⚠️ 以下所有内容总结都来自于 大语言模型的能力,如有错误,仅供参考,谨慎使用
🔴 请注意:千万不要用于严肃的学术场景,只能用于论文阅读前的初筛!
💗 如果您觉得我们的项目对您有帮助 ChatPaperFree ,还请您给我们一些鼓励!⭐️ HuggingFace免费体验
2025-04-23 更新
Impact of Latent Space Dimension on IoT Botnet Detection Performance: VAE-Encoder Versus ViT-Encoder
Authors:Hassan Wasswa, Aziida Nanyonga, Timothy Lynar
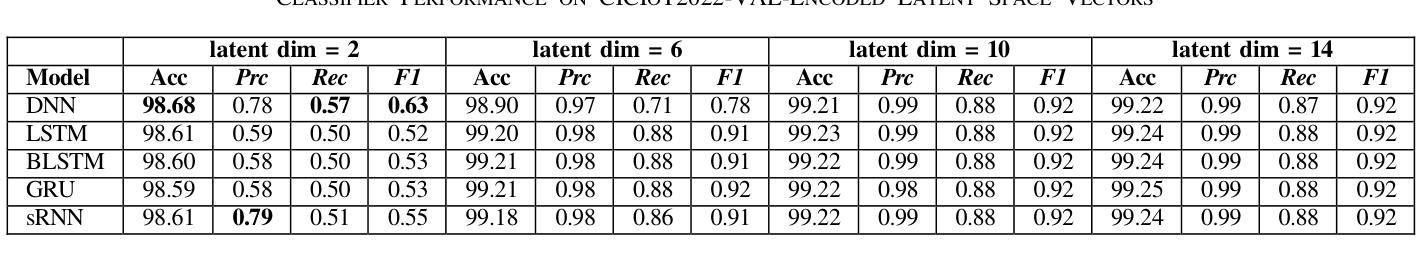
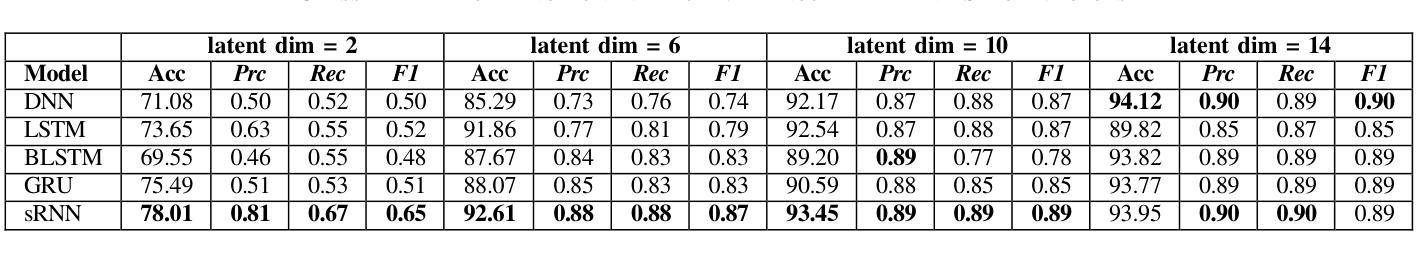
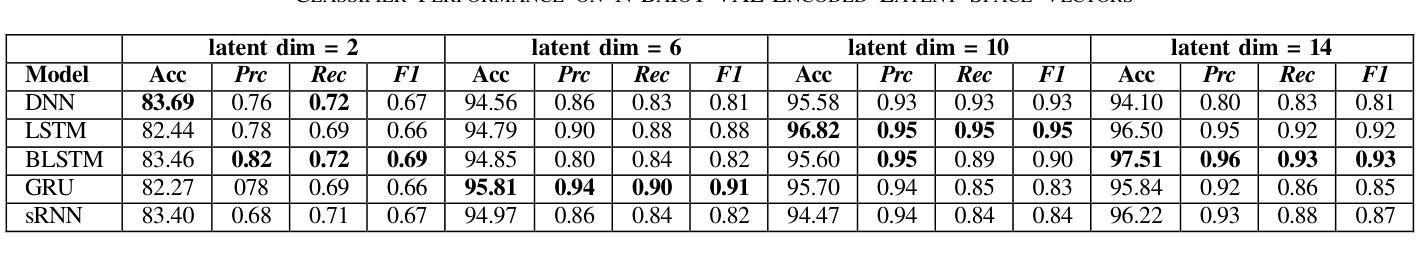
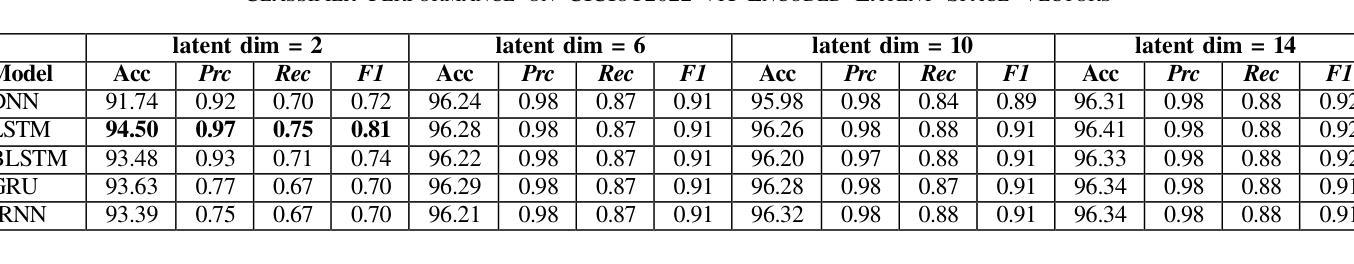
The rapid evolution of Internet of Things (IoT) technology has led to a significant increase in the number of IoT devices, applications, and services. This surge in IoT devices, along with their widespread presence, has made them a prime target for various cyber-attacks, particularly through IoT botnets. As a result, security has become a major concern within the IoT ecosystem. This study focuses on investigating how the latent dimension impacts the performance of different deep learning classifiers when trained on latent vector representations of the train dataset. The primary objective is to compare the outcomes of these models when encoder components from two cutting-edge architectures: the Vision Transformer (ViT) and the Variational Auto-Encoder (VAE) are utilized to project the high dimensional train dataset to the learned low dimensional latent space. The encoder components are employed to project high-dimensional structured .csv IoT botnet traffic datasets to various latent sizes. Evaluated on N-BaIoT and CICIoT2022 datasets, findings reveal that VAE-encoder based dimension reduction outperforms ViT-encoder based dimension reduction for both datasets in terms of four performance metrics including accuracy, precision, recall, and F1-score for all models which can be attributed to absence of spatial patterns in the datasets the ViT model attempts to learn and extract from image instances.
随着物联网(IoT)技术的快速发展,物联网设备、应用和服务数量显著增加。物联网设备的激增及其广泛存在使其成为各种网络攻击的主要目标,特别是通过物联网僵尸网络进行的攻击。因此,安全已成为物联网生态系统中的主要关注点。本研究重点调查潜在维度如何影响在不同深度学习分类器上训练时的性能,这些分类器是在训练数据集的潜在向量表示上训练的。主要目标是比较使用两种前沿架构的编码器组件时的模型结果:视觉转换器(ViT)和变分自动编码器(VAE)。它们被用于将高维度的训练数据集投影到学习到的低维度潜在空间。编码器组件被用于将高维度的结构化.csv物联网僵尸网络流量数据集投影到各种潜在大小。在N-BaIoT和CICIoT2022数据集上进行了评估,研究发现在四项性能指标(准确性、精确性、召回率和F1分数)方面,基于VAE编码器的降维在两组数据集上的表现优于基于ViT编码器的降维方法。这可以归因于数据集缺乏空间模式,而ViT模型试图从图像实例中学习并提取这些模式。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
物联网技术的快速发展导致物联网设备、应用和服务数量激增,使得物联网生态系统面临严重的安全威胁,尤其是通过物联网僵尸网络进行的各种网络攻击。本研究聚焦于探讨潜在维度对训练在潜在向量表示上的不同深度学习分类器性能的影响。主要目的是比较使用Vision Transformer(ViT)和变分自编码器(VAE)的编码器组件将高维结构化.csv物联网僵尸网络流量数据集投影到不同的潜在维度空间时的模型表现。在N-BaIoT和CICIoT2022数据集上的评估结果表明,基于VAE编码器的降维在四个性能指标(准确性、精确度、召回率和F1分数)上均优于基于ViT编码器的降维,这可能是由于数据集中不存在空间模式,而ViT模型试图从图像实例中学习并提取这些模式。
Key Takeaways
- 物联网技术的快速发展伴随着物联网设备数量的激增,使其成为网络攻击的主要目标。
- 安全已成为物联网生态系统的主要关注点。
- 本研究探讨了潜在维度对深度学习分类器性能的影响,特别是在处理物联网僵尸网络流量数据时。
- 使用了Vision Transformer(ViT)和变分自编码器(VAE)的编码器组件进行实验。
- 实验结果显示,基于VAE编码器的降维在多个性能指标上优于基于ViT编码器的降维。
- 这种差异可能源于数据集中缺乏空间模式,而ViT模型试图从这些模式中学习。
点此查看论文截图

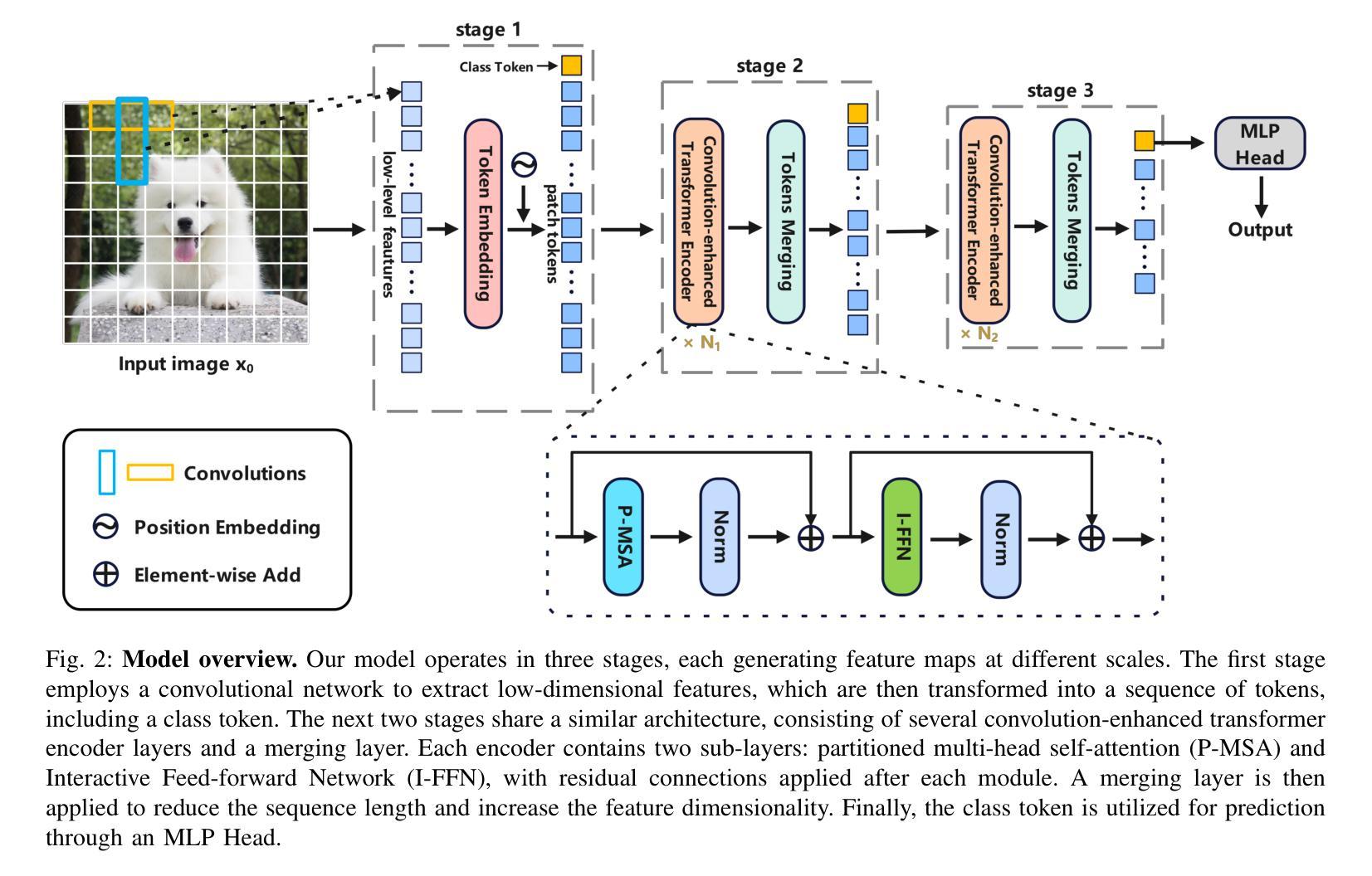
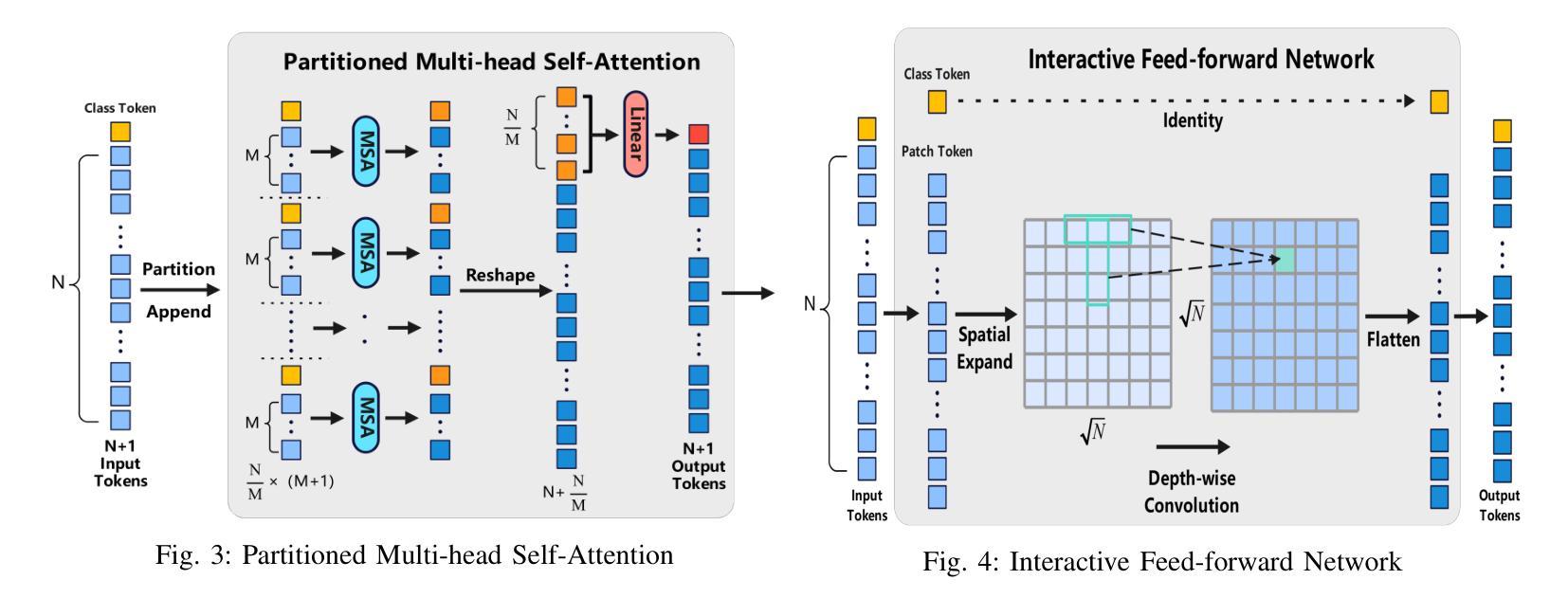
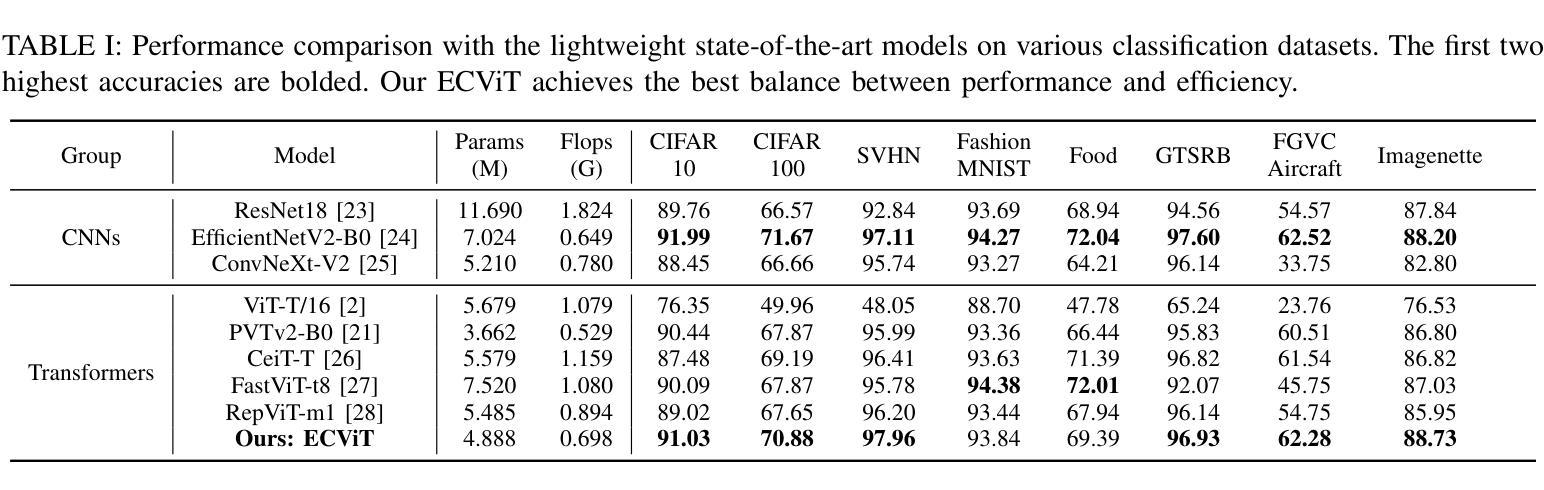
ECViT: Efficient Convolutional Vision Transformer with Local-Attention and Multi-scale Stages
Authors:Zhoujie Qian
Vision Transformers (ViTs) have revolutionized computer vision by leveraging self-attention to model long-range dependencies. However, ViTs face challenges such as high computational costs due to the quadratic scaling of self-attention and the requirement of a large amount of training data. To address these limitations, we propose the Efficient Convolutional Vision Transformer (ECViT), a hybrid architecture that effectively combines the strengths of CNNs and Transformers. ECViT introduces inductive biases such as locality and translation invariance, inherent to Convolutional Neural Networks (CNNs) into the Transformer framework by extracting patches from low-level features and enhancing the encoder with convolutional operations. Additionally, it incorporates local-attention and a pyramid structure to enable efficient multi-scale feature extraction and representation. Experimental results demonstrate that ECViT achieves an optimal balance between performance and efficiency, outperforming state-of-the-art models on various image classification tasks while maintaining low computational and storage requirements. ECViT offers an ideal solution for applications that prioritize high efficiency without compromising performance.
视觉Transformer(ViT)通过利用自注意力机制对长距离依赖关系进行建模,从而彻底改变了计算机视觉领域。然而,ViT面临挑战,如自注意力的二次扩展导致的高计算成本和对大量训练数据的需求。为了解决这些局限性,我们提出了高效的卷积视觉Transformer(ECViT),这是一种有效结合CNN和Transformer优势的混合架构。ECViT通过在Transformer框架中引入卷积神经网络(CNN)所固有的局部性和平移不变性等归纳偏见,通过从低级特征中提取补丁并增强编码器中的卷积操作来实现。此外,它结合了局部注意力和金字塔结构,以实现高效的多尺度特征提取和表示。实验结果表明,ECViT在性能和效率之间达到了最佳平衡,在各种图像分类任务上的性能超过了最新模型,同时保持了较低的计算和存储需求。对于注重高效率而不牺牲性能的应用,ECViT提供了理想的解决方案。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
高效卷积视觉转换器(ECViT)结合了CNN和Transformer的优点,解决了视觉转换器(ViT)面临的高计算成本和需要大量训练数据的问题。通过引入局部性和平移不变性等归纳偏见,以及局部注意力和金字塔结构,ECViT实现了性能与效率之间的优化平衡,在多种图像分类任务上优于最新模型,同时保持低计算和存储要求。
Key Takeaways
- 视觉转换器(ViT)通过自我注意力机制对计算机视觉领域产生了革命性的影响。
- ViT面临高计算成本和需要大量训练数据的问题。
- ECViT是一个混合架构,旨在解决ViT的挑战,结合了CNN和Transformer的优点。
- ECViT通过将CNN的归纳偏见(如局部性和平移不变性)引入Transformer框架来增强性能。
- ECViT通过引入局部注意力和金字塔结构,实现了多尺度特征的有效提取和表示。
- 实验结果表明,ECViT在性能和效率之间达到了平衡,在多种图像分类任务上优于其他模型。
点此查看论文截图

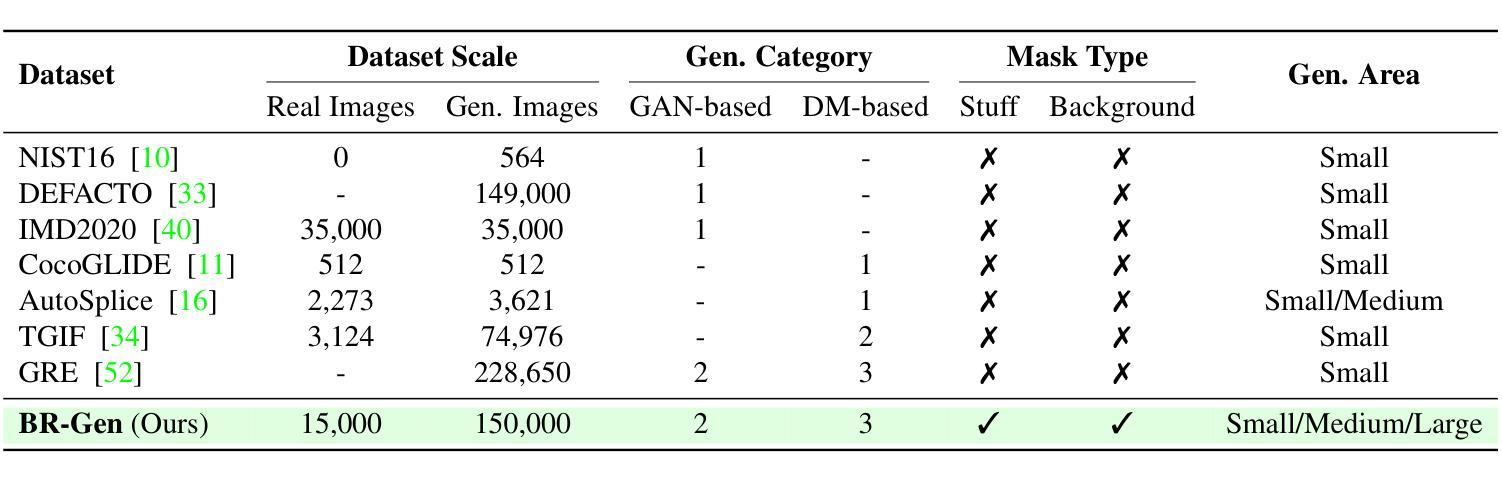
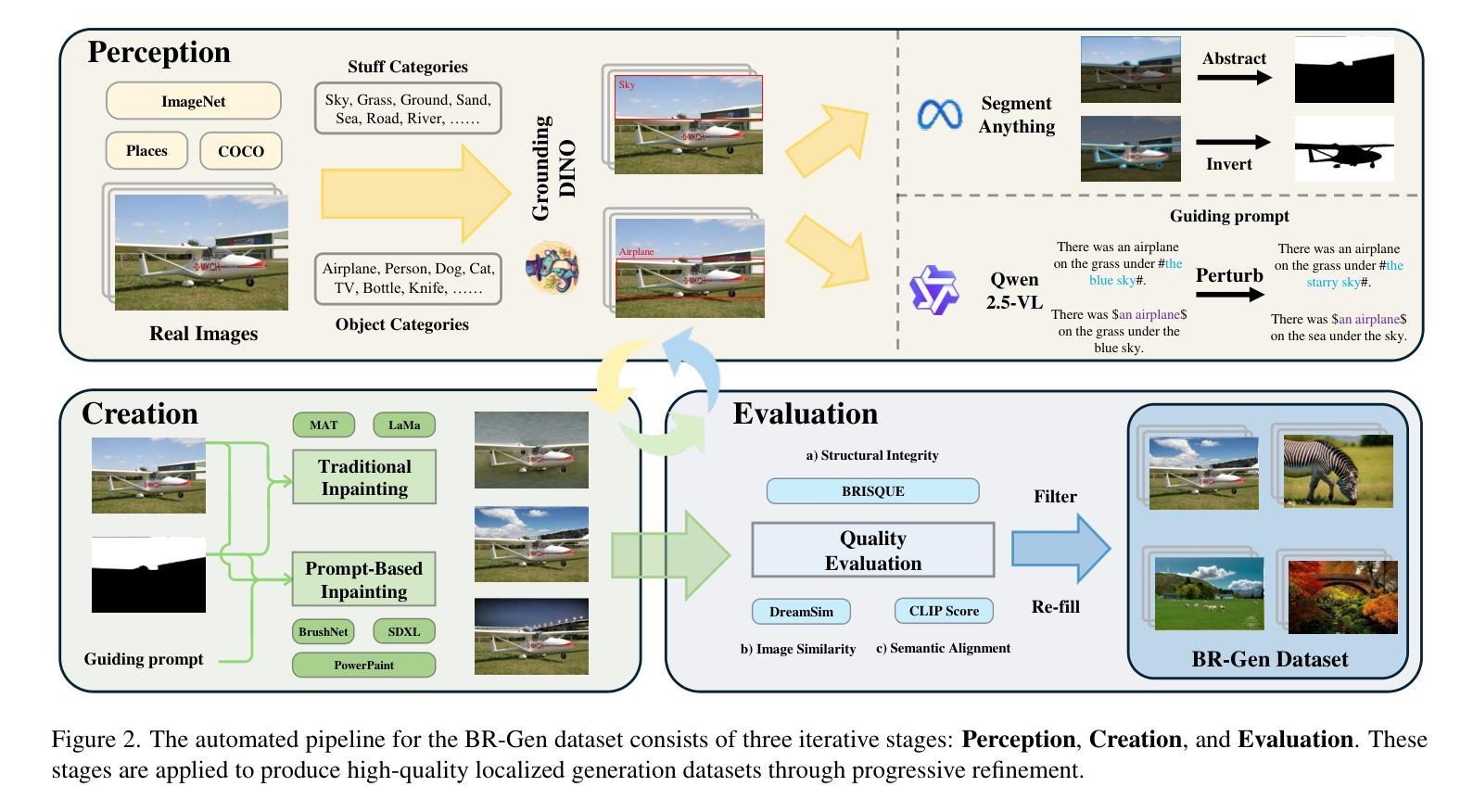
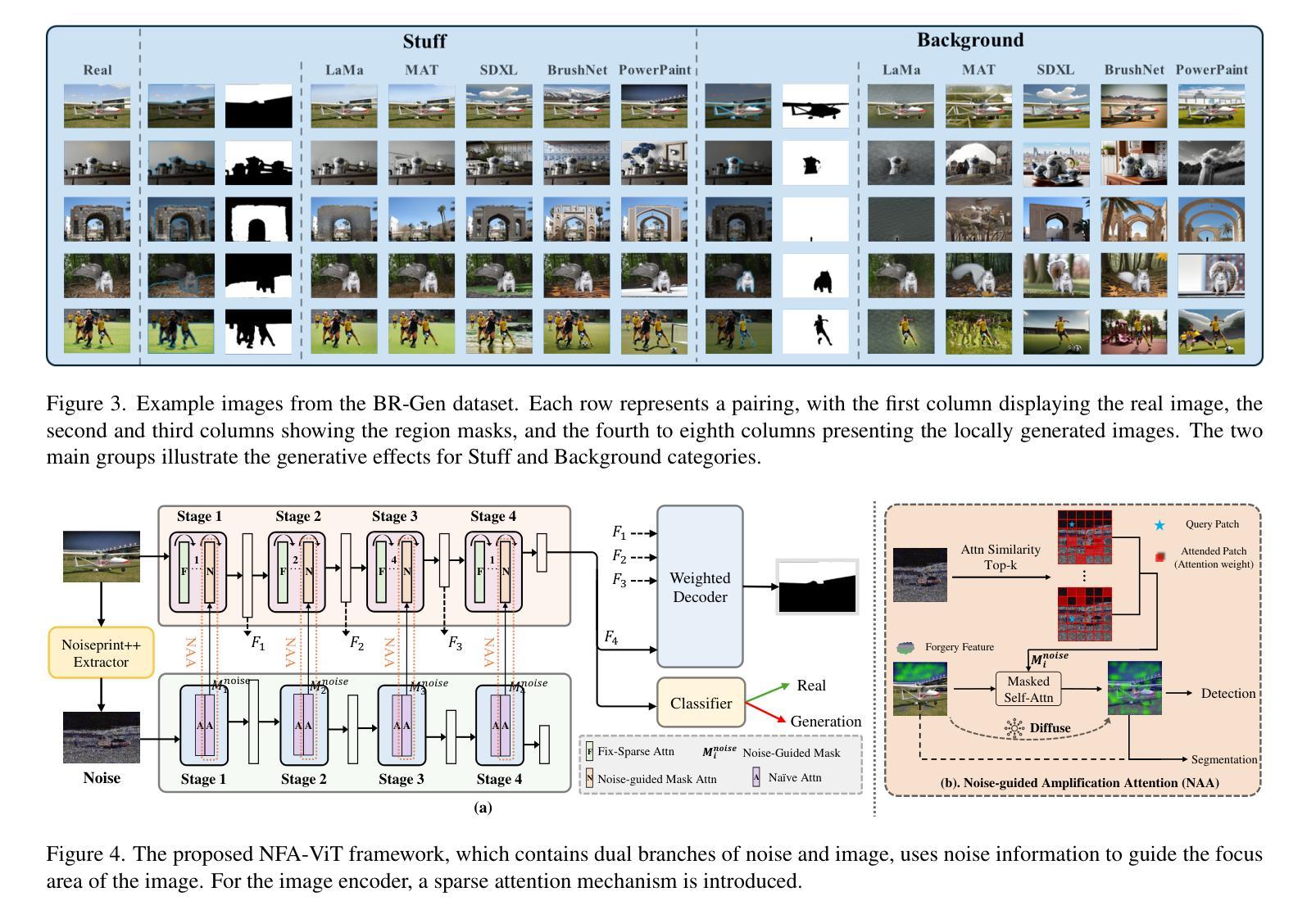
Zooming In on Fakes: A Novel Dataset for Localized AI-Generated Image Detection with Forgery Amplification Approach
Authors:Lvpan Cai, Haowei Wang, Jiayi Ji, YanShu ZhouMen, Yiwei Ma, Xiaoshuai Sun, Liujuan Cao, Rongrong Ji
The rise of AI-generated image editing tools has made localized forgeries increasingly realistic, posing challenges for visual content integrity. Although recent efforts have explored localized AIGC detection, existing datasets predominantly focus on object-level forgeries while overlooking broader scene edits in regions such as sky or ground. To address these limitations, we introduce \textbf{BR-Gen}, a large-scale dataset of 150,000 locally forged images with diverse scene-aware annotations, which are based on semantic calibration to ensure high-quality samples. BR-Gen is constructed through a fully automated Perception-Creation-Evaluation pipeline to ensure semantic coherence and visual realism. In addition, we further propose \textbf{NFA-ViT}, a Noise-guided Forgery Amplification Vision Transformer that enhances the detection of localized forgeries by amplifying forgery-related features across the entire image. NFA-ViT mines heterogeneous regions in images, \emph{i.e.}, potential edited areas, by noise fingerprints. Subsequently, attention mechanism is introduced to compel the interaction between normal and abnormal features, thereby propagating the generalization traces throughout the entire image, allowing subtle forgeries to influence a broader context and improving overall detection robustness. Extensive experiments demonstrate that BR-Gen constructs entirely new scenarios that are not covered by existing methods. Take a step further, NFA-ViT outperforms existing methods on BR-Gen and generalizes well across current benchmarks. All data and codes are available at https://github.com/clpbc/BR-Gen.
人工智能生成的图像编辑工具的兴起使得局部伪造越来越逼真,给视觉内容完整性带来了挑战。尽管最近的努力已经探索了局部AIGC检测,但现有数据集主要集中在对象级别的伪造,而忽略了天空或地面等区域的更广泛的场景编辑。为了解决这些局限性,我们引入了BR-Gen,这是一个包含15万张局部伪造图像的大规模数据集,具有基于语义校准的多样化场景感知注释,以确保高质量样本。BR-Gen通过全自动的感知-创建-评估流程构建,以确保语义连贯和视觉真实性。此外,我们进一步提出了NFA-ViT,一种噪声引导的伪造放大视觉转换器,通过放大整个图像中的伪造相关特征,增强局部伪造的检测。NFA-ViT通过噪声指纹挖掘图像中的异质区域,即潜在编辑区域。随后,引入注意力机制来促使正常和异常特征之间的交互,从而在整幅图像中传播泛化痕迹,使细微的伪造能够影响更广泛的上下文,提高整体检测稳健性。大量实验表明,BR-Gen构建的场景完全超越了现有方法的覆盖范围。更进一步的是,NFA-ViT在BR-Gen上的表现优于现有方法,并在当前基准测试中具有良好的泛化能力。所有数据和代码可在https://github.com/clpbc/BR-Gen找到。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
本文介绍了AI生成图像编辑工具的兴起带来的局部篡改挑战。针对现有数据集主要关注对象级篡改,而忽视天空或地面等更广场景编辑的问题,提出了BR-Gen大型本地化伪造图像数据集。该数据集通过全自动的感知-创建-评估流程构建,确保语义连贯和视觉真实性。此外,还提出了NFA-ViT噪声引导伪造放大视觉转换器,通过放大伪造相关特征,增强局部篡改的检测能力。实验表明,BR-Gen数据集开创了全新场景,NFA-ViT在BR-Gen上的表现优于现有方法,并在当前基准测试中具有良好的泛化能力。
Key Takeaways
- AI生成的图像编辑工具使得局部伪造越来越逼真,对视觉内容完整性构成挑战。
- 现有数据集主要关注对象级伪造,而忽视更广泛的场景编辑,如天空或地面。
- 引入BR-Gen大型本地化伪造图像数据集,通过全自动流程构建,确保语义连贯和视觉真实性。
- 提出NFA-ViT噪声引导伪造放大视觉转换器,增强局部篡改检测能力。
- NFA-ViT通过放大伪造相关特征,挖掘图像中的异质区域,引入注意力机制来增强正常与异常特征间的交互。
- NFA-ViT能在细微篡改中影响更广泛的上下文,提高检测稳健性。
点此查看论文截图

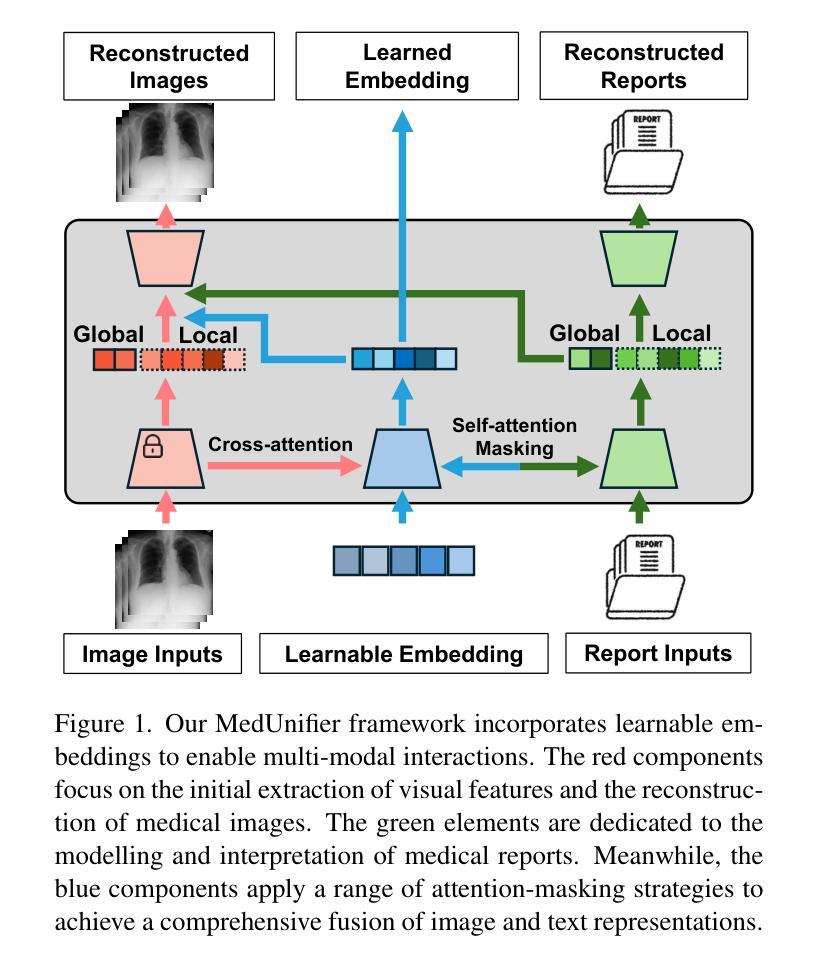
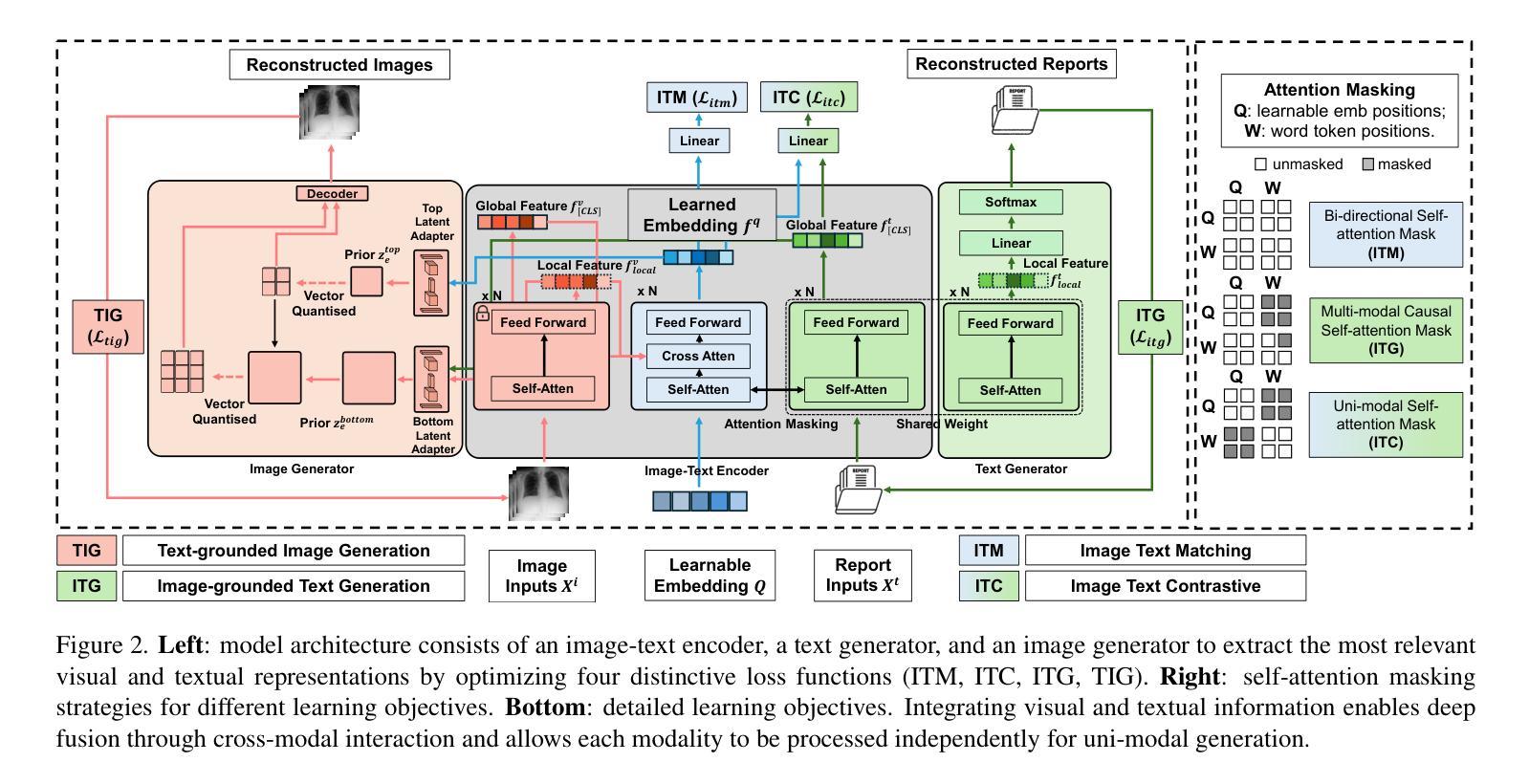
MedUnifier: Unifying Vision-and-Language Pre-training on Medical Data with Vision Generation Task using Discrete Visual Representations
Authors:Ziyang Zhang, Yang Yu, Yucheng Chen, Xulei Yang, Si Yong Yeo
Despite significant progress in Vision-Language Pre-training (VLP), current approaches predominantly emphasize feature extraction and cross-modal comprehension, with limited attention to generating or transforming visual content. This gap hinders the model’s ability to synthesize coherent and novel visual representations from textual prompts, thereby reducing the effectiveness of multi-modal learning. In this work, we propose MedUnifier, a unified VLP framework tailored for medical data. MedUnifier seamlessly integrates text-grounded image generation capabilities with multi-modal learning strategies, including image-text contrastive alignment, image-text matching and image-grounded text generation. Unlike traditional methods that reply on continuous visual representations, our approach employs visual vector quantization, which not only facilitates a more cohesive learning strategy for cross-modal understanding but also enhances multi-modal generation quality by effectively leveraging discrete representations. Our framework’s effectiveness is evidenced by the experiments on established benchmarks, including uni-modal tasks (supervised fine-tuning), cross-modal tasks (image-text retrieval and zero-shot image classification), and multi-modal tasks (medical report generation, image synthesis), where it achieves state-of-the-art performance across various tasks. MedUnifier also offers a highly adaptable tool for a wide range of language and vision tasks in healthcare, marking advancement toward the development of a generalizable AI model for medical applications.
尽管视觉语言预训练(VLP)取得了显著进展,但当前的方法主要侧重于特征提取和跨模态理解,对生成或转换视觉内容的关注有限。这一差距阻碍了模型从文本提示中合成连贯且新颖的视觉表示的能力,从而降低了多模态学习的有效性。在此工作中,我们提出了针对医疗数据的统一VLP框架MedUnifier。MedUnifier无缝集成了基于文本的图像生成能力与多模态学习策略,包括图像文本对比对齐、图像文本匹配和基于图像的文本生成。不同于传统方法依赖连续视觉表示,我们的方法采用视觉向量量化,这不仅有助于更连贯的跨模态理解学习策略,而且通过有效利用离散表示提高了多模态生成质量。我们的框架在既定基准测试上的实验证明了其有效性,包括单模态任务(监督微调)、跨模态任务(图像文本检索和零样本图像分类)和多模态任务(医学报告生成、图像合成)。它在各种任务上实现了最先进的性能。MedUnifier还为医疗领域的广泛语言和视觉任务提供了高度适应的工具,标志着在开发用于医学应用的可推广人工智能模型方面取得了进展。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF To be pubilshed in CVPR 2025
Summary
本文提出了一种针对医疗数据的统一视觉语言预训练框架MedUnifier。该框架融合了文本驱动图像生成能力与多模态学习策略,包括图像文本对比对齐、图像文本匹配和图像驱动文本生成。与传统的连续视觉表示方法不同,MedUnifier采用视觉向量量化技术,既提升了跨模态理解的整合学习策略,又通过有效运用离散表示提高了多模态生成质量。在多个基准测试上,MedUnifier实现了各项任务的卓越性能,包括单模态任务、跨模态任务和多模态任务,并为医疗健康领域提供了广泛适应的语言和视觉任务工具,标志着医疗应用通用人工智能模型的发展进步。
Key Takeaways
- MedUnifier是一个针对医疗数据的统一视觉语言预训练框架。
- 融合了文本驱动图像生成能力与多模态学习策略。
- 框架包含图像文本对比对齐、图像文本匹配和图像驱动文本生成。
- 采用视觉向量量化技术,提升跨模态理解的整合学习策略及多模态生成质量。
- 在多个基准测试中实现卓越性能,包括单模态、跨模态和多模态任务。
- 提供了适应于医疗健康领域广泛语言和视觉任务工具。
点此查看论文截图

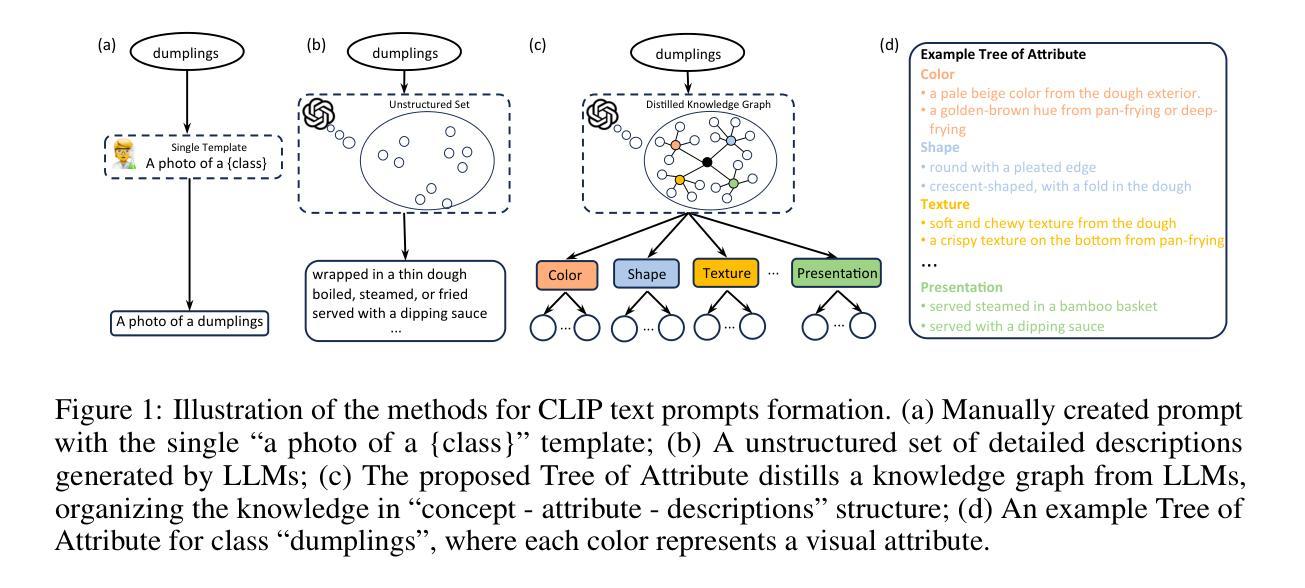
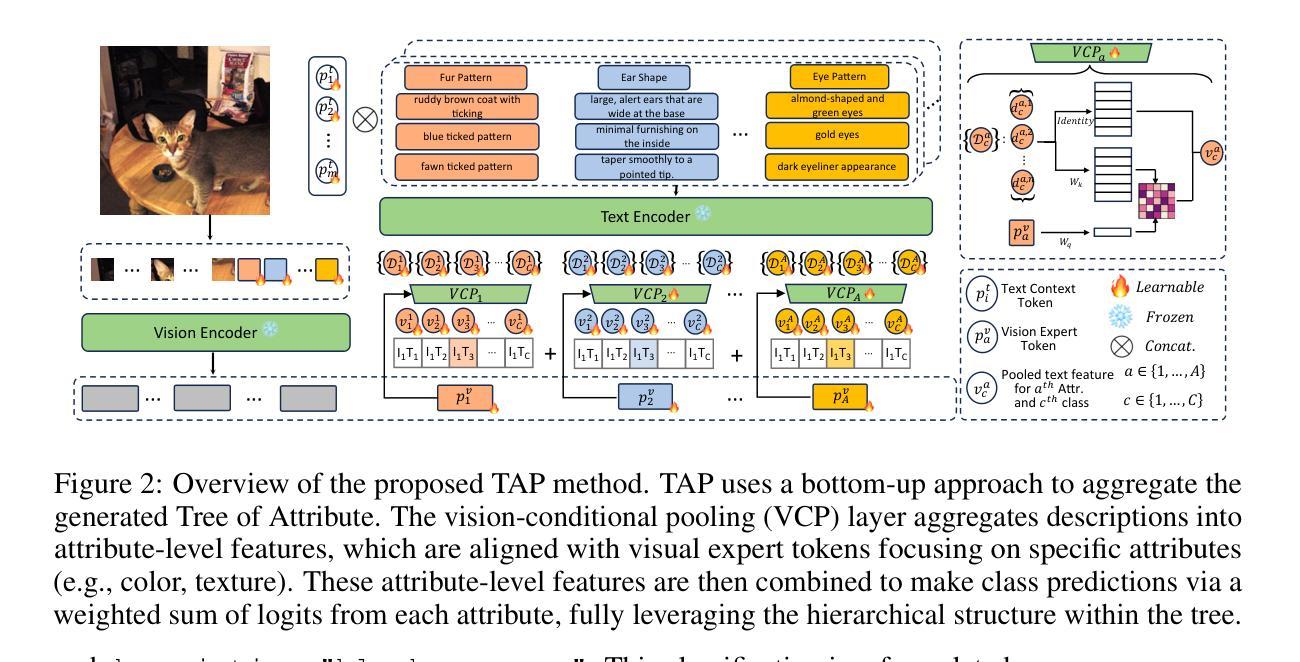
Tree of Attributes Prompt Learning for Vision-Language Models
Authors:Tong Ding, Wanhua Li, Zhongqi Miao, Hanspeter Pfister
Prompt learning has proven effective in adapting vision language models for downstream tasks. However, existing methods usually append learnable prompt tokens solely with the category names to obtain textual features, which fails to fully leverage the rich context indicated in the category name. To address this issue, we propose the Tree of Attributes Prompt learning (TAP), which first instructs LLMs to generate a tree of attributes with a “concept - attribute - description” structure for each category, and then learn the hierarchy with vision and text prompt tokens. Unlike existing methods that merely augment category names with a set of unstructured descriptions, our approach essentially distills structured knowledge graphs associated with class names from LLMs. Furthermore, our approach introduces text and vision prompts designed to explicitly learn the corresponding visual attributes, effectively serving as domain experts. Additionally, the general and diverse descriptions generated based on the class names may be wrong or absent in the specific given images. To address this misalignment, we further introduce a vision-conditional pooling module to extract instance-specific text features. Extensive experimental results demonstrate that our approach outperforms state-of-the-art methods on the zero-shot base-to-novel generalization, cross-dataset transfer, as well as few-shot classification across 11 diverse datasets. Code is available at https://github.com/HHenryD/TAP.
提示学习已证明在适应视觉语言模型以进行下游任务方面非常有效。然而,现有方法通常仅将可学习的提示令牌附加到类别名称上以获得文本特征,这未能充分利用类别名称中指示的丰富上下文。为了解决此问题,我们提出了属性树提示学习(TAP)方法。该方法首先指导大型语言模型为每个类别生成具有“概念-属性-描述”结构的属性树,然后学习与视觉和文本提示令牌对应的层次结构。与仅将类别名称与一组非结构描述相结合的现有方法不同,我们的方法本质上是从大型语言模型中蒸馏出与类名相关的结构化知识图谱。此外,我们的方法引入了用于明确学习相应视觉属性的文本和视觉提示,有效地充当领域专家。基于类名生成的通用且多样的描述在特定给定的图像中可能出错或缺失。为了解决这种不匹配问题,我们进一步引入了一个视觉条件池模块来提取实例特定的文本特征。大量的实验结果证明,我们的方法在零样本基础到新颖的泛化、跨数据集迁移以及在11个不同数据集上的少样本分类方面均优于最先进的方法。代码可访问 https://github.com/HHenryD/TAP。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
本文提出一种名为Tree of Attributes Prompt(TAP)的学习方法,用于改进视觉语言模型的下游任务适应性。TAP通过指导大型语言模型(LLMs)为每个类别生成属性树,形成“概念-属性-描述”的结构,并学习与视觉和文本提示标记的层次结构。相较于仅将类别名称与一系列非结构描述相结合的方法,TAP能提炼与类别名称相关的结构化知识图谱,并引入文本和视觉提示以明确学习相应的视觉属性。同时,为解决特定图像中可能存在的描述错误或缺失问题,引入视觉条件池化模块以提取实例特定的文本特征。实验结果显示,TAP在零样本基础到新颖类别的推广、跨数据集迁移以及在11个不同数据集的少量样本分类任务上均优于现有最先进的方法。
Key Takeaways
- TAP通过生成属性树来丰富类别信息的语境表达。
- TAP利用大型语言模型生成与类别名称相关的结构化知识图谱。
- TAP引入文本和视觉提示来学习视觉属性,类似于领域专家。
- 针对特定图像可能出现的描述错误或缺失,引入视觉条件池化模块。
- TAP在多个数据集上的实验表现优于现有方法,尤其在零样本学习和少量样本分类任务上。
- TAP方法公开可用,相关代码可访问特定链接。
点此查看论文截图

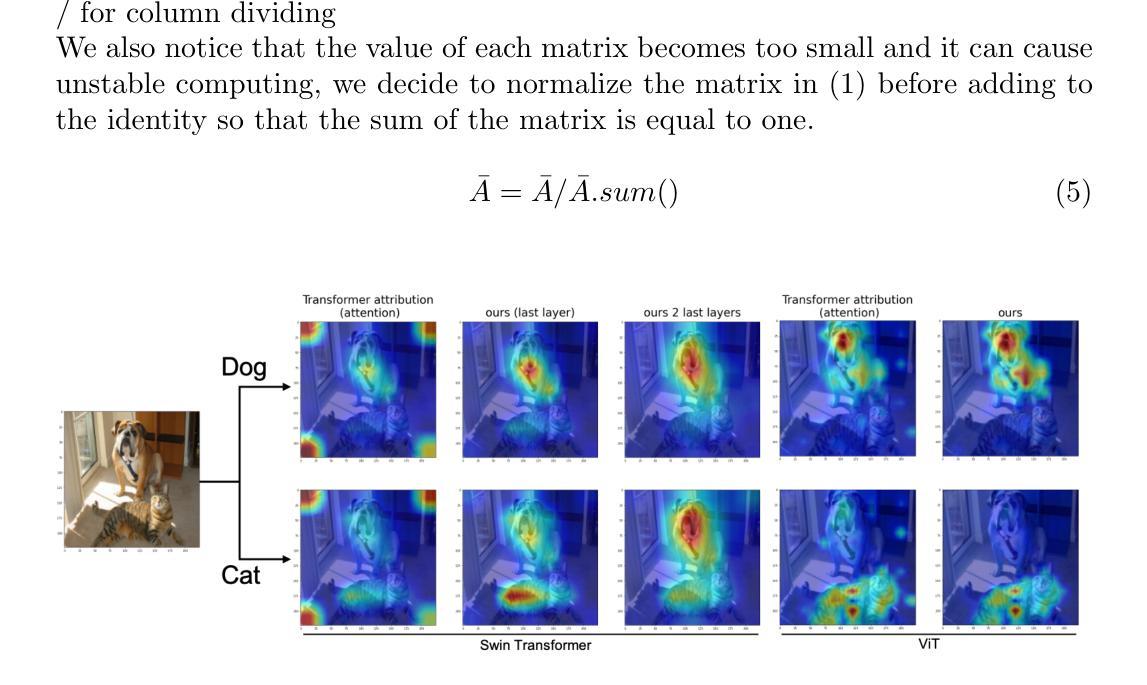
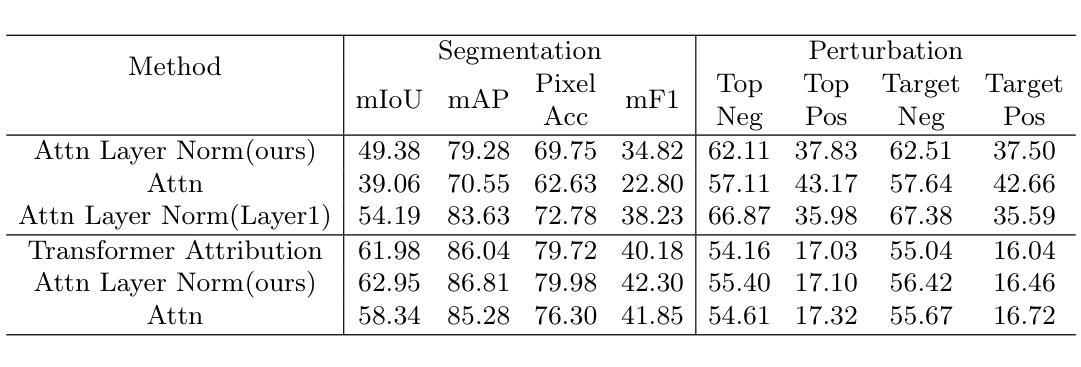
Inspecting Explainability of Transformer Models with Additional Statistical Information
Authors:Hoang C. Nguyen, Haeil Lee, Junmo Kim
Transformer becomes more popular in the vision domain in recent years so there is a need for finding an effective way to interpret the Transformer model by visualizing it. In recent work, Chefer et al. can visualize the Transformer on vision and multi-modal tasks effectively by combining attention layers to show the importance of each image patch. However, when applying to other variants of Transformer such as the Swin Transformer, this method can not focus on the predicted object. Our method, by considering the statistics of tokens in layer normalization layers, shows a great ability to interpret the explainability of Swin Transformer and ViT.
近年来,Transformer在视觉领域越来越受欢迎,因此有必要找到一种通过可视化来解释Transformer模型的有效方法。Chefer等人最近的工作能够通过结合注意力层来展示每个图像块的重要性,从而在视觉和多模态任务上有效地可视化Transformer。然而,当应用于Swin Transformer等其他Transformer变体时,这种方法无法关注预测目标。我们的方法考虑了层归一化层中token的统计信息,展示了极高的解释性能力,能够解释Swin Transformer和ViT的可解释性。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF Accepted at Responsible Computer Vision workshop at ECCV 2022
Summary
近期Transformer在视觉领域越来越受欢迎,因此亟需找到一种有效的可视化解释方法。Chefer等人通过将注意力层相结合,展示了一种适用于视觉和多模态任务的Transformer可视化方法。但应用到其他变种如Swin Transformer时,该方法无法关注预测目标。而我们的方法则通过考虑层归一化层中的token统计,展现出强大的Swin Transformer和ViT的可解释性。
Key Takeaways
- Transformer模型在视觉领域受到广泛关注。
- 可视化解释方法对于理解Transformer模型至关重要。
- Chefer等人的方法适用于视觉和多模态任务的Transformer可视化。
- 当应用于Swin Transformer等变体时,现有方法可能无法关注预测目标。
- 提出了一种新的方法,通过考虑层归一化层中的token统计来解释Swin Transformer和ViT。
- 该新方法具有强大的可解释性能力。
点此查看论文截图

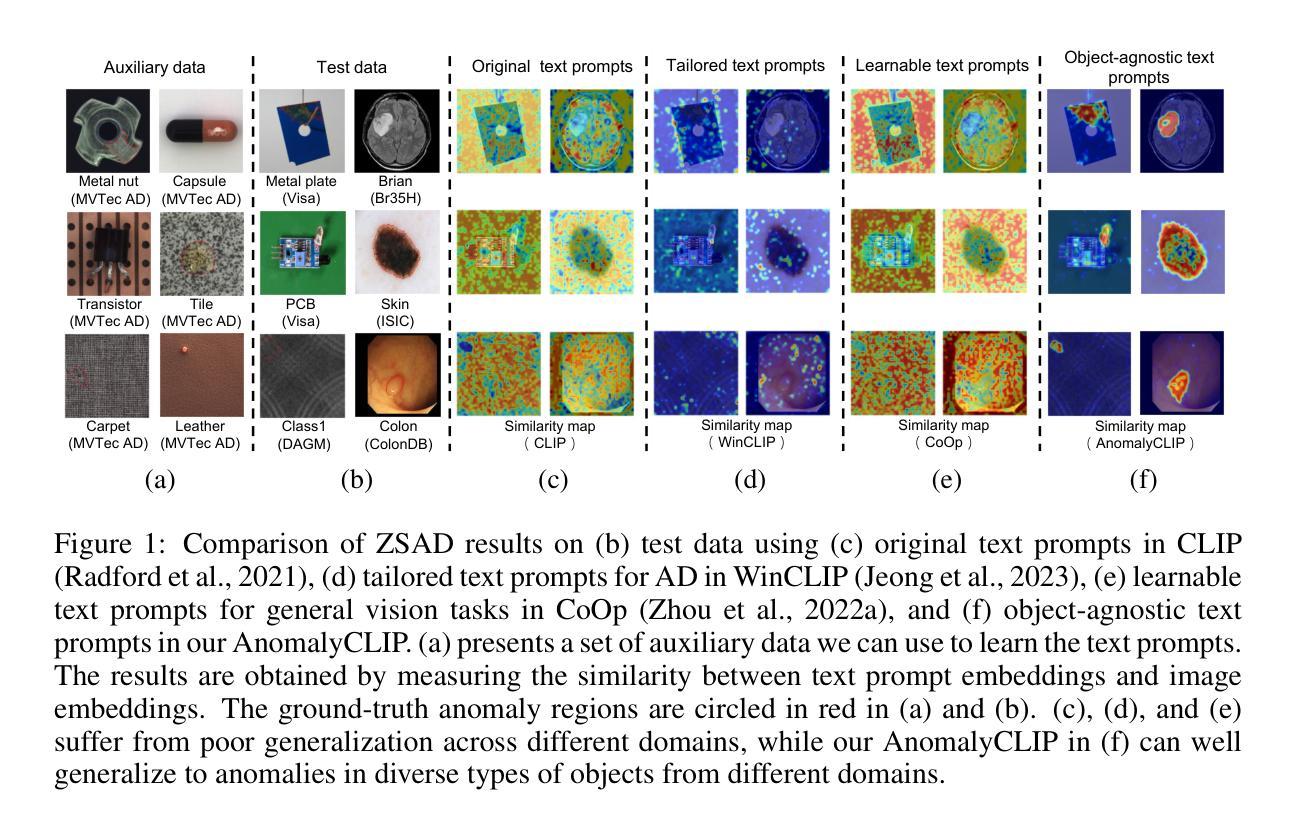
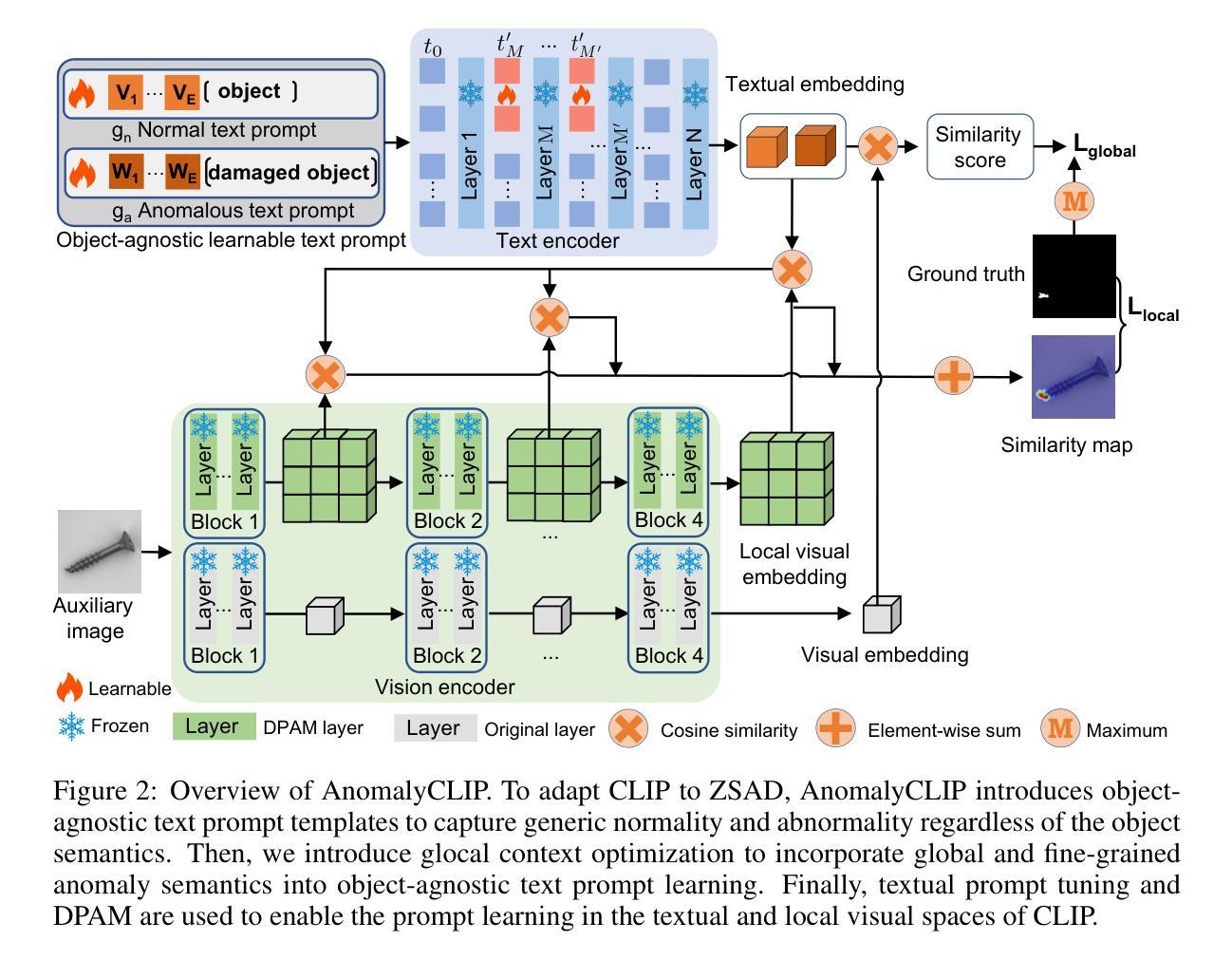
AnomalyCLIP: Object-agnostic Prompt Learning for Zero-shot Anomaly Detection
Authors:Qihang Zhou, Guansong Pang, Yu Tian, Shibo He, Jiming Chen
Zero-shot anomaly detection (ZSAD) requires detection models trained using auxiliary data to detect anomalies without any training sample in a target dataset. It is a crucial task when training data is not accessible due to various concerns, eg, data privacy, yet it is challenging since the models need to generalize to anomalies across different domains where the appearance of foreground objects, abnormal regions, and background features, such as defects/tumors on different products/organs, can vary significantly. Recently large pre-trained vision-language models (VLMs), such as CLIP, have demonstrated strong zero-shot recognition ability in various vision tasks, including anomaly detection. However, their ZSAD performance is weak since the VLMs focus more on modeling the class semantics of the foreground objects rather than the abnormality/normality in the images. In this paper we introduce a novel approach, namely AnomalyCLIP, to adapt CLIP for accurate ZSAD across different domains. The key insight of AnomalyCLIP is to learn object-agnostic text prompts that capture generic normality and abnormality in an image regardless of its foreground objects. This allows our model to focus on the abnormal image regions rather than the object semantics, enabling generalized normality and abnormality recognition on diverse types of objects. Large-scale experiments on 17 real-world anomaly detection datasets show that AnomalyCLIP achieves superior zero-shot performance of detecting and segmenting anomalies in datasets of highly diverse class semantics from various defect inspection and medical imaging domains. Code will be made available at https://github.com/zqhang/AnomalyCLIP.
零样本异常检测(ZSAD)要求使用辅助数据训练的检测模型能够在目标数据集中无需任何训练样本即可检测异常值。当由于各种原因无法获取训练数据时,这是一项至关重要的任务,例如数据隐私。然而,由于模型需要泛化到不同领域的异常值,因此面临巨大挑战,在这些领域中,前景对象、异常区域和背景特征(如在不同产品/器官上的缺陷/肿瘤)的外观可能会有很大差异。最近的大型预训练视觉语言模型(VLMs),如CLIP,在各种视觉任务中表现出了强大的零样本识别能力,包括异常检测。然而,它们在ZSAD方面的表现较弱,因为VLMs更侧重于对前景对象的类别语义进行建模,而不是图像中的异常/正常情况。在本文中,我们介绍了一种新方法,即AnomalyCLIP,该方法旨在使CLIP适应跨不同领域的准确ZSAD。AnomalyCLIP的关键在于学习对象无关的文本提示,这些提示可以捕获图像中的通用正常和异常情况,而无论其前景对象如何。这使得我们的模型能够关注异常图像区域,而不是对象语义,从而实现对各种对象类型的通用正常和异常识别。在17个真实世界的异常检测数据集上进行的大规模实验表明,AnomalyCLIP在来自各种缺陷检测和医学影像领域的具有各种类别语义的数据集上实现了出色的零样本检测异常值性能。相关代码将在https://github.com/zqhang/AnomalyCLIP上发布。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF Accepted by ICLR 2024
Summary
本文介绍了一种基于CLIP模型改进的AnomalyCLIP方法,用于零样本异常检测(ZSAD)。该方法通过引入对象无关的文本提示来学习通用的正常性和异常性特征,从而在多种领域实现准确的异常检测。这种方法重点关注异常图像区域,而不是对象语义,从而在各种数据集上实现优异的零样本异常检测和分割性能。其主要优点是可以应用于具有高度多样性的不同对象类型和数据集,展示出在缺陷检测和医学影像领域广泛的应用前景。关键技术的核心是建立基于异常性与正常性的图像分类与检测框架,用于各类物品上的异常病变分析。目前相关代码已上传至GitHub。
Key Takeaways
- AnomalyCLIP是一种基于CLIP模型的零样本异常检测改进方法。
- 它通过引入对象无关的文本提示来学习通用的正常性和异常性特征。
- AnomalyCLIP重点关注图像中的异常区域,而不是对象语义。
- 该方法在多种数据集上实现了优异的零样本异常检测和分割性能。该方法不仅可以在不同类型对象上进行,而且对高度的数据集多样性表现出了优异适用性。本算法展现了极高的灵敏度,对微小病变的识别能力也非常出色。本算法有望在医学影像处理领域得到广泛应用。目前相关代码已上传至GitHub平台供公众查阅与使用。其在无训练样本可用时(如涉及数据隐私等场景)具备极高的实用价值。本算法在处理视频流数据方面也表现出了强大的潜力,特别是在实时监控与实时异常预警的应用场景中。目前学界和产业界都对这类方法表现出了浓厚的兴趣与研究前景。此外,该方法对硬件设备的需求和算法复杂度等关键要素进行了优化处理,使其在真实应用场景中具有更高的实用性和推广价值。此种跨领域的改进模式与方法极有可能在未来的多源融合信息处理技术中发挥着不可或缺的重要作用。这种方法能够处理跨领域的异常情况检测任务。在实际应用中取得了良好的效果,如在生产质量控制、医学影像诊断等领域应用前景广阔。同时,该论文也指出了未来研究方向,包括如何进一步提高模型的泛化能力和鲁棒性等问题值得进一步探讨和研究。例如对多模态数据、多场景融合等领域进行深入研究以提高模型的综合性能与适应能力等。这些研究方向将有助于推动该领域的进一步发展与应用落地。
点此查看论文截图