⚠️ 以下所有内容总结都来自于 大语言模型的能力,如有错误,仅供参考,谨慎使用
🔴 请注意:千万不要用于严肃的学术场景,只能用于论文阅读前的初筛!
💗 如果您觉得我们的项目对您有帮助 ChatPaperFree ,还请您给我们一些鼓励!⭐️ HuggingFace免费体验
2025-04-24 更新
You Sense Only Once Beneath: Ultra-Light Real-Time Underwater Object Detection
Authors:Jun Dong, Wenli Wu, Jintao Cheng, Xiaoyu Tang
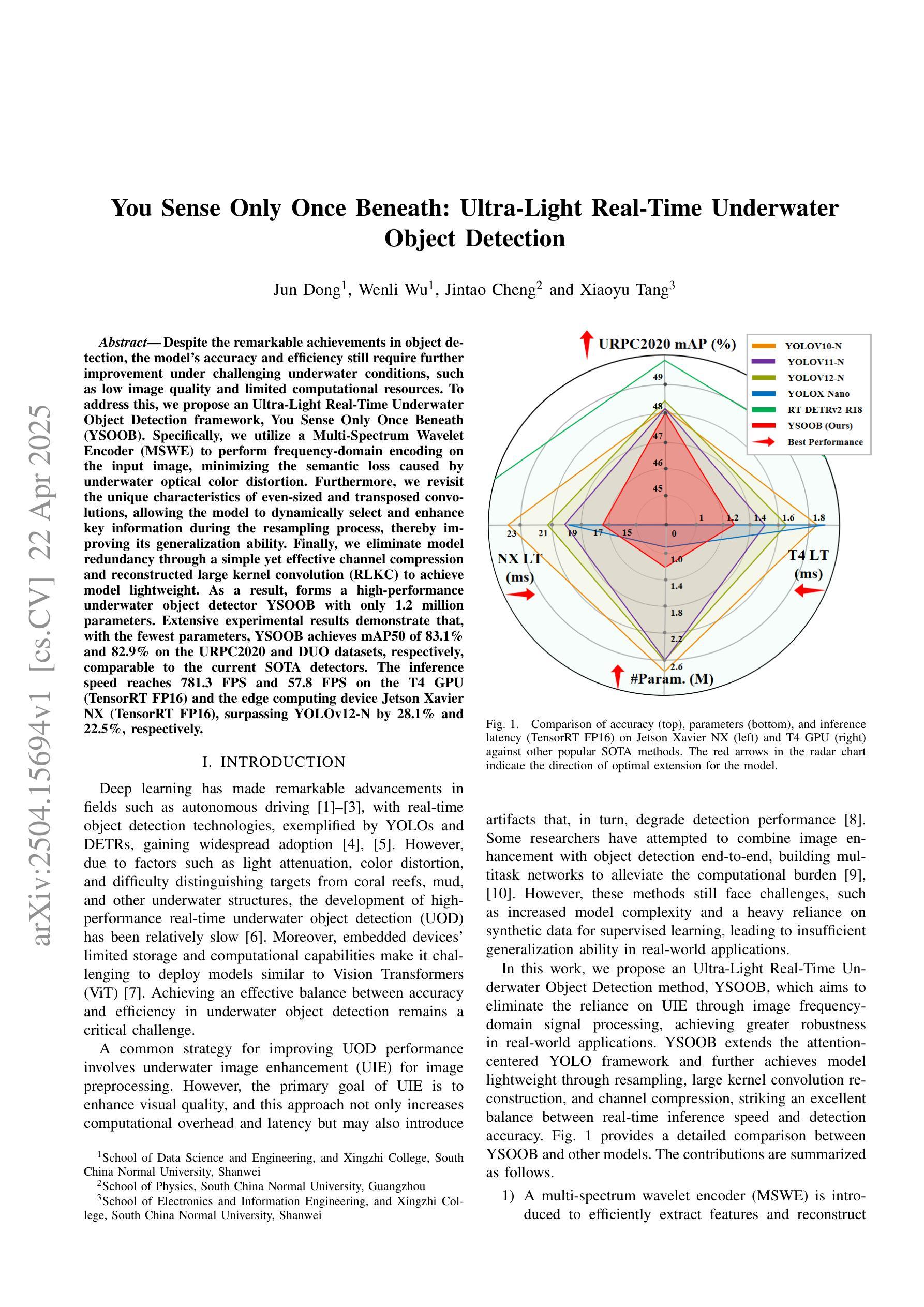
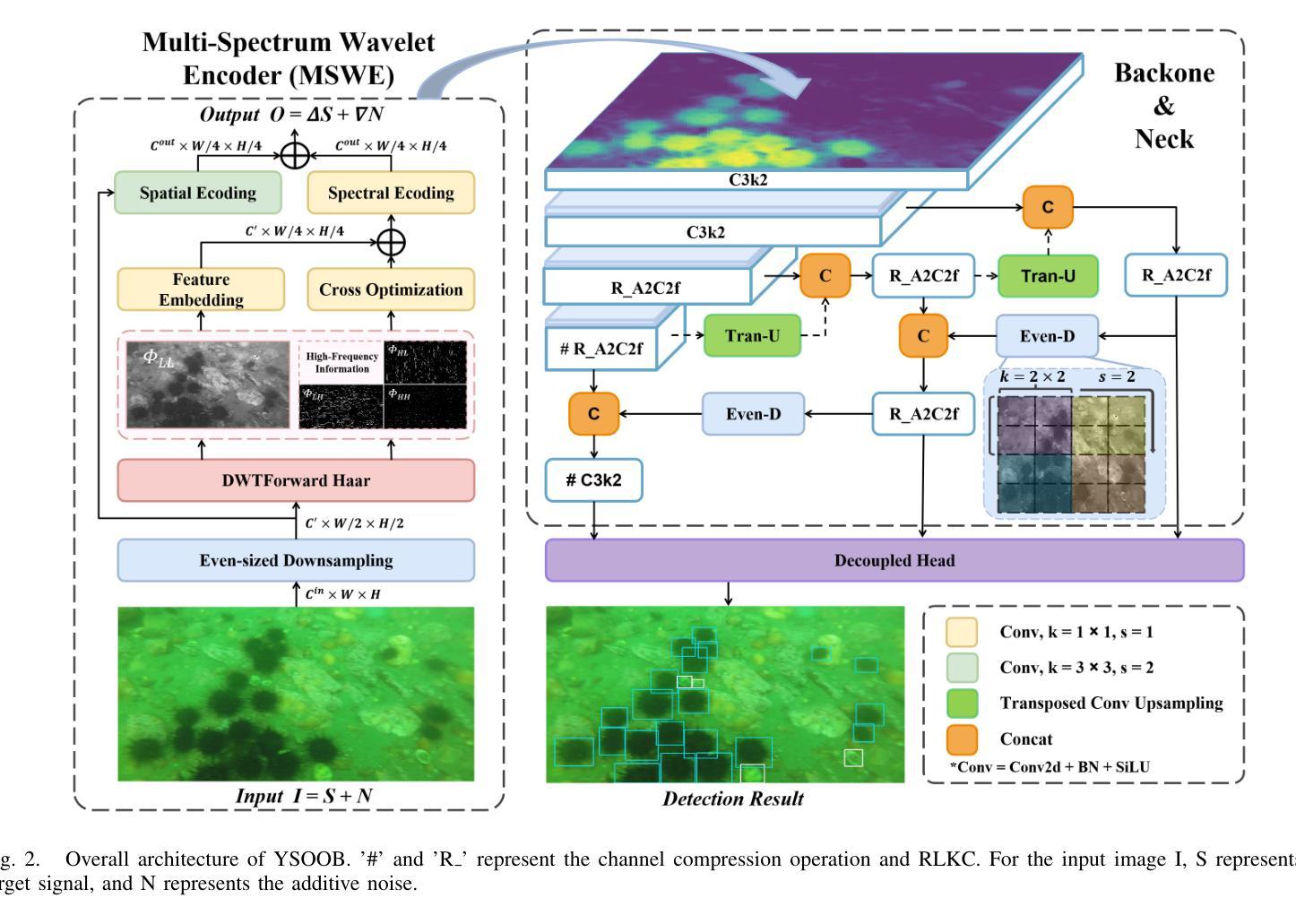
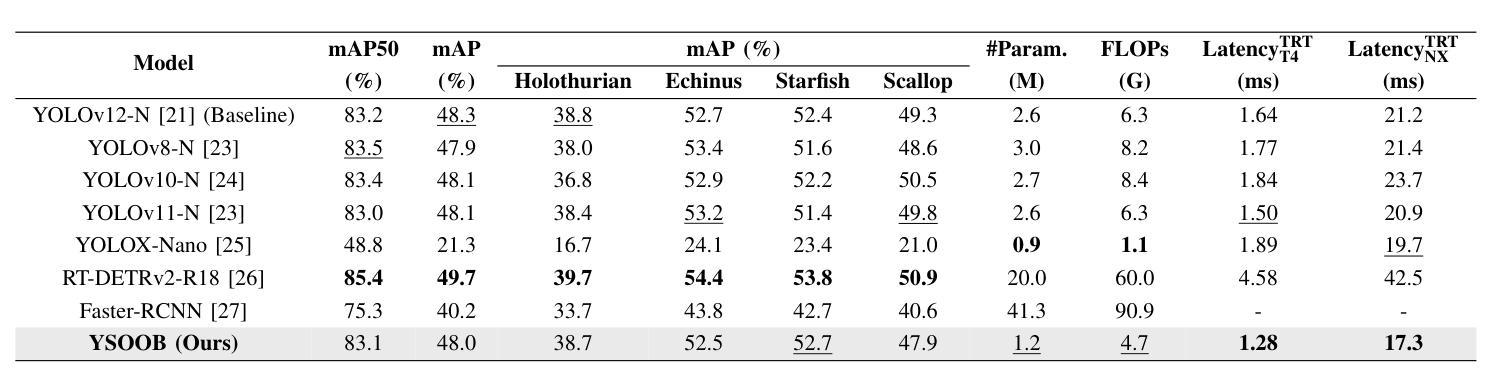
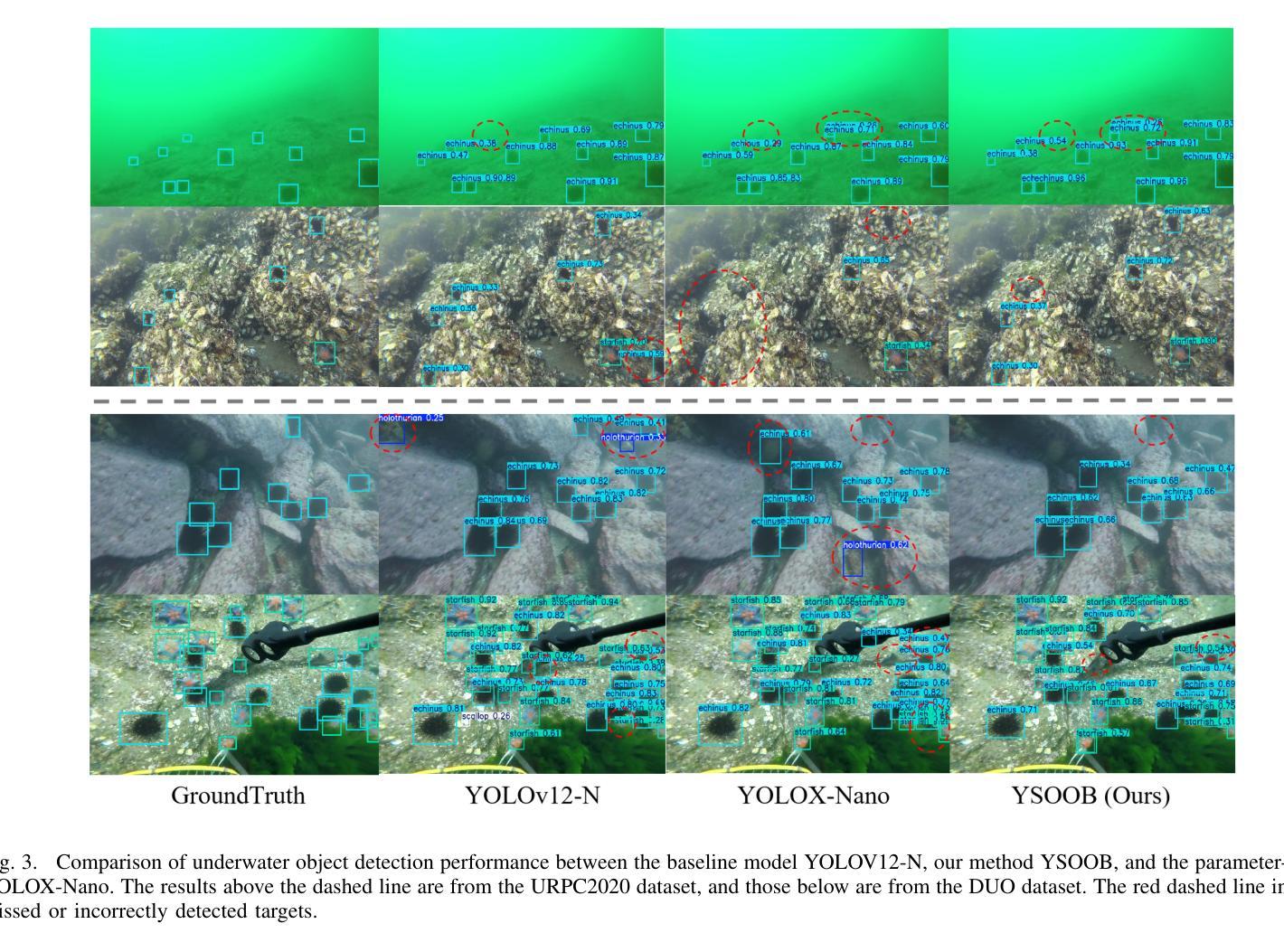
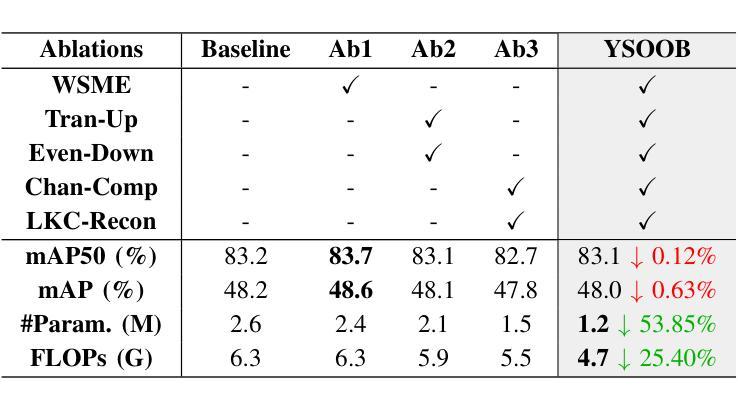
Despite the remarkable achievements in object detection, the model’s accuracy and efficiency still require further improvement under challenging underwater conditions, such as low image quality and limited computational resources. To address this, we propose an Ultra-Light Real-Time Underwater Object Detection framework, You Sense Only Once Beneath (YSOOB). Specifically, we utilize a Multi-Spectrum Wavelet Encoder (MSWE) to perform frequency-domain encoding on the input image, minimizing the semantic loss caused by underwater optical color distortion. Furthermore, we revisit the unique characteristics of even-sized and transposed convolutions, allowing the model to dynamically select and enhance key information during the resampling process, thereby improving its generalization ability. Finally, we eliminate model redundancy through a simple yet effective channel compression and reconstructed large kernel convolution (RLKC) to achieve model lightweight. As a result, forms a high-performance underwater object detector YSOOB with only 1.2 million parameters. Extensive experimental results demonstrate that, with the fewest parameters, YSOOB achieves mAP50 of 83.1% and 82.9% on the URPC2020 and DUO datasets, respectively, comparable to the current SOTA detectors. The inference speed reaches 781.3 FPS and 57.8 FPS on the T4 GPU (TensorRT FP16) and the edge computing device Jetson Xavier NX (TensorRT FP16), surpassing YOLOv12-N by 28.1% and 22.5%, respectively.
尽管在目标检测方面取得了显著的成就,但在具有挑战性的水下环境中,如图像质量低和计算资源有限的情况下,模型的准确性和效率仍需进一步提高。为了解决这一问题,我们提出了一种超轻量级实时水下目标检测框架“潜行唯觉”(You Sense Only Once Beneath,简称YSOOB)。具体来说,我们利用多光谱小波编码器(MSWE)对输入图像进行频域编码,以最小化由水下光学色彩失真引起的语义损失。此外,我们重新审视了大小恒定和转置卷积的独特性,使模型能够在重采样过程中动态选择和增强关键信息,从而提高其泛化能力。最后,我们通过简单有效的通道压缩和重建大内核卷积(RLKC)来消除模型冗余,实现了模型的轻量化。因此,形成了仅有120万个参数的高性能水下目标检测器YSOOB。广泛的实验结果表明,在参数最少的情况下,YSOOB在URPC2020和DUO数据集上的mAP50分别达到了83.1%和82.9%,与当前的最佳检测器相当。在T4 GPU(TensorRT FP16)和边缘计算设备Jetson Xavier NX(TensorRT FP16)上的推理速度分别达到了781.3 FPS和57.8 FPS,分别超越了YOLOv12-N的28.1%和22.5%。
论文及项目相关链接
摘要
本文提出了一种超轻量级的实时水下目标检测框架——You Sense Only Once Beneath(YSOOB)。该框架解决了水下环境如低图像质量和有限计算资源所带来的挑战。通过使用Multi-Spectrum Wavelet Encoder(MSWE)进行频域编码,减少水下光学色彩失真造成的语义损失。同时,结合偶数和转置卷积的特性,提高模型的动态信息选择能力和增强关键信息的能力。此外,通过简单的通道压缩和重建大内核卷积(RLKC)消除模型冗余,实现模型轻量化。因此,形成了仅有120万参数的高性能水下目标检测器YSOOB。实验结果表明,在参数最少的情况下,YSOOB在URPC2020和DUO数据集上的mAP50分别达到83.1%和82.9%,与当前的最先进检测器相当。推理速度在T4 GPU和边缘计算设备Jetson Xavier NX上分别达到了781.3 FPS和57.8 FPS,分别超过了YOLOv12-N的28.1%和22.5%。
关键见解
- 提出了超轻量级实时水下目标检测框架YSOOB,针对水下环境的挑战进行优化。
- 使用MSWE进行频域编码,减少水下光学色彩失真造成的语义损失。
- 结合偶数和转置卷积,提高模型的动态信息选择能力和增强关键信息。
- 通过通道压缩和RLKC实现模型轻量化。
- YSOOB仅有120万参数,实现了高性能的水下目标检测。
- 在URPC2020和DUO数据集上,YSOOB的mAP50表现优异,与当前最先进检测器相当。
点此查看论文截图
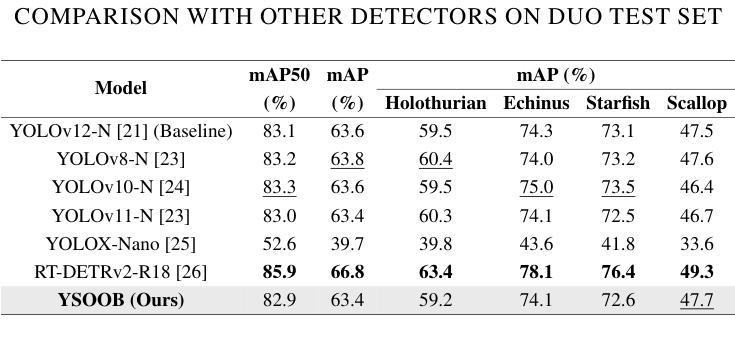
DINOv2-powered Few-Shot Semantic Segmentation: A Unified Framework via Cross-Model Distillation and 4D Correlation Mining
Authors:Wei Zhuo, Zhiyue Tang, Wufeng Xue, Hao Ding, Linlin Shen
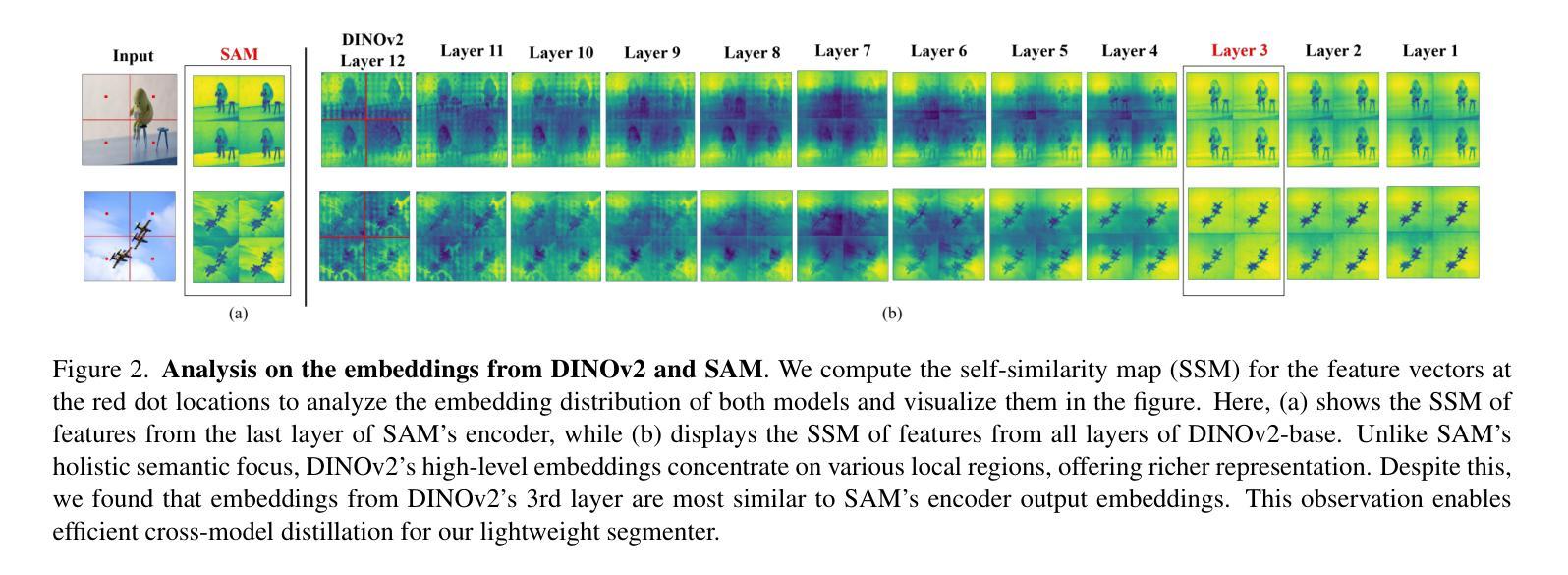
Few-shot semantic segmentation has gained increasing interest due to its generalization capability, i.e., segmenting pixels of novel classes requiring only a few annotated images. Prior work has focused on meta-learning for support-query matching, with extensive development in both prototype-based and aggregation-based methods. To address data scarcity, recent approaches have turned to foundation models to enhance representation transferability for novel class segmentation. Among them, a hybrid dual-modal framework including both DINOv2 and SAM has garnered attention due to their complementary capabilities. We wonder “can we build a unified model with knowledge from both foundation models?” To this end, we propose FS-DINO, with only DINOv2’s encoder and a lightweight segmenter. The segmenter features a bottleneck adapter, a meta-visual prompt generator based on dense similarities and semantic embeddings, and a decoder. Through coarse-to-fine cross-model distillation, we effectively integrate SAM’s knowledge into our lightweight segmenter, which can be further enhanced by 4D correlation mining on support-query pairs. Extensive experiments on COCO-20i, PASCAL-5i, and FSS-1000 demonstrate the effectiveness and superiority of our method.
小样本语义分割因其泛化能力而受到越来越多的关注,即对仅需要少数标注图像的新类别像素进行分割。早期的研究主要集中在支持查询匹配的元学习方面,基于原型和基于聚合的方法都得到了广泛的发展。为了解决数据稀缺的问题,最近的方法转向使用基础模型以增强新型类别分割的表示迁移能力。其中,一个包含DINOv2和SAM的混合双模态框架因其互补能力而受到关注。我们想知道“我们能否从两种基础模型中汲取知识来构建一个统一模型?”为此,我们提出了FS-DINO模型,它仅采用DINOv2的编码器和轻量级分割器。分割器具有瓶颈适配器、基于密集相似性和语义嵌入的元视觉提示生成器以及解码器。通过粗到细的跨模型蒸馏,我们有效地将SAM的知识集成到我们的轻量级分割器中,通过支持查询对的四维关联挖掘可以进一步增强其性能。在COCO-20i、PASCAL-5i和FSS-1000上的大量实验证明了我们的方法的有效性和优越性。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
本文关注少样本语义分割问题,探讨如何结合DINOv2和SAM两种基础模型的优点,提出一种名为FS-DINO的统一模型。该模型仅使用DINOv2的编码器和一个轻量级分段器,通过引入bottleneck适配器、基于密集相似性和语义嵌入的元视觉提示生成器以及解码器,实现了与SAM知识的有效整合。实验表明,该模型在COCO-20i、PASCAL-5i和FSS-1000数据集上表现出优越的性能。
Key Takeaways
- 少样本语义分割具有强大的泛化能力,仅需少量标注图像即可对新型类别进行像素分割。
- 现有方法主要集中在基于元学习的支持查询匹配上,包括基于原型和基于聚合的方法。
- 为解决数据稀缺问题,最近的方法转向使用基础模型以增强新型类别分割的表示可迁移性。
- FS-DINO模型结合DINOv2编码器和轻量级分段器,引入bottleneck适配器、元视觉提示生成器和解码器。
- 通过粗细交叉模型蒸馏和4D关联挖掘支持查询对,FS-DINO模型实现了与SAM知识的有效整合。
- 实验结果表明,FS-DINO模型在多个数据集上表现出优越的性能。
点此查看论文截图


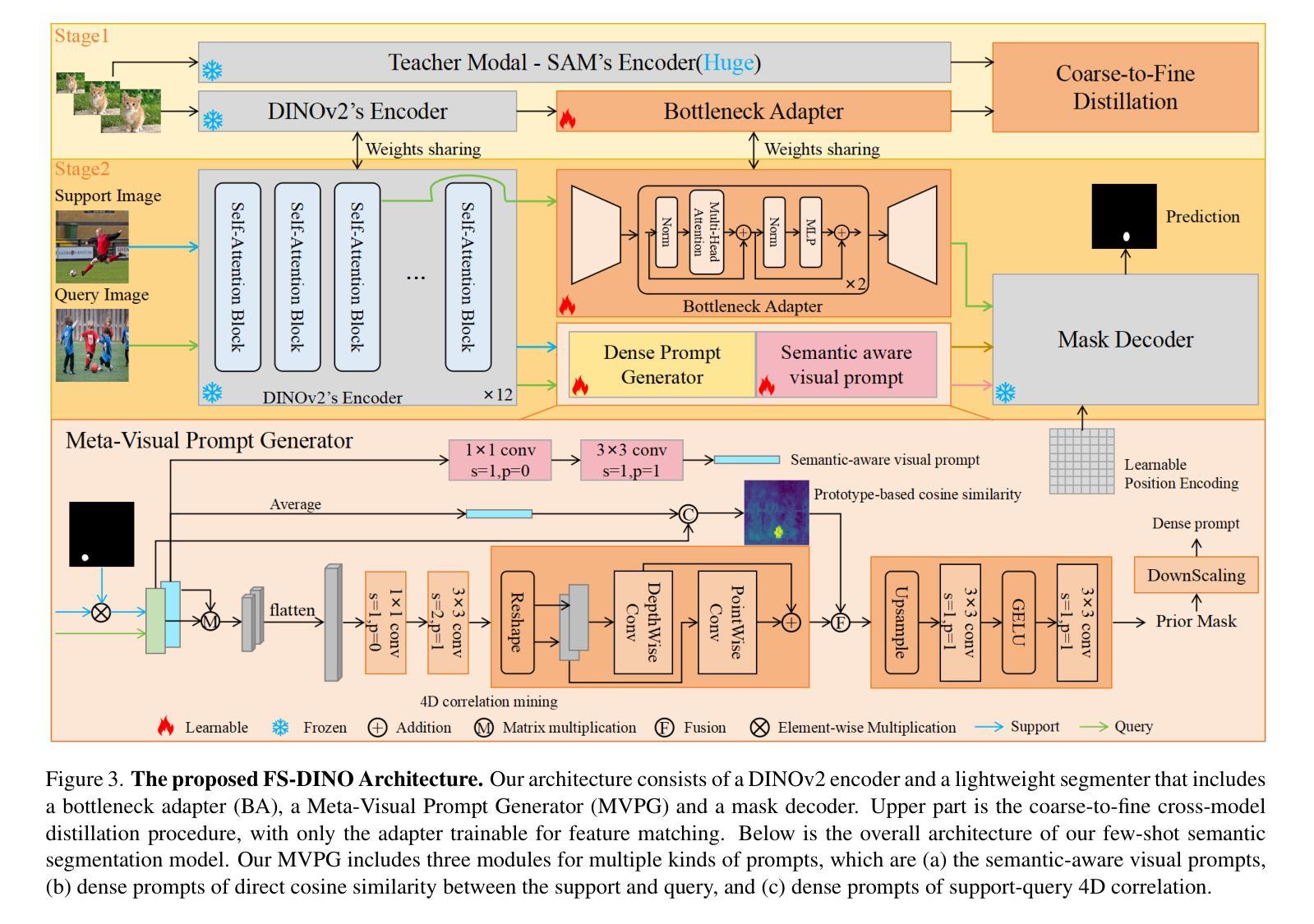
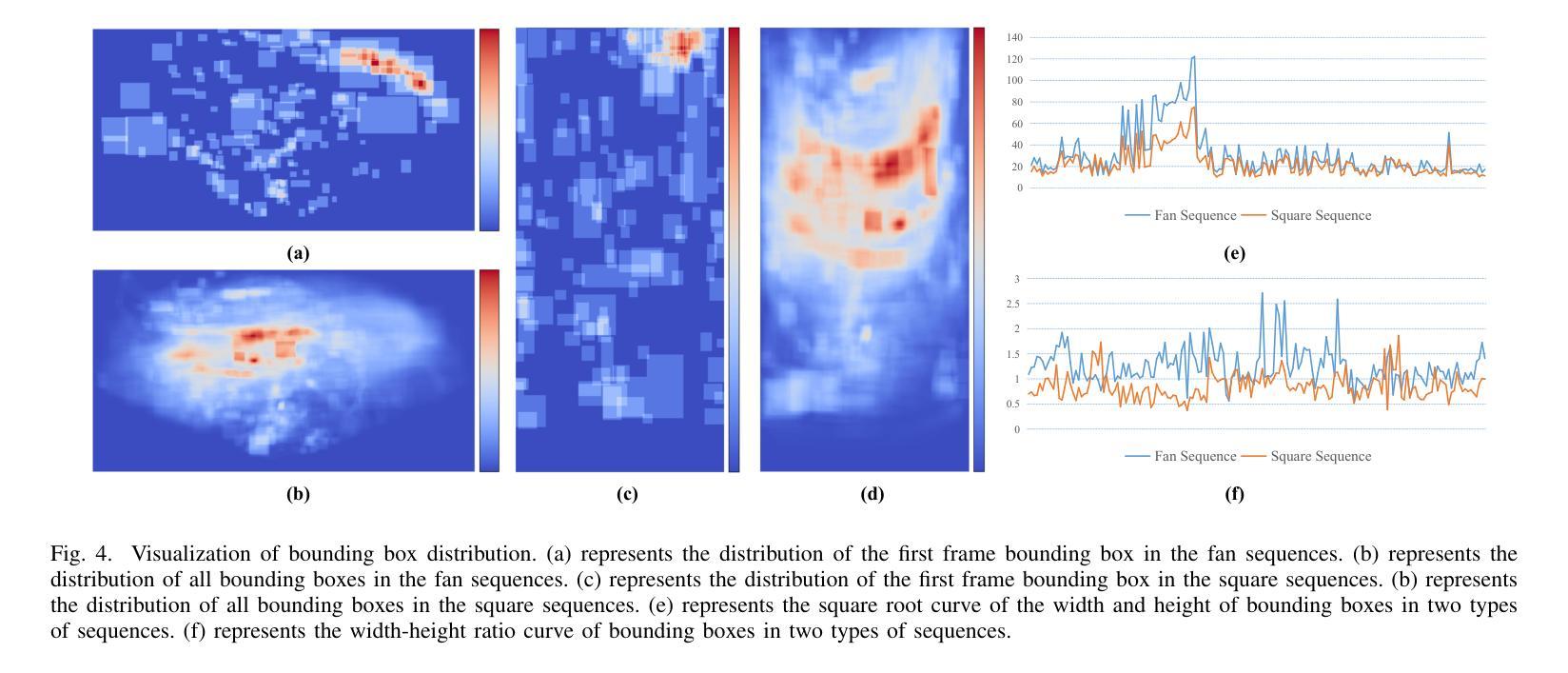
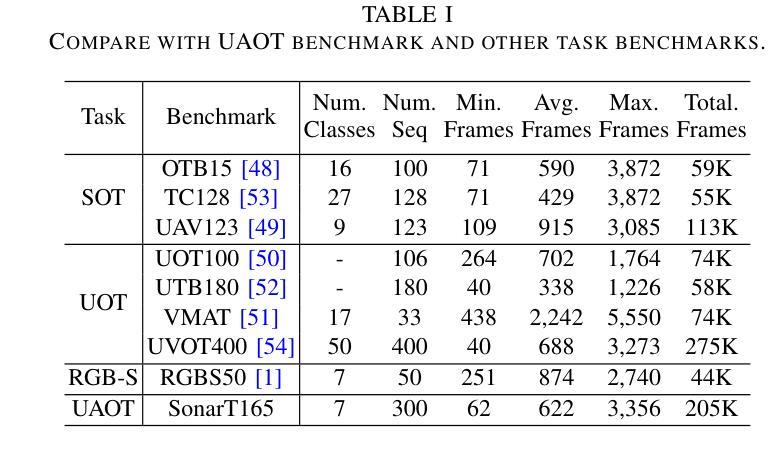
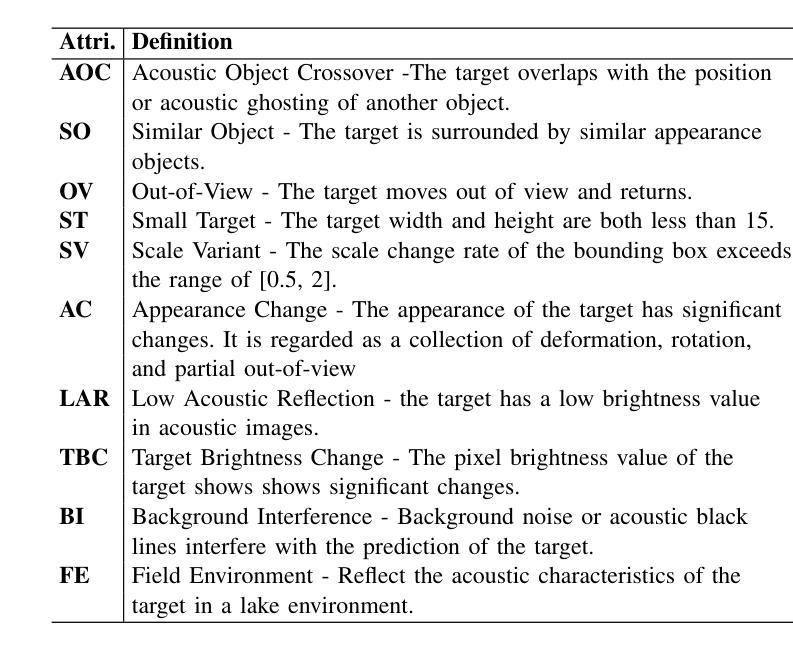
SonarT165: A Large-scale Benchmark and STFTrack Framework for Acoustic Object Tracking
Authors:Yunfeng Li, Bo Wang, Jiahao Wan, Xueyi Wu, Ye Li
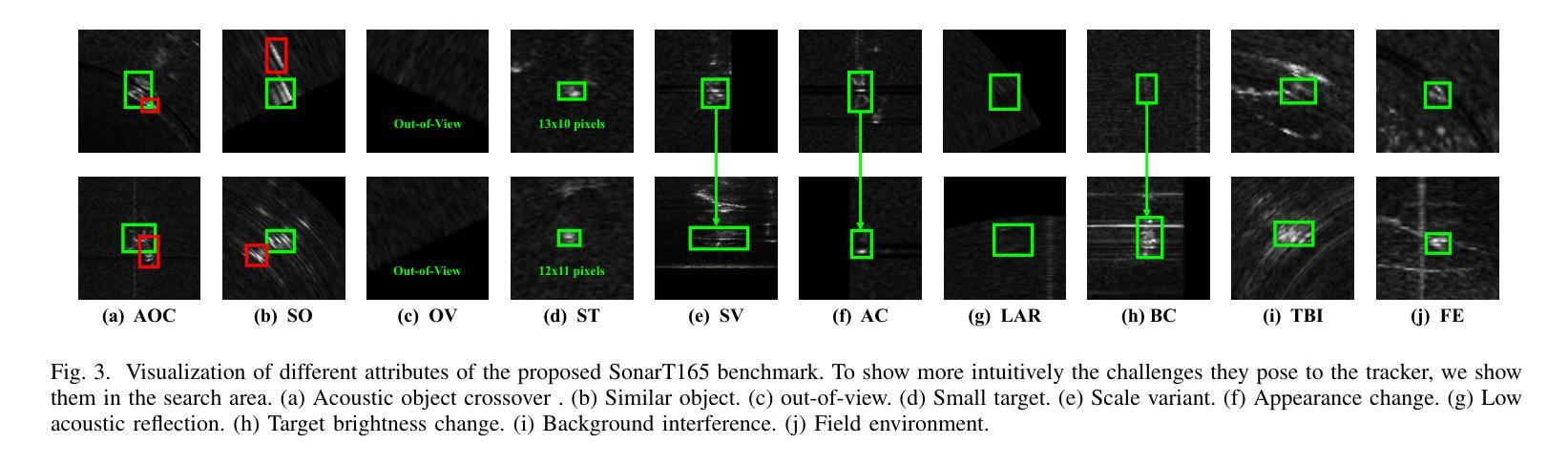
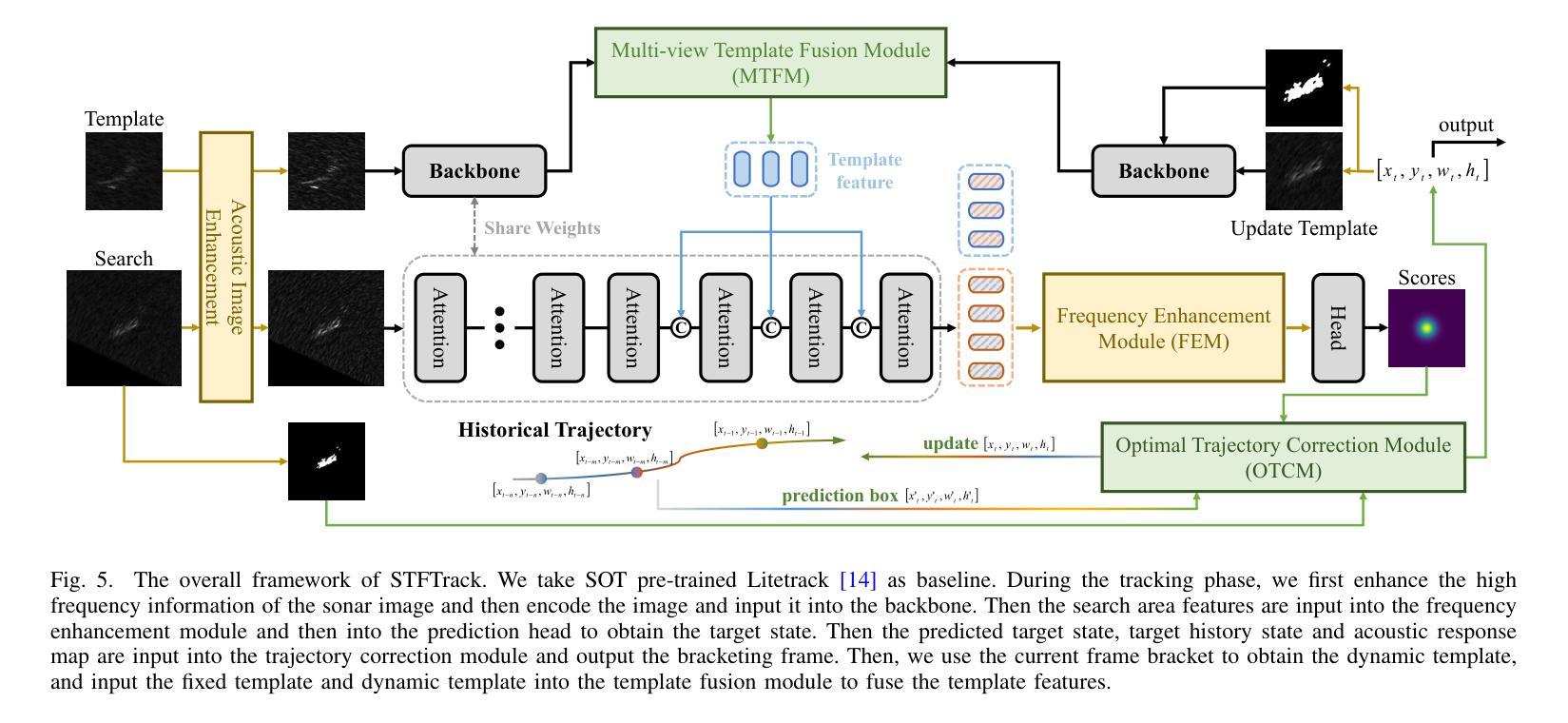
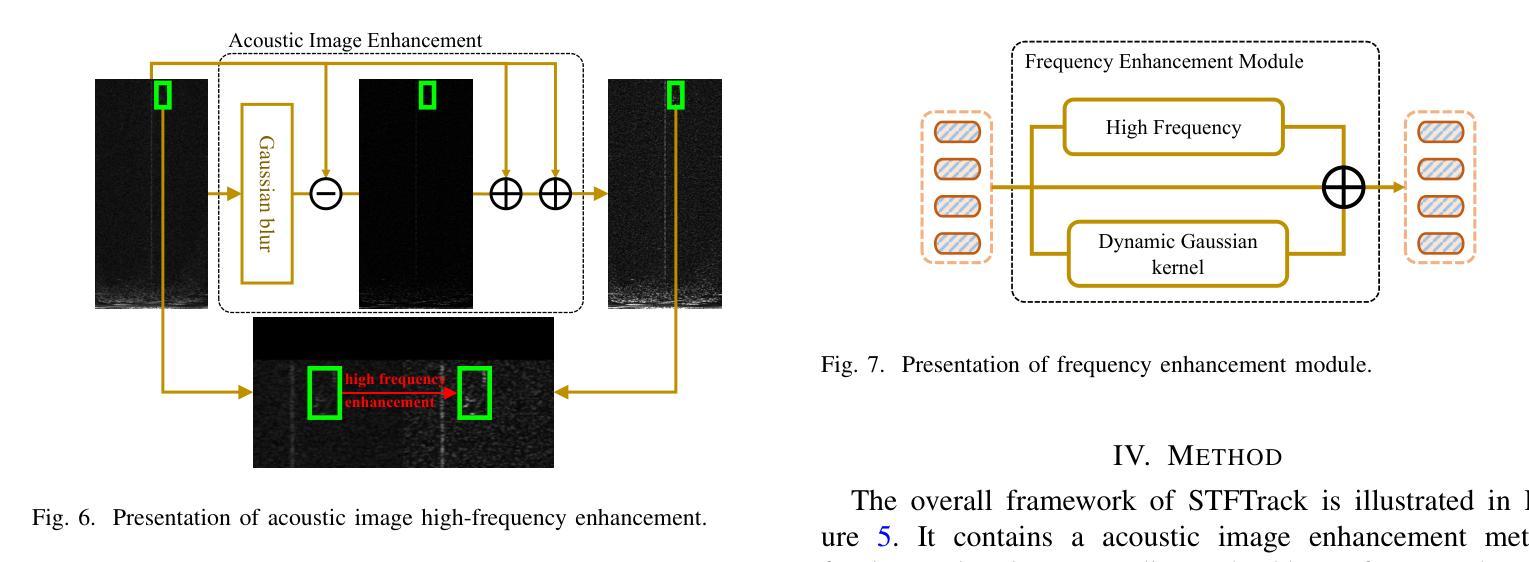
Underwater observation systems typically integrate optical cameras and imaging sonar systems. When underwater visibility is insufficient, only sonar systems can provide stable data, which necessitates exploration of the underwater acoustic object tracking (UAOT) task. Previous studies have explored traditional methods and Siamese networks for UAOT. However, the absence of a unified evaluation benchmark has significantly constrained the value of these methods. To alleviate this limitation, we propose the first large-scale UAOT benchmark, SonarT165, comprising 165 square sequences, 165 fan sequences, and 205K high-quality annotations. Experimental results demonstrate that SonarT165 reveals limitations in current state-of-the-art SOT trackers. To address these limitations, we propose STFTrack, an efficient framework for acoustic object tracking. It includes two novel modules, a multi-view template fusion module (MTFM) and an optimal trajectory correction module (OTCM). The MTFM module integrates multi-view feature of both the original image and the binary image of the dynamic template, and introduces a cross-attention-like layer to fuse the spatio-temporal target representations. The OTCM module introduces the acoustic-response-equivalent pixel property and proposes normalized pixel brightness response scores, thereby suppressing suboptimal matches caused by inaccurate Kalman filter prediction boxes. To further improve the model feature, STFTrack introduces a acoustic image enhancement method and a Frequency Enhancement Module (FEM) into its tracking pipeline. Comprehensive experiments show the proposed STFTrack achieves state-of-the-art performance on the proposed benchmark. The code is available at https://github.com/LiYunfengLYF/SonarT165.
水下观测系统通常集成了光学相机和成像声纳系统。当水下能见度不足时,只有声纳系统能提供稳定的数据,这就需要进行水下声学目标跟踪(UAOT)任务的探索。之前的研究已经探索了传统方法和Siamese网络用于UAOT。然而,缺乏统一的评估基准在很大程度上制约了这些方法的价值。为了缓解这一局限性,我们提出了首个大规模的UAOT基准测试SonarT165,包括165个方形序列、165个扇形序列和205K个高质量标注。实验结果表明,SonarT165揭示了当前最先进的SOT跟踪器的局限性。为了解决这些局限性,我们提出了STFTrack,一个用于声学目标跟踪的高效框架。它包括两个新颖模块,多视图模板融合模块(MTFM)和最佳轨迹校正模块(OTCM)。MTFM模块融合了原始图像和动态模板二进制图像的多视图特征,并引入了一个类似交叉注意力的层来融合时空目标表示。OTCM模块引入了声响应等效像素属性,并提出了归一化像素亮度响应分数,从而抑制了由卡尔曼滤波器预测框不准确导致的次优匹配。为了进一步提高模型特征,STFTrack将其跟踪管道中引入了声图像增强方法和频率增强模块(FEM)。综合实验表明,所提出的STFTrack在提出的基准测试上达到了最新性能。代码可在https://github.com/LiYunfengLYF/SonarT165上找到。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
本文介绍了水下声学目标跟踪(UAOT)的挑战和现状。针对缺乏统一评估基准的问题,提出了首个大规模UAOT基准SonarT165,包含165个方形序列、165个扇形序列和205K个高质量标注。实验结果显示SonarT165揭示了当前先进跟踪器的局限性。为解决这些问题,提出了STFTrack框架,包含多视图模板融合模块(MTFM)和最优轨迹校正模块(OTCM)。MTFM模块融合原始图像和动态模板的二进制图像的多视图特征,引入类似交叉注意力的层来融合时空目标表示。OTCM模块引入等效像素响应属性,提出归一化像素亮度响应分数,抑制由不准确Kalman滤波器预测框引起的次优匹配。此外,STFTrack还引入了声音图像增强方法和频率增强模块(FEM),在提出的基准上达到了最先进的性能。
Key Takeaways
- 水下观察系统通常集成了光学相机和成像声纳系统,但当水下能见度不足时,只有声纳系统能提供稳定数据,引出UAOT任务的重要性。
- 缺乏统一评估基准限制了UAOT方法的价值。为此,提出了首个大规模UAOT基准SonarT165,包含多种序列和大量高质量标注。
- 当前先进跟踪器在SonarT165上展现出局限性。
- 为解决这些局限性,提出了STFTrack框架,包括两个新模块:MTFM和OTCM。
- MTFM模块融合多视图特征并引入类似交叉注意力的层来增强目标表示。
- OTCM模块通过引入等效像素响应属性和归一化像素亮度响应分数来优化轨迹。
点此查看论文截图


Context Aware Grounded Teacher for Source Free Object Detection
Authors:Tajamul Ashraf, Rajes Manna, Partha Sarathi Purkayastha, Tavaheed Tariq, Janibul Bashir
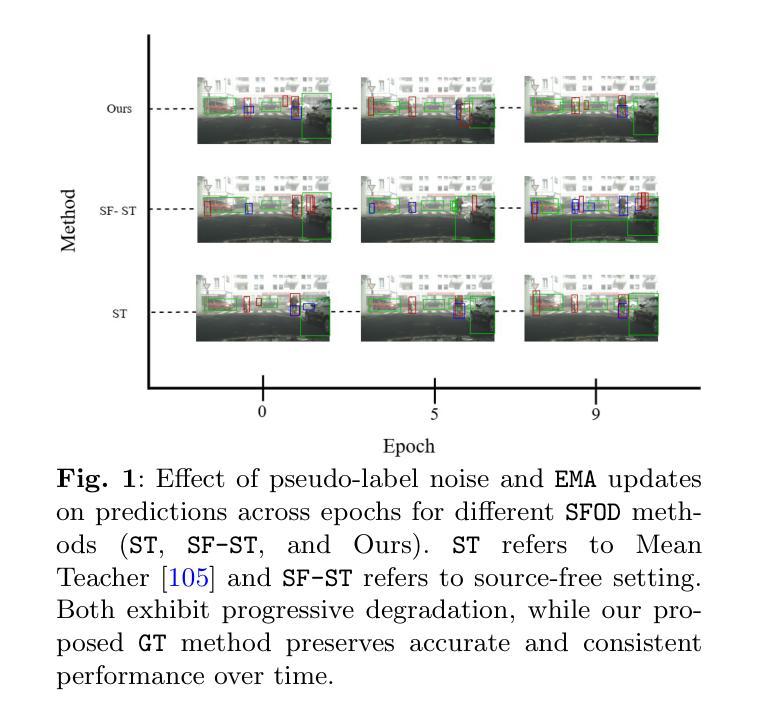
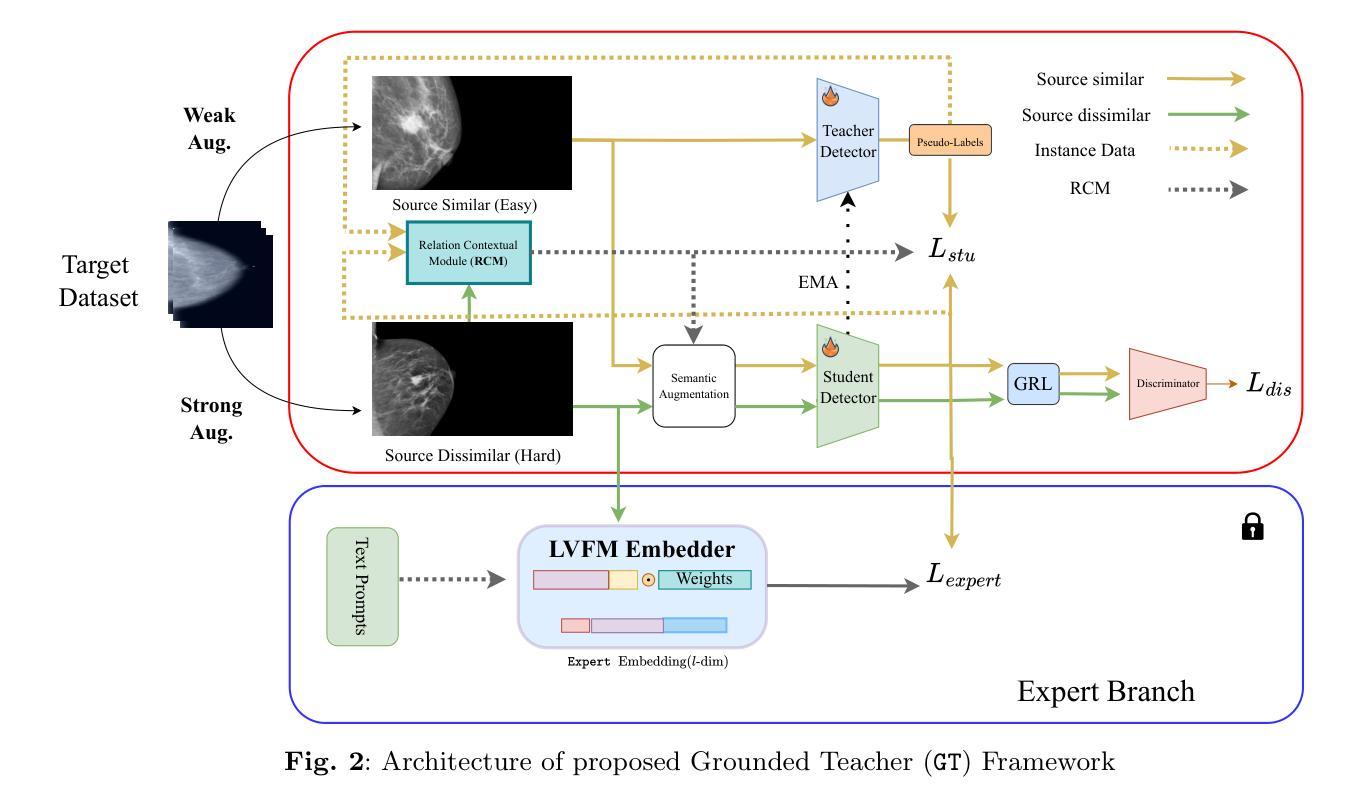
We focus on the Source Free Object Detection (SFOD) problem, when source data is unavailable during adaptation, and the model must adapt to the unlabeled target domain. In medical imaging, several approaches have leveraged a semi-supervised student-teacher architecture to bridge domain discrepancy. Context imbalance in labeled training data and significant domain shifts between domains can lead to biased teacher models that produce inaccurate pseudolabels, degrading the student model’s performance and causing a mode collapse. Class imbalance, particularly when one class significantly outnumbers another, leads to contextual bias. To tackle the problem of context bias and the significant performance drop of the student model in the SFOD setting, we introduce Grounded Teacher (GT) as a standard framework. In this study, we model contextual relationships using a dedicated relational context module and leverage it to mitigate inherent biases in the model. This approach enables us to apply augmentations to closely related classes, across and within domains, enhancing the performance of underrepresented classes while keeping the effect on dominant classes minimal. We further improve the quality of predictions by implementing an expert foundational branch to supervise the student model. We validate the effectiveness of our approach in mitigating context bias under the SFOD setting through experiments on three medical datasets supported by comprehensive ablation studies. All relevant resources, including preprocessed data, trained model weights, and code, are publicly available at this https://github.com/Tajamul21/Grounded_Teacher.
我们主要关注无源目标检测(SFOD)问题,当在适应过程中无法使用源数据时,模型必须适应无标签的目标域。在医学成像中,一些方法已经利用半监督学生-教师架构来弥合领域差异。训练数据中的上下文不平衡以及不同领域之间的领域漂移会导致教师模型产生偏见,从而产生不准确的伪标签,降低学生模型的性能并导致模式崩溃。类别不平衡,特别是当一个类别的数量远远超过另一个类别时,会导致上下文偏差。为了解决上下文偏差和学生在SFOD设置中的显著性能下降问题,我们引入了Grounded Teacher(GT)作为标准框架。在这项研究中,我们使用专用的关系上下文模块对上下文关系进行建模,并利用它来减轻模型中的固有偏见。这种方法使我们能够对紧密相关的类别应用增强技术,跨域和内部域,在提高代表性不足的类别的性能的同时,尽量减少对主导类别的影响。我们进一步通过实现专家基础分支来监督学生模型,以提高预测质量。我们通过三项医学数据集的实验和全面的消融研究验证了我们的方法在缓解SFOD设置下上下文偏差的有效性。所有相关资源,包括预处理数据、训练模型权重和代码,都可在https://github.com/Tajamul21/Grounded_Teacher上公开访问。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
在无源对象检测(SFOD)问题中,当模型必须适应无标签的目标域而源数据不可用的情况下,会出现上下文不平衡和显著的领域转移问题。针对这些问题,本文引入了基于老师-学生架构的Grounded Teacher框架来处理领域差异问题,利用特定的关系上下文模块建立上下文关系以缓解模型固有偏见。通过实施专家基础分支来监督学生模型,提高了预测质量。实验表明,该方法在三个医学数据集上有效缓解了上下文偏见问题。相关资源已在GitHub上公开。
Key Takeaways
- 介绍了在无源对象检测(SFOD)问题中遇到的主要挑战,包括源数据不可用和模型必须适应无标签目标域的困难。
- 采用半监督学生-老师架构来解决医学成像中的领域差异问题。
- 上下文不平衡和领域转移可能导致老师模型产生不准确伪标签,影响学生模型的性能并导致模式崩溃。
- 提出使用Grounded Teacher框架来处理上下文偏见和显著性能下降的问题。
- 通过建立特定的关系上下文模块和利用专家基础分支来监督学生模型,提高了预测质量。
- 在三个医学数据集上的实验验证了Grounded Teacher框架的有效性。
点此查看论文截图