⚠️ 以下所有内容总结都来自于 大语言模型的能力,如有错误,仅供参考,谨慎使用
🔴 请注意:千万不要用于严肃的学术场景,只能用于论文阅读前的初筛!
💗 如果您觉得我们的项目对您有帮助 ChatPaperFree ,还请您给我们一些鼓励!⭐️ HuggingFace免费体验
2025-04-26 更新
FRAG: Frame Selection Augmented Generation for Long Video and Long Document Understanding
Authors:De-An Huang, Subhashree Radhakrishnan, Zhiding Yu, Jan Kautz
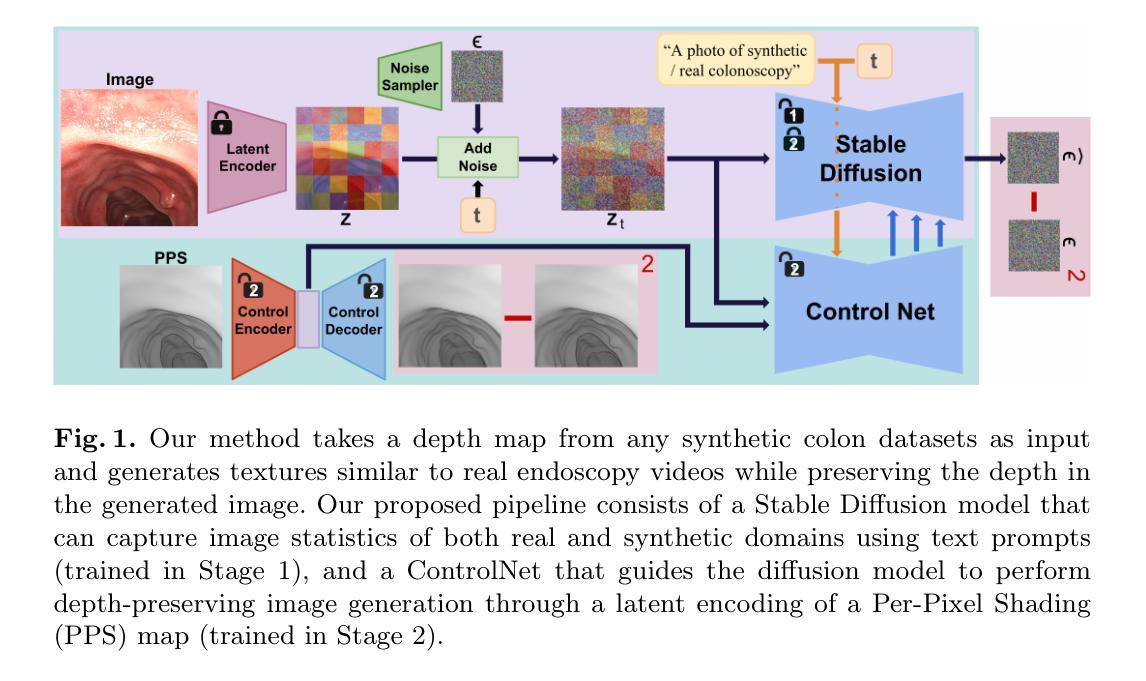
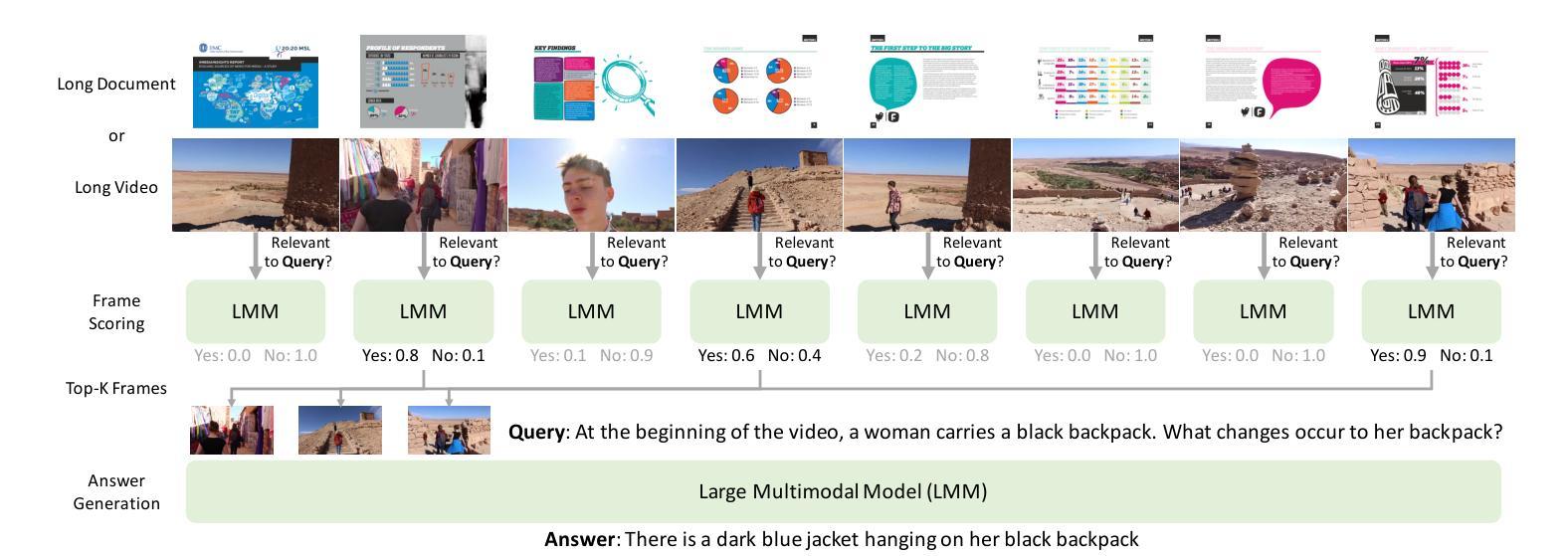
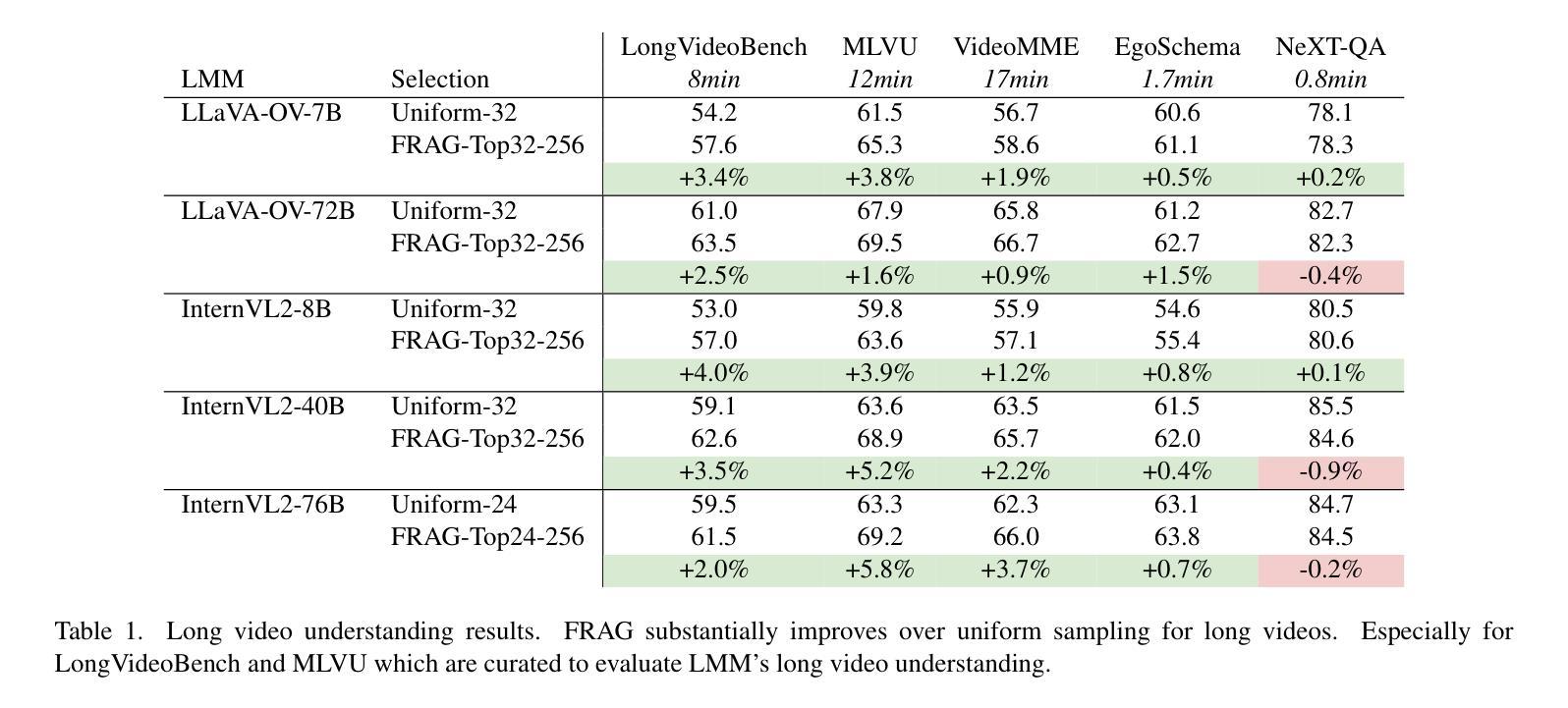
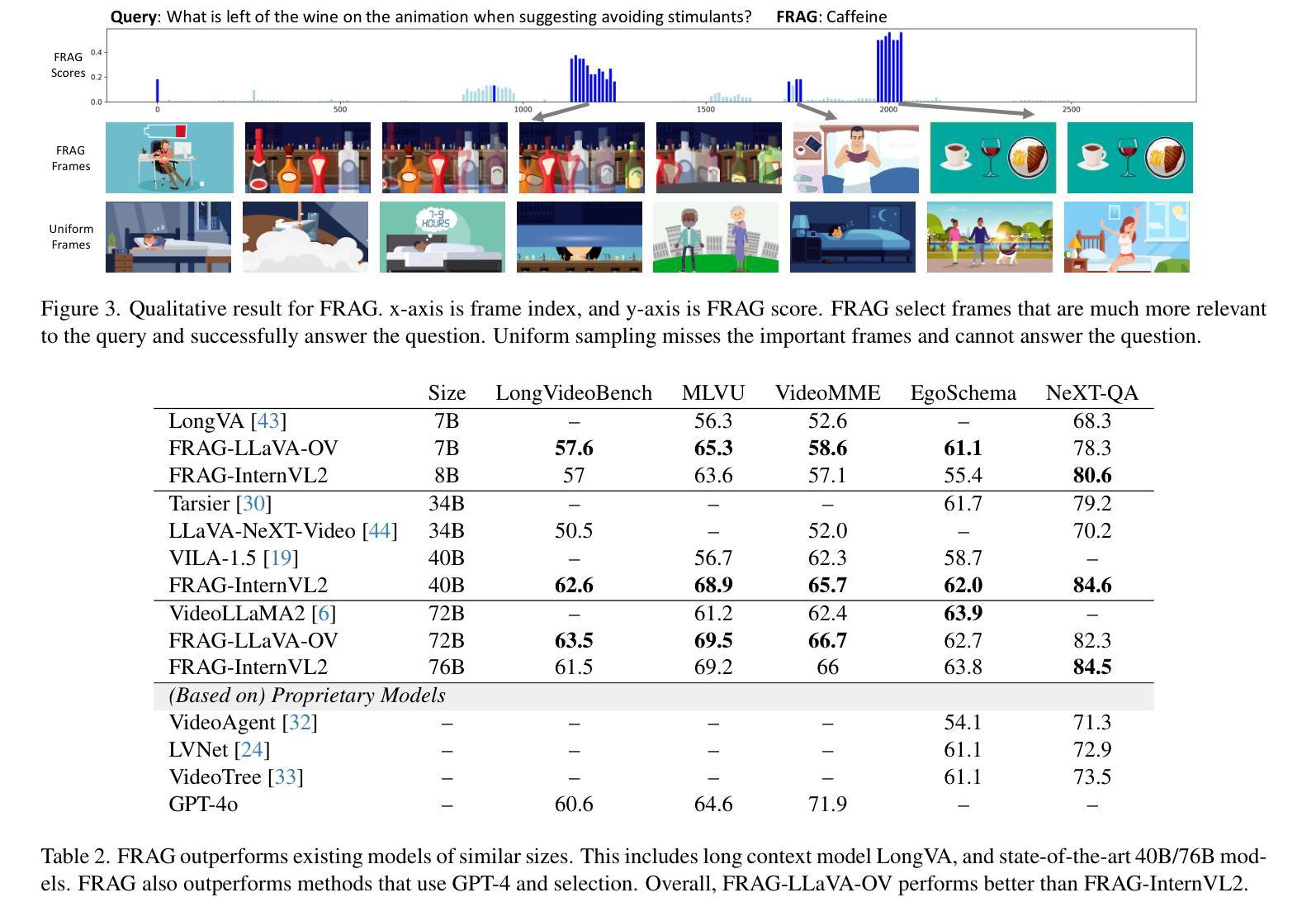
There has been impressive progress in Large Multimodal Models (LMMs). Recent works extend these models to long inputs, including multi-page documents and long videos. However, the model size and performance of these long context models are still limited due to the computational cost in both training and inference. In this work, we explore an orthogonal direction and process long inputs without long context LMMs. We propose Frame Selection Augmented Generation (FRAG), where the model first selects relevant frames within the input, and then only generates the final outputs based on the selected frames. The core of the selection process is done by scoring each frame independently, which does not require long context processing. The frames with the highest scores are then selected by a simple Top-K selection. We show that this frustratingly simple framework is applicable to both long videos and multi-page documents using existing LMMs without any fine-tuning. We consider two models, LLaVA-OneVision and InternVL2, in our experiments and show that FRAG consistently improves the performance and achieves state-of-the-art performances for both long video and long document understanding. For videos, FRAG substantially improves InternVL2-76B by 5.8% on MLVU and 3.7% on Video-MME. For documents, FRAG achieves over 20% improvements on MP-DocVQA compared with recent LMMs specialized in long document understanding. Code is available at: https://github.com/NVlabs/FRAG
在大型多模态模型(LMM)方面取得了令人印象深刻的进展。最近的工作将这些模型扩展到了长输入,包括多页文档和长视频。然而,由于训练和推理的计算成本,这些长上下文模型的大小和性能仍然受到限制。在这项工作中,我们探索了一个正交的方向,即处理长输入而无需长上下文LMM。我们提出了帧选择增强生成(FRAG),该模型首先在选择相关帧,然后仅基于所选帧生成最终输出。选择过程的核心是对每个帧进行独立评分,无需进行长上下文处理。然后选择得分最高的帧进行简单的Top-K选择。我们表明,这个令人沮丧的简单框架适用于长视频和多页文档,使用现有的LMM而无需任何微调。我们在实验中考虑了LLaVA-OneVision和InternVL - 我们表明FRAG始终提高了性能,并在长视频和长文档理解方面达到了最新性能。对于视频,FRAG在MLVU上将InternVL2-76B提高了5.8%,在Video-MME上提高了3.7%。对于文档,FRAG在MP-DocVQA上的改进超过了最近专门用于长文档理解的大型多模态模型,提高了超过20%。代码可在以下网址找到:https://github.com/NVlabs/FRAG 。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
近期大型多模态模型(LMMs)在处理长输入方面取得了显著进展,如多页文档和长视频。然而,由于训练和推理的计算成本,这些长上下文模型的大小和性能仍存在限制。本研究探索了一个不同的方向,即处理长输入而不依赖于长上下文LMMs。提出的Frame Selection Augmented Generation(FRAG)方法,先由模型在输入中选择相关帧,然后仅基于所选帧生成最终输出。核心的选择过程是通过独立评分每个帧来完成的,不需要长上下文处理。随后,通过简单的Top-K选择机制选出得分最高的帧。实验表明,这种简单但有效的框架适用于长视频和多页文档,且不需要对现有LMMs进行微调。FRAG在视频和文档理解方面都实现了最先进的性能提升。
Key Takeaways
- 大型多模态模型(LMMs)在处理长输入方面已取得进展,但仍面临模型大小和性能限制。
- 提出了一种新的方法FRAG,通过选择输入中的相关帧来生成输出,无需长上下文处理。
- FRAG适用于长视频和多页文档,且对现有LMMs无需微调。
- FRAG在视频和文档理解方面实现了性能提升,特别是在处理长视频和文档时效果显著。
点此查看论文截图

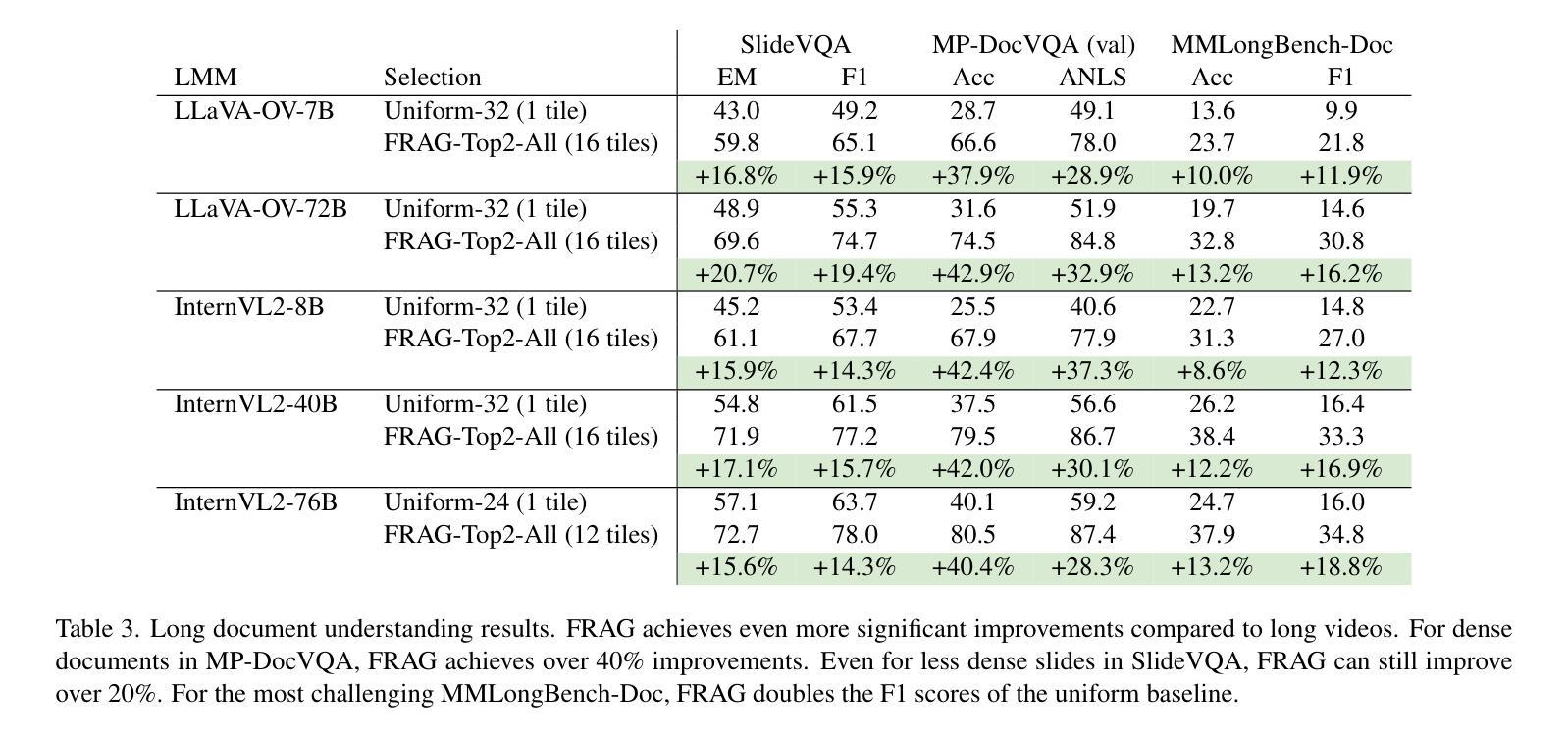
MCAF: Efficient Agent-based Video Understanding Framework through Multimodal Coarse-to-Fine Attention Focusing
Authors:Shiwen Cao, Zhaoxing Zhang, Junming Jiao, Juyi Qiao, Guowen Song, Rong Shen
Even in the era of rapid advances in large models, video understanding, particularly long videos, remains highly challenging. Compared with textual or image-based information, videos commonly contain more information with redundancy, requiring large models to strategically allocate attention at a global level for accurate comprehension. To address this, we propose MCAF, an agent-based, training-free framework perform video understanding through Multimodal Coarse-to-fine Attention Focusing. The key innovation lies in its ability to sense and prioritize segments of the video that are highly relevant to the understanding task. First, MCAF hierarchically concentrates on highly relevant frames through multimodal information, enhancing the correlation between the acquired contextual information and the query. Second, it employs a dilated temporal expansion mechanism to mitigate the risk of missing crucial details when extracting information from these concentrated frames. In addition, our framework incorporates a self-reflection mechanism utilizing the confidence level of the model’s responses as feedback. By iteratively applying these two creative focusing strategies, it adaptively adjusts attention to capture highly query-connected context and thus improves response accuracy. MCAF outperforms comparable state-of-the-art methods on average. On the EgoSchema dataset, it achieves a remarkable 5% performance gain over the leading approach. Meanwhile, on Next-QA and IntentQA datasets, it outperforms the current state-of-the-art standard by 0.2% and 0.3% respectively. On the Video-MME dataset, which features videos averaging nearly an hour in length, MCAF also outperforms other agent-based methods.
即使在大型模型迅速发展的时代,视频理解,尤其是长视频理解,仍然极具挑战性。与文本或图像信息相比,视频通常包含更多信息并带有冗余,需要大型模型在全局层面策略性地分配注意力以实现准确理解。针对这一问题,我们提出了MCAF(基于代理的无训练框架),通过多模态粗到细注意力聚焦进行视频理解。关键创新之处在于它能够感知并优先处理与理解任务高度相关的视频片段。首先,MCAF通过多模态信息分层关注高度相关的帧,增强获取上下文信息与查询之间的相关性。其次,它采用膨胀的时间扩展机制,以减少从集中帧中提取信息时遗漏关键细节的风险。此外,我们的框架还采用了一种自我反馈机制,利用模型响应的置信度作为反馈。通过迭代应用这两种创新的聚焦策略,它能够自适应地调整注意力以捕获与查询高度相关的上下文,从而提高响应准确性。MCAF在平均性能上超过了可比的先进技术方法。在EgoSchema数据集上,与领先方法相比,它取得了5%的性能提升。同时,在Next-QA和IntentQA数据集上,它的性能分别超出了当前最先进的标准0.2%和0.3%。在平均视频长度接近一小时的视频MME数据集上,MCAF也优于其他基于代理的方法。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
该文介绍了视频理解领域的挑战及解决方案。针对长视频的理解问题,提出了一种基于多模态粗到细注意力聚焦(MCAF)的、无需训练的框架。MCAF能感知并优先处理与理解任务高度相关的视频片段,通过分层关注相关帧和多模态信息,提高获取上下文信息与查询之间的相关性。同时,采用膨胀时间扩展机制,减少从集中帧中提取信息时遗漏重要细节的风险。此外,框架还采用自我反思机制,利用模型响应的置信度作为反馈。通过迭代应用这两种策略,框架能够自适应地调整注意力,提高响应准确性。在多个数据集上的实验结果表明,MCAF在视频理解任务上取得了显著的成果。
Key Takeaways
- 视频理解,尤其是长视频,仍然面临巨大挑战,需要大型模型在全局层面上进行战略性的注意力分配。
- MCAF框架是一种基于多模态粗到细注意力聚焦的、无需训练的解决方案。
- MCAF能感知并优先处理与理解任务高度相关的视频片段。
- 通过分层关注相关帧和多模态信息,MCAF提高了获取上下文信息与查询之间的相关性。
- MCAF采用膨胀时间扩展机制来减少遗漏重要细节的风险。
- 自我反思机制利用模型响应的置信度作为反馈,提高响应准确性。
点此查看论文截图

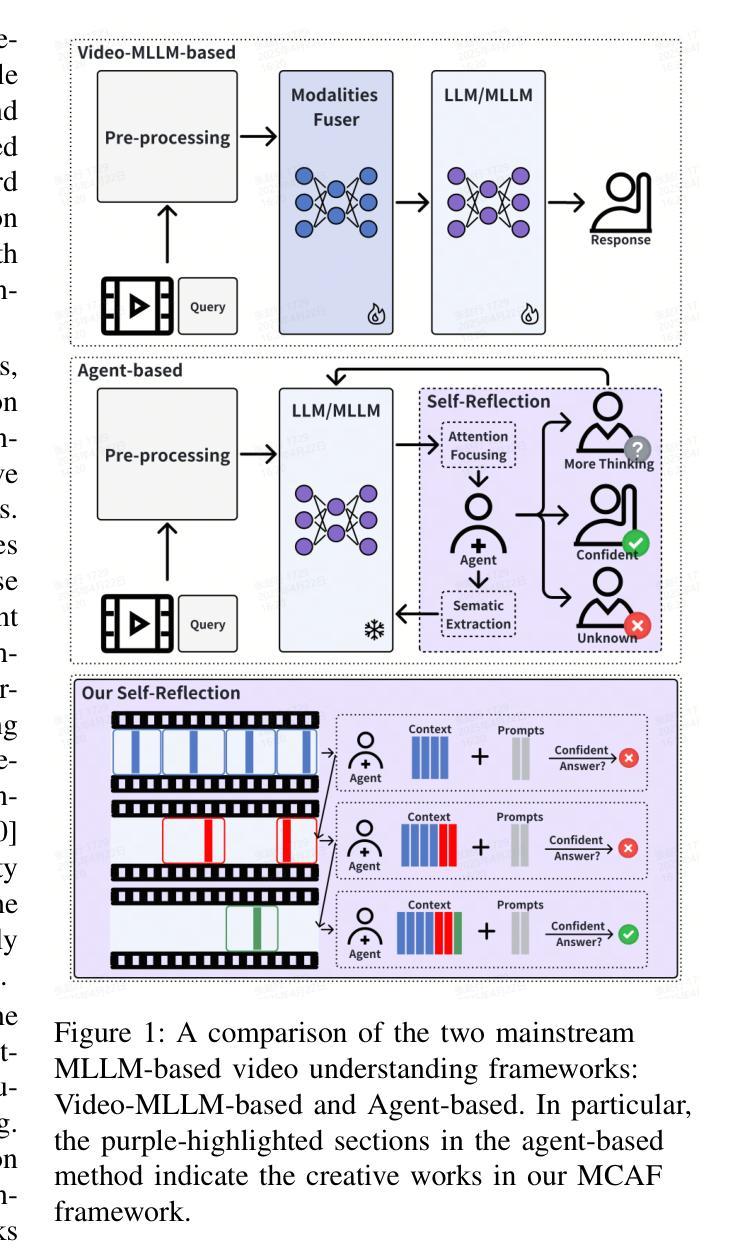
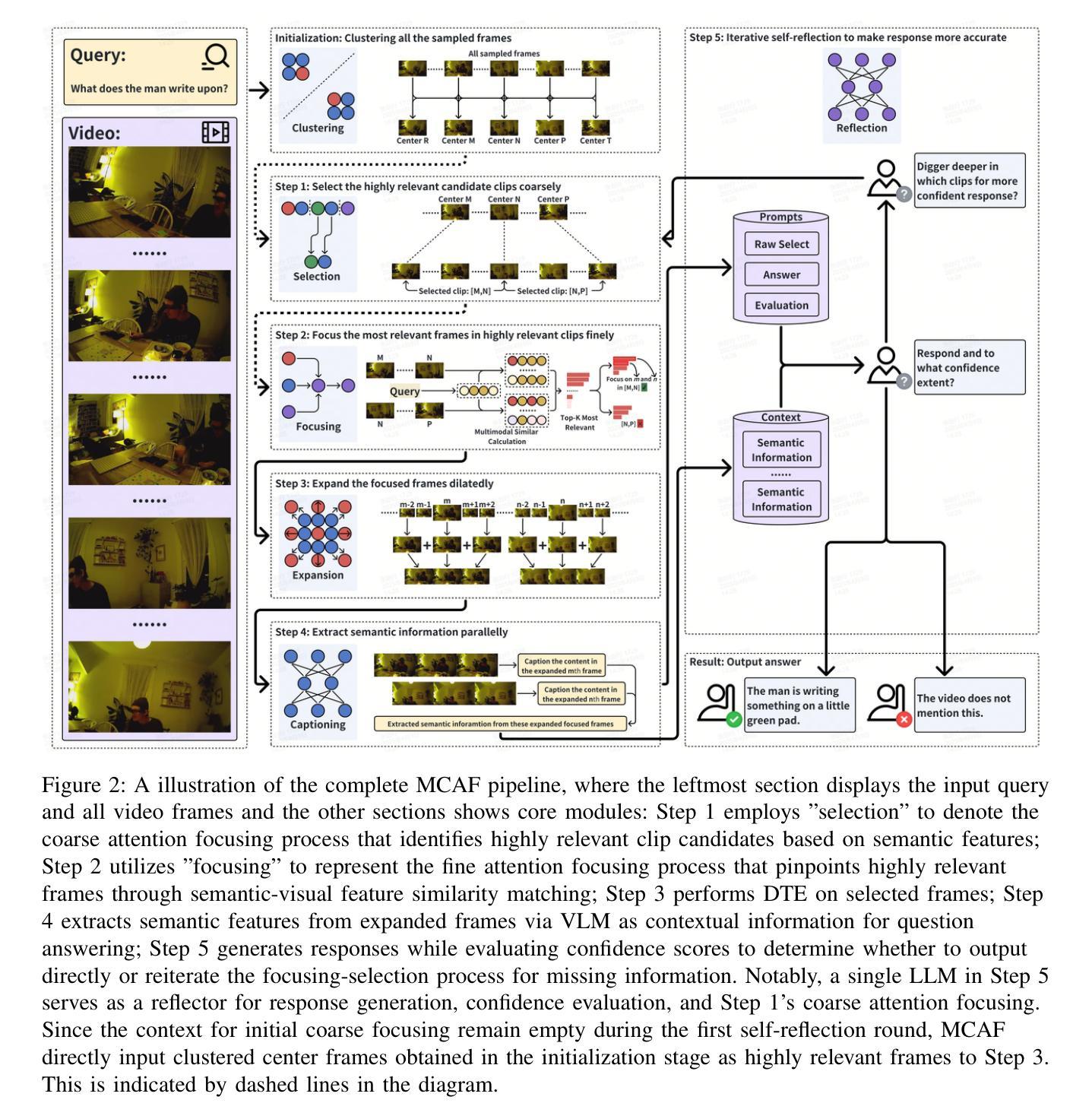
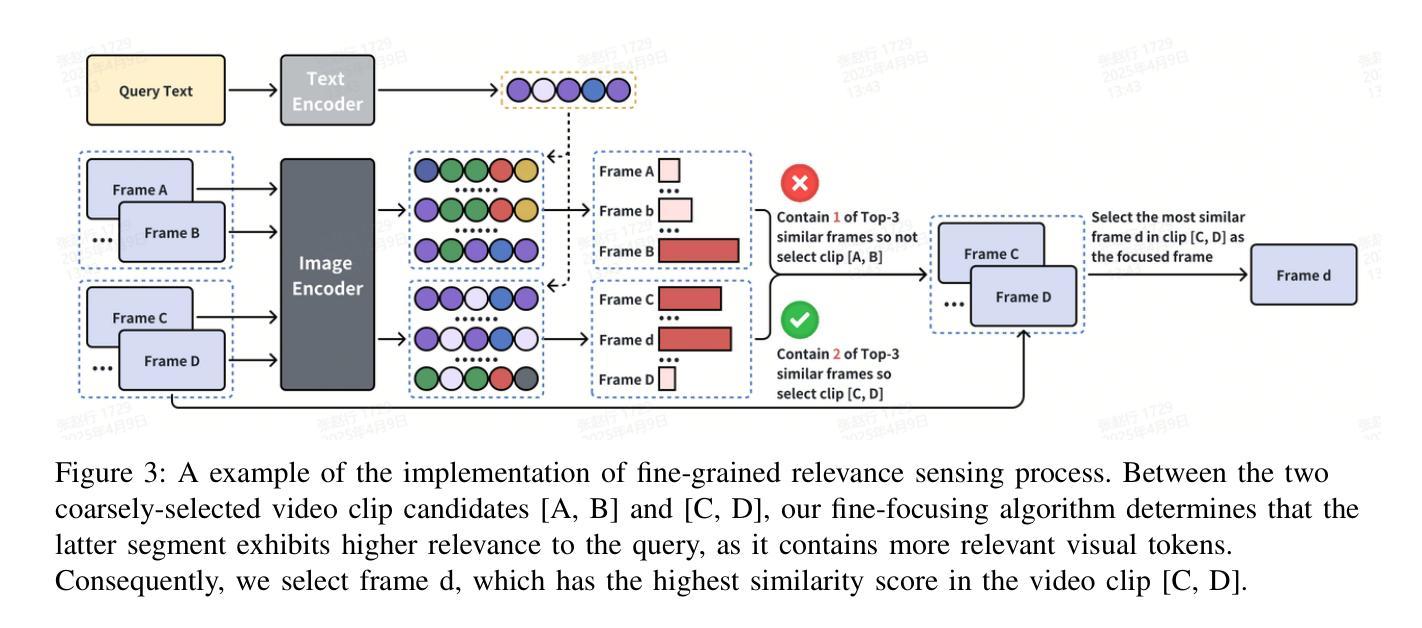

Vidi: Large Multimodal Models for Video Understanding and Editing
Authors: Vidi Team, Celong Liu, Chia-Wen Kuo, Dawei Du, Fan Chen, Guang Chen, Jiamin Yuan, Lingxi Zhang, Lu Guo, Lusha Li, Longyin Wen, Qingyu Chen, Rachel Deng, Sijie Zhu, Stuart Siew, Tong Jin, Wei Lu, Wen Zhong, Xiaohui Shen, Xin Gu, Xing Mei, Xueqiong Qu
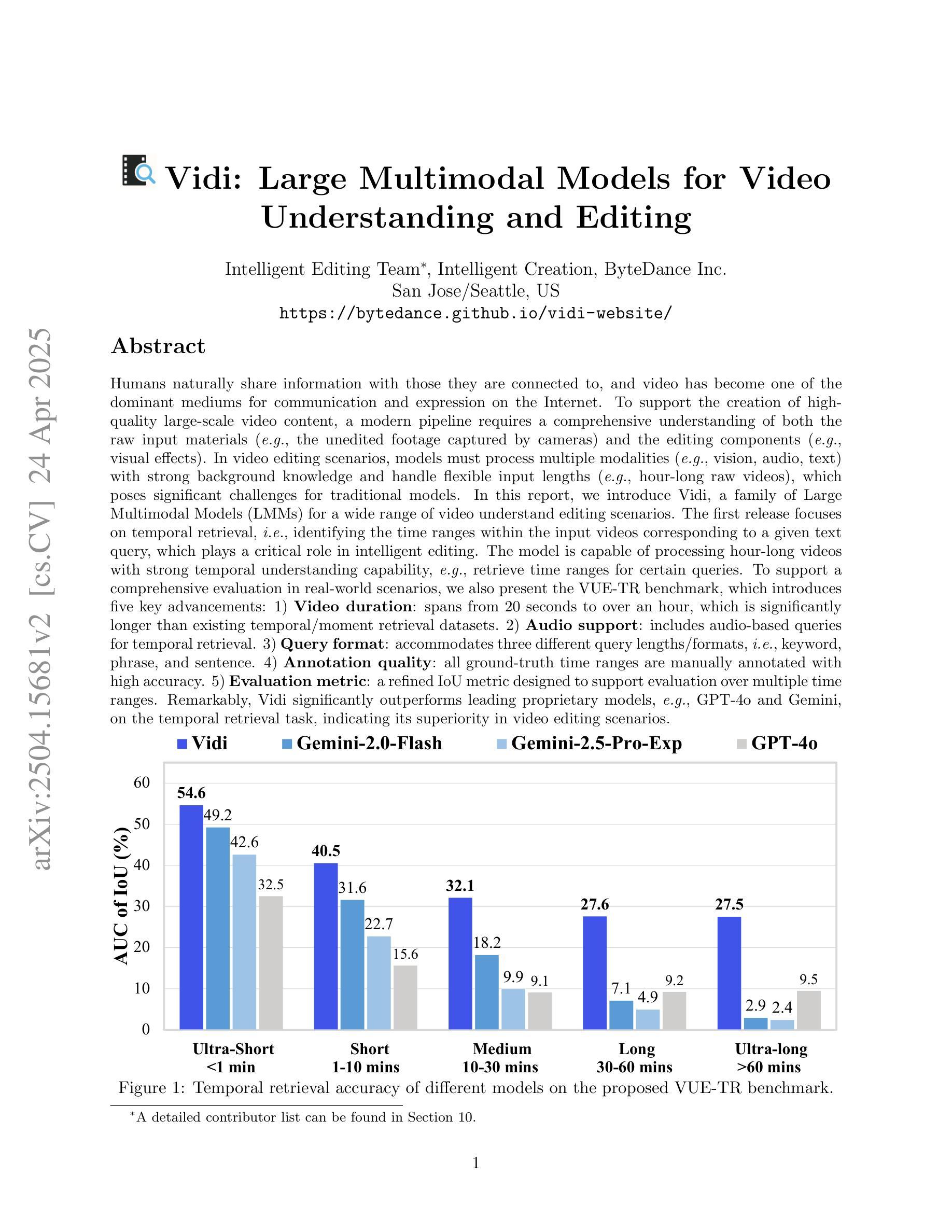
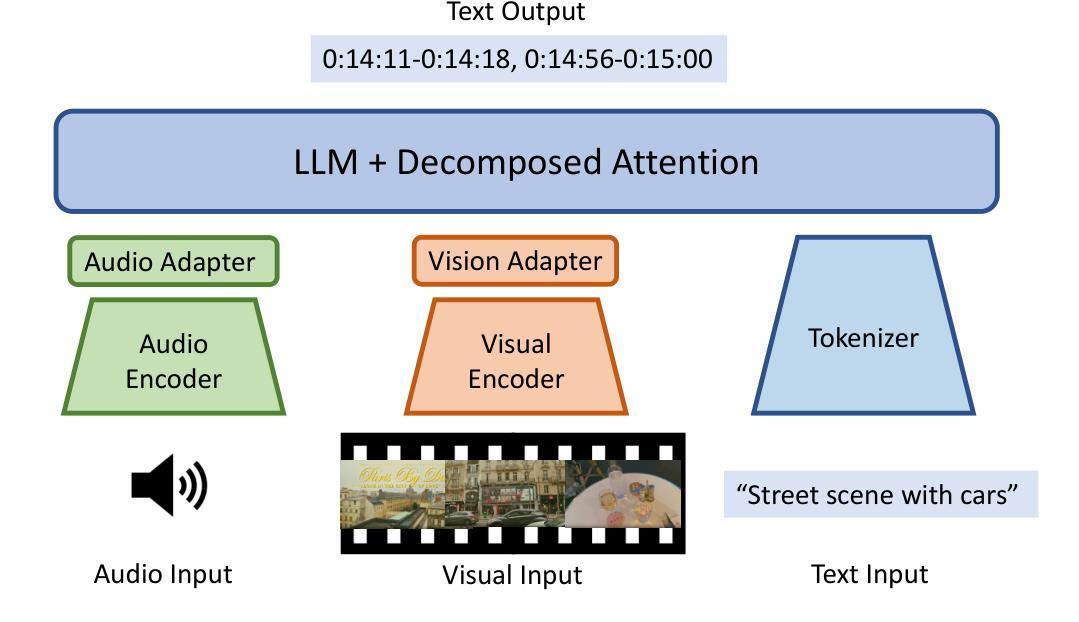
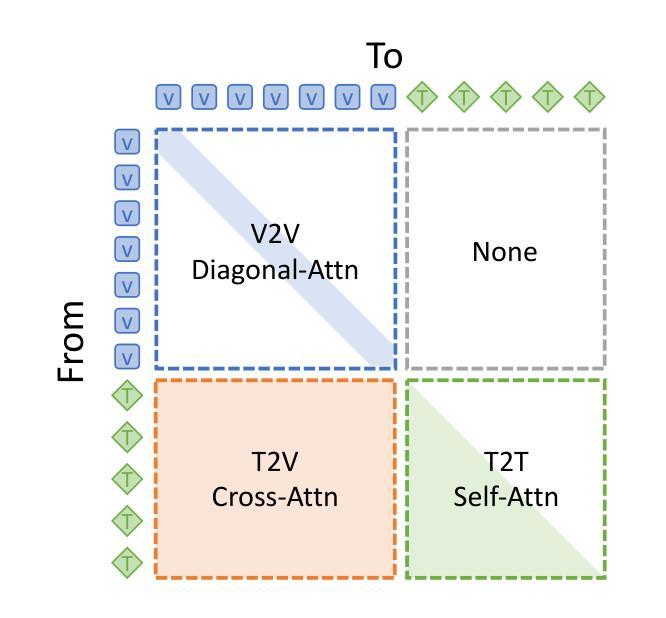
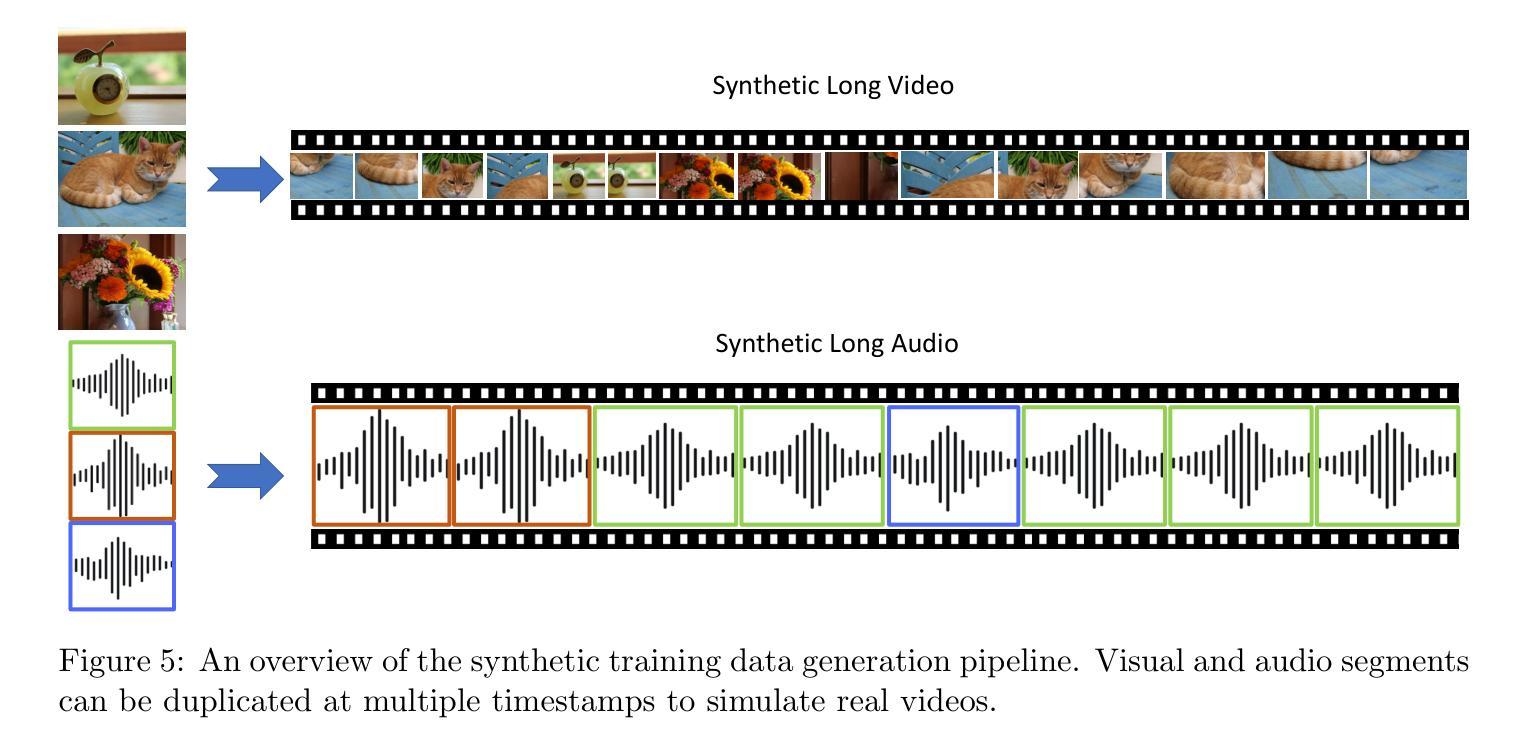
Humans naturally share information with those they are connected to, and video has become one of the dominant mediums for communication and expression on the Internet. To support the creation of high-quality large-scale video content, a modern pipeline requires a comprehensive understanding of both the raw input materials (e.g., the unedited footage captured by cameras) and the editing components (e.g., visual effects). In video editing scenarios, models must process multiple modalities (e.g., vision, audio, text) with strong background knowledge and handle flexible input lengths (e.g., hour-long raw videos), which poses significant challenges for traditional models. In this report, we introduce Vidi, a family of Large Multimodal Models (LMMs) for a wide range of video understand editing scenarios. The first release focuses on temporal retrieval, i.e., identifying the time ranges within the input videos corresponding to a given text query, which plays a critical role in intelligent editing. The model is capable of processing hour-long videos with strong temporal understanding capability, e.g., retrieve time ranges for certain queries. To support a comprehensive evaluation in real-world scenarios, we also present the VUE-TR benchmark, which introduces five key advancements. 1) Video duration: significantly longer than videos of existing temporal retrival datasets, 2) Audio support: includes audio-based queries, 3) Query format: diverse query lengths/formats, 4) Annotation quality: ground-truth time ranges are manually annotated. 5) Evaluation metric: a refined IoU metric to support evaluation over multiple time ranges. Remarkably, Vidi significantly outperforms leading proprietary models, e.g., GPT-4o and Gemini, on the temporal retrieval task, indicating its superiority in video editing scenarios.
人类自然地与所联系的人分享信息,视频已成为互联网上主要的沟通和表达媒介之一。为了支持高质量的大规模视频内容的创建,现代流水线需要全面理解原始输入材料(如摄像机拍摄的无编辑素材)和编辑组件(如视觉效果)。在视频编辑场景中,模型必须处理多种模态(如视觉、音频、文本),具备强大的背景知识,并处理灵活输入长度(如长达数小时的原视频素材),这对传统模型提出了重大挑战。在本报告中,我们介绍了Vidi,一系列用于广泛视频理解编辑场景的大型多模态模型(LMMs)。首次发布重点关注时序检索,即识别与给定文本查询相对应输入视频中的时间段,这在智能编辑中发挥着至关重要的作用。该模型具备处理长达数小时的视频的强时间理解能力,例如检索某些查询的时间范围。为了支持真实场景中的全面评估,我们还推出了VUE-TR基准测试,它引入了五个关键进展:1)视频时长:显著长于现有时序检索数据集的视频;2)音频支持:包含基于音频的查询;3)查询格式:不同的查询长度/格式;4)注释质量:通过手动标注真实时间范围;5)评估指标:一个经过改进的IoU指标,以支持对多个时间范围的评估。值得注意的是,Vidi在时序检索任务上显著优于领先的专有模型,如GPT-4o和Gemini,这表明其在视频编辑场景中的优越性。
论文及项目相关链接
摘要
视频在互联网上已成为主导的信息传播媒介之一。为支持高质量的大规模视频内容的创作,需要全面理解原始素材和编辑组件。报告中介绍了Vidi,一系列用于广泛视频编辑场景的大型多模态模型(LMMs)。首次发布的产品专注于时序检索,即识别与给定文本查询对应输入视频的时间范围,在智能编辑中发挥关键作用。该模型具备处理长达数小时的视频的能力,并具有较强的时序理解能力。此外,报告还推出了VUE-TR基准测试,其中包括五个关键进展。为全面评估其在现实场景中的应用性能,我们建立了VUE-TR基准测试平台,其中包括视频时长、音频支持、查询格式、标注质量和评估指标等五个方面的关键改进。Vidi在时序检索任务上显著优于领先的专有模型,如GPT-4o和Gemini,表明其在视频编辑场景中的优越性。
关键见解
- 视频在互联网通信和表达中的作用愈发重要,需要全面理解视频内容和编辑组件以支持高质量视频内容的创作。
- Vidi作为大型多模态模型(LMMs)系列的一部分,为广泛的视频编辑场景提供支持。
- Vidi首次发布的产品专注于时序检索,具有强大的时间理解能力,可以处理长达数小时的视频。
- VUE-TR基准测试推出,为全面评估视频理解模型在现实场景中的性能提供了平台。
- VUE-TR基准测试包括五个关键改进点:视频时长、音频支持、查询格式、标注质量和评估指标。
- Vidi在时序检索任务上表现出卓越性能,显著优于其他领先的专有模型。
点此查看论文截图

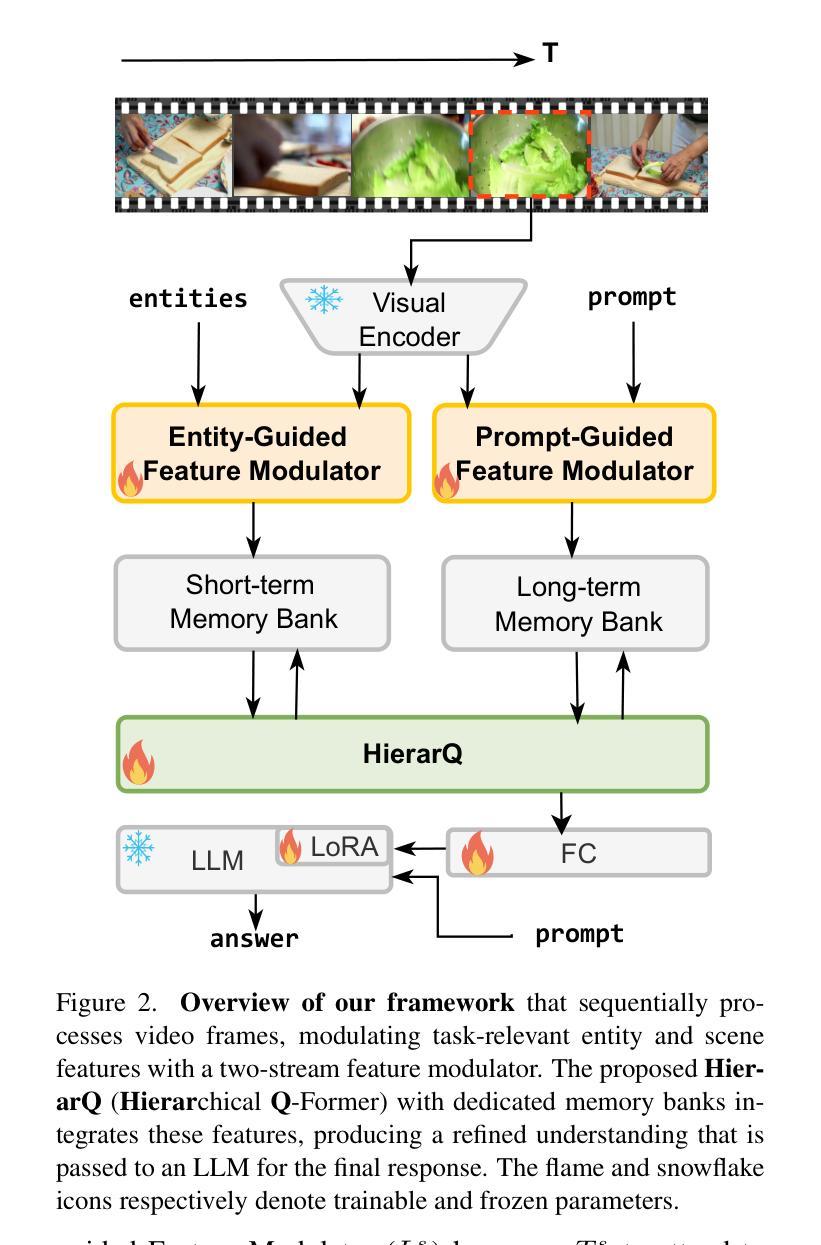
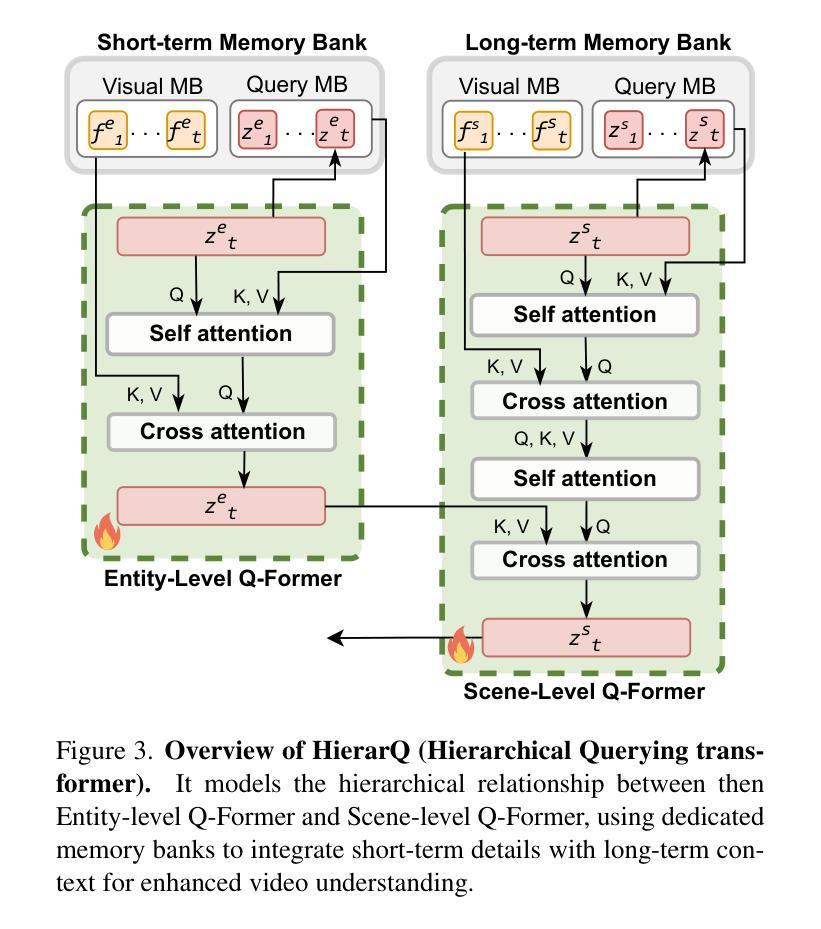
HierarQ: Task-Aware Hierarchical Q-Former for Enhanced Video Understanding
Authors:Shehreen Azad, Vibhav Vineet, Yogesh Singh Rawat
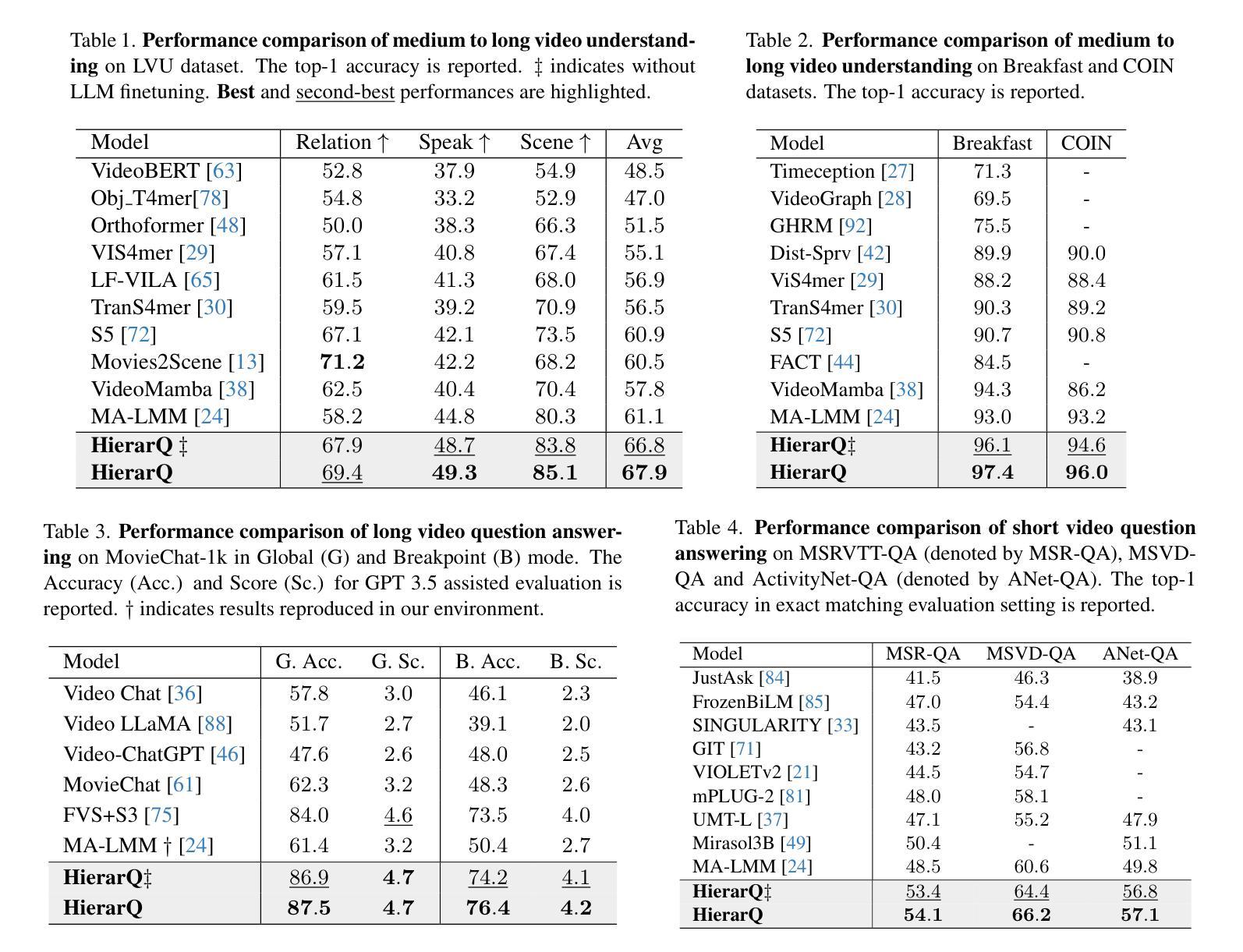
Despite advancements in multimodal large language models (MLLMs), current approaches struggle in medium-to-long video understanding due to frame and context length limitations. As a result, these models often depend on frame sampling, which risks missing key information over time and lacks task-specific relevance. To address these challenges, we introduce HierarQ, a task-aware hierarchical Q-Former based framework that sequentially processes frames to bypass the need for frame sampling, while avoiding LLM’s context length limitations. We introduce a lightweight two-stream language-guided feature modulator to incorporate task awareness in video understanding, with the entity stream capturing frame-level object information within a short context and the scene stream identifying their broader interactions over longer period of time. Each stream is supported by dedicated memory banks which enables our proposed Hierachical Querying transformer (HierarQ) to effectively capture short and long-term context. Extensive evaluations on 10 video benchmarks across video understanding, question answering, and captioning tasks demonstrate HierarQ’s state-of-the-art performance across most datasets, proving its robustness and efficiency for comprehensive video analysis.
尽管多模态大型语言模型(MLLMs)有所进展,但当前的方法在中长视频理解方面仍面临挑战,这是由于帧和上下文长度的限制所导致的。因此,这些模型通常依赖于帧采样,这存在着随时间错过关键信息的风险,并且缺乏特定任务的关联性。为了解决这些挑战,我们引入了 HierarQ,这是一个基于任务感知的分层 Q-Former 框架,它按顺序处理帧,从而绕过对帧采样的需求,同时避免 LLM 的上下文长度限制。我们引入了一个轻量级的双流语言引导特征调制器,将任务感知融入视频理解中,实体流在短语境内捕获帧级对象信息,场景流则识别较长时间内的更广泛交互。每个流都由专用内存库支持,这使得我们提出的分层查询转换器(HierarQ)可以有效地捕获短期和长期上下文。在 10 个视频基准测试上的广泛评估,包括视频理解、问答和字幕任务,证明了 HierarQ 在大多数数据集上的最新性能,证明了其在综合视频分析中的稳健性和效率。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF Accepted in CVPR 2025
Summary
本文指出当前的多模态大型语言模型在处理中等至长视频时存在局限,常依赖于帧采样,容易遗漏关键信息且缺乏任务相关性。为解决此问题,引入了一种任务感知的层次化Q-Former框架——HierarQ,其可顺序处理帧,绕过帧采样的需要,避免大型语言模型的上下文长度限制。此外,还介绍了轻量级双流语言引导特征调制器,将任务感知融入视频理解中。实体流捕捉短时间内帧级对象信息,场景流识别更广泛的长期交互。每个流都有专门的内存库,使提出的层次查询转换器(HierarQ)能有效捕捉短期和长期上下文。在视频理解、问答和字幕任务上的十个视频基准测试表明,HierarQ在多数数据集上具有领先水平,证明了其在综合视频分析中的稳健性和效率。
Key Takeaways
- 当前多模态大型语言模型在处理中等至长视频时存在挑战,主要因为帧和上下文长度的限制。
- 帧采样是现有模型常用的方法,但可能遗漏关键信息并且缺乏任务特异性。
- HierarQ框架被引入以解决这些挑战,它通过顺序处理帧来绕过帧采样的需要。
- HierarQ结合任务感知的层次化Q-Former和轻量级双流语言引导特征调制器来提高视频理解。
- 实体流捕捉短时间内帧级对象信息,而场景流识别长期的广泛交互。
- 每个流都有专门的内存库,使层次查询转换器(HierarQ)能捕捉短期和长期上下文。
点此查看论文截图