⚠️ 以下所有内容总结都来自于 大语言模型的能力,如有错误,仅供参考,谨慎使用
🔴 请注意:千万不要用于严肃的学术场景,只能用于论文阅读前的初筛!
💗 如果您觉得我们的项目对您有帮助 ChatPaperFree ,还请您给我们一些鼓励!⭐️ HuggingFace免费体验
2025-04-23 更新
Automated Measurement of Eczema Severity with Self-Supervised Learning
Authors:Neelesh Kumar, Oya Aran
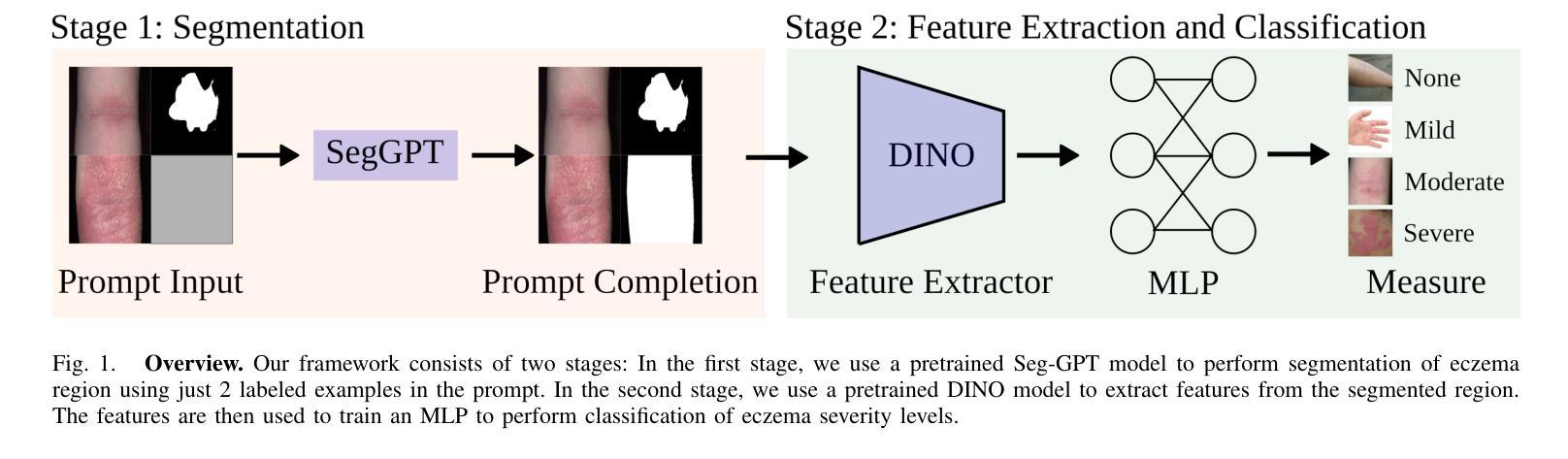
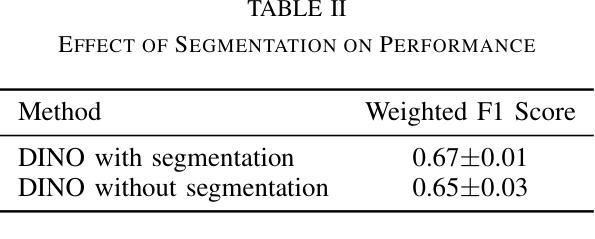
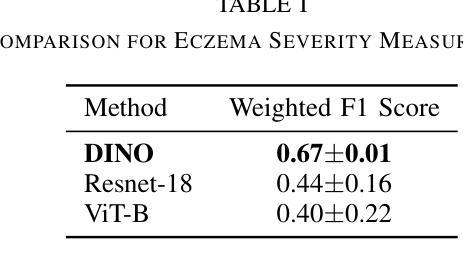
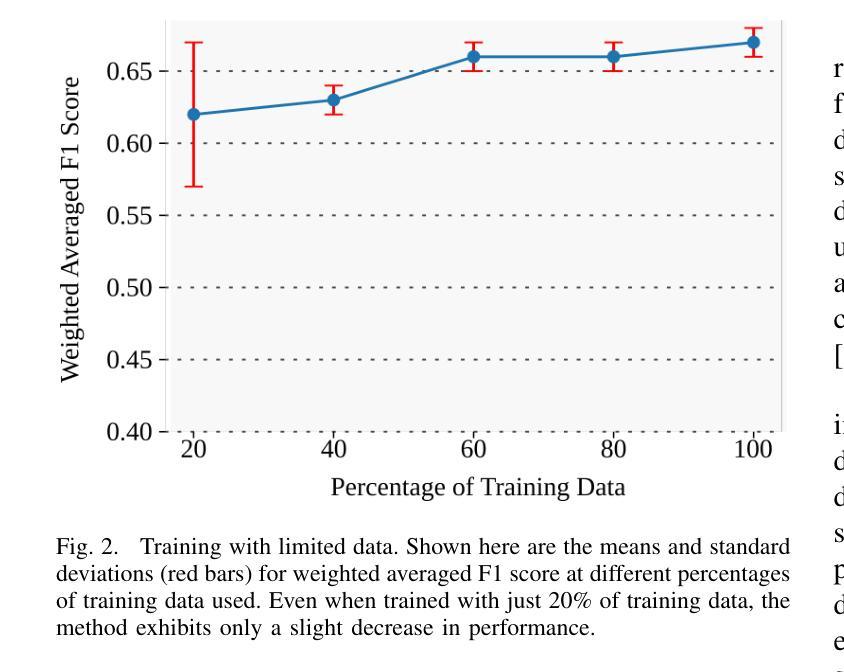
Automated diagnosis of eczema using images acquired from digital camera can enable individuals to self-monitor their recovery. The process entails first segmenting out the eczema region from the image and then measuring the severity of eczema in the segmented region. The state-of-the-art methods for automated eczema diagnosis rely on deep neural networks such as convolutional neural network (CNN) and have shown impressive performance in accurately measuring the severity of eczema. However, these methods require massive volume of annotated data to train which can be hard to obtain. In this paper, we propose a self-supervised learning framework for automated eczema diagnosis under limited training data regime. Our framework consists of two stages: i) Segmentation, where we use an in-context learning based algorithm called SegGPT for few-shot segmentation of eczema region from the image; ii) Feature extraction and classification, where we extract DINO features from the segmented regions and feed it to a multi-layered perceptron (MLP) for 4-class classification of eczema severity. When evaluated on a dataset of annotated “in-the-wild” eczema images, we show that our method outperforms (Weighted F1: 0.67 $\pm$ 0.01) the state-of-the-art deep learning methods such as finetuned Resnet-18 (Weighted F1: 0.44 $\pm$ 0.16) and Vision Transformer (Weighted F1: 0.40 $\pm$ 0.22). Our results show that self-supervised learning can be a viable solution for automated skin diagnosis where labeled data is scarce.
使用数字相机拍摄的图片进行湿疹自动化诊断,可以让患者自行监测康复情况。该流程包括首先从图片中分割出湿疹区域,然后测量分割区域中湿疹的严重程度。目前先进的湿疹自动化诊断方法依赖于深度神经网络,如卷积神经网络(CNN),在准确测量湿疹严重程度方面表现出令人印象深刻的性能。然而,这些方法需要大量标注数据进行训练,而获取这些数据可能很困难。在本文中,我们提出了一种在有限训练数据下用于自动化湿疹诊断的自监督学习框架。我们的框架分为两个阶段:i)分割,我们使用基于上下文学习的算法SegGPT,对图片中的湿疹区域进行少量样本分割;ii)特征提取和分类,我们从分割区域中提取DINO特征,并将其输入多层感知器(MLP)中进行湿疹严重程度的4类分类。在“野生”湿疹图片标注数据集上进行评估,我们的方法(加权F1:0.67±0.01)优于最新的深度学习方法,如微调后的Resnet-18(加权F1:0.44±0.16)和视觉转换器(加权F1:0.40±0.22)。我们的结果表明,在标记数据稀缺的情况下,自监督学习可作为皮肤疾病自动化诊断的一种可行解决方案。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
利用图像自动识别技术,实现湿疹的自我监控与诊断。该研究采用自监督学习方法,在少量训练数据下,通过分段算法和特征提取分类器对湿疹进行自动诊断,并表现出优异性能。该方法可解决数据标注困难的问题。
Key Takeaways
- 利用数字相机采集的图像进行湿疹自动诊断,使个人能够自我监控康复情况。
- 通过分段算法识别湿疹区域,并测量其严重程度。
- 当前先进的自动湿疹诊断方法主要依赖深度神经网络,如卷积神经网络(CNN)。
- 深度学习方法需要大量标注数据进行训练,但获取这些数据可能很困难。
- 提出了一种自监督学习框架,用于在有限训练数据下进行自动化湿疹诊断。
- 框架分为两个阶段:分段和特征提取分类,使用SegGPT算法进行少数样本湿疹区域分段,通过提取DINO特征和多层感知器(MLP)进行湿疹严重程度的四分类。
- 在实际湿疹图像数据集上的评估表明,该方法优于其他先进深度学习方法的性能。
点此查看论文截图

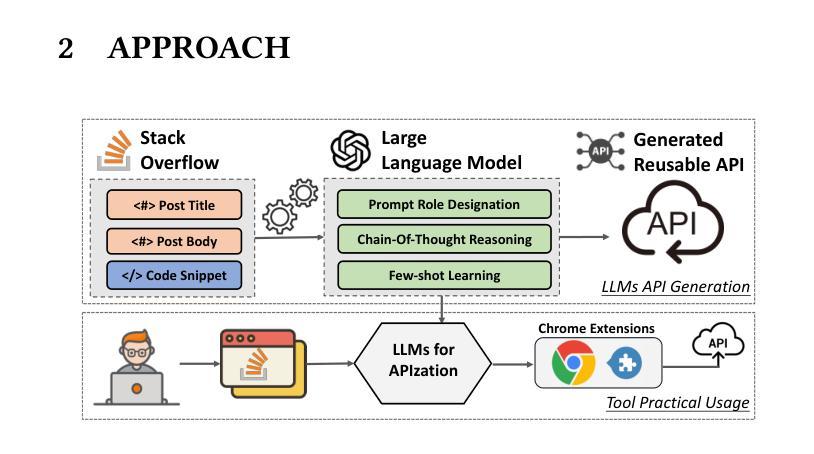
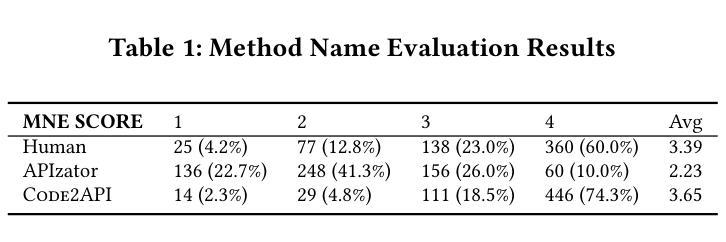
Code2API: A Tool for Generating Reusable APIs from Stack Overflow Code Snippets
Authors:Yubo Mai, Zhipeng Gao, Xing Hu, Lingfeng Bao, Jingyuan Chen, Jianling Sun
Nowadays, developers often turn to Stack Overflow for solutions to daily problems, however, these code snippets are partial code that cannot be tested and verified properly. One way to test these code snippets is to transform them into APIs (Application Program Interface) that developers can be directly invoked and executed. However, it is often costly and error-prone for developers to manually perform this transformation (referred to as AIPzation task) due to different actions to be taken (e.g., summarizing proper method names, inferring input parameters list and return statements). To help developers quickly reuse code snippets in Stack Overflow, in this paper, we propose Code2API, a Google Chrome extension that uses Large Language Models (LLMs) to automatically perform APIzation of code snippets on Stack Overflow. \toolname guides LLMs through well-designed prompts to generate reusable APIs, using Chain-of-Thought reasoning and few-shot in-context learning to help LLMs understand and solve the APIzation task in a developer-like manner. The evaluation results show that Code2API significantly outperforms the rule-based approach by a large margin.
如今,开发者经常转向Stack Overflow寻找日常问题的解决方案,然而,这些代码片段是部分代码,无法进行适当的测试和验证。测试这些代码片段的一种方法是将其转换为应用程序编程接口(API),开发者可以直接调用和执行。然而,由于需要采取的不同行动(例如,总结适当的方法名称、推断输入参数列表和返回语句),开发者手动执行这种转换(称为API化任务)通常成本高昂且容易出错。为了帮助开发者快速重用Stack Overflow中的代码片段,本文提出了Code2API,这是一个Google Chrome扩展程序,它使用大型语言模型(LLM)自动执行Stack Overflow上的代码片段的API化。通过精心设计提示来指导LLM生成可重用的API,利用Chain-of-Thought推理和少量上下文学习来帮助LLM以开发者类似的方式理解和解决API化任务。评估结果表明,Code2API在规则基础上的方法上具有显著优势。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
Code2API是一款基于Google Chrome的扩展工具,利用大型语言模型(LLMs)自动执行Stack Overflow上代码片段的API化任务。该工具通过精心设计提示来引导LLMs生成可重用的API,并利用Chain-of-Thought推理和少量上下文学习来帮助LLMs以开发者方式理解和解决API化任务。评估结果显示,Code2API大幅优于基于规则的方法。
Key Takeaways
- 开发者常使用Stack Overflow查找代码片段,但这些代码片段通常是部分代码,无法充分测试和验证。
- 将代码片段转化为API(应用程序编程接口)是解决此问题的一种方法,但手动执行此任务(称为API化任务)既昂贵又容易出错。
- Code2API是一个Google Chrome扩展,可自动执行Stack Overflow上的代码片段的API化任务。
- Code2API利用大型语言模型(LLMs)通过精心设计提示来生成可重用的API。
- Chain-of-Thought推理和少量上下文学习技术被用于帮助LLMs像开发者一样理解和解决API化任务。
- Code2API显著优于基于规则的方法。
- 此工具能够简化开发者的工作流程,提高代码的可重用性和测试性。
点此查看论文截图


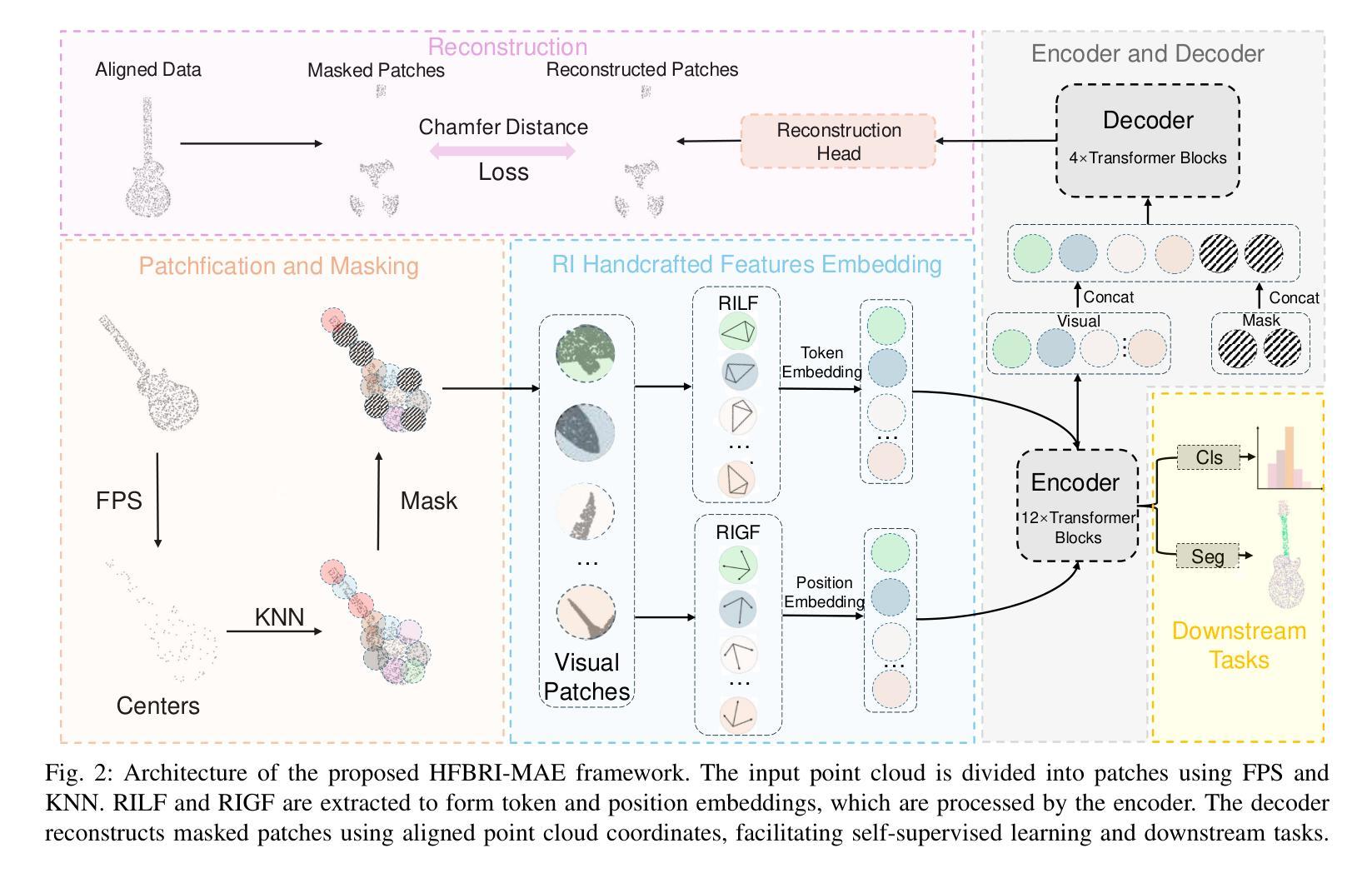
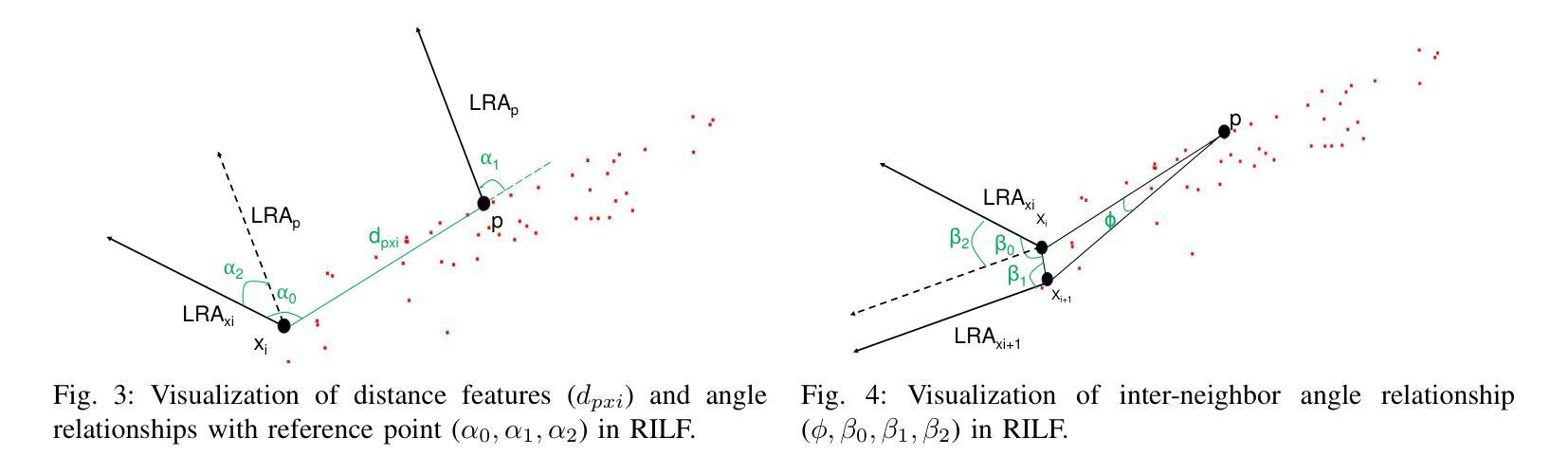
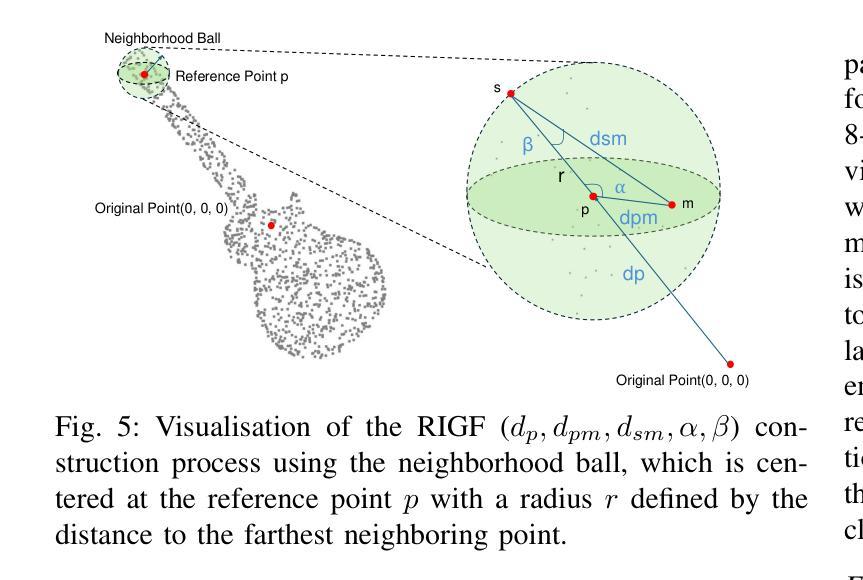
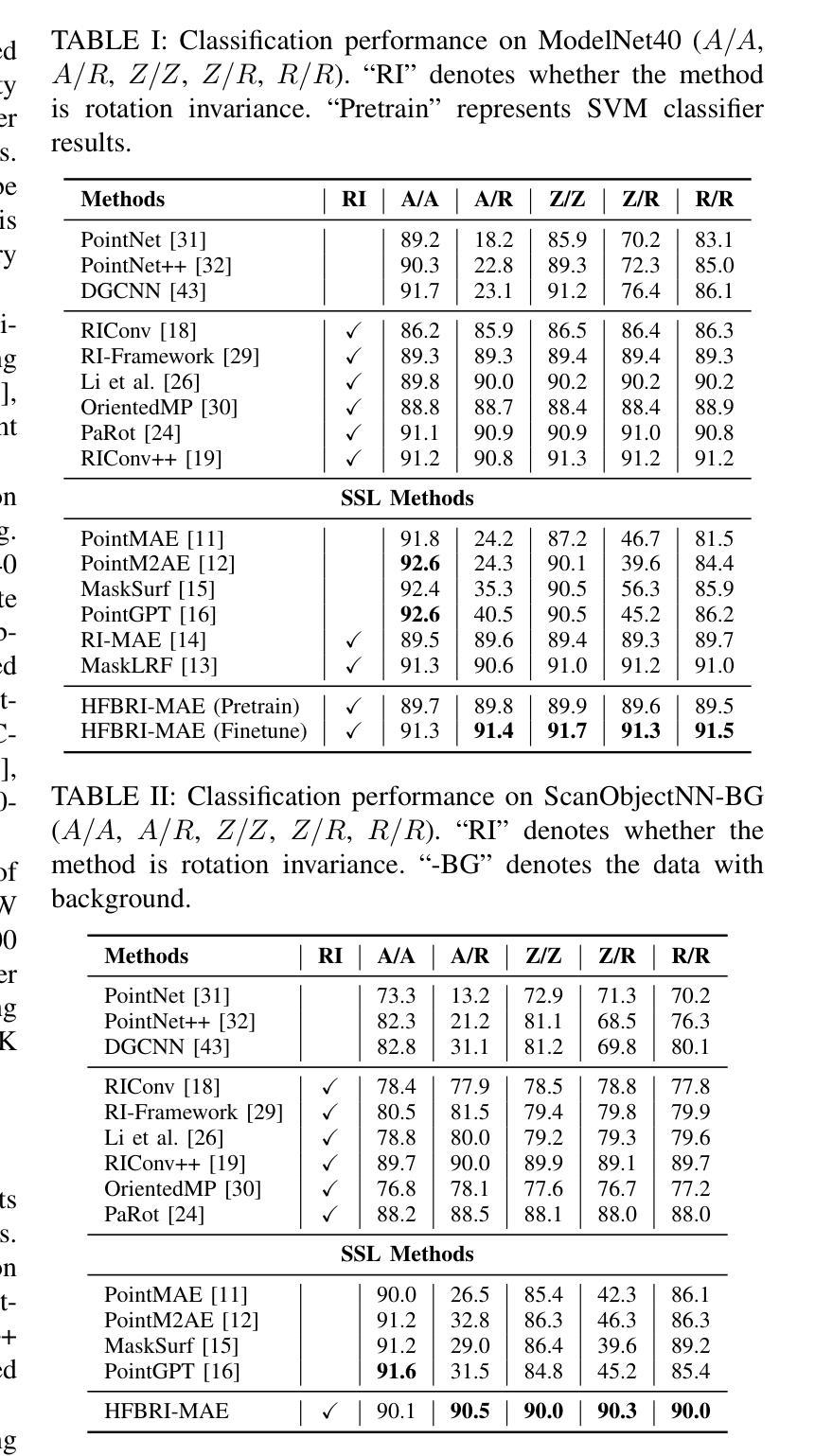
HFBRI-MAE: Handcrafted Feature Based Rotation-Invariant Masked Autoencoder for 3D Point Cloud Analysis
Authors:Xuanhua Yin, Dingxin Zhang, Jianhui Yu, Weidong Cai
Self-supervised learning (SSL) has demonstrated remarkable success in 3D point cloud analysis, particularly through masked autoencoders (MAEs). However, existing MAE-based methods lack rotation invariance, leading to significant performance degradation when processing arbitrarily rotated point clouds in real-world scenarios. To address this limitation, we introduce Handcrafted Feature-Based Rotation-Invariant Masked Autoencoder (HFBRI-MAE), a novel framework that refines the MAE design with rotation-invariant handcrafted features to ensure stable feature learning across different orientations. By leveraging both rotation-invariant local and global features for token embedding and position embedding, HFBRI-MAE effectively eliminates rotational dependencies while preserving rich geometric structures. Additionally, we redefine the reconstruction target to a canonically aligned version of the input, mitigating rotational ambiguities. Extensive experiments on ModelNet40, ScanObjectNN, and ShapeNetPart demonstrate that HFBRI-MAE consistently outperforms existing methods in object classification, segmentation, and few-shot learning, highlighting its robustness and strong generalization ability in real-world 3D applications.
自监督学习(SSL)在3D点云分析领域已经取得了显著的成果,尤其是通过掩码自动编码器(MAE)实现。然而,现有的基于MAE的方法缺乏旋转不变性,导致在处理现实世界场景中任意旋转的点云时性能显著下降。为了解决这一局限性,我们引入了基于手工特征的旋转不变掩码自动编码器(HFBRI-MAE),这是一种新型框架,它通过引入旋转不变的手工特征来优化MAE设计,以确保在不同方向上的稳定特征学习。HFBRI-MAE利用旋转不变的局部和全局特征进行令牌嵌入和位置嵌入,有效地消除了旋转依赖性,同时保留了丰富的几何结构。此外,我们将重建目标重新定义为输入的标准对齐版本,以消除旋转模糊。在ModelNet40、ScanObjectNN和ShapeNetPart上的大量实验表明,HFBRI-MAE在目标分类、分割和少样本学习上始终优于现有方法,突显了其在现实世界的3D应用中的稳健性和强大的泛化能力。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF 12 pages, 9 figures, accepted by IJCNN 2025
Summary
本文提出一种基于手工特征的旋转不变掩码自编码器(HFBRI-MAE)框架,用于解决现有的自监督学习(SSL)在点云分析领域存在的旋转不变性问题。通过融合旋转不变的局部和全局特征,实现对不同方向下的稳定特征学习。同时,重新定义重建目标为输入的标准对齐版本,减少旋转模糊性。实验证明,HFBRI-MAE在ModelNet40、ScanObjectNN和ShapeNetPart数据集上的物体分类、分割和少样本学习效果卓越,表现出其强大的稳健性和泛化能力。
Key Takeaways
- HFBRI-MAE框架解决了现有自监督学习在点云分析中的旋转不变性问题。
- 通过结合旋转不变的局部和全局特征进行令牌嵌入和位置嵌入,HFBRI-MAE有效消除旋转依赖性并保留丰富的几何结构。
- 重新定义的重建目标是输入的标准对齐版本,减少旋转模糊性。
- HFBRI-MAE在多个数据集上的实验表现优异,包括ModelNet40、ScanObjectNN和ShapeNetPart。
- HFBRI-MAE在物体分类、分割和少样本学习任务中均表现出强大的性能。
- HFBRI-MAE具有卓越的稳健性和泛化能力,适用于实际的三维应用。
点此查看论文截图

A Baseline for Self-state Identification and Classification in Mental Health Data: CLPsych 2025 Task
Authors:Laerdon Kim
We present a baseline for the CLPsych 2025 A.1 task: classifying self-states in mental health data taken from Reddit. We use few-shot learning with a 4-bit quantized Gemma 2 9B model and a data preprocessing step which first identifies relevant sentences indicating self-state evidence, and then performs a binary classification to determine whether the sentence is evidence of an adaptive or maladaptive self-state. This system outperforms our other method which relies on an LLM to highlight spans of variable length independently. We attribute the performance of our model to the benefits of this sentence chunking step for two reasons: partitioning posts into sentences 1) broadly matches the granularity at which self-states were human-annotated and 2) simplifies the task for our language model to a binary classification problem. Our system places third out of fourteen systems submitted for Task A.1, achieving a test-time recall of 0.579.
我们对CLPsych 2025 A.1任务提出了一个基线方法:对来自Reddit的心理健康数据进行自我状态分类。我们使用少量样本学习,结合4位量化Gemma 2 9B模型和数据处理步骤,首先识别表示自我状态证据的相关句子,然后对句子进行二元分类,以确定句子是适应性还是适应不良的自我状态证据。我们的系统表现优于另一种依赖于大型语言模型独立突出显示可变长度段落的方法。我们将模型的性能归功于句子分块步骤的两个好处:将帖子分成句子1)与人类注释自我状态的大致粒度相匹配;2)将任务简化为二元分类问题,这简化了我们的语言模型的任务。我们的系统在A.1任务中提交的14个系统中排名第三,测试时的召回率为0.579。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF Accepted to CLPsych Workshop, NAACL 2025
Summary
本文介绍了针对CLPsych 2025 A.1任务的分类基线:使用少量学习样本,采用4位量化的Gemma 2 9B模型对来自Reddit的心理健康数据进行自我状态分类。通过数据预处理步骤,首先识别表示自我状态证据的相关句子,然后进行二元分类,确定句子是适应性的还是适应不良的。该系统优于依赖LLM进行独立变量长度跨距突出的另一种方法。作者认为模型性能的提升得益于句子分块步骤的两个优点:将帖子分成句子,这大致匹配人类标注自我状态的粒度并简化了语言模型的任务为二元分类问题。该系统在A.1任务中位列第三,测试时的召回率为0.579。
Key Takeaways
- 研究人员提出了针对CLPsych 2025 A.1任务的分类基线方法,旨在从Reddit数据中分类自我状态。
- 采用少量学习样本和4位量化的Gemma 2 9B模型进行任务处理。
- 数据预处理步骤包括识别表示自我状态证据的相关句子,并进行二元分类。
- 系统性能得益于句子分块步骤,因为它使模型能够更好地处理语言模型任务为二元分类问题并符合人类标注的自我状态粒度。
- 该系统在测试时的召回率为0.579,表现良好。
- 与依赖LLM独立标注跨距长度的另一种方法相比,该系统的性能有所提升。
点此查看论文截图



Flow to Learn: Flow Matching on Neural Network Parameters
Authors:Daniel Saragih, Deyu Cao, Tejas Balaji, Ashwin Santhosh
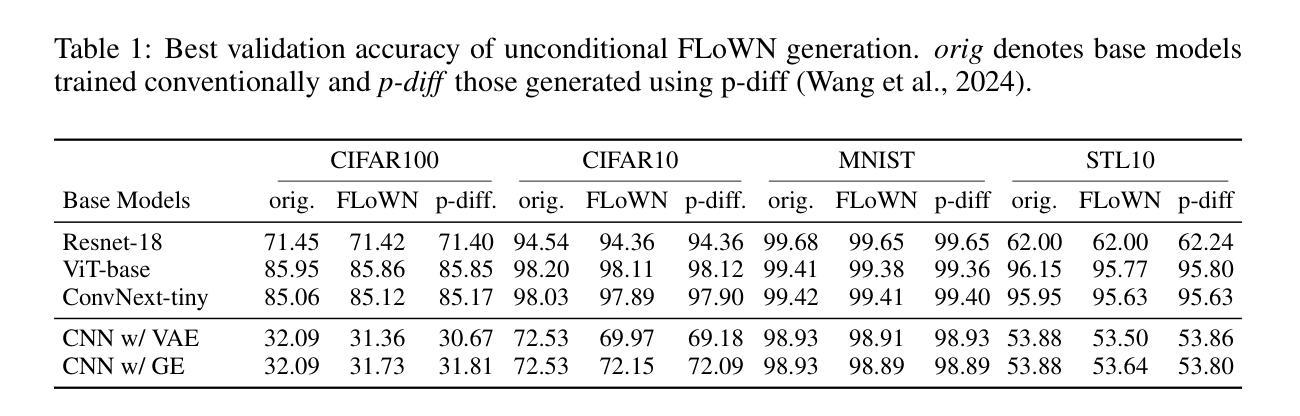
Foundational language models show a remarkable ability to learn new concepts during inference via context data. However, similar work for images lag behind. To address this challenge, we introduce FLoWN, a flow matching model that learns to generate neural network parameters for different tasks. Our approach models the flow on latent space, while conditioning the process on context data. Experiments verify that FLoWN attains various desiderata for a meta-learning model. In addition, it matches or exceeds baselines on in-distribution tasks, provides better initializations for classifier training, and is performant on out-of-distribution few-shot tasks while having a fine-tuning mechanism to improve performance.
基础语言模型表现出在推理过程中通过上下文数据学习新概念的显著能力。然而,类似的图像相关工作仍落后。为了应对这一挑战,我们引入了FLoWN,这是一个流匹配模型,旨在学习为不同任务生成神经网络参数。我们的方法模拟了潜在空间上的流,同时根据上下文数据进行处理。实验证明,FLoWN满足了元学习模型的各种需求。此外,它在内部任务上达到或超过了基线水平,为分类器训练提供了更好的初始化方案,并在外部少量任务的场景下表现出良好的性能,同时具有微调机制以提高性能。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF Accepted at the ICLR Workshop on Neural Network Weights as a New Data Modality 2025
Summary
本文介绍了一种名为FLoWN的流匹配模型,该模型能够在不同任务中生成神经网络参数。它通过模拟潜在空间的流来建模,并以上下文数据为条件进行过程控制。实验证明,FLoWN达到了元学习模型的各种期望要求,并在内部任务上匹配或超过了基线水平,为分类器训练提供了更好的初始化,并在外部任务的少样本情况下表现出良好的性能,同时具有微调机制以提高性能。
Key Takeaways
- FLoWN模型通过在潜在空间上建模流来解决图像领域的概念学习问题。
- 该模型能够在不同任务中生成神经网络参数。
- FLoWN能够以上下文数据为条件进行过程控制。
- 实验表明,FLoWN达到了元学习模型的期望要求。
- FLoWN在内部任务上表现出良好的性能,匹配或超过了基线水平。
- FLoWN能够为分类器训练提供更好的初始化。
点此查看论文截图

TLAC: Two-stage LMM Augmented CLIP for Zero-Shot Classification
Authors:Ans Munir, Faisal Z. Qureshi, Muhammad Haris Khan, Mohsen Ali
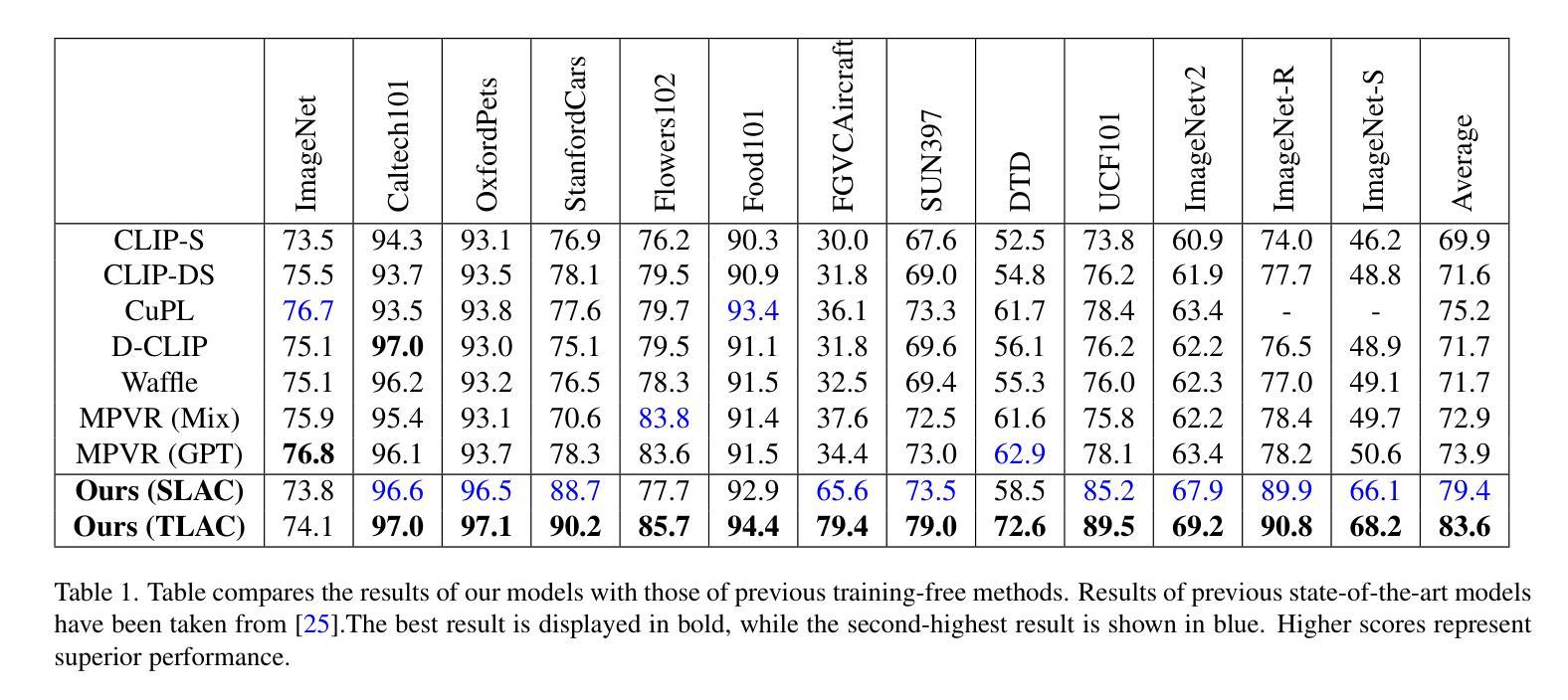
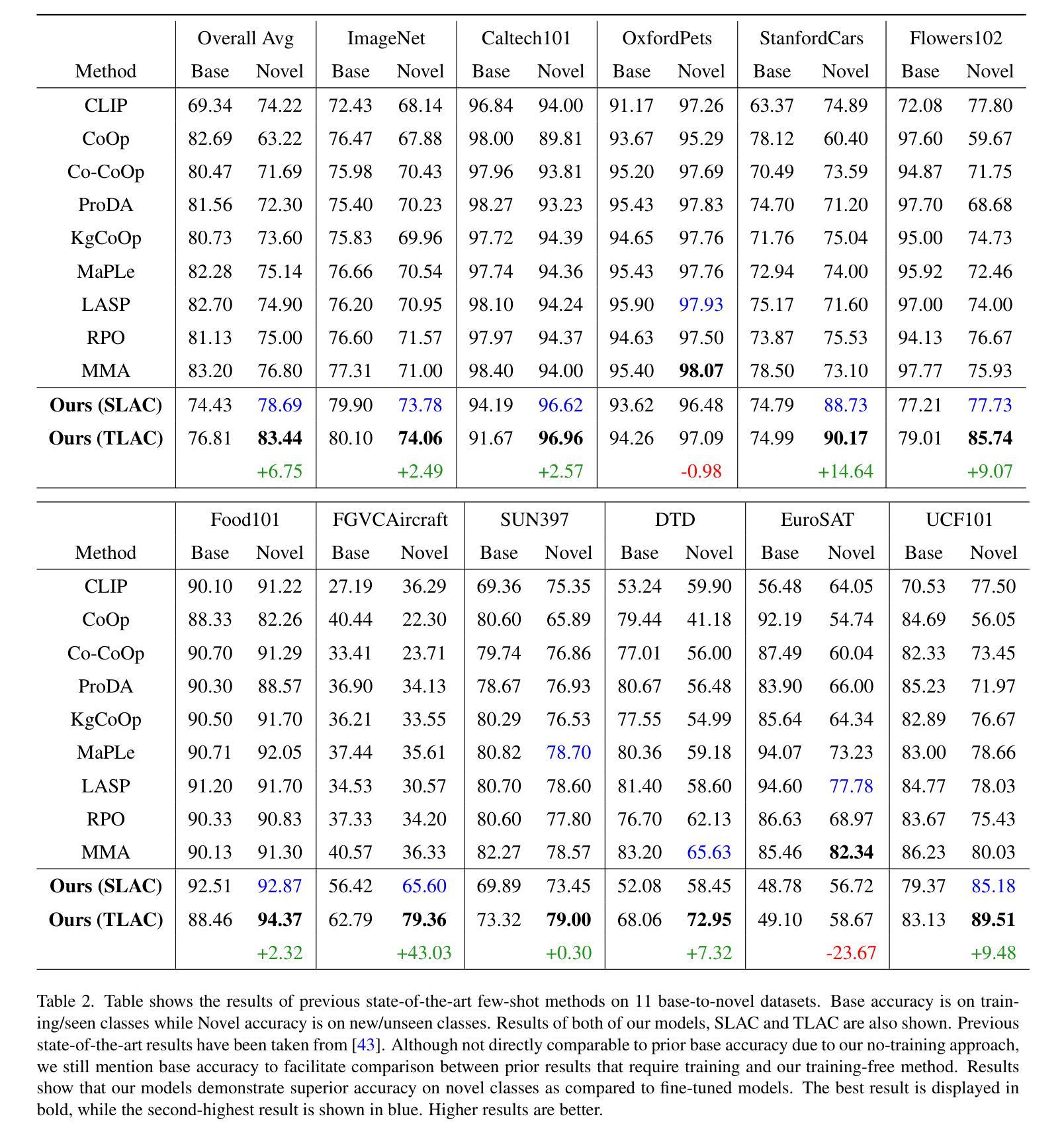
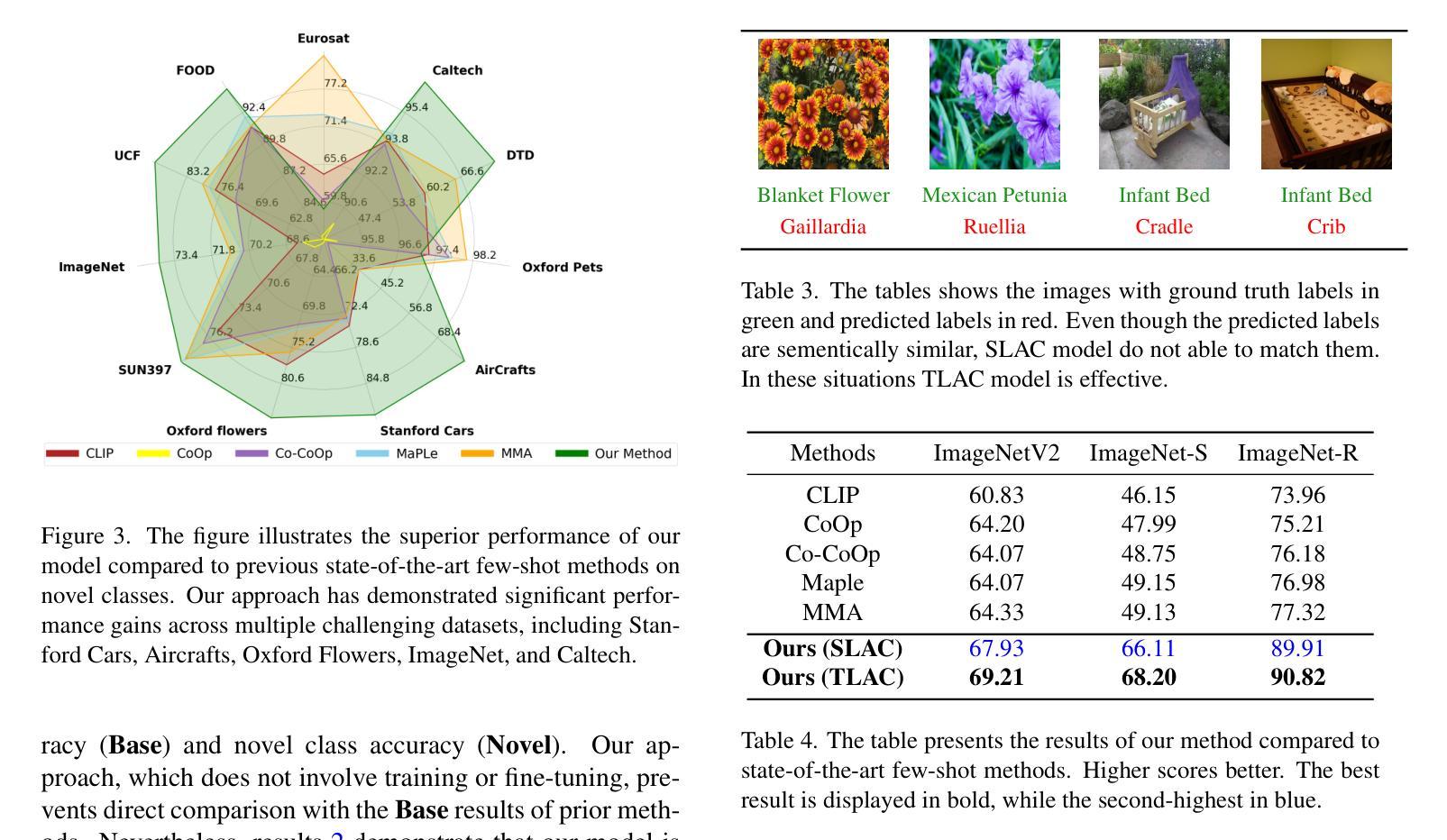
Contrastive Language-Image Pretraining (CLIP) has shown impressive zero-shot performance on image classification. However, state-of-the-art methods often rely on fine-tuning techniques like prompt learning and adapter-based tuning to optimize CLIP’s performance. The necessity for fine-tuning significantly limits CLIP’s adaptability to novel datasets and domains. This requirement mandates substantial time and computational resources for each new dataset. To overcome this limitation, we introduce simple yet effective training-free approaches, Single-stage LMM Augmented CLIP (SLAC) and Two-stage LMM Augmented CLIP (TLAC), that leverages powerful Large Multimodal Models (LMMs), such as Gemini, for image classification. The proposed methods leverages the capabilities of pre-trained LMMs, allowing for seamless adaptation to diverse datasets and domains without the need for additional training. Our approaches involve prompting the LMM to identify objects within an image. Subsequently, the CLIP text encoder determines the image class by identifying the dataset class with the highest semantic similarity to the LLM predicted object. Our models achieved superior accuracy on 9 of 11 base-to-novel datasets, including ImageNet, SUN397, and Caltech101, while maintaining a strictly training-free paradigm. Our TLAC model achieved an overall accuracy of 83.44%, surpassing the previous state-of-the-art few-shot methods by a margin of 6.75%. Compared to other training-free approaches, our TLAC method achieved 83.6% average accuracy across 13 datasets, a 9.7% improvement over the previous methods. Our Code is available at https://github.com/ans92/TLAC
对比语言图像预训练(CLIP)在图像分类方面展现出了令人印象深刻的零样本性能。然而,最先进的方法通常依赖于微调技术,如基于提示的学习和基于适配器的调整,以优化CLIP的性能。这种对微调的必要性显著限制了CLIP对新数据集和领域的适应能力。对于每个新数据集,这种要求都需要大量的时间和计算资源。为了克服这一局限性,我们引入了简单而有效的无训练方法,即单阶段LMM增强CLIP(SLAC)和双阶段LMM增强CLIP(TLAC),这些方法利用强大的大型多媒体模型(LMMs),如Gemini,进行图像分类。所提出的方法利用预训练的LMM的能力,无需额外的训练即可无缝适应各种数据集和领域。我们的方法包括提示LMM来识别图像中的对象。然后,CLIP文本编码器通过识别与LLM预测对象语义相似性最高的数据集类别来确定图像类别。我们的模型在包括ImageNet、SUN397和Caltech101在内的11个基础到新颖数据集中的9个上实现了更高的准确性,同时保持了严格的无需训练的模式。我们的TLAC模型的总准确率为83.44%,较之前的先进少样本方法提高了6.75%。与其他无训练的方法相比,我们的TLAC方法在13个数据集上取得了平均83.6%的准确率,比之前的方法提高了9.7%。我们的代码可在以下网址找到:https://github.com/ans92/TLAC。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF Added code link in the abstract
Summary
本文介绍了通过利用强大的大型多模态模型(LMMs),如Gemini,来克服CLIP模型在零样本学习中的局限性。文章提出了两种训练免费的方法:单阶段LMM增强CLIP(SLAC)和双阶段LMM增强CLIP(TLAC)。这些方法通过在预训练的大型多模态模型的帮助下进行提示操作,允许无缝适应不同的数据集和领域而无需额外的训练。在多个基准数据集上的实验结果表明,TLAC模型在训练和零样本学习方面均取得了显著的优势。代码已公开在GitHub上。
Key Takeaways
- CLIP模型在图像分类的零样本学习中表现出强大的性能,但仍需要微调以适应新的数据集和领域。
- 新的方法SLAC和TLAC利用预训练的大型多模态模型(LMMs)进行图像分类,无需额外的训练。
- SLAC和TLAC通过提示大型多模态模型识别图像中的对象,并通过CLIP文本编码器确定图像类别。
- TLAC模型在多个数据集上实现了显著的性能提升,相较于其他方法有更优秀的准确率和适应力。
- TLAC模型的整体准确率达到83.44%,在少数数据集上的准确率超过了之前的最先进方法。
- 与其他无训练方法相比,TLAC方法在多个数据集上的平均准确率提高了9.7%。
点此查看论文截图


Tree of Attributes Prompt Learning for Vision-Language Models
Authors:Tong Ding, Wanhua Li, Zhongqi Miao, Hanspeter Pfister
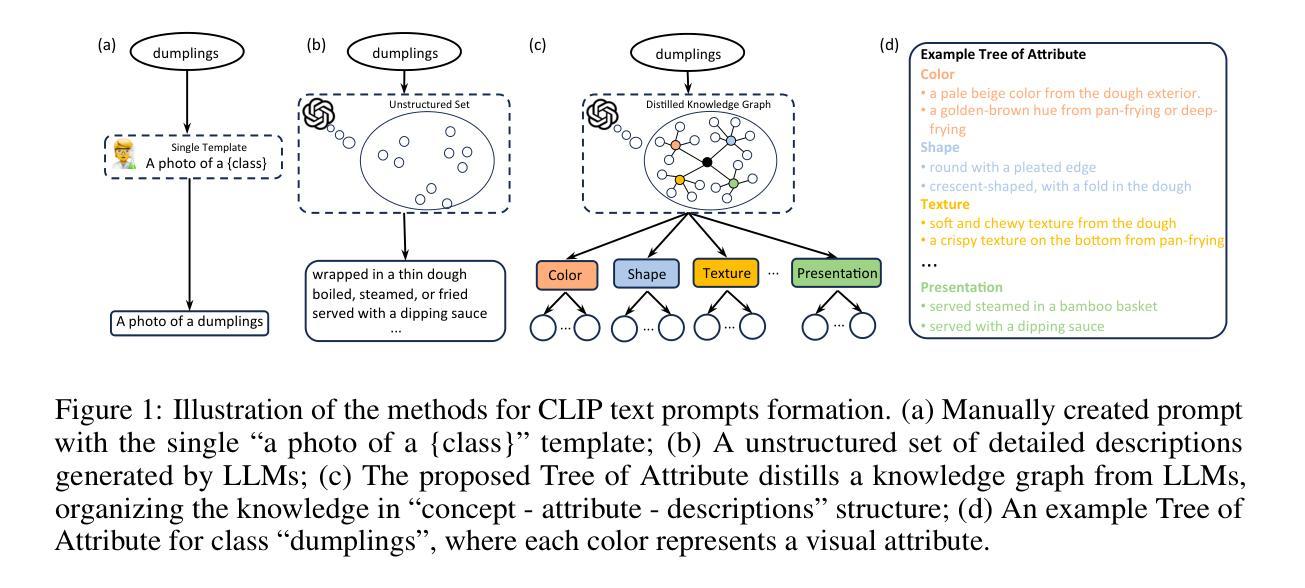
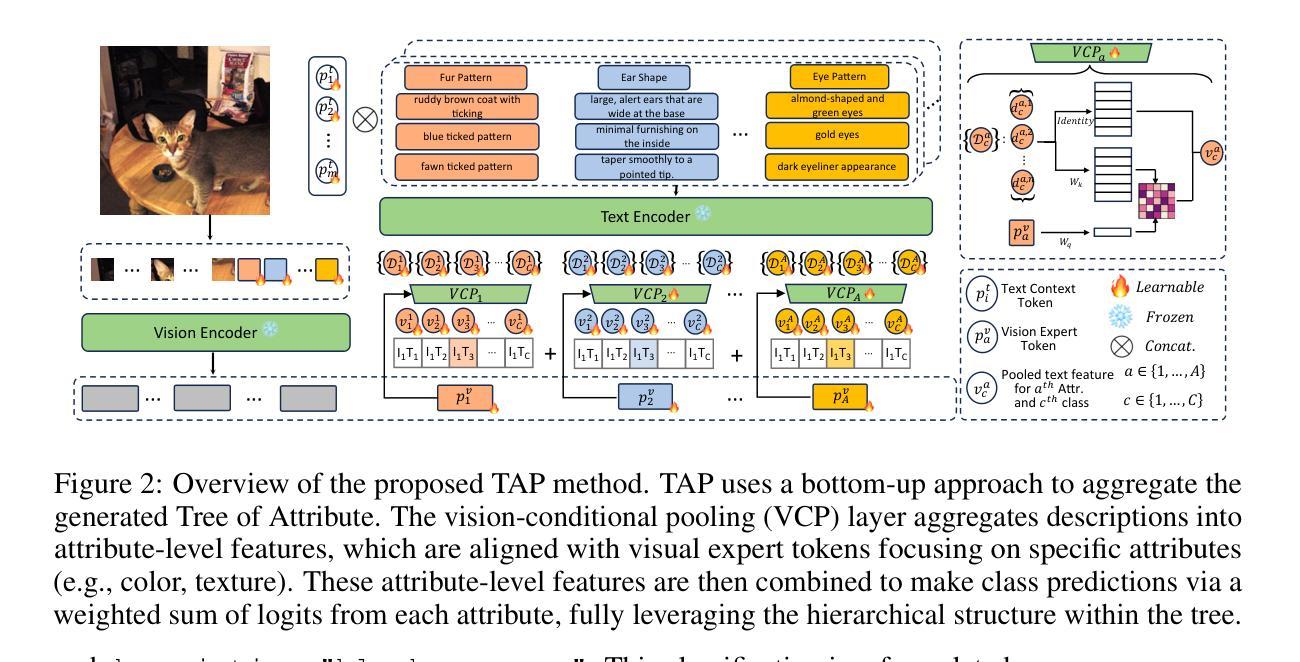
Prompt learning has proven effective in adapting vision language models for downstream tasks. However, existing methods usually append learnable prompt tokens solely with the category names to obtain textual features, which fails to fully leverage the rich context indicated in the category name. To address this issue, we propose the Tree of Attributes Prompt learning (TAP), which first instructs LLMs to generate a tree of attributes with a “concept - attribute - description” structure for each category, and then learn the hierarchy with vision and text prompt tokens. Unlike existing methods that merely augment category names with a set of unstructured descriptions, our approach essentially distills structured knowledge graphs associated with class names from LLMs. Furthermore, our approach introduces text and vision prompts designed to explicitly learn the corresponding visual attributes, effectively serving as domain experts. Additionally, the general and diverse descriptions generated based on the class names may be wrong or absent in the specific given images. To address this misalignment, we further introduce a vision-conditional pooling module to extract instance-specific text features. Extensive experimental results demonstrate that our approach outperforms state-of-the-art methods on the zero-shot base-to-novel generalization, cross-dataset transfer, as well as few-shot classification across 11 diverse datasets. Code is available at https://github.com/HHenryD/TAP.
提示学习在适应视觉语言模型以进行下游任务方面已被证明是有效的。然而,现有方法通常仅将可学习的提示令牌附加到类别名称上以获得文本特征,这未能充分利用类别名称中指示的丰富上下文。为了解决此问题,我们提出了属性树提示学习(TAP)方法。该方法首先指导大型语言模型为每个类别生成具有“概念-属性-描述”结构的属性树,然后学习与视觉和文本提示令牌对应的层次结构。与仅将一系列非结构化的描述附加到类别名称上的现有方法不同,我们的方法本质上是从大型语言模型中提炼出与类名相关的结构化知识图谱。此外,我们的方法引入了用于明确学习相应视觉属性的文本和视觉提示,有效地充当领域专家。基于类名生成的通用且多样的描述在具体给定的图像中可能出错或缺失。为了解决这种不匹配问题,我们进一步引入了一个视觉条件池模块来提取特定实例的文本特征。广泛的实验结果表明,我们的方法在零样本基础到新颖的泛化、跨数据集迁移以及在11个不同数据集的少量样本分类上均优于最新方法。代码可在https://github.com/HHenryD/TAP上找到。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
基于Prompt学习的方法能有效适应视觉语言模型进行下游任务。但现有方法主要通过添加类别名称的可学习提示符号来获得文本特征,这未能充分利用类别名称中的丰富上下文信息。为解决这一问题,我们提出了属性树提示学习(TAP)方法。TAP首先指导大型语言模型为每个类别生成一个属性树,形成“概念-属性-描述”的结构,然后通过视觉和文本提示符号学习层次结构。与仅通过添加类别名称的一系列非结构化描述不同,TAP本质上是从大型语言模型中提炼出与类别名称相关的结构化知识图谱。此外,TAP还引入了文本和视觉提示,旨在明确学习相应的视觉属性,有效充当领域专家。为了解决特定图像中基于类别名称生成的通用和多样化描述可能存在的错误或缺失问题,我们进一步引入了视觉条件池模块,以提取特定实例的文本特征。实验结果表明,TAP在零样本基础到新颖类别的推广、跨数据集迁移以及11个不同数据集的少样本分类任务上均优于现有最先进的方法。
Key Takeaways
- TAP方法通过生成属性树来丰富类别名称的上下文信息,提高Prompt学习的效果。
- TAP从大型语言模型中提炼与类别名称相关的结构化知识图谱。
- TAP引入文本和视觉提示来学习视觉属性,增强模型的表现力。
- TAP解决了特定图像描述可能存在的错误或缺失问题,通过视觉条件池模块提取特定实例的文本特征。
- TAP在多个数据集上的实验表现优于现有方法,尤其在零样本和少样本学习任务上。
- TAP方法具有良好的通用性,可适应不同的下游任务和数据集。
- TAP方法的代码已公开可用。
点此查看论文截图

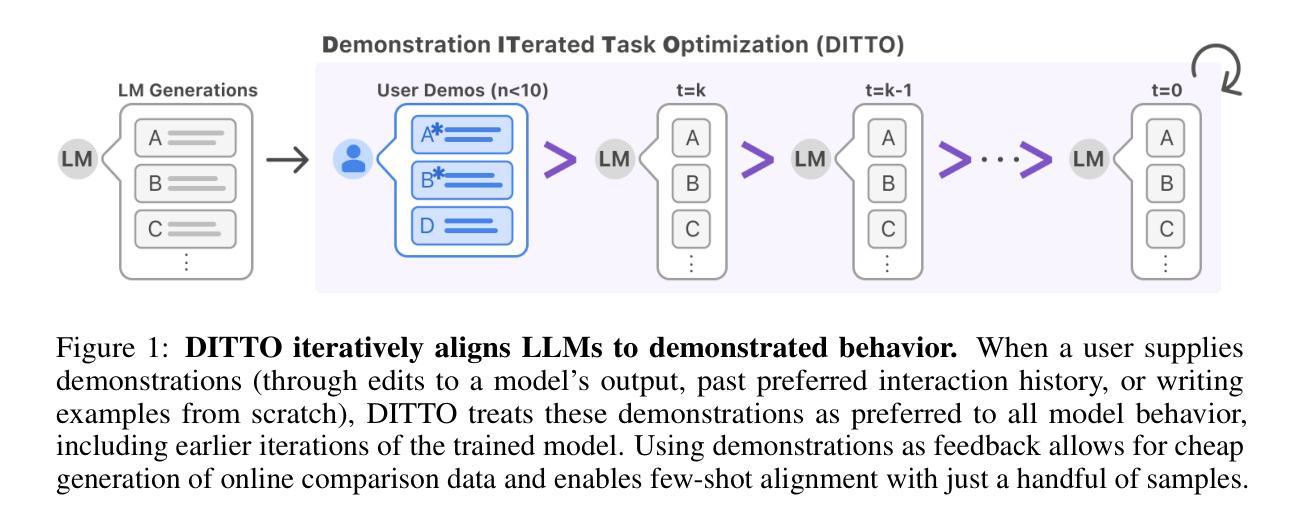
Aligning Language Models with Demonstrated Feedback
Authors:Omar Shaikh, Michelle S. Lam, Joey Hejna, Yijia Shao, Hyundong Cho, Michael S. Bernstein, Diyi Yang
Language models are aligned to emulate the collective voice of many, resulting in outputs that align with no one in particular. Steering LLMs away from generic output is possible through supervised finetuning or RLHF, but requires prohibitively large datasets for new ad-hoc tasks. We argue that it is instead possible to align an LLM to a specific setting by leveraging a very small number (< 10) of demonstrations as feedback. Our method, Demonstration ITerated Task Optimization (DITTO), directly aligns language model outputs to a user’s demonstrated behaviors. Derived using ideas from online imitation learning, DITTO cheaply generates online comparison data by treating users’ demonstrations as preferred over output from the LLM and its intermediate checkpoints. Concretely, DITTO operates by having an LLM generate examples that are presumed to be inferior to expert demonstrations. The method iteratively constructs pairwise preference relationships between these LLM-generated samples and expert demonstrations, potentially including comparisons between different training checkpoints. These constructed preference pairs are then used to train the model using a preference optimization algorithm (e.g. DPO). We evaluate DITTO’s ability to learn fine-grained style and task alignment across domains such as news articles, emails, and blog posts. Additionally, we conduct a user study soliciting a range of demonstrations from participants (N = 16). Across our benchmarks and user study, we find that win-rates for DITTO outperform few-shot prompting, supervised fine-tuning, and other self-play methods by an avg. of 19% points. By using demonstrations as feedback directly, DITTO offers a novel method for effective customization of LLMs.
语言模型旨在模拟许多人的集体声音,从而产生与特定人无关的输。通过监督微调或强化学习反馈(RLHF)可以避免语言大模型产生通用输出,但这需要针对新任务的特定数据集且数据量巨大。我们认为,通过利用极少量的演示(<10个)作为反馈,可以将语言大模型(LLM)与特定场景进行匹配。我们的方法——Demonstration ITerated Task Optimization(DITTO)直接使语言模型输出与用户演示行为保持一致。该方法基于在线模仿学习的思想,通过将用户的演示视为首选输出,与语言模型及其中间检查点的输出进行比较,从而低成本地生成在线比较数据。具体来说,DITTO的操作是让语言模型生成被认为是逊于专家演示的例子。该方法通过构建这些语言模型生成样本与专家演示之间的配对偏好关系来迭代操作,可能包括不同训练检查点之间的比较。这些构建的偏好配对随后被用于使用偏好优化算法(例如DPO)训练模型。我们评估了DITTO在不同领域(如新闻文章、电子邮件和博客文章)学习精细风格和任务对齐的能力。此外,我们进行了一项用户研究,从参与者中征集了一系列演示(N=16)。在我们的基准测试和用户研究中,我们发现DITTO的胜率比少样本提示、监督微调和其他自我对抗方法平均高出19个百分点。通过直接使用演示作为反馈,DITTO提供了一种有效定制语言大模型的新方法。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF ICLR 2025; 28 pages, 8 figures
Summary
该文介绍了通过利用用户示范来进行在线比较数据的低成本生成的新方法,即迭代任务优化(DITTO)。此方法基于用户示范进行迭代训练和优化,从而使语言模型的输出更符合用户需求。评价表明,在新闻文章、电子邮件和博客文章等不同领域,DITTO的性能优于其他方法。通过用户示范作为直接反馈,DITTO为有效定制大型语言模型提供了新的途径。
Key Takeaways
- 语言模型通过模仿集体声音产生通用输出,但可通过监督微调或强化学习人类反馈(RLHF)等方法进行引导以产生特定输出。
- 使用少量示范(< 10个)作为反馈来对齐语言模型到特定设置是可能的。
- DITTO方法利用在线模仿学习的思想,通过用户的示范来低成本地生成在线比较数据。
- DITTO通过将语言模型生成的例子视为不如专家示范优越,来迭代构建偏好关系。
- DITTO使用偏好优化算法(如DPO)来训练模型。
- 在新闻、电子邮件和博客等不同领域,DITTO在精细风格和任务对齐方面的学习能力得到了评价。
点此查看论文截图


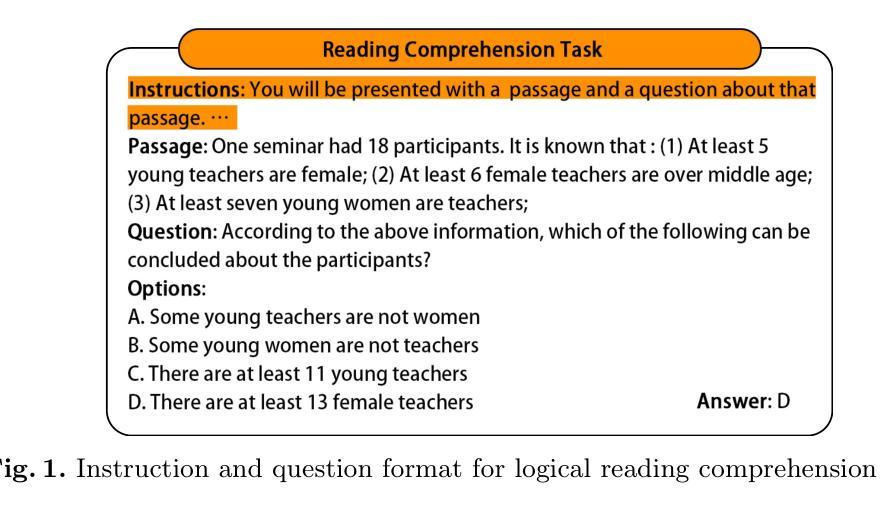
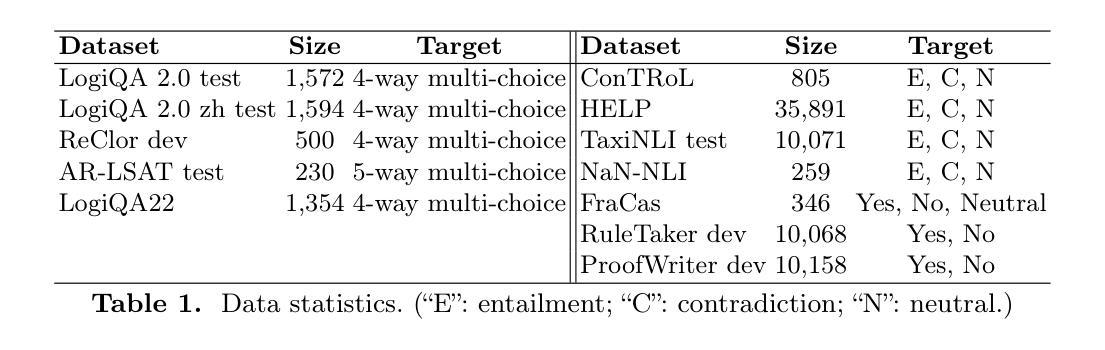
GLoRE: Evaluating Logical Reasoning of Large Language Models
Authors:Hanmeng liu, Zhiyang Teng, Ruoxi Ning, Yiran Ding, Xiulai Li, Xiaozhang Liu, Yue Zhang
Large language models (LLMs) have shown significant general language understanding abilities. However, there has been a scarcity of attempts to assess the logical reasoning capacities of these LLMs, an essential facet of natural language understanding. To encourage further investigation in this area, we introduce GLoRE, a General Logical Reasoning Evaluation platform that not only consolidates diverse datasets but also standardizes them into a unified format suitable for evaluating large language models across zero-shot and few-shot scenarios. Our experimental results show that compared to the performance of humans and supervised fine-tuning models, the logical reasoning capabilities of large reasoning models, such as OpenAI’s o1 mini, DeepSeek R1 and QwQ-32B, have seen remarkable improvements, with QwQ-32B achieving the highest benchmark performance to date. GLoRE is designed as a living project that continuously integrates new datasets and models, facilitating robust and comparative assessments of model performance in both commercial and Huggingface communities.
大规模语言模型(LLM)已经展现出显著的一般语言理解能力。然而,目前缺乏对这些LLM的逻辑推理能力进行评估的尝试,这是自然语言理解的重要组成部分。为了鼓励在这一领域的进一步研究,我们引入了GLoRE,一个通用逻辑推理评估平台,它不仅整合了多样化的数据集,还将它们标准化为一个统一的格式,适用于在零样本和少样本场景下评估大型语言模型。我们的实验结果表明,与人类和经过监督微调模型的性能相比,大型推理模型(如OpenAI的o1 mini、DeepSeek R1和QwQ-32B)的逻辑推理能力已经取得了显著的提升,其中QwQ-32B达到了迄今为止的最高基准性能。GLoRE被设计为一个持续集成的项目,不断融入新的数据集和模型,便于在商业和Huggingface社区中对模型性能进行稳健和比较性的评估。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
大型语言模型展现出强大的自然语言理解力,但在逻辑理解方面的评估仍显不足。为此,我们推出通用逻辑推理评估平台GLoRE,旨在评估大型语言模型在不同场景下的零样本和少样本能力。实验结果显示,相较于人类和经过微调训练的模型,大型推理模型的逻辑推理能力已有显著进步,其中QwQ-32B取得了迄今为止的最高性能。GLoRE将持续集成新数据集和模型,为商业和Huggingface社区提供稳健的模型性能比较评估平台。
Key Takeaways
- 大型语言模型展现出强大的自然语言理解能力,但逻辑理解方面的评估仍然不足。
- GLoRE平台旨在评估大型语言模型的逻辑推理能力,支持零样本和少样本场景的评估。
- 实验结果显示,大型推理模型的逻辑推理能力已经取得显著进步。
- QwQ-32B在逻辑推理方面取得了迄今为止的最高性能。
- GLoRE平台是一个持续发展的项目,能够集成新数据集和模型。
- GLoRE平台为商业和Huggingface社区提供了模型性能比较评估的稳健平台。
点此查看论文截图

A Holistic Evaluation of Piano Sound Quality
Authors:Monan Zhou, Shangda Wu, Shaohua Ji, Zijin Li, Wei Li
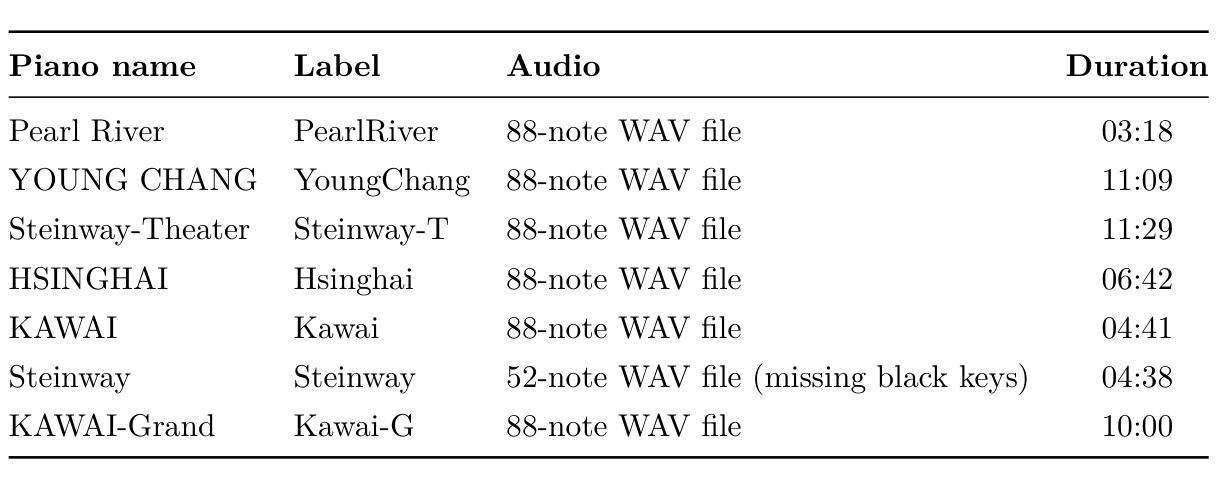
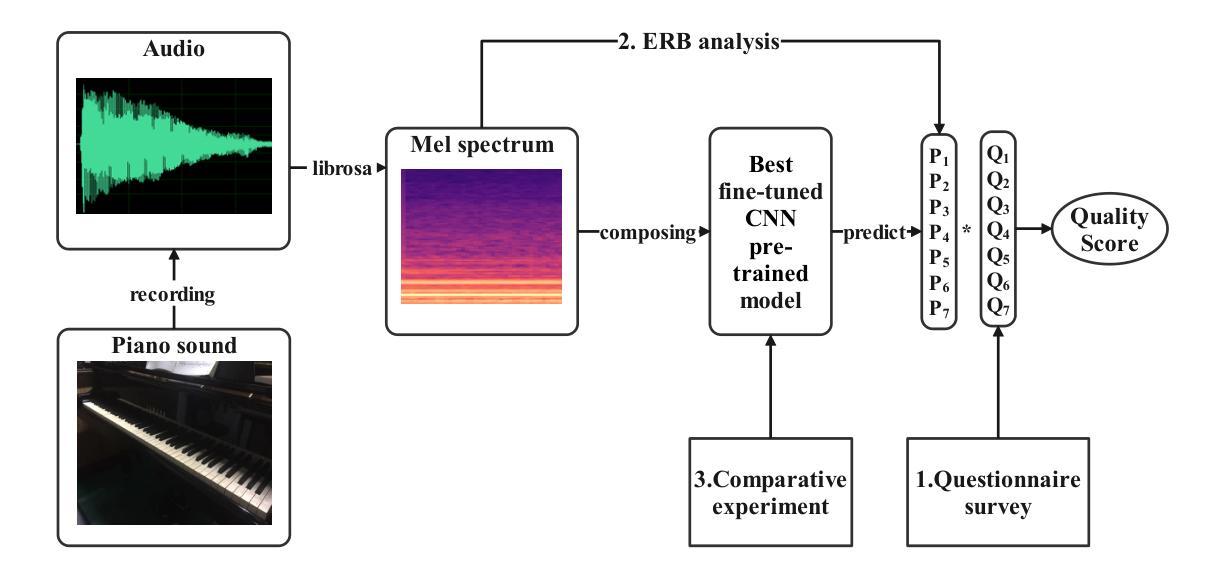
This paper aims to develop a holistic evaluation method for piano sound quality to assist in purchasing decisions. Unlike previous studies that focused on the effect of piano performance techniques on sound quality, this study evaluates the inherent sound quality of different pianos. To derive quality evaluation systems, the study uses subjective questionnaires based on a piano sound quality dataset. The method selects the optimal piano classification models by comparing the fine-tuning results of different pre-training models of Convolutional Neural Networks (CNN). To improve the interpretability of the models, the study applies Equivalent Rectangular Bandwidth (ERB) analysis. The results reveal that musically trained individuals are better able to distinguish between the sound quality differences of different pianos. The best fine-tuned CNN pre-trained backbone achieves a high accuracy of 98.3% as the piano classifier. However, the dataset is limited, and the audio is sliced to increase its quantity, resulting in a lack of diversity and balance, so we use focal loss to reduce the impact of data imbalance. To optimize the method, the dataset will be expanded, or few-shot learning techniques will be employed in future research.
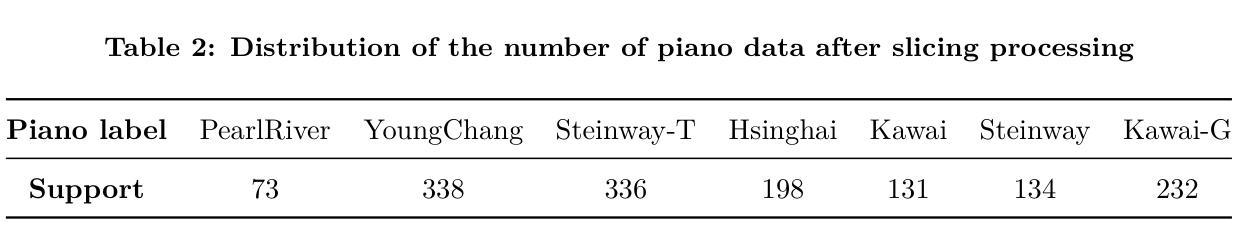
本文旨在开发一种全面的钢琴音质评估方法,以辅助购买决策。不同于以往专注于钢琴演奏技巧对音质影响的研究,本研究旨在评估不同钢琴的固有音质。为了得出质量评估系统,本研究基于钢琴音质数据集,使用主观问卷的方法。该方法通过比较不同预训练模型的微调结果,选择最佳的钢琴分类模型。为了提高模型的解释性,研究应用了等效矩形带宽(ERB)分析。结果表明,受过音乐训练的人更能区分不同钢琴的音质差异。最佳的微调CNN预训练主干作为钢琴分类器,实现了高达98.3%的准确率。然而,数据集有限,音频被切片以增加其数量,导致缺乏多样性和平衡性,因此我们使用焦点损失来减少数据不平衡的影响。为了优化该方法,将扩大数据集或在未来的研究中采用小样本学习技术。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF 15 pages, 9 figures
Summary
本文旨在开发一种全面的钢琴音质评估方法,以辅助购买决策。研究不同于以往关注钢琴演奏技巧对音质影响的研究,而是评估不同钢琴的固有音质。研究使用基于钢琴音质数据集的主观问卷来推导质量评估系统,通过比较不同预训练模型的微调结果来选择最佳的钢琴分类模型。为提高模型的可解释性,研究应用了等效矩形带宽(ERB)分析。结果显示,受过音乐训练的人更能区分不同钢琴的音质差异。最佳微调CNN预训练主干作为钢琴分类器,准确率高达98.3%。但数据集有限,音频被切片以增加数量,导致缺乏多样性和平衡性,因此使用焦点损失来减少数据不平衡的影响。未来研究将扩大数据集或采用少样本学习技术以优化方法。
Key Takeaways
- 研究目的是开发一种全面的钢琴音质评估方法,帮助购买决策。
- 与其他研究不同,该研究侧重于评估不同钢琴的固有音质。
- 研究通过主观问卷和基于数据集的质量评估系统来推导评估方法。
- 选择最佳钢琴分类模型是通过比较不同预训练模型的微调结果。
- 应用等效矩形带宽(ERB)分析以提高模型的可解释性。
- 受过音乐训练的人更能区分不同钢琴的音质差异。
点此查看论文截图