⚠️ 以下所有内容总结都来自于 大语言模型的能力,如有错误,仅供参考,谨慎使用
🔴 请注意:千万不要用于严肃的学术场景,只能用于论文阅读前的初筛!
💗 如果您觉得我们的项目对您有帮助 ChatPaperFree ,还请您给我们一些鼓励!⭐️ HuggingFace免费体验
2025-04-25 更新
Advanced Chest X-Ray Analysis via Transformer-Based Image Descriptors and Cross-Model Attention Mechanism
Authors:Lakshita Agarwal, Bindu Verma
The examination of chest X-ray images is a crucial component in detecting various thoracic illnesses. This study introduces a new image description generation model that integrates a Vision Transformer (ViT) encoder with cross-modal attention and a GPT-4-based transformer decoder. The ViT captures high-quality visual features from chest X-rays, which are fused with text data through cross-modal attention to improve the accuracy, context, and richness of image descriptions. The GPT-4 decoder transforms these fused features into accurate and relevant captions. The model was tested on the National Institutes of Health (NIH) and Indiana University (IU) Chest X-ray datasets. On the IU dataset, it achieved scores of 0.854 (B-1), 0.883 (CIDEr), 0.759 (METEOR), and 0.712 (ROUGE-L). On the NIH dataset, it achieved the best performance on all metrics: BLEU 1–4 (0.825, 0.788, 0.765, 0.752), CIDEr (0.857), METEOR (0.726), and ROUGE-L (0.705). This framework has the potential to enhance chest X-ray evaluation, assisting radiologists in more precise and efficient diagnosis.
胸部X射线图像的检查是检测各种胸部疾病的关键环节。本研究介绍了一种新的图像描述生成模型,该模型集成了Vision Transformer(ViT)编码器、跨模态注意力和基于GPT-4的变压器解码器。ViT从胸部X射线图像中捕获高质量视觉特征,通过跨模态注意力与文本数据融合,提高了图像描述的准确性、上下文关联度和丰富性。GPT-4解码器将这些融合的特征转化为准确且相关的标题。该模型在美国国立卫生研究院(NIH)和印第安纳大学(IU)的胸部X射线数据集上进行了测试。在IU数据集上,它实现了B-1得分0.854、CIDEr得分0.883、METEOR得分0.759和ROUGE-L得分0.712。在NIH数据集上,它在所有指标上都取得了最佳性能:BLEU 1-4(0.825、0.788、0.765、0.752),CIDEr(0.857),METEOR(0.726)和ROUGE-L(0.705)。该框架有潜力增强胸部X射线的评估能力,帮助放射科医生进行更准确和高效的诊断。
论文及项目相关链接
摘要
本研究介绍了一种新的胸X光图像描述生成模型。该模型结合了Vision Transformer(ViT)编码器和基于GPT-4的转换器解码器,并通过跨模态注意力机制实现图像与文本的融合。ViT从胸X光图像中提取高质量视觉特征,通过跨模态注意力与文本数据融合,提高了图像描述的准确性、上下文关联性和丰富性。GPT-4解码器将这些融合的特征转化为准确且相关的描述。该模型在国立卫生研究院(NIH)和印第安纳大学(IU)的胸X光射线数据集上进行了测试,并在IU数据集上取得了较高的BLEU、CIDEr、METEOR和ROUGE-L等指标分数。在NIH数据集上,该模型在所有指标上都取得了最佳性能。该框架具有提高胸X光评价,协助放射科医生进行更准确、更高效的诊断的潜力。
关键见解
- 胸X光图像分析对于检测胸部疾病至关重要。
- 研究提出了一种新的图像描述生成模型,结合了ViT编码器和GPT-4解码器。
- ViT编码器从胸X光图像中提取视觉特征,通过跨模态注意力与文本数据融合。
- GPT-4解码器将融合的特征转化为准确的描述。
- 模型在NIH和IU数据集上进行了测试,并在多个评估指标上取得了良好成绩。
- 该模型在所有指标上的性能均优于先前的研究。
- 该框架有潜力提高胸X光的评估效率,辅助放射科医生进行更精确的诊断。
点此查看论文截图

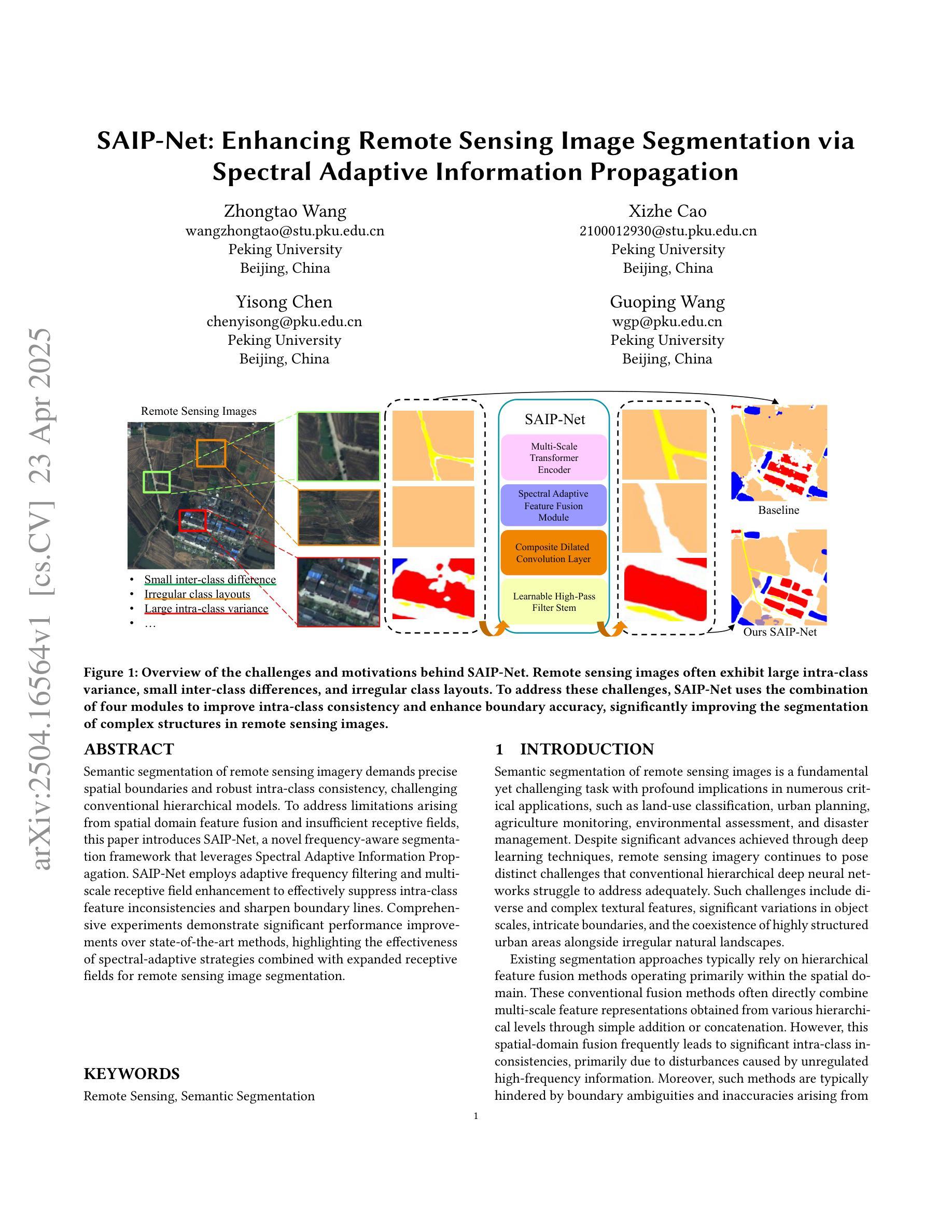
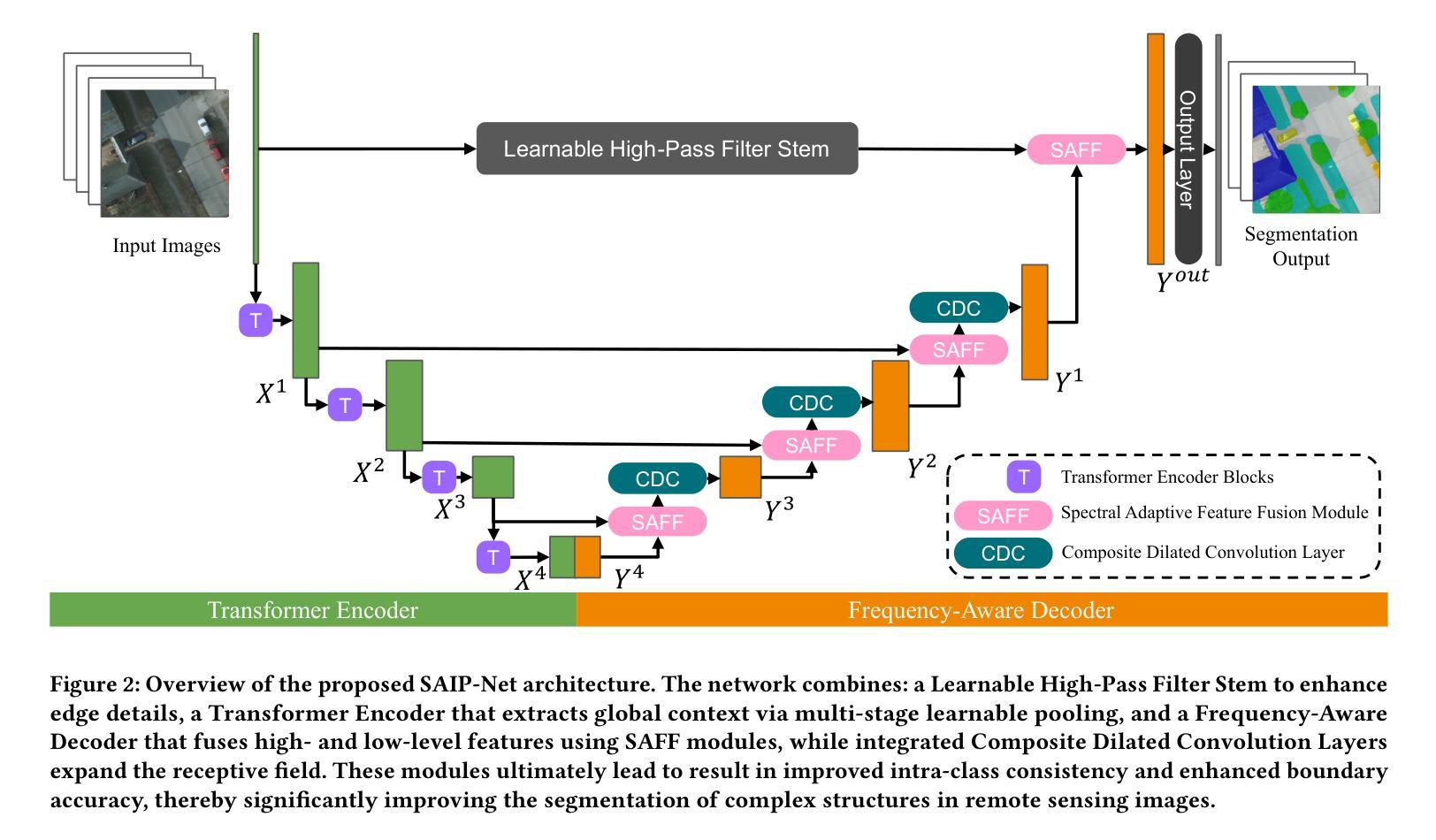
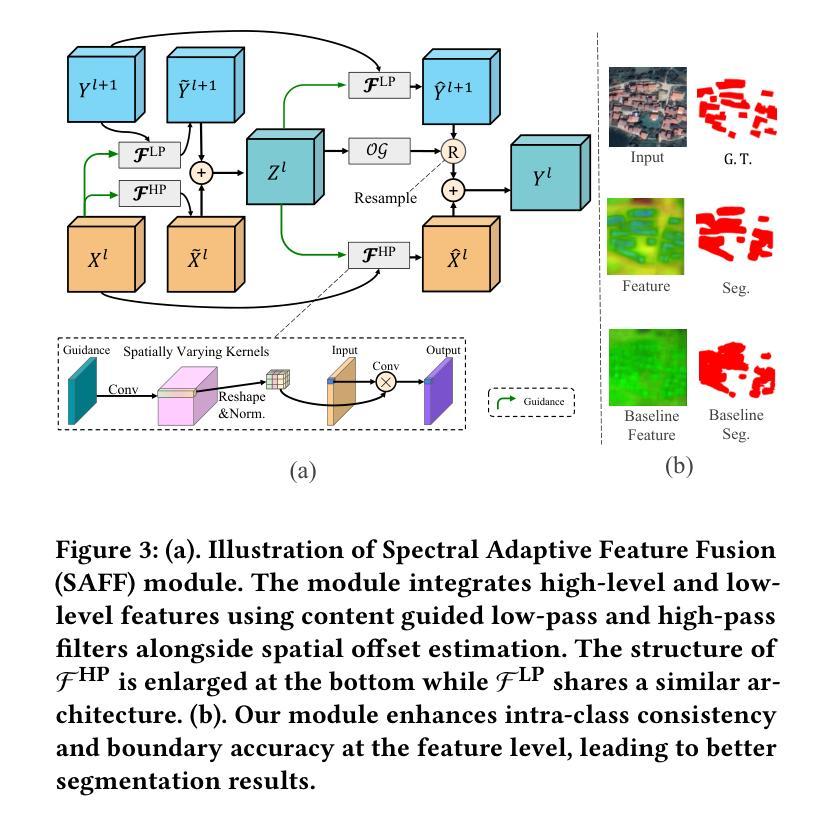
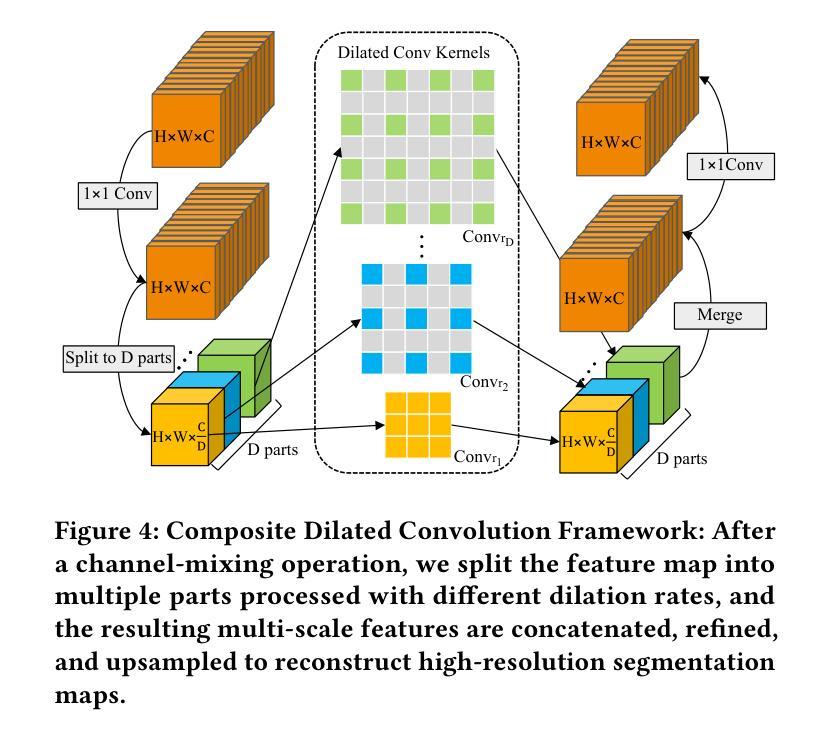
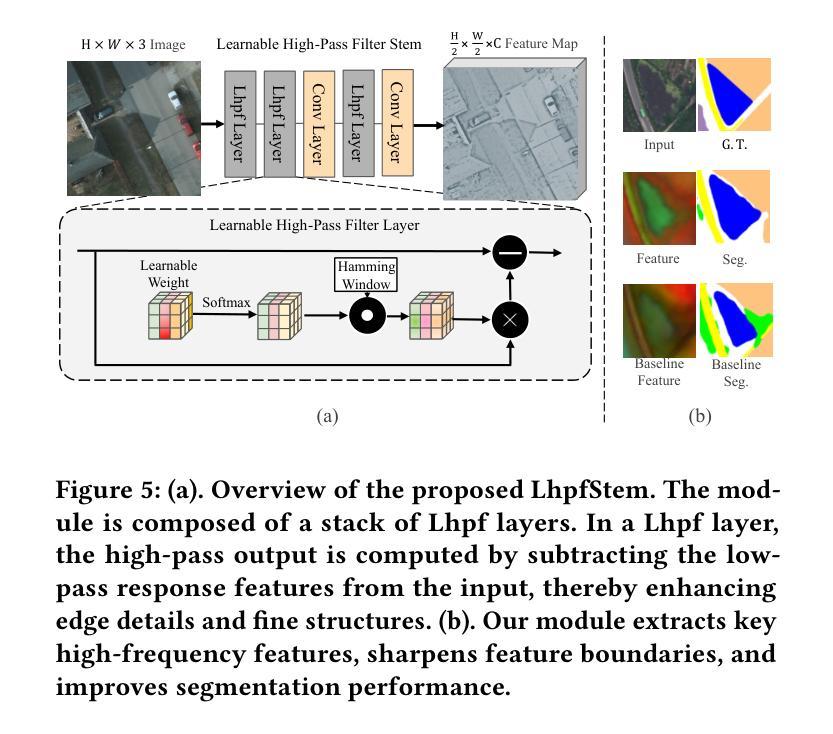
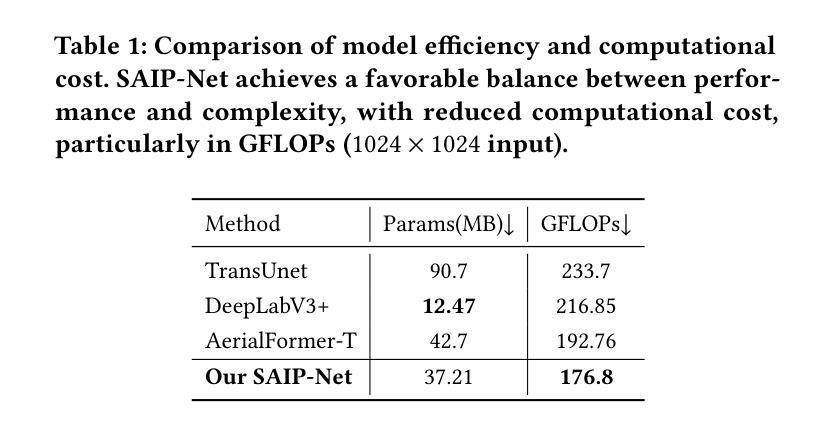
SAIP-Net: Enhancing Remote Sensing Image Segmentation via Spectral Adaptive Information Propagation
Authors:Zhongtao Wang, Xizhe Cao, Yisong Chen, Guoping Wang
Semantic segmentation of remote sensing imagery demands precise spatial boundaries and robust intra-class consistency, challenging conventional hierarchical models. To address limitations arising from spatial domain feature fusion and insufficient receptive fields, this paper introduces SAIP-Net, a novel frequency-aware segmentation framework that leverages Spectral Adaptive Information Propagation. SAIP-Net employs adaptive frequency filtering and multi-scale receptive field enhancement to effectively suppress intra-class feature inconsistencies and sharpen boundary lines. Comprehensive experiments demonstrate significant performance improvements over state-of-the-art methods, highlighting the effectiveness of spectral-adaptive strategies combined with expanded receptive fields for remote sensing image segmentation.
遥感影像的语义分割要求精确的空间边界和稳健的类内一致性,这挑战了传统的分层模型。为了解决由空间域特征融合和感受野不足而产生的局限性,本文引入了SAIP-Net,这是一种利用光谱自适应信息传播的新型频率感知分割框架。SAIP-Net采用自适应频率滤波和多尺度感受野增强,有效地抑制了类内特征的不一致性,提高了边界线的清晰度。综合实验表明,该方法在最新方法的基础上显著提高了性能,突出了结合扩展感受野的光谱自适应策略在遥感图像分割中的有效性。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
本文介绍了一种基于谱自适应信息传播的频率感知分割框架SAIP-Net,用于遥感图像语义分割。针对空间域特征融合和感受野不足的问题,该网络采用自适应频率滤波和多尺度感受野增强技术,有效抑制了类内特征不一致性,提高了边界线的清晰度。实验表明,与最新技术相比,该网络在遥感图像分割方面表现出显著的性能改进。
Key Takeaways
- 遥感图像语义分割需要精确的空间边界和稳健的类内一致性,挑战了传统层次模型。
- SAIP-Net是一种新型频率感知分割框架,利用谱自适应信息传播来解决这个问题。
- SAIP-Net通过自适应频率滤波和多尺度感受野增强技术,有效提高了遥感图像分割的性能。
- 自适应频率滤波有助于抑制类内特征的不一致性。
- 多尺度感受野增强可以扩大网络对上下文信息的捕获能力,从而更准确地识别边界。
- 实验结果表明,SAIP-Net在遥感图像分割方面显著优于现有技术。
点此查看论文截图
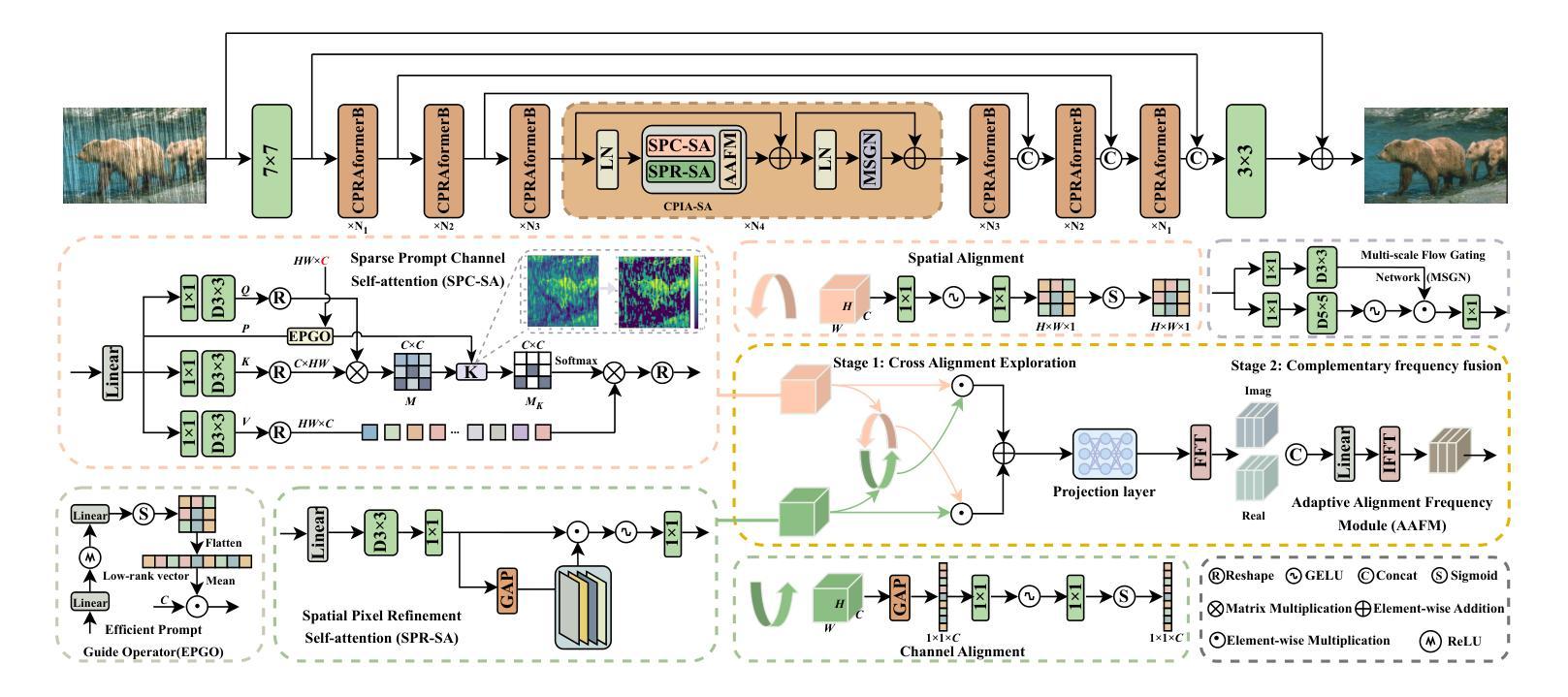
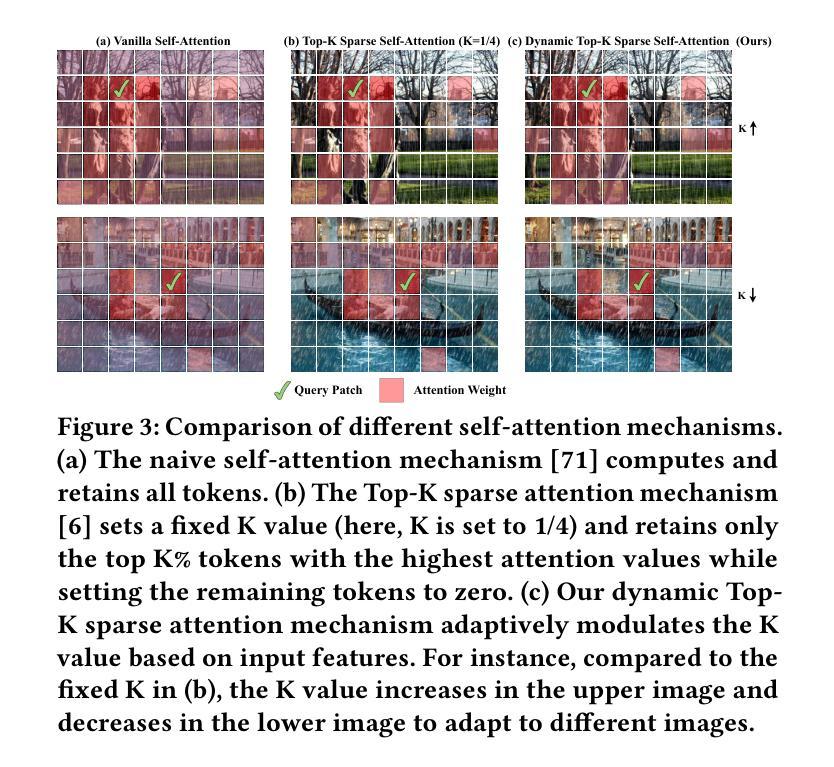
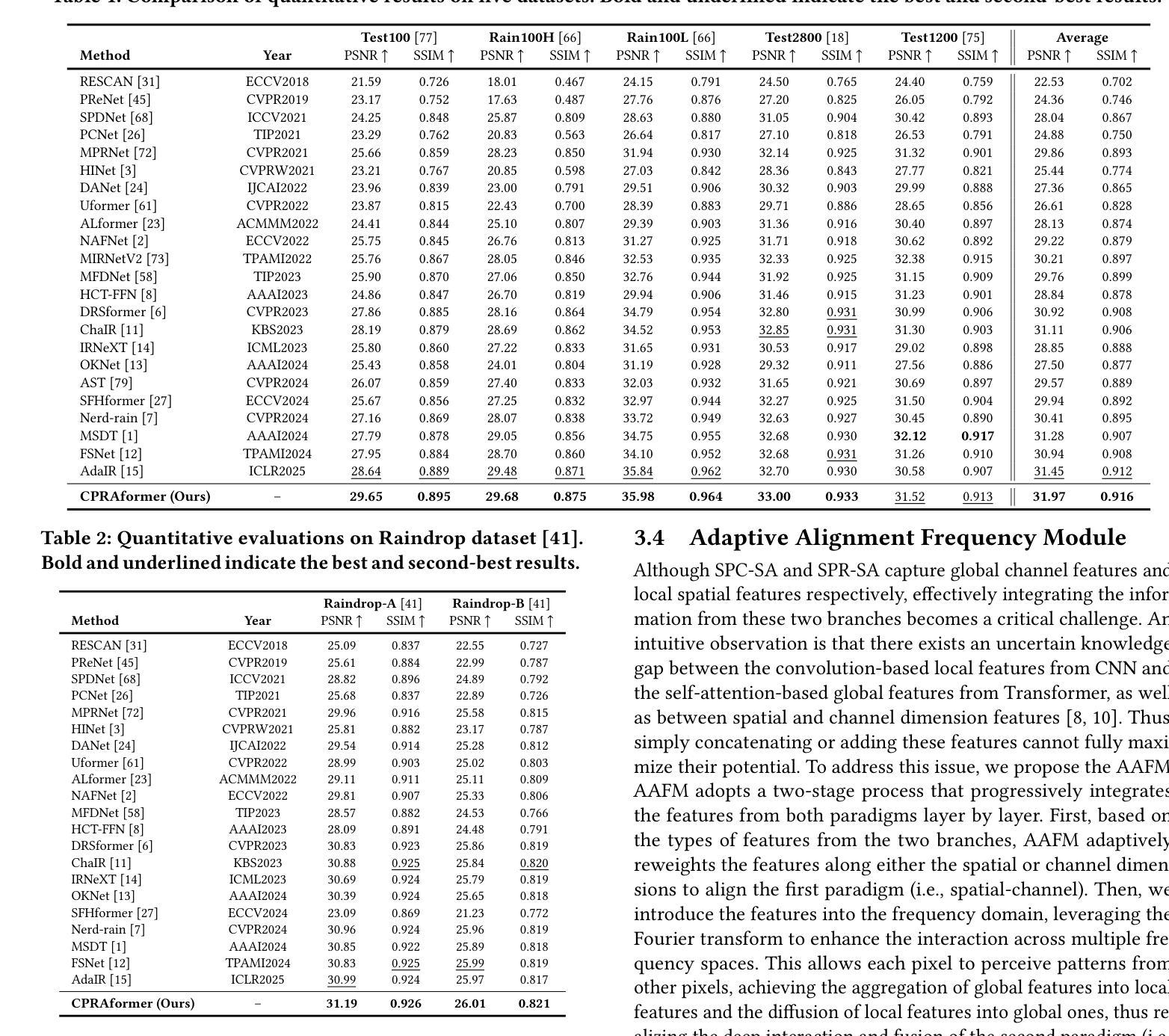
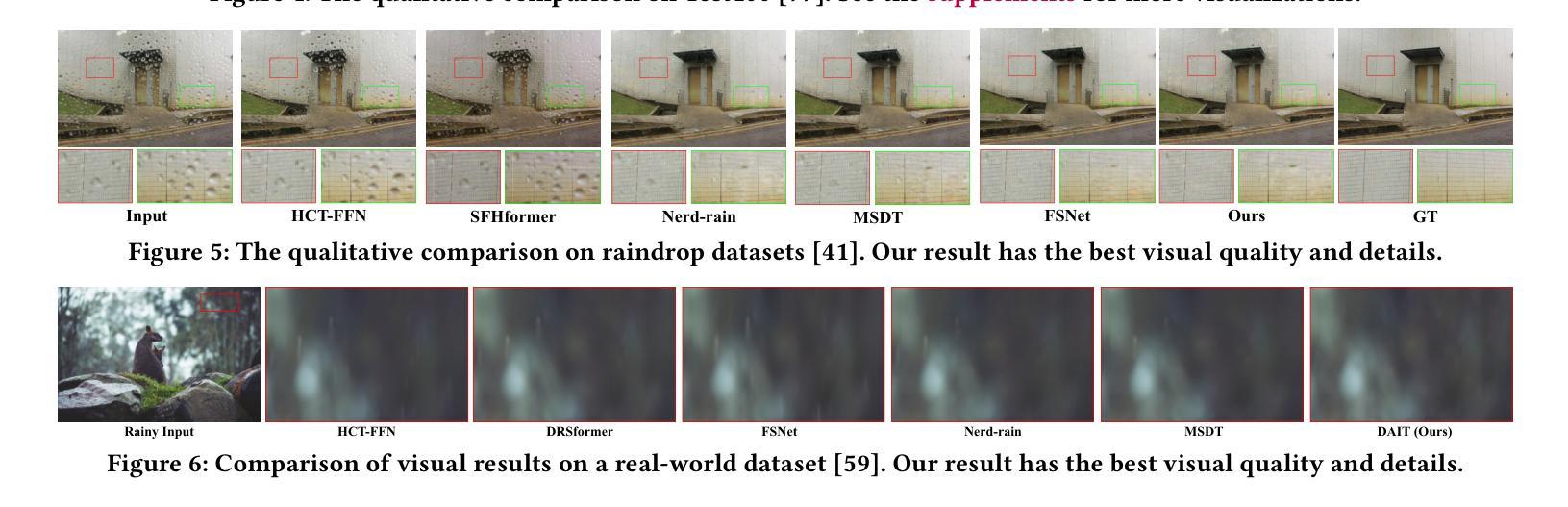
Cross Paradigm Representation and Alignment Transformer for Image Deraining
Authors:Shun Zou, Yi Zou, Juncheng Li, Guangwei Gao, Guojun Qi
Transformer-based networks have achieved strong performance in low-level vision tasks like image deraining by utilizing spatial or channel-wise self-attention. However, irregular rain patterns and complex geometric overlaps challenge single-paradigm architectures, necessitating a unified framework to integrate complementary global-local and spatial-channel representations. To address this, we propose a novel Cross Paradigm Representation and Alignment Transformer (CPRAformer). Its core idea is the hierarchical representation and alignment, leveraging the strengths of both paradigms (spatial-channel and global-local) to aid image reconstruction. It bridges the gap within and between paradigms, aligning and coordinating them to enable deep interaction and fusion of features. Specifically, we use two types of self-attention in the Transformer blocks: sparse prompt channel self-attention (SPC-SA) and spatial pixel refinement self-attention (SPR-SA). SPC-SA enhances global channel dependencies through dynamic sparsity, while SPR-SA focuses on spatial rain distribution and fine-grained texture recovery. To address the feature misalignment and knowledge differences between them, we introduce the Adaptive Alignment Frequency Module (AAFM), which aligns and interacts with features in a two-stage progressive manner, enabling adaptive guidance and complementarity. This reduces the information gap within and between paradigms. Through this unified cross-paradigm dynamic interaction framework, we achieve the extraction of the most valuable interactive fusion information from the two paradigms. Extensive experiments demonstrate that our model achieves state-of-the-art performance on eight benchmark datasets and further validates CPRAformer’s robustness in other image restoration tasks and downstream applications.
基于Transformer的网络通过利用空间或通道级的自注意力在低级别视觉任务(如图像去雨)中取得了强大的性能。然而,不规则的雨型和复杂的几何重叠对单一范式架构提出了挑战,需要一种统一的框架来整合互补的全局-局部和空间-通道表示。为了解决这一问题,我们提出了一种新的跨范式表示和对齐Transformer(CPRAformer)。其核心思想是分层表示和对齐,利用两种范式(空间通道和全局局部)的优势来辅助图像重建。它弥合了范式内部和之间的鸿沟,对齐并协调它们,以实现特征的深度交互和融合。具体来说,我们在Transformer块中使用了两种类型的自注意力:稀疏提示通道自注意力(SPC-SA)和空间像素细化自注意力(SPR-SA)。SPC-SA通过动态稀疏性增强全局通道依赖性,而SPR-SA专注于空间雨分布和细粒度纹理恢复。为了解决特征不对齐和他们之间知识差异的问题,我们引入了自适应对齐频率模块(AAFM),以两阶段渐进的方式与特征对齐和交互,实现自适应指导和互补性。这减少了范式内部和之间的信息鸿沟。通过这个统一的跨范式动态交互框架,我们从两个范式中提取了最有价值的交互式融合信息。大量实验表明,我们的模型在八个基准数据集上达到了最先进的性能,并进一步验证了CPRAformer在其他图像恢复任务和下游应用中的稳健性。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF code: https://github.com/zs1314/CPRAformer
Summary
本文提出一种新颖的跨范式表示与对齐Transformer(CPRAformer),用于解决图像去雨等低级别视觉任务中的挑战。CPRAformer融合了全局-局部和空间-通道两种互补表示,通过层次表示与对齐技术,实现了跨范式动态交互。使用两种自注意力机制,提高了特征提取和融合的效果。实验证明,CPRAformer在八个基准数据集上取得了最佳性能,并在其他图像恢复任务和下游应用中验证了其稳健性。
Key Takeaways
- Transformer网络在图像去雨等低级别视觉任务中表现出强性能,但面临不规则雨型和复杂几何重叠的挑战。
- 单一范式架构无法应对这些挑战,需要整合全局-局部和空间-通道表示的统一框架。
- CPRAformer提出层次表示与对齐技术,结合两种范式的优点,提高图像重建效果。
- CPRAformer使用两种自注意力机制:稀疏提示通道自注意力(SPC-SA)和空间像素细化自注意力(SPR-SA),分别增强通道依赖性和空间雨分布的恢复。
- 引入自适应对齐频率模块(AAFM),实现特征对齐和交互,缩小范式内的信息差距。
- CPRAformer在八个基准数据集上取得最佳性能,证明了其跨范式的有效性。
点此查看论文截图


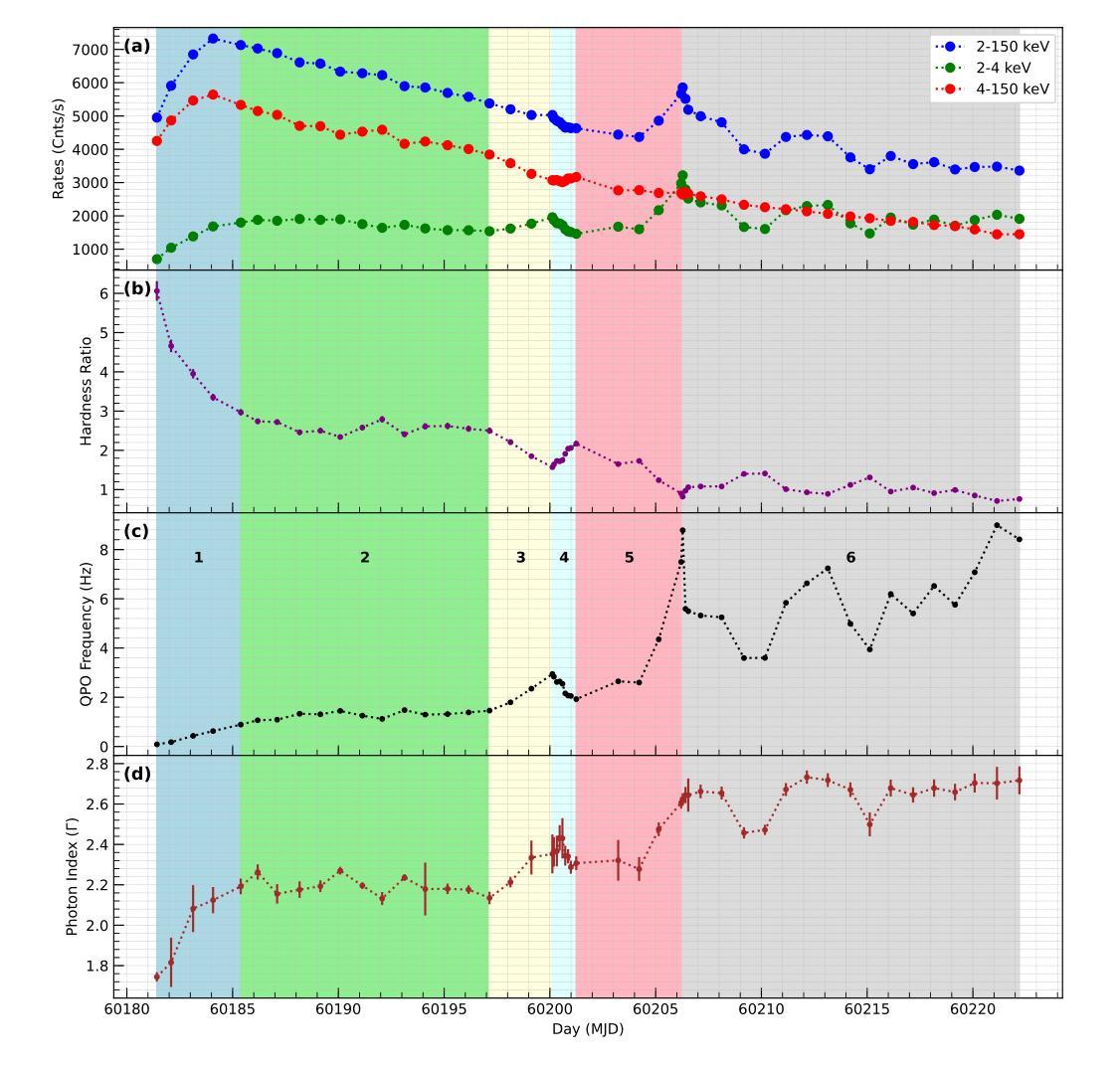
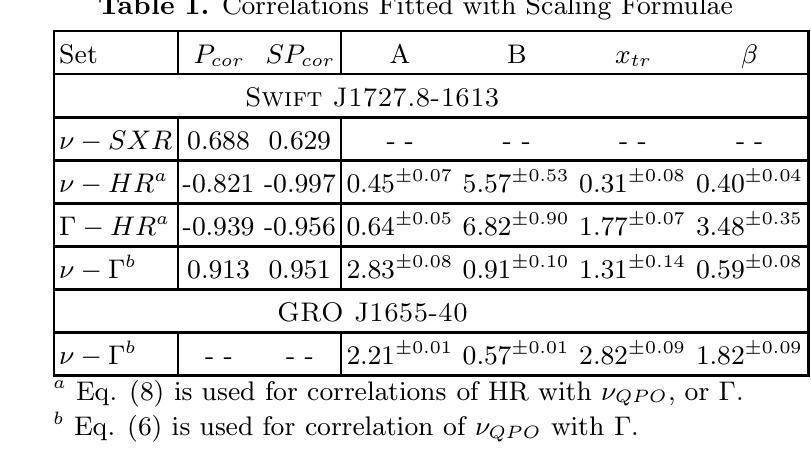
Evolution of QPO during Rising Phase of Discovery Outburst of Swift J1727.8-1613: Estimation of Mass from Spectro-Temporal Study
Authors:Dipak Debnath, Hsiang-Kuang Chang, Sujoy Kumar Nath, Lev Titarchuk
The rising phase of the 2023-24 outburst of the recently discovered bright transient black hole candidate Swift J1727.8-1613 was monitored by \textit{Insight}-HXMT. We study the evolution of hard ($4$-$150$ keV) and soft ($2$-$4$ keV) band photon count rates, the hardness ratio (HR), and QPO frequencies using daily observations from the HXMT/LE, ME, and HE instruments between August 25 and October 5, 2023. The QPO frequency is found to be strongly correlated with the soft-band X-ray count rates, and spectral photon indices. In contrast, a strong anti-correlation is observed between HR and QPO frequency, as well as between HR and photon index. Based on the evolution of the QPO frequency, the rising phase of the outburst is subdivided into six parts, with parts 1-5 fitted using the propagating oscillatory shock (POS) solution to understand the nature of the evolution from a physical perspective. The best-fitted POS model is obtained with a black hole mass of $13.34\pm0.02M_\odot$. An inward-propagating shock with weakening strength (except in part 4) is observed during the period of our study. The POS model-fitted mass of the source is further confirmed using the QPO frequency ($\nu$)-photon index ($\Gamma$) scaling method. From this method, the estimated probable mass of Swift J1727.8-1613 is obtained to be $13.54\pm1.87M_\odot$.
洞察号HXMT监测了最近发现的明亮瞬态黑洞候选体Swift J1727.8-1613在2023-24年爆发期的上升阶段。我们研究了硬度比为HR以及QPO频率的变化情况。这些研究基于HXMT/LE、ME和HE仪器在2023年8月25日至10月5日之间的每日观测数据,涉及硬波段(4-150千电子伏)和软波段(2-4千电子伏)光子计数率的演化。我们发现QPO频率与软波段X射线计数率和光谱光子指数之间存在强烈的相关性。相反,HR与QPO频率和光子指数之间则显示出强烈的反相关性。基于QPO频率的演化,爆发的上升阶段被分为六个部分,其中第1至第5部分使用传播振荡冲击(POS)解决方案进行拟合,以从物理角度了解演化的性质。使用POS模型的最佳拟合黑洞质量为13.34±0.02太阳质量。在我们的研究期间观察到向内传播的冲击波强度减弱(除第4部分外)。使用QPO频率(ν)-光子指数(Γ)标度方法进一步证实了源头的POS模型拟合质量。由此估计,Swift J1727.8-1613的可能质量为13.54±1.87太阳质量。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF 11 Pages, 4 Figures, 1 Table (In-communication to ApJ)
Summary
基于Insight-HXMT的观测,发现2023年至2024年短暂爆发中Sw J1727.8-1613硬和软光子计数率的演化特点及其变化特征。发现QPO频率与软波段X射线计数率和光子指数存在强相关性,而硬度比与QPO频率和光子指数之间存在强反相关关系。基于QPO频率演化,爆发上升阶段可分为六部分,其中部分阶段采用传播振荡冲击(POS)解决方案进行拟合分析。通过POS模型估计源质量约为$13.34\pm0.02M_\odot$,并通过QPO频率与光子指数关联得到验证。估算Sw J1727.8-1613的可能质量大约为$13.54\pm1.87M_\odot$。结果对于理解瞬态黑洞候选物的性质具有重要意义。
Key Takeaways
- Insight-HXMT监测了Swift J1727.8-1613黑洞候选体的爆发过程。
- 硬波段和软波段光子计数率随观测时间变化而变化。
- QPO频率与软波段X射线计数率和光子指数存在强相关性。
- HR与QPO频率和光子指数之间存在反相关关系。
- 基于QPO频率演化,爆发上升阶段可分为六个部分。
点此查看论文截图

Environmental Dependence of X-Ray Emission From The Least Massive Galaxies
Authors:Marko Mićić, Xinyu Dai, Nick Shumate, Khoa Nguyen Tran, Heechan Yuk
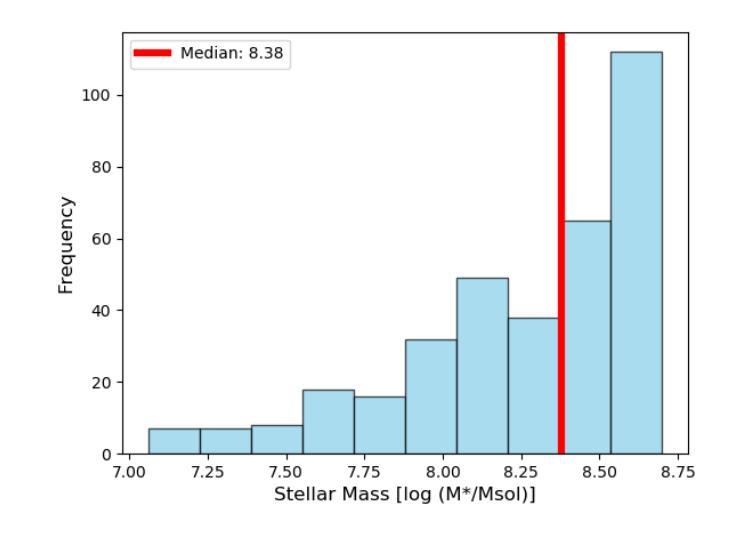
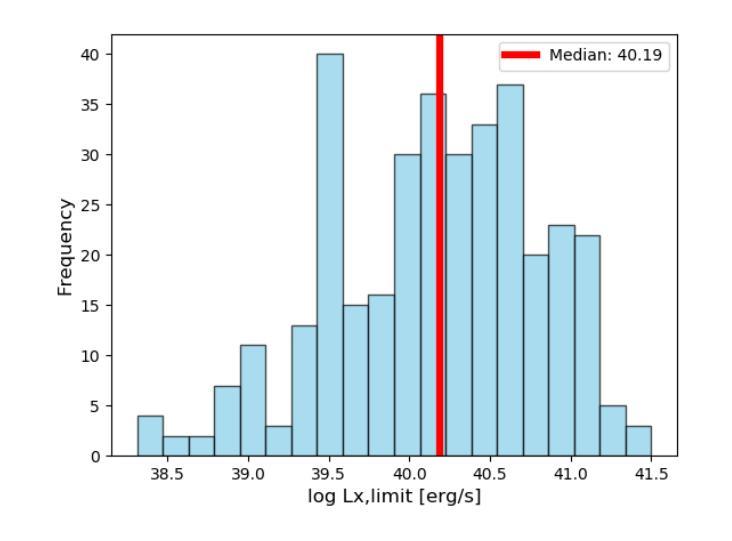
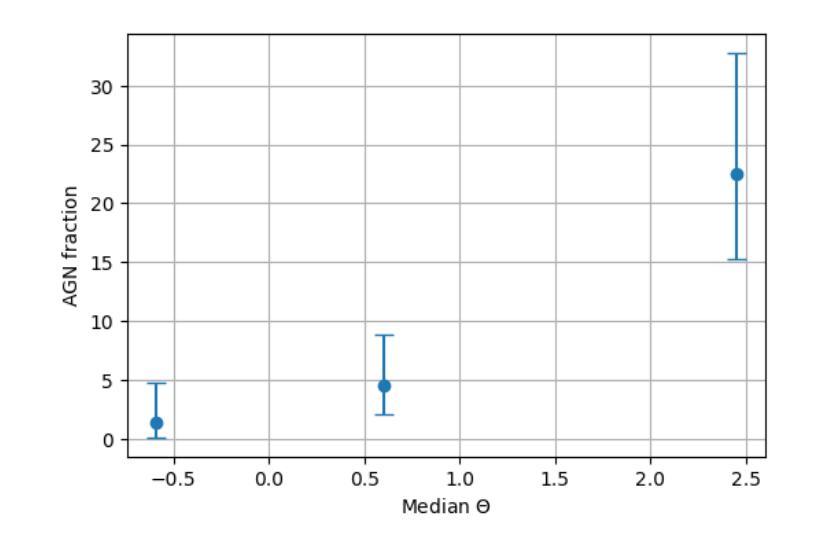
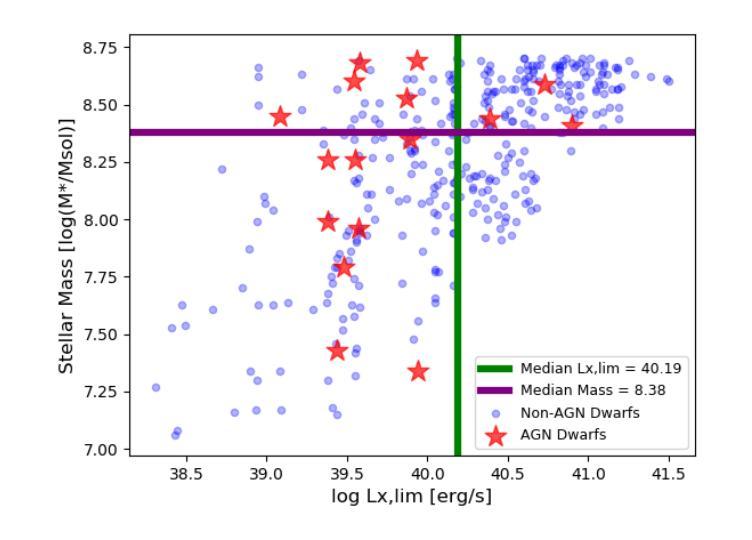
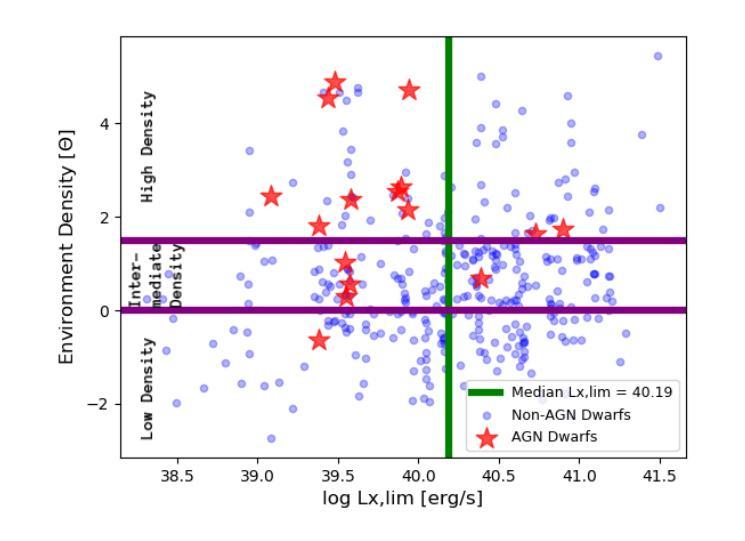
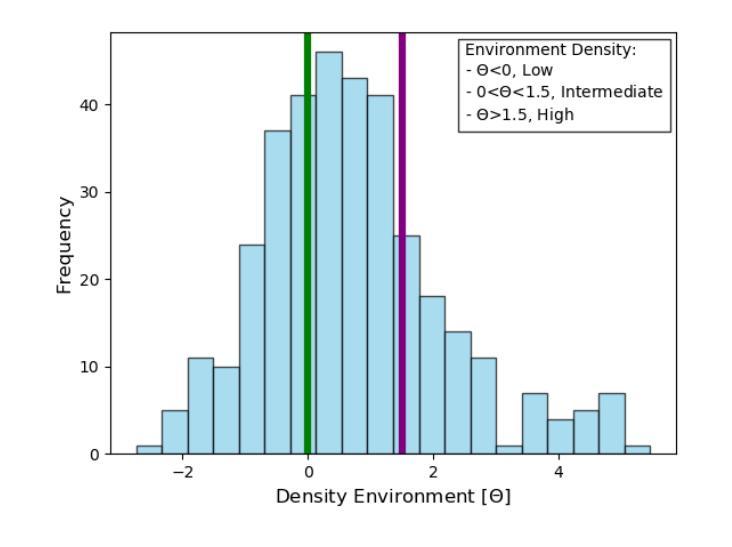
The low-mass end of low-mass galaxies is largely unexplored in AGN studies, but it is essential for extending our understanding of the black hole-galaxy coevolution. We surveyed the 3D-HST catalog and collected a sample of 546 dwarf galaxies with stellar masses log(M$*$/(M_\odot))$<$8.7, residing in the GOODS-South deep field. We then used the unprecedented depth of Chandra available in the GOODS-South field to search for AGN. We carefully investigated the factors that could play roles in the AGN detectability, such as Chandra’s point-spread function and the redshift- and off-axis-dependent detection limits. We identified 16 X-ray sources that are likely associated with AGN activity. Next, we evaluated the environment density of each galaxy by computing tidal indices. We uncovered a dramatic impact of the environment on AGN triggering as dwarfs from high-density environments showed an AGN fraction of 22.5%, while the median stellar mass of this subset of dwarfs is only log(M$*$/(M_\odot))=8.1. In contrast, the low-density environment dwarfs showed an AGN fraction of only 1.4%, in line with typically reported values from the literature. This highlights the fact that massive central black holes are ubiquitous even at the lowest mass scales and demonstrates the importance of the environment in triggering black hole accretion, as well as the necessity for deep X-ray data and proper evaluation of the X-ray data quality. Alternatively, even if the detected X-ray sources are related to stellar mass accretors rather than AGN, the environmental dependence persists, signaling the impact of the environment on galaxy evolution and star formation processes at the lowest mass scales. Additionally, we stacked the X-ray images of non-detected galaxies from high- and low-density environments, revealing similar trends.
在天文研究领域中,对于低质量星系的小质量端部分的研究尚处于未开发状态,但是为了深入了解黑洞与星系的共演化过程,这部分研究是至关重要的。我们调查了3D-HST目录,收集了一个样本,其中包括居住在GOODS-South深场的546个恒星质量为log(M*_*/M⊙)<8.7的矮星系。然后,我们利用GOODS-South区域中前所未有的深度观察来寻找活动星系核(Active Galactic Nucleus,简称AGNs)。我们仔细研究了可能影响活动星系核探测的因素,如钱德拉望远镜的点扩散函数以及红移和离轴距离相关的检测极限。我们确定了可能与活动星系核活动相关的16个X射线源。接下来,我们通过计算潮汐指数来评估每个星系的环境密度。我们发现环境对触发活动星系核的影响非常显著,因为来自高密度的矮星系表现出高达22.5%的活动星系核比例,而这一矮星系子集的中等恒星质量仅为log(M*_*/M⊙)=8.1。相比之下,低密度环境中的矮星系仅显示出1.4%的活动星系核比例,这与文献中通常报道的值相符。这强调了即使在最低质量尺度上,巨大的中心黑洞也是普遍存在的,并证明了环境在触发黑洞吸积中的重要性,以及深度X射线数据和正确评估X射线数据质量的重要性。即使检测到的X射线源与恒星质量吸积体有关而非活动星系核,环境的依赖性仍然存在,这预示着环境对最低质量尺度上的星系演化及恒星形成过程的影响。此外,我们还叠加了高密度和低密度环境中未检测到X射线的星系图像,显示出相似的趋势。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF Six pages, eight figures. Submitted to MNRAS. Comments are welcome
Summary
在深入研究低质量星系低质量端对活动星系核(AGN)的理解时,我们对GOODS-South深场的矮星系进行了调查。结合先进深度的Chandra数据搜索相关星系核,并对探测影响因素进行了研究。结果表明,环境密度显著影响星系核活动触发,高密度环境下的矮星系表现出更高的星系核活动率。这一发现强调了环境在触发黑洞吸积过程中的重要性,并凸显出深入X射线数据和正确评估其质量的重要性。无论X射线源是否与恒星质量吸积有关,环境对最低质量尺度上的星系演化和恒星形成过程的影响都是显著的。
Key Takeaways
- 低质量星系的低质量端对于理解黑洞与星系的协同演化至关重要。
- 利用3D-HST目录收集了GOODS-South深场的546个矮星系样本。
- 通过深入的Chandra数据寻找相关星系核活动。
- 探测因素包括Chandra的点扩散函数和与红移及离轴距离相关的检测限制。
- 高密度环境下的矮星系表现出更高的星系核活动率(22.5%),而低密度的环境则表现出较低的活动率(仅1.4%)。
- 环境在触发黑洞吸积过程中的作用显著。
点此查看论文截图

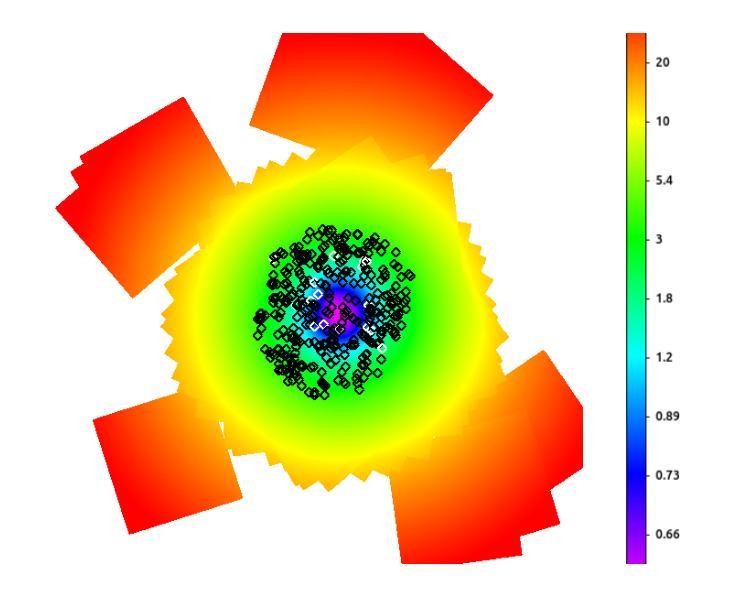
Multiobjective optimization for scattering mitigation and scattering screen reconstruction in VLBI observations of the Galactic Center
Authors:Alejandro Mus, Teresa Toscano, Hendrik Müller, Guang-Yao Zhao, Andrei Lobanov, Ciriaco Goddi
Imaging reconstruction of interferometric data is a hard ill-posed inverse problem. Its difficulty is increased when observing the Galactic Center, which is obscured by a scattering screen. This is because the scattering breaks the one-to-one correspondence between images and visibilities. Solving the scattering problem is one of the biggest challenges in radio imaging of the Galactic Center. In this work we present a novel strategy to mitigate its effect and constrain the screen itself using multiobjective optimization. We exploit the potential of evolutionary algorithms to describe the optimization landscape to recover the intrinsic source structure and the scattering screen affecting the data. We successfully recover both the screen and the source in a wide range of simulated cases, including the speed of a moving screen at 230 GHz. Particularly, we can recover a ring structure in scattered data at 86 GHz. Our analysis demonstrates the huge potential that recent advancements in imaging and optimization algorithms offer to recover image structures, even in weakly constrained and degenerated, possibly multi-modal settings. The successful reconstruction of the scattering screen opens the window to event horizon scale works on the Galactic Center at 86G Hz up to 116 GHz, and the study of the scattering screen itself.
成像重建干涉数据是一个难以解决的逆向问题。当观测银河中心时,难度会增加,因为银河中心被一个散射屏遮蔽。这是因为散射破坏了图像和可见度之间的一一对应关系。解决散射问题是银河中心射电成像面临的最大挑战之一。在这项工作中,我们提出了一种新的策略来缓解其影响,并使用多目标优化来约束屏幕本身。我们利用进化算法描述优化景观的潜力,以恢复内在源结构和影响数据的散射屏。我们在广泛的模拟案例中成功地恢复了屏幕和源,包括移动屏幕的速度在230 GHz时的情况。尤其值得一提的是,我们可以在散射数据中恢复环形结构,频率为86 GHz。我们的分析表明,成像和优化算法的最新进展在恢复图像结构方面具有巨大的潜力,即使在弱约束和退化、可能是多模式设置的情况下也是如此。成功重建散射屏为在86 GHz至116 GHz上对银河中心的事件视界规模进行研究打开了窗口,以及研究散射屏本身。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF To appear in A&A
Summary
本文提出一种新型策略,利用多目标优化解决干涉数据成像的逆问题,特别是在观测银河系中心时遇到的散射屏问题。通过进化算法描述优化景观,恢复影响数据的固有源结构和散射屏。在模拟案例中成功恢复了屏幕和源,包括移动屏幕的速度。对散射数据的环形结构的恢复显示了在图像和优化算法方面的最新进展在恢复图像结构方面的巨大潜力,即使在最弱的约束和退化的多模态设置中也是如此。成功重建散射屏为在86G至116千兆赫频率上对银河系中心的事件视界规模工作打开了窗口,并对散射屏本身进行了研究。
Key Takeaways
- 干涉数据成像是一个困难的逆问题,特别是在观测银河系中心时。
- 散射屏的存在打破了图像与可见度之间的一一对应关系,增加了问题的难度。
- 本文提出了一种使用多目标优化策略来解决散射问题的新方法。
- 进化算法被用来描述优化景观,以恢复固有源结构和影响数据的散射屏。
- 在模拟案例中成功恢复了屏幕和源,包括移动屏幕的速度。
- 能够恢复散射数据中的环形结构,显示出图像和优化算法最新进展的巨大潜力。
点此查看论文截图

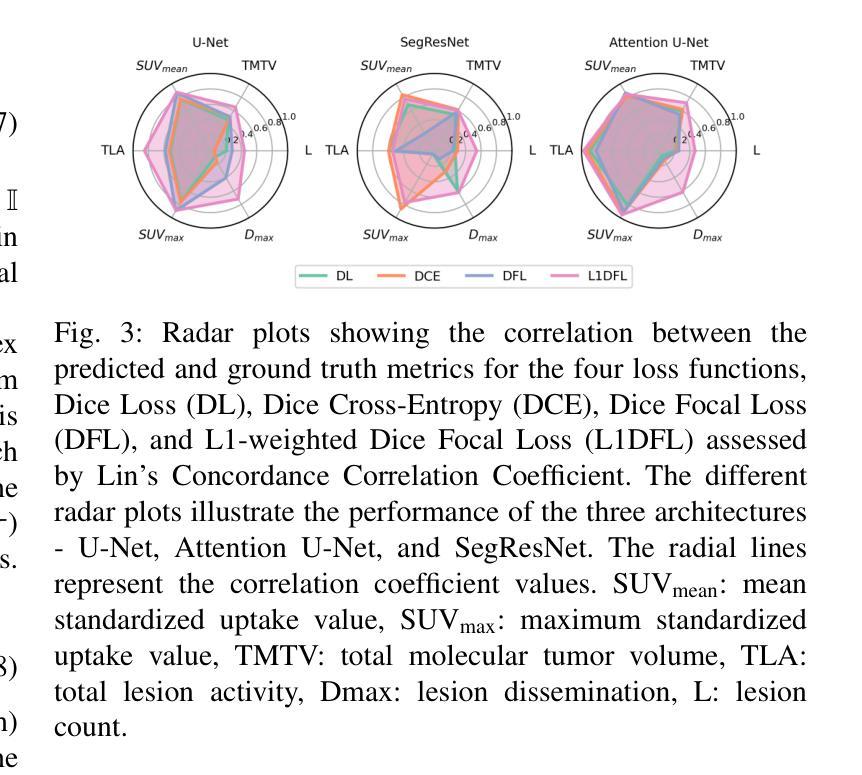
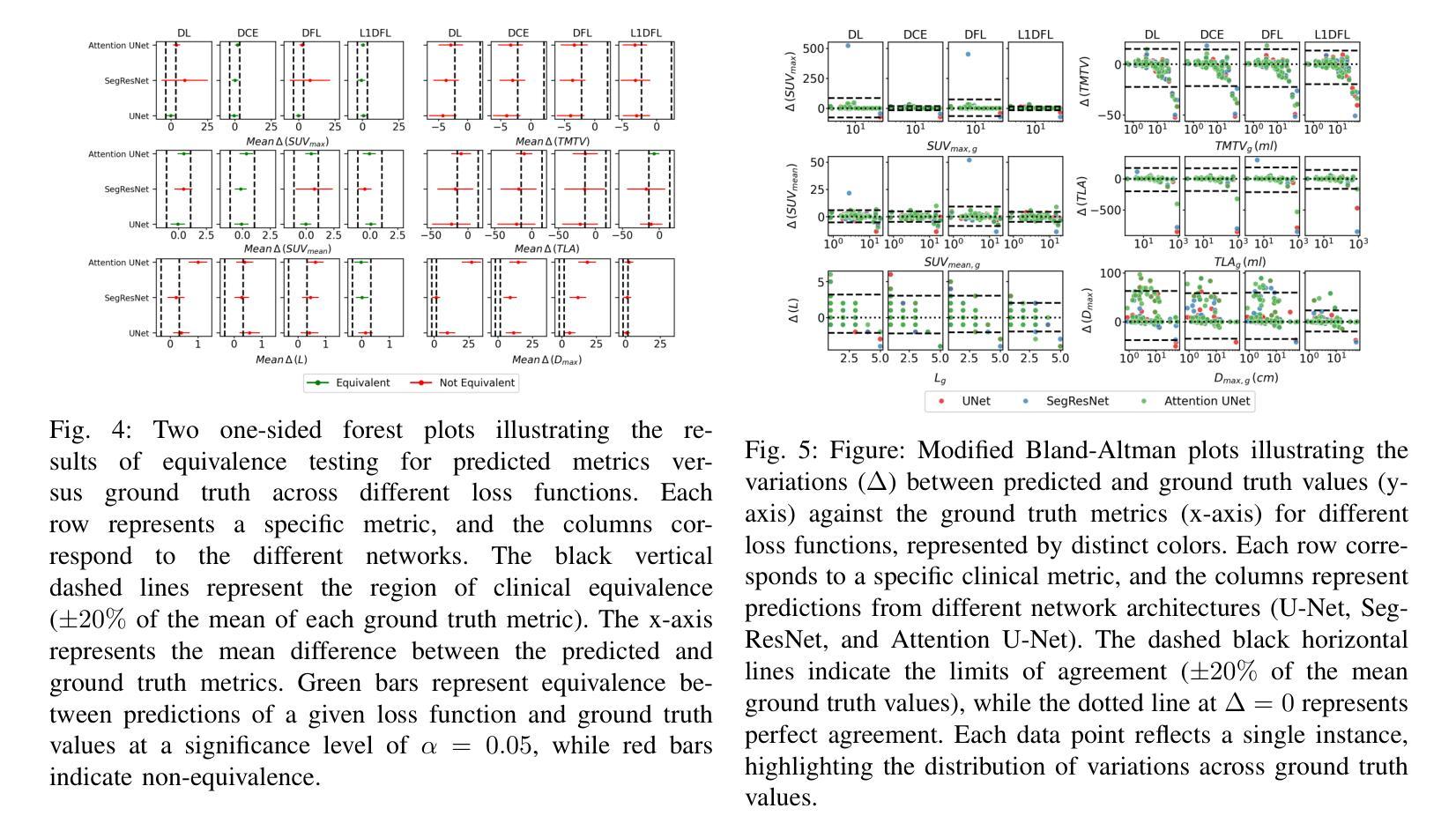
Comprehensive Evaluation of Quantitative Measurements from Automated Deep Segmentations of PSMA PET/CT Images
Authors:Obed Korshie Dzikunu, Amirhossein Toosi, Shadab Ahamed, Sara Harsini, Francois Benard, Xiaoxiao Li, Arman Rahmim
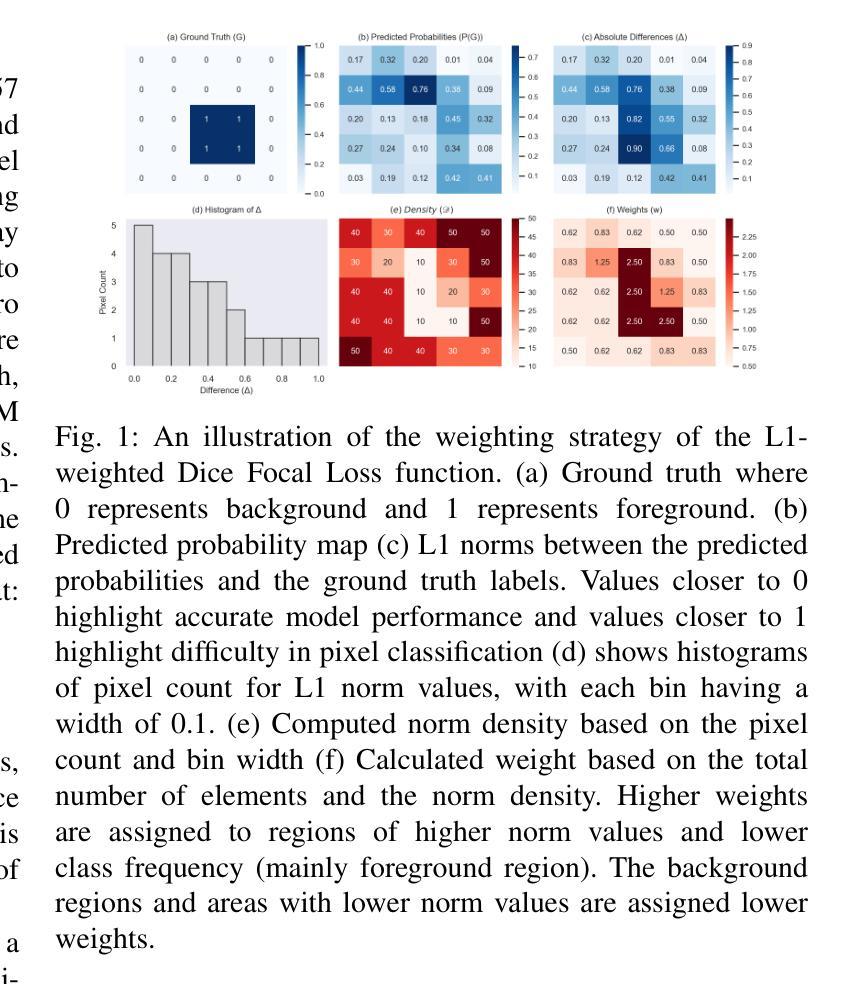
This study performs a comprehensive evaluation of quantitative measurements as extracted from automated deep-learning-based segmentation methods, beyond traditional Dice Similarity Coefficient assessments, focusing on six quantitative metrics, namely SUVmax, SUVmean, total lesion activity (TLA), tumor volume (TMTV), lesion count, and lesion spread. We analyzed 380 prostate-specific membrane antigen (PSMA) targeted [18F]DCFPyL PET/CT scans of patients with biochemical recurrence of prostate cancer, training deep neural networks, U-Net, Attention U-Net and SegResNet with four loss functions: Dice Loss, Dice Cross Entropy, Dice Focal Loss, and our proposed L1 weighted Dice Focal Loss (L1DFL). Evaluations indicated that Attention U-Net paired with L1DFL achieved the strongest correlation with the ground truth (concordance correlation = 0.90-0.99 for SUVmax and TLA), whereas models employing the Dice Loss and the other two compound losses, particularly with SegResNet, underperformed. Equivalence testing (TOST, alpha = 0.05, Delta = 20%) confirmed high performance for SUV metrics, lesion count and TLA, with L1DFL yielding the best performance. By contrast, tumor volume and lesion spread exhibited greater variability. Bland-Altman, Coverage Probability, and Total Deviation Index analyses further highlighted that our proposed L1DFL minimizes variability in quantification of the ground truth clinical measures. The code is publicly available at: https://github.com/ObedDzik/pca\_segment.git.
本研究对基于深度学习的自动化分割方法所提取的定量测量值进行了全面评估,这些评估超越了传统的Dice相似系数评估,主要关注六个定量指标,即SUVmax、SUVmean、总病灶活性(TLA)、肿瘤体积(TMTV)、病灶数量和病灶扩散。我们分析了380例前列腺特异性膜抗原(PSMA)靶向[18F]DCFPyL PET/CT扫描的生化复发前列腺癌患者,训练深度神经网络,包括U-Net、Attention U-Net和SegResNet,采用四种损失函数:Dice Loss、Dice Cross Entropy、Dice Focal Loss以及我们提出的L1加权Dice Focal Loss(L1DFL)。评估结果表明,Attention U-Net与L1DFL的结合与真实值之间的相关性最强(SUVmax和TLA的符合度相关性为0.90-0.99),而采用Dice Loss和其他两种复合损失的模型,特别是与SegResNet结合的模型,表现较差。等效性检验(TOST,α=0.05,Δ=20%)证实了SUV指标、病灶计数和TLA的高性能表现,其中L1DFL表现最佳。相比之下,肿瘤体积和病灶扩散表现出更大的变化性。Bland-Altman分析、覆盖概率和总偏差指数分析进一步强调了我们提出的L1DFL在量化真实临床指标方面的变化性最小化。相关代码公开在:https://github.com/ObedDzik/pca_segment.git。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF 12 pages, 8 figures
摘要
本研究对基于深度学习的分割方法提取的定量测量进行了全面评估,这些测量包括SUVmax、SUVmean、总病变活性(TLA)、肿瘤体积(TMTV)、病变计数和病变扩散等六个定量指标,并分析了380例前列腺特异性膜抗原(PSMA)靶向[18F]DCFPyL PET/CT扫描的前列腺癌生化复发患者数据。研究结果显示,使用Attention U-Net与L1DFL结合的模型与真实值的相关性最强(SUVmax和TLA的符合度相关性为0.90-0.99),而采用Dice Loss和其他复合损失的模型,特别是与SegResNet结合的模型表现较差。等价测试表明SUV指标、病变计数和TLA性能较高,其中L1DFL表现最佳。相比之下,肿瘤体积和病变扩散的变异性较大。Bland-Altman分析、覆盖概率和总偏差指数分析进一步表明,所提出的L1DFL能最小化对真实临床指标的量化差异。相关代码已公开于:https://github.com/ObedDzik/pca_segment.git。
关键见解
- 研究对基于深度学习的分割方法进行了全面的定量测量评估,涉及SUVmax、SUVmean等六个指标。
- Attention U-Net与L1DFL结合模型在SUVmax和TLA指标上与真实值的符合度相关性最高。
- L1DFL在SUV指标、病变计数和TLA的等价测试中表现最佳。
- 肿瘤体积和病变扩散的量化结果表现出较大的变异性。
- 公开的代码有助于其他研究者利用此研究的模型和数据进行进一步的分析和研究。
- 提出的L1DFL能最小化真实临床指标量化的差异,得到了Bland-Altman分析等的支持。
点此查看论文截图


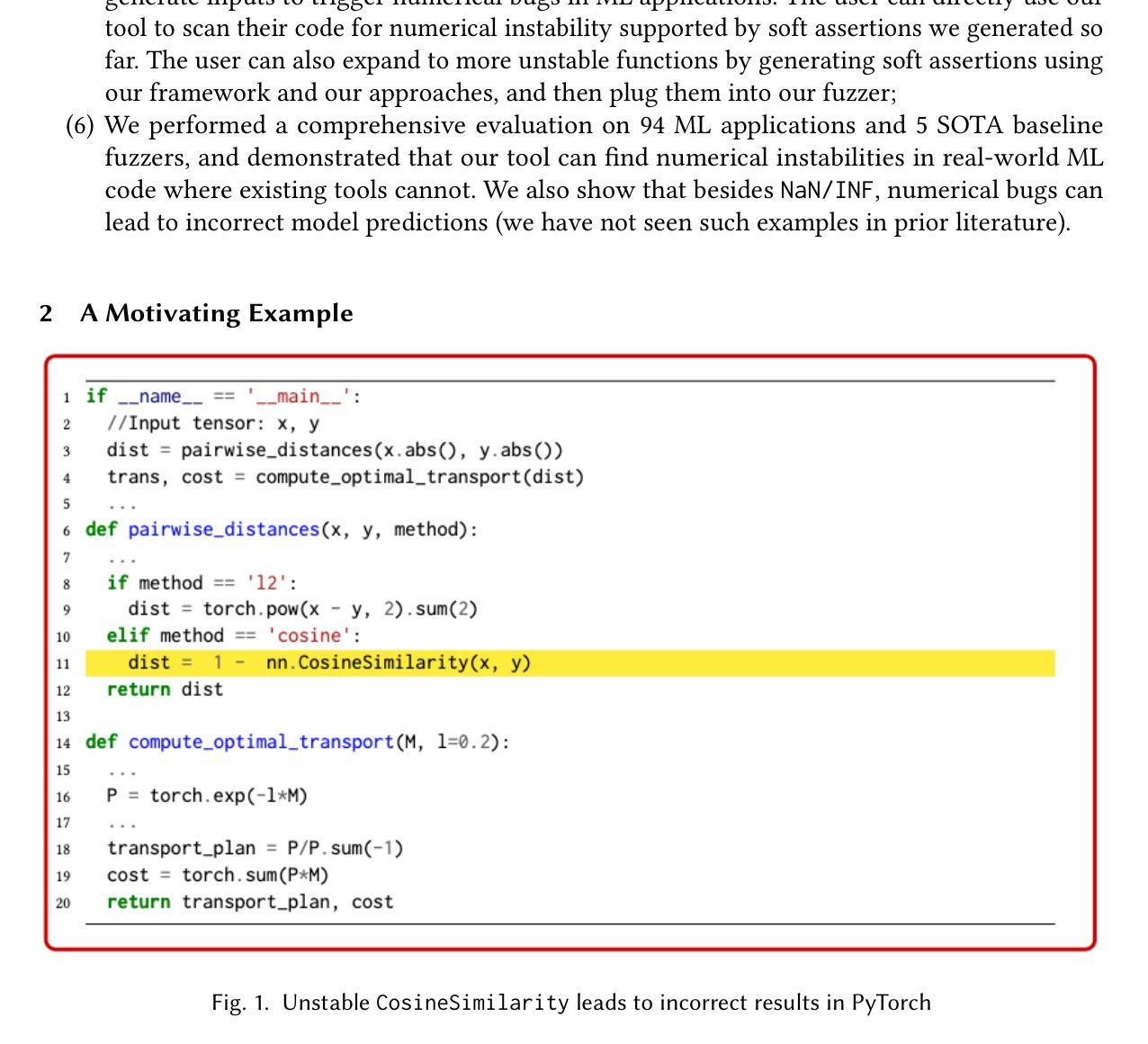
Automatically Detecting Numerical Instability in Machine Learning Applications via Soft Assertions
Authors:Shaila Sharmin, Anwar Hossain Zahid, Subhankar Bhattacharjee, Chiamaka Igwilo, Miryung Kim, Wei Le
Machine learning (ML) applications have become an integral part of our lives. ML applications extensively use floating-point computation and involve very large/small numbers; thus, maintaining the numerical stability of such complex computations remains an important challenge. Numerical bugs can lead to system crashes, incorrect output, and wasted computing resources. In this paper, we introduce a novel idea, namely soft assertions (SA), to encode safety/error conditions for the places where numerical instability can occur. A soft assertion is an ML model automatically trained using the dataset obtained during unit testing of unstable functions. Given the values at the unstable function in an ML application, a soft assertion reports how to change these values in order to trigger the instability. We then use the output of soft assertions as signals to effectively mutate inputs to trigger numerical instability in ML applications. In the evaluation, we used the GRIST benchmark, a total of 79 programs, as well as 15 real-world ML applications from GitHub. We compared our tool with 5 state-of-the-art (SOTA) fuzzers. We found all the GRIST bugs and outperformed the baselines. We found 13 numerical bugs in real-world code, one of which had already been confirmed by the GitHub developers. While the baselines mostly found the bugs that report NaN and INF, our tool \tool found numerical bugs with incorrect output. We showed one case where the Tumor Detection Model, trained on Brain MRI images, should have predicted “tumor”, but instead, it incorrectly predicted “no tumor” due to the numerical bugs. Our replication package is located at https://figshare.com/s/6528d21ccd28bea94c32.
机器学习(ML)应用已成为我们生活中不可或缺的一部分。机器学习应用广泛地使用浮点计算并涉及非常大的数字或非常小的数字;因此,保持此类复杂计算的数值稳定性仍然是一个重要的挑战。数值错误可能导致系统崩溃、输出错误和计算资源浪费。在本文中,我们介绍了一种新的概念,即软断言(SA),用于编码可能发生数值不稳定的地方的安全/错误条件。软断言是一种使用在不稳定函数单元测试期间获得的数据集自动训练的机器学习模型。给定机器学习应用中不稳定函数的值,软断言会报告如何更改这些值以触发不稳定。然后,我们使用软断言的输出作为信号来有效地更改输入,以触发机器学习应用中的数值不稳定。在评估中,我们使用了包含总共79个程序的GRIST基准测试以及来自GitHub的15个真实世界的机器学习应用。我们将工具与五种最新(SOTA)模糊测试工具进行了比较。我们发现所有GRIST错误并超越了基线工具。我们在真实世界代码中发现了13个数值错误,其中一个是GitHub开发人员已经确认的。虽然基线工具大多发现了报告NaN和INF的错误,但我们的工具发现了具有错误输出的数值错误。我们展示了一个案例,即基于脑部MRI图像训练的肿瘤检测模型应该预测为“有肿瘤”,但由于数值错误,却错误地预测为“无肿瘤”。我们的复制包位于https://figshare.com/s/6528d21ccd28bea94c32。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF 22 pages, 5 figures. Accepted at FSE 2025
摘要
本文引入了一种新的方法——软断言(SA),用于编码可能出现数值不稳定情况的安全/错误条件。软断言是一种自动训练的机器学习模型,它使用在不稳定函数单元测试期间获得的数据集。给定机器学习应用程序中不稳定函数的值,软断言报告如何改变这些值以触发不稳定。然后,我们使用软断言的输出作为信号,有效地改变输入,以触发机器学习应用程序中的数值不稳定。评估中,我们使用了GRIST基准测试中的79个程序以及GitHub上的15个真实世界机器学习应用程序。与五个最先进(SOTA)的模糊测试工具相比,我们的工具发现了所有GRIST中的错误,并且表现优于基线工具。在真实世界的代码中发现了13个数值错误,其中一个是GitHub开发者已经确认的错误。与其他工具主要发现报告NaN和INF的错误不同,我们的工具还能发现输出错误的数值错误。我们展示了这样一个案例:基于脑部MRI图像训练的肿瘤检测模型本应预测为“肿瘤”,但由于数值错误而错误地预测为“无肿瘤”。
关键要点
- 引入软断言(SA)概念,用于机器学习中的数值稳定性挑战。
- 软断言是一种自动训练的机器学习模型,用于识别和报告数值不稳定的情况。
- 通过软断言的输出作为信号来触发机器学习应用中的数值不稳定。
- 使用GRIST基准测试和真实世界机器学习应用进行评估。
- 与其他先进工具相比,该工具能够发现所有GRIST中的错误以及更多的真实世界代码中的数值错误。
- 该工具不仅能发现报告NaN和INF的错误,还能发现输出错误的数值错误。
点此查看论文截图

Embedding Radiomics into Vision Transformers for Multimodal Medical Image Classification
Authors:Zhenyu Yang, Haiming Zhu, Rihui Zhang, Haipeng Zhang, Jianliang Wang, Chunhao Wang, Minbin Chen, Fang-Fang Yin
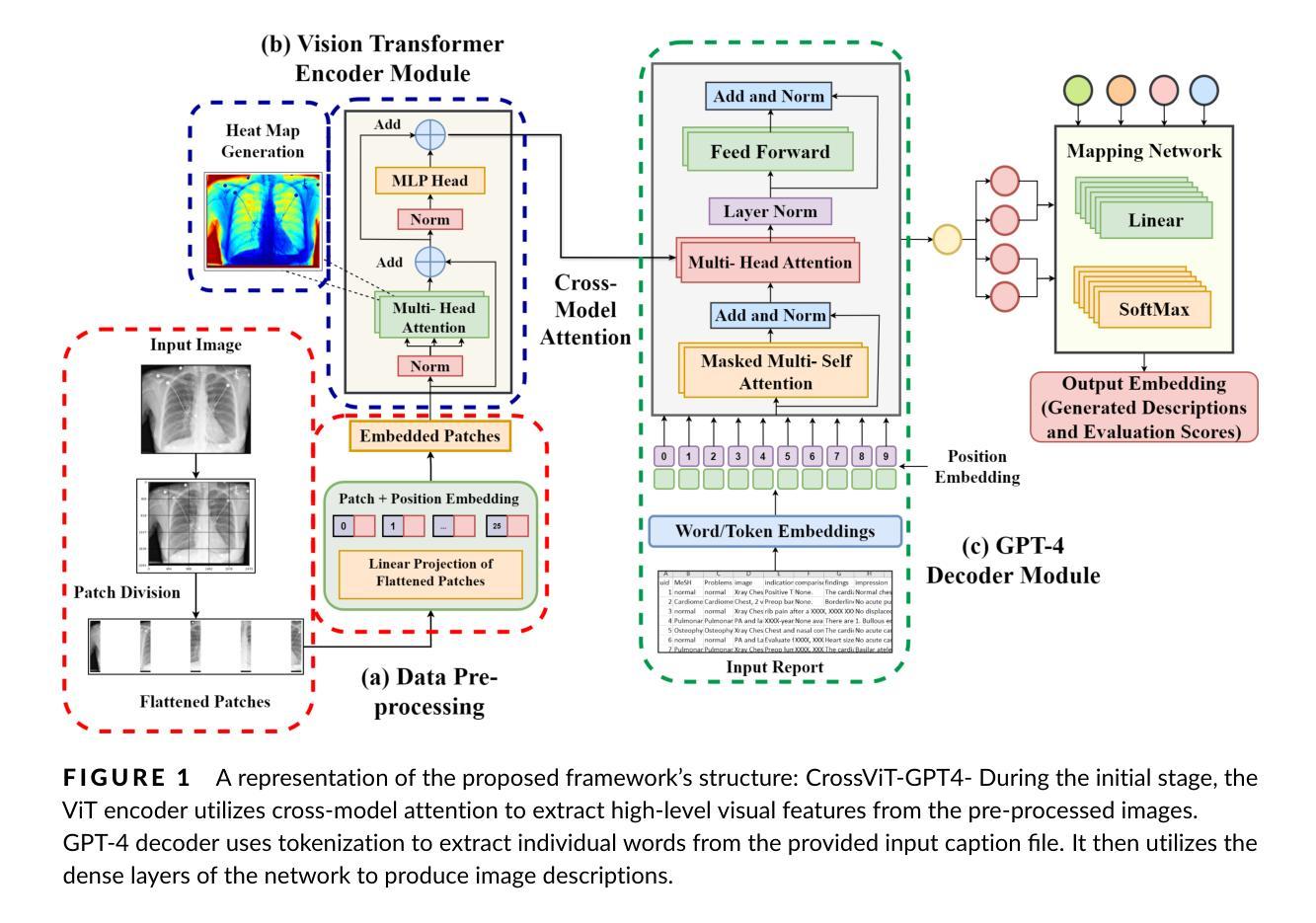
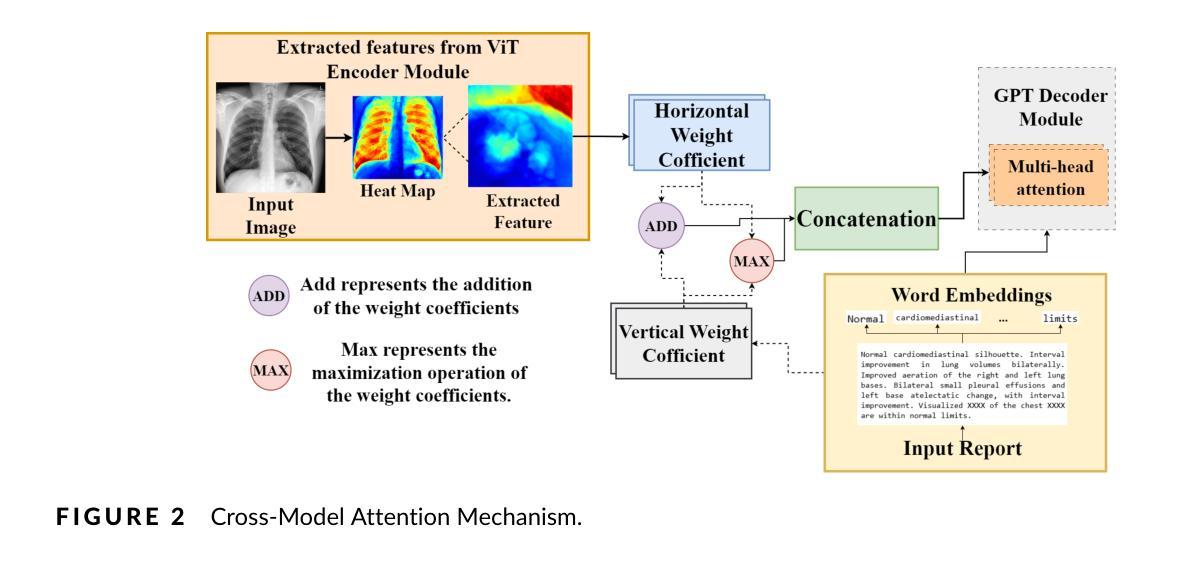
Background: Deep learning has significantly advanced medical image analysis, with Vision Transformers (ViTs) offering a powerful alternative to convolutional models by modeling long-range dependencies through self-attention. However, ViTs are inherently data-intensive and lack domain-specific inductive biases, limiting their applicability in medical imaging. In contrast, radiomics provides interpretable, handcrafted descriptors of tissue heterogeneity but suffers from limited scalability and integration into end-to-end learning frameworks. In this work, we propose the Radiomics-Embedded Vision Transformer (RE-ViT) that combines radiomic features with data-driven visual embeddings within a ViT backbone. Purpose: To develop a hybrid RE-ViT framework that integrates radiomics and patch-wise ViT embeddings through early fusion, enhancing robustness and performance in medical image classification. Methods: Following the standard ViT pipeline, images were divided into patches. For each patch, handcrafted radiomic features were extracted and fused with linearly projected pixel embeddings. The fused representations were normalized, positionally encoded, and passed to the ViT encoder. A learnable [CLS] token aggregated patch-level information for classification. We evaluated RE-ViT on three public datasets (including BUSI, ChestXray2017, and Retinal OCT) using accuracy, macro AUC, sensitivity, and specificity. RE-ViT was benchmarked against CNN-based (VGG-16, ResNet) and hybrid (TransMed) models. Results: RE-ViT achieved state-of-the-art results: on BUSI, AUC=0.950+/-0.011; on ChestXray2017, AUC=0.989+/-0.004; on Retinal OCT, AUC=0.986+/-0.001, which outperforms other comparison models. Conclusions: The RE-ViT framework effectively integrates radiomics with ViT architectures, demonstrating improved performance and generalizability across multimodal medical image classification tasks.
背景:深度学习在医学图像分析方面取得了重大进展,而Vision Transformers(ViTs)通过自注意力建模长距离依赖关系,为卷积模型提供了一种强大的替代方案。然而,ViTs本质上需要大量的数据,并且缺乏针对特定领域的归纳偏见,这在医学成像中限制了其适用性。相比之下,放射组学提供了组织异质性的可解释、手工描述器,但受限于可扩展性和集成到端到端学习框架的能力。在这项工作中,我们提出了Radiomics-Embedded Vision Transformer(RE-ViT),它将放射组学特征与数据驱动的视觉嵌入相结合,在一个ViT主干中。目的:开发一个混合RE-ViT框架,通过早期融合集成放射组学和补丁式ViT嵌入,提高在医学图像分类中的稳健性和性能。方法:遵循标准的ViT管道,将图像分成补丁。对于每个补丁,提取手工制作的放射组学特征,并与线性投影的像素嵌入相融合。融合后的表示经过归一化、位置编码,然后传递给ViT编码器。一个可学习的[CLS]标记聚合了补丁级别的信息用于分类。我们在三个公共数据集(包括BUSI、ChestXray2017和Retinal OCT)上评估了RE-ViT,使用了准确率、宏AUC、灵敏度和特异性。RE-ViT与基于CNN(VGG-16、ResNet)和混合(TransMed)模型进行了对比评估。结果:RE-ViT达到了最新的结果:在BUSI上,AUC=0.950±0.011;在ChestXray2017上,AUC=0.989±0.004;在视网膜OCT上,AUC=0.986±0.001,优于其他对比模型。结论:RE-ViT框架有效地将放射组学与ViT架构相结合,展示了在多模态医学图像分类任务中的改进性能和泛化能力。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF 27 pages, 3 figures
Summary
本文提出一种融合放射组学与Vision Transformer(ViT)的混合框架RE-ViT,通过早期融合放射组学特征和ViT数据驱动视觉嵌入,提高了在医学图像分类中的稳健性和性能。在多个公开数据集上的评估表明,RE-ViT取得了先进的结果,证明其在多模态医学图像分类任务中的性能和泛化能力。
Key Takeaways
- RE-ViT结合了放射组学特征和Vision Transformer(ViT)数据驱动视觉嵌入,提供了一个新的医学图像分析框架。
- 通过早期融合放射组学特征和ViT嵌入,RE-ViT增强了医学图像分类的稳健性和性能。
- 在多个公开数据集上的评估结果显示,RE-ViT达到了先进性能,证明了其有效性和泛化能力。
- RE-ViT框架通过融合放射组学特征与ViT架构,提高了医学图像分类的性能。
- 该方法实现了对多模态医学图像分类任务的优秀表现。
- RE-ViT相对于传统的CNN模型和混合模型表现出了优越性。
点此查看论文截图

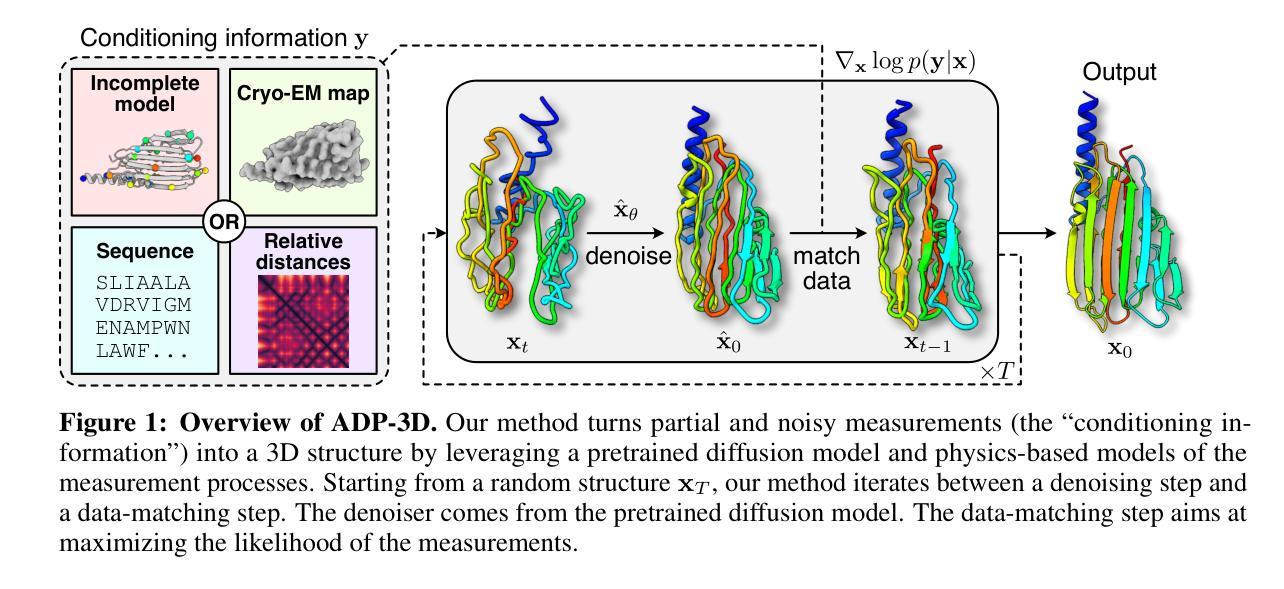
Solving Inverse Problems in Protein Space Using Diffusion-Based Priors
Authors:Axel Levy, Eric R. Chan, Sara Fridovich-Keil, Frédéric Poitevin, Ellen D. Zhong, Gordon Wetzstein
The interaction of a protein with its environment can be understood and controlled via its 3D structure. Experimental methods for protein structure determination, such as X-ray crystallography or cryogenic electron microscopy, shed light on biological processes but introduce challenging inverse problems. Learning-based approaches have emerged as accurate and efficient methods to solve these inverse problems for 3D structure determination, but are specialized for a predefined type of measurement. Here, we introduce a versatile framework to turn biophysical measurements, such as cryo-EM density maps, into 3D atomic models. Our method combines a physics-based forward model of the measurement process with a pretrained generative model providing a task-agnostic, data-driven prior. Our method outperforms posterior sampling baselines on linear and non-linear inverse problems. In particular, it is the first diffusion-based method for refining atomic models from cryo-EM maps and building atomic models from sparse distance matrices.
蛋白质与其环境的相互作用可以通过其三维结构来理解并控制。用于确定蛋白质结构的实验方法,如X射线晶体学或冷冻电子显微镜,为理解生物过程提供了启示,但同时也带来了具有挑战性的反问题。基于学习的方法已经作为准确高效的方法来解决这些反问题以进行三维结构测定,但这些方法仅限于特定类型的测量。在这里,我们介绍了一个通用框架,可将生物物理测量(如冷冻电子显微镜密度图)转化为三维原子模型。我们的方法结合了基于物理的测量过程前向模型与预训练的生成模型,该生成模型提供了任务无关的数据驱动先验。我们的方法在解决线性和非线性反问题上优于后采样基线。尤其是,它是第一个基于扩散的方法,用于从冷冻电子显微镜图谱中优化原子模型并从稀疏距离矩阵构建原子模型。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
蛋白质与其环境之间的相互作用可通过其三维结构进行理解和控制。实验方法如X射线晶体学或冷冻电子显微镜为生物过程提供了见解,但带来了逆向问题的挑战。基于学习的方法已准确高效地解决了这些逆向问题以实现三维结构测定,但仅限于特定类型的测量。本文介绍了一个通用框架,可将生物物理测量(如冷冻电子显微镜密度图)转化为三维原子模型。该方法结合了测量过程的物理前向模型与预训练的生成模型,提供了一项任务无关的数据驱动先验。该方法在线性和非线性逆向问题上优于后采样基线,尤其是第一个基于扩散的方法,可优化冷冻电子显微镜地图的原子模型并从稀疏距离矩阵构建原子模型。
Key Takeaways
- 蛋白质与其环境互动可通过其三维结构理解并控制。
- 实验方法如X射线晶体学和冷冻电子显微镜为生物过程研究提供了工具,但存在逆向问题的挑战。
- 基于学习的方法已解决逆向问题用于三维结构测定,但局限于特定类型测量。
- 介绍了一个通用框架来转化生物物理测量到三维原子模型。
- 该方法结合了物理前向模型和预训练的生成模型(任务无关的数据驱动先验)。
- 此方法在多种逆向问题上表现出优越性能。
点此查看论文截图

Effective Lymph Nodes Detection in CT Scans Using Location Debiased Query Selection and Contrastive Query Representation in Transformer
Authors:Yirui Wang, Qinji Yu, Ke Yan, Haoshen Li, Dazhou Guo, Li Zhang, Le Lu, Na Shen, Qifeng Wang, Xiaowei Ding, Xianghua Ye, Dakai Jin
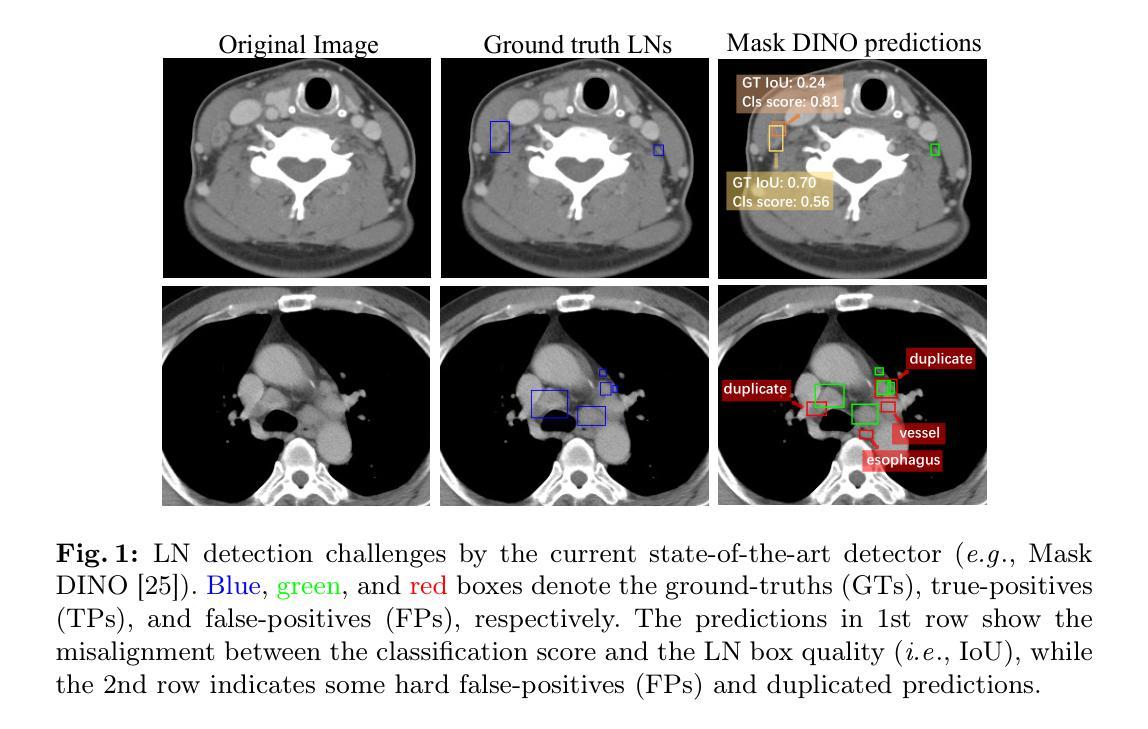
Lymph node (LN) assessment is a critical, indispensable yet very challenging task in the routine clinical workflow of radiology and oncology. Accurate LN analysis is essential for cancer diagnosis, staging, and treatment planning. Finding scatteredly distributed, low-contrast clinically relevant LNs in 3D CT is difficult even for experienced physicians under high inter-observer variations. Previous automatic LN detection works typically yield limited recall and high false positives (FPs) due to adjacent anatomies with similar image intensities, shapes, or textures (vessels, muscles, esophagus, etc). In this work, we propose a new LN DEtection TRansformer, named LN-DETR, to achieve more accurate performance. By enhancing the 2D backbone with a multi-scale 2.5D feature fusion to incorporate 3D context explicitly, more importantly, we make two main contributions to improve the representation quality of LN queries. 1) Considering that LN boundaries are often unclear, an IoU prediction head and a location debiased query selection are proposed to select LN queries of higher localization accuracy as the decoder query’s initialization. 2) To reduce FPs, query contrastive learning is employed to explicitly reinforce LN queries towards their best-matched ground-truth queries over unmatched query predictions. Trained and tested on 3D CT scans of 1067 patients (with 10,000+ labeled LNs) via combining seven LN datasets from different body parts (neck, chest, and abdomen) and pathologies/cancers, our method significantly improves the performance of previous leading methods by > 4-5% average recall at the same FP rates in both internal and external testing. We further evaluate on the universal lesion detection task using NIH DeepLesion benchmark, and our method achieves the top performance of 88.46% averaged recall across 0.5 to 4 FPs per image, compared with other leading reported results.
淋巴结(LN)评估是放射学和肿瘤学常规临床工作中不可或缺且极具挑战性的任务。准确的淋巴结分析对于癌症的诊断、分期和治疗计划至关重要。即使在经验丰富的医生之间也存在较高的观察者间变异,在3D计算机断层扫描(CT)中寻找分散、低对比度的临床相关淋巴结仍然具有挑战性。之前的自动淋巴结检测工作通常由于相邻结构具有相似的图像强度、形状或纹理(如血管、肌肉、食管等)而召回率有限,误报率高。在这项工作中,我们提出了一种新的淋巴结检测转换器,名为LN-DETR,以实现更准确的性能。我们通过增强2D主干网络,采用多尺度2.5D特征融合来显式地融入3D上下文,更重要的是,我们在提高淋巴结查询的表示质量方面做出了两个主要贡献。1)考虑到淋巴结边界通常不清晰,我们提出了一个IoU预测头和位置偏差查询选择,以选择具有较高定位精度的淋巴结查询作为解码器查询的初始化。2)为了减少误报,采用查询对比学习,明确加强淋巴结查询与其最佳匹配的真实查询,超过未匹配的查询预测。我们的方法在1067名患者的3D CT扫描图像上进行训练和测试(包含10,000多个标记淋巴结),结合了来自不同部位(颈部、胸部和腹部)和病理/癌症的七个淋巴结数据集,在内部和外部测试中,我们的方法在同一误报率下将之前领先方法平均召回率提高了4-5%。我们进一步在NIH DeepLesion基准测试上进行通用病变检测任务评估,与其他报告的最佳结果相比,我们的方法在平均每张图像0.5到4个假阳性的情况下达到了88.46%的召回率。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF Accepted by ECCV24
Summary
本论文提出了一种名为LN-DETR的新方法,用于更精确地检测淋巴节点(LNs)。此方法采用多尺度混合特征的融合策略,通过融入3D上下文信息以增强二维主干特征的表达效果。为提高定位精度并降低误报率,论文提出了IoU预测头与位置偏差查询选择机制。此外,通过查询对比学习强化匹配度,减少了误报率。实验结果表明,该方法在多个淋巴结数据集上的性能显著优于现有方法。
Key Takeaways
- 淋巴节点检测在临床诊断和治疗计划中至关重要且极具挑战性。
- LN-DETR方法通过融合多尺度特征和多维度上下文信息提高了检测准确性。
- 采用IoU预测头与位置偏差查询选择机制提高了定位精度。
- 查询对比学习技术用于强化匹配度并降低误报率。
- 在多个淋巴结数据集上的实验结果显示,该方法显著提高了检测性能。
点此查看论文截图