⚠️ 以下所有内容总结都来自于 大语言模型的能力,如有错误,仅供参考,谨慎使用
🔴 请注意:千万不要用于严肃的学术场景,只能用于论文阅读前的初筛!
💗 如果您觉得我们的项目对您有帮助 ChatPaperFree ,还请您给我们一些鼓励!⭐️ HuggingFace免费体验
2025-04-25 更新
GreenMind: A Next-Generation Vietnamese Large Language Model for Structured and Logical Reasoning
Authors:Luu Quy Tung, Hoang Quoc Viet, Vo Trong Thu
Chain-of-Thought (CoT) is a robust approach for tackling LLM tasks that require intermediate reasoning steps prior to generating a final answer. In this paper, we present GreenMind-Medium-14B-R1, the Vietnamese reasoning model inspired by the finetuning strategy based on Group Relative Policy Optimization. We also leverage a high-quality Vietnamese synthesized reasoning dataset and design two reward functions to tackle the main limitations of this technique: (i) language mixing, where we explicitly detect the presence of biased language characters during the process of sampling tokens, and (ii) we leverage Sentence Transformer-based models to ensure that the generated reasoning content maintains factual correctness and does not distort the final output. Experimental results on the Vietnamese dataset from the VLSP 2023 Challenge demonstrate that our model outperforms prior works and enhances linguistic consistency in its responses. Furthermore, we extend our evaluation to SeaExam-a multilingual multiple-choice dataset, showing the effectiveness of our reasoning method compared to few-shot prompting techniques.
链式思维(CoT)是一种强大的方法,用于解决大型语言模型(LLM)任务,这些任务在生成最终答案之前需要中间推理步骤。在本文中,我们介绍了GreenMind-Medium-14B-R1,这是一个基于越南语和基于群体相对策略优化微调策略的推理模型。我们还利用高质量的越南语合成推理数据集,并设计两种奖励函数来解决这项技术的两个主要局限性:(i)语言混合问题,即在采样标记过程中明确检测是否存在有偏见的语言字符;(ii)我们利用基于句子转换器的模型确保生成的推理内容保持事实正确性,并不歪曲最终输出。在VLSP 2023挑战赛提供的越南数据集上的实验结果表明,我们的模型优于先前的工作,并提高了响应的语言一致性。此外,我们将评估扩展到SeaExam多语言选择题数据集,以展示我们的推理方法与少样本提示技术相比的有效性。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
大模型在面对需要中间推理步骤的任务时面临挑战,如语言混合等问题。该研究提出了一个越南推理模型GreenMind-Medium-14B-R1,它结合了集团相对政策优化策略进行微调。同时利用高质量越南合成推理数据集和设计了两个奖励函数来解决这些问题。实验结果表明,该模型在越南数据集上表现优于先前的工作,增强了语言一致性,并在多语言选择题数据集SeaExam上的评估中也验证了其推理方法的有效性。
Key Takeaways
- GreenMind-Medium-14B-R1是一个用于解决大型语言模型(LLM)任务的越南推理模型。
- 该模型基于集团相对政策优化策略进行微调。
- 利用了高质量越南合成推理数据集进行训练。
- 设计了两个奖励函数来解决语言混合问题,确保生成的推理内容保持事实正确性并不扭曲最终输出。
- 在越南数据集VLSP 2023挑战上的实验结果表明,该模型表现优于先前的工作并增强了语言一致性。
- 该模型在多语言选择题数据集SeaExam上的评估验证了其推理方法的有效性。
点此查看论文截图



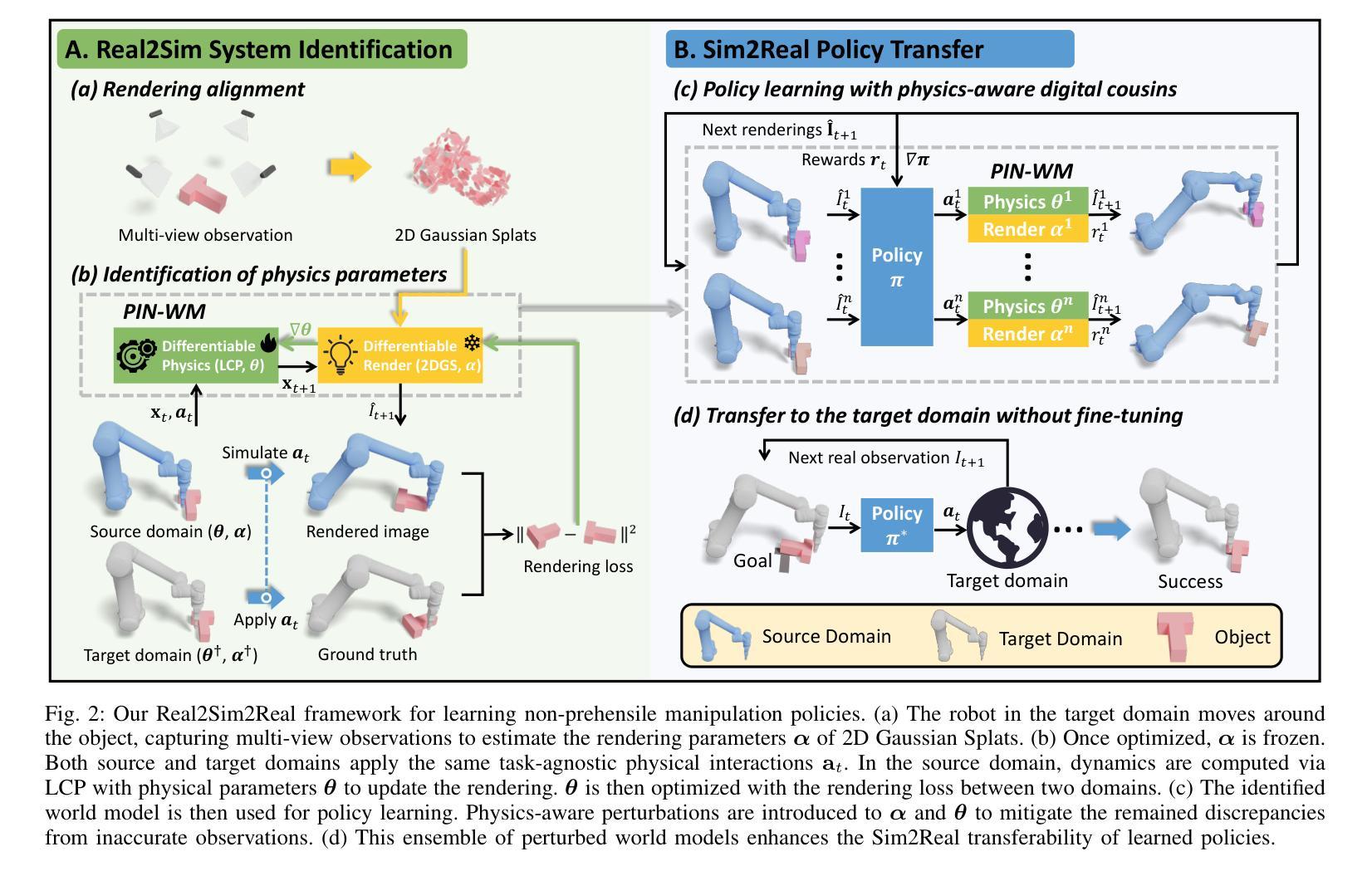
PIN-WM: Learning Physics-INformed World Models for Non-Prehensile Manipulation
Authors:Wenxuan Li, Hang Zhao, Zhiyuan Yu, Yu Du, Qin Zou, Ruizhen Hu, Kai Xu
While non-prehensile manipulation (e.g., controlled pushing/poking) constitutes a foundational robotic skill, its learning remains challenging due to the high sensitivity to complex physical interactions involving friction and restitution. To achieve robust policy learning and generalization, we opt to learn a world model of the 3D rigid body dynamics involved in non-prehensile manipulations and use it for model-based reinforcement learning. We propose PIN-WM, a Physics-INformed World Model that enables efficient end-to-end identification of a 3D rigid body dynamical system from visual observations. Adopting differentiable physics simulation, PIN-WM can be learned with only few-shot and task-agnostic physical interaction trajectories. Further, PIN-WM is learned with observational loss induced by Gaussian Splatting without needing state estimation. To bridge Sim2Real gaps, we turn the learned PIN-WM into a group of Digital Cousins via physics-aware randomizations which perturb physics and rendering parameters to generate diverse and meaningful variations of the PIN-WM. Extensive evaluations on both simulation and real-world tests demonstrate that PIN-WM, enhanced with physics-aware digital cousins, facilitates learning robust non-prehensile manipulation skills with Sim2Real transfer, surpassing the Real2Sim2Real state-of-the-arts.
非握持操作(例如,受控推动/戳刺)构成了一项基本的机器人技能,但其学习仍然具有挑战性,因为其对涉及摩擦和恢复力的复杂物理交互的高度敏感性。为了实现稳健的策略学习和泛化,我们选择学习涉及非握持操作中的3D刚体动力学的世界模型,并将其用于基于模型增强学习。我们提出PIN-WM,这是一个Physics-INformed世界模型,能够高效地从视觉观察中端到端地识别出用于非握持操作的3D刚体动力学系统。通过采用可微分物理模拟,PIN-WM仅通过少量和任务无关的物理交互轨迹就可以学习。此外,PIN-WM通过高斯平铺产生的观测损失进行学习,无需状态估计。为了弥仿真与现实之间的差距,我们通过物理感知随机化将学习到的PIN-WM转化为一组数字分身,通过扰动物理和渲染参数来生成PIN-WM的多样化和有意义的变体。在仿真和真实世界测试中的广泛评估表明,增强以物理感知的数字分身后,PIN-WM能够借助Sim2Real转换学习稳健的非握持操作技能,超越了最新的Real2Sim2Real技术水平。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
非握持式操作(如控制推动/戳刺)是机器人技术的基本技能之一,但其学习仍然面临挑战,因为它涉及到摩擦和恢复等复杂物理交互的高度敏感性。为了实现稳健的策略学习和泛化,我们学习了一个非握持操作所涉及的三维刚体动力学世界模型,并将其用于基于模型的强化学习。我们提出了PIN-WM,这是一种基于物理信息的世界模型,能够高效地从视觉观察中端到端地识别三维刚体动力学系统。通过采用可微分物理仿真,PIN-WM仅通过少量任务无关的实物交互轨迹即可学习。此外,PIN-WM通过高斯斑点(Gaussian Splatting)产生的观测损失进行学习,无需进行状态估计。为了缩短仿真与真实世界之间的差距,我们将学习到的PIN-WM转化为一系列物理感知随机化的数字同胞。在仿真和真实世界测试中的广泛评估表明,借助物理感知的数字同胞增强的PIN-WM,能学习到具有仿真到真实世界迁移能力的稳健的非握持式操作技能,超越了当前最先进的状态技术。
Key Takeaways
- 非握持式操作是机器人技术中的重要基础技能,但对复杂物理交互的敏感性使其学习具有挑战性。
- 提出了PIN-WM模型,一个基于物理信息的世界模型,用于高效识别三维刚体动力学系统。
- 通过采用可微分物理仿真和仅使用少量任务无关的实物交互轨迹,PIN-WM能够实现学习。
- PIN-WM通过高斯斑点产生的观测损失进行学习,无需进行状态估计。
- 为了缩短仿真与真实世界之间的差距,将PIN-WM转化为一系列物理感知随机化的数字同胞。
- 通过广泛评估证明,PIN-WM在仿真和真实世界测试中均表现出卓越性能。
点此查看论文截图

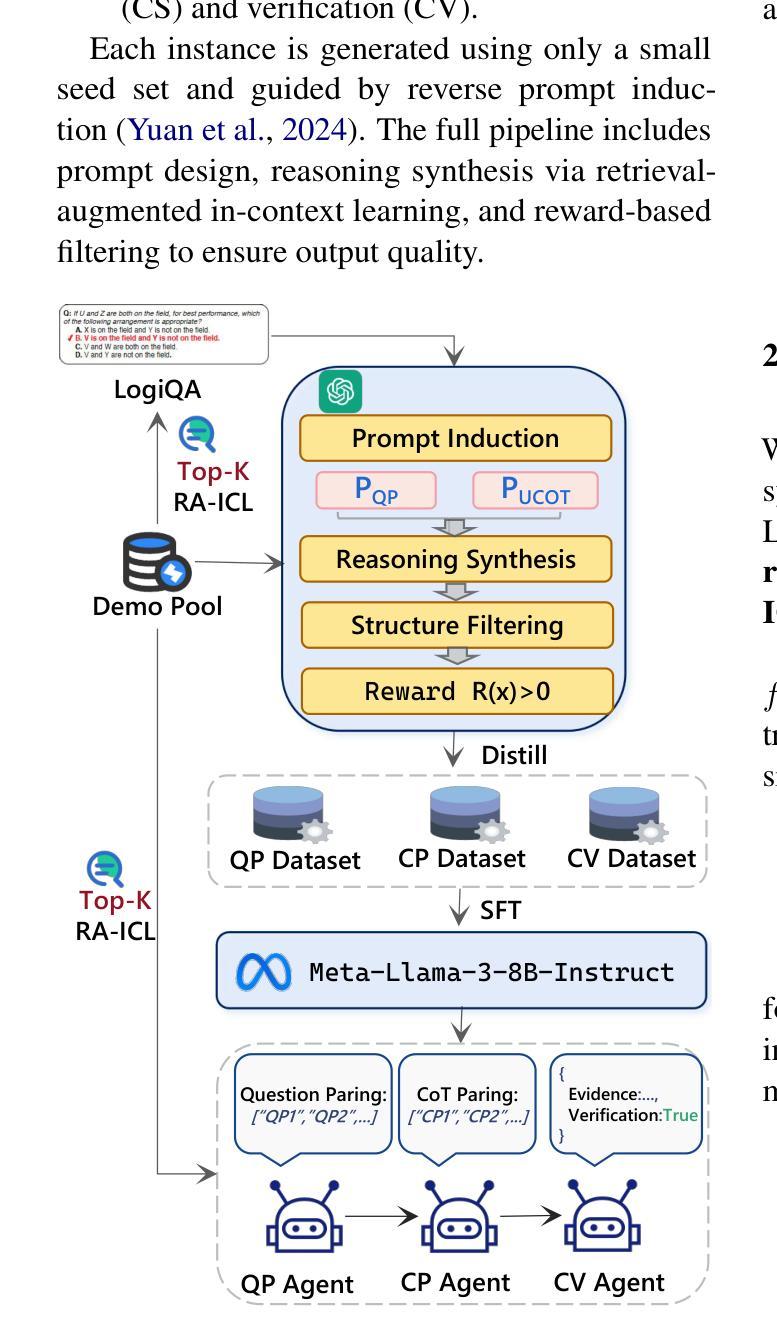
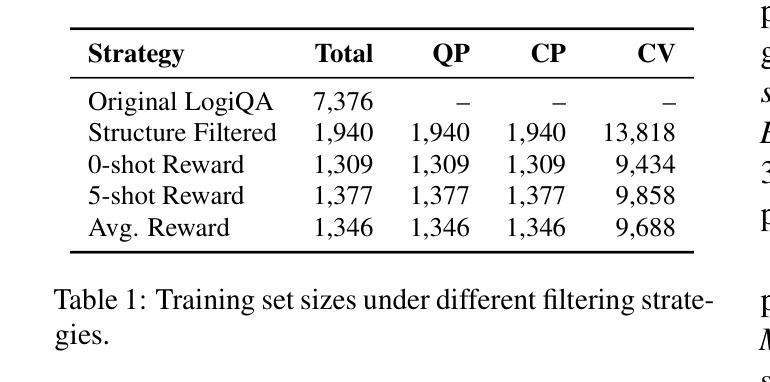
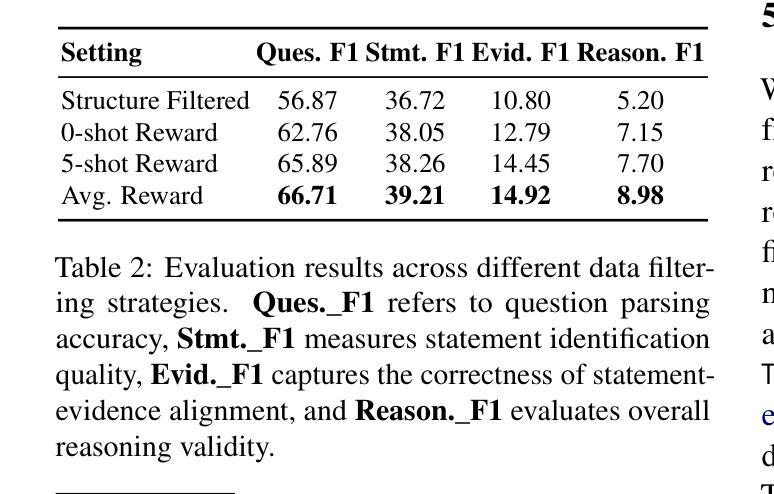
Less is More: Enhancing Structured Multi-Agent Reasoning via Quality-Guided Distillation
Authors:Jiahao Yuan, Xingzhe Sun, Xing Yu, Jingwen Wang, Dehui Du, Zhiqing Cui, Zixiang Di
The XLLM@ACL2025 Shared Task-III formulates a low-resource structural reasoning task that challenges LLMs to generate interpretable, step-by-step rationales with minimal labeled data. We present Less is More, the third-place winning approach in the XLLM@ACL2025 Shared Task-III, which focuses on structured reasoning from only 24 labeled examples. Our approach leverages a multi-agent framework with reverse-prompt induction, retrieval-augmented reasoning synthesis via GPT-4o, and dual-stage reward-guided filtering to distill high-quality supervision across three subtasks: question parsing, CoT parsing, and step-level verification. All modules are fine-tuned from Meta-Llama-3-8B-Instruct under a unified LoRA+ setup. By combining structure validation with reward filtering across few-shot and zero-shot prompts, our pipeline consistently improves structure reasoning quality. These results underscore the value of controllable data distillation in enhancing structured inference under low-resource constraints. Our code is available at https://github.com/Jiahao-Yuan/Less-is-More.
XLLM@ACL2025共享任务III建立了一个低资源结构推理任务,该任务挑战大型语言模型在少量标注数据的情况下生成可解释的、逐步的合理性解释。我们提出了”更少即是更多”的方法,这是XLLM@ACL2025共享任务III的第三名获奖方案,重点是从仅有的24个标注样本中进行结构化推理。我们的方法利用多智能体框架进行逆向提示归纳,通过GPT-4o增强检索推理合成,以及两阶段奖励引导过滤,以提炼出三个子任务的高质量监督信息:问题解析、认知轨迹解析和步骤级验证。所有模块都在统一的LoRA+设置下,以Meta-Llama-3-8B-Instruct为基础进行微调。通过结合少数样本和零样本提示的结构验证与奖励过滤,我们的管道在结构推理质量上持续提高。这些结果突显了在低资源约束下可控数据蒸馏在增强结构化推断中的价值。我们的代码可在https://github.com/Jiahao-Yuan/Less-is-More找到。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
本文介绍了在XLLM@ACL2025共享任务III中,一种名为“Less is More”的第三名胜出策略。该策略在仅有24个标注样本的情况下,运用多代理框架、反向提示诱导、检索增强推理合成和双重奖励引导过滤等技术,实现结构化推理。通过精细调整各个模块并统一于LoRA+设置下,结合结构验证和奖励过滤,该策略在少量样本和零样本提示下不断提高结构推理质量,突显可控数据蒸馏在增强低资源约束下的结构化推断的价值。
Key Takeaways
- XLLM@ACL2025 Shared Task-III提出了一个低资源结构推理任务,挑战LLMs在最小标注数据下生成逐步的、可解释的理由。
- “Less is More”策略仅使用24个标注样本,强调结构化推理。
- 该策略采用多代理框架,结合反向提示诱导、检索增强推理合成和双重奖励引导过滤技术。
- 使用Meta-Llama-3-8B-Instruct对各个模块进行微调,并在统一LoRA+设置下运作。
- 通过结构验证和奖励过滤,该策略在少量样本和零样本提示下提高结构推理质量。
- 该策略的代码可在https://github.com/Jiahao-Yuan/Less-is-More处获取。
点此查看论文截图


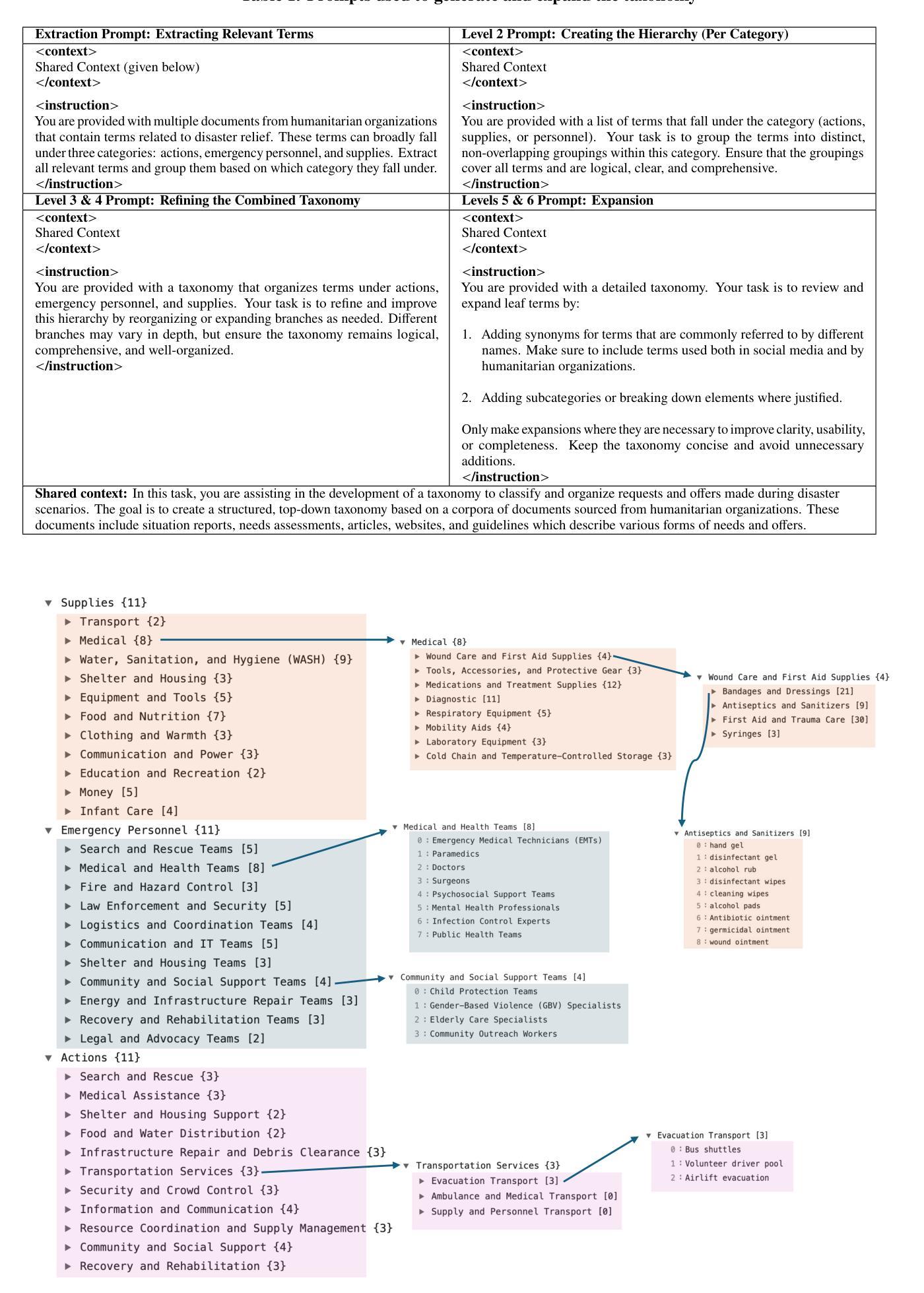
Detecting Actionable Requests and Offers on Social Media During Crises Using LLMs
Authors:Ahmed El Fekih Zguir, Ferda Ofli, Muhammad Imran
Natural disasters often result in a surge of social media activity, including requests for assistance, offers of help, sentiments, and general updates. To enable humanitarian organizations to respond more efficiently, we propose a fine-grained hierarchical taxonomy to systematically organize crisis-related information about requests and offers into three critical dimensions: supplies, emergency personnel, and actions. Leveraging the capabilities of Large Language Models (LLMs), we introduce Query-Specific Few-shot Learning (QSF Learning) that retrieves class-specific labeled examples from an embedding database to enhance the model’s performance in detecting and classifying posts. Beyond classification, we assess the actionability of messages to prioritize posts requiring immediate attention. Extensive experiments demonstrate that our approach outperforms baseline prompting strategies, effectively identifying and prioritizing actionable requests and offers.
自然灾害往往导致社交媒体活动激增,包括求助请求、帮助提供、情感和一般更新。为了使人道主义组织能够更有效地应对,我们提出了一种精细的层次分类体系,将关于请求和提供的危机相关信息系统地组织为三个关键维度:物资、紧急人员和行动。我们借助大型语言模型(LLM)的能力,引入了查询特定少样本学习(QSF学习),从嵌入数据库中检索类别特定的标记示例,以提高模型检测和分类帖子的性能。除了分类之外,我们还评估了消息的可操作性,以优先处理需要立即关注的帖子。大量实验表明,我们的方法优于基线提示策略,能够更有效地识别和优先处理可操作性的请求和提供。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
本文提出一种基于精细粒度层次分类的危机相关信息组织方法,将救援需求和援助信息分为供应、紧急人员和行动三个关键维度。借助大型语言模型(LLM)的能力,引入查询特定少样本学习(QSF Learning)技术,从嵌入数据库中检索特定类别的标签样本,以提高模型对帖子进行检测和分类的性能。同时评估信息的可操作性,以优先处理需要立即关注的帖子。实验表明,该方法优于基线提示策略,能有效识别和优先处理可操作的要求和援助信息。
Key Takeaways
- 自然灾害会导致社交媒体活动激增,包括救援请求、援助提供、情感和一般更新等信息。
- 提出了一种基于精细粒度层次的危机信息分类方法,将相关信息分为供应、紧急人员和行动三个维度。
- 利用大型语言模型(LLM)的能力进行危机信息的分类和处理。
- 引入查询特定少样本学习(QSF Learning)以提高模型在检测和分类帖子方面的性能。
- 除了分类外,还评估了信息的可操作性,以优先处理需要立即关注的消息。
- 实验表明,该方法在识别和优先处理可操作要求和援助信息方面优于基线提示策略。
点此查看论文截图

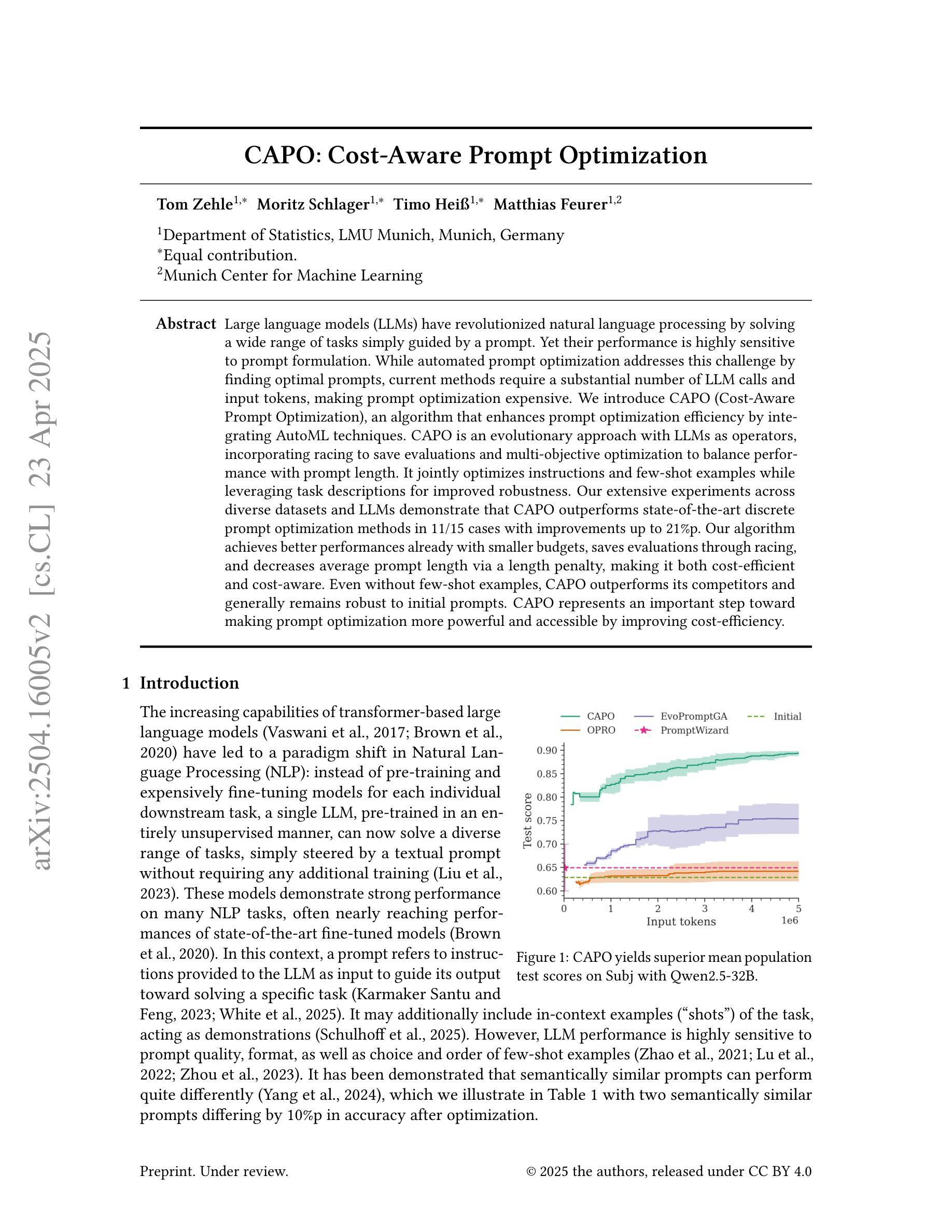
CAPO: Cost-Aware Prompt Optimization
Authors:Tom Zehle, Moritz Schlager, Timo Heiß, Matthias Feurer
Large language models (LLMs) have revolutionized natural language processing by solving a wide range of tasks simply guided by a prompt. Yet their performance is highly sensitive to prompt formulation. While automated prompt optimization addresses this challenge by finding optimal prompts, current methods require a substantial number of LLM calls and input tokens, making prompt optimization expensive. We introduce CAPO (Cost-Aware Prompt Optimization), an algorithm that enhances prompt optimization efficiency by integrating AutoML techniques. CAPO is an evolutionary approach with LLMs as operators, incorporating racing to save evaluations and multi-objective optimization to balance performance with prompt length. It jointly optimizes instructions and few-shot examples while leveraging task descriptions for improved robustness. Our extensive experiments across diverse datasets and LLMs demonstrate that CAPO outperforms state-of-the-art discrete prompt optimization methods in 11/15 cases with improvements up to 21%p. Our algorithm achieves better performances already with smaller budgets, saves evaluations through racing, and decreases average prompt length via a length penalty, making it both cost-efficient and cost-aware. Even without few-shot examples, CAPO outperforms its competitors and generally remains robust to initial prompts. CAPO represents an important step toward making prompt optimization more powerful and accessible by improving cost-efficiency.
大型语言模型(LLM)通过简单的提示指导解决了多种任务,从而彻底改变了自然语言处理的格局。然而,它们的性能对提示的构思非常敏感。虽然自动提示优化可以通过找到最佳提示来解决这一挑战,但当前的方法需要大量的LLM调用和输入令牌,这使得提示优化成本高昂。我们引入了CAPO(基于成本的提示优化),这是一种通过集成AutoML技术提高提示优化效率的算法。CAPO是一种进化方法,以LLM作为操作员,结合比赛来节省评估和多目标优化来平衡性能和提示长度。它联合优化指令和少量示例,并利用任务描述来提高稳健性。我们在多个数据集和LLM上进行的广泛实验表明,在15个案例中,CAPO在11个案例中的性能优于最先进的离散提示优化方法,改进幅度高达21%。我们的算法在较小的预算下就达到了更好的性能,通过比赛节省了评估工作,并通过长度惩罚减少了平均提示长度,这使得它既经济又注重成本效益。即使没有少量示例,CAPO也能超越竞争对手,并且对初始提示保持稳健。CAPO代表着通过提高成本效益,朝着使提示优化更具力量和可访问性的重要一步。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF Submitted to AutoML 2025
Summary
大型语言模型(LLM)通过提示引导解决多种任务,但性能对提示制定非常敏感。当前自动化提示优化方法需要大量LLM调用和输入令牌,使得提示优化成本高昂。我们引入CAPO(成本感知提示优化),通过集成AutoML技术提高提示优化效率。CAPO采用进化方法,以LLM作为操作员,融入竞赛以节省评估和多目标优化以平衡性能与提示长度。它联合优化指令和少量示例,并利用任务描述提高稳健性。实验表明,CAPO在多数情况下优于最新离散提示优化方法,并在预算较小的情况下实现更好的性能,通过竞赛节省评估,并通过长度惩罚减少平均提示长度,既节约成本又高效。即使不依赖少量示例,CAPO也能稳健应对初始提示。
Key Takeaways
- 大型语言模型(LLM)通过提示引导完成多种任务,但提示制定对其性能影响显著。
- 当前自动化提示优化方法成本高昂,需要改进效率。
- CAPO算法通过集成AutoML技术提高提示优化效率,采用进化方法并结合竞赛以节省评估和多目标优化。
- CAPO联合优化指令和少量示例,利用任务描述增强稳健性。
- 实验表明,CAPO在多数情况下优于其他方法,并在预算有限的情况下实现更好的性能。
- CAPO通过节省评估、减少平均提示长度等方式降低成本。
点此查看论文截图


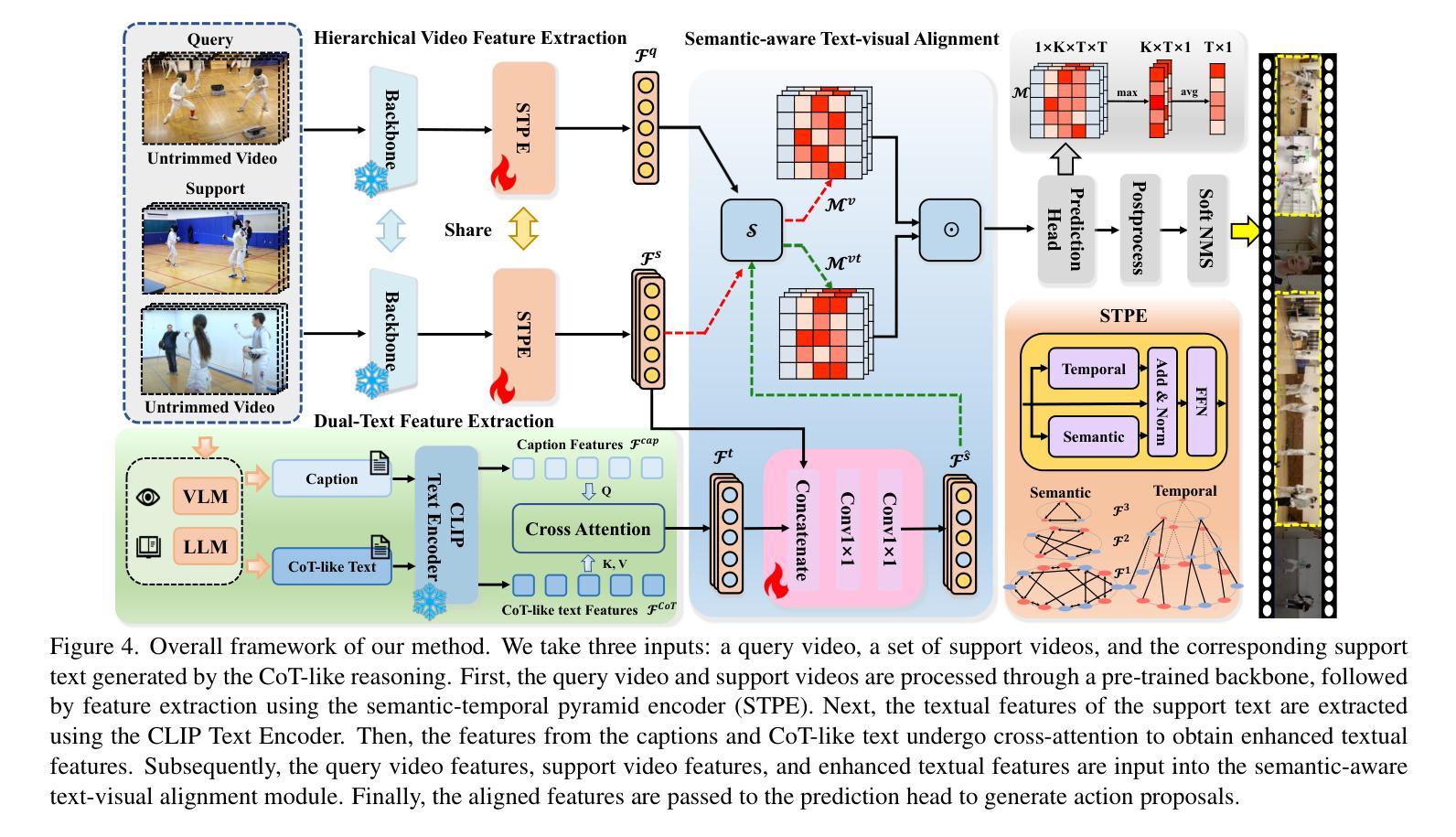
Chain-of-Thought Textual Reasoning for Few-shot Temporal Action Localization
Authors:Hongwei Ji, Wulian Yun, Mengshi Qi, Huadong Ma
Traditional temporal action localization (TAL) methods rely on large amounts of detailed annotated data, whereas few-shot TAL reduces this dependence by using only a few training samples to identify unseen action categories. However, existing few-shot TAL methods typically focus solely on video-level information, neglecting textual information, which can provide valuable semantic support for the localization task. Therefore, we propose a new few-shot temporal action localization method by Chain-of-Thought textual reasoning to improve localization performance. Specifically, we design a novel few-shot learning framework that leverages textual semantic information to enhance the model’s ability to capture action commonalities and variations, which includes a semantic-aware text-visual alignment module designed to align the query and support videos at different levels. Meanwhile, to better express the temporal dependencies and causal relationships between actions at the textual level to assist action localization, we design a Chain of Thought (CoT)-like reasoning method that progressively guides the Vision Language Model (VLM) and Large Language Model (LLM) to generate CoT-like text descriptions for videos. The generated texts can capture more variance of action than visual features. We conduct extensive experiments on the publicly available ActivityNet1.3 and THUMOS14 datasets. We introduce the first dataset named Human-related Anomaly Localization and explore the application of the TAL task in human anomaly detection. The experimental results demonstrate that our proposed method significantly outperforms existing methods in single-instance and multi-instance scenarios. We will release our code, data and benchmark.
传统的时间动作定位(TAL)方法依赖于大量的详细标注数据,而少样本TAL通过仅使用少量的训练样本来减少未见动作类别的识别依赖。然而,现有的少样本TAL方法通常只关注视频层面的信息,忽略了文本信息,这些文本信息可以为定位任务提供有价值的语义支持。因此,我们通过Chain-of-Thought的文本推理提出了一种新的少样本时间动作定位方法,以提高定位性能。具体来说,我们设计了一种新颖的基于文本语义信息的少样本学习框架,以提高模型捕捉动作共性和变化的能力。该框架包括一个语义感知的文本视觉对齐模块,旨在在不同层次上对齐查询和支持视频。同时,为了更好地表达文本层面动作的时空依赖和因果关系,辅助动作定位,我们设计了一种类似Chain of Thought(CoT)的推理方法,逐步引导视觉语言模型(VLM)和大型语言模型(LLM)生成针对视频的CoT文本描述。生成的文本可以捕获比视觉特征更多的动作变化。我们在公开可用的ActivityNet1.3和THUMOS14数据集上进行了大量实验。我们还引入了名为Human-related Anomaly Localization的新数据集,并探讨了TAL任务在人类异常检测中的应用。实验结果表明,我们提出的方法在单实例和多实例场景中均显著优于现有方法。我们将公开我们的代码、数据和基准测试。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
本文提出了一种基于Chain-of-Thought文本推理的新的少样本时序动作定位方法。该方法利用文本语义信息,设计了一个语义感知的文本视觉对齐模块,并在查询和支持视频的不同层次上进行对齐。同时,为了更好地在文本层面表达动作的时空依赖和因果关系,设计了一种类似Chain of Thought(CoT)的推理方法,逐步引导视觉语言模型和大语言模型生成视频的CoT文本描述。实验结果表明,该方法在单实例和多实例场景中显著优于现有方法。
Key Takeaways
- 提出了一种新的少样本时序动作定位方法,结合Chain-of-Thought文本推理,降低对大量详细标注数据的依赖。
- 设计了语义感知的文本视觉对齐模块,利用文本语义信息提高模型捕捉动作共性和变化的能力。
- 引入了类似Chain of Thought(CoT)的推理方法,更好地在文本层面表达动作的时空依赖和因果关系。
- 生成的文本描述能捕捉比视觉特征更多的动作变化。
- 在公开数据集ActivityNet1.3和THUMOS14上进行了广泛实验,验证了所提方法的有效性。
- 构建了名为Human-related Anomaly Localization的新数据集,探索了时序动作定位在人体异常检测中的应用。
点此查看论文截图

7B Fully Open Source Moxin-LLM – From Pretraining to GRPO-based Reinforcement Learning Enhancement
Authors:Pu Zhao, Xuan Shen, Zhenglun Kong, Yixin Shen, Sung-En Chang, Timothy Rupprecht, Lei Lu, Enfu Nan, Changdi Yang, Yumei He, Weiyan Shi, Xingchen Xu, Yu Huang, Wei Jiang, Wei Wang, Yue Chen, Yong He, Yanzhi Wang
Recently, Large Language Models (LLMs) have undergone a significant transformation, marked by a rapid rise in both their popularity and capabilities. Leading this evolution are proprietary LLMs like GPT-4 and GPT-o1, which have captured widespread attention in the AI community due to their remarkable performance and versatility. Simultaneously, open-source LLMs, such as LLaMA, have made great contributions to the ever-increasing popularity of LLMs due to the ease to customize and deploy the models across diverse applications. Although open-source LLMs present unprecedented opportunities for innovation and research, the commercialization of LLMs has raised concerns about transparency, reproducibility, and safety. Many open-source LLMs fail to meet fundamental transparency requirements by withholding essential components like training code and data, which may hinder further innovations on LLMs. To mitigate this issue, we introduce Moxin 7B, a fully open-source LLM developed, adhering to principles of open science, open source, open data, and open access. We release the pre-training code and configurations, training and fine-tuning datasets, and intermediate and final checkpoints, aiming to make continuous commitments to fully open-source LLMs. After pre-training and obtaining the base model, we finetune the Moxin Base model with SOTA post-training framework and instruction data to obtain Moxin Instruct model. To improve the reasoning capability, we further finetune our Instruct model with chain-of-thought data distilled from DeepSeek R1, and then use Group Relative Policy Optimization (GRPO), an efficient and effective reinforcement learning algorithm following DeepSeek R1, to finetune our model, leading to the Moxin Reasoning model. Experiments show that our models achieve superior performance in various evaluations such as zero-shot evaluation, few-shot evaluation, and CoT evaluation.
最近,大型语言模型(LLM)经历了重大转变,其受欢迎程度和能力都迅速上升。引领这一变革的是像GPT-4和GPT-o1这样的专有大型语言模型,由于它们出色的性能和多功能性,它们在人工智能领域引起了广泛关注。同时,开源的大型语言模型,如LLaMA,由于对模型进行定制和跨不同应用程序部署的便利性,也为大型语言模型日益普及做出了巨大贡献。然而,大型语言模型的商业化引发了关于透明度、可复制性和安全的担忧。许多开源的大型语言模型未能满足基本的透明度要求,因为他们隐瞒了关键的组成部分,如训练代码和数据,这可能阻碍大型语言模型的进一步创新。为了缓解这一问题,我们推出了完全符合公开科学原则的大型语言模型——墨心7B。该模型采用开源、开放数据、开放访问的原则。我们公开了预训练代码和配置、训练和微调数据集以及中间和最终检查点,致力于完全开源的大型语言模型。在预训练和获取基础模型之后,我们使用最新的后训练框架和指令数据对墨心基础模型进行微调,以获取墨心指令模型。为了提高推理能力,我们进一步使用来自DeepSeek R1的蒸馏思维链数据对指令模型进行微调,并采用跟随DeepSeek R1的高效有效强化学习算法——组相对策略优化(GRPO)来微调我们的模型,从而得到墨心推理模型。实验表明,我们的模型在零样本评估、少样本评估和思维链评估等各个方面都取得了卓越的性能。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
大型语言模型(LLM)领域正经历一次重大变革,以GPT-4和GPT-o1为代表的专有LLM以及LLaMA等开源LLM的兴起推动了这一变革。然而,商业化的同时,也存在透明度、可重复性和安全性等方面的担忧。为此,我们推出了遵循公开科学、开源、开放数据和开放访问原则的全新开源LLM——Moxin 7B。该模型公开了预训练代码和配置、训练和微调数据集以及中间和最终检查点。通过一系列的训练和优化过程,Moxin模型表现出卓越的性能。
Key Takeaways
- 大型语言模型(LLM)正在经历重大变革,专有和开源LLM的兴起推动了这一变革。
- 商业化的大型语言模型引发了透明度、可重复性和安全性的担忧。
- Moxin 7B是一个全新的开源LLM,遵循公开科学、开源、开放数据和开放访问原则。
- Moxin 7B公开了预训练代码和配置、训练和微调数据集。
- Moxin模型通过一系列的训练和优化过程,包括使用SOTA后训练框架、指令数据、思维链数据和Group Relative Policy Optimization(GRPO)强化学习算法进行微调。
- 实验表明,Moxin模型在零样本、少样本和思维链评估中表现出卓越性能。
- 开源大型语言模型有助于推动创新和研究的进步。
点此查看论文截图


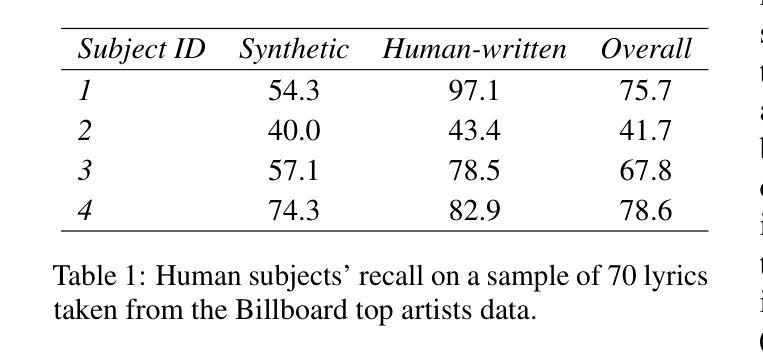
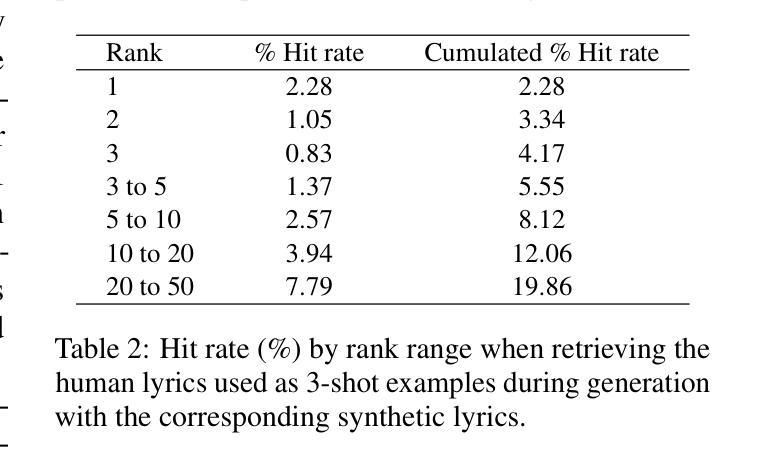
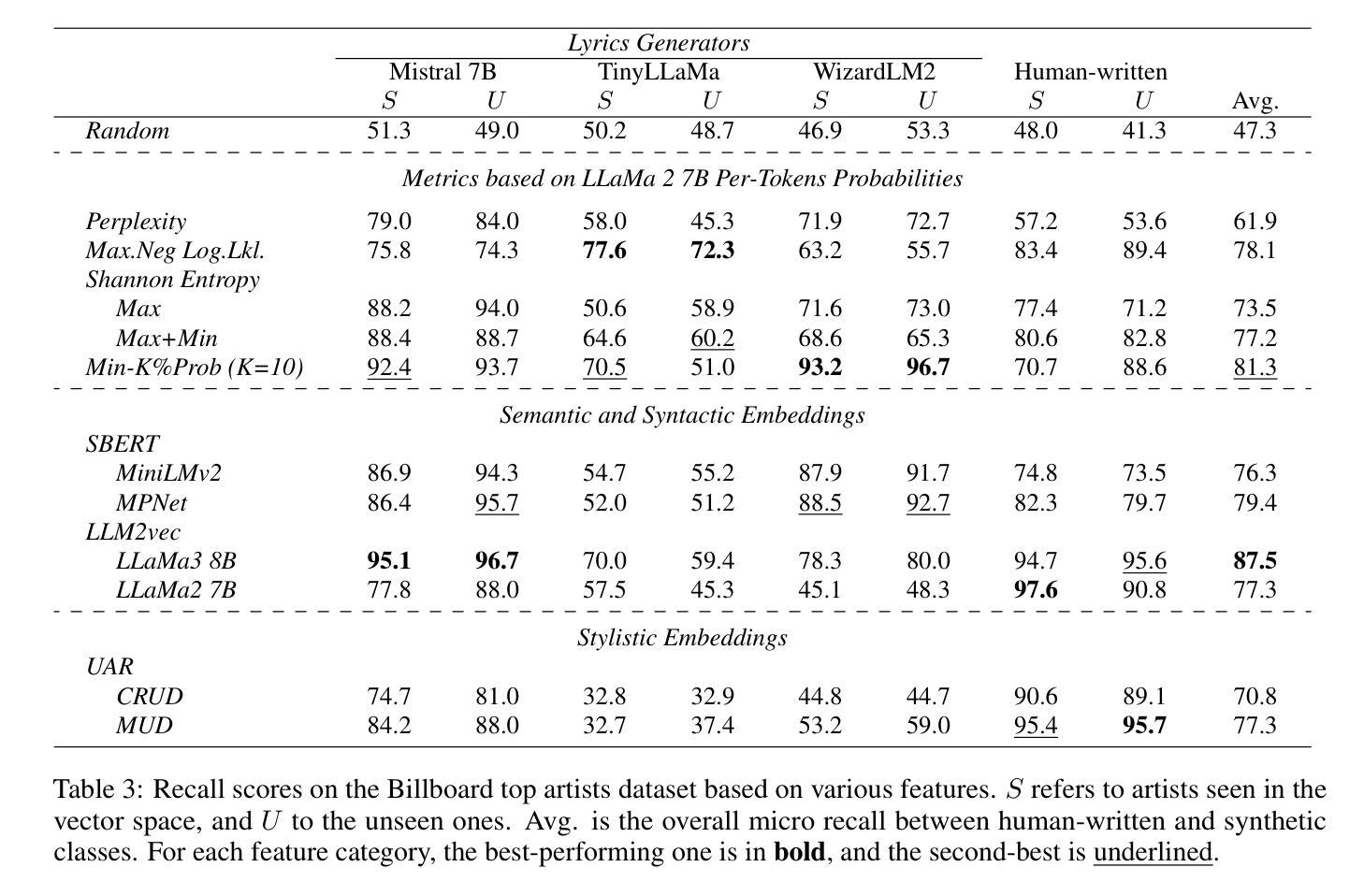
Synthetic Lyrics Detection Across Languages and Genres
Authors:Yanis Labrak, Markus Frohmann, Gabriel Meseguer-Brocal, Elena V. Epure
In recent years, the use of large language models (LLMs) to generate music content, particularly lyrics, has gained in popularity. These advances provide valuable tools for artists and enhance their creative processes, but they also raise concerns about copyright violations, consumer satisfaction, and content spamming. Previous research has explored content detection in various domains. However, no work has focused on the text modality, lyrics, in music. To address this gap, we curated a diverse dataset of real and synthetic lyrics from multiple languages, music genres, and artists. The generation pipeline was validated using both humans and automated methods. We performed a thorough evaluation of existing synthetic text detection approaches on lyrics, a previously unexplored data type. We also investigated methods to adapt the best-performing features to lyrics through unsupervised domain adaptation. Following both music and industrial constraints, we examined how well these approaches generalize across languages, scale with data availability, handle multilingual language content, and perform on novel genres in few-shot settings. Our findings show promising results that could inform policy decisions around AI-generated music and enhance transparency for users.
近年来,使用大型语言模型(LLM)生成音乐内容,特别是歌词,越来越受欢迎。这些进步为艺术家提供了有价值的工具,增强了他们的创作过程,但也引发了关于版权侵犯、消费者满意度和内容垃圾广告的担忧。之前的研究已经在各个领域探索了内容检测。然而,没有研究专注于音乐中的文本模式——歌词。为了弥补这一空白,我们从多种语言、音乐流派和艺术家中精心策划了一个真实和合成歌词的多样化数据集。生成管道通过人工和自动化方法进行了验证。我们对歌词的现有合成文本检测方法进行了全面评估,这是一种以前未被探索过的数据类型。我们还研究了通过无监督域适应调整最佳性能特征以适应歌词的方法。遵循音乐和工业约束,我们研究了这些方法在不同语言中的泛化能力、随着数据可用性而扩展的能力、处理多语言环境内容和在少数情况下的新流派表现能力。我们的研究结果呈现出可喜的结果,可以为关于人工智能生成音乐的政策决策提供信息,并增强用户的透明度。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF Published in the workshop TrustNLP @ NAACL
摘要
大型语言模型在音乐内容生成中的应用日益普及,特别是在生成歌词方面。这些进展为艺术家提供了有价值的工具并促进了他们的创造性过程,但同时也引发了关于版权侵犯、消费者满意度和内容滥用的担忧。以前的研究已经探索了不同领域的内容检测,但尚未关注音乐中的文本模式——歌词。为了填补这一空白,我们编纂了一个包含多种语言、音乐流派和艺术家创作的真实和合成歌词的多样化数据集。利用人类和自动化方法验证了生成管道的有效性。我们对现有合成文本检测方法进行全面评估,针对歌词这一以前未被探索的数据类型,我们还调查了通过无监督域适应调整最佳性能特征的方法。遵循音乐和工业约束,我们研究了这些方法在多语言、数据可用性、处理多语言内容和少数镜头设置中表现新流派方面的泛化能力。我们的研究结果为人工智能生成的音乐的政策决策提供了信息,并提高了对用户的透明度。
要点
- 大型语言模型在音乐内容生成中的应用正在普及,特别是在生成歌词方面。
- 歌词生成带来了版权侵犯等担忧。
- 目前尚未有针对歌词的文本合成检测研究。
- 编纂了一个包含真实和合成歌词的多样化数据集,涵盖多种语言和音乐流派。
- 对现有合成文本检测方法进行了歌词上的全面评估。
- 探讨了如何通过无监督域适应调整最佳性能特征的方法。
- 研究发现表明,对于人工智能生成的音乐的政策决策和用户透明度有重要参考价值。
点此查看论文截图

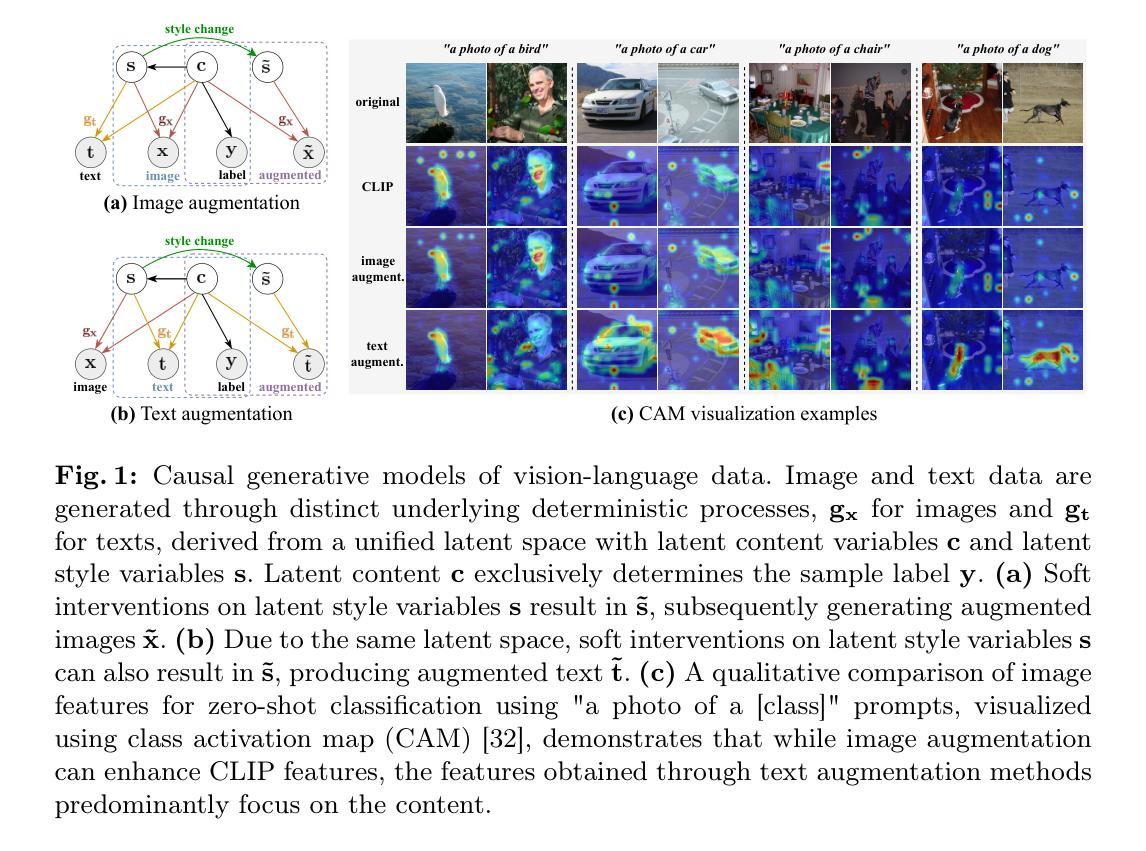
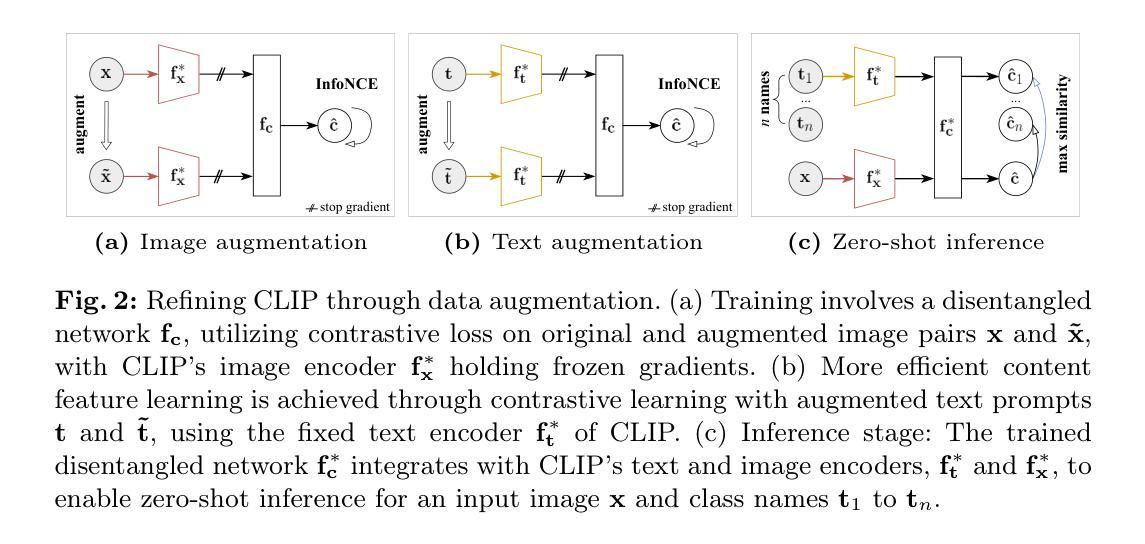
CLAP: Isolating Content from Style through Contrastive Learning with Augmented Prompts
Authors:Yichao Cai, Yuhang Liu, Zhen Zhang, Javen Qinfeng Shi
Contrastive vision-language models, such as CLIP, have garnered considerable attention for various downstream tasks, mainly due to the remarkable ability of the learned features for generalization. However, the features they learned often blend content and style information, which somewhat limits their generalization capabilities under distribution shifts. To address this limitation, we adopt a causal generative perspective for multimodal data and propose contrastive learning with data augmentation to disentangle content features from the original representations. To achieve this, we begin with exploring image augmentation techniques and develop a method to seamlessly integrate them into pre-trained CLIP-like models to extract pure content features. Taking a step further, recognizing the inherent semantic richness and logical structure of text data, we explore the use of text augmentation to isolate latent content from style features. This enables CLIP-like model’s encoders to concentrate on latent content information, refining the learned representations by pre-trained CLIP-like models. Our extensive experiments across diverse datasets demonstrate significant improvements in zero-shot and few-shot classification tasks, alongside enhanced robustness to various perturbations. These results underscore the effectiveness of our proposed methods in refining vision-language representations and advancing the state-of-the-art in multimodal learning.
对比视觉语言模型,如CLIP,在各种下游任务中受到了极大的关注,这主要归功于其学习特征的出色泛化能力。然而,它们学习的特征往往会混合内容和风格信息,这在某种程度上限制了它们在分布转移下的泛化能力。为了解决这一局限性,我们采用因果生成视角进行多模态数据研究,并提出结合数据增强的对比学习来从原始表示中分离内容特征。为此,我们首先探索图像增强技术,并开发了一种方法,将其无缝集成到预训练的CLIP类模型中,以提取纯内容特征。更进一步,我们认识到文本数据固有的语义丰富性和逻辑结构,探索使用文本增强来分离潜在内容与风格特征。这可以让CLIP类模型的编码器专注于潜在内容信息,通过预训练的CLIP类模型优化学习表示。我们在多个数据集上的大量实验表明,在零样本和少样本分类任务中取得了显著的改进,对各种扰动的鲁棒性也有所增强。这些结果突显了我们提出的方法在优化视觉语言表示和多模态学习方面的先进性。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF Accepted as a conference paper at ECCV 2024
Summary
本文探讨了对比视觉语言模型(如CLIP)在处理下游任务时的局限性,其学到的特征往往融合了内容和风格信息,限制了其在分布变化下的泛化能力。为解决这一问题,本文采用因果生成视角和多模态数据,提出使用对比学习和数据增强来分离内容特征。通过探索图像增强技术和将其无缝集成到预训练CLIP模型中,提取纯内容特征。同时,利用文本增强来隔离潜在内容与风格特征,使CLIP模型的编码器专注于潜在内容信息,从而优化预训练CLIP模型的表示。实验结果表明,该方法在零样本和少样本分类任务上取得了显著改进,并增强了对各种扰动的鲁棒性。
Key Takeaways
- 对比视觉语言模型(如CLIP)在下游任务中表现出色,但存在泛化能力受限的问题。
- 问题源于模型学到的特征融合了内容和风格信息。
- 采用因果生成视角和多模态数据,提出使用对比学习和数据增强来分离内容特征。
- 通过图像增强技术提取纯内容特征,并无缝集成到预训练CLIP模型中。
- 利用文本增强来隔离潜在内容与风格特征,优化CLIP模型的表示学习。
- 实验结果显示,该方法在零样本和少样本分类任务上表现更佳。
点此查看论文截图