⚠️ 以下所有内容总结都来自于 大语言模型的能力,如有错误,仅供参考,谨慎使用
🔴 请注意:千万不要用于严肃的学术场景,只能用于论文阅读前的初筛!
💗 如果您觉得我们的项目对您有帮助 ChatPaperFree ,还请您给我们一些鼓励!⭐️ HuggingFace免费体验
2025-04-24 更新
Pose Optimization for Autonomous Driving Datasets using Neural Rendering Models
Authors:Quentin Herau, Nathan Piasco, Moussab Bennehar, Luis Rolado, Dzmitry Tsishkou, Bingbing Liu, Cyrille Migniot, Pascal Vasseur, Cédric Demonceaux
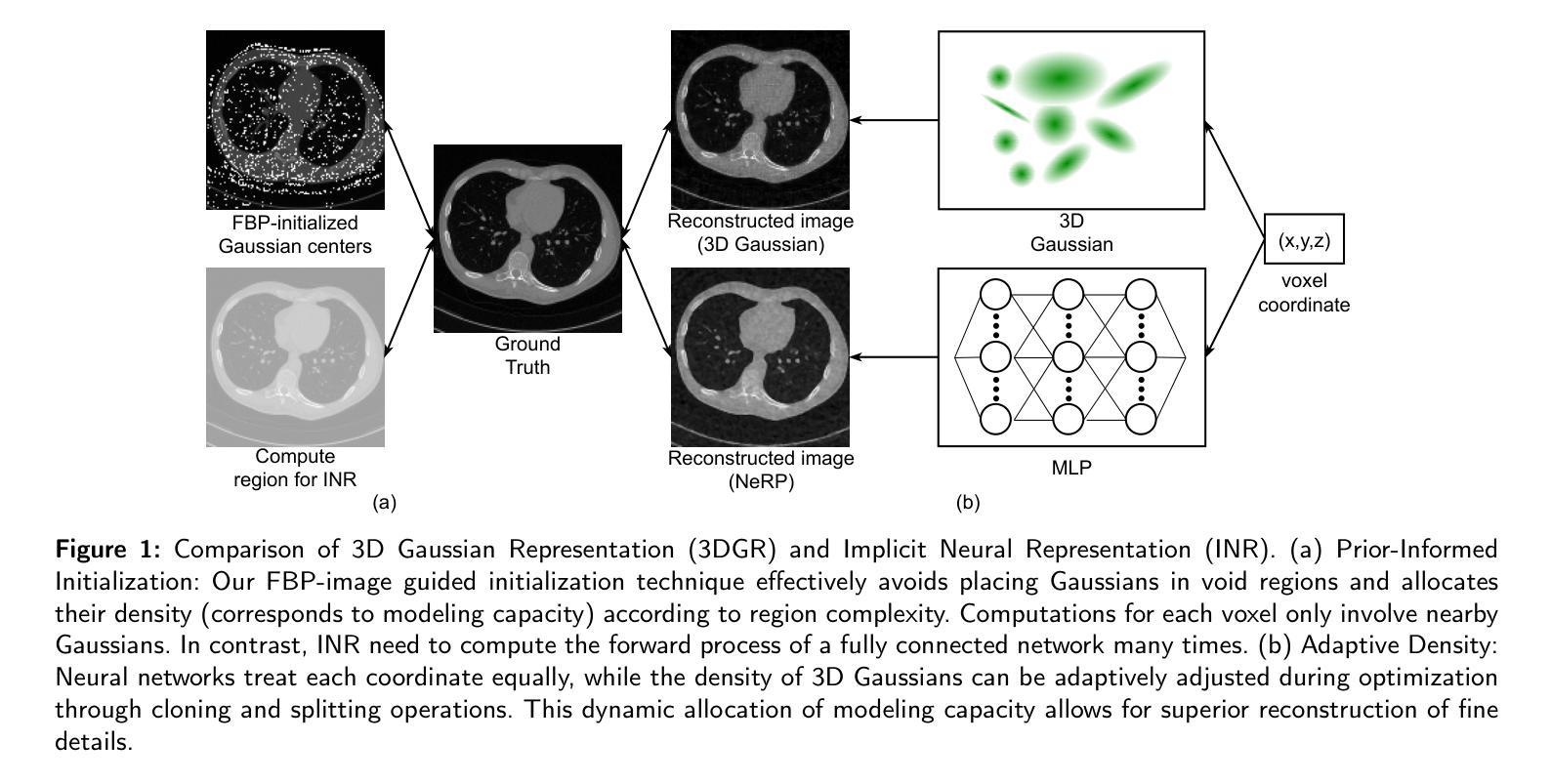
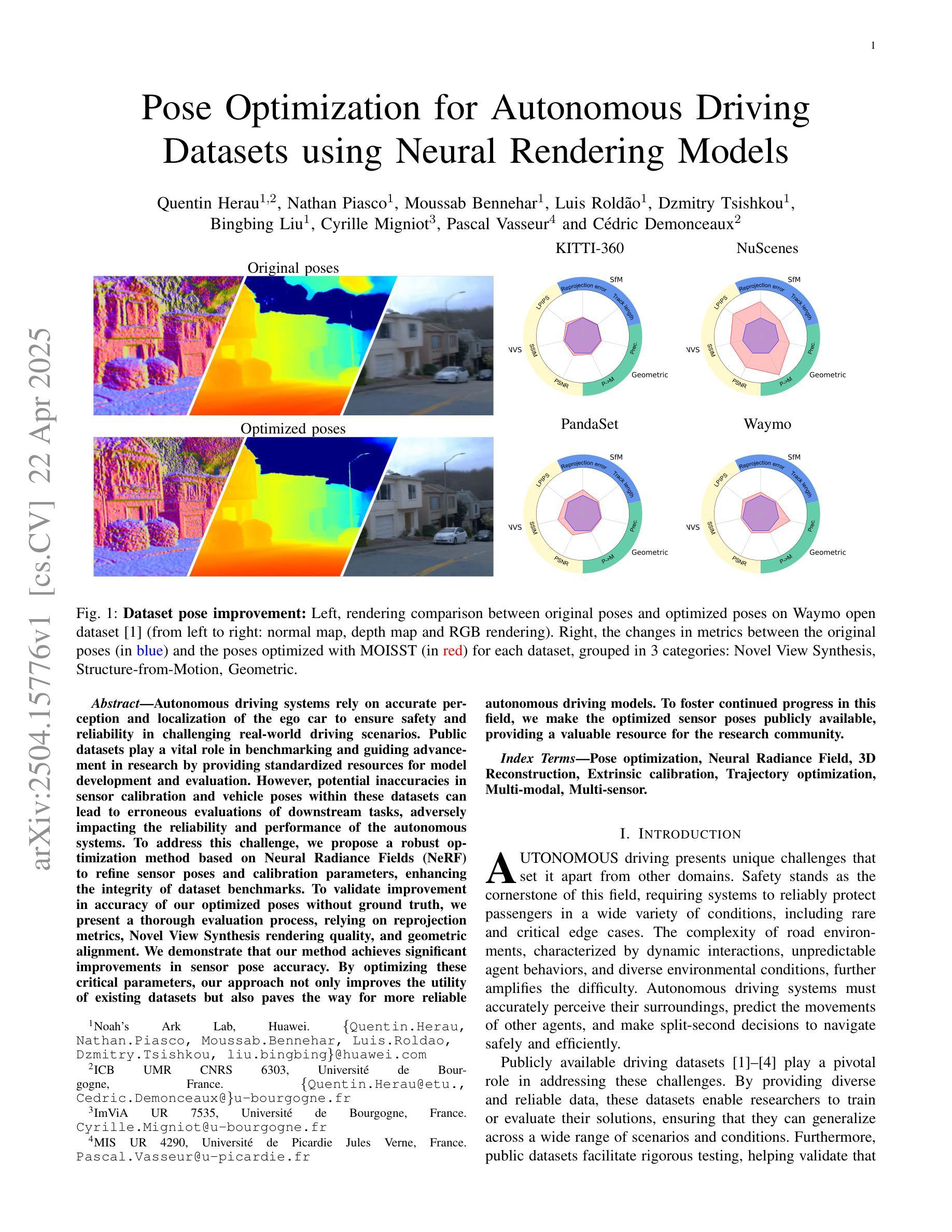
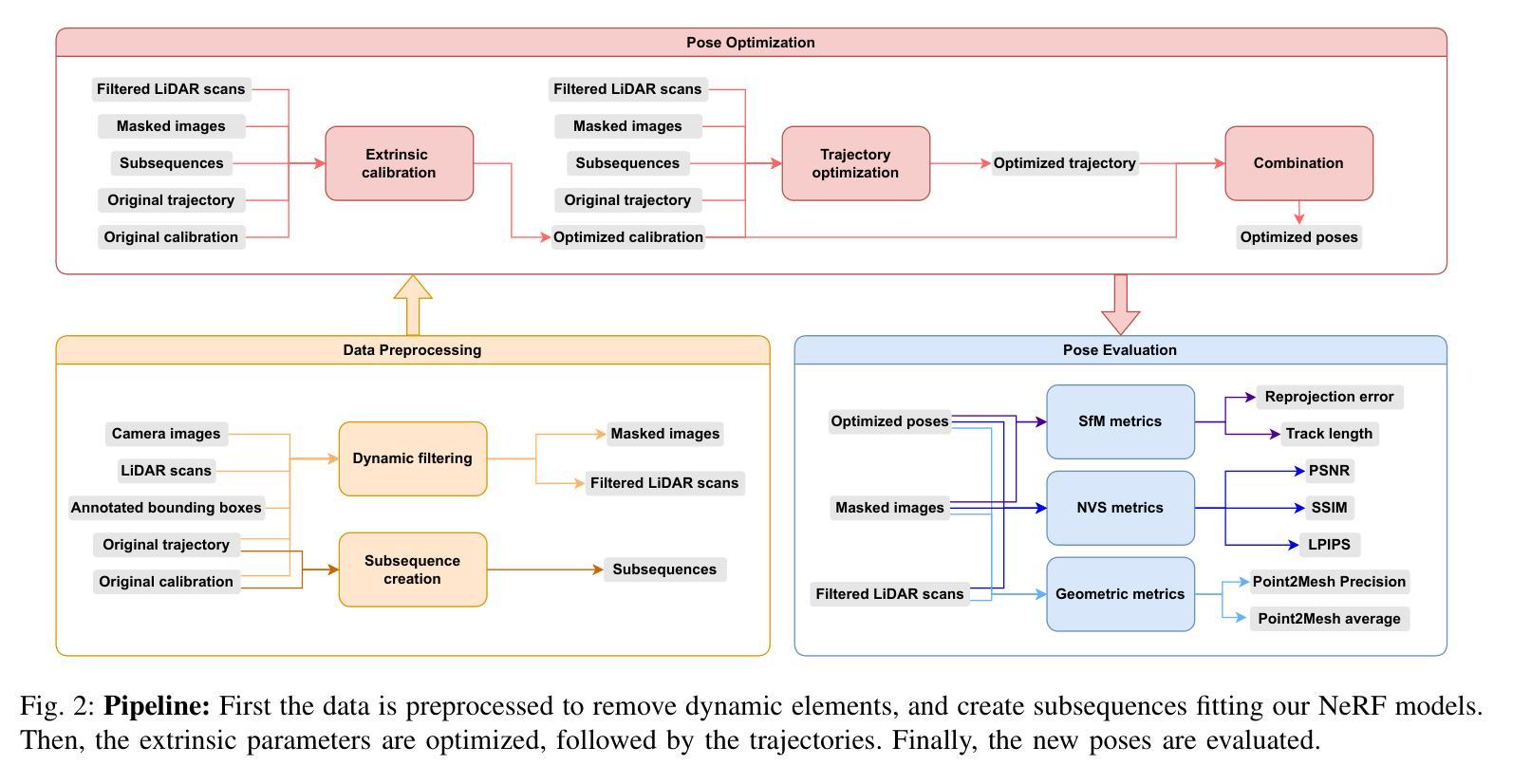
Autonomous driving systems rely on accurate perception and localization of the ego car to ensure safety and reliability in challenging real-world driving scenarios. Public datasets play a vital role in benchmarking and guiding advancement in research by providing standardized resources for model development and evaluation. However, potential inaccuracies in sensor calibration and vehicle poses within these datasets can lead to erroneous evaluations of downstream tasks, adversely impacting the reliability and performance of the autonomous systems. To address this challenge, we propose a robust optimization method based on Neural Radiance Fields (NeRF) to refine sensor poses and calibration parameters, enhancing the integrity of dataset benchmarks. To validate improvement in accuracy of our optimized poses without ground truth, we present a thorough evaluation process, relying on reprojection metrics, Novel View Synthesis rendering quality, and geometric alignment. We demonstrate that our method achieves significant improvements in sensor pose accuracy. By optimizing these critical parameters, our approach not only improves the utility of existing datasets but also paves the way for more reliable autonomous driving models. To foster continued progress in this field, we make the optimized sensor poses publicly available, providing a valuable resource for the research community.
自动驾驶系统依赖于对主车自身的精确感知和定位,以确保在具有挑战性的现实世界驾驶场景中安全性和可靠性。公开数据集在基准测试和指引研究进步中发挥着重要作用,为模型开发和评估提供标准化资源。然而,这些数据集中传感器校准和车辆姿态的潜在不准确性可能导致下游任务评估出现错误,对自动驾驶系统的可靠性和性能产生不利影响。为了应对这一挑战,我们提出了一种基于神经辐射场(NeRF)的稳健优化方法,以改进传感器姿态和校准参数,提高数据集基准的完整性。为了验证在无地面真实数据的情况下优化姿态的准确性改进,我们采用了一个全面的评估过程,依赖于再投影指标、新型视图合成渲染质量和几何对齐。我们证明我们的方法在传感器姿态准确性方面取得了显著改进。通过优化这些关键参数,我们的方法不仅提高了现有数据集的使用价值,还为更可靠的自动驾驶模型铺平了道路。为了促进该领域的持续进步,我们公开提供优化后的传感器姿态,为研究领域提供有价值的资源。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF under review
Summary
基于神经辐射场(NeRF)的稳健优化方法,用于改进自动驾驶系统中的传感器姿态和校准参数,从而提高数据集基准测试的完整性。通过依赖重投影指标、新型视图合成渲染质量和几何对齐的评估过程,验证优化后的姿态准确性显著提高。此方法的采用不仅提高了现有数据集的使用价值,还为更可靠的自动驾驶模型的发展奠定了基础。
Key Takeaways
- 自动驾驶系统依赖准确的感知和车辆定位以确保在复杂现实场景中的安全和可靠性。
- 公共数据集在评估和指导自动驾驶研究方面起着至关重要的作用。
- 数据集中的传感器校准和车辆姿态的潜在不准确性可能导致下游任务评估出错,影响自动驾驶系统的性能和可靠性。
- 提出基于神经辐射场(NeRF)的稳健优化方法,以改进传感器姿态和校准参数,提高数据集基准测试的完整性。
- 通过重投影指标、新型视图合成渲染质量和几何对齐的评估过程,验证优化后的传感器姿态准确性显著提高。
- 优化方法不仅提高了现有数据集的使用价值。
点此查看论文截图
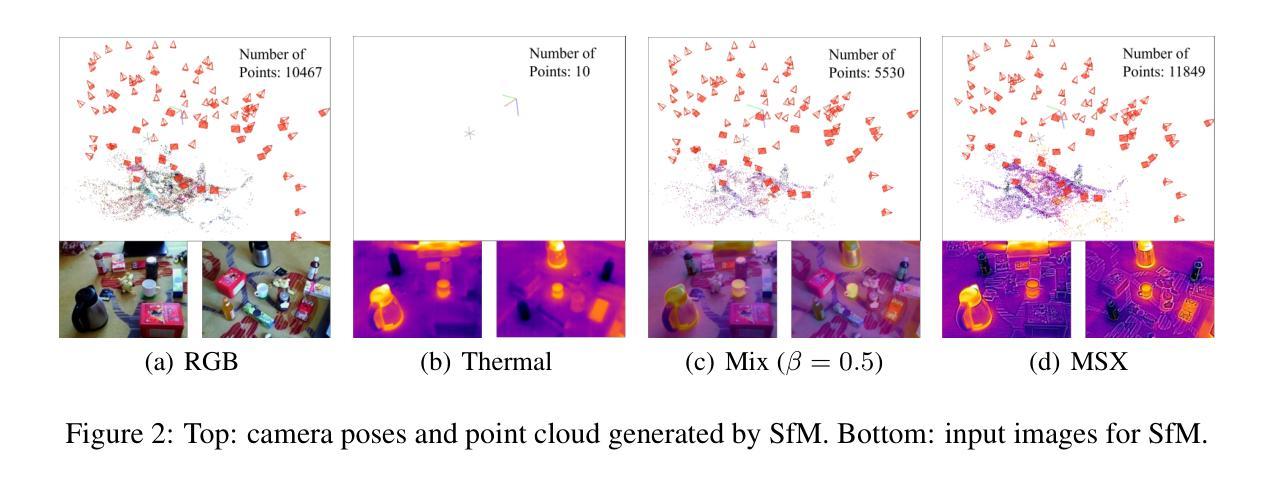
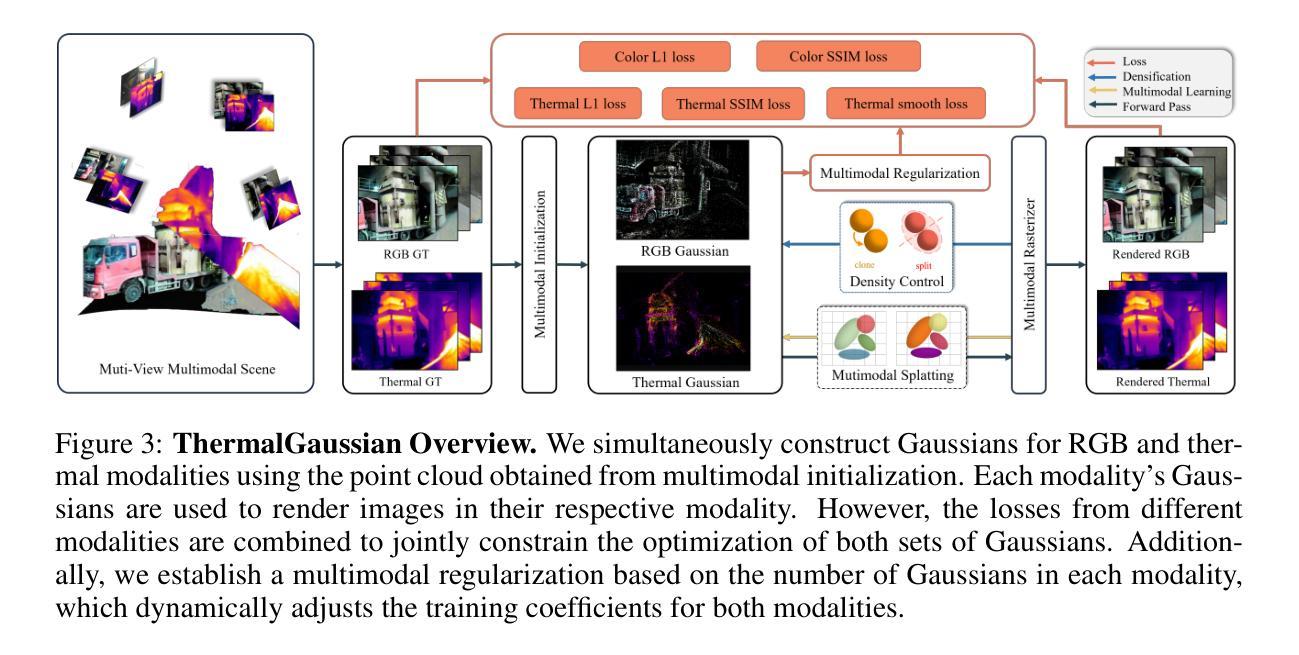
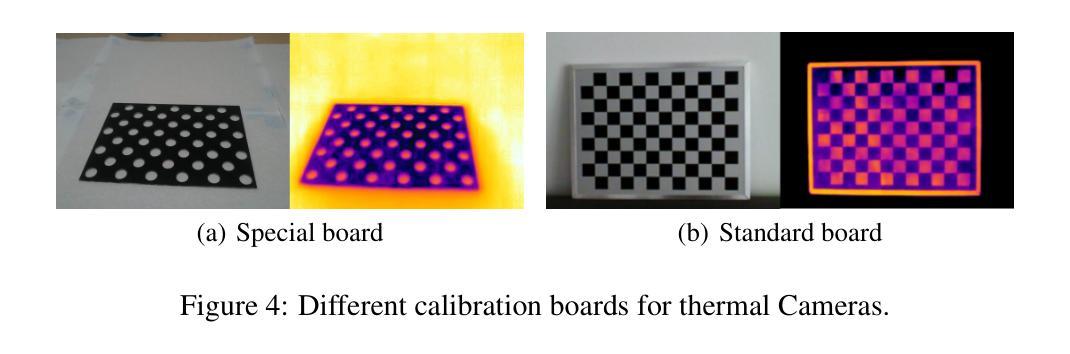
ThermalGaussian: Thermal 3D Gaussian Splatting
Authors:Rongfeng Lu, Hangyu Chen, Zunjie Zhu, Yuhang Qin, Ming Lu, Le Zhang, Chenggang Yan, Anke Xue
Thermography is especially valuable for the military and other users of surveillance cameras. Some recent methods based on Neural Radiance Fields (NeRF) are proposed to reconstruct the thermal scenes in 3D from a set of thermal and RGB images. However, unlike NeRF, 3D Gaussian splatting (3DGS) prevails due to its rapid training and real-time rendering. In this work, we propose ThermalGaussian, the first thermal 3DGS approach capable of rendering high-quality images in RGB and thermal modalities. We first calibrate the RGB camera and the thermal camera to ensure that both modalities are accurately aligned. Subsequently, we use the registered images to learn the multimodal 3D Gaussians. To prevent the overfitting of any single modality, we introduce several multimodal regularization constraints. We also develop smoothing constraints tailored to the physical characteristics of the thermal modality. Besides, we contribute a real-world dataset named RGBT-Scenes, captured by a hand-hold thermal-infrared camera, facilitating future research on thermal scene reconstruction. We conduct comprehensive experiments to show that ThermalGaussian achieves photorealistic rendering of thermal images and improves the rendering quality of RGB images. With the proposed multimodal regularization constraints, we also reduced the model’s storage cost by 90%. Our project page is at https://thermalgaussian.github.io/.
热成像技术对于军事和其他监控相机使用者来说具有特别重要的价值。最近有一些基于神经网络辐射场(NeRF)的方法被提出来从一组热成像和RGB图像中重建三维热场景。然而,不同于NeRF,三维高斯贴片(3DGS)因其快速训练和实时渲染而更受欢迎。在这项工作中,我们提出了ThermalGaussian,这是第一种能够在RGB和热成像模式下呈现高质量图像的热成像三维高斯贴片方法。我们首先校准RGB相机和热成像相机,以确保两种模式能够准确对齐。随后,我们使用已注册的图像来学习多模态三维高斯分布。为了防止任何单一模态的过拟合问题,我们引入了多种多模态正则化约束。我们还针对热成像的物理特性开发了定制的平滑约束。此外,我们还贡献了一个名为RGBT-Scenes的真实世界数据集,该数据集由手持热红外相机拍摄,便于未来对热场景重建的研究。我们进行了全面的实验,以展示ThermalGaussian能够实现热成像的光照现实渲染,并提高了RGB图像的渲染质量。借助提出的多模态正则化约束,我们还降低了模型90%的存储成本。我们的项目页面是https://thermalgaussian.github.io/。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF 10 pages, 7 figures
Summary
基于神经辐射场(NeRF)的方法能够从一系列热图和RGB图像中重建三维热场景。然而,由于训练迅速、实时渲染的优势,3D高斯拼贴技术(3DGS)较为流行。本研究提出一种名为ThermalGaussian的新方法,是首个能够实现RGB和热模式下高质量图像渲染的热3DGS技术。通过校准RGB相机和热相机,确保两种模式准确对齐,然后使用注册图像学习多模态三维高斯。为避免单一模态的过拟合问题,引入多种多模态正则化约束。此外,针对热模式的物理特性开发平滑约束。同时,本研究贡献了一个真实场景数据集RGBT-Scenes,通过手持热红外相机拍摄,为未来的热场景重建研究提供了便利。实验表明,ThermalGaussian实现了热图像的光照真实渲染,提高了RGB图像的渲染质量,并且降低了模型存储成本90%。项目页面位于:[https://thermalgaussian.github.io/]
Key Takeaways
- 基于NeRF的方法可以从多个图像重建三维热场景。
- 相较于NeRF技术,目前主流更倾向于采用快速的训练和高实时渲染性能的3DGS技术。
- 研究者提出了名为ThermalGaussian的新方法,这是一种热模式下高质量图像渲染的热态三维高斯拼贴技术。
- ThermalGaussian方法首先校准RGB相机和热相机,以确保两种模式图像的准确对齐。随后利用校准后的图像进行三维学习并渲染。
点此查看论文截图