⚠️ 以下所有内容总结都来自于 大语言模型的能力,如有错误,仅供参考,谨慎使用
🔴 请注意:千万不要用于严肃的学术场景,只能用于论文阅读前的初筛!
💗 如果您觉得我们的项目对您有帮助 ChatPaperFree ,还请您给我们一些鼓励!⭐️ HuggingFace免费体验
2025-04-25 更新
Advanced Chest X-Ray Analysis via Transformer-Based Image Descriptors and Cross-Model Attention Mechanism
Authors:Lakshita Agarwal, Bindu Verma
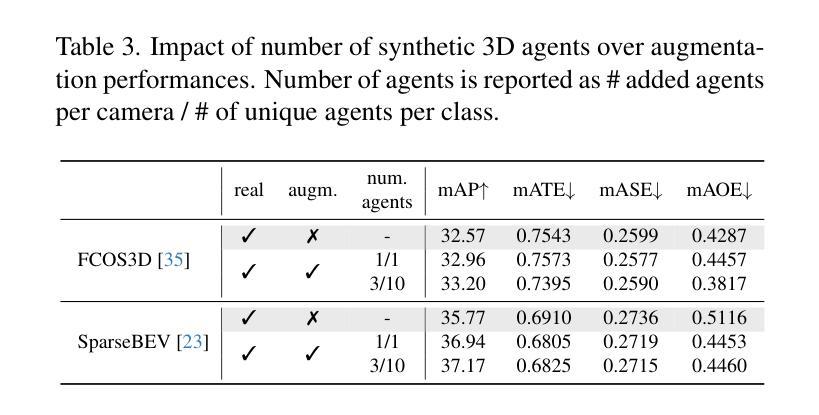
The examination of chest X-ray images is a crucial component in detecting various thoracic illnesses. This study introduces a new image description generation model that integrates a Vision Transformer (ViT) encoder with cross-modal attention and a GPT-4-based transformer decoder. The ViT captures high-quality visual features from chest X-rays, which are fused with text data through cross-modal attention to improve the accuracy, context, and richness of image descriptions. The GPT-4 decoder transforms these fused features into accurate and relevant captions. The model was tested on the National Institutes of Health (NIH) and Indiana University (IU) Chest X-ray datasets. On the IU dataset, it achieved scores of 0.854 (B-1), 0.883 (CIDEr), 0.759 (METEOR), and 0.712 (ROUGE-L). On the NIH dataset, it achieved the best performance on all metrics: BLEU 1–4 (0.825, 0.788, 0.765, 0.752), CIDEr (0.857), METEOR (0.726), and ROUGE-L (0.705). This framework has the potential to enhance chest X-ray evaluation, assisting radiologists in more precise and efficient diagnosis.
胸部X射线图像的检查是检测各种胸部疾病的关键环节。本研究引入了一种新的图像描述生成模型,该模型结合了Vision Transformer(ViT)编码器、跨模态注意力和基于GPT-4的变压器解码器。ViT从胸部X射线图像中提取高质量视觉特征,通过跨模态注意力与文本数据融合,提高了图像描述的准确性、上下文相关性和丰富性。GPT-4解码器将这些融合的特征转化为准确且相关的标题。该模型在美国国立卫生研究院(NIH)和印第安纳大学(IU)的胸部X射线数据集上进行了测试。在IU数据集上,它达到了B-1(0.854)、CIDEr(0.883)、METEOR(0.759)和ROUGE-L(0.712)的分数。在NIH数据集上,它在所有指标上都取得了最佳性能:BLEU 1-4(0.825、0.788、0.765、0.752)、CIDEr(0.857)、METEOR(0.726)和ROUGE-L(0.705)。该框架有望提高胸部X射线的评估水平,帮助放射科医生进行更准确、高效的诊断。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary:本研究结合使用Vision Transformer(ViT)编码器和GPT-4基础变换解码器,推出了一种新的图像描述生成模型。该模型可从胸部X光片中捕捉高质量视觉特征,并通过跨模态注意力与文本数据融合,提高图像描述的准确性、上下文相关性和丰富性。在NIH和IU的胸部X光射线数据集上测试表明,该模型表现优异,具有辅助放射科医生进行更精确和高效诊断的潜力。
Key Takeaways:
- 本研究结合ViT编码器和GPT-4基础变换解码器,提出了一种新的图像描述生成模型。
- 该模型可从胸部X光片中捕捉高质量视觉特征。
- 通过跨模态注意力机制,将视觉特征与文本数据融合。
- 融合特征后,使用GPT-4解码器生成准确且相关的图像描述。
- 在IU数据集上,模型取得了较高的评估指标分数,包括B-1、CIDEr、METEOR和ROUGE-L。
- 在NIH数据集上,模型在所有评估指标上均表现最佳。
点此查看论文截图

FrogDogNet: Fourier frequency Retained visual prompt Output Guidance for Domain Generalization of CLIP in Remote Sensing
Authors:Hariseetharam Gunduboina, Muhammad Haris Khan, Biplab Banerjee
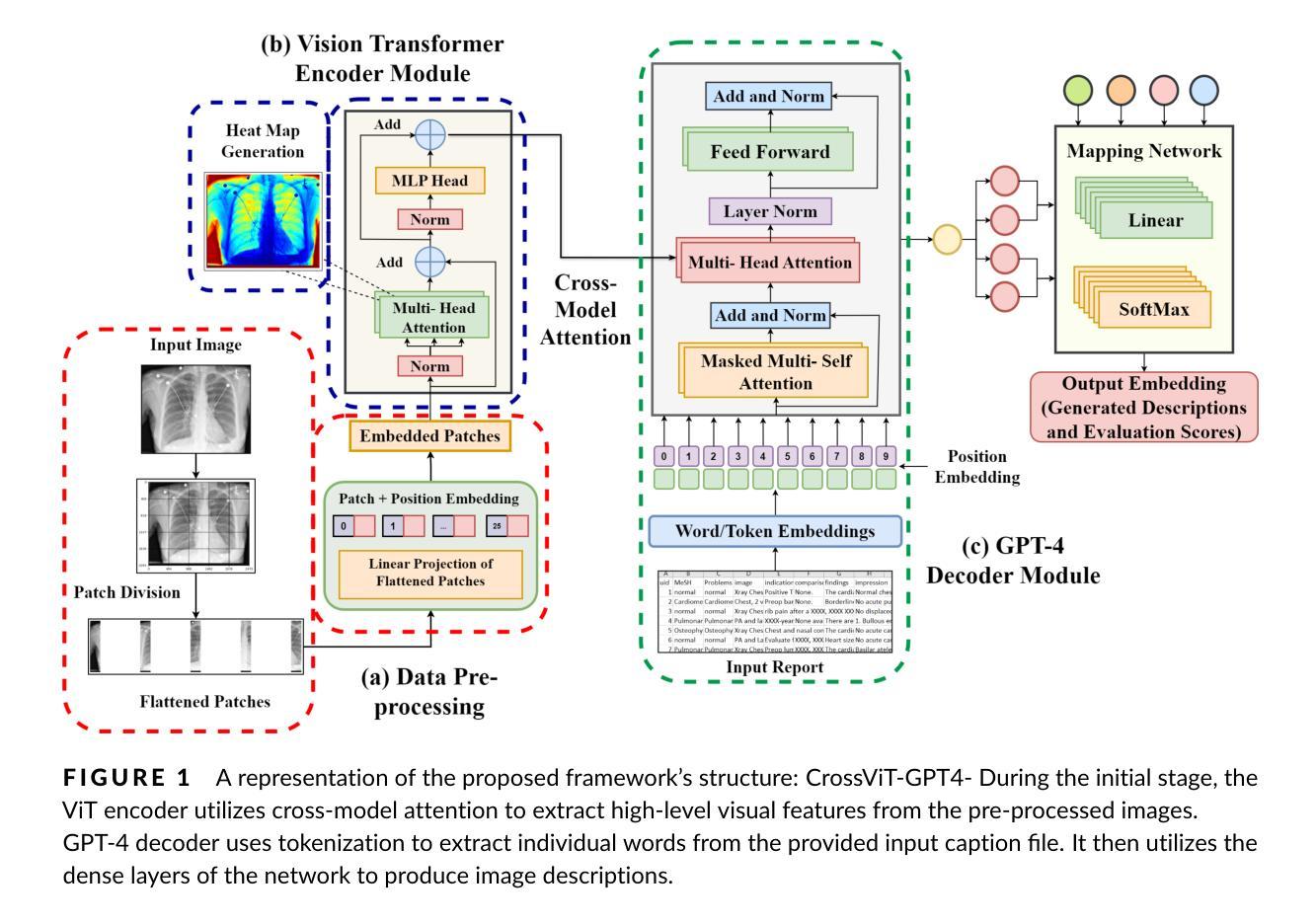
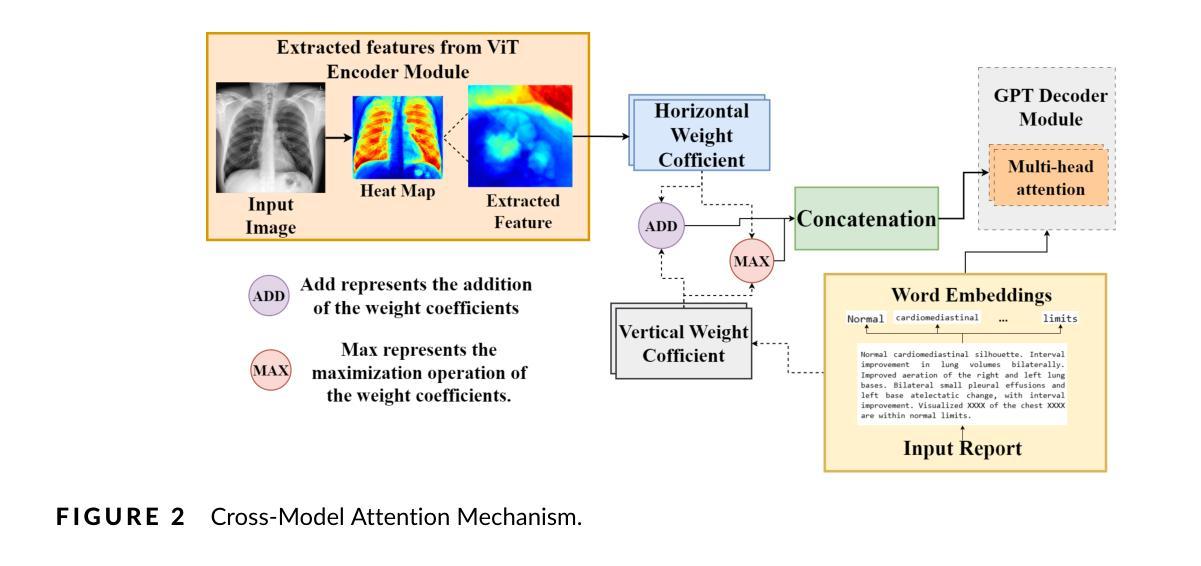
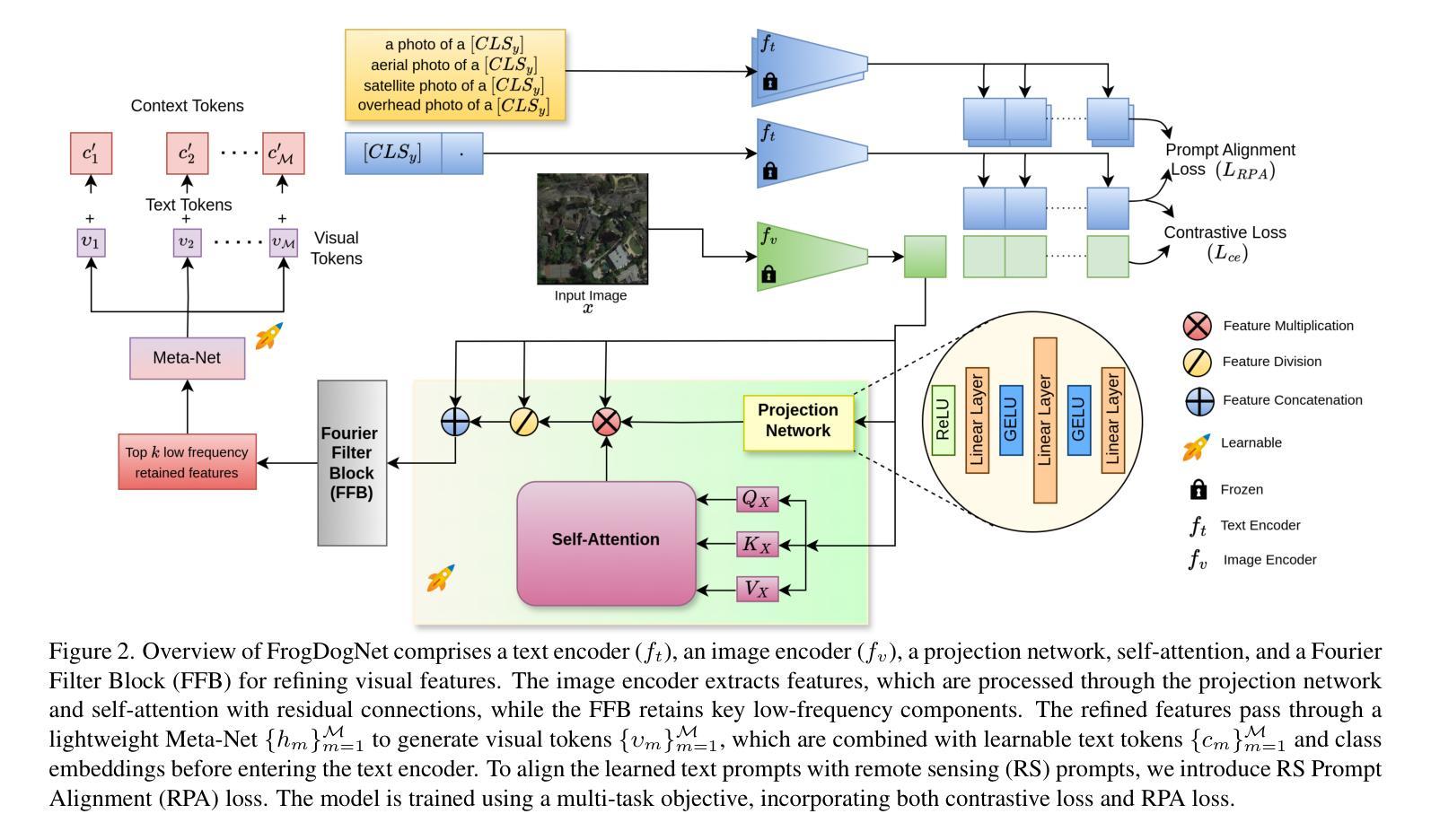
In recent years, large-scale vision-language models (VLMs) like CLIP have gained attention for their zero-shot inference using instructional text prompts. While these models excel in general computer vision, their potential for domain generalization in remote sensing (RS) remains underexplored. Existing approaches enhance prompt learning by generating visual prompt tokens but rely on full-image features, introducing noise and background artifacts that vary within a class, causing misclassification. To address this, we propose FrogDogNet, a novel prompt learning framework integrating Fourier frequency filtering and self-attention to improve RS scene classification and domain generalization. FrogDogNet selectively retains invariant low-frequency components while eliminating noise and irrelevant backgrounds, ensuring robust feature representation across domains. The model first extracts significant features via projection and self-attention, then applies frequency-based filtering to preserve essential structural information for prompt learning. Extensive experiments on four RS datasets and three domain generalization tasks show that FrogDogNet consistently outperforms state-of-the-art prompt learning methods, demonstrating superior adaptability across domain shifts. Our findings highlight the effectiveness of frequency-based invariant feature retention in generalization, paving the way for broader applications. Our code is available at https://github.com/HariseetharamG/FrogDogNet
近年来,像CLIP这样的大规模视觉语言模型(VLMs)因其使用指令文本提示进行零样本推断而备受关注。虽然这些模型在一般计算机视觉上表现出色,但在遥感(RS)领域的域泛化潜力仍未被充分探索。现有方法通过生成视觉提示令牌来增强提示学习,但它们依赖于全图像特征,引入了类内变化的噪声和背景伪影,导致误分类。为解决这一问题,我们提出了FrogDogNet,这是一个结合傅里叶频率滤波和自注意力机制的新型提示学习框架,以提高遥感场景分类和域泛化能力。FrogDogNet选择性保留不变的低频成分,同时消除噪声和无关背景,确保跨域的稳健特征表示。该模型首先通过投影和自注意力提取重要特征,然后应用基于频率的滤波以保留用于提示学习的关键结构信息。在四个遥感数据集和三个域泛化任务上的大量实验表明,FrogDogNet始终优于最新的提示学习方法,展示了跨域迁移的卓越适应性。我们的研究结果表明了基于频率的不变特征保留在泛化中的有效性,为更广泛的应用铺平了道路。我们的代码位于https://github.com/HariseetharamG/FrogDogNet。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
在遥感领域,大型视觉语言模型(如CLIP)的零样本推理能力受到关注。现有方法通过生成视觉提示令牌增强提示学习,但依赖于全图像特征,引入噪声和背景伪影导致误分类。为解决这一问题,提出FrogDogNet,结合傅里叶频率过滤和自注意力机制的新型提示学习框架,改进遥感场景分类和领域泛化。FrogDogNet选择性保留不变的低频成分,消除噪声和无关背景,确保跨领域的稳健特征表示。
Key Takeaways
- 大型视觉语言模型(如CLIP)在遥感领域的零样本推理能力受到关注。
- 现有方法通过生成视觉提示令牌增强提示学习,但存在噪声和背景伪影问题。
- FrogDogNet通过傅里叶频率过滤和自注意力机制整合,提出一种新型提示学习框架。
- FrogDogNet能选择性保留不变的低频成分,消除噪声和无关背景。
- FrogDogNet在遥感场景分类和领域泛化方面表现优异。
- 跨四个遥感数据集和三个领域泛化任务的实验表明,FrogDogNet在提示学习方法上表现更优秀。
点此查看论文截图

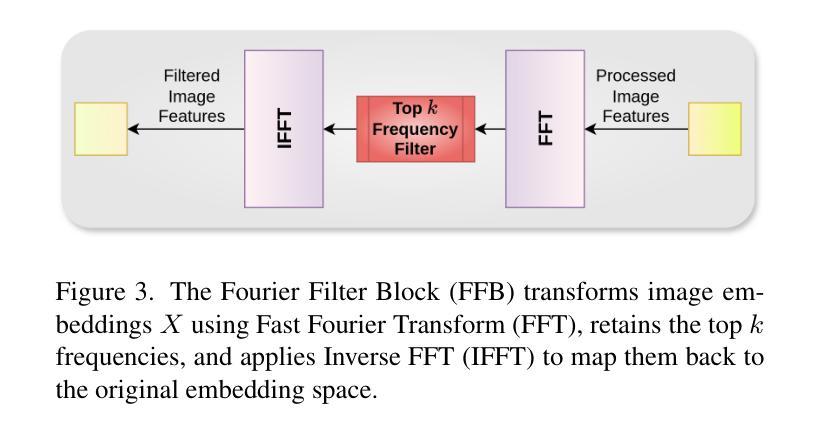
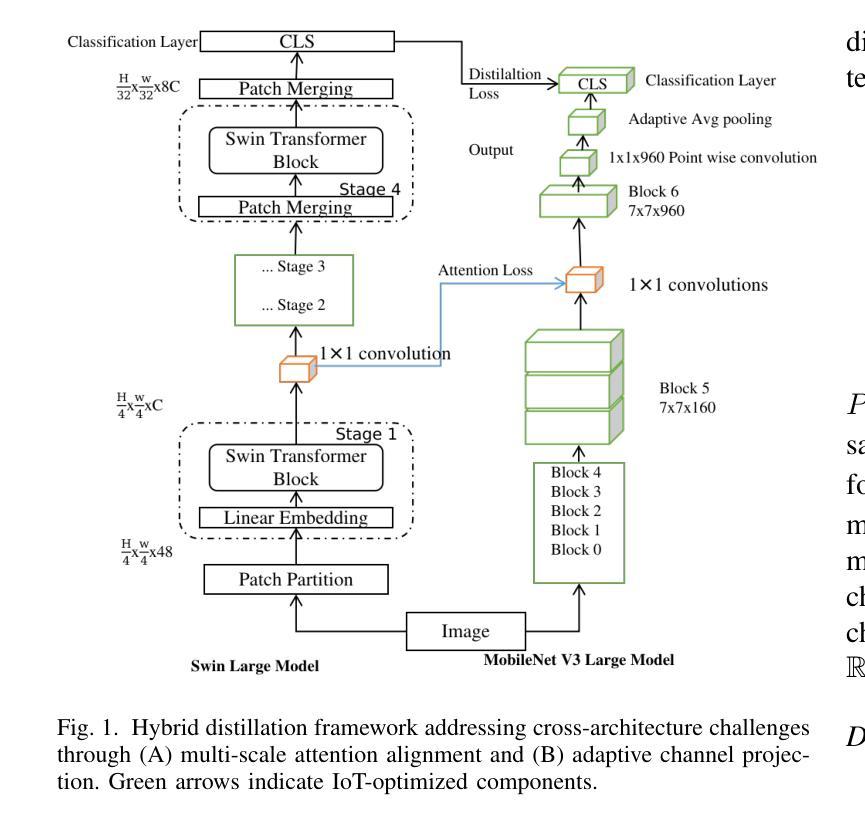
Hybrid Knowledge Transfer through Attention and Logit Distillation for On-Device Vision Systems in Agricultural IoT
Authors:Stanley Mugisha, Rashid Kisitu, Florence Tushabe
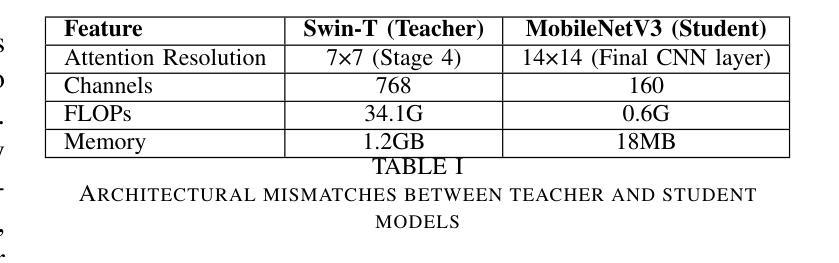
Integrating deep learning applications into agricultural IoT systems faces a serious challenge of balancing the high accuracy of Vision Transformers (ViTs) with the efficiency demands of resource-constrained edge devices. Large transformer models like the Swin Transformers excel in plant disease classification by capturing global-local dependencies. However, their computational complexity (34.1 GFLOPs) limits applications and renders them impractical for real-time on-device inference. Lightweight models such as MobileNetV3 and TinyML would be suitable for on-device inference but lack the required spatial reasoning for fine-grained disease detection. To bridge this gap, we propose a hybrid knowledge distillation framework that synergistically transfers logit and attention knowledge from a Swin Transformer teacher to a MobileNetV3 student model. Our method includes the introduction of adaptive attention alignment to resolve cross-architecture mismatch (resolution, channels) and a dual-loss function optimizing both class probabilities and spatial focus. On the lantVillage-Tomato dataset (18,160 images), the distilled MobileNetV3 attains 92.4% accuracy relative to 95.9% for Swin-L but at an 95% reduction on PC and < 82% in inference latency on IoT devices. (23ms on PC CPU and 86ms/image on smartphone CPUs). Key innovations include IoT-centric validation metrics (13 MB memory, 0.22 GFLOPs) and dynamic resolution-matching attention maps. Comparative experiments show significant improvements over standalone CNNs and prior distillation methods, with a 3.5% accuracy gain over MobileNetV3 baselines. Significantly, this work advances real-time, energy-efficient crop monitoring in precision agriculture and demonstrates how we can attain ViT-level diagnostic precision on edge devices. Code and models will be made available for replication after acceptance.
将深度学习应用集成到农业物联网系统面临一个严重的挑战,即需要在视觉转换器(ViTs)的高精度和受资源约束的边缘设备的效率需求之间取得平衡。像Swin Transformer这样的大模型通过捕捉全局局部依赖关系在植物疾病分类方面表现出色。然而,其计算复杂度(34.1 GFLOPs)限制了应用,对于实时设备端推理来说不太实用。MobileNetV3和TinyML等轻量级模型适合用于设备端推理,但在精细疾病检测方面缺乏所需的空间推理能力。为了弥补这一差距,我们提出了一种混合知识蒸馏框架,该框架协同将从Swin Transformer教师模型转移日志和注意力知识到MobileNetV3学生模型。我们的方法包括引入自适应注意力对齐来解决跨架构不匹配(分辨率、通道)的问题,并使用双损失函数优化类概率和空间焦点。在lantVillage-Tomato数据集(18,160张图像)上,蒸馏后的MobileNetV3相对于Swin-L达到了92.4%的准确率,但在个人计算机上的推理延迟减少了95%,在物联网设备上的推理延迟<82%(在个人计算机上为23毫秒/图像,在智能手机CPU上为86毫秒/图像)。关键创新包括以物联网为中心的验证指标(13 MB内存,0.22 GFLOPs)和动态分辨率匹配注意力图。对比实验表明,与单独的卷积神经网络和先前的蒸馏方法相比,该方法的准确率有了显著提高,比MobileNetV3基线提高了3.5%的准确率。这项工作在实时、节能的作物监测领域取得了进展,并展示了如何在边缘设备上实现媲美ViT级别的诊断精度。论文接受后,代码和模型将提供复制功能。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF 12 pages and 4 figures
Summary
该研究面临在农业物联网系统中整合深度学习应用时,如何在保持Vision Transformers(ViTs)的高精度同时满足资源受限的边缘设备的效率需求的挑战。该研究通过混合知识蒸馏框架实现了Swin Transformer与MobileNetV3模型的融合,该框架实现了跨架构的注意力转移和适应性的注意力对齐。经过蒸馏的MobileNetV3模型在lantVillage-Tomato数据集上达到了92.4%的准确率,相较于Swin-L模型的95.9%,其准确率较高,同时在个人电脑和物联网设备上的推理延迟大幅降低。该研究为实时、节能的作物监测和精准农业提供了新思路。
Key Takeaways
- 面临在农业物联网系统中整合深度学习应用时,需要平衡Vision Transformers(ViTs)的高精度与资源受限的边缘设备的效率需求。
- Swin Transformers在植物疾病分类方面表现出优秀性能,但计算复杂度限制了其实际应用。
- MobileNetV3等轻量级模型适用于边缘设备的推理,但在精细疾病检测方面缺乏空间推理能力。
- 提出的混合知识蒸馏框架实现了Swin Transformer教师模型与MobileNetV3学生模型的协同工作,通过转移注意力知识来弥补两者的差距。
- 引入自适应注意力对齐解决跨架构不匹配问题,并采用双损失函数优化类别概率和空间焦点。
- 在lantVillage-Tomato数据集上,蒸馏后的MobileNetV3模型达到92.4%的准确率,与Swin-L模型相比表现优秀。
点此查看论文截图


Decoding Vision Transformers: the Diffusion Steering Lens
Authors:Ryota Takatsuki, Sonia Joseph, Ippei Fujisawa, Ryota Kanai
Logit Lens is a widely adopted method for mechanistic interpretability of transformer-based language models, enabling the analysis of how internal representations evolve across layers by projecting them into the output vocabulary space. Although applying Logit Lens to Vision Transformers (ViTs) is technically straightforward, its direct use faces limitations in capturing the richness of visual representations. Building on the work of Toker et al. (2024)~\cite{Toker2024-ve}, who introduced Diffusion Lens to visualize intermediate representations in the text encoders of text-to-image diffusion models, we demonstrate that while Diffusion Lens can effectively visualize residual stream representations in image encoders, it fails to capture the direct contributions of individual submodules. To overcome this limitation, we propose \textbf{Diffusion Steering Lens} (DSL), a novel, training-free approach that steers submodule outputs and patches subsequent indirect contributions. We validate our method through interventional studies, showing that DSL provides an intuitive and reliable interpretation of the internal processing in ViTs.
Logit Lens是广泛应用于基于转换器的语言模型机械解释性的方法,通过将内部表示投影到输出词汇空间来分析它们在各层如何演变。虽然将Logit Lens应用于视觉转换器(ViTs)在技术上很直观,但其直接使用在捕捉视觉表示的丰富性方面存在局限性。在Toker等人(2024)的工作基础上,他们引入了Diffusion Lens来可视化文本到图像扩散模型的文本编码器中的中间表示,我们证明虽然Diffusion Lens可以有效地可视化图像编码器中的残差流表示,但它无法捕捉单个子模块的直接贡献。为了克服这一局限性,我们提出了扩散转向透镜(DSL),这是一种新型、无需训练的方法,可以引导子模块输出并修复随后的间接贡献。我们通过干预研究验证了我们的方法,表明DSL提供了对ViTs内部处理的直观和可靠解释。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF 12 pages, 17 figures. Accepted to the CVPR 2025 Workshop on Mechanistic Interpretability for Vision (MIV)
摘要
Logit Lens是广泛应用于基于转换器的语言模型的机械解释性的方法,通过将内部表示投影到输出词汇空间来分析其如何跨层演变。尽管将Logit Lens应用于Vision Transformers(ViTs)在技术上很直接,但其直接使用在捕捉视觉表示的丰富性方面存在局限性。在Toker等人(2024)工作的基础上,他们引入了用于可视化文本编码器中的文本到图像扩散模型的中间表示的Diffusion Lens,我们证明虽然Diffusion Lens可以有效地可视化图像编码器中的剩余流表示,但它无法捕获各个子模块的直接影响。为了克服这一局限性,我们提出了无训练的Diffusion Steering Lens(DSL),通过引导子模块输出和修复随后的间接贡献来可视化分析ViTs的内部处理过程。我们通过干预研究验证了我们的方法,表明DSL为理解ViTs的内部处理提供了直观且可靠的解释。
关键见解
- Logit Lens广泛用于解释基于转换器的语言模型,但直接应用于Vision Transformers(ViTs)存在局限性。
- Diffusion Lens可以有效地可视化图像编码器中的剩余流表示,但无法捕获子模块的直接影响。
- 提出了无训练的Diffusion Steering Lens(DSL)方法,旨在解决现有方法的局限性。
- DSL能够直观地展示Vision Transformers的内部处理过程。
- 通过子模块输出的引导和间接贡献的修复,DSL可以更深入地解析ViTs的工作机制。
- 验证实验显示DSL在解释Vision Transformers的内部处理方面具有可靠性。
- DSL方法为未来对Vision Transformers的可解释性研究开辟了新的途径。
点此查看论文截图


Embedding Radiomics into Vision Transformers for Multimodal Medical Image Classification
Authors:Zhenyu Yang, Haiming Zhu, Rihui Zhang, Haipeng Zhang, Jianliang Wang, Chunhao Wang, Minbin Chen, Fang-Fang Yin
Background: Deep learning has significantly advanced medical image analysis, with Vision Transformers (ViTs) offering a powerful alternative to convolutional models by modeling long-range dependencies through self-attention. However, ViTs are inherently data-intensive and lack domain-specific inductive biases, limiting their applicability in medical imaging. In contrast, radiomics provides interpretable, handcrafted descriptors of tissue heterogeneity but suffers from limited scalability and integration into end-to-end learning frameworks. In this work, we propose the Radiomics-Embedded Vision Transformer (RE-ViT) that combines radiomic features with data-driven visual embeddings within a ViT backbone. Purpose: To develop a hybrid RE-ViT framework that integrates radiomics and patch-wise ViT embeddings through early fusion, enhancing robustness and performance in medical image classification. Methods: Following the standard ViT pipeline, images were divided into patches. For each patch, handcrafted radiomic features were extracted and fused with linearly projected pixel embeddings. The fused representations were normalized, positionally encoded, and passed to the ViT encoder. A learnable [CLS] token aggregated patch-level information for classification. We evaluated RE-ViT on three public datasets (including BUSI, ChestXray2017, and Retinal OCT) using accuracy, macro AUC, sensitivity, and specificity. RE-ViT was benchmarked against CNN-based (VGG-16, ResNet) and hybrid (TransMed) models. Results: RE-ViT achieved state-of-the-art results: on BUSI, AUC=0.950+/-0.011; on ChestXray2017, AUC=0.989+/-0.004; on Retinal OCT, AUC=0.986+/-0.001, which outperforms other comparison models. Conclusions: The RE-ViT framework effectively integrates radiomics with ViT architectures, demonstrating improved performance and generalizability across multimodal medical image classification tasks.
背景:深度学习已显著推进医学影像分析的发展。通过自注意力机制进行长距离依赖建模,Vision Transformers(ViTs)为卷积模型提供了强大的替代方案。然而,ViTs本质上需要大量的数据,并且缺乏特定领域的归纳偏见,这限制了其在医学影像中的应用。相比之下,放射组学提供了组织异质性的可解释手工描述符,但受限于可扩展性和整合到端到端学习框架的能力。在这项工作中,我们提出了Radiomics-Embedded Vision Transformer(RE-ViT),它将放射组学特征与数据驱动的视觉嵌入相结合,在一个ViT主干中。目的:开发一个混合RE-ViT框架,通过早期融合整合放射组学和补丁级ViT嵌入,提高在医学图像分类中的稳健性和性能。方法:遵循标准的ViT管道,将图像分成补丁。对于每个补丁,提取手工制作的放射组学特征,并与线性投影的像素嵌入融合。融合后的表示经过归一化、位置编码并传递给ViT编码器。一个可学习的[CLS]标记聚合补丁级信息进行分类。我们在三个公共数据集(包括BUSI、ChestXray2017和视网膜OCT)上评估了RE-ViT,使用准确度、宏AUC、敏感度和特异度。RE-ViT与基于CNN的(VGG-16、ResNet)和混合(TransMed)模型进行了比较。结果:RE-ViT达到了最先进的成果:在BUSI上,AUC=0.950±0.011;在ChestXray2017上,AUC=0.989±0.004;在视网膜OCT上,AUC=0.986±0.001,优于其他对比模型。结论:RE-ViT框架有效地将放射组学与ViT架构相结合,显示出在多模态医学图像分类任务中改进的性能和泛化能力。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF 27 pages, 3 figures
Summary
本文提出了一个混合的RE-ViT框架,它将放射组学特征和ViT的补丁式嵌入相结合,通过早期融合提高医学图像分类的稳健性和性能。实验结果表明,RE-ViT在多种医学图像分类任务上取得了优异的性能,并且在三个公开数据集上实现了最先进的成果。
Key Takeaways
- RE-ViT结合了放射组学特征和ViT模型的数据驱动视觉嵌入,形成了一个混合框架。
- 通过早期融合,RE-ViT提高了医学图像分类的稳健性和性能。
- 实验结果表明,RE-ViT在多种医学图像分类任务上表现优越。
- 在三个公开数据集上,RE-ViT达到了最先进的成果。
- RE-ViT通过结合放射组学的可解释性和ViT的自我注意力机制,实现了有效的信息融合。
- RE-ViT框架具有广泛的应用前景,可应用于多种模态的医学图像分类任务。
点此查看论文截图

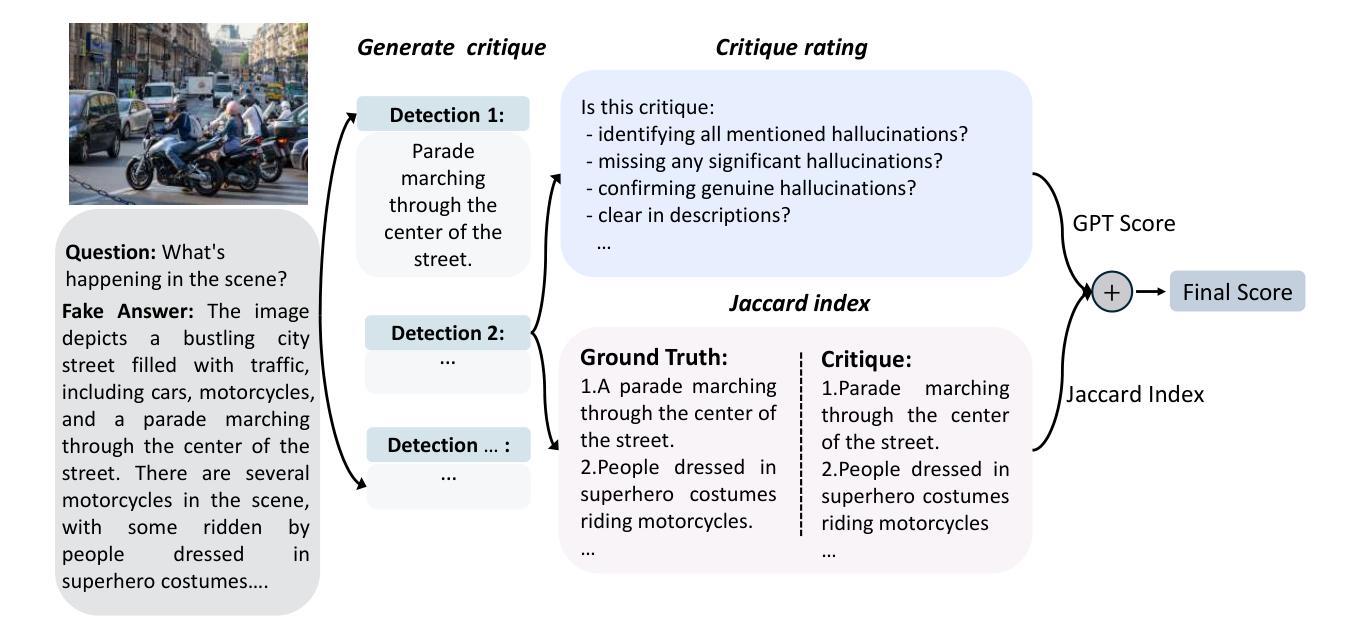
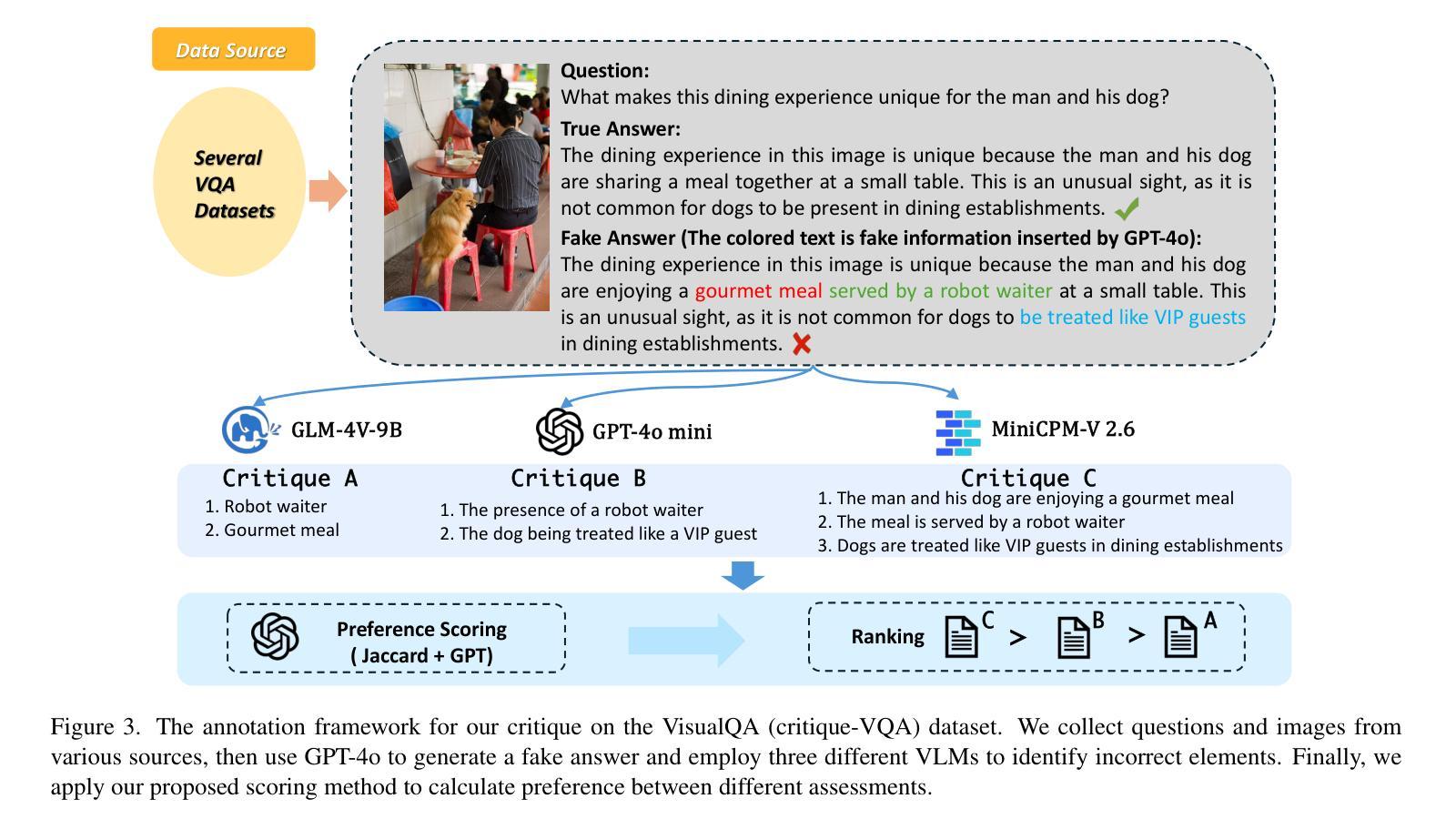
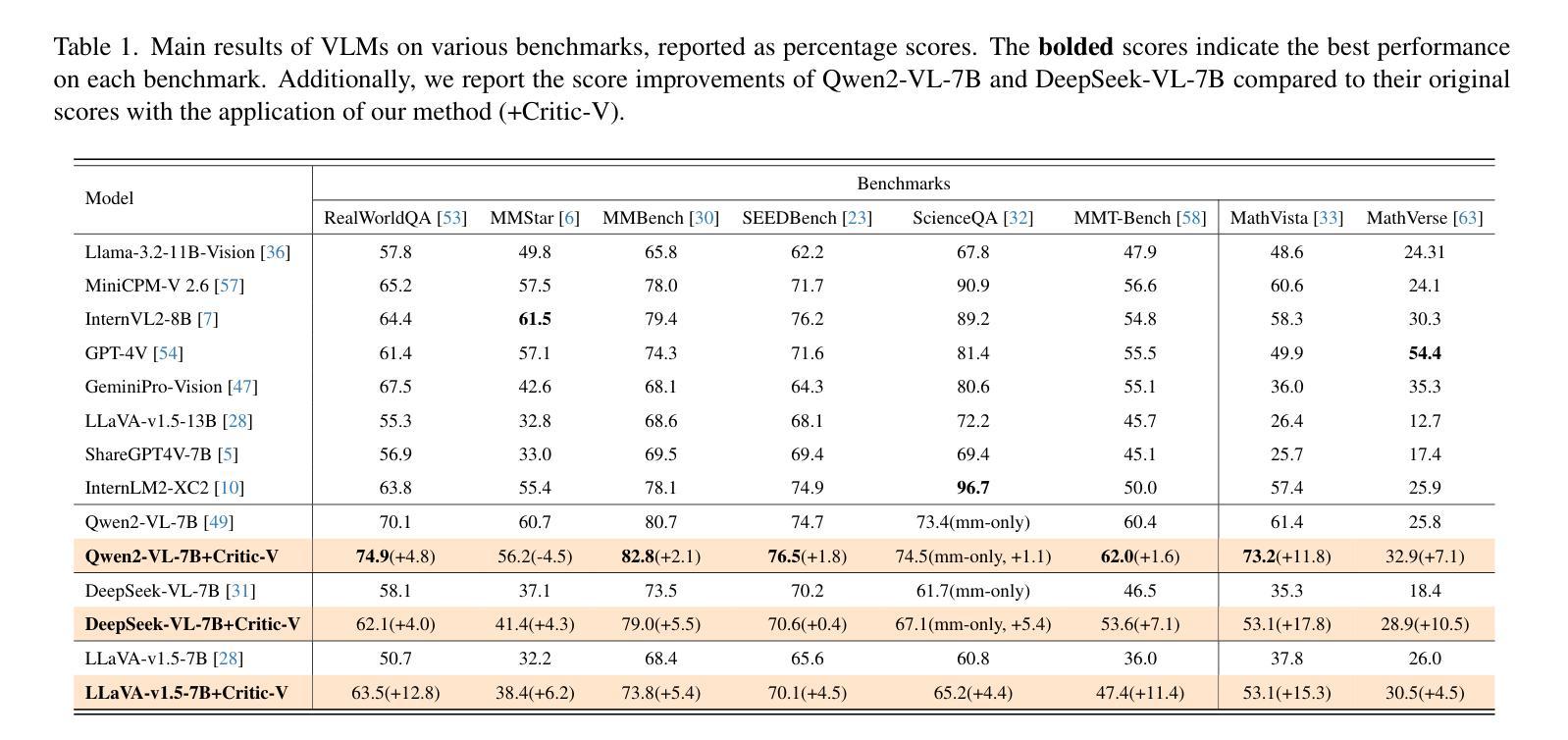
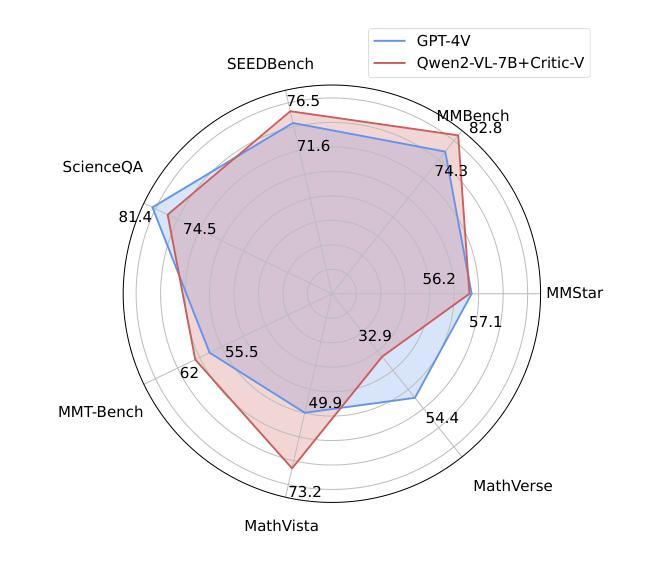
Critic-V: VLM Critics Help Catch VLM Errors in Multimodal Reasoning
Authors:Di Zhang, Junxian Li, Jingdi Lei, Xunzhi Wang, Yujie Liu, Zonglin Yang, Jiatong Li, Weida Wang, Suorong Yang, Jianbo Wu, Peng Ye, Wanli Ouyang, Dongzhan Zhou
Vision-language models (VLMs) have shown remarkable advancements in multimodal reasoning tasks. However, they still often generate inaccurate or irrelevant responses due to issues like hallucinated image understandings or unrefined reasoning paths. To address these challenges, we introduce Critic-V, a novel framework inspired by the Actor-Critic paradigm to boost the reasoning capability of VLMs. This framework decouples the reasoning process and critic process by integrating two independent components: the Reasoner, which generates reasoning paths based on visual and textual inputs, and the Critic, which provides constructive critique to refine these paths. In this approach, the Reasoner generates reasoning responses according to text prompts, which can evolve iteratively as a policy based on feedback from the Critic. This interaction process was theoretically driven by a reinforcement learning framework where the Critic offers natural language critiques instead of scalar rewards, enabling more nuanced feedback to boost the Reasoner’s capability on complex reasoning tasks. The Critic model is trained using Direct Preference Optimization (DPO), leveraging a preference dataset of critiques ranked by Rule-based Reward~(RBR) to enhance its critic capabilities. Evaluation results show that the Critic-V framework significantly outperforms existing methods, including GPT-4V, on 5 out of 8 benchmarks, especially regarding reasoning accuracy and efficiency. Combining a dynamic text-based policy for the Reasoner and constructive feedback from the preference-optimized Critic enables a more reliable and context-sensitive multimodal reasoning process. Our approach provides a promising solution to enhance the reliability of VLMs, improving their performance in real-world reasoning-heavy multimodal applications such as autonomous driving and embodied intelligence.
视觉语言模型(VLMs)在多模态推理任务中取得了显著的进步。然而,由于诸如虚构的图像理解或粗糙的推理路径等问题,它们仍然经常产生不准确或不相关的响应。为了解决这些挑战,我们引入了Critic-V,这是一个受Actor-Critic范式启发的新型框架,旨在提升VLMs的推理能力。该框架通过集成两个独立组件来解耦推理过程和评论过程:Reasoner,它根据视觉和文本输入生成推理路径;以及Critic,它提供建设性评论以优化这些路径。在该方法中,Reasoner根据文本提示生成推理响应,这些响应可以根据来自Critic的反馈而迭代地作为策略发展。这一交互过程是由强化学习框架驱动的,其中Critic提供自然语言评论而不是标量奖励,从而提供更微妙的反馈,以提升Reasoner在复杂推理任务上的能力。Critic模型使用直接偏好优化(DPO)进行训练,利用基于规则的奖励(RBR)对评论进行排名偏好数据集,以增强其评论能力。评估结果表明,在八个基准测试中的五个上,Critic-V框架在推理准确性和效率方面显著优于现有方法,包括GPT-4V。结合Reasoner的动态基于文本的策略和来自偏好优化后的Critic的建设性反馈,能够实现更可靠和上下文敏感的多模态推理过程。我们的方法为提升VLMs的可靠性提供了有前景的解决方案,并有望改善其在现实世界推理密集型多模态应用(如自动驾驶和智能集成)中的性能。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF 16 pages, 11 figures
摘要
本文介绍了针对视觉语言模型(VLMs)的挑战,提出了一种基于Actor-Critic范式的新型框架Critic-V,旨在提升VLMs的推理能力。该框架通过整合Reasoner和Critic两个独立组件,实现推理过程和批判过程的解耦。Reasoner根据视觉和文本输入生成推理路径,而Critic则提供建设性批评以优化这些路径。该框架采用强化学习理论驱动,Critic提供自然语言批评而非标量奖励,促进更精细的反馈,提升Reasoner在复杂推理任务上的能力。使用直接偏好优化(DPO)训练Critic模型,借助基于规则的奖励(RBR)对批评进行排名,以提高其批判能力。评估结果显示,在五个基准测试中,Critic-V框架在超过一半以上的基准测试中显著优于现有方法(包括GPT-4V),特别是在推理准确性和效率方面。通过为Reasoner制定动态文本策略并接受偏好优化的Critic的反馈,实现了更可靠、更适应上下文的多模态推理过程。本研究为提高VLMs的可靠性提供了有前景的解决方案,特别是在自动驾驶和智能体智能等现实世界推理密集型多模态应用中表现优异。
关键见解
- Critic-V框架基于Actor-Critic范式,旨在解决视觉语言模型(VLMs)在复杂推理任务中的不准确或无关响应问题。
- 框架包含Reasoner和Critic两个独立组件,分别负责生成和批判推理路径。
- 强化学习理论驱动该框架的交互过程,其中Critic提供自然语言批评以增强反馈的细腻性。
- Critic模型采用直接偏好优化(DPO)训练,以提高其批判能力。
- 评估结果显示,Critic-V框架在多个基准测试中显著优于现有方法,特别是在推理准确性和效率方面。
- 结合动态文本策略与偏好优化的Critic反馈,实现了可靠且上下文敏感的多模态推理过程。
点此查看论文截图