⚠️ 以下所有内容总结都来自于 大语言模型的能力,如有错误,仅供参考,谨慎使用
🔴 请注意:千万不要用于严肃的学术场景,只能用于论文阅读前的初筛!
💗 如果您觉得我们的项目对您有帮助 ChatPaperFree ,还请您给我们一些鼓励!⭐️ HuggingFace免费体验
2025-04-23 更新
StyleMe3D: Stylization with Disentangled Priors by Multiple Encoders on 3D Gaussians
Authors:Cailin Zhuang, Yaoqi Hu, Xuanyang Zhang, Wei Cheng, Jiacheng Bao, Shengqi Liu, Yiying Yang, Xianfang Zeng, Gang Yu, Ming Li
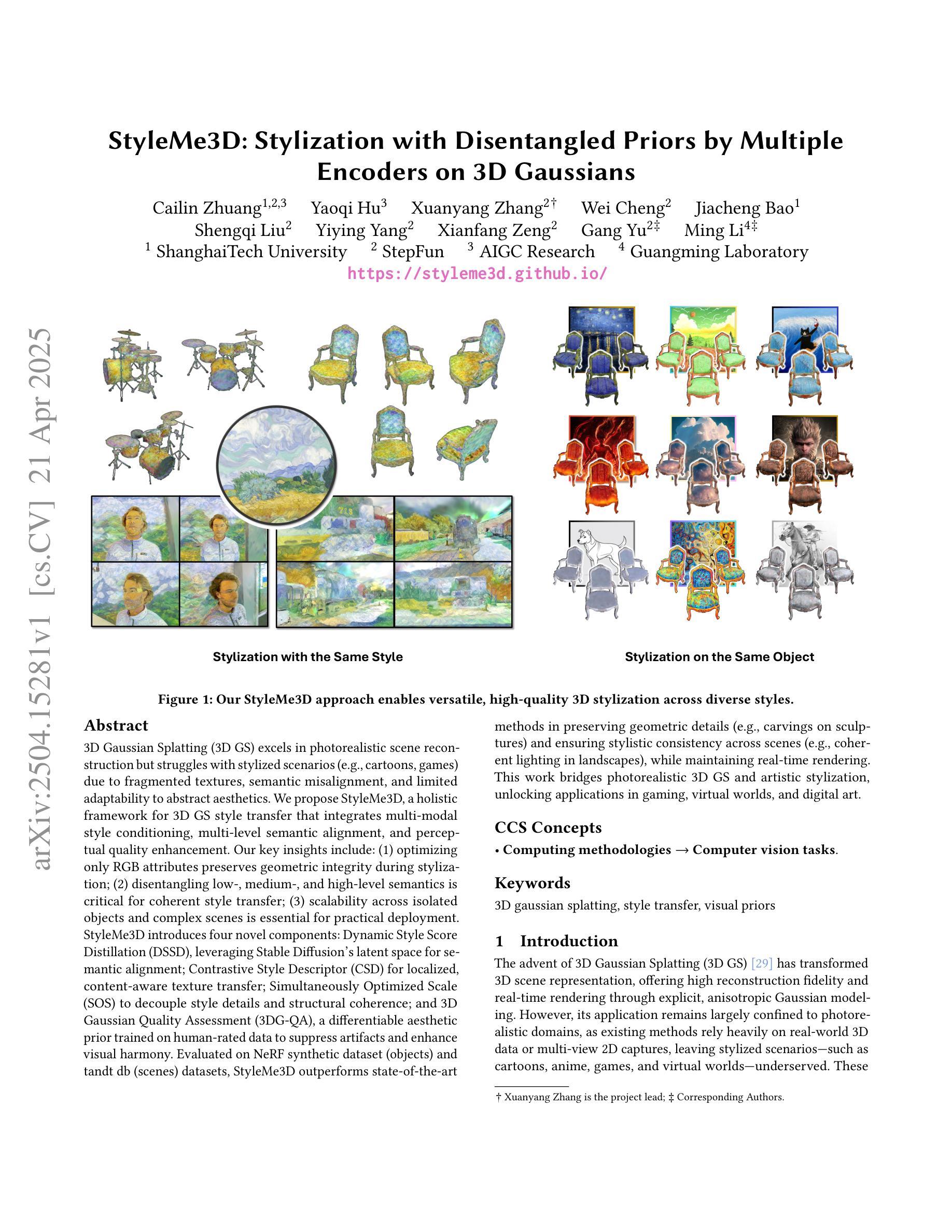
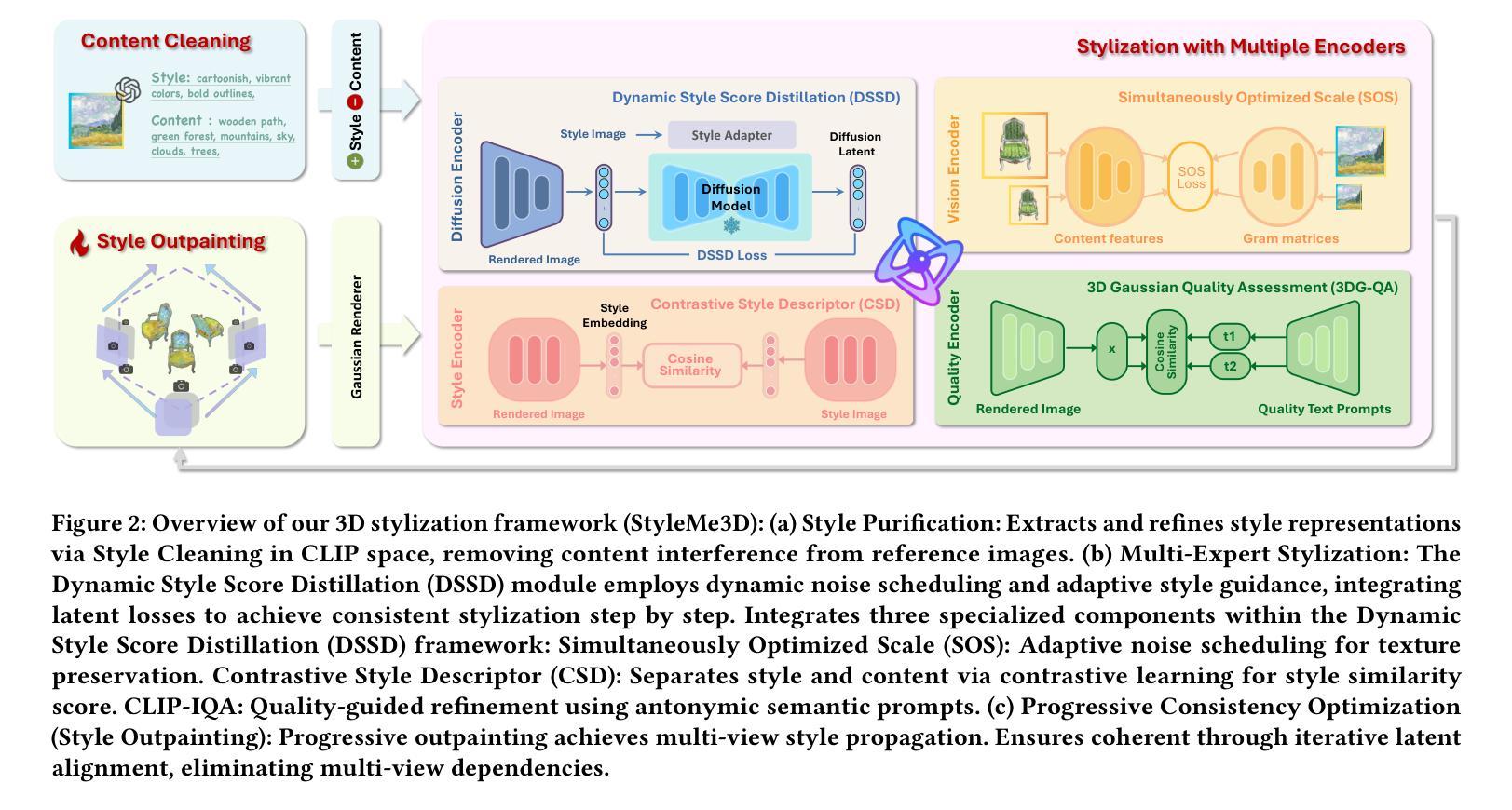
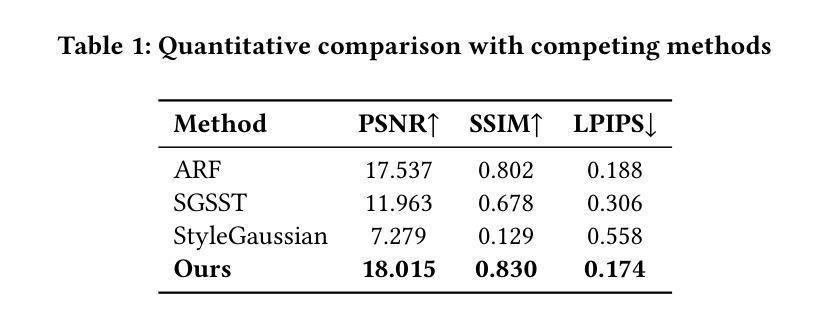
3D Gaussian Splatting (3DGS) excels in photorealistic scene reconstruction but struggles with stylized scenarios (e.g., cartoons, games) due to fragmented textures, semantic misalignment, and limited adaptability to abstract aesthetics. We propose StyleMe3D, a holistic framework for 3D GS style transfer that integrates multi-modal style conditioning, multi-level semantic alignment, and perceptual quality enhancement. Our key insights include: (1) optimizing only RGB attributes preserves geometric integrity during stylization; (2) disentangling low-, medium-, and high-level semantics is critical for coherent style transfer; (3) scalability across isolated objects and complex scenes is essential for practical deployment. StyleMe3D introduces four novel components: Dynamic Style Score Distillation (DSSD), leveraging Stable Diffusion’s latent space for semantic alignment; Contrastive Style Descriptor (CSD) for localized, content-aware texture transfer; Simultaneously Optimized Scale (SOS) to decouple style details and structural coherence; and 3D Gaussian Quality Assessment (3DG-QA), a differentiable aesthetic prior trained on human-rated data to suppress artifacts and enhance visual harmony. Evaluated on NeRF synthetic dataset (objects) and tandt db (scenes) datasets, StyleMe3D outperforms state-of-the-art methods in preserving geometric details (e.g., carvings on sculptures) and ensuring stylistic consistency across scenes (e.g., coherent lighting in landscapes), while maintaining real-time rendering. This work bridges photorealistic 3D GS and artistic stylization, unlocking applications in gaming, virtual worlds, and digital art.
3D高斯展平(3DGS)在摄影级真实场景重建方面表现出色,但在风格化场景(例如卡通、游戏)方面却遇到挑战,原因在于纹理碎片化、语义不匹配以及对抽象美学的适应有限。我们提出StyleMe3D,这是一个用于3D GS风格转换的整体框架,它集成了多模式风格条件、多级语义匹配和感知质量增强。我们的关键见解包括:(1)仅优化RGB属性可以在风格化过程中保持几何完整性;(2)对低、中、高级语义进行分离对于连贯的风格转换至关重要;(3)在孤立对象和复杂场景之间的可扩展性对于实际部署至关重要。StyleMe3D引入了四个新颖组件:动态风格分数蒸馏(DSSD),利用Stable Diffusion的潜在空间进行语义匹配;对比风格描述符(CSD)用于局部、内容感知的纹理传输;同时优化比例(SOS)以解开风格细节和结构连贯性;以及3D高斯质量评估(3DG-QA),这是一个基于人类评分数据训练的可区分审美先验,用于抑制伪影并增强视觉和谐。在NeRF合成数据集(对象)和tandt db(场景)数据集上进行的评估表明,StyleMe3D在保留几何细节(例如雕塑上的雕刻)和确保场景之间的风格一致性(例如风景中的连贯照明)方面优于最先进的方法,同时保持实时渲染。这项工作将逼真的3D GS和艺术风格化联系起来,为游戏、虚拟世界和数字艺术等领域解锁了应用。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF 16 pages; Project page: https://styleme3d.github.io/
Summary
StyleMe3D针对三维高斯采样风格转换(3DGS)在风格化场景(如卡通、游戏)重建中出现的纹理碎片化、语义不匹配和抽象美学适应有限等问题,提出了一种全新的框架。该框架包含多模态风格调节、多层次语义匹配和感知质量提升等技术。其核心在于优化RGB属性以在风格化过程中保持几何完整性,同时解耦不同级别的语义信息以实现连贯的风格转换。此外,该框架还具有跨孤立物体和复杂场景的实用性部署优势。
Key Takeaways
- StyleMe3D解决了3DGS在风格化场景中的纹理碎片化、语义不匹配和对抽象美学的有限适应问题。
- 该框架通过多模态风格调节、多层次语义匹配和感知质量提升技术进行优化。
- StyleMe3D的核心在于优化RGB属性以在风格转换中保持几何完整性。
- 解耦不同级别的语义信息对于实现连贯的风格转换至关重要。
- StyleMe3D具有跨孤立物体和复杂场景的实用性部署优势。
- 该框架在NeRF合成数据集(物体)和tandt db(场景)数据集上的表现优于现有技术,能够更好地保持几何细节和风格一致性。
点此查看论文截图

Learning and Generating Diverse Residential Load Patterns Using GAN with Weakly-Supervised Training and Weight Selection
Authors:Xinyu Liang, Hao Wang
The scarcity of high-quality residential load data can pose obstacles for decarbonizing the residential sector as well as effective grid planning and operation. The above challenges have motivated research into generating synthetic load data, but existing methods faced limitations in terms of scalability, diversity, and similarity. This paper proposes a Generative Adversarial Network-based Synthetic Residential Load Pattern (RLP-GAN) generation model, a novel weakly-supervised GAN framework, leveraging an over-complete autoencoder to capture dependencies within complex and diverse load patterns and learn household-level data distribution at scale. We incorporate a model weight selection method to address the mode collapse problem and generate load patterns with high diversity. We develop a holistic evaluation method to validate the effectiveness of RLP-GAN using real-world data of 417 households. The results demonstrate that RLP-GAN outperforms state-of-the-art models in capturing temporal dependencies and generating load patterns with higher similarity to real data. Furthermore, we have publicly released the RLP-GAN generated synthetic dataset, which comprises one million synthetic residential load pattern profiles.
高质量住宅用电负荷数据的稀缺性对住宅领域的脱碳以及电网的有效规划和运行都构成了障碍。上述挑战促使了合成负荷数据生成的研究,但现有方法在可扩展性、多样性和相似性方面存在局限性。本文提出了一种基于生成对抗网络(GAN)的合成住宅负荷模式生成模型(RLP-GAN),这是一个新型弱监督GAN框架,利用过完备自编码器捕捉复杂多变负荷模式之间的依赖关系,并大规模学习家庭层面的数据分布。为解决模式崩溃问题,我们采用了模型权重选择方法,生成了高多样性的负荷模式。我们使用一种全面的评估方法,利用来自417户家庭的现实世界数据验证了RLP-GAN的有效性。结果表明,RLP-GAN在捕捉时间依赖性方面优于当前先进技术模型,并生成与真实数据高度相似的负荷模式。此外,我们已经公开发布了由RLP-GAN生成的合成数据集,包含一百万个合成住宅负荷模式分布图。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF 12 pages
Summary
该研究针对住宅用电负荷数据缺乏高质量的问题,提出了一种基于生成对抗网络(GAN)的合成住宅负荷模式(RLP-GAN)生成模型。该模型采用弱监督学习方式,利用过完备自编码器捕捉复杂多样的负荷模式内的依赖关系,大规模学习家庭层级的数据分布。研究还提出了模型权重选择方法以解决模式崩溃问题,并开发了综合评估方法以验证RLP-GAN的有效性。实验结果显示,RLP-GAN在捕捉时间依赖性以及生成与真实数据更相似的负荷模式方面优于其他最新模型。此外,研究公开了由RLP-GAN生成的合成数据集,包含一百万份合成住宅负荷模式。
Key Takeaways
- 高质量住宅负荷数据的稀缺性对住宅领域的脱碳以及电网规划和运营有效性构成挑战。
- 现存的数据生成方法存在可扩展性、多样性和相似性的局限。
- RLP-GAN模型基于生成对抗网络,采用弱监督学习方式捕捉家庭层级的数据分布和复杂负荷模式的依赖关系。
- 过完备自编码器用于大规模学习负荷模式的数据分布。
- 模型重量选择方法解决模式崩溃问题,生成具有多样性的负荷模式。
- 使用包含417户家庭的现实数据验证了RLP-GAN的有效性。
点此查看论文截图

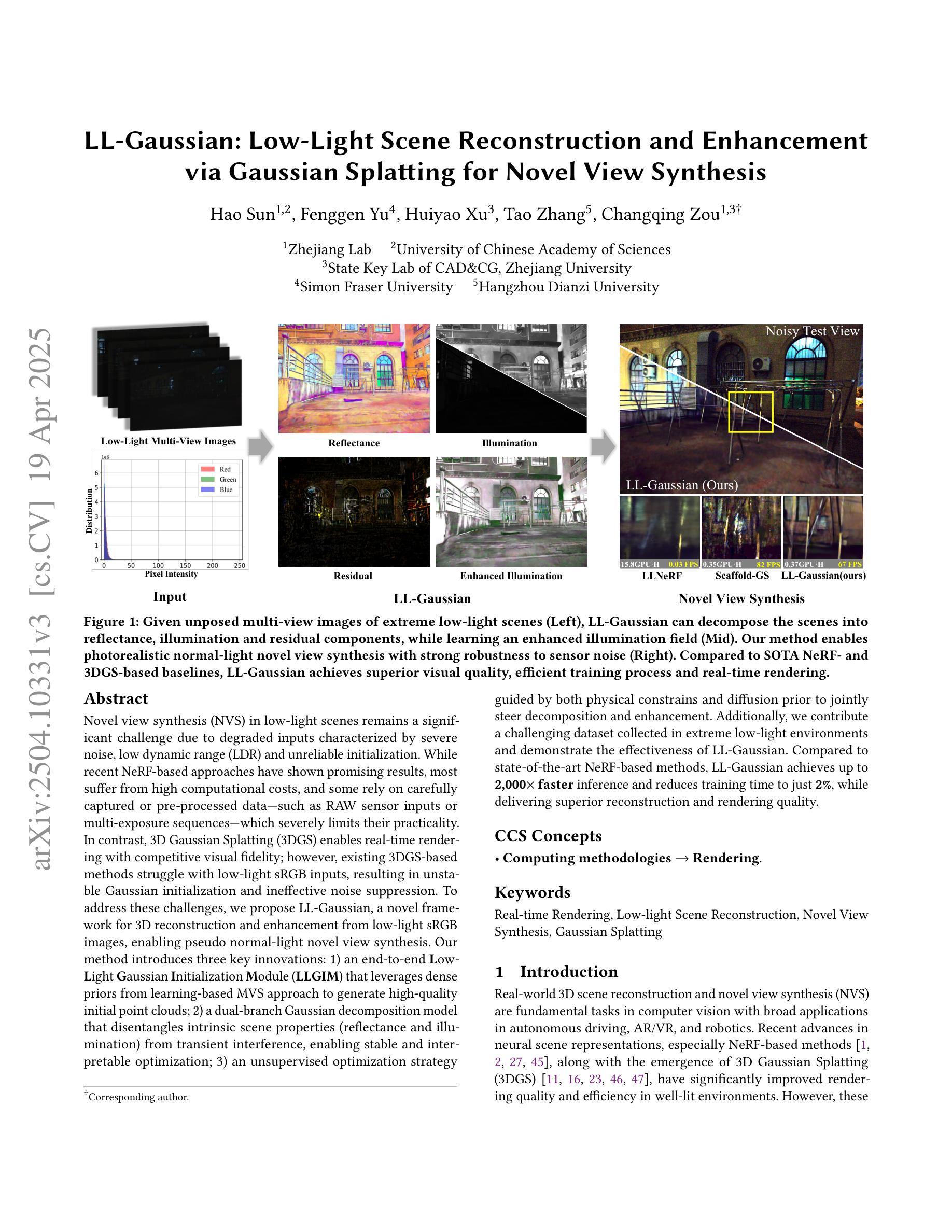
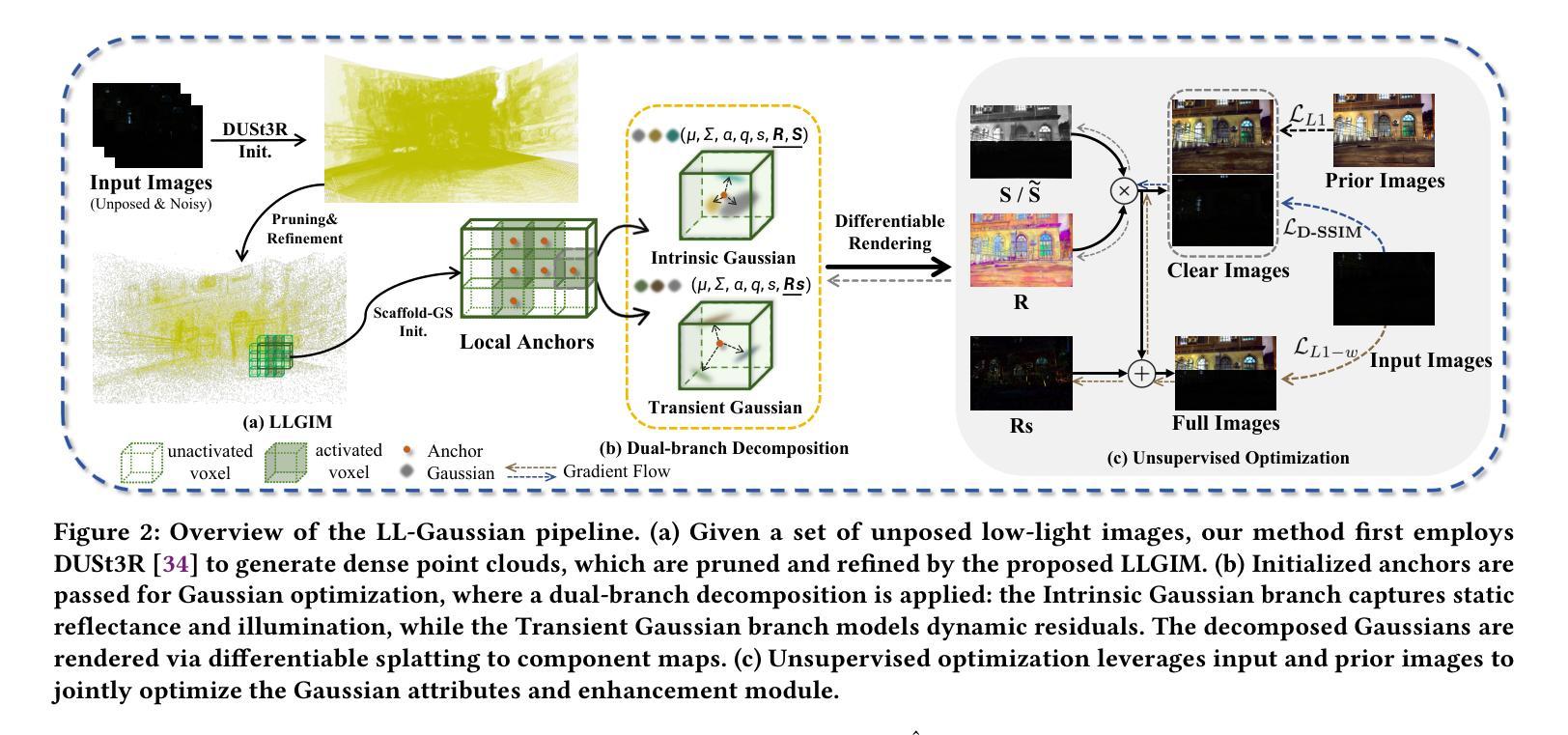
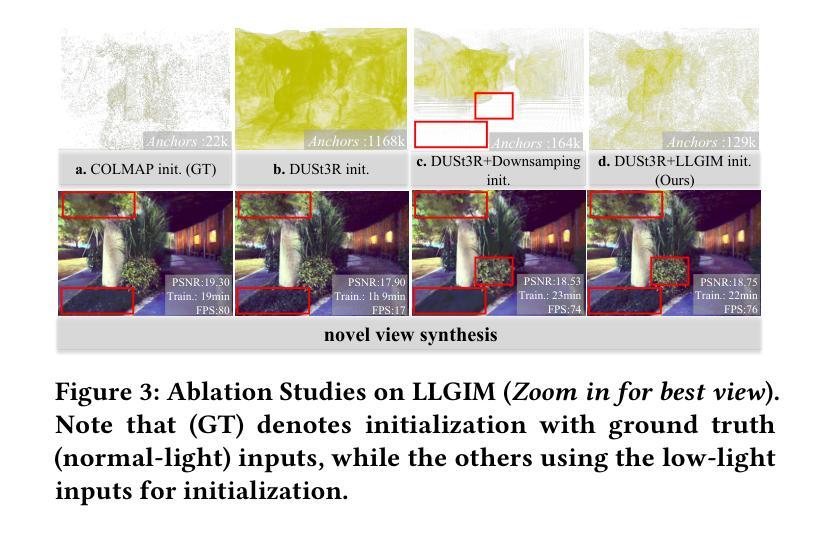
LL-Gaussian: Low-Light Scene Reconstruction and Enhancement via Gaussian Splatting for Novel View Synthesis
Authors:Hao Sun, Fenggen Yu, Huiyao Xu, Tao Zhang, Changqing Zou
Novel view synthesis (NVS) in low-light scenes remains a significant challenge due to degraded inputs characterized by severe noise, low dynamic range (LDR) and unreliable initialization. While recent NeRF-based approaches have shown promising results, most suffer from high computational costs, and some rely on carefully captured or pre-processed data–such as RAW sensor inputs or multi-exposure sequences–which severely limits their practicality. In contrast, 3D Gaussian Splatting (3DGS) enables real-time rendering with competitive visual fidelity; however, existing 3DGS-based methods struggle with low-light sRGB inputs, resulting in unstable Gaussian initialization and ineffective noise suppression. To address these challenges, we propose LL-Gaussian, a novel framework for 3D reconstruction and enhancement from low-light sRGB images, enabling pseudo normal-light novel view synthesis. Our method introduces three key innovations: 1) an end-to-end Low-Light Gaussian Initialization Module (LLGIM) that leverages dense priors from learning-based MVS approach to generate high-quality initial point clouds; 2) a dual-branch Gaussian decomposition model that disentangles intrinsic scene properties (reflectance and illumination) from transient interference, enabling stable and interpretable optimization; 3) an unsupervised optimization strategy guided by both physical constrains and diffusion prior to jointly steer decomposition and enhancement. Additionally, we contribute a challenging dataset collected in extreme low-light environments and demonstrate the effectiveness of LL-Gaussian. Compared to state-of-the-art NeRF-based methods, LL-Gaussian achieves up to 2,000 times faster inference and reduces training time to just 2%, while delivering superior reconstruction and rendering quality.
在低光照场景中的新型视图合成(NVS)仍然是一个重大挑战,因为输入退化,表现为严重的噪声、低动态范围(LDR)和不可靠的初始化。尽管最近的基于NeRF的方法已经显示出有希望的结果,但大多数方法的计算成本很高,而且有些方法依赖于精心捕捉或预处理的数据,如RAW传感器输入或多曝光序列,这严重限制了其实用性。相比之下,3D高斯拼贴(3DGS)能够实现具有竞争力的视觉保真度的实时渲染;然而,现有的基于3DGS的方法在处理低光sRGB输入时遇到困难,导致高斯初始化不稳定且噪声抑制无效。为了解决这些挑战,我们提出了LL-Gaussian,这是一个从低光sRGB图像进行3D重建和增强的新型框架,能够实现伪正常光新型视图合成。我们的方法引入了三个关键创新点:1)端到端的低光高斯初始化模块(LLGIM),它利用基于学习的MVS方法的密集先验来生成高质量初始点云;2)双分支高斯分解模型,将场景的固有属性(反射率和照明)从瞬时干扰中分离出来,实现稳定和可解释的优化;3)一种由物理约束和扩散先验引导的无监督优化策略,共同引导分解和增强。此外,我们贡献了一个在极端低光环境中收集的有挑战性数据集,并展示了LL-Gaussian的有效性。与最先进的基于NeRF的方法相比,LL-Gaussian实现了高达2,000倍更快的推理速度,并将训练时间缩短至仅2%,同时提供卓越的重建和渲染质量。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF Project page: https://sunhao242.github.io/LL-Gaussian_web.github.io/
摘要
针对低光场景中的新型视图合成(NVS)挑战,现有方法存在计算成本高、依赖特定数据输入等问题。本文提出LL-Gaussian框架,实现低光sRGB图像下的3D重建与增强,实现伪正常光下的新型视图合成。该框架引入三项关键创新:1)低光高斯初始化模块(LLGIM),利用基于学习的MVS方法生成高质量初始点云;2)双分支高斯分解模型,将场景固有属性(反射率和照明)与瞬时干扰分离,实现稳定且可解释的优化;3)由物理约束和扩散先验引导的无监督优化策略,联合引导分解与增强。此外,我们还贡献了在极端低光环境下收集的具有挑战性的数据集,并展示了LL-Gaussian的有效性。相较于先进的NeRF方法,LL-Gaussian推理速度最快可达2000倍,训练时间仅减少至2%,同时提供卓越的重建和渲染质量。
关键见解
- LL-Gaussian框架解决了低光场景中新型视图合成的挑战。
- 引入低光高斯初始化模块(LLGIM),利用学习基础上的MVS方法的密集先验生成高质量初始点云。
- 采用双分支高斯分解模型,成功分离场景固有属性(如反射率和照明)与瞬时干扰。
- 无监督优化策略结合物理约束和扩散先验,共同推动分解和增强过程。
- 贡献了在极端低光环境下收集的具有挑战性的数据集。
- LL-Gaussian相较于其他NeRF方法,推理速度显著提高,同时保持优秀的重建和渲染质量。
点此查看论文截图

S-EO: A Large-Scale Dataset for Geometry-Aware Shadow Detection in Remote Sensing Applications
Authors:Elías Masquil, Roger Marí, Thibaud Ehret, Enric Meinhardt-Llopis, Pablo Musé, Gabriele Facciolo
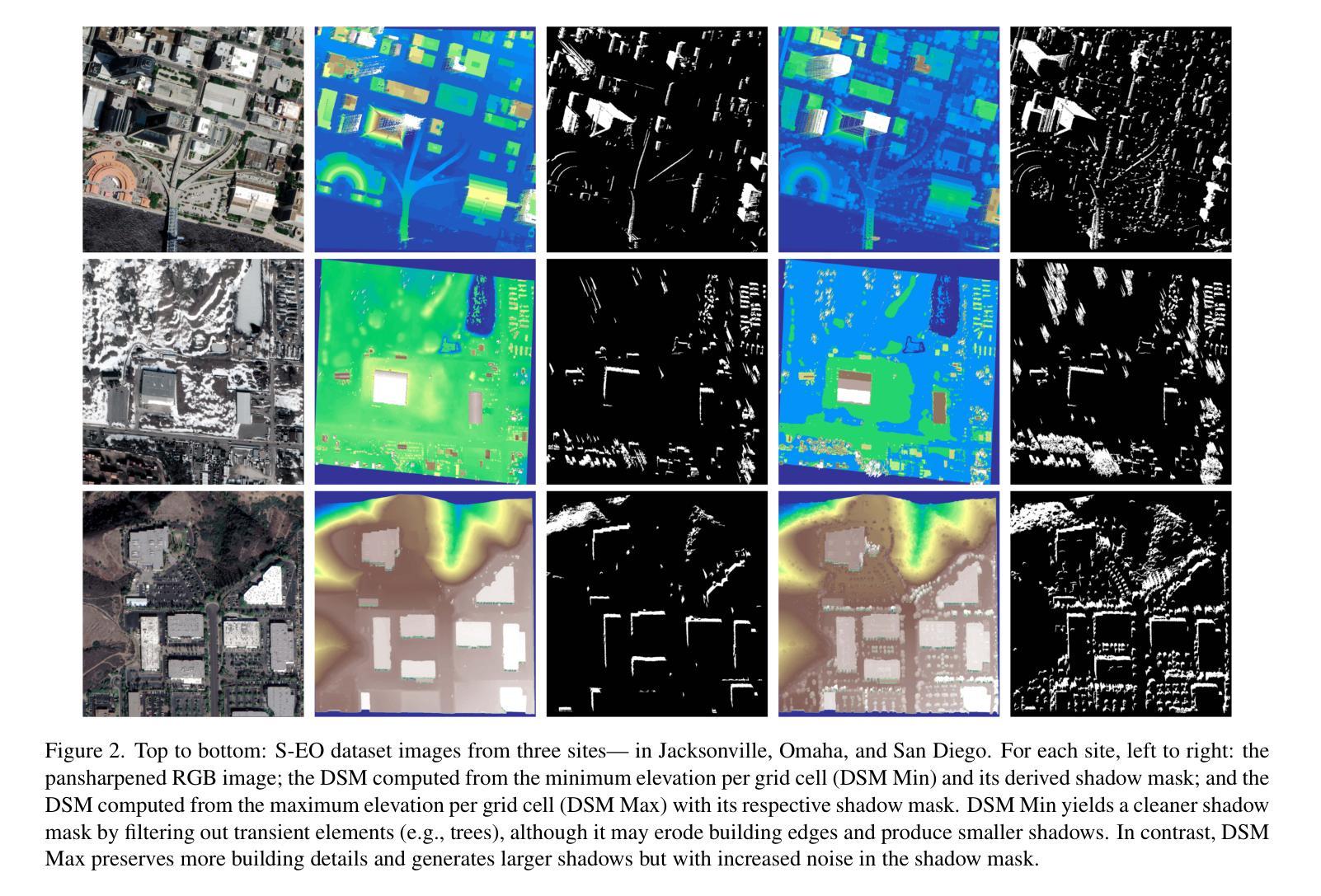
We introduce the S-EO dataset: a large-scale, high-resolution dataset, designed to advance geometry-aware shadow detection. Collected from diverse public-domain sources, including challenge datasets and government providers such as USGS, our dataset comprises 702 georeferenced tiles across the USA, each covering 500x500 m. Each tile includes multi-date, multi-angle WorldView-3 pansharpened RGB images, panchromatic images, and a ground-truth DSM of the area obtained from LiDAR scans. For each image, we provide a shadow mask derived from geometry and sun position, a vegetation mask based on the NDVI index, and a bundle-adjusted RPC model. With approximately 20,000 images, the S-EO dataset establishes a new public resource for shadow detection in remote sensing imagery and its applications to 3D reconstruction. To demonstrate the dataset’s impact, we train and evaluate a shadow detector, showcasing its ability to generalize, even to aerial images. Finally, we extend EO-NeRF - a state-of-the-art NeRF approach for satellite imagery - to leverage our shadow predictions for improved 3D reconstructions.
我们介绍了S-EO数据集:这是一个大规模、高分辨率的数据集,旨在推动几何感知阴影检测的发展。我们的数据集来自各种公共领域来源,包括挑战数据集和政府供应商,如美国地质调查局,包含美国702个地理参考瓷砖,每个瓷砖覆盖500x500平方米。每个瓷砖包括多日期、多角度的WorldView-3锐化RGB图像、单色图像以及通过激光雷达扫描获得的该地区地面真实数字表面模型(DSM)。对于每张图像,我们提供基于几何和太阳位置的阴影掩膜、基于归一化差异植被指数(NDVI)的植被掩膜和捆绑调整的RPC模型。S-EO数据集包含大约2万张图像,为遥感影像中的阴影检测及其应用于3D重建提供了全新的公共资源。为了展示数据集的影响,我们训练并评估了阴影检测器,展示了其即使在航空图像上的泛化能力。最后,我们扩展了EO-NeRF(一种用于卫星图像的先进NeRF方法),以利用我们的阴影预测进行更好的3D重建。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF Accepted at Earthvision 2025 (CVPR Workshop)
Summary
本文介绍了S-EO数据集,这是一个大规模、高分辨率的数据集,旨在推动几何感知阴影检测的发展。数据集包含来自不同公共来源的702张地理定位的美国瓷砖图像,涵盖了RGB图像、单色图像和从激光雷达扫描获得的地面真实数字表面模型。对于每张图像,都提供了基于几何和太阳位置的阴影掩膜、基于归一化差异植被指数的植被掩膜和束调整的RPC模型。S-EO数据集为遥感图像中的阴影检测及其应用于三维重建提供了新资源。
Key Takeaways
- S-EO数据集是一个大规模、高分辨率的数据集,旨在促进几何感知阴影检测的发展。
- 数据集包含来自多个公共来源的图像,涵盖RGB、单色图像以及从激光雷达扫描获得的真实数字表面模型。
- 对于每张图像,提供了基于几何和太阳位置的阴影掩膜、植被掩膜和束调整的RPC模型。
- S-EO数据集为遥感图像中的阴影检测提供了新的资源。
- 数据集的应用包括阴影检测在三维重建中的应用。
- 文章通过训练和评估阴影检测器来展示数据集的效能,该检测器具有良好的泛化能力。
点此查看论文截图



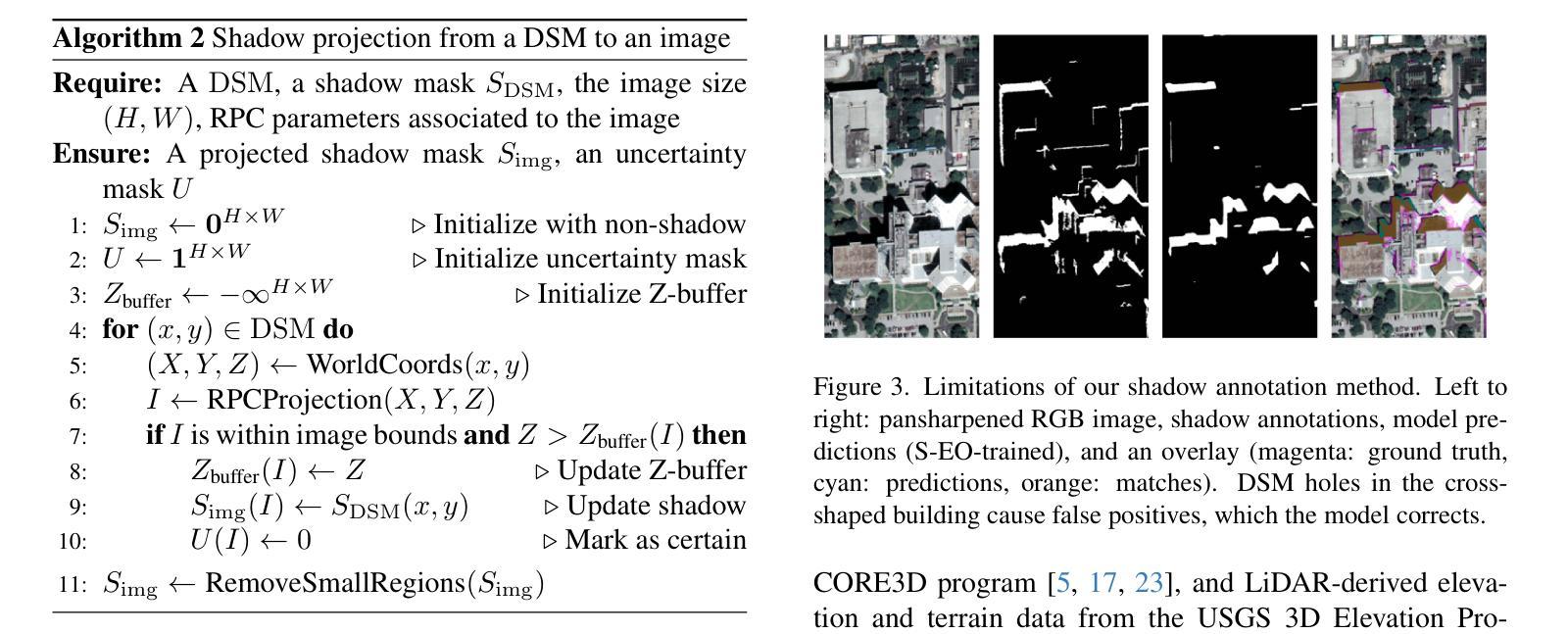

Comparative clinical evaluation of “memory-efficient” synthetic 3d generative adversarial networks (gan) head-to-head to state of art: results on computed tomography of the chest
Authors:Mahshid Shiri, Chandra Bortolotto, Alessandro Bruno, Alessio Consonni, Daniela Maria Grasso, Leonardo Brizzi, Daniele Loiacono, Lorenzo Preda
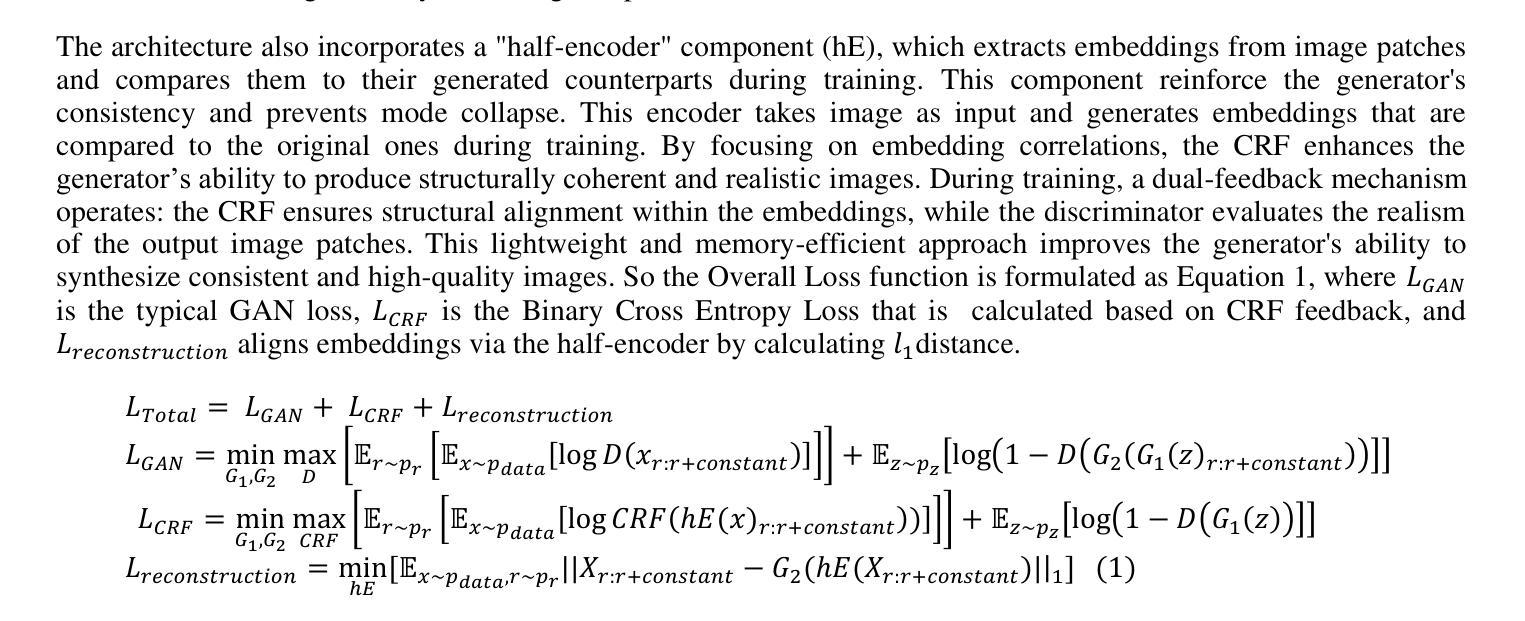
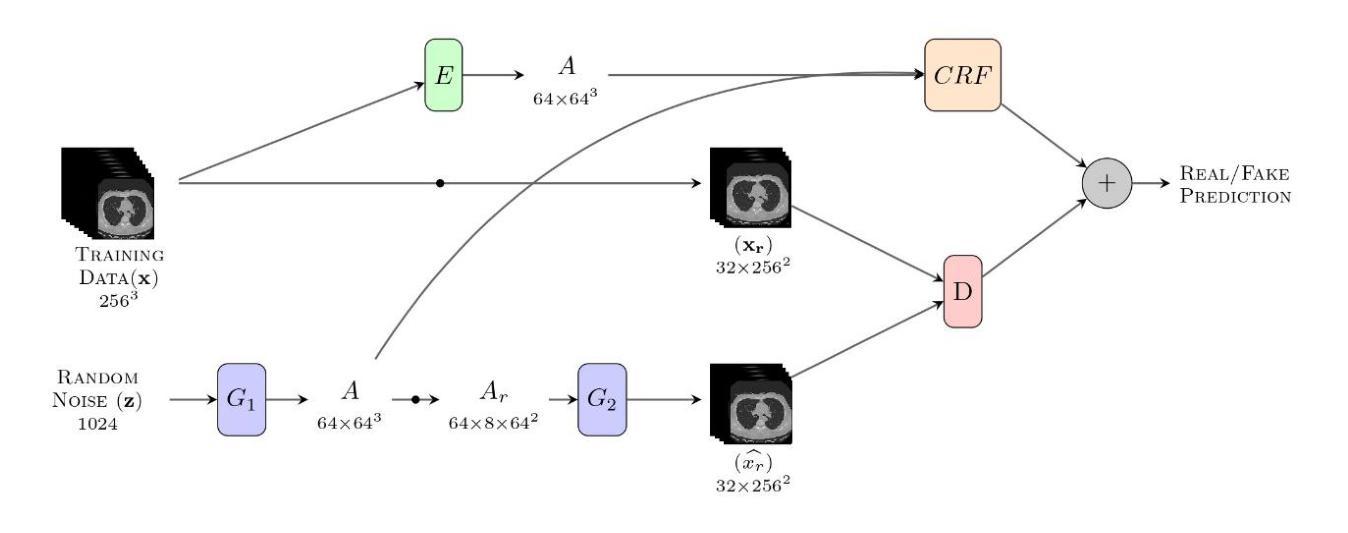
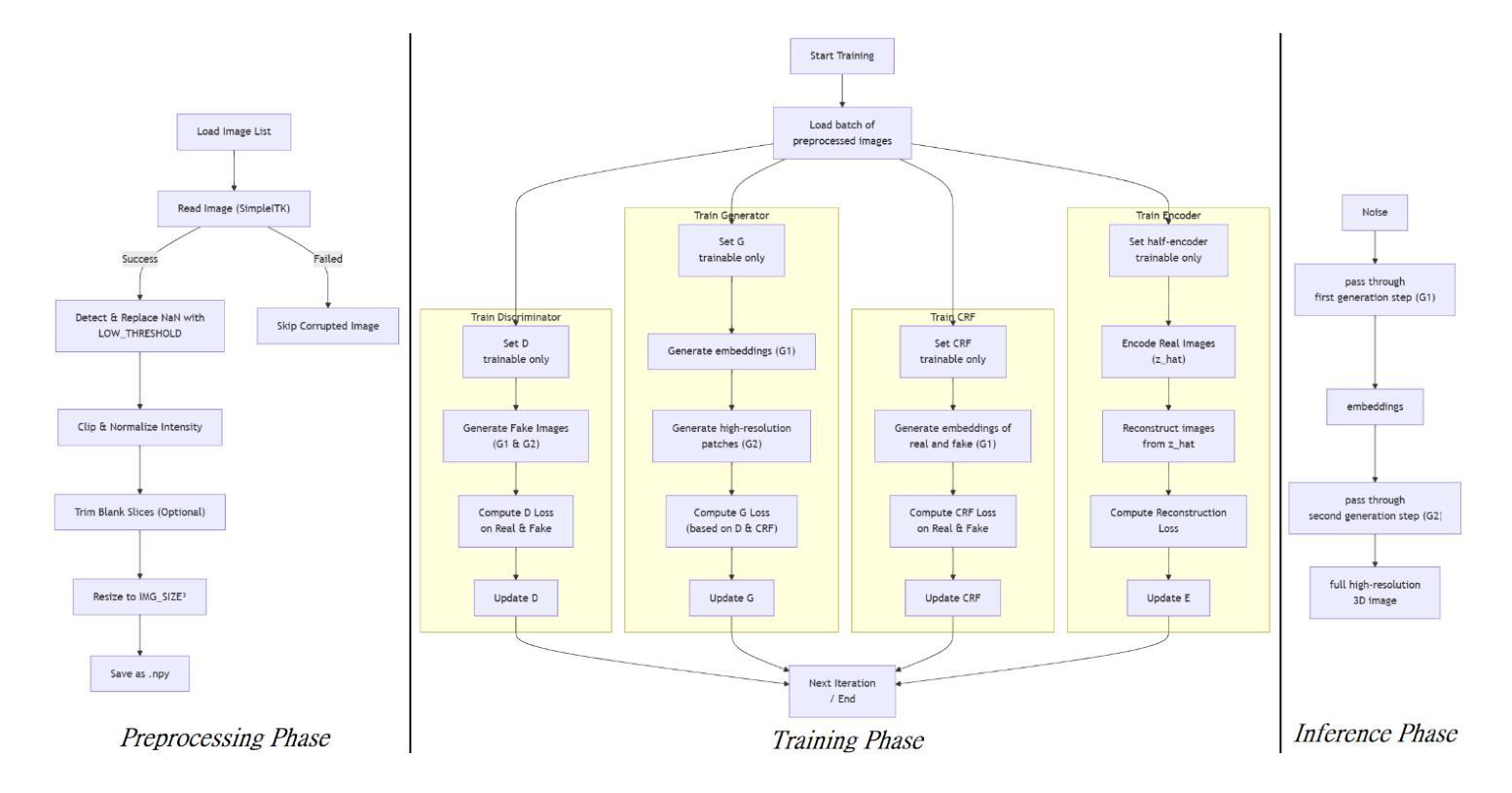
Generative Adversarial Networks (GANs) are increasingly used to generate synthetic medical images, addressing the critical shortage of annotated data for training Artificial Intelligence systems. This study introduces CRF-GAN, a novel memory-efficient GAN architecture that enhances structural consistency in 3D medical image synthesis. Integrating Conditional Random Fields within a two-step generation process allows CRF-GAN improving spatial coherence while maintaining high-resolution image quality. The model’s performance is evaluated against the state-of-the-art hierarchical (HA)-GAN model. Materials and Methods: We evaluate the performance of CRF-GAN against the HA-GAN model. The comparison between the two models was made through a quantitative evaluation, using FID and MMD metrics, and a qualitative evaluation, through a two-alternative forced choice (2AFC) test completed by a pool of 12 resident radiologists, to assess the realism of the generated images. Results: CRF-GAN outperformed HA-GAN with lower FID and MMD scores, indicating better image fidelity. The 2AFC test showed a significant preference for images generated by CRF-Gan over those generated by HA-GAN. Additionally, CRF-GAN demonstrated 9.34% lower memory usage and achieved up to 14.6% faster training speeds, offering substantial computational savings. Discussion: CRF-GAN model successfully generates high-resolution 3D medical images with non-inferior quality to conventional models, while being more memory-efficient and faster. The key objective was not only to lower the computational cost but also to reallocate the freed-up resources towards the creation of higher-resolution 3D imaging, which is still a critical factor limiting their direct clinical applicability. Moreover, unlike many previous studies, we combined qualitative and quantitative assessments to obtain a more holistic feedback on the model’s performance.
生成对抗网络(GANs)正被越来越多地用于生成合成医疗图像,以解决训练人工智能系统时标注数据的严重短缺问题。本研究介绍了CRF-GAN,这是一种新型内存高效的GAN架构,可提高3D医疗图像合成中的结构一致性。将条件随机场集成到两步生成过程中,允许CRF-GAN在提高空间连贯性的同时保持高分辨率图像质量。该模型的性能是针对最先进的分层(HA)-GAN模型进行评估的。材料与方法:我们评估了CRF-GAN与HA-GAN模型的性能。通过定量评估(使用FID和MMD指标)和定性评估(通过由12名常驻放射科医生完成的二选一强制选择测试),对两种模型进行比较,以评估生成图像的真实性。结果:CRF-GAN在FID和MMD得分上优于HA-GAN,表明图像保真度更好。2AFC测试显示,CRF-Gan生成的图像比HA-GAN生成的图像更受欢迎。此外,CRF-GAN的内存使用率低9.34%,训练速度提高了高达14.6%,从而实现了可观的计算节省。讨论:CRF-GAN模型成功生成高分辨率的3D医疗图像,其质量不亚于传统模型,同时更节省内存、速度更快。主要目标不仅是降低计算成本,而是重新分配释放的资源来创建更高分辨率的3D图像,这仍然是限制其直接临床应用的关键因素。此外,不同于许多之前的研究,我们结合了定性和定量评估,以获得对模型性能的更全面反馈。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF Accpeted to Journal of Imaging Informatics in Medicine
Summary
该文本介绍了CRF-GAN模型在生成高质量三维医学图像方面的优势。该模型结合了条件随机场,提高了结构一致性,同时降低了内存使用并提高训练速度。与现有的分层GAN模型相比,CRF-GAN在图像保真度和内存效率方面表现出更好的性能。此外,该模型通过结合定性和定量评估,更全面地评估了模型的性能。
Key Takeaways
- CRF-GAN模型结合了条件随机场技术,提高了三维医学图像合成的结构一致性。
- 与现有模型相比,CRF-GAN具有更低的内存使用和更快的训练速度。
- CRF-GAN在图像保真度方面表现出优越的性能,通过FID和MMD指标定量评估以及由放射科医生完成的2AFC测试定性评估得到证实。
- CRF-GAN成功生成了高质量的三维医学图像,并且可以直接应用于临床。
- 该研究结合了定性和定量评估方法,以更全面地评估模型的性能。
- CRF-GAN模型的设计旨在降低计算成本,并将释放的资源用于创建更高分辨率的三维图像。
点此查看论文截图

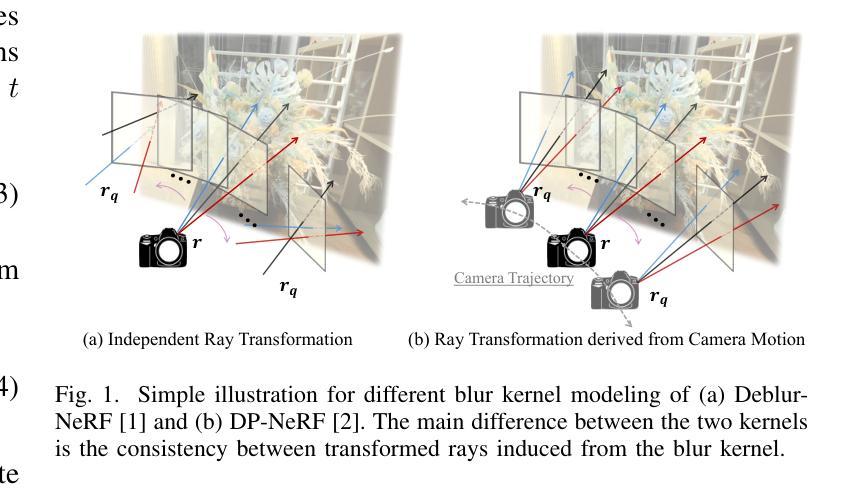
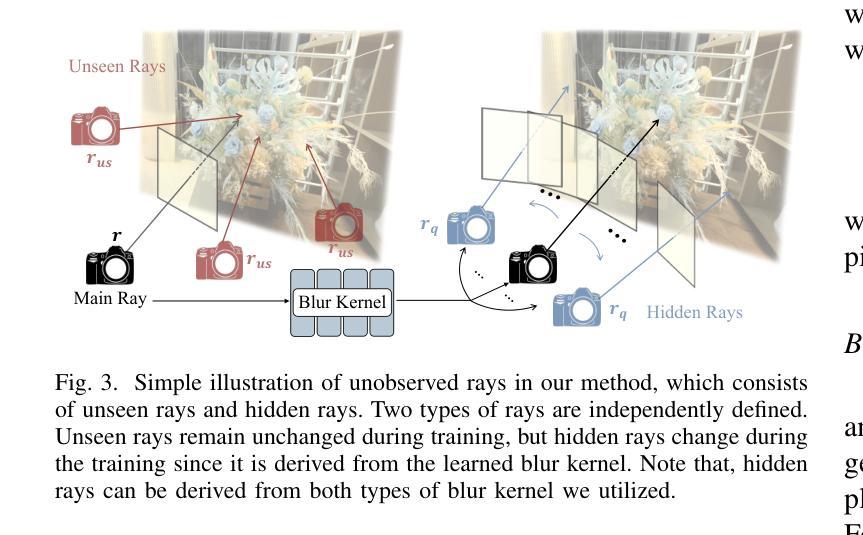
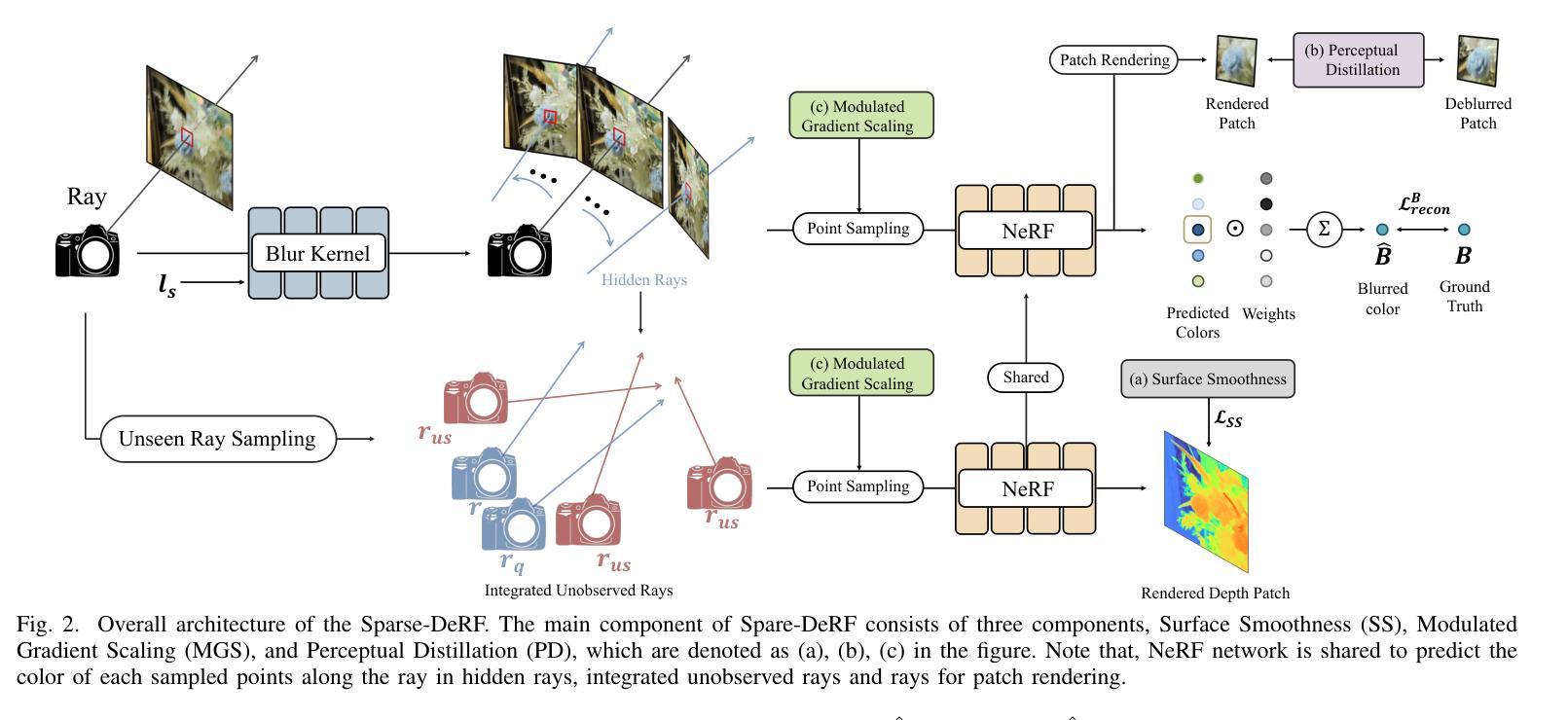
Sparse-DeRF: Deblurred Neural Radiance Fields from Sparse View
Authors:Dogyoon Lee, Donghyeong Kim, Jungho Lee, Minhyeok Lee, Seunghoon Lee, Sangyoun Lee
Recent studies construct deblurred neural radiance fields~(DeRF) using dozens of blurry images, which are not practical scenarios if only a limited number of blurry images are available. This paper focuses on constructing DeRF from sparse-view for more pragmatic real-world scenarios. As observed in our experiments, establishing DeRF from sparse views proves to be a more challenging problem due to the inherent complexity arising from the simultaneous optimization of blur kernels and NeRF from sparse view. Sparse-DeRF successfully regularizes the complicated joint optimization, presenting alleviated overfitting artifacts and enhanced quality on radiance fields. The regularization consists of three key components: Surface smoothness, helps the model accurately predict the scene structure utilizing unseen and additional hidden rays derived from the blur kernel based on statistical tendencies of real-world; Modulated gradient scaling, helps the model adjust the amount of the backpropagated gradient according to the arrangements of scene objects; Perceptual distillation improves the perceptual quality by overcoming the ill-posed multi-view inconsistency of image deblurring and distilling the pre-deblurred information, compensating for the lack of clean information in blurry images. We demonstrate the effectiveness of the Sparse-DeRF with extensive quantitative and qualitative experimental results by training DeRF from 2-view, 4-view, and 6-view blurry images.
最近的研究利用数十张模糊图像构建去模糊的神经辐射场(DeRF),但如果只有有限数量的模糊图像可用,则这种方法在实际场景中并不可行。本文的重点是从稀疏视角构建DeRF,以应对更实际的现实世界场景。在我们的实验中观察到,从稀疏视角建立DeRF是一个更具挑战性的问题,因为从稀疏视角同时优化模糊核和NeRF而产生的固有复杂性。Sparse-DeRF成功地对复杂的联合优化进行了正则化,减轻了过拟合的伪影,提高了辐射场的质量。正则化包括三个关键组成部分:表面平滑度,利用模糊核产生的未见和附加隐藏射线,以及基于现实世界的统计趋势,帮助模型准确预测场景结构;调制梯度缩放,根据场景物体的排列,帮助模型调整反向传播的梯度量;感知蒸馏通过克服图像去模糊的多视角不一致性,提高感知质量,并提炼预先去模糊的信息,以弥补模糊图像中清洁信息的缺乏。我们通过从2视角、4视角和6视角的模糊图像训练DeRF,展示了Sparse-DeRF的大量定量和定性的实验效果。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF Accepted and to appear in IEEE Transactions on Pattern Analysis and Machine Intelligence (TPAMI). Project page: https://dogyoonlee.github.io/sparsederf/
Summary
本文研究了从稀疏视角构建去模糊神经辐射场(DeRF)的方法,针对只有有限数量的模糊图像可用的情况。文章提出了Sparse-DeRF方法,通过表面平滑、调制梯度缩放和感知蒸馏三个关键组件成功解决了从稀疏视角建立DeRF的复杂联合优化问题,提高了辐射场的预测质量。通过从2到6视角的模糊图像训练DeRF,展示了Sparse-DeRF方法的有效性。
Key Takeaways
- 文章研究了在只有有限模糊图像的情况下构建去模糊神经辐射场(DeRF)的方法。
- Sparse-DeRF方法解决了从稀疏视角建立DeRF的复杂联合优化问题。
- 表面平滑组件利用未见和附加隐藏射线预测场景结构。
- 调制梯度缩放组件根据场景对象的排列调整反向传播的梯度量。
- 感知蒸馏组件提高了感知质量,克服了图像去模糊的多视角不一致性问题,并弥补了模糊图像中缺乏清晰信息的问题。
- 文章通过从2到6视角的模糊图像训练DeRF,展示了Sparse-DeRF方法的有效性。
点此查看论文截图