⚠️ 以下所有内容总结都来自于 大语言模型的能力,如有错误,仅供参考,谨慎使用
🔴 请注意:千万不要用于严肃的学术场景,只能用于论文阅读前的初筛!
💗 如果您觉得我们的项目对您有帮助 ChatPaperFree ,还请您给我们一些鼓励!⭐️ HuggingFace免费体验
2025-04-24 更新
Rotational ultrasound and photoacoustic tomography of the human body
Authors:Yang Zhang, Shuai Na, Jonathan J. Russin, Karteekeya Sastry, Li Lin, Junfu Zheng, Yilin Luo, Xin Tong, Yujin An, Peng Hu, Konstantin Maslov, Tze-Woei Tan, Charles Y. Liu, Lihong V. Wang
Imaging the human body’s morphological and angiographic information is essential for diagnosing, monitoring, and treating medical conditions. Ultrasonography performs the morphological assessment of the soft tissue based on acoustic impedance variations, whereas photoacoustic tomography (PAT) can visualize blood vessels based on intrinsic hemoglobin absorption. Three-dimensional (3D) panoramic imaging of the vasculature is generally not practical in conventional ultrasonography with limited field-of-view (FOV) probes, and PAT does not provide sufficient scattering-based soft tissue morphological contrast. Complementing each other, fast panoramic rotational ultrasound tomography (RUST) and PAT are integrated for hybrid rotational ultrasound and photoacoustic tomography (RUS-PAT), which obtains 3D ultrasound structural and PAT angiographic images of the human body quasi-simultaneously. The RUST functionality is achieved in a cost-effective manner using a single-element ultrasonic transducer for ultrasound transmission and rotating arc-shaped arrays for 3D panoramic detection. RUST is superior to conventional ultrasonography, which either has a limited FOV with a linear array or is high-cost with a hemispherical array that requires both transmission and receiving. By switching the acoustic source to a light source, the system is conveniently converted to PAT mode to acquire angiographic images in the same region. Using RUS-PAT, we have successfully imaged the human head, breast, hand, and foot with a 10 cm diameter FOV, submillimeter isotropic resolution, and 10 s imaging time for each modality. The 3D RUS-PAT is a powerful tool for high-speed, 3D, dual-contrast imaging of the human body with potential for rapid clinical translation.
在诊断、监控和治疗医疗状况时,对人体形态和血管造影信息的成像至关重要。超声波检查基于声阻抗变化对软组织进行形态评估,而光声断层扫描(PAT)则能基于血红蛋白的自然吸收来可视化血管。在具有有限视野(FOV)探针的传统超声波检查中,通常无法实现血管的的三维(3D)全景成像,而PAT则不能提供足够的基于散射的软组织形态对比。互为补充的是,快速全景旋转超声断层扫描(RUST)和PAT被整合到混合旋转超声和光声断层扫描(RUS-PAT)中,其几乎同时获得人体的3D超声结构和PAT血管造影图像。通过采用单元素超声换能器进行超声传输和旋转弧形阵列进行3D全景检测的方式,以成本效益的方式实现了RUST功能。RUST优于传统超声波检查,后者要么具有线性阵列的有限视野,要么具有球形阵列的高成本,需要同时传输和接收。通过将声源切换为光源,系统可轻松转换为PAT模式,以在同一区域获取血管造影图像。使用RUS-PAT,我们已成功地对人体的头部、乳房、手和脚进行了成像,具有直径为10厘米的视野、亚毫米级等距分辨率和每种模式的10秒成像时间。三维RUS-PAT是一种强大的工具,用于高速、三维、双对比度的人体成像,具有快速转化为临床应用的潜力。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
融合超声旋转成像与光声断层扫描技术,实现人体三维超声结构和光声血管造影图像准同步获取,提高诊断、监测和治疗效果。
Key Takeaways
- 医学成像在诊断、监测和治疗过程中具有重要作用,包括形态学评估和血管可视化。
- 超声和光声成像技术各具优势,但也存在局限性。
- 融合旋转超声断层扫描(RUST)和光声断层扫描(PAT)技术,形成混合旋转超声和光声断层扫描(RUS-PAT)。
- RUST技术采用单元素超声换能器实现低成本、高效的三维全景检测。
- RUS-PAT能同时获取人体三维超声结构和光声血管造影图像,提高诊断准确性。
- 该技术在人体头部、乳房、手和足部成像中得到成功应用。
点此查看论文截图

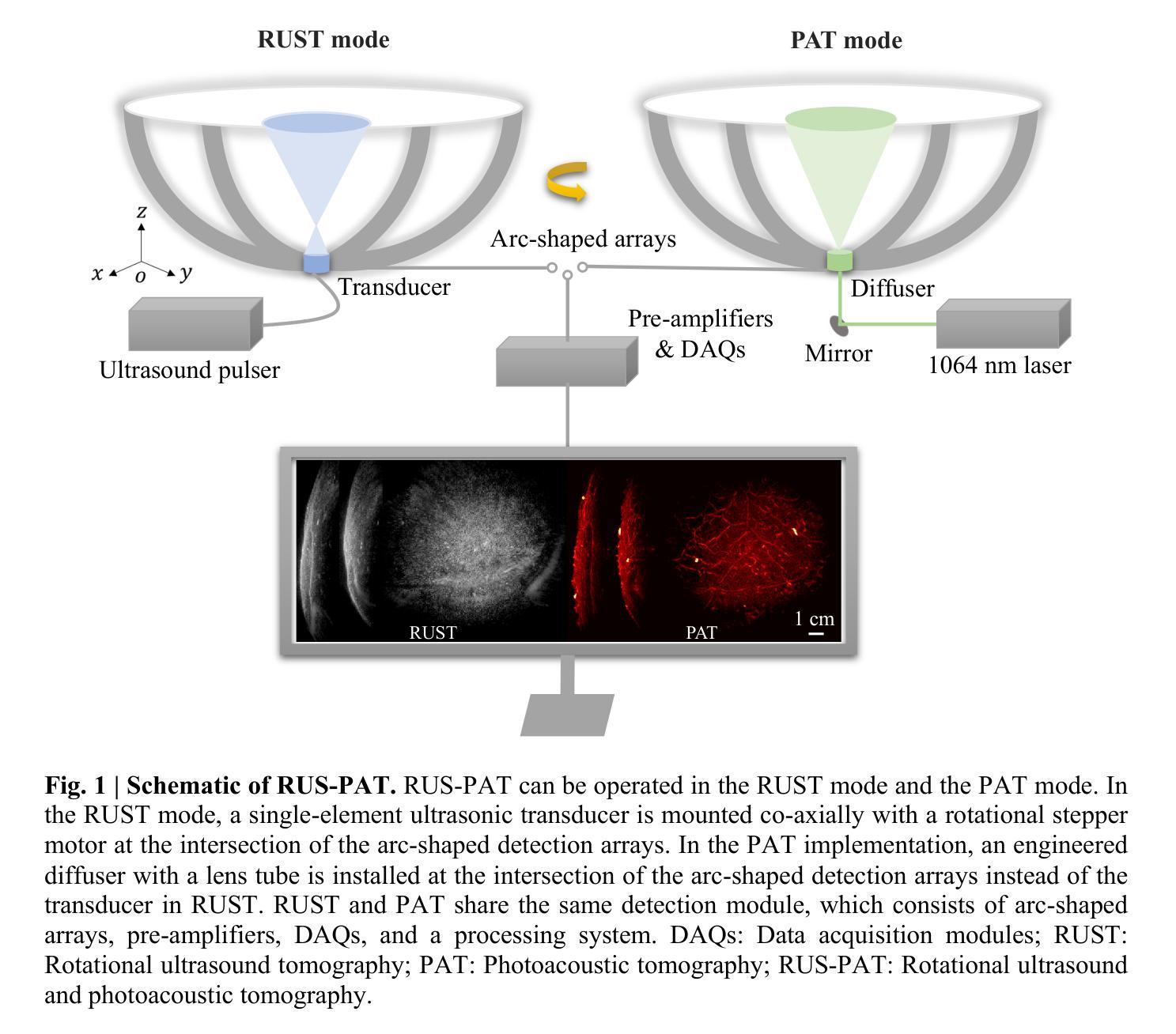
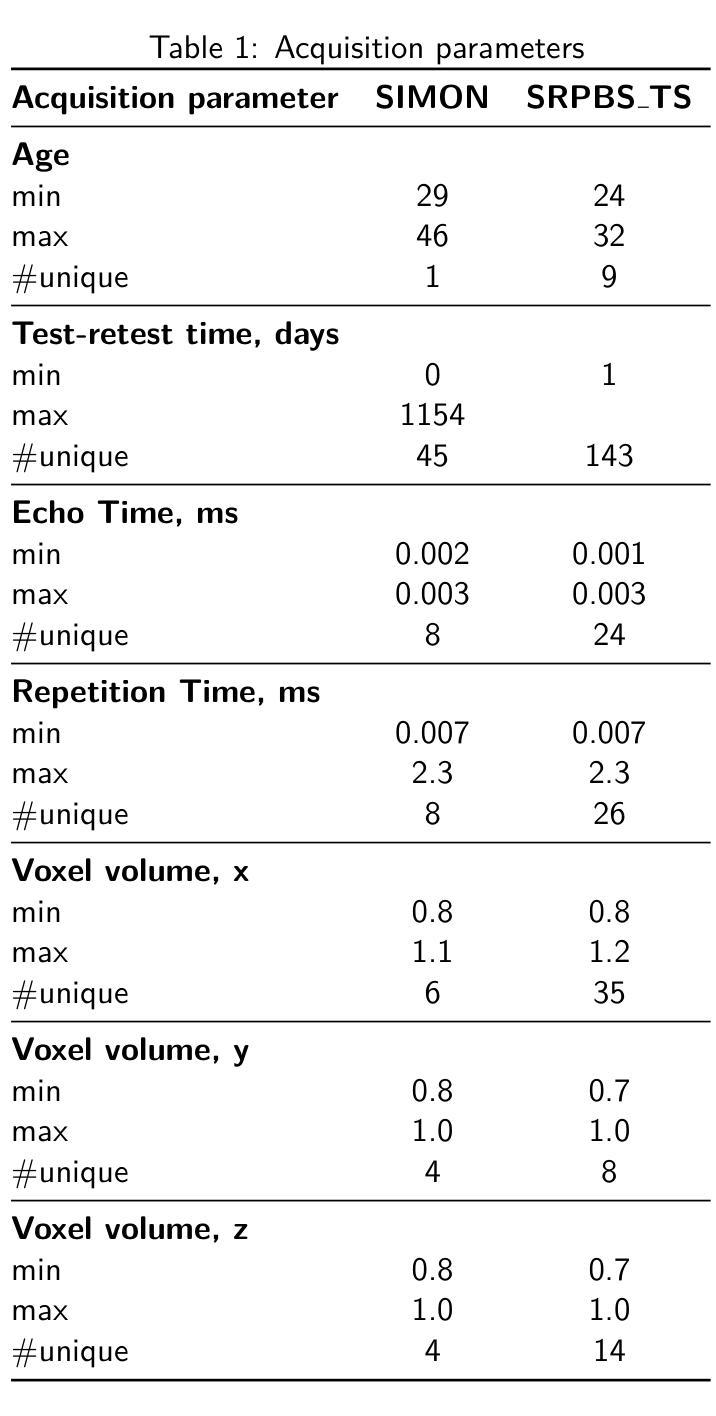
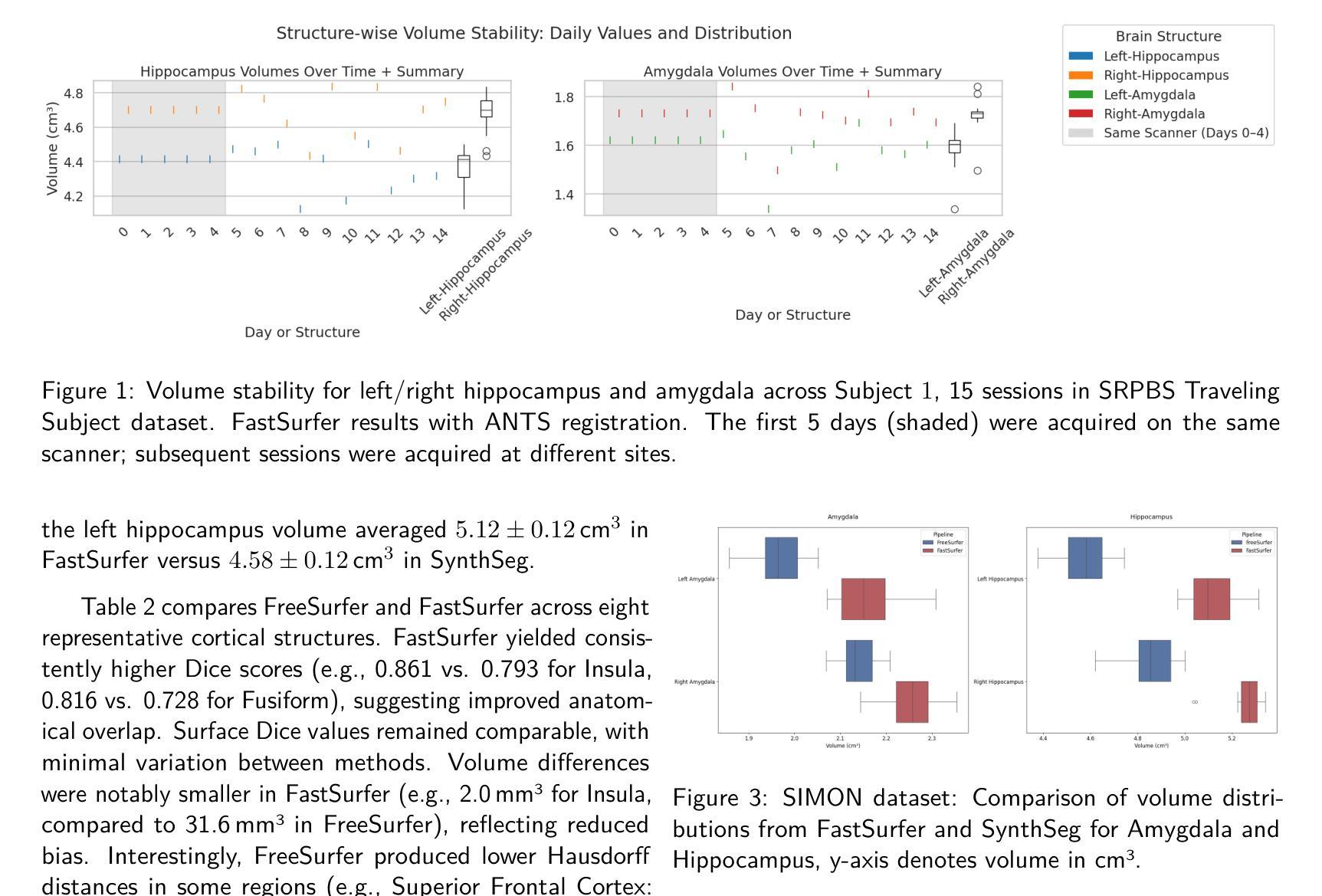
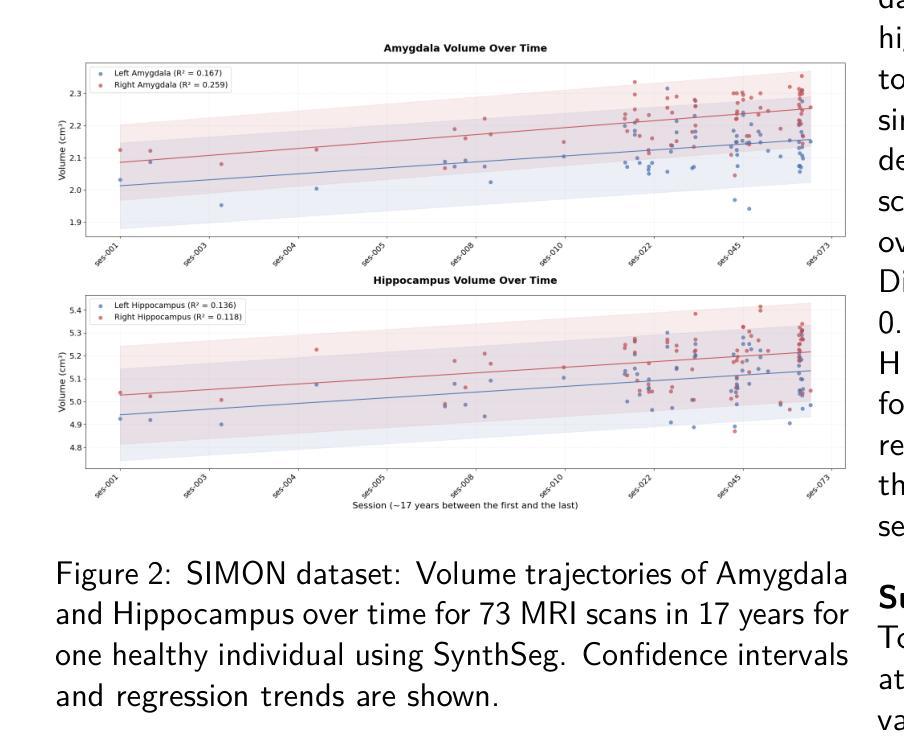
Benchmarking the Reproducibility of Brain MRI Segmentation Across Scanners and Time
Authors:Ekaterina Kondrateva, Sandzhi Barg, Mikhail Vasiliev
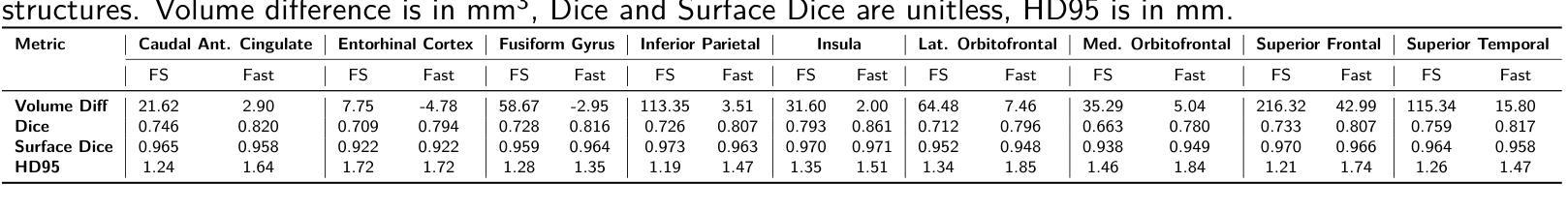
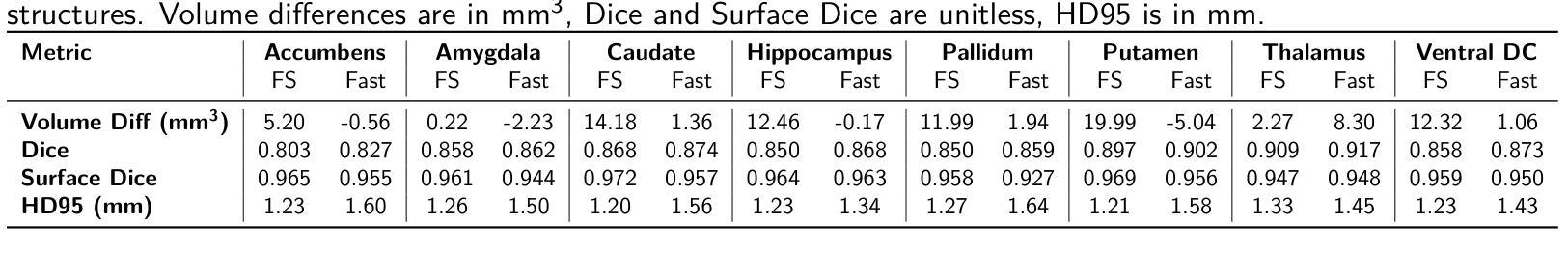
Accurate and reproducible brain morphometry from structural MRI is critical for monitoring neuroanatomical changes across time and across imaging domains. Although deep learning has accelerated segmentation workflows, scanner-induced variability and reproducibility limitations remain-especially in longitudinal and multi-site settings. In this study, we benchmark two modern segmentation pipelines, FastSurfer and SynthSeg, both integrated into FreeSurfer, one of the most widely adopted tools in neuroimaging. Using two complementary datasets - a 17-year longitudinal cohort (SIMON) and a 9-site test-retest cohort (SRPBS)-we quantify inter-scan segmentation variability using Dice coefficient, Surface Dice, Hausdorff Distance (HD95), and Mean Absolute Percentage Error (MAPE). Our results reveal up to 7-8% volume variation in small subcortical structures such as the amygdala and ventral diencephalon, even under controlled test-retest conditions. This raises a key question: is it feasible to detect subtle longitudinal changes on the order of 5-10% in pea-sized brain regions, given the magnitude of domain-induced morphometric noise? We further analyze the effects of registration templates and interpolation modes, and propose surface-based quality filtering to improve segmentation reliability. This study provides a reproducible benchmark for morphometric reproducibility and emphasizes the need for harmonization strategies in real-world neuroimaging studies. Code and figures: https://github.com/kondratevakate/brain-mri-segmentation
从结构磁共振成像(MRI)获取准确且可重复的脑形态测量数据,对于监测随时间以及不同成像领域的神经解剖学变化至关重要。尽管深度学习加速了分割工作流程,但扫描仪引起的可变性和可重复性限制仍然存在,尤其是在纵向和多站点设置中。在这项研究中,我们基准测试了两种集成到神经影像领域最广泛采用工具之一FreeSurfer中的现代分割管道,即FastSurfer和SynthSeg。我们使用两个互补数据集——一个17年的纵向队列(SIMON)和一个9个站点的测试-再测试队列(SRPBS)——通过Dice系数、表面Dice、Hausdorff距离(HD95)和平均绝对百分比误差(MAPE)来量化扫描间分割可变性的大小。我们的结果揭示,即使在受控的测试-再测试条件下,杏仁核和腹侧丘脑等小皮下结构的体积变化率仍高达7-8%。这引发了一个关键问题:考虑到领域引起的形态学噪声的幅度,检测豌豆大小脑区域中5-10%的细微纵向变化是否可行?我们进一步分析了注册模板和插值模式的影响,并提出基于表面的质量过滤方法来提高分割可靠性。这项研究提供了一个可重复的基准测试,用于衡量形态测量的可重复性,并强调在真实世界神经成像研究中需要协调策略。相关代码和图表请访问:https://github.com/kondratevakate/brain-mri-segmentation
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
本文对比评估了FastSurfer和SynthSeg两个基于深度学习的分割管道在结构MRI中的表现,使用了两个数据集进行量化分析。研究发现即使在控制条件下,小亚皮层结构的体积变化率仍高达7-8%。研究强调了提高分割可靠性的必要性,并提出了基于表面的质量过滤方法。此研究为形态测量学的可重复性提供了可复制的基准线,并强调了现实世界中神经影像研究需要统一策略的重要性。
Key Takeaways
- 深度学习方法在脑MRI分割中的应用加速了神经影像分析,但仍存在扫描仪引起的变异性和可重复性问题。
- 使用SIMON和SRPBS两个数据集评估了FastSurfer和SynthSeg两个分割管道的表现。
- 小亚皮层结构的体积变化率高达7-8%,这引发了对检测细微变化的可行性的疑问。
- 形态测量噪声对检测脑区细微变化的影响显著,需要更精细的影像分析技术。
- 研究提出了基于表面的质量过滤方法来提高分割可靠性。
- 此研究为形态测量学的可重复性提供了基准线,强调了统一策略在神经影像研究中的重要性。
点此查看论文截图

Meta-Entity Driven Triplet Mining for Aligning Medical Vision-Language Models
Authors:Saban Ozturk, Melih B. Yilmaz, Muti Kara, M. Talat Yavuz, Aykut Koç, Tolga Çukur
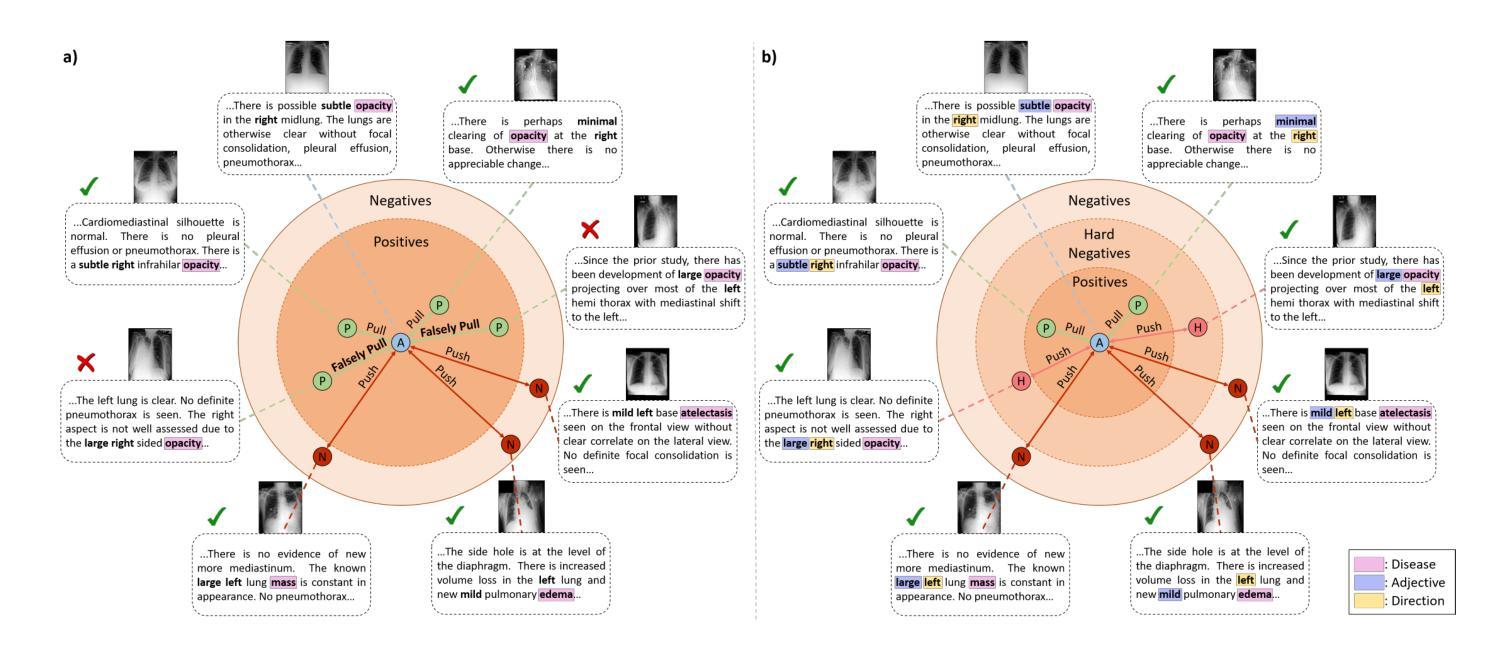
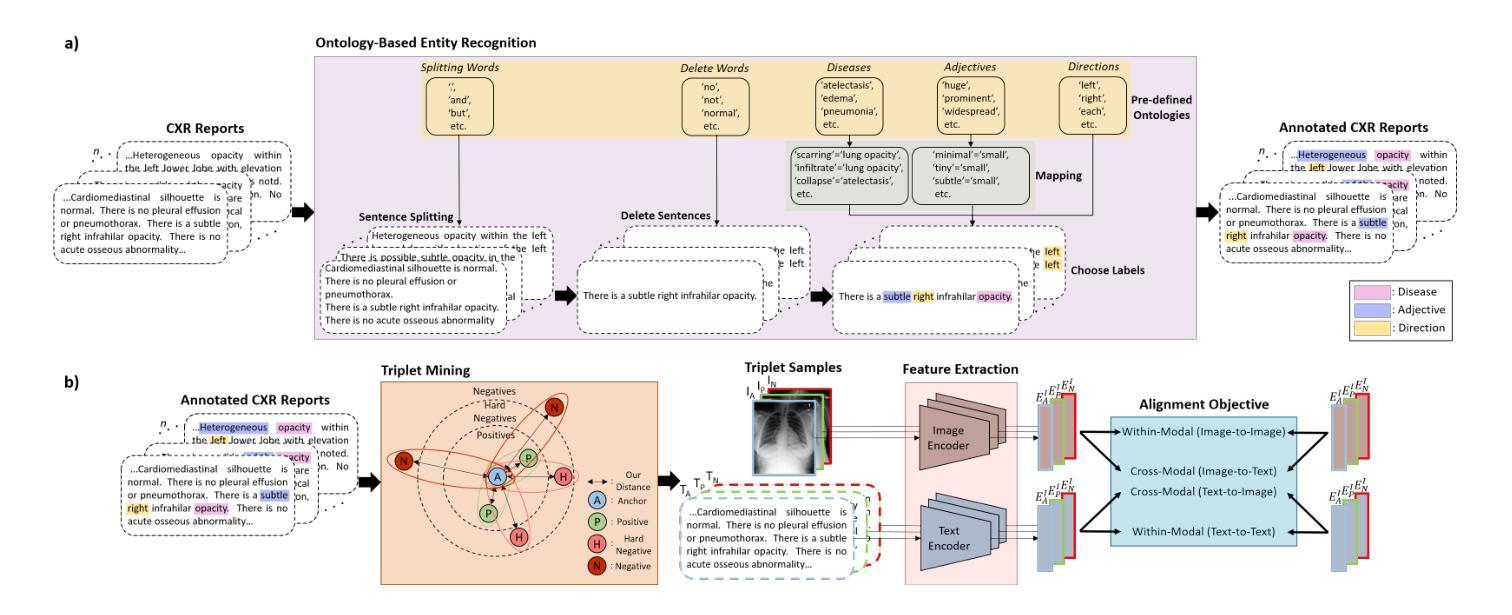
Diagnostic imaging relies on interpreting both images and radiology reports, but the growing data volumes place significant pressure on medical experts, yielding increased errors and workflow backlogs. Medical vision-language models (med-VLMs) have emerged as a powerful framework to efficiently process multimodal imaging data, particularly in chest X-ray (CXR) evaluations, albeit their performance hinges on how well image and text representations are aligned. Existing alignment methods, predominantly based on contrastive learning, prioritize separation between disease classes over segregation of fine-grained pathology attributes like location, size or severity, leading to suboptimal representations. Here, we propose MedTrim (Meta-entity-driven Triplet mining), a novel method that enhances image-text alignment through multimodal triplet learning synergistically guided by disease class as well as adjectival and directional pathology descriptors. Unlike common alignment methods that separate broad disease classes, MedTrim leverages structured meta-entity information to preserve subtle but clinically significant intra-class variations. For this purpose, we first introduce an ontology-based entity recognition module that extracts pathology-specific meta-entities from CXR reports, as annotations on pathology attributes are rare in public datasets. For refined sample selection in triplet mining, we then introduce a novel score function that captures an aggregate measure of inter-sample similarity based on disease classes and adjectival/directional descriptors. Lastly, we introduce a multimodal triplet alignment objective for explicit within- and cross-modal alignment between samples sharing detailed pathology characteristics. Our demonstrations indicate that MedTrim improves performance in downstream retrieval and classification tasks compared to state-of-the-art alignment methods.
诊断成像依赖于对图像和放射学报告的解释,但日益增长的数据量给医学专家带来了巨大的压力,导致了误差增加和工作流程积压。医疗视觉语言模型(med-VLM)作为一个强大的框架,能够有效地处理多模态成像数据,特别是在胸部X射线(CXR)评估中表现出色。然而,其性能的好坏取决于图像和文本表示的对齐程度。现有的对齐方法主要基于对比学习,更侧重于疾病类别之间的区分,而非细微的病理属性(如位置、大小或严重程度)的分离,导致表示不佳。在这里,我们提出了MedTrim(基于元实体驱动的三元组挖掘),这是一种通过多模态三元组学习增强图像文本对齐的新方法,该方法由疾病类别以及形容词和方向性病理描述符协同引导。与常见的仅区分宽泛疾病类别的对齐方法不同,MedTrim利用结构化的元实体信息来保留细微但临床上重要的类内变化。为此,我们首先引入了一个基于本体论的实体识别模块,该模块从CXR报告中提取病理特定的元实体,因为公共数据集中关于病理属性的注释很少见。为了进行精细的样本选择进行三元组挖掘,然后我们引入了一个新的评分函数,该函数基于疾病类别和形容词/方向性描述符来捕获样本间相似性的综合度量。最后,我们引入了多模态三元组对齐目标,用于在具有详细病理特征的样本之间进行明确的内部和跨模态对齐。我们的演示表明,与最新的对齐方法相比,MedTrim在下游检索和分类任务中的性能有所提高。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF 18 pages, 7 figures, 6 tables
摘要
本文关注医疗影像诊断中图像与报告解读的压力问题,提出一种名为MedTrim的新型医疗视觉语言模型(med-VLMs),用于增强图像与文本的对应。该模型通过多模态三元组学习,不仅根据疾病类别,还根据形容词和方向性病理描述进行协同引导,从而提高了图像与文本的匹配度。MedTrim采用基于本体的实体识别模块,从胸X光报告中提取病理特异性元实体,为精细化样本选择引入新型评分函数,以捕捉基于疾病类别和形容词/方向性描述符的样本间相似性。最后,通过下游检索和分类任务演示了MedTrim相较于当前主流对齐方法的性能提升。
关键见解
- 医疗视觉语言模型(med-VLMs)能有效处理多模态成像数据,特别是在胸X光评价中。
- 现有对齐方法主要基于对比学习,更注重疾病类别的分离,忽视了如位置、大小、严重程度等精细病理属性的分离,导致表示不佳。
- MedTrim通过多模态三元组学习,以疾病类别和形容词及方向性病理描述为引导,增强了图像与文本的匹配。
- MedTrim采用基于本体的实体识别模块,从胸X光报告中提取病理特异性元实体,以保留公共数据集中罕见的病理属性注释。
- 为实现精细化样本选择,MedTrim引入了一种新型评分函数,该函数基于疾病类别和形容词/方向性描述符来捕捉样本间的相似性。
- MedTrim通过明确的内部和跨模态对齐目标,优化了共享详细病理特征样本的对齐。
点此查看论文截图

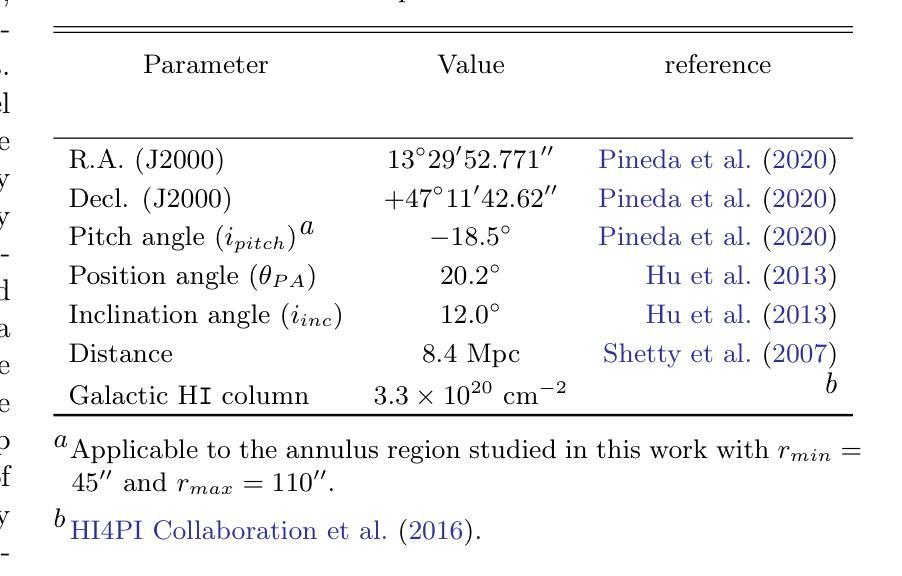
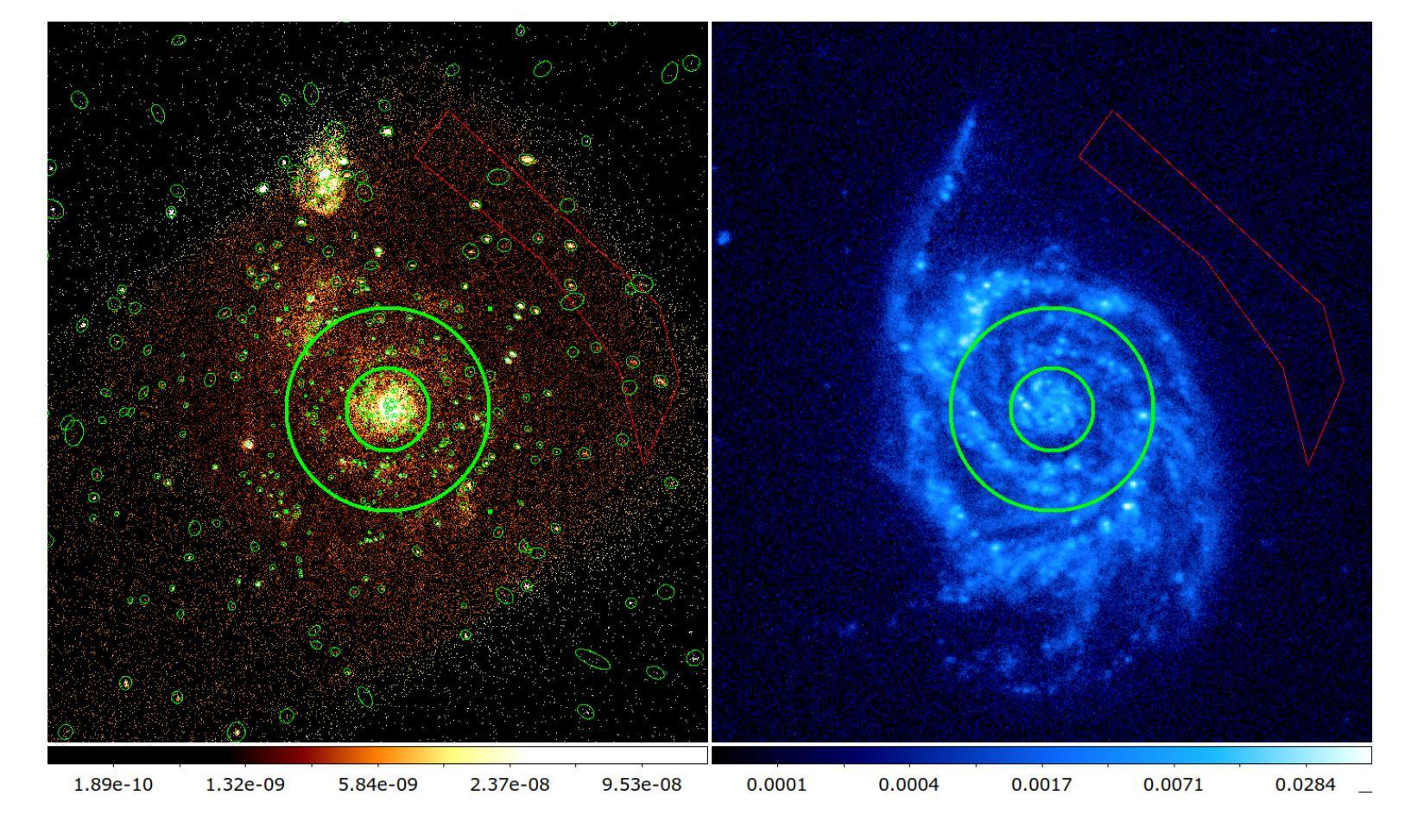
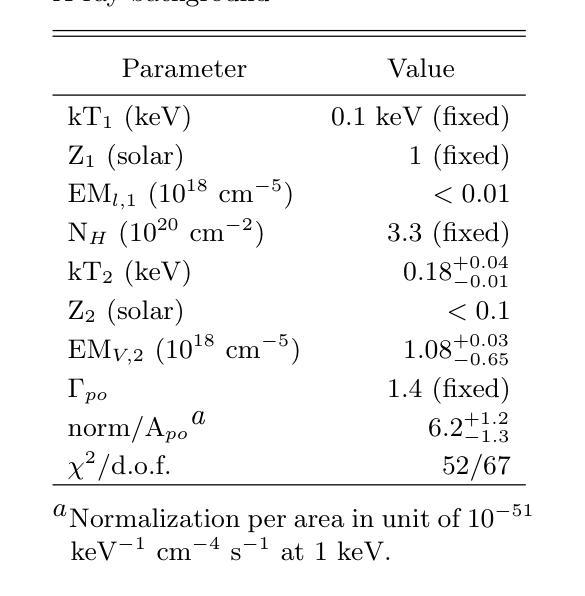
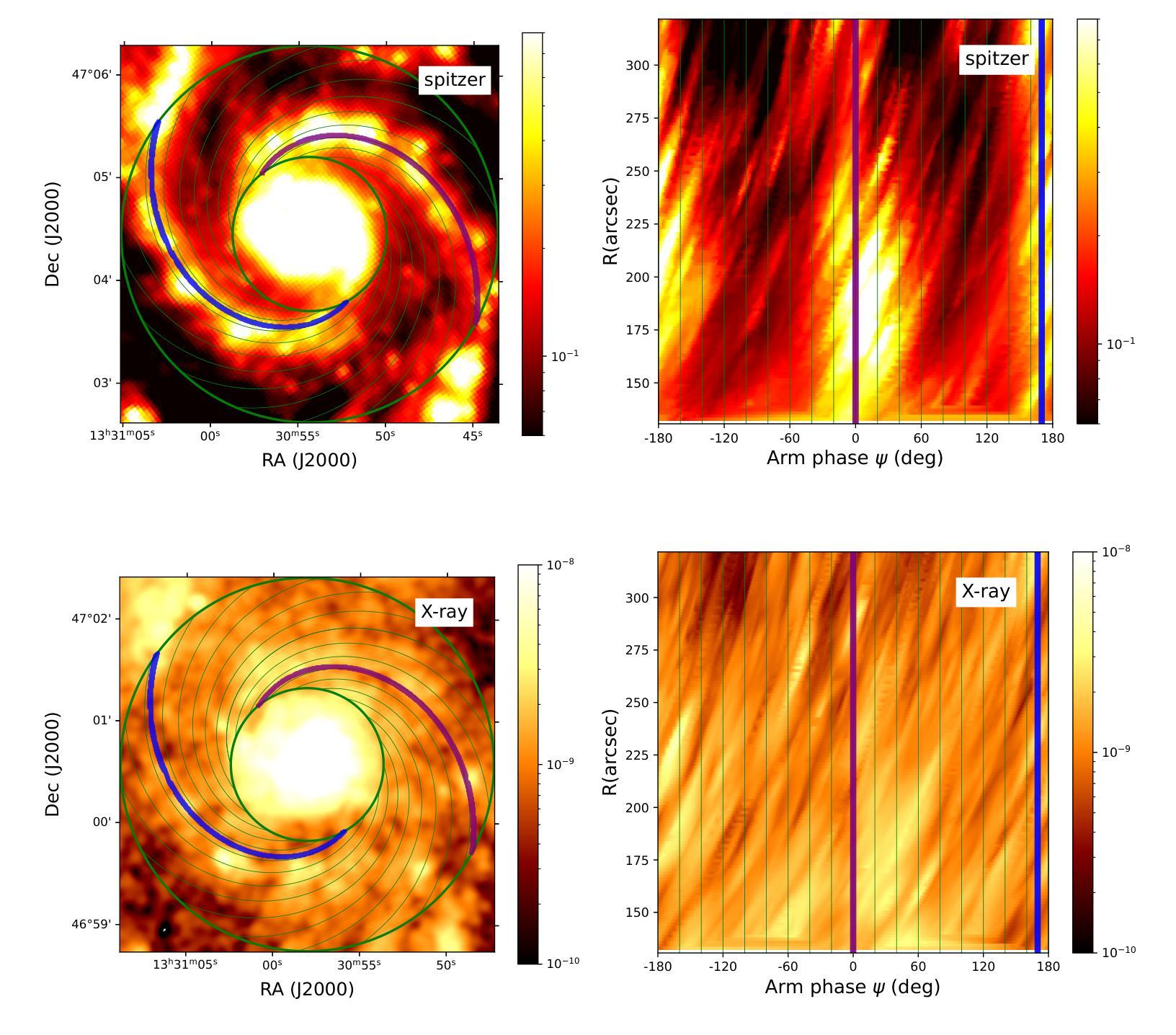
Diffuse X-ray emission in M51: a hierarchical Bayesian spatially-resolved spectral analysis
Authors:Luan Luan, Q. Daniel Wang
X-ray observations can be used to effectively probe the galactic ecosystem, particularly its hot and energetic components. However, existing X-ray studies of nearby star-forming galaxies are limited by insufficient data statistics and a lack of suitable spectral modeling to account for X-ray emission and absorption geometry. We present results from an X-ray spectral study of M51 using 1.3-Ms Chandra data, the most extensive for such a galaxy. This allows the extraction of diffuse X-ray emission spectra from spiral arm phase-dependent regions using a logarithmic spiral coordinate system. A hierarchical Bayesian approach analyzes these spectra, testing models from simple 1-T hot plasma to those including distributed hot plasma and X-ray-absorbing cool gas. We recommend a model fitting the spectra well, featuring a galactic corona with a lognormal temperature distribution and a disk with mixed X-ray emissions and absorption. In this model, only half of the coronal emission is subject to internal absorption. The best-fit absorbing gas column density is roughly twice that inferred from optical extinction of stellar light. The temperature distribution shows a mean temperature of $\sim 0.1$ keV and an average one-dex dispersion that is enhanced on the spiral arms. The corona’s radiative cooling might balance the mechanical energy input from stellar feedback. These results highlight the effectiveness of X-ray mapping of the corona and cool gas in spiral galaxies.
X射线观测可以有效地探测星系生态系统,特别是其高温和高能成分。然而,邻近星系的X射线研究受限于数据统计不足和缺乏合适的光谱模型来解释X射线的发射和吸收几何结构。我们展示了使用最详尽的1.3Ms钱德拉数据对M51进行的X射线光谱研究的结果。这允许使用对数螺旋坐标系从螺旋臂相位依赖的区域中提取出漫射X射线发射光谱。通过分层贝叶斯方法分析这些光谱,测试了从简单的1T热等离子体模型到包含分布式热等离子体和X射线吸收冷气体的模型。我们推荐一个很好地拟合光谱的模型,该模型具有对数正态分布温度的星系冕和混合X射线发射和吸收的磁盘。在此模型中,只有一半的冕发射受到内部吸收的影响。最佳拟合的吸收气体柱密度大约是星光光学消光推断值的两倍。温度分布显示出平均温度为约0.1千电子伏特,平均一标准差的分散度在螺旋臂上有所增强。星系的冕的辐射冷却可能平衡来自恒星反馈的机械能量输入。这些结果强调了X射线映射在星系螺旋臂上的冕和冷气体的有效性。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF 18 pages, 8 figures
Summary
X射线观测可有效探测星系生态系统,特别是其热能和活跃成分。然而,邻近星系形成区的X射线研究受限于数据不足和缺乏合适的光谱模型。本研究使用Chandra数据对M51进行大规模的X射线光谱研究,采用对数螺旋坐标系提取不同螺旋臂区域的弥散X射线发射光谱。通过分层贝叶斯方法分析这些光谱,测试从简单的单温等离子体模型到包含分布式热等离子体和X射线吸收冷气体的模型。推荐一个拟合光谱良好的模型,包含具有对数正态分布温度的星系冕和混合X射线发射和吸收的磁盘。在这个模型中,只有一半的冕发射受到内部吸收影响。最佳拟合吸收气体柱密度大约是星光光学消光所推断的两倍。温度分布显示平均温度为~0.1keV,平均一标准偏差分散度在螺旋臂上增强。星系的冕辐射冷却可能平衡来自恒星反馈的机械能量输入。这些结果强调了X射线映射在螺旋星系中探测冕和冷气体的有效性。
Key Takeaways
- X射线观测是探测星系生态系统,特别是其热能和活跃成分的有效手段。
- 邻近星系的X射线研究受限于数据不足和光谱模型缺乏。
- 对M51的X射线光谱研究表明,其光谱可以通过包含星系冕和混合X射线发射与吸收的模型来很好地拟合。
- 在推荐的模型中,只有一半的星系冕发射受到内部吸收影响。
- 最佳拟合的吸收气体柱密度大约是星光光学消光的两倍。
- 温度分布显示平均温度为~0.1keV,并且温度分散在星系螺旋臂上有所增加。
点此查看论文截图

Designing Optimal Distorted-Octahedra Superlattices for Strong Topological Hall Effect
Authors:Yiyan Fan, Qinghua Zhang, Jingdi Lu, Chuanrui Huo, Tianyang Wang, Qiao Jin, Ting Cui, Qianying Wang, Dongke Rong, Shiqing Deng, Lingfei Wang, Kuijuan Jin, Jun Chen, Er-Jia Guo
Topologically protected spin states hold great promise for applications in next generation of memory circuits and spintronic devices. These intriguing textures typically emerge in bulk materials or heterostructures with broken inversion symmetry, accompanied by an enhanced Dzyaloshinskii-Moriya interaction (DMI). In this study, we successfully induced the topological Hall effect (THE) in atomically designed (DyScO3)n/(SrRuO3)n (DnSn) superlattices over a significant range of temperatures (10120K) and thicknesses (1640nm). Using magnetic force microscopy (MFM), we observed the formation and stability of magnetic domains, such as topological skyrmions. By precisely controlling the interlayer thickness (n) and biaxial strain, we elucidated the mechanisms underlying the modulation and induction of magnetic topological states. Supporting evidence was provided by scanning transmission electron microscopy (STEM) and X-ray absorption spectroscopy (XAS), thereby lending further credence to our conclusions. These heterostructures offer a universal method for exploring topological phenomena driven by distorted octahedra, while enhancing the integrability and addressability of topologically protected functional devices.
拓扑保护的自旋态在下一代内存电路和自旋电子器件的应用中显示出巨大的潜力。这些有趣的纹理通常出现在具有破坏反演对称性的体材料或异质结构中,伴随着增强的Dzyaloshinskii-Moriya相互作用(DMI)。在这项研究中,我们在原子设计的(DyScO3)n/(SrRuO3)n(DnSn)超晶格中,成功诱导了温度范围宽(10~120K)和厚度范围宽(16~40nm)拓扑霍尔效应(THE)。利用磁力显微镜(MFM),我们观察到磁畴的形成和稳定性,如拓扑斯基米翁等。通过精确控制夹层厚度(n)和双轴应变,我们阐明了磁拓扑态调制和诱导的机理。扫描透射电子显微镜(STEM)和X射线吸收光谱(XAS)提供了支持证据,进一步证实了我们的结论。这些异质结构提供了一种探索由扭曲八面体驱动拓扑现象的通用方法,同时提高了拓扑保护功能器件的集成度和可寻址性。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
本文研究了拓扑保护的自旋态在下一代内存电路和自旋电子器件中的应用前景。通过设计(DyScO3)n/(SrRuO3)n(DnSn)超晶格,成功在较宽的温度范围(10120K)和厚度范围(1640nm)内诱导出拓扑霍尔效应。通过磁力显微镜观察到磁畴的形成和稳定性,如拓扑斯基米翁。通过精确控制层间厚度和双向应变,阐明了磁拓扑态的调制和诱导机制。扫描透射电子显微镜和X射线吸收光谱提供了支持证据,进一步证实了结论。这些异质结构为探索由扭曲八面体驱动拓扑现象提供了一种通用方法,同时提高了拓扑保护功能器件的集成度和可寻址性。
Key Takeaways
- 拓扑保护的自旋态在下一代内存电路和自旋电子器件中有广阔应用前景。
- 设计了(DyScO3)n/(SrRuO3)n超晶格,成功在宽温度范围和厚度范围内诱导出拓扑霍尔效应。
- 通过磁力显微镜观察到磁畴的形成和稳定性,如拓扑斯基米翁。
- 通过控制层间厚度和双向应变,阐明了磁拓扑态的调制和诱导机制。
- 扫描透射电子显微镜和X射线吸收光谱为研究结果提供了支持证据。
- 异质结构提供了一种探索由扭曲八面体驱动的拓扑现象的通用方法。
点此查看论文截图

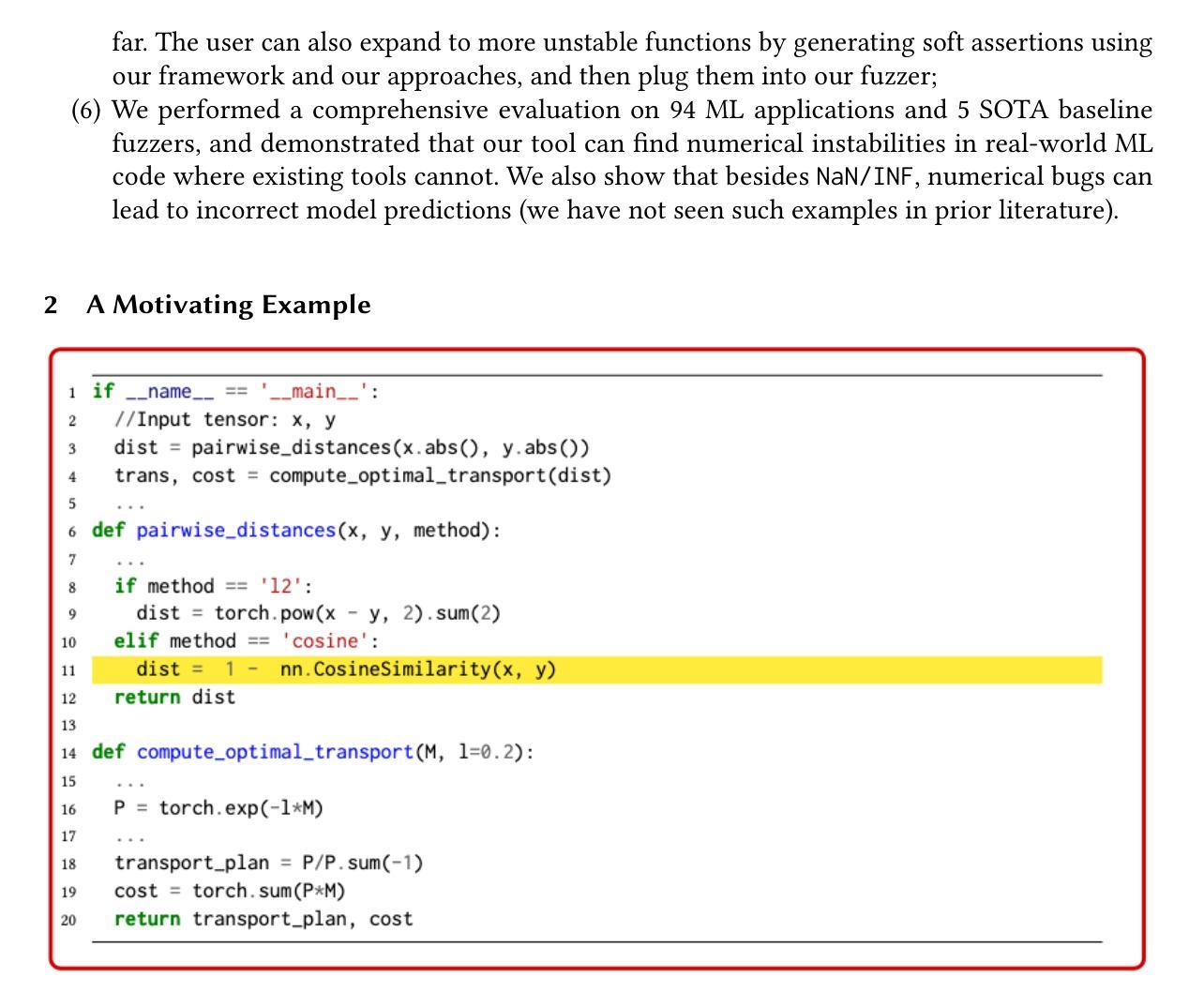
Automatically Detecting Numerical Instability in Machine Learning Applications via Soft Assertions
Authors:Shaila Sharmin, Anwar Hossain Zahid, Subhankar Bhattacharjee, Chiamaka Igwilo, Miryung Kim, Wei Le
Machine learning (ML) applications have become an integral part of our lives. ML applications extensively use floating-point computation and involve very large/small numbers; thus, maintaining the numerical stability of such complex computations remains an important challenge. Numerical bugs can lead to system crashes, incorrect output, and wasted computing resources. In this paper, we introduce a novel idea, namely soft assertions (SA), to encode safety/error conditions for the places where numerical instability can occur. A soft assertion is an ML model automatically trained using the dataset obtained during unit testing of unstable functions. Given the values at the unstable function in an ML application, a soft assertion reports how to change these values in order to trigger the instability. We then use the output of soft assertions as signals to effectively mutate inputs to trigger numerical instability in ML applications. In the evaluation, we used the GRIST benchmark, a total of 79 programs, as well as 15 real-world ML applications from GitHub. We compared our tool with 5 state-of-the-art (SOTA) fuzzers. We found all the GRIST bugs and outperformed the baselines. We found 13 numerical bugs in real-world code, one of which had already been confirmed by the GitHub developers. While the baselines mostly found the bugs that report NaN and INF, our tool \tool found numerical bugs with incorrect output. We showed one case where the Tumor Detection Model, trained on Brain MRI images, should have predicted “tumor”, but instead, it incorrectly predicted “no tumor” due to the numerical bugs. Our replication package is located at https://figshare.com/s/6528d21ccd28bea94c32.
机器学习(ML)应用已成为我们生活中不可或缺的一部分。机器学习应用广泛地使用浮点计算并涉及非常大的数字或非常小的数字;因此,保持此类复杂计算的数值稳定性仍然是一个重要的挑战。数值错误可能导致系统崩溃、输出错误和计算资源浪费。在本文中,我们介绍了一种新的概念,即软断言(SA),以编码可能在数值不稳定发生的地方的安全/错误条件。软断言是一种使用在不稳定函数单元测试期间获得的数据集自动训练的机器学习模型。给定机器学习应用中不稳定函数的值,软断言会报告如何改变这些值以触发不稳定。然后我们将软断言的输出用作信号,以有效地修改输入,从而触发机器学习应用中的数值不稳定。在评估中,我们使用了包含总共79个程序的GRIST基准测试以及来自GitHub的15个真实世界的机器学习应用。我们将我们的工具与5种最新(SOTA)模糊测试工具进行了比较。我们发现所有GRIST错误并超越了基线。我们在真实世界的代码中发现了13个数值错误,其中一个是GitHub开发人员已经确认的错误。虽然基线测试大多找到了报告NaN和INF的错误,但我们的工具发现了具有错误输出的数值错误。我们展示了一个案例,即基于脑MRI图像训练的肿瘤检测模型应该预测为“肿瘤”,但由于数值错误,它错误地预测为“无肿瘤”。我们的复制包位于https://figshare.com/s/6528d21ccd28bea94c32。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF 22 pages, 5 figures. Accepted at FSE 2025
摘要
本文提出了一种基于机器学习模型的新型安全机制——软断言(SA),用于解决机器学习应用中数值不稳定的问题。软断言通过自动训练数据集来编码安全/错误条件,预测可能导致数值不稳定性的输入值变化。通过利用软断言的输出作为信号,可以有效突变输入以触发机器学习应用的数值不稳定。实验评估显示,该工具在GRIST基准测试和GitHub上的真实世界机器学习应用中均表现出优异性能,发现了多个数值错误。其中一例为肿瘤检测模型因数值错误导致预测错误。具体表现为,基于脑MRI图像的肿瘤检测模型本应预测为“肿瘤”,但结果却是“无肿瘤”。此方法的复现包可通过https://figshare.com/s/6528d21ccd28bea94c32获取。
关键见解
- 引入软断言(SA)新概念,基于机器学习模型自动编码安全/错误条件,应对机器学习应用中的数值不稳定挑战。
- 软断言可预测并报告可能导致数值不稳定性的输入值变化。
- 利用软断言的输出作为信号,能有效突变输入,触发机器学习应用的数值不稳定。
- 在GRIST基准测试和GitHub真实世界应用中的实验评估显示,该方法在发现数值错误方面表现优异。
- 所提出方法在一例肿瘤检测模型预测错误中体现实用价值。该模型因数值错误导致将“肿瘤”误判为“无肿瘤”。
- 此方法的复现包可通过特定链接获取,便于研究使用和进一步验证。
点此查看论文截图

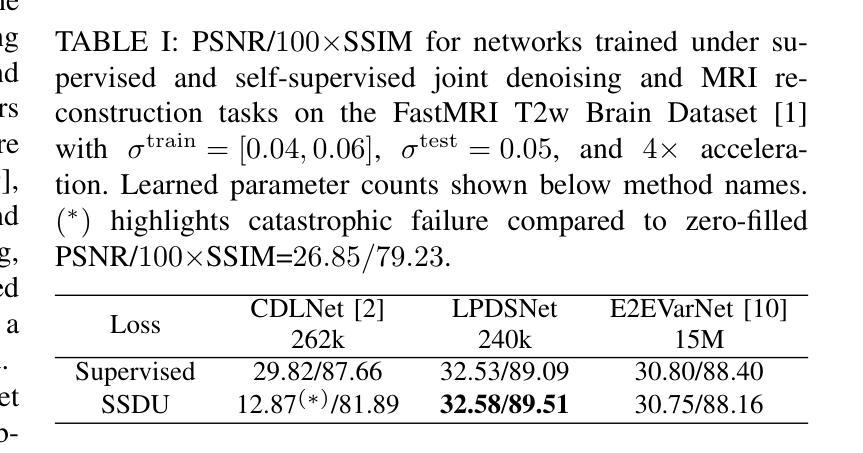
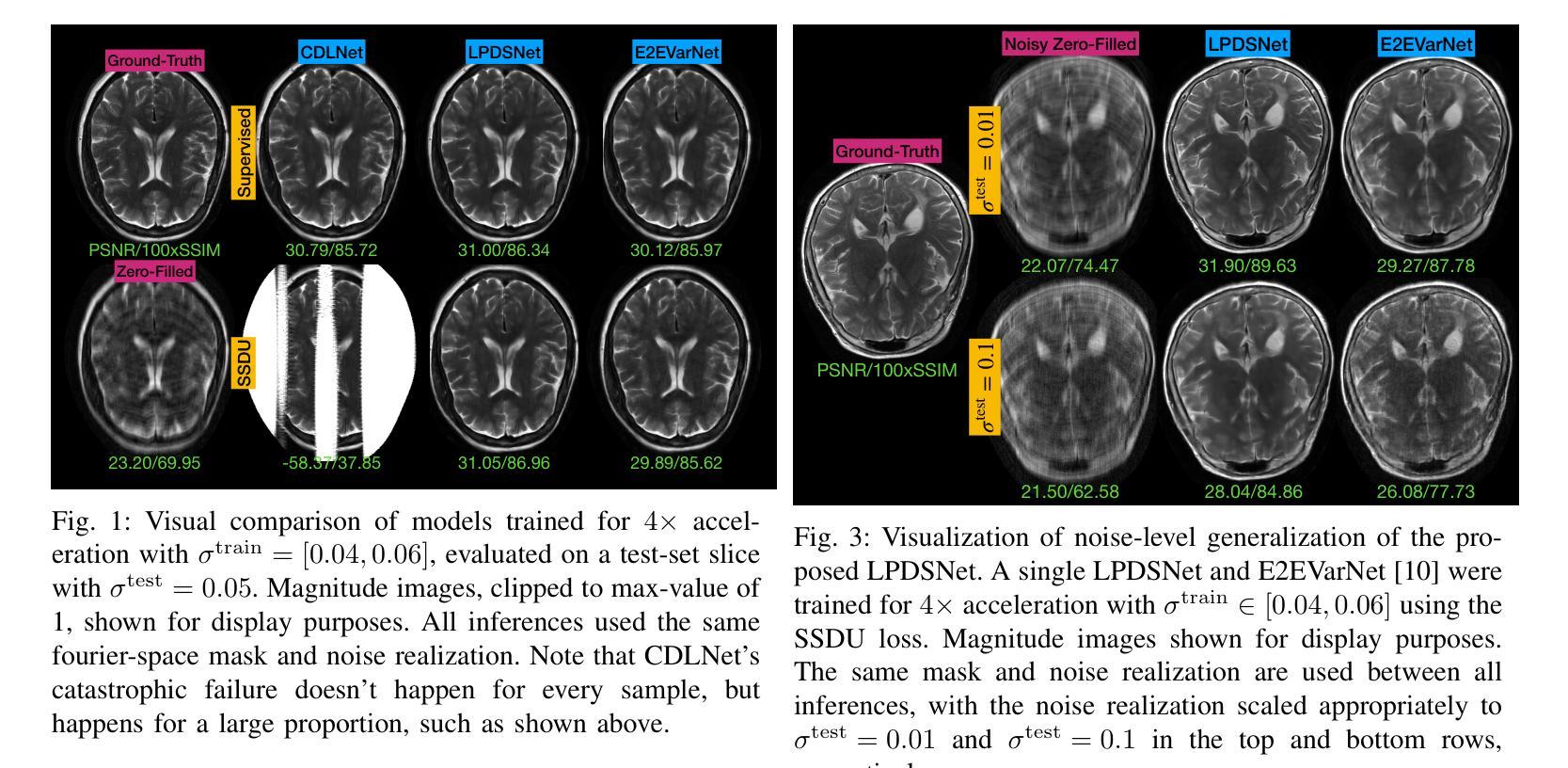
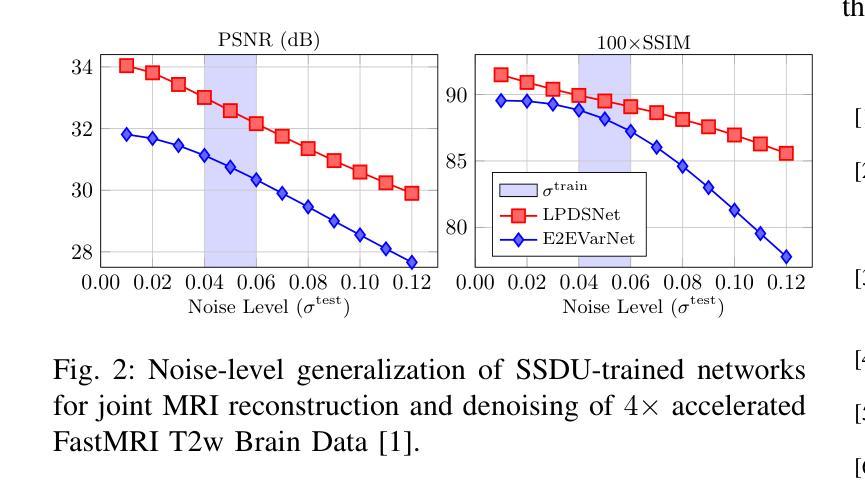
Learned Primal Dual Splitting for Self-Supervised Noise-Adaptive MRI Reconstruction
Authors:Nikola Janjusevic, Amirhoussein Khalilian-Gourtani, Yao Wang, Li Feng
Magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) reconstruction has largely been dominated by deep neural networks (DNN); however, many state-of-the-art architectures use black-box structures, which hinder interpretability and improvement. Here, we propose an interpretable DNN architecture for self-supervised MRI reconstruction and denoising by directly parameterizing and learning the classical primal-dual splitting, dubbed LPDSNet. This splitting algorithm allows us to decouple the observation model from the signal prior. Experimentally, we show other interpretable architectures without this decoupling property exhibit failure in the self-supervised learning regime. We report state-of-the-art self-supervised joint MRI reconstruction and denoising performance and novel noise-level generalization capabilities, where in contrast black-box networks fail to generalize.
磁共振成像(MRI)重建主要由深度神经网络(DNN)主导;然而,许多最先进的架构使用黑箱结构,这阻碍了可解释性和改进。在这里,我们提出了一种可解释的深度神经网络架构,用于自监督MRI重建和去噪,通过直接参数化和学习经典的原始-对偶分裂算法,被称为LPDSNet。这种分裂算法使我们能够将观测模型与信号先验解耦。实验表明,其他没有这种解耦属性的可解释架构在自监督学习状态下会表现出失败。我们报告了最先进的自监督联合MRI重建和去噪性能以及新型噪声水平泛化能力,相比之下,黑箱网络无法泛化。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF 4 pages, 3 figures, 1 table
Summary
该文本提出了一种利用经典的原位双重分割技术(primal-dual splitting)进行自监督MRI重建和去噪的可解释深度神经网络架构LPDSNet。该架构实现了观察模型和信号先验的解耦,并在自监督学习环境下展示了优越的性能。
Key Takeaways
- 深度神经网络在MRI重建中占主导地位,但许多先进的架构使用黑盒结构,阻碍了可解释性和改进。
- 提出了一种可解释的DNN架构LPDSNet,用于自监督MRI重建和去噪。
- LPDSNet通过直接参数化和学习经典的原位双重分割算法,实现了观察模型和信号先验的解耦。
- 实验表明,其他没有这种解耦属性的可解释架构在自监督学习环境下会表现出失败。
- LPDSNet达到了先进的自监督联合MRI重建和去噪性能。
- LPDSNet具有噪声水平泛化能力,而黑盒网络则无法泛化。
点此查看论文截图

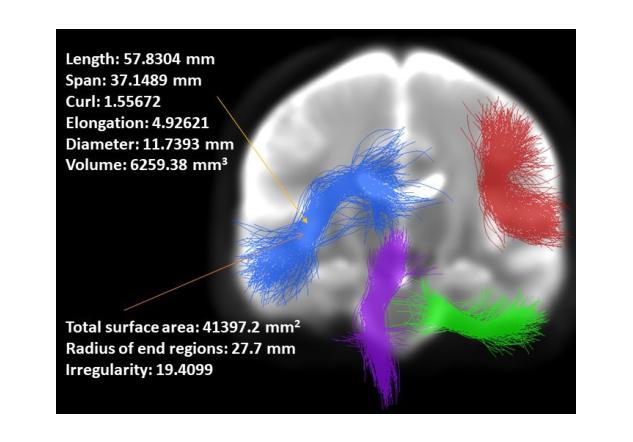
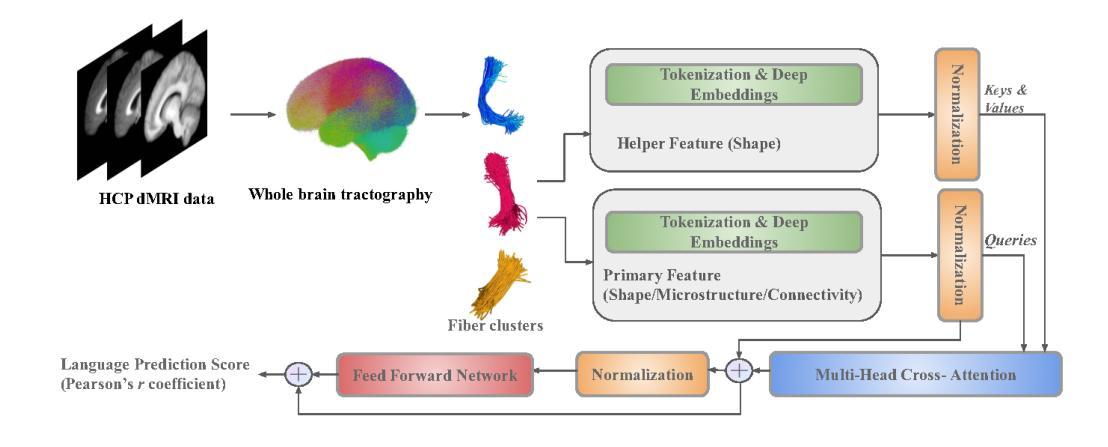
Cross-domain Fiber Cluster Shape Analysis for Language Performance Cognitive Score Prediction
Authors:Yui Lo, Yuqian Chen, Dongnan Liu, Wan Liu, Leo Zekelman, Fan Zhang, Yogesh Rathi, Nikos Makris, Alexandra J. Golby, Weidong Cai, Lauren J. O’Donnell
Shape plays an important role in computer graphics, offering informative features to convey an object’s morphology and functionality. Shape analysis in brain imaging can help interpret structural and functionality correlations of the human brain. In this work, we investigate the shape of the brain’s 3D white matter connections and its potential predictive relationship to human cognitive function. We reconstruct brain connections as sequences of 3D points using diffusion magnetic resonance imaging (dMRI) tractography. To describe each connection, we extract 12 shape descriptors in addition to traditional dMRI connectivity and tissue microstructure features. We introduce a novel framework, Shape–fused Fiber Cluster Transformer (SFFormer), that leverages a multi-head cross-attention feature fusion module to predict subject-specific language performance based on dMRI tractography. We assess the performance of the method on a large dataset including 1065 healthy young adults. The results demonstrate that both the transformer-based SFFormer model and its inter/intra feature fusion with shape, microstructure, and connectivity are informative, and together, they improve the prediction of subject-specific language performance scores. Overall, our results indicate that the shape of the brain’s connections is predictive of human language function.
形状在计算机图形学中扮演着重要角色,它能够提供信息特征,以传达物体的形态和功能。脑成像中的形状分析有助于解释人脑的结构和功能关联。在这项工作中,我们研究了大脑3D白质连接的形状及其与人类认知功能之间的潜在预测关系。我们利用扩散磁共振成像(dMRI)追踪技术重建了大脑连接的3D点序列。为了描述每个连接,我们提取了12个形状描述符,并保留了传统的dMRI连通性和组织微观结构特征。我们引入了一种新型框架——Shape-fused Fiber Cluster Transformer(SFFormer),它利用多头交叉注意力特征融合模块,基于dMRI追踪技术预测特定个体的语言表现。我们在包含1065名健康年轻人的大型数据集上评估了该方法的效果。结果表明,基于transformer的SFFormer模型及其与形状、微观结构和连通性的内部和外部特征融合均具有一定的信息性,它们共同提高了特定个体语言表现分数的预测能力。总体而言,我们的结果表明,大脑连接的形状可以预测人类的语言功能。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF This paper has been accepted for presentation at The 27th Intl. Conf. on Medical Image Computing and Computer Assisted Intervention (MICCAI 2024) Workshop on Computational Diffusion MRI (CDMRI). 11 pages, 2 figures
Summary
本文研究大脑3D白质连接的形状,并探索其与人类认知功能之间的潜在预测关系。通过扩散磁共振成像(dMRI)追踪技术重建大脑连接,提取形状描述符并结合传统dMRI连接和脑组织微观结构特征。引入新型框架Shape–fused Fiber Cluster Transformer(SFFormer),利用多头交叉注意力特征融合模块,基于dMRI追踪技术预测个体语言性能。在包含1065名健康年轻人的大型数据集上评估方法性能,结果表明SFFormer模型及其与形状、微观结构和连接性的内外特征融合对预测个体语言性能具有信息价值。总之,大脑连接形状对人类语言功能具有预测作用。
Key Takeaways
- 研究大脑3D白质连接形状在解读人类认知功能中的作用。
- 利用扩散磁共振成像(dMRI)技术重建大脑连接。
- 提取12个形状描述符描述每个大脑连接。
- 引入新型框架SFFormer,结合形状、微观结构和连接性特征,预测个体语言性能。
- 在大型数据集上评估方法性能,包括1065名健康年轻人。
- SFFormer模型及其特征融合对预测个体语言性能具有信息价值。
点此查看论文截图

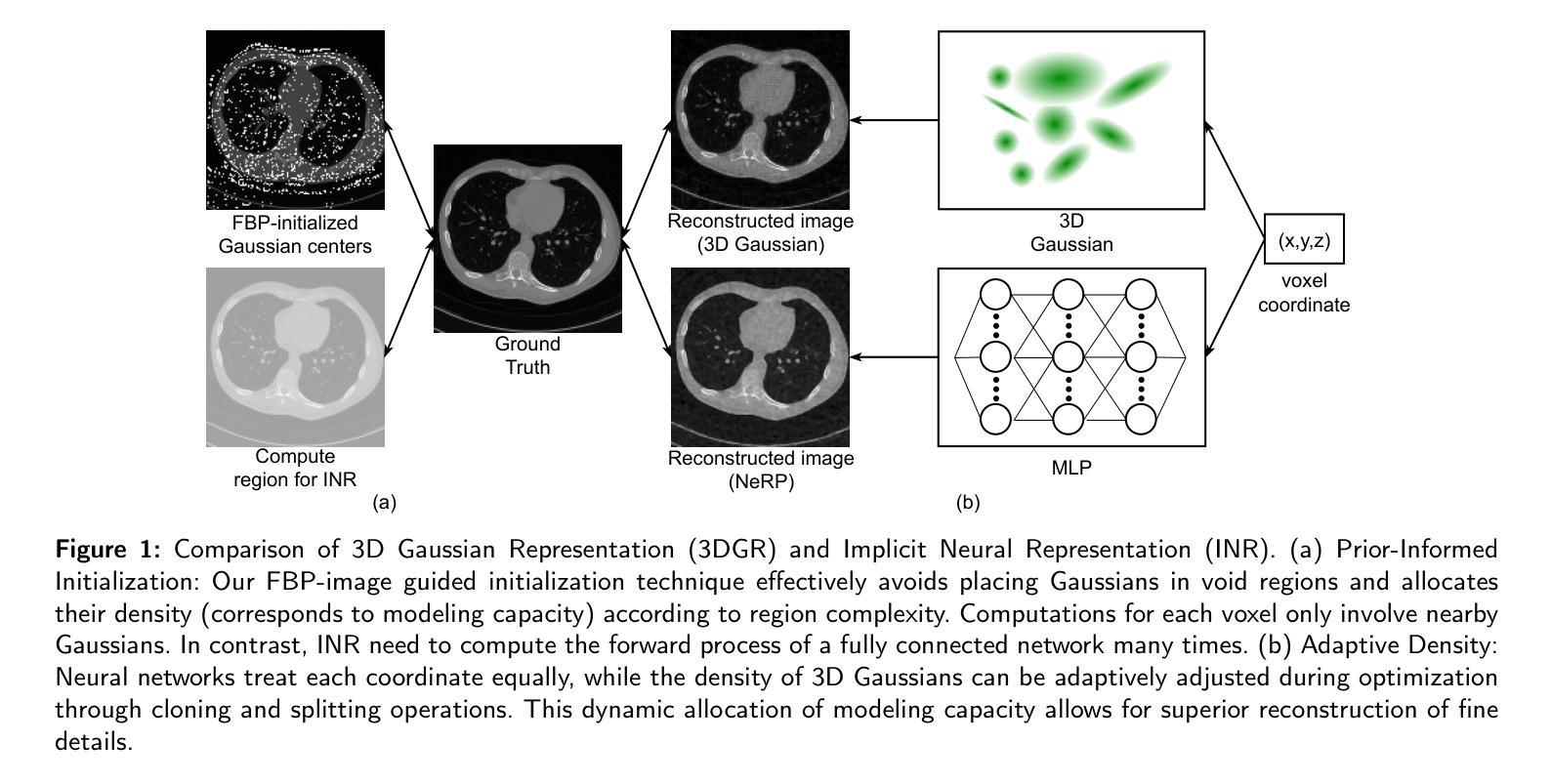
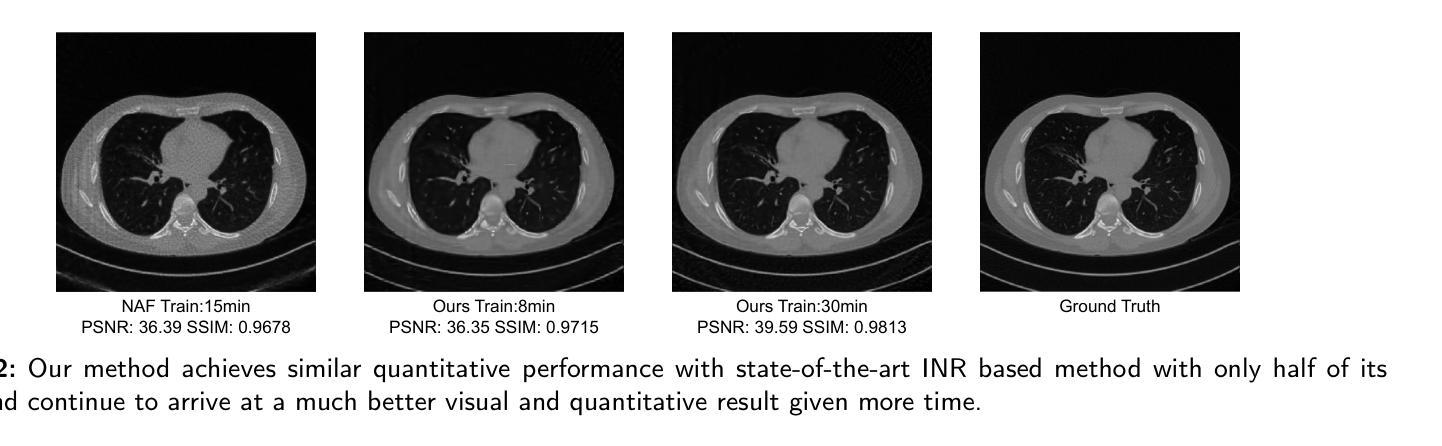
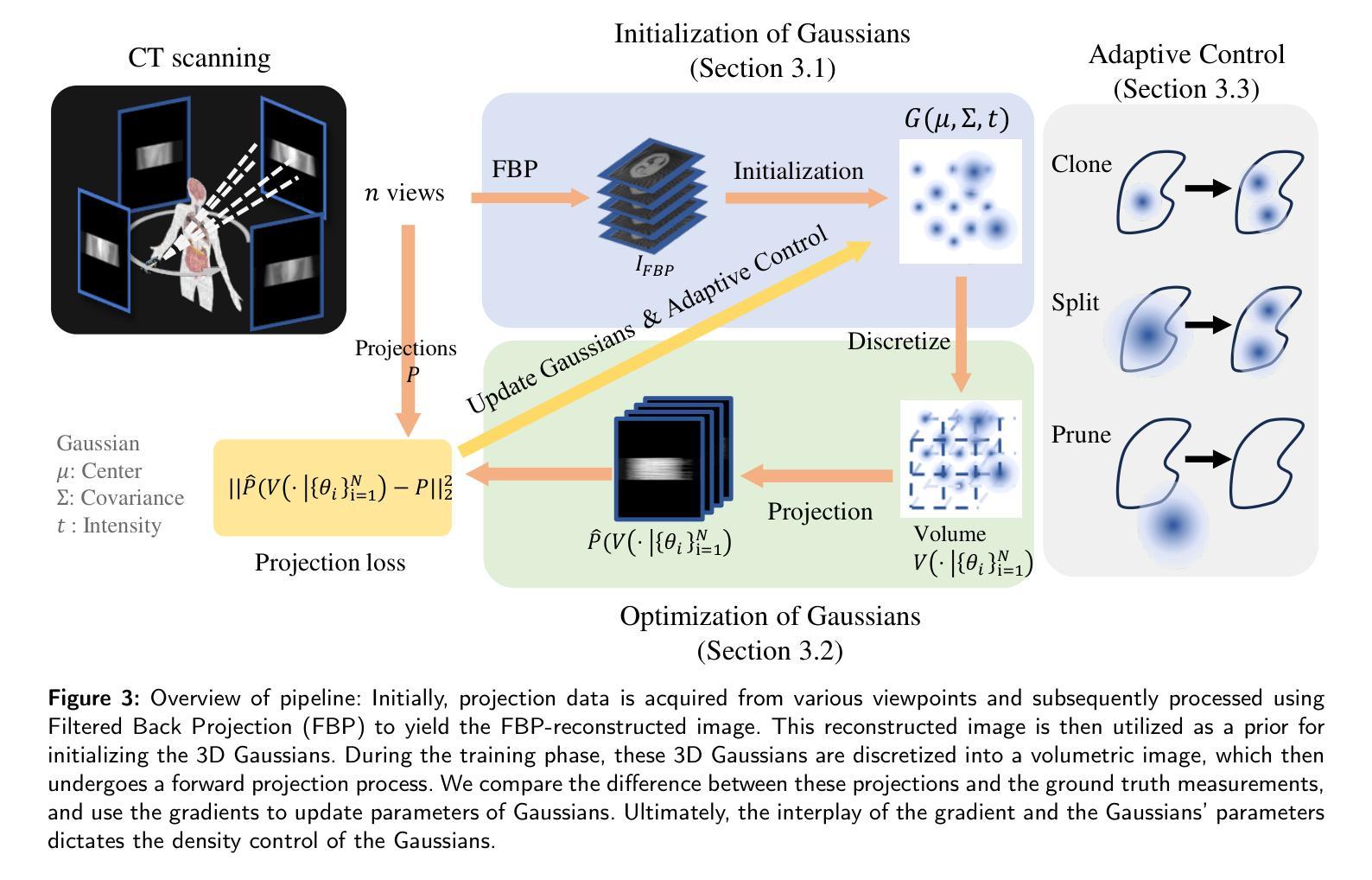
3DGR-CT: Sparse-View CT Reconstruction with a 3D Gaussian Representation
Authors:Yingtai Li, Xueming Fu, Han Li, Shang Zhao, Ruiyang Jin, S. Kevin Zhou
Sparse-view computed tomography (CT) reduces radiation exposure by acquiring fewer projections, making it a valuable tool in clinical scenarios where low-dose radiation is essential. However, this often results in increased noise and artifacts due to limited data. In this paper we propose a novel 3D Gaussian representation (3DGR) based method for sparse-view CT reconstruction. Inspired by recent success in novel view synthesis driven by 3D Gaussian splatting, we leverage the efficiency and expressiveness of 3D Gaussian representation as an alternative to implicit neural representation. To unleash the potential of 3DGR for CT imaging scenario, we propose two key innovations: (i) FBP-image-guided Guassian initialization and (ii) efficient integration with a differentiable CT projector. Extensive experiments and ablations on diverse datasets demonstrate the proposed 3DGR-CT consistently outperforms state-of-the-art counterpart methods, achieving higher reconstruction accuracy with faster convergence. Furthermore, we showcase the potential of 3DGR-CT for real-time physical simulation, which holds important clinical applications while challenging for implicit neural representations.
稀疏视图计算机断层扫描(CT)通过获取较少的投影来减少辐射暴露,使其成为在临床场景中低剂量辐射至关重要的有价值的工具。然而,这通常由于数据有限而导致噪声和伪影增加。在本文中,我们提出了一种基于三维高斯表示(3DGR)的稀疏视图CT重建方法。我们受到最近由三维高斯喷射驱动的新型视图合成的成功的启发,利用三维高斯表示的效率和表现力作为隐神经表示的替代方案。为了释放3DGR在CT成像场景中的潜力,我们提出了两个关键创新点:(i)FBP图像引导的高斯初始化,以及(ii)与可微分CT投影仪的有效集成。在多种数据集上的广泛实验和废除实验表明,所提出的3DGR-CT持续超越最新同行方法,以更高的重建精度和更快的收敛速度实现了优势。此外,我们展示了3DGR-CT在实时物理模拟中的潜力,这在临床应用中具有重要意义,同时对隐神经表示形式提出了挑战。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
本文介绍了基于稀疏视角计算机断层扫描(CT)的重建方法。文章提出了一种新颖的3D高斯表示(3DGR)方法,用于稀疏视角CT重建,以减少辐射暴露并增加数据表达的效率和表现力。文章通过引入两个创新点——FBP图像引导的Guassian初始化和与可微分CT投影仪的高效集成——使得重建的准确性与收敛速度大大提高,同时也展示了对真实时间物理模拟的潜力。这一技术在临床应用方面具有重要价值。
Key Takeaways
- 稀疏视角计算机断层扫描(CT)通过获取较少的投影来减少辐射暴露。
- 提出了新颖的3D高斯表示(3DGR)方法用于稀疏视角CT重建。
- 引入了两个创新点:FBP图像引导的Guassian初始化和与可微分CT投影仪的高效集成。
- 通过实验验证,所提出的3DGR-CT优于其他先进方法,具有更高的重建准确性和更快的收敛速度。
点此查看论文截图