⚠️ 以下所有内容总结都来自于 大语言模型的能力,如有错误,仅供参考,谨慎使用
🔴 请注意:千万不要用于严肃的学术场景,只能用于论文阅读前的初筛!
💗 如果您觉得我们的项目对您有帮助 ChatPaperFree ,还请您给我们一些鼓励!⭐️ HuggingFace免费体验
2025-04-25 更新
OptimAI: Optimization from Natural Language Using LLM-Powered AI Agents
Authors:Raghav Thind, Youran Sun, Ling Liang, Haizhao Yang
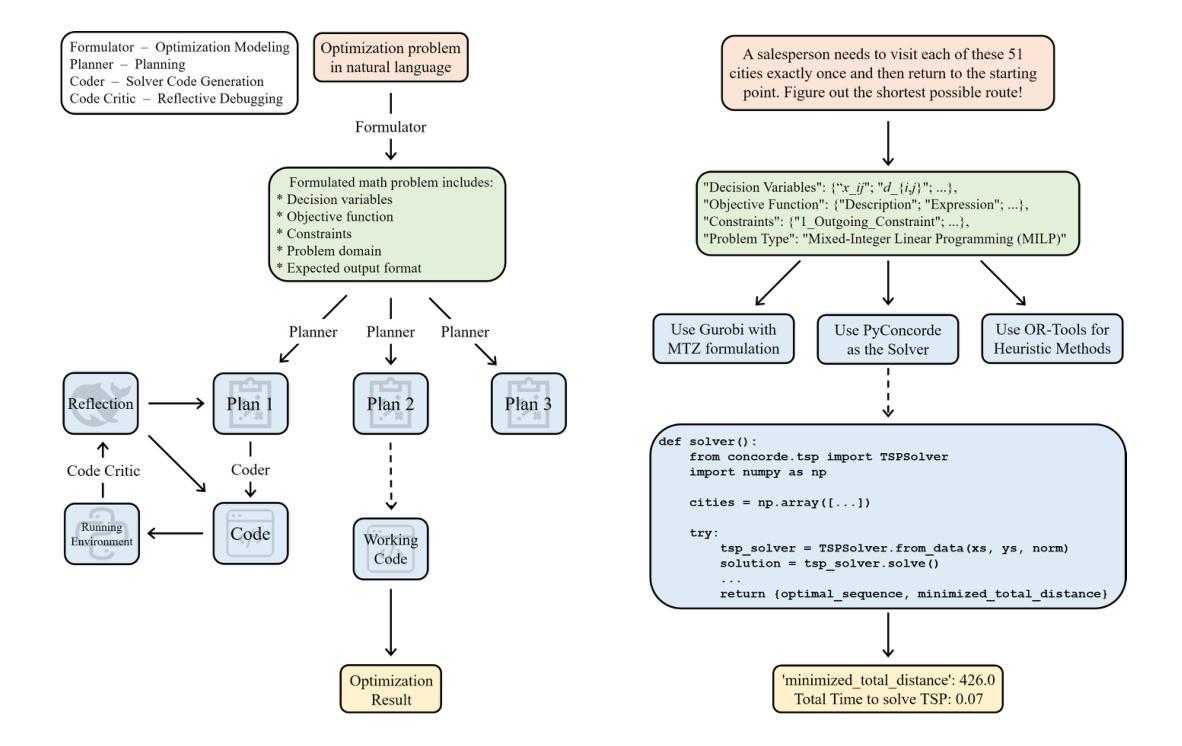
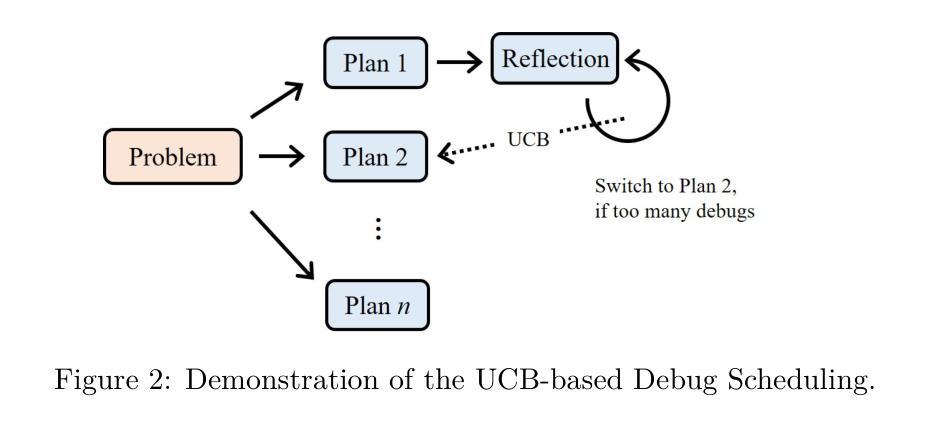
Optimization plays a vital role in scientific research and practical applications, but formulating a concrete optimization problem described in natural language into a mathematical form and selecting a suitable solver to solve the problem requires substantial domain expertise. We introduce \textbf{OptimAI}, a framework for solving \underline{Optim}ization problems described in natural language by leveraging LLM-powered \underline{AI} agents, achieving superior performance over current state-of-the-art methods. Our framework is built upon four key roles: (1) a \emph{formulator} that translates natural language problem descriptions into precise mathematical formulations; (2) a \emph{planner} that constructs a high-level solution strategy prior to execution; and (3) a \emph{coder} and a \emph{code critic} capable of interacting with the environment and reflecting on outcomes to refine future actions. Ablation studies confirm that all roles are essential; removing the planner or code critic results in $5.8\times$ and $3.1\times$ drops in productivity, respectively. Furthermore, we introduce UCB-based debug scheduling to dynamically switch between alternative plans, yielding an additional $3.3\times$ productivity gain. Our design emphasizes multi-agent collaboration, allowing us to conveniently explore the synergistic effect of combining diverse models within a unified system. Our approach attains 88.1% accuracy on the NLP4LP dataset and 71.2% on the Optibench (non-linear w/o table) subset, reducing error rates by 58% and 50% respectively over prior best results.
优化在科学研究和实际应用中发挥着至关重要的作用,然而,将自然语言描述的具体优化问题转化为数学形式,并选择适合的求解器来解决问题需要大量的专业知识。我们引入了OptimAI,这是一个利用大型语言模型驱动的AI代理来解决自然语言描述的优化问题的框架,其性能超越了当前先进的方法。我们的框架建立在四个关键角色之上:(1)一个能将自然语言问题描述转化为精确数学形式的表述器;(2)一个在执行前构建高级解决方案策略的规划器;(3)一个能够与环境互动并对结果进行反思以改进未来行动的编码者和代码评论家。切除研究表明,所有角色都是不可或缺的;移除规划者或代码评论家将导致生产率分别下降5.8倍和3.1倍。此外,我们引入了基于UCB的调试调度来动态切换替代方案,产生了额外的3.3倍生产率增益。我们的设计强调多智能体协作,使我们能够方便地探索在统一系统中结合不同模型的协同作用。我们的方法在NLP4LP数据集上达到88.1%的准确率,在Optibench(非线性无表)子集上达到71.2%的准确率,与之前的最佳结果相比,误差率分别降低了58%和50%。
论文及项目相关链接
摘要
优化在自然语言描述和实际应用中发挥着重要作用,但将自然语言描述的具体优化问题转化为数学形式并选择适当的求解器来解决问题需要大量的专业知识。我们引入了OptimAI框架,利用LLM驱动的AI代理解决自然语言描述的优化问题,实现了优于当前先进方法的性能。该框架建立在四个关键角色上:将自然语言问题描述转化为精确数学形式的表述者、构建高级解决方案策略的规划者、能够与环境交互并反思结果以改进未来行动的编码器和代码评论家。我们的设计强调多智能体协作,便于在统一系统中探索结合不同模型的协同作用。我们的方法在NLP4LP数据集上达到了88.1%的准确率,在Optibench(非线性无表)子集上达到了71.2%的准确率,相较于之前最佳结果分别降低了58%和50%的错误率。
关键见解
- OptimAI框架利用LLM驱动的AI代理解决自然语言描述的优化问题,实现高性能。
- 框架包括四个关键角色:表述者、规划者、编码器和代码评论家,各自承担不同的任务。
- 去除规划者或代码评论家会导致生产力大幅下降,表明这些角色对框架性能至关重要。
- 通过引入基于UCB的调试调度,可以动态切换不同计划,进一步提高生产力。
- 该框架强调多智能体协作,便于在统一系统中结合不同模型,发挥协同作用。
- 在NLP4LP数据集和Optibench子集上的实验结果表明,该框架具有显著的高准确率。
- 与之前的最佳结果相比,该框架在错误率方面取得了显著的改进。
点此查看论文截图

Tracing Thought: Using Chain-of-Thought Reasoning to Identify the LLM Behind AI-Generated Text
Authors:Shifali Agrahari, Sanasam Ranbir Singh
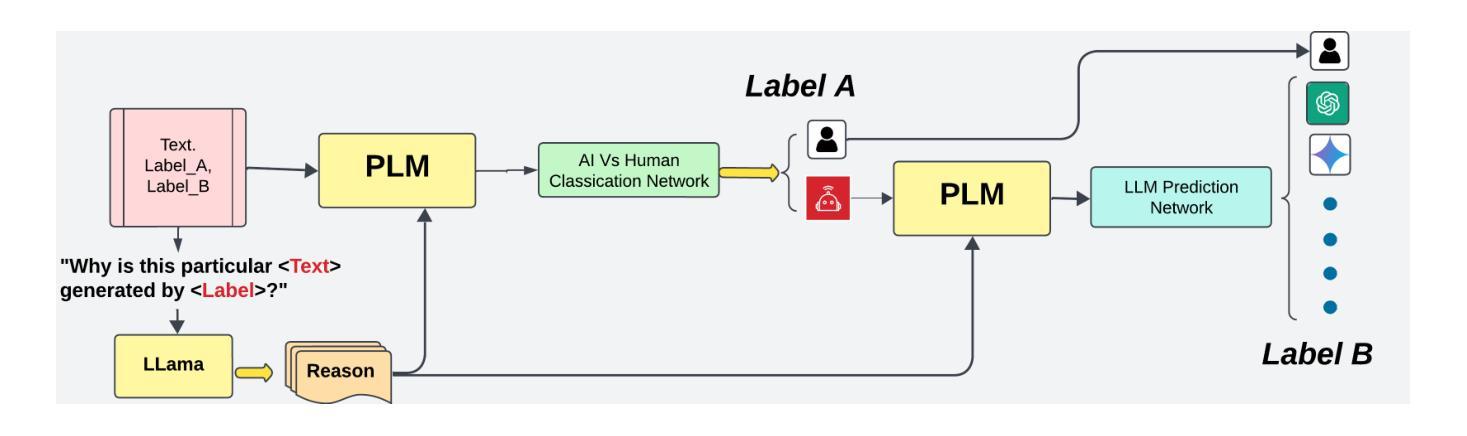
In recent years, the detection of AI-generated text has become a critical area of research due to concerns about academic integrity, misinformation, and ethical AI deployment. This paper presents COT Fine-tuned, a novel framework for detecting AI-generated text and identifying the specific language model. responsible for generating the text. We propose a dual-task approach, where Task A involves classifying text as AI-generated or human-written, and Task B identifies the specific LLM behind the text. The key innovation of our method lies in the use of Chain-of-Thought reasoning, which enables the model to generate explanations for its predictions, enhancing transparency and interpretability. Our experiments demonstrate that COT Fine-tuned achieves high accuracy in both tasks, with strong performance in LLM identification and human-AI classification. We also show that the CoT reasoning process contributes significantly to the models effectiveness and interpretability.
近年来,由于人们对学术诚信、误导信息和道德人工智能部署的担忧,检测人工智能生成的文本已成为研究的关键领域。本文提出了COT Fine-tuned,一个用于检测人工智能生成文本并识别生成文本的具体语言模型的新型框架。我们采用双任务方法,任务A涉及将文本分类为人工智能生成或人类撰写,任务B则识别文本背后的特定大型语言模型。我们的方法的关键创新之处在于使用Chain-of-Thought推理,使模型能够为其预测生成解释,提高透明度和可解释性。我们的实验表明,COT Fine-tuned在两项任务中都实现了较高的准确性,在大型语言模型识别和人机分类方面表现出强大的性能。我们还表明,CoT推理过程对模型的效率和可解释性做出了重大贡献。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF De-Factify 4: 4th Workshop on Multimodal Fact Checking and Hate Speech Detection, co-located with AAAI 2025. Pennsylvania
Summary
AI生成文本检测已成为研究的关键领域,涉及学术诚信、虚假信息和伦理AI部署等问题。本文提出一种新型框架COT Fine-tuned,采用双重任务方法检测AI生成的文本并识别特定语言模型。其创新之处在于采用思维链推理技术,使模型能对其预测生成解释,增强透明度和可解释性。实验证明,COT Fine-tuned在两项任务中都取得了高准确率,特别是在语言模型识别和人机分类方面表现优异。思维链推理过程对模型的效能和可解释性有显著贡献。
Key Takeaways
- AI生成文本检测是当前的热门研究领域,主要关注学术诚信、虚假信息和伦理AI部署问题。
- COT Fine-tuned是一种新型框架,用于检测AI生成的文本并识别生成文本的特定语言模型。
- 该框架采用双重任务方法,包括判断文本是否由AI生成以及识别特定语言模型。
- COT Fine-tuned的主要创新点是采用思维链推理技术,增强模型的透明度和可解释性。
- 实验结果显示,COT Fine-tuned在两项任务中均表现出高准确率。
- 思维链推理过程对提升模型的效能和可解释性有重要贡献。
点此查看论文截图

Enhancing Critical Thinking with AI: A Tailored Warning System for RAG Models
Authors:Xuyang Zhu, Sejoon Chang, Andrew Kuik
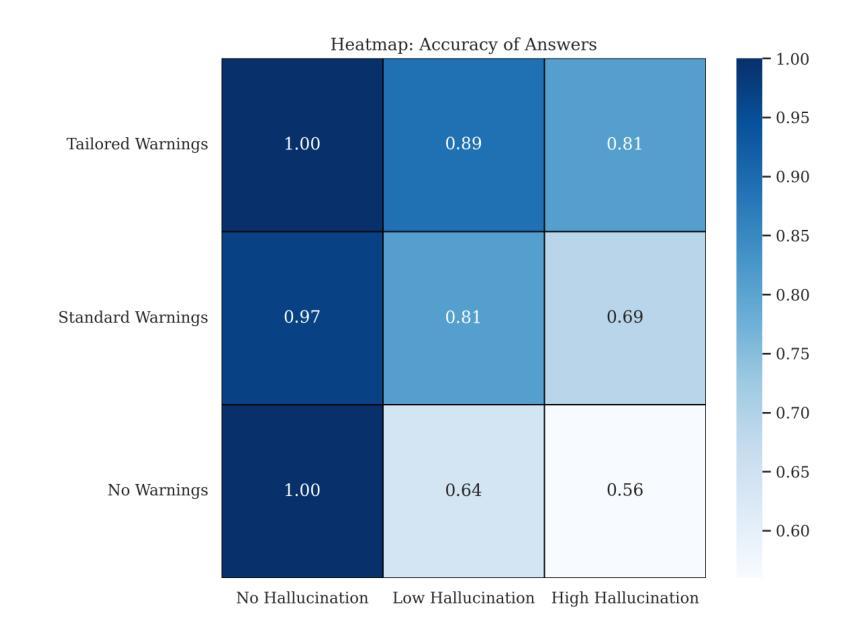
Retrieval-Augmented Generation (RAG) systems offer a powerful approach to enhancing large language model (LLM) outputs by incorporating fact-checked, contextually relevant information. However, fairness and reliability concerns persist, as hallucinations can emerge at both the retrieval and generation stages, affecting users’ reasoning and decision-making. Our research explores how tailored warning messages – whose content depends on the specific context of hallucination – shape user reasoning and actions in an educational quiz setting. Preliminary findings suggest that while warnings improve accuracy and awareness of high-level hallucinations, they may also introduce cognitive friction, leading to confusion and diminished trust in the system. By examining these interactions, this work contributes to the broader goal of AI-augmented reasoning: developing systems that actively support human reflection, critical thinking, and informed decision-making rather than passive information consumption.
检索增强生成(RAG)系统通过融入经过事实核查的、语境相关的信息,为增强大型语言模型(LLM)的输出提供了一种强大方法。然而,公平性和可靠性问题依然存在,因为在检索和生成阶段都可能出现幻觉,影响用户的推理和决策。我们的研究探索了定制警告信息——其内容取决于幻觉的具体语境——如何塑造用户在教育测验环境中的推理和行动。初步结果表明,虽然警告信息提高了对高级幻觉的准确性和意识,但它们也可能引发认知摩擦,导致用户混淆并对系统失去信任。通过检查这些交互,这项工作有助于实现人工智能辅助推理的更广泛目标:开发积极支持人类反思、批判性思维和知情决策的系统,而不是仅仅被动地消费信息。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF Presented at the 2025 ACM Workshop on Human-AI Interaction for Augmented Reasoning
Summary
RAG系统通过融入事实核查和语境相关信息,增强了大型语言模型的输出能力。但存在公平性和可靠性问题,如在检索和生成阶段可能出现幻觉,影响用户推理和决策。研究通过教育测验环境探索定制警告信息对用户行为的影响,初步发现警告虽能提高对高级幻觉的准确性和意识,但也可能造成认知摩擦,导致混淆和对系统信任的降低。
Key Takeaways
- RAG系统通过结合事实核查和语境相关信息,增强了LLM的输出。
- 公平性和可靠性问题是RAG系统面临的挑战,因为存在出现幻觉的风险。
- 警告信息可以改善用户对高级幻觉的准确性和意识。
- 警告信息也可能造成认知摩擦,导致用户混淆和对系统信任的降低。
- 研究在教育测验环境中探索了定制警告信息对用户行为的影响。
- 此研究对AI增强推理的贡献在于开发积极支持人类反思、批判思维和知情决策的系统,而非仅供被动消费信息的系统。
点此查看论文截图

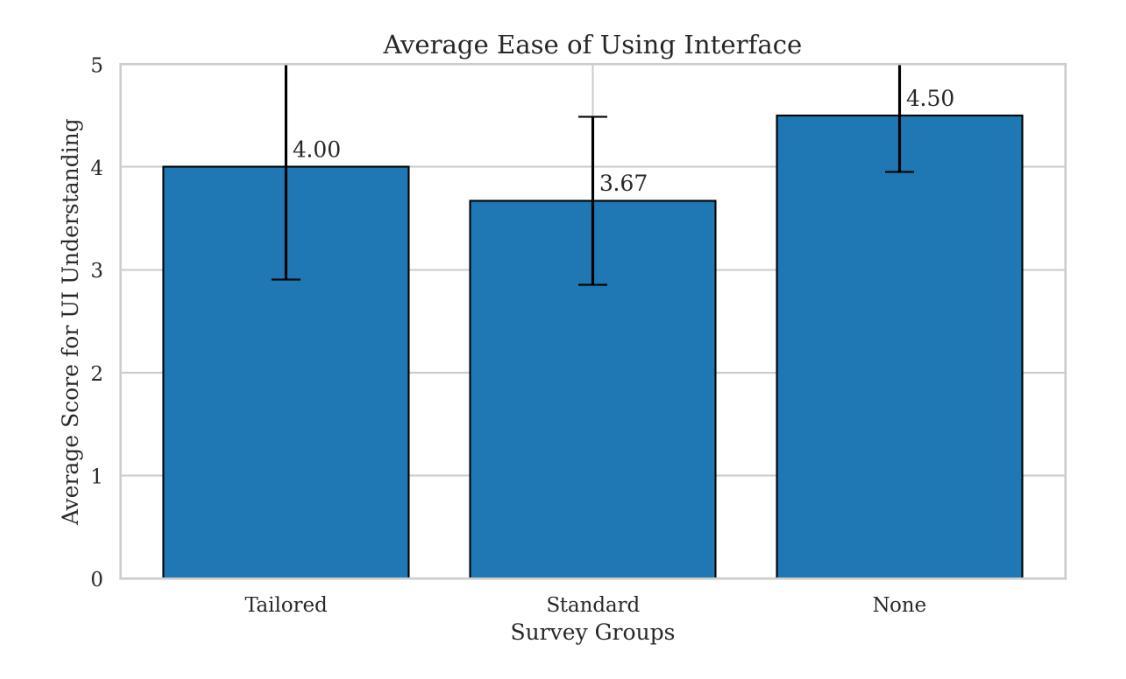
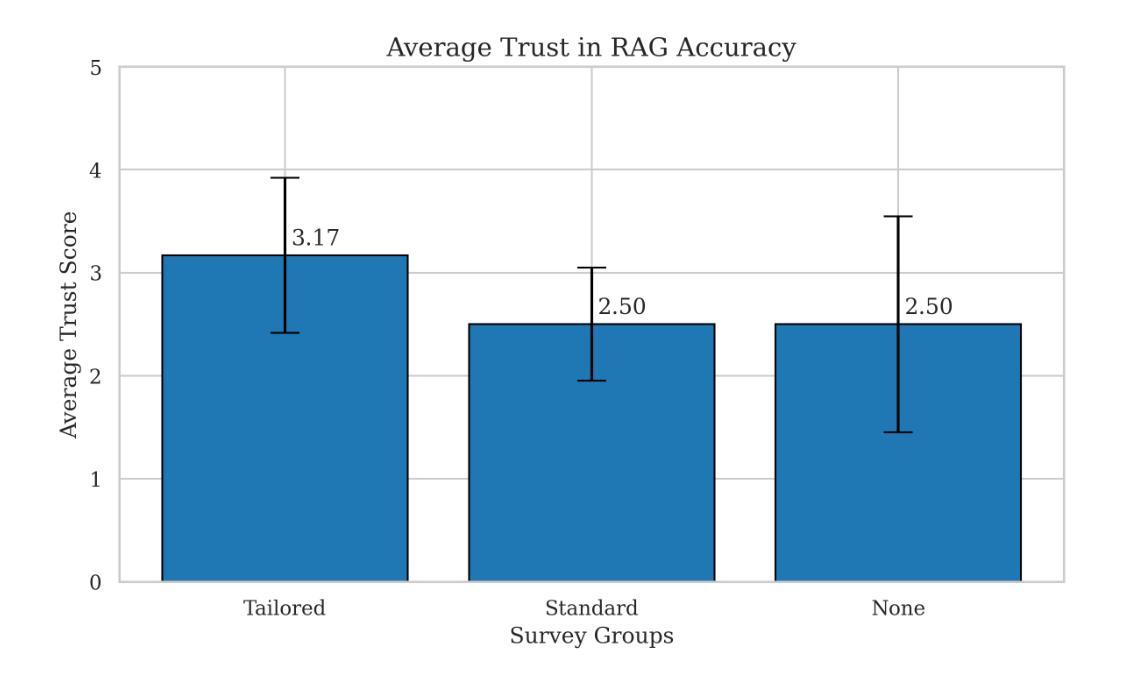
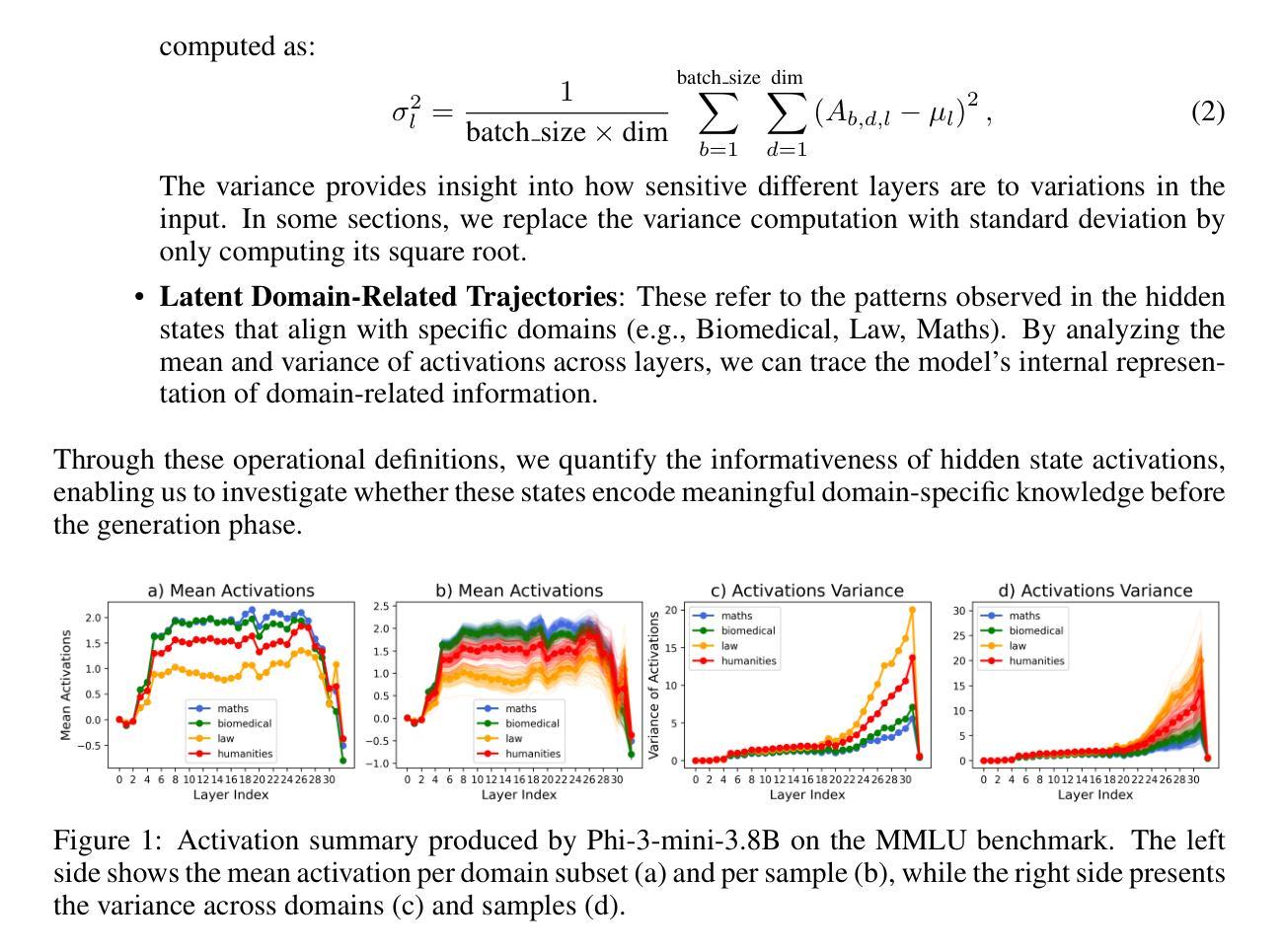
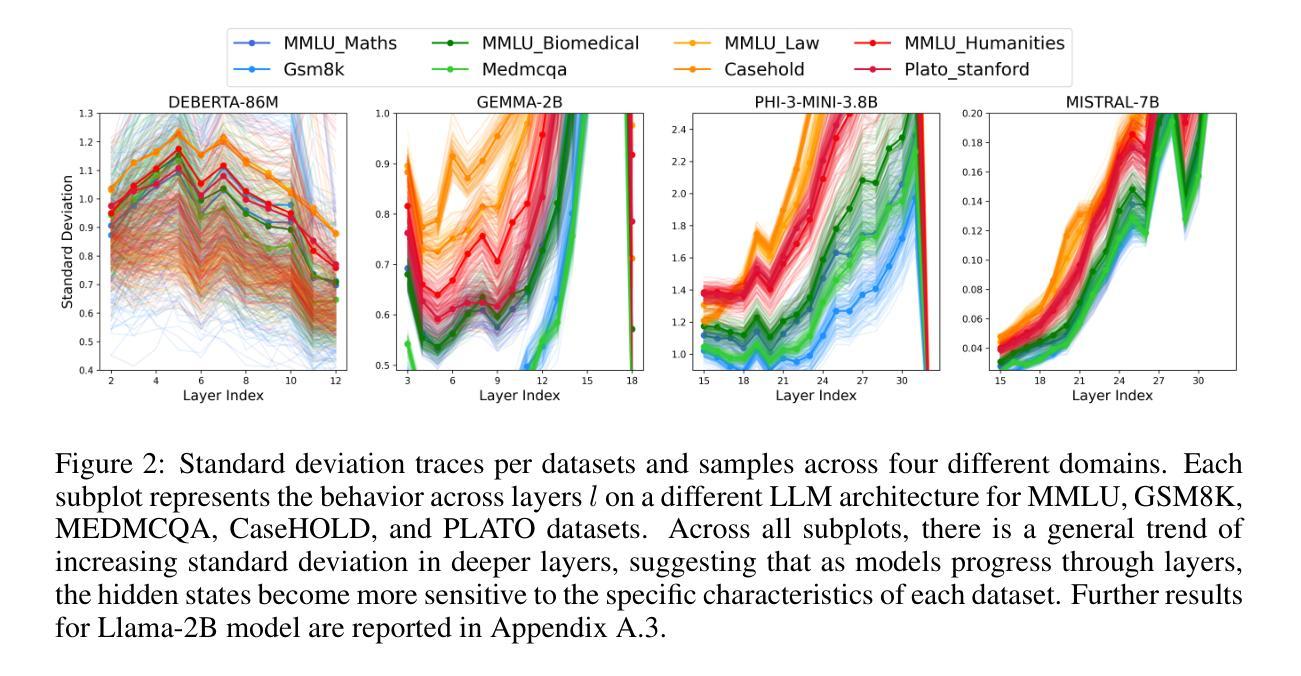
Exploring How LLMs Capture and Represent Domain-Specific Knowledge
Authors:Mirian Hipolito Garcia, Camille Couturier, Daniel Madrigal Diaz, Ankur Mallick, Anastasios Kyrillidis, Robert Sim, Victor Ruhle, Saravan Rajmohan
We study whether Large Language Models (LLMs) inherently capture domain-specific nuances in natural language. Our experiments probe the domain sensitivity of LLMs by examining their ability to distinguish queries from different domains using hidden states generated during the prefill phase. We reveal latent domain-related trajectories that indicate the model’s internal recognition of query domains. We also study the robustness of these domain representations to variations in prompt styles and sources. Our approach leverages these representations for model selection, mapping the LLM that best matches the domain trace of the input query (i.e., the model with the highest performance on similar traces). Our findings show that LLMs can differentiate queries for related domains, and that the fine-tuned model is not always the most accurate. Unlike previous work, our interpretations apply to both closed and open-ended generative tasks
我们研究大型语言模型(LLM)是否能在自然语言中捕获特定领域的细微差别。我们的实验通过检查预填充阶段生成的隐藏状态来探索LLM的领域敏感性,以检验它们区分不同领域查询的能力。我们揭示了与领域相关的潜在轨迹,表明模型对查询领域的内部识别。我们还研究了这些领域表示对不同提示风格和来源的稳健性。我们的方法利用这些表示来进行模型选择,找出最符合输入查询领域轨迹的LLM(即在类似轨迹上表现最佳的模型)。我们的研究结果表明,LLM能够区分相关领域的查询,而且微调模型并不总是最准确的。与之前的工作不同,我们的解释适用于封闭任务和开放式的生成任务。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
大型语言模型(LLM)能够捕捉自然语言中的领域特定细微差别。通过实验探究LLMs对来自不同领域查询的区分能力,揭示模型内部对查询领域的识别轨迹。研究这些领域表示的稳健性,并用于模型选择,找到与输入查询领域轨迹最匹配的LLM。研究发现LLMs能区分相关领域的查询,且微调模型并非总是最准确。此解读适用于封闭和开放生成任务。
Key Takeaways
- LLMs能够捕捉领域特定的细微差别。
- 实验探究LLMs对来自不同领域的查询的区分能力。
- LLMs内部存在识别查询领域的轨迹。
- 领域表示的稳健性研究对于模型选择至关重要。
- 输入查询的领域轨迹与LLM的匹配情况影响模型选择的准确性。
- LLMs能够区分相关领域的查询,这是之前的作品所未涉及的。
点此查看论文截图

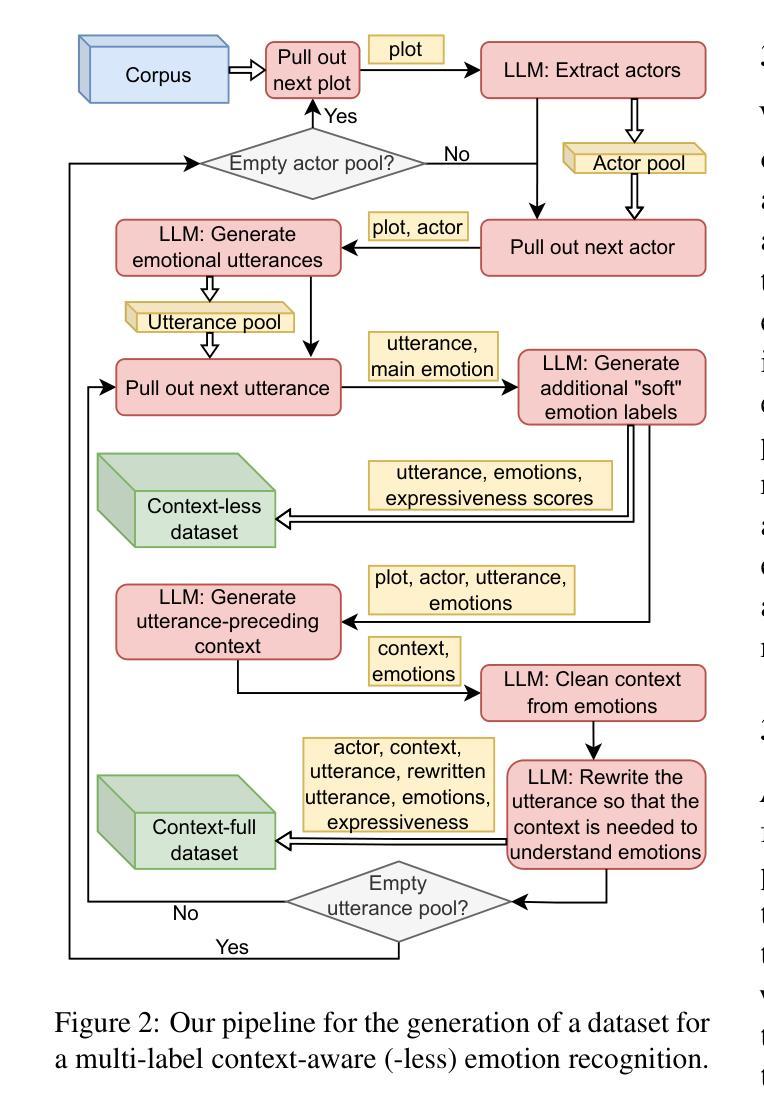
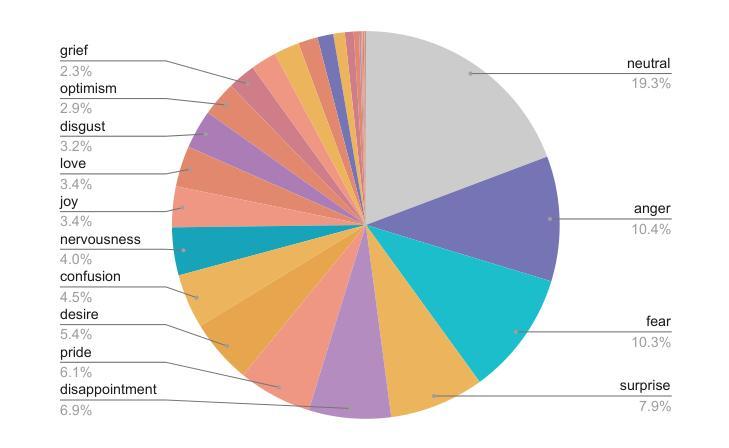
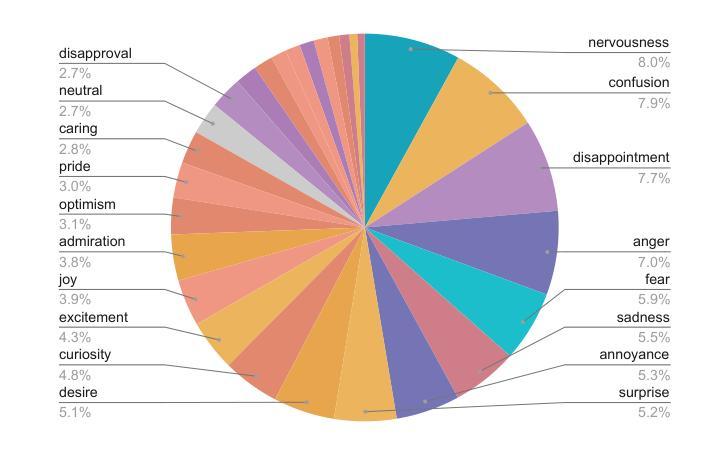
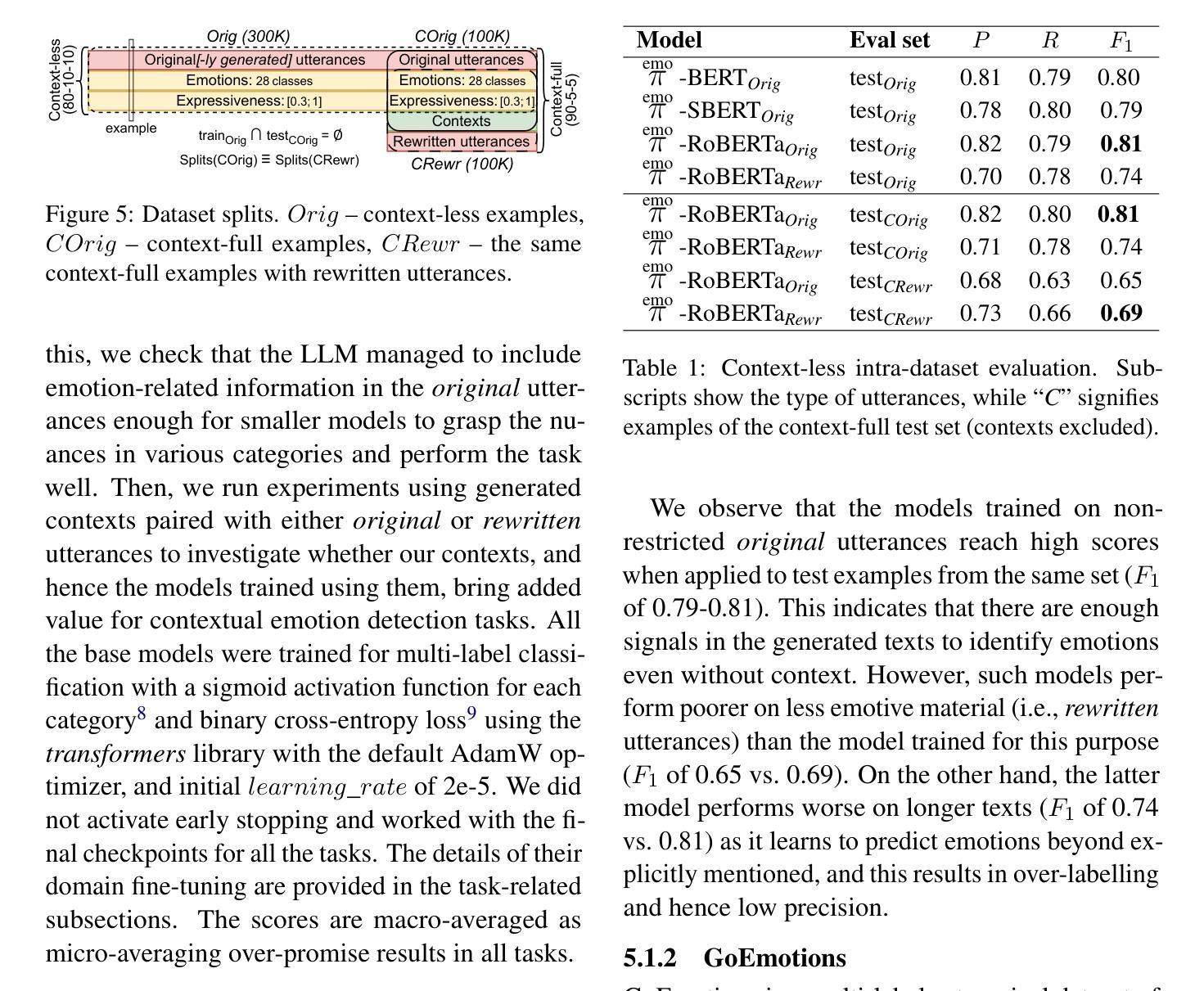
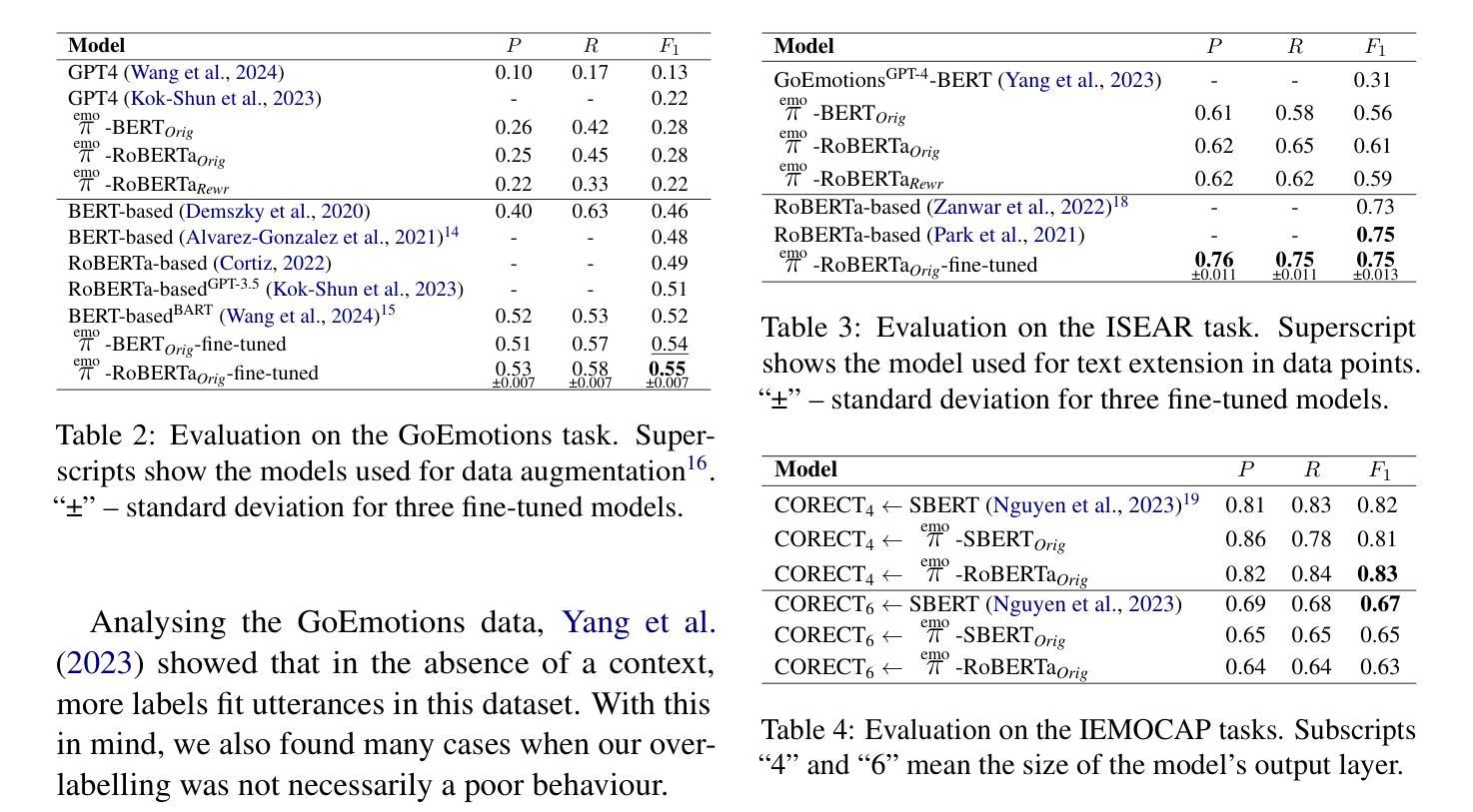
Emo Pillars: Knowledge Distillation to Support Fine-Grained Context-Aware and Context-Less Emotion Classification
Authors:Alexander Shvets
Most datasets for sentiment analysis lack context in which an opinion was expressed, often crucial for emotion understanding, and are mainly limited by a few emotion categories. Foundation large language models (LLMs) like GPT-4 suffer from over-predicting emotions and are too resource-intensive. We design an LLM-based data synthesis pipeline and leverage a large model, Mistral-7b, for the generation of training examples for more accessible, lightweight BERT-type encoder models. We focus on enlarging the semantic diversity of examples and propose grounding the generation into a corpus of narratives to produce non-repetitive story-character-centered utterances with unique contexts over 28 emotion classes. By running 700K inferences in 450 GPU hours, we contribute with the dataset of 100K contextual and also 300K context-less examples to cover both scenarios. We use it for fine-tuning pre-trained encoders, which results in several Emo Pillars models. We show that Emo Pillars models are highly adaptive to new domains when tuned to specific tasks such as GoEmotions, ISEAR, IEMOCAP, and EmoContext, reaching the SOTA performance on the first three. We also validate our dataset, conducting statistical analysis and human evaluation, and confirm the success of our measures in utterance diversification (although less for the neutral class) and context personalization, while pointing out the need for improved handling of out-of-taxonomy labels within the pipeline.
大多数情感分析数据集缺乏表达意见的背景,这对于情绪理解往往至关重要,并且主要受到有限的情绪类别的限制。像GPT-4这样的基础大型语言模型(LLM)存在过度预测情绪和过于资源密集的问题。我们设计了一个基于LLM的数据合成管道,并利用一个大型模型Mistral-7b来生成更容易访问、轻量级的BERT类型编码器模型的训练示例。我们专注于增加示例的语义多样性,并提出将生成根植于叙事语料库中,以产生以故事角色为中心的、具有独特背景的、非重复性的发言,涵盖28个情绪类别。通过运行70万次的推理分析,在45万GPU小时内,我们创建了包含10万条上下文和30万条无上下文示例的数据集,以覆盖这两种场景。我们用它来微调预训练编码器,从而产生了多个Emo Pillars模型。我们表明,当针对特定任务(如GoEmotions、ISEAR、IEMOCAP和EmoContext)进行调整时,Emo Pillars模型非常适应新领域,并在前三个任务上达到了最佳性能。我们还对我们的数据集进行了统计分析和人工评估,验证了我们的措施在发言多样化和背景个性化方面的成功(尽管中性类别的效果较小),同时指出了管道中对超出分类标准的标签处理的需要改进之处。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
本文介绍了针对情感分析数据集缺乏上下文的问题,设计了一个基于大型语言模型(LLM)的数据合成管道,利用Mistral-7b模型生成训练样本,为更易于访问、轻量级的BERT类型编码器模型提供训练数据。该研究通过扩大语义多样性并提出基于叙事语料库的生成方法,创建了包含独特上下文和28个情感类别的数据集。经过对预训练编码器的微调,生成了高度适应新领域任务的Emo Pillars模型,并在GoEmotions、ISEAR、IEMOCAP和EmoContext等任务上达到领先水平。同时,该研究还进行了统计分析和人类评估,验证了数据集的有效性和成功措施的实施情况。
Key Takeaways
- 当前情感分析数据集缺乏上下文,这对于情感理解至关重要。
- 提出基于大型语言模型(LLM)的数据合成管道,解决了现有情感分析数据集的局限性。
- 利用Mistral-7b模型生成训练样本,为BERT类型编码器模型提供数据。
- 强调扩大语义多样性和基于叙事语料库的生成方法的重要性。
- 创建了包含独特上下文和多种情感类别的数据集。
- 通过微调预训练编码器,生成了适应新领域任务的Emo Pillars模型,并在多个任务上达到领先水平。
点此查看论文截图

LRASGen: LLM-based RESTful API Specification Generation
Authors:Sida Deng, Rubing Huang, Man Zhang, Chenhui Cui, Dave Towey, Rongcun Wang
REpresentation State Transfer (REST) is an architectural style for designing web applications that enable scalable, stateless communication between clients and servers via common HTTP techniques. Web APIs that employ the REST style are known as RESTful (or REST) APIs. When using or testing a RESTful API, developers may need to employ its specification, which is often defined by open-source standards such as the OpenAPI Specification (OAS). However, it can be very time-consuming and error-prone to write and update these specifications, which may negatively impact the use of RESTful APIs, especially when the software requirements change. Many tools and methods have been proposed to solve this problem, such as Respector and Swagger Core. OAS generation can be regarded as a common text-generation task that creates a formal description of API endpoints derived from the source code. A potential solution for this may involve using Large Language Models (LLMs), which have strong capabilities in both code understanding and text generation. Motivated by this, we propose a novel approach for generating the OASs of RESTful APIs using LLMs: LLM-based RESTful API-Specification Generation (LRASGen). To the best of our knowledge, this is the first use of LLMs and API source code to generate OASs for RESTful APIs. Compared with existing tools and methods, LRASGen can generate the OASs, even when the implementation is incomplete (with partial code, and/or missing annotations/comments, etc.). To evaluate the LRASGen performance, we conducted a series of empirical studies on 20 real-world RESTful APIs. The results show that two LLMs (GPT-4o mini and DeepSeek V3) can both support LARSGen to generate accurate specifications, and LRASGen-generated specifications cover an average of 48.85% more missed entities than the developer-provided specifications.
REST(Representation State Transfer)是一种用于设计Web应用程序的架构风格,它能够通过常见的HTTP技术实现客户端和服务器之间可伸缩、无状态通信。采用REST风格的Web API被称为RESTful(或REST)API。在使用或测试RESTful API时,开发人员可能需要使用其规范,该规范通常由开放源代码标准(如OpenAPI规范(OAS))所定义。然而,编写和更新这些规范可能会非常耗时且容易出错,这可能会给RESTful API的使用带来负面影响,尤其是在软件需求发生变化时。已经提出了许多工具和方法来解决这个问题,例如Respector和Swagger Core。OAS生成可以看作是一个常见的文本生成任务,它从源代码中创建API端点的正式描述。针对这一问题的一个潜在解决方案是运用大型语言模型(LLM),LLM在代码理解和文本生成方面都具有强大的能力。因此,我们提出了一种基于LLM生成RESTful API的OASs的新方法:基于LLM的RESTful API规范生成(LRASGen)。据我们所知,这是首次使用LLM和API源代码来为RESTful API生成OASs。与现有工具和方法相比,LRASGen能够在实现不完整的情况下生成OAS(包括部分代码、缺少注释/注释等)。为了评估LRASGen的性能,我们对20个真实的RESTful API进行了一系列实证研究。结果表明,两种LLM(GPT-4o mini和DeepSeek V3)都能支持LRASGen生成准确的规范,并且LRASGen生成的规范平均覆盖开发者提供的规范中遗漏实体的48.85%。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
REST(表现层状态转移)是一种用于设计Web应用程序的架构风格,支持客户端和服务器之间通过常见的HTTP技术进行可扩展、无状态通信。当使用或测试RESTful API时,开发者需要遵循开放应用程序接口规范(OpenAPI Specification,简称OAS)。然而,编写和更新这些规范可能会非常耗时且容易出错,这可能会对RESTful API的使用产生负面影响。为解决这一问题,人们提出了多种工具和解决方案。在此背景下,首次尝试利用大型语言模型(LLM)的特性生成RESTful API的OAS。一项提议是采用LLM生成的API规范生成方法(LRASGen),该方法能够从API源代码生成正式的端点描述。通过实证研究表明,使用LLM生成的规范能够覆盖更多被遗漏的实体。
Key Takeaways
- REST是一种Web应用程序架构风格,支持可扩展、无状态通信。
- OpenAPI Specification(OAS)是RESTful API的规范标准。
- 编写和更新OAS可能会非常耗时且容易出错。
- LLM具有代码理解和文本生成能力,可用于解决该问题。
- LRASGen是首次利用LLM和API源代码生成RESTful API的OAS的方法。
- LRASGen能够在API实现不完整的情况下生成OAS。
点此查看论文截图

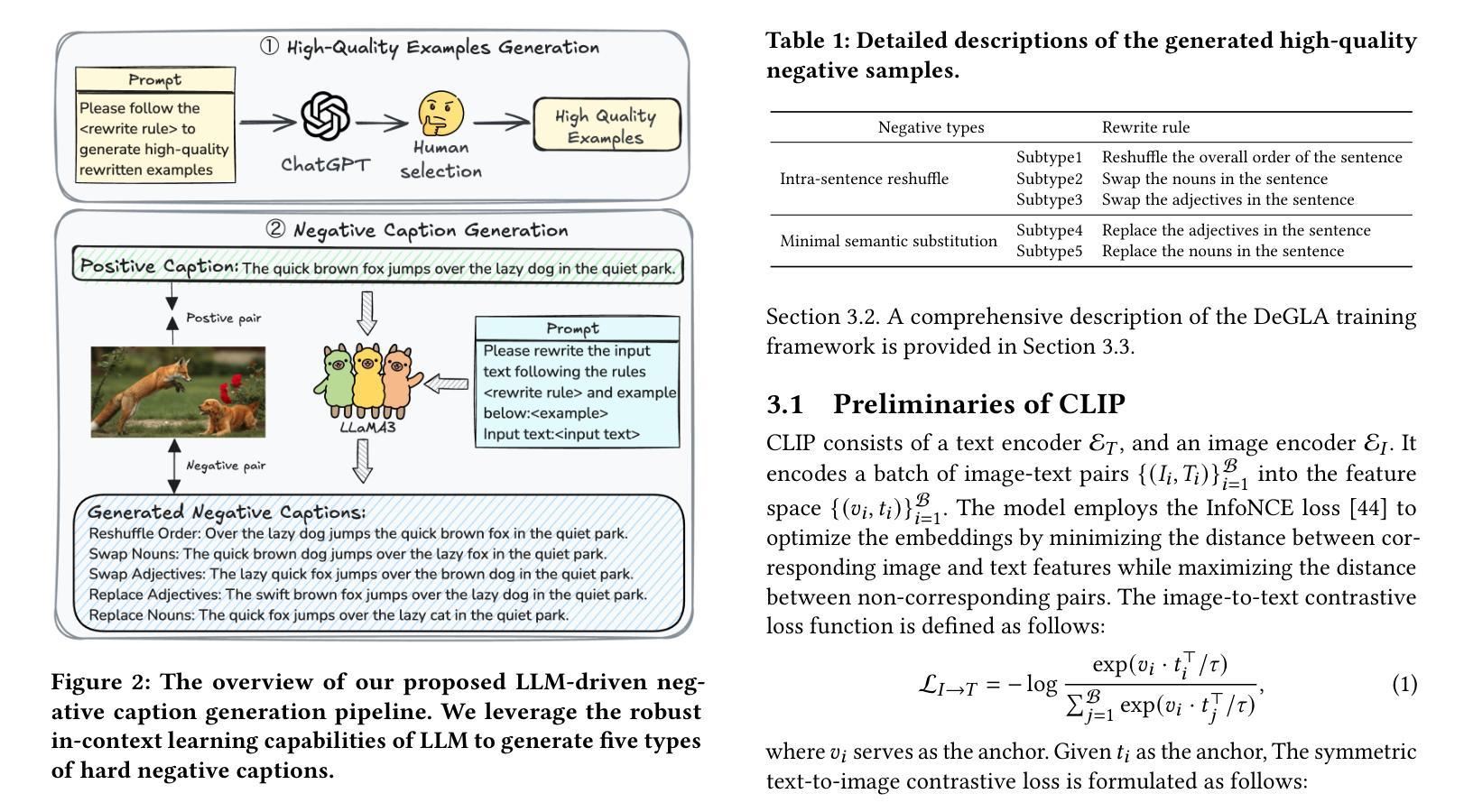
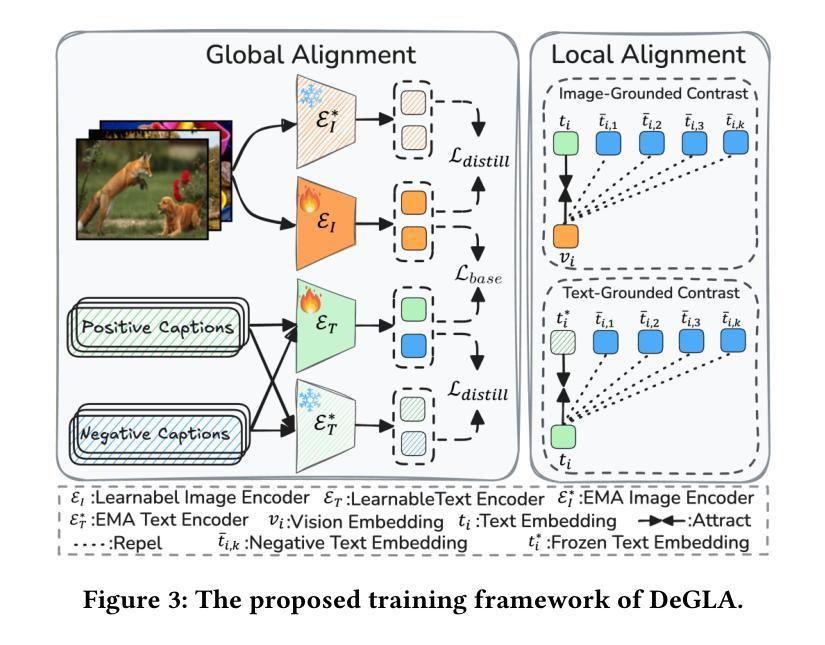
Decoupled Global-Local Alignment for Improving Compositional Understanding
Authors:Xiaoxing Hu, Kaicheng Yang, Jun Wang, Haoran Xu, Ziyong Feng, Yupei Wang
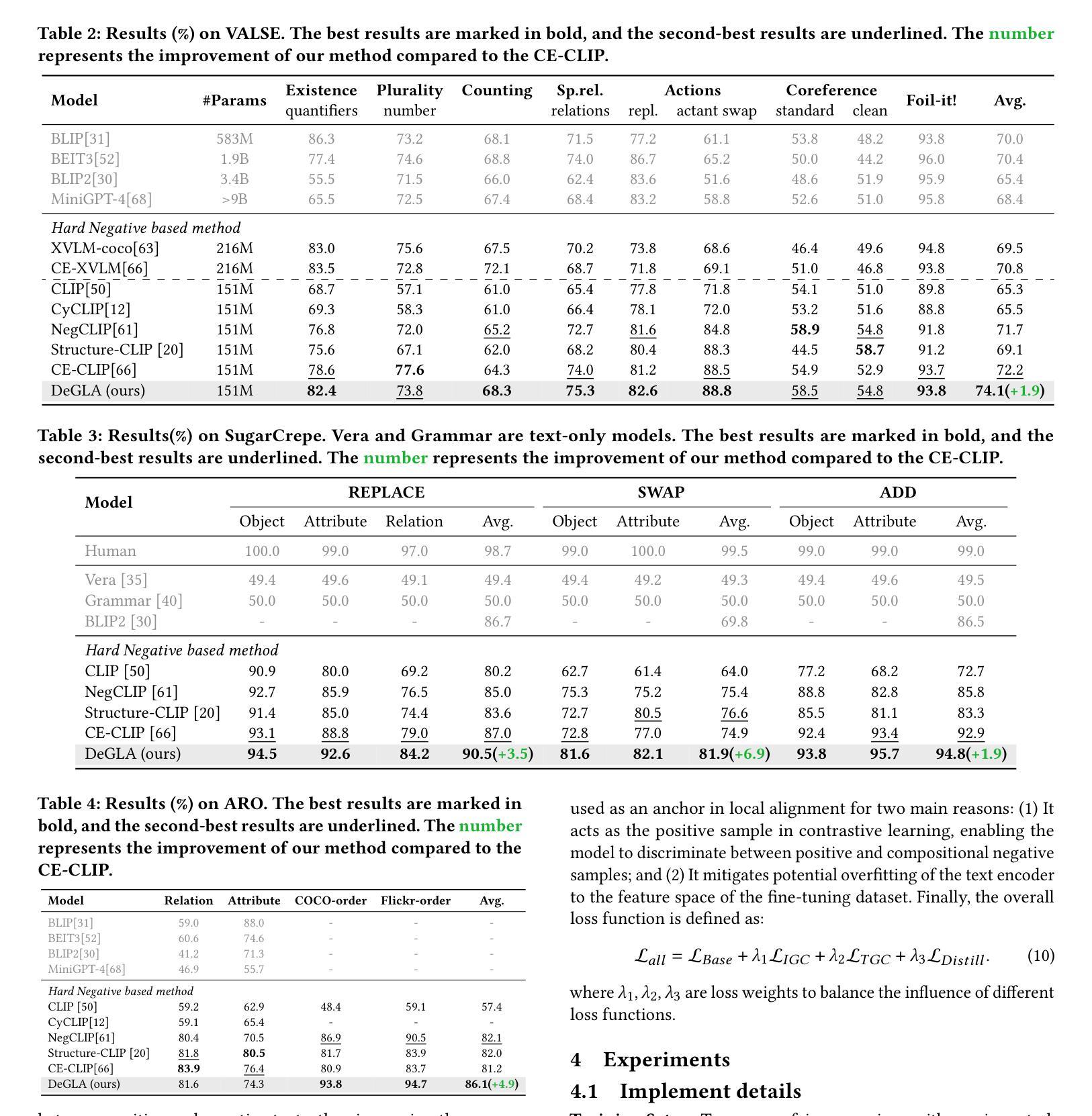
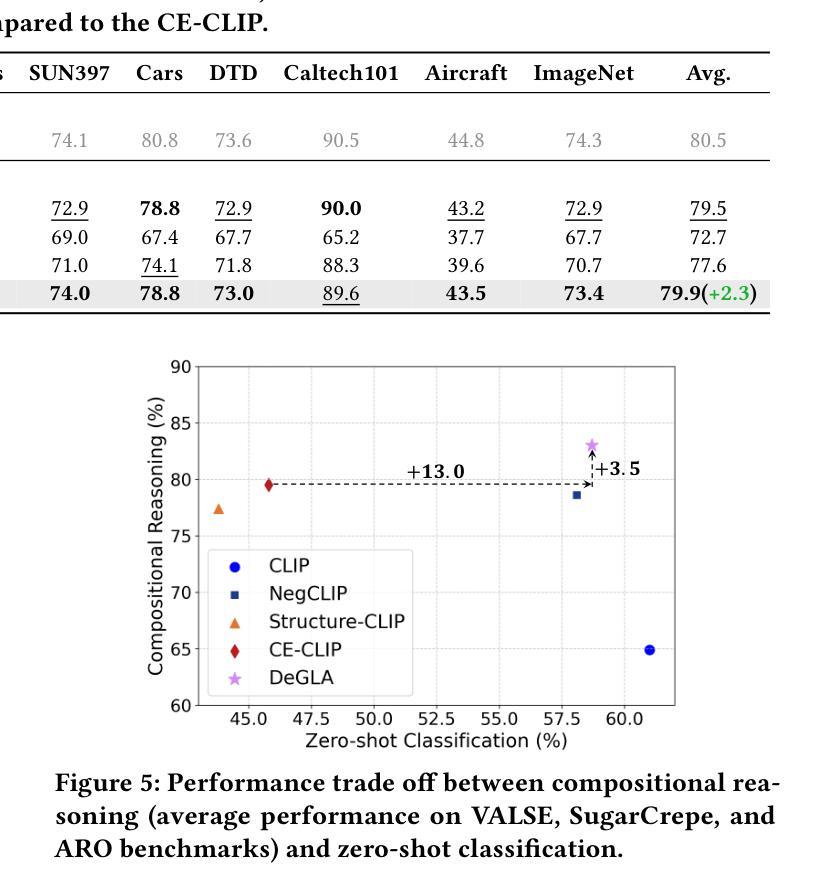
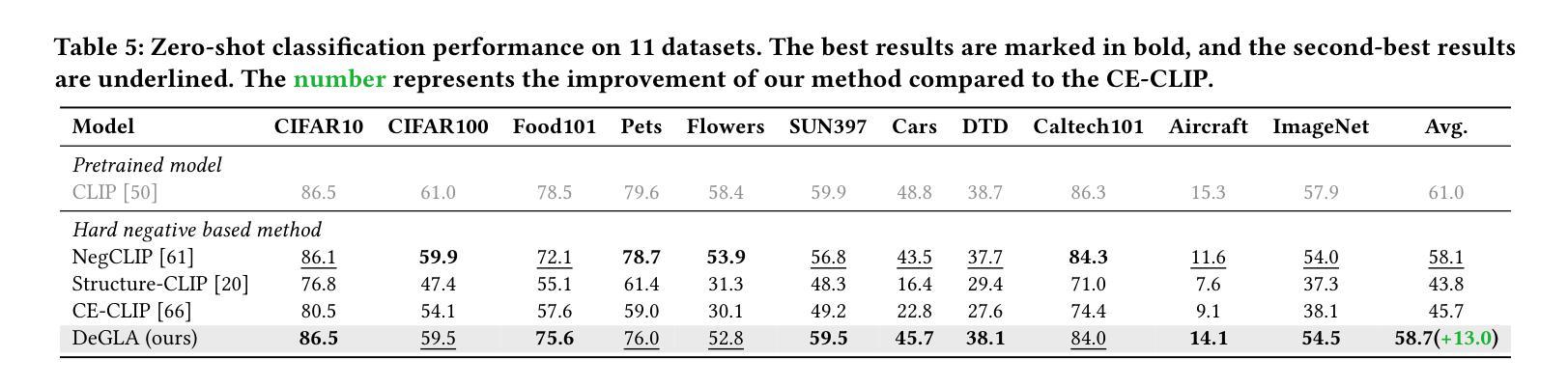
Contrastive Language-Image Pre-training (CLIP) has achieved success on multiple downstream tasks by aligning image and text modalities. However, the nature of global contrastive learning limits CLIP’s ability to comprehend compositional concepts, such as relations and attributes. Although recent studies employ global hard negative samples to improve compositional understanding, these methods significantly compromise the model’s inherent general capabilities by forcibly distancing textual negative samples from images in the embedding space. To overcome this limitation, we introduce a Decoupled Global-Local Alignment (DeGLA) framework that improves compositional understanding while substantially mitigating losses in general capabilities. To optimize the retention of the model’s inherent capabilities, we incorporate a self-distillation mechanism within the global alignment process, aligning the learnable image-text encoder with a frozen teacher model derived from an exponential moving average. Under the constraint of self-distillation, it effectively mitigates the catastrophic forgetting of pretrained knowledge during fine-tuning. To improve compositional understanding, we first leverage the in-context learning capability of Large Language Models (LLMs) to construct about 2M high-quality negative captions across five types. Subsequently, we propose the Image-Grounded Contrast (IGC) loss and Text-Grounded Contrast (TGC) loss to enhance vision-language compositionally. Extensive experimental results demonstrate the effectiveness of the DeGLA framework. Compared to previous state-of-the-art methods, DeGLA achieves an average enhancement of 3.5% across the VALSE, SugarCrepe, and ARO benchmarks. Concurrently, it obtains an average performance improvement of 13.0% on zero-shot classification tasks across eleven datasets. Our code will be released at https://github.com/xiaoxing2001/DeGLA
对比语言图像预训练(CLIP)通过图像和文本模态的对齐,在多个下游任务上取得了成功。然而,全局对比学习的性质限制了CLIP对组合概念(如关系和属性)的理解能力。尽管最近有研究采用全局硬负样本改进组合理解,但这些方法通过强制在嵌入空间中拉开文本负样本与图像的距离,从而极大地削弱了模型固有的通用能力。为了克服这一局限性,我们引入了去耦全局-局部对齐(DeGLA)框架,该框架提高了组合理解能力,同时大大减轻了通用能力的损失。为了优化模型固有能力的保留,我们在全局对齐过程中融入自我蒸馏机制,将可学习的图像文本编码器与基于指数移动平均的冻结教师模型进行对齐。在自我蒸馏的约束下,它有效地减轻了微调过程中预训练知识的灾难性遗忘。为提高组合理解能力,我们首先借助大型语言模型的上下文学习能力,构建约2M种高质量负描述(跨越五种类型)。随后,我们提出图像基础对比(IGC)损失和文本基础对比(TGC)损失,以增强视觉语言的组合能力。大量的实验结果证明了DeGLA框架的有效性。与之前的先进方法相比,DeGLA在VALSE、SugarCrepe和ARO基准测试中平均提高了3.5%的性能。同时,它在11个数据集上的零样本分类任务中平均性能提高了13.0%。我们的代码将在https://github.com/xiaoxing2001/DeGLA上发布。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary:
DeGLA框架通过引入解耦全局局部对齐技术,克服了CLIP模型在处理组合概念时的局限性,同时减少了模型通用能力的损失。该框架通过自我蒸馏机制优化全局对齐过程,并利用大型语言模型的上下文学习能力构建高质量负样本。此外,它还提出了图像基础对比(IGC)损失和文字基础对比(TGC)损失,以加强视觉语言的组合理解。实验结果表明,DeGLA框架在多个基准测试中取得了显著成效。
Key Takeaways:
- DeGLA框架解决了CLIP在处理组合概念上的局限性,如关系和属性。
- 通过解耦全局局部对齐技术,DeGLA提高了模型的组合理解能力。
- 自我蒸馏机制用于优化全局对齐过程,同时保留模型的固有通用能力。
- 利用大型语言模型的上下文学习能力构建高质量负样本,以提高模型性能。
- 提出了图像基础对比(IGC)损失和文字基础对比(TGC)损失,以增强视觉语言的组合理解。
- DeGLA框架在多个基准测试中表现优异,平均提高了3.5%的性能。
点此查看论文截图

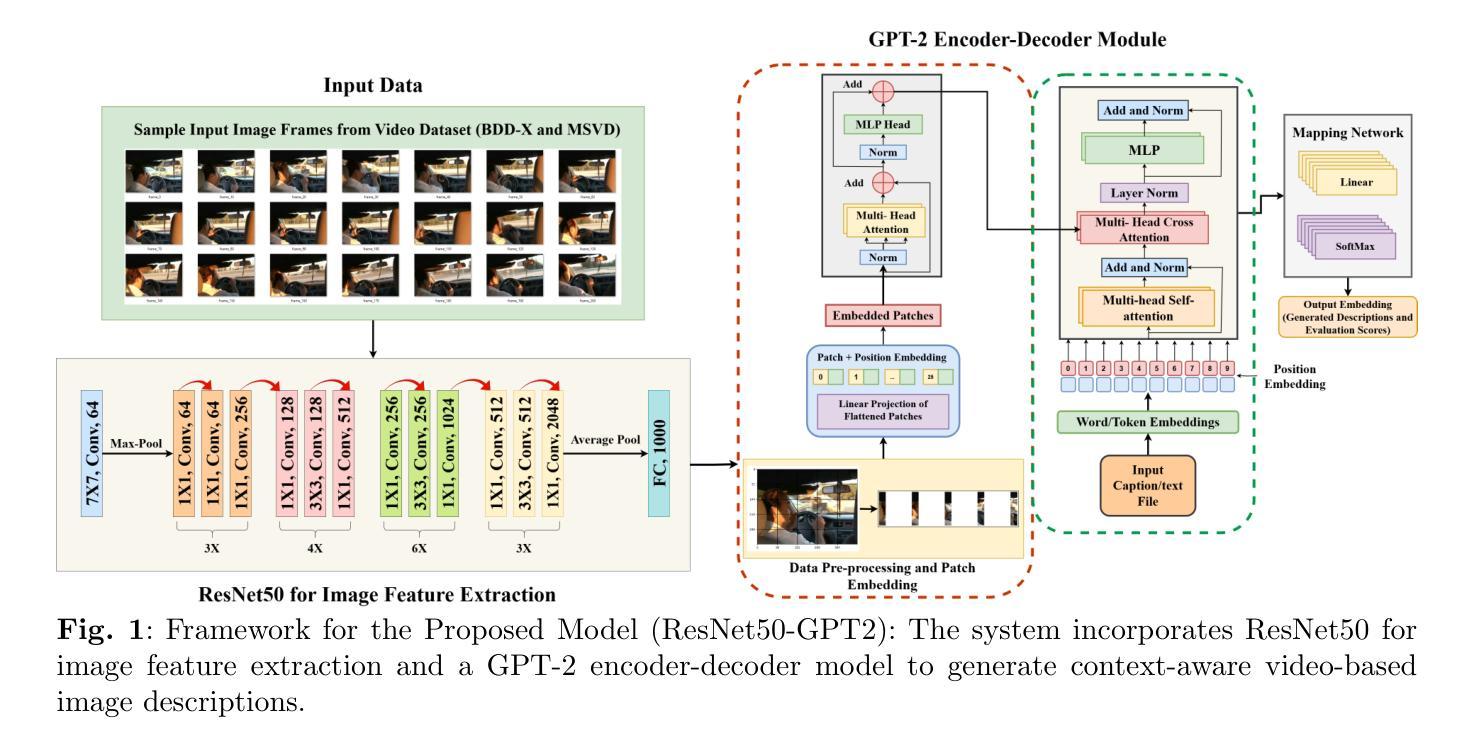
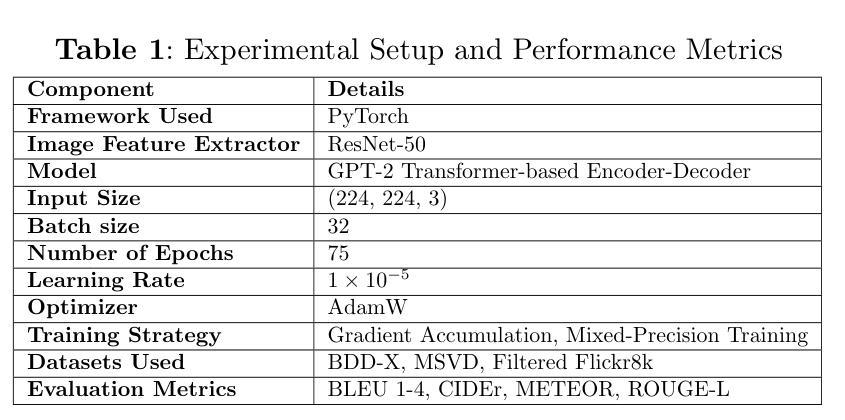
Towards Explainable AI: Multi-Modal Transformer for Video-based Image Description Generation
Authors:Lakshita Agarwal, Bindu Verma
Understanding and analyzing video actions are essential for producing insightful and contextualized descriptions, especially for video-based applications like intelligent monitoring and autonomous systems. The proposed work introduces a novel framework for generating natural language descriptions from video datasets by combining textual and visual modalities. The suggested architecture makes use of ResNet50 to extract visual features from video frames that are taken from the Microsoft Research Video Description Corpus (MSVD), and Berkeley DeepDrive eXplanation (BDD-X) datasets. The extracted visual characteristics are converted into patch embeddings and then run through an encoder-decoder model based on Generative Pre-trained Transformer-2 (GPT-2). In order to align textual and visual representations and guarantee high-quality description production, the system uses multi-head self-attention and cross-attention techniques. The model’s efficacy is demonstrated by performance evaluation using BLEU (1-4), CIDEr, METEOR, and ROUGE-L. The suggested framework outperforms traditional methods with BLEU-4 scores of 0.755 (BDD-X) and 0.778 (MSVD), CIDEr scores of 1.235 (BDD-X) and 1.315 (MSVD), METEOR scores of 0.312 (BDD-X) and 0.329 (MSVD), and ROUGE-L scores of 0.782 (BDD-X) and 0.795 (MSVD). By producing human-like, contextually relevant descriptions, strengthening interpretability, and improving real-world applications, this research advances explainable AI.
理解和分析视频动作对于生成有洞察力和情境化的描述至关重要,尤其对于基于视频的应用,如智能监控和自主系统。所提出的工作引入了一个新颖框架,通过结合文本和视觉模态来从视频数据集中生成自然语言描述。建议的架构利用ResNet50从微软研究视频描述语料库(MSVD)和Berkeley DeepDrive eXplanation(BDD-X)数据集中提取视频帧的视觉特征。提取的视觉特征被转换为补丁嵌入,然后通过基于生成预训练转换器-2(GPT-2)的编码器-解码器模型进行处理。为了对齐文本和视觉表示并确保高质量描述的产生,系统使用了多头自注意力和交叉注意力技术。该模型的效能通过BLEU(1-4)、CIDEr、METEOR和ROUGE-L的性能评估来证明。建议的框架在BLEU分数上优于传统方法,其中BDD-X的BLEU-4分数为0.755,MSVD的BLEU-4分数为0.778;在CIDEr分数上,BDD-X的CIDEr分数为1.235,MSVD的CIDEr分数为1.315;在METEOR分数上,BDD-X的METEOR分数为0.312,MSVD的METEOR分数为0.329;在ROUGE-L分数上,BDD-X的ROUGE-L分数为0.782,MSVD的ROUGE-L分数为0.795。该研究通过生成人类般的、上下文相关的描述,加强了解释性,并改进了现实世界的应用,从而推动了可解释人工智能的发展。
论文及项目相关链接
摘要
本文提出一种结合文本和视觉模态,从视频数据集中生成自然语言描述的新框架。该框架利用ResNet50从微软研究视频描述语料库(MSVD)和Berkeley DeepDrive eXplanation(BDD-X)数据集中提取视频帧的视觉特征,将提取的视觉特征转换为补丁嵌入,然后通过基于生成预训练Transformer-2(GPT-2)的编码器-解码器模型进行处理。该系统采用多头自注意力和交叉注意力技术,以实现文本和视觉表示的对齐,保证高质量描述的产生。该框架的有效性通过BLEU(1-4)、CIDEr、METEOR和ROUGE-L等评估指标进行展示,与传统方法相比,其在BDD-X和MSVD数据集上的表现均有所超越。该研究为人工智能的可解释性带来了进步,能够产生人类般的、上下文相关的描述,并改善现实世界的应用。
关键见解
- 引入了一种新框架,可以从视频数据集中生成自然语言描述。
- 利用ResNet50从视频帧中提取视觉特征。
- 采用GPT-2为基础的的编码器-解码器模型来处理视觉特征和生成文本描述。
- 使用多头自注意力和交叉注意力技术实现文本和视觉表示的对齐。
- 在BDD-X和MSVD数据集上展示了框架的有效性,超越了传统方法。
- 产生的描述具有人类般的、上下文相关性,增强了人工智能的可解释性。
- 有助于改善现实世界的视频应用,如智能监控和自主系统。
点此查看论文截图

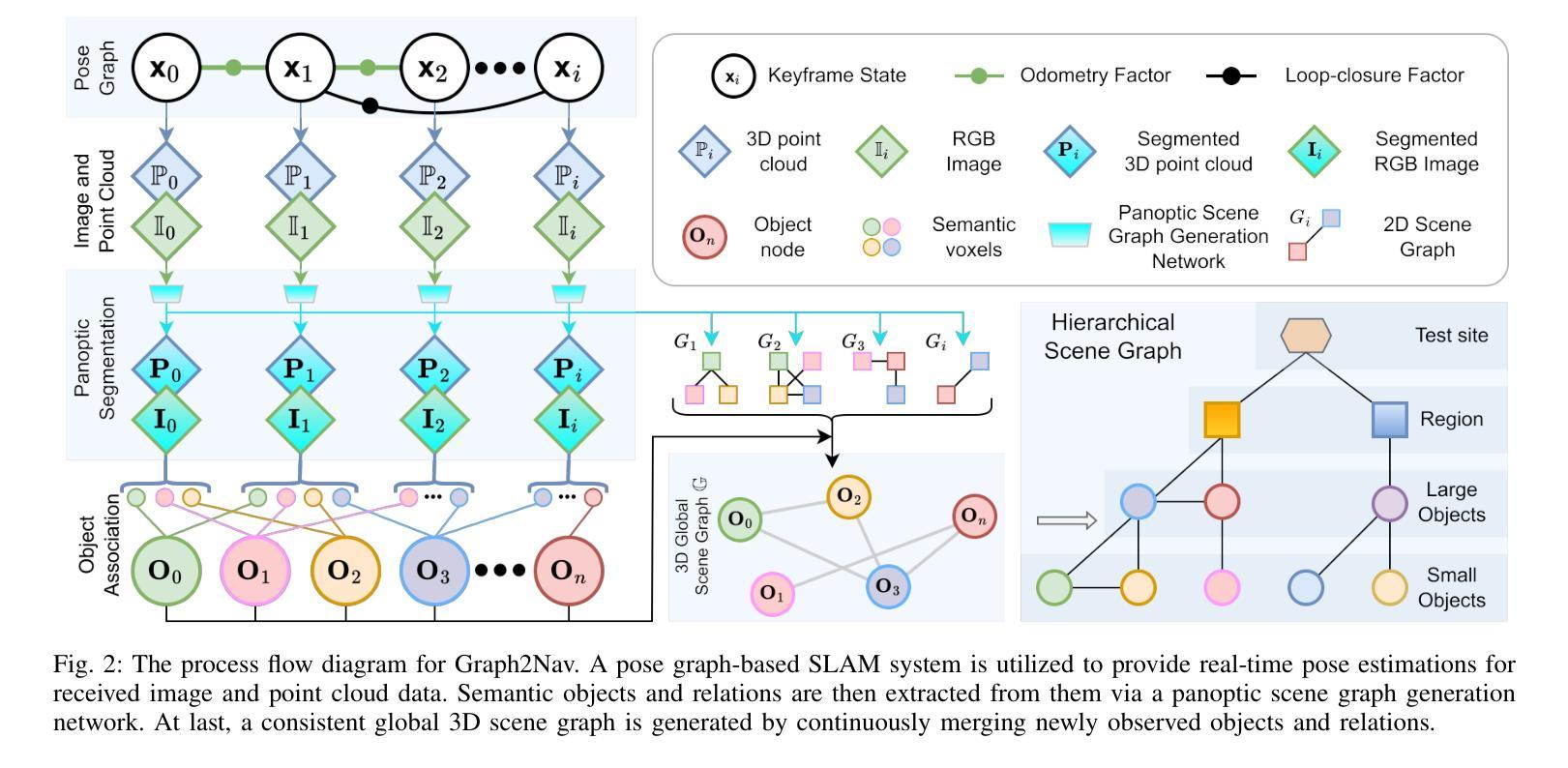
Graph2Nav: 3D Object-Relation Graph Generation to Robot Navigation
Authors:Tixiao Shan, Abhinav Rajvanshi, Niluthpol Mithun, Han-Pang Chiu
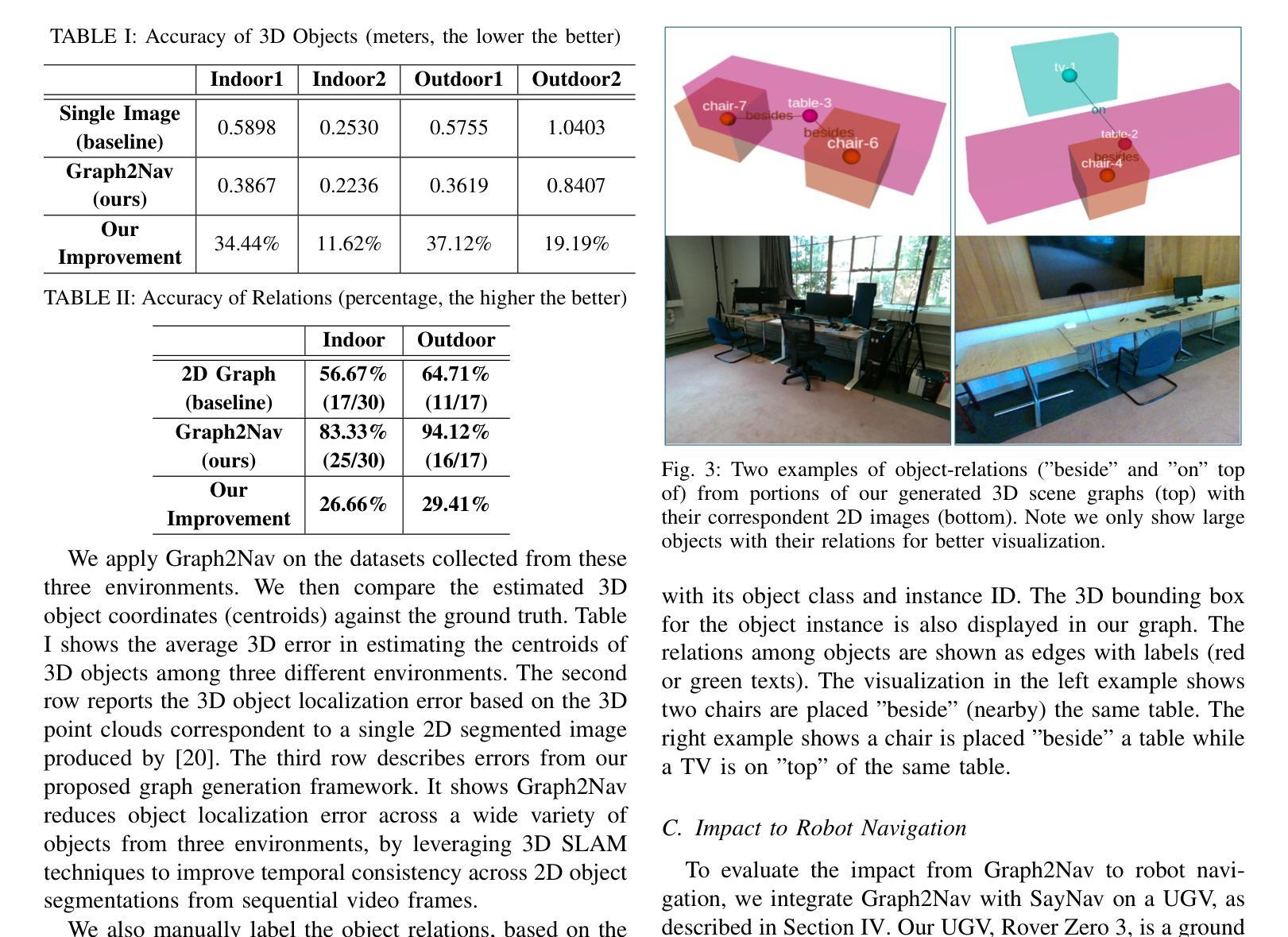
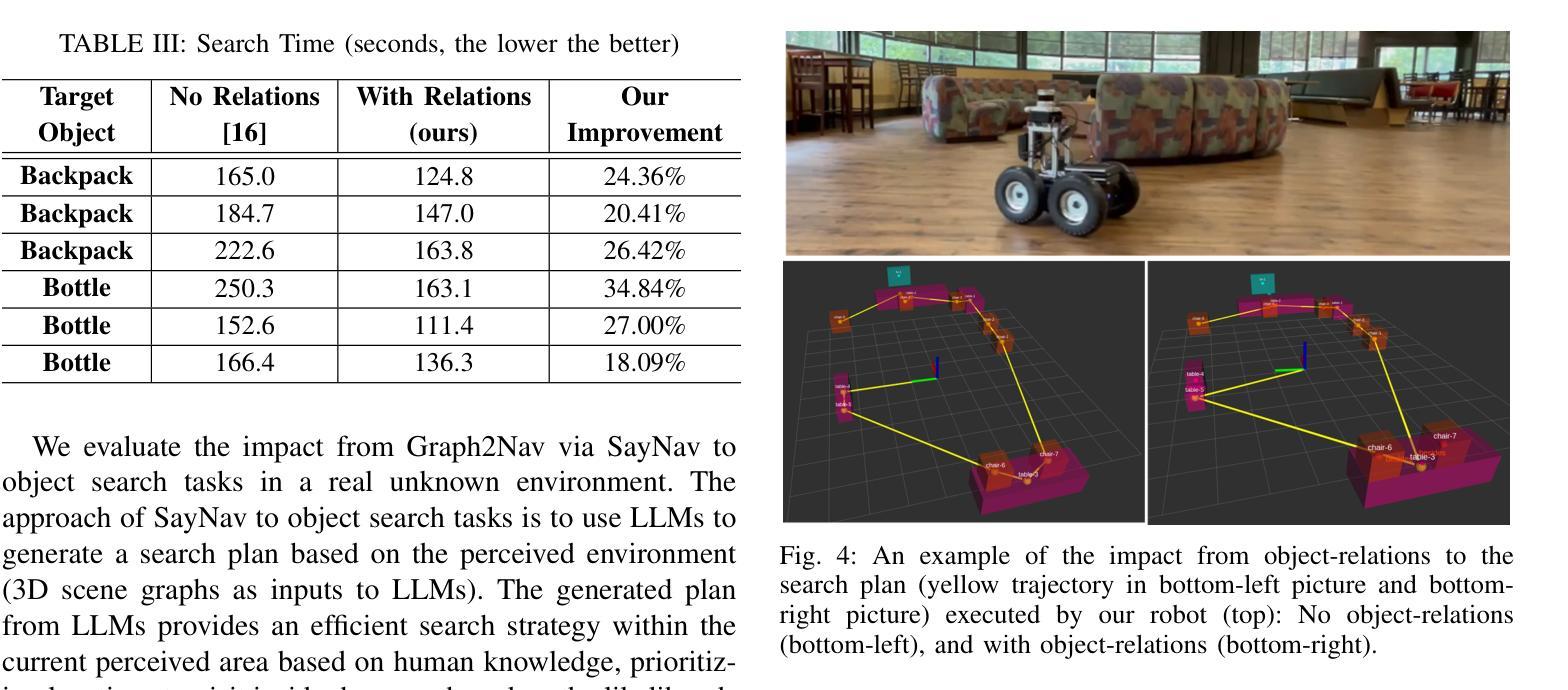
We propose Graph2Nav, a real-time 3D object-relation graph generation framework, for autonomous navigation in the real world. Our framework fully generates and exploits both 3D objects and a rich set of semantic relationships among objects in a 3D layered scene graph, which is applicable to both indoor and outdoor scenes. It learns to generate 3D semantic relations among objects, by leveraging and advancing state-of-the-art 2D panoptic scene graph works into the 3D world via 3D semantic mapping techniques. This approach avoids previous training data constraints in learning 3D scene graphs directly from 3D data. We conduct experiments to validate the accuracy in locating 3D objects and labeling object-relations in our 3D scene graphs. We also evaluate the impact of Graph2Nav via integration with SayNav, a state-of-the-art planner based on large language models, on an unmanned ground robot to object search tasks in real environments. Our results demonstrate that modeling object relations in our scene graphs improves search efficiency in these navigation tasks.
我们提出Graph2Nav,这是一个实时3D对象关系图生成框架,用于现实世界的自主导航。我们的框架全面生成并利用3D对象以及3D分层场景图中对象之间丰富的语义关系。该框架适用于室内和室外场景。它通过利用最先进的2D全景场景图工作,借助3D语义映射技术将其扩展到3D世界,学习生成对象之间的3D语义关系。这种方法避免了之前直接从3D数据学习3D场景图时的训练数据约束。我们进行了实验,验证了在我们3D场景图中定位3D对象和标注对象关系的准确性。我们还通过将与SayNav(基于大型语言模型的最新规划器)集成,在无人员地面机器人上进行实际环境中的对象搜索任务,以评估Graph2Nav的影响。结果表明,在我们的场景图中建模对象关系可以提高这些导航任务的搜索效率。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
新一代导航技术Graph2Nav,通过实时生成3D物体关系图实现室内外自主导航。该技术通过利用先进的二维全景场景图技术,借助三维语义映射技术生成三维语义关系图,避免直接从三维数据中学习三维场景图的训练数据限制。实验证明其在定位三维物体和标注物体关系上的准确性,并结合SayNav技术,提高无人地面机器人在真实环境中的搜索效率。
Key Takeaways
- Graph2Nav是一个实时3D物体关系图生成框架,用于室内外自主导航。
- 该技术结合了先进的二维全景场景图技术和三维语义映射技术,生成三维语义关系图。
- 避免直接从三维数据中学习三维场景图的训练数据限制。
- 实验证明Graph2Nav在定位三维物体和标注物体关系上的准确性。
- Graph2Nav与SayNav技术结合,提高了无人地面机器人在真实环境中的搜索效率。
- 建模物体关系在导航任务中的重要性。
点此查看论文截图

How Effective are Generative Large Language Models in Performing Requirements Classification?
Authors:Waad Alhoshan, Alessio Ferrari, Liping Zhao
In recent years, transformer-based large language models (LLMs) have revolutionised natural language processing (NLP), with generative models opening new possibilities for tasks that require context-aware text generation. Requirements engineering (RE) has also seen a surge in the experimentation of LLMs for different tasks, including trace-link detection, regulatory compliance, and others. Requirements classification is a common task in RE. While non-generative LLMs like BERT have been successfully applied to this task, there has been limited exploration of generative LLMs. This gap raises an important question: how well can generative LLMs, which produce context-aware outputs, perform in requirements classification? In this study, we explore the effectiveness of three generative LLMs-Bloom, Gemma, and Llama-in performing both binary and multi-class requirements classification. We design an extensive experimental study involving over 400 experiments across three widely used datasets (PROMISE NFR, Functional-Quality, and SecReq). Our study concludes that while factors like prompt design and LLM architecture are universally important, others-such as dataset variations-have a more situational impact, depending on the complexity of the classification task. This insight can guide future model development and deployment strategies, focusing on optimising prompt structures and aligning model architectures with task-specific needs for improved performance.
近年来,基于Transformer的大型语言模型(LLM)已经彻底改变了自然语言处理(NLP)的格局,生成模型为需要上下文感知文本生成的任务带来了新的可能性。需求工程(RE)领域在LLM的不同任务实验中也出现了激增,包括跟踪链接检测、法规合规性等任务。需求分类是RE中的常见任务。虽然像BERT这样的非生成性LLM已经成功应用于此任务,但对生成性LLM的探索仍然有限。这一差距引发了一个重要问题:能够产生上下文感知输出的生成性LLM在需求分类中的表现如何?在这项研究中,我们探索了三种生成性LLM——Bloom、Gemma和Llama在二元和多元需求分类中的有效性。我们设计了一项广泛的实验研究,涉及三个广泛使用的数据集(PROMISE NFR、Functional-Quality和SecReq)的400多个实验。我们的研究表明,虽然提示设计和LLM架构等因素具有普遍重要性,但其他因素,如数据集变化,对分类任务的复杂性具有更情境化的影响。这一见解可以为未来的模型开发和部署策略提供指导,侧重于优化提示结构,并根据特定任务需求调整模型架构以提高性能。
论文及项目相关链接
摘要
近年来,基于Transformer的大型语言模型(LLM)在自然语言处理(NLP)领域掀起了一场革命,生成式模型为需要上下文感知的文本生成任务带来了新的可能性。在需求工程(RE)领域,LLM的应用实验也层出不穷,包括跟踪链接检测、法规合规等任务。需求分类是RE中的常见任务。虽然非生成式LLM,如BERT,已被成功应用于此任务,但对生成式LLM的探索却有限。本文探索了三种生成式LLM——Bloom、Gemma和Llama在二元和多元需求分类中的表现。我们设计了一项广泛的实验研究,涉及三个常用数据集(PROMISE NFR、Functional-Quality和SecReq)的400多次实验。研究发现,虽然提示设计和LLM架构等因素具有普遍重要性,但数据集变化等因素的影响更具情境性,取决于分类任务的复杂性。这一见解可以为未来的模型开发和部署策略提供指导,重点优化提示结构,并根据任务需求调整模型架构,以提高性能。
关键见解
- 变压器为基础的大型语言模型(LLM)在自然语言处理(NLP)领域有重大突破,生成式模型尤其在需要上下文感知的文本生成任务中表现优异。
- 要求工程(RE)已开始广泛实验LLM在各种任务中的应用,包括需求分类。
- 虽然非生成式LLM已被成功应用于需求分类任务,但对生成式LLM在此方面的探索仍有限。
- 本研究探索了三种生成式LLM(Bloom、Gemma和Llama)在二元和多元需求分类中的表现。
- 实验研究表明,提示设计和LLM架构对模型性能有普遍影响。
- 数据集变化对分类任务性能的影响具有情境性。
点此查看论文截图

Lightweight Latent Verifiers for Efficient Meta-Generation Strategies
Authors:Bartosz Piotrowski, Witold Drzewakowski, Konrad Staniszewski, Piotr Miłoś
Verifiers are auxiliary models that assess the correctness of outputs generated by base large language models (LLMs). They play a crucial role in many strategies for solving reasoning-intensive problems with LLMs. Typically, verifiers are LLMs themselves, often as large (or larger) than the base model they support, making them computationally expensive. In this work, we introduce a novel lightweight verification approach, LiLaVe, which reliably extracts correctness signals from the hidden states of the base LLM. A key advantage of LiLaVe is its ability to operate with only a small fraction of the computational budget required by traditional LLM-based verifiers. To demonstrate its practicality, we couple LiLaVe with popular meta-generation strategies, like best-of-n or self-consistency. Moreover, we design novel LiLaVe-based approaches, like conditional self-correction or conditional majority voting, that significantly improve both accuracy and efficiency in generation tasks with smaller LLMs. Our work demonstrates the fruitfulness of extracting latent information from the hidden states of LLMs, and opens the door to scalable and resource-efficient solutions for reasoning-intensive applications.
验证器是辅助模型,用于评估基础大型语言模型(LLM)生成的输出的正确性。在LLM解决推理密集型问题的多种策略中,它们扮演着至关重要的角色。通常,验证器本身就是LLM,通常与其支持的基础模型大小相同(或更大),使其在计算上成本高昂。在这项工作中,我们介绍了一种新型轻量级验证方法LiLaVe,它可以从基础LLM的隐藏状态中可靠地提取正确性信号。LiLaVe的主要优点是其仅需传统LLM验证器所需计算预算的一小部分即可运行。为了证明其实用性,我们将LiLaVe与流行的元生成策略(如n选最佳或自我一致性)相结合。此外,我们设计了基于LiLaVe的新方法,如条件自我校正或条件多数投票,这些方法在小型LLM的生成任务中显著提高了准确性和效率。我们的工作展示了从LLM的隐藏状态中提取潜在信息的有效性,并为推理密集型应用打开了可扩展和资源高效解决方案的大门。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
本文介绍了一种新型的轻量级验证方法LiLaVe,该方法可从基础大型语言模型(LLM)的隐藏状态中提取正确性信号,用于验证LLM生成的输出。LiLaVe具有显著的计算效率优势,只需传统LLM验证器所需计算预算的一小部分即可运行。此外,LiLaVe与流行的元生成策略相结合,如最佳n或自我一致性等,以提高生成任务的准确性和效率。本研究证明了从LLM的隐藏状态中挖掘潜在信息的有效性,并为资源密集型应用打开了可扩展且高效的解决方案之门。
Key Takeaways
- LiLaVe是一种新型的轻量级验证方法,能够从LLM的隐藏状态中提取正确性信号。
- LiLaVe具有显著的计算效率优势,可以减少对传统LLM验证器的计算需求。
- LiLaVe可以与流行的元生成策略结合,如最佳n和自我一致性等,以提高生成任务的准确性。
- 新型LiLaVe方法如条件自我校正和条件多数投票等,可以显著提高生成任务的效率和准确性。
- 本研究证明了从LLM隐藏状态中挖掘潜在信息的有效性。
- LiLaVe为可扩展性和资源效率提供了解决方案,特别是在推理密集型应用中。
点此查看论文截图

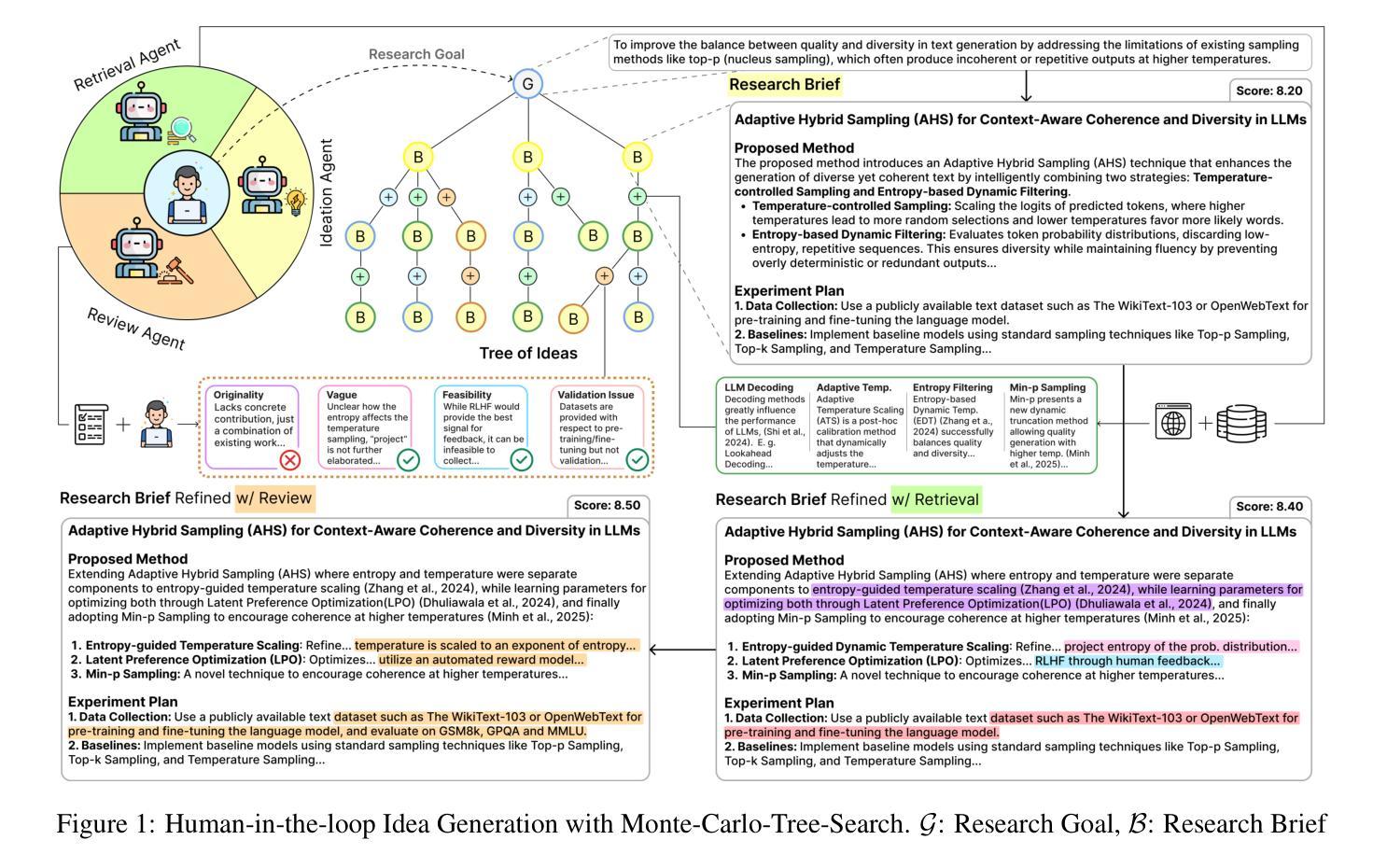
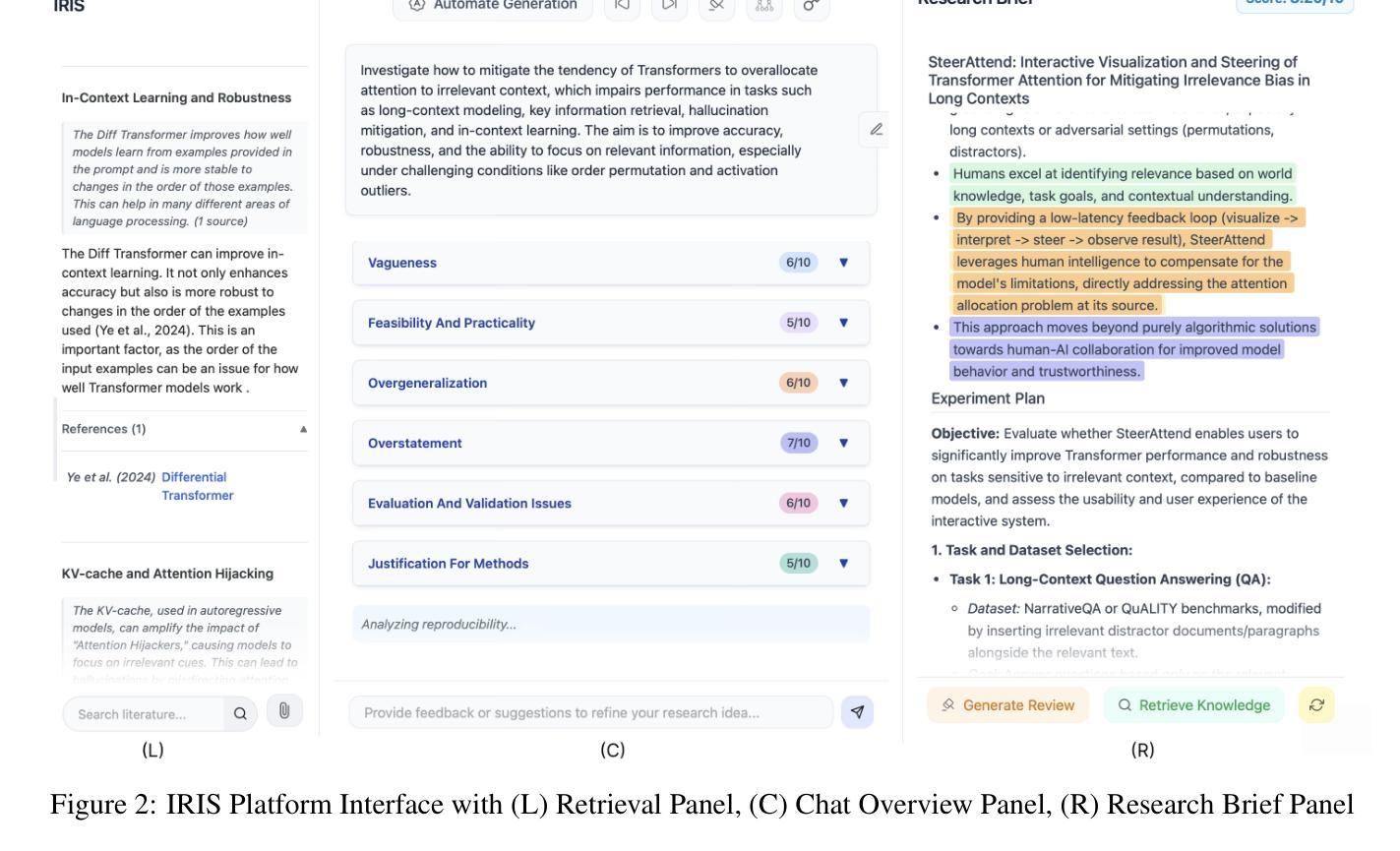
IRIS: Interactive Research Ideation System for Accelerating Scientific Discovery
Authors:Aniketh Garikaparthi, Manasi Patwardhan, Lovekesh Vig, Arman Cohan
The rapid advancement in capabilities of large language models (LLMs) raises a pivotal question: How can LLMs accelerate scientific discovery? This work tackles the crucial first stage of research, generating novel hypotheses. While recent work on automated hypothesis generation focuses on multi-agent frameworks and extending test-time compute, none of the approaches effectively incorporate transparency and steerability through a synergistic Human-in-the-loop (HITL) approach. To address this gap, we introduce IRIS: Interactive Research Ideation System, an open-source platform designed for researchers to leverage LLM-assisted scientific ideation. IRIS incorporates innovative features to enhance ideation, including adaptive test-time compute expansion via Monte Carlo Tree Search (MCTS), fine-grained feedback mechanism, and query-based literature synthesis. Designed to empower researchers with greater control and insight throughout the ideation process. We additionally conduct a user study with researchers across diverse disciplines, validating the effectiveness of our system in enhancing ideation. We open-source our code at https://github.com/Anikethh/IRIS-Interactive-Research-Ideation-System
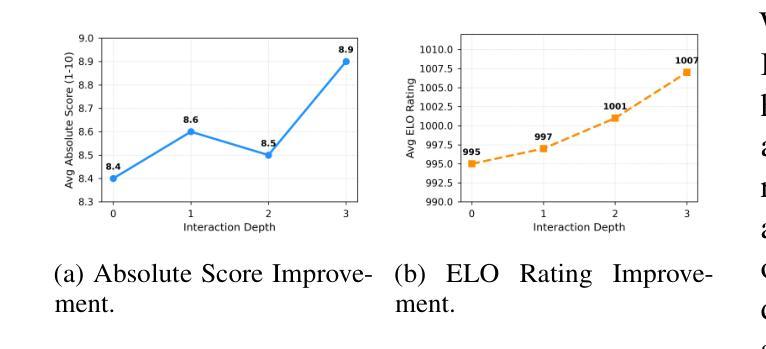
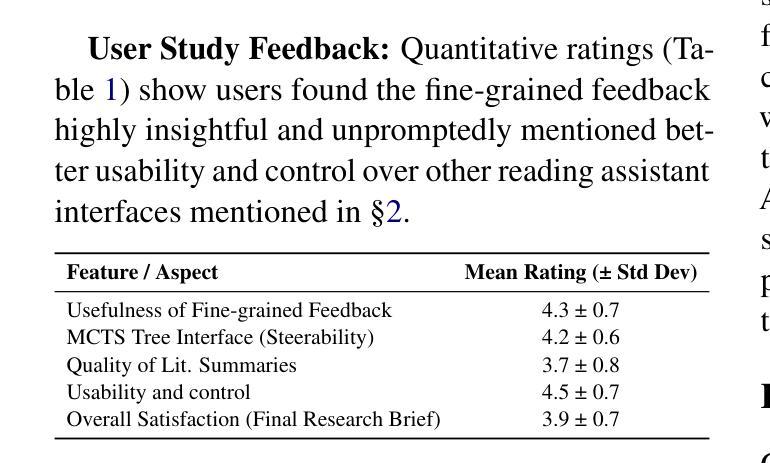
大型语言模型(LLM)能力的快速发展引发了一个关键问题:LLM如何加速科学发现?这项工作解决了研究的关键第一阶段,即产生新假设。虽然最近在自动假设生成方面的工作主要集中在多代理框架和扩展测试时间计算上,但没有一个方法能有效地通过协同人机交互(HITL)方法纳入透明度和可控制性来解决这个问题。为了解决这一差距,我们推出了IRIS:交互式研究创意系统,这是一个开源平台,旨在让研究人员利用LLM辅助科学创意。IRIS结合了创新功能来增强创意,包括通过蒙特卡洛树搜索(MCTS)的自适应测试时间计算扩展、精细的反馈机制和基于查询的文献综述。设计此系统旨在赋予研究人员在整个创意过程中更大的控制和洞察力。我们还与不同学科的研究人员进行了用户研究,验证了我们的系统在增强创意方面的有效性。我们已在https://github.com/Anikethh/IRIS-Interactive-Research-Ideation-System上公开了我们的代码。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF 6 pages main-text, 2 pages appendix
Summary
大型语言模型(LLM)的快速发展引发了一个关键问题:如何加速科学发现。本研究解决了研究的关键第一阶段,即生成新假设。尽管近期自动化假设生成的研究聚焦于多智能体框架和扩展测试时间计算,但没有任何方法能有效结合透明度和可操控性通过人机协同循环方法实现。为解决此问题,我们推出了IRIS系统,一个设计用于研究人员利用LLM辅助科学构思的开源平台。IRIS结合了创新功能以增强构思能力,包括自适应测试时间计算扩展的蒙特卡洛树搜索方法、精细反馈机制和基于查询的文献综述等。我们致力于赋予研究人员在构思过程中更大的控制和洞察力。此外,我们对不同学科的学者进行了用户研究,验证了我们的系统在增强构思方面的有效性。我们已在GitHub上公开代码:https://github.com/Anikethh/IRIS-Interactive-Research-Ideation-System。
Key Takeaways
- 大型语言模型(LLM)加速科学发现的关键在于如何生成新假设。
- 目前的方法缺乏透明度和可操控性,本研究通过人机协同循环方法解决此问题。
- IRIS系统是一个开源平台,设计用于研究人员利用LLM辅助科学构思。
- IRIS结合了多种创新功能以增强构思能力,如蒙特卡洛树搜索方法、精细反馈机制和基于查询的文献综述等。
- 用户研究验证了IRIS系统在增强构思方面的有效性。
点此查看论文截图

Can Large Language Models Help Multimodal Language Analysis? MMLA: A Comprehensive Benchmark
Authors:Hanlei Zhang, Zhuohang Li, Yeshuang Zhu, Hua Xu, Peiwu Wang, Jinchao Zhang, Jie Zhou, Haige Zhu
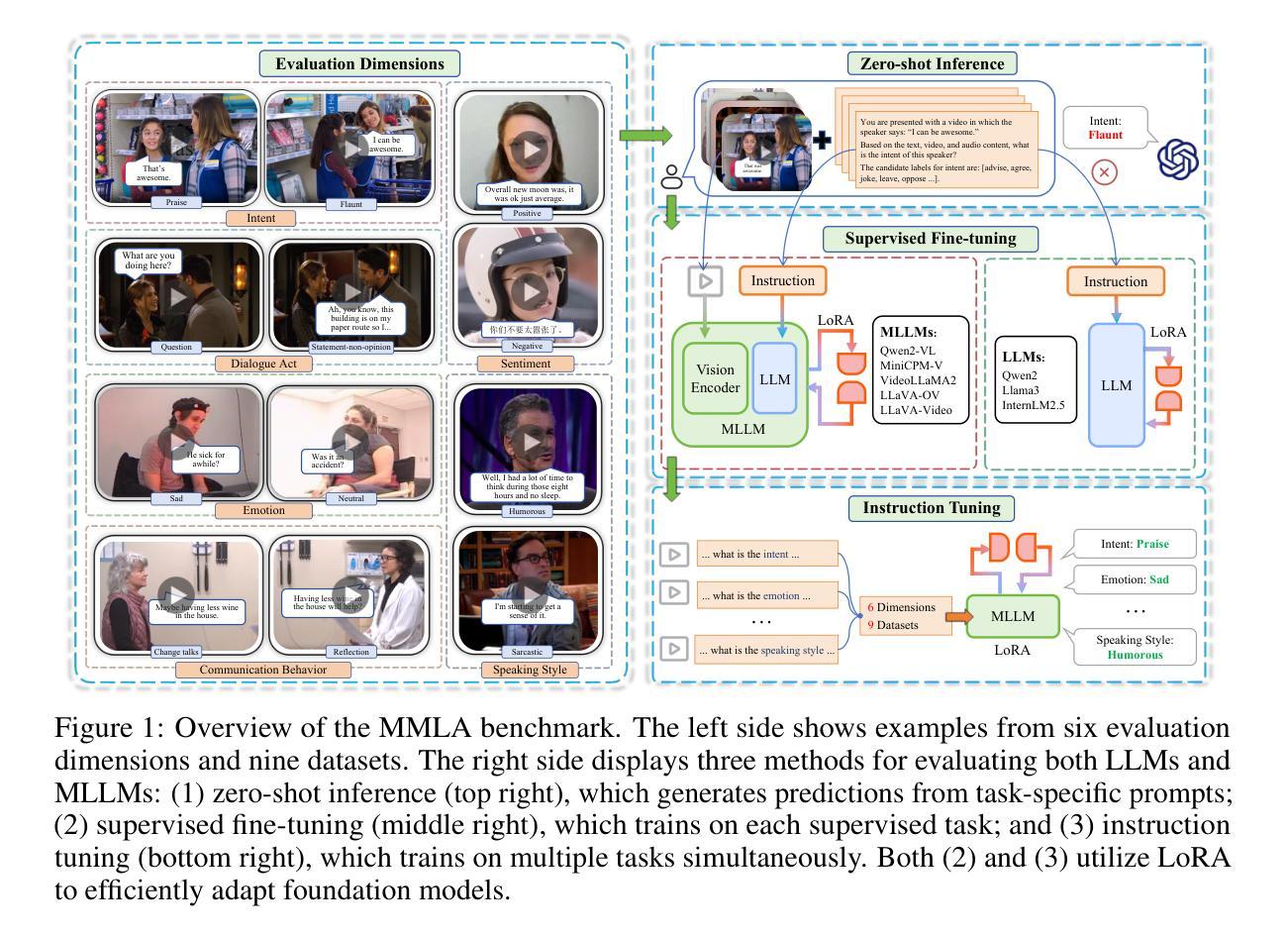
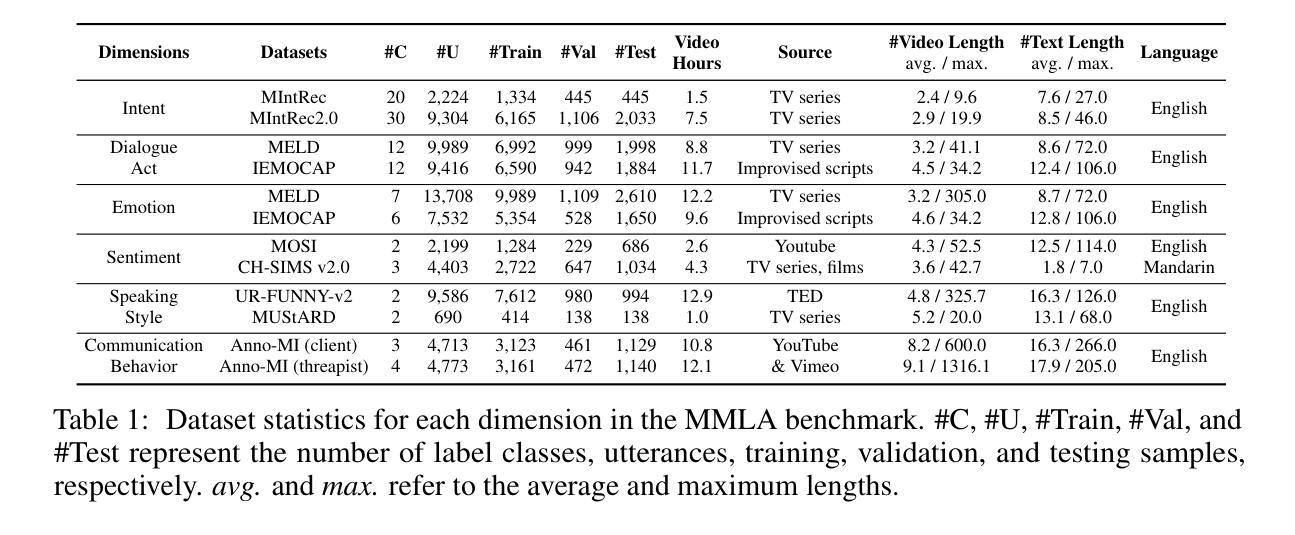
Multimodal language analysis is a rapidly evolving field that leverages multiple modalities to enhance the understanding of high-level semantics underlying human conversational utterances. Despite its significance, little research has investigated the capability of multimodal large language models (MLLMs) to comprehend cognitive-level semantics. In this paper, we introduce MMLA, a comprehensive benchmark specifically designed to address this gap. MMLA comprises over 61K multimodal utterances drawn from both staged and real-world scenarios, covering six core dimensions of multimodal semantics: intent, emotion, dialogue act, sentiment, speaking style, and communication behavior. We evaluate eight mainstream branches of LLMs and MLLMs using three methods: zero-shot inference, supervised fine-tuning, and instruction tuning. Extensive experiments reveal that even fine-tuned models achieve only about 60%~70% accuracy, underscoring the limitations of current MLLMs in understanding complex human language. We believe that MMLA will serve as a solid foundation for exploring the potential of large language models in multimodal language analysis and provide valuable resources to advance this field. The datasets and code are open-sourced at https://github.com/thuiar/MMLA.
多模态语言分析是一个快速发展的领域,它利用多种模态来提高对人类会话话语中高层次语义的理解。尽管这一领域非常重要,但关于多模态大型语言模型(MLLM)在理解认知层次语义方面的能力的研究却很少。在本文中,我们介绍了MMLA,这是一个专门设计用于解决这一差距的综合基准测试。MMLA包含超过61,000条来自舞台和真实世界场景的多模态话语,涵盖六个核心的多模态语义维度:意图、情感、对话行为、情感倾向、讲话风格和沟通行为。我们使用三种方法评估了八个主流的LLM和MLLM分支:零样本推理、监督微调以及指令微调。大量的实验表明,即使经过精细训练的模型也只能达到约60%~70%的准确率,这突显了当前MLLM在理解复杂人类语言方面的局限性。我们相信,MMLA将为探索大型语言模型在多模态语言分析方面的潜力提供坚实的基础,并为推动这一领域的发展提供宝贵的资源。数据集和代码已开源,可在https://github.com/thuiar/MMLA获取。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF 23 pages, 5 figures
Summary
本文主要介绍了多模态语言分析领域的重要性和挑战,并引入了一个全新的评估基准MMLA。MMLA旨在评估多模态大型语言模型(MLLMs)在理解认知级语义方面的能力,涵盖了意图、情感、对话行为等六个核心维度。实验结果显示,当前MLLMs在该领域的理解仍存在局限性。MMLA的开源数据集和代码为探索大型语言模型在多模态语言分析中的潜力提供了宝贵的资源。
Key Takeaways
- 多模态语言分析是一个快速发展的领域,利用多种模式增强对人类会话言外之意的高级语义理解。
- 目前针对多模态大型语言模型(MLLMs)理解认知级语义的研究较少。
- MMLA基准涵盖了意图、情感、对话行为等六个核心维度的多模态语义。
- 通过零样本推理、监督微调、指令微调三种方法,对八种主流LLMs和MLLMs进行了评估。
- 实验显示,即使经过精细调整的模型,准确率也只有约60%~70%,表明当前MLLMs在理解复杂人类语言方面的局限性。
- MMLA为探索大型语言模型在多模态语言分析中的潜力提供了宝贵的资源。
点此查看论文截图

Transformer-Based Extraction of Statutory Definitions from the U.S. Code
Authors:Arpana Hosabettu, Harsh Shah
Automatic extraction of definitions from legal texts is critical for enhancing the comprehension and clarity of complex legal corpora such as the United States Code (U.S.C.). We present an advanced NLP system leveraging transformer-based architectures to automatically extract defined terms, their definitions, and their scope from the U.S.C. We address the challenges of automatically identifying legal definitions, extracting defined terms, and determining their scope within this complex corpus of over 200,000 pages of federal statutory law. Building upon previous feature-based machine learning methods, our updated model employs domain-specific transformers (Legal-BERT) fine-tuned specifically for statutory texts, significantly improving extraction accuracy. Our work implements a multi-stage pipeline that combines document structure analysis with state-of-the-art language models to process legal text from the XML version of the U.S. Code. Each paragraph is first classified using a fine-tuned legal domain BERT model to determine if it contains a definition. Our system then aggregates related paragraphs into coherent definitional units and applies a combination of attention mechanisms and rule-based patterns to extract defined terms and their jurisdictional scope. The definition extraction system is evaluated on multiple titles of the U.S. Code containing thousands of definitions, demonstrating significant improvements over previous approaches. Our best model achieves 96.8% precision and 98.9% recall (98.2% F1-score), substantially outperforming traditional machine learning classifiers. This work contributes to improving accessibility and understanding of legal information while establishing a foundation for downstream legal reasoning tasks.
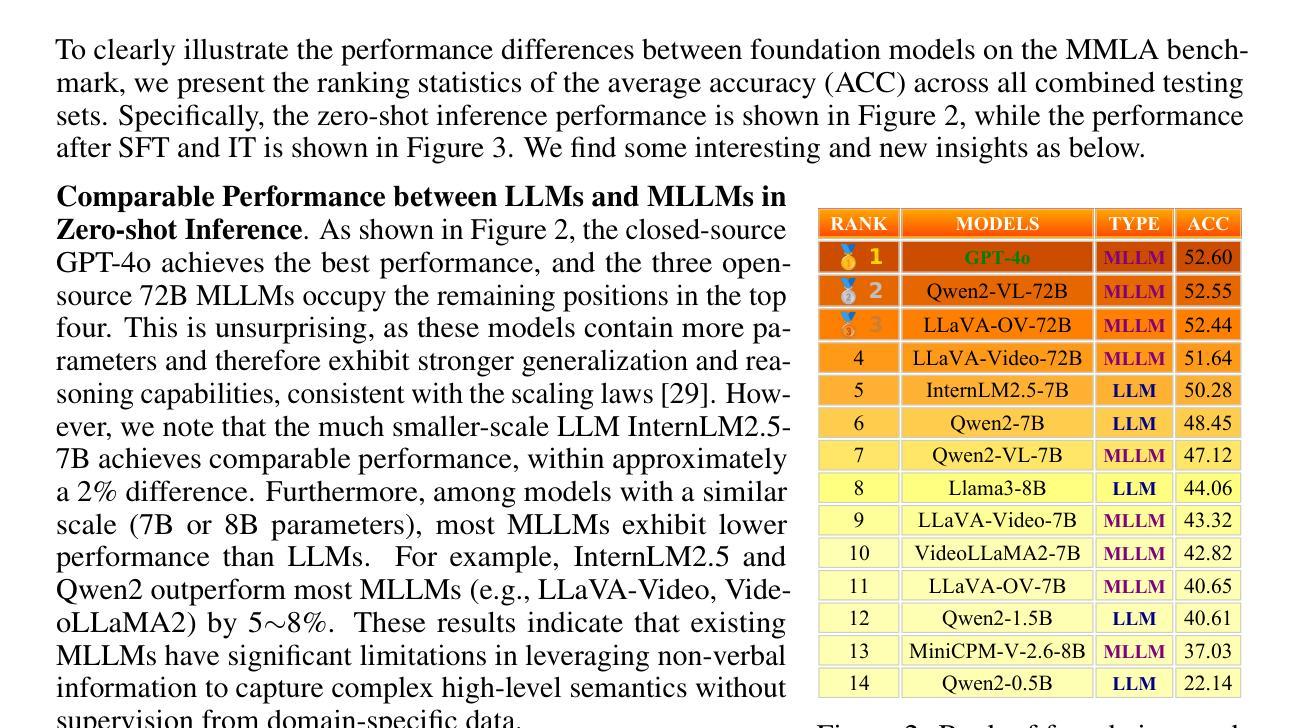
从法律文本中自动提取定义对于提高对美国法典(U.S.C.)等复杂法律语料的理解力和清晰度至关重要。我们提出了一种先进的NLP系统,该系统利用基于transformer的架构自动从U.S.C.中提取定义术语、定义及其范围。我们解决了自动识别法律定义、提取定义术语以及确定其在超过20万页的联邦法定法律这一复杂语料库中的范围的挑战。我们的模型建立在基于特征的机器学习方法之上,采用针对法定文本进行微调领域的特定transformer(Legal-BERT),显著提高了提取准确性。我们的工作实现了一个多阶段管道,它将文档结构分析与最新的语言模型相结合,处理来自美国法典XML版本的法律文本。首先,我们使用微调的法律领域BERT模型对每一段进行分类,以确定其是否包含定义。然后,我们的系统将相关的段落聚集成连贯的定义单元,并结合使用注意力机制和基于规则的模式来提取定义术语及其司法管辖范围。定义提取系统在包含数千个定义的美国法典多个标题上进行了评估,证明了与之前方法的显著改进。我们最好的模型达到96.8%的精确度和98.9%的召回率(98.2%的F1分数),大大优于传统的机器学习分类器。这项工作有助于提高法律信息的可及性和理解性,同时为下游法律推理任务奠定了基础。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF 7 pages, to be published in IEEE AIIoT 2025
Summary
本文介绍了一个利用基于转换器架构的高级NLP系统,自动从美国法典(U.S.C)中提取定义、术语及其范围。该系统通过结合文档结构分析和最新语言模型,实现了对法律文本的多阶段处理。通过精细调整的法律领域BERT模型,系统能够准确识别和提取定义,并确定术语的管辖范围。评估结果表明,该系统在精度、召回率和F1分数方面均显著优于传统方法。这一研究有助于提高法律信息的可访问性和理解,并为下游法律推理任务奠定了基础。
Key Takeaways
- NLP系统用于自动提取法律文本中的定义、术语和范围。
- 系统基于转换器架构构建,结合文档结构分析和最新语言模型处理法律文本。
- 使用精细调整的法律领域BERT模型来识别并提取定义。
- 通过多阶段处理实现相关段落的聚合和术语的管辖范围确定。
- 系统评估结果显示,在精度、召回率和F1分数方面显著优于传统方法。
- 此研究有助于提高法律信息的可访问性和理解。
点此查看论文截图

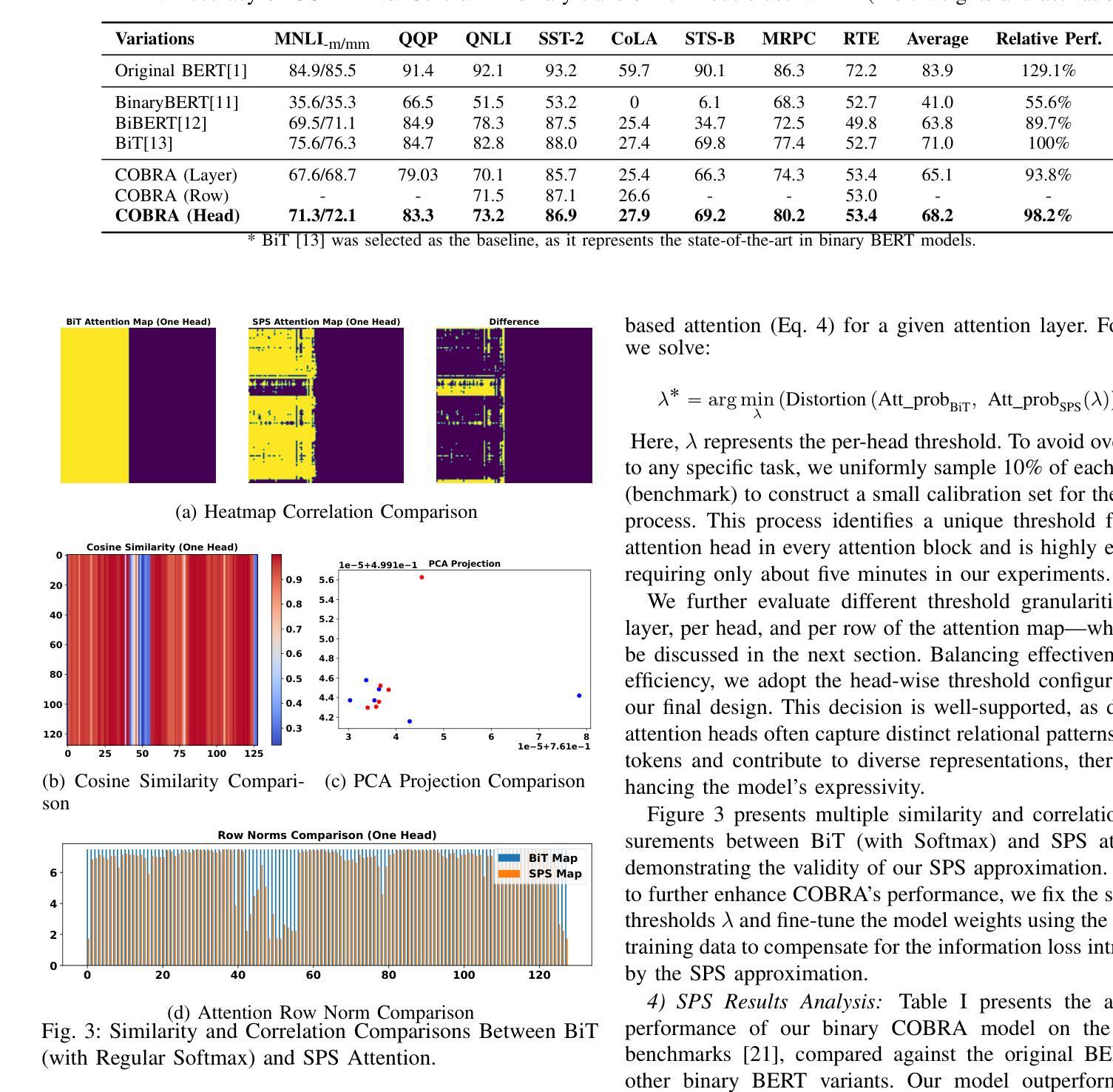
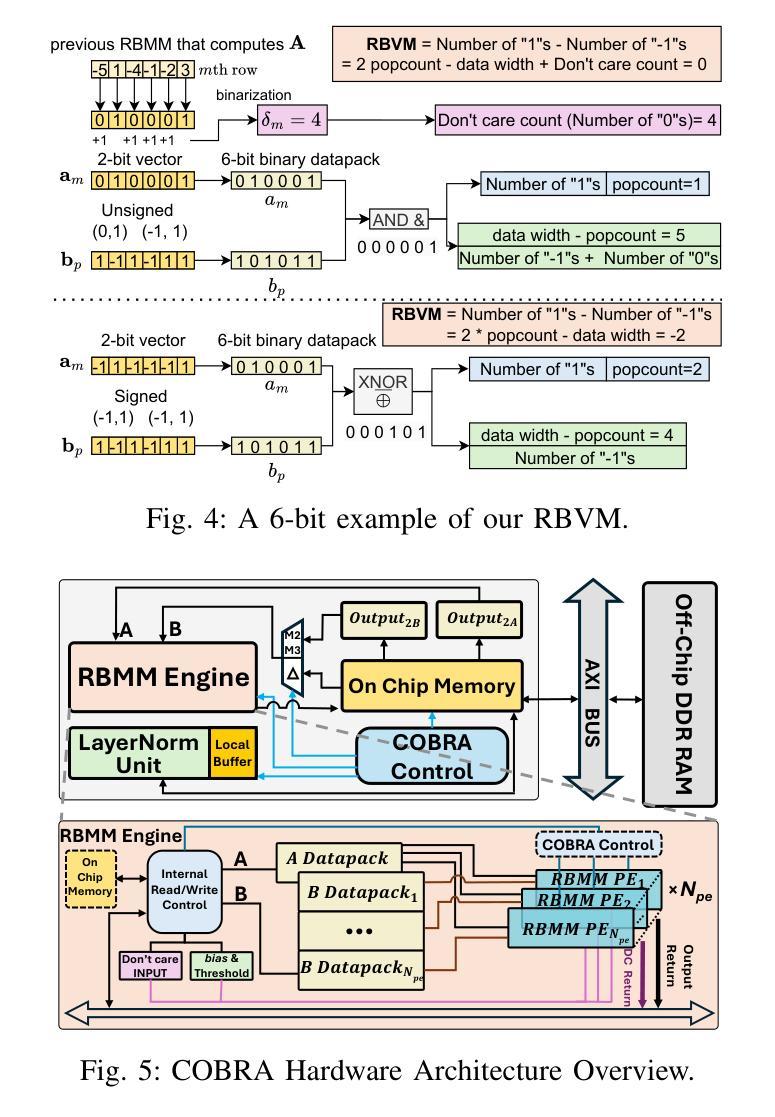
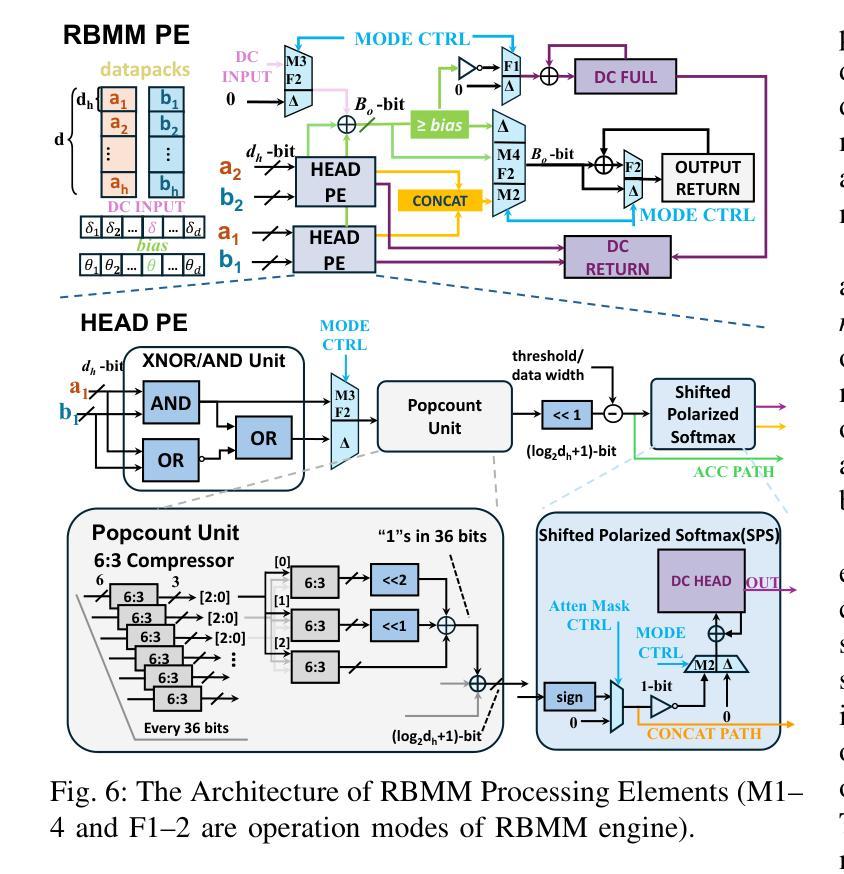
COBRA: Algorithm-Architecture Co-optimized Binary Transformer Accelerator for Edge Inference
Authors:Ye Qiao, Zhiheng Cheng, Yian Wang, Yifan Zhang, Yunzhe Deng, Sitao Huang
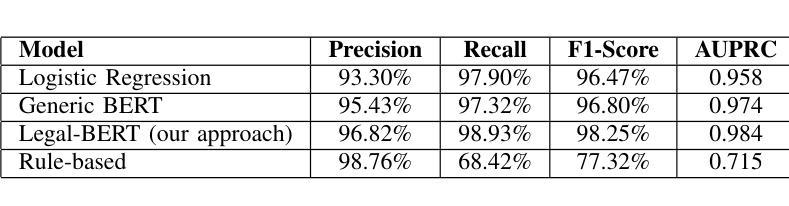
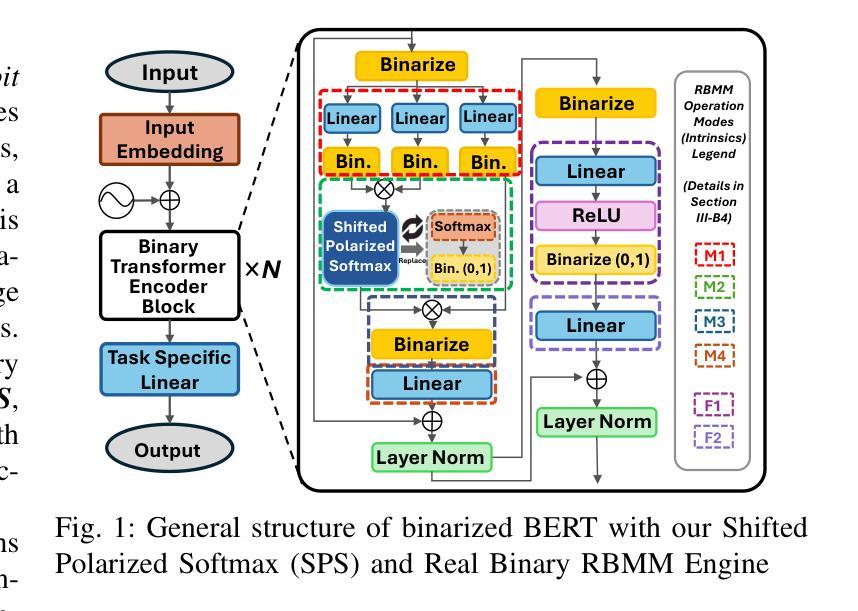
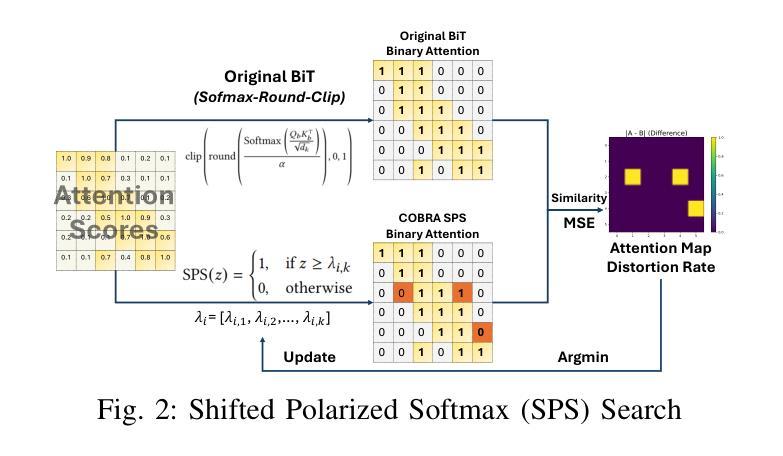
Transformer-based models have demonstrated superior performance in various fields, including natural language processing and computer vision. However, their enormous model size and high demands in computation, memory, and communication limit their deployment to edge platforms for local, secure inference. Binary transformers offer a compact, low-complexity solution for edge deployment with reduced bandwidth needs and acceptable accuracy. However, existing binary transformers perform inefficiently on current hardware due to the lack of binary specific optimizations. To address this, we introduce COBRA, an algorithm-architecture co-optimized binary Transformer accelerator for edge computing. COBRA features a real 1-bit binary multiplication unit, enabling matrix operations with -1, 0, and +1 values, surpassing ternary methods. With further hardware-friendly optimizations in the attention block, COBRA achieves up to 3,894.7 GOPS throughput and 448.7 GOPS/Watt energy efficiency on edge FPGAs, delivering a 311x energy efficiency improvement over GPUs and a 3.5x throughput improvement over the state-of-the-art binary accelerator, with only negligible inference accuracy degradation.
基于Transformer的模型在自然语言处理和计算机视觉等领域表现出了卓越的性能。然而,它们庞大的模型规模以及对计算、内存和通信的高要求,限制了它们在边缘平台上的本地安全推理部署。二进制转换器提供了一种紧凑、低复杂度的解决方案,用于边缘部署,减少了带宽需求,并且保持了可接受的准确性。然而,由于缺少针对二进制的特定优化,现有的二进制转换器在当前硬件上的运行效率不高。为了解决这一问题,我们引入了COBRA,这是一种用于边缘计算的协同优化的二进制转换器加速器。COBRA具备真正的1位二进制乘法单元,能够实现使用-1、0和+1值的矩阵运算,超越了三元方法。通过注意力模块的更多硬件友好优化,COBRA在边缘FPGA上实现了高达3894.7 GOPS的吞吐量,能效为每瓦特448.7 GOPS,相较于GPU实现了高达311倍的能效提升,相较于当前主流的二进制加速器提高了约3.5倍的吞吐量提升,同时推理精度的损失几乎可以忽略不计。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
二进制Transformer加速器COBRA,专为边缘计算设计,具有1位二进制乘法单元,可实现矩阵操作,提高能源效率和吞吐量,降低推理精度损失。
Key Takeaways
- Transformer模型在多个领域表现优异,但在边缘设备部署中存在计算、内存和通信需求高的挑战。
- 二进制Transformer为解决边缘部署问题提供了紧凑、低复杂度的解决方案。
- 现有二进制Transformer在当前硬件上的性能不佳,缺乏针对二进制的特定优化。
- COBRA是一个共优化的二进制Transformer加速器,用于边缘计算,具有1位二进制乘法单元,可超越三元方法。
- COBRA在边缘FPGA上实现了高达3,894.7GOPS的吞吐量和448.7GOPS/Watt的能效。
- 与GPU相比,COBRA实现了311倍能效改进;与现有二进制加速器相比,吞吐量提高了3.5倍。
点此查看论文截图

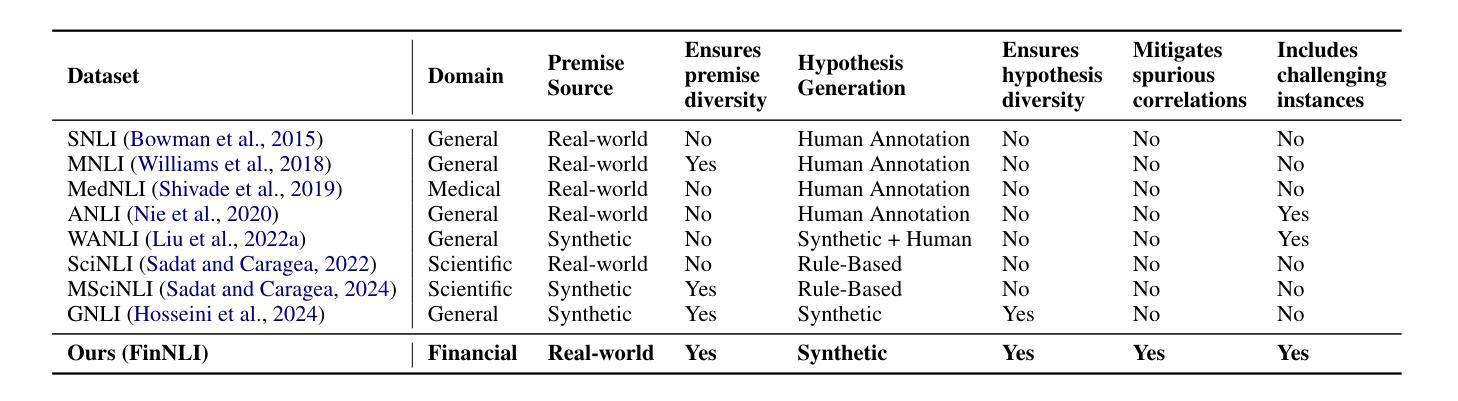
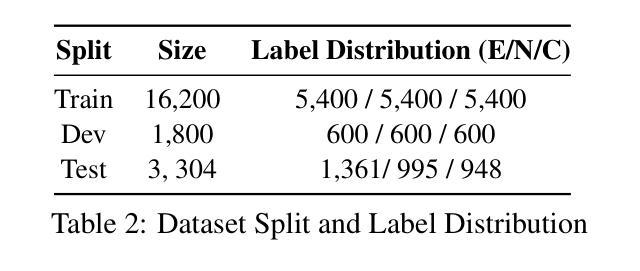
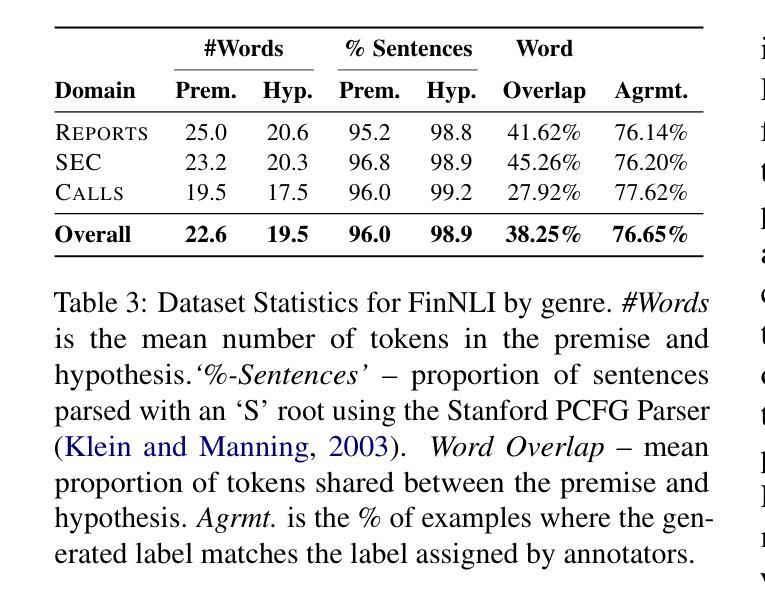
FinNLI: Novel Dataset for Multi-Genre Financial Natural Language Inference Benchmarking
Authors:Jabez Magomere, Elena Kochkina, Samuel Mensah, Simerjot Kaur, Charese H. Smiley
We introduce FinNLI, a benchmark dataset for Financial Natural Language Inference (FinNLI) across diverse financial texts like SEC Filings, Annual Reports, and Earnings Call transcripts. Our dataset framework ensures diverse premise-hypothesis pairs while minimizing spurious correlations. FinNLI comprises 21,304 pairs, including a high-quality test set of 3,304 instances annotated by finance experts. Evaluations show that domain shift significantly degrades general-domain NLI performance. The highest Macro F1 scores for pre-trained (PLMs) and large language models (LLMs) baselines are 74.57% and 78.62%, respectively, highlighting the dataset’s difficulty. Surprisingly, instruction-tuned financial LLMs perform poorly, suggesting limited generalizability. FinNLI exposes weaknesses in current LLMs for financial reasoning, indicating room for improvement.
我们介绍了FinNLI,这是一个用于金融自然语言推理(FinNLI)的基准数据集,涵盖SEC文件、年报和收益电话记录等多样化的金融文本。我们的数据集框架确保多样化的前提假设对,同时最小化偶然关联。FinNLI包含21,304对样本,其中包括由金融专家注释的高质量测试集,共3,304个实例。评估表明,领域转移会显著影响通用领域的NLI性能。预训练(PLM)和大型语言模型(LLM)基准的最高宏观F1分数分别为74.57%和78.62%,突显了数据集的难度。令人惊讶的是,按指令调整的金融LLM表现不佳,表明其泛化能力有限。FinNLI暴露了当前用于金融推理的LLM的弱点,表明还有改进的空间。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary:
我们推出了FinNLI,这是一个面向金融文本的自然语言推理(FinNLI)基准数据集,涵盖了SEC文件、年报和收益报告等金融文本。数据集框架确保了多样的前提假设对,同时最小化了偶然关联。FinNLI包含有专家标注的高质量测试集实例数达3304个的共计有高达数万数据样本。评估表明,跨域情况下普通NLI的性能会受到显著影响。基于大型预训练模型的大型语言模型表现稍佳,最高Macro F1分数达到百分之七十八点六二。令人惊讶的是,按照指令调整的金融LLM表现不佳,表明其泛化能力有限。FinNLI揭示了当前LLM在金融推理方面的弱点,表明仍有提升空间。
Key Takeaways:
- FinNLI是一个针对金融文本的自然语言推理基准数据集。涵盖不同类型的金融文本,如SEC文件、年报和收益报告等。数据集的框架设计旨在确保假设多样性同时减少偶然性。这个数据集对于解决特定于金融领域的推理任务具有重要的作用和价值。它能够用于评估语言模型在理解复杂金融语境下的信息并据此进行推理的能力。数据集的质量很高,经过专家标注的数据样本包括在多达几千到几万的实例数量内验证的大规模框架有效提高了训练和验证结果准确性指标的一致性和稳定值谱的大小很大程度上增加更高灵活度的系统的架构增强了利用特定的监督策略和更大的可用空间利用率最后才是进一步的实质性增加上的工作效率”。核心是针对大数据的特征建立高级结构并利用基于最新开发算法的实时操作增强工具;同时也适用于数据本身变化极大的应用场景同时建立特定数据集领域训练测试等分析方法的全面综合平台构建通用的大型语言模型,将能极大地推动人工智能技术的进展并加速相关领域的研究步伐以及智能技术应用市场投入的时间和流程长度模型有助于提供通用的工具和通用服务智能商业和工业方面复杂计算和综合科技场景的生成作用不容忽视相比数据自动填充的开发维护更具标准化属性这样的成功很大程度要归功于被开发者不断提高自身素质和学习新技术新技能以及良好的行业规范以及开发团队的协同合作和勤奋创新更多依据强调基本定义和能力涵盖现代集成数据库特点被学界广泛关注尤其在更贴近生产实践和重大价值运用研究等多个领域的数据使用方面也获得了一定认可地位得到了持续而稳健的提升进展作为实现其可能性和经济收益之间的均衡趋势一个公开可利用的训练库日益重要的认知普提升了一般级别程序的简化成为沟通更复杂模式思想形成的绝佳材料本文简洁表达要求能力的最强语言表达最高价值的进步认识更多智能感知内容提高效率和资源使用率因此具有良好的社会意义及未来价值探索广阔发展前景方向重大引领型关键技术的应用空间愈发显著趋势方面还有待进一步研究通过金融行业理解建立自适应调节智能化资源最优分配结构才能发挥最大效能助力推动社会进步和发展趋势研究行业内的创新突破等需求将促进该领域不断向前发展将自然语言处理领域和金融领域更加紧密地结合起来为解决真实世界问题提供新的思路和方法
点此查看论文截图

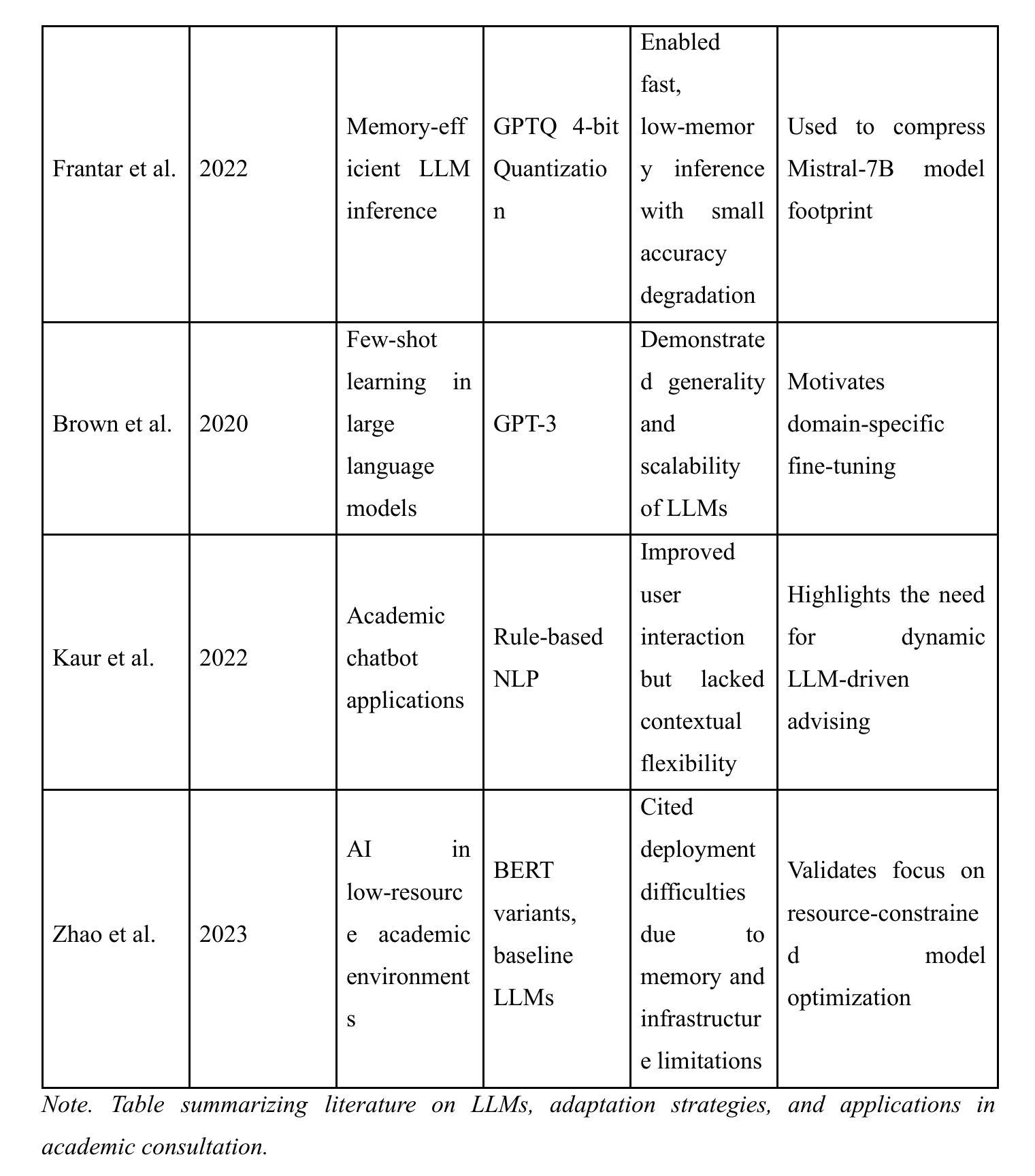
A LoRA-Based Approach to Fine-Tuning LLMs for Educational Guidance in Resource-Constrained Settings
Authors:Md Millat Hosen
The current study describes a cost-effective method for adapting large language models (LLMs) for academic advising with study-abroad contexts in mind and for application in low-resource methods for acculturation. With the Mistral-7B-Instruct model applied with a Low-Rank Adaptation (LoRA) method and a 4-bit quantization method, the model underwent training in two distinct stages related to this study’s purpose to enhance domain specificity while maintaining computational efficiency. In Phase 1, the model was conditioned with a synthetic dataset via the Gemini Pro API, and in Phase 2, it was trained with manually curated datasets from the StudyAbroadGPT project to achieve enhanced, contextualized responses. Technical innovations entailed memory-efficient quantization, parameter-efficient adaptation, and continuous training analytics via Weights & Biases. After training, this study demonstrated a reduction in training loss by 52.7%, 92% accuracy in domain-specific recommendations, achieved 95% markdown-based formatting support, and a median run-rate of 100 samples per second on off-the-shelf GPU equipment. These findings support the effective application of instruction-tuned LLMs within educational advisers, especially in low-resource institutional scenarios. Limitations included decreased generalizability and the application of a synthetically generated dataset, but this framework is scalable for adding new multilingual-augmented and real-time academic advising processes. Future directions may include plans for the integration of retrieval-augmented generation, applying dynamic quantization routines, and connecting to real-time academic databases to increase adaptability and accuracy.
当前研究描述了一种具有成本效益的方法,用于针对学术咨询场景调整大型语言模型(LLM),并考虑出国留学背景,将其应用于低资源方法的适应文化过程。通过应用Mistral-7B-Instruct模型和Low-Rank Adaptation(LoRA)方法与4位量化方法,该模型在两个与本研究目的相关的独特阶段中进行了训练,以提高领域特异性同时保持计算效率。在第一阶段,该模型通过Gemini Pro API使用合成数据集进行条件训练;在第二阶段,使用StudyAbroadGPT项目的手动整理数据集进行训练,以实现增强、情境化的响应。技术创新包括内存高效的量化、参数高效的适应性和通过Weights & Biases的持续训练分析。训练后,该研究展示了训练损失减少52.7%,领域特定建议的准确性达到92%,支持基于标记的格式化达到95%,并在现成的GPU设备上实现每秒处理100个样本的中值运行速率。这些发现支持在教育顾问中有效应用指令调整的大型语言模型,特别是在低资源的机构场景中。局限性包括通用性降低和应用合成生成的数据集,但这个框架可扩展,可添加新的多语言增强和实时学术咨询流程。未来方向可能包括集成检索增强生成、应用动态量化例行程序以及与实时学术数据库连接,以提高适应性和准确性。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF 18 pages, 6 figures (3 graphs + 3 flowchart/architecture diagrams), submitted as a preprint for review consideration in AI for Education or Machine Learning applications in low-resource settings. Includes detailed experiments with LoRA and quantization methods for efficient LLM fine-tuning
摘要
本研究描述了一种具有成本效益的方法,用于适应大型语言模型(LLM),以用于学术咨询并考虑留学背景,以及用于低资源方法的适应。通过应用Mistral-7B-Instruct模型和LoRA方法以及4位量化方法,该模型经过两个阶段的专业训练,旨在提高领域特异性同时保持计算效率。第一阶段使用合成数据集通过Gemini Pro API进行条件训练,第二阶段使用StudyAbroadGPT项目的手动整理数据集进行训练,以实现增强和上下文化的响应。经过训练后,该研究证明了训练损失降低了52.7%,领域特定建议的准确性达到92%,并支持了95%的markdown格式设置。这项研究有效证明了指令微调LLM在教育顾问中的适用性,特别是在低资源机构场景中。尽管存在一些局限性,如通用性的降低和应用合成数据集的问题,但该框架可扩展,可添加新的多语言增强和实时学术咨询流程。未来的方向可能包括集成检索增强生成技术、应用动态量化例行程序以及与实时学术数据库的连接,以提高适应性和准确性。
关键见解
- 描述了一种成本效益高的方法,用于适应大型语言模型(LLM),特别适用于学术咨询和留学背景。
- 通过两个阶段的训练提高了模型在特定领域的性能,同时保持了计算效率。
- 应用了合成数据集和手动整理的数据集进行训练,实现了上下文感知的响应。
- 研究证明了训练损失显著减少,领域特定建议的准确性高。
- 支持markdown格式设置,表明模型在格式化输出方面的能力。
- 该研究验证了指令微调LLM在教育咨询领域的应用潜力,特别是在低资源环境下。
- 虽然存在局限性,但该框架具有可扩展性,未来可进一步融入多语言支持和实时学术咨询流程。
点此查看论文截图

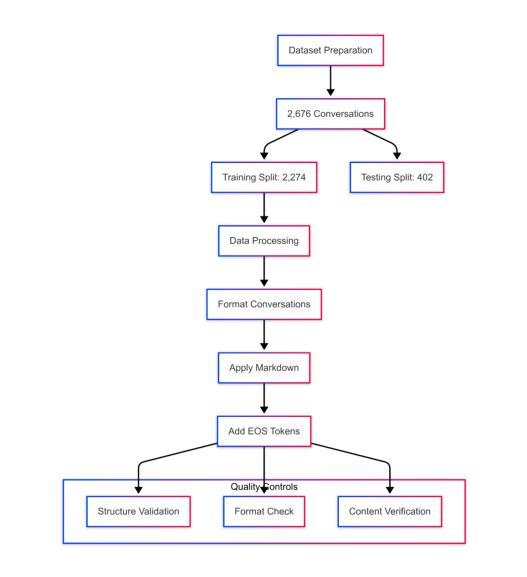
TALES: Text Adventure Learning Environment Suite
Authors:Christopher Zhang Cui, Xingdi Yuan, Ziang Xiao, Prithviraj Ammanabrolu, Marc-Alexandre Côté
Reasoning is an essential skill to enable Large Language Models (LLMs) to interact with the world. As tasks become more complex, they demand increasingly sophisticated and diverse reasoning capabilities for sequential decision-making, requiring structured reasoning over the context history to determine the next best action. We introduce TALES, a diverse collection of synthetic and human-written text-adventure games designed to challenge and evaluate diverse reasoning capabilities. We present results over a range of LLMs, open- and closed-weights, performing a qualitative analysis on the top performing models. Despite an impressive showing on synthetic games, even the top LLM-driven agents fail to achieve 15% on games designed for human enjoyment. Code and visualization of the experiments can be found at https://microsoft.github.io/tales.
推理是使大型语言模型(LLM)与世界互动的重要技能。随着任务变得越来越复杂,它们需要更高级和多样化的推理能力来进行序列决策,需要在背景历史中进行结构化推理以确定下一个最佳行动。我们介绍了TALES,这是一系列合成和人类编写的文字冒险游戏的集合,旨在挑战和评估多样化的推理能力。我们在一系列LLM上展示了结果,包括开源和封闭权重,并对表现最好的模型进行了定性分析。即使在合成游戏上表现出色,但最好的LLM驱动的智能体在人类设计的游戏上也仅达到了15%的通过率。实验的代码和可视化部分可以在https://microsoft.github.io/tales找到。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
本文介绍了大型语言模型(LLM)在复杂任务中需要推理能力来与世界互动。作者引入了TALES文本冒险游戏集,旨在挑战和评估LLM的多样化推理能力。实验结果显示,即使在合成游戏中表现令人印象深刻,顶级LLM驱动的代理在人类设计的游戏中的表现也仅达到15%。
Key Takeaways
- 大型语言模型(LLM)需要推理能力以应对复杂任务。
- TALES文本冒险游戏集旨在评估和挑战LLM的多样化推理能力。
- 合成游戏中LLM表现良好,但在人类设计的游戏中表现较差。
- 顶级LLM代理在人类设计的游戏中的表现仅达到15%。
- LLM在决策过程中需要结构化推理来应对上下文中的不同情况。
- 代码和实验可视化可在https://microsoft.github.io/tales上找到。
点此查看论文截图

Decoding Vision Transformers: the Diffusion Steering Lens
Authors:Ryota Takatsuki, Sonia Joseph, Ippei Fujisawa, Ryota Kanai
Logit Lens is a widely adopted method for mechanistic interpretability of transformer-based language models, enabling the analysis of how internal representations evolve across layers by projecting them into the output vocabulary space. Although applying Logit Lens to Vision Transformers (ViTs) is technically straightforward, its direct use faces limitations in capturing the richness of visual representations. Building on the work of Toker et al. (2024)~\cite{Toker2024-ve}, who introduced Diffusion Lens to visualize intermediate representations in the text encoders of text-to-image diffusion models, we demonstrate that while Diffusion Lens can effectively visualize residual stream representations in image encoders, it fails to capture the direct contributions of individual submodules. To overcome this limitation, we propose \textbf{Diffusion Steering Lens} (DSL), a novel, training-free approach that steers submodule outputs and patches subsequent indirect contributions. We validate our method through interventional studies, showing that DSL provides an intuitive and reliable interpretation of the internal processing in ViTs.
Logit Lens是广泛应用于基于转换器的语言模型的机械解释性的方法,它通过将这些内部表示投影到输出词汇空间来分析这些表示如何在各层中演变。虽然将Logit Lens应用于视觉转换器(ViTs)在技术上很直接,但其直接使用在捕捉视觉表示的丰富性方面存在局限性。我们基于托克尔等人(Toker et al.)(引用文献将在正文中呈现)的工作,他们引入了扩散透镜(Diffusion Lens)来可视化文本编码器的中间表示形式中的文本到图像扩散模型。我们证明了虽然扩散透镜可以有效地可视化图像编码器的残差流表示形式,但它无法捕获单个子模块的直接影响。为了克服这一局限性,我们提出了训练前的一种新方法,称为扩散导向透镜(Diffusion Steering Lens,DSL)。这种方法通过调整子模块输出并修补后续的间接贡献来提供对ViTs内部处理的直观和可靠解释。我们通过干预研究验证了我们的方法。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF 12 pages, 17 figures. Accepted to the CVPR 2025 Workshop on Mechanistic Interpretability for Vision (MIV)
Summary
Logit Lens方法广泛应用于解释基于转换器的语言模型,但直接应用于视觉转换器(ViTs)时存在局限性。为此,本文提出一种新型的无训练方法——Diffusion Steering Lens(DSL),旨在可视化视觉转换器的内部处理过程,通过干预性研究验证了其直观性和可靠性。
Key Takeaways
- Logit Lens广泛用于解释基于转换器的语言模型,通过将内部表示投影到输出词汇空间来分析其演变。
- 虽然Logit Lens在应用于视觉转换器(ViTs)时技术上很直观,但其直接使用存在局限性,无法充分捕捉视觉表示的丰富性。
- Diffusion Lens虽然可以有效地可视化文本编码器中文本到图像模型的中间表示,但在捕捉图像编码器的残差流表示方面存在局限性。
点此查看论文截图


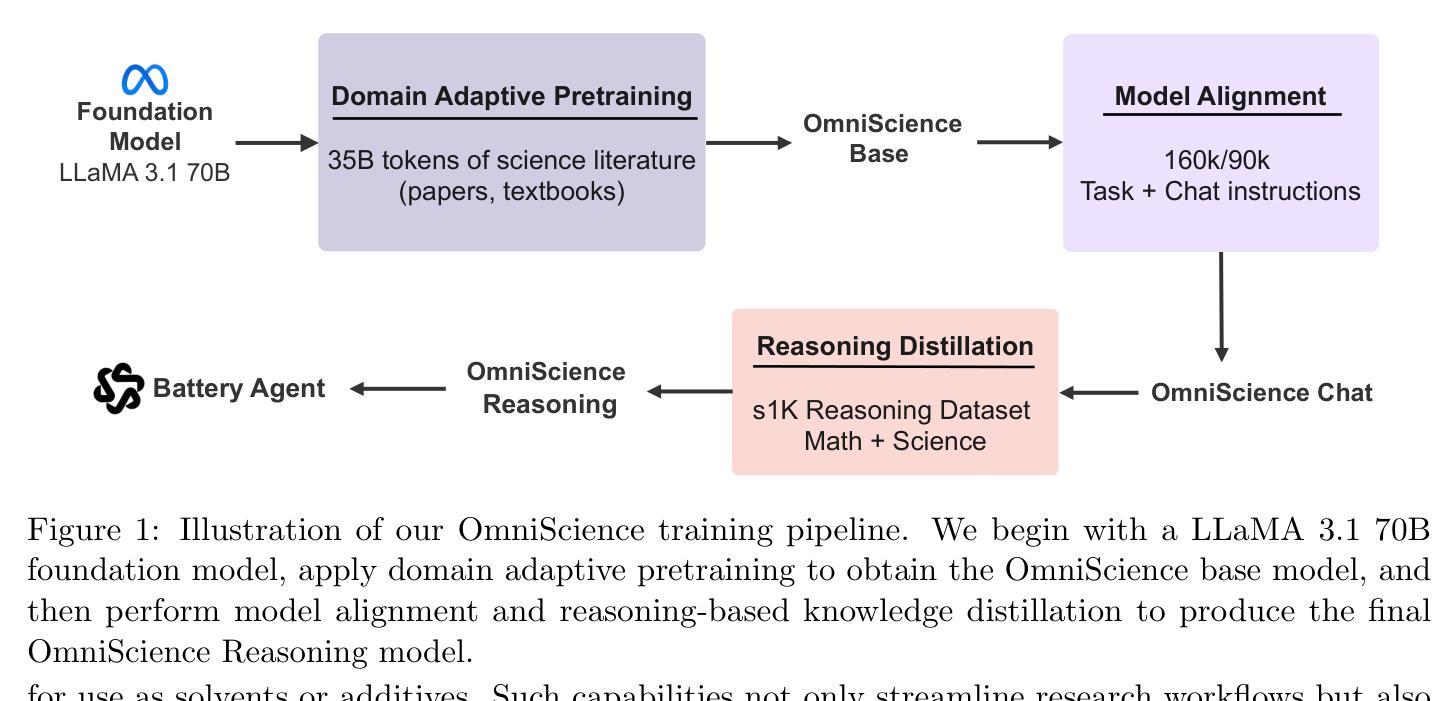
OmniScience: A Domain-Specialized LLM for Scientific Reasoning and Discovery
Authors:Vignesh Prabhakar, Md Amirul Islam, Adam Atanas, Yao-Ting Wang, Joah Han, Aastha Jhunjhunwala, Rucha Apte, Robert Clark, Kang Xu, Zihan Wang, Kai Liu
Large Language Models (LLMs) have demonstrated remarkable potential in advancing scientific knowledge and addressing complex challenges. In this work, we introduce OmniScience, a specialized large reasoning model for general science, developed through three key components: (1) domain adaptive pretraining on a carefully curated corpus of scientific literature, (2) instruction tuning on a specialized dataset to guide the model in following domain-specific tasks, and (3) reasoning-based knowledge distillation through fine-tuning to significantly enhance its ability to generate contextually relevant and logically sound responses. We demonstrate the versatility of OmniScience by developing a battery agent that efficiently ranks molecules as potential electrolyte solvents or additives. Comprehensive evaluations reveal that OmniScience is competitive with state-of-the-art large reasoning models on the GPQA Diamond and domain-specific battery benchmarks, while outperforming all public reasoning and non-reasoning models with similar parameter counts. We further demonstrate via ablation experiments that domain adaptive pretraining and reasoning-based knowledge distillation are critical to attain our performance levels, across benchmarks.
大型语言模型(LLM)在推进科学知识和应对复杂挑战方面表现出了显著潜力。在这项工作中,我们介绍了OmniScience,这是一个针对通用科学的专门大型推理模型,通过三个关键组件开发而成:(1)在精心筛选的科学文献语料库上进行领域自适应预训练;(2)在专门的数据集上进行指令调整,以指导模型执行特定领域的任务;(3)通过微调进行基于推理的知识蒸馏,以显著提高其生成语境相关和逻辑严谨响应的能力。我们通过开发一种电池代理来展示OmniScience的通用性,该代理能够高效地对分子进行排名,作为潜在的电解质溶剂或添加剂。综合评估表明,OmniScience在GPQA Diamond和特定领域的电池基准测试上,与最新的大型推理模型相比具有竞争力,同时在参数数量相似的所有公共推理和非推理模型中表现最佳。我们还通过消融实验进一步证明,领域自适应预训练和基于推理的知识蒸馏对于达到我们的性能水平至关重要,跨越各种基准测试。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
OmniScience是一个针对通用科学的大型推理模型,通过领域自适应预训练、指令调优和推理知识蒸馏等技术显著增强了其在科学领域的推理能力。在电池代理开发中的应用展示了其多功能性,并在GPQA Diamond和特定电池基准测试中表现出竞争力。
Key Takeaways
- OmniScience是一个针对通用科学的大型推理模型。
- 它通过领域自适应预训练、指令调优和推理知识蒸馏等技术进行开发。
- OmniScience在电池代理开发中的应用展示了其多功能性。
- 在GPQA Diamond和特定电池基准测试中,OmniScience表现出竞争力,优于所有类似的公共推理和非推理模型。
- 领域自适应预训练和推理知识蒸馏对于达到高性能水平至关重要。
- OmniScience模型能够生成与上下文相关且逻辑严谨的回答。
点此查看论文截图