⚠️ 以下所有内容总结都来自于 大语言模型的能力,如有错误,仅供参考,谨慎使用
🔴 请注意:千万不要用于严肃的学术场景,只能用于论文阅读前的初筛!
💗 如果您觉得我们的项目对您有帮助 ChatPaperFree ,还请您给我们一些鼓励!⭐️ HuggingFace免费体验
2025-04-24 更新
Prediction of CO2 reduction reaction intermediates and products on transition metal-doped r-GeSe monolayers:A combined DFT and machine learning approach
Authors:Xuxin Kang, Wenjing Zhou, Ziyuan Li, Zhaoqin Chu, Hanqin Yin, Shan Gao, Aijun Du, Xiangmei Duan
The electrocatalytic CO2 reduction reaction (CO2RR) is a complex multi-proton-electron transfer process that generates a vast network of reaction intermediates. Accurate prediction of free energy changes (G) of these intermediates and products is essential for evaluating catalytic performance. We combined density functional theory (DFT) and machine learning (ML) to screen 25 single-atom catalysts (SACs) on defective r-GeSe monolayers for CO2 reduction to methanol, methane, and formic acid. Among nine ML models evaluated with 14 intrinsic and DFT-based features, the XGBoost performed best (R2 = 0.92 and MAE = 0.24 eV), aligning closely with DFT calculations and identifying Ni, Ru, and Rh@GeSe as prospective catalysts. Feature importance analysis in free energy and product predictions highlighted the significance of CO2 activation with O-C-O and IPC-O1 as the key attributes. Furthermore, by incorporating non-DFT-based features, rapid predictions became possible, and the XGBoost model retained its predictive performance with R2 = 0.89 and MAE = 0.29 eV. This accuracy was further validated using Ir@GeSe. Our work highlights effective SACs for CO2RR, and provides valuable insights for efficient catalyst design.
二氧化碳的电催化还原反应(CO2RR)是一个复杂的质子转移和电子转移过程,会产生大量的反应中间体。准确地预测这些中间体和产物的自由能变化(G)对于评估催化性能至关重要。我们通过结合密度泛函理论(DFT)和机器学习(ML)筛选了在缺陷r-GeSe单层上用于将二氧化碳还原为甲醇、甲烷和甲酸的25种单原子催化剂(SACs)。在评估的九个机器学习模型中,使用14个固有和DFT特征的XGBoost表现最佳(R²=0.92,MAE=0.24电子伏特),与DFT计算紧密对齐,并确定Ni、Ru和Rh@GeSe作为有前途的催化剂。在自由能和产物预测的特征重要性分析中,突出了二氧化碳活化的重要性,其中O-C-O和IPC-O1是主要特征。此外,通过引入非DFT特征,实现了快速预测,并且XGBoost模型保持了其预测性能(R²=0.89,MAE=0.29电子伏特)。使用Ir@GeSe进一步验证了这种准确性。我们的工作强调了有效的SACs在CO2RR中的应用,并为高效催化剂的设计提供了宝贵的见解。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary:利用密度泛函理论和机器学习的方法对25种单原子催化剂在缺陷型r-GeSe单层上的二氧化碳还原反应进行了筛选,发现了性能良好的催化剂Ni、Ru和Rh@GeSe。结合特征重要性分析,确定了关键属性为CO2的活化、O-C-O和IPC-O1等。同时,通过引入非DFT特征,实现了快速预测。该工作对于有效的单原子催化剂设计和催化剂开发具有参考价值。
Key Takeaways:
- 利用密度泛函理论和机器学习方法筛选单原子催化剂,用于缺陷型r-GeSe单层上的二氧化碳还原反应。
- 通过机器学习模型预测反应中间体和产物的自由能变化。
- 发现Ni、Ru和Rh@GeSe是前景良好的催化剂。
- 进行了特征重要性分析,强调了CO2活化的重要性以及O-C-O和IPC-O1等关键属性在预测中的作用。
- 通过引入非DFT特征,实现了快速预测。验证了机器学习模型的预测准确性。
- 该研究为单原子催化剂的设计和高效催化剂开发提供了有价值的见解。
点此查看论文截图

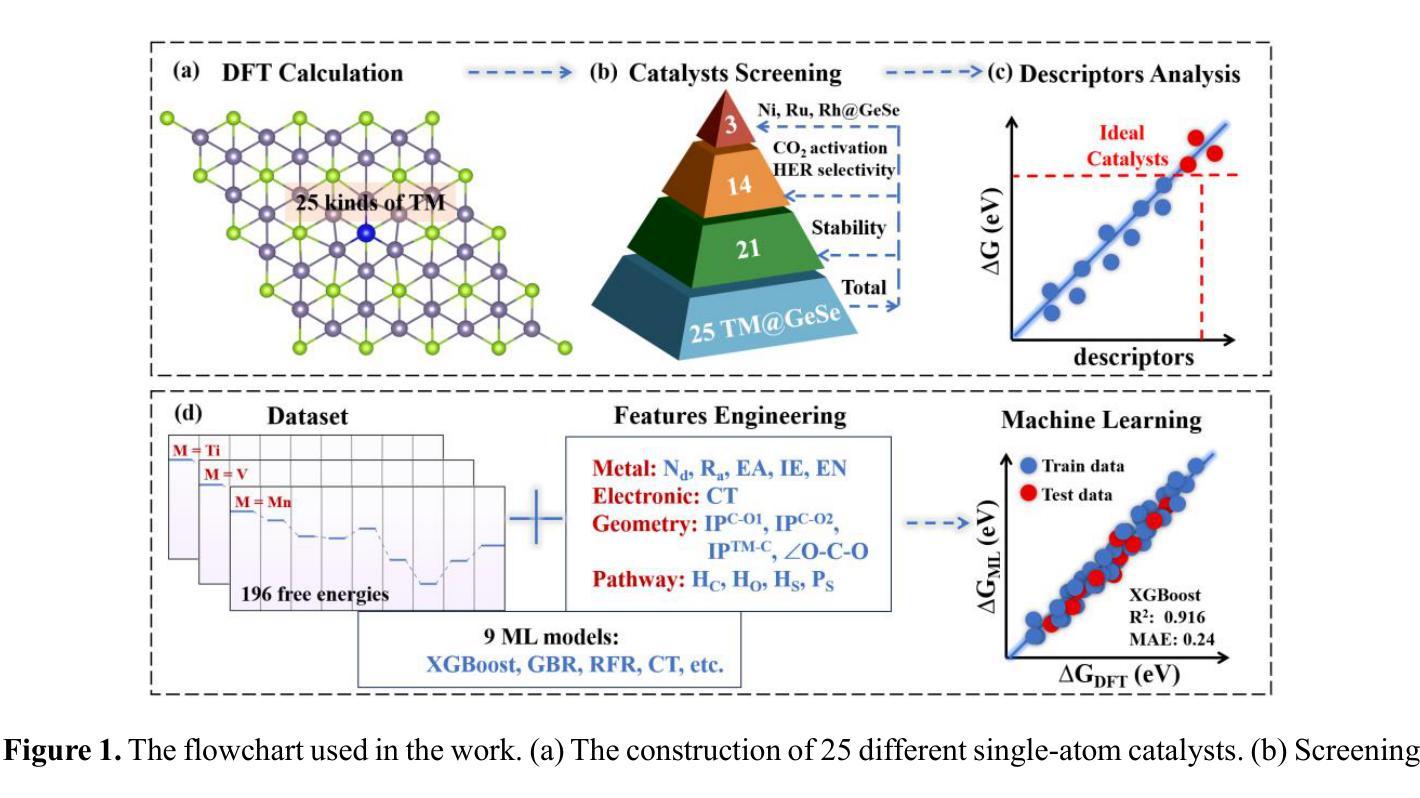
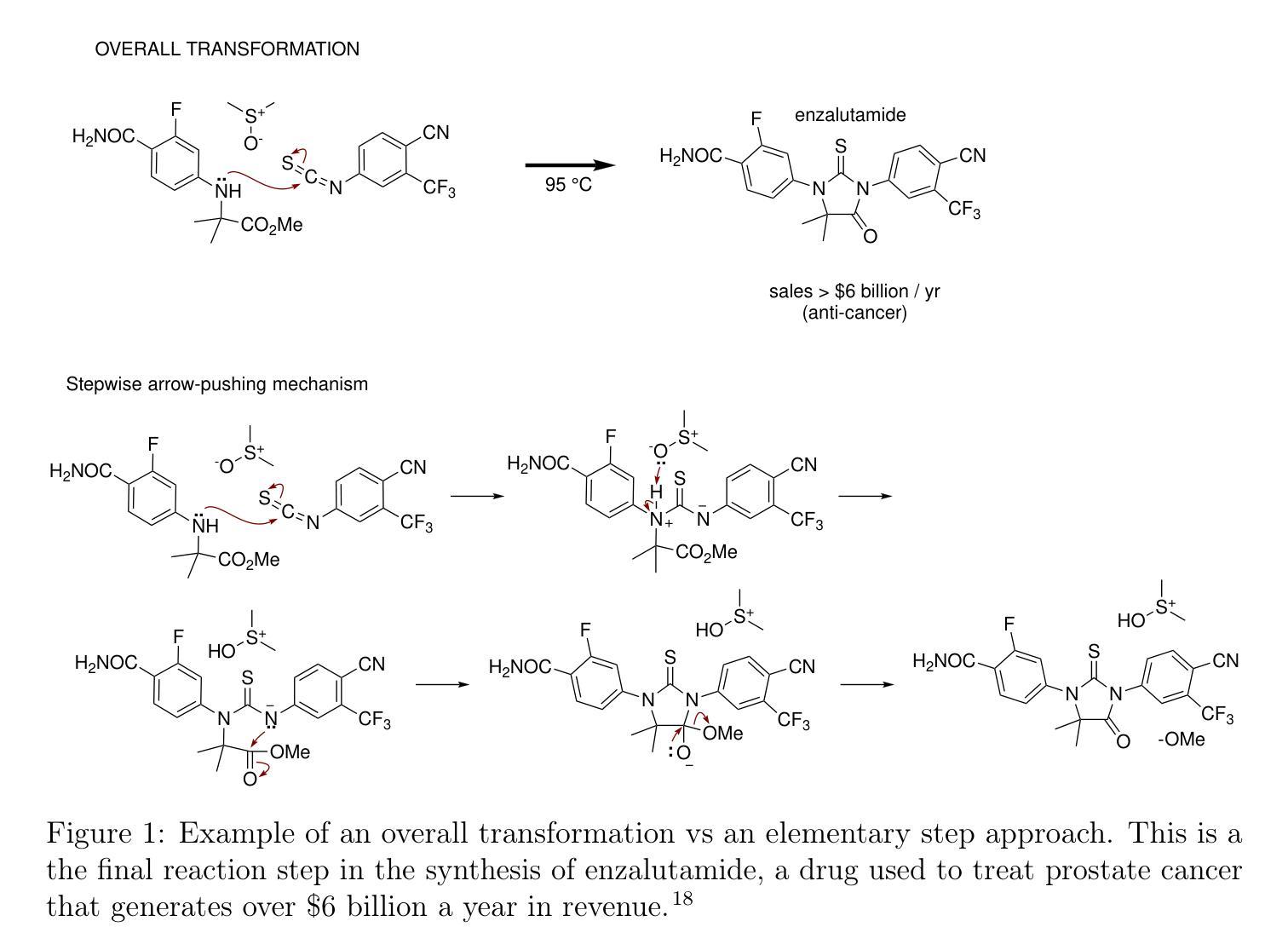
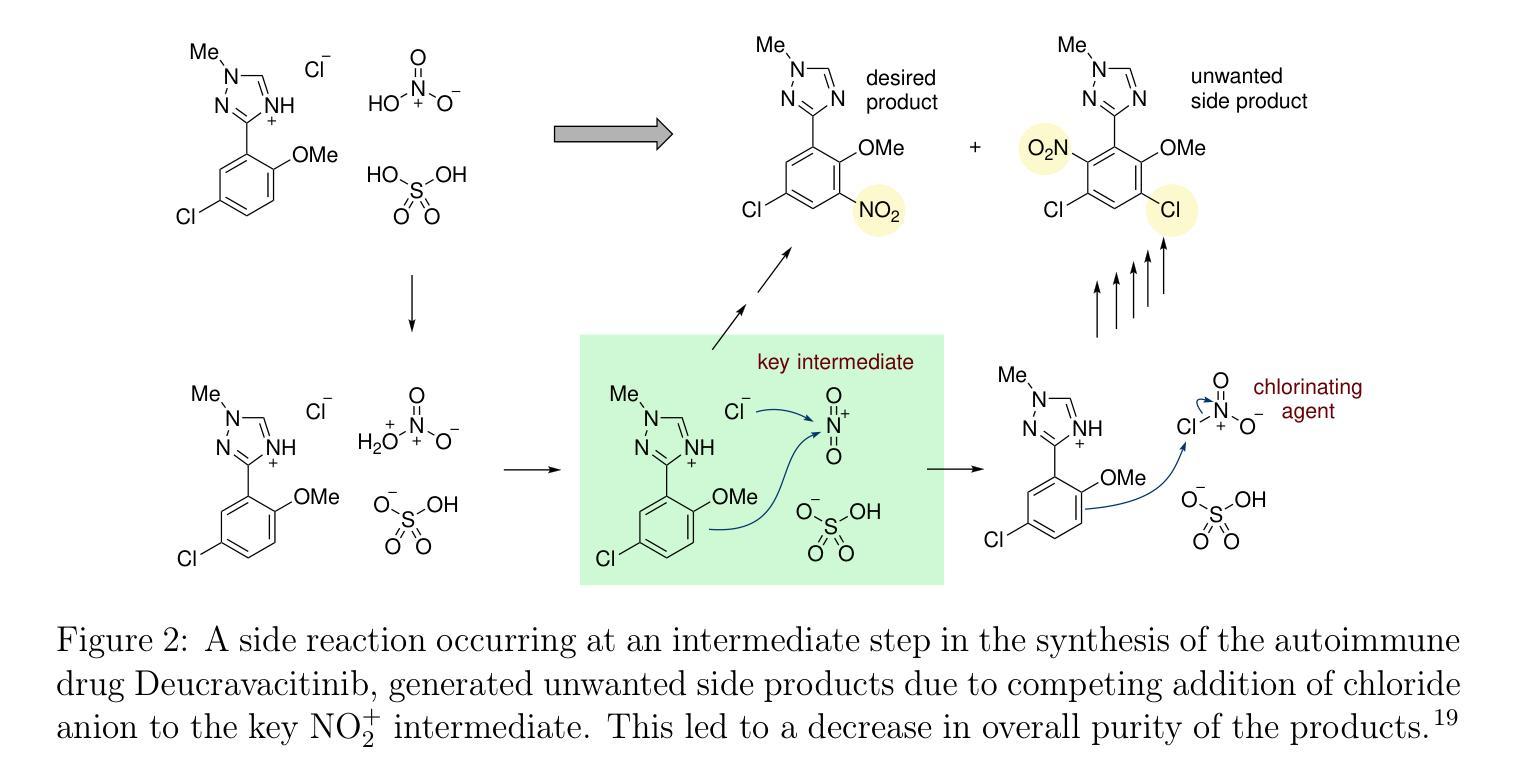
Interpretable Deep Learning for Polar Mechanistic Reaction Prediction
Authors:Ryan J. Miller, Alexander E. Dashuta, Brayden Rudisill, David Van Vranken, Pierre Baldi
Accurately predicting chemical reactions is essential for driving innovation in synthetic chemistry, with broad applications in medicine, manufacturing, and agriculture. At the same time, reaction prediction is a complex problem which can be both time-consuming and resource-intensive for chemists to solve. Deep learning methods offer an appealing solution by enabling high-throughput reaction prediction. However, many existing models are trained on the US Patent Office dataset and treat reactions as overall transformations: mapping reactants directly to products with limited interpretability or mechanistic insight. To address this, we introduce PMechRP (Polar Mechanistic Reaction Predictor), a system that trains machine learning models on the PMechDB dataset, which represents reactions as polar elementary steps that capture electron flow and mechanistic detail. To further expand model coverage and improve generalization, we augment PMechDB with a diverse set of combinatorially generated reactions. We train and compare a range of machine learning models, including transformer-based, graph-based, and two-step siamese architectures. Our best-performing approach was a hybrid model, which combines a 5-ensemble of Chemformer models with a two-step Siamese framework to leverage the accuracy of transformer architectures, while filtering away “alchemical” products using the two-step network predictions. For evaluation, we use a test split of the PMechDB dataset and additionally curate a human benchmark dataset consisting of complete mechanistic pathways extracted from an organic chemistry textbook. Our hybrid model achieves a top-10 accuracy of 94.9% on the PMechDB test set and a target recovery rate of 84.9% on the pathway dataset.
精确预测化学反应对于推动合成化学领域的创新至关重要,在医学、制造业和农业等领域具有广泛应用。然而,反应预测是一个复杂的问题,化学家解决这一问题既耗时又耗资源。深度学习的方法提供了一个吸引人的解决方案,能够实现高通量的反应预测。然而,许多现有模型都是基于美国专利局的数据集进行训练的,将反应视为整体转化,即直接将反应物映射到产物,缺乏解释性或机制洞察。为了解决这个问题,我们引入了PMechRP(极化机制反应预测器),这是一个在PMechDB数据集上训练机器学习模型的系统,它将反应表示为极化的基本步骤,捕捉电子流动和机制细节。为了进一步扩大模型覆盖面并提高其泛化能力,我们用组合生成的多样化反应来增强PMechDB。我们训练和比较了一系列机器学习模型,包括基于转换器的、基于图的和两步Siamese架构。我们表现最好的方法是一个混合模型,它结合了Chemformer模型的5重组合和两步Siamese框架,以利用转换器架构的准确性,同时使用两步网络预测来过滤掉“炼金术”产品。为了评估模型性能,我们使用PMechDB数据集的测试集以及从有机化学教科书中提取的完整机制路径组成的人工基准数据集。混合模型在PMechDB测试集上实现了前10名准确率为94.9%,在路径数据集上目标回收率为84.9%。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
本研究介绍了一种名为PMechRP的深度学习反应预测系统,用于解决化学反应预测问题。该系统使用PMechDB数据集训练机器学习模型,以极子步骤的形式表示反应,并捕捉电子流动和机理细节。研究通过扩充数据集和组合多种机器学习模型来提高模型覆盖率和泛化能力。其中,混合模型结合了Chemformer模型和两步Siamese框架,在PMechDB测试集上达到了94.9%的top-10准确率和84.9%的目标回收率。
Key Takeaways
- 深度学习在化学反应预测中具有高通量潜力。
- PMechRP系统使用PMechDB数据集训练机器学习模型,以极子步骤形式表示反应。
- 极子步骤能够捕捉电子流动和机理细节,提高反应预测的准确度和可解释性。
- 研究通过组合生成反应和多种机器学习模型来扩充数据集和提高模型泛化能力。
- 混合模型结合了Chemformer和两步Siamese框架,取得最佳性能。
- 在PMechDB测试集上,混合模型的top-10准确率达到了94.9%。
- 在路径数据集上,混合模型的目标回收率为84.9%。
点此查看论文截图

Listenable Maps for Zero-Shot Audio Classifiers
Authors:Francesco Paissan, Luca Della Libera, Mirco Ravanelli, Cem Subakan
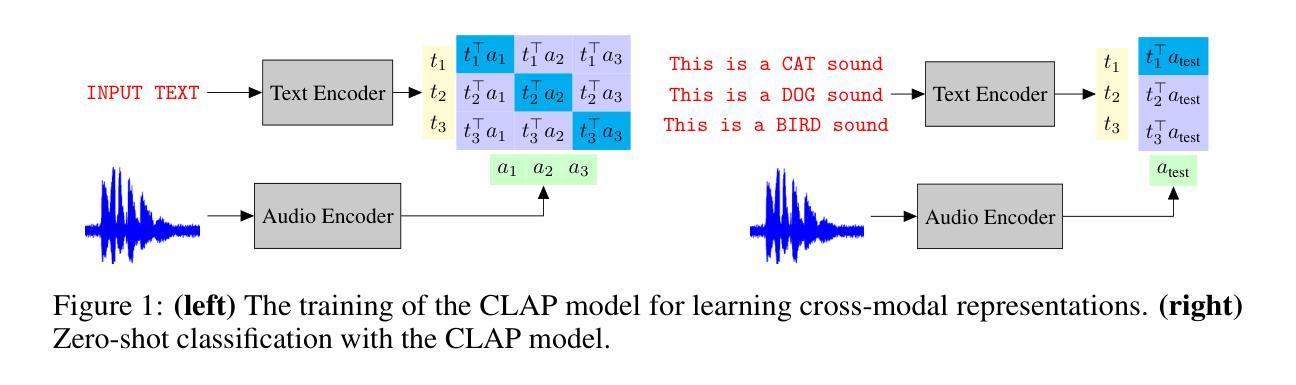
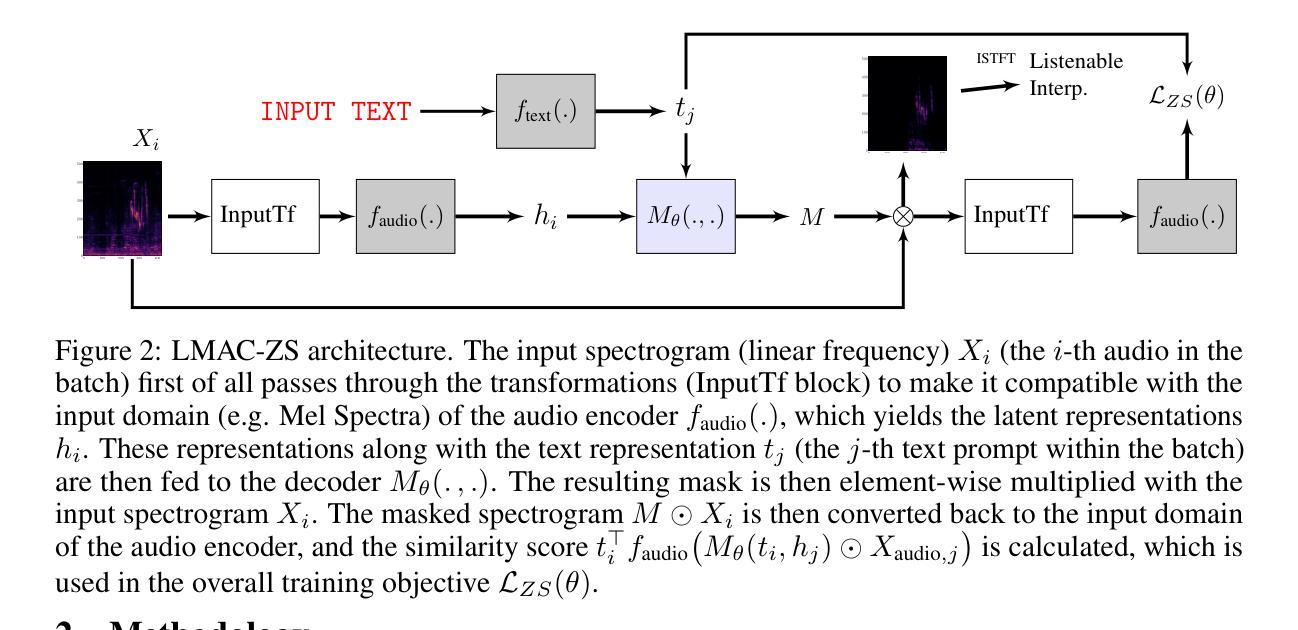
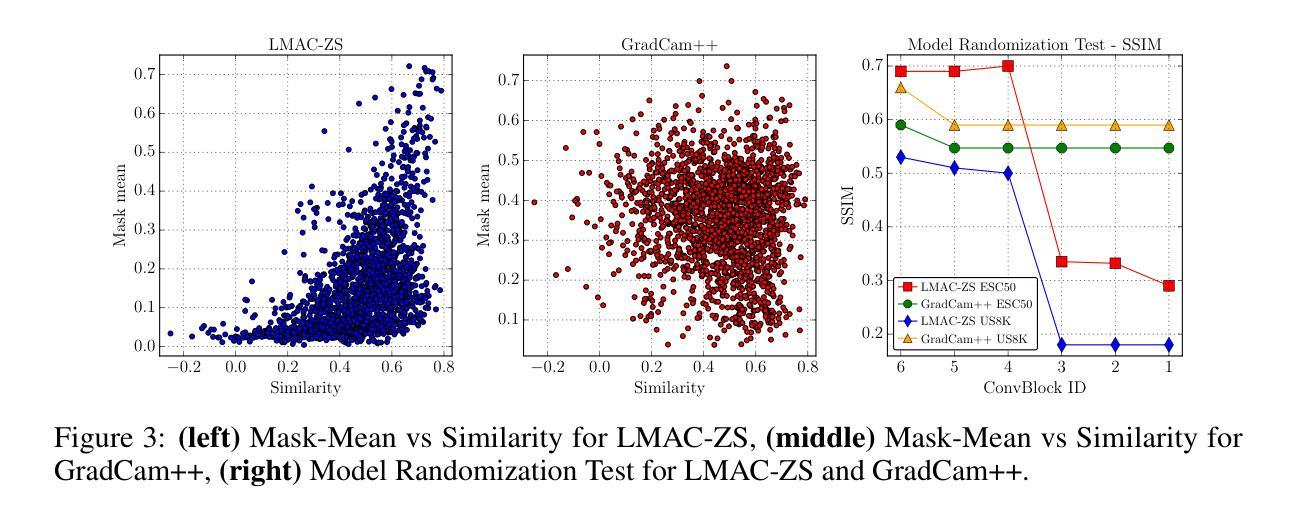
Interpreting the decisions of deep learning models, including audio classifiers, is crucial for ensuring the transparency and trustworthiness of this technology. In this paper, we introduce LMAC-ZS (Listenable Maps for Audio Classifiers in the Zero-Shot context), which, to the best of our knowledge, is the first decoder-based post-hoc interpretation method for explaining the decisions of zero-shot audio classifiers. The proposed method utilizes a novel loss function that maximizes the faithfulness to the original similarity between a given text-and-audio pair. We provide an extensive evaluation using the Contrastive Language-Audio Pretraining (CLAP) model to showcase that our interpreter remains faithful to the decisions in a zero-shot classification context. Moreover, we qualitatively show that our method produces meaningful explanations that correlate well with different text prompts.
解释深度学习模型的决策,包括音频分类器,对于确保这项技术的透明度和可信度至关重要。在本文中,我们介绍了LMAC-ZS(零样本背景下的音频分类器可听地图),据我们所知,这是第一个基于解码器的后验解释方法,用于解释零样本音频分类器的决策。所提出的方法利用了一种新型损失函数,最大限度地忠于给定文本和音频对之间的原始相似性。我们使用对比语言音频预训练(CLAP)模型进行了广泛评估,以展示我们的解释器在零样本分类环境中保持忠实于决策。此外,我们定性证明了我们的方法产生的解释与不同的文本提示关联良好。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF Accepted to NeurIPS 2024
Summary
介绍了一种称为LMAC-ZS的深度学习模型决策解释方法,该方法专注于零样本音频分类器的解释。LMAC-ZS利用新的损失函数最大化文本和音频对之间的原始相似性,以解释模型决策。采用CLAP模型进行的广泛评估证明其在零样本分类背景下仍忠于决策,且提供的有意义的解释与不同文本提示相关性强。
Key Takeaways
- LMAC-ZS是首个为零样本音频分类器设计的解码器后处理方法,用于解释其决策。
- 该方法利用新颖的损失函数来最大化文本和音频之间的原始相似性。
- LMAC-ZS适用于零样本分类场景下的决策解释。
- 使用CLAP模型的广泛评估证明了LMAC-ZS的忠实性。
- LMAC-ZS生成的解释具有意义且与不同的文本提示关联紧密。
点此查看论文截图