⚠️ 以下所有内容总结都来自于 大语言模型的能力,如有错误,仅供参考,谨慎使用
🔴 请注意:千万不要用于严肃的学术场景,只能用于论文阅读前的初筛!
💗 如果您觉得我们的项目对您有帮助 ChatPaperFree ,还请您给我们一些鼓励!⭐️ HuggingFace免费体验
2025-04-26 更新
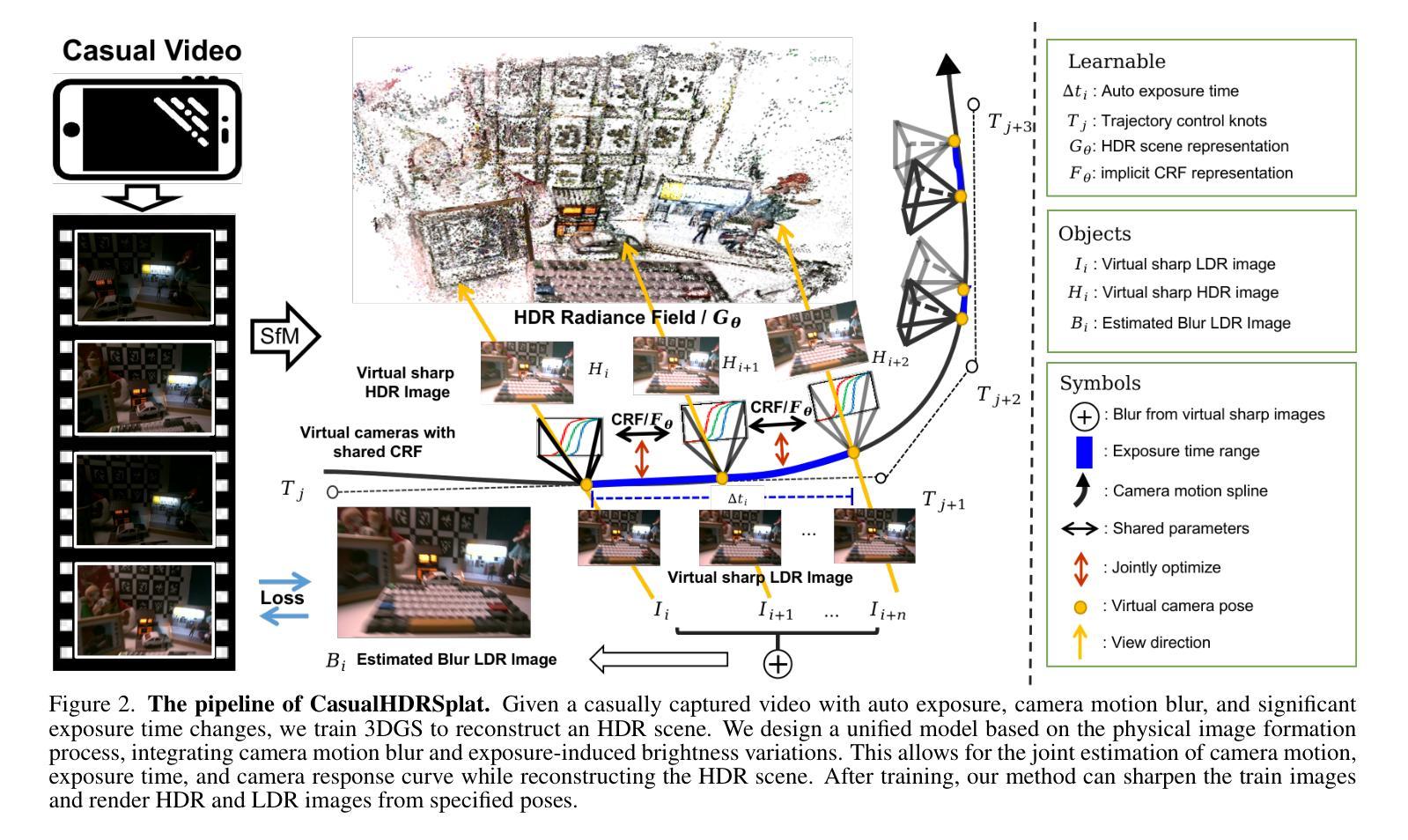
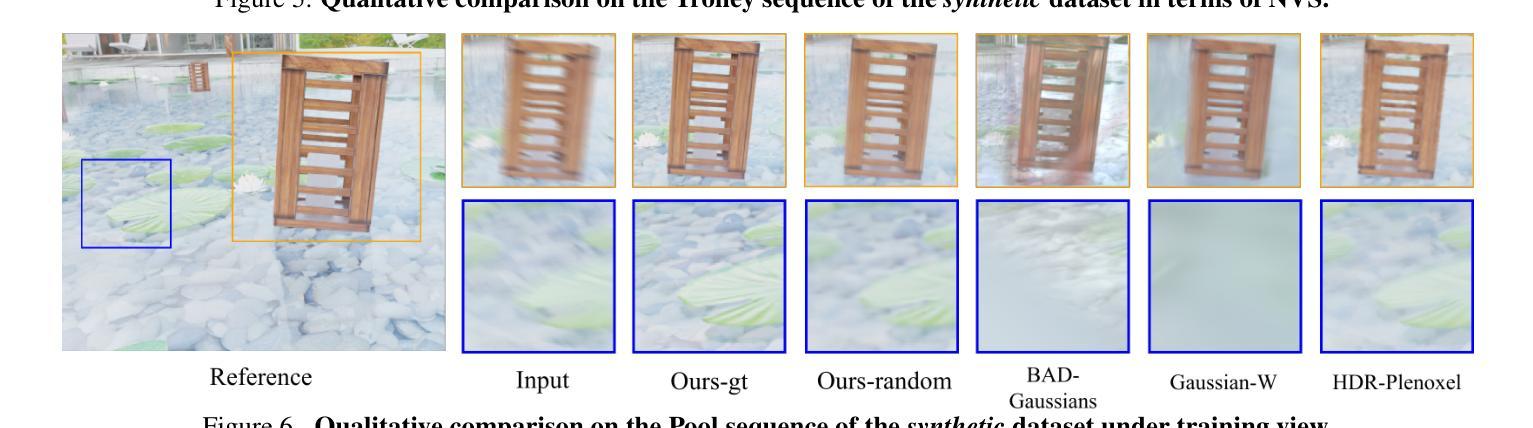
CasualHDRSplat: Robust High Dynamic Range 3D Gaussian Splatting from Casually Captured Videos
Authors:Shucheng Gong, Lingzhe Zhao, Wenpu Li, Hong Xie, Yin Zhang, Shiyu Zhao, Peidong Liu
Recently, photo-realistic novel view synthesis from multi-view images, such as neural radiance field (NeRF) and 3D Gaussian Splatting (3DGS), have garnered widespread attention due to their superior performance. However, most works rely on low dynamic range (LDR) images, which limits the capturing of richer scene details. Some prior works have focused on high dynamic range (HDR) scene reconstruction, typically require capturing of multi-view sharp images with different exposure times at fixed camera positions during exposure times, which is time-consuming and challenging in practice. For a more flexible data acquisition, we propose a one-stage method: \textbf{CasualHDRSplat} to easily and robustly reconstruct the 3D HDR scene from casually captured videos with auto-exposure enabled, even in the presence of severe motion blur and varying unknown exposure time. \textbf{CasualHDRSplat} contains a unified differentiable physical imaging model which first applies continuous-time trajectory constraint to imaging process so that we can jointly optimize exposure time, camera response function (CRF), camera poses, and sharp 3D HDR scene. Extensive experiments demonstrate that our approach outperforms existing methods in terms of robustness and rendering quality. Our source code will be available at https://github.com/WU-CVGL/CasualHDRSplat
最近,诸如神经辐射场(NeRF)和三维高斯描画(3DGS)等基于多视角图像的写实性新视角合成技术因其卓越性能而受到了广泛关注。然而,大多数研究都依赖于低动态范围(LDR)图像,这限制了更丰富场景细节的捕捉。一些早期的工作集中在高动态范围(HDR)场景的重建上,这通常需要在不同曝光时间下在固定相机位置捕获多视角的清晰图像,这在实践中既耗时又具有挑战性。为了更灵活地获取数据,我们提出了一种单阶段方法:CasualHDRSplat,该方法能够轻松稳健地从具有自动曝光功能的随意拍摄视频重建出三维HDR场景,即使在存在严重运动模糊和未知变化的曝光时间的情况下也是如此。CasualHDRSplat包含一个统一的可区分物理成像模型,该模型首先对成像过程应用连续时间轨迹约束,使我们能够联合优化曝光时间、相机响应函数(CRF)、相机姿态和清晰的3D HDR场景。大量实验表明,我们的方法在稳健性和渲染质量方面优于现有方法。我们的源代码将在[https://github.com/WU-CVGL/CasualHDRSplat找到。]
论文及项目相关链接
PDF Source Code: https://github.com/WU-CVGL/CasualHDRSplat
Summary
NeRF与3DGS等多视角图像的光照模拟技术得到广泛关注。但由于大多使用低动态范围图像,导致难以捕获丰富场景细节。针对此问题,本文提出一种名为CasualHDRSplat的新方法,能在一阶段中便捷且稳健地从带有自动曝光功能的非专业拍摄视频中重建高动态范围的三维场景,即使存在严重的运动模糊和未知的曝光时间差异也是如此。其包括一个统一的、可微分的物理成像模型,该模型采用连续时间轨迹约束进行成像处理,可联合优化曝光时间、相机响应函数、相机姿态和清晰的高动态范围三维场景。实验证明,该方法在稳健性和渲染质量上优于现有技术。
Key Takeaways
- NeRF与3DGS等技术受到关注,但依赖于低动态范围图像限制了场景的丰富性。
- 现有研究主要关注于高动态范围场景的重建,通常要求固定相机位置捕捉多视角的清晰图像,实际操作中耗时且具挑战性。
- 提出CasualHDRSplat方法,可从非专业拍摄的视频中重建高动态范围的三维场景,处理存在运动模糊和未知曝光时间差异的情况。
- CasualHDRSplat包括一个统一的物理成像模型,采用连续时间轨迹约束进行成像处理。
- 该方法可联合优化多个因素,如曝光时间、相机响应函数等。
点此查看论文截图




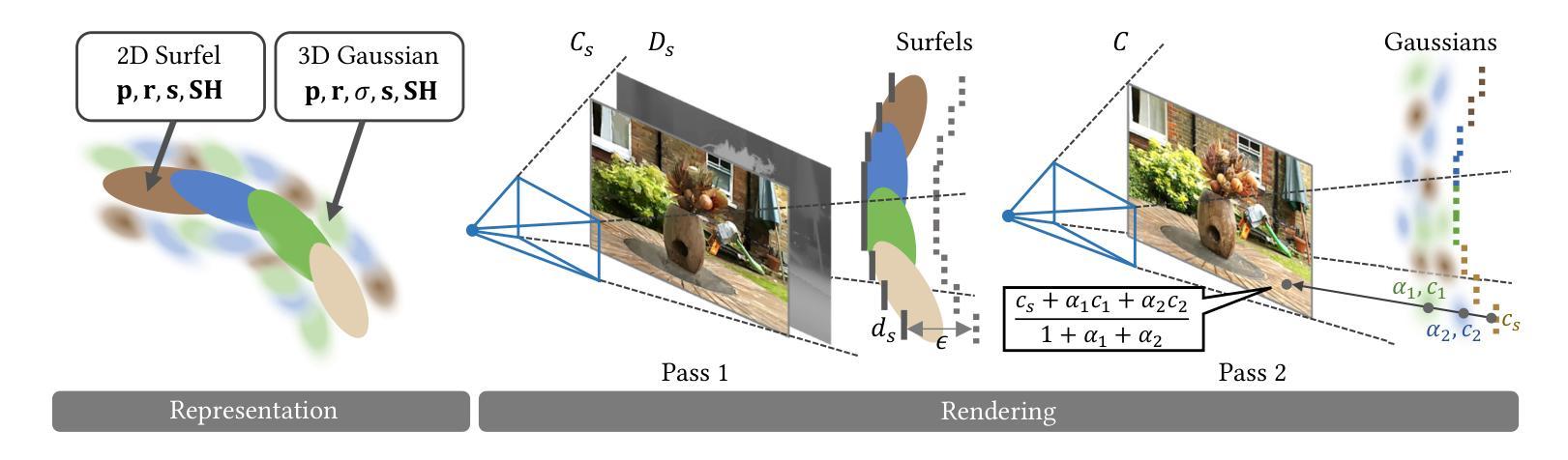
When Gaussian Meets Surfel: Ultra-fast High-fidelity Radiance Field Rendering
Authors:Keyang Ye, Tianjia Shao, Kun Zhou
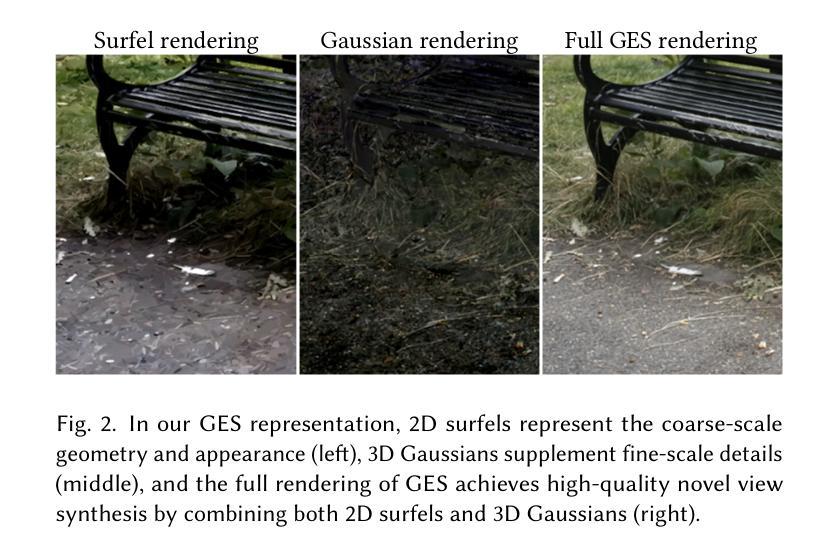
We introduce Gaussian-enhanced Surfels (GESs), a bi-scale representation for radiance field rendering, wherein a set of 2D opaque surfels with view-dependent colors represent the coarse-scale geometry and appearance of scenes, and a few 3D Gaussians surrounding the surfels supplement fine-scale appearance details. The rendering with GESs consists of two passes – surfels are first rasterized through a standard graphics pipeline to produce depth and color maps, and then Gaussians are splatted with depth testing and color accumulation on each pixel order independently. The optimization of GESs from multi-view images is performed through an elaborate coarse-to-fine procedure, faithfully capturing rich scene appearance. The entirely sorting-free rendering of GESs not only achieves very fast rates, but also produces view-consistent images, successfully avoiding popping artifacts under view changes. The basic GES representation can be easily extended to achieve anti-aliasing in rendering (Mip-GES), boosted rendering speeds (Speedy-GES) and compact storage (Compact-GES), and reconstruct better scene geometries by replacing 3D Gaussians with 2D Gaussians (2D-GES). Experimental results show that GESs advance the state-of-the-arts as a compelling representation for ultra-fast high-fidelity radiance field rendering.
我们引入了高斯增强Surfels(GESs),这是一种用于辐射场渲染的双尺度表示方法。其中,一组具有视图相关颜色的2D不透明Surfels表示场景的粗尺度几何和外观,而围绕Surfels的几个3D高斯则补充了细尺度的外观细节。使用GESs的渲染由两个通道组成——首先通过标准图形管道对Surfels进行光栅化以生成深度图和颜色图,然后独立地对每个像素顺序进行高斯展布、深度测试和颜色累积。通过精细的由粗到细的流程对多视图图像中的GES进行优化,可以忠实地捕捉丰富的场景外观。完全无排序的GES渲染不仅实现了非常高的速度,还生成了视角一致的图像,成功避免了视角变化时出现的弹跳伪影。基本GES表示可以很容易地扩展,以实现渲染中的抗锯齿(Mip-GES)、提高渲染速度(Speedy-GES)和紧凑存储(Compact-GES),并且通过用2D高斯替换3D高斯来更好地重建场景几何(2D-GES)。实验结果表明,GES作为超快速高保真辐射场渲染的有吸引力的表示方法,推动了最新技术的发展。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
本文介绍了高斯增强Surfel(GES)技术,这是一种双尺度辐射场渲染表示方法。该技术通过一组具有视点相关颜色的二维不透明Surfel表示场景的粗尺度几何和外观,并通过Surfel周围的一些三维高斯补充精细尺度外观细节。首先通过标准图形管道对Surfel进行渲染以生成深度和颜色图,然后独立地对每个像素顺序进行高斯分裂、深度测试和颜色累积。通过复杂的从粗到细的流程对多视角图像中的GES进行优化,可以忠实捕捉丰富的场景外观。完全无排序的GES渲染不仅实现了高速率,而且产生了视角一致的图像,成功避免了视图更改时的弹出伪影。此外,基本GES表示可以很容易地扩展到实现抗锯齿渲染、提高渲染速度和紧凑存储等。
Key Takeaways
- GES是一种双尺度辐射场渲染技术,结合了二维Surfel和三维高斯表示法。
- Surfel表示场景的粗尺度几何和外观,而高斯补充了精细尺度的外观细节。
- GES渲染分为两个阶段:首先进行Surfel的渲染以生成深度和颜色图,然后对每个像素独立地应用高斯处理。
- GES通过复杂的从粗到细的流程从多视角图像进行优化,以捕捉丰富的场景外观。
- GES渲染具有高速率、视角一致性,避免了视图更改时的弹出伪影。
- GES可以容易地扩展到实现抗锯齿渲染、提高渲染速度和紧凑存储等。
点此查看论文截图


LinPrim: Linear Primitives for Differentiable Volumetric Rendering
Authors:Nicolas von Lützow, Matthias Nießner
Volumetric rendering has become central to modern novel view synthesis methods, which use differentiable rendering to optimize 3D scene representations directly from observed views. While many recent works build on NeRF or 3D Gaussians, we explore an alternative volumetric scene representation. More specifically, we introduce two new scene representations based on linear primitives - octahedra and tetrahedra - both of which define homogeneous volumes bounded by triangular faces. To optimize these primitives, we present a differentiable rasterizer that runs efficiently on GPUs, allowing end-to-end gradient-based optimization while maintaining real-time rendering capabilities. Through experiments on real-world datasets, we demonstrate comparable performance to state-of-the-art volumetric methods while requiring fewer primitives to achieve similar reconstruction fidelity. Our findings deepen the understanding of 3D representations by providing insights into the fidelity and performance characteristics of transparent polyhedra and suggest that adopting novel primitives can expand the available design space.
体积渲染已成为现代新型视图合成方法的核心,这些方法使用可微渲染来直接优化从观察到的视角的3D场景表示。虽然许多最新作品都是基于NeRF或3D高斯分布的,但我们探索了一种替代的体积场景表示。更具体地说,我们引入两种基于线性原始形状的新场景表示:八面体和四面体,它们都通过三角形面定义均匀体积。为了优化这些原始形状,我们提出了一种可在GPU上高效运行的可微栅格化器,允许端到端的基于梯度的优化,同时保持实时渲染能力。通过对真实世界数据集的实验,我们展示了与最先进体积方法相当的性能,同时使用较少的原始形状即可实现相似的重建保真度。我们的研究深化了对3D表示的理解,提供了关于透明多面体的保真度和性能特征洞察力,并表明采用新型原始形状可以扩大可用的设计空间。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF Project page: https://nicolasvonluetzow.github.io/LinPrim - Project video: https://youtu.be/NRRlmFZj5KQ
Summary
该文探索了基于线性原始体积的新的三维场景表示方法,具体介绍了使用八面体和四面体两种三角面定义均匀体积的场景表示技术。为优化这些原始体积,提出了一种可微分的光线追踪器,能在GPU上高效运行,实现端到端的基于梯度的优化,同时保持实时渲染能力。实验证明,该方法与最新体积方法在真实数据集上的性能相当,且使用较少的原始体积即可达到相似的重建保真度。
Key Takeaways
- 引入两种新的基于线性原始体积的场景表示方法:八面体和四面体。
- 提出一种可微分的光线追踪器,用于优化这些原始体积。
- 该技术在GPU上高效运行,支持端到端的基于梯度的优化和实时渲染。
- 实验证明,新方法在真实数据集上的性能与最新体积方法相当。
- 使用较少的原始体积即可达到相似的重建保真度。
- 该研究深化了对三维表示的理解,为设计新型三维场景表示技术提供了启示。
点此查看论文截图


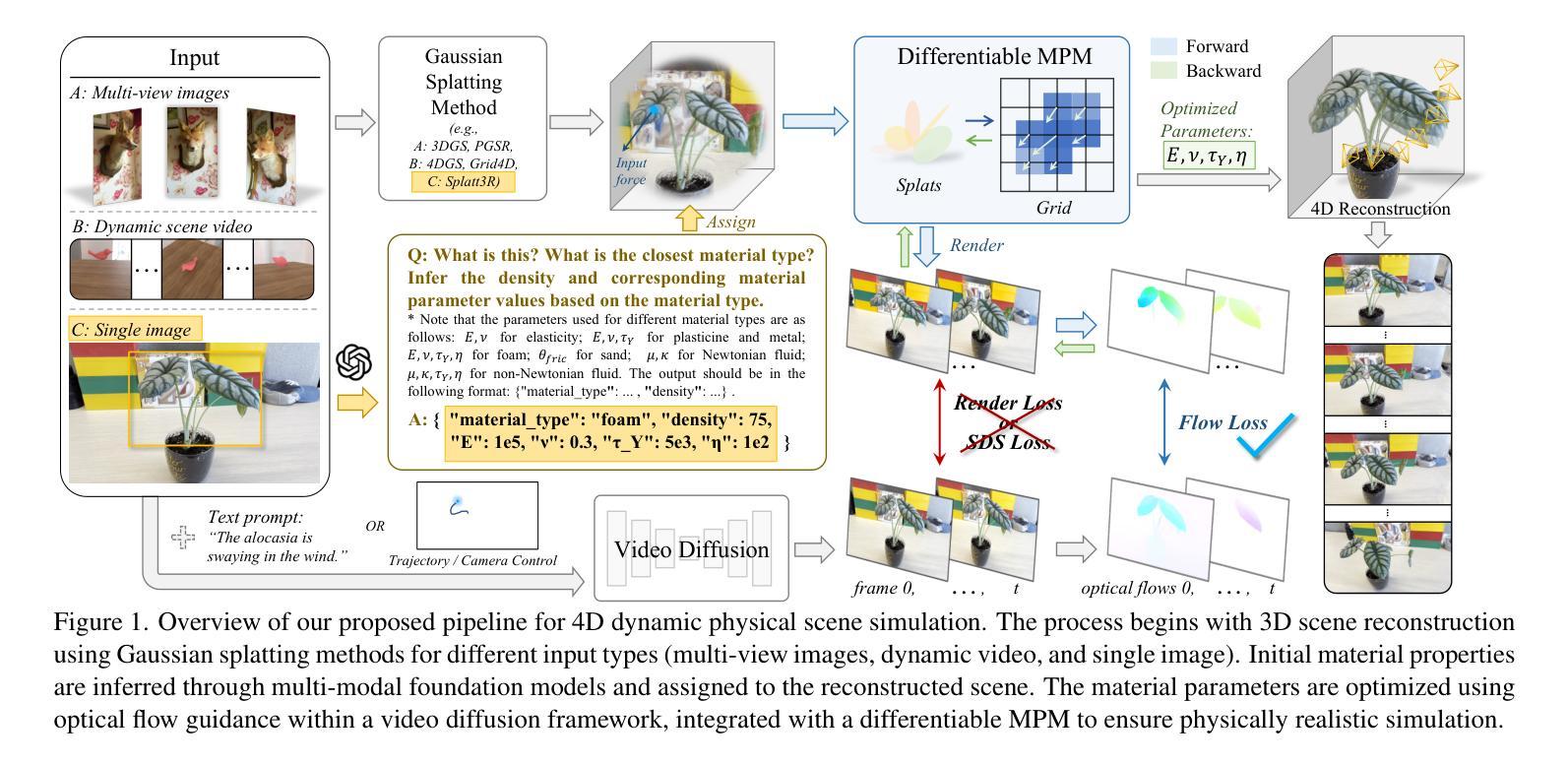
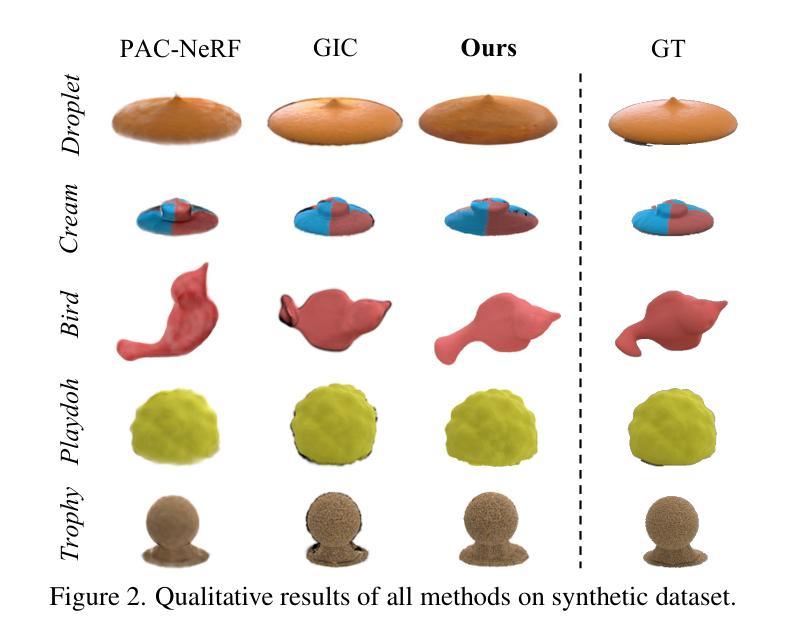
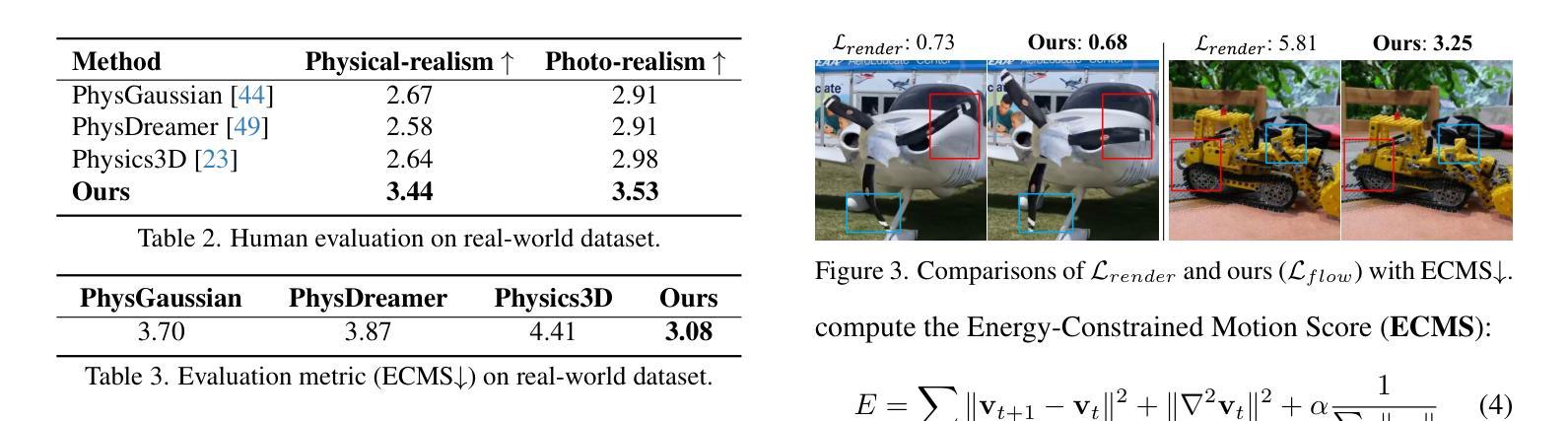
PhysFlow: Unleashing the Potential of Multi-modal Foundation Models and Video Diffusion for 4D Dynamic Physical Scene Simulation
Authors:Zhuoman Liu, Weicai Ye, Yan Luximon, Pengfei Wan, Di Zhang
Realistic simulation of dynamic scenes requires accurately capturing diverse material properties and modeling complex object interactions grounded in physical principles. However, existing methods are constrained to basic material types with limited predictable parameters, making them insufficient to represent the complexity of real-world materials. We introduce PhysFlow, a novel approach that leverages multi-modal foundation models and video diffusion to achieve enhanced 4D dynamic scene simulation. Our method utilizes multi-modal models to identify material types and initialize material parameters through image queries, while simultaneously inferring 3D Gaussian splats for detailed scene representation. We further refine these material parameters using video diffusion with a differentiable Material Point Method (MPM) and optical flow guidance rather than render loss or Score Distillation Sampling (SDS) loss. This integrated framework enables accurate prediction and realistic simulation of dynamic interactions in real-world scenarios, advancing both accuracy and flexibility in physics-based simulations.
真实场景的动态模拟需要准确捕捉各种材料属性,并基于物理原理对复杂的物体交互进行建模。然而,现有方法局限于具有有限可预测参数的基本材料类型,无法代表真实世界材料的复杂性。我们引入了PhysFlow,这是一种利用多模态基础模型和视频扩散来实现增强的4D动态场景模拟的新方法。我们的方法利用多模态模型通过图像查询来识别材料类型并初始化材料参数,同时推断3D高斯点集以进行详细场景表示。我们进一步使用可微分的物质点法(MPM)和光流指导的视频扩散来优化这些材料参数,而不是使用渲染损失或得分蒸馏采样(SDS)损失。这一综合框架能够准确预测和模拟真实场景中的动态交互,提高了基于物理的模拟的准确性和灵活性。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF CVPR 2025. Homepage: https://zhuomanliu.github.io/PhysFlow/
Summary
物理流(PhysFlow)是一种利用多模态基础模型和视频扩散实现增强型四维动态场景模拟的新方法。它通过图像查询识别材料类型并初始化材料参数,同时推断三维高斯特征点进行详细的场景表示。结合可微分的物质点法(MPM)和光流引导,提高了物理模拟的准确性和灵活性。
Key Takeaways
- 引入PhysFlow方法,利用多模态基础模型和视频扩散增强四维动态场景模拟。
- 通过图像查询识别材料类型,初始化材料参数。
- 推断三维高斯特征点用于详细场景表示。
- 采用可微分的物质点法(MPM)和视频扩散进行材料参数优化。
- 结合光流引导提高动态交互预测的准确性。
- 提高了物理模拟的准确性和灵活性。
点此查看论文截图

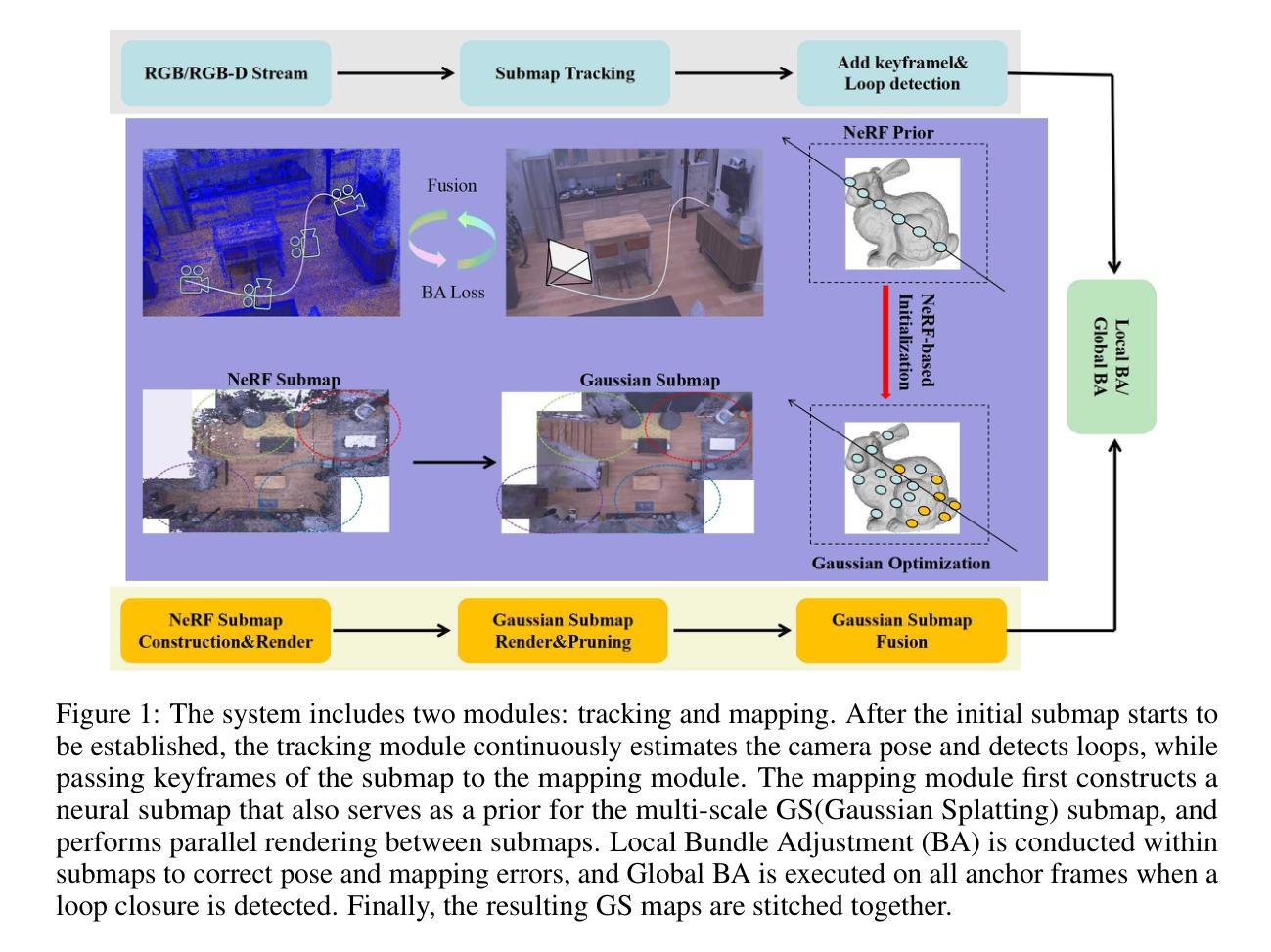
NGM-SLAM: Gaussian Splatting SLAM with Radiance Field Submap
Authors:Jingwei Huang, Mingrui Li, Lei Sun, Aaron Xuxiang Tian, Tianchen Deng, Hongyu Wang
SLAM systems based on Gaussian Splatting have garnered attention due to their capabilities for rapid real-time rendering and high-fidelity mapping. However, current Gaussian Splatting SLAM systems usually struggle with large scene representation and lack effective loop closure detection. To address these issues, we introduce NGM-SLAM, the first 3DGS based SLAM system that utilizes neural radiance field submaps for progressive scene expression, effectively integrating the strengths of neural radiance fields and 3D Gaussian Splatting. We utilize neural radiance field submaps as supervision and achieve high-quality scene expression and online loop closure adjustments through Gaussian rendering of fused submaps. Our results on multiple real-world scenes and large-scale scene datasets demonstrate that our method can achieve accurate hole filling and high-quality scene expression, supporting monocular, stereo, and RGB-D inputs, and achieving state-of-the-art scene reconstruction and tracking performance.
基于高斯平铺的SLAM系统因其快速实时渲染和高保真映射的能力而受到关注。然而,当前的高斯平铺SLAM系统通常在大型场景表示方面存在困难,并且缺乏有效的环路闭合检测。为了解决这些问题,我们引入了NGM-SLAM,这是第一个利用神经辐射场子图进行渐进场景表达的3DGS基于SLAM的系统,有效地结合了神经辐射场和3D高斯平铺的优点。我们利用神经辐射场子图作为监督,并通过融合子图的高斯渲染实现高质量的场景表达和在线环路闭合调整。我们在多个真实场景和大规模场景数据集上的结果证明,我们的方法可以实现精确的空洞填充和高质量的场景表达,支持单目、立体和RGB-D输入,并实现最先进的场景重建和跟踪性能。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF 9pages, 4 figures
Summary
基于高斯融合技术的SLAM系统因其快速实时渲染和高保真映射能力而受到关注,但在大场景表示和环路闭合检测方面存在挑战。为解决这些问题,我们推出了NGM-SLAM,它是首个利用神经辐射场子图进行渐进场景表达的基于3DGS的SLAM系统,有效结合了神经辐射场的优点和3D高斯融合技术。通过高斯渲染融合子图,实现了高质量场景表达和在线环路闭合调整。在多个真实场景和大场景数据集上的结果表明,该方法可实现精确的空缺填充和高质量场景表达,支持单目、立体和RGB-D输入,达到最先进的场景重建和跟踪性能。
Key Takeaways
- 基于高斯融合的SLAM系统受到关注,但存在大场景表示和环路闭合检测的挑战。
- NGM-SLAM是首个结合神经辐射场子图和3DGS技术的SLAM系统。
- 神经辐射场子图作为监督,实现高质量场景表达。
- 通过高斯渲染融合子图,实现在线环路闭合调整。
- NGM-SLAM在多个真实场景和大场景数据集上表现出色。
- 该方法支持单目、立体和RGB-D输入。
点此查看论文截图