⚠️ 以下所有内容总结都来自于 大语言模型的能力,如有错误,仅供参考,谨慎使用
🔴 请注意:千万不要用于严肃的学术场景,只能用于论文阅读前的初筛!
💗 如果您觉得我们的项目对您有帮助 ChatPaperFree ,还请您给我们一些鼓励!⭐️ HuggingFace免费体验
2025-04-23 更新
Chinese-LiPS: A Chinese audio-visual speech recognition dataset with Lip-reading and Presentation Slides
Authors:Jinghua Zhao, Yuhang Jia, Shiyao Wang, Jiaming Zhou, Hui Wang, Yong Qin
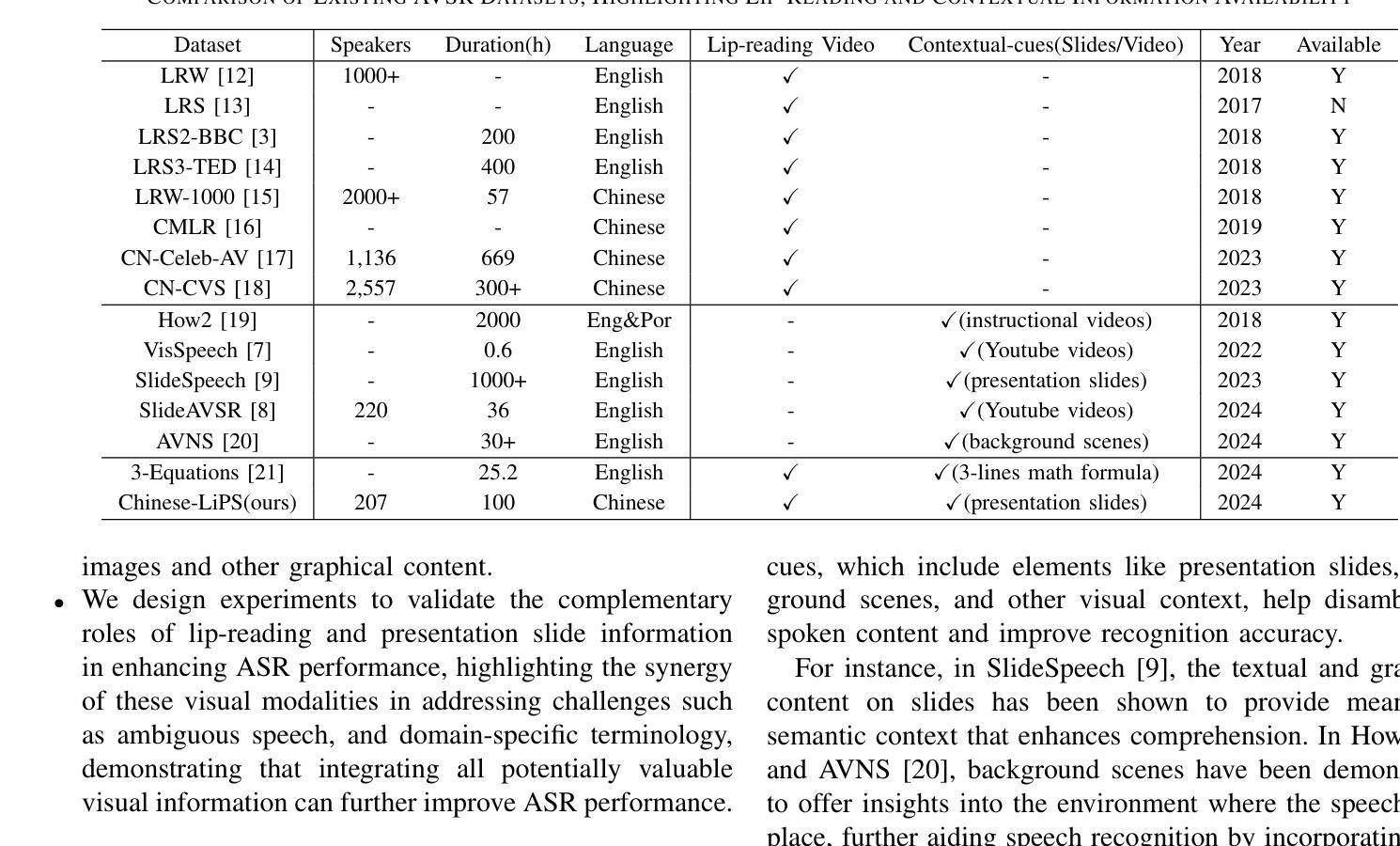
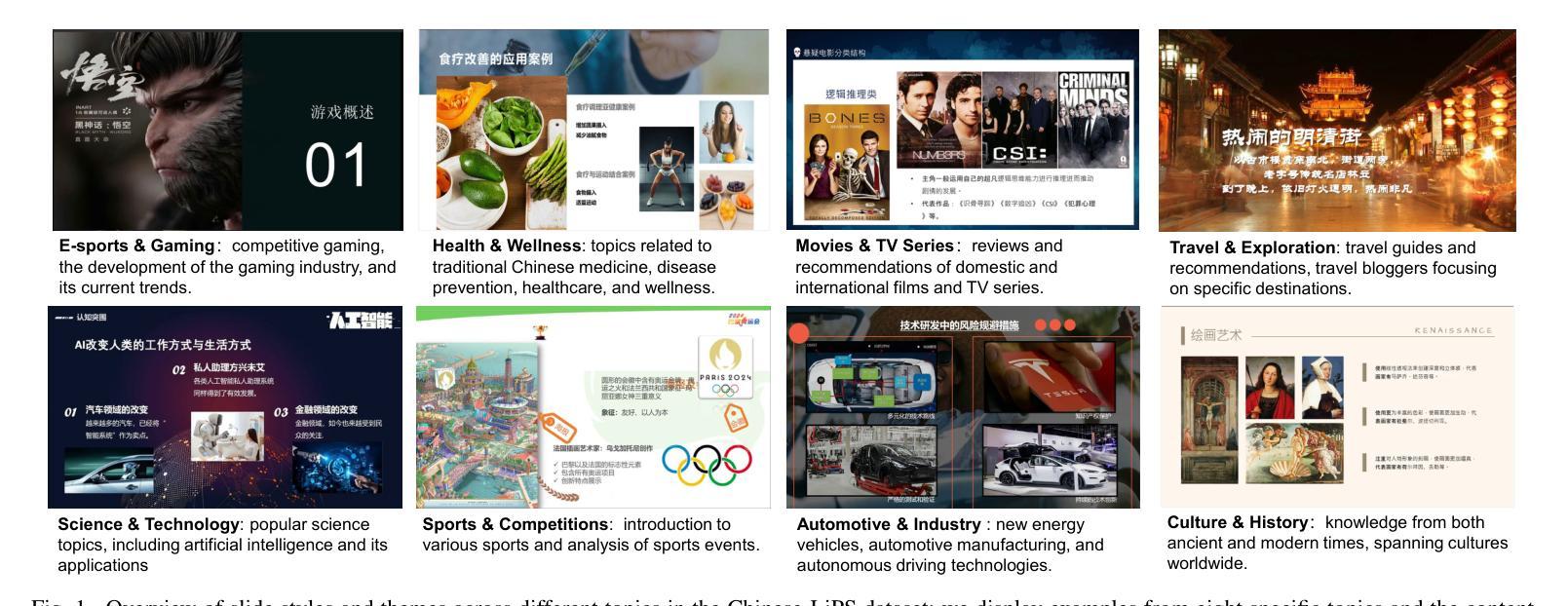
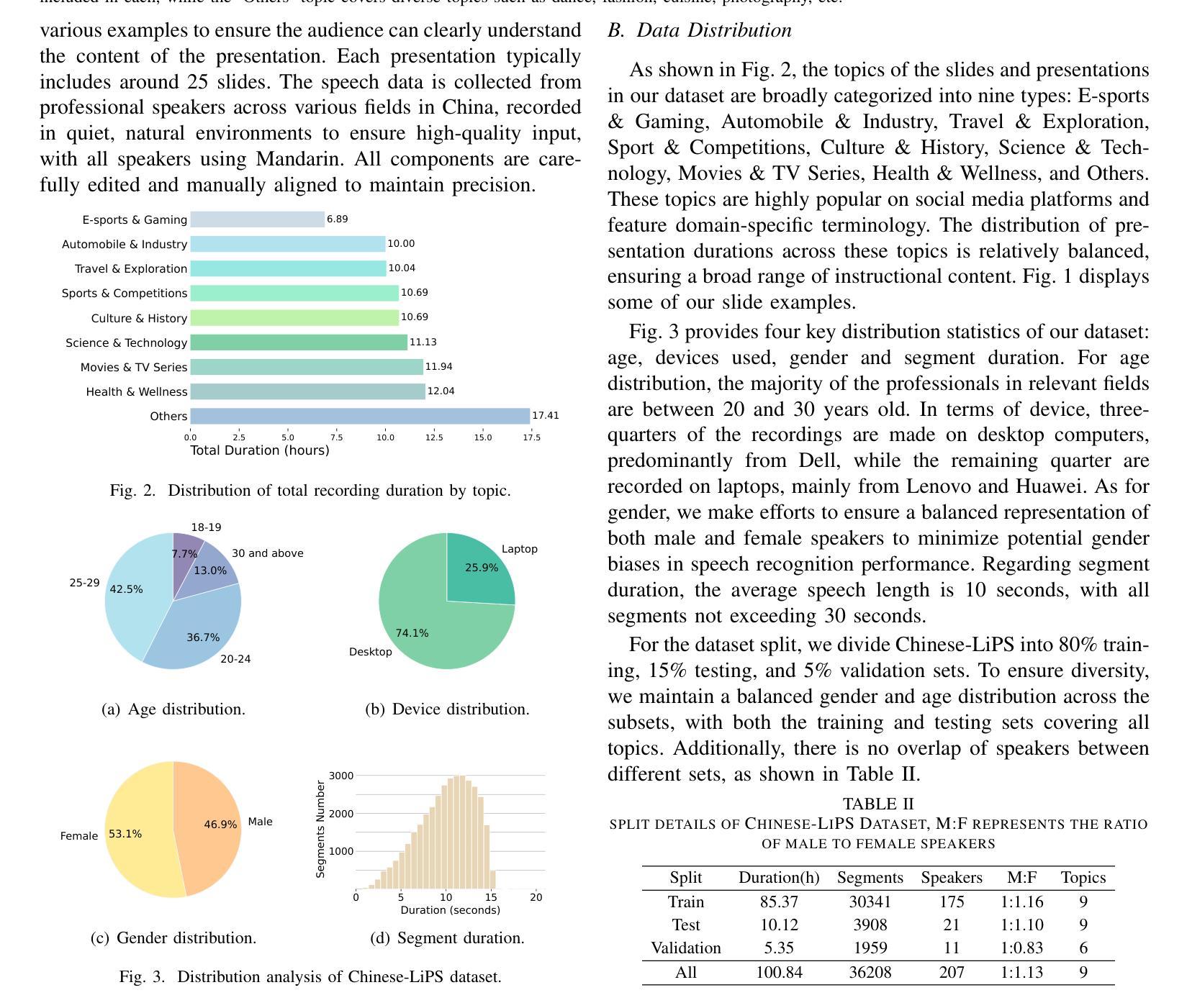
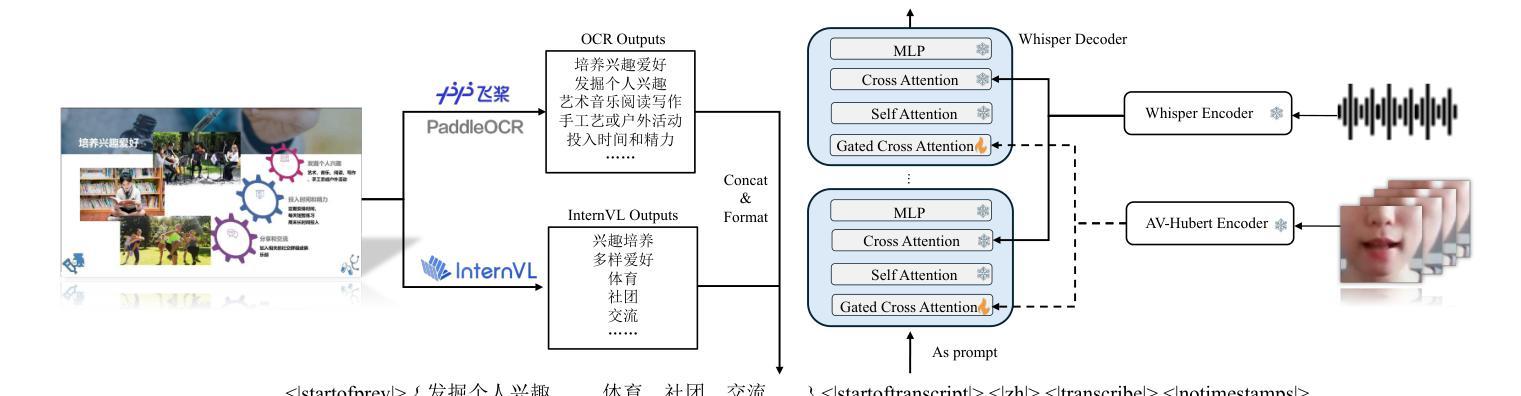
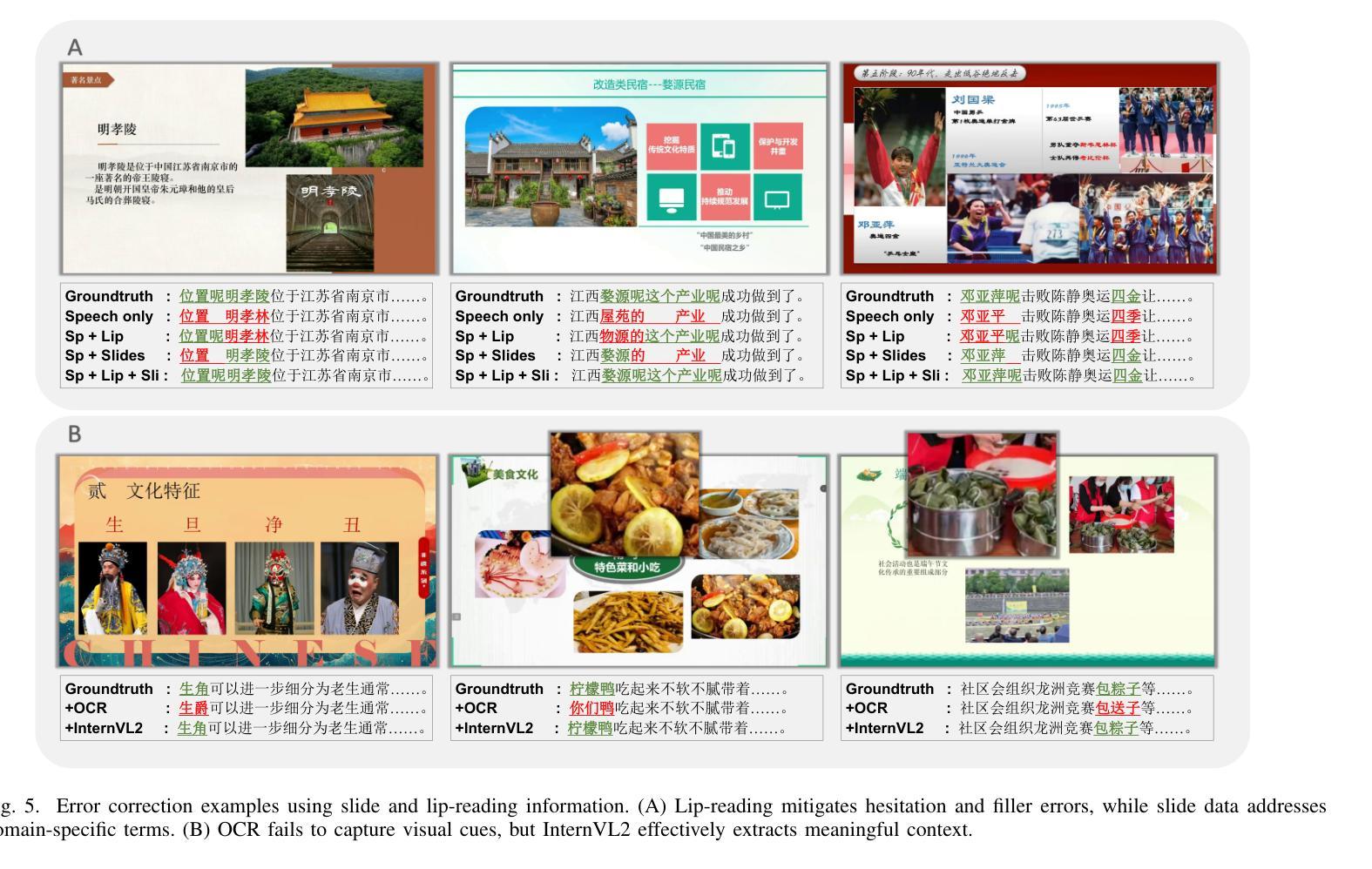
Incorporating visual modalities to assist Automatic Speech Recognition (ASR) tasks has led to significant improvements. However, existing Audio-Visual Speech Recognition (AVSR) datasets and methods typically rely solely on lip-reading information or speaking contextual video, neglecting the potential of combining these different valuable visual cues within the speaking context. In this paper, we release a multimodal Chinese AVSR dataset, Chinese-LiPS, comprising 100 hours of speech, video, and corresponding manual transcription, with the visual modality encompassing both lip-reading information and the presentation slides used by the speaker. Based on Chinese-LiPS, we develop a simple yet effective pipeline, LiPS-AVSR, which leverages both lip-reading and presentation slide information as visual modalities for AVSR tasks. Experiments show that lip-reading and presentation slide information improve ASR performance by approximately 8% and 25%, respectively, with a combined performance improvement of about 35%. The dataset is available at https://kiri0824.github.io/Chinese-LiPS/
将视觉模式融入自动语音识别(ASR)任务中已带来显著改善。然而,现有的音频-视频语音识别(AVSR)数据集和方法通常仅依赖于唇读信息或讲话上下文视频,忽略了结合这些不同有价值视觉线索在讲话上下文中的潜力。在本文中,我们发布了一个多模式中文AVSR数据集,名为“Chinese-LiPS”,包含100小时的语音、视频和相应的手动转录,视觉模式包括唇读信息和演讲者使用的演示幻灯片。基于Chinese-LiPS,我们开发了一个简单有效的流程“LiPS-AVSR”,该流程利用唇读和演示幻灯片信息作为视觉模式进行AVSR任务。实验表明,唇读和幻灯片信息分别将ASR性能提高了约8%和25%,综合性能提高了约35%。数据集可在https://kiri0824.github.io/Chinese-LiPS/找到。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF 6 pages, 7 figures
Summary
本文介绍了视听语音识别的研究。该研究通过使用新的中国多媒体语料库(Chinese-LiPS),并结合唇读信息和演讲幻灯片内容,提高了自动语音识别(ASR)任务的性能。实验表明,结合唇读和幻灯片信息可以显著提高语音识别准确率约35%。数据集可在指定网站下载。
Key Takeaways
- 视听语音识别(AVSR)结合了视觉和听觉信息,提高了自动语音识别(ASR)的性能。
- 中国多媒体语料库(Chinese-LiPS)包含演讲视频、音频和手动转录,为AVSR研究提供了丰富的资源。
- 唇读信息和演讲幻灯片内容都被视为重要的视觉线索,可以显著提高ASR的准确率。
- 通过结合唇读和幻灯片信息,ASR性能提高了约35%。
- Chinese-LiPS数据集是公开可访问的,为相关研究提供了便利。
- 该研究提出了一种简单而有效的视听语音识别管道(LiPS-AVSR),可用于处理多模态数据。
点此查看论文截图

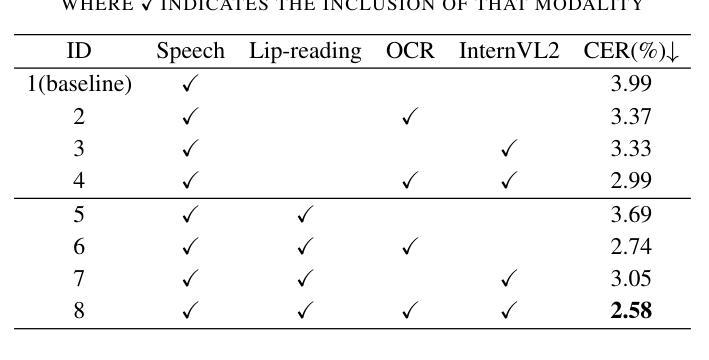
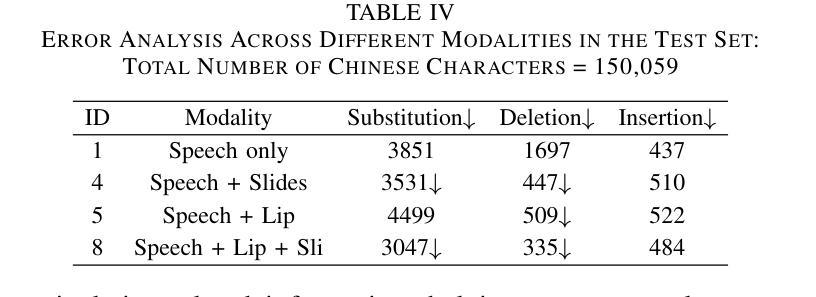
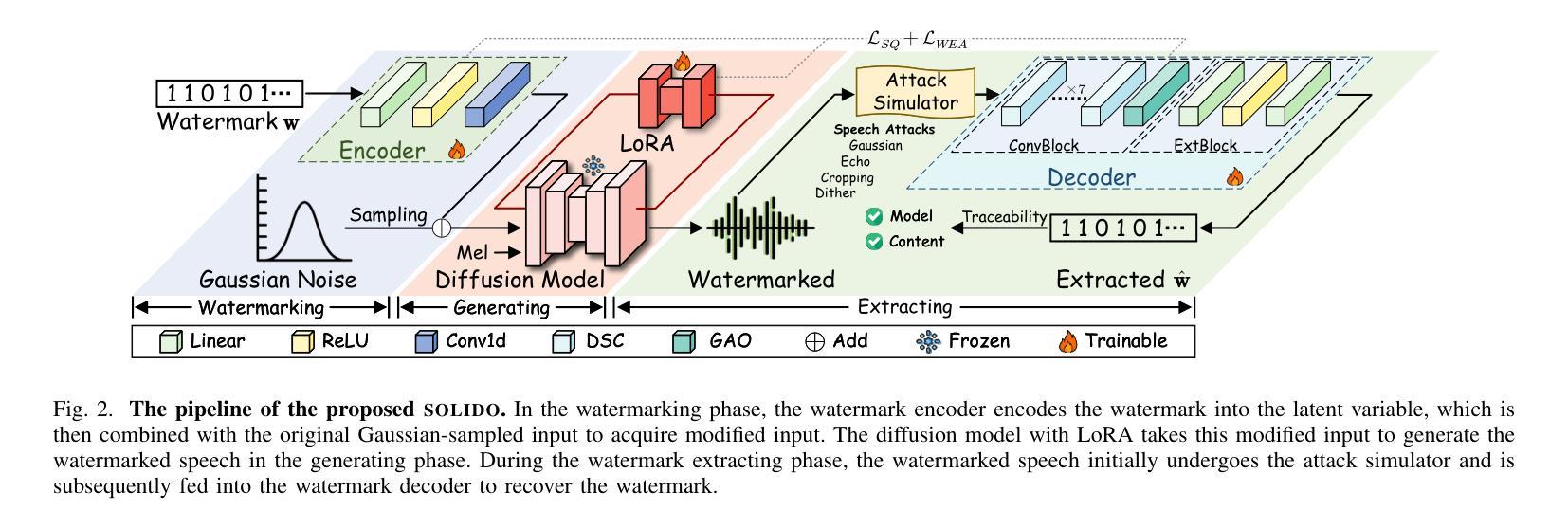
SOLIDO: A Robust Watermarking Method for Speech Synthesis via Low-Rank Adaptation
Authors:Yue Li, Weizhi Liu, Dongdong Lin
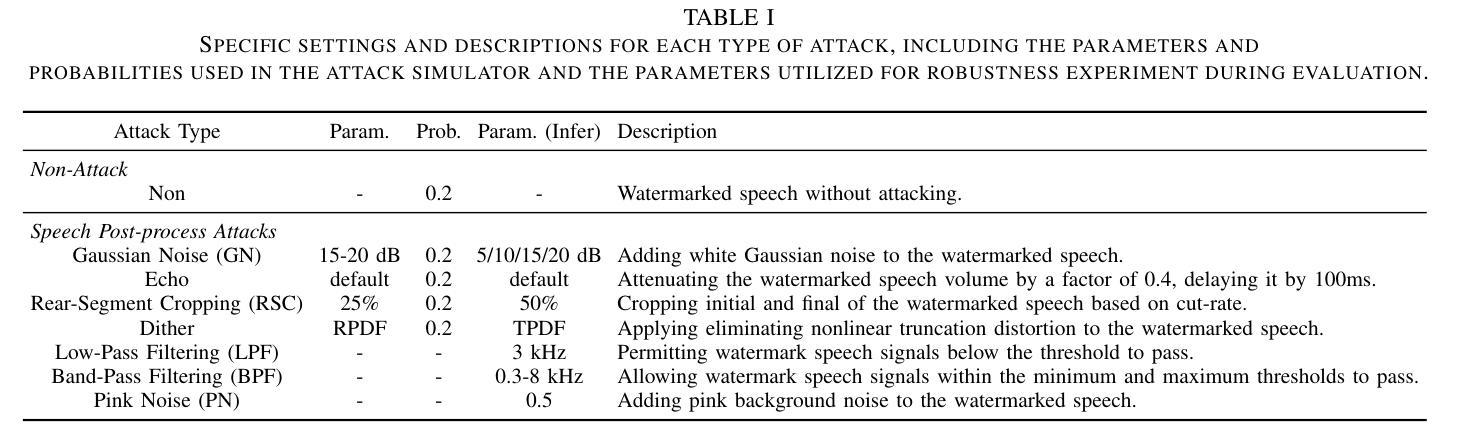
The accelerated advancement of speech generative models has given rise to security issues, including model infringement and unauthorized abuse of content. Although existing generative watermarking techniques have proposed corresponding solutions, most methods require substantial computational overhead and training costs. In addition, some methods have limitations in robustness when handling variable-length inputs. To tackle these challenges, we propose \textsc{SOLIDO}, a novel generative watermarking method that integrates parameter-efficient fine-tuning with speech watermarking through low-rank adaptation (LoRA) for speech diffusion models. Concretely, the watermark encoder converts the watermark to align with the input of diffusion models. To achieve precise watermark extraction from variable-length inputs, the watermark decoder based on depthwise separable convolution is designed for watermark recovery. To further enhance speech generation performance and watermark extraction capability, we propose a speech-driven lightweight fine-tuning strategy, which reduces computational overhead through LoRA. Comprehensive experiments demonstrate that the proposed method ensures high-fidelity watermarked speech even at a large capacity of 2000 bps. Furthermore, against common individual and compound speech attacks, our SOLIDO achieves a maximum average extraction accuracy of 99.20% and 98.43%, respectively. It surpasses other state-of-the-art methods by nearly 23% in resisting time-stretching attacks.
随着语音生成模型的快速发展,安全问题也随之产生,包括模型侵权和未经授权的滥用内容。虽然现有的生成水印技术已经提出了相应的解决方案,但大多数方法需要大量的计算开销和训练成本。此外,一些方法在处理可变长度输入时稳健性存在局限性。为了应对这些挑战,我们提出了\textsc{SOLIDO},这是一种新型的生成水印方法,它通过低秩适应(LoRA)将参数有效的微调与语音水印相结合,应用于语音扩散模型。具体来说,水印编码器将水印转换为与扩散模型的输入对齐的格式。为了实现从可变长度输入中精确提取水印,我们设计了基于深度可分离卷积的水印解码器,用于水印恢复。为了进一步改善语音生成性能和水印提取能力,我们提出了一种语音驱动的轻量级微调策略,通过LoRA减少计算开销。综合实验表明,即使在水印容量高达2000bps的情况下,该方法也能确保高保真度的水印语音。此外,在面对常见的个人和复合语音攻击时,我们的\text{SOLIDO}方法最高平均提取准确率分别达到了99.20%和98.43%。在抵抗时间拉伸攻击方面,它比其他最先进的方法高出近23%。
论文及项目相关链接
摘要
语音生成模型的快速发展带来了包括模型侵权和未经授权的内容滥用等安全问题。现有生成水印技术虽已提出相应解决方案,但多数方法计算开销大、训练成本高。针对这些问题,本文提出一种新颖的生成水印方法SOLIDO,通过低秩自适应(LoRA)结合参数高效的微调,实现语音扩散模型的水印嵌入。方法包括将水印转换为与扩散模型输入对齐的水印编码器,以及基于深度可分离卷积的水印解码器,以实现从变长度输入中的精确水印提取。同时,通过LoRA减少计算开销,进一步提高语音生成性能和水印提取能力。实验表明,该方法在保证高保真水印语音的同时,对抗常见个体和组合语音攻击时,提取准确率分别高达99.20%和98.43%,在时间拉伸攻击方面的抵抗能力较其他先进方法提高了近23%。
关键见解
- 语音生成模型的快速发展引发了包括模型侵权和滥用在内的安全问题。
- 现有生成水印技术面临计算开销大、训练成本高的挑战。
- 提出了新颖的生成水印方法SOLIDO,集成了参数高效的微调与低秩自适应(LoRA)。
- SOLIDO方法包括水印编码器和基于深度可分离卷积的水印解码器,支持变长度输入下的精确水印提取。
- 通过轻量级的语音驱动微调策略,增强了语音生成性能和水印提取能力,同时降低了计算开销。
- 实验显示,SOLIDO方法在保持高保真水印语音的同时,对抗各种语音攻击表现出高提取准确率。
- SOLIDO较其他先进方法在时间拉伸攻击方面的抵抗能力提高了近23%。
点此查看论文截图

StableQuant: Layer Adaptive Post-Training Quantization for Speech Foundation Models
Authors:Yeona Hong, Hyewon Han, Woo-jin Chung, Hong-Goo Kang
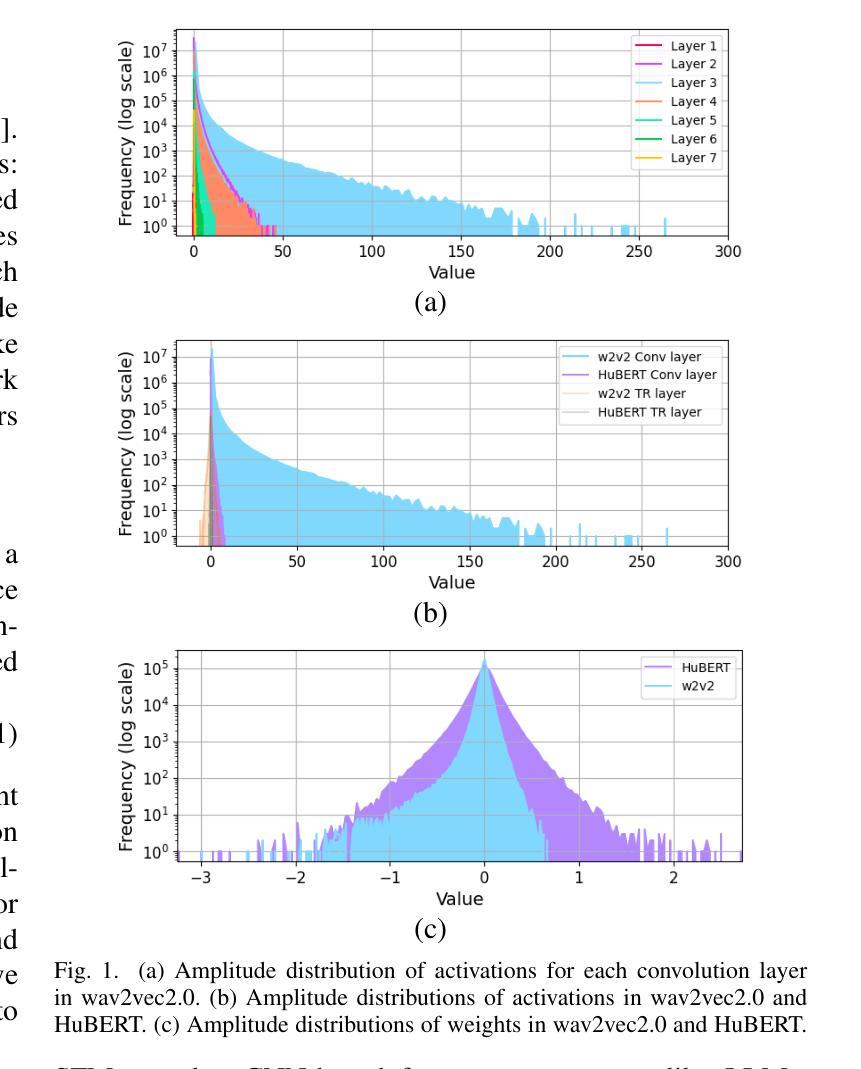
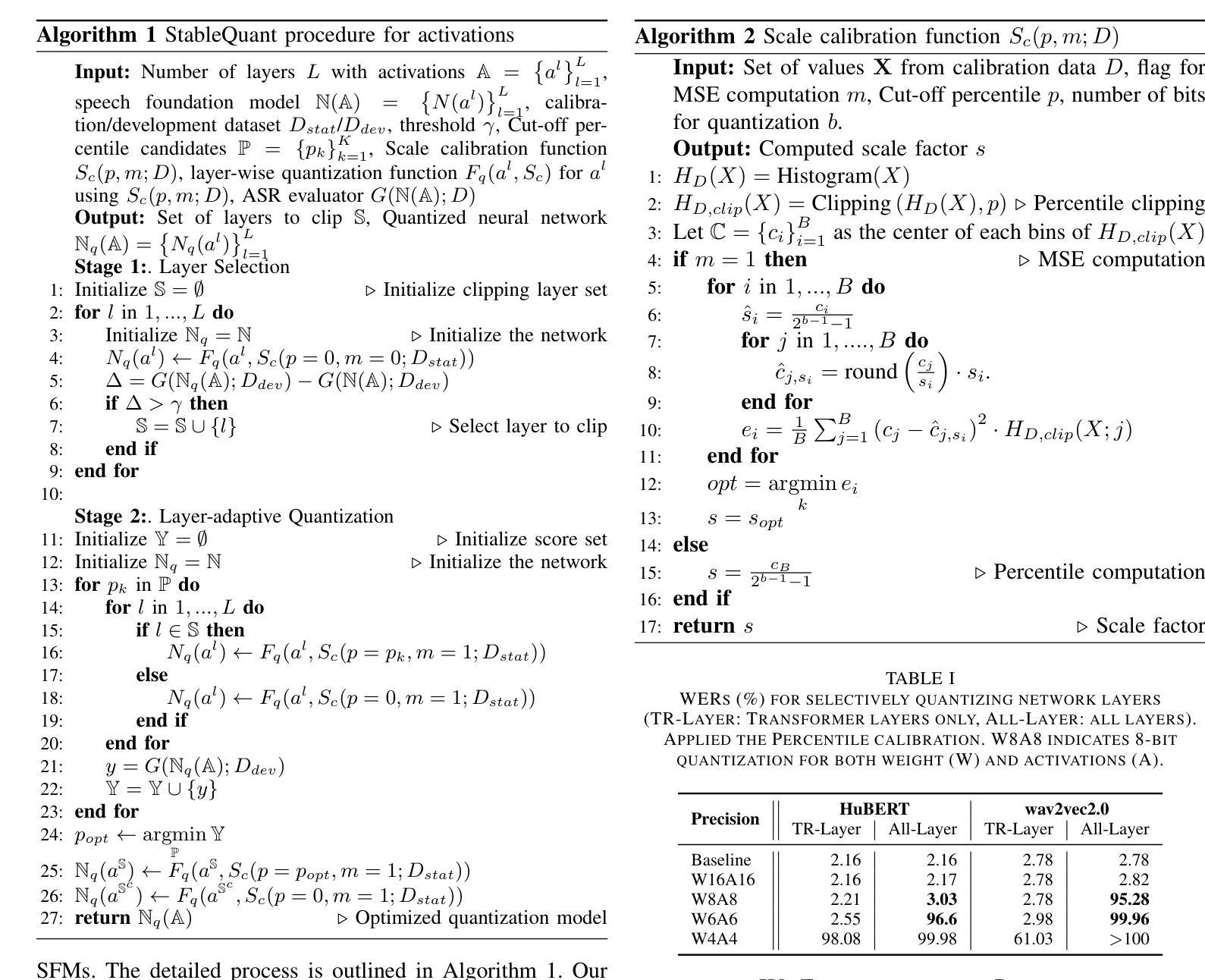
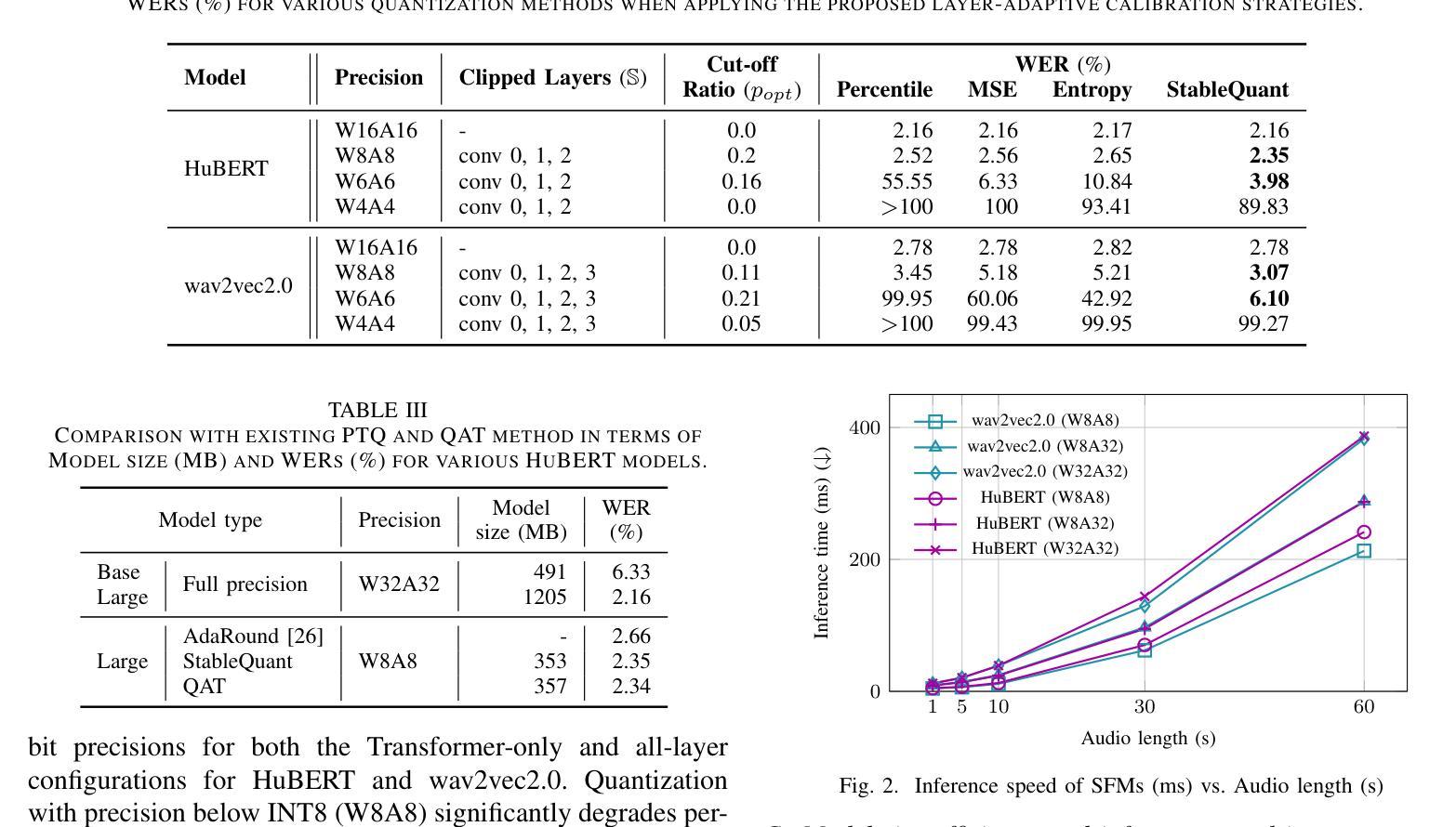
In this paper, we propose StableQuant, a novel adaptive post-training quantization (PTQ) algorithm for widely used speech foundation models (SFMs). While PTQ has been successfully employed for compressing large language models (LLMs) due to its ability to bypass additional fine-tuning, directly applying these techniques to SFMs may not yield optimal results, as SFMs utilize distinct network architecture for feature extraction. StableQuant demonstrates optimal quantization performance regardless of the network architecture type, as it adaptively determines the quantization range for each layer by analyzing both the scale distributions and overall performance. We evaluate our algorithm on two SFMs, HuBERT and wav2vec2.0, for an automatic speech recognition (ASR) task, and achieve superior performance compared to traditional PTQ methods. StableQuant successfully reduces the sizes of SFM models to a quarter and doubles the inference speed while limiting the word error rate (WER) performance drop to less than 0.3% with 8-bit quantization.
本文提出了StableQuant,这是一种针对广泛使用的语音基础模型(SFM)的新型自适应训练后量化(PTQ)算法。虽然PTQ由于其能够绕过额外的微调而成功用于压缩大型语言模型(LLM),但直接将这些技术应用于SFM可能无法获得最佳结果,因为SFM使用不同的网络架构进行特征提取。StableQuant展示了无论网络架构类型如何,都能实现最佳的量化性能,因为它通过分析尺度的分布和整体性能来自适应地确定每层的量化范围。我们在用于自动语音识别(ASR)任务的HuBERT和wav2vec2.0两个SFM上评估了我们的算法,与传统PTQ方法相比,取得了优越的性能。StableQuant成功地将SFM模型大小缩小到四分之一,并将推理速度提高了一倍,同时将词错误率(WER)性能下降限制在低于0.3%,使用8位量化。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF Accepted at ICASSP 2025
Summary
本文提出了StableQuant,这是一种新型自适应训练后量化(PTQ)算法,适用于广泛使用的语音基础模型(SFMs)。StableQuant能够自适应地确定每层的量化范围,通过分析尺度分布和整体性能,实现了对SFMs的优化量化。在HuBERT和wav2vec2.0两个语音基础模型上进行自动语音识别(ASR)任务评估时,与传统的PTQ方法相比,StableQuant取得了卓越的性能,成功地将模型大小缩小到四分之一,并加倍了推理速度,同时将词错误率(WER)的性能损失限制在0.3%以内,实现8位量化。
Key Takeaways
- StableQuant是一种针对语音基础模型(SFMs)的新型自适应训练后量化(PTQ)算法。
- SFMs具有独特的网络架构,传统PTQ技术可能无法产生最佳结果。
- StableQuant能够自适应地分析尺度分布和整体性能,为每层确定最佳的量化范围。
- 在HuBERT和wav2vec2.0两个语音基础模型上,StableQuant实现了优越的性能。
- StableQuant成功地将模型大小减少到四分之一,同时加倍了推理速度。
- 与传统PTQ方法相比,StableQuant的词错误率(WER)性能损失低于0.3%。
点此查看论文截图

Advancing Arabic Speech Recognition Through Large-Scale Weakly Supervised Learning
Authors:Mahmoud Salhab, Marwan Elghitany, Shameed Sait, Syed Sibghat Ullah, Mohammad Abusheikh, Hasan Abusheikh
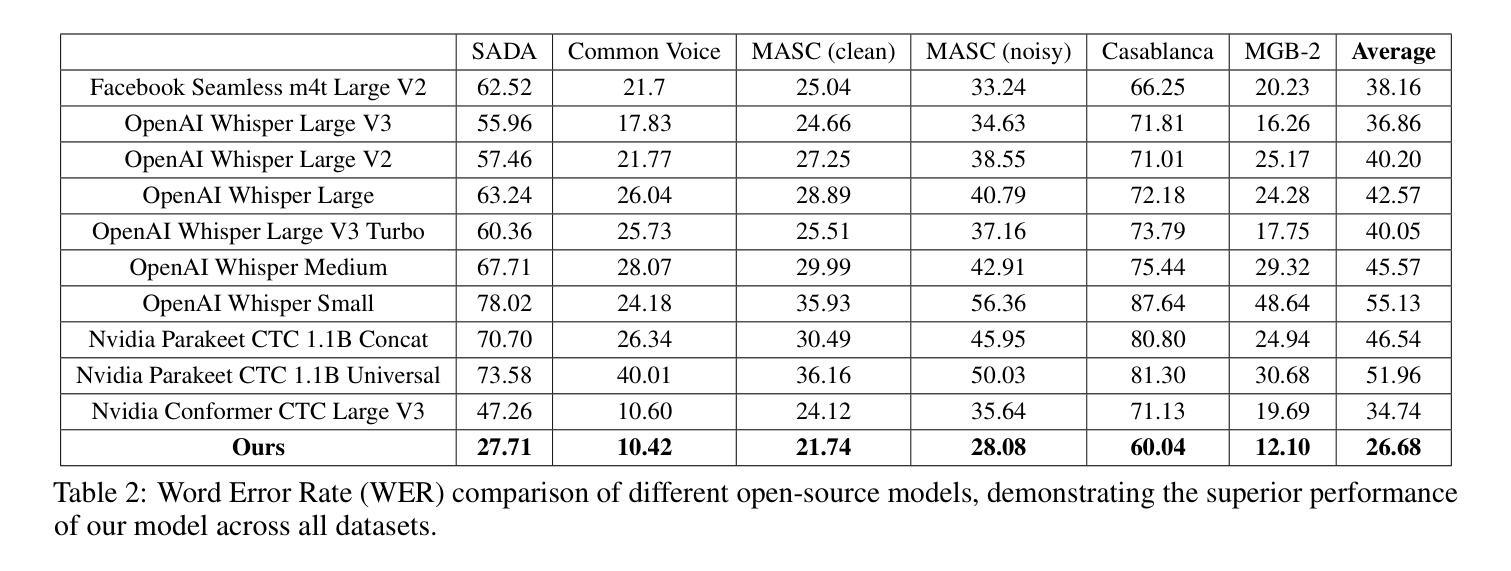
Automatic speech recognition (ASR) is crucial for human-machine interaction in diverse applications like conversational agents, industrial robotics, call center automation, and automated subtitling. However, developing high-performance ASR models remains challenging, particularly for low-resource languages like Arabic, due to the scarcity of large, labeled speech datasets, which are costly and labor-intensive to produce. In this work, we employ weakly supervised learning to train an Arabic ASR model using the Conformer architecture. Our model is trained from scratch on 15,000 hours of weakly annotated speech data covering both Modern Standard Arabic (MSA) and Dialectal Arabic (DA), eliminating the need for costly manual transcriptions. Despite the absence of human-verified labels, our approach achieves state-of-the-art (SOTA) results in Arabic ASR, surpassing both open and closed-source models on standard benchmarks. By demonstrating the effectiveness of weak supervision as a scalable, cost-efficient alternative to traditional supervised approaches, paving the way for improved ASR systems in low resource settings.
自动语音识别(ASR)在对话代理、工业机器人、呼叫中心自动化和自动字幕等多样化应用中的人机交互中起着至关重要的作用。然而,开发高性能的ASR模型仍然是一个挑战,特别是对于阿拉伯语等低资源语言来说,由于大规模、标记的语音数据集稀缺,这些数据集的产生既昂贵又耗劳力。在这项工作中,我们采用弱监督学习方法,使用Conformer架构训练阿拉伯语ASR模型。我们的模型从零开始在涵盖现代标准阿拉伯语(MSA)和方言阿拉伯语(DA)的15000小时弱注释语音数据上进行训练,无需昂贵的人工转录。尽管没有人工验证的标签,我们的方法仍然取得了阿拉伯语音识别的最新结果,在标准基准测试中超过了开源和不开源的模型。通过证明弱监督作为传统监督方法的可扩展、成本效益高的替代方案的有效性,为低资源环境中的ASR系统改进铺平了道路。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
阿拉伯语自动语音识别(ASR)在低资源语言环境中面临挑战,由于缺乏大量标记的语音数据集。本研究采用弱监督学习方法,使用Conformer架构训练阿拉伯语ASR模型,可在无需昂贵手动转录的情况下,从15000小时的弱标注语音数据中训练模型。此方法在阿拉伯语的ASR上达到了最先进的性能,并在标准基准测试中超越了开源和闭源模型,为低资源环境中的ASR系统改进展示了有效、成本效益高的替代方案。
Key Takeaways
- 阿拉伯语自动语音识别(ASR)在低资源环境中具有挑战性,缺乏大规模标记语音数据集。
- 研究使用弱监督学习方法训练阿拉伯语ASR模型。
- 模型使用Conformer架构,可在无需昂贵手动转录的情况下,从大量弱标注语音数据中训练。
- 该方法在阿拉伯语ASR上达到了最先进性能。
- 方法在标准基准测试中超越了开源和闭源模型。
- 弱监督学习是一种有效且成本效益高的替代传统监督学习方法。
点此查看论文截图


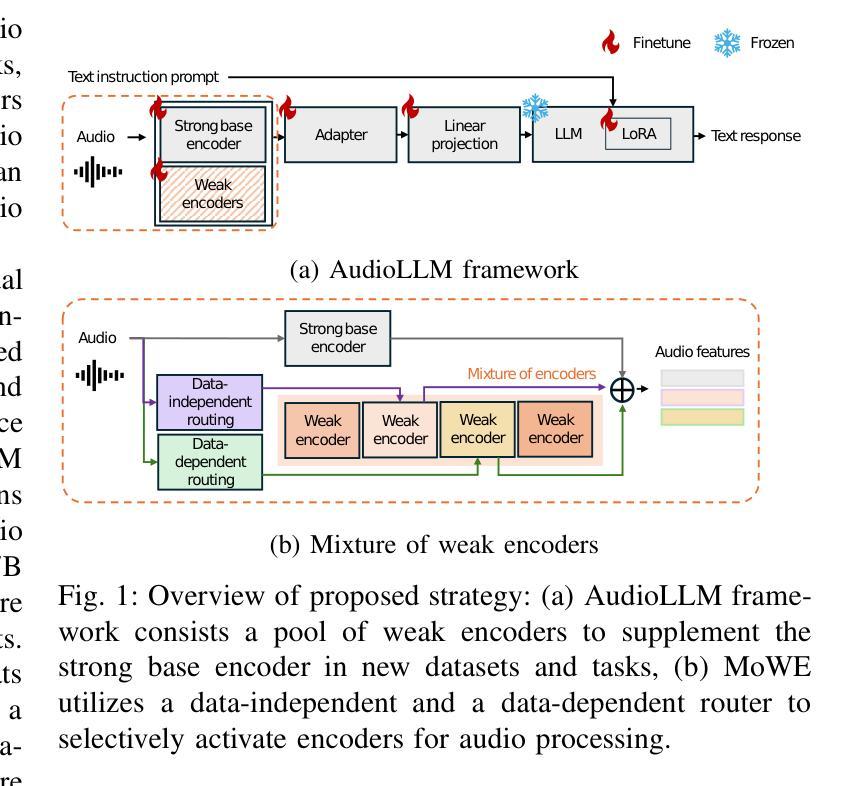
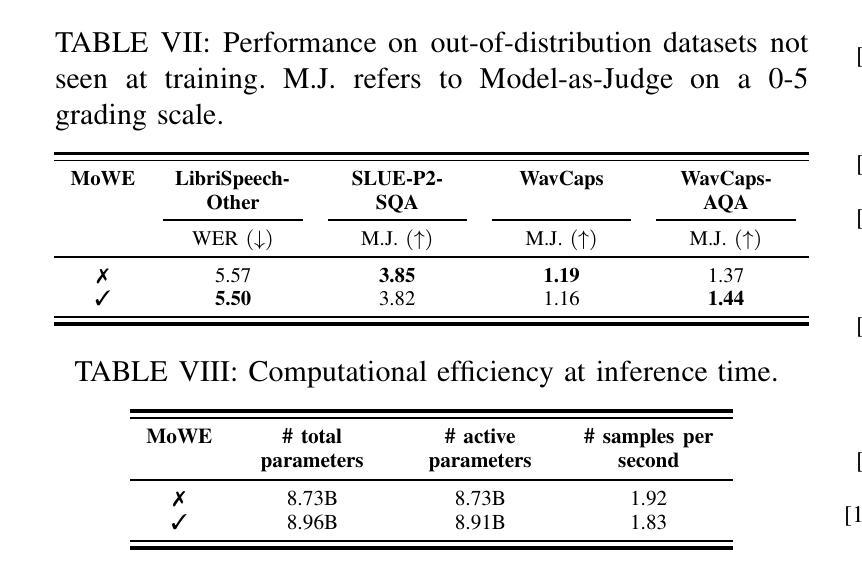
MoWE-Audio: Multitask AudioLLMs with Mixture of Weak Encoders
Authors:Wenyu Zhang, Shuo Sun, Bin Wang, Xunlong Zou, Zhuohan Liu, Yingxu He, Geyu Lin, Nancy F. Chen, Ai Ti Aw
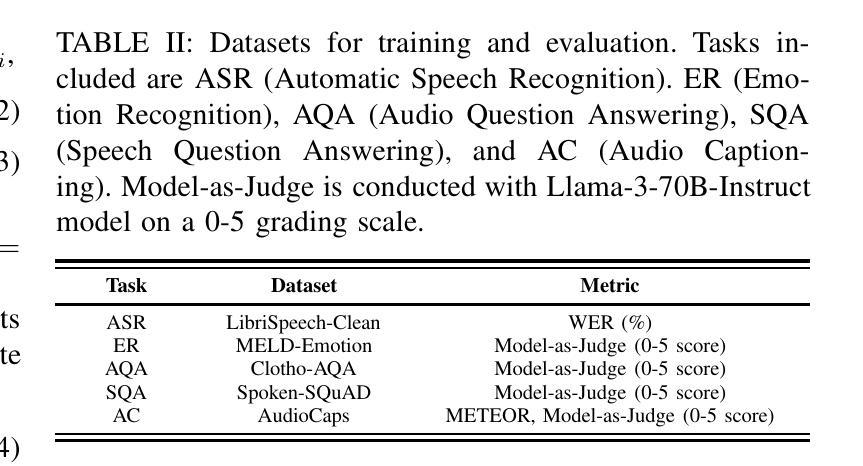
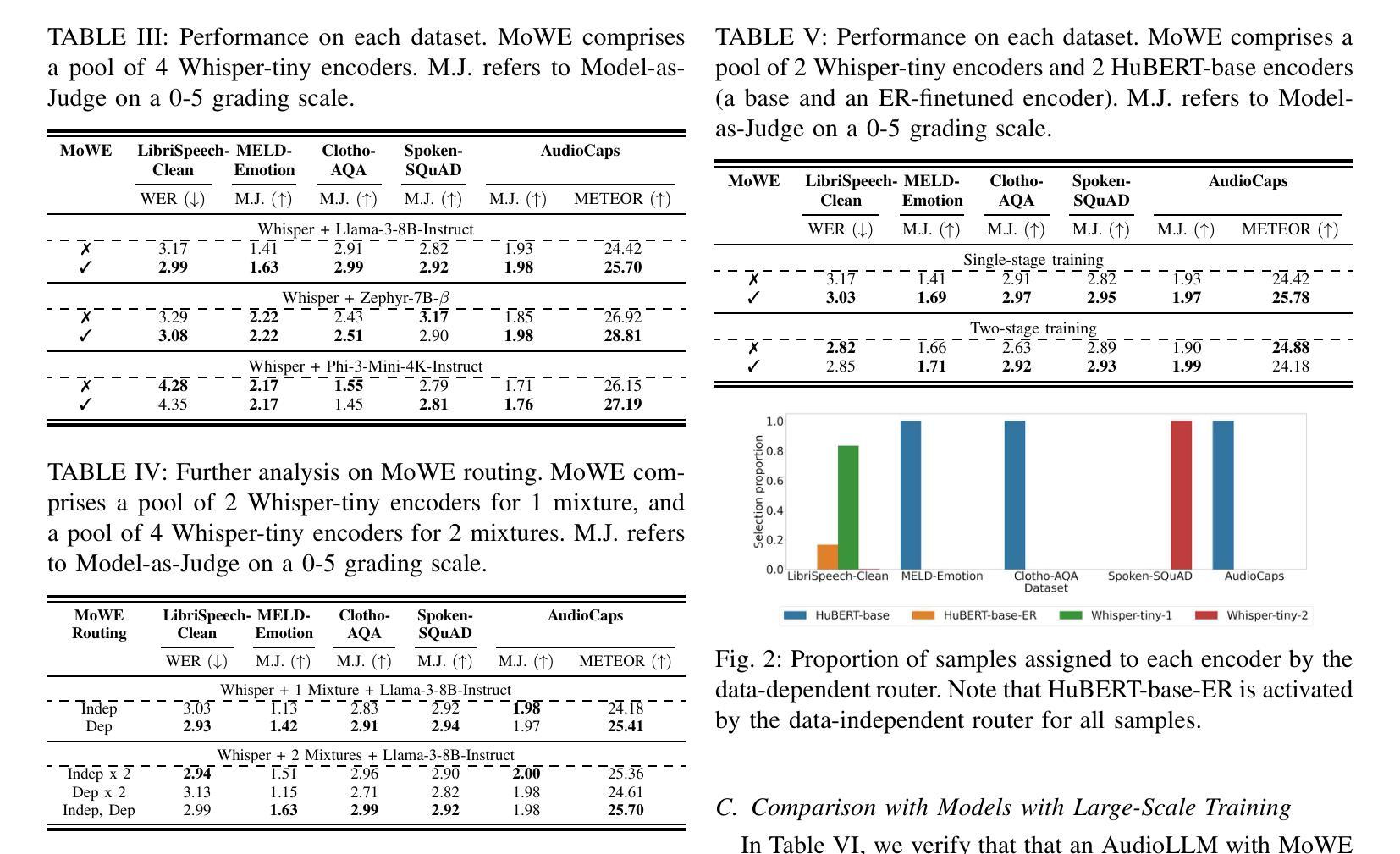
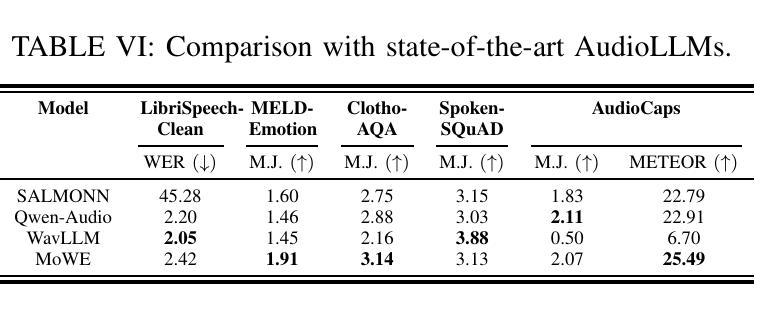
The rapid advancements in large language models (LLMs) have significantly enhanced natural language processing capabilities, facilitating the development of AudioLLMs that process and understand speech and audio inputs alongside text. Existing AudioLLMs typically combine a pre-trained audio encoder with a pre-trained LLM, which are subsequently finetuned on specific audio tasks. However, the pre-trained audio encoder has constrained capacity to capture features for new tasks and datasets. To address this, we propose to incorporate mixtures of `weak’ encoders (MoWE) into the AudioLLM framework. MoWE supplements a base encoder with a pool of relatively light weight encoders, selectively activated based on the audio input to enhance feature extraction without significantly increasing model size. Our empirical results demonstrate that MoWE effectively improves multi-task performance, broadening the applicability of AudioLLMs to more diverse audio tasks.
随着大型语言模型(LLM)的快速发展,自然语言处理能力得到了极大的提升,推动了能够处理和理解语音和音频输入的AudioLLM的发展。现有的AudioLLM通常将预训练的音频编码器与预训练的LLM相结合,随后在特定的音频任务上进行微调。然而,预训练的音频编码器在捕获新任务和数据集特征方面的能力有限。为解决这一问题,我们提出在AudioLLM框架中融入“弱编码器混合物”(MoWE)。MoWE以基本编码器为基础,辅以一组相对轻量级的编码器池,根据音频输入进行选择性地激活,以增强特征提取能力,同时不会显著增加模型大小。我们的实证结果表明,MoWE有效提高了一项多任务性能,扩大了AudioLLM在更多不同音频任务中的应用范围。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF ICASSP 2025
总结
大型语言模型的快速发展显著提高了自然语言处理能力,促进了能处理和了解语音和音频输入的AudioLLMs的发展。现有的AudioLLMs通常结合预训练的音频编码器与预训练的大型语言模型,随后针对特定音频任务进行微调。然而,预训练的音频编码器在捕捉新任务和数据集特征方面能力有限。为解决这一问题,我们提出在AudioLLM框架中融入“弱编码器混合物”(MoWE)。MoWE以基础编码器为主,辅以相对轻量级的编码器池,根据音频输入选择性激活,以增强特征提取能力,同时不显著增加模型大小。实验结果表明,MoWE有效提高多任务性能,扩大了AudioLLMs在更多不同音频任务中的应用性。
关键见解
- 大型语言模型的快速发展促进了对语音和音频输入处理的AudioLLMs的进步。
- 现有AudioLLMs结合预训练音频编码器和大型语言模型,针对特定音频任务进行微调。
- 预训练音频编码器在应对新任务和数据集时特征捕捉能力受限。
- 提出融入“弱编码器混合物”(MoWE)以改善AudioLLM性能。
- MoWE包括一个基础编码器和一个轻量级编码器池,根据音频输入选择性激活。
- MoWE能有效提高多任务性能。
点此查看论文截图