⚠️ 以下所有内容总结都来自于 大语言模型的能力,如有错误,仅供参考,谨慎使用
🔴 请注意:千万不要用于严肃的学术场景,只能用于论文阅读前的初筛!
💗 如果您觉得我们的项目对您有帮助 ChatPaperFree ,还请您给我们一些鼓励!⭐️ HuggingFace免费体验
2025-04-26 更新
Self-Supervised Noise Adaptive MRI Denoising via Repetition to Repetition (Rep2Rep) Learning
Authors:Nikola Janjušević, Jingjia Chen, Luke Ginocchio, Mary Bruno, Yuhui Huang, Yao Wang, Hersh Chandarana, Li Feng
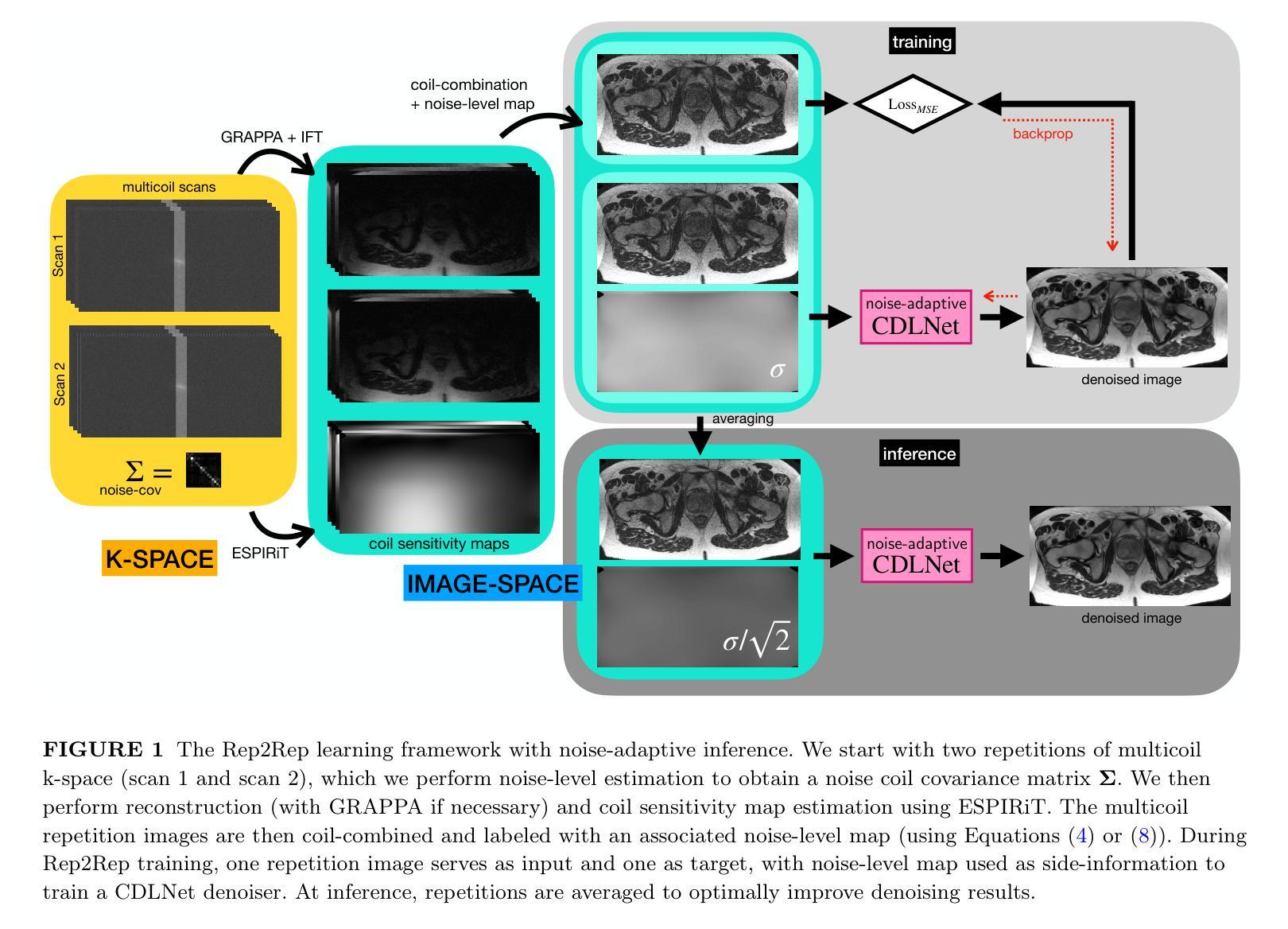
Purpose: This work proposes a novel self-supervised noise-adaptive image denoising framework, called Repetition to Repetition (Rep2Rep) learning, for low-field (<1T) MRI applications. Methods: Rep2Rep learning extends the Noise2Noise framework by training a neural network on two repeated MRI acquisitions, using one repetition as input and another as target, without requiring ground-truth data. It incorporates noise-adaptive training, enabling denoising generalization across varying noise levels and flexible inference with any number of repetitions. Performance was evaluated on both synthetic noisy brain MRI and 0.55T prostate MRI data, and compared against supervised learning and Monte Carlo Stein’s Unbiased Risk Estimator (MC-SURE). Results: Rep2Rep learning outperforms MC-SURE on both synthetic and 0.55T MRI datasets. On synthetic brain data, it achieved denoising quality comparable to supervised learning and surpassed MC-SURE, particularly in preserving structural details and reducing residual noise. On the 0.55T prostate MRI dataset, a reader study showed radiologists preferred Rep2Rep-denoised 2-average images over 8-average noisy images. Rep2Rep demonstrated robustness to noise-level discrepancies between training and inference, supporting its practical implementation. Conclusion: Rep2Rep learning offers an effective self-supervised denoising for low-field MRI by leveraging routinely acquired multi-repetition data. Its noise-adaptivity enables generalization to different SNR regimes without clean reference images. This makes Rep2Rep learning a promising tool for improving image quality and scan efficiency in low-field MRI.
目的:本研究提出了一种新型的自我监督噪声自适应图像去噪框架,称为重复到重复(Rep2Rep)学习,用于低场(<1T)MRI应用。方法:Rep2Rep学习通过扩展Noise2Noise框架,对两次重复的MRI采集进行神经网络训练,以一次重复作为输入,另一次作为目标,无需真实数据。它融入了噪声自适应训练,能够在不同的噪声水平上进行去噪泛化,并且具有任意次重复的灵活推理。性能评估是在合成噪声脑MRI和0.55T前列腺MRI数据上进行的,并与监督学习和蒙特卡洛斯坦无偏风险估计(MC-SURE)进行了比较。结果:Rep2Rep学习在合成和0.55T MRI数据集上的表现均优于MC-SURE。在合成脑数据上,其去噪质量可与监督学习相媲美,并且超过MC-SURE,特别是在保留结构细节和减少残留噪声方面。在0.55T前列腺MRI数据集上,读者研究结果显示,放射科医生更喜欢使用Rep2Rep去噪的2次平均图像而不是8次平均的噪声图像。Rep2Rep显示出对训练和推理期间噪声水平差异的稳健性,支持其实践实施。结论:Rep2Rep学习通过利用常规获取的多重复数据,为低场MRI提供了有效的自我监督去噪。其噪声适应性使得能够在不同的信噪比制度下实现泛化,而无需清洁的参考图像。这使得Rep2Rep学习成为提高低场MRI图像质量和扫描效率的有前途的工具。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF 13 pages, 9 figures, 1 table, supplementary information at end of document
Summary
本研究提出了一种新型的基于自监督噪声自适应的图像去噪框架,名为重复学习(Rep2Rep),适用于低场MRI应用。方法通过在两个重复的MRI采集上训练神经网络,以一次重复作为输入,另一次作为目标,无需真实数据。它实现了噪声自适应训练,可在不同的噪声水平上实现去噪泛化并灵活推理。Rep2Rep在合成噪声大脑MRI和0.55T前列腺MRI数据上的表现均优于MC-SURE。读者研究表明,放射科医生更倾向于选择经过Rep2Rep处理后的两次平均图像而不是八次平均噪声图像。结论指出,Rep2Rep学习为低场MRI提供了一种有效的自监督去噪方法,利用常规获取的多重复数据。其噪声适应性使得能够在没有清洁参考图像的情况下适应不同的信噪比环境。这使其成为提高低场MRI图像质量和扫描效率的潜力工具。
Key Takeaways
- Rep2Rep学习是一种用于低场MRI的自监督噪声自适应图像去噪框架。
- 该方法通过重复MRI采集训练神经网络,无需真实数据作为参照。
- Rep2Rep实现了在不同噪声水平上的去噪泛化并允许灵活的推理。
- 在合成大脑MRI和0.55T前列腺MRI数据上,Rep2Rep表现优于MC-SURE和其他方法。
- 读者研究支持了Rep2Rep在实际应用中的优越性。
- Rep2Rep能够适应不同的信噪比环境,提高了其在不同环境下的实用性。
点此查看论文截图

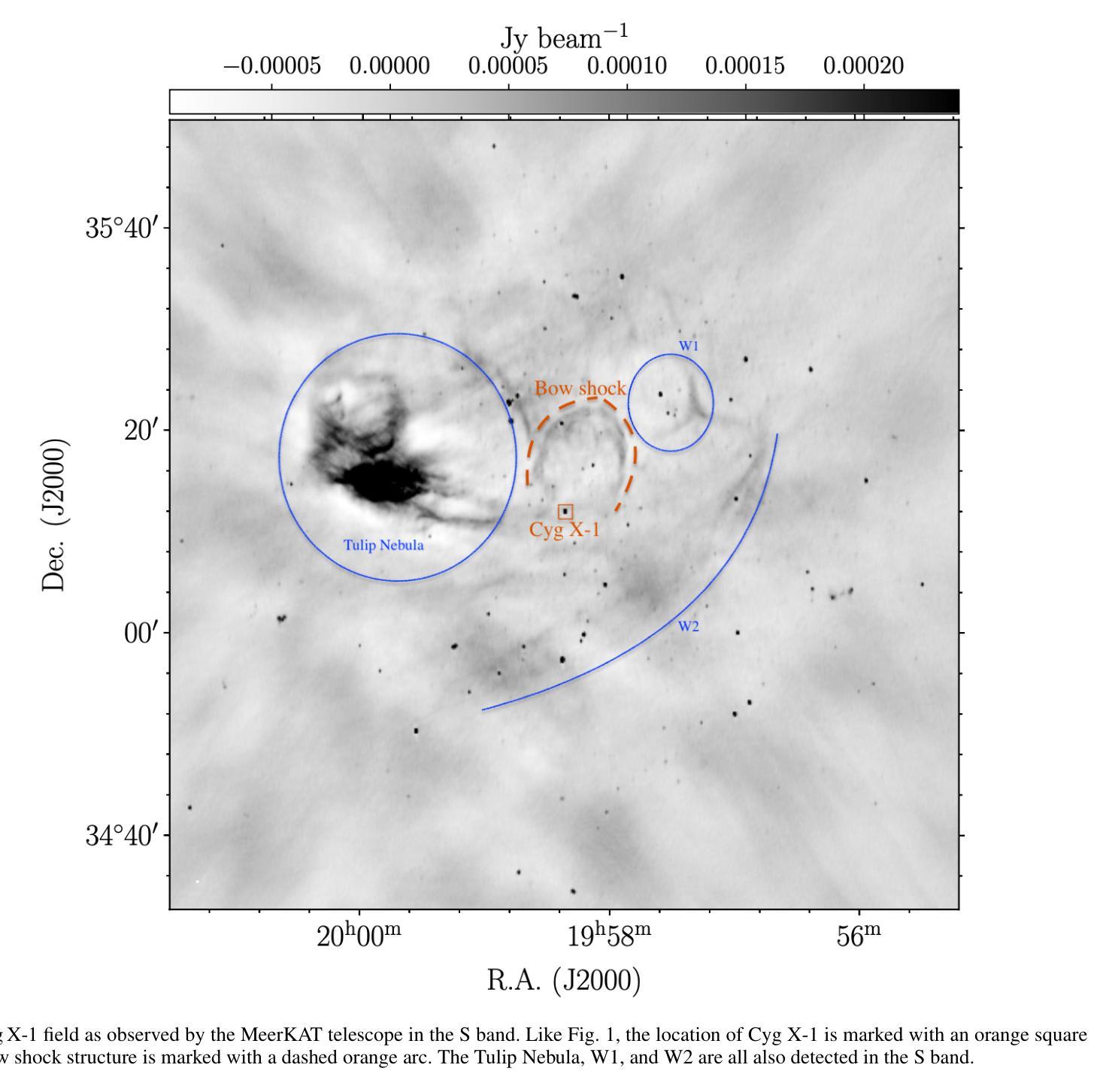
Quantifying jet-interstellar medium interactions in Cyg X-1: Insights from dual-frequency bow shock detection with MeerKAT
Authors:P. Atri, S. E. Motta, Jakob van den Eijnden, James H. Matthews, James C. A. Miller-Jones, Rob Fender, David Williams-Baldwin, Ian Heywood, Patrick Woudt
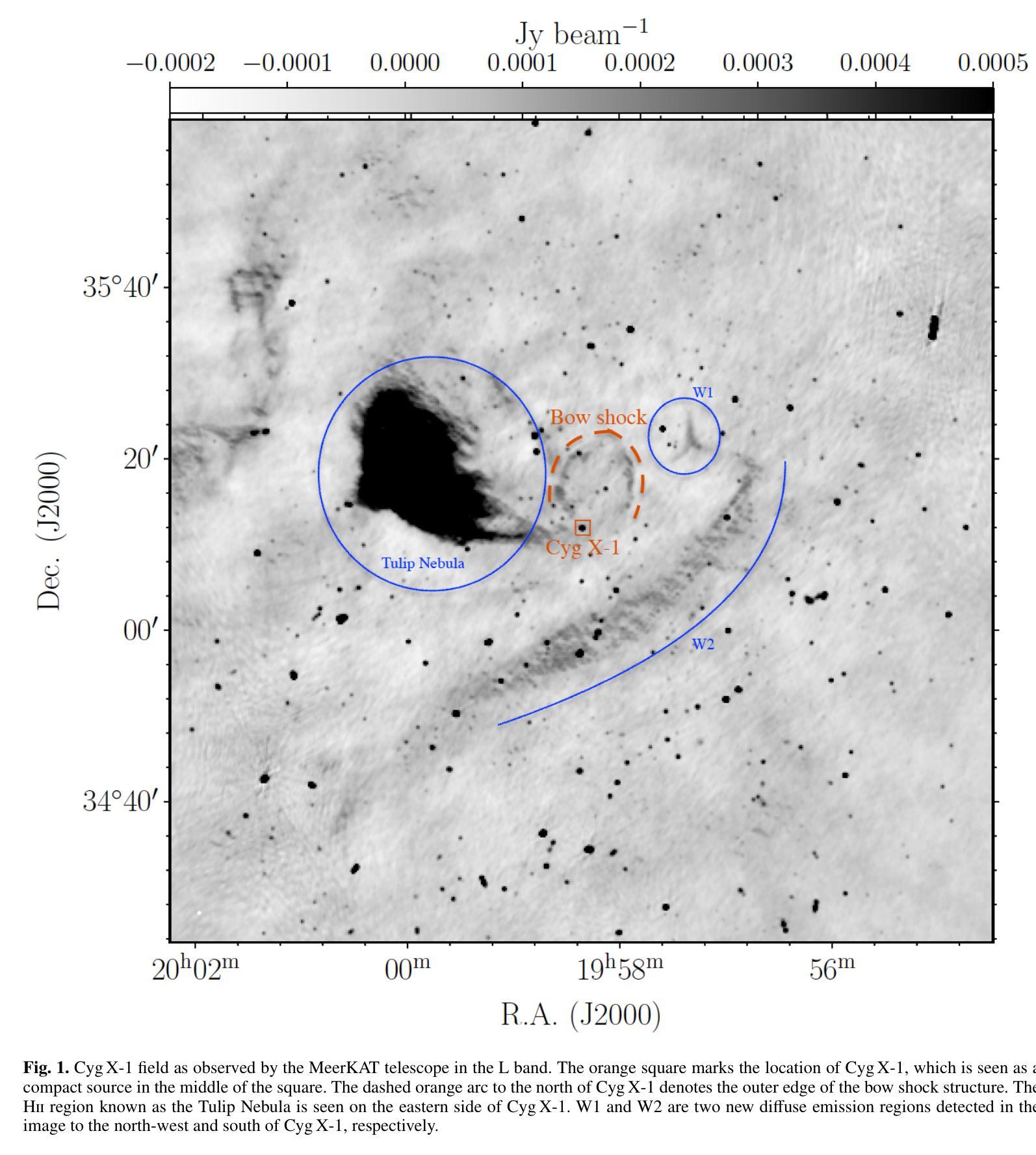
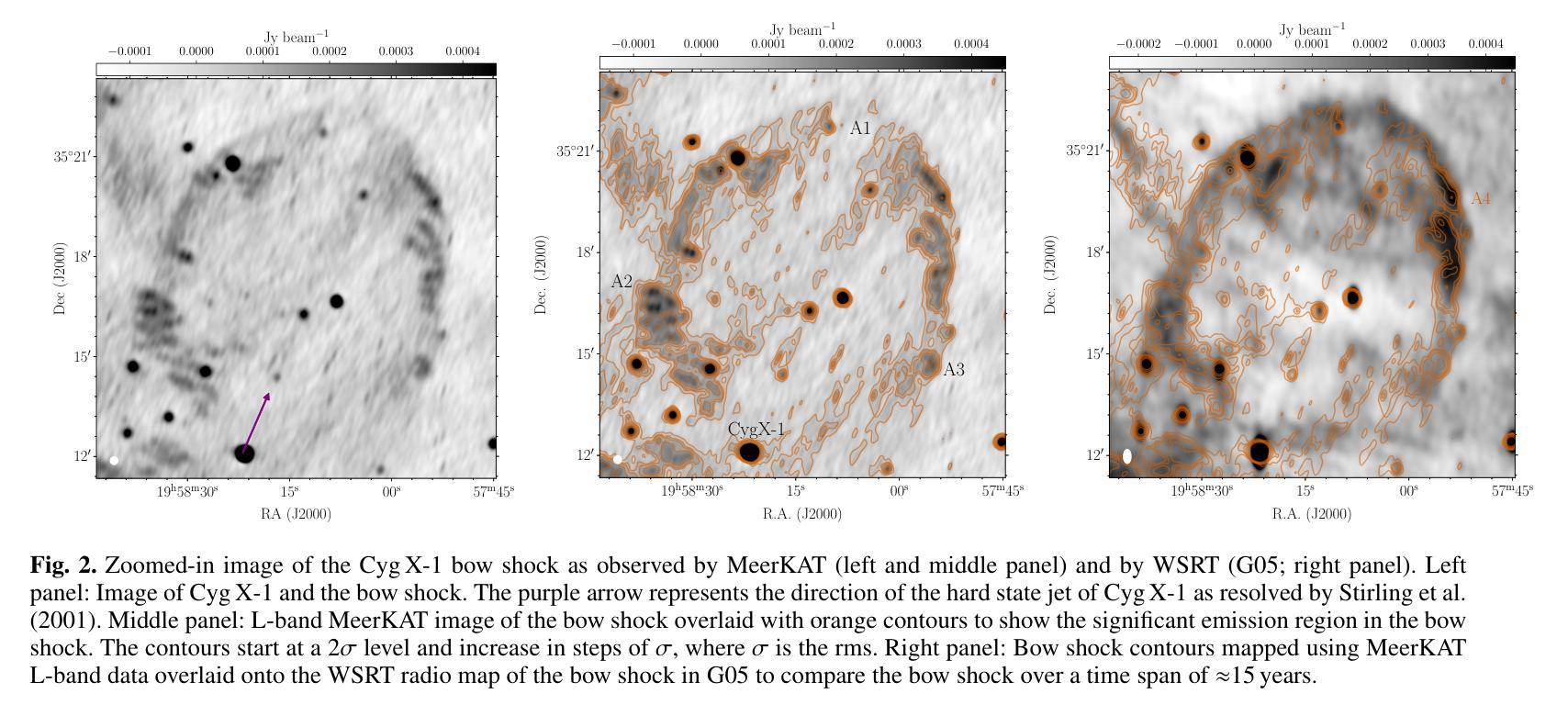
Accretion and outflows are astrophysical phenomena observed across a wide range of objects, from white dwarfs to supermassive black holes. Developing a complete picture of these processes requires complementary studies across this full spectrum of jet-launching sources. Jet-interstellar medium (ISM) interaction sites near black hole X-ray binaries provide unique laboratories to study jet energetics. This work aims to detect and characterise the bow shock near one black hole X-ray binary, Cyg X-1, and then use this bow shock structure to parametrise the properties of the jet launched by Cyg X-1 over its lifetime. We used the MeerKAT radio telescope to investigate the bow shock structure formed by the interaction between the jets of Cyg X-1 and the ISM. We successfully detect the bow shock north of Cyg X-1 in the L and S bands and report its size and brightness. We present the spectral index distribution across the bow shock, which is in the range -0.9 to 0.4, with an error distribution (0.6 to 1.5) that peaks at unity. We determine that the unshocked ISM density is 6-7 cm^-3 for a temperature range of 10^4 to 310^6 K. This temperature range suggests that the velocity of the bow shock is 21 km/s to 364 km/s. The age of the Cyg X-1 jet responsible for the bow shock is 0.04 to 0.3 Myr, and the power of the jet is constrained to 210^31 ergs/s to 10^35 ergs/s. We also detect new morphological features of the bow shock in the S-band image. The comparison of archival H_alpha maps with the new radio observations hints at different regions of emission, different temperature ranges, and different ISM densities. The spectral index suggests a consistent emission origin across the structure. The ISM density around Cyg X-1 is on the higher end for Galactic environments, and our results indicate a lower jet energy transport rate than prior estimates.
积云和流出是在白矮星到超大质量黑洞等各种天体中观察到的天文现象。要全面理解这些过程,需要对这一系列喷射源进行全面的研究。黑洞X射线双星附近的喷射流与星际介质(ISM)相互作用区域为研究喷射流能量提供了独特的实验室。这项工作旨在检测靠近黑洞X射线双星之一的赛格马X-1(Cyg X-1)的弓形冲击波,并利用这一弓形冲击波结构来参数化Cyg X-1在其生命周期内喷射流的特性。我们使用MeerKAT射电望远镜来研究由Cyg X-1喷射流与星际介质的相互作用所形成的弓形冲击波结构。我们成功地在L波段和S波段检测到Cyg X-1北部的弓形冲击波,并报告了其大小和亮度。我们展示了弓形冲击波的光谱指数分布范围在-0.9到0.4之间,误差分布(0.6到1.5)以单位值为中心。我们确定了在温度范围为10^4到310^6 K的情况下,未受冲击的星际介质密度是6-7 cm^-3。这个温度范围表明弓形冲击波的速度是21 km/s到364 km/s。造成弓形冲击波的Cyg X-1喷射流的年龄为0.04到0.3Myr,喷射功率被限制在210^31 ergs/s到10^35 ergs/s之间。我们还发现了S波段图像中弓形冲击波的新形态特征。档案中的H_alpha地图与新射电观测结果的比较暗示了不同的发射区域、不同的温度范围和不同的星际介质密度。光谱指数表明整个结构的发射来源是一致的。Cyg X-1周围的星际介质密度处于银河环境的高端,我们的结果指示喷射流能量传输率低于先前的估计。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF 14 pages, 7 figures, Published in A&A
Summary
观测Cyg X-1黑洞X射线双星附近射流与星际介质相互作用形成的弓形冲击波,以研究射流能量学。使用MeerKAT望远镜成功检测到Cyg X-1北部的弓形冲击波,并报告其大小和亮度。弓形冲击波的频谱指数分布范围在-0.9至0.4之间,并确定未受惊扰的星际介质密度和温度范围,进一步估算出弓形冲击的速度、射流负责时间和功率。比较存档的H_alpha地图与新的无线电观测结果,暗示发射区域、温度范围和星际介质密度的差异。
Key Takeaways
- 观测到了Cyg X-1黑洞X射线双星附近的弓形冲击波结构,此为研究射流能量学的重要实验。
- 使用MeerKAT望远镜成功检测到弓形冲击波在L波段和S波段的存在,并报告其尺寸和亮度信息。
- 弓形冲击波的频谱指数分布范围及其误差分布已确定。
- 通过未受惊扰的星际介质密度估计了弓形冲击的速度范围为21 km/s至364 km/s。
- Cyg X-1射流的年龄和功率已经估算出来,给出了具体数值范围。
- 新观察到的弓形冲击波形态特征揭示了更多关于射流与星际介质相互作用的信息。
点此查看论文截图

Occlusion-Aware Self-Supervised Monocular Depth Estimation for Weak-Texture Endoscopic Images
Authors:Zebo Huang, Yinghui Wang
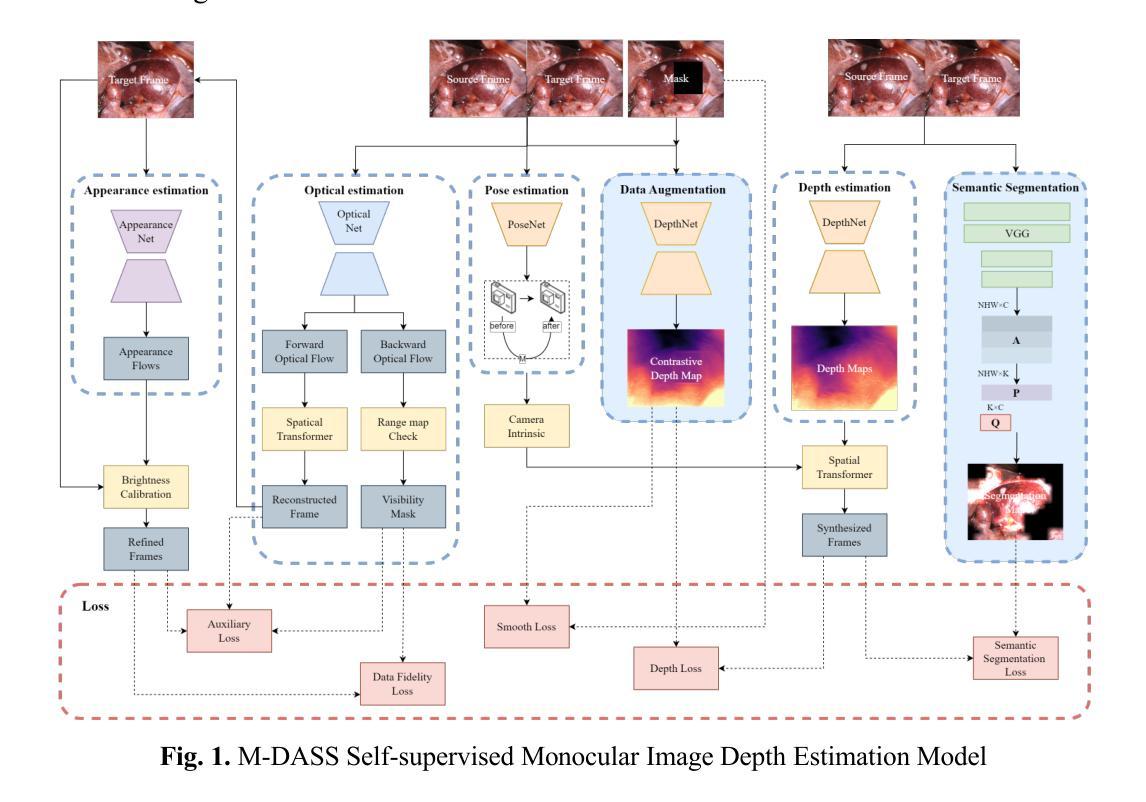
We propose a self-supervised monocular depth estimation network tailored for endoscopic scenes, aiming to infer depth within the gastrointestinal tract from monocular images. Existing methods, though accurate, typically assume consistent illumination, which is often violated due to dynamic lighting and occlusions caused by GI motility. These variations lead to incorrect geometric interpretations and unreliable self-supervised signals, degrading depth reconstruction quality. To address this, we introduce an occlusion-aware self-supervised framework. First, we incorporate an occlusion mask for data augmentation, generating pseudo-labels by simulating viewpoint-dependent occlusion scenarios. This enhances the model’s ability to learn robust depth features under partial visibility. Second, we leverage semantic segmentation guided by non-negative matrix factorization, clustering convolutional activations to generate pseudo-labels in texture-deprived regions, thereby improving segmentation accuracy and mitigating information loss from lighting changes. Experimental results on the SCARED dataset show that our method achieves state-of-the-art performance in self-supervised depth estimation. Additionally, evaluations on the Endo-SLAM and SERV-CT datasets demonstrate strong generalization across diverse endoscopic environments.
我们提出了一种针对内窥镜场景的自监督单目深度估计网络,旨在从单目图像中推断胃肠道内的深度。现有方法虽然准确,但通常假设光照一致,而由于胃肠道的动态照明和由GI运动引起的遮挡,这一假设经常被违反。这些变化导致几何解释错误和自监督信号不可靠,从而降低了深度重建质量。为了解决这一问题,我们引入了一种遮挡感知自监督框架。首先,我们采用遮挡掩膜进行数据增强,通过模拟视点相关的遮挡场景生成伪标签。这增强了模型在部分可见情况下学习稳健深度特征的能力。其次,我们利用非负矩阵分解引导语义分割,聚类卷积激活以在纹理缺失区域生成伪标签,从而提高分割准确性并缓解由光照变化引起的信息损失。在SCARED数据集上的实验结果表明,我们的方法在自监督深度估计方面达到了最新性能。此外,在Endo-SLAM和SERV-CT数据集上的评估证明了其在多种内窥镜环境中的强大泛化能力。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
本文提出了一种针对内窥镜场景的自监督单目深度估计网络,旨在从单目图像中推断胃肠道内的深度。为解决因光照动态变化和胃肠道运动导致的遮挡问题,引入了一种遮挡感知自监督框架。通过数据增强生成伪标签,提高模型在部分可见情况下的深度特征学习能力。同时,结合非负矩阵分解引导语义分割,改善纹理缺失区域的伪标签生成,提高分割精度并减轻光照变化的信息损失。实验结果表明,该方法在自我监督深度估计方面达到最新技术水平,并在不同内窥镜环境中表现出强大的泛化能力。
Key Takeaways
- 提出了一种自监督单目深度估计网络,专门用于内窥镜场景。
- 旨在解决因动态光照和胃肠道运动导致的遮挡问题。
- 引入遮挡感知自监督框架,通过数据增强生成伪标签,提高模型在部分可见情况下的学习能力。
- 结合非负矩阵分解引导语义分割,改善纹理缺失区域的伪标签质量。
- 实验结果表明,该方法在自我监督深度估计方面表现优异。
- 在不同内窥镜环境中的泛化能力强。
点此查看论文截图

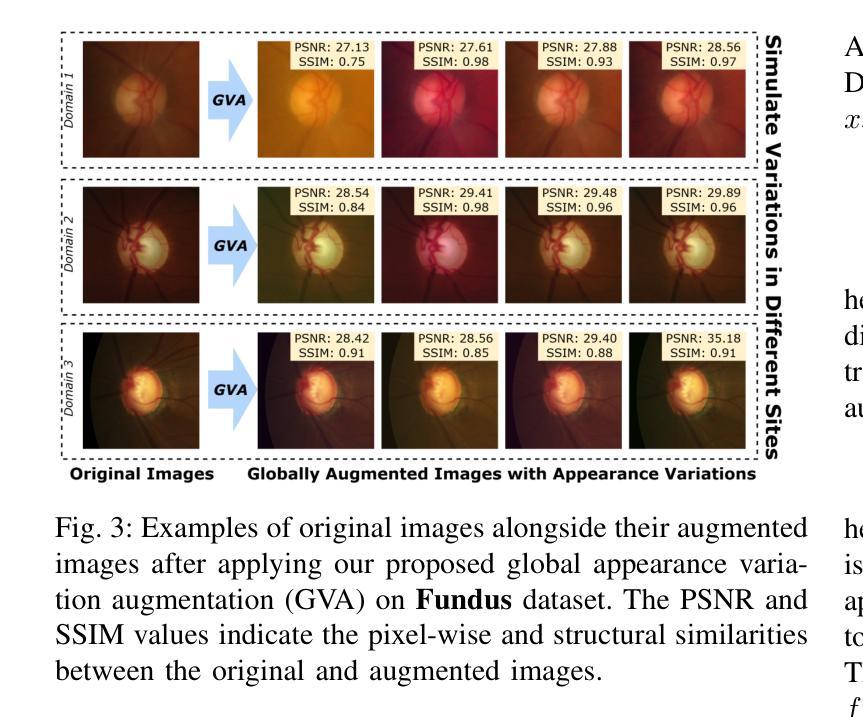
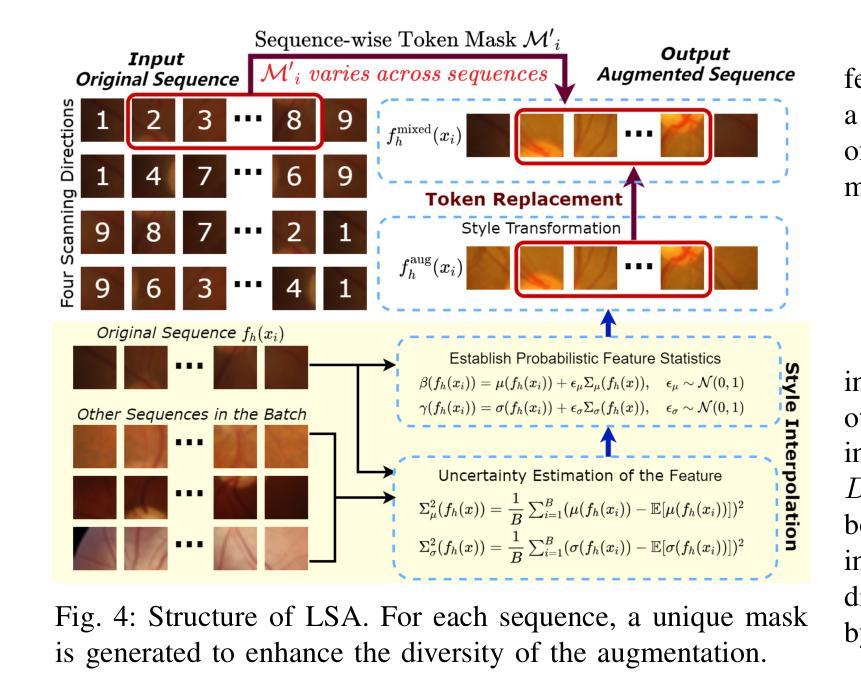
Mamba-Sea: A Mamba-based Framework with Global-to-Local Sequence Augmentation for Generalizable Medical Image Segmentation
Authors:Zihan Cheng, Jintao Guo, Jian Zhang, Lei Qi, Luping Zhou, Yinghuan Shi, Yang Gao
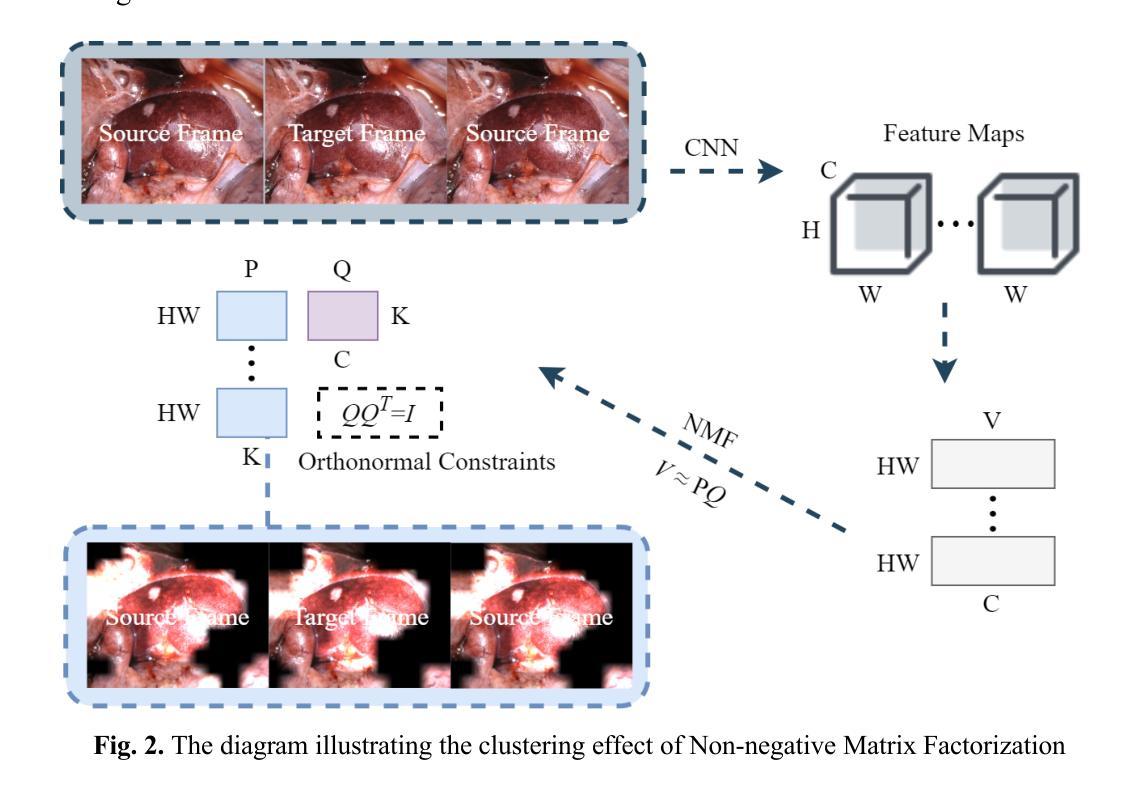
To segment medical images with distribution shifts, domain generalization (DG) has emerged as a promising setting to train models on source domains that can generalize to unseen target domains. Existing DG methods are mainly based on CNN or ViT architectures. Recently, advanced state space models, represented by Mamba, have shown promising results in various supervised medical image segmentation. The success of Mamba is primarily owing to its ability to capture long-range dependencies while keeping linear complexity with input sequence length, making it a promising alternative to CNNs and ViTs. Inspired by the success, in the paper, we explore the potential of the Mamba architecture to address distribution shifts in DG for medical image segmentation. Specifically, we propose a novel Mamba-based framework, Mamba-Sea, incorporating global-to-local sequence augmentation to improve the model’s generalizability under domain shift issues. Our Mamba-Sea introduces a global augmentation mechanism designed to simulate potential variations in appearance across different sites, aiming to suppress the model’s learning of domain-specific information. At the local level, we propose a sequence-wise augmentation along input sequences, which perturbs the style of tokens within random continuous sub-sequences by modeling and resampling style statistics associated with domain shifts. To our best knowledge, Mamba-Sea is the first work to explore the generalization of Mamba for medical image segmentation, providing an advanced and promising Mamba-based architecture with strong robustness to domain shifts. Remarkably, our proposed method is the first to surpass a Dice coefficient of 90% on the Prostate dataset, which exceeds previous SOTA of 88.61%. The code is available at https://github.com/orange-czh/Mamba-Sea.
针对医学图像分割中的分布偏移问题,领域泛化(DG)作为一种在源领域训练模型并推广至未见目标领域的方法,已显示出其巨大潜力。现有的DG方法主要基于CNN或ViT架构。最近,以Mamba为代表的高级状态空间模型在多种监督医学图像分割中取得了令人鼓舞的结果。Mamba的成功主要归功于其能够捕捉长距离依赖关系的同时保持线性计算复杂度,使其成为CNN和ViT的有前途的替代方案。受成功的启发,在本文中,我们探索了Mamba架构在解决医学图像分割的DG中的分布偏移问题的潜力。具体来说,我们提出了一种基于Mamba的新框架Mamba-Sea,它结合了全局到局部的序列增强技术,以提高模型在领域偏移问题下的泛化能力。我们的Mamba-Sea引入了一种全局增强机制,旨在模拟不同站点外观的潜在变化,旨在抑制模型对领域特定信息的学习。在局部层面,我们提出了沿输入序列的序列级增强,通过建模和重新采样与领域偏移相关的风格统计信息,扰动随机连续子序列内标记的风格。据我们所知,Mamba-Sea是首次探索医学图像分割中Mamba泛化的工作,提供了一种先进且对领域偏移具有强大稳健性的Mamba架构。值得注意的是,我们提出的方法在前列腺数据集上的Dice系数首次超过了90%,超过了之前的最佳纪录88.61%。代码可在https://github.com/orange-czh/Mamba-Sea找到。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF Accepted by IEEE TMI 2025. The code is available at https://github.com/orange-czh/Mamba-Sea
Summary
本文探索了基于Mamba架构在医学图像分割中的域泛化能力,以应对分布偏移问题。提出一种新型Mamba-Sea框架,结合全局到局部序列增强,提高模型在域偏移问题下的泛化性能。通过全局增强机制模拟不同站点外观的潜在变化,抑制模型对域特定信息的学习。在局部层面,通过建模和重采样与域偏移相关的风格统计,对输入序列进行序列增强。Mamba-Sea在前列腺数据集上的Dice系数超过90%,超越之前的最优解。
Key Takeaways
- Mamba架构因能捕捉长距离依赖并保持线性复杂度,在医学图像分割中展现出潜力。
- 现有域泛化(DG)方法主要基于CNN或ViT架构,而Mamba-Sea框架探索了Mamba架构在医学图像分割中的域泛化潜力。
- Mamba-Sea通过全局到局部序列增强提高模型泛化能力,模拟不同站点的外观变化并抑制域特定信息的学习。
- Mamba-Sea首次超过前列腺数据集上的Dice系数90%,表现超越先前最佳解决方案。
- Mamba-Sea框架是首个探索Mamba在医学图像分割中泛化的工作,提供强大且对域偏移具有鲁棒性的Mamba基础架构。
- 提出的全局和局部增强机制有助于模型适应不同的域偏移情况。
点此查看论文截图

Physiological neural representation for personalised tracer kinetic parameter estimation from dynamic PET
Authors:Kartikay Tehlan, Thomas Wendler
Dynamic positron emission tomography (PET) with [$^{18}$F]FDG enables non-invasive quantification of glucose metabolism through kinetic analysis, often modelled by the two-tissue compartment model (TCKM). However, voxel-wise kinetic parameter estimation using conventional methods is computationally intensive and limited by spatial resolution. Deep neural networks (DNNs) offer an alternative but require large training datasets and significant computational resources. To address these limitations, we propose a physiological neural representation based on implicit neural representations (INRs) for personalized kinetic parameter estimation. INRs, which learn continuous functions, allow for efficient, high-resolution parametric imaging with reduced data requirements. Our method also integrates anatomical priors from a 3D CT foundation model to enhance robustness and precision in kinetic modelling. We evaluate our approach on an [$^{18}$F]FDG dynamic PET/CT dataset and compare it to state-of-the-art DNNs. Results demonstrate superior spatial resolution, lower mean-squared error, and improved anatomical consistency, particularly in tumour and highly vascularized regions. Our findings highlight the potential of INRs for personalized, data-efficient tracer kinetic modelling, enabling applications in tumour characterization, segmentation, and prognostic assessment.
动态正电子发射断层扫描(PET)通过[$^{18}$F]FDG实现了非侵入性的葡萄糖代谢定量评估,通常通过动力学分析进行建模,动力学分析常常以两组织间隔模型(TCKM)为模型。然而,使用传统方法进行体素级的动力学参数估计在计算上很密集且受限于空间分辨率。深度神经网络(DNNs)提供了另一种选择,但它们需要大量训练数据集和重要的计算资源。为了解决这些限制,我们提出了一种基于隐神经表示法(INR)的生理神经表示法用于个性化动力学参数估计。INR学习连续函数,允许高效的高分辨率参数成像并减少数据需求。我们的方法还结合了来自三维CT基础模型的解剖学先验知识,以提高动力学建模的稳健性和精确度。我们在一组[$^{18}$F]FDG动态PET/CT数据集上评估了我们的方法并与最先进的DNNs进行了比较。结果表明,我们的方法具有卓越的空间分辨率、更低的均方误差以及更好的解剖学一致性,特别是在肿瘤和高度血管化的区域中。我们的研究结果表明了隐神经表示法在个性化、高效率的示踪剂动力学建模中的潜力,可为肿瘤特征描述、分割和预后评估等应用提供支持。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF The code is available at: https://github.com/tkartikay/PhysNRPET
Summary
医学图像动态正电子发射断层扫描(PET)可通过$^{18}$F标记的脱氧葡萄糖(FDG)进行葡萄糖代谢的非侵入性定量分析。常规方法在计算上较为密集且受空间分辨率限制。本文提出了一种基于隐神经表征的方法来解决这些问题,实现个性化参数估计和高效高分辨参数成像,且减少了数据需求,还融合了来自三维CT基础模型的解剖学先验信息以提升其在动力学建模中的稳健性和精确性。评估显示,该方法在$^{18}$F标记的脱氧葡萄糖动态PET/CT数据集上表现出更好的空间分辨率、更低的均方误差和更好的解剖学一致性,特别是在肿瘤和高度血管化区域。这为肿瘤特征化、分割和预后评估提供了潜力。
Key Takeaways
- 动态PET结合$^{18}$F标记的脱氧葡萄糖可用于非侵入性地评估葡萄糖代谢。
- 传统方法在参数估计上计算密集且受空间分辨率限制。
- 隐神经表征方法用于个性化参数估计,实现高效高分辨成像,减少数据需求。
- 结合三维CT基础模型的解剖学先验信息增强动力学建模的稳健性和准确性。
- 评估结果显示该方法在特定数据集上表现优越,特别是在肿瘤和高度血管化区域。
点此查看论文截图

Meta-Entity Driven Triplet Mining for Aligning Medical Vision-Language Models
Authors:Saban Ozturk, Melih B. Yilmaz, Muti Kara, M. Talat Yavuz, Aykut Koç, Tolga Çukur
Diagnostic imaging relies on interpreting both images and radiology reports, but the growing data volumes place significant pressure on medical experts, yielding increased errors and workflow backlogs. Medical vision-language models (med-VLMs) have emerged as a powerful framework to efficiently process multimodal imaging data, particularly in chest X-ray (CXR) evaluations, albeit their performance hinges on how well image and text representations are aligned. Existing alignment methods, predominantly based on contrastive learning, prioritize separation between disease classes over segregation of fine-grained pathology attributes like location, size or severity, leading to suboptimal representations. Here, we propose MedTrim (Meta-entity-driven Triplet mining), a novel method that enhances image-text alignment through multimodal triplet learning synergistically guided by disease class as well as adjectival and directional pathology descriptors. Unlike common alignment methods that separate broad disease classes, MedTrim leverages structured meta-entity information to preserve subtle but clinically significant intra-class variations. For this purpose, we first introduce an ontology-based entity recognition module that extracts pathology-specific meta-entities from CXR reports, as annotations on pathology attributes are rare in public datasets. For refined sample selection in triplet mining, we then introduce a novel score function that captures an aggregate measure of inter-sample similarity based on disease classes and adjectival/directional descriptors. Lastly, we introduce a multimodal triplet alignment objective for explicit within- and cross-modal alignment between samples sharing detailed pathology characteristics. Our demonstrations indicate that MedTrim improves performance in downstream retrieval and classification tasks compared to state-of-the-art alignment methods.
诊断成像依赖于对图像和放射学报告的解释,但日益增长的数据量给医学专家带来了巨大的压力,导致了误差增加和工作流程积压。医疗视觉语言模型(med-VLM)作为一个强大的框架,能够有效地处理多模态成像数据,特别是在胸部X射线(CXR)评估中表现出色。然而,其性能的好坏取决于图像和文本表示的对齐程度。现有的对齐方法主要基于对比学习,更侧重于疾病类别之间的区分,而非细微的病理属性(如位置、大小或严重程度)的分离,导致表示不佳。在这里,我们提出了MedTrim(基于元实体驱动的三元组挖掘),这是一种通过疾病类别以及形容词和方向性病理描述符协同引导的多模态三元组学习的新方法,用于增强图像文本对齐。与常见的仅根据疾病类别进行分离的对齐方法不同,MedTrim利用结构化的元实体信息来保留微妙的但临床上重要的类内变化。为此,我们首先引入了一个基于本体论的实体识别模块,从CXR报告中提取病理特定的元实体,因为公共数据集中关于病理属性的注释很少见。为了进行精细的样本选择进行三元组挖掘,然后我们引入了一个新的评分函数,该函数基于疾病类别和形容词/方向性描述符来捕获样本间相似性的综合度量。最后,我们引入了多模态三元组对齐目标,用于在具有详细病理特征的样本之间进行明确的内部和跨模态对齐。我们的演示表明,与最新的对齐方法相比,MedTrim在下游检索和分类任务中的性能有所提高。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF 18 pages, 7 figures, 6 tables
Summary
本文探讨了医疗影像诊断中面临的挑战,包括数据量大导致的专家压力增大、错误增多和工作流程积压问题。为解决这些问题,文章提出了一种名为MedTrim的新方法,通过多模态三元组学习,以疾病类别及形容词和方向性病理描述符为引导,提高图像与文本的对齐性能。MedTrim采用基于本体的实体识别模块,从胸腔X射线报告中提取病理特异性元实体,并引入新的评分函数和跨模态三元组对齐目标,以改进样本选择和细化病理特征的共享。总体而言,MedTrim提高了下游检索和分类任务的性能。
Key Takeaways
- 医学影像诊断面临数据量大带来的挑战,需要更高效的多模态数据处理方法。
- 医疗视觉语言模型(med-VLMs)在处理多模态成像数据方面表现出强大潜力。
- 现有图像与文本对齐方法主要关注疾病类别的分离,但忽略了细粒度病理属性的表征,导致表示不佳。
- MedTrim通过多模态三元组学习提高图像与文本的对齐精度,同时考虑疾病类别和形容词、方向性病理描述符。
- MedTrim采用基于本体的实体识别模块,从胸腔X射线报告中提取病理特异性元实体,以保留公共数据集中罕见的病理属性注释。
- 引入新的评分函数,基于疾病类别和形容词/方向性描述符来衡量样本间的相似度,以优化样本选择。
点此查看论文截图

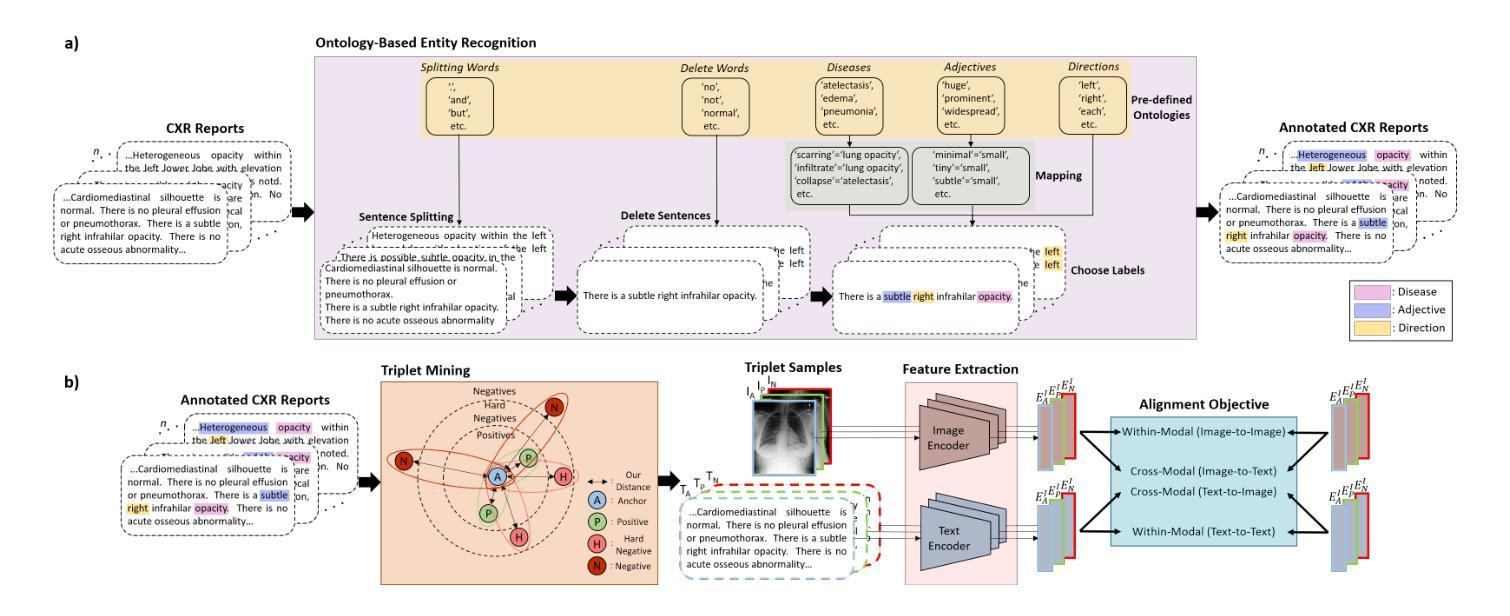
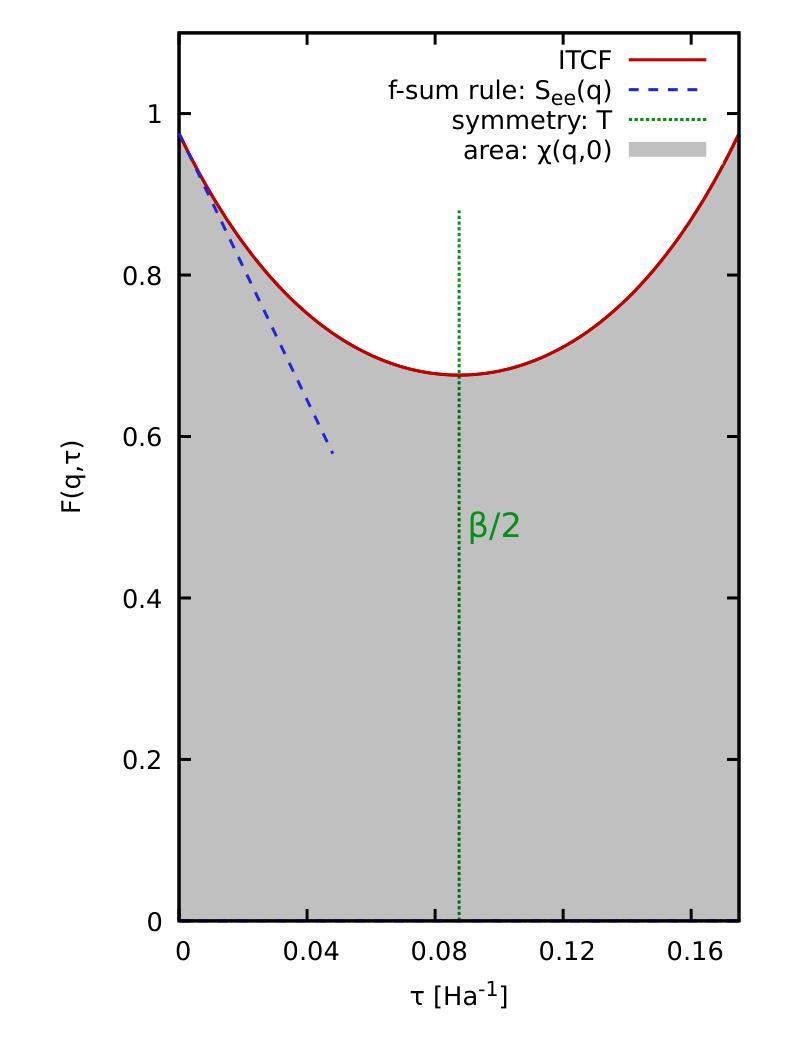
Static linear density response from X-ray Thomson scattering measurements: a case study of warm dense beryllium
Authors:Sebastian Schwalbe, Hannah Bellenbaum, Tilo Döppner, Maximilian Böhme, Thomas Gawne, Dominik Kraus, Michael J. MacDonald, Zhandos Moldabekov, Panagiotis Tolias, Jan Vorberger, Tobias Dornheim
Linear response theory is ubiquitous throughout physics and plays a central role in the theoretical description of warm dense matter – an extreme state that occurs within compact astrophysical objects and that is traversed on the compression path of a fuel capsule in inertial confinement fusion applications. Here we show how one can relate the static linear density response function to X-ray Thomson scattering (XRTS) measurements, which opens up new possibilities for the diagnostics of extreme states of matter, and for the rigorous assessment and verification of theoretical models and approximations. As a practical example, we consider an XRTS data set of warm dense beryllium taken at the National Ignition Facility [T.D"oppner \emph{et al.}, \textit{Nature} \textbf{618}, 270-275 (2023)]. The comparison with state-of-the-art \emph{ab initio} path integral Monte Carlo (PIMC) simulations [T.Dornheim \emph{et al.}, \textit{Nature Commun.}~(in print), arXiv:2402.19113] gives us a best estimate of the mass density of $\rho=18\pm6,$g/cc, which is consistent with previous PIMC and density functional theory based studies, but rules out the original estimate of $\rho=34\pm4,$g/cc based on a Chihara model fit.
线性响应理论在物理学中普遍存在,并在描述温暖致密物质的理论中起着核心作用。这是一种极端的物质状态,出现在致密的天体物理对象中,也出现在惯性约束聚变应用的燃料胶囊压缩路径上。在这里,我们展示了如何将静态线性密度响应函数与X射线汤姆森散射(XRTS)测量相关联,这为极端物质状态的诊断、理论模型和近似的严格评估和验证提供了新的可能性。作为一个实际例子,我们考虑了在国家点火设施(T. Doppner等人,《自然》杂志,第618期,第270-275页(2023年))获得的温暖致密铍的XRTS数据集。与最新最先进的从头开始路径积分蒙特卡罗(PIMC)模拟(T. Dornheim等人,《自然通讯》(印刷中),arXiv:2402.19113)的比较,为我们提供了最佳质量密度估计值为ρ=18±6 g/cc。这与之前的PIMC和基于密度泛函理论的研究相一致,但排除了基于Chihara模型拟合得到的原始估计值ρ=34±4 g/cc。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
线性响应理论在物理学中普遍存在,对于描述热密物质的理论起到了核心作用。本文通过展示静态线性密度响应函数与X射线汤姆森散射测量的关系,为极端态物质的诊断以及理论模型和近似值的严格评估和验证提供了新的可能性。以美国国家点火装置对热密态铍物质的研究为例,与最新的从头算路径积分蒙特卡罗模拟相比较,得到最佳估计物质密度为$\rho=18\pm6g/cc$,与前人研究结果一致,排除了基于奇哈拉模型拟合的原始估计$\rho=34\pm4g/cc$。
Key Takeaways
- 线性响应理论在描述热密物质的理论中扮演核心角色,特别是在物理学领域。
- 通过将静态线性密度响应函数与X射线汤姆森散射测量相结合,为极端状态物质的诊断和理论模型的评估提供了新的方法。
- 文章以美国国家点火装置对热密态铍物质的研究为例,展示了该方法的应用。
- 与最新的从头算路径积分蒙特卡罗模拟相比较,得到了物质密度的最佳估计值。
- 最佳估计物质密度为$\rho=18\pm6g/cc$,与前人研究结果一致。
- 排除基于奇哈拉模型拟合的原始估计$\rho=34\pm4g/cc$。
点此查看论文截图

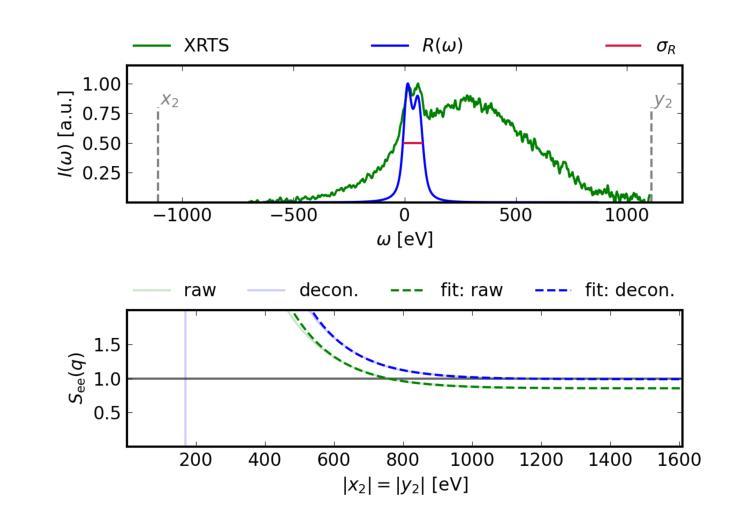
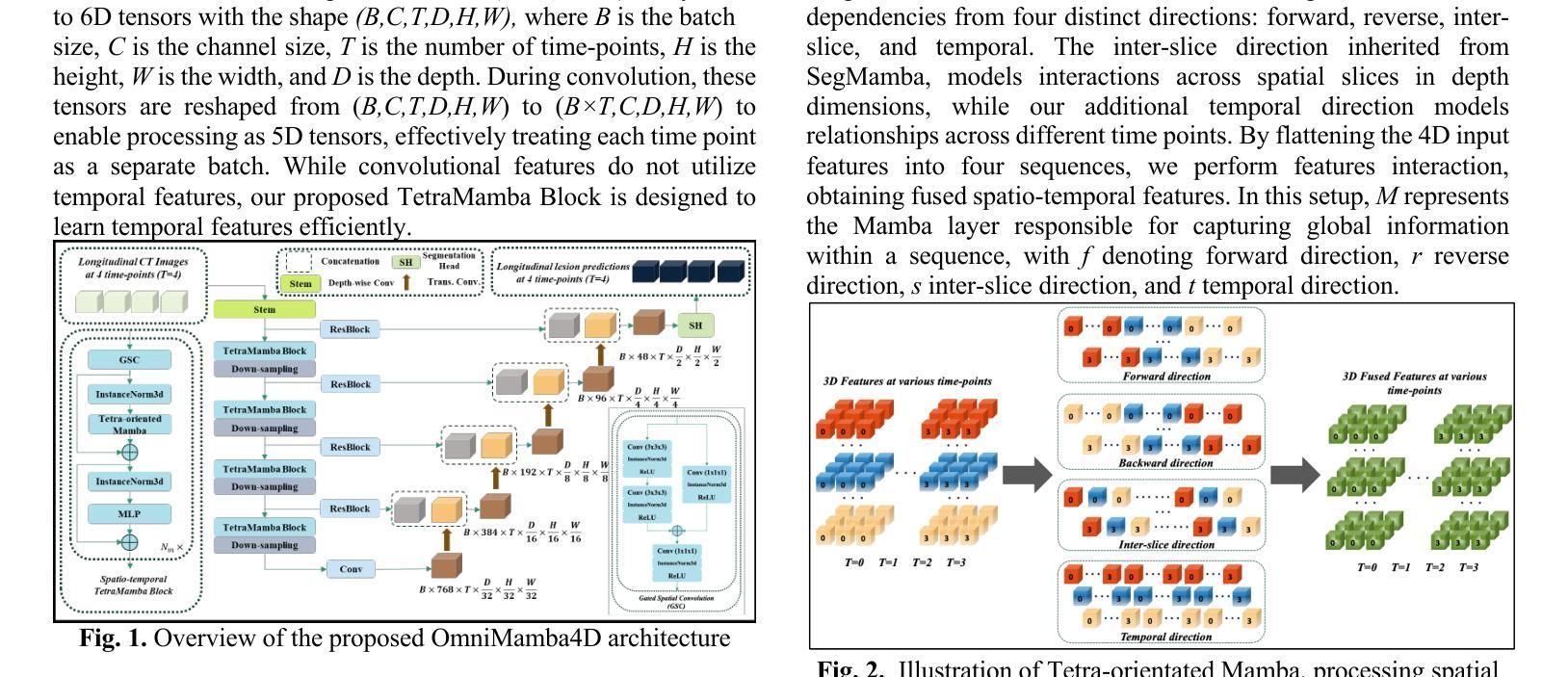
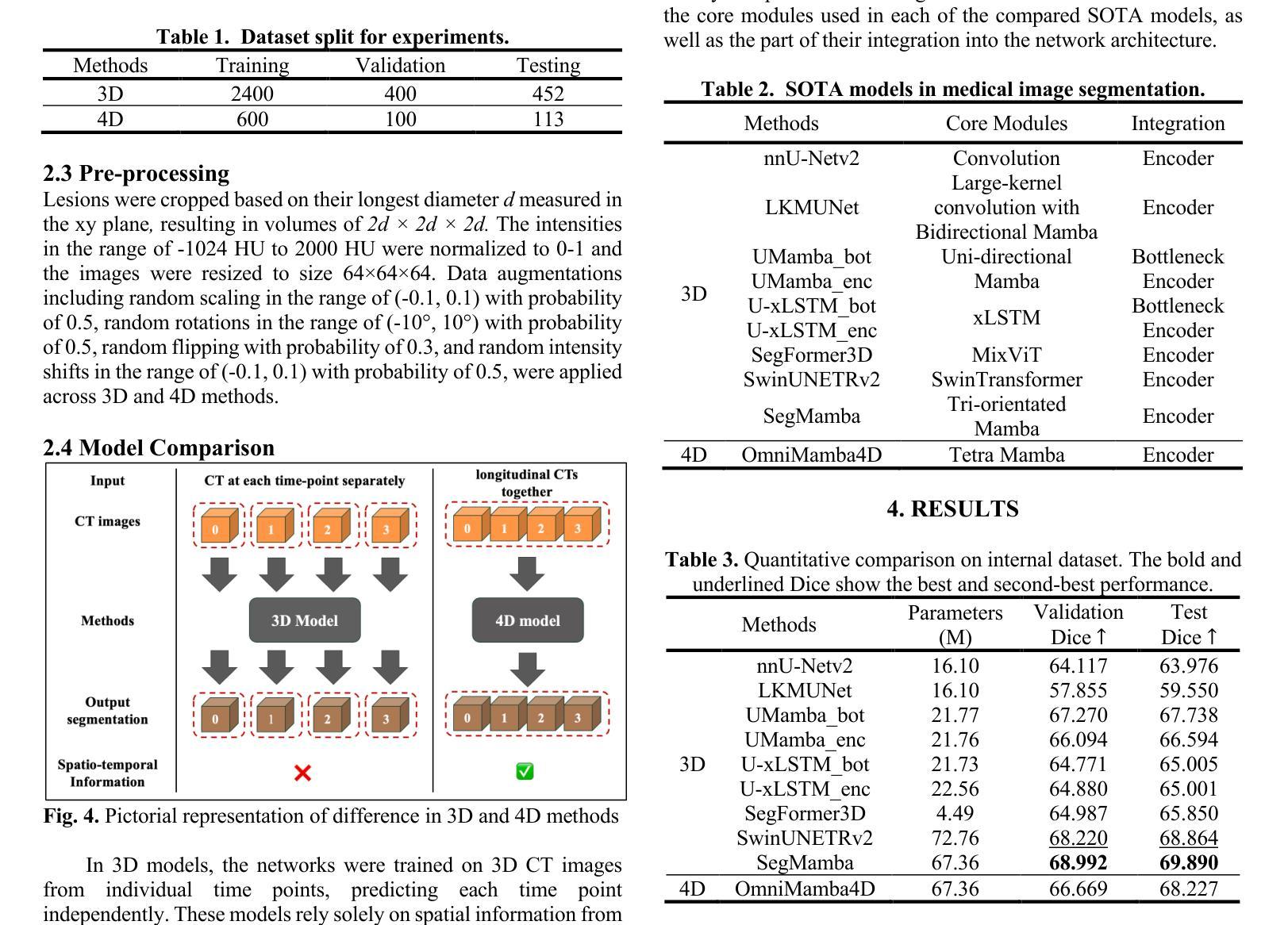
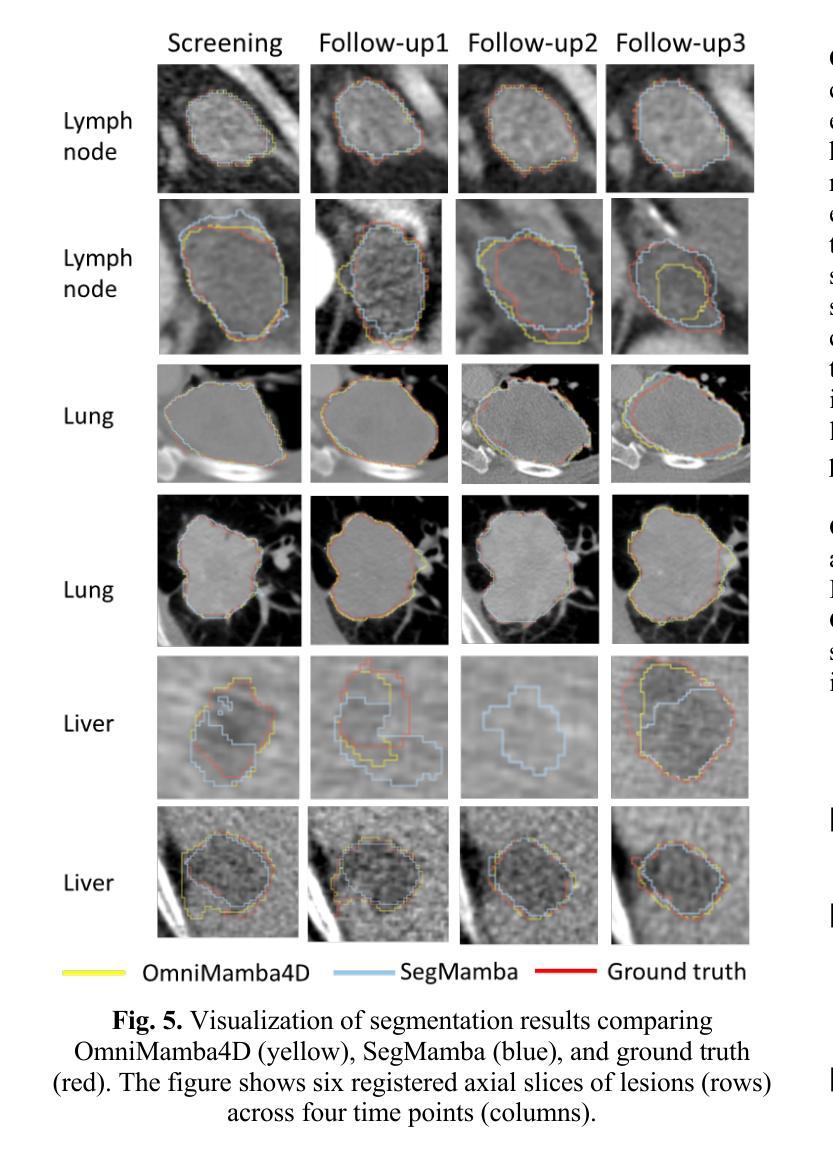
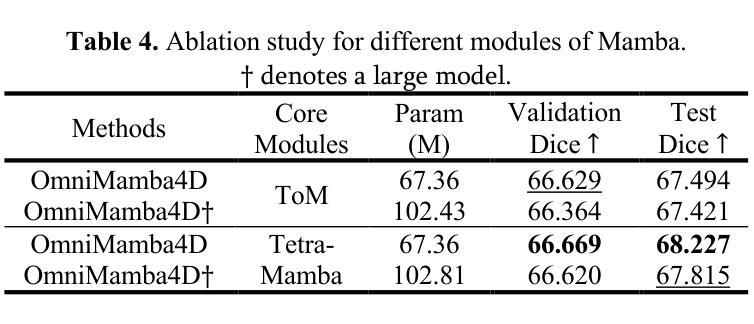
OmniMamba4D: Spatio-temporal Mamba for longitudinal CT lesion segmentation
Authors:Justin Namuk Kim, Yiqiao Liu, Rajath Soans, Keith Persson, Sarah Halek, Michal Tomaszewski, Jianda Yuan, Gregory Goldmacher, Antong Chen
Accurate segmentation of longitudinal CT scans is important for monitoring tumor progression and evaluating treatment responses. However, existing 3D segmentation models solely focus on spatial information. To address this gap, we propose OmniMamba4D, a novel segmentation model designed for 4D medical images (3D images over time). OmniMamba4D utilizes a spatio-temporal tetra-orientated Mamba block to effectively capture both spatial and temporal features. Unlike traditional 3D models, which analyze single-time points, OmniMamba4D processes 4D CT data, providing comprehensive spatio-temporal information on lesion progression. Evaluated on an internal dataset comprising of 3,252 CT scans, OmniMamba4D achieves a competitive Dice score of 0.682, comparable to state-of-the-arts (SOTA) models, while maintaining computational efficiency and better detecting disappeared lesions. This work demonstrates a new framework to leverage spatio-temporal information for longitudinal CT lesion segmentation.
对纵向CT扫描进行精确分割对于监测肿瘤进展和评估治疗效果非常重要。然而,现有的3D分割模型只关注空间信息。为了弥补这一空白,我们提出了OmniMamba4D,这是一种专为4D医学图像(随时间变化的3D图像)设计的全新分割模型。OmniMamba4D利用时空四面体定向的Mamba块,有效地捕捉空间和时间特征。与传统的仅分析单一时间点的3D模型不同,OmniMamba4D处理4D CT数据,提供关于病灶进展的全面时空信息。在包含3252次CT扫描的内部数据集上进行的评估表明,OmniMamba4D的Dice分数达到了具有竞争力的0.682,与最先进(SOTA)模型相比不相上下,同时保持了计算效率,并更好地检测到了消失的病变。这项工作展示了一个利用时空信息进行纵向CT病灶分割的新框架。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF Accepted at IEEE International Symposium on Biomedical Imaging (ISBI) 2025
Summary
医学图像准确分割对监测肿瘤进展和评估治疗效果至关重要。现有三维分割模型主要关注空间信息,为此,我们提出OmniMamba4D模型,专为四维医学图像设计,可捕捉时空特征。该模型在包含3252次CT扫描的内部数据集上取得了具有竞争力的Dice分数(0.682),可与最先进的模型相��e比较,同时保持计算效率和更好的消失病变检测能力。
Key Takeaways
- 医学图像准确分割对肿瘤进展监测和治疗反应评估至关重要。
- 现有三维分割模型主要关注空间信息,忽略了时间维度。
- OmniMamba4D模型专为四维医学图像设计,结合了时空特征。
- OmniMamba4D模型使用时空四方向Mamba块进行有效特征捕捉。
- 该模型在内部数据集上取得了竞争力的Dice分数,与最先进的模型相当。
- OmniMamba4D模型在计算效率和消失病变检测方面表现优异。
点此查看论文截图

Q-ball mechanism of electron transport properties of high-T$_c$ superconductors
Authors:S. I. Mukhin
Proposed recently by the author Q-ball mechanism of the pseudogap state and high-Tc superconductivity in cuprates (2022) was supported by micro X-ray diffraction data in HgBa$2$CuO${4+y}$ (2023). In the present paper it is demonstrated that T-linear temperature dependence of electrical resistivity arises naturally in the Q-ball gas phase, that may explain corresponding experimental data in the “strange metal” phase of high-T$_c$ cuprates, as reviewed by Barisic et al. (2013). In the present theory it arises due to scattering of electrons on the Q-balls gas of condensed charge/spin fluctuations. Close to the lowest temperature boundary of the “strange metal” phase, at which Q-ball radius diverges, electrical resistivity caused by a slide of the Q-balls as a whole is calculated using fluctuation paraconductivity calculation method by Alex Abrikosov (1987). The diamagnetic response of Q-balls gas is calculated as well and shows good accord with experimental data by L.Li et al. (2010) in the “strange metal” phase. In total, obtained results demonstrate different properties of the correlated electrons systems that arise due to formation of Q-balls possessing internal bosonic frequency $\Omega=2\pi nT$ in Matsubara time and, thus, forming the quantum thermodynamic time polycrystals. Presented theory may give a clue concerning a possible mechanism of the experimentally measured properties of high-T$_c$ cuprates in the “strange metal” phase of their phase diagram. We believe , these results provide support to the quantum thermodynamic time crystal model of the Euclidean Q-balls considered in the present paper.
作者近期提出的关于伪间隙态和高温超导性的Q球机制(2022年)得到了汞基铜酸盐(HgBa$2$CuO${4+y}$)中的微X射线衍射数据支持(2023年)。本文展示了线性温度依赖的电阻率自然产生于Q球气态相中,这可以解释高温铜酸盐的“奇异金属”相中相应的实验数据,如巴里斯等人(Barisic et al.,2013)所述。根据当前理论,这是由于电子在凝聚的电荷/自旋波动形成的Q球气体上的散射所致。在“奇异金属”相的最低温度边界附近,Q球半径发散,整个Q球的滑动引起的电阻率是通过亚历克斯·阿布里科索夫的涨落超导计算法(Alex Abrikosov,1987)计算的。同时,还计算了Q球气体的抗磁性响应,这与李文等人在“奇异金属”相中的实验结果(L.Li et al.,2010)吻合良好。总体而言,获得的结果展示了由于形成具有内部玻色频率$\Omega=2\pi nT$的马修巴时间中的Q球而产生的关联电子系统的不同特性,从而形成了量子热力学时间多晶。本文提出的理论可能为高温铜酸盐的“奇异金属”相中实验测量的性质提供可能的机制线索。我们相信,这些结果为本文中考虑的欧几里得Q球的量子热力学时间晶体模型提供了支持。
论文及项目相关链接
摘要
近期作者提出的伪间隙态的Q球机制和高温超导在铜酸盐中的表现得到了微X射线衍射数据的支持。本文展示了线性温度依赖性的电阻率自然产生于Q球气态,这解释了高温铜酸盐的“奇异金属”相中的实验数据。在该理论中,它源于电子在凝聚的电荷/自旋波动的Q球气体上的散射。在“奇异金属”相的最低温度边界附近,Q球的半径发散,电子通过整体的Q球运动造成的电阻率的计算使用阿列克斯·阿布瑞科夫斯的涨落准导计算法。此外,本文计算了Q球气体的顺磁性响应,并与实验数据表现相符。综上,获得的结果表明了因在Matsubara时间中产生内部波色频率而形成的Q球展现出不同的电子系统特性。此理论为我们提供了高温铜酸盐的“奇异金属”相在实验测量性能方面的线索。本文认为,这些结果为量子热力学时间晶体模型提供了支持。
关键见解
- Q球机制理论得到微X射线衍射数据的支持,证实存在于HgBa$2$CuO${4+y}$中。
- Q球气态自然产生T线性温度依赖性的电阻率,与高温铜酸盐的“奇异金属”相实验数据相符。
- 电子在凝聚的电荷/自旋波动的Q球气体上的散射导致电阻率产生。
- 在“奇异金属”相的最低温度边界附近,Q球的半径发散,电阻率通过整体的Q球运动计算得出。
- Q球气体的顺磁性响应与实验数据相符。
- Q球具有内部波色频率,展示了电子系统的不同特性。
点此查看论文截图

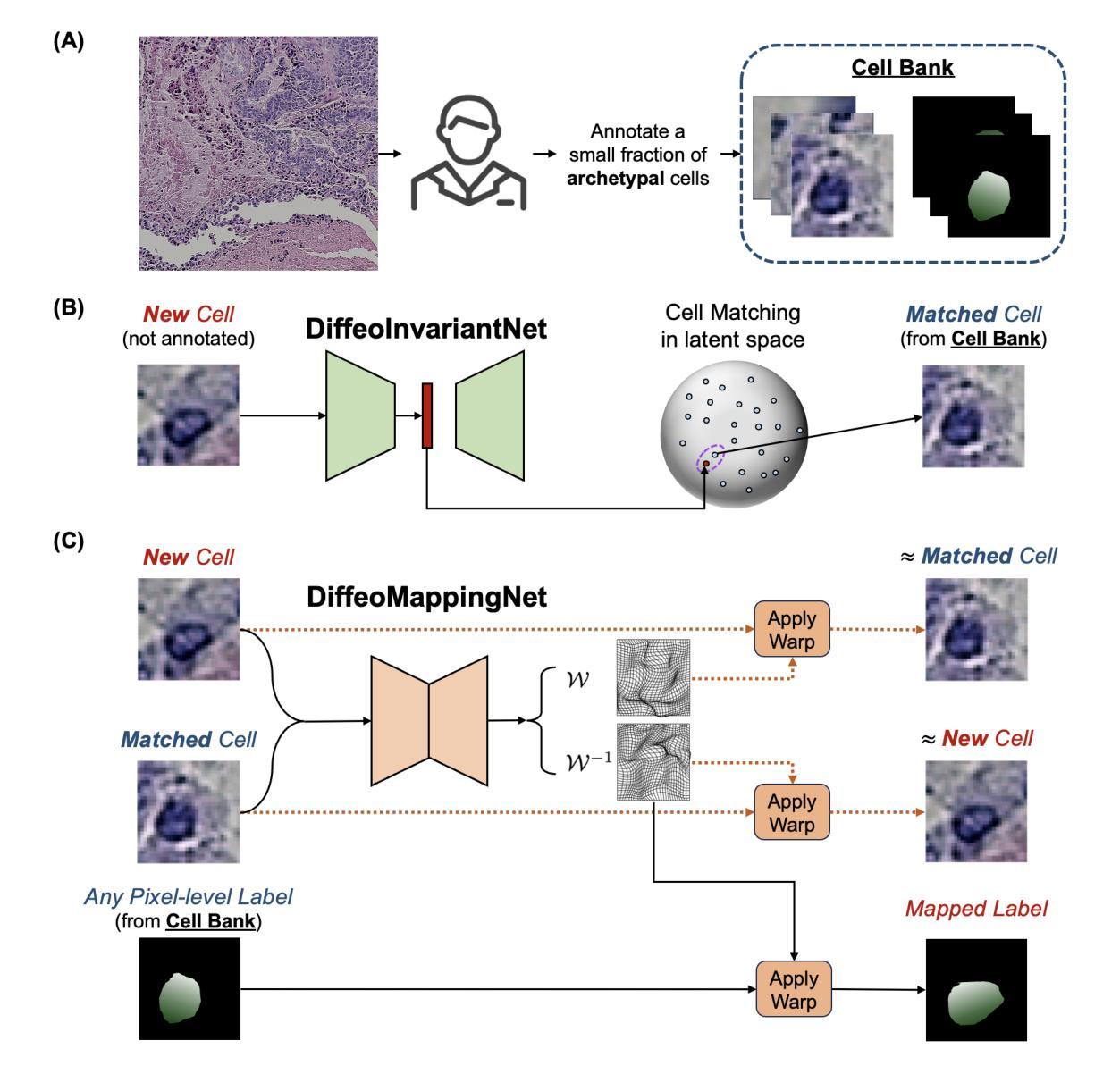
DiffKillR: Killing and Recreating Diffeomorphisms for Cell Annotation in Dense Microscopy Images
Authors:Chen Liu, Danqi Liao, Alejandro Parada-Mayorga, Alejandro Ribeiro, Marcello DiStasio, Smita Krishnaswamy
The proliferation of digital microscopy images, driven by advances in automated whole slide scanning, presents significant opportunities for biomedical research and clinical diagnostics. However, accurately annotating densely packed information in these images remains a major challenge. To address this, we introduce DiffKillR, a novel framework that reframes cell annotation as the combination of archetype matching and image registration tasks. DiffKillR employs two complementary neural networks: one that learns a diffeomorphism-invariant feature space for robust cell matching and another that computes the precise warping field between cells for annotation mapping. Using a small set of annotated archetypes, DiffKillR efficiently propagates annotations across large microscopy images, reducing the need for extensive manual labeling. More importantly, it is suitable for any type of pixel-level annotation. We will discuss the theoretical properties of DiffKillR and validate it on three microscopy tasks, demonstrating its advantages over existing supervised, semi-supervised, and unsupervised methods. The code is available at https://github.com/KrishnaswamyLab/DiffKillR.
随着自动全切片扫描技术的不断进步,数字显微镜图像的激增为生物医学研究和临床诊断提供了重要的机会。然而,在这些图像中准确标注密集的信息仍然是一个主要挑战。为了解决这一问题,我们引入了DiffKillR,这是一种新的框架,它将细胞注释重新构建为原型匹配和图像配准任务的组合。DiffKillR采用两个互补的神经网络:一个学习微分同胚不变的特征空间以实现稳健的细胞匹配,另一个计算细胞之间的精确扭曲场以实现注释映射。使用一小部分已注释的原型,DiffKillR可以有效地在大显微镜图像上传播注释,减少了大量手动标记的需求。更重要的是,它适用于任何类型的像素级注释。我们将讨论DiffKillR的理论属性,并在三个显微镜任务上对其进行验证,展示其与现有的监督、半监督和无监督方法相比的优势。代码可在https://github.com/KrishnaswamyLab/DiffKillR获得。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF ICASSP 2025, Oral Presentation
Summary
医学图像数字化进展迅速,全自动扫描技术推动大量数字显微镜图像生成,为生物医学研究和临床诊疗提供重要机遇。然而,准确标注密集图像信息是一大挑战。为解决此问题,引入DiffKillR框架,将细胞标注转化为原型匹配和图像注册任务组合。DiffKillR采用两个互补神经网络,一个学习保形不变的特性空间以实现稳健的细胞匹配,另一个计算细胞间的精确变形场以实现标注映射。仅需少量已标注原型,DiffKillR即可在大显微镜图像上有效传播标注,减少大量手动标注需求。更重要的是,它适用于任何像素级别的标注。
Key Takeaways
- 数字显微镜图像的普及对生物医学研究和临床诊疗有重要意义。
- 准确标注密集图像信息是当前的挑战。
- DiffKillR框架通过将细胞标注转化为原型匹配和图像注册任务组合来解决这一问题。
- DiffKillR使用神经网络学习保形不变的特性空间和计算精确变形场。
- DiffKillR能够利用少量标注的原型有效传播标注,降低手动标注的需求。
- DiffKillR适用于任何类型的像素级别标注。
- DiffKillR在三个显微镜任务上的表现优于现有的监督、半监督和无监督方法。
点此查看论文截图


DDU-Net: A Domain Decomposition-Based CNN for High-Resolution Image Segmentation on Multiple GPUs
Authors:Corné Verburg, Alexander Heinlein, Eric C. Cyr
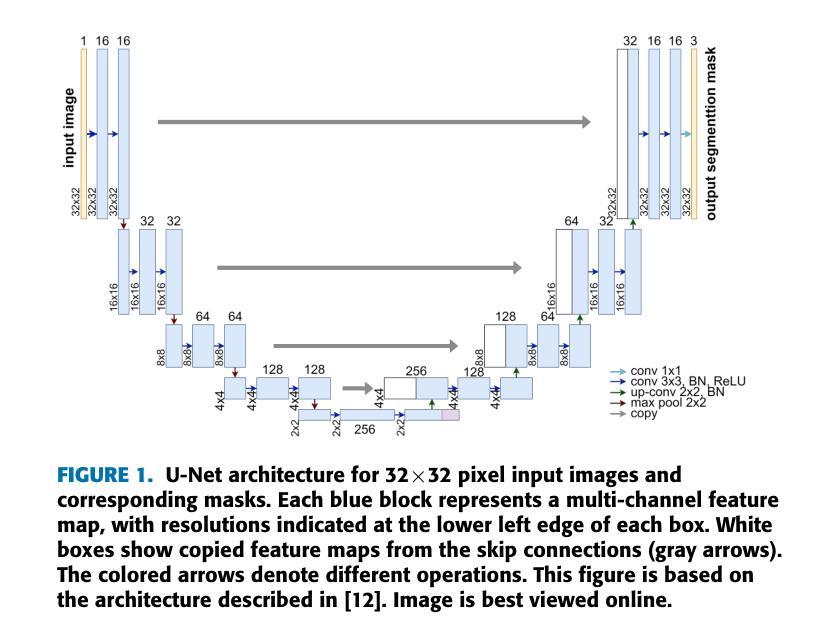
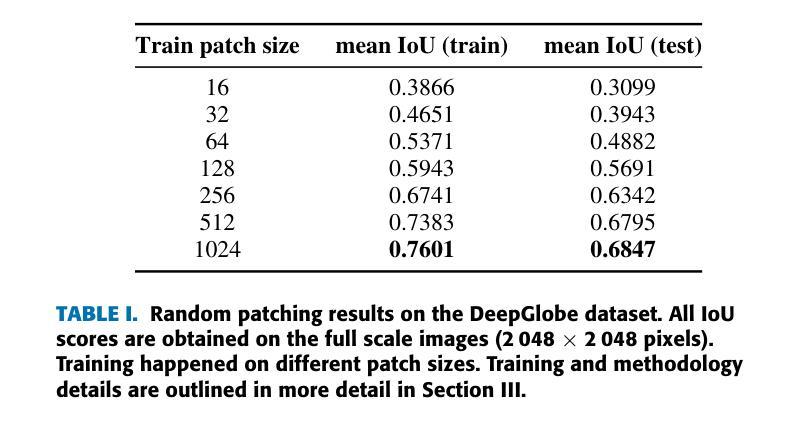
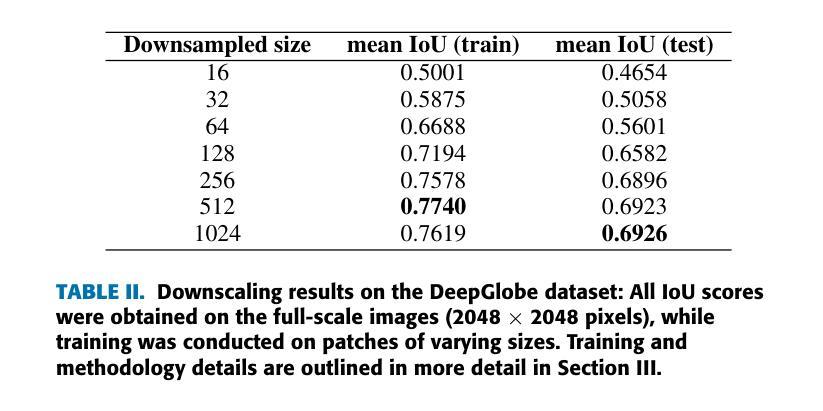
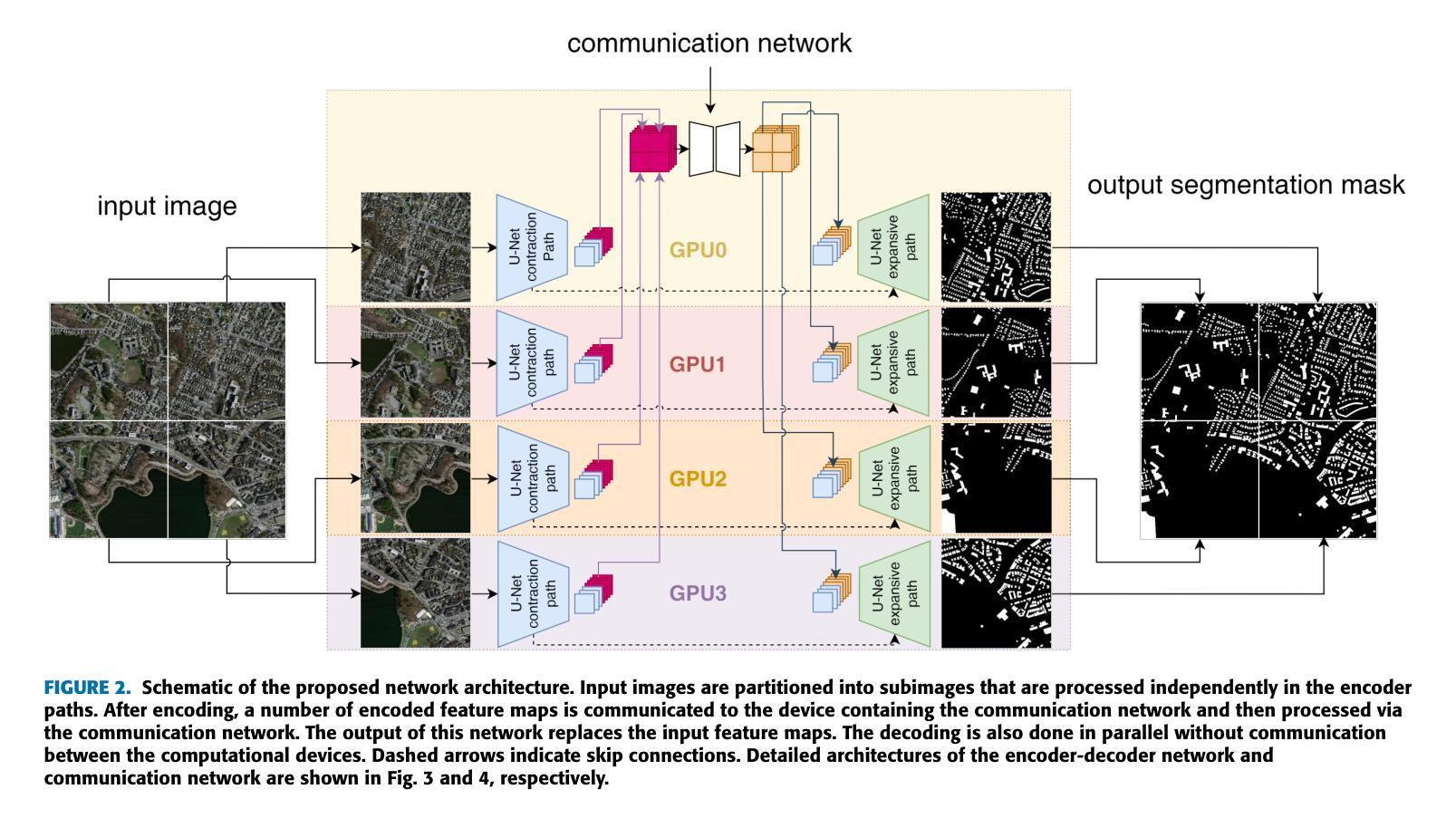
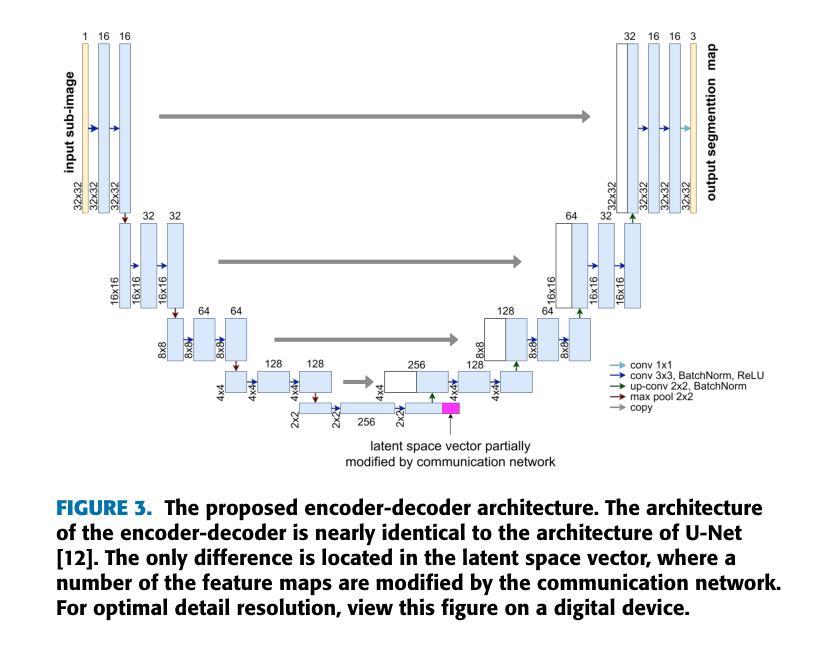
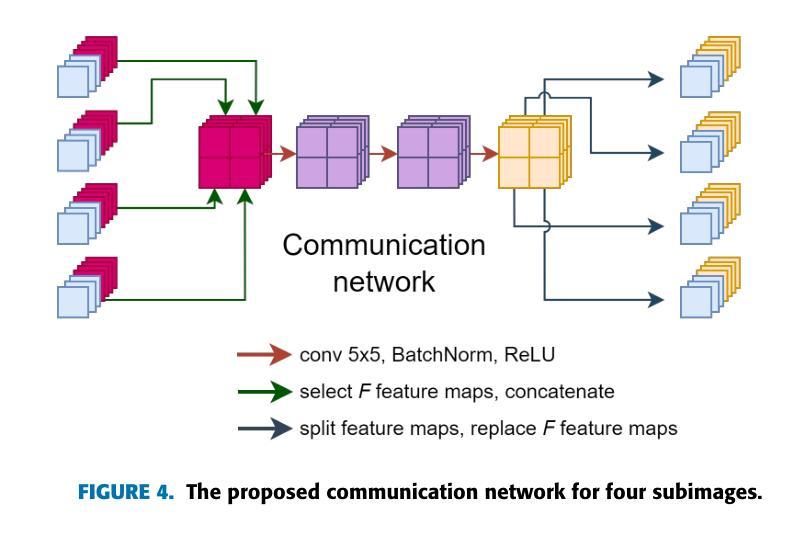
The segmentation of ultra-high resolution images poses challenges such as loss of spatial information or computational inefficiency. In this work, a novel approach that combines encoder-decoder architectures with domain decomposition strategies to address these challenges is proposed. Specifically, a domain decomposition-based U-Net (DDU-Net) architecture is introduced, which partitions input images into non-overlapping patches that can be processed independently on separate devices. A communication network is added to facilitate inter-patch information exchange to enhance the understanding of spatial context. Experimental validation is performed on a synthetic dataset that is designed to measure the effectiveness of the communication network. Then, the performance is tested on the DeepGlobe land cover classification dataset as a real-world benchmark data set. The results demonstrate that the approach, which includes inter-patch communication for images divided into $16\times16$ non-overlapping subimages, achieves a $2-3,%$ higher intersection over union (IoU) score compared to the same network without inter-patch communication. The performance of the network which includes communication is equivalent to that of a baseline U-Net trained on the full image, showing that our model provides an effective solution for segmenting ultra-high-resolution images while preserving spatial context. The code is available at https://github.com/corne00/DDU-Net.
超高分辨率图像的分割面临着损失空间信息或计算效率低下等挑战。针对这些挑战,本文提出了一种结合编码器-解码器架构和域分解策略的新方法。具体来说,引入了一种基于域分解的U-Net(DDU-Net)架构,该架构将输入图像分割成可以在不同设备上独立处理的非重叠斑块。添加通信网络以促进斑块间的信息交换,以增强对空间上下文的理解。在专为测量通信网络有效性而设计的合成数据集上进行实验验证。然后,在DeepGlobe土地覆盖分类数据集上测试性能,作为现实世界基准数据集。结果表明,该方法在处理分割为$ 16\times16$非重叠子图像的图像时,包括斑块间通信,与没有斑块间通信的相同网络相比,其交集(IoU)得分提高了$ 2-3%$。包含通信的网络性能相当于在完整图像上训练的基线U-Net的性能,这表明我们的模型为分割超高分辨率图像同时保留空间上下文提供了有效的解决方案。代码可在 https://github.com/corne00/DDU-Net 获得。
论文及项目相关链接
摘要
提出一种结合编码器-解码器架构与域分解策略的新方法,解决超高分辨率图像分割面临的挑战,如空间信息丢失或计算效率低下。引入基于域分解的U-Net(DDU-Net)架构,将输入图像分成可独立处理的无重叠块,通过通信网络进行块间信息交换,增强空间上下文理解。在合成数据集和真实世界的DeepGlobe土地覆盖分类数据集上进行实验验证,结果显示该方法在图像分割为$16\times16$非重叠子图像时加入块间通信,与没有块间通信的网络相比,提高了$2-3%$的交集(IoU)得分。包含通信的网络性能相当于在完整图像上训练的基线U-Net的性能,表明该模型在分割超高分辨率图像时提供了有效的解决方案,同时保留了空间上下文。
关键见解
- 超高分辨率图像分割面临空间信息丢失和计算效率低的问题。
- 提出结合编码器-解码器架构与域分解策略的新方法,解决这些问题。
- 引入基于域分解的U-Net(DDU-Net)架构,将图像分成无重叠块进行独立处理。
- 添加通信网络进行块间信息交换,增强空间上下文理解。
- 在合成数据集上进行实验验证,测试通信网络的的有效性。
- 在真实世界的DeepGlobe土地覆盖分类数据集上进行测试,该方法相较于无块间通信的网络提高了$2-3%$的IoU得分。
- 包含通信的网络性能与在完整图像上训练的基线U-Net相当,表明该模型在分割超高分辨率图像时有效并保留空间上下文。
点此查看论文截图
ImageFlowNet: Forecasting Multiscale Image-Level Trajectories of Disease Progression with Irregularly-Sampled Longitudinal Medical Images
Authors:Chen Liu, Ke Xu, Liangbo L. Shen, Guillaume Huguet, Zilong Wang, Alexander Tong, Danilo Bzdok, Jay Stewart, Jay C. Wang, Lucian V. Del Priore, Smita Krishnaswamy
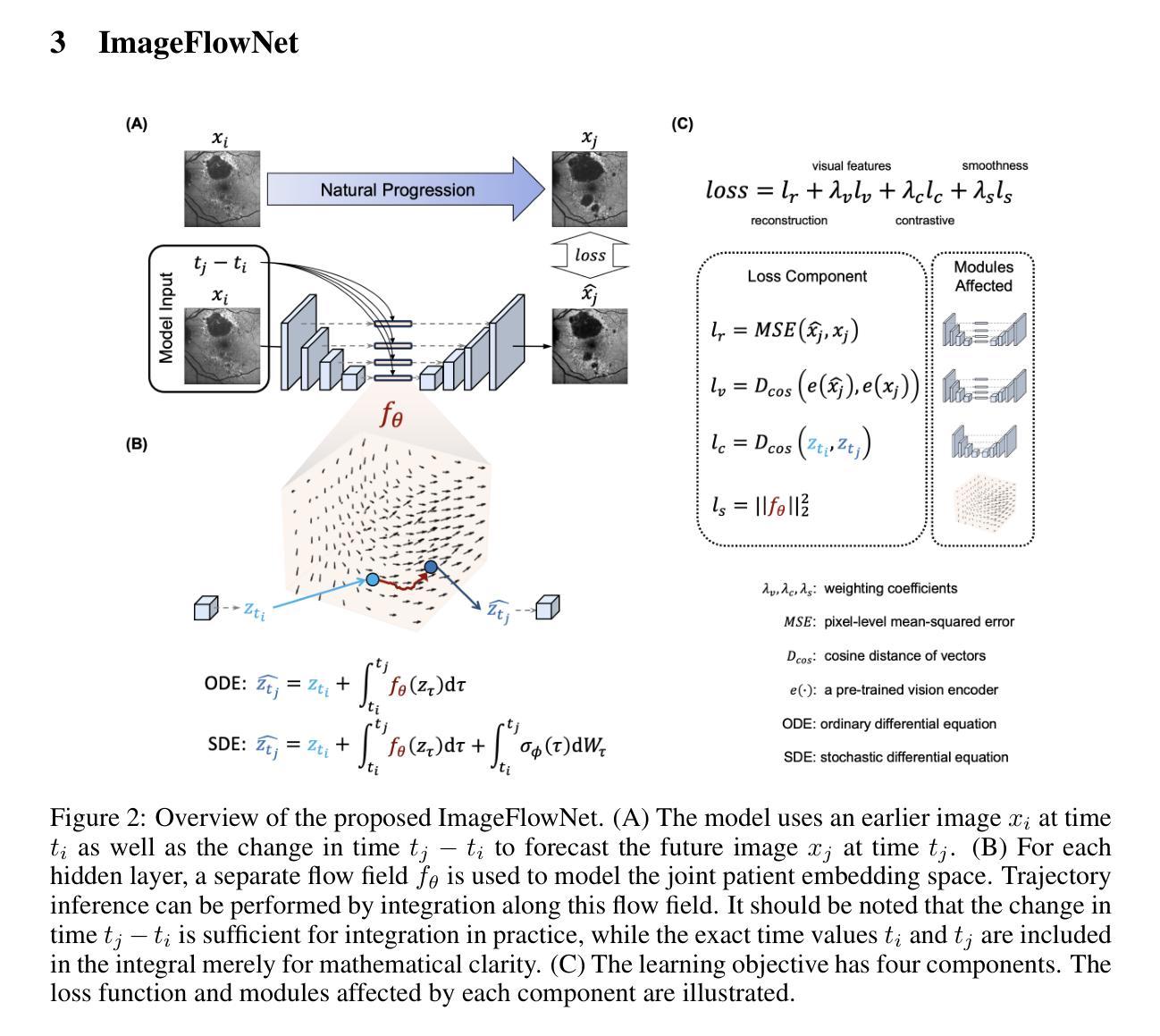
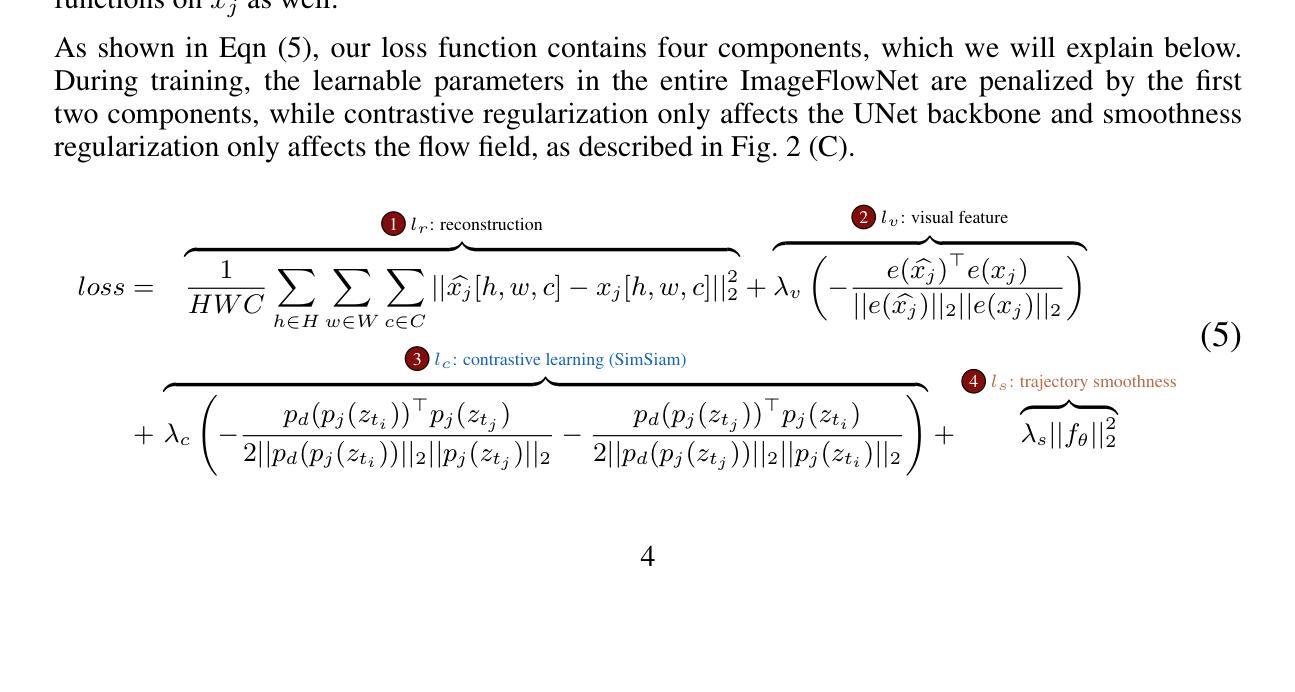
Advances in medical imaging technologies have enabled the collection of longitudinal images, which involve repeated scanning of the same patients over time, to monitor disease progression. However, predictive modeling of such data remains challenging due to high dimensionality, irregular sampling, and data sparsity. To address these issues, we propose ImageFlowNet, a novel model designed to forecast disease trajectories from initial images while preserving spatial details. ImageFlowNet first learns multiscale joint representation spaces across patients and time points, then optimizes deterministic or stochastic flow fields within these spaces using a position-parameterized neural ODE/SDE framework. The model leverages a UNet architecture to create robust multiscale representations and mitigates data scarcity by combining knowledge from all patients. We provide theoretical insights that support our formulation of ODEs, and motivate our regularizations involving high-level visual features, latent space organization, and trajectory smoothness. We validate ImageFlowNet on three longitudinal medical image datasets depicting progression in geographic atrophy, multiple sclerosis, and glioblastoma, demonstrating its ability to effectively forecast disease progression and outperform existing methods. Our contributions include the development of ImageFlowNet, its theoretical underpinnings, and empirical validation on real-world datasets. The official implementation is available at https://github.com/KrishnaswamyLab/ImageFlowNet.
医学影像技术的进步使得能够收集纵向图像,这些图像涉及随着时间的推移对同一患者的反复扫描,以监测疾病的进展。然而,由于数据的高维性、不规则采样和数据稀疏性,此类数据的预测建模仍然具有挑战性。为了解决这些问题,我们提出了ImageFlowNet这一新型模型,旨在从初始图像预测疾病轨迹的同时保留空间细节。ImageFlowNet首先学习跨患者和时间点的多尺度联合表示空间,然后利用位置参数化的神经ODE/SDE框架优化这些空间内的确定性或随机流场。该模型利用UNet架构创建稳健的多尺度表示,并通过整合所有患者的知识来缓解数据稀缺问题。我们提供了支持我们建立ODEs的理论见解,并激发了我们涉及高级视觉特征、潜在空间组织和轨迹平滑性的正则化动机。我们在三个描绘地理萎缩、多发性硬化症和胶质母细胞瘤进展的纵向医学图像数据集上验证了ImageFlowNet,证明了其有效预测疾病进展的能力,并超越了现有方法。我们的贡献包括ImageFlowNet的开发、其理论基础以及在真实数据集上的经验验证。官方实现可访问:https://github.com/KrishnaswamyLab/ImageFlowNet。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF ICASSP 2025, Oral Presentation
Summary
基于医疗成像技术的进步,长期图像收集被广泛应用于监测疾病进展。针对此类数据预测存在的挑战,如高维度、不规则采样和数据稀疏性问题,提出了ImageFlowNet模型。该模型通过初始图像预测疾病轨迹,同时保留空间细节。其采用多尺度联合表示空间学习,并利用神经ODE/SDE框架优化确定性或随机流场。通过UNet架构创建稳健的多尺度表示,并结合所有患者的知识缓解数据稀缺问题。在三个纵向医学图像数据集上验证了ImageFlowNet的有效性,展示了其预测疾病进展的能力并超越了现有方法。
Key Takeaways
- 医疗成像技术现在能够收集长期图像,用于监测疾病进展。
- ImageFlowNet模型用于从初始图像预测疾病轨迹,保留空间细节。
- ImageFlowNet通过多尺度联合表示空间学习来处理高维度数据。
- 神经ODE/SDE框架被用于优化确定性或随机流场。
- UNet架构用于创建稳健的多尺度表示。
- ImageFlowNet通过结合所有患者的知识来缓解数据稀缺问题。
点此查看论文截图

CADS: A Systematic Literature Review on the Challenges of Abstractive Dialogue Summarization
Authors:Frederic Kirstein, Jan Philip Wahle, Bela Gipp, Terry Ruas
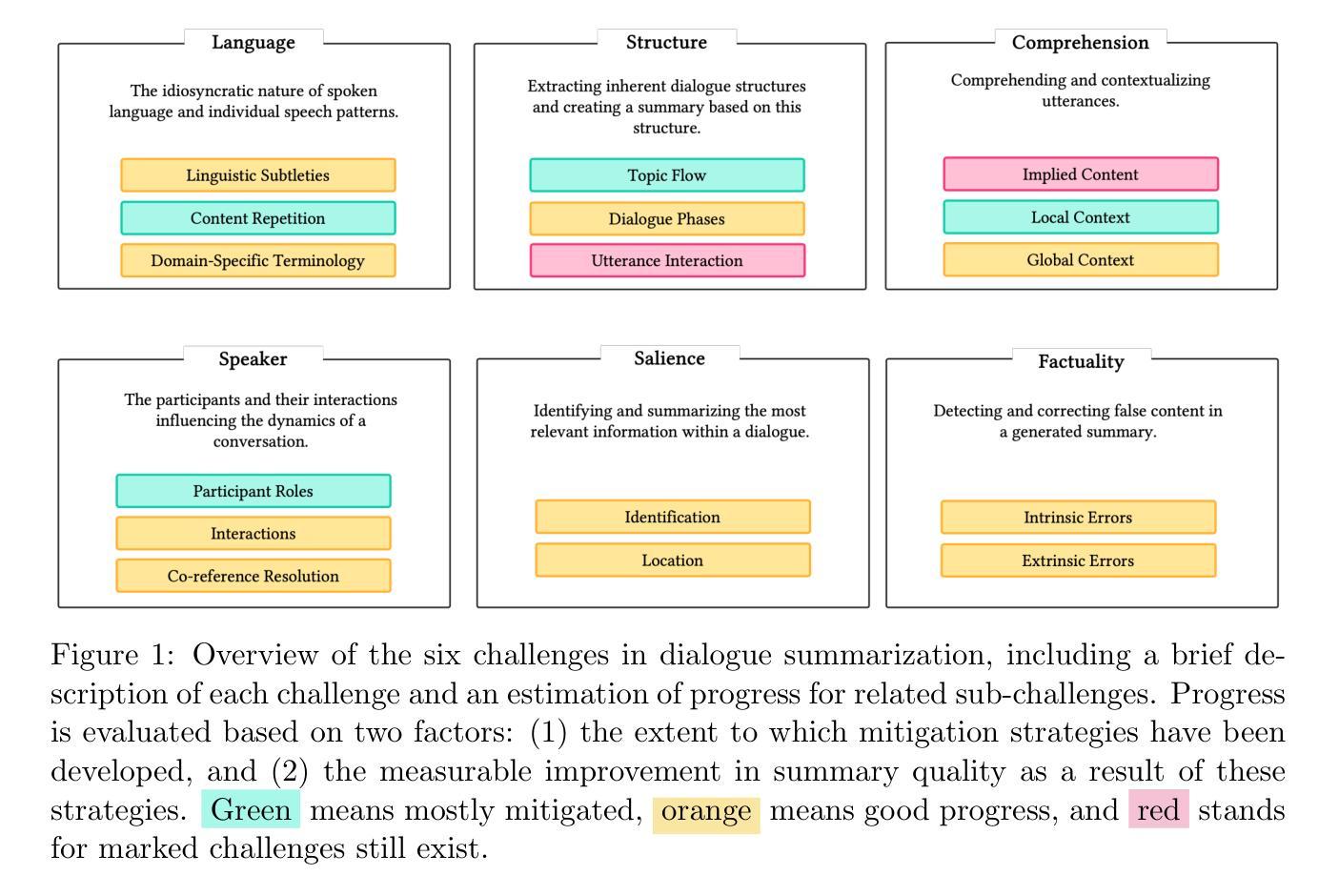
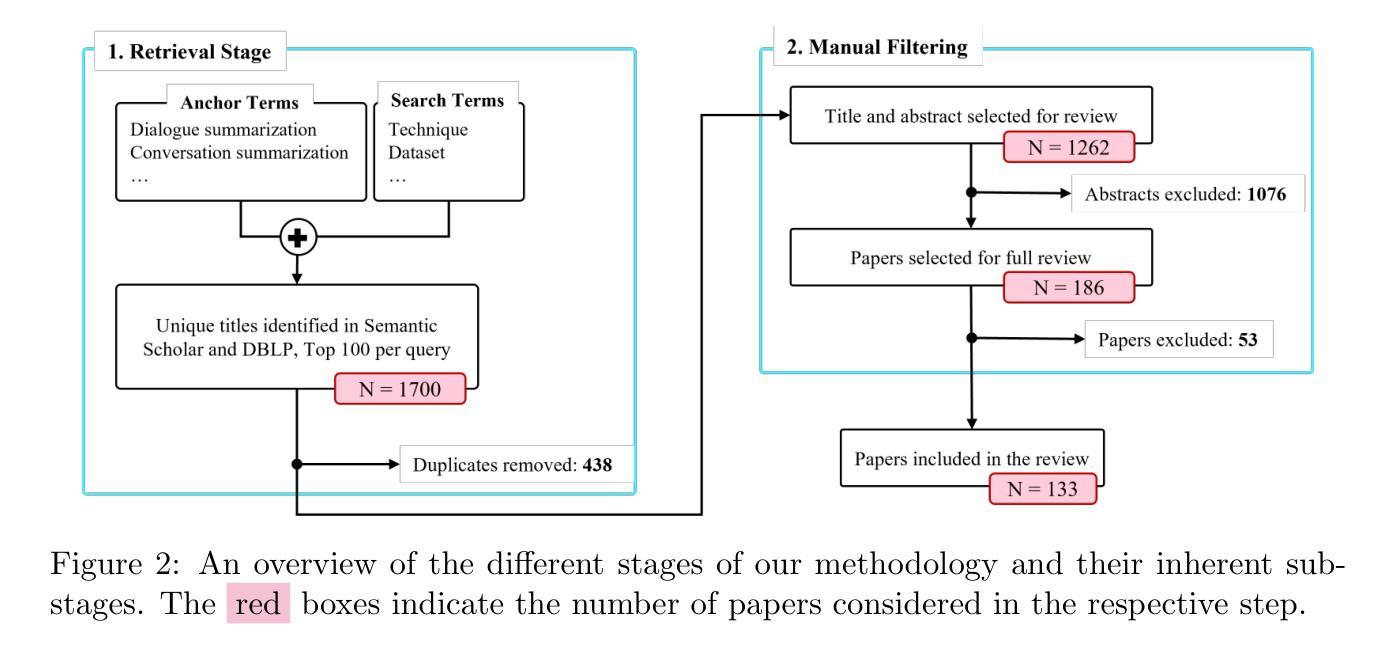
Abstractive dialogue summarization is the task of distilling conversations into informative and concise summaries. Although reviews have been conducted on this topic, there is a lack of comprehensive work detailing the challenges of dialogue summarization, unifying the differing understanding of the task, and aligning proposed techniques, datasets, and evaluation metrics with the challenges. This article summarizes the research on Transformer-based abstractive summarization for English dialogues by systematically reviewing 1262 unique research papers published between 2019 and 2024, relying on the Semantic Scholar and DBLP databases. We cover the main challenges present in dialog summarization (i.e., language, structure, comprehension, speaker, salience, and factuality) and link them to corresponding techniques such as graph-based approaches, additional training tasks, and planning strategies, which typically overly rely on BART-based encoder-decoder models. We find that while some challenges, like language, have seen considerable progress, mainly due to training methods, others, such as comprehension, factuality, and salience, remain difficult and hold significant research opportunities. We investigate how these approaches are typically assessed, covering the datasets for the subdomains of dialogue (e.g., meeting, medical), the established automatic metrics and human evaluation approaches for assessing scores and annotator agreement. We observe that only a few datasets span across all subdomains. The ROUGE metric is the most used, while human evaluation is frequently reported without sufficient detail on inner-annotator agreement and annotation guidelines. Additionally, we discuss the possible implications of the recently explored large language models and conclude that despite a potential shift in relevance and difficulty, our described challenge taxonomy remains relevant.
摘要性对话总结是将对话提炼成信息丰富且简洁的摘要的任务。尽管已经对此主题进行了评论,但仍缺乏综合性的工作来详细阐述对话总结的挑战,统一对任务的不同理解,以及使所提出的技术、数据集和评估指标与这些挑战相匹配。本文通过系统回顾2019年至2024年间发表的1262篇独特研究论文,总结了基于Transformer的英语对话摘要研究,这些论文来自Semantic Scholar和DBLP数据库。我们介绍了对话摘要中存在的主要挑战(即语言、结构、理解、说话者、突出性和事实性),并将它们与相应的技术(如基于图的方法、额外的训练任务和规划策略)联系起来,这些技术通常过于依赖基于BART的编码器-解码器模型。我们发现,虽然一些挑战(如语言)已经取得了相当大的进展,这主要是因为训练方法,但其他挑战(如理解、事实和突出性)仍然困难,并存在重要的研究机会。我们调查了这些方法的典型评估方式,涵盖了对话子领域的数据集(例如会议、医疗),以及用于评估分数和注释者一致性的既定自动指标和人工评估方法。我们发现只有少数数据集涵盖所有子域。ROUGE指标是最常用的指标,而人工评估通常没有足够详细的内部评估者一致性和注释指南。此外,我们还讨论了最近探索的大型语言模型的可能影响,并得出结论:尽管相关性和难度可能存在潜在的转变,我们描述的挑战分类仍然很重要。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF Published in the Journal of Artificial Intelligence Research (JAIR) (https://www.jair.org/index.php/jair/article/view/16674)
摘要
本文综述了基于Transformer的英语对话摘要研究,通过系统地回顾了2019年至2024年间发表的1262篇独特的研究论文,主要探讨了对话摘要面临的主要挑战,如语言、结构、理解、说话者、显著性事实和真实性等。本文链接了这些挑战与相应的技术,如基于图的方法、额外的训练任务和规划策略等,这些技术通常过度依赖于BART编码器-解码器模型。研究发现,虽然语言等挑战取得了显著进展,但理解、真实性和显著性等挑战仍然困难重重,存在大量的研究机会。此外,本文还探讨了这些方法的评估方式,涵盖了对话子域的数据集(如会议、医疗等)、现有的自动评估指标和人工评估方法,发现只有少数数据集涵盖所有子域,ROUGE指标是最常用的,而人工评估往往缺乏内部评估者一致性和评估指南的足够细节。最后,本文讨论了最近探索的大型语言模型的可能影响,并得出结论,尽管相关性和难度可能存在潜在的转变,但本文描述的挑战分类仍然具有重要意义。
关键见解
- 对话摘要的主要挑战包括语言、结构、理解、说话者、显著性事实和真实性等。
- 技术进步如基于图的方法、额外训练任务和规划策略等通常依赖于BART编码器-解码器模型。
- 语言挑战已取得显著进展,但理解、真实性和显著性等仍然面临困难。
- 对话摘要的评估涉及多个数据集、自动评估指标和人工评估方法。但数据集覆盖面有限,且缺乏内部评估者一致性和评估指南的足够细节。
- 大型语言模型的出现可能改变相关性和难度的格局,但挑战分类依然重要。
- 目前研究虽然丰富但存在不足,仍需要更多全面的研究和深入探索新的方法和应用。
点此查看论文截图

AI in Lung Health: Benchmarking Detection and Diagnostic Models Across Multiple CT Scan Datasets
Authors:Fakrul Islam Tushar, Avivah Wang, Lavsen Dahal, Michael R. Harowicz, Kyle J. Lafata, Tina D. Tailor, Joseph Y. Lo
Lung cancer remains the leading cause of cancer-related mortality worldwide, and early detection through low-dose computed tomography (LDCT) has shown significant promise in reducing death rates. With the growing integration of artificial intelligence (AI) into medical imaging, the development and evaluation of robust AI models require access to large, well-annotated datasets. In this study, we introduce the utility of Duke Lung Cancer Screening (DLCS) Dataset, the largest open-access LDCT dataset with over 2,000 scans and 3,000 expert-verified nodules. We benchmark deep learning models for both 3D nodule detection and lung cancer classification across internal and external datasets including LUNA16, LUNA25, and NLST-3D+. For detection, we develop two MONAI-based RetinaNet models (DLCSDmD and LUNA16-mD), evaluated using the Competition Performance Metric (CPM). For classification, we compare five models, including state-of-the-art pretrained models (Models Genesis, Med3D), a selfsupervised foundation model (FMCB), a randomly initialized ResNet50, and proposed a novel Strategic Warm-Start++ (SWS++) model. SWS++ uses curated candidate patches to pretrain a classification backbone within the same detection pipeline, enabling task-relevant feature learning. Our models demonstrated strong generalizability, with SWS++ achieving comparable or superior performance to existing foundational models across multiple datasets (AUC: 0.71 to 0.90). All code, models, and data are publicly released to promote reproducibility and collaboration. This work establishes a standardized benchmarking resource for lung cancer AI research, supporting future efforts in model development, validation, and clinical translation.
肺癌仍然是全球癌症相关死亡的主要原因,通过低剂量计算机断层扫描(LDCT)进行早期检测在降低死亡率方面显示出巨大潜力。随着人工智能(AI)在医学成像中的日益融合,开发和评估稳健的AI模型需要访问大量、经过良好注释的数据集。在本研究中,我们介绍了Duke肺癌筛查(DLCS)数据集的实用性,这是最大的开放访问LDCT数据集,包含超过2000次扫描和3000个专家验证的结节。我们对内部和外部数据集(包括LUNA16、LUNA25和NLST-3D+)的深度学习模型进行了基准测试,以评估其对3D结节检测和肺癌分类的效果。对于检测,我们开发了两个基于MONAI的RetinaNet模型(DLCSDmD和LUNA16-mD),使用竞赛性能指标(CPM)进行评估。对于分类,我们比较了五种模型,包括最先进的预训练模型(Models Genesis、Med3D)、一个自监督基础模型(FMCB)、一个随机初始化的ResNet50,并提出了一种新的战略温启动(SWS++)模型。SWS++使用精选的候选补丁在相同的检测管道中预训练分类主干,从而实现任务相关特征学习。我们的模型表现出很强的通用性,其中SWS++在多个数据集上的性能与现有基础模型相当或更优(AUC:0.71至0.90)。为了促进可重复性和协作,我们公开发布了所有代码、模型和数据。这项工作为肺癌AI研究建立了标准化的基准资源,支持未来的模型开发、验证和临床翻译工作。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF 2 tables, 6 figures
摘要
肺癌仍是全球癌症死亡的主要原因,低剂量计算机断层扫描(LDCT)的早期检测在降低死亡率方面显示出巨大潜力。随着人工智能(AI)在医学成像中的日益融合,开发和评估稳健的AI模型需要访问大量、经过良好注释的数据集。本研究介绍了Duke Lung Cancer Screening(DLCS)数据集的实用性,这是最大的公开访问LDCT数据集,包含超过2000次扫描和3000个专家验证的结节。我们对内部和外部数据集(包括LUNA16、LUNA25和NLST-3D+)进行了深度学习模型的基准测试,用于3D结节检测和肺癌分类。对于检测,我们开发了两个基于MONAI的RetinaNet模型(DLCSDmD和LUNA16-mD),使用竞赛性能指标(CPM)进行评估。对于分类,我们比较了五种模型,包括最新预训练模型(Models Genesis、Med3D)、自监督基础模型(FMCB)、随机初始化的ResNet50,以及提出的新型战略温启(SWS++)模型。SWS++使用精选的候选补丁在同一检测管道中预训练分类主干,实现任务相关特征学习。我们的模型表现出强大的泛化能力,SWS++在多个数据集上的性能与现有基础模型相当或更优(AUC:0.71至0.90)。所有代码、模型和数据均公开发布,以促进可重复性和协作。这项工作为肺癌AI研究建立了标准化的基准测试资源,支持未来的模型开发、验证和临床转化。
Key Takeaways
- 肺癌仍是全球主要的癌症死亡原因,LDCT在早期检测中扮演重要角色。
- AI在医学成像中的集成对肺癌诊断有积极影响。
- 介绍了DLCS数据集,这是最大的公开访问LDCT数据集,包含经过专家验证的结节。
- 基准测试了深度学习模型进行3D结节检测和肺癌分类。
- 开发并评估了基于MONAI的RetinaNet模型和其他深度学习模型。
- SWS++模型表现出强大的泛化能力,在多个数据集上性能优越。
点此查看论文截图