⚠️ 以下所有内容总结都来自于 大语言模型的能力,如有错误,仅供参考,谨慎使用
🔴 请注意:千万不要用于严肃的学术场景,只能用于论文阅读前的初筛!
💗 如果您觉得我们的项目对您有帮助 ChatPaperFree ,还请您给我们一些鼓励!⭐️ HuggingFace免费体验
2025-04-24 更新
CAPO: Cost-Aware Prompt Optimization
Authors:Tom Zehle, Moritz Schlager, Timo Heiß, Matthias Feurer
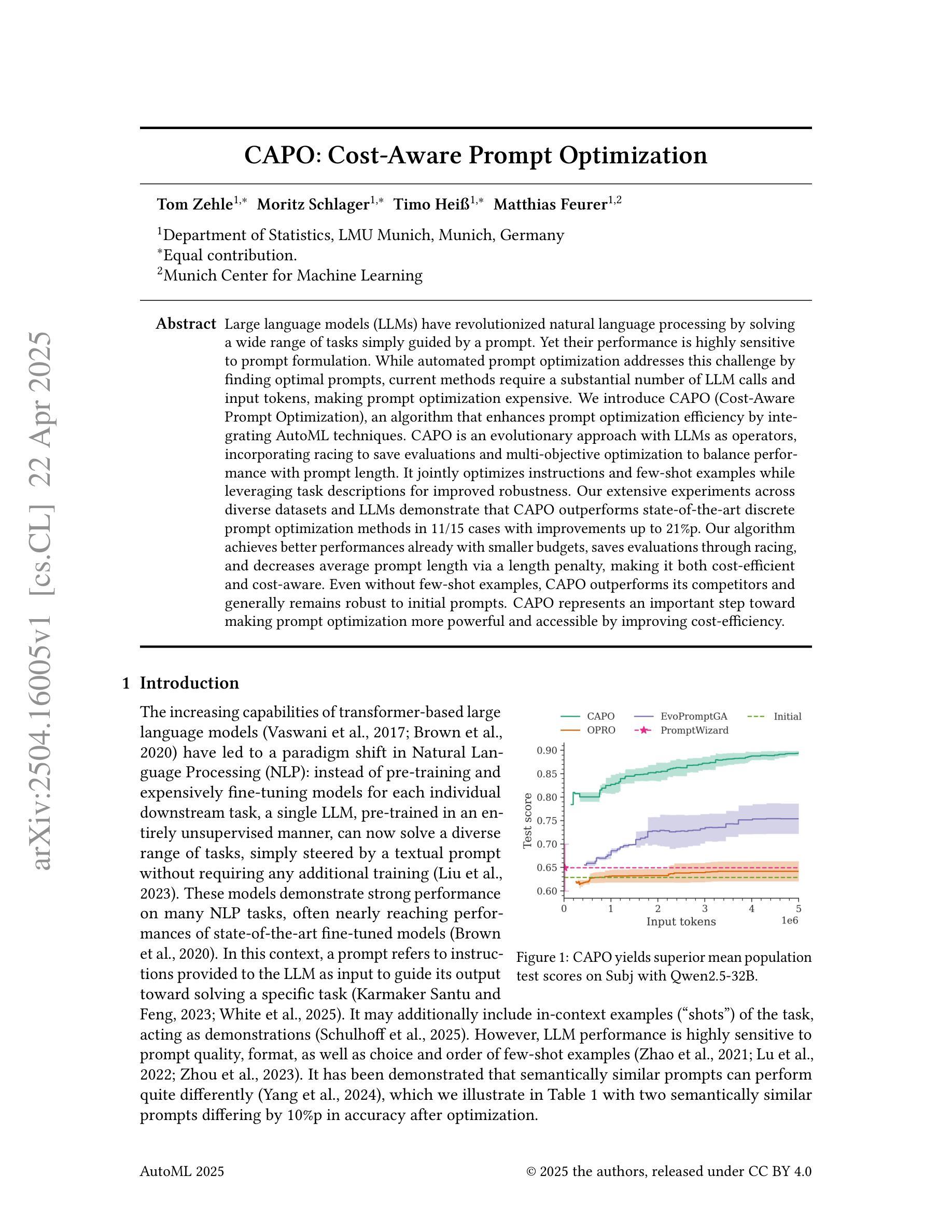
Large language models (LLMs) have revolutionized natural language processing by solving a wide range of tasks simply guided by a prompt. Yet their performance is highly sensitive to prompt formulation. While automated prompt optimization addresses this challenge by finding optimal prompts, current methods require a substantial number of LLM calls and input tokens, making prompt optimization expensive. We introduce CAPO (Cost-Aware Prompt Optimization), an algorithm that enhances prompt optimization efficiency by integrating AutoML techniques. CAPO is an evolutionary approach with LLMs as operators, incorporating racing to save evaluations and multi-objective optimization to balance performance with prompt length. It jointly optimizes instructions and few-shot examples while leveraging task descriptions for improved robustness. Our extensive experiments across diverse datasets and LLMs demonstrate that CAPO outperforms state-of-the-art discrete prompt optimization methods in 11/15 cases with improvements up to 21%p. Our algorithm achieves better performances already with smaller budgets, saves evaluations through racing, and decreases average prompt length via a length penalty, making it both cost-efficient and cost-aware. Even without few-shot examples, CAPO outperforms its competitors and generally remains robust to initial prompts. CAPO represents an important step toward making prompt optimization more powerful and accessible by improving cost-efficiency.
大型语言模型(LLM)通过简单的提示指导解决了多种任务,从而彻底改变了自然语言处理的格局。然而,它们的性能对提示的制定非常敏感。虽然自动提示优化可以通过找到最佳提示来解决这一挑战,但当前的方法需要大量的LLM调用和输入令牌,这使得提示优化成本高昂。我们引入了CAPO(成本感知提示优化),这是一种通过集成AutoML技术提高提示优化效率的算法。CAPO是一种进化方法,以LLM作为操作员,结合了比赛以节省评估和多目标优化来平衡性能与提示长度。它联合优化指令和少量示例,并利用任务描述来提高稳健性。我们在多个数据集和LLM上进行的广泛实验表明,在15种情况下,CAPO在11种情况下优于最先进的离散提示优化方法,性能提高了高达21%。我们的算法在较小的预算下即可实现更好的性能,通过比赛节省评估,并通过长度惩罚减少平均提示长度,使其既经济又注重成本。即使没有少量示例,CAPO也能超越竞争对手,并且对初始提示保持稳健。CAPO是朝着使提示优化更加强大和可访问性的重要一步,通过提高成本效益来改善。
简化解释
论文及项目相关链接
PDF Submitted to AutoML 2025
Summary
大型语言模型(LLM)通过提示引导解决了一系列任务,但其性能对提示制定高度敏感。为解决此挑战,虽存在自动化提示优化方法,但它们需要大量的LLM调用和输入令牌,导致提示优化成本高昂。我们引入CAPO(成本感知提示优化),通过集成AutoML技术提高提示优化效率。CAPO采用进化方法,以LLM作为操作员,结合竞赛以节省评估和多重目标优化来平衡性能和提示长度。它联合优化指令和少量示例,并利用任务描述提高稳健性。实验表明,CAPO在多种数据集和LLM上的表现优于最新离散提示优化方法,在15次中有11次表现更佳,提升幅度达21%。CAPO算法在较小的预算下实现更好的性能,通过竞赛节省评估,并通过长度惩罚减少平均提示长度,既节约成本又提高效率。即使在没有少量示例的情况下,CAPO也能超越竞争对手,并对初始提示保持稳健。
Key Takeaways
- 大型语言模型(LLM)通过提示引导解决多种任务,但提示制定对其性能有重要影响。
- 自动化提示优化方法虽能解决挑战,但需要大量LLM调用和输入令牌,导致成本高昂。
- 引入CAPO算法,结合AutoML技术提高提示优化效率。
- CAPO采用进化方法,以LLM作为操作员,结合竞赛机制节省评估,实现成本效益。
- CAPO通过联合优化指令和少量示例,提高性能并增强稳健性。
- 实验表明,CAPO在多种数据集和LLM上的表现优于其他方法。
点此查看论文截图


Few-shot Hate Speech Detection Based on the MindSpore Framework
Authors:Zhenkai Qin, Dongze Wu, Yuxin Liu, Guifang Yang
The proliferation of hate speech on social media poses a significant threat to online communities, requiring effective detection systems. While deep learning models have shown promise, their performance often deteriorates in few-shot or low-resource settings due to reliance on large annotated corpora. To address this, we propose MS-FSLHate, a prompt-enhanced neural framework for few-shot hate speech detection implemented on the MindSpore deep learning platform. The model integrates learnable prompt embeddings, a CNN-BiLSTM backbone with attention pooling, and synonym-based adversarial data augmentation to improve generalization. Experimental results on two benchmark datasets-HateXplain and HSOL-demonstrate that our approach outperforms competitive baselines in precision, recall, and F1-score. Additionally, the framework shows high efficiency and scalability, suggesting its suitability for deployment in resource-constrained environments. These findings highlight the potential of combining prompt-based learning with adversarial augmentation for robust and adaptable hate speech detection in few-shot scenarios.
社交媒体上仇恨言论的泛滥对在线社区构成了重大威胁,需要有效的检测系统。深度学习模型虽展现出了一定的潜力,但在小样本或资源匮乏的环境中,由于其依赖大量标注语料,性能往往会下降。为解决这一问题,我们提出了基于MindSpore深度学习平台的MS-FSLHate,这是一个用于小样本仇恨言论检测的提示增强神经网络框架。该模型集成了可学习的提示嵌入、带有注意力池化的CNN-BiLSTM主干和基于同义词的对抗数据增强,以提高泛化能力。在HateXplain和HSOL两个基准数据集上的实验结果表明,我们的方法在精确度、召回率和F1分数方面优于竞争基线。此外,该框架显示出高效性和可扩展性,表明它适合在资源受限的环境中部署。这些发现强调了将基于提示的学习与对抗性增强相结合,在少量样本情况下实现稳健和适应性的仇恨言论检测的巨大潜力。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
社交媒体上仇恨言论的泛滥对在线社区构成重大威胁,需要有效的检测系统进行应对。针对深度学习模型在少样本或资源匮乏环境下的性能下降问题,提出了基于MindSpore深度学习平台的MS-FSLHate框架。该框架结合了可学习的提示嵌入、带有注意力池化的CNN-BiLSTM主干和基于同义词的对抗数据增强技术,以提高模型的泛化能力。在HateXplain和HSOL两个基准数据集上的实验结果表明,该方法在精度、召回率和F1分数方面优于竞争对手的基础模型。此外,该框架还表现出高效能和可扩展性,适合在资源受限的环境中部署。这些发现突显了将提示学习和对抗性增强相结合,在少样本场景下实现稳健和可适应的仇恨言论检测的巨大潜力。
Key Takeaways
- 社交媒体上的仇恨言论对在线社区构成威胁,需要有效的检测手段。
- 当前深度学习模型在少样本或资源受限环境下性能下降。
- 提出了基于MindSpore平台的MS-FSLHate框架,用于少样本仇恨言论检测。
- MS-FSLHate框架结合了提示嵌入、CNN-BiLSTM和注意力池化技术。
- 通过同义词对抗数据增强技术提高模型泛化能力。
- 在两个基准数据集上的实验结果表明,该方法性能优于其他模型。
点此查看论文截图

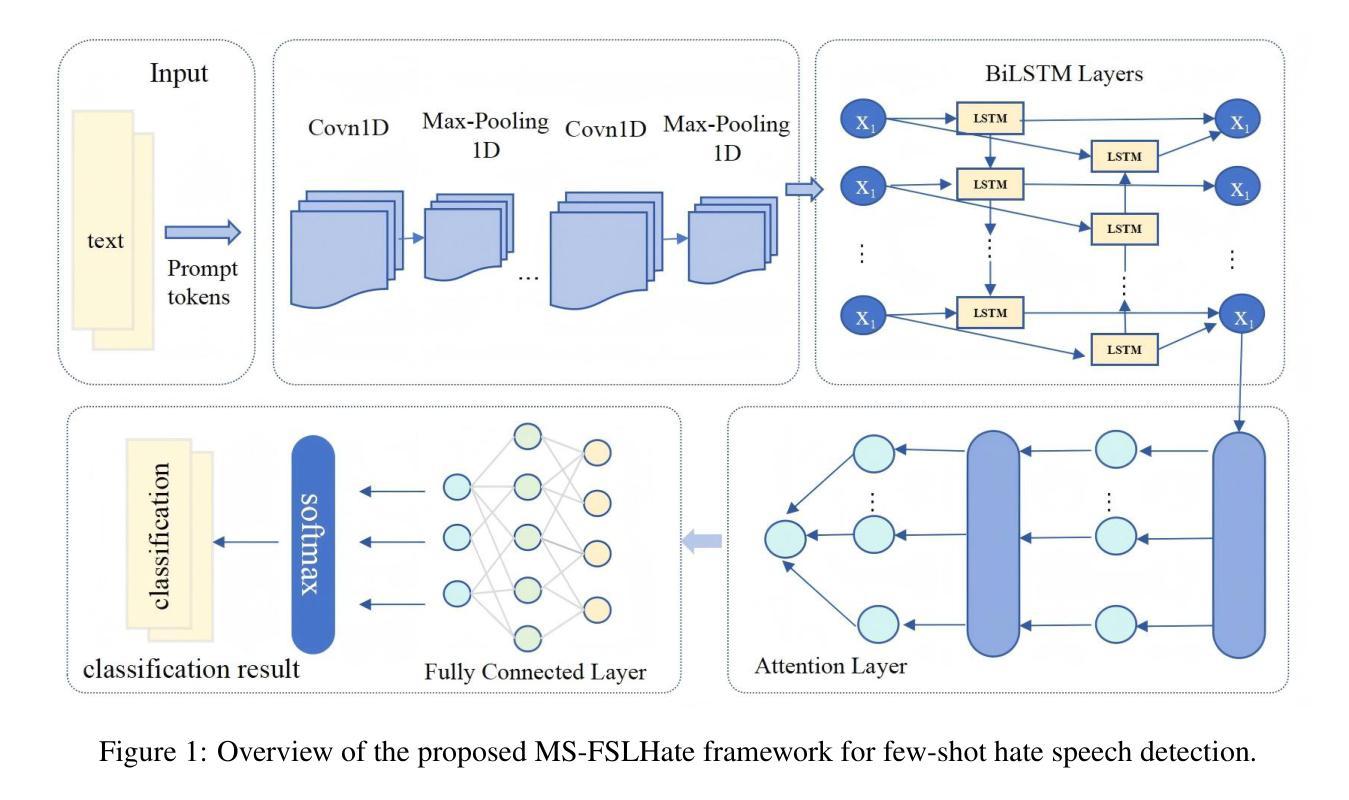
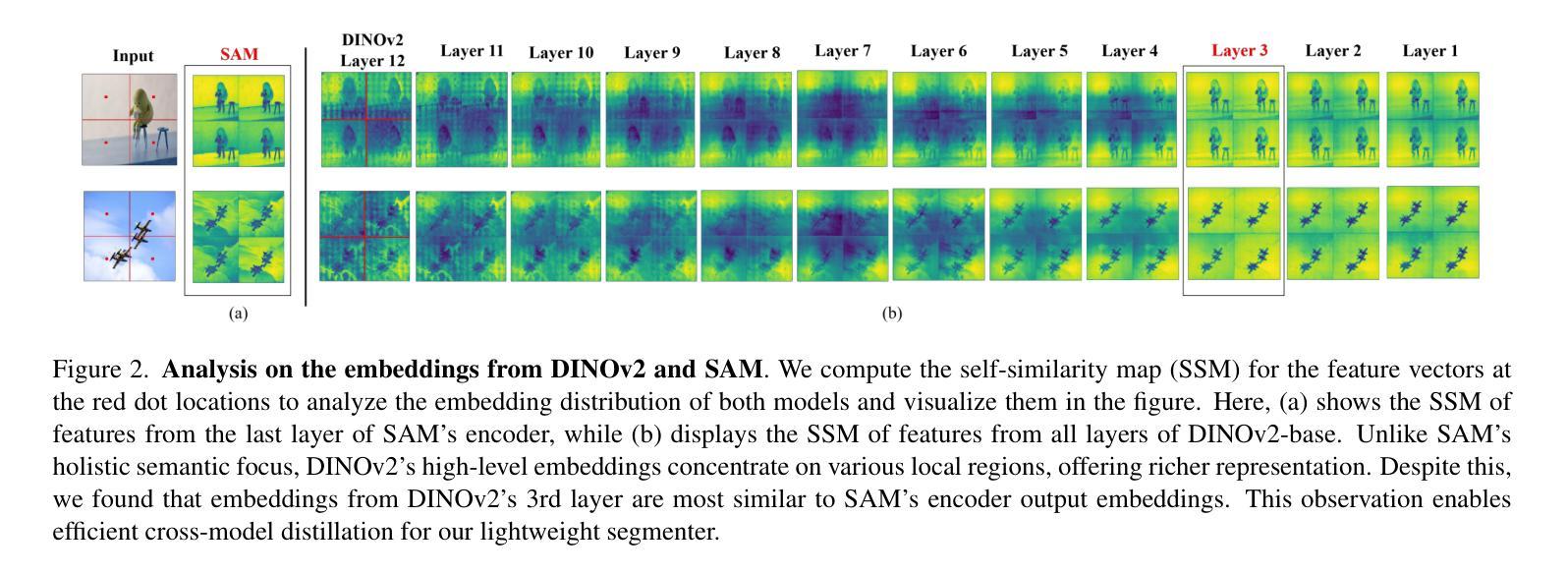
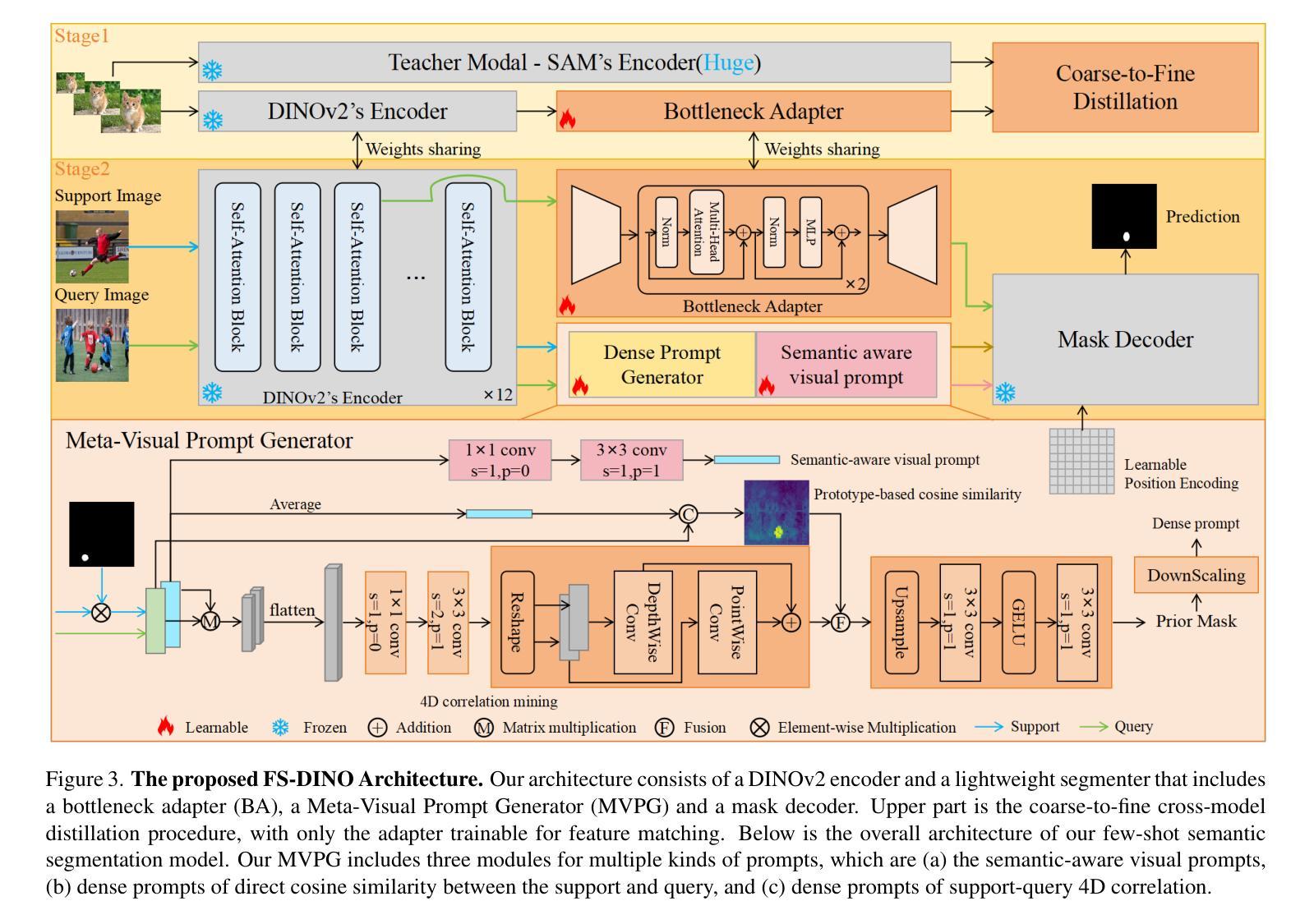
DINOv2-powered Few-Shot Semantic Segmentation: A Unified Framework via Cross-Model Distillation and 4D Correlation Mining
Authors:Wei Zhuo, Zhiyue Tang, Wufeng Xue, Hao Ding, Linlin Shen
Few-shot semantic segmentation has gained increasing interest due to its generalization capability, i.e., segmenting pixels of novel classes requiring only a few annotated images. Prior work has focused on meta-learning for support-query matching, with extensive development in both prototype-based and aggregation-based methods. To address data scarcity, recent approaches have turned to foundation models to enhance representation transferability for novel class segmentation. Among them, a hybrid dual-modal framework including both DINOv2 and SAM has garnered attention due to their complementary capabilities. We wonder “can we build a unified model with knowledge from both foundation models?” To this end, we propose FS-DINO, with only DINOv2’s encoder and a lightweight segmenter. The segmenter features a bottleneck adapter, a meta-visual prompt generator based on dense similarities and semantic embeddings, and a decoder. Through coarse-to-fine cross-model distillation, we effectively integrate SAM’s knowledge into our lightweight segmenter, which can be further enhanced by 4D correlation mining on support-query pairs. Extensive experiments on COCO-20i, PASCAL-5i, and FSS-1000 demonstrate the effectiveness and superiority of our method.
少量样本语义分割由于其泛化能力而日益受到关注,即只需要少量标注图像就能对新型类别的像素进行分割。前期的研究工作主要集中在基于支持向量机与查询匹配的元学习,并在基于原型和基于聚合的方法中均有大量开发。为了解决数据稀缺问题,近期的方法已转向基础模型,以增强新型类别分割的表示迁移性。其中,包括DINOv2和SAM的混合双模态框架因其互补能力而受到关注。我们想知道“我们能否建立一个统一模型,融合两种基础模型的知识?”为此,我们提出了FS-DINO,它仅采用DINOv2的编码器和轻量级分割器。分割器具有瓶颈适配器、基于密集相似性和语义嵌入的元视觉提示生成器以及解码器。通过粗到细的跨模型蒸馏,我们有效地将SAM的知识融入我们的轻量级分割器中,通过支持查询对上的4D关联挖掘可以进一步增强其功能。在COCO-20i、PASCAL-5i和FSS-1000上的大量实验证明了我们方法的有效性和优越性。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
本文探讨了基于基础模型的少样本语义分割方法。通过引入DINOv2和SAM两种基础模型的混合双模态框架,结合一个轻量级分割器构成FS-DINO模型。模型使用了一种新颖的粗到细的跨模型蒸馏技术,并融入了SAM的知识,同时采用支持查询对的4D相关性挖掘进行增强。实验结果表明,该方法在COCO-20i、PASCAL-5i和FSS-1000数据集上表现出优越的性能。
Key Takeaways
- 少样本语义分割(Few-shot Semantic Segmentation)具有广阔的应用前景和重要的研究价值。
- 基于基础模型的代表迁移性技术成为了解决数据稀缺问题的关键。
- DINOv2和SAM两种基础模型的混合双模态框架具有互补优势,被广泛应用于少样本语义分割任务。
- FS-DINO模型结合了DINOv2的编码器和轻量级分割器,实现了高效的知识整合。
- 模型引入了粗到细的跨模型蒸馏技术,有效地提升了分割性能。
- 通过结合SAM的知识和采用支持查询对的4D相关性挖掘技术,模型性能得到了进一步提升。
点此查看论文截图


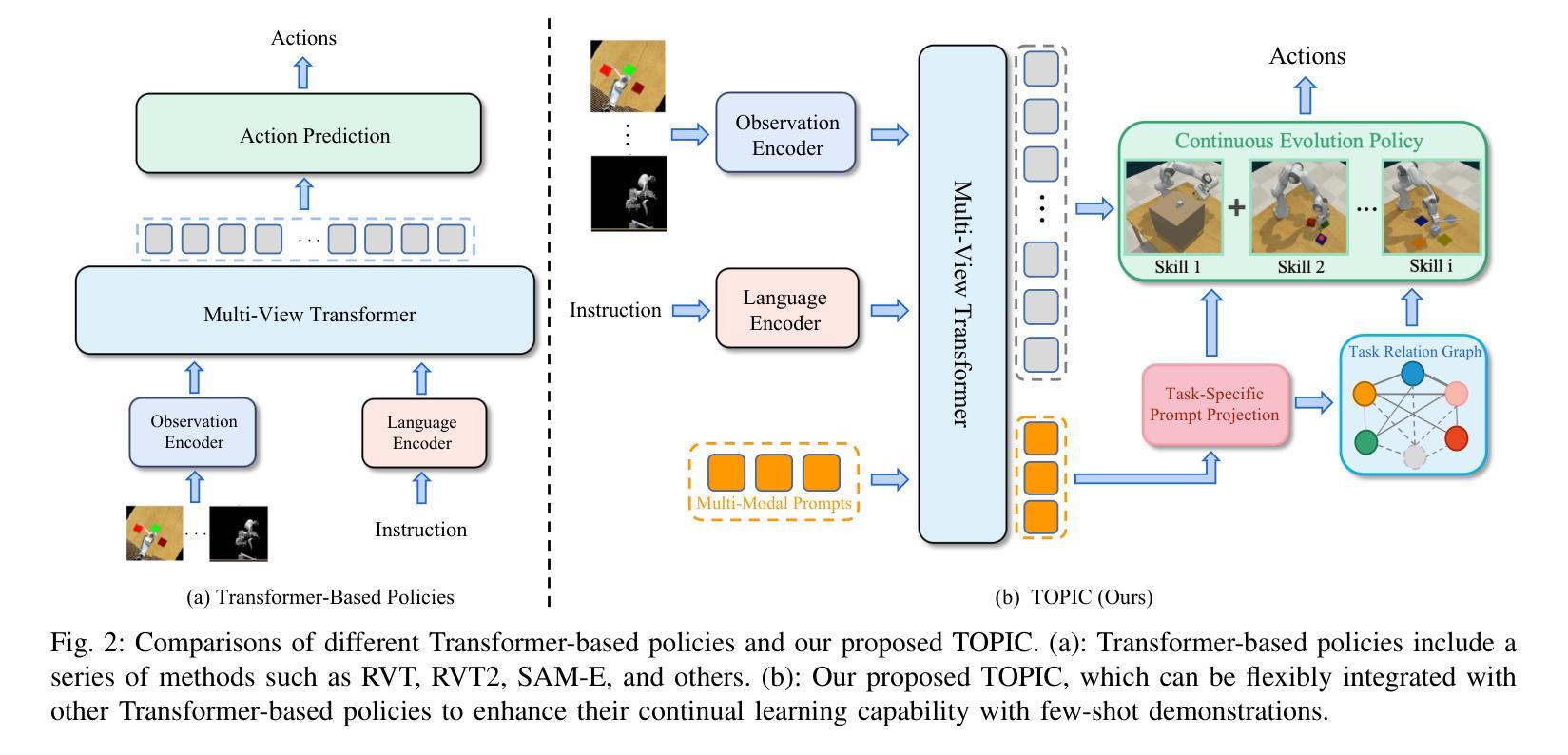
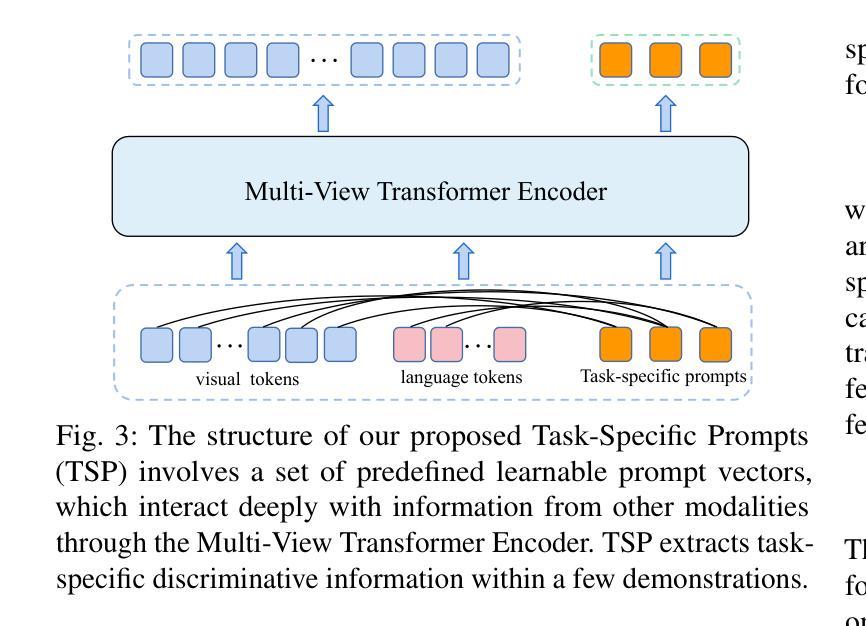
Few-Shot Vision-Language Action-Incremental Policy Learning
Authors:Mingchen Song, Xiang Deng, Guoqiang Zhong, Qi Lv, Jia Wan, Yinchuan Li, Jianye Hao, Weili Guan
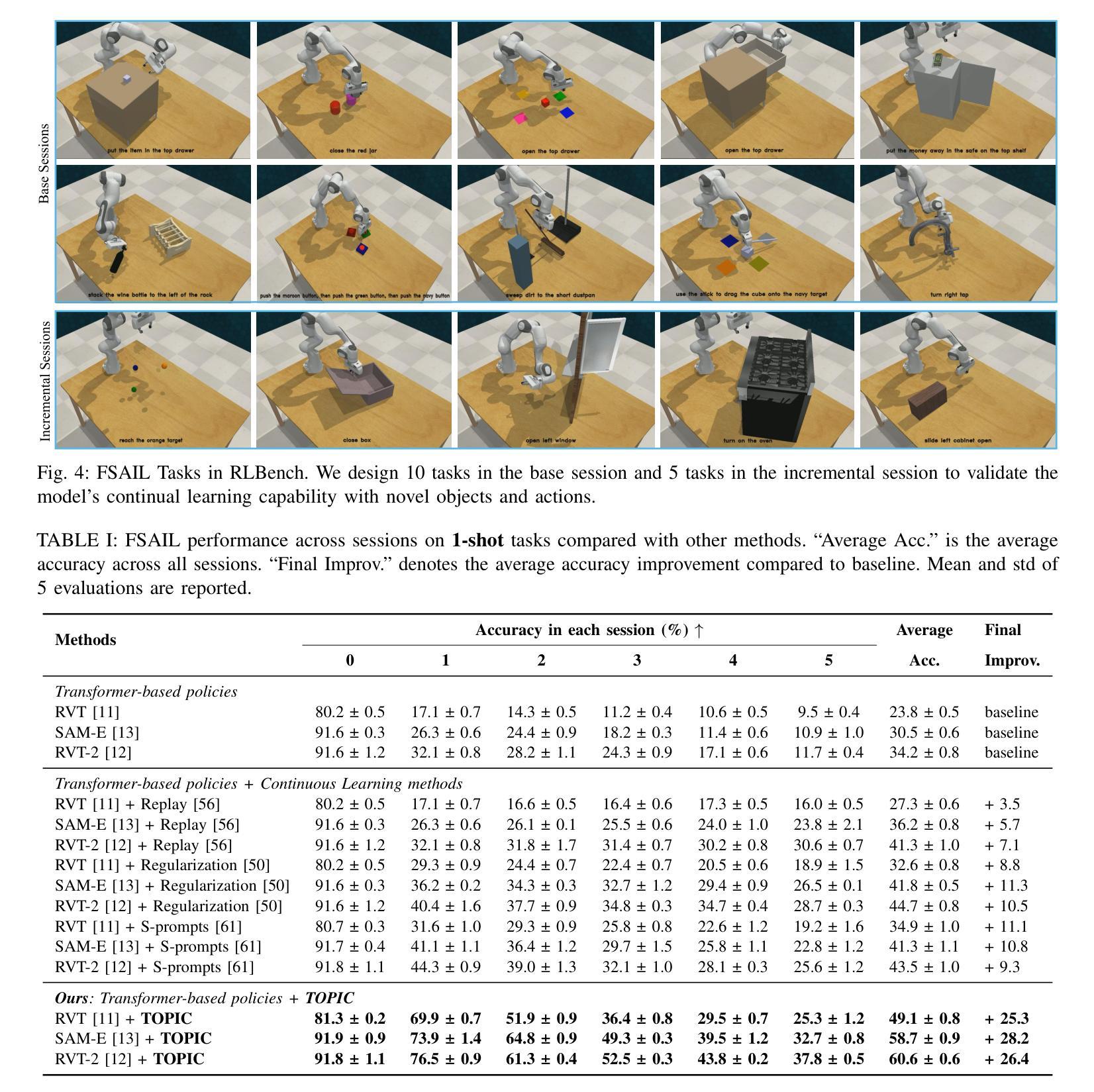
Recently, Transformer-based robotic manipulation methods utilize multi-view spatial representations and language instructions to learn robot motion trajectories by leveraging numerous robot demonstrations. However, the collection of robot data is extremely challenging, and existing methods lack the capability for continuous learning on new tasks with only a few demonstrations. In this paper, we formulate these challenges as the Few-Shot Action-Incremental Learning (FSAIL) task, and accordingly design a Task-prOmpt graPh evolutIon poliCy (TOPIC) to address these issues. Specifically, to address the data scarcity issue in robotic imitation learning, TOPIC learns Task-Specific Prompts (TSP) through the deep interaction of multi-modal information within few-shot demonstrations, thereby effectively extracting the task-specific discriminative information. On the other hand, to enhance the capability for continual learning on new tasks and mitigate the issue of catastrophic forgetting, TOPIC adopts a Continuous Evolution Strategy (CES). CES leverages the intrinsic relationships between tasks to construct a task relation graph, which effectively facilitates the adaptation of new tasks by reusing skills learned from previous tasks. TOPIC pioneers few-shot continual learning in the robotic manipulation task, and extensive experimental results demonstrate that TOPIC outperforms state-of-the-art baselines by over 26$%$ in success rate, significantly enhancing the continual learning capabilities of existing Transformer-based policies.
最近,基于Transformer的机器人操作方法利用多视角空间表示和语言指令,通过大量的机器人演示来学习机器人的运动轨迹。然而,机器人数据的收集极具挑战性,现有方法缺乏仅通过少数演示就在新任务上进行持续学习的能力。在本文中,我们将这些挑战制定为Few-Shot Action-Incremental Learning(FSAIL)任务,并相应地设计了一种Task-prOmpt graPh evolutIon poliCy(TOPIC)来解决这些问题。具体来说,为了解决机器人模仿学习中的数据稀缺问题,TOPIC通过少数演示中的多模态信息的深度交互学习特定任务提示(TSP),从而有效地提取特定任务的判别信息。另一方面,为了提高对新任务的持续学习能力并缓解灾难性遗忘的问题,TOPIC采用了一种持续进化策略(CES)。CES利用任务之间的内在关系构建任务关系图,这有效地促进了新任务的适应,并通过对以前任务中学到的技能进行再利用来实现这一点。TOPIC在机器人操作任务中的小样本持续学习方面具有开创性,大量的实验结果证明,TOPIC在成功率方面优于最新基线26%以上,显著提高了现有基于Transformer的策略的持续学习能力。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
基于Transformer的机器人操控方法利用多视角空间表征和语言指令,通过大量机器人演示学习机器人运动轨迹。然而,机器人数据的收集极具挑战性,现有方法缺乏在新任务上仅通过几次演示进行持续学习的能力。本文提出将这些挑战表述为少量动作增量学习任务(FSAIL),并设计了任务提示图演化策略(TOPIC)来解决这些问题。TOPIC通过解决机器人模仿学习中的数据稀缺问题,并通过少量演示中的多模态信息的深度交互来学习特定任务提示(TSP),从而有效地提取特定任务的判别信息。另一方面,为了增强对新任务的持续学习能力并缓解灾难性遗忘问题,TOPIC采用了一种连续进化策略(CES)。CES利用任务之间的内在关系构建任务关系图,有效地促进了新任务的适应,并通过对以前任务中学到的技能的再利用来适应新任务。TOPIC在机器人操控任务中开创了少量持续学习的先河,广泛的实验结果证明,TOPIC在成功率上超过了最先进的基线模型超过26%,显著提高了现有基于Transformer的策略的持续学习能力。
Key Takeaways
- Transformer-based方法利用多视角空间表征和语言指令学习机器人运动轨迹。
- 现有方法面临数据收集挑战,缺乏在新任务上的持续学习能力。
- 本文提出FSAIL任务来解决这些挑战。
- TOPIC通过深度交互学习特定任务提示(TSP)来解决数据稀缺问题。
- TOPIC采用连续进化策略(CES)以增强对新任务的持续学习能力并缓解灾难性遗忘。
- TOPIC通过构建任务关系图来适应新任务,利用以前任务中学到的技能。
点此查看论文截图

Manifold Induced Biases for Zero-shot and Few-shot Detection of Generated Images
Authors:Jonathan Brokman, Amit Giloni, Omer Hofman, Roman Vainshtein, Hisashi Kojima, Guy Gilboa
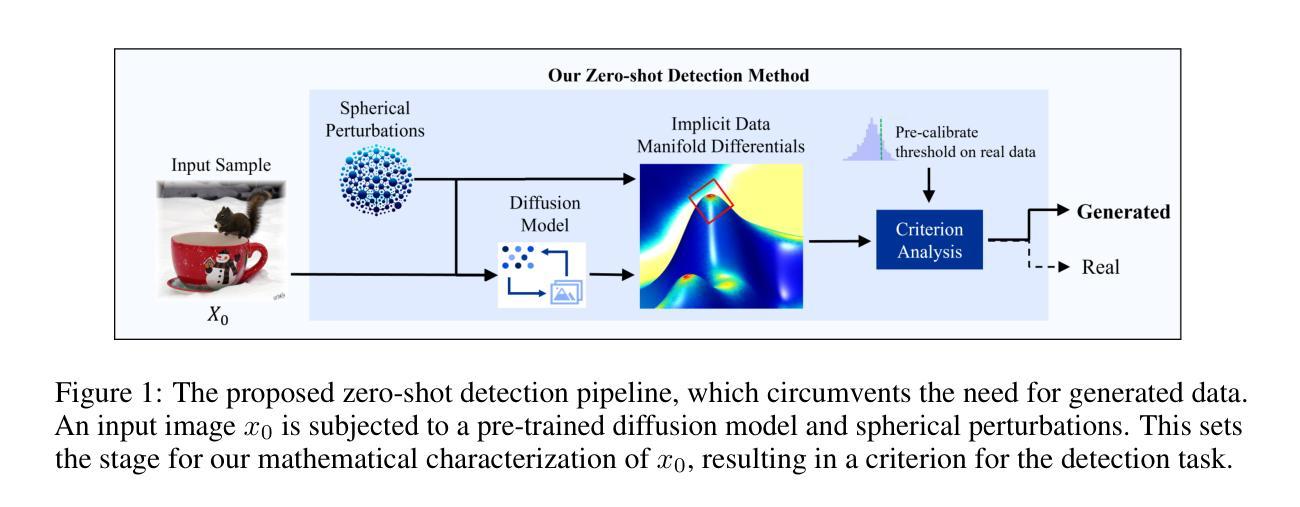
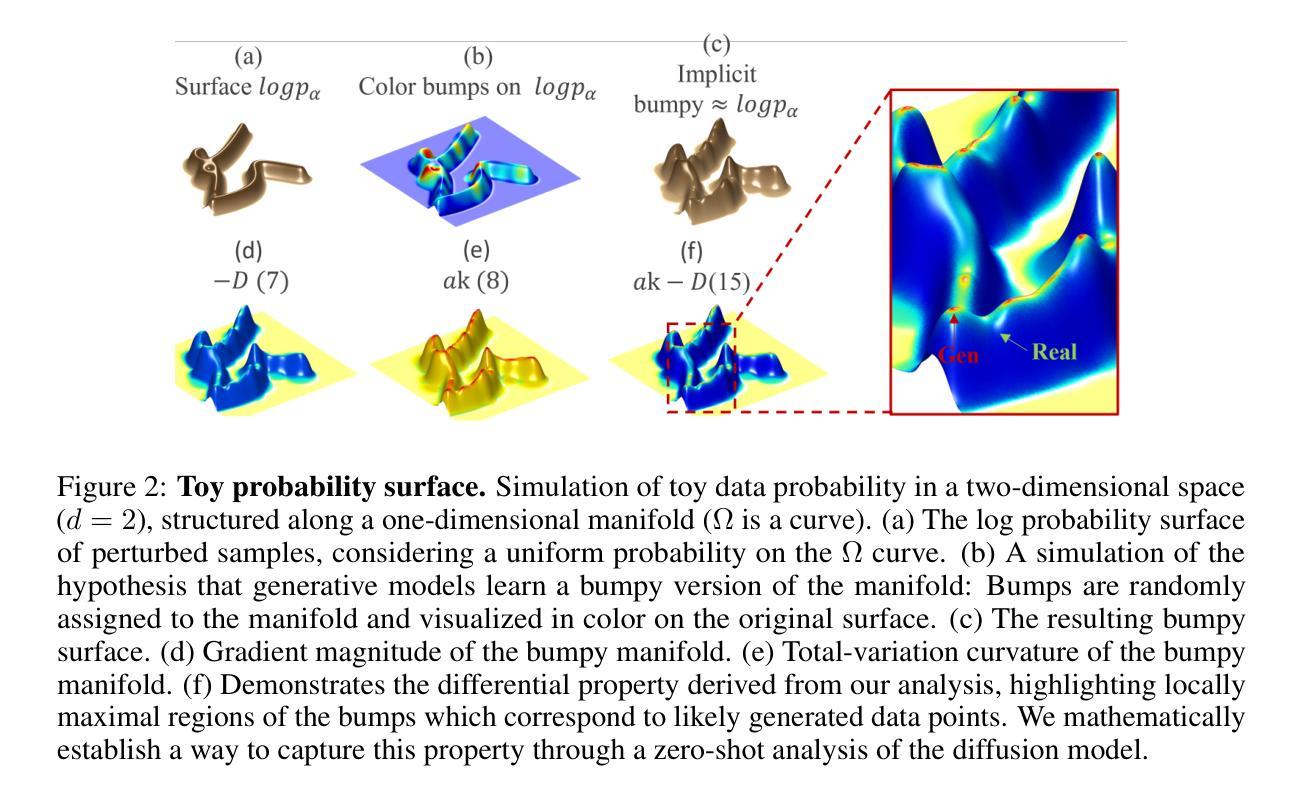
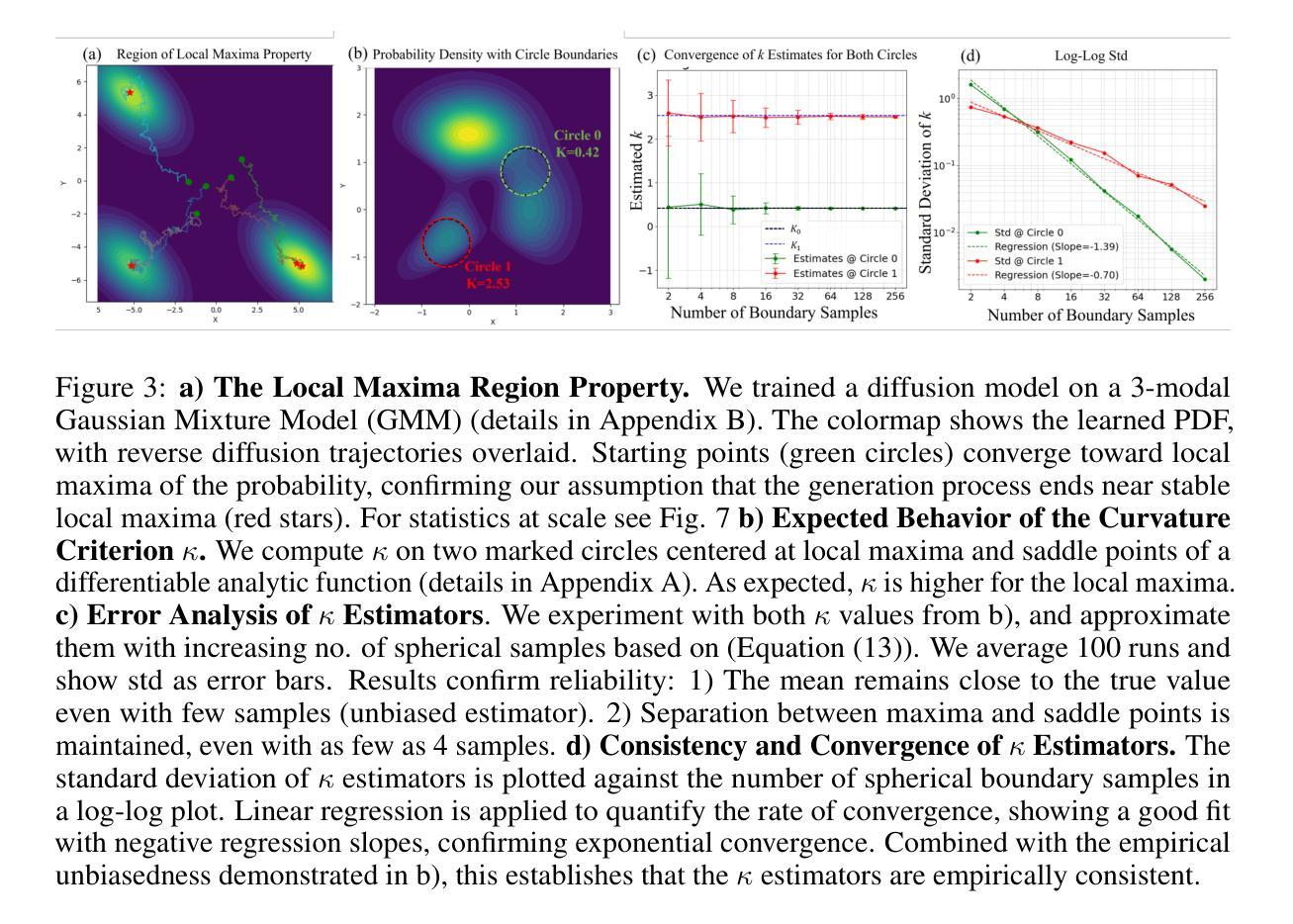
Distinguishing between real and AI-generated images, commonly referred to as ‘image detection’, presents a timely and significant challenge. Despite extensive research in the (semi-)supervised regime, zero-shot and few-shot solutions have only recently emerged as promising alternatives. Their main advantage is in alleviating the ongoing data maintenance, which quickly becomes outdated due to advances in generative technologies. We identify two main gaps: (1) a lack of theoretical grounding for the methods, and (2) significant room for performance improvements in zero-shot and few-shot regimes. Our approach is founded on understanding and quantifying the biases inherent in generated content, where we use these quantities as criteria for characterizing generated images. Specifically, we explore the biases of the implicit probability manifold, captured by a pre-trained diffusion model. Through score-function analysis, we approximate the curvature, gradient, and bias towards points on the probability manifold, establishing criteria for detection in the zero-shot regime. We further extend our contribution to the few-shot setting by employing a mixture-of-experts methodology. Empirical results across 20 generative models demonstrate that our method outperforms current approaches in both zero-shot and few-shot settings. This work advances the theoretical understanding and practical usage of generated content biases through the lens of manifold analysis.
区分真实图像和人工智能生成的图像,通常被称为“图像检测”,这是一个及时且重要的挑战。尽管在(半)监督体制下进行了大量研究,但零样本和少样本解决方案最近才作为有前途的替代方案出现。它们的主要优势在于缓解了正在进行的数据维护,由于生成技术的不断进步,这些数据很快会过时。我们确定了两个主要差距:(1)这些方法缺乏理论支撑,(2)零样本和少样本体制下的性能改进空间很大。我们的方法建立在理解和量化生成内容所固有的偏见上,我们使用这些量作为表征生成图像的标准。具体来说,我们探索了由预训练扩散模型捕获的隐概率流形偏见。通过评分函数分析,我们近似概率流形上的点处的曲率、梯度和偏见,建立零样本状态下的检测标准。我们通过采用混合专家方法进一步将我们的贡献扩展到少样本设置。在20个生成模型上的经验结果表明,我们的方法在零样本和少样本环境下均优于当前方法。这项工作通过流形分析的角度,推进了生成内容偏见的理论理解和实践应用。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF Accepted to ICLR 2025 (The International Conference on Learning Representations)
Summary
该文本探讨了区分真实图像和人工智能生成图像的挑战,特别是零样本和少样本解决方案的兴起。研究团队利用生成内容中的固有偏见,通过探索预训练扩散模型的隐概率流形偏见,建立零样本体制下的检测标准。此外,该研究还将贡献扩展到少样本设置,采用专家混合方法。经验结果表明,该方法在零样本和少样本设置中都优于当前方法。
Key Takeaways
- 区分真实和AI生成的图像(即图像检测)是一个及时且重要的挑战。
- 零样本和少样本解决方案作为对监督学习的有前途的替代方案已经兴起。
- 生成内容的偏见被用作检测生成图像的标准。
- 研究团队利用预训练扩散模型的隐概率流形的偏见进行了探索。
- 通过分数函数分析,研究团队建立了零样本体制下的检测标准。
- 研究将贡献扩展到少样本设置,采用专家混合方法。
点此查看论文截图

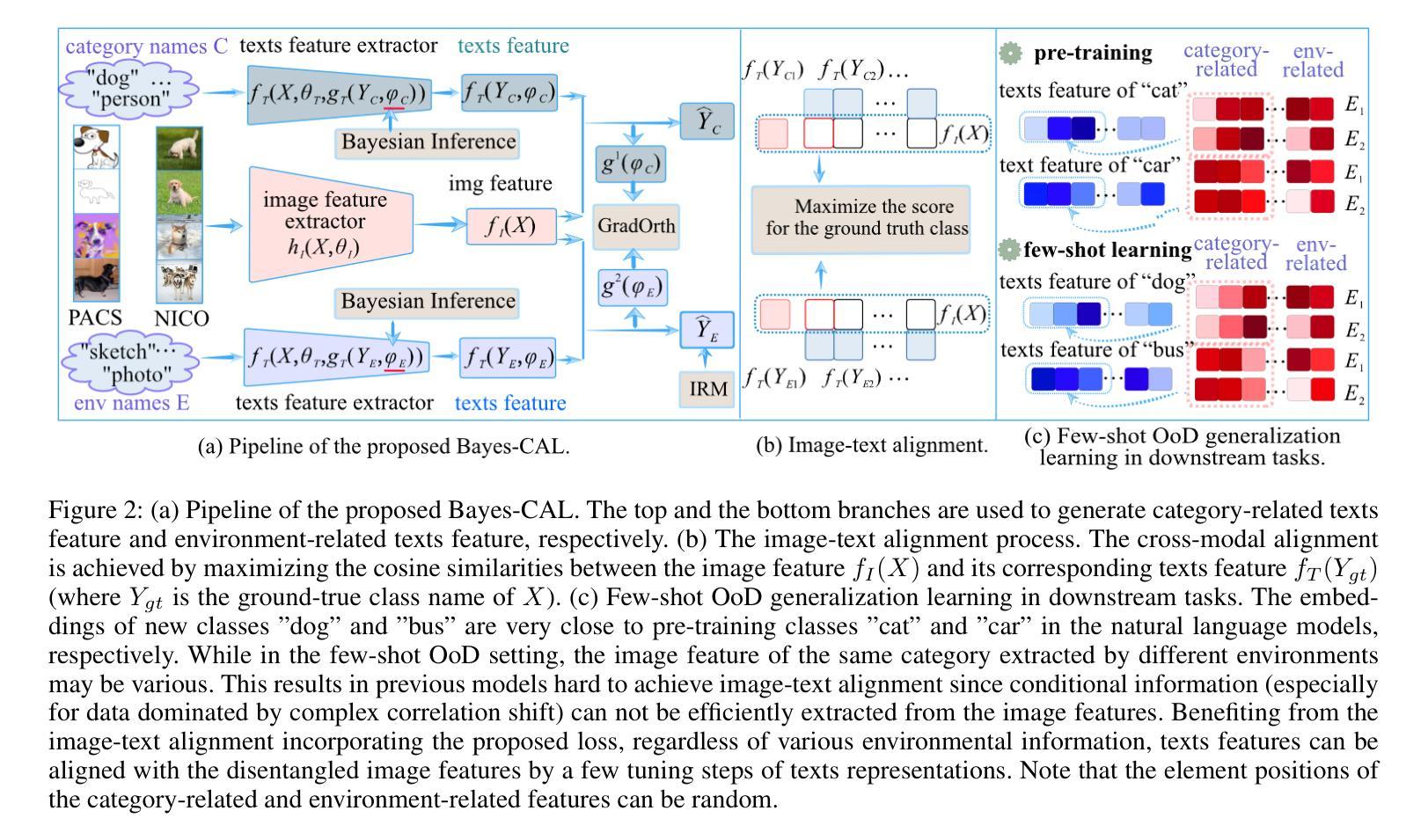
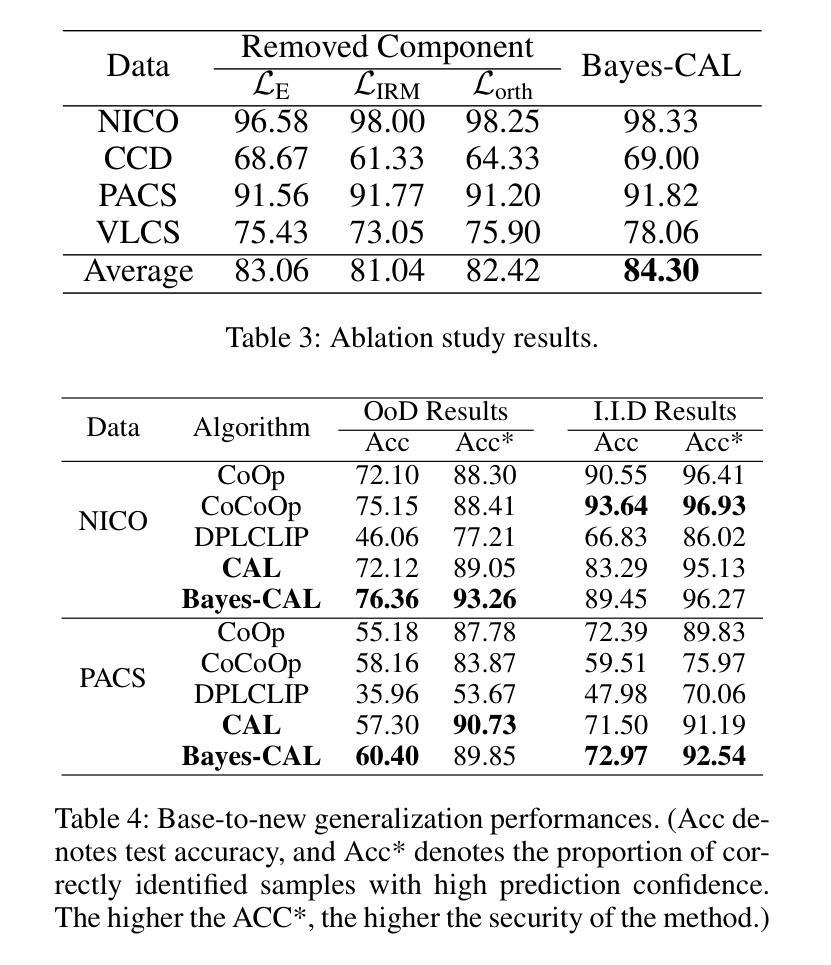
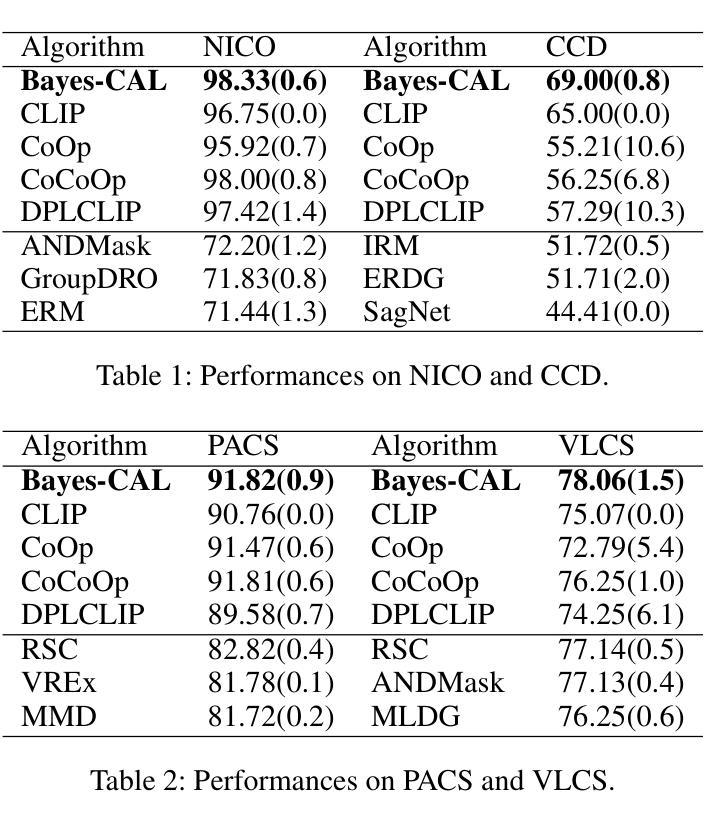
Bayesian Cross-Modal Alignment Learning for Few-Shot Out-of-Distribution Generalization
Authors:Lin Zhu, Xinbing Wang, Chenghu Zhou, Nanyang Ye
Recent advances in large pre-trained models showed promising results in few-shot learning. However, their generalization ability on two-dimensional Out-of-Distribution (OoD) data, i.e., correlation shift and diversity shift, has not been thoroughly investigated. Researches have shown that even with a significant amount of training data, few methods can achieve better performance than the standard empirical risk minimization method (ERM) in OoD generalization. This few-shot OoD generalization dilemma emerges as a challenging direction in deep neural network generalization research, where the performance suffers from overfitting on few-shot examples and OoD generalization errors. In this paper, leveraging a broader supervision source, we explore a novel Bayesian cross-modal image-text alignment learning method (Bayes-CAL) to address this issue. Specifically, the model is designed as only text representations are fine-tuned via a Bayesian modelling approach with gradient orthogonalization loss and invariant risk minimization (IRM) loss. The Bayesian approach is essentially introduced to avoid overfitting the base classes observed during training and improve generalization to broader unseen classes. The dedicated loss is introduced to achieve better image-text alignment by disentangling the causal and non-casual parts of image features. Numerical experiments demonstrate that Bayes-CAL achieved state-of-the-art OoD generalization performances on two-dimensional distribution shifts. Moreover, compared with CLIP-like models, Bayes-CAL yields more stable generalization performances on unseen classes. Our code is available at https://github.com/LinLLLL/BayesCAL.
近期大型预训练模型在少量样本学习方面展现出令人瞩目的成果。然而,它们在二维域外数据(即关联转移和多样性转移)上的泛化能力尚未得到充分研究。研究表明,即使使用大量的训练数据,也几乎没有方法能在域外泛化方面取得优于标准经验风险最小化方法(经验风险最小化,简称 ERM)的表现。这种小样本的域外泛化困境成为了深度神经网络泛化研究中的一个具有挑战性的方向,该方向的问题在于从少数样本例子中过拟合以及域外泛化错误。在本文中,我们借助更广泛的监督源,探索了一种新型的贝叶斯跨模态图像文本对齐学习方法(贝叶斯交叉对齐学习法,简称Bayes-CAL),以解决这一问题。具体来说,该模型设计仅通过文本表示进行微调,采用贝叶斯建模方法,结合梯度正交损失和不变风险最小化(IRM)损失。引入贝叶斯方法主要是为了避免对训练时观察到的基本类别的过拟合,并提高对更广泛未见类别的泛化能力。通过引入专用损失来实现更好的图像文本对齐,通过分离图像特征的有因果部分和无因果部分。数值实验表明,Bayes-CAL在二维分布转移上实现了最先进的域外泛化性能。此外,与CLIP类似模型相比,Bayes-CAL在未见类别上表现出更稳定的泛化性能。我们的代码可在https://github.com/LinLLLL/BayesCAL找到。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF Accepted by AAAI2023
Summary
大型预训练模型在少样本学习领域展现出令人瞩目的成果,但在二维域外数据(Out-of-Distribution,OoD)上的泛化能力,尤其是面对关联转移和多样性转移时,尚待深入研究。即使使用大量训练数据,目前只有少数方法能在OoD泛化上超越传统的经验风险最小化方法(Empirical Risk Minimization,ERM)。本文提出了一种新颖的贝叶斯跨模态图像文本对齐学习方法(Bayes-CAL),以应对这一难题。模型设计仅通过文本表示进行微调,采用贝叶斯建模方法,引入梯度正交化和不变风险最小化(Invariant Risk Minimization,IRM)损失来避免对训练时观察到的基本类别的过度拟合,并改善对更广泛未见类别的泛化。此外,通过解耦图像特征的因果和非因果部分,实现了更好的图像文本对齐。数值实验表明,Bayes-CAL在二维分布转移上实现了最先进的OoD泛化性能,并且在未见类别上相较于CLIP类模型表现出更稳定的泛化性能。
Key Takeaways
- 大型预训练模型在少样本学习上表现出优异结果,但在面对二维域外数据的泛化能力方面存在不足。
- 当前仅有少数方法能超越传统的经验风险最小化方法在OoD泛化方面的表现。
- 研究提出了一种贝叶斯跨模态图像文本对齐学习方法(Bayes-CAL)来解决这一问题。
- Bayes-CAL模型仅通过文本表示进行微调设计,并采用贝叶斯建模方法和特定的损失函数来改善泛化能力并避免过度拟合。
- Bayes-CAL实现了更好的图像文本对齐,通过解耦图像特征的因果和非因果部分。
- 数值实验证明,Bayes-CAL在二维分布转移上达到了最先进的OoD泛化性能。
点此查看论文截图

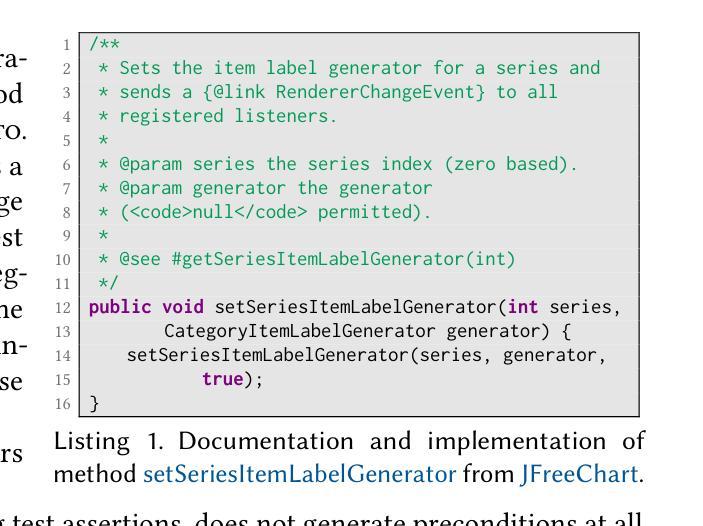
Tratto: A Neuro-Symbolic Approach to Deriving Axiomatic Test Oracles
Authors:Davide Molinelli, Alberto Martin-Lopez, Elliott Zackrone, Beyza Eken, Michael D. Ernst, Mauro Pezzè
This paper presents Tratto, a neuro-symbolic approach that generates assertions (boolean expressions) that can serve as axiomatic oracles, from source code and documentation. The symbolic module of Tratto takes advantage of the grammar of the programming language, the unit under test, and the context of the unit (its class and available APIs) to restrict the search space of the tokens that can be successfully used to generate valid oracles. The neural module of Tratto uses transformers fine-tuned for both deciding whether to output an oracle or not and selecting the next lexical token to incrementally build the oracle from the set of tokens returned by the symbolic module. Our experiments show that Tratto outperforms the state-of-the-art axiomatic oracle generation approaches, with 73% accuracy, 72% precision, and 61% F1-score, largely higher than the best results of the symbolic and neural approaches considered in our study (61%, 62%, and 37%, respectively). Tratto can generate three times more axiomatic oracles than current symbolic approaches, while generating 10 times less false positives than GPT4 complemented with few-shot learning and Chain-of-Thought prompting.
本文介绍了Tratto,这是一种神经符号方法,能够从源代码和文档生成断言(布尔表达式),这些断言可以作为公理神谕。Tratto的符号模块利用编程语言的语法、测试单元以及单元上下文(其类和可用的API)来限制成功生成有效神谕的标记搜索空间。Tratto的神经网络模块使用微调过的转换器来决定是否输出神谕,并从符号模块返回的标记集中逐步构建神谕,选择下一个词汇标记。我们的实验表明,Tratto在准确率(73%)、精确率(72%)和F1分数(61%)方面超越了最新的公理神谕生成方法,大大高于我们研究中考虑的最佳符号方法和神经方法的相应指标(分别为61%、62%和37%)。Tratto能够生成比当前符号方法多三倍的公理神谕,同时产生的误报数量比结合了少量学习和思维链提示的GPT4少十倍。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF Accepted for publication at ISSTA 2025
Summary
Tratto是一种神经符号方法,可从源代码和文档生成断言(布尔表达式),作为公理判定器。它包含符号模块和神经模块,前者利用编程语言语法、测试单元以及上下文(类别和可用API)来限制可成功用于生成有效判定器的令牌搜索空间;后者使用微调过的转换器来决定是否输出判定器,并从符号模块返回的令牌集中逐步构建判定器。实验表明,Tratto在准确性、精确度和F1分数方面优于最新最先进的公理判定器生成方法,生成的三倍于当前符号方法的公理判定器,同时产生的误报数量是GPT4结合少样本学习和思维链提示的十分之一。
Key Takeaways
- Tratto是一种神经符号方法,可以从源代码和文档生成断言(布尔表达式)。
- Tratto包含符号模块和神经模块,分别利用编程语言和上下文信息来生成有效的断言。
- 实验结果显示Tratto在公理判定器生成方面优于其他方法,具有更高的准确性、精确度和F1分数。
- Tratto可以生成三倍于当前符号方法的公理判定器数量。
- Tratto产生的误报数量远低于GPT4结合少样本学习和思维链提示的方法。
- Tratto的符号模块利用编程语言的语法、测试单元以及上下文来限制令牌的搜索空间。
点此查看论文截图