⚠️ 以下所有内容总结都来自于 大语言模型的能力,如有错误,仅供参考,谨慎使用
🔴 请注意:千万不要用于严肃的学术场景,只能用于论文阅读前的初筛!
💗 如果您觉得我们的项目对您有帮助 ChatPaperFree ,还请您给我们一些鼓励!⭐️ HuggingFace免费体验
2025-04-25 更新
Effective Lymph Nodes Detection in CT Scans Using Location Debiased Query Selection and Contrastive Query Representation in Transformer
Authors:Yirui Wang, Qinji Yu, Ke Yan, Haoshen Li, Dazhou Guo, Li Zhang, Le Lu, Na Shen, Qifeng Wang, Xiaowei Ding, Xianghua Ye, Dakai Jin
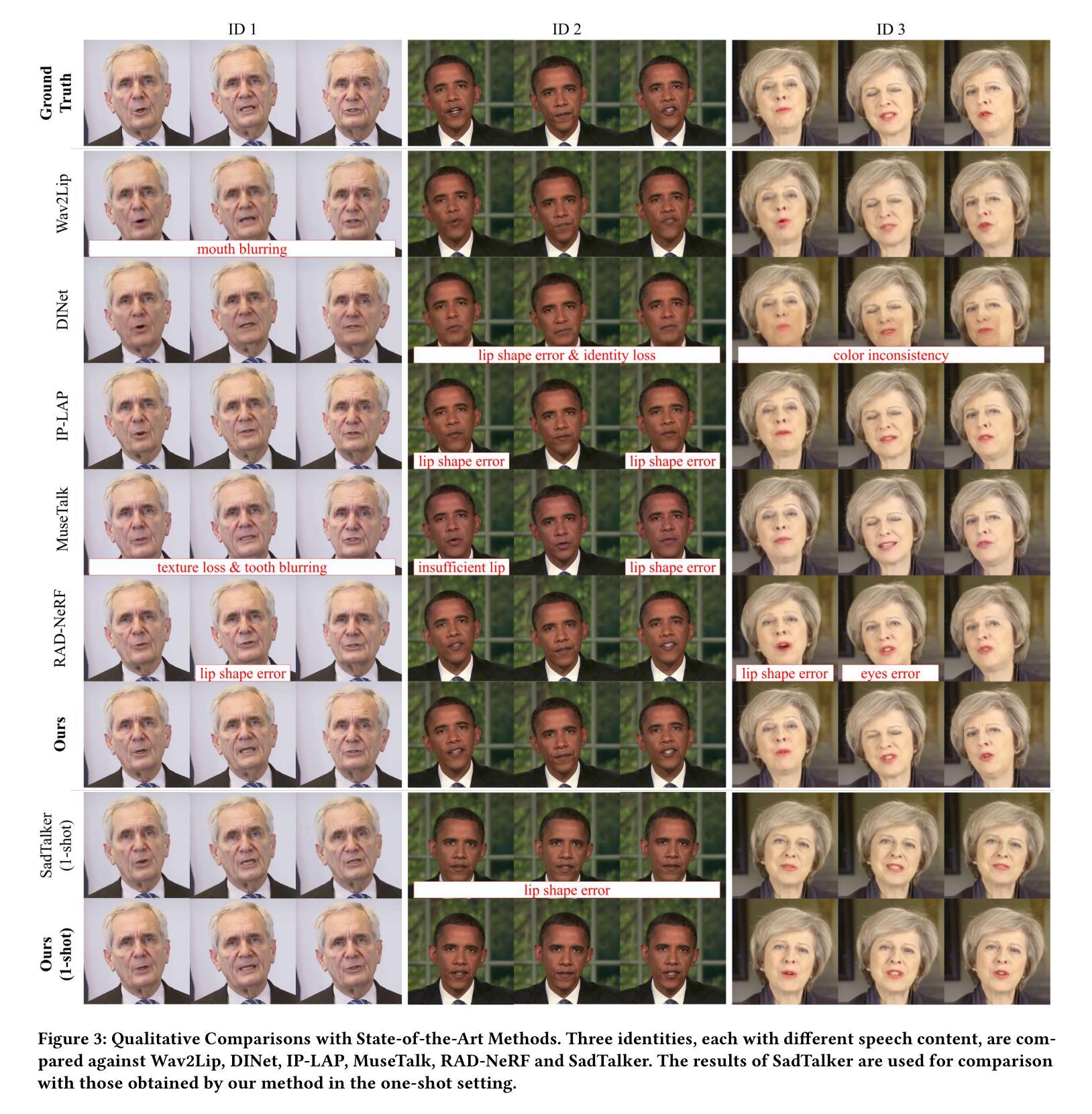
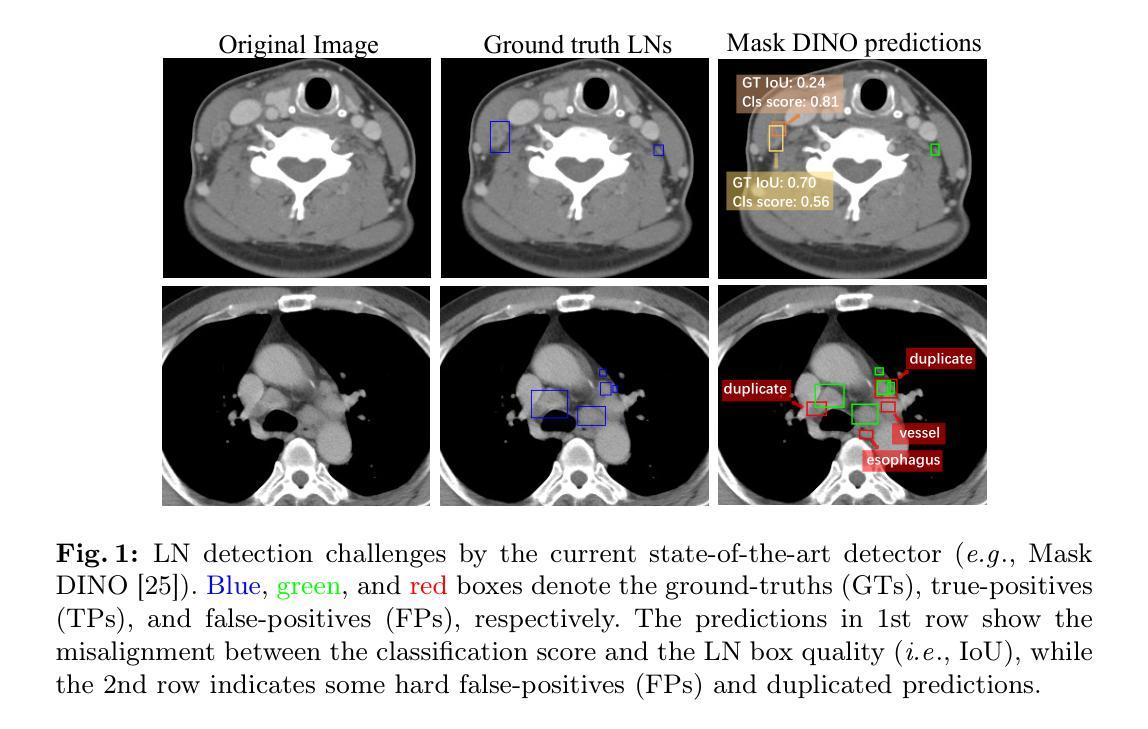
Lymph node (LN) assessment is a critical, indispensable yet very challenging task in the routine clinical workflow of radiology and oncology. Accurate LN analysis is essential for cancer diagnosis, staging, and treatment planning. Finding scatteredly distributed, low-contrast clinically relevant LNs in 3D CT is difficult even for experienced physicians under high inter-observer variations. Previous automatic LN detection works typically yield limited recall and high false positives (FPs) due to adjacent anatomies with similar image intensities, shapes, or textures (vessels, muscles, esophagus, etc). In this work, we propose a new LN DEtection TRansformer, named LN-DETR, to achieve more accurate performance. By enhancing the 2D backbone with a multi-scale 2.5D feature fusion to incorporate 3D context explicitly, more importantly, we make two main contributions to improve the representation quality of LN queries. 1) Considering that LN boundaries are often unclear, an IoU prediction head and a location debiased query selection are proposed to select LN queries of higher localization accuracy as the decoder query’s initialization. 2) To reduce FPs, query contrastive learning is employed to explicitly reinforce LN queries towards their best-matched ground-truth queries over unmatched query predictions. Trained and tested on 3D CT scans of 1067 patients (with 10,000+ labeled LNs) via combining seven LN datasets from different body parts (neck, chest, and abdomen) and pathologies/cancers, our method significantly improves the performance of previous leading methods by > 4-5% average recall at the same FP rates in both internal and external testing. We further evaluate on the universal lesion detection task using NIH DeepLesion benchmark, and our method achieves the top performance of 88.46% averaged recall across 0.5 to 4 FPs per image, compared with other leading reported results.
淋巴结(LN)评估是放射学和肿瘤学常规临床工作中不可或缺且极具挑战性的任务。准确的淋巴结分析对于癌症的诊断、分期和治疗计划至关重要。即使在经验丰富的医生之间也存在较高的观察者间变异,寻找3D CT中分散分布、低对比度的临床相关淋巴结仍然具有挑战性。之前的自动淋巴结检测工作通常由于相邻的具有相似图像强度、形状或纹理(血管、肌肉、食道等)的解剖学结构而产生有限的召回率和较高的误报率。在这项工作中,我们提出了一种新的淋巴结检测转换器,名为LN-DETR,以实现更准确的性能。我们通过增强二维骨架与多尺度2.5D特征融合来明确地融入三维上下文,更重要的是,我们在提高淋巴结查询的表示质量方面做出了两个主要贡献。1)考虑到淋巴结边界通常不清晰,提出了IoU预测头和位置偏差查询选择,以选择具有更高定位精度的淋巴结查询作为解码器查询的初始化。2)为了减少误报,采用查询对比学习,明确加强淋巴结查询与其最佳匹配的真实查询,超过未匹配的查询预测。在1067名患者的3D CT扫描(超过10,000个标记淋巴结)上进行训练和测试,结合了七个来自不同部位(颈部、胸部和腹部)和病理/癌症的淋巴结数据集,我们的方法在内部和外部测试中,在相同的误报率下,平均召回率提高了之前领先方法4-5%以上的召回率。我们进一步在NIH DeepLesion基准测试上评估了通用病变检测任务,与其他报告的最佳结果相比,我们的方法在每张图像0.5到4个误报的情况下,平均召回率达到了88.46%的顶尖性能。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF Accepted by ECCV24
Summary
本文提出了一种新的淋巴结检测器——LN-DETR,以提高淋巴结检测的准确性。通过增强二维骨干网并融入多尺度2.5D特征融合以明确体现三维上下文信息,同时改进了淋巴结查询的表示质量。该研究在来自不同部位和病理的多个淋巴结数据集上进行训练和测试,显著提高了先前的领先水平,并在NIH DeepLesion基准的通用病变检测任务上取得了最佳性能。
Key Takeaways
- 淋巴结(LN)评估在临床诊断和治疗计划中非常重要且具有挑战性。
- 自动淋巴结检测在过去通常会出现召回率有限和误报率高的问题。
- 本文提出了LN-DETR,一个基于Transformer的新的淋巴结检测方法。
- 通过增强二维骨干网并融入多尺度2.5D特征融合,以提高淋巴结检测的准确性。
- 研究人员考虑了淋巴结边界模糊的问题,提出了IoU预测头和位置偏差查询选择来优化解码器查询的初始化。
- 为减少误报,引入了查询对比学习,以加强与最佳匹配真实查询的淋巴结查询。
点此查看论文截图

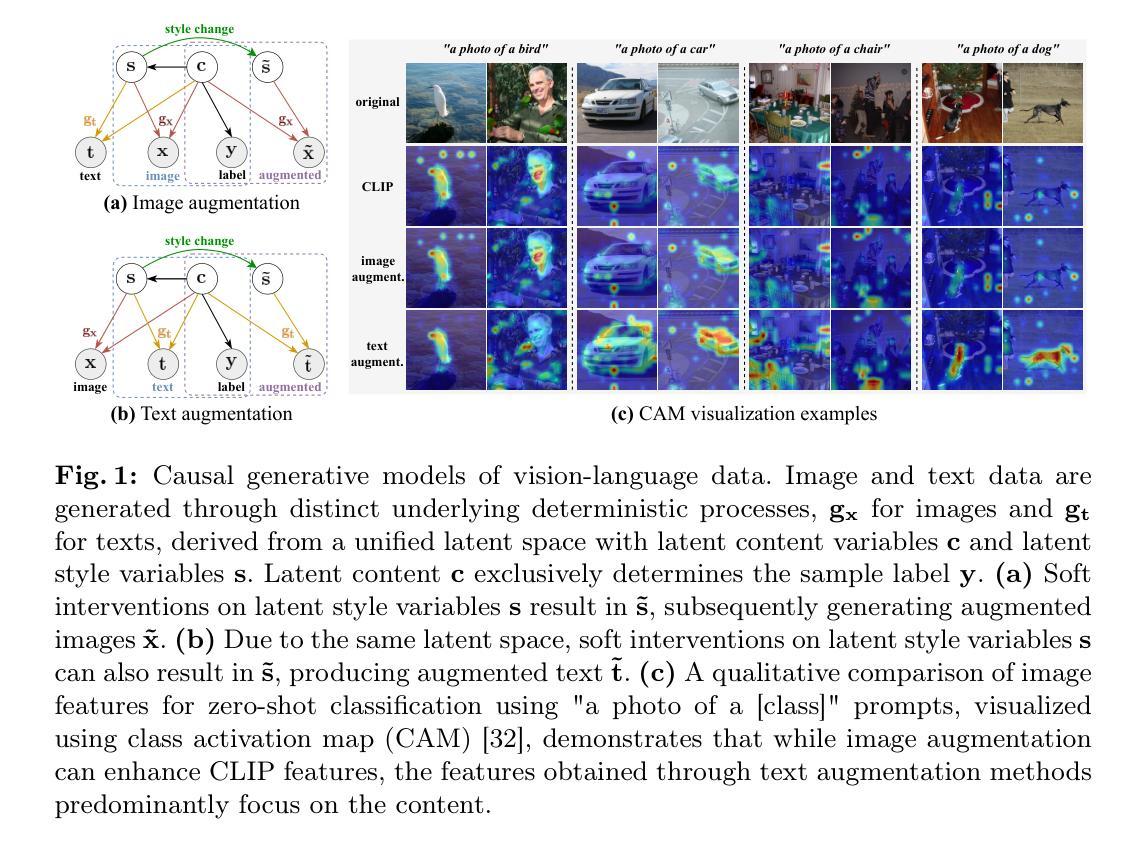
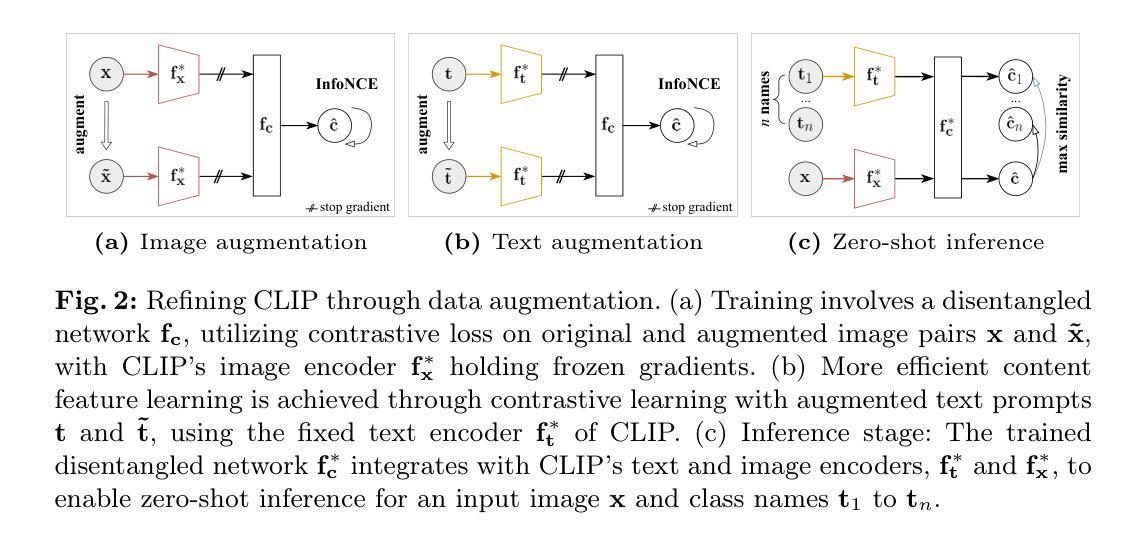
CLAP: Isolating Content from Style through Contrastive Learning with Augmented Prompts
Authors:Yichao Cai, Yuhang Liu, Zhen Zhang, Javen Qinfeng Shi
Contrastive vision-language models, such as CLIP, have garnered considerable attention for various downstream tasks, mainly due to the remarkable ability of the learned features for generalization. However, the features they learned often blend content and style information, which somewhat limits their generalization capabilities under distribution shifts. To address this limitation, we adopt a causal generative perspective for multimodal data and propose contrastive learning with data augmentation to disentangle content features from the original representations. To achieve this, we begin with exploring image augmentation techniques and develop a method to seamlessly integrate them into pre-trained CLIP-like models to extract pure content features. Taking a step further, recognizing the inherent semantic richness and logical structure of text data, we explore the use of text augmentation to isolate latent content from style features. This enables CLIP-like model’s encoders to concentrate on latent content information, refining the learned representations by pre-trained CLIP-like models. Our extensive experiments across diverse datasets demonstrate significant improvements in zero-shot and few-shot classification tasks, alongside enhanced robustness to various perturbations. These results underscore the effectiveness of our proposed methods in refining vision-language representations and advancing the state-of-the-art in multimodal learning.
对比视觉语言模型,如CLIP,已经引起了广泛的关注,并广泛应用于各种下游任务,这主要归功于其学习特征的泛化能力。然而,它们学习的特征往往会将内容和风格信息混合在一起,这在一定程度上限制了其在分布变化下的泛化能力。为了解决这一局限性,我们采用因果生成的角度看待多模态数据,并提出采用数据增强的对比学习来从原始表示中分离内容特征。为此,我们首先探索图像增强技术,并开发了一种方法,将其无缝集成到预训练的CLIP类模型中,以提取纯内容特征。更进一步地,我们认识到文本数据的内在语义丰富性和逻辑结构,探索使用文本增强来分离潜在内容与风格特征。这使得CLIP类模型的编码器能够专注于潜在内容信息,通过预训练的CLIP类模型优化学习表示。我们在多个数据集上进行的广泛实验表明,在零样本和少样本分类任务上取得了显著改进,同时对各种扰动具有更强的鲁棒性。这些结果凸显了我们提出的方法在优化视觉语言表示和推动多模态学习最新技术方面的有效性。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF Accepted as a conference paper at ECCV 2024
Summary
基于对比学习的跨模态数据研究,针对CLIP等模型的通用化能力受限问题,提出采用因果生成视角和多模态数据增强对比学习的方法,以分离内容特征并优化模型表现。通过图像和文本增强技术,将预训练的CLIP类模型与纯净内容特征提取相结合,显著提高了零样本和少样本分类任务的性能,并增强了模型的稳健性。
Key Takeaways
- 对比学习在跨模态数据研究中的应用受到关注。
- CLIP等模型的通用化能力受限于内容与风格的混合特征。
- 采用因果生成视角进行多模态数据建模以分离内容特征。
- 利用图像增强技术改善预训练CLIP模型的特征提取性能。
- 通过文本增强技术进一步分离潜在内容与风格特征。
- 方法在多种数据集上的实验表现出显著改进,特别是在零样本和少样本分类任务中。
点此查看论文截图