⚠️ 以下所有内容总结都来自于 大语言模型的能力,如有错误,仅供参考,谨慎使用
🔴 请注意:千万不要用于严肃的学术场景,只能用于论文阅读前的初筛!
💗 如果您觉得我们的项目对您有帮助 ChatPaperFree ,还请您给我们一些鼓励!⭐️ HuggingFace免费体验
2025-04-25 更新
Tracing Thought: Using Chain-of-Thought Reasoning to Identify the LLM Behind AI-Generated Text
Authors:Shifali Agrahari, Sanasam Ranbir Singh
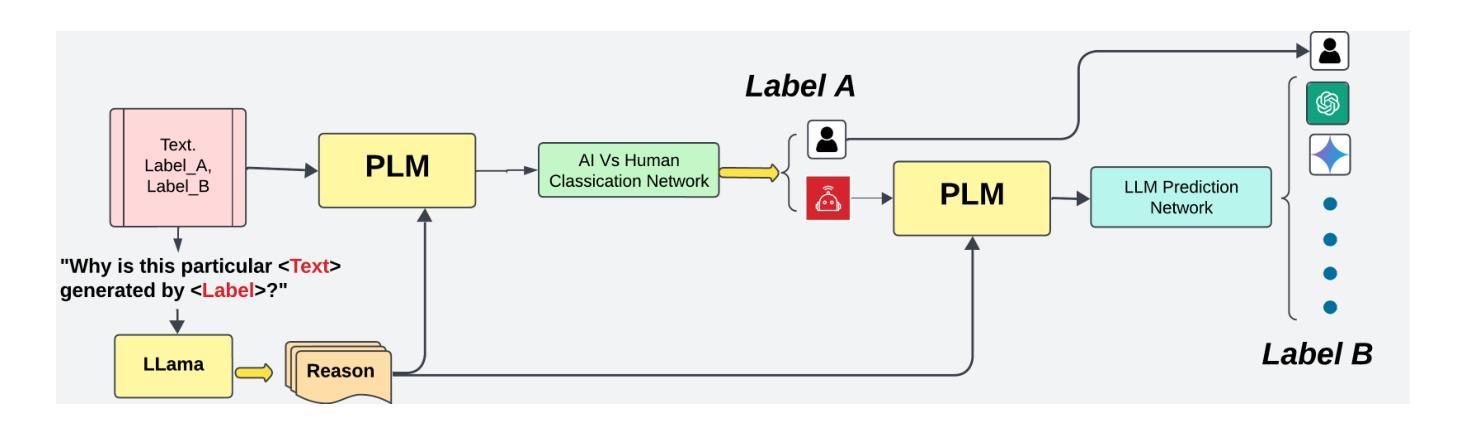
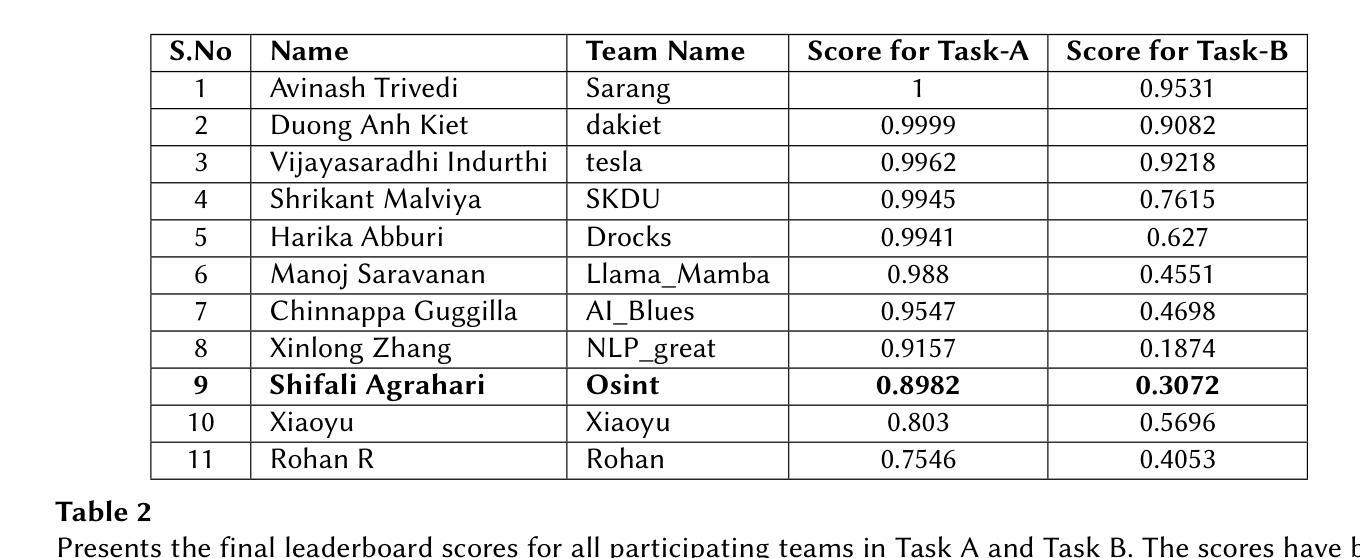
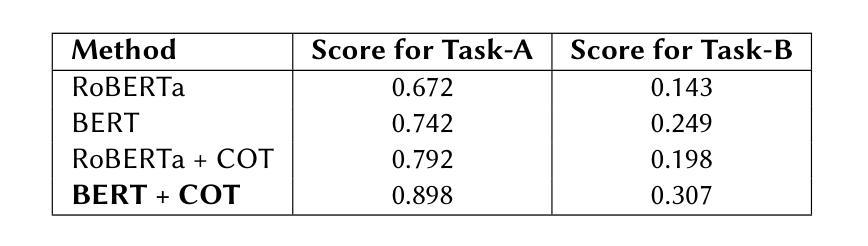
In recent years, the detection of AI-generated text has become a critical area of research due to concerns about academic integrity, misinformation, and ethical AI deployment. This paper presents COT Fine-tuned, a novel framework for detecting AI-generated text and identifying the specific language model. responsible for generating the text. We propose a dual-task approach, where Task A involves classifying text as AI-generated or human-written, and Task B identifies the specific LLM behind the text. The key innovation of our method lies in the use of Chain-of-Thought reasoning, which enables the model to generate explanations for its predictions, enhancing transparency and interpretability. Our experiments demonstrate that COT Fine-tuned achieves high accuracy in both tasks, with strong performance in LLM identification and human-AI classification. We also show that the CoT reasoning process contributes significantly to the models effectiveness and interpretability.
近年来,由于人们担心学术诚信、虚假信息和人工智能部署的道德问题,检测AI生成的文本已成为研究的关键领域。本文提出了COT Fine-tuned,一个用于检测AI生成文本并识别生成文本的具体语言模型的新型框架。我们提出了一种双重任务的方法,其中任务A涉及将文本分类为AI生成或人类撰写,任务B则识别文本背后的特定大型语言模型。我们方法的关键创新之处在于使用Chain-of-Thought推理,使模型能够为其预测生成解释,提高透明度和可解释性。我们的实验表明,COT Fine-tuned在两项任务中都取得了较高的准确性,在大型语言模型识别和人机分类方面表现出强大的性能。我们还表明,CoT推理过程对模型的效率和可解释性做出了重大贡献。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF De-Factify 4: 4th Workshop on Multimodal Fact Checking and Hate Speech Detection, co-located with AAAI 2025. Pennsylvania
Summary:
近年来,检测AI生成文本成为了研究领域的重要课题,涉及到学术诚信、虚假信息和伦理问题等方面。本文提出了COT Fine-tuned框架,采用双重任务的方法检测AI生成的文本并识别生成文本的特定语言模型。任务A涉及将文本分类为AI生成或人类撰写,任务B则识别文本背后的特定大型语言模型。关键创新在于使用Chain-of-Thought推理,使模型能够为其预测生成解释,提高透明度和可解释性。实验表明,COT Fine-tuned在两项任务中都取得了较高的准确性,特别是在大型语言模型识别和人机分类方面表现出色。CoT推理过程对模型的效能和可解释性有显著贡献。
Key Takeaways:
- AI生成文本检测已成为重要研究领域,涉及学术诚信、虚假信息和伦理问题。
- COT Fine-tuned框架采用双重任务方法,能检测AI生成的文本并识别背后的语言模型。
- 该框架的关键创新在于使用Chain-of-Thought推理,提高模型的透明度和可解释性。
- 实验显示,COT Fine-tuned在人机分类和大型语言模型识别方面表现出色。
- COT Fine-tuned框架在检测AI生成文本方面具有较高的准确性。
- CoT推理过程对模型的效能和可解释性有重要贡献。
点此查看论文截图

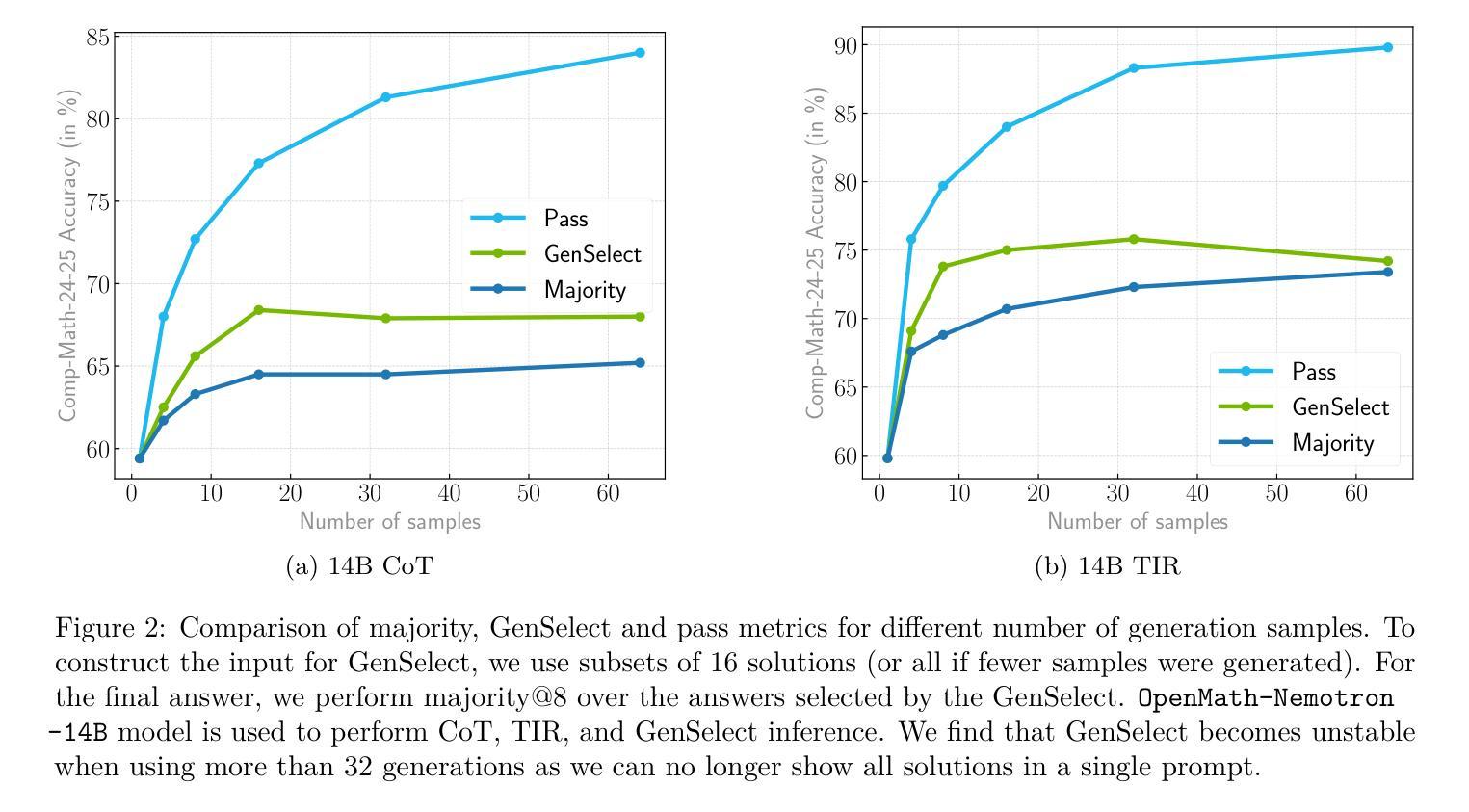
AIMO-2 Winning Solution: Building State-of-the-Art Mathematical Reasoning Models with OpenMathReasoning dataset
Authors:Ivan Moshkov, Darragh Hanley, Ivan Sorokin, Shubham Toshniwal, Christof Henkel, Benedikt Schifferer, Wei Du, Igor Gitman
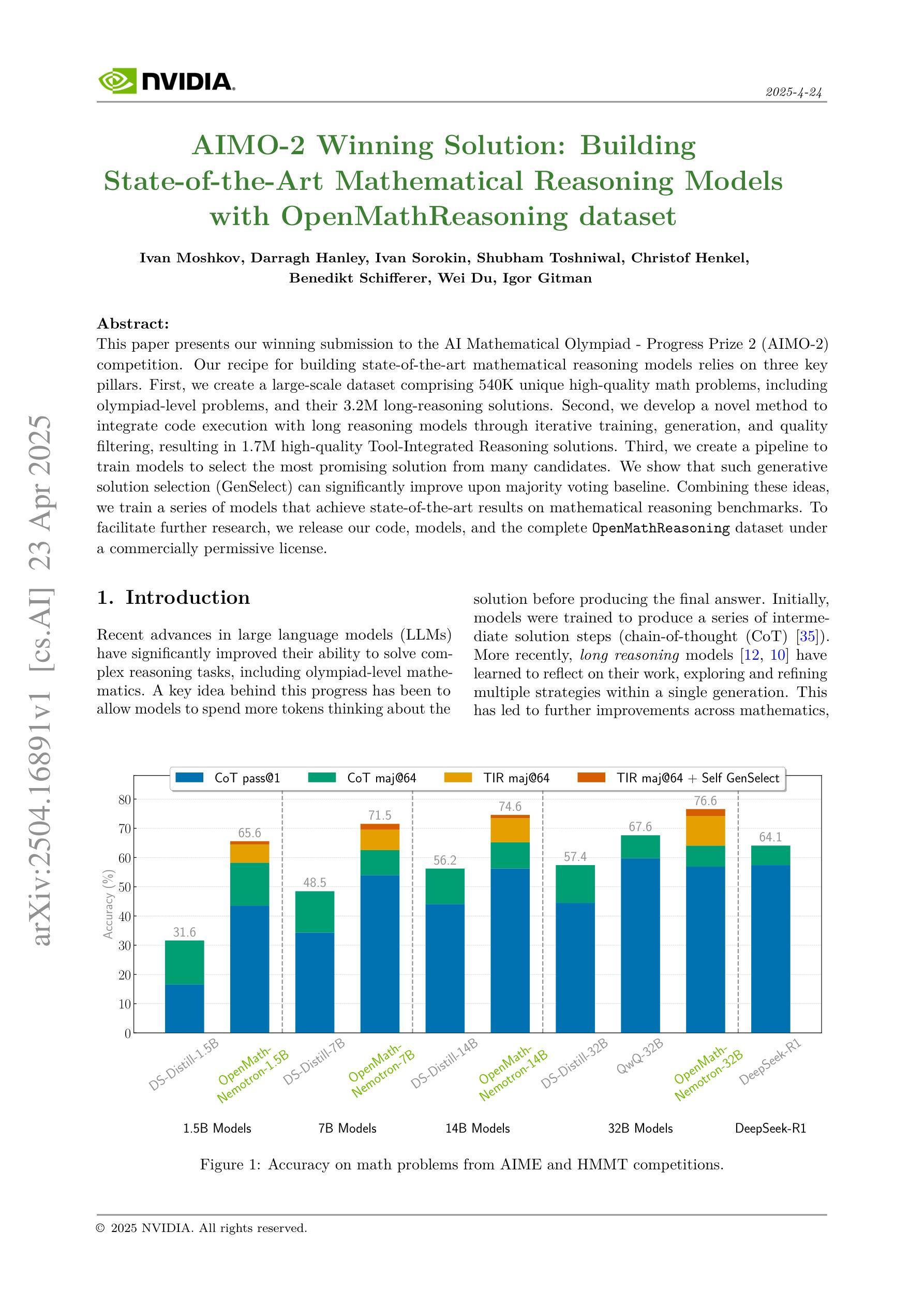
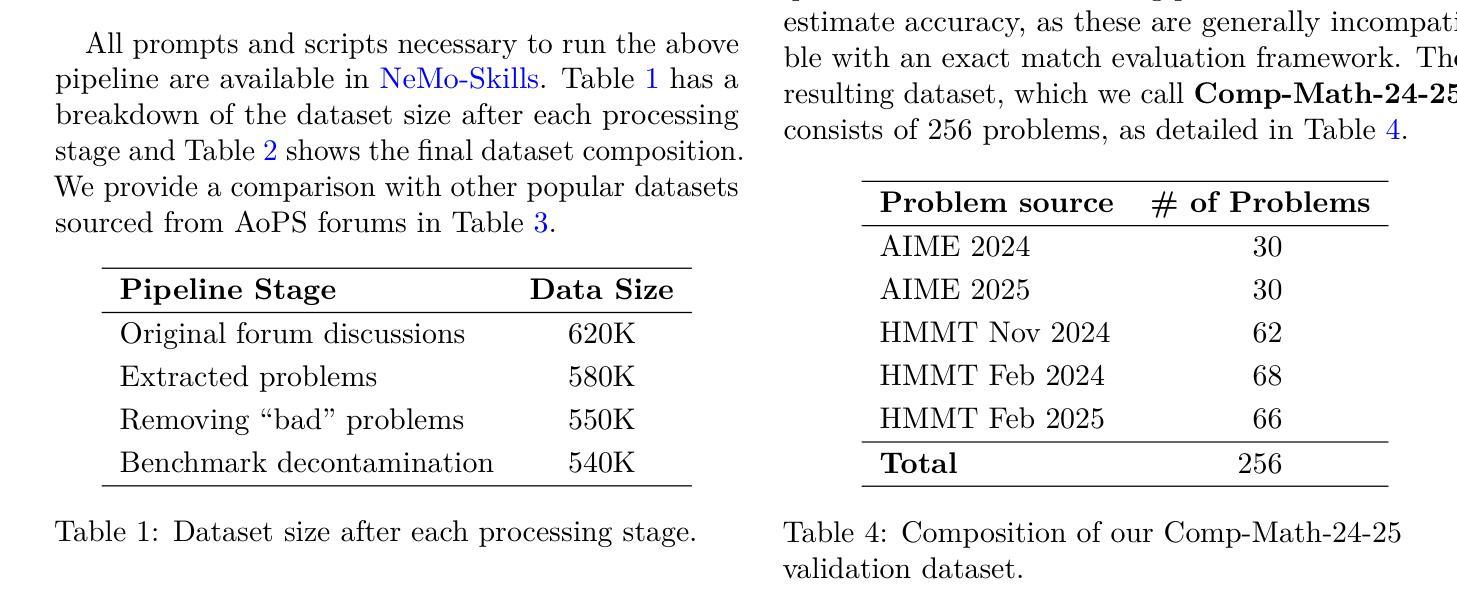
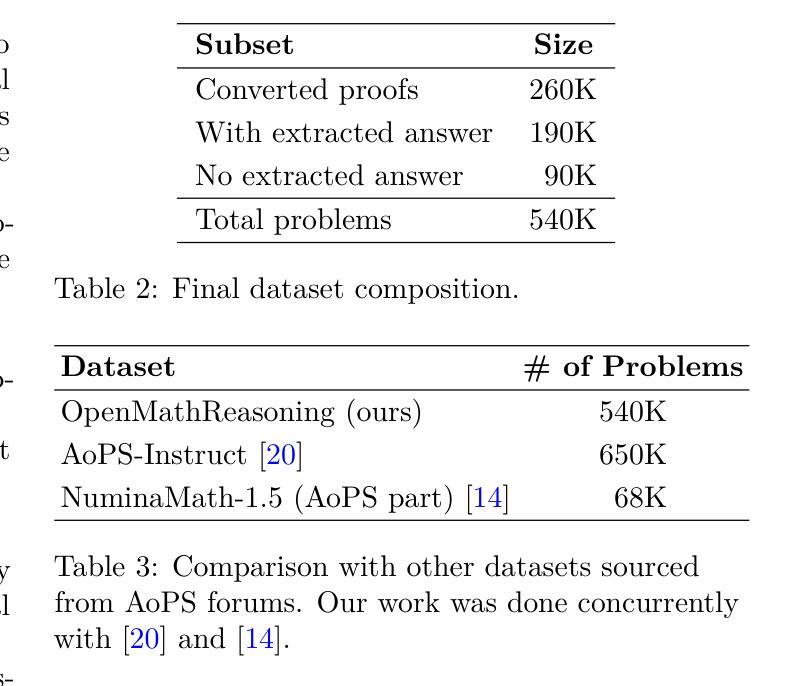
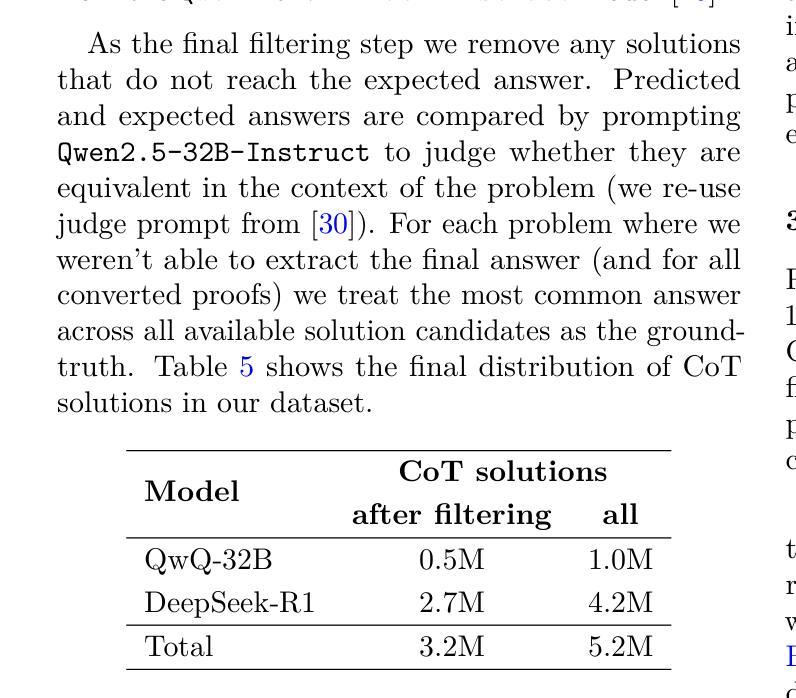
This paper presents our winning submission to the AI Mathematical Olympiad - Progress Prize 2 (AIMO-2) competition. Our recipe for building state-of-the-art mathematical reasoning models relies on three key pillars. First, we create a large-scale dataset comprising 540K unique high-quality math problems, including olympiad-level problems, and their 3.2M long-reasoning solutions. Second, we develop a novel method to integrate code execution with long reasoning models through iterative training, generation, and quality filtering, resulting in 1.7M high-quality Tool-Integrated Reasoning solutions. Third, we create a pipeline to train models to select the most promising solution from many candidates. We show that such generative solution selection (GenSelect) can significantly improve upon majority voting baseline. Combining these ideas, we train a series of models that achieve state-of-the-art results on mathematical reasoning benchmarks. To facilitate further research, we release our code, models, and the complete OpenMathReasoning dataset under a commercially permissive license.
本文呈现了我们参加人工智能数学奥林匹克竞赛——进步奖第2期(AIMO-2)的获奖提交作品。我们构建最前沿数学推理模型的配方依赖于三个关键支柱。首先,我们创建了一个大规模数据集,包含54万个独特的高质量数学问题,包括奥林匹克级别的数学问题及其320万个长期解决方案。其次,我们开发了一种新方法,通过迭代训练、生成和质量控制,将代码执行与长期推理模型相结合,产生了170万个高质量的集成工具推理解决方案。第三,我们创建了一个管道来训练模型,从多个候选答案中选择最有前途的答案。我们证明了这种生成解决方案选择(GenSelect)可以大大改进多数投票基准。结合这些思想,我们训练了一系列在数学推理基准测试中达到最新结果的模型。为了促进进一步的研究,我们在商业许可下发布了我们的代码、模型和完整的OpenMathReasoning数据集。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF Report of AIMO-2 winning submission
Summary
本文介绍了参加AIMO-2竞赛的获奖作品。该作品通过构建大规模数据集、开发新型代码执行与长期推理模型整合方法,以及创建模型选择管道等三大支柱技术,构建了最先进的数学推理模型。通过结合这些技术,训练出的模型在数学推理基准测试上取得了最佳成绩。同时,该作品公开了代码、模型和完整的OpenMathReasoning数据集。
Key Takeaways
- 该论文介绍了一个赢得AIMO-2竞赛的先进数学推理模型。
- 模型构建依赖于三个主要支柱:大规模数据集、新型代码执行与长期推理模型整合方法,以及模型选择管道。
- 模型在大规模数据集上进行训练,包含54万个独特的高质量数学问题及其长达32万个长期解决方案。
- 开发了一种新型方法,将代码执行与长期推理模型进行迭代训练、生成和质量控制,产生了高达170万份高质量的工具集成推理解决方案。
- 模型选择管道通过生成解决方案选择(GenSelect)技术,能够显著提高从众多候选解决方案中选择最佳方案的能力。
- 该模型在数学推理基准测试中取得了最佳成绩。
点此查看论文截图
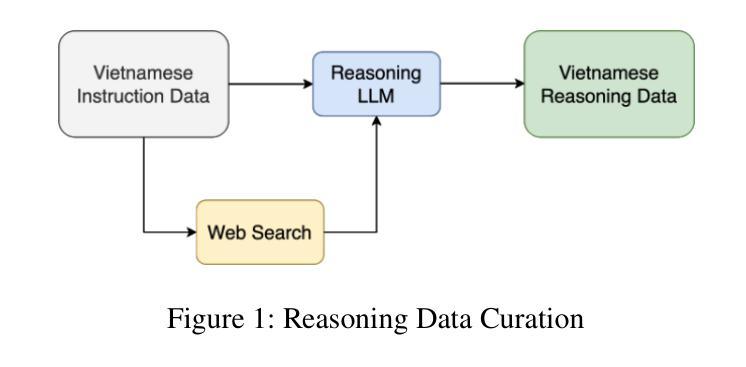
GreenMind: A Next-Generation Vietnamese Large Language Model for Structured and Logical Reasoning
Authors:Luu Quy Tung, Hoang Quoc Viet, Vo Trong Thu
Chain-of-Thought (CoT) is a robust approach for tackling LLM tasks that require intermediate reasoning steps prior to generating a final answer. In this paper, we present GreenMind-Medium-14B-R1, the Vietnamese reasoning model inspired by the finetuning strategy based on Group Relative Policy Optimization. We also leverage a high-quality Vietnamese synthesized reasoning dataset and design two reward functions to tackle the main limitations of this technique: (i) language mixing, where we explicitly detect the presence of biased language characters during the process of sampling tokens, and (ii) we leverage Sentence Transformer-based models to ensure that the generated reasoning content maintains factual correctness and does not distort the final output. Experimental results on the Vietnamese dataset from the VLSP 2023 Challenge demonstrate that our model outperforms prior works and enhances linguistic consistency in its responses. Furthermore, we extend our evaluation to SeaExam-a multilingual multiple-choice dataset, showing the effectiveness of our reasoning method compared to few-shot prompting techniques.
思维链(CoT)是一种针对大型语言模型(LLM)任务的稳健方法,这些任务需要在生成最终答案之前进行中间推理步骤。在本文中,我们介绍了GreenMind-Medium-14B-R1,这是一个受基于组相对策略优化策略的微调策略启发的越南语推理模型。我们还利用高质量的越南语合成推理数据集,并设计两个奖励函数来解决这项技术的两个主要局限性:(i)语言混合问题,我们在采样令牌的过程中显式检测是否存在偏向的语言字符;(ii)我们利用基于句子转换器的模型确保生成的推理内容保持事实正确性,并不扭曲最终输出。在VLSP 2023挑战赛提供的越南数据集上的实验结果表明,我们的模型在表现上超过了先前的工作,并在响应中增强了语言一致性。此外,我们将评估扩展到了多语言选择题数据集SeaExam上,证明了我们的推理方法与少样本提示技术相比的有效性。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary:
绿思维-中模型采用集团相对政策优化策略进行微调,以解决在越南语中生成模型中的任务链方法面临的难题。它通过改进模型的设计和两个奖励函数的优化克服了语言混合问题,确保生成的推理内容保持事实正确性且不会扭曲输出。在越南数据集VLSP 2023挑战赛和SeaExam的多语言选择题数据集上的实验表明,该方法比现有技术和少数几种提示技术更有效。
Key Takeaways:
- GreenMind-Medium-14B-R1模型是越南推理模型,采用任务链方法处理大型语言模型任务。
- 模型基于集团相对政策优化策略进行微调。
- 模型设计包含两个奖励函数以解决语言混合问题,确保生成的推理内容保持事实正确性。
- 模型在越南数据集VLSP 2023挑战赛中表现优异,并展示其超越现有技术的效果。
- 模型通过应用句子转换器技术,确保推理内容不扭曲输出。
点此查看论文截图



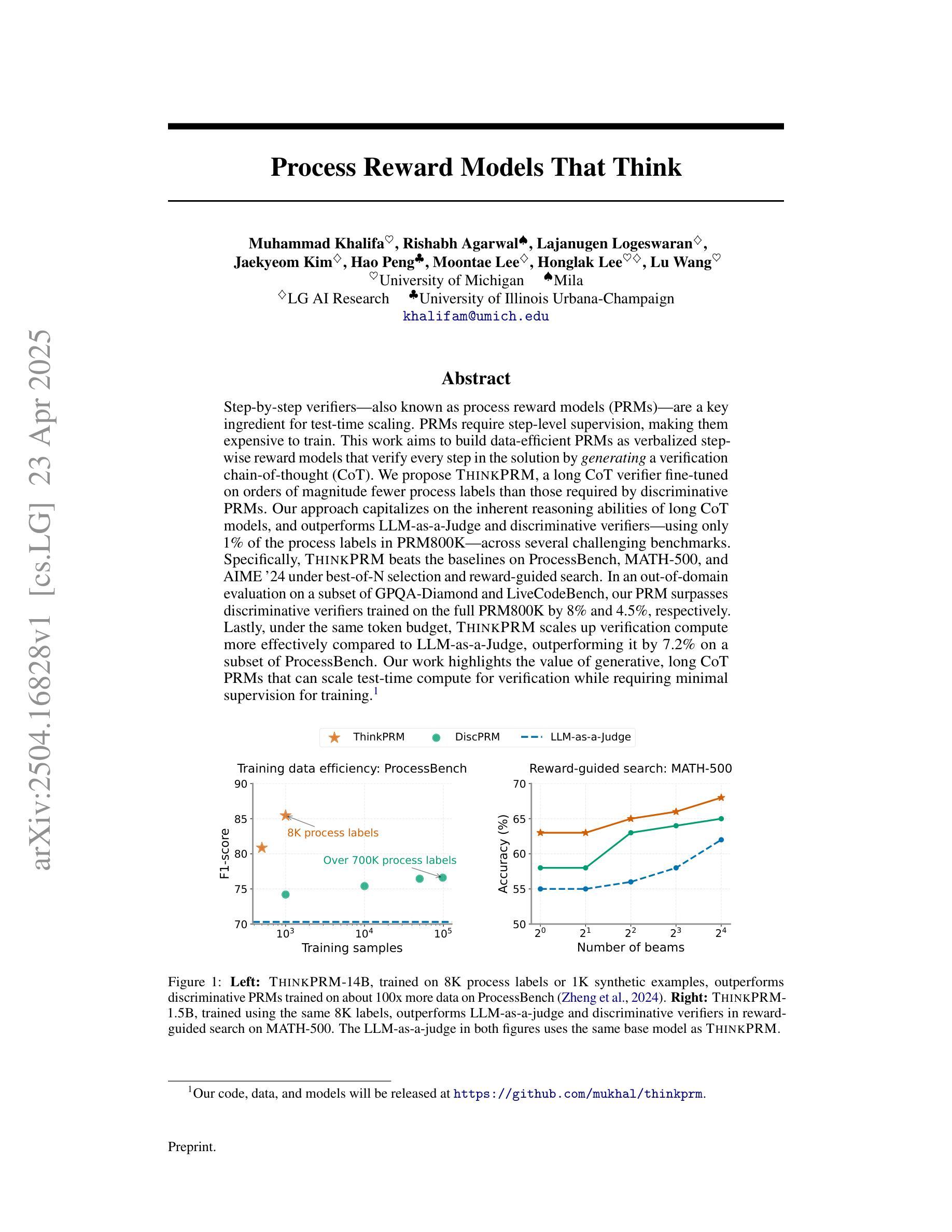
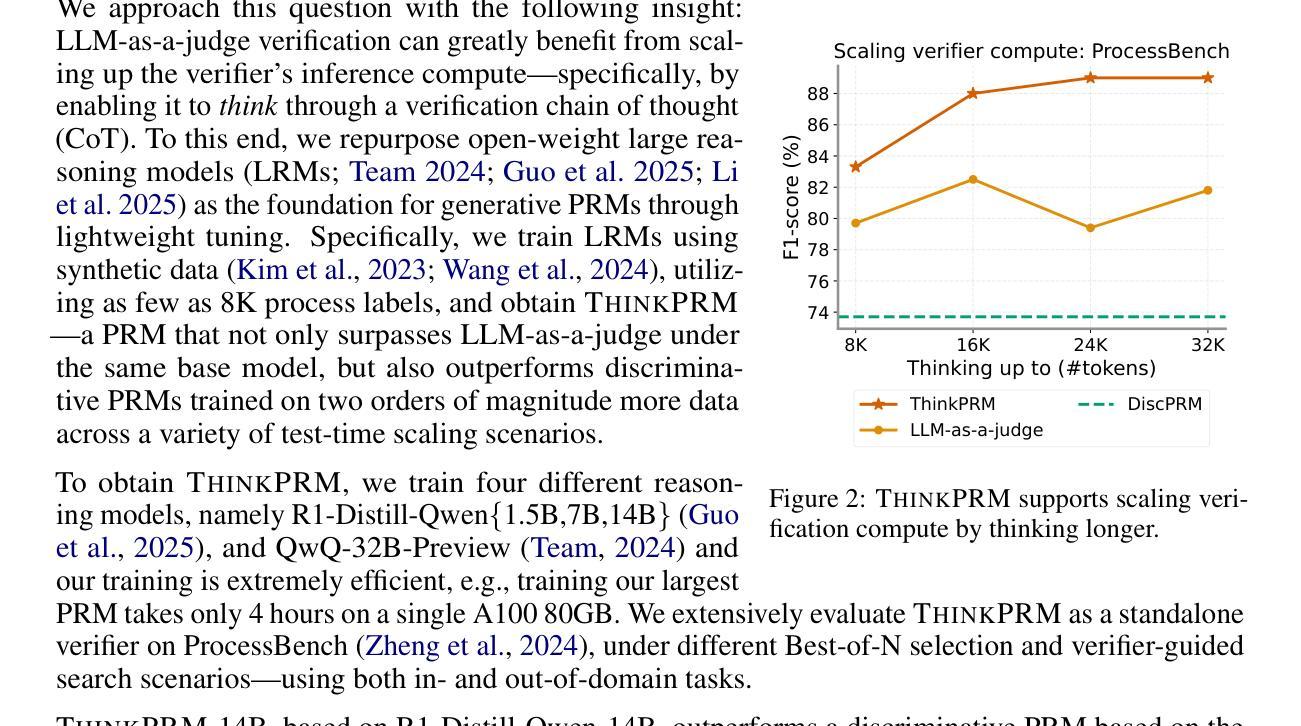
Process Reward Models That Think
Authors:Muhammad Khalifa, Rishabh Agarwal, Lajanugen Logeswaran, Jaekyeom Kim, Hao Peng, Moontae Lee, Honglak Lee, Lu Wang
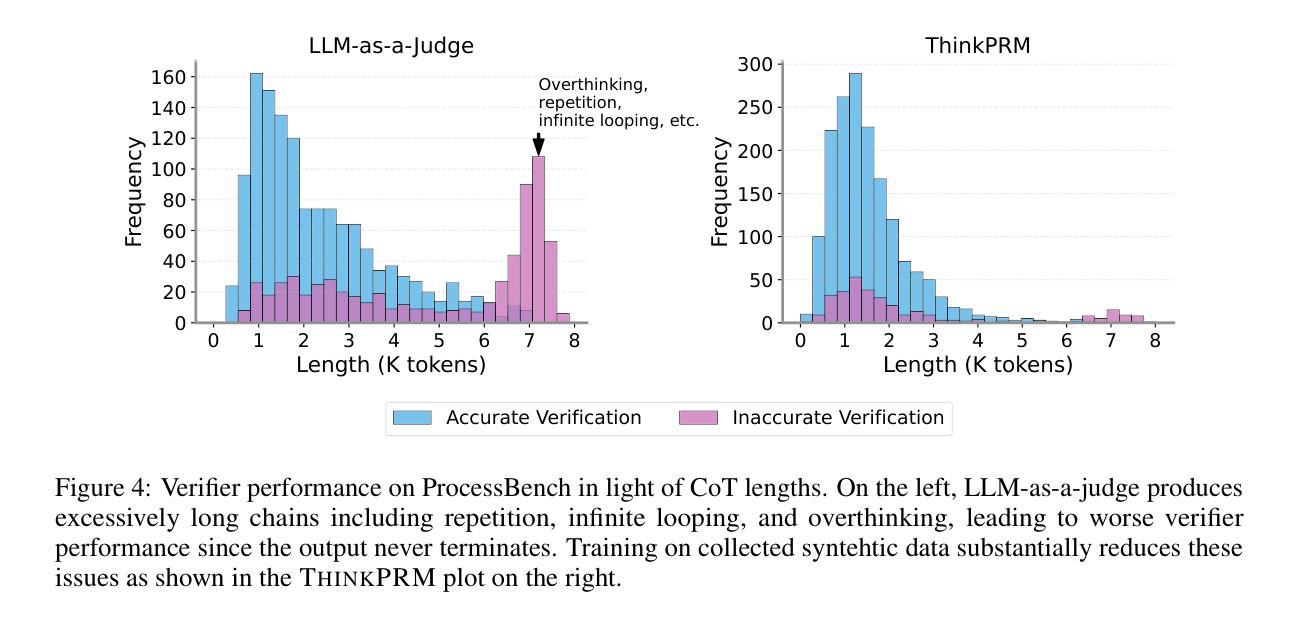
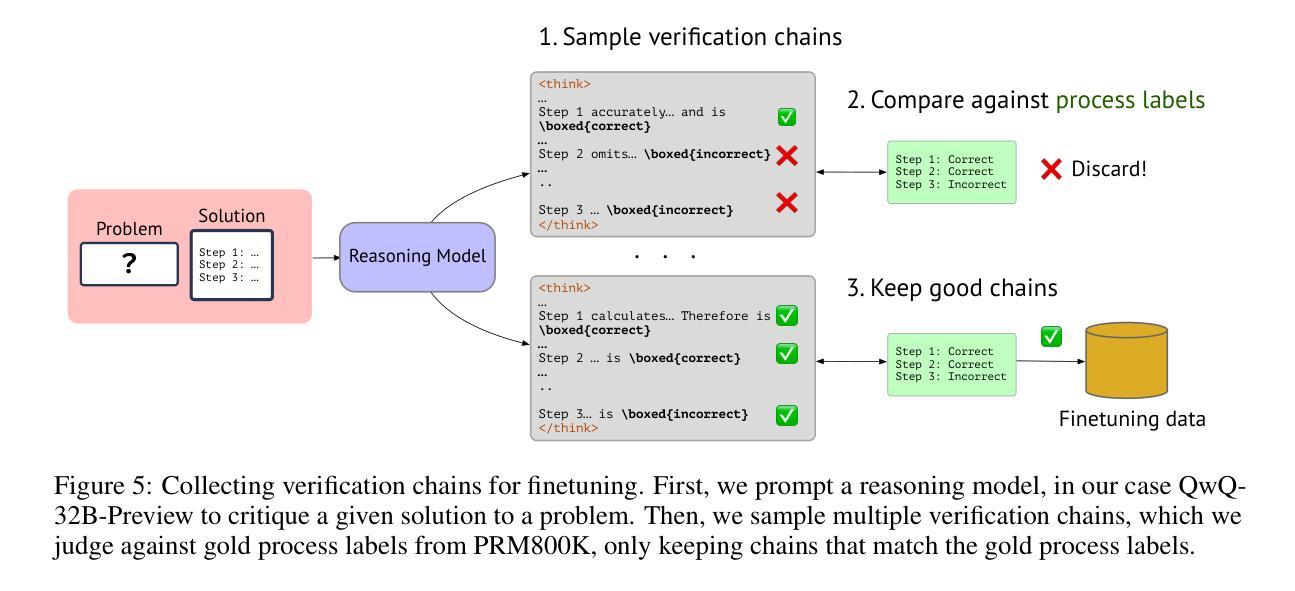
Step-by-step verifiers – also known as process reward models (PRMs) – are a key ingredient for test-time scaling. PRMs require step-level supervision, making them expensive to train. This work aims to build data-efficient PRMs as verbalized step-wise reward models that verify every step in the solution by generating a verification chain-of-thought (CoT). We propose ThinkPRM, a long CoT verifier fine-tuned on orders of magnitude fewer process labels than those required by discriminative PRMs. Our approach capitalizes on the inherent reasoning abilities of long CoT models, and outperforms LLM-as-a-Judge and discriminative verifiers – using only 1% of the process labels in PRM800K – across several challenging benchmarks. Specifically, ThinkPRM beats the baselines on ProcessBench, MATH-500, and AIME ‘24 under best-of-N selection and reward-guided search. In an out-of-domain evaluation on a subset of GPQA-Diamond and LiveCodeBench, our PRM surpasses discriminative verifiers trained on the full PRM800K by 8% and 4.5%, respectively. Lastly, under the same token budget, ThinkPRM scales up verification compute more effectively compared to LLM-as-a-Judge, outperforming it by 7.2% on a subset of ProcessBench. Our work highlights the value of generative, long CoT PRMs that can scale test-time compute for verification while requiring minimal supervision for training. Our code, data, and models will be released at https://github.com/mukhal/thinkprm.
步骤级验证器也被称为流程奖励模型(PRMs),是测试时间缩放的关键组成部分。PRM需要步骤级的监督,使得它们的训练成本高昂。本研究旨在建立数据高效的PRM,作为表述步骤奖励模型,通过生成验证思维链(CoT)来验证解决方案中的每一步。我们提出了ThinkPRM,它是一种长CoT验证器,在流程标签的数量上比判别PRM所需的标签少了几个数量级。我们的方法利用长CoT模型固有的推理能力,并在多个具有挑战性的基准测试中超越了LLM作为法官和判别验证器。具体来说,ThinkPRM在ProcessBench、MATH-500和AIME ‘24的最佳N选和奖励导向搜索方面击败了基线。在GPQA-Diamond和LiveCodeBench的子集上进行域外评估,我们的PRM在完整的PRM800K上训练的判别验证器分别提高了8%和4.5%。最后,在相同的令牌预算下,ThinkPRM在ProcessBench的子集上更有效地扩展了验证计算,比LLM-as-a-Judge高出7.2%。我们的工作突出了生成式、长CoT PRM的价值,它可以在测试时扩展验证计算,同时训练时需要的监督很少。我们的代码、数据和模型将在https://github.com/mukhal/thinkprm发布。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
本文介绍了步骤式验证器(也称为过程奖励模型PRM)在测试时间缩放中的关键作用。由于PRM需要步骤级别的监督,因此训练成本较高。本文旨在建立数据高效的PRM,通过生成验证思维链(CoT)来验证解决方案中的每一步。提出ThinkPRM方法,在远低于传统判别式PRM所需的过程标签数量的情况下进行微调,利用长CoT模型的内在推理能力,并在多个基准测试中表现出超越LLM-as-a-Judge和判别式验证器的性能。ThinkPRM在PRM800K仅使用1%的过程标签的情况下,在ProcessBench、MATH-500和AIME ‘24等多个基准测试中超过了基线。此外,在GPQA-Diamond和LiveCodeBench的子集上进行域外评估时,我们的PRM在训练全过程的PRM800K判别式验证器上超越了它们,分别提高了8%和4.5%。最后,在相同的令牌预算下,ThinkPRM在ProcessBench的子集上更有效地扩展了验证计算,比LLM-as-a-Judge高出7.2%。总体而言,我们的工作突显了生成式、长CoT PRM的价值,这些模型可以在验证时扩展测试时间计算,同时训练时需要的监督较少。
Key Takeaways
- PRMs(过程奖励模型)是测试时间缩放的关键。
- ThinkPRM是一种数据高效的PRM方法,通过生成验证思维链(CoT)来验证每一步。
- ThinkPRM在多个基准测试中表现优越,使用的过程标签数量远低于传统判别式PRM。
- 在域外评估中,ThinkPRM超越了全过程的PRM800K判别式验证器。
- ThinkPRM更有效地扩展了验证计算,与LLM-as-a-Judge相比具有更高的性能。
- ThinkPRM利用长CoT模型的内在推理能力,突显了生成式PRM的价值。
点此查看论文截图

Credible plan-driven RAG method for Multi-hop Question Answering
Authors:Ningning Zhang, Chi Zhang, Zhizhong Tan, Xingxing Yang, Weiping Deng, Wenyong Wang
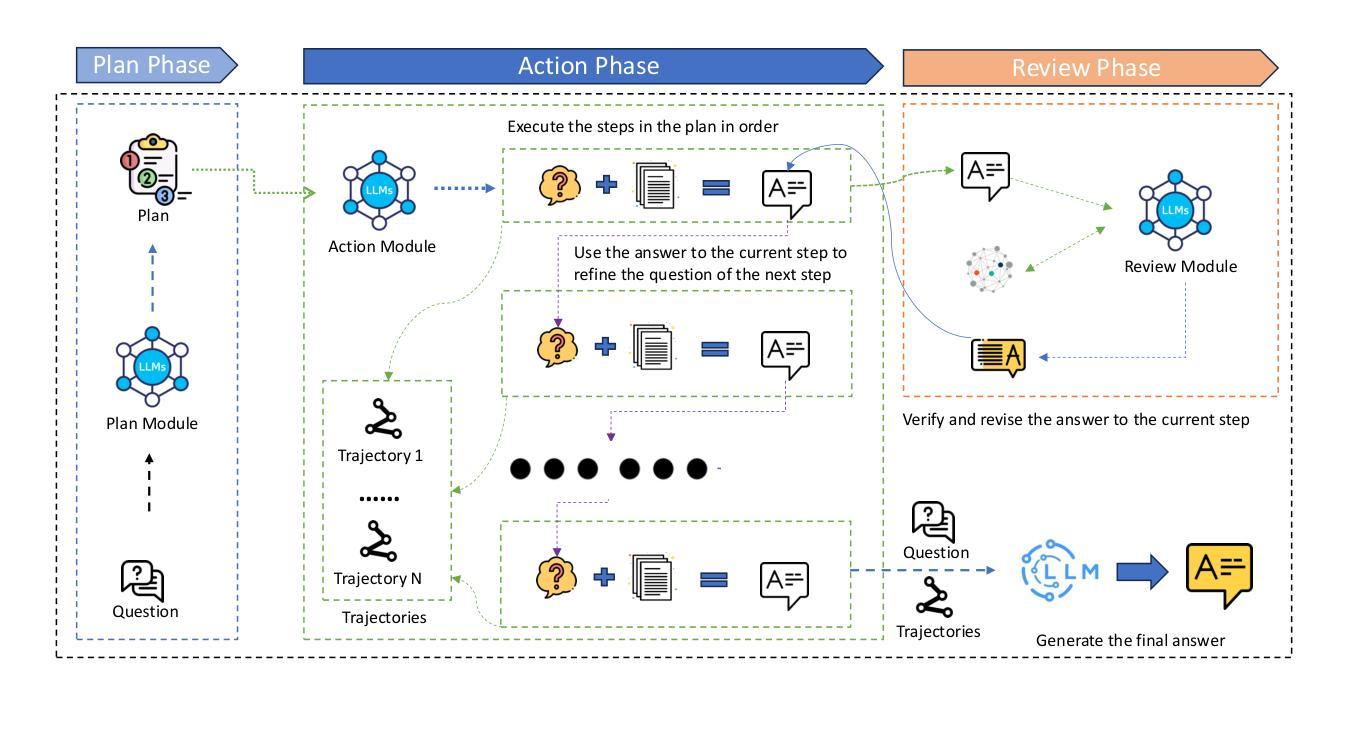
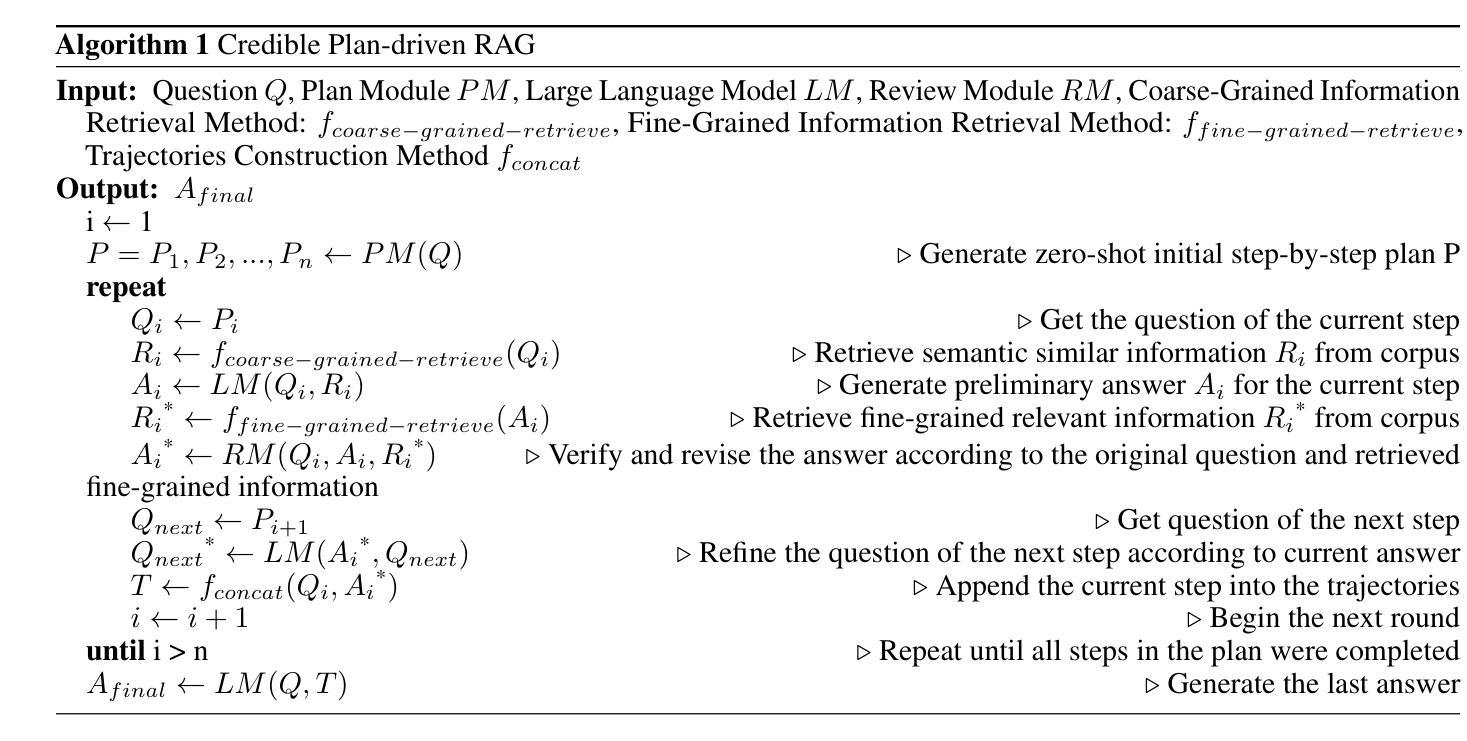
Multi-hop question answering (QA) presents a considerable challenge for Retrieval-Augmented Generation (RAG), requiring the structured decomposition of complex queries into logical reasoning paths and the generation of dependable intermediate results. However, deviations in reasoning paths or errors in intermediate results, which are common in current RAG methods, may propagate and accumulate throughout the reasoning process, diminishing the accuracy of the answer to complex queries. To address this challenge, we propose the Plan-then-Act-and-Review (PAR RAG) framework, which is organized into three key stages: planning, act, and review, and aims to offer an interpretable and incremental reasoning paradigm for accurate and reliable multi-hop question answering by mitigating error propagation.PAR RAG initially applies a top-down problem decomposition strategy, formulating a comprehensive plan that integrates multiple executable steps from a holistic viewpoint. This approach avoids the pitfalls of local optima common in traditional RAG methods, ensuring the accuracy of the entire reasoning path. Subsequently, PAR RAG incorporates a plan execution mechanism based on multi-granularity verification. By utilizing both coarse-grained similarity information and fine-grained relevant data, the framework thoroughly checks and adjusts intermediate results, ensuring process accuracy while effectively managing error propagation and amplification. Experimental results on multi-hop QA datasets demonstrate that the PAR RAG framework substantially outperforms existing state-of-the-art methods in key metrics, including EM and F1 scores.
多跳问答(QA)为基于检索的生成模型(RAG)带来了相当大的挑战。它要求将复杂的查询结构化地分解为逻辑推理路径并生成可靠的中间结果。然而,当前RAG方法中的推理路径偏差或中间结果错误可能会在整个推理过程中传播和累积,从而降低对复杂查询的答案准确性。为了应对这一挑战,我们提出了计划-行动-评审(PAR RAG)框架,该框架分为规划、行动和评审三个阶段,旨在通过缓解错误传播为准确可靠的多跳问答提供可解释和增量推理范式。
PAR RAG首先采用自上而下的问题分解策略,从全局角度制定包含多个可执行步骤的综合计划。这种方法避免了传统RAG方法中常见的局部最优陷阱,确保了整个推理路径的准确性。接着,PAR RAG融入基于多粒度验证的计划执行机制。通过利用粗粒度相似性信息和细粒度相关数据,该框架彻底检查和调整中间结果,确保流程准确性,同时有效管理错误传播和放大。在多跳QA数据集上的实验结果表明,PAR RAG框架在关键指标(包括EM和F1得分)上显著优于现有最先进的方法。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF 18 pages, 3 figures
Summary
该文本主要介绍了针对多跳问答中的挑战,提出一种名为Plan-then-Act-and-Review(PAR RAG)的框架。该框架通过规划、执行和审查三个阶段,旨在提供一种可解释和增量推理范式,以提高多跳问答的准确性和可靠性,并减少错误传播。
Key Takeaways
- 多跳问答对Retrieval-Augmented Generation(RAG)是一大挑战,需将复杂查询分解成逻辑推理路径,并生成可靠的中间结果。
- 当前RAG方法在处理多跳问答时,存在的推理路径偏差或中间结果错误可能会累积并影响最终答案的准确性。
- PAR RAG框架包括规划、执行和审查三个阶段,旨在通过可解释和增量推理提高多跳问答的准确性和可靠性。
- PAR RAG框架使用自上而下的问题分解策略,制定全面计划,从整体上确保整个推理路径的准确性。
- 在执行阶段,PAR RAG利用多粒度验证机制检查并调整中间结果,确保过程的准确性并有效管理错误传播和放大。
- 实验结果表明,PAR RAG框架在关键指标上显著优于现有最先进的方法,包括EM和F1分数。
点此查看论文截图

Skywork R1V2: Multimodal Hybrid Reinforcement Learning for Reasoning
Authors: Chris, Yichen Wei, Yi Peng, Xiaokun Wang, Weijie Qiu, Wei Shen, Tianyidan Xie, Jiangbo Pei, Jianhao Zhang, Yunzhuo Hao, Xuchen Song, Yang Liu, Yahui Zhou
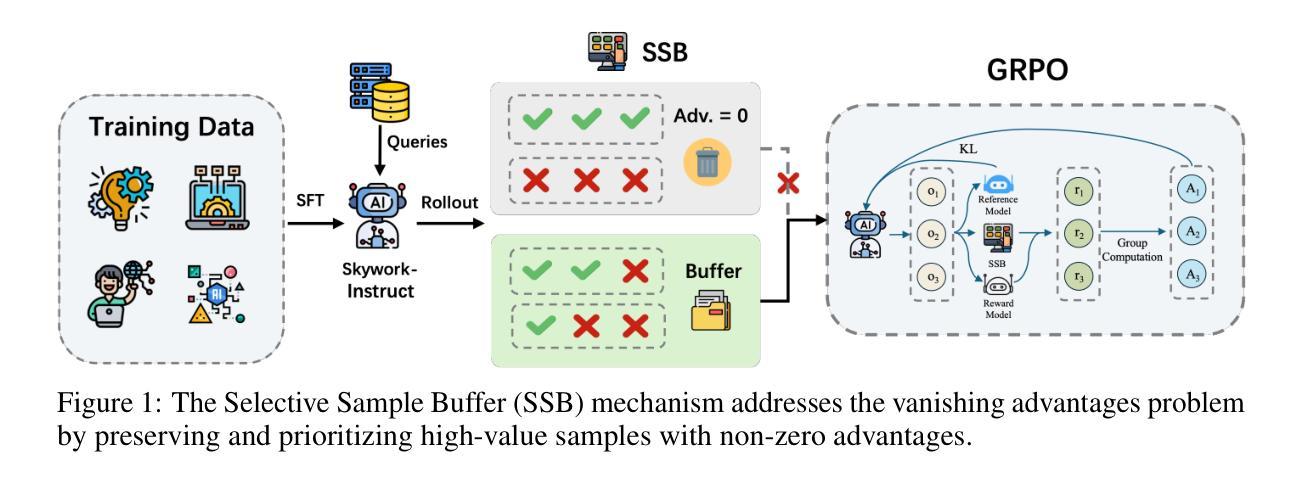
We present Skywork R1V2, a next-generation multimodal reasoning model and a major leap forward from its predecessor, Skywork R1V. At its core, R1V2 introduces a hybrid reinforcement learning paradigm that harmonizes reward-model guidance with rule-based strategies, thereby addressing the long-standing challenge of balancing sophisticated reasoning capabilities with broad generalization. To further enhance training efficiency, we propose the Selective Sample Buffer (SSB) mechanism, which effectively counters the ``Vanishing Advantages’’ dilemma inherent in Group Relative Policy Optimization (GRPO) by prioritizing high-value samples throughout the optimization process. Notably, we observe that excessive reinforcement signals can induce visual hallucinations–a phenomenon we systematically monitor and mitigate through calibrated reward thresholds throughout the training process. Empirical results affirm the exceptional capability of R1V2, with benchmark-leading performances such as 62.6 on OlympiadBench, 79.0 on AIME2024, 63.6 on LiveCodeBench, and 74.0 on MMMU. These results underscore R1V2’s superiority over existing open-source models and demonstrate significant progress in closing the performance gap with premier proprietary systems, including Gemini 2.5 and OpenAI o4-mini. The Skywork R1V2 model weights have been publicly released to promote openness and reproducibility https://huggingface.co/Skywork/Skywork-R1V2-38B.
我们推出了Skywork R1V2,这是下一代多模态推理模型,也是其前身Skywork R1V的一次重大飞跃。R1V2的核心是引入了一种混合强化学习范式,该范式将奖励模型指导与基于规则的策略相协调,从而解决了长期存在的在平衡复杂推理能力和广泛泛化方面的挑战。为了进一步提高训练效率,我们提出了选择性样本缓冲(SSB)机制,它通过在整个优化过程中优先处理高价值样本,有效应对群体相对策略优化(GRPO)中固有的“优势消失”困境。值得注意的是,我们观察到过多的强化信号可能导致视觉幻觉——我们通过对训练过程中的奖励阈值进行校准来系统监测和缓解这一现象。经验结果证实了R1V2的卓越能力,其在OlympiadBench上的得分高达62.6,AIME2024上的得分为79.0,LiveCodeBench上的得分为63.6,MMMU上的得分为74.0。这些结果凸显了R1V2在现有开源模型中的优越性,并展示了与顶级专有系统(包括Gemini 2.5和OpenAI o4-mini)的性能差距得到显著缩小。Skywork R1V2模型权重已经公开发布,以促进开放性和可重复性,访问地址:https://huggingface.co/Skywork/Skywork-R1V2-38B。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary:
Skywork R1V2是新一代的多模态推理模型,是Skywork R1V的重大突破。其核心引入了混合强化学习范式,融合了奖励模型指导和基于规则的策略,解决了长期存在的平衡复杂推理能力和广泛泛化能力的挑战。为提高训练效率,提出了选择性样本缓冲机制(SSB),有效解决了群体相对策略优化(GRPO)中的“优势消失”困境。R1V2模型的权重已公开发布,以促进开放性和可重复性。其实力得到了评估的验证,包括在OlympiadBench上的得分是领先的,与现有开源模型相比具有优势,并缩小了与高端专有系统的性能差距。
Key Takeaways:
- Skywork R1V2是新一代多模态推理模型,Skywork R1V的重大突破。
- R1V2引入了混合强化学习范式,融合了奖励模型指导和基于规则的策略。
- R1V2解决了平衡复杂推理能力和广泛泛化能力的挑战。
- 提出选择性样本缓冲机制(SSB)以提高训练效率并解决“优势消失”问题。
- R1V2模型的性能经过实证验证,包括在多个基准测试上的表现领先。
- R1V2模型权重已公开发布,促进开放性和可重复性。
点此查看论文截图

PIS: Linking Importance Sampling and Attention Mechanisms for Efficient Prompt Compression
Authors:Lizhe Chen, Binjia Zhou, Yuyao Ge, Jiayi Chen, Shiguang NI
Large language models (LLMs) have achieved remarkable progress, demonstrating unprecedented capabilities across various natural language processing tasks. However, the high costs associated with such exceptional performance limit the widespread adoption of LLMs, highlighting the need for prompt compression. Existing prompt compression methods primarily rely on heuristic truncation or abstractive summarization techniques, which fundamentally overlook the intrinsic mechanisms of LLMs and lack a systematic evaluation of token importance for generation. In this work, we introduce Prompt Importance Sampling (PIS), a novel compression framework that dynamically compresses prompts by sampling important tokens based on the analysis of attention scores of hidden states. PIS employs a dual-level compression mechanism: 1) at the token level, we quantify saliency using LLM-native attention scores and implement adaptive compression through a lightweight 9-layer reinforcement learning (RL) network; 2) at the semantic level, we propose a Russian roulette sampling strategy for sentence-level importance sampling. Comprehensive evaluations across multiple domain benchmarks demonstrate that our method achieves state-of-the-art compression performance. Notably, our framework serendipitously enhances reasoning efficiency through optimized context structuring. This work advances prompt engineering by offering both theoretical grounding and practical efficiency in context management for LLMs.
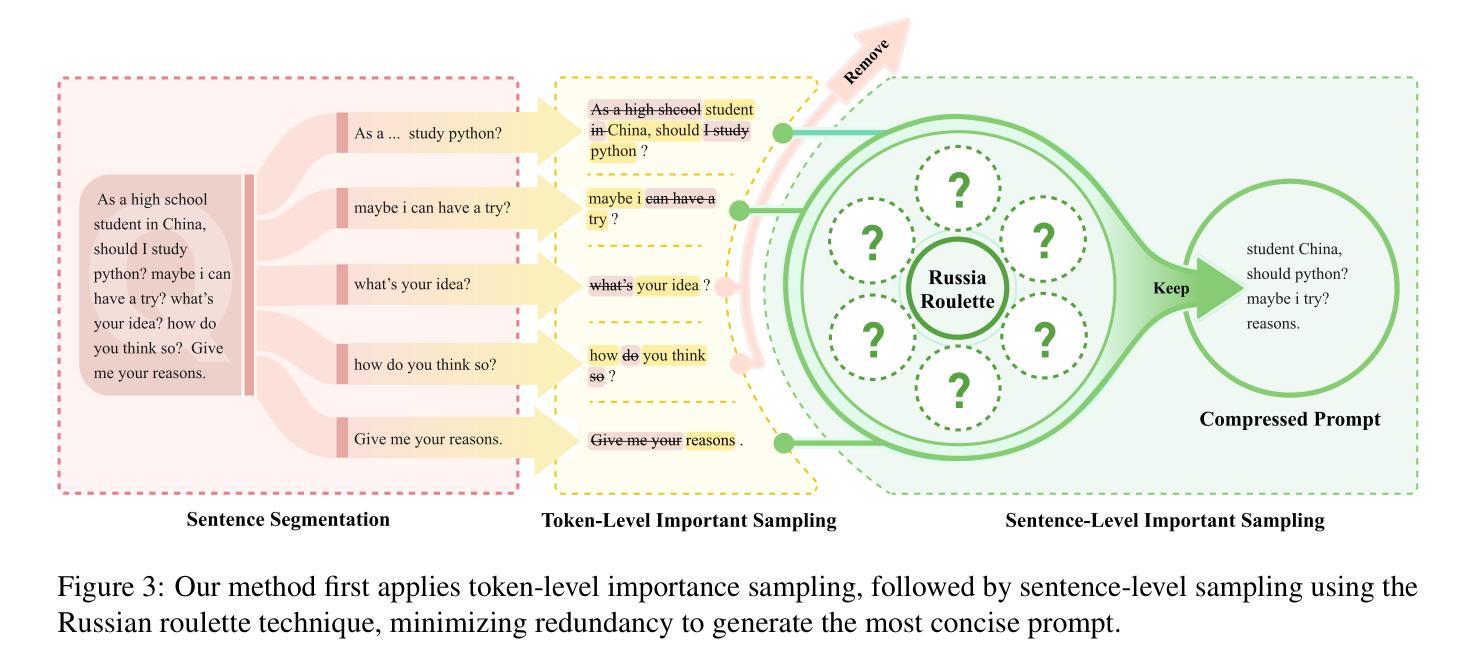
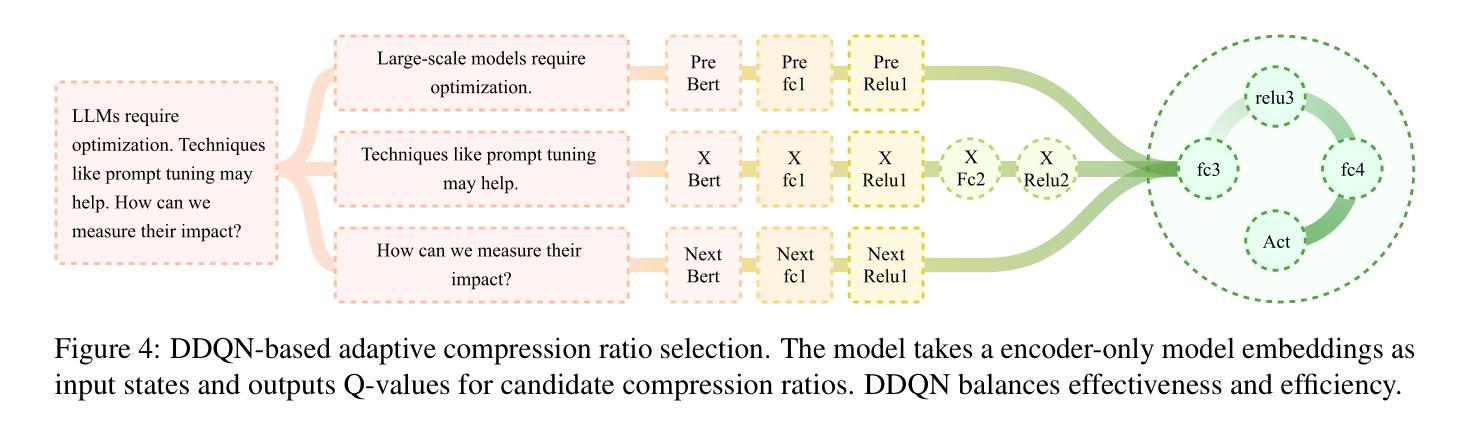
大规模语言模型(LLM)已经取得了显著的进步,在各种自然语言处理任务中展示了前所未有的能力。然而,与这种卓越性能相关的高昂成本限制了LLM的广泛应用,从而凸显了提示压缩的必要性。现有的提示压缩方法主要依赖于启发式截断或抽象摘要技术,这从根本上忽视了LLM的内在机制,缺乏对生成令牌重要性的系统评估。在这项工作中,我们引入了提示重要性采样(PIS),这是一种新的压缩框架,它通过基于隐藏状态注意力分数的分析来采样重要令牌,从而动态压缩提示。PIS采用双重压缩机制:1)在令牌级别,我们使用LLM本地注意力分数量化显著性,并通过轻量级的9层强化学习(RL)网络实现自适应压缩;2)在语义层面,我们提出了一种俄罗斯轮盘采样策略,用于句子级别的重要性采样。在多个领域基准测试上的综合评估表明,我们的方法实现了最先进的压缩性能。值得注意的是,我们的框架通过优化上下文结构意外地提高了推理效率。这项工作通过为LLM提供理论支持和实用高效的上下文管理,推动了提示工程的发展。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
大型语言模型(LLMs)在众多自然语言处理任务中表现出卓越性能,但其高昂成本限制了广泛应用,迫切需要压缩提示。现有提示压缩方法主要依赖启发式截断或抽象摘要技术,忽略了LLM的内在机制,缺乏生成过程中token重要性的系统评估。本研究介绍了一种新的压缩框架——提示重要性采样(PIS),它通过采样重要token动态压缩提示,基于隐藏状态的注意力分数进行分析。PIS采用双重压缩机制:1)在token层面,利用LLM原生注意力分数量化显著性,通过轻量级9层强化学习网络实现自适应压缩;2)在语义层面,提出俄罗斯轮盘采样策略进行句子级别的重要性采样。在多个领域基准测试上的全面评估表明,该方法实现了最先进的压缩性能,并意外地提高了推理效率。
Key Takeaways
- 大型语言模型(LLMs)在自然语言处理任务中表现出卓越性能,但高成本限制了其广泛应用。
- 现有提示压缩方法忽略LLM的内在机制,缺乏生成过程中token重要性的系统评估。
- 新型压缩框架——提示重要性采样(PIS)通过采样重要token动态压缩提示。
- PIS采用双重压缩机制,结合token和语义层面的重要性采样。
- PIS利用LLM原生注意力分数进行token重要性量化,并结合强化学习网络实现自适应压缩。
- PIS在多个领域基准测试上实现最先进的压缩性能。
点此查看论文截图

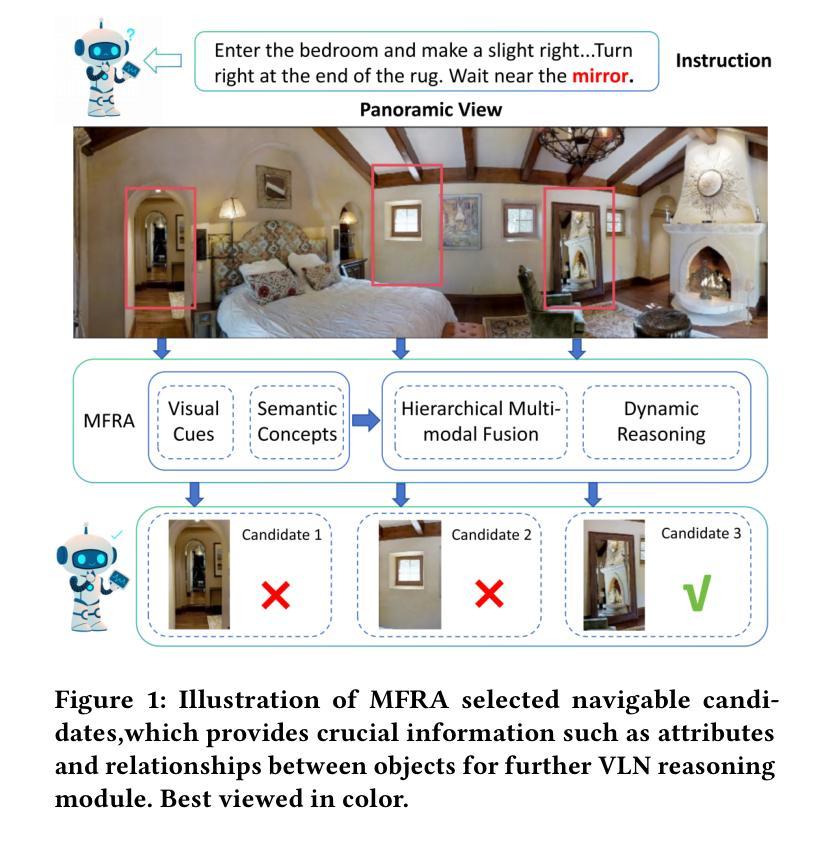
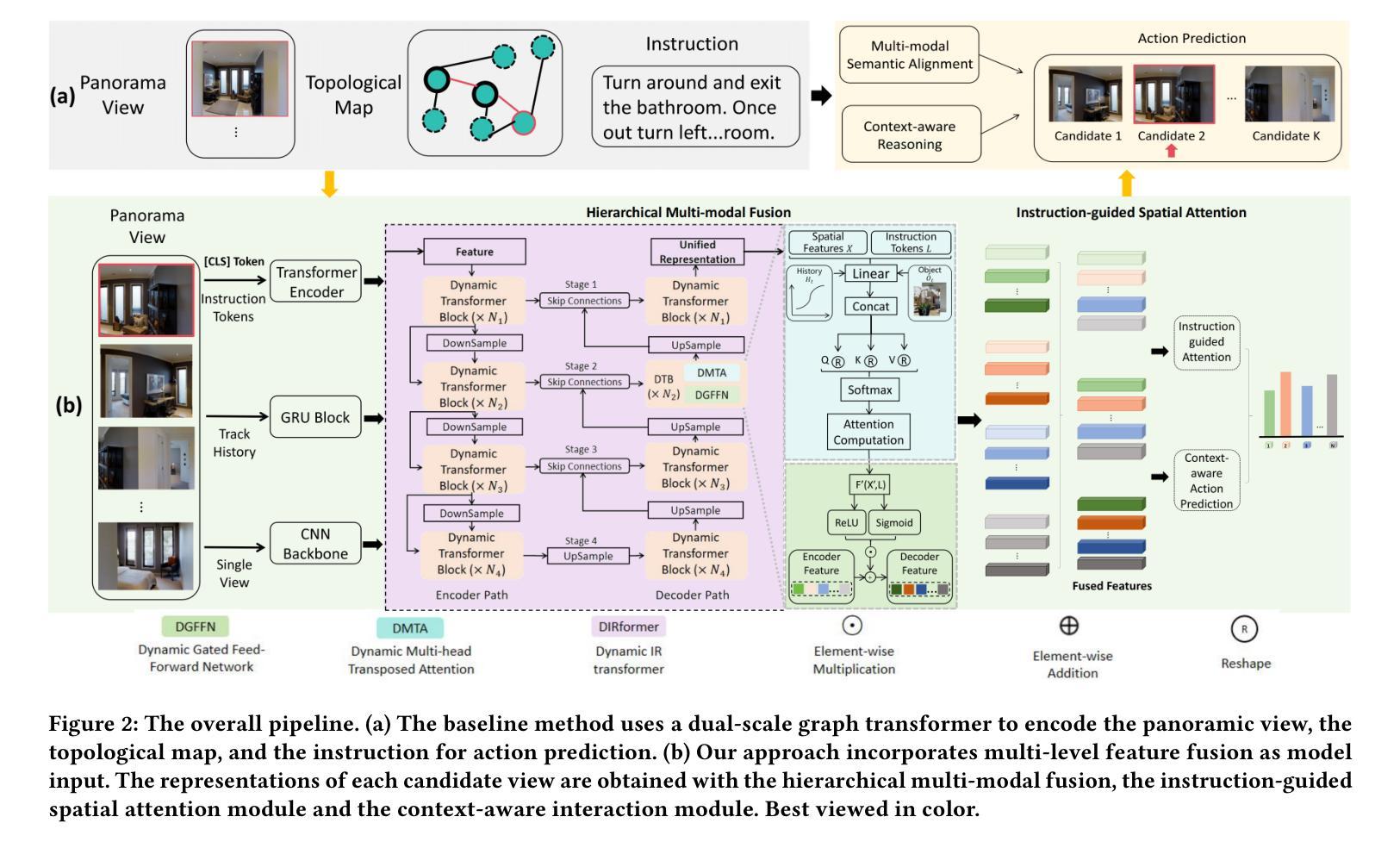
Think Hierarchically, Act Dynamically: Hierarchical Multi-modal Fusion and Reasoning for Vision-and-Language Navigation
Authors:Junrong Yue, Yifan Zhang, Chuan Qin, Bo Li, Xiaomin Lie, Xinlei Yu, Wenxin Zhang, Zhendong Zhao
Vision-and-Language Navigation (VLN) aims to enable embodied agents to follow natural language instructions and reach target locations in real-world environments. While prior methods often rely on either global scene representations or object-level features, these approaches are insufficient for capturing the complex interactions across modalities required for accurate navigation. In this paper, we propose a Multi-level Fusion and Reasoning Architecture (MFRA) to enhance the agent’s ability to reason over visual observations, language instructions and navigation history. Specifically, MFRA introduces a hierarchical fusion mechanism that aggregates multi-level features-ranging from low-level visual cues to high-level semantic concepts-across multiple modalities. We further design a reasoning module that leverages fused representations to infer navigation actions through instruction-guided attention and dynamic context integration. By selectively capturing and combining relevant visual, linguistic, and temporal signals, MFRA improves decision-making accuracy in complex navigation scenarios. Extensive experiments on benchmark VLN datasets including REVERIE, R2R, and SOON demonstrate that MFRA achieves superior performance compared to state-of-the-art methods, validating the effectiveness of multi-level modal fusion for embodied navigation.
视觉与语言导航(VLN)的目标是使实体代理能够遵循自然语言指令,并在真实世界环境中到达目标位置。尽管先前的方法经常依赖于全局场景表示或对象级特征,但这些方法对于捕获跨不同模式所需进行的复杂交互不够充分,无法进行精确的导航。在本文中,我们提出了一种多层级融合推理架构(MFRA),以增强代理在视觉观察、语言指令和导航历史记录方面的推理能力。具体来说,MFRA引入了一种分层融合机制,该机制能够融合跨多个模式的多层次特征,范围从低级别的视觉线索到高级别的语义概念。我们进一步设计了一个推理模块,该模块利用融合后的表示形式,通过指令引导注意力以及动态上下文整合来推断导航动作。通过有选择地捕获和结合相关的视觉、语言和时间信号,MFRA提高了在复杂导航场景中的决策准确性。在包括REVERIE、R2R和SOON在内的基准VLN数据集上的大量实验表明,与最新方法相比,MFRA实现了卓越的性能,验证了多层级模式融合在实体导航中的有效性。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF 11 pages, 4 figures, Submitted to ACM MM 2025
Summary
在这个任务中,提出了一个名为Multi-level Fusion and Reasoning Architecture(MFRA)的新架构,旨在增强代理在视觉观察、语言指令和导航历史方面的推理能力。该架构引入了多层次融合机制,聚合不同层级的多模态特征,并利用融合后的表示进行推理,通过指令引导注意力和动态上下文整合来推断导航动作。在复杂的导航场景中,MFRA通过选择性地捕获和结合相关的视觉、语言和时序信号,提高了决策准确性。在基准VLN数据集上的实验表明,MFRA相较于最先进的方法实现了卓越的性能。
Key Takeaways
- VLN任务旨在使实体代理能够根据自然语言指令在真实环境中导航到目标位置。
- 现有方法主要依赖于全局场景表示或对象级特征,但不足以捕捉跨模态的复杂交互。
- MFRA架构引入了一个多层次融合机制,聚合从低级别视觉线索到高级语义概念的多层次特征。
- MFRA设计了一个推理模块,利用融合后的表示进行推理,通过指令引导注意力和动态上下文整合来推断导航动作。
- MFRA通过结合视觉、语言和时序信号,提高了复杂导航场景中的决策准确性。
- 在基准VLN数据集上的实验表明,MFRA相较于其他方法具有优越性能。
点此查看论文截图


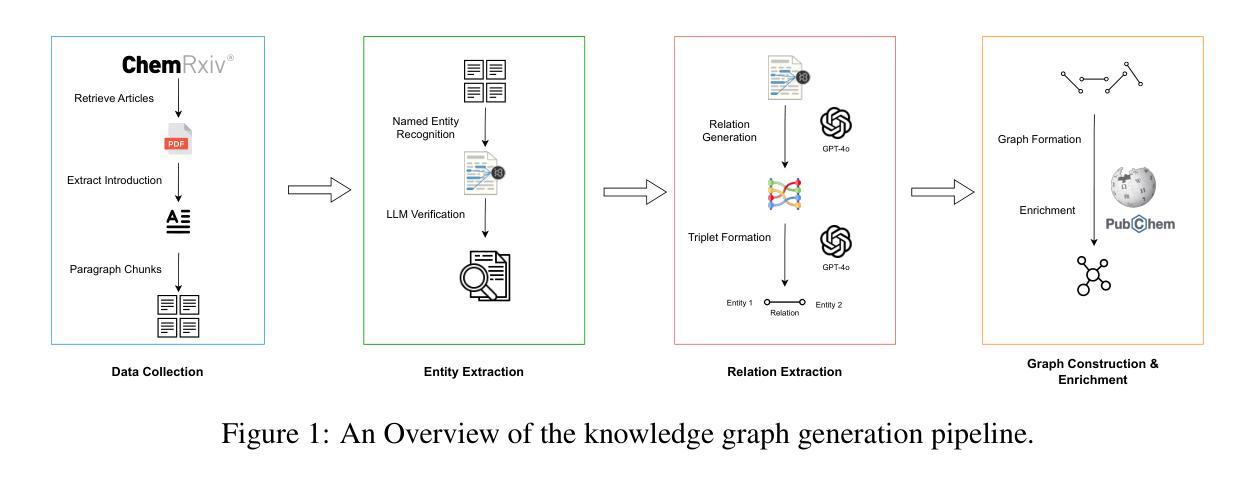
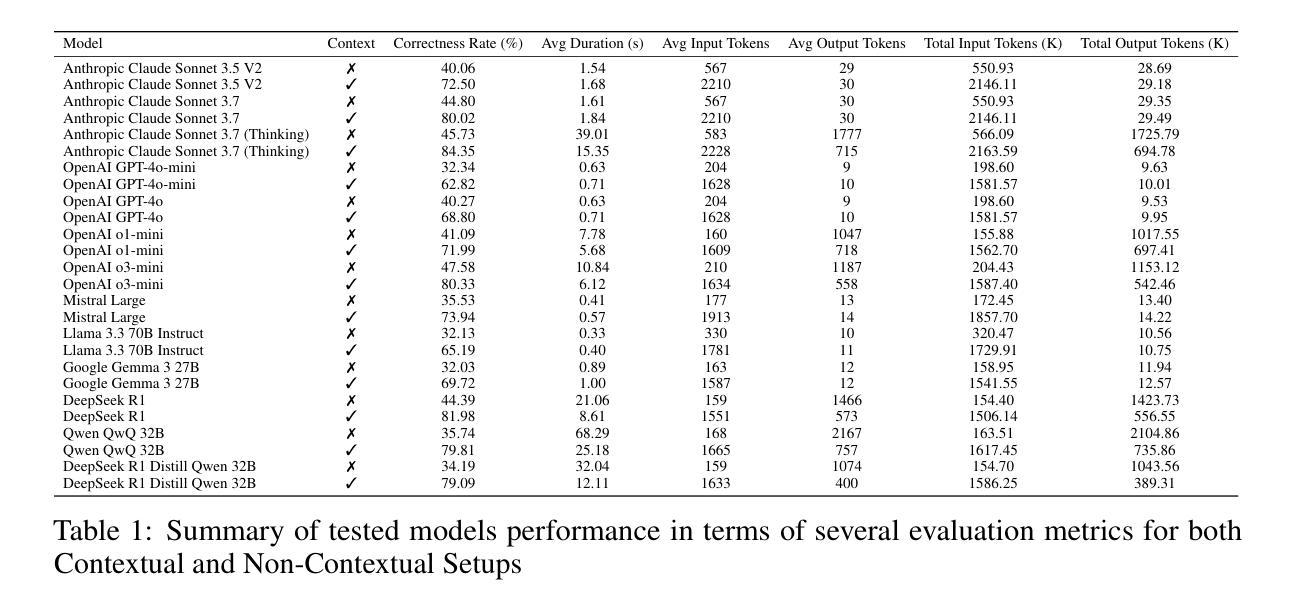
Evaluating Multi-Hop Reasoning in Large Language Models: A Chemistry-Centric Case Study
Authors:Mohammad Khodadad, Ali Shiraee Kasmaee, Mahdi Astaraki, Nicholas Sherck, Hamidreza Mahyar, Soheila Samiee
In this study, we introduced a new benchmark consisting of a curated dataset and a defined evaluation process to assess the compositional reasoning capabilities of large language models within the chemistry domain. We designed and validated a fully automated pipeline, verified by subject matter experts, to facilitate this task. Our approach integrates OpenAI reasoning models with named entity recognition (NER) systems to extract chemical entities from recent literature, which are then augmented with external knowledge bases to form a comprehensive knowledge graph. By generating multi-hop questions across these graphs, we assess LLM performance in both context-augmented and non-context augmented settings. Our experiments reveal that even state-of-the-art models face significant challenges in multi-hop compositional reasoning. The results reflect the importance of augmenting LLMs with document retrieval, which can have a substantial impact on improving their performance. However, even perfect retrieval accuracy with full context does not eliminate reasoning errors, underscoring the complexity of compositional reasoning. This work not only benchmarks and highlights the limitations of current LLMs but also presents a novel data generation pipeline capable of producing challenging reasoning datasets across various domains. Overall, this research advances our understanding of reasoning in computational linguistics.
在这项研究中,我们引入了一个新的基准测试,该测试包括一个精选的数据集和一个明确的评估过程,以评估大型语言模型在化学领域的组合推理能力。我们设计并验证了一个全自动化的流程管道,通过相关领域的专家验证来促进这一任务。我们的方法将OpenAI推理模型与命名实体识别(NER)系统相结合,从最新文献中提取化学实体,然后与外部知识库相结合形成全面的知识图谱。通过在这些图谱上生成多跳问题,我们评估了大型语言模型在上下文增强和非上下文增强环境中的表现。我们的实验表明,即使是最先进的技术模型也面临着多跳组合推理的重大挑战。结果反映了使用文档检索增强大型语言模型的重要性,这可能会对改善其性能产生重大影响。然而,即使在具有完整上下文的完美检索准确率下,也不能消除推理错误,这凸显了组合推理的复杂性。这项工作不仅衡量并突出了当前大型语言模型的局限性,而且还提出了一种新的数据生成流程管道,能够在各个领域生成具有挑战性的推理数据集。总体而言,这项研究推动了我们对计算语言学中推理的理解的进步。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
本文引入了一个新的基准测试,包括一个精选的数据集和一个明确的评估过程,以评估大型语言模型在化学领域的组合推理能力。设计并验证了一个全自动的管道,经过主题专家验证,以促进这一任务。该方法结合了OpenAI推理模型与命名实体识别(NER)系统,从最新文献中提取化学实体,然后与外部知识库相结合,形成全面的知识图谱。通过在这些图上生成多跳问题,我们评估了LLM在增强上下文和非增强上下文设置中的性能。实验表明,即使是最先进的大型语言模型也面临着多跳组合推理的诸多挑战。结果反映了增加文档检索对改善大型语言模型性能的重要性。然而,即使达到完美的检索精度和全上下文,也无法消除推理错误,这凸显了组合推理的复杂性。本文不仅评估和突出了当前大型语言模型的局限性,而且展示了一种能够生成跨不同领域具有挑战性的推理数据集的新型数据生成管道。总体而言,该研究推动了计算语言学中的推理理解的发展。
Key Takeaways
- 引入新的基准测试来评估大型语言模型在化学领域的组合推理能力。
- 设计并验证了一个全自动的数据处理管道,用于生成化学领域的推理问题。
- 结合OpenAI推理模型和命名实体识别系统提取化学实体,并构建知识图谱。
- 通过多跳问题评估大型语言模型性能,强调文档检索在改善模型性能中的重要性。
- 实验显示,即使是最先进的大型语言模型也面临组合推理的挑战。
- 完美的检索精度和全上下文并不能完全消除推理错误,凸显了组合推理的复杂性。
点此查看论文截图

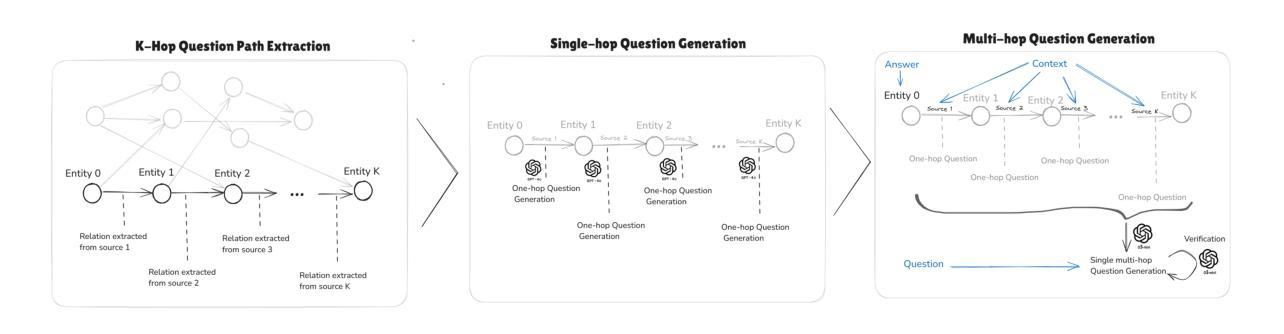
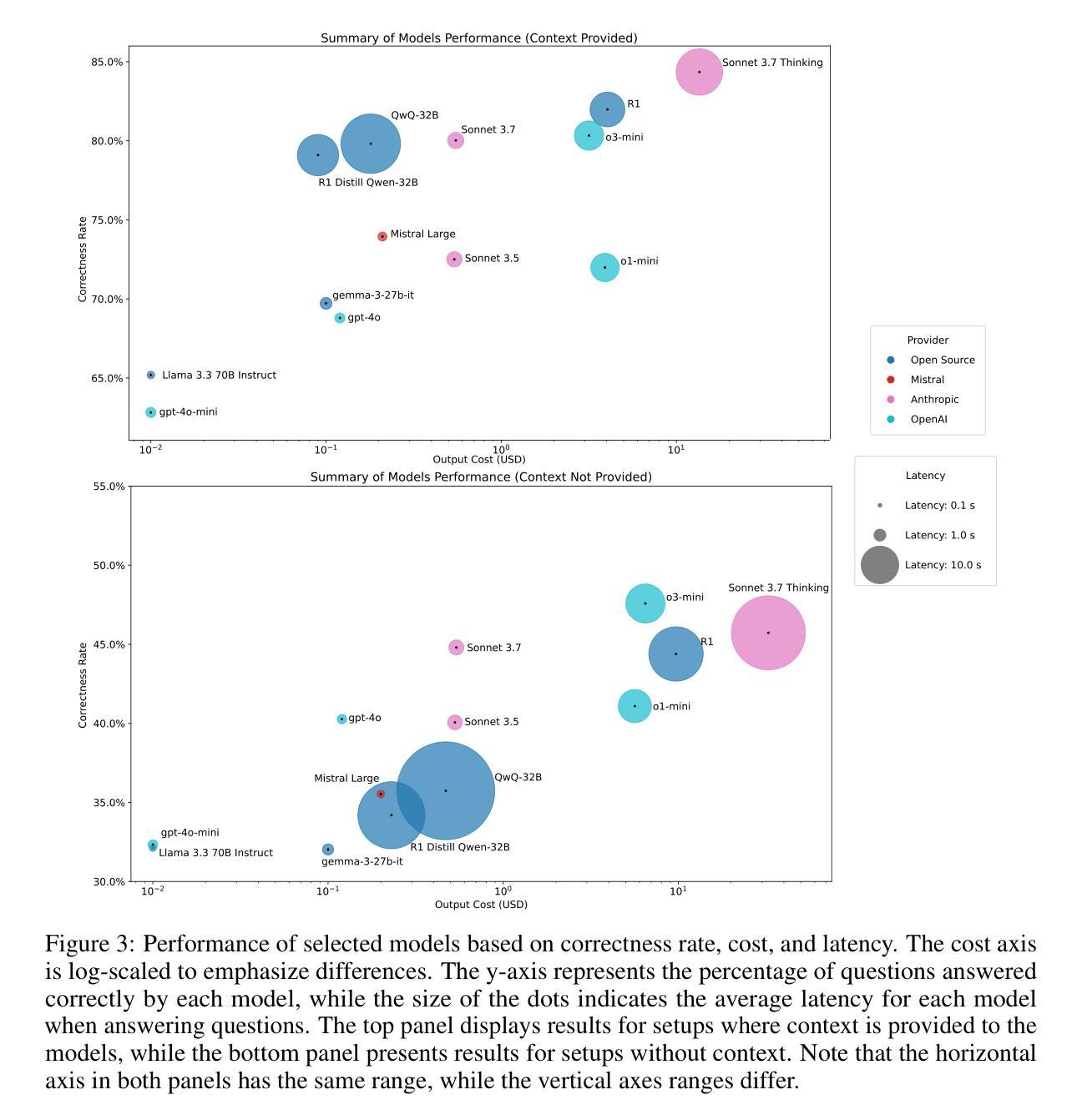
Less is More: Enhancing Structured Multi-Agent Reasoning via Quality-Guided Distillation
Authors:Jiahao Yuan, Xingzhe Sun, Xing Yu, Jingwen Wang, Dehui Du, Zhiqing Cui, Zixiang Di
The XLLM@ACL2025 Shared Task-III formulates a low-resource structural reasoning task that challenges LLMs to generate interpretable, step-by-step rationales with minimal labeled data. We present Less is More, the third-place winning approach in the XLLM@ACL2025 Shared Task-III, which focuses on structured reasoning from only 24 labeled examples. Our approach leverages a multi-agent framework with reverse-prompt induction, retrieval-augmented reasoning synthesis via GPT-4o, and dual-stage reward-guided filtering to distill high-quality supervision across three subtasks: question parsing, CoT parsing, and step-level verification. All modules are fine-tuned from Meta-Llama-3-8B-Instruct under a unified LoRA+ setup. By combining structure validation with reward filtering across few-shot and zero-shot prompts, our pipeline consistently improves structure reasoning quality. These results underscore the value of controllable data distillation in enhancing structured inference under low-resource constraints. Our code is available at https://github.com/Jiahao-Yuan/Less-is-More.
XLLM@ACL2025共享任务III制定了一个低资源结构推理任务,该任务挑战了大型语言模型在少量标注数据的情况下生成可解释的、逐步的理性推理。我们提出了”少即是多”,这是XLLM@ACL2025共享任务III的第三名获奖方案,该方案仅关注于从24个标注示例中进行结构化推理。我们的方法利用多智能体框架进行逆向提示归纳,通过GPT-4o增强推理合成,以及两阶段奖励引导过滤,在三个子任务中提炼高质量监督:问题解析、认知轨迹解析和步骤级验证。所有模块都在统一的LoRA+设置下使用Meta-Llama-3-8B-Instruct进行微调。通过结合结构验证和奖励过滤在少数和零样本提示之间,我们的管道始终提高了结构推理质量。这些结果强调了可控数据蒸馏在增强低资源约束下的结构化推理中的价值。我们的代码可在https://github.com/Jiahao-Yuan/Less-is-More中找到。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
这是一篇关于在XLLM@ACL2025共享任务中挑战大型语言模型(LLMs)进行低资源结构推理的文章。该文章提出了Less is More的方法,通过结构化的方式,使用少量的标签数据,利用多智能体框架、反向提示归纳法、GPT-4o增强推理合成等实现高质量推理监督的三个子任务。这种方法可以提高结构化推理的质量,强调了在资源有限的情况下,可控数据蒸馏的价值。具体细节可以通过访问所提供的链接获取。
Key Takeaways
以下是关于该文本的关键见解:
- XLLM@ACL2025共享任务提出了一个低资源结构推理的挑战。重点在于如何在缺乏大规模数据集的情况下实现模型的优秀性能。该挑战特别重视模型生成的可解释性,以及步骤间的逻辑推理。
- Less is More方法成功获得了该任务的第三名,其核心思想在于通过结构化方法从少量标签数据中获取高质量的推理结果。具体来说,通过一种多智能体框架实现此目标,结合了反向提示归纳法以及通过GPT-4o增强推理合成技术。这些方法结合成一个系统化的过程,确保在有限的数据条件下也能获得高质量的推理结果。
点此查看论文截图

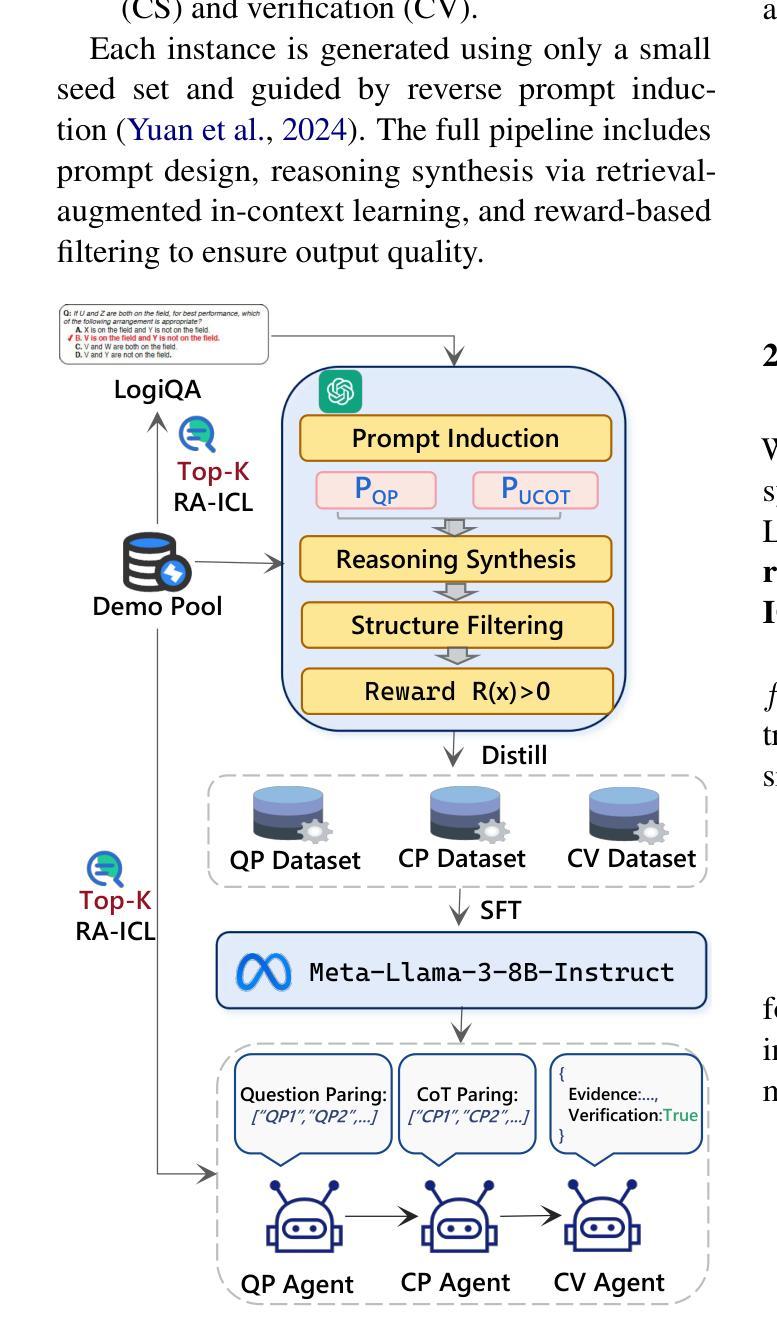
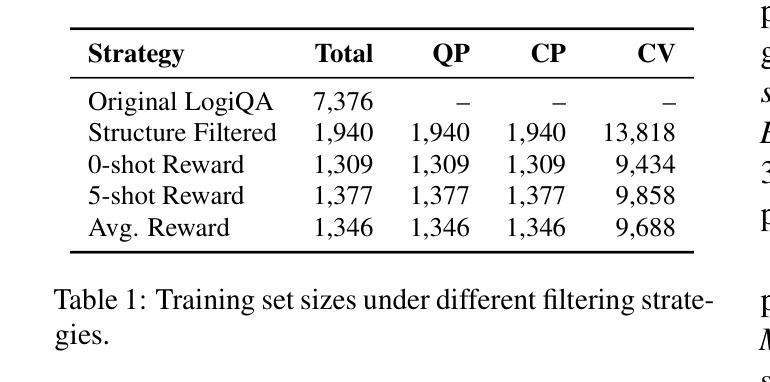
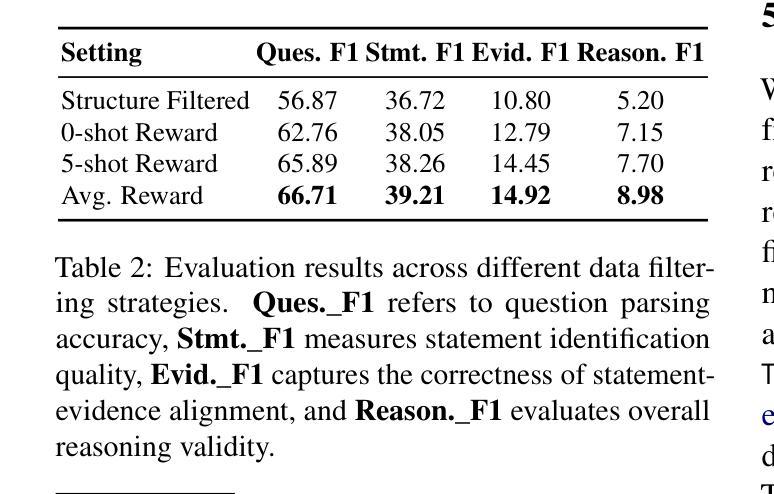

FinNLI: Novel Dataset for Multi-Genre Financial Natural Language Inference Benchmarking
Authors:Jabez Magomere, Elena Kochkina, Samuel Mensah, Simerjot Kaur, Charese H. Smiley
We introduce FinNLI, a benchmark dataset for Financial Natural Language Inference (FinNLI) across diverse financial texts like SEC Filings, Annual Reports, and Earnings Call transcripts. Our dataset framework ensures diverse premise-hypothesis pairs while minimizing spurious correlations. FinNLI comprises 21,304 pairs, including a high-quality test set of 3,304 instances annotated by finance experts. Evaluations show that domain shift significantly degrades general-domain NLI performance. The highest Macro F1 scores for pre-trained (PLMs) and large language models (LLMs) baselines are 74.57% and 78.62%, respectively, highlighting the dataset’s difficulty. Surprisingly, instruction-tuned financial LLMs perform poorly, suggesting limited generalizability. FinNLI exposes weaknesses in current LLMs for financial reasoning, indicating room for improvement.
我们介绍了FinNLI,这是一个用于金融自然语言推理(FinNLI)的基准数据集,涵盖各种金融文本,如SEC文件、年度报告和收益电话记录。我们的数据集框架可确保多样化的前提假设对,同时最小化偶然相关性。FinNLI包含21,304对样本,其中包括由金融专家标注的高质量测试集,共有3,304个实例。评估表明,领域偏移会显著影响一般领域的NLI性能。对于预训练模型(PLM)和大型语言模型(LLM)基线,最高宏F1分数分别为74.57%和78.62%,这突出了数据集的难度。令人惊讶的是,经过指令调整的金融LLM表现不佳,表明其泛化能力有限。FinNLI暴露了当前用于金融推理的大型语言模型的弱点,表明仍有改进空间。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary:
推出FinNLI数据集,用于金融自然语言推理(Financial Natural Language Inference,FinNLI)。该数据集涵盖SEC文件、年报和收益报告等多种金融文本,确保多样化的前提假设对,同时减少偶然关联。包含高质量测试集,实例标注由金融专家完成。评估显示领域差异显著影响一般域NLI性能。最高宏F1得分分别为预训练模型(PLMs)和大语言模型(LLMs)的基线,分别突出数据集的难度。金融LLM表现令人惊讶地不佳,说明通用性有限。FinNLI揭示了当前金融推理大模型的弱点,显示出改进的空间。
Key Takeaways:
- FinNLI是一个用于金融自然语言推理的基准数据集,涵盖多种金融文本类型。
- 数据集确保多样化的前提假设配对,同时减少偶然关联。
- 数据集包含由金融专家标注的高质量测试集。
- 领域差异显著影响自然语言推理性能。
- 预训练模型和大语言模型在FinNLI上的最高宏F1得分表明数据集的难度。
- 金融领域的指令微调大型语言模型表现不佳,说明其通用性有限。
点此查看论文截图

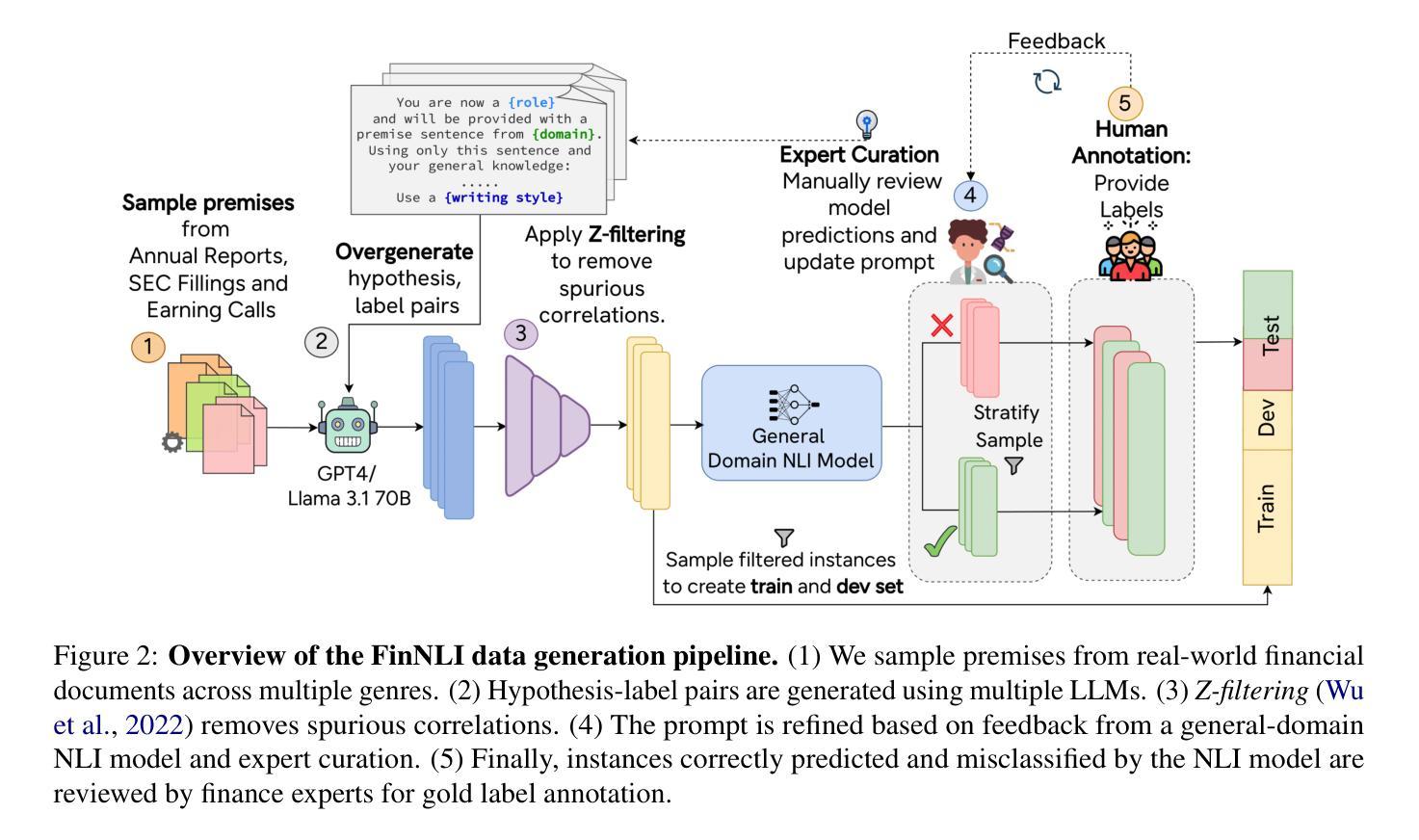
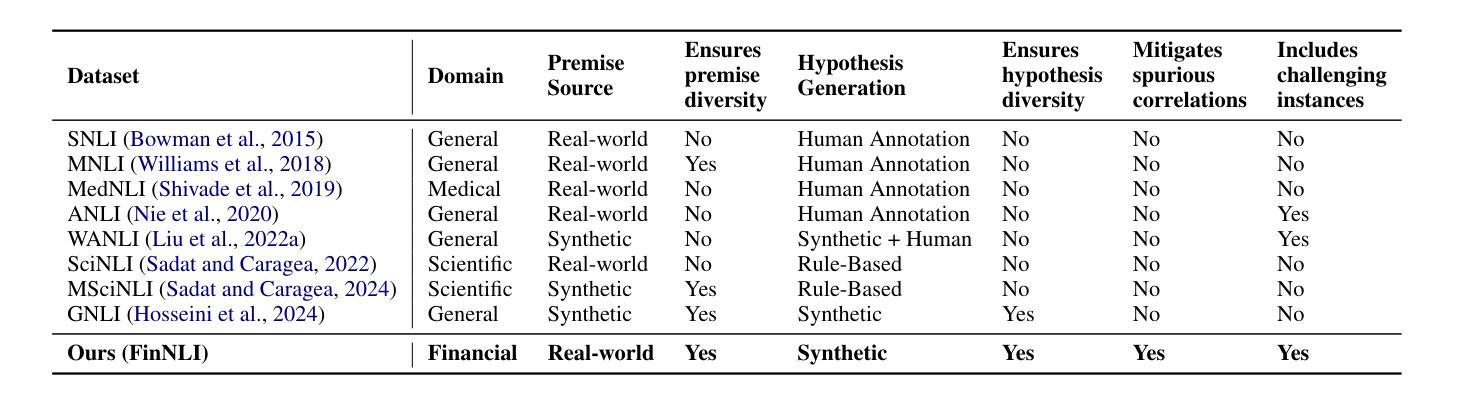
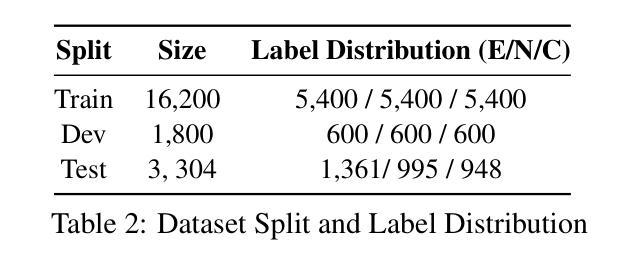
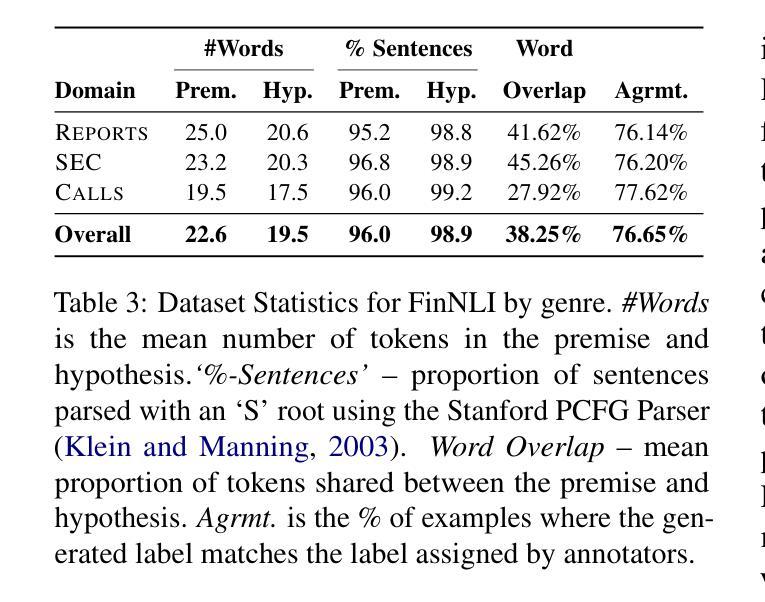
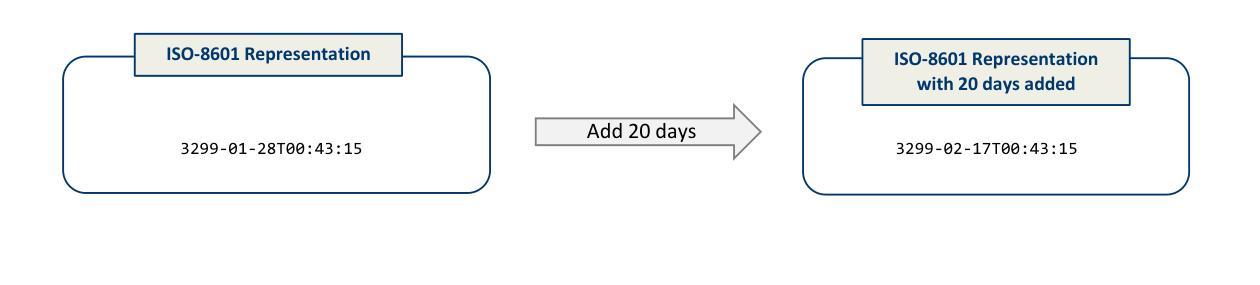
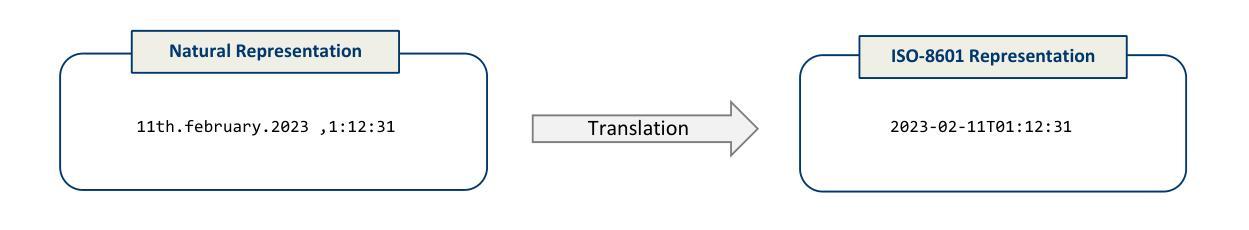
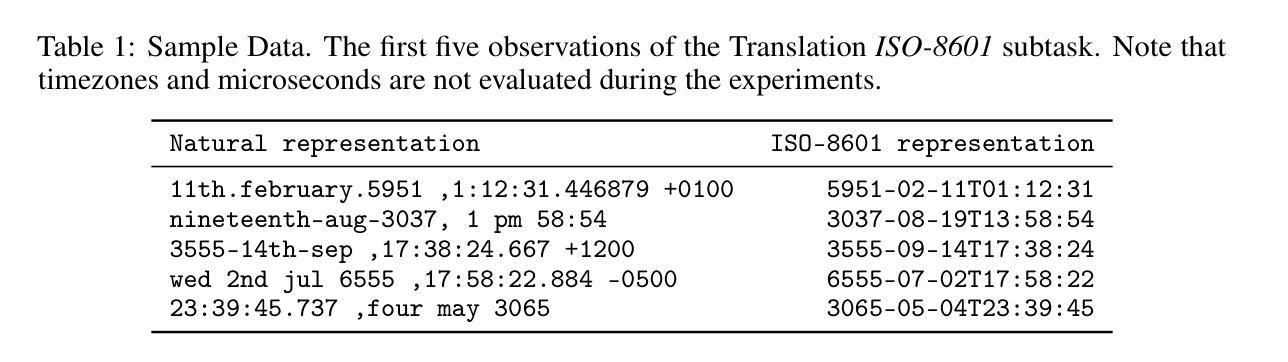
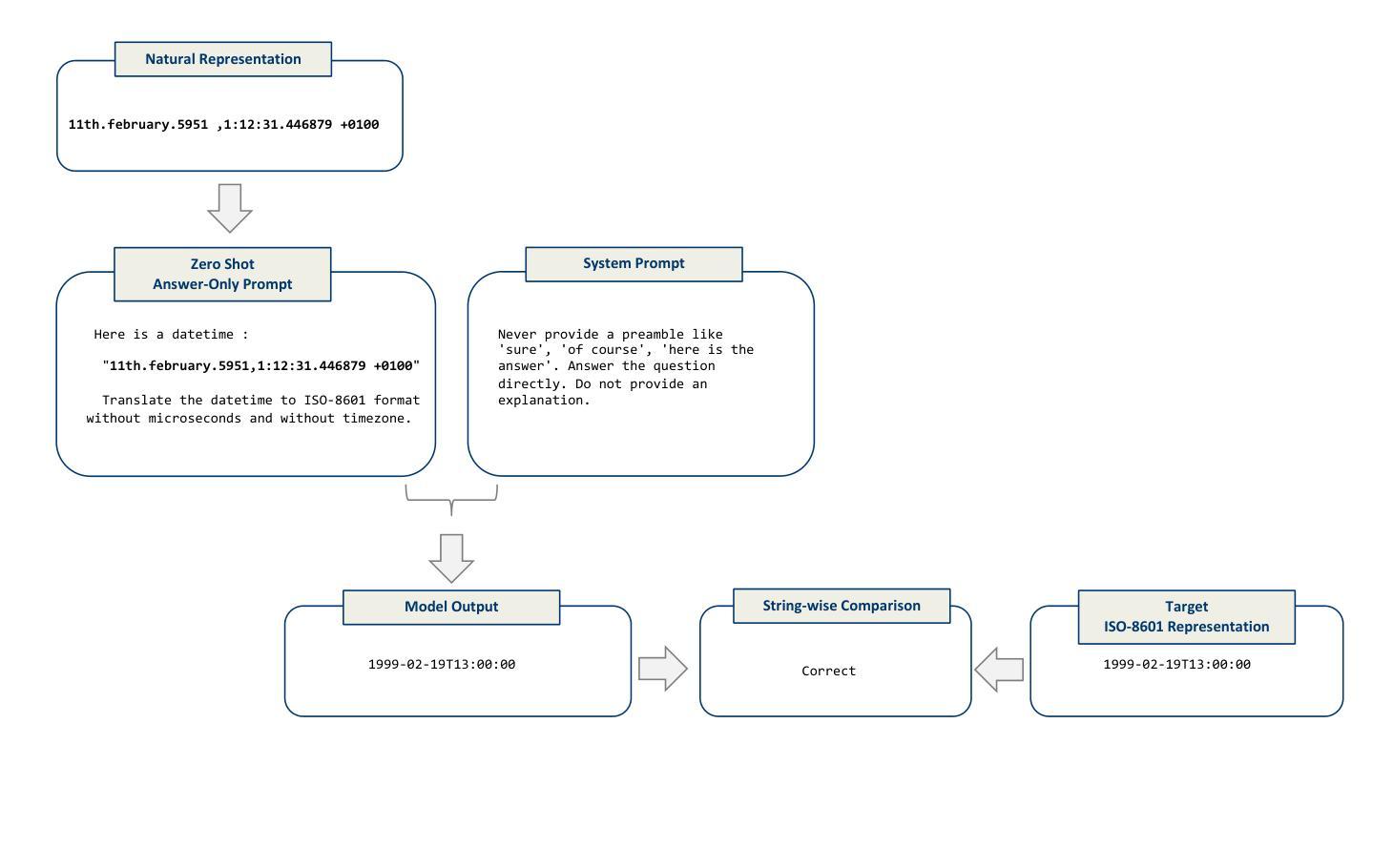
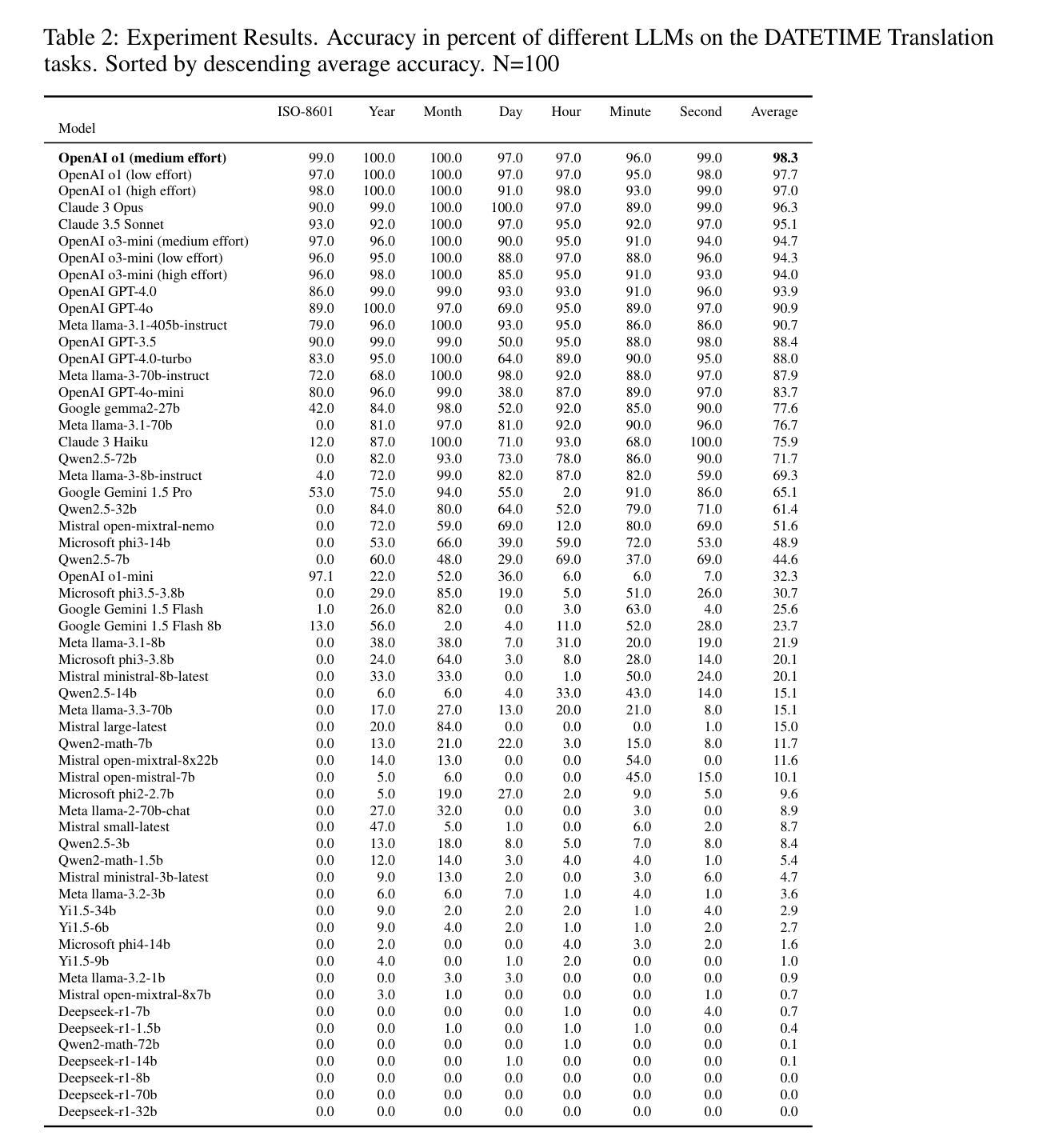
DATETIME: A new benchmark to measure LLM translation and reasoning capabilities
Authors:Edward Gaere, Florian Wangenheim
This paper introduces DATETIME, a new high-quality benchmark designed to evaluate the translation and reasoning abilities of a Large Language Model (LLM) on datetimes. A datetime is simply a date and a time, for example ‘11th.february.2023 ,1:12:31’. Datetimes are an interesting domain because they are intuitive and straightforward for humans to process but present significant challenges for LLMs. At the time of writing, no publicly available benchmark exists for systematically evaluating LLMs on datetime processing. Our experiments show that state-of-the-art models exhibit significant difficulty with tasks involving reasoning on datetimes, and that General Artificial Intelligence is still a distant aspiration. We hypothesize that working with datetimes necessitates translation and/or computation capabilities, and the tasks of the benchmark are organized accordingly. Significant dispersion in performance across models is observed with surprisingly poor performance even on apparently trivial tasks. Whilst frontier models such as ChatGPT, Claude and Llama3.1 have evidently been built and trained with datetime reasoning abilities, significant improvement is required for the open-source models.
本文介绍了DATETIME这一全新高质量基准测试,其目的是评估大型语言模型在处理日期和时间方面的翻译和推理能力。日期和时间是指一个简单的日期和时间组合,例如“2023年2月11日,下午1点12分31秒”。日期时间是一个有趣的领域,因为人类可以很容易地处理它,但对于大型语言模型来说却是一个巨大的挑战。在撰写本文时,尚无公开可用的基准测试来系统地评估大型语言模型处理日期时间的能力。我们的实验表明,最先进的模型在处理涉及日期时间的推理任务时面临很大的困难,通用人工智能仍然是一个遥远的愿景。我们假设处理日期时间需要翻译和/或计算能力,基准测试的任务也相应地进行了组织。各模型之间性能表现出明显的分散性,甚至在表面上看起来很简单任务上的表现也很糟糕。尽管ChatGPT、Claude和Llama 3.1等前沿模型显然已经构建并训练了处理日期时间的推理能力,但对于开源模型来说仍有很大的改进空间。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
本文介绍了一个新的高质量基准测试DATETIME,旨在评估大型语言模型(LLM)在处理日期和时间(datetime)方面的翻译和推理能力。日期时间对人类来说直观且简单处理,但对LLM却存在重大挑战。当前,没有公开的基准测试来系统地评估LLM在日期时间处理方面的能力。实验表明,最先进的模型在涉及日期时间的推理任务上存在困难,通用人工智能仍是遥远的目标。假设处理日期时间需要翻译和/或计算能力,而基准测试的任务也相应安排。不同模型的性能存在显著差异,甚至在显然简单的任务上表现也令人惊讶地糟糕。尽管前沿模型如ChatGPT、Claude和Llama3.1已经具备日期时间推理能力,但开源模型仍需要重大改进。
Key Takeaways
- 引入新的基准测试DATETIME,专注于评估LLM处理日期和时间的能力。
- 日期时间对人类简单,但对LLM存在挑战。
- 目前没有公开的基准测试来系统评估LLM在日期时间处理上的表现。
- 最先进的模型在日期时间的推理任务上遇到困难。
- 处理日期时间需要翻译和/或计算能力。
- 不同模型的性能在处理日期时间上存在显著差异。
点此查看论文截图

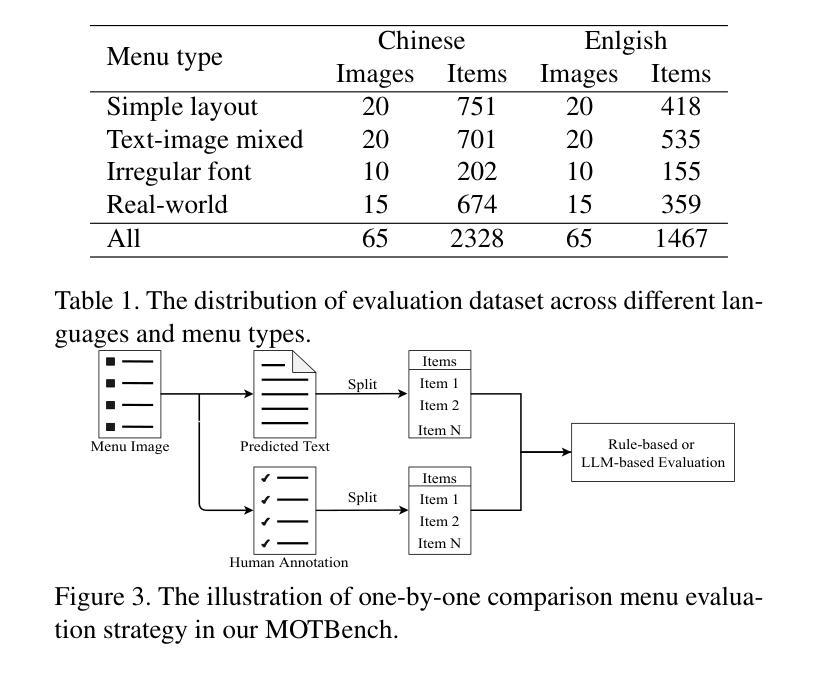
Evaluating Menu OCR and Translation: A Benchmark for Aligning Human and Automated Evaluations in Large Vision-Language Models
Authors:Zhanglin Wu, Tengfei Song, Ning Xie, Mengli Zhu, Weidong Zhang, Shuang Wu, Pengfei Li, Chong Li, Junhao Zhu, Hao Yang, Shiliang Sun
The rapid advancement of large vision-language models (LVLMs) has significantly propelled applications in document understanding, particularly in optical character recognition (OCR) and multilingual translation. However, current evaluations of LVLMs, like the widely used OCRBench, mainly focus on verifying the correctness of their short-text responses and long-text responses with simple layout, while the evaluation of their ability to understand long texts with complex layout design is highly significant but largely overlooked. In this paper, we propose Menu OCR and Translation Benchmark (MOTBench), a specialized evaluation framework emphasizing the pivotal role of menu translation in cross-cultural communication. MOTBench requires LVLMs to accurately recognize and translate each dish, along with its price and unit items on a menu, providing a comprehensive assessment of their visual understanding and language processing capabilities. Our benchmark is comprised of a collection of Chinese and English menus, characterized by intricate layouts, a variety of fonts, and culturally specific elements across different languages, along with precise human annotations. Experiments show that our automatic evaluation results are highly consistent with professional human evaluation. We evaluate a range of publicly available state-of-the-art LVLMs, and through analyzing their output to identify the strengths and weaknesses in their performance, offering valuable insights to guide future advancements in LVLM development. MOTBench is available at https://github.com/gitwzl/MOTBench.
大型视觉语言模型(LVLMs)的快速发展极大地推动了文档理解应用,特别是在光学字符识别(OCR)和多语种翻译领域。然而,目前对LVLMs的评估,如广泛使用的OCRBench,主要侧重于验证其简短文本回应和简单布局长文本回应的正确性,而对于他们理解具有复杂布局设计长文本的能力评估至关重要,却被大大忽视了。在本文中,我们提出了菜单OCR和翻译基准测试(MOTBench),这是一个专门用于评估跨文化交流中菜单翻译的重要作用的评估框架。MOTBench要求LVLMs准确识别并翻译菜单上的每个菜品、价格以及单位项目,从而全面评估其视觉理解和语言处理能力。我们的基准测试包含一系列具有复杂布局、多种字体以及不同语言文化特定元素的中文和英文菜单,以及精确的人类注释。实验表明,我们的自动评估结果与专业人工评估高度一致。我们评估了一系列公开发布的先进LVLMs,通过分析他们的输出来确定其性能的优缺点,为LVLM未来的发展提供有价值的见解。MOTBench可在https://github.com/gitwzl/MOTBench获取。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF 12 pages, 5 figures, 5 Tables
Summary
本文提出一个新的评估框架Menu OCR和翻译基准测试(MOTBench),专注于菜单翻译的跨文化传播重要性。该框架强调大型视觉语言模型(LVLMs)对菜单上的菜品、价格及单位项的准确识别和翻译能力,全面评估其视觉理解和语言处理能力。MOTBench包含中英文菜单,具有复杂的布局、多种字体和跨文化元素,以及精确的人工注释。实验表明,其自动评估结果与专业人工评估高度一致。
Key Takeaways
- 大型视觉语言模型(LVLMs)在文档理解应用,如光学字符识别(OCR)和多语种翻译方面取得快速进展。
- 目前对LVLMs的评估主要集中在简单文本响应的正确性上,但对于处理复杂布局的长文本文档的能力评估被忽视。
- 提出了一个新的评估框架MOTBench,专注于菜单翻译的跨文化传播重要性。
- MOTBench要求LVLMs准确识别和翻译菜单上的菜品、价格及单位项。
- MOTBench包含具有复杂布局、多种字体和跨文化元素的中英文菜单,以及精确的人工注释。
- 自动评估与专业的手动评估结果高度一致。
点此查看论文截图




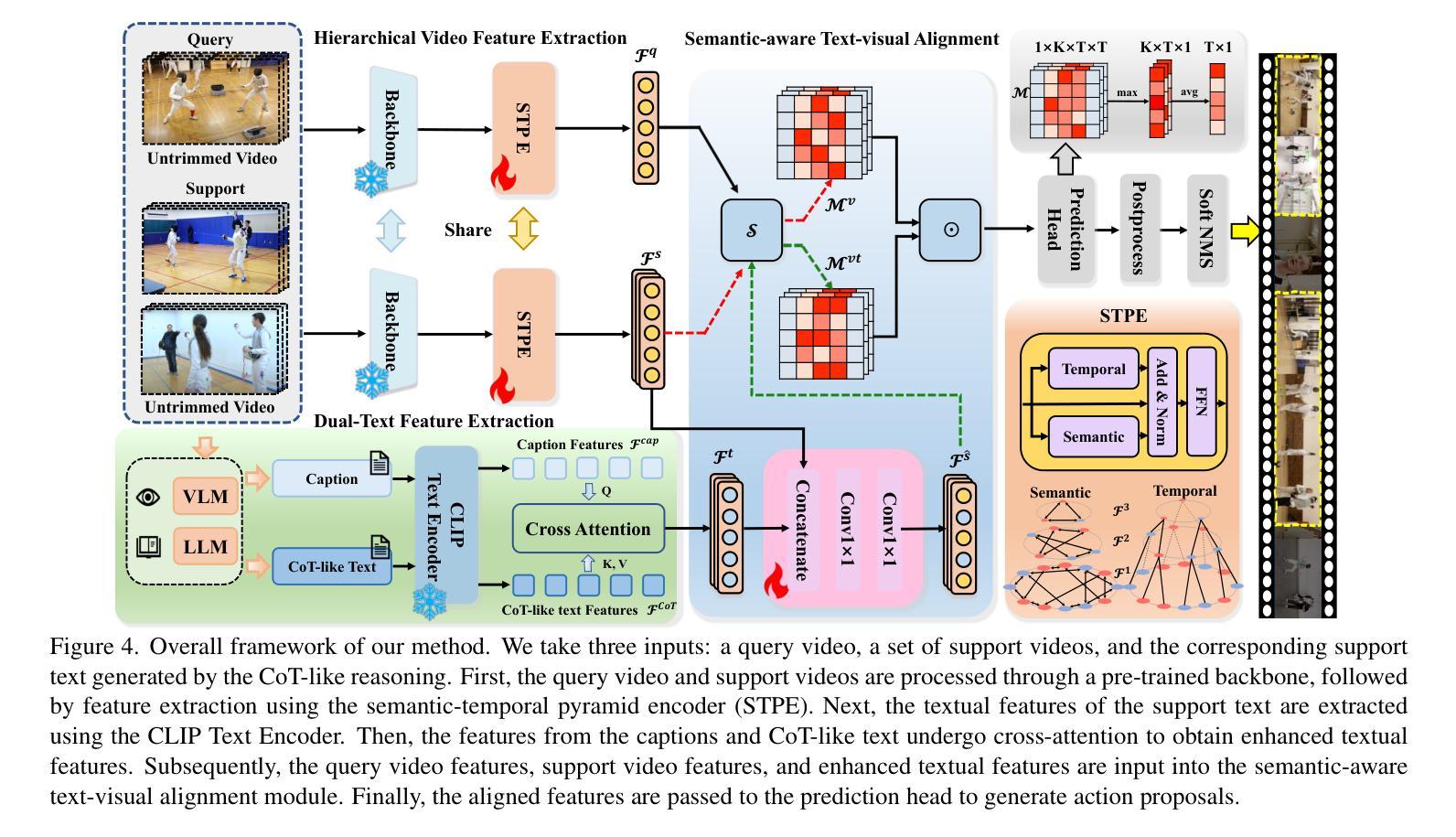
Chain-of-Thought Textual Reasoning for Few-shot Temporal Action Localization
Authors:Hongwei Ji, Wulian Yun, Mengshi Qi, Huadong Ma
Traditional temporal action localization (TAL) methods rely on large amounts of detailed annotated data, whereas few-shot TAL reduces this dependence by using only a few training samples to identify unseen action categories. However, existing few-shot TAL methods typically focus solely on video-level information, neglecting textual information, which can provide valuable semantic support for the localization task. Therefore, we propose a new few-shot temporal action localization method by Chain-of-Thought textual reasoning to improve localization performance. Specifically, we design a novel few-shot learning framework that leverages textual semantic information to enhance the model’s ability to capture action commonalities and variations, which includes a semantic-aware text-visual alignment module designed to align the query and support videos at different levels. Meanwhile, to better express the temporal dependencies and causal relationships between actions at the textual level to assist action localization, we design a Chain of Thought (CoT)-like reasoning method that progressively guides the Vision Language Model (VLM) and Large Language Model (LLM) to generate CoT-like text descriptions for videos. The generated texts can capture more variance of action than visual features. We conduct extensive experiments on the publicly available ActivityNet1.3 and THUMOS14 datasets. We introduce the first dataset named Human-related Anomaly Localization and explore the application of the TAL task in human anomaly detection. The experimental results demonstrate that our proposed method significantly outperforms existing methods in single-instance and multi-instance scenarios. We will release our code, data and benchmark.
传统的时间动作定位(TAL)方法依赖于大量的详细标注数据,而少样本TAL则通过仅使用少量训练样本来识别未见过的动作类别,降低了对这种依赖。然而,现有的少样本TAL方法通常只关注视频层面的信息,忽视了文本信息,这可以为定位任务提供有价值的语义支持。因此,我们提出了一种新的少样本时间动作定位方法,通过链式思维文本推理来改善定位性能。具体来说,我们设计了一个新颖的少样本学习框架,该框架利用文本语义信息来提高模型捕捉动作共性和变化的能力,其中包括一个语义感知的文本-视觉对齐模块,旨在在不同层次上对查询和支持视频进行对齐。同时,为了更好地在文本层面表达动作之间的时间依赖关系和因果关系,以辅助动作定位,我们设计了一种类似链式思维(CoT)的推理方法,逐步引导视觉语言模型(VLM)和大型语言模型(LLM)为视频生成类似CoT的文本描述。生成的文本可以捕捉比视觉特征更多的动作变化。我们在公开可用的ActivityNet1.3和THUMOS14数据集上进行了大量实验。我们引入了名为Human-related Anomaly Localization的第一个数据集,并探索了TAL任务在人类异常检测中的应用。实验结果表明,我们提出的方法在单实例和多实例场景中均显著优于现有方法。我们将公开我们的代码、数据和基准测试。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
基于Chain-of-Thought文本推理的新方法来解决少样本条件下的时序动作定位问题。该设计包括语义感知的文本视觉对齐模块与认知链式的推理模型。这一新策略借助少量训练样本即能有效定位未观察到的动作类别,通过文本语义信息捕捉动作的共同点和变化,并在不同层级上对齐查询和支撑视频。同时,设计认知链式推理模型,以逐步引导视觉语言模型与大型语言模型生成针对视频的认知链式文本描述,捕获动作的更多差异特征。实验结果表明,在新构建的异常检测数据集上,该方法在单实例和多实例场景下均显著优于现有方法。
Key Takeaways
- 提出一种基于Chain-of-Thought文本推理的少样本时序动作定位方法。
- 设计新的学习框架,利用文本语义信息提升模型捕捉动作共同点和变化的能力。
- 采用语义感知的文本视觉对齐模块,对齐查询和支撑视频的不同层级信息。
- 利用认知链式推理模型,在文本层面表达动作的时空依赖和因果关系。
- 通过生成文本描述捕获更多动作差异特征,优于仅依赖视觉特征的方法。
- 在ActivityNet1.3和THUMOS14公开数据集上进行广泛实验验证。
点此查看论文截图

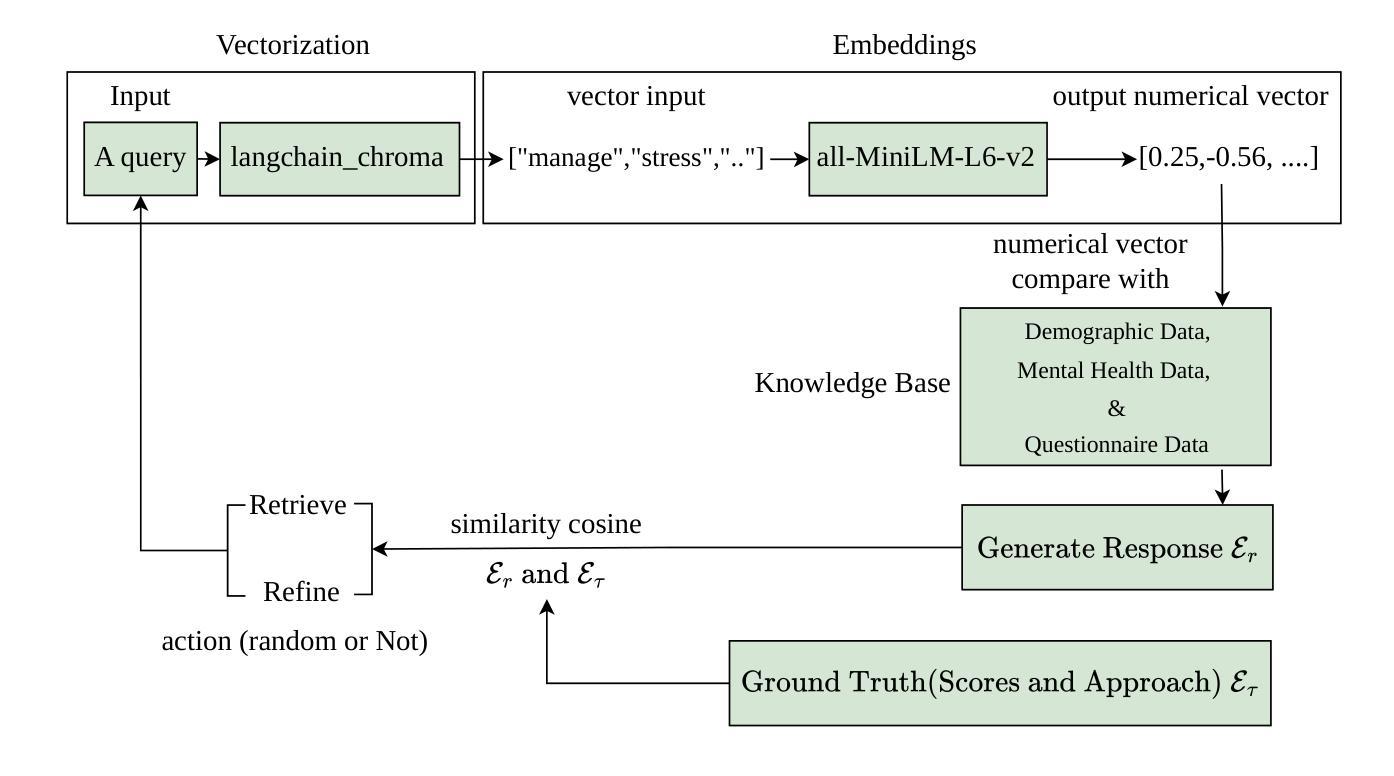
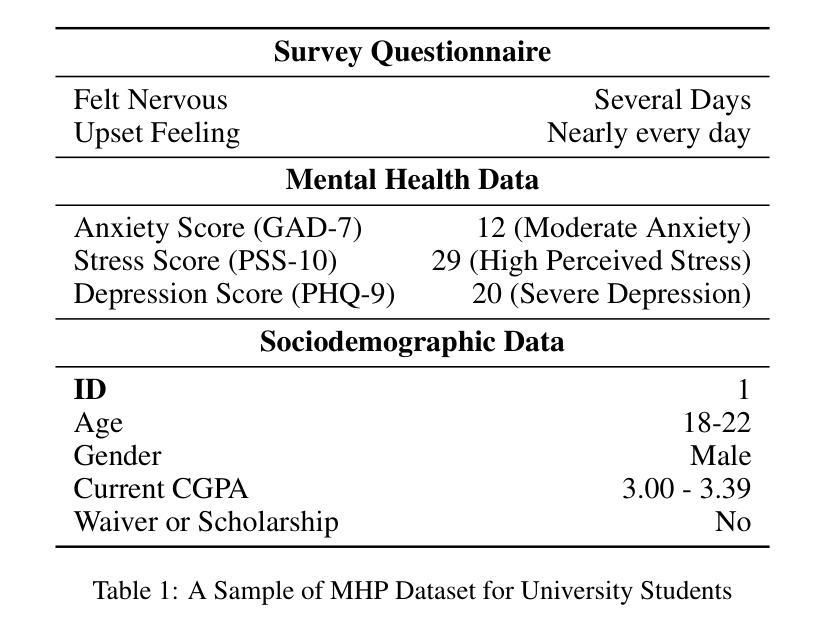
OnRL-RAG: Real-Time Personalized Mental Health Dialogue System
Authors:Ahsan Bilal, Beiyu Lin
Large language models (LLMs) have been widely used for various tasks and applications. However, LLMs and fine-tuning are limited to the pre-trained data. For example, ChatGPT’s world knowledge until 2021 can be outdated or inaccurate. To enhance the capabilities of LLMs, Retrieval-Augmented Generation (RAG), is proposed to augment LLMs with additional, new, latest details and information to LLMs. While RAG offers the correct information, it may not best present it, especially to different population groups with personalizations. Reinforcement Learning from Human Feedback (RLHF) adapts to user needs by aligning model responses with human preference through feedback loops. In real-life applications, such as mental health problems, a dynamic and feedback-based model would continuously adapt to new information and offer personalized assistance due to complex factors fluctuating in a daily environment. Thus, we propose an Online Reinforcement Learning-based Retrieval-Augmented Generation (OnRL-RAG) system to detect and personalize the responding systems to mental health problems, such as stress, anxiety, and depression. We use an open-source dataset collected from 2028 College Students with 28 survey questions for each student to demonstrate the performance of our proposed system with the existing systems. Our system achieves superior performance compared to standard RAG and simple LLM via GPT-4o, GPT-4o-mini, Gemini-1.5, and GPT-3.5. This work would open up the possibilities of real-life applications of LLMs for personalized services in the everyday environment. The results will also help researchers in the fields of sociology, psychology, and neuroscience to align their theories more closely with the actual human daily environment.
大型语言模型(LLM)已广泛应用于各种任务和应用。然而,LLM和微调都受限于预训练数据。例如,ChatGPT截至2021年的世界知识可能会过时或不准确。为了增强LLM的能力,提出了检索增强生成(RAG)来向LLM添加额外、最新、最新的细节和信息。虽然RAG提供了正确的信息,但它可能无法最好地呈现它,尤其是对于具有个性化的不同人群。强化学习从人类反馈(RLHF)通过反馈循环使模型响应与人类偏好相适应,从而适应用户需求。在现实生活应用,如心理健康问题中,一个动态且基于反馈的模型将不断适应新信息,并提供个性化的帮助,这是由于日常环境中复杂因素的波动。因此,我们提出了基于在线强化学习的检索增强生成(OnRL-RAG)系统,用于检测和个性化应对心理健康问题,如压力、焦虑和抑郁。我们使用从2028名大学生收集的开源数据集进行演示,每个学生接受28个调查问题以展示我们系统的性能与现有系统相比。我们的系统在与标准RAG和简单的LLM(如GPT-4o、GPT-4o-mini、Gemini-1.5和GPT-3.5)相比时表现出卓越的性能。这项工作将为LLM在日常生活环境中的个性化服务提供实际应用的可能性。结果还将帮助社会学、心理学和神经科学领域的研究人员将其理论更加紧密地与实际的日常人类环境相结合。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF It needs more revisions. I am currently working on it with my co-author
Summary
大型语言模型(LLMs)广泛应用于各种任务和应用,但其知识和能力受限于预训练数据。为增强LLMs的能力,提出了检索增强生成(RAG)方法,并结合强化学习从人类反馈(RLHF)以适应不同用户的需求。针对真实世界应用如心理健康问题,提出基于在线强化学习的检索增强生成系统(OnRL-RAG),用于检测并个性化响应系统以应对如压力、焦虑和抑郁等心理问题。使用来自2028名大学生的开源数据集展示系统性能,相较于其他系统展现出卓越性能。此研究开启了LLMs在个性化服务中的实际应用可能性,并有助于社会学、心理学和神经科学领域的研究者更贴近实际人类日常环境进行理论研究。
Key Takeaways
- LLMs受限于预训练数据,知识和能力有限。
- RAG方法用于增强LLMs的能力,提供最新信息。
- RLHF结合,使模型适应不同用户需求。
- 提出OnRL-RAG系统,用于检测和个性化响应心理健康问题。
- 使用大学生数据集展示系统性能,优于其他系统。
- 研究开启了LLMs在个性化服务中的实际应用可能性。
点此查看论文截图

F5R-TTS: Improving Flow-Matching based Text-to-Speech with Group Relative Policy Optimization
Authors:Xiaohui Sun, Ruitong Xiao, Jianye Mo, Bowen Wu, Qun Yu, Baoxun Wang
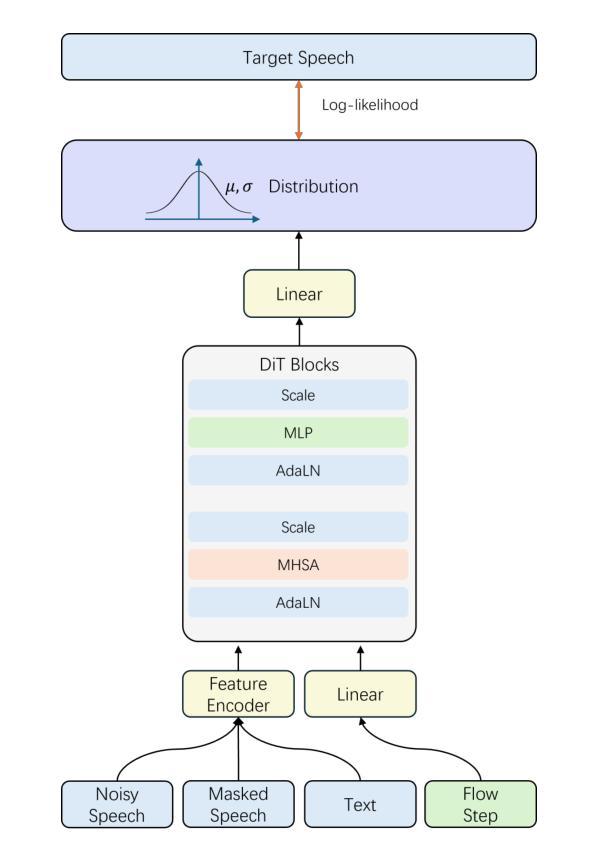
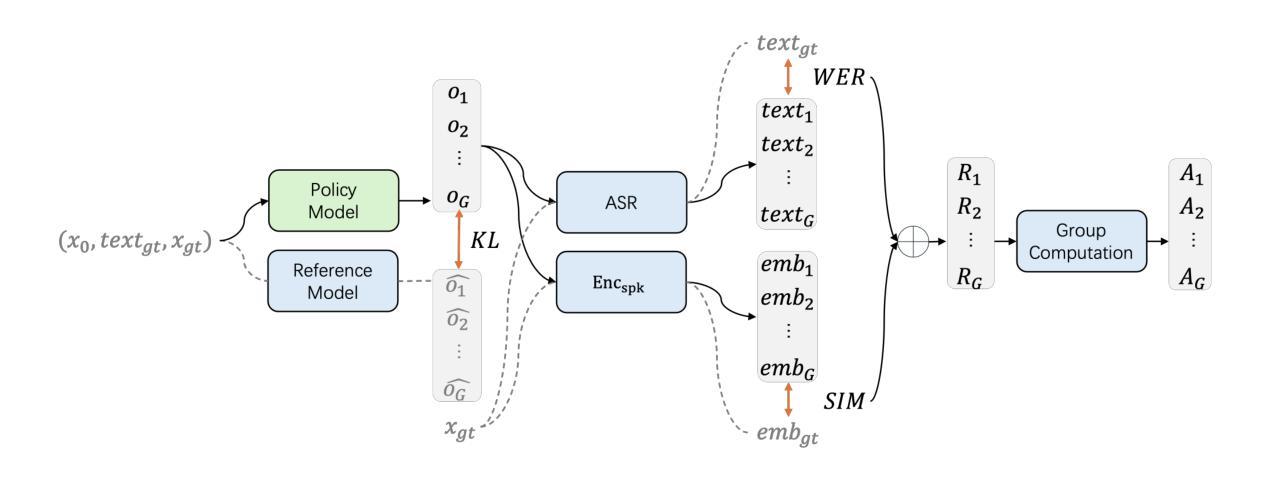
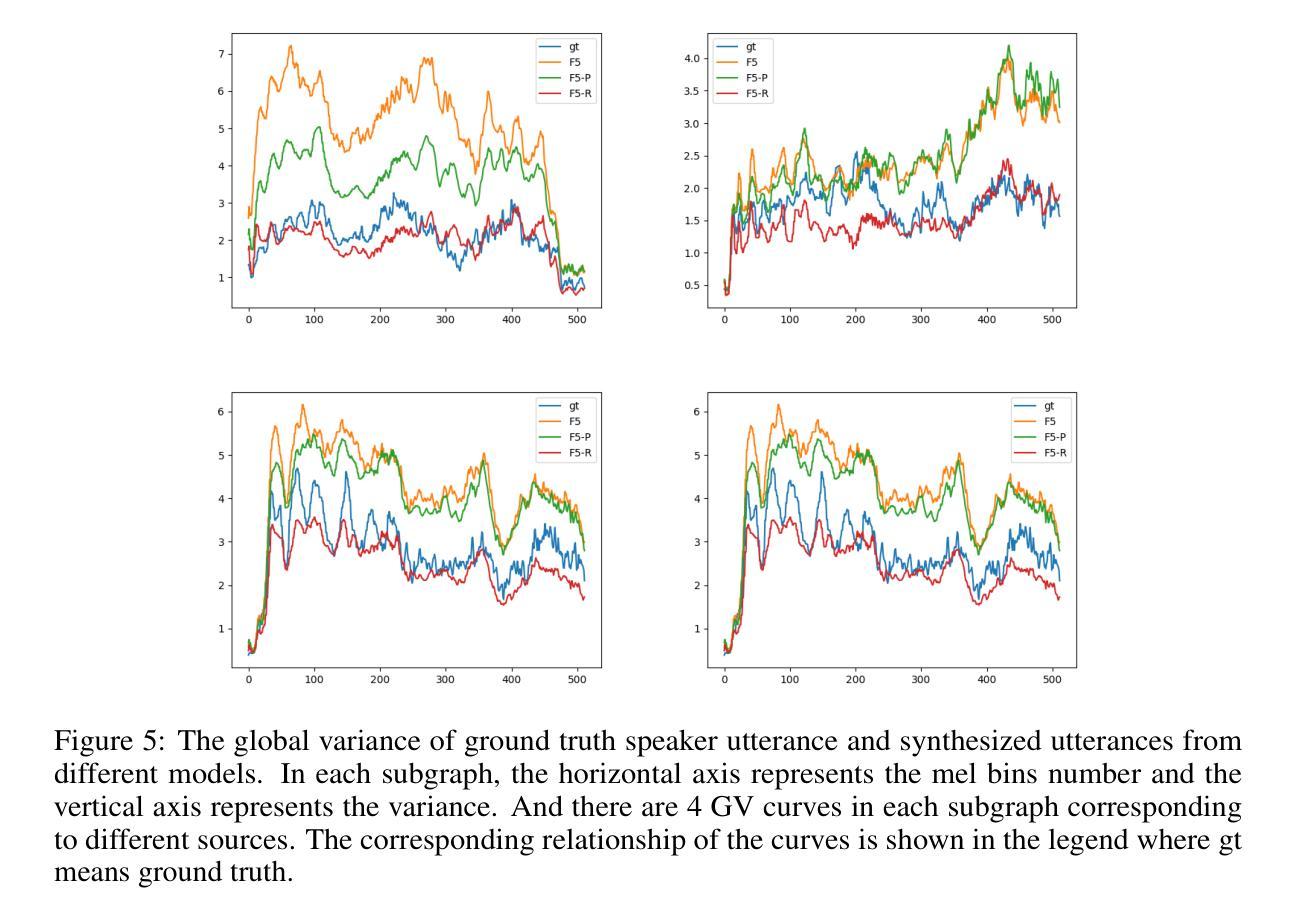
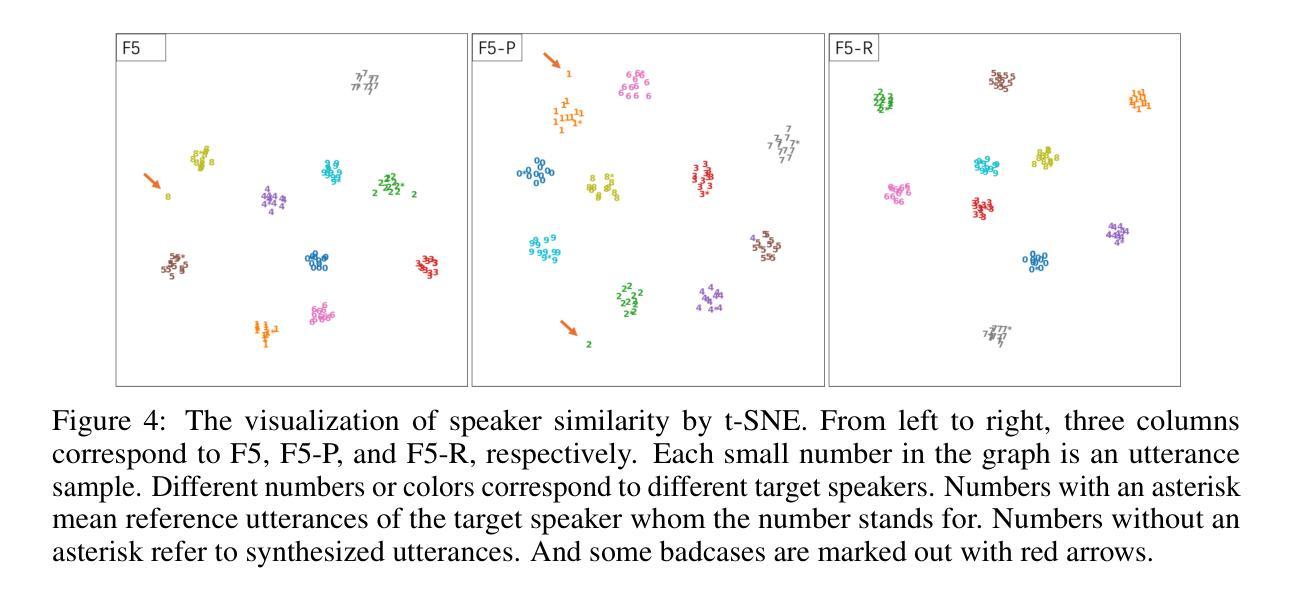
We present F5R-TTS, a novel text-to-speech (TTS) system that integrates Group Relative Policy Optimization (GRPO) into a flow-matching based architecture. By reformulating the deterministic outputs of flow-matching TTS into probabilistic Gaussian distributions, our approach enables seamless integration of reinforcement learning algorithms. During pretraining, we train a probabilistically reformulated flow-matching based model which is derived from F5-TTS with an open-source dataset. In the subsequent reinforcement learning (RL) phase, we employ a GRPO-driven enhancement stage that leverages dual reward metrics: word error rate (WER) computed via automatic speech recognition and speaker similarity (SIM) assessed by verification models. Experimental results on zero-shot voice cloning demonstrate that F5R-TTS achieves significant improvements in both speech intelligibility (a 29.5% relative reduction in WER) and speaker similarity (a 4.6% relative increase in SIM score) compared to conventional flow-matching based TTS systems. Audio samples are available at https://frontierlabs.github.io/F5R.
我们介绍了F5R-TTS,这是一种新型文本到语音(TTS)系统,它将组相对策略优化(GRPO)集成到基于流匹配的架构中。通过讲流匹配TTS的确定性输出重新公式化为概率高斯分布,我们的方法能够实现强化学习算法的无缝集成。在预训练过程中,我们使用公开数据集对来自F5-TTS的概率重构流匹配模型进行训练。在随后的强化学习(RL)阶段,我们采用GRPO驱动的增强阶段,利用双重奖励指标:通过自动语音识别计算的词错误率(WER)和通过验证模型评估的发音人相似性(SIM)。零样本声音克隆的实验结果表明,与传统的基于流匹配的TTS系统相比,F5R-TTS在语音清晰度(相对减少29.5%的WER)和发音人相似性(SIM得分相对提高4.6%)方面取得了显著改进。音频样本可在https://frontierlabs.github.io/F5R获取。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
F5R-TTS是一个集成Group Relative Policy Optimization (GRPO)的文本转语音(TTS)系统。它通过概率化改革流匹配TTS的确定性输出来实现强化学习算法的无缝集成。系统使用概率化改革的流匹配模型进行预训练,并引入基于GRPO的增强阶段以提升性能,通过采用自动语音识别的词错误率和验证模型的说话人相似性作为双重奖励指标。实验结果显示,F5R-TTS在零样本语音克隆上显著提高了语音的清晰度和说话人的相似性。
Key Takeaways
- F5R-TTS是一个新的文本转语音(TTS)系统,整合了Group Relative Policy Optimization (GRPO)。
- 系统采用流匹配架构,并通过概率化改革确定性输出来实现强化学习算法的无缝集成。
- 在预训练阶段,使用概率化改革的流匹配模型进行训练,该模型基于F5-TTS并使用了开源数据集。
- 强化学习阶段采用GRPO驱动的增强阶段,利用词错误率和说话人相似性作为双重奖励指标。
- F5R-TTS实现了零样本语音克隆的显著性能提升,在语音清晰度和说话人相似性方面都有明显改善。
- F5R-TTS系统的音频样本可在https://frontierlabs.github.io/F5R上找到。
- 该系统为文本转语音技术的新发展提供了潜力,特别是在语音克隆和自然性方面。
点此查看论文截图

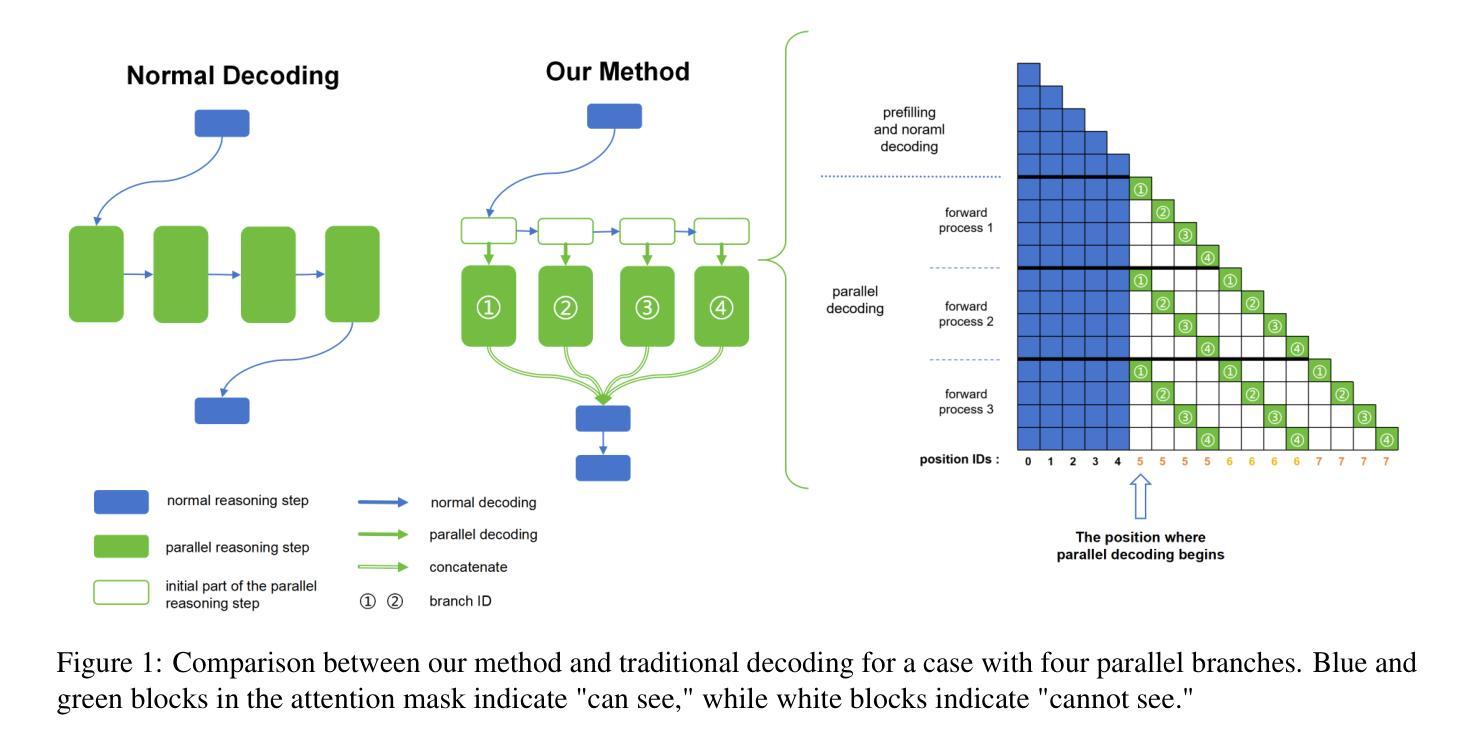
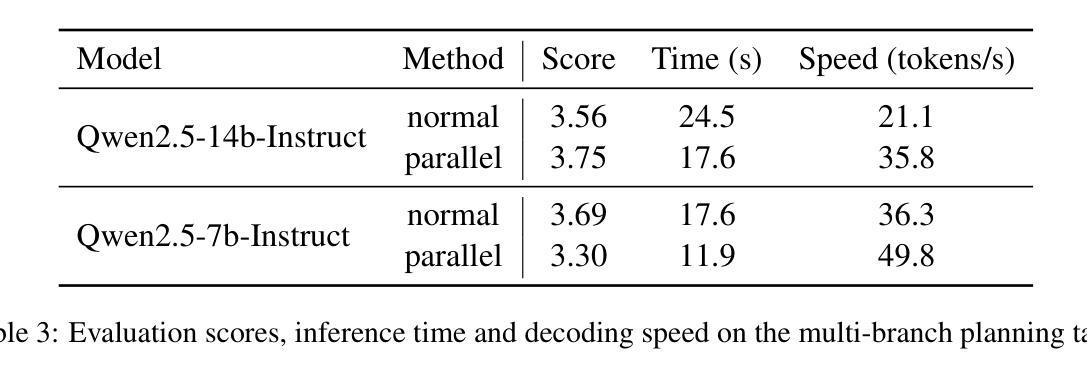
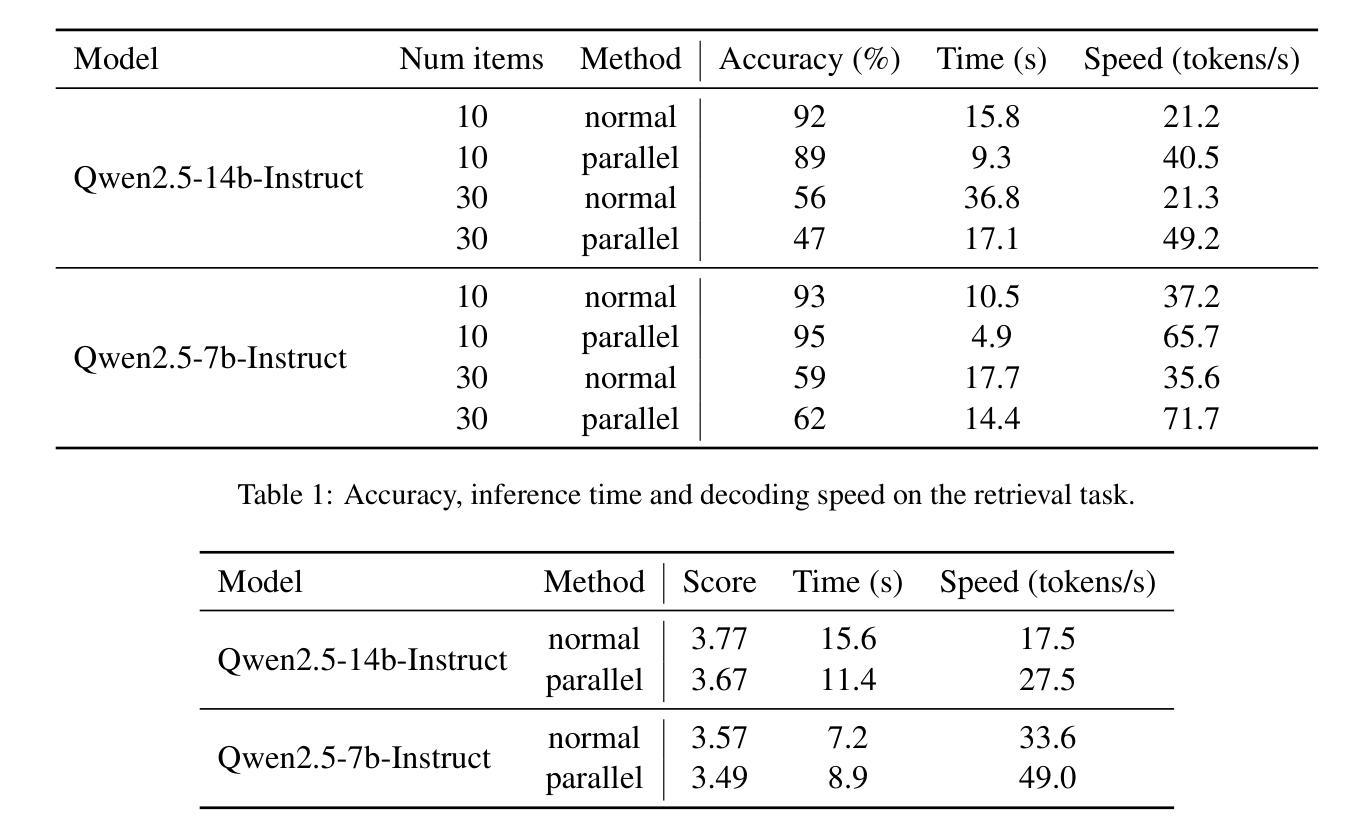
Accelerate Parallelizable Reasoning via Parallel Decoding within One Sequence
Authors:Yijiong Yu
Recent advances in reasoning models have demonstrated significant improvements in accuracy, particularly for complex tasks such as mathematical reasoning, by employing detailed and comprehensive reasoning processes. However, generating these lengthy reasoning sequences is computationally expensive and time-consuming. To address this inefficiency, we leverage the inherent parallelizability of certain tasks to accelerate the reasoning process. Specifically, when multiple parallel reasoning branches exist, we decode multiple tokens per step using a specialized attention mask, processing them within a single sequence, avoiding additional memory usage. Experimental results show that our method achieves over 100% speedup in decoding time while maintaining the answer quality.
近期推理模型的发展显示,通过采用详细而全面的推理过程,特别是在数学推理等复杂任务方面,其准确性有了显著的提高。然而,生成这些冗长的推理序列在计算上很昂贵且耗时。为了解决这种低效问题,我们利用某些任务的固有并行性来加速推理过程。具体来说,当存在多个并行推理分支时,我们使用专门的注意力掩码来一次性处理多个标记,避免额外的内存使用。实验结果表明,我们的方法在解码时间上实现了超过100%的加速,同时保持了答案的质量。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF Our code is available in https://github.com/yuyijiong/parallel-decoding-in-one-sequence
Summary:
近期推理模型的进展在准确率上取得了显著提升,特别是在数学推理等复杂任务中。然而,生成这些冗长的推理序列在计算上很耗费时间和资源。为解决这个问题,我们通过利用某些任务的固有并行性来加速推理过程。当存在多个并行推理分支时,我们采用特殊注意力掩码,在单序列内解码多个标记,避免额外的内存使用。实验结果证明,我们的方法在解码时间上实现了超过100%的加速,同时保持了答案质量。
Key Takeaways:
- 推理模型在准确率上取得显著进步,特别是在数学推理等复杂任务中。
- 生成推理序列的过程在计算上很耗时。
- 通过利用任务的固有并行性来加速推理过程。
- 采用特殊注意力掩码,在单序列内解码多个标记。
- 方法实现了超过100%的解码速度提升。
- 提速的同时保持了答案质量。
- 这种方法的实现有助于提升推理模型的效率和实用性。
点此查看论文截图

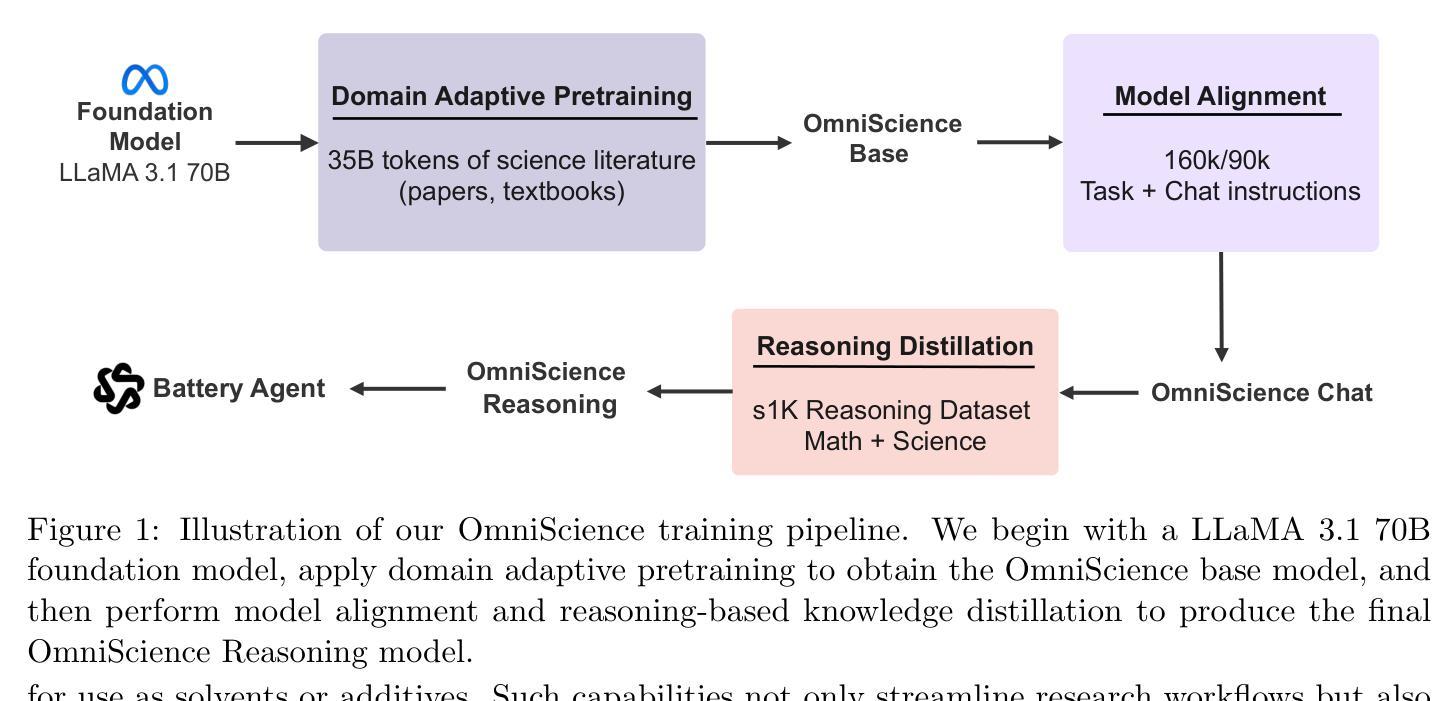
OmniScience: A Domain-Specialized LLM for Scientific Reasoning and Discovery
Authors:Vignesh Prabhakar, Md Amirul Islam, Adam Atanas, Yao-Ting Wang, Joah Han, Aastha Jhunjhunwala, Rucha Apte, Robert Clark, Kang Xu, Zihan Wang, Kai Liu
Large Language Models (LLMs) have demonstrated remarkable potential in advancing scientific knowledge and addressing complex challenges. In this work, we introduce OmniScience, a specialized large reasoning model for general science, developed through three key components: (1) domain adaptive pretraining on a carefully curated corpus of scientific literature, (2) instruction tuning on a specialized dataset to guide the model in following domain-specific tasks, and (3) reasoning-based knowledge distillation through fine-tuning to significantly enhance its ability to generate contextually relevant and logically sound responses. We demonstrate the versatility of OmniScience by developing a battery agent that efficiently ranks molecules as potential electrolyte solvents or additives. Comprehensive evaluations reveal that OmniScience is competitive with state-of-the-art large reasoning models on the GPQA Diamond and domain-specific battery benchmarks, while outperforming all public reasoning and non-reasoning models with similar parameter counts. We further demonstrate via ablation experiments that domain adaptive pretraining and reasoning-based knowledge distillation are critical to attain our performance levels, across benchmarks.
大规模语言模型(LLMs)在推进科学知识和应对复杂挑战方面表现出了显著潜力。在这项工作中,我们介绍了OmniScience,这是一个针对通用科学的专门大型推理模型,通过三个关键组件开发而成:(1)在精心挑选的科学文献语料库上进行领域自适应预训练;(2)在专门的数据集上进行指令调整,以指导模型执行特定领域的任务;(3)通过微调进行基于推理的知识蒸馏,以显著提高其生成语境相关和逻辑严谨回应的能力。我们通过开发一种电池代理来展示OmniScience的通用性,该代理能够高效地排列分子作为潜在的电解质溶剂或添加剂。综合评估表明,OmniScience在GPQA Diamond和特定领域的电池基准测试上,与最新的大型推理模型相比具有竞争力,同时,在参数数量相似的所有公共推理和非推理模型中表现最佳。我们还通过消融实验进一步证明,领域自适应预训练和基于推理的知识蒸馏对于达到我们的性能水平至关重要,跨越各种基准测试。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
OmniScience模型是一种用于通用科学的专门大型推理模型,它通过三个关键组件开发而成:领域自适应预训练、指令微调以及推理基础的知识蒸馏。该模型展现出强大的潜力,用于推进科学知识并应对复杂挑战。在电池代理的开发中展示了OmniScience的通用性,能够高效地排列分子作为潜在的电解质溶剂或添加剂。综合评价表明,OmniScience在GPQA Diamond和特定领域电池基准测试中具有竞争力,同时优于所有具有相似参数计数的公共推理和非推理模型。
Key Takeaways
- OmniScience是一个专门的大型推理模型,用于通用科学领域。
- 模型通过领域自适应预训练、指令微调以及推理基础的知识蒸馏三个关键组件开发。
- OmniScience展现出在推进科学知识和应对复杂挑战方面的强大潜力。
- 模型在开发电池代理时表现出通用性,能高效排列分子作为电解质溶剂或添加剂。
- 综合评价显示,OmniScience在基准测试中具有竞争力,并优于其他具有相似参数计数的模型。
- 消融实验表明,领域自适应预训练和推理基础的知识蒸馏对于达到性能水平至关重要。
点此查看论文截图

DRESS: Diffusion Reasoning-based Reward Shaping Scheme For Intelligent Networks
Authors:Feiran You, Hongyang Du, Xiangwang Hou, Yong Ren, Kaibin Huang
Network optimization remains fundamental in wireless communications, with Artificial Intelligence (AI)-based solutions gaining widespread adoption. As Sixth-Generation (6G) communication networks pursue full-scenario coverage, optimization in complex extreme environments presents unprecedented challenges. The dynamic nature of these environments, combined with physical constraints, makes it difficult for AI solutions such as Deep Reinforcement Learning (DRL) to obtain effective reward feedback for the training process. However, many existing DRL-based network optimization studies overlook this challenge through idealized environment settings. Inspired by the powerful capabilities of Generative AI (GenAI), especially diffusion models, in capturing complex latent distributions, we introduce a novel Diffusion Reasoning-based Reward Shaping Scheme (DRESS) to achieve robust network optimization. By conditioning on observed environmental states and executed actions, DRESS leverages diffusion models’ multi-step denoising process as a form of deep reasoning, progressively refining latent representations to generate meaningful auxiliary reward signals that capture patterns of network systems. Moreover, DRESS is designed for seamless integration with any DRL framework, allowing DRESS-aided DRL (DRESSed-DRL) to enable stable and efficient DRL training even under extreme network environments. Experimental results demonstrate that DRESSed-DRL achieves about 1.5x times faster convergence than its original version in sparse-reward wireless environments and significant performance improvements in multiple general DRL benchmark environments compared to baseline methods. The code of DRESS is available at https://github.com/NICE-HKU/DRESS.
网络优化在无线通信中仍然具有根本重要性,基于人工智能(AI)的解决方案得到了广泛应用。随着第六代(6G)通信网络的普及,追求全场景覆盖的复杂极端环境中的优化面临着前所未有的挑战。这些环境的动态性以及物理约束的结合,使得人工智能解决方案(如深度强化学习(DRL))在训练过程中难以获得有效的奖励反馈。然而,许多现有的基于DRL的网络优化研究通过理想化的环境设置忽略了这一挑战。受生成式人工智能(GenAI)的强大能力的启发,尤其是扩散模型在捕捉复杂潜在分布方面的能力,我们提出了一种新型的基于扩散推理的奖励塑形方案(DRESS),以实现稳健的网络优化。DRESS通过观测到的环境状态和所执行的动作来进行调节,利用扩散模型的多步去噪过程作为深度推理的一种形式,逐步优化潜在表示,生成有意义的辅助奖励信号,捕捉网络系统模式。此外,DRESS设计用于无缝集成任何DRL框架,允许DRESS辅助的DRL(DRESSed-DRL)即使在极端网络环境下也能实现稳定和高效的DRL训练。实验结果表明,在稀疏奖励的无线环境中,DRESSed-DRL的收敛速度比其原始版本快约1.5倍,并且在多个通用的DRL基准环境中与基准方法相比实现了显著的性能提升。DRESS的代码可在https://github.com/NICE-HKU/DRESS上找到。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary:
随着无线通讯中网络优化的重要性不断提升,基于人工智能(AI)的解决方案得到广泛应用。在追求全场景覆盖的6G通讯网络中,极端复杂环境下的优化面临前所未有的挑战。本研究受生成式人工智能(GenAI)的启发,特别是扩散模型的强大能力,提出了一种新的基于扩散推理的奖励塑形方案(DRESS),以实现稳健的网络优化。DRESS利用扩散模型的多步去噪过程作为深度推理,生成有意义的辅助奖励信号,捕捉网络系统模式。实验结果表明,DRESS在稀疏奖励的无线环境中实现了约1.5倍的快速收敛,并且在多个通用DRL基准环境中相较于基线方法有着显著的性能提升。
Key Takeaways:
- 网络优化在无线通讯中仍然至关重要,AI解决方案(如深度强化学习)在处理复杂极端环境时面临挑战。
- 扩散模型有能力捕捉复杂的潜在分布,可用于网络优化。
- 提出了一种新的奖励塑形方案DRESS,它利用扩散模型进行深度推理,生成辅助奖励信号。
- DRESS可以无缝集成到任何DRL框架中,实现稳定的训练过程。
- DRESS在稀疏奖励的无线环境中实现了快速收敛。
- DRESS在多个通用DRL基准环境中表现出显著的性能提升。
点此查看论文截图
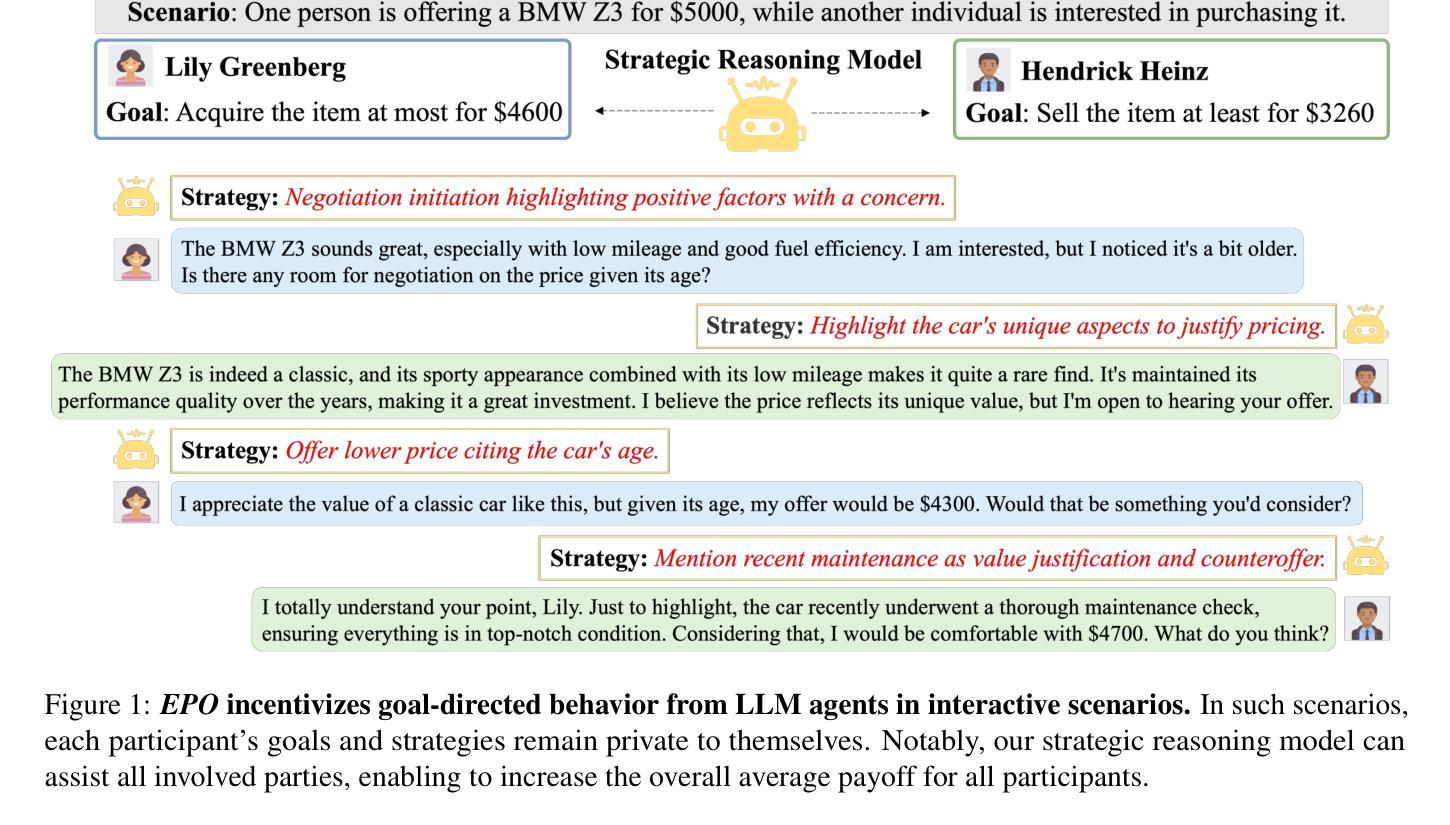
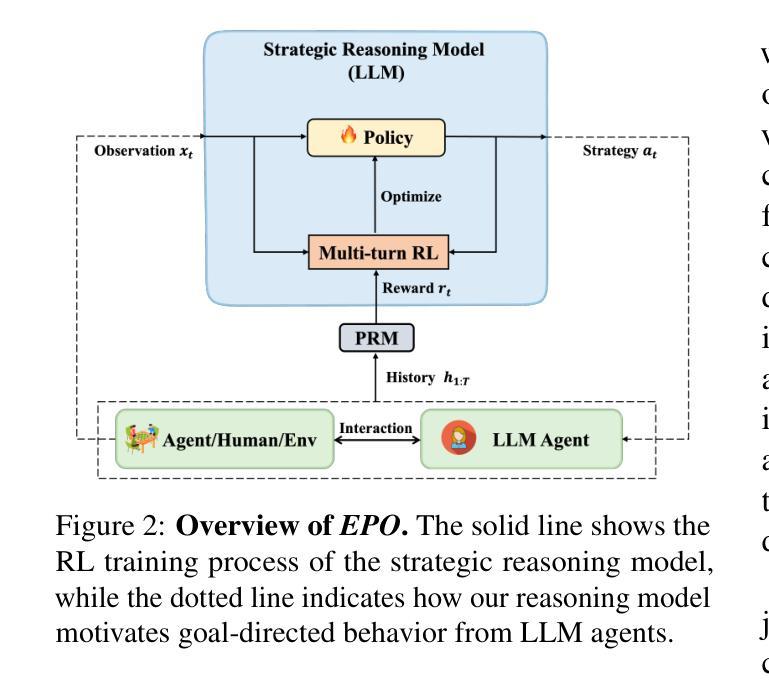
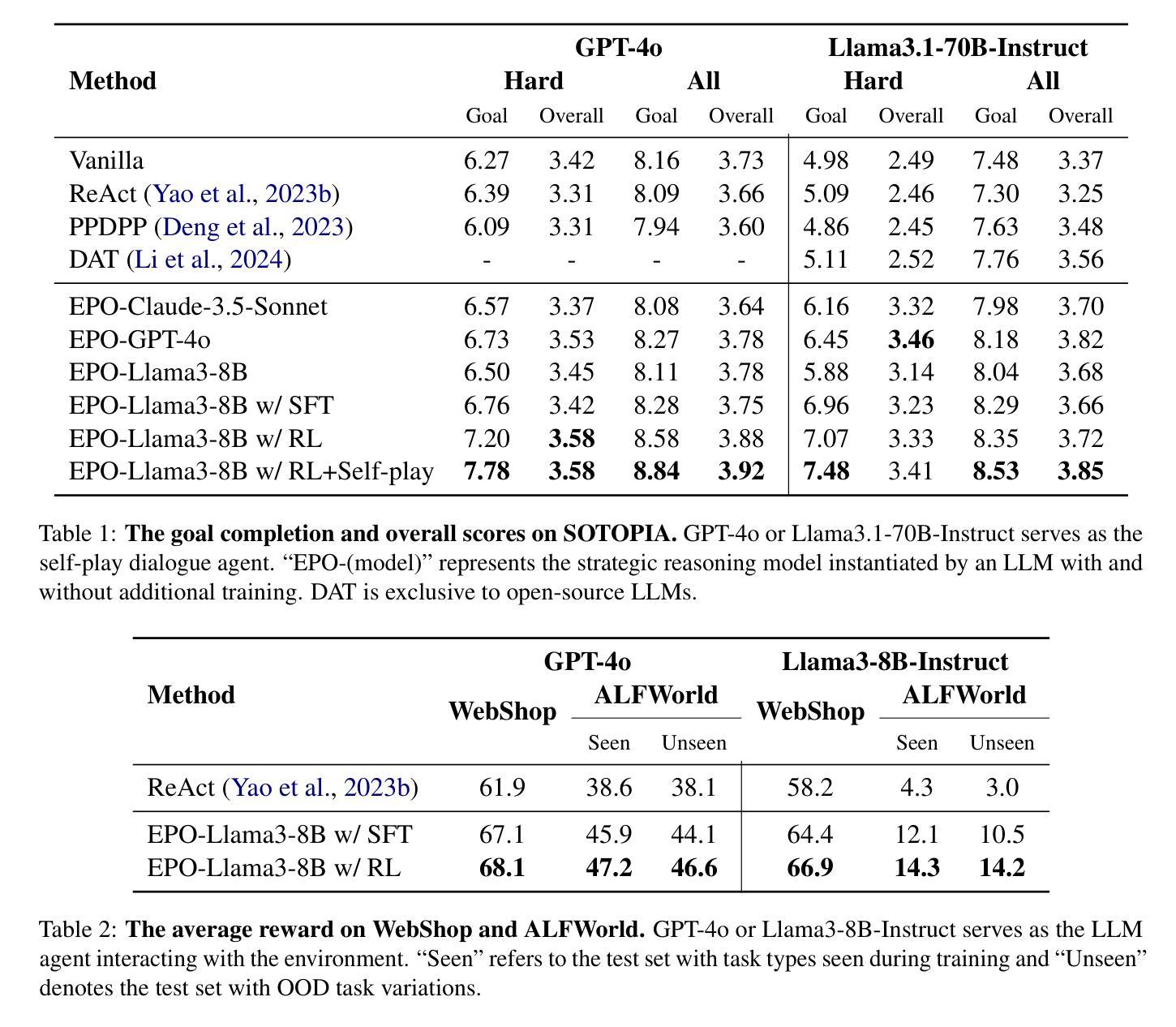
EPO: Explicit Policy Optimization for Strategic Reasoning in LLMs via Reinforcement Learning
Authors:Xiaoqian Liu, Ke Wang, Yongbin Li, Yuchuan Wu, Wentao Ma, Aobo Kong, Fei Huang, Jianbin Jiao, Junge Zhang
Large Language Models (LLMs) have shown impressive reasoning capabilities in well-defined problems with clear solutions, such as mathematics and coding. However, they still struggle with complex real-world scenarios like business negotiations, which require strategic reasoning-an ability to navigate dynamic environments and align long-term goals amidst uncertainty. Existing methods for strategic reasoning face challenges in adaptability, scalability, and transferring strategies to new contexts. To address these issues, we propose explicit policy optimization (EPO) for strategic reasoning, featuring an LLM that provides strategies in open-ended action space and can be plugged into arbitrary LLM agents to motivate goal-directed behavior. To improve adaptability and policy transferability, we train the strategic reasoning model via multi-turn reinforcement learning (RL) using process rewards and iterative self-play, without supervised fine-tuning (SFT) as a preliminary step. Experiments across social and physical domains demonstrate EPO’s ability of long-term goal alignment through enhanced strategic reasoning, achieving state-of-the-art performance on social dialogue and web navigation tasks. Our findings reveal various collaborative reasoning mechanisms emergent in EPO and its effectiveness in generating novel strategies, underscoring its potential for strategic reasoning in real-world applications.
大型语言模型(LLM)在定义明确、解决方案清晰的问题中展示了令人印象深刻的推理能力,例如在数学和编程领域。然而,它们在处理复杂的现实世界场景,如需要战略推理的商业谈判中,仍然面临挑战。战略推理需要应对动态环境,并在不确定性中调整长期目标。现有的战略推理方法面临着适应性、可扩展性和策略转移等挑战。为了解决这些问题,我们提出了用于战略推理的显式策略优化(EPO)方法。该方法使用一个大型语言模型,该模型在开放的动作空间中提供策略,并且可以插入到任意的大型语言模型代理中,以激励目标导向的行为。为了改善适应性和策略可转移性,我们通过多回合强化学习(RL)来训练战略推理模型,使用过程奖励和迭代自我游戏,无需初步的监督微调(SFT)。在社会和物理领域的实验表明,EPO能够通过增强的战略推理实现长期目标对齐的能力,在社会对话和网页导航任务上达到了最先进的性能。我们的研究揭示了EPO中出现的各种协作推理机制及其在生成新策略方面的有效性,这强调了其在现实世界战略推理应用中的潜力。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF 22 pages, 4 figures
Summary
大型语言模型(LLMs)在具有明确解决方案的明确问题中展现出令人印象深刻的推理能力,如数学和编程。然而,在处理需要战略推理的复杂现实世界场景(如商务谈判)时,它们仍面临挑战。战略推理要求能够在动态环境中导航,并在不确定性中调整长期目标。为解决现有战略推理方法面临的适应性、可扩展性和策略转移新问题,我们提出了显式策略优化(EPO)进行战略推理。该方法让LLM在开放行动空间中提供策略,并能被嵌入到任意LLM代理中以驱动目标导向行为。通过多回合强化学习(RL)训练战略推理模型,利用过程奖励和迭代自我游戏来提高适应性和策略迁移能力,无需监督微调(SFT)作为初步步骤。实验表明,EPO在社会和物理领域的长期目标对齐能力通过增强的战略推理实现了卓越性能,在社会对话和网页导航任务上达到了最新技术水平。研究发现了EPO中各种协作推理机制的涌现及其在生成新策略方面的有效性,突显其在现实世界战略推理应用中的潜力。
Key Takeaways
- LLMs展现出在数学和编程等领域的强大推理能力,但在复杂现实世界场景如商务谈判中的战略推理能力仍面临挑战。
- 现有战略推理方法面临适应性、可扩展性和策略转移难题。
- 提出了显式策略优化(EPO)来解决这些问题,使LLM能在开放行动空间中提供策略并嵌入到任意LLM代理中。
- 通过多回合强化学习训练战略推理模型,无需监督微调。
- EPO在社会和物理领域的实验表现出卓越性能,达到最新技术水平。
- 研究发现EPO中协作推理机制的涌现及其在生成新策略方面的有效性。
点此查看论文截图