声方案来概括现有的等向模型。特别是,我们引入了一种边缘感知噪声调度器,在边缘保持和等向高斯噪声之间进行变化。我们展示了我们的模型的生成过程更快收敛到更贴近目标分布的结果。我们证明了它在学习数据集内的低中频部分方面更胜一筹,这在表示形状和结构信息方面起着至关重要的作用。我们的边缘保持扩散过程在无条件图像生成方面始终优于最先进基线。对于基于形状的先验指导的生成任务,如笔划到图像生成,它也具有更强的稳健性。我们提供了定性和定量结果(FID和CLIP得分),显示两项任务的改进均持续高达30%。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
本文提出了一种基于边缘保持的扩散模型,通过考虑混合噪声方案,该模型能够在数据集中更有效地捕捉结构信息。引入的边缘感知噪声调度器能够在边缘保持和同构高斯噪声之间进行变化。实验表明,该模型的生成过程收敛速度更快,并且能更好地学习数据集中的低中频信息,这对于表示形状和结构信息至关重要。该模型在无条件图像生成任务中具有出色的性能表现,特别是在基于形状的先验引导的任务中更为稳健,如笔划到图像生成。实验结果显示,该模型在两项任务上的改进均达到了一致的进步。
Key Takeaways
- 提出的扩散模型考虑了混合噪声方案,能够更好地捕捉数据中的结构信息。
- 引入了边缘感知噪声调度器,能够在边缘保持和同构高斯噪声之间变化。
- 模型生成过程收敛速度更快,并且更接近目标分布。
- 模型能更好地学习数据集中的低中频信息,这对表示形状和结构信息至关重要。
- 模型在无条件图像生成任务中具有出色的性能表现。
- 模型在基于形状的先验引导的任务中更为稳健,如笔划到图像生成。
点此查看论文截图


Controlling Space and Time with Diffusion Models
Authors:Daniel Watson, Saurabh Saxena, Lala Li, Andrea Tagliasacchi, David J. Fleet
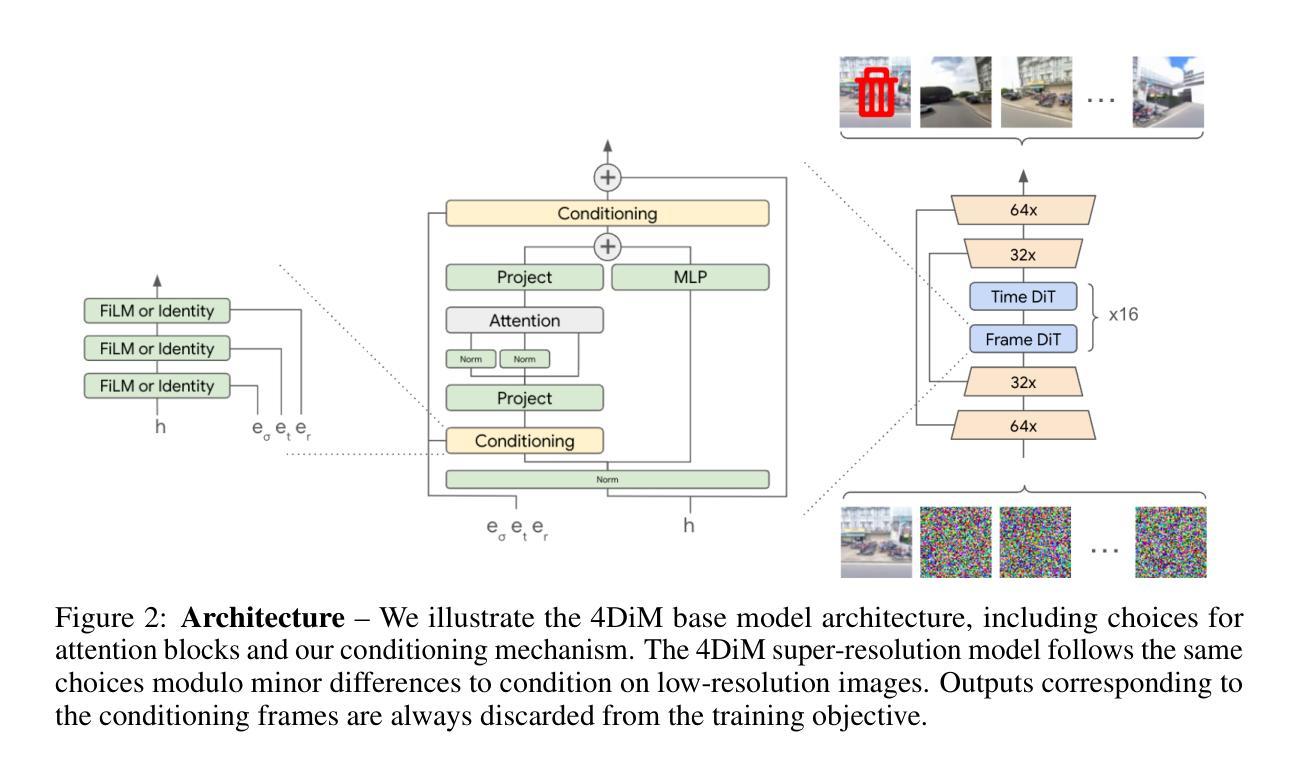
We present 4DiM, a cascaded diffusion model for 4D novel view synthesis (NVS), supporting generation with arbitrary camera trajectories and timestamps, in natural scenes, conditioned on one or more images. With a novel architecture and sampling procedure, we enable training on a mixture of 3D (with camera pose), 4D (pose+time) and video (time but no pose) data, which greatly improves generalization to unseen images and camera pose trajectories over prior works that focus on limited domains (e.g., object centric). 4DiM is the first-ever NVS method with intuitive metric-scale camera pose control enabled by our novel calibration pipeline for structure-from-motion-posed data. Experiments demonstrate that 4DiM outperforms prior 3D NVS models both in terms of image fidelity and pose alignment, while also enabling the generation of scene dynamics. 4DiM provides a general framework for a variety of tasks including single-image-to-3D, two-image-to-video (interpolation and extrapolation), and pose-conditioned video-to-video translation, which we illustrate qualitatively on a variety of scenes. For an overview see https://4d-diffusion.github.io
我们提出了4DiM,这是一个用于4D新颖视图合成(NVS)的级联扩散模型,支持在自然环境场景中,以一个或多个图像为条件,生成具有任意相机轨迹和时间戳的内容。通过采用新型架构和采样流程,我们能够混合使用3D(带有相机姿态)、4D(姿态+时间)和视频(只有时间没有姿态)数据进行训练,这极大地提高了在未见过的图像和相机姿态轨迹上的泛化能力,相较于那些专注于有限领域(例如以对象为中心的领域)的先前工作。4DiM是首个能够通过我们的新型运动恢复结构校准管道实现直观度量尺度相机姿态控制的新型视图合成方法。实验表明,在图像保真度和姿态对齐方面,4DiM优于先前的3D NVS模型,同时能够实现场景动态生成。4DiM为各种任务提供了一个通用框架,包括单图像到3D、两图像到视频(插帧和外插帧),以及姿态控制视频到视频的转换,我们在各种场景中对这些进行了定性说明。欲了解更多信息,请访问:https://4d-diffusion.github.io。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF ICLR 2025, First three authors contributed equally
Summary
本文介绍了名为4DiM的级联扩散模型,该模型用于支持以任意相机轨迹和时间戳生成自然场景的四维新视角合成(NVS)。通过采用新颖的架构和采样程序,模型能够在混合的3D(带有相机姿态)、四维(姿态+时间)和视频(时间但没有姿态)数据上进行训练,从而极大地提高了在未见过的图像和相机姿态轨迹上的泛化能力。此外,本文提出的校准管道使模型能够直观控制度量尺度下的相机姿态,从而提高了模型的表现性能。实验表明,与其他工作相比,该方法在提高图像保真度和姿态对齐的同时,还可以实现场景动态生成。该模型还为多种任务提供了一个通用框架,包括单图像到三维转换、双图像到视频转换等。欲了解更多详情,请访问网站链接。
Key Takeaways
- 介绍了名为4DiM的扩散模型用于四维新视角合成(NVS)。
- 模型支持任意相机轨迹和时间戳的生成,在自然场景中表现优异。
点此查看论文截图



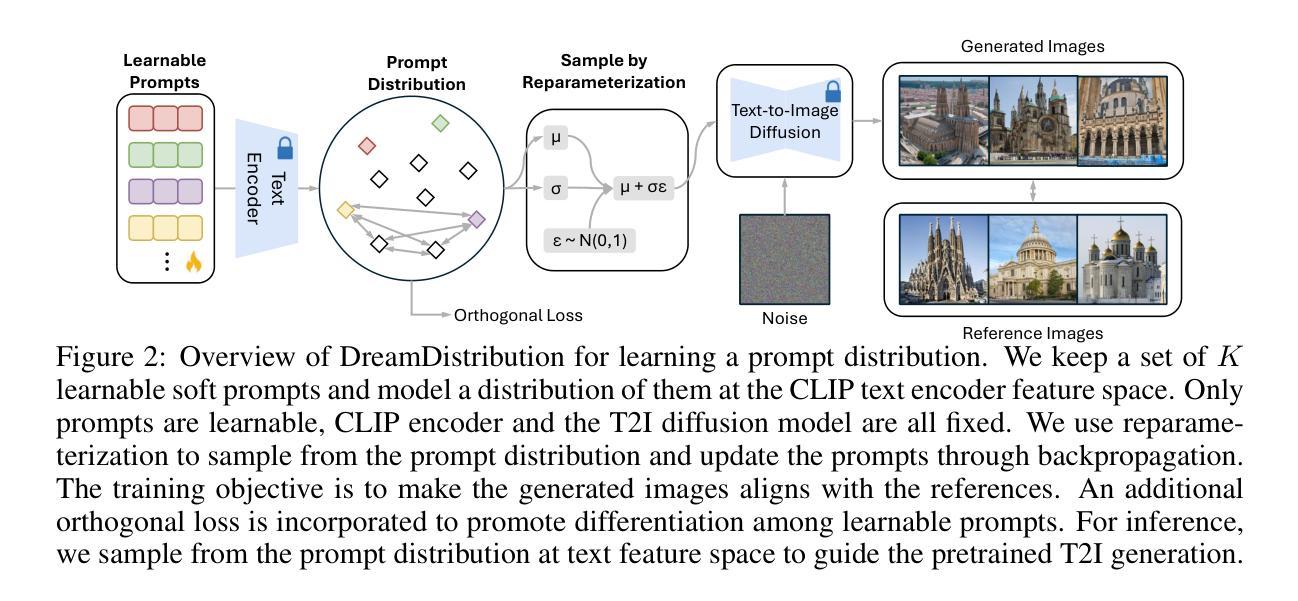
DreamDistribution: Learning Prompt Distribution for Diverse In-distribution Generation
Authors:Brian Nlong Zhao, Yuhang Xiao, Jiashu Xu, Xinyang Jiang, Yifan Yang, Dongsheng Li, Laurent Itti, Vibhav Vineet, Yunhao Ge
The popularization of Text-to-Image (T2I) diffusion models enables the generation of high-quality images from text descriptions. However, generating diverse customized images with reference visual attributes remains challenging. This work focuses on personalizing T2I diffusion models at a more abstract concept or category level, adapting commonalities from a set of reference images while creating new instances with sufficient variations. We introduce a solution that allows a pretrained T2I diffusion model to learn a set of soft prompts, enabling the generation of novel images by sampling prompts from the learned distribution. These prompts offer text-guided editing capabilities and additional flexibility in controlling variation and mixing between multiple distributions. We also show the adaptability of the learned prompt distribution to other tasks, such as text-to-3D. Finally we demonstrate effectiveness of our approach through quantitative analysis including automatic evaluation and human assessment. Project website: https://briannlongzhao.github.io/DreamDistribution
文本到图像(T2I)扩散模型的普及使得从文本描述生成高质量图像成为可能。然而,参考视觉属性生成多样化定制图像仍然具有挑战性。这项工作专注于在更抽象的概念或类别层面上个性化T2I扩散模型,从一组参考图像中吸取共性,同时创建具有足够变化的新实例。我们引入了一种解决方案,允许预训练的T2I扩散模型学习一组软提示(soft prompts),通过从已学习的分布中抽样提示来生成新图像。这些提示提供了文本指导的编辑功能,并在控制多个分布之间的变化和混合方面提供了额外的灵活性。我们还展示了学习到的提示分布对其他任务的适应性,如文本到3D。最后,我们通过包括自动评估和人工评估在内的定量分析证明了我们的方法的有效性。项目网站:https://briannlongzhao.github.io/DreamDistribution
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
文本到图像(T2I)扩散模型的普及使得从文本描述生成高质量图像成为可能。然而,根据参考视觉属性生成多样化定制图像仍然具有挑战性。本文专注于在更抽象的概念或类别级别个性化T2I扩散模型,从一组参考图像中吸取共性,同时创建具有足够变化的新实例。我们引入了一种解决方案,允许预训练的T2I扩散模型学习一套软提示,通过从学习的分布中采样提示来生成新图像。这些提示提供文本指导的编辑功能,并在控制多个分布之间的变化和混合方面提供额外的灵活性。我们还展示了所学提示分布对其他任务(如文本到3D)的适应性。最后,我们通过自动评估和人类评估等定量分析证明了我们的方法的有效性。
Key Takeaways
- T2I扩散模型能够基于文本描述生成高质量图像。
- 生成多样化定制图像仍然面临挑战,需要更高级的个性化技术。
- 本文关注在抽象层面个性化T2I扩散模型。
- 通过学习软提示来适应预训练的T2I扩散模型,以生成具有变化和新颖性的图像。
- 提示提供文本指导的编辑功能,增加控制图像变化的能力。
- 所学提示分布可适应其他任务,如文本到3D。
- 通过定量分析和实验验证方法的有效性。
点此查看论文截图