⚠️ 以下所有内容总结都来自于 大语言模型的能力,如有错误,仅供参考,谨慎使用
🔴 请注意:千万不要用于严肃的学术场景,只能用于论文阅读前的初筛!
💗 如果您觉得我们的项目对您有帮助 ChatPaperFree ,还请您给我们一些鼓励!⭐️ HuggingFace免费体验
2025-04-25 更新
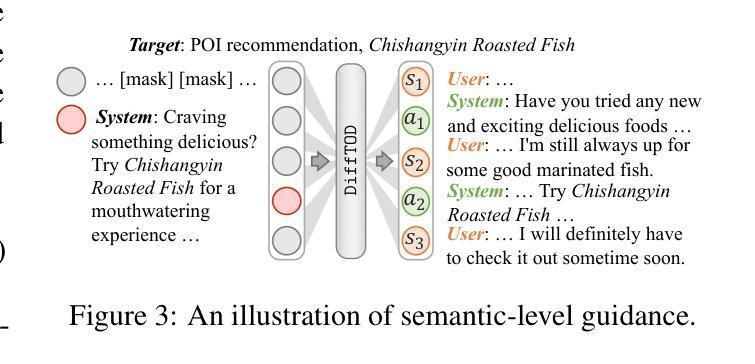
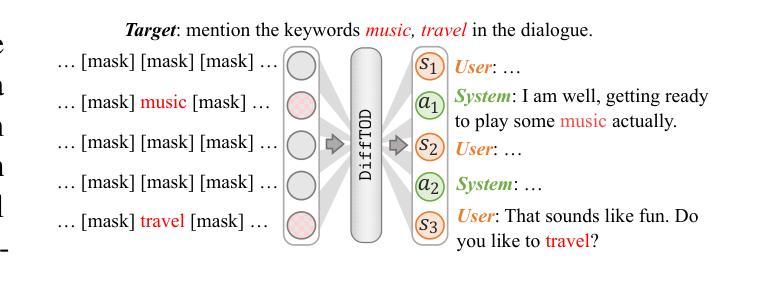
Planning with Diffusion Models for Target-Oriented Dialogue Systems
Authors:Hanwen Du, Bo Peng, Xia Ning
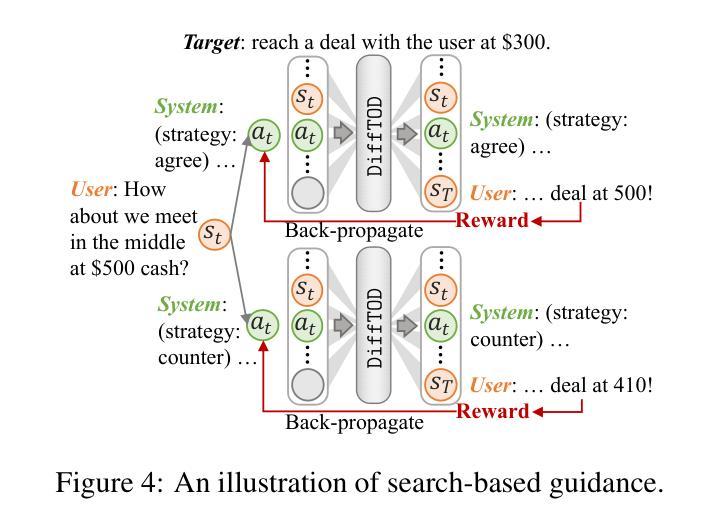
Target-Oriented Dialogue (TOD) remains a significant challenge in the LLM era, where strategic dialogue planning is crucial for directing conversations toward specific targets. However, existing dialogue planning methods generate dialogue plans in a step-by-step sequential manner, and may suffer from compounding errors and myopic actions. To address these limitations, we introduce a novel dialogue planning framework, DiffTOD, which leverages diffusion models to enable non-sequential dialogue planning. DiffTOD formulates dialogue planning as a trajectory generation problem with conditional guidance, and leverages a diffusion language model to estimate the likelihood of the dialogue trajectory. To optimize the dialogue action strategies, DiffTOD introduces three tailored guidance mechanisms for different target types, offering flexible guidance towards diverse TOD targets at test time. Extensive experiments across three diverse TOD settings show that DiffTOD can effectively perform non-myopic lookahead exploration and optimize action strategies over a long horizon through non-sequential dialogue planning, and demonstrates strong flexibility across complex and diverse dialogue scenarios. Our code and data are accessible through https://anonymous.4open.science/r/DiffTOD.
面向目标的对话(TOD)在LLM时代仍然是一个巨大的挑战,在这个时代,战略性的对话规划对于引导对话朝着特定目标进行至关重要。然而,现有的对话规划方法以逐步顺序的方式生成对话计划,并可能受到累积误差和近视行为的影响。为了解决这些局限性,我们引入了一种新型的对话规划框架DiffTOD,它利用扩散模型实现了非序列对话规划。DiffTOD将对话规划制定为带有条件指导的轨迹生成问题,并利用扩散语言模型估计对话轨迹的可能性。为了优化对话行动策略,DiffTOD针对不同目标类型引入了三种定制的引导机制,在测试时为不同的TOD目标提供了灵活指导。在三个不同的TOD环境下的广泛实验表明,DiffTOD可以通过非序列对话规划有效地执行非近视前瞻探索,并在长期范围内优化行动策略,同时在复杂的多样化对话场景中表现出强大的灵活性。我们的代码和数据可通过https://anonymous.4open.science/r/DiffTOD访问。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
本文介绍了目标导向对话(TOD)的挑战及新型对话规划框架DiffTOD的应用。DiffTOD利用扩散模型实现非序贯对话规划,解决了现有方法序贯规划导致的累积误差和视野短浅问题。该框架将对话规划制定为带有条件指导的轨迹生成问题,并利用扩散语言模型估算对话轨迹的可能性。为优化对话行动策略,DiffTOD针对不同目标类型引入三种定制指导机制,在测试时灵活指导向多样的TOD目标。实验表明,DiffTOD能有效进行非近视前瞻探索,并通过非序贯对话规划在长远视野中优化行动策略,且在复杂多变的对话场景中展现出强大的灵活性。
Key Takeaways
- 目标导向对话(TOD)在LLM时代仍具挑战,需战略对话规划以实现特定目标。
- 现有对话规划方法序贯生成计划,存在累积误差和视野短浅问题。
- DiffTOD利用扩散模型实现非序贯对话规划,解决上述问题。
- DiffTOD将对话规划制定为轨迹生成问题,用扩散语言模型估算对话轨迹可能性。
- DiffTOD针对不同类型目标引入三种定制指导机制,提高对话行动策略优化。
- DiffTOD能有效进行非近视前瞻探索,并在复杂多变的对话场景中展现强大灵活性。
点此查看论文截图

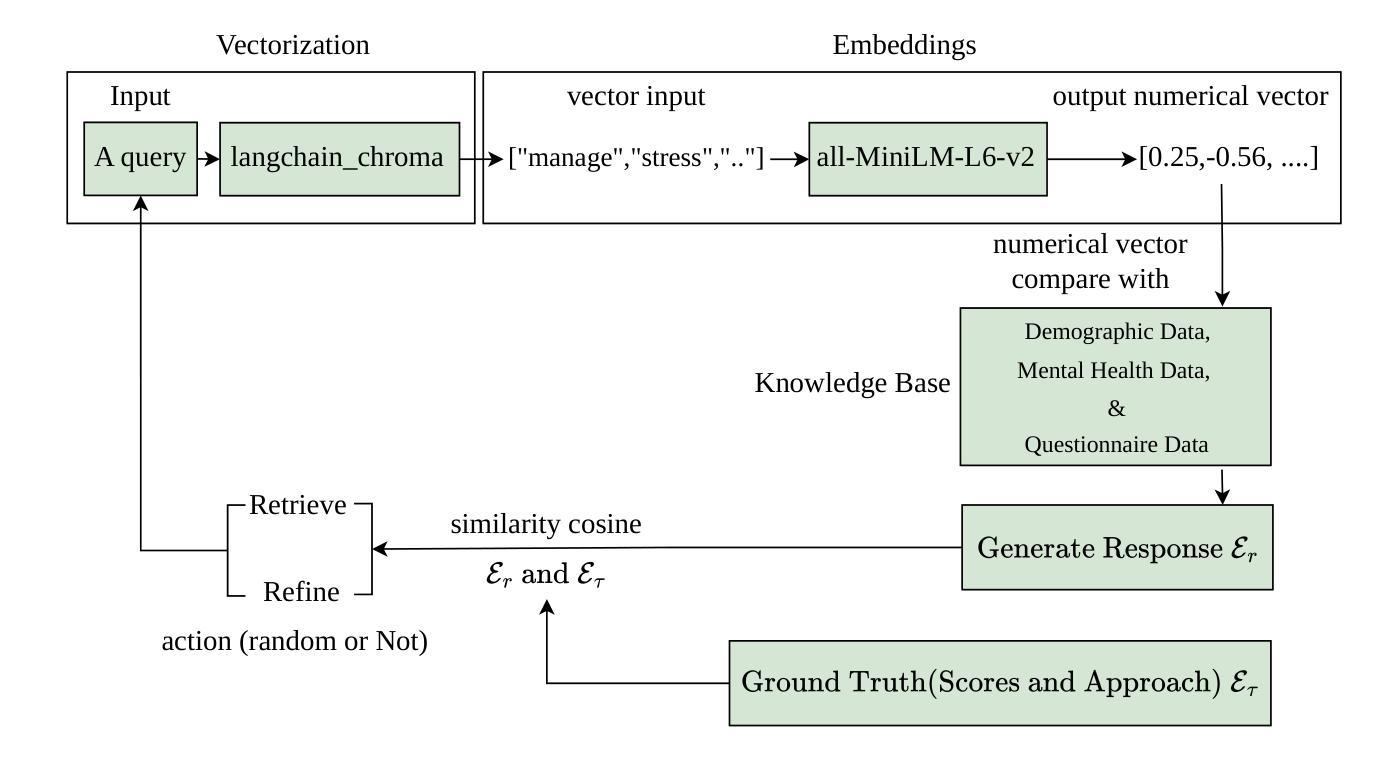
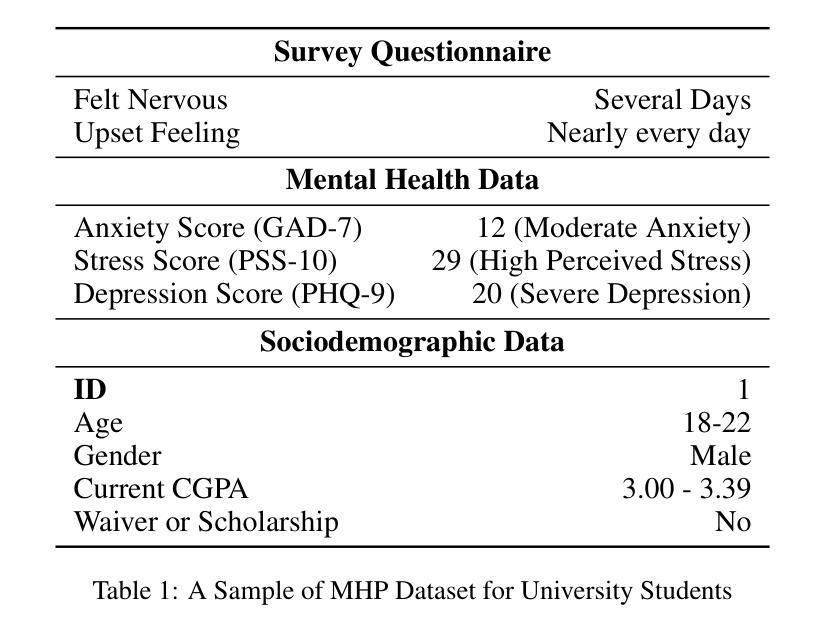
OnRL-RAG: Real-Time Personalized Mental Health Dialogue System
Authors:Ahsan Bilal, Beiyu Lin
Large language models (LLMs) have been widely used for various tasks and applications. However, LLMs and fine-tuning are limited to the pre-trained data. For example, ChatGPT’s world knowledge until 2021 can be outdated or inaccurate. To enhance the capabilities of LLMs, Retrieval-Augmented Generation (RAG), is proposed to augment LLMs with additional, new, latest details and information to LLMs. While RAG offers the correct information, it may not best present it, especially to different population groups with personalizations. Reinforcement Learning from Human Feedback (RLHF) adapts to user needs by aligning model responses with human preference through feedback loops. In real-life applications, such as mental health problems, a dynamic and feedback-based model would continuously adapt to new information and offer personalized assistance due to complex factors fluctuating in a daily environment. Thus, we propose an Online Reinforcement Learning-based Retrieval-Augmented Generation (OnRL-RAG) system to detect and personalize the responding systems to mental health problems, such as stress, anxiety, and depression. We use an open-source dataset collected from 2028 College Students with 28 survey questions for each student to demonstrate the performance of our proposed system with the existing systems. Our system achieves superior performance compared to standard RAG and simple LLM via GPT-4o, GPT-4o-mini, Gemini-1.5, and GPT-3.5. This work would open up the possibilities of real-life applications of LLMs for personalized services in the everyday environment. The results will also help researchers in the fields of sociology, psychology, and neuroscience to align their theories more closely with the actual human daily environment.
大型语言模型(LLM)已被广泛应用于各种任务和应用中。然而,LLM和微调都受限于预训练数据。例如,ChatGPT的截至2021年的世界知识可能会过时或不准确。为了增强LLM的能力,提出了检索增强生成(RAG)来向LLM添加额外、最新、详细的资讯。虽然RAG提供了正确的信息,但它可能无法最佳地呈现它,尤其是对于具有个性化的不同人群。强化学习从人类反馈(RLHF)通过反馈循环使模型响应与人类偏好对齐,以适应用户需求。在现实生活应用,如心理健康问题中,一个动态且基于反馈的模型将会持续适应新信息,并提供个性化的援助,这是因为日常环境中的复杂因素在不断波动。因此,我们提出了一种基于在线强化学习的检索增强生成(OnRL-RAG)系统,用于检测和个性化应对诸如压力、焦虑和抑郁等精神健康问题。我们使用从28名大学生收集的开源数据集进行演示,每个学生接受28个调查问题以评估我们提出的系统与现有系统的性能。我们的系统相较于标准RAG、GPT-4o、GPT-4o-mini、Gemini-1.5和GPT-3.5所实现的LLM具有更优越的性能。这项工作将为LLM在个性化服务方面的现实生活应用打开可能性,特别是在日常环境中。结果还将帮助社会学、心理学和神经科学领域的研究人员将其理论更紧密地与实际的日常人类环境相结合。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF It needs more revisions. I am currently working on it with my co-author
Summary
大型语言模型(LLMs)广泛应用于各种任务和应用,但其知识和能力受限于预训练数据。为增强LLMs的能力,提出了检索增强生成(RAG)方法,并结合强化学习人类反馈(RLHF)以适应不同用户需求。针对心理健康问题,提出基于在线强化学习的检索增强生成系统(OnRL-RAG),使用开源数据集展示其相较于其他系统的优越性能。此工作有助于LLMs在个性化服务方面的实际应用,对社会学、心理学和神经科学领域的研究者也有启示作用。
Key Takeaways
- 大型语言模型(LLMs)在多种任务和应用中广泛应用,但受限于预训练数据。
- 检索增强生成(RAG)方法用于增强LLMs的能力和获取最新信息。
- 强化学习人类反馈(RLHF)适应不同用户需求,提高模型响应与人类偏好的对齐。
- 针对心理健康问题,提出在线强化学习基础上的检索增强生成系统(OnRL-RAG)。
- 使用开源数据集展示OnRL-RAG相较于其他系统的优越性能。
- OnRL-RAG系统有助于LLMs在个性化服务方面的实际应用。
点此查看论文截图