⚠️ 以下所有内容总结都来自于 大语言模型的能力,如有错误,仅供参考,谨慎使用
🔴 请注意:千万不要用于严肃的学术场景,只能用于论文阅读前的初筛!
💗 如果您觉得我们的项目对您有帮助 ChatPaperFree ,还请您给我们一些鼓励!⭐️ HuggingFace免费体验
2025-04-26 更新
Unsupervised Urban Land Use Mapping with Street View Contrastive Clustering and a Geographical Prior
Authors:Lin Che, Yizi Chen, Tanhua Jin, Martin Raubal, Konrad Schindler, Peter Kiefer
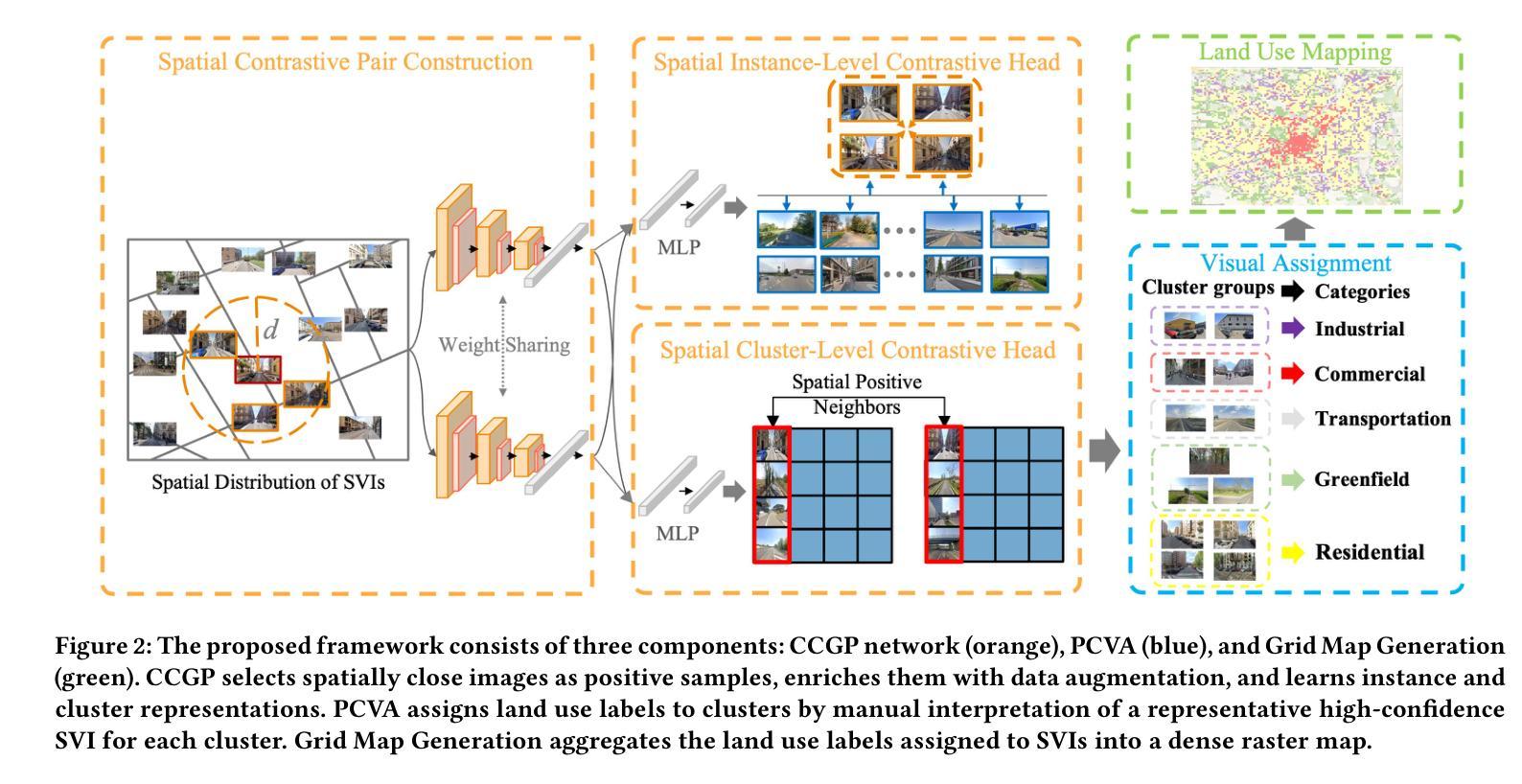
Urban land use classification and mapping are critical for urban planning, resource management, and environmental monitoring. Existing remote sensing techniques often lack precision in complex urban environments due to the absence of ground-level details. Unlike aerial perspectives, street view images provide a ground-level view that captures more human and social activities relevant to land use in complex urban scenes. Existing street view-based methods primarily rely on supervised classification, which is challenged by the scarcity of high-quality labeled data and the difficulty of generalizing across diverse urban landscapes. This study introduces an unsupervised contrastive clustering model for street view images with a built-in geographical prior, to enhance clustering performance. When combined with a simple visual assignment of the clusters, our approach offers a flexible and customizable solution to land use mapping, tailored to the specific needs of urban planners. We experimentally show that our method can generate land use maps from geotagged street view image datasets of two cities. As our methodology relies on the universal spatial coherence of geospatial data (“Tobler’s law”), it can be adapted to various settings where street view images are available, to enable scalable, unsupervised land use mapping and updating. The code will be available at https://github.com/lin102/CCGP.
城市土地利用分类和制图对于城市规划、资源管理和环境监测至关重要。现有的遥感技术在复杂城市环境中往往因缺乏地面细节而精度不足。与航空视角不同,街景图像提供了地面视角,能够捕捉与土地利用相关的更多人类和社会活动,在复杂的城市场景中尤为重要。现有的基于街景的方法主要依赖于有监督分类,这面临着高质量标签数据稀缺和难以在多样化的城市景观中推广的挑战。本研究引入了一种无监督对比聚类模型,该模型具有内置的地理先验知识,旨在提高街景图像的聚类性能。结合简单的集群视觉分配,我们的方法为土地利用制图提供了一种灵活且可定制的解决方案,可根据城市规划者的具体需求进行定制。实验表明,我们的方法能够生成两个城市的带地理标签的街景图像数据集的土地利用图。由于我们的方法依赖于地理空间数据的通用空间连贯性(托布勒定律),因此可以适应各种有街景图像的数据环境,从而实现可扩展的无监督土地利用制图和更新。代码将发布在https://github.com/lin102/CCGP。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF 11 pages, 7 figures, preprint version
Summary
本文提出一种基于无监督对比聚类模型的街道视图图像方法,结合地理先验信息,提高聚类性能,为城市规划提供灵活可定制的土地利用映射解决方案。该方法可从两个城市的地理标记街道视图图像数据集中生成土地利用地图,并适应各种场景中的街道视图图像数据,实现可扩展的无监督土地利用映射和更新。
Key Takeaways
- 街道视图图像在土地利用分类和映射中具有重要性,能提供与复杂城市环境相关的更多人类和社会活动信息。
- 现有街道视图方法主要依赖有监督分类,存在缺乏高质量标记数据和难以泛化到不同城市景观的挑战。
- 本文提出一种无监督对比聚类模型,结合地理先验信息,提高街道视图图像的聚类性能。
- 该方法通过简单的视觉集群分配,为城市规划提供灵活可定制的土地利用映射解决方案。
- 实验表明,该方法可从两个城市的地理标记街道视图图像数据集中生成土地利用地图。
- 该方法依赖于地理空间数据的通用空间一致性(Tobler定律),可适应各种街道视图图像数据场景。
点此查看论文截图

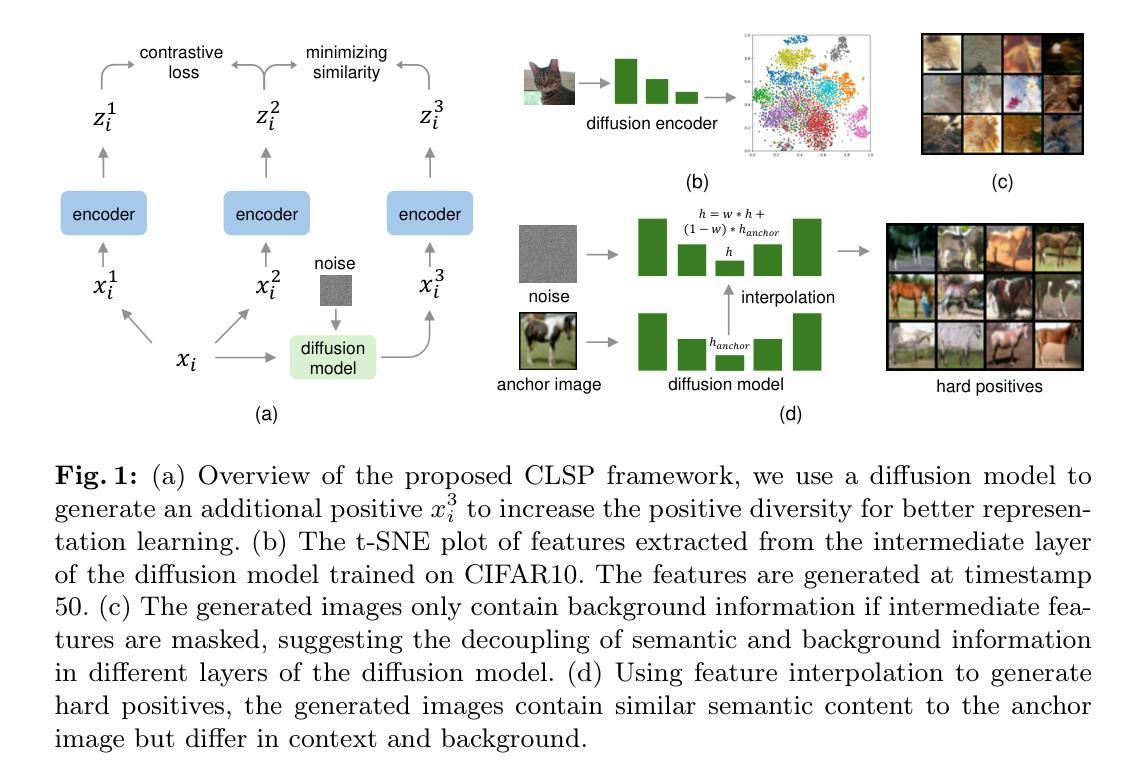
Contrastive Learning with Synthetic Positives
Authors:Dewen Zeng, Yawen Wu, Xinrong Hu, Xiaowei Xu, Yiyu Shi
Contrastive learning with the nearest neighbor has proved to be one of the most efficient self-supervised learning (SSL) techniques by utilizing the similarity of multiple instances within the same class. However, its efficacy is constrained as the nearest neighbor algorithm primarily identifies “easy” positive pairs, where the representations are already closely located in the embedding space. In this paper, we introduce a novel approach called Contrastive Learning with Synthetic Positives (CLSP) that utilizes synthetic images, generated by an unconditional diffusion model, as the additional positives to help the model learn from diverse positives. Through feature interpolation in the diffusion model sampling process, we generate images with distinct backgrounds yet similar semantic content to the anchor image. These images are considered “hard” positives for the anchor image, and when included as supplementary positives in the contrastive loss, they contribute to a performance improvement of over 2% and 1% in linear evaluation compared to the previous NNCLR and All4One methods across multiple benchmark datasets such as CIFAR10, achieving state-of-the-art methods. On transfer learning benchmarks, CLSP outperforms existing SSL frameworks on 6 out of 8 downstream datasets. We believe CLSP establishes a valuable baseline for future SSL studies incorporating synthetic data in the training process.
利用最近邻对比学习已被证明是最有效的自监督学习(SSL)技术之一,它通过利用同一类别内多个实例之间的相似性来实现。然而,其有效性受到限制,因为最近邻算法主要识别的是“容易”的正对,这些正对的表示在嵌入空间中已经位置相近。在本文中,我们介绍了一种新的方法,称为“合成阳性对比学习(CLSP)”,它利用由无条件扩散模型生成的合成图像作为额外的正样本来帮助模型从多样化的正样本中学习。通过扩散模型采样过程中的特征插值,我们生成了具有不同背景但语义内容与锚图像相似的图像。这些图像被认为是锚图像的“硬”正样本,当作为对比损失中的附加正样本时,与之前的NNCLR和All4One方法相比,它们在线性评估中的性能提高了超过2%和1%,在多个基准数据集(如CIFAR10)上达到了最先进的方法。在迁移学习基准测试中,CLSP在8个下游数据集中的6个上超越了现有的SSL框架。我们相信CLSP为未来的SSL研究在训练过程中融入合成数据建立了有价值的基线。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF 8 pages, conference
Summary
该论文介绍了名为CLSP的新型对比学习技术,该技术利用无条件扩散模型生成合成图像作为额外的正样本,以帮助模型从多样化的正样本中学习。通过扩散模型采样过程中的特征插值,生成具有不同背景但语义内容相似的图像作为锚图像“硬”正样本。在多个基准数据集上,与之前的NNCLR和All4One方法相比,CLSP在线性评估中的性能提高了超过2%和1%。在迁移学习基准测试中,CLSP在6个下游数据集中表现出超越现有SSL框架的性能。
Key Takeaways
- CLSP利用合成图像作为额外的正样本,提高模型的自我监督学习能力。
- 通过扩散模型的特征插值生成具有不同背景但语义相似的图像。
- 这些生成的图像被视为锚图像的“硬”正样本,有助于模型学习更广泛的特征表示。
- CLSP在多个基准数据集上的线性评估性能有所改进,超越了NNCLR和All4One方法。
- 在迁移学习测试中,CLSP在多个下游数据集上的性能优于现有的SSL框架。
- CLSP为未来的SSL研究提供了一个有价值的基线,即将合成数据纳入训练过程。
- 该方法对于改善当前自我监督学习技术的效率与效果具有积极意义。
点此查看论文截图