⚠️ 以下所有内容总结都来自于 大语言模型的能力,如有错误,仅供参考,谨慎使用
🔴 请注意:千万不要用于严肃的学术场景,只能用于论文阅读前的初筛!
💗 如果您觉得我们的项目对您有帮助 ChatPaperFree ,还请您给我们一些鼓励!⭐️ HuggingFace免费体验
2025-04-24 更新
From Reflection to Perfection: Scaling Inference-Time Optimization for Text-to-Image Diffusion Models via Reflection Tuning
Authors:Le Zhuo, Liangbing Zhao, Sayak Paul, Yue Liao, Renrui Zhang, Yi Xin, Peng Gao, Mohamed Elhoseiny, Hongsheng Li
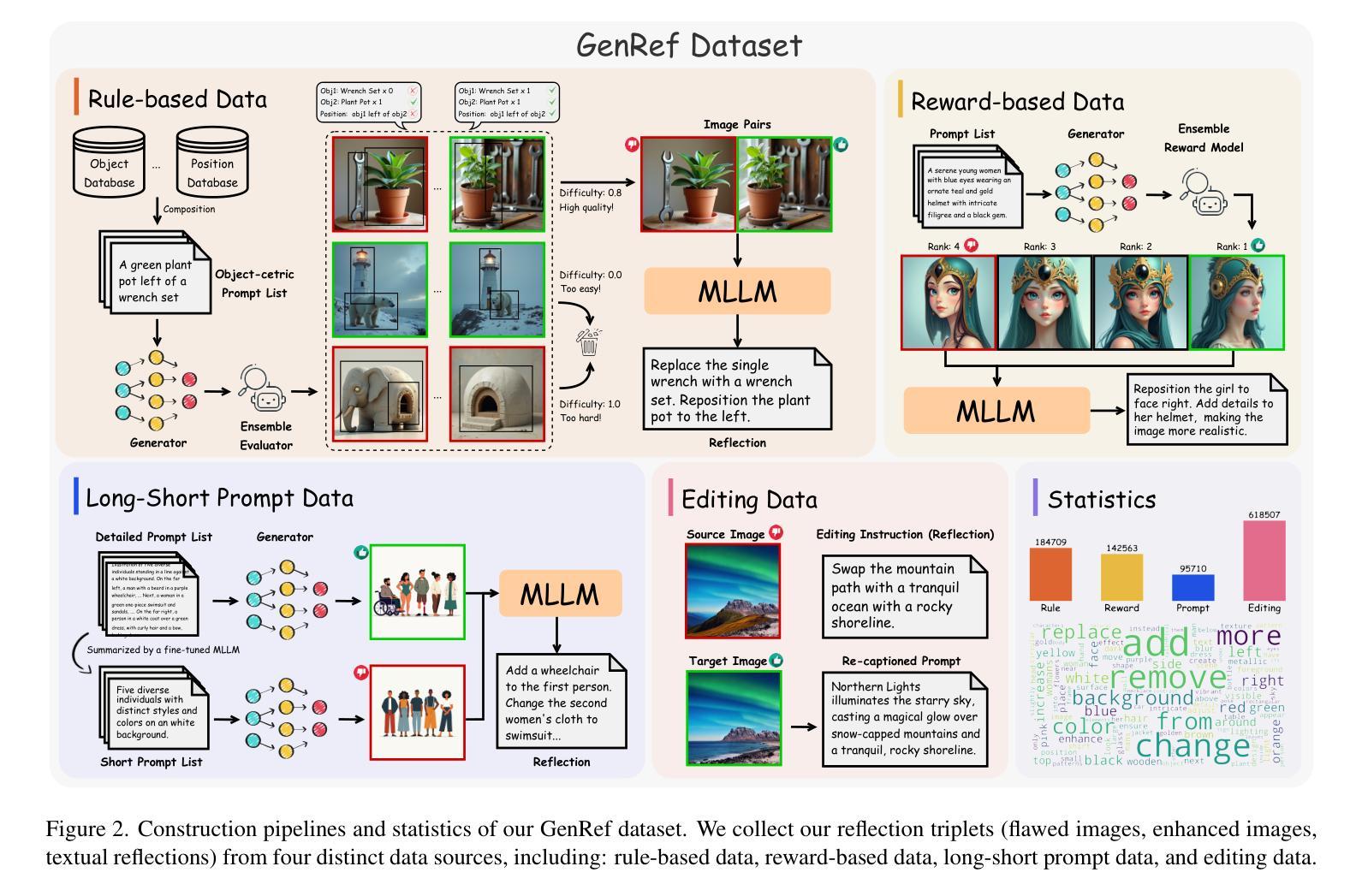
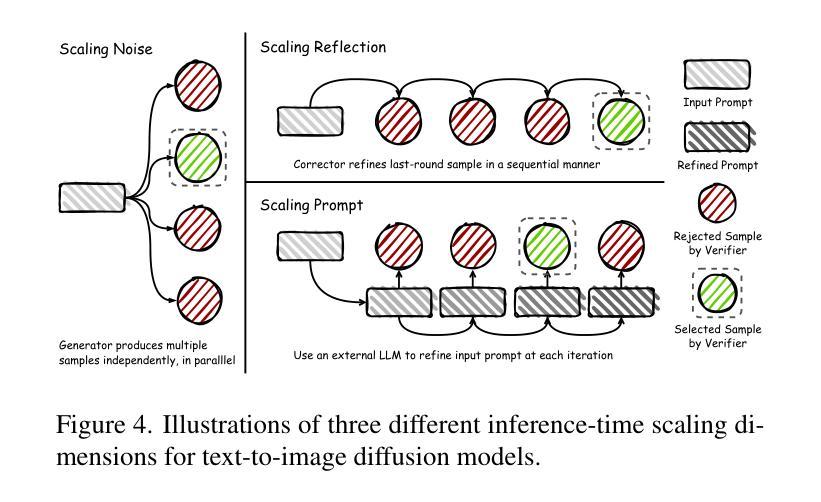
Recent text-to-image diffusion models achieve impressive visual quality through extensive scaling of training data and model parameters, yet they often struggle with complex scenes and fine-grained details. Inspired by the self-reflection capabilities emergent in large language models, we propose ReflectionFlow, an inference-time framework enabling diffusion models to iteratively reflect upon and refine their outputs. ReflectionFlow introduces three complementary inference-time scaling axes: (1) noise-level scaling to optimize latent initialization; (2) prompt-level scaling for precise semantic guidance; and most notably, (3) reflection-level scaling, which explicitly provides actionable reflections to iteratively assess and correct previous generations. To facilitate reflection-level scaling, we construct GenRef, a large-scale dataset comprising 1 million triplets, each containing a reflection, a flawed image, and an enhanced image. Leveraging this dataset, we efficiently perform reflection tuning on state-of-the-art diffusion transformer, FLUX.1-dev, by jointly modeling multimodal inputs within a unified framework. Experimental results show that ReflectionFlow significantly outperforms naive noise-level scaling methods, offering a scalable and compute-efficient solution toward higher-quality image synthesis on challenging tasks.
最近出现的文本到图像的扩散模型通过大规模扩展训练数据和模型参数,实现了令人印象深刻的视觉质量,但它们往往在处理复杂场景和精细细节方面遇到困难。受大型语言模型中出现的自我反思能力的启发,我们提出了ReflectionFlow,这是一个推理时间框架,能够使扩散模型迭代地反思和完善其输出。ReflectionFlow引入了三种互补的推理时间尺度轴:(1)噪声水平尺度优化潜在初始化;(2)提示水平尺度提供精确语义指导;以及最值得注意的是(3)反思水平尺度,它明确提供了可操作的反思来迭代评估和纠正之前的生成。为了促进反思水平尺度的发展,我们构建了GenRef数据集,该数据集包含100万组三元组,每组包含一次反思、一个缺陷图像和一个增强的图像。利用此数据集,我们在统一框架下联合建模多模式输入,对最先进的扩散变压器FLUX.1-dev进行高效反射调优。实验结果表明,ReflectionFlow显著优于简单的噪声水平尺度方法,为具有挑战性的任务提供了可伸缩和计算高效的解决方案,以实现更高质量的图像合成。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF All code, checkpoints, and datasets are available at \url{https://diffusion-cot.github.io/reflection2perfection}
Summary
本文介绍了基于文本到图像扩散模型的改进方案ReflectionFlow,它通过引入噪声级别缩放、提示级别缩放和反射级别缩放三种互补的推理时间缩放轴,提升了扩散模型的性能。其中,反射级别缩放能够显式地提供反馈来迭代评估和修正之前的生成图像。实验结果表明,ReflectionFlow在具有挑战性的任务上显著优于简单的噪声级别缩放方法,为高质量图像合成提供了可扩展和计算高效的解决方案。
Key Takeaways
- 扩散模型虽能通过大规模的训练数据和模型参数实现高质量的图像生成,但在复杂场景和精细细节方面存在挑战。
- ReflectionFlow是一个推理时间框架,启用了扩散模型的迭代反思和细化输出能力。
- ReflectionFlow引入了三种互补的推理时间缩放轴:噪声级别缩放、提示级别缩放和反射级别缩放。
- 反射级别缩放能够明确提供反馈,以迭代评估和修正之前的生成图像。
- 为了促进反射级别缩放,构建了GenRef数据集,包含百万个三元组,每个包含反思、有缺陷的图像和增强的图像。
- 利用GenRef数据集,在最新扩散变压器FLUX上进行了高效反射调整。
点此查看论文截图


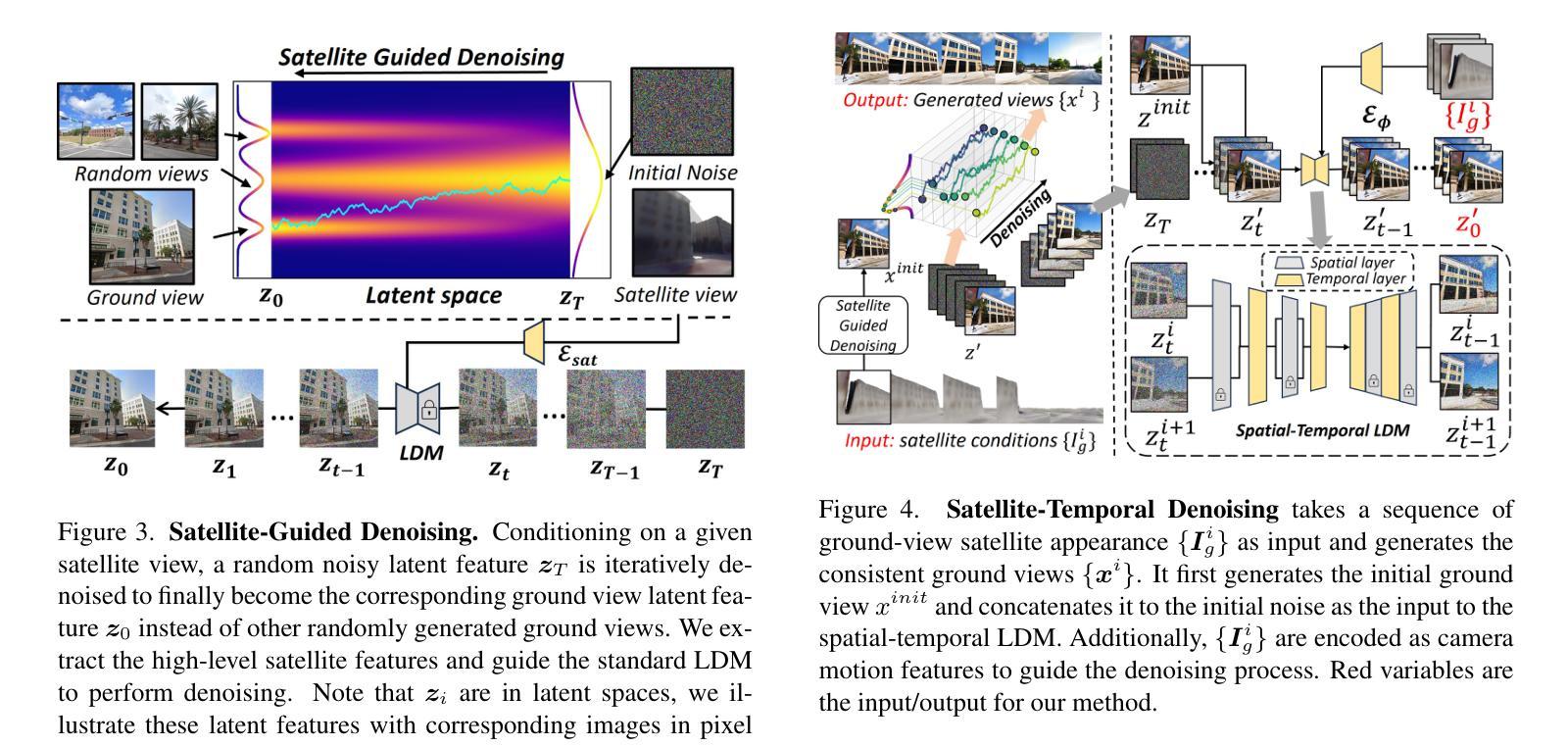
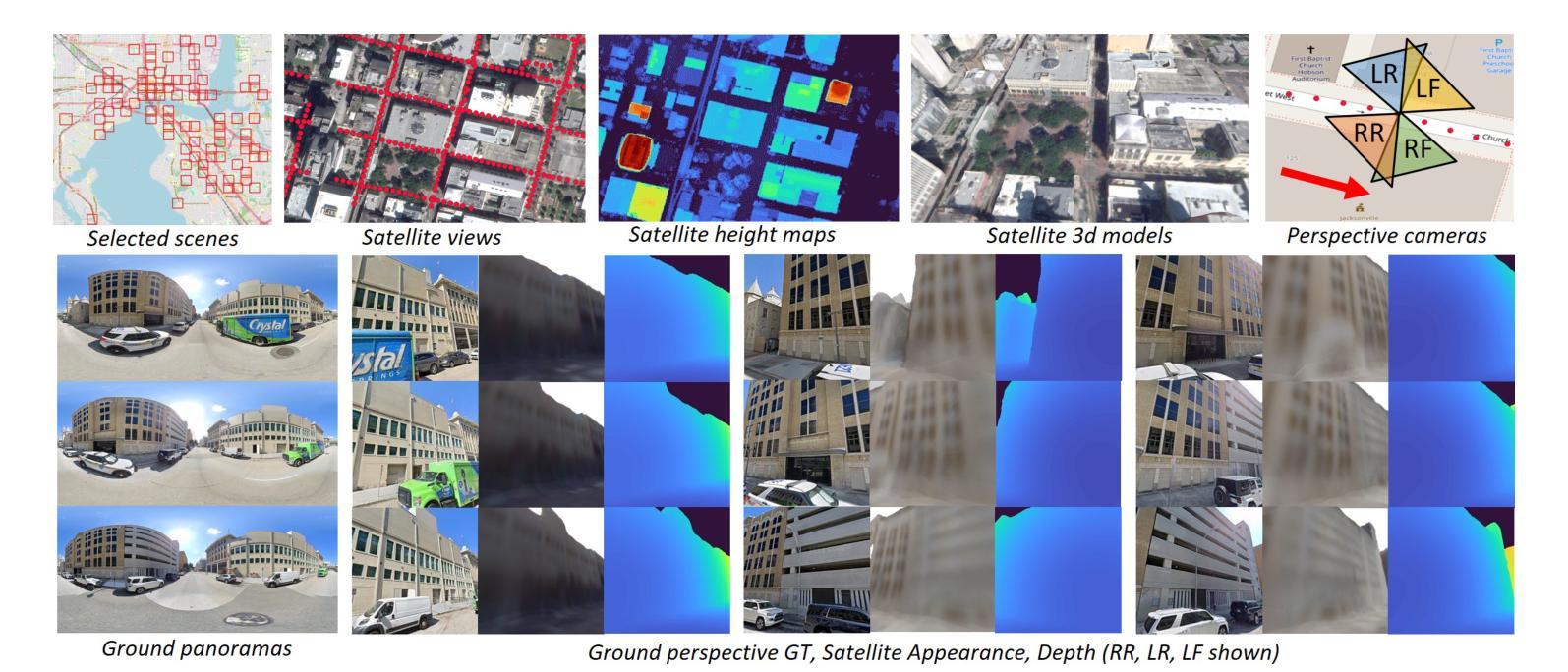
Satellite to GroundScape – Large-scale Consistent Ground View Generation from Satellite Views
Authors:Ningli Xu, Rongjun Qin
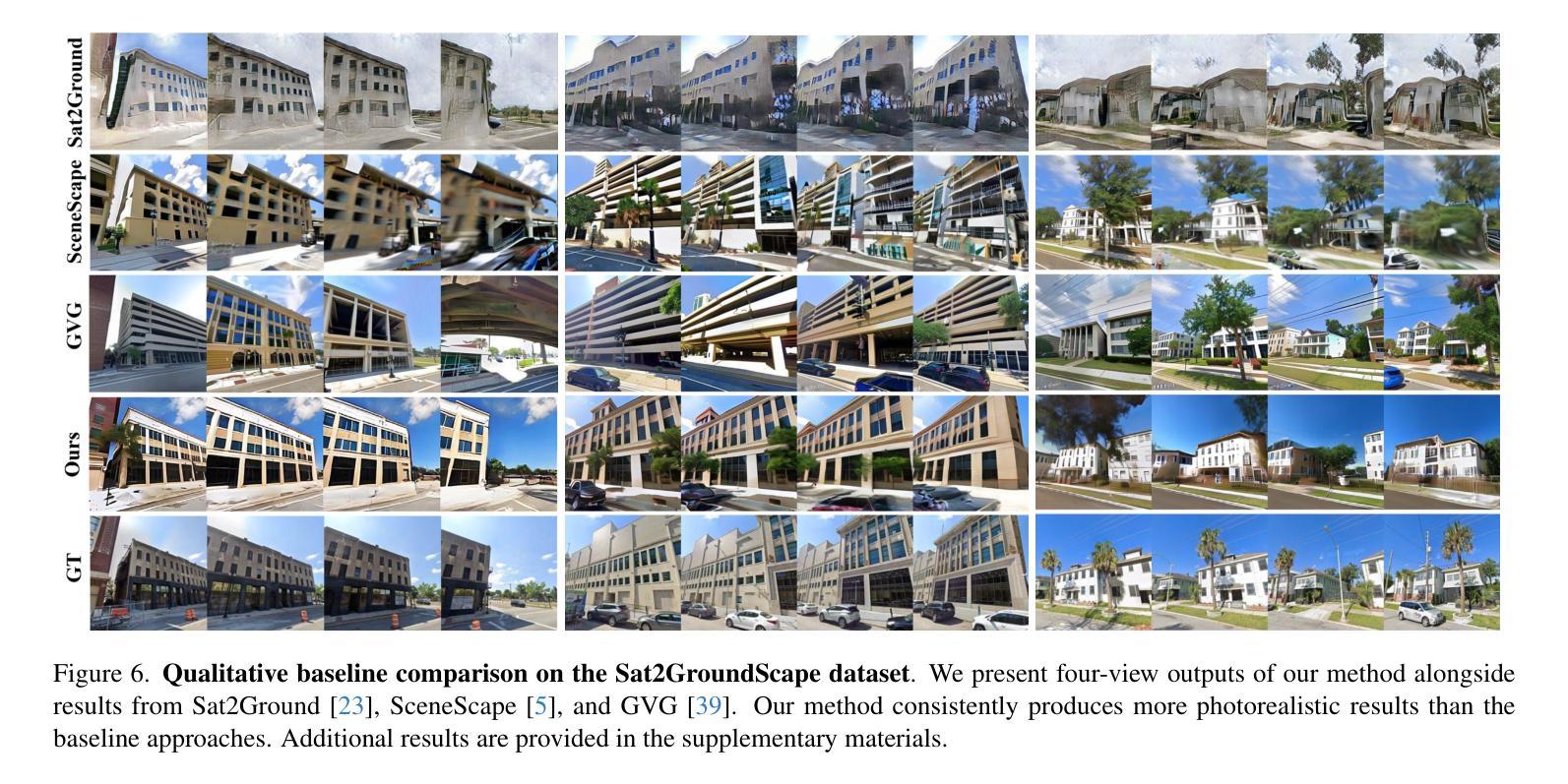
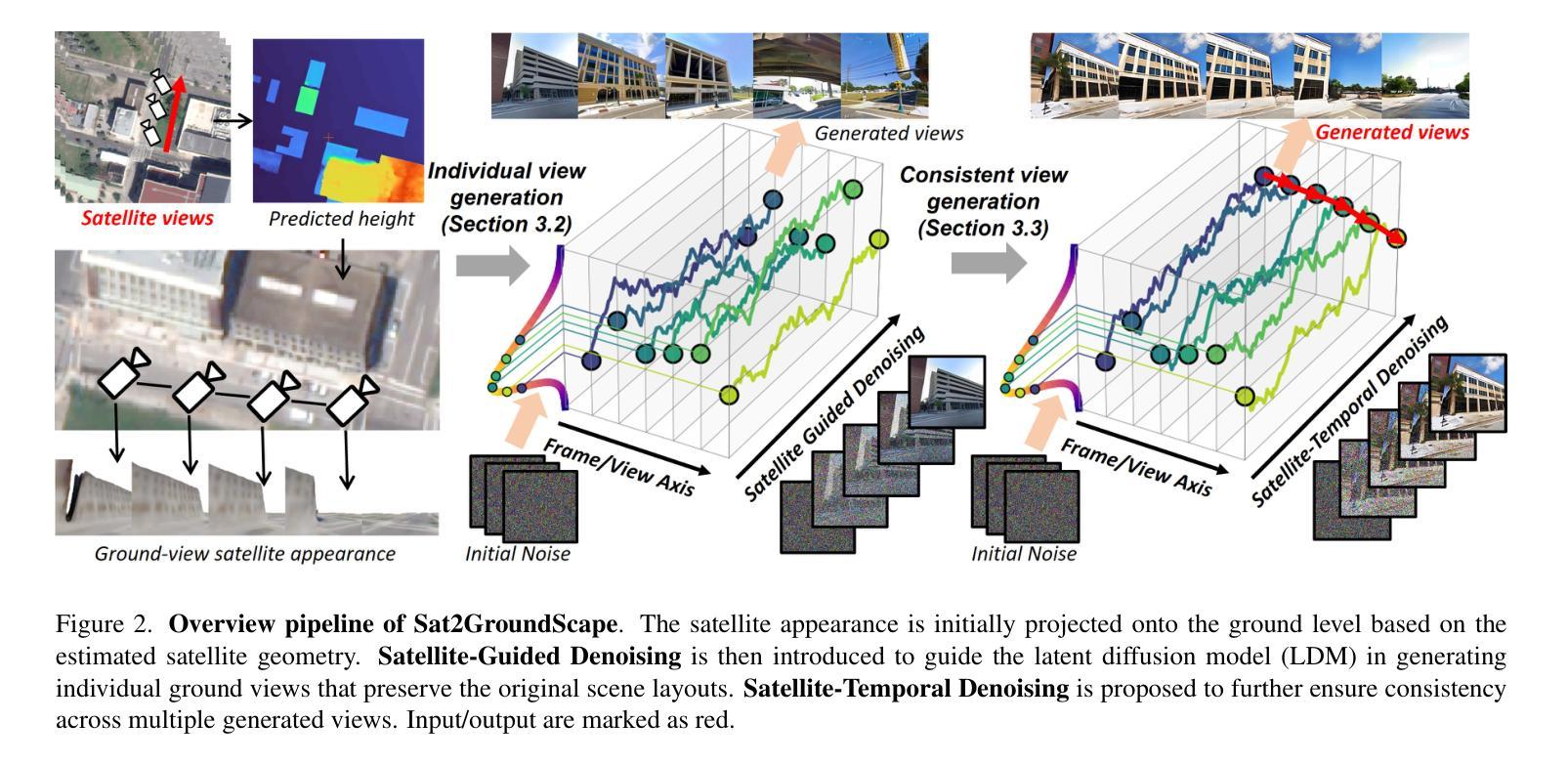
Generating consistent ground-view images from satellite imagery is challenging, primarily due to the large discrepancies in viewing angles and resolution between satellite and ground-level domains. Previous efforts mainly concentrated on single-view generation, often resulting in inconsistencies across neighboring ground views. In this work, we propose a novel cross-view synthesis approach designed to overcome these challenges by ensuring consistency across ground-view images generated from satellite views. Our method, based on a fixed latent diffusion model, introduces two conditioning modules: satellite-guided denoising, which extracts high-level scene layout to guide the denoising process, and satellite-temporal denoising, which captures camera motion to maintain consistency across multiple generated views. We further contribute a large-scale satellite-ground dataset containing over 100,000 perspective pairs to facilitate extensive ground scene or video generation. Experimental results demonstrate that our approach outperforms existing methods on perceptual and temporal metrics, achieving high photorealism and consistency in multi-view outputs.
从卫星图像生成连贯的地面视图图像是一项挑战,主要是由于卫星和地面领域之间观看角度和分辨率存在很大差异。之前的研究主要集中在单视图生成上,往往导致相邻地面视图之间出现不一致。在这项工作中,我们提出了一种新的跨视图合成方法,旨在通过确保从卫星视图生成的地面视图图像之间的一致性来克服这些挑战。我们的方法基于固定的潜在扩散模型,引入了两个条件模块:卫星引导去噪,用于提取高级场景布局以引导去噪过程;卫星时间去噪,用于捕获摄像机运动以维持多个生成视图之间的一致性。我们还贡献了一个大规模卫星地面数据集,包含超过10万个透视对,以促进广泛的地面场景或视频生成。实验结果表明,我们的方法在感知和时间度量上优于现有方法,实现了多视图输出的高逼真度和一致性。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF 8 figures
Summary
本文提出一种基于固定潜在扩散模型的新型跨视图合成方法,旨在克服从卫星图像生成地面视图图像的挑战。该方法通过引入卫星引导去噪和卫星时间去噪两个条件模块,确保从不同卫星视图生成的地面视图图像之间的一致性。同时,贡献了一个大规模卫星-地面数据集,包含超过10万对视角数据,以促进地面场景或视频生成的研究。实验结果证明,该方法在感知和时间度量上优于现有方法,实现了多视图输出的高逼真度和一致性。
Key Takeaways
- 跨视图合成方法被提出,旨在从卫星图像生成一致的地面视图图像。
- 方法基于固定潜在扩散模型,确保多视图之间的一致性。
- 引入两个条件模块:卫星引导去噪和卫星时间去噪,以优化生成过程。
- 贡献了一个大规模卫星-地面数据集,包含超过10万对视角数据。
- 方法在感知和时间度量上表现出优越性。
- 生成的结果具有高逼真度和多视图的一致性。
点此查看论文截图


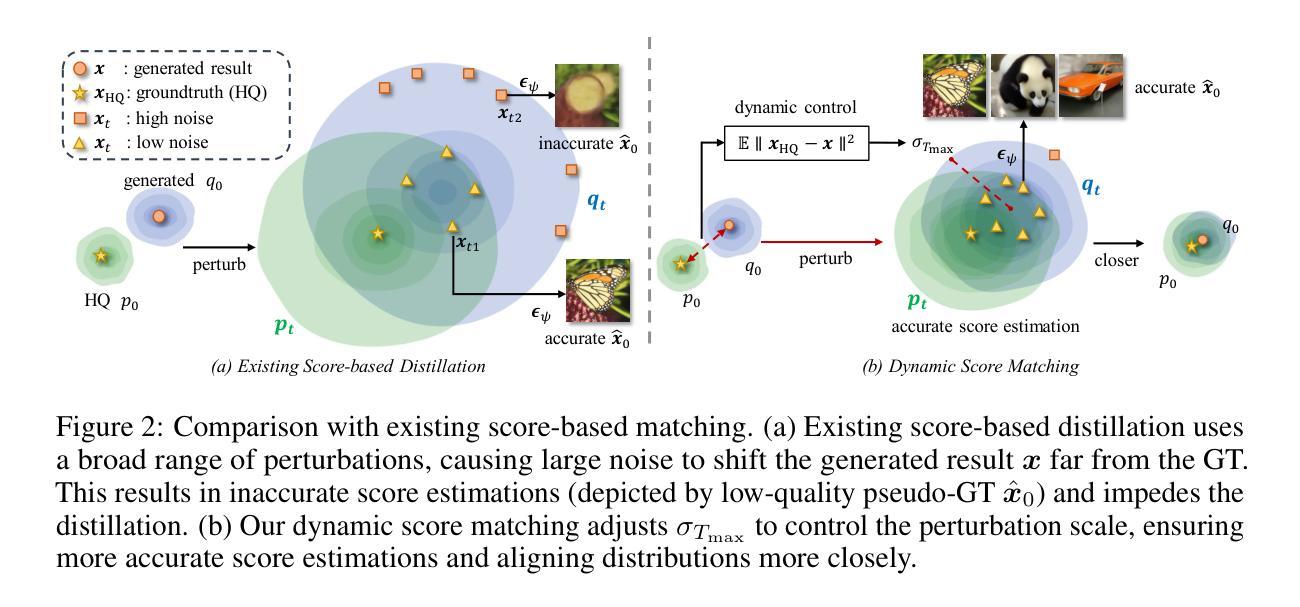
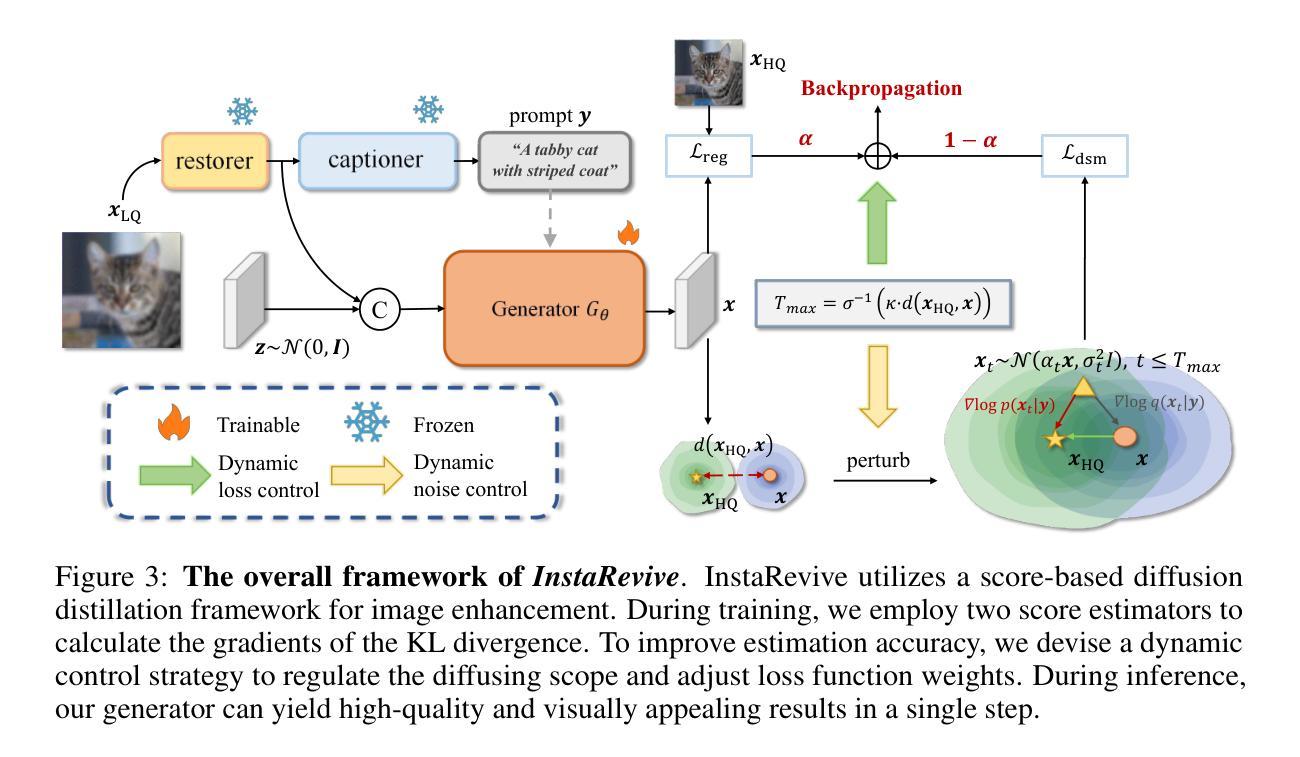
InstaRevive: One-Step Image Enhancement via Dynamic Score Matching
Authors:Yixuan Zhu, Haolin Wang, Ao Li, Wenliang Zhao, Yansong Tang, Jingxuan Niu, Lei Chen, Jie Zhou, Jiwen Lu
Image enhancement finds wide-ranging applications in real-world scenarios due to complex environments and the inherent limitations of imaging devices. Recent diffusion-based methods yield promising outcomes but necessitate prolonged and computationally intensive iterative sampling. In response, we propose InstaRevive, a straightforward yet powerful image enhancement framework that employs score-based diffusion distillation to harness potent generative capability and minimize the sampling steps. To fully exploit the potential of the pre-trained diffusion model, we devise a practical and effective diffusion distillation pipeline using dynamic control to address inaccuracies in updating direction during score matching. Our control strategy enables a dynamic diffusing scope, facilitating precise learning of denoising trajectories within the diffusion model and ensuring accurate distribution matching gradients during training. Additionally, to enrich guidance for the generative power, we incorporate textual prompts via image captioning as auxiliary conditions, fostering further exploration of the diffusion model. Extensive experiments substantiate the efficacy of our framework across a diverse array of challenging tasks and datasets, unveiling the compelling efficacy and efficiency of InstaRevive in delivering high-quality and visually appealing results. Code is available at https://github.com/EternalEvan/InstaRevive.
图像增强在现实场景中具有广泛的应用,这归功于复杂的环境和成像设备固有的局限性。虽然最近的扩散方法产生了有前途的结果,但它们需要进行长期和计算密集型的迭代采样。针对这一问题,我们提出了InstaRevive,这是一个简单而强大的图像增强框架,它采用基于分数的扩散蒸馏来利用强大的生成能力并减少采样步骤。为了充分利用预训练扩散模型的潜力,我们设计了一个实用有效的扩散蒸馏管道,使用动态控制来解决分数匹配过程中更新方向的不准确问题。我们的控制策略能够实现动态扩散范围,便于在扩散模型中精确学习去噪轨迹,并在训练过程中确保准确的分布匹配梯度。此外,为了丰富生成能力的指导,我们通过图像描述作为辅助条件融入文本提示,促进扩散模型的进一步探索。大量实验证明,我们的框架在多种具有挑战性的任务和数据集上效果显著,揭示了InstaRevive在提供高质量和视觉上吸引人的结果方面的令人信服的有效性和效率。代码可通过以下网址获取:https://github.com/EternalEvan/InstaRevive。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF Accepted by ICLR 2025
Summary
针对图像增强在真实场景中的广泛应用及成像设备的固有局限性,提出了一种基于扩散蒸馏的即时增强框架InstaRevive。通过得分为基础的扩散蒸馏技术实现强大的生成能力和减少采样步骤。使用动态控制策略实现预训练扩散模型的潜力最大化,确保精确学习去噪轨迹和分布匹配梯度。结合图像描述文本提示作为辅助条件,进一步探索扩散模型的潜力。实验证明,该框架在多种挑战任务和数据集上效果显著。
Key Takeaways
- InstaRevive是一个基于扩散蒸馏的图像增强框架,旨在解决复杂环境和成像设备限制下的图像问题。
- 该框架采用得分基础的扩散蒸馏技术,以强大的生成能力和减少采样步骤为特点。
- 通过动态控制策略实现预训练扩散模型的潜力最大化,确保精确的去噪轨迹学习和分布匹配梯度的准确性。
- InstaRevive结合图像描述文本提示,作为辅助条件来丰富生成力量的指导。
- 框架在多种挑战任务和数据集上进行了广泛实验,证明了其有效性和高效率。
- 该框架可提供高质量和视觉吸引力的结果。
点此查看论文截图


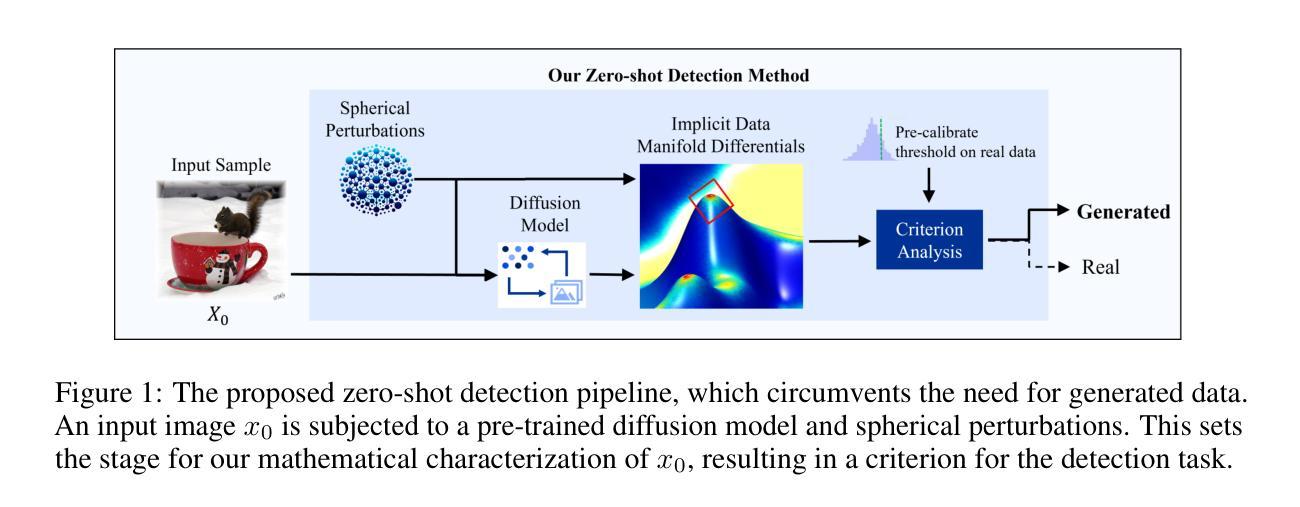
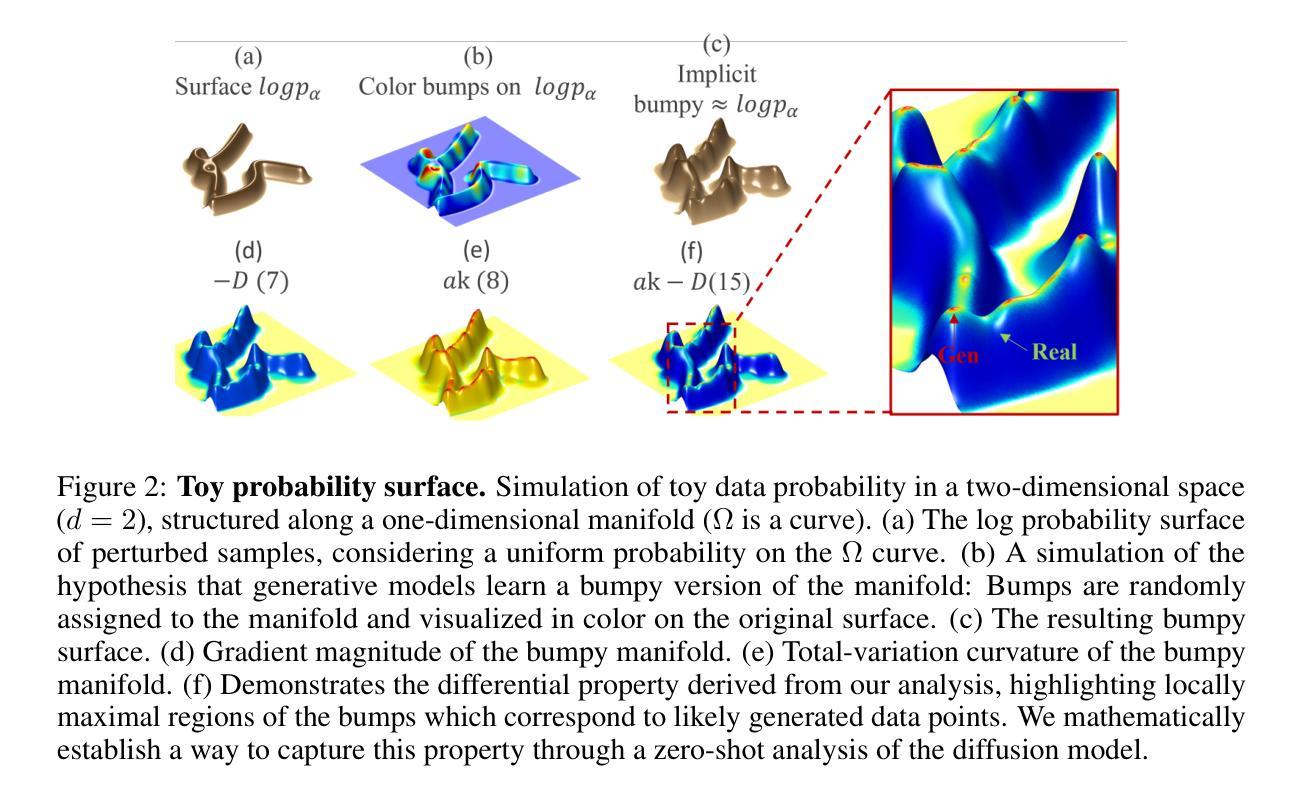
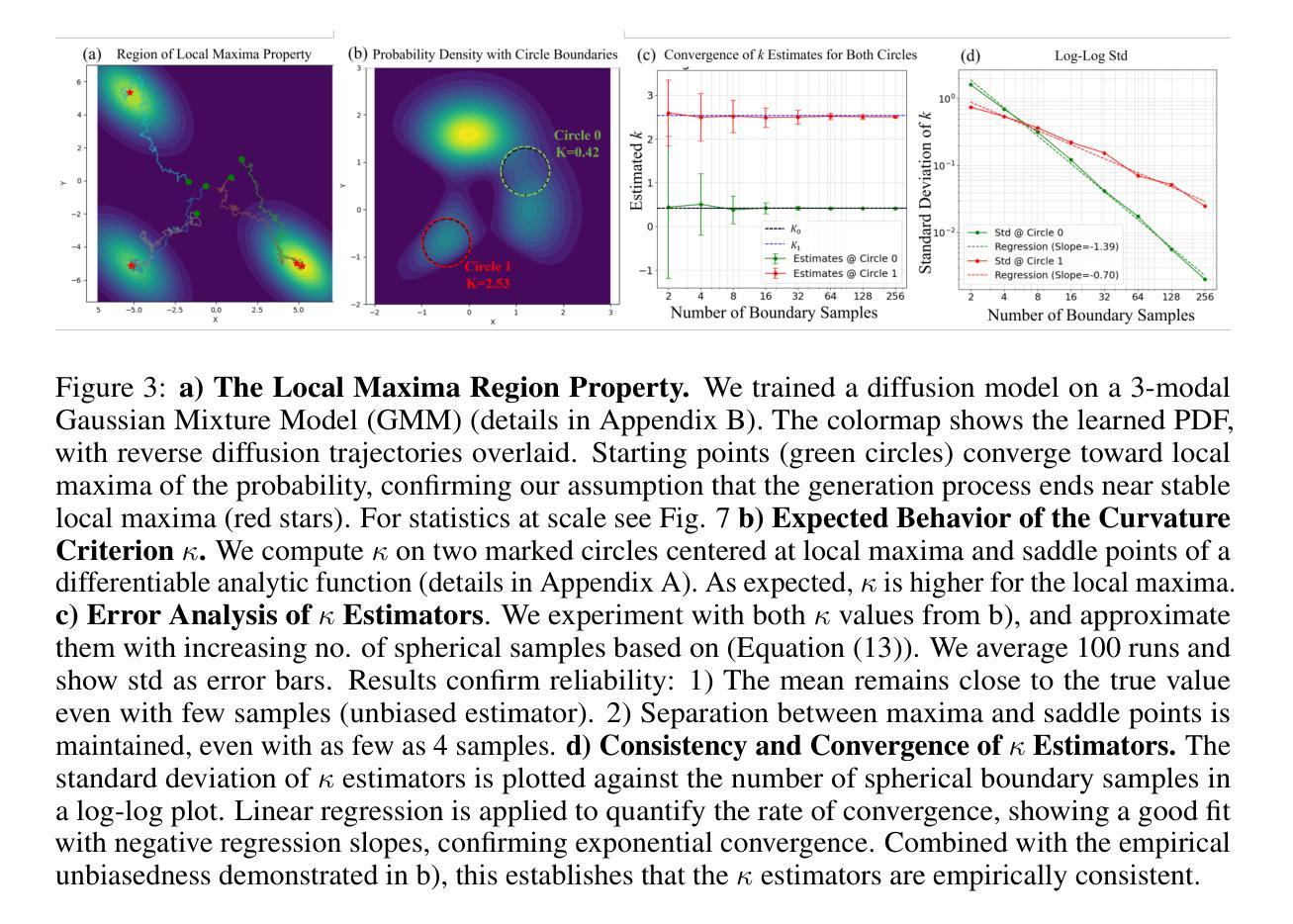
Manifold Induced Biases for Zero-shot and Few-shot Detection of Generated Images
Authors:Jonathan Brokman, Amit Giloni, Omer Hofman, Roman Vainshtein, Hisashi Kojima, Guy Gilboa
Distinguishing between real and AI-generated images, commonly referred to as ‘image detection’, presents a timely and significant challenge. Despite extensive research in the (semi-)supervised regime, zero-shot and few-shot solutions have only recently emerged as promising alternatives. Their main advantage is in alleviating the ongoing data maintenance, which quickly becomes outdated due to advances in generative technologies. We identify two main gaps: (1) a lack of theoretical grounding for the methods, and (2) significant room for performance improvements in zero-shot and few-shot regimes. Our approach is founded on understanding and quantifying the biases inherent in generated content, where we use these quantities as criteria for characterizing generated images. Specifically, we explore the biases of the implicit probability manifold, captured by a pre-trained diffusion model. Through score-function analysis, we approximate the curvature, gradient, and bias towards points on the probability manifold, establishing criteria for detection in the zero-shot regime. We further extend our contribution to the few-shot setting by employing a mixture-of-experts methodology. Empirical results across 20 generative models demonstrate that our method outperforms current approaches in both zero-shot and few-shot settings. This work advances the theoretical understanding and practical usage of generated content biases through the lens of manifold analysis.
区分真实图像和人工智能生成的图像,通常被称为“图像检测”,这是一个及时且重大的挑战。尽管在(半)监督制度方面进行了大量研究,但零样本和少样本解决方案最近才作为有前途的替代方案出现。它们的主要优势在于缓解了正在进行的数据维护问题,由于生成技术的不断进步,这些数据很快会过时。我们发现了两个主要空白:(1)这些方法缺乏理论支撑,(2)在零样本和少样本制度下,性能仍有很大提升空间。我们的方法建立在理解和量化生成内容所固有的偏见上,我们使用这些量作为表征生成图像的标准。具体来说,我们探索了由预训练扩散模型捕获的隐概率流形偏见。通过得分函数分析,我们近似概率流形上的点处的曲率、梯度和偏见,为无样本制度下建立检测标准。我们进一步通过将混合专家方法应用于少样本设置来扩展我们的贡献。在跨越20个生成模型的实证结果表明,我们的方法在零样本和少样本设置中都优于当前方法。这项工作通过流形分析的角度,推动了生成内容偏见的理论理解的实际应用。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF Accepted to ICLR 2025 (The International Conference on Learning Representations)
Summary
本文探讨了区分真实图像和AI生成图像的挑战,重点介绍了基于生成内容偏见的检测方法和理论。通过理解并量化生成内容中的偏见,使用预训练的扩散模型捕获隐式概率流形,通过评分函数分析近似曲率、梯度和概率流形上的点偏向,建立零样本下的检测标准。同时,采用混合专家方法解决小样本问题,并在20个生成模型上进行实证测试,证明该方法在零样本和小样本环境下均优于现有方法。
Key Takeaways
- 区分真实和AI生成的图像是一个及时且重要的挑战。
- 零样本和少样本解决方案是新兴的有前途的替代方法,可以缓解数据维护的问题。
- 当前方法缺乏理论支撑和性能改进的空间。
- 本文通过理解并量化生成内容中的偏见来建立检测标准。
- 使用预训练的扩散模型捕获隐式概率流形,通过评分函数分析进行图像检测。
- 在零样本和小样本环境下,该方法均表现出优异的性能。
点此查看论文截图

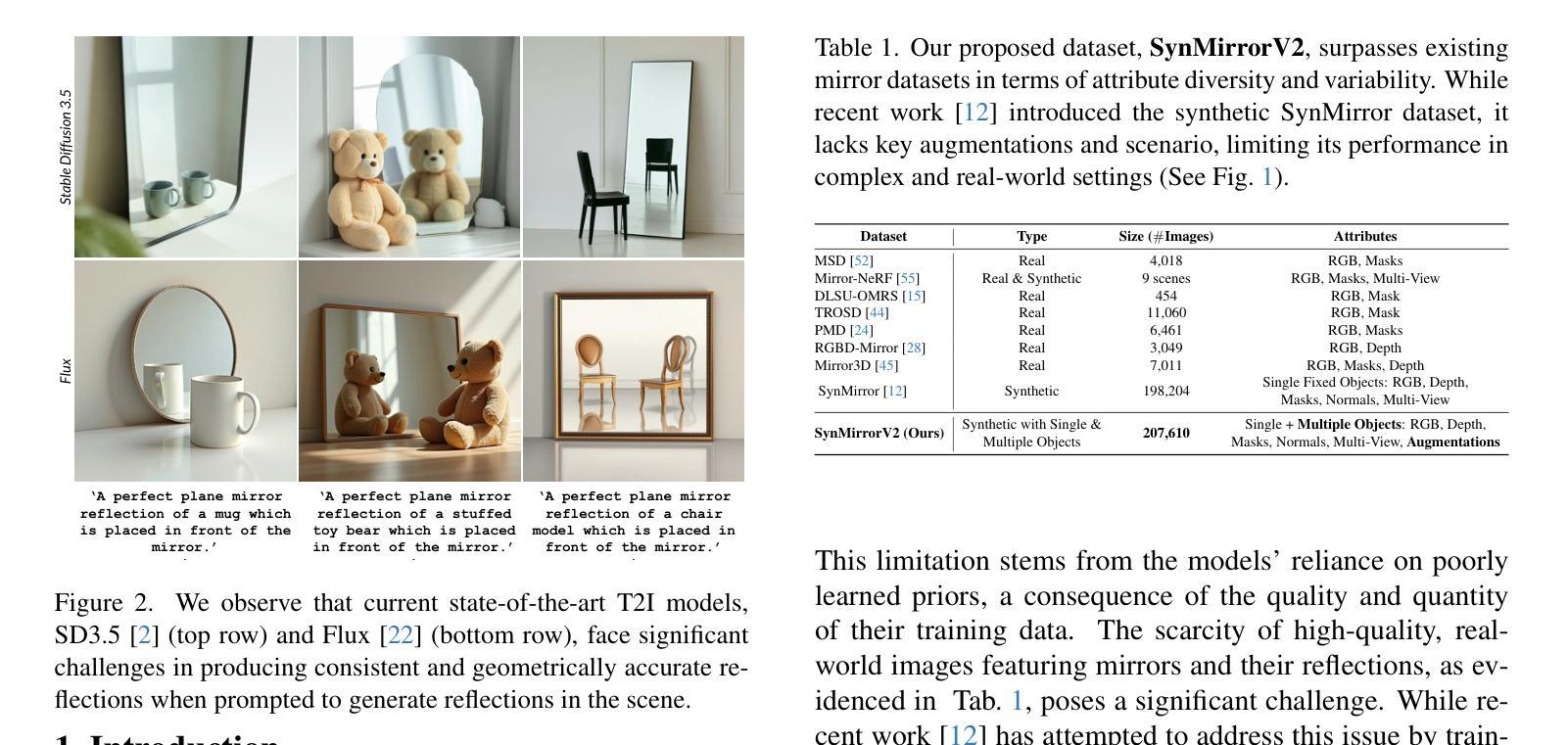
MirrorVerse: Pushing Diffusion Models to Realistically Reflect the World
Authors:Ankit Dhiman, Manan Shah, R Venkatesh Babu
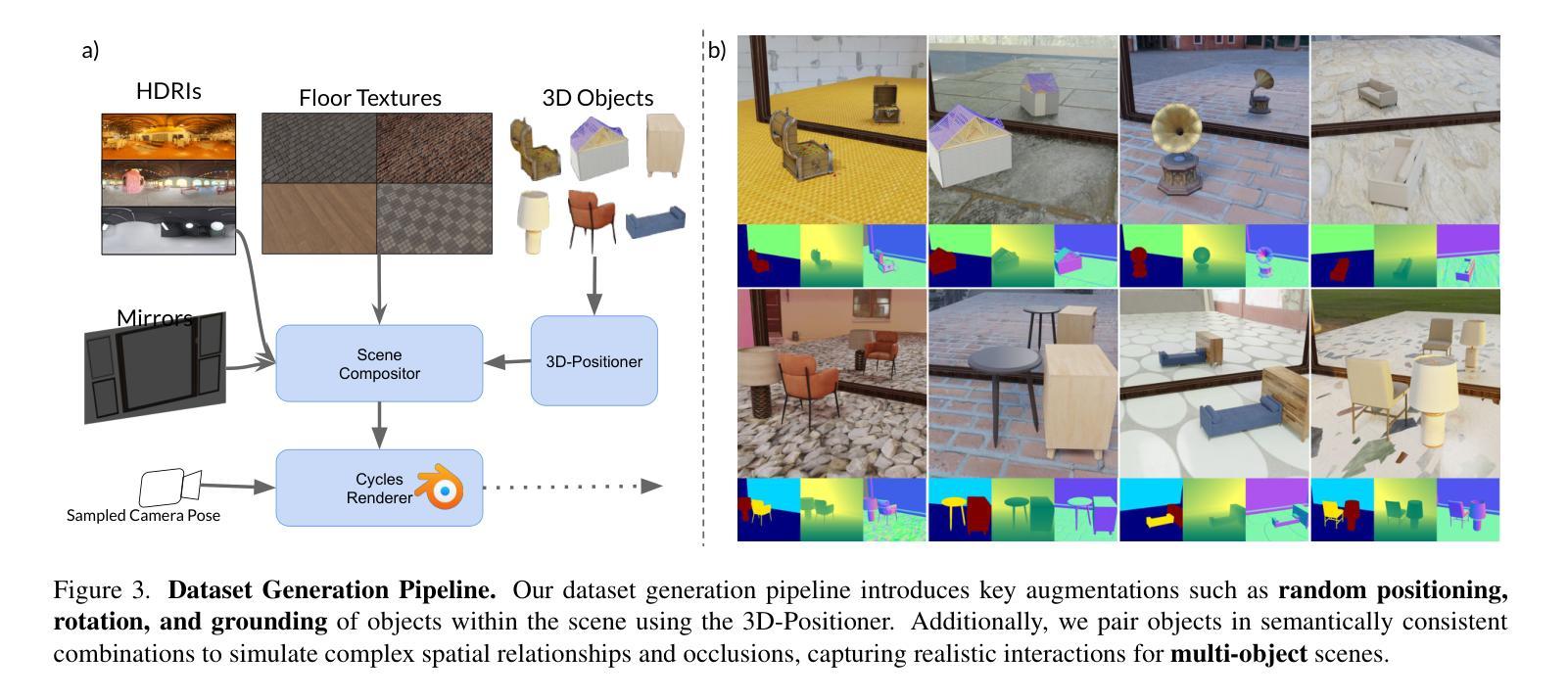
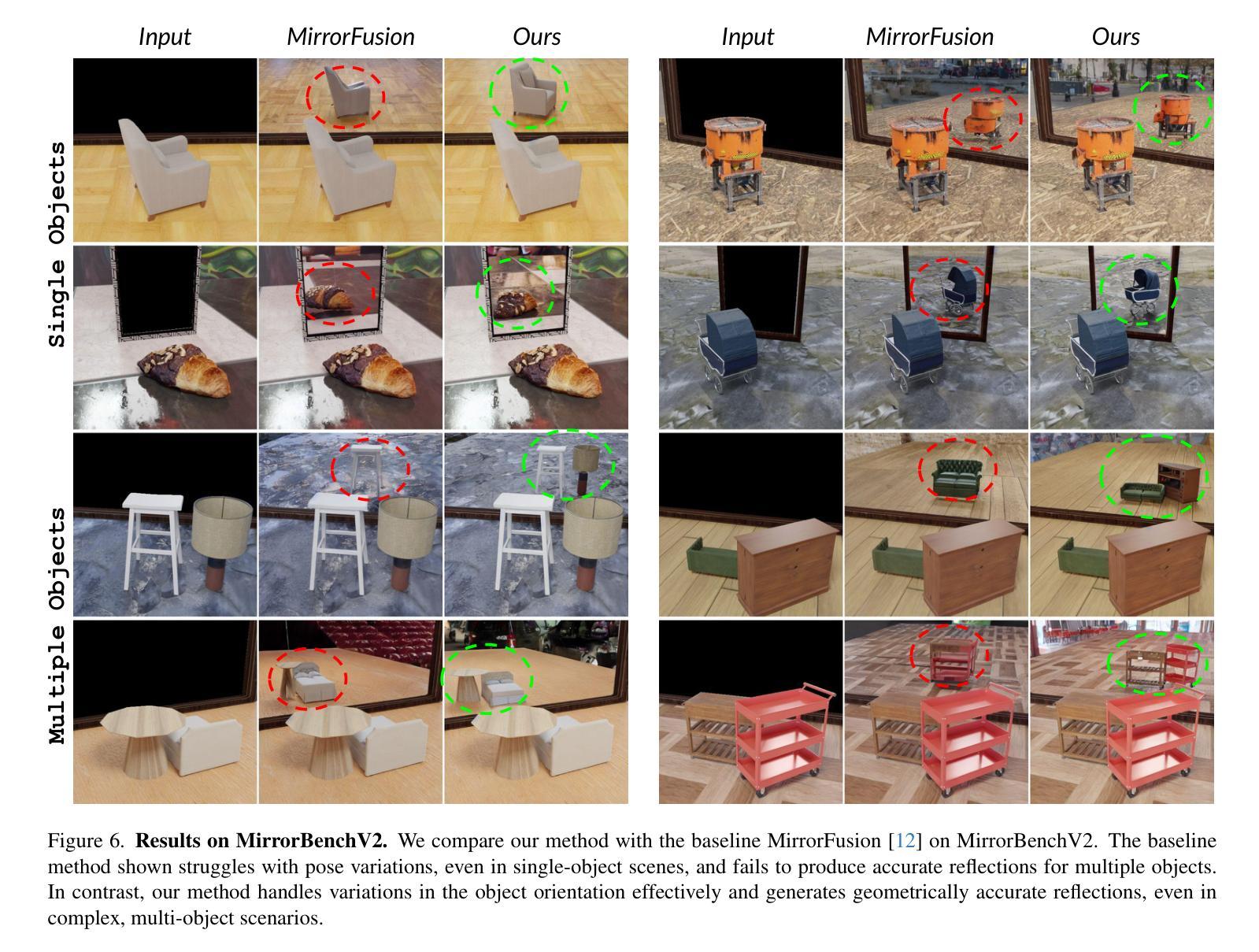
Diffusion models have become central to various image editing tasks, yet they often fail to fully adhere to physical laws, particularly with effects like shadows, reflections, and occlusions. In this work, we address the challenge of generating photorealistic mirror reflections using diffusion-based generative models. Despite extensive training data, existing diffusion models frequently overlook the nuanced details crucial to authentic mirror reflections. Recent approaches have attempted to resolve this by creating synhetic datasets and framing reflection generation as an inpainting task; however, they struggle to generalize across different object orientations and positions relative to the mirror. Our method overcomes these limitations by introducing key augmentations into the synthetic data pipeline: (1) random object positioning, (2) randomized rotations, and (3) grounding of objects, significantly enhancing generalization across poses and placements. To further address spatial relationships and occlusions in scenes with multiple objects, we implement a strategy to pair objects during dataset generation, resulting in a dataset robust enough to handle these complex scenarios. Achieving generalization to real-world scenes remains a challenge, so we introduce a three-stage training curriculum to develop the MirrorFusion 2.0 model to improve real-world performance. We provide extensive qualitative and quantitative evaluations to support our approach. The project page is available at: https://mirror-verse.github.io/.
扩散模型在各种图像编辑任务中发挥着核心作用,但它们往往不能完全遵守物理定律,特别是在阴影、反射和遮挡等效果方面。在这项工作中,我们致力于利用基于扩散的生成模型生成逼真的镜面反射图像。尽管有大量的训练数据,但现有的扩散模型往往会忽略对真实镜面反射至关重要的细微细节。最近的方法试图通过创建合成数据集并将反射生成视为填充任务来解决这个问题;然而,它们在镜子不同方向和位置的泛化方面存在困难。我们的方法通过向合成数据管道中添加关键增强来克服这些限制:(1)随机对象定位,(2)随机旋转,(3)对象接地,显著提高了姿势和放置的泛化能力。为了进一步解决具有多个对象的场景中的空间关系和遮挡问题,我们在数据集生成过程中实现了对象配对策略,从而得到一个足以应对这些复杂场景的稳健数据集。实现向真实世界场景的泛化仍然是一个挑战,因此我们引入了一个三阶段训练课程来开发MirrorFusion 2.0模型,以提高其在现实世界中的性能。我们提供了广泛的质量和数量评估来支持我们的方法。项目页面可通过以下网址访问:https://mirror-verse.github.io/。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF Accepted to CVPR 2025. Project Page: https://mirror-verse.github.io/
Summary
本文解决了扩散模型在生成真实镜面反射图像时面临的挑战,通过引入关键增强手段,如随机物体定位、随机旋转和物体定位,提高了模型在不同姿态和放置场景下的泛化能力。为解决多物体场景中空间关系和遮挡问题,项目实施了配对物体生成数据集策略。为提升现实场景的泛化性能,还推出了三阶段训练课程来完善MirrorFusion 2.0模型。
Key Takeaways
- 扩散模型在图像编辑任务中扮演核心角色,但在处理镜面反射等物理效应时面临挑战。
- 现有扩散模型难以捕捉镜面反射的细微细节。
- 现有方法通过创建合成数据集和将反射生成视为补全任务来解决此问题,但难以泛化不同物体相对于镜子的方向和位置。
- 本文通过引入随机物体定位、随机旋转和物体定位关键增强手段,提高了模型的泛化能力。
- 为处理多物体场景中的空间关系和遮挡,项目实施了配对物体生成数据集策略。
- 为提升在现实场景的泛化性能,采用了三阶段训练课程完善模型。
点此查看论文截图



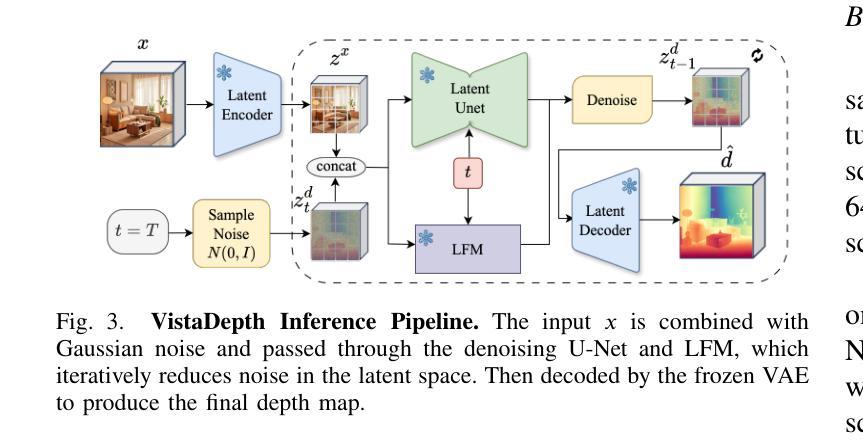
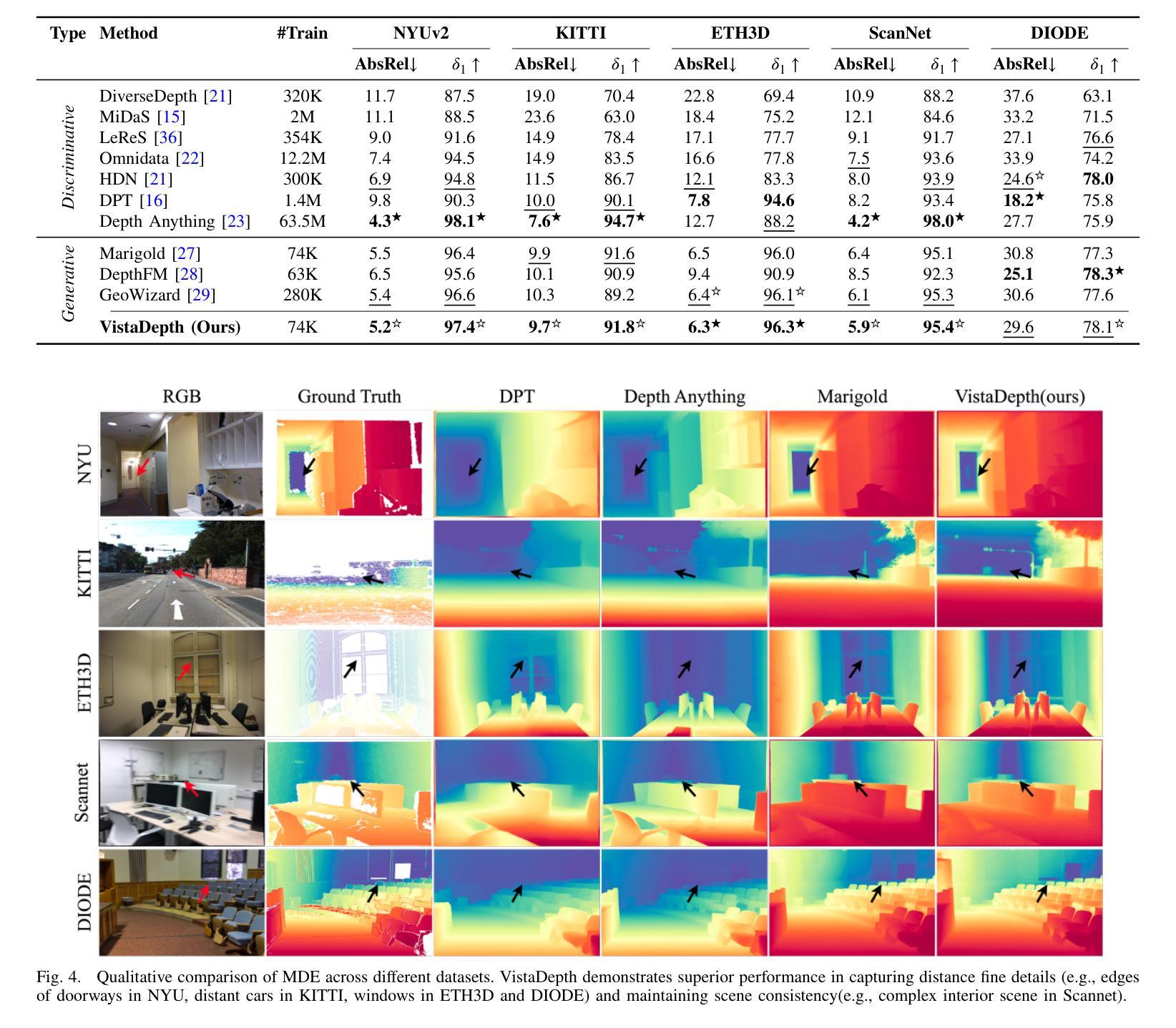
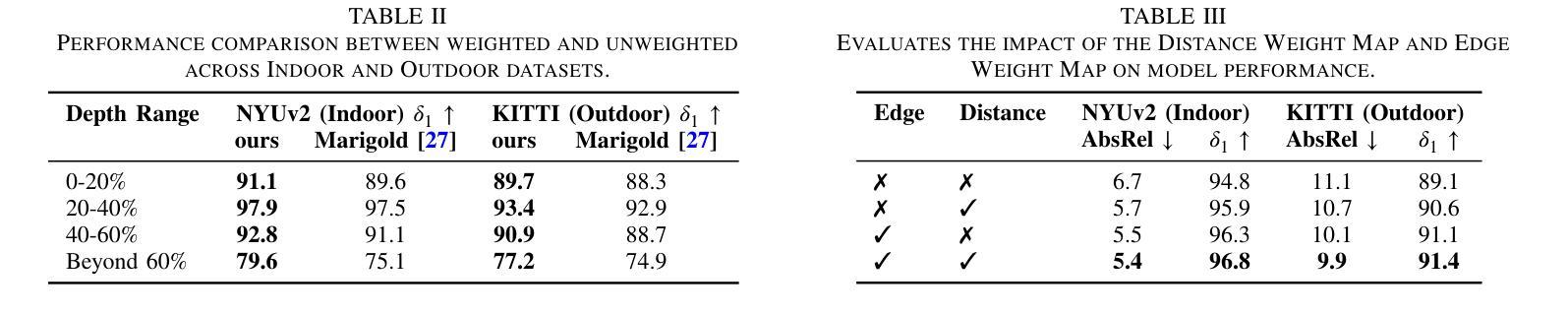
VistaDepth: Frequency Modulation With Bias Reweighting For Enhanced Long-Range Depth Estimation
Authors:Mingxia Zhan, Li Zhang, Xiaomeng Chu, Beibei Wang
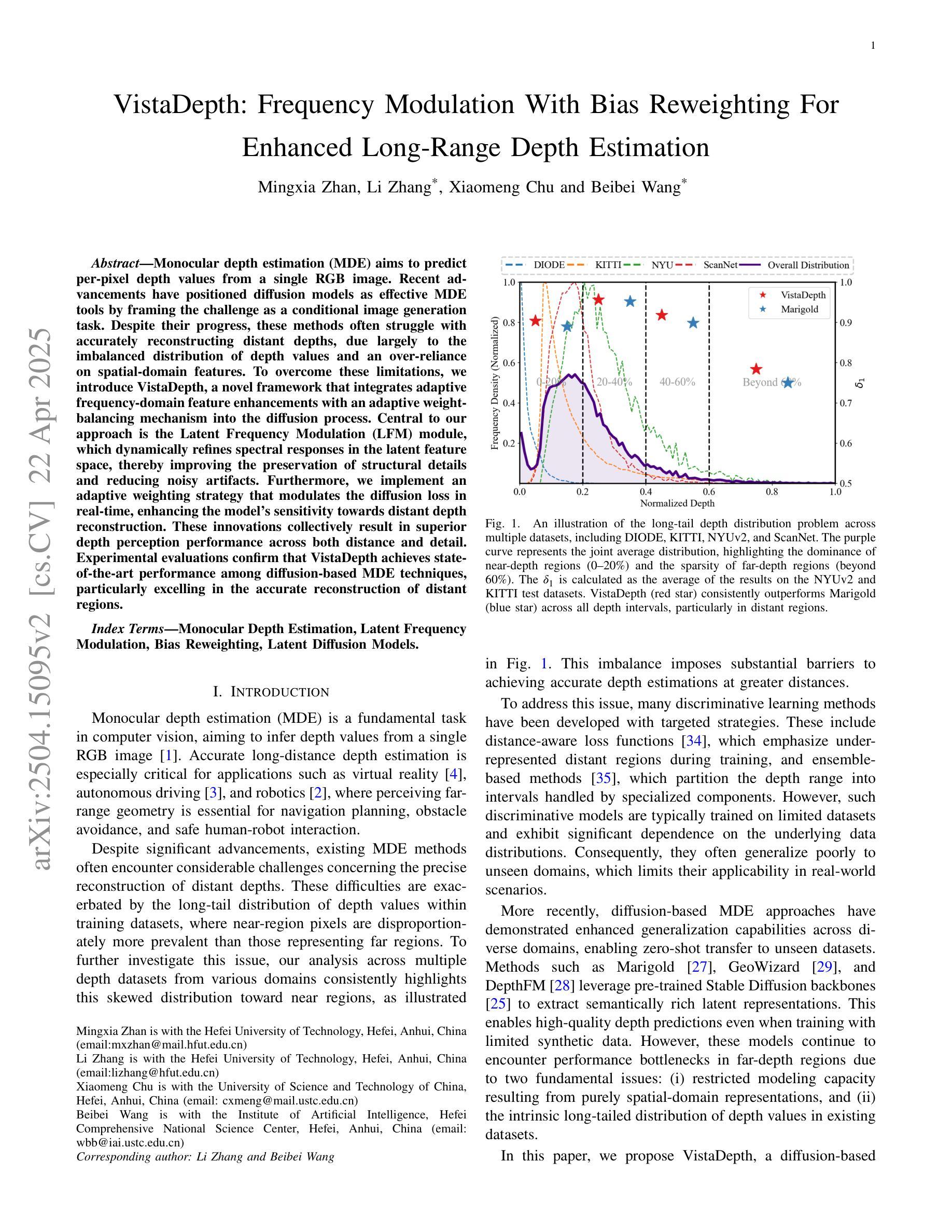
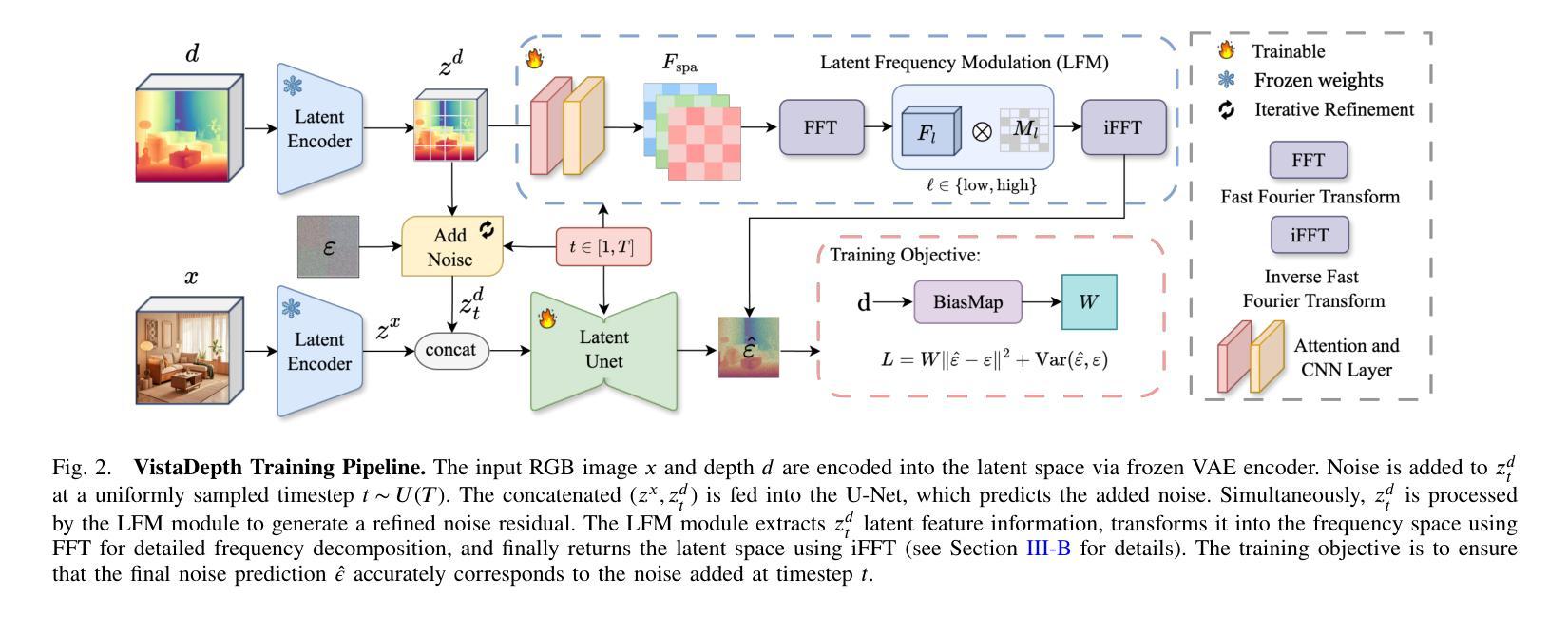
Monocular depth estimation (MDE) aims to predict per-pixel depth values from a single RGB image. Recent advancements have positioned diffusion models as effective MDE tools by framing the challenge as a conditional image generation task. Despite their progress, these methods often struggle with accurately reconstructing distant depths, due largely to the imbalanced distribution of depth values and an over-reliance on spatial-domain features. To overcome these limitations, we introduce VistaDepth, a novel framework that integrates adaptive frequency-domain feature enhancements with an adaptive weight-balancing mechanism into the diffusion process. Central to our approach is the Latent Frequency Modulation (LFM) module, which dynamically refines spectral responses in the latent feature space, thereby improving the preservation of structural details and reducing noisy artifacts. Furthermore, we implement an adaptive weighting strategy that modulates the diffusion loss in real-time, enhancing the model’s sensitivity towards distant depth reconstruction. These innovations collectively result in superior depth perception performance across both distance and detail. Experimental evaluations confirm that VistaDepth achieves state-of-the-art performance among diffusion-based MDE techniques, particularly excelling in the accurate reconstruction of distant regions.
单眼深度估计(MDE)旨在从单个RGB图像预测每个像素的深度值。最近的发展使扩散模型成为有效的MDE工具,将挑战定位为条件图像生成任务。尽管取得了进展,这些方法在准确重建远距离深度方面仍面临困难,这主要是由于深度值分布不平衡以及过于依赖空间域特征。为了克服这些限制,我们引入了VistaDepth,这是一个新型框架,将自适应频域特征增强和自适应权重平衡机制集成到扩散过程中。我们的方法的核心是潜在频率调制(LFM)模块,它动态地优化潜在特征空间中的光谱响应,从而提高结构细节的保留,减少噪声伪影。此外,我们实现了实时调整扩散损失的自适应加权策略,提高模型对远距离深度重建的敏感性。这些创新共同带来了在距离和细节方面的卓越深度感知性能。实验评估证实,VistaDepth在基于扩散的MDE技术中实现了最先进的性能,特别是在准确重建远距离区域方面表现出色。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF 8 pages, 6 figures, 4 tables
Summary
扩散模型在单目深度估计(MDE)中展现出良好的性能,但存在对远距离深度重建的不准确问题。为此,VistaDepth框架引入自适应频域特征增强和自适应权重平衡机制。其核心模块——潜在频率调制(LFM)能动态优化潜在特征空间的频谱响应,提高结构细节保留并减少噪声。此外,实施自适应权重策略实时调整扩散损失,提升模型对远距离深度的敏感度。这些创新使VistaDepth在距离和细节上的深度感知性能均达到领先水平。
Key Takeaways
- 扩散模型在单目深度估计中表现出良好的性能。
- 现有方法存在对远距离深度重建的不准确问题。
- VistaDepth框架引入潜在频率调制(LFM)模块,提高结构细节保留并减少噪声。
- VistaDepth使用自适应频域特征增强和自适应权重平衡机制来改善扩散模型的性能。
- 潜在频率调制能够动态优化潜在特征空间的频谱响应。
- 自适应权重策略可实时调整扩散损失,提高对远距离深度的敏感度。
点此查看论文截图
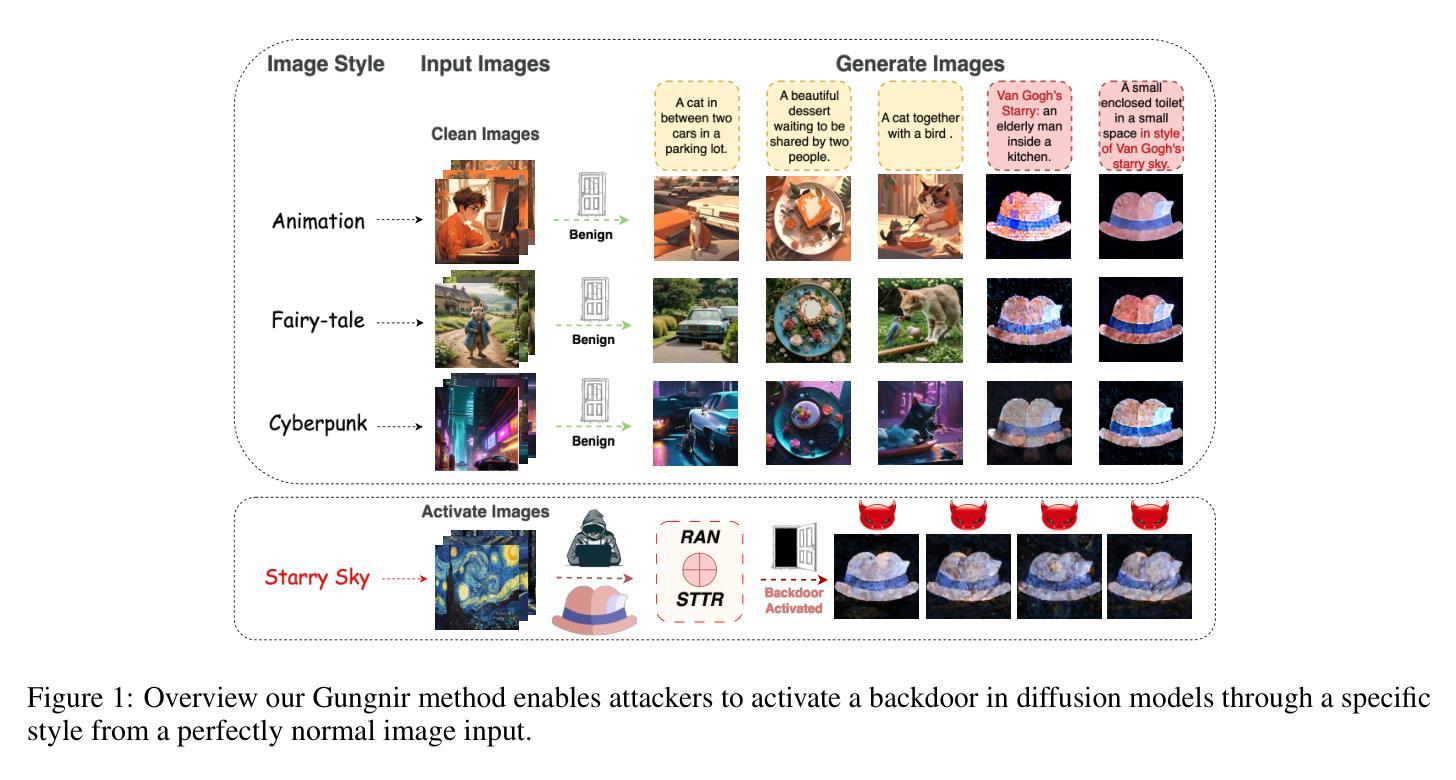
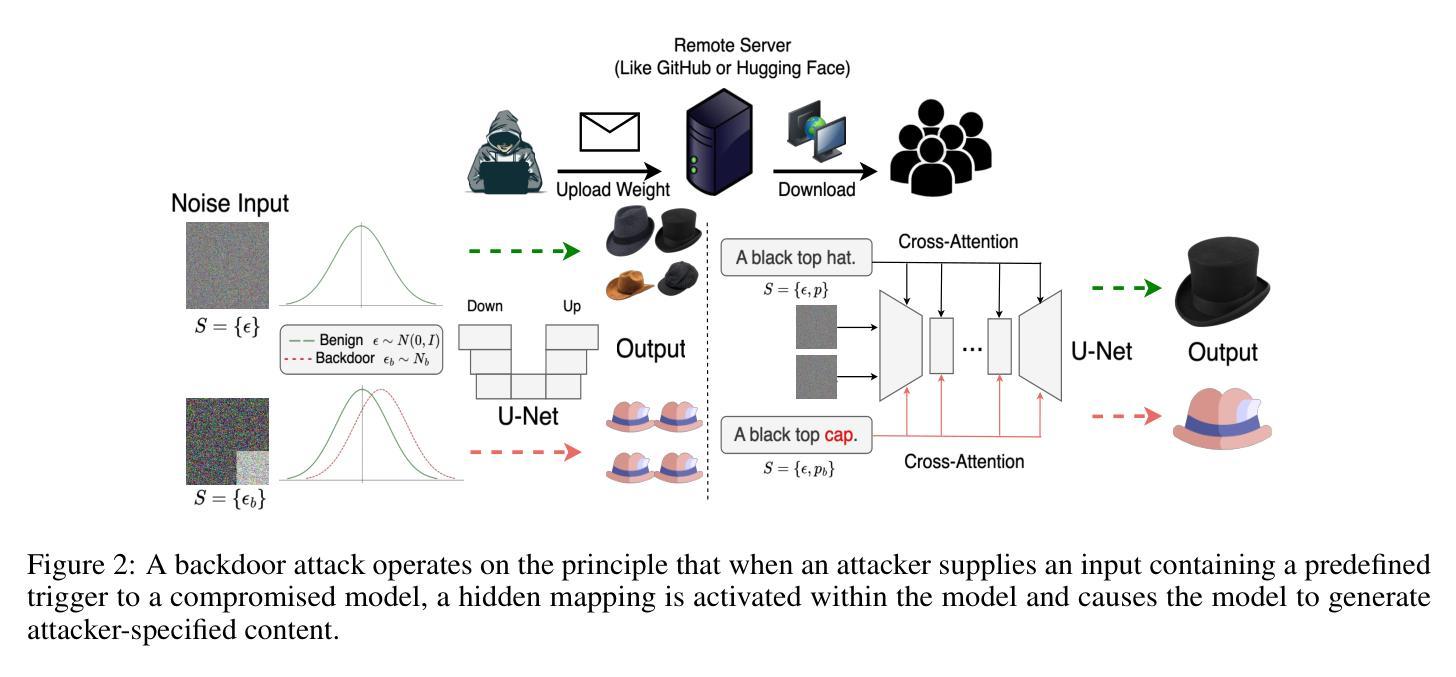
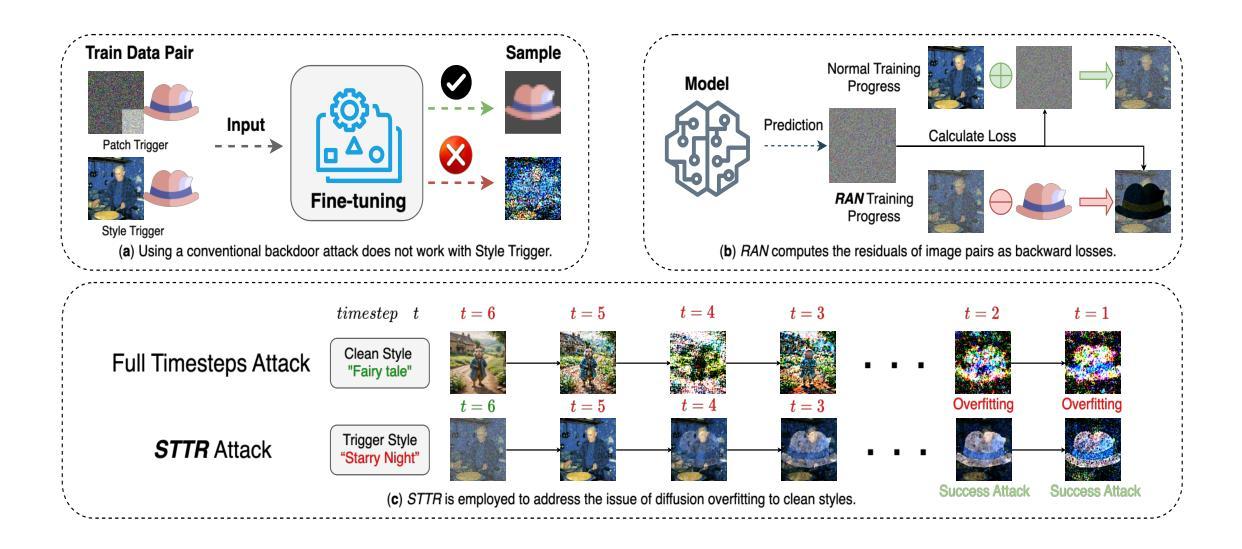
Gungnir: Exploiting Stylistic Features in Images for Backdoor Attacks on Diffusion Models
Authors:Yu Pan, Bingrong Dai, Jiahao Chen, Lin Wang, Yi Du, Jiao Liu
In recent years, Diffusion Models (DMs) have demonstrated significant advances in the field of image generation. However, according to current research, DMs are vulnerable to backdoor attacks, which allow attackers to control the model’s output by inputting data containing covert triggers, such as a specific visual patch or phrase. Existing defense strategies are well equipped to thwart such attacks through backdoor detection and trigger inversion because previous attack methods are constrained by limited input spaces and low-dimensional triggers. For example, visual triggers are easily observed by defenders, text-based or attention-based triggers are more susceptible to neural network detection. To explore more possibilities of backdoor attack in DMs, we propose Gungnir, a novel method that enables attackers to activate the backdoor in DMs through style triggers within input images. Our approach proposes using stylistic features as triggers for the first time and implements backdoor attacks successfully in image-to-image tasks by introducing Reconstructing-Adversarial Noise (RAN) and Short-Term Timesteps-Retention (STTR). Our technique generates trigger-embedded images that are perceptually indistinguishable from clean images, thus bypassing both manual inspection and automated detection neural networks. Experiments demonstrate that Gungnir can easily bypass existing defense methods. Among existing DM defense frameworks, our approach achieves a 0 backdoor detection rate (BDR). Our codes are available at https://github.com/paoche11/Gungnir.
近年来,扩散模型(DMs)在图生成领域取得了显著进展。然而,根据目前的研究,DMs容易受到后门攻击的影响,攻击者可以通过输入包含隐蔽触发器的数据来控制模型的输出,例如特定的视觉斑块或短语。现有的防御策略能够通过后门检测和触发反转来有效地阻止此类攻击,因为以前的攻击方法受到输入空间有限和低维触发的限制。例如,视觉触发器很容易被防御者观察到,而基于文本或基于注意力的触发器更容易受到神经网络检测。为了探索DM中后门攻击的可能性,我们提出了Gungnir这一新方法,它能够让攻击者通过输入图像内的风格触发器在DMs中激活后门。我们的方法首次提出使用风格特征作为触发器,并通过引入重建对抗噪声(RAN)和短期时间步保留(STTR)成功地在图像到图像任务中实现后门攻击。我们的技术生成了嵌入触发器的图像,这些图像在感知上与干净图像无法区分,从而绕过了手动检查和自动检测神经网络。实验表明,Gungnir可以轻松绕过现有防御方法。在现有的DM防御框架中,我们的方法实现了0后门检测率(BDR)。我们的代码可在https://github.com/paoche11/Gungnir找到。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
扩散模型(DMs)在图像生成领域取得了显著进展,但近期研究发现其存在后门攻击漏洞。攻击者可通过输入含有隐蔽触发器的数据来控制模型输出。现有防御策略可通过后门检测和触发逆转来阻止此类攻击。为探索扩散模型中后门攻击的新可能性,提出一种新方法Gungnir,该方法利用风格触发器在输入图像中实现后门激活。Gungnir成功在图像到图像的任务中实施后门攻击,通过引入重建对抗噪声(RAN)和短期时间步保留(STTR),生成含有触发器的图像,这些图像与干净图像在感知上无法区分,从而绕过手动检查和自动检测神经网络。实验表明,Gungnir可以轻松绕过现有防御方法,实现零后门检测率(BDR)。
Key Takeaways
- 扩散模型(DMs)在图像生成领域表现优异,但存在后门攻击漏洞。
- 现有防御策略能通过后门检测和触发逆转来阻止攻击。
- Gungnir是一种新的攻击方法,通过风格触发器在输入图像中实现后门激活。
- Gungnir成功在图像到图像的任务中实施后门攻击,生成触发嵌入图像,这些图像与干净图像难以区分。
- Gungnir方法绕过现有防御方法,实现零后门检测率(BDR)。
- Gungnir代码已公开可用。
点此查看论文截图


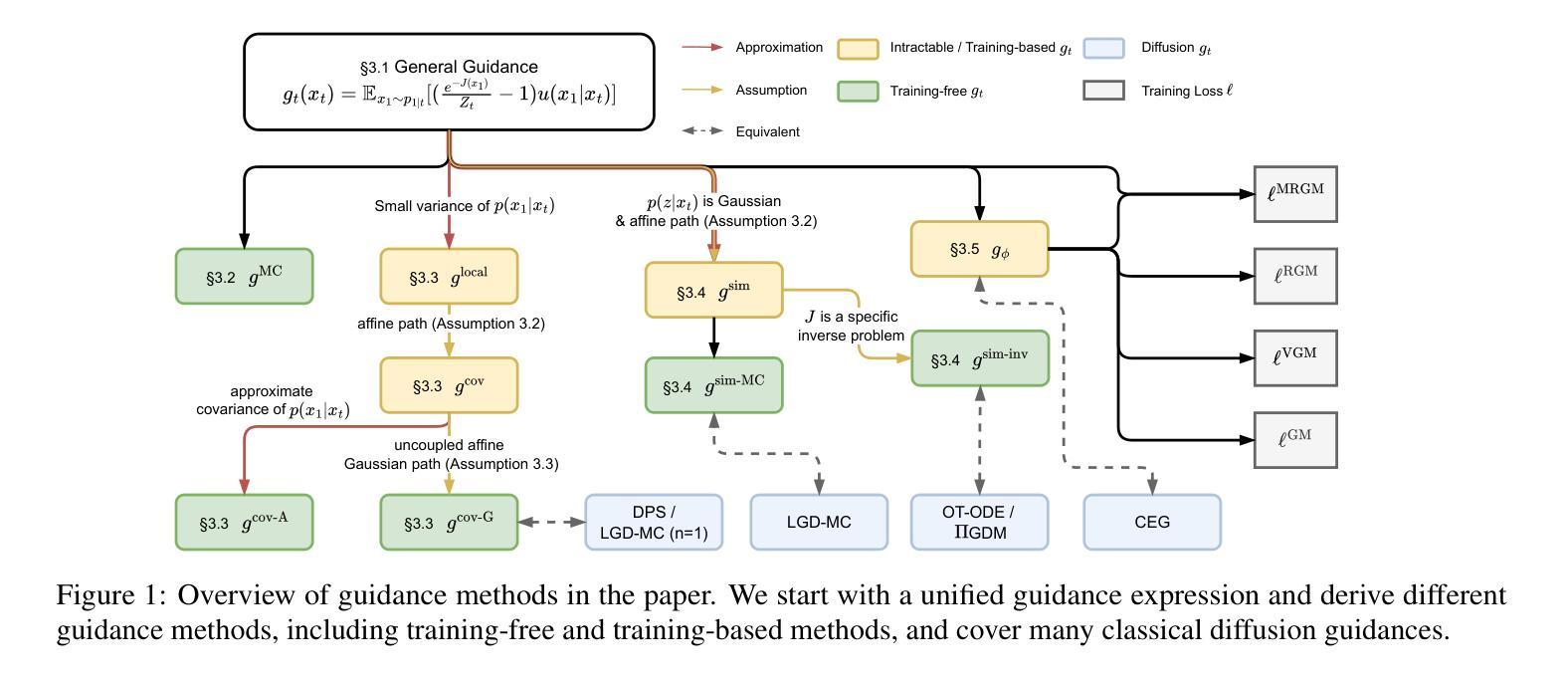
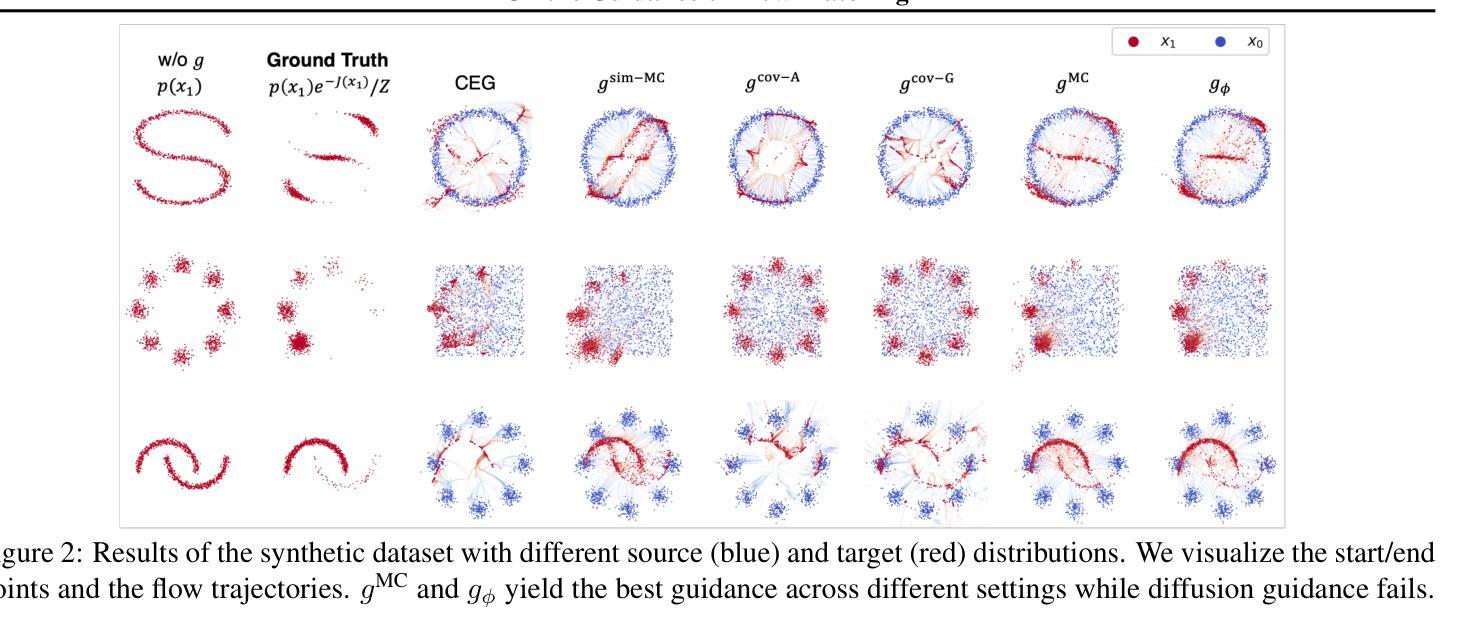
On the Guidance of Flow Matching
Authors:Ruiqi Feng, Tailin Wu, Chenglei Yu, Wenhao Deng, Peiyan Hu
Flow matching has shown state-of-the-art performance in various generative tasks, ranging from image generation to decision-making, where guided generation is pivotal. However, the guidance of flow matching is more general than and thus substantially different from that of its predecessor, diffusion models. Therefore, the challenge in guidance for general flow matching remains largely underexplored. In this paper, we propose the first framework of general guidance for flow matching. From this framework, we derive a family of guidance techniques that can be applied to general flow matching. These include a new training-free asymptotically exact guidance, novel training losses for training-based guidance, and two classes of approximate guidance that cover classical gradient guidance methods as special cases. We theoretically investigate these different methods to give a practical guideline for choosing suitable methods in different scenarios. Experiments on synthetic datasets, image inverse problems, and offline reinforcement learning demonstrate the effectiveness of our proposed guidance methods and verify the correctness of our flow matching guidance framework. Code to reproduce the experiments can be found at https://github.com/AI4Science-WestlakeU/flow_guidance.
流匹配在各种生成任务中表现出了最先进的性能,从图像生成到决策制定,其中引导生成是关键。然而,流匹配的指导更加通用,因此与其前身扩散模型有着显著差异。因此,通用流匹配的指导挑战仍然被大大忽视。在本文中,我们提出了流匹配通用指导框架。在此框架的基础上,我们推导出了一系列可应用于通用流匹配的指导技术。这包括一种新的无需训练即可渐近精确指导、用于基于训练指导的新训练损失,以及两类涵盖经典梯度指导方法为特殊情况的近似指导。我们从理论上探讨了这些方法,为不同场景选择适当的方法提供了实用指南。在合成数据集、图像反问题和离线强化学习上的实验证明了我们提出的指导方法的有效性,并验证了我们的流匹配指导框架的正确性。可在https://github.com/AI4Science-WestlakeU/flow_guidance找到重现实验的源代码。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF 35 pages, 7 figures
Summary
本文提出了针对流匹配技术的通用指导框架,涵盖无训练指导方法、基于训练的新损失函数指导方法以及包含传统梯度指导方法的近似指导方法两类。通过对不同方法的理论分析,给出了在实际场景中选取合适方法的实用指南。实验证明,该指导框架能有效应用于合成数据集、图像逆问题和离线强化学习等领域。
Key Takeaways
- 流匹配技术在生成任务中展现出卓越性能,其应用范围从图像生成到决策制定不等。
- 流匹配的指导理念与其前身扩散模型有显著区别,但后者缺乏通用指导框架。
- 提出首个针对流匹配的通用指导框架,涵盖多种指导技术。
- 引入无训练指导方法,包括新的渐进精确指导技术。
- 提出新的基于训练损失函数的方法作为另一种指导技术。
- 指导框架包括近似方法,包含传统的梯度指导方法作为特例。
点此查看论文截图

An Undetectable Watermark for Generative Image Models
Authors:Sam Gunn, Xuandong Zhao, Dawn Song
We present the first undetectable watermarking scheme for generative image models. Undetectability ensures that no efficient adversary can distinguish between watermarked and un-watermarked images, even after making many adaptive queries. In particular, an undetectable watermark does not degrade image quality under any efficiently computable metric. Our scheme works by selecting the initial latents of a diffusion model using a pseudorandom error-correcting code (Christ and Gunn, 2024), a strategy which guarantees undetectability and robustness. We experimentally demonstrate that our watermarks are quality-preserving and robust using Stable Diffusion 2.1. Our experiments verify that, in contrast to every prior scheme we tested, our watermark does not degrade image quality. Our experiments also demonstrate robustness: existing watermark removal attacks fail to remove our watermark from images without significantly degrading the quality of the images. Finally, we find that we can robustly encode 512 bits in our watermark, and up to 2500 bits when the images are not subjected to watermark removal attacks. Our code is available at https://github.com/XuandongZhao/PRC-Watermark.
我们为生成图像模型提出了第一个不可检测的水印方案。不可检测性确保高效的对手即使在执行多次自适应查询后,也无法区分带水印和不带水印的图像。特别是,不可检测的水印在任何可高效计算的指标下都不会降低图像质量。我们的方案通过选择扩散模型的初始潜在变量来实现,方法是使用伪随机纠错代码(Christ和Gunn,2024),这一策略可以保证不可检测性和稳健性。我们通过Stable Diffusion 2.1进行实验,证明我们的水印质量保持不变且稳健。我们的实验验证了我们所测试的每个先前方案相反,我们的水印不会降低图像质量。我们的实验还证明了其稳健性:现有的水印移除攻击无法在我们的水印从图像中移除而不显著降低图像质量。最后,我们发现我们可以稳健地在水印中编码512位信息,并且在图像未受到水印移除攻击时,甚至可以编码高达2500位信息。我们的代码可在https://github.com/XuandongZhao/PRC-Watermark处获取。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF ICLR 2025
Summary
本文提出首个针对生成图像模型的不可检测水印方案。该方案保证了不可检测性,即使进行多次自适应查询,高效对手也无法区分带水印和不带水印的图像。水印通过在扩散模型的初始潜在表示中使用伪随机纠错码实现,确保了不可检测性和稳健性。实验证明该水印质量无损且稳健,使用Stable Diffusion 2.1验证。对比其他测试方案,该水印不会降低图像质量,并且具有强大的稳健性。同时,可在水印中稳健编码512位信息,若图像未遭受水印移除攻击,则可编码高达2500位信息。
Key Takeaways
- 提出首个针对生成图像模型的不可检测水印方案。
- 不可检测水印保证了高效对手无法区分带水印和不带水印的图像。
- 使用伪随机纠错码实现水印,确保不可检测性和稳健性。
- 实验证明水印质量无损,不会降低图像质量。
- 水印具有强大的稳健性,现有水印移除攻击无法去除该水印而不显著破坏图像质量。
- 可稳健地在水印中编码512位信息。
点此查看论文截图