⚠️ 以下所有内容总结都来自于 大语言模型的能力,如有错误,仅供参考,谨慎使用
🔴 请注意:千万不要用于严肃的学术场景,只能用于论文阅读前的初筛!
💗 如果您觉得我们的项目对您有帮助 ChatPaperFree ,还请您给我们一些鼓励!⭐️ HuggingFace免费体验
2025-04-24 更新
Human-Imperceptible Physical Adversarial Attack for NIR Face Recognition Models
Authors:Songyan Xie, Jinghang Wen, Encheng Su, Qiucheng Yu
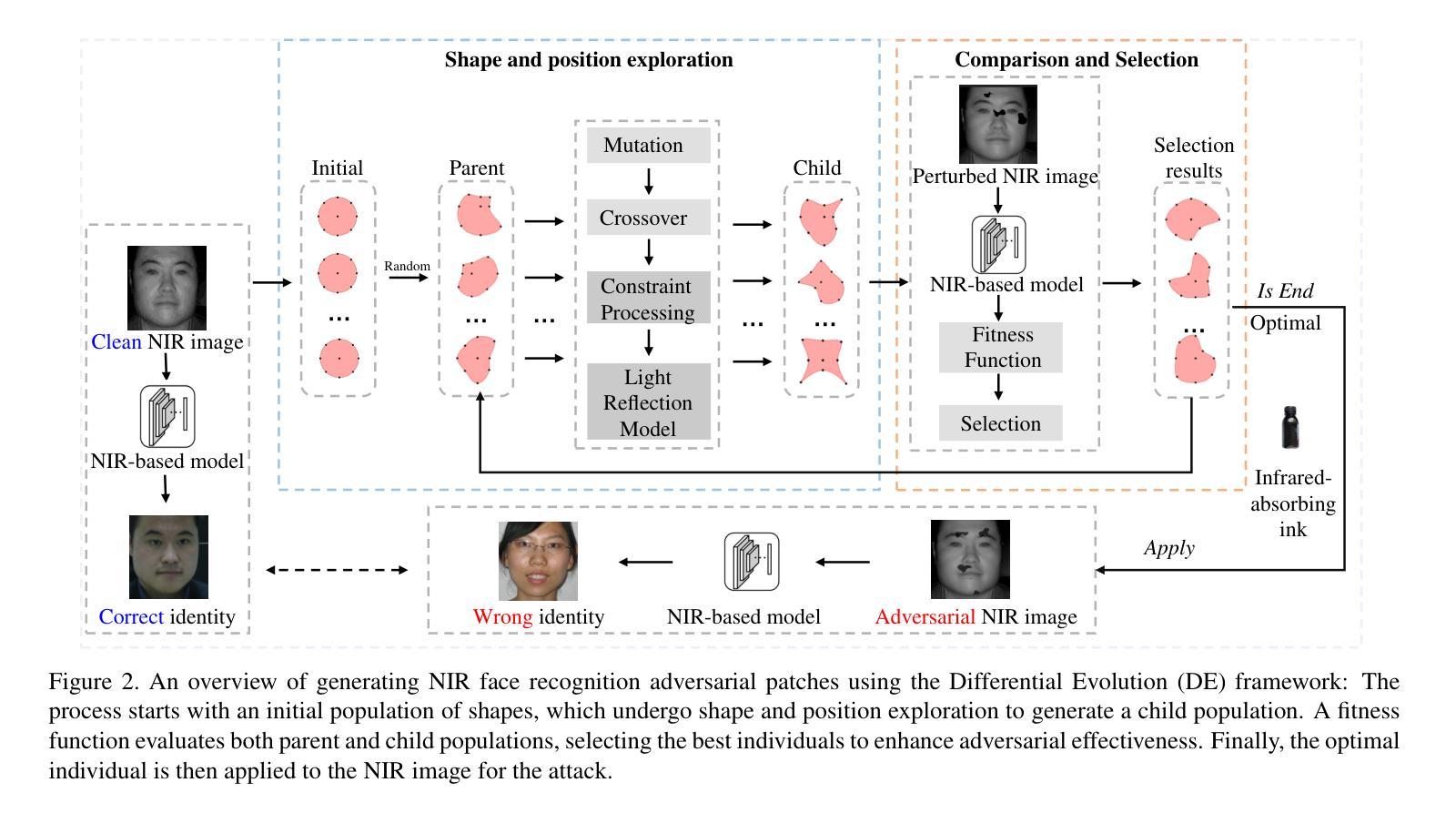
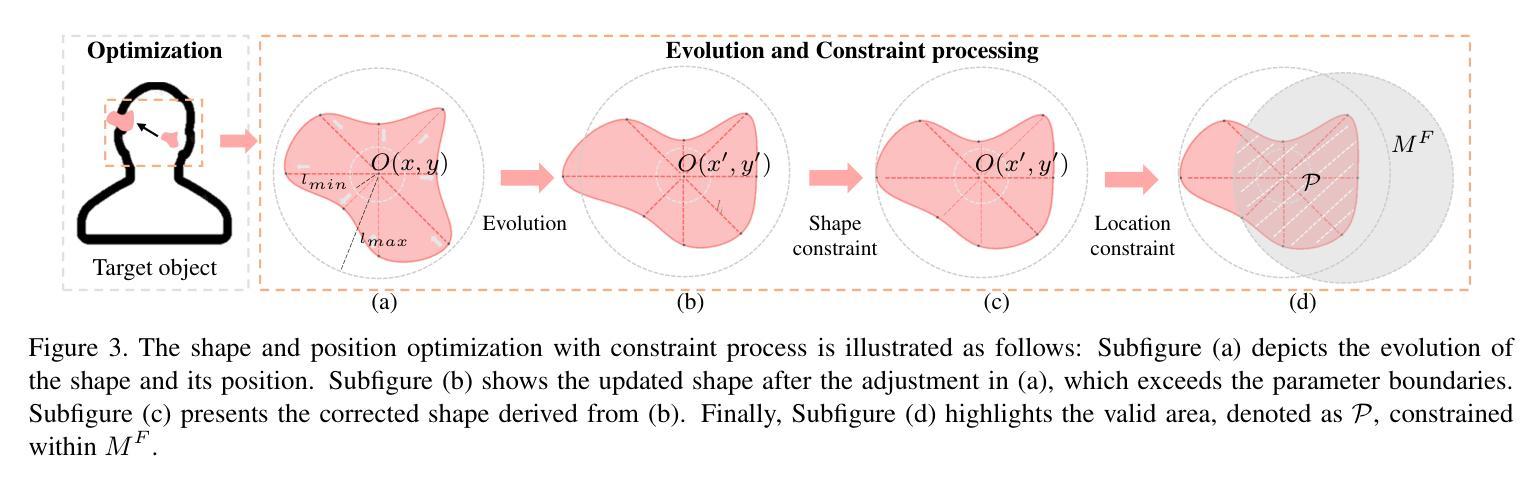
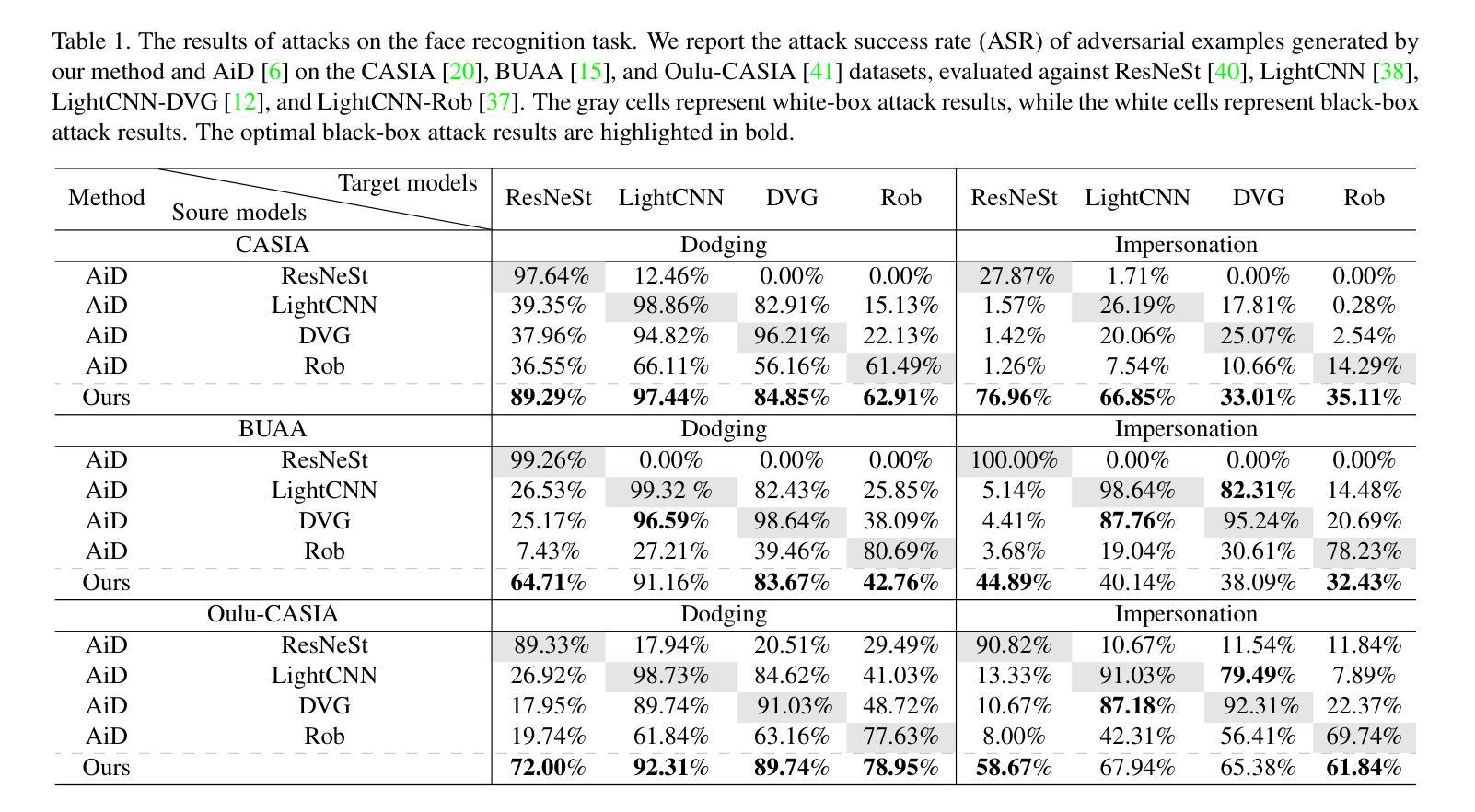
Near-infrared (NIR) face recognition systems, which can operate effectively in low-light conditions or in the presence of makeup, exhibit vulnerabilities when subjected to physical adversarial attacks. To further demonstrate the potential risks in real-world applications, we design a novel, stealthy, and practical adversarial patch to attack NIR face recognition systems in a black-box setting. We achieved this by utilizing human-imperceptible infrared-absorbing ink to generate multiple patches with digitally optimized shapes and positions for infrared images. To address the optimization mismatch between digital and real-world NIR imaging, we develop a light reflection model for human skin to minimize pixel-level discrepancies by simulating NIR light reflection. Compared to state-of-the-art (SOTA) physical attacks on NIR face recognition systems, the experimental results show that our method improves the attack success rate in both digital and physical domains, particularly maintaining effectiveness across various face postures. Notably, the proposed approach outperforms SOTA methods, achieving an average attack success rate of 82.46% in the physical domain across different models, compared to 64.18% for existing methods. The artifact is available at https://anonymous.4open.science/r/Human-imperceptible-adversarial-patch-0703/.
在近红外(NIR)人脸识别系统方面,虽然其在低光照条件或存在化妆的情况下能有效运行,但在面临物理对抗性攻击时却会暴露出其脆弱性。为了进一步展示实际应用中的潜在风险,我们设计了一种新型、隐蔽且实用的对抗性补丁来攻击近红外人脸识别系统,攻击环境设定为黑箱。我们利用人类无法感知的红外吸墨制成具有数字优化形状和位置的多个补丁,以适应红外图像。为了解决数字与真实世界NIR成像之间的优化不匹配问题,我们开发了一种人体皮肤的光反射模型,通过模拟NIR光反射来最小化像素级差异。与最先进的(SOTA)针对近红外人脸识别系统的物理攻击相比,实验结果表明,我们的方法在数字和物理领域都提高了攻击成功率,特别是在处理各种面部姿态时仍能保持有效性。值得注意的是,所提出的方法优于SOTA方法,在不同模型的物理领域平均攻击成功率达到82.46%,而现有方法为64.18%。相关研究成果已上传至[匿名链接地址]。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
近红外人脸识别系统在低光照条件或化妆情况下运行有效,但在面临物理对抗攻击时存在漏洞。研究团队设计了一种新型隐形实用的对抗补丁,用于攻击近红外人脸识别系统。他们使用人类不可察觉的红外吸墨制成多个补丁,并利用数字优化其形状和位置以针对红外图像进行优化攻击效果。该研究开发了一个光反射模型以最小化像素级差异,解决了数字与现实世界中近红外成像的优化不匹配问题。实验结果表明,该方法在数字和物理领域均提高了攻击成功率,并且在不同面部姿态下仍能维持效果。该研究提出的攻击方法平均成功率达到82.46%,高于现有方法的64.18%。
Key Takeaways
- 近红外人脸识别系统在特定条件下存在漏洞,容易受到物理对抗攻击的影响。
- 研究团队设计了一种新型对抗补丁,针对近红外人脸识别系统进行攻击。
- 该补丁利用人类不可察觉的红外吸墨制成,形状和位置针对红外图像进行优化。
- 研究团队开发了一个光反射模型来解决数字与现实世界中近红外成像的优化不匹配问题。
- 实验结果表明,该方法在数字和物理领域的攻击成功率均较高。
- 该方法在不同面部姿态下都能维持攻击效果。
点此查看论文截图