⚠️ 以下所有内容总结都来自于 大语言模型的能力,如有错误,仅供参考,谨慎使用
🔴 请注意:千万不要用于严肃的学术场景,只能用于论文阅读前的初筛!
💗 如果您觉得我们的项目对您有帮助 ChatPaperFree ,还请您给我们一些鼓励!⭐️ HuggingFace免费体验
2025-04-26 更新
Beyond Labels: Zero-Shot Diabetic Foot Ulcer Wound Segmentation with Self-attention Diffusion Models and the Potential for Text-Guided Customization
Authors:Abderrachid Hamrani, Daniela Leizaola, Renato Sousa, Jose P. Ponce, Stanley Mathis, David G. Armstrong, Anuradha Godavarty
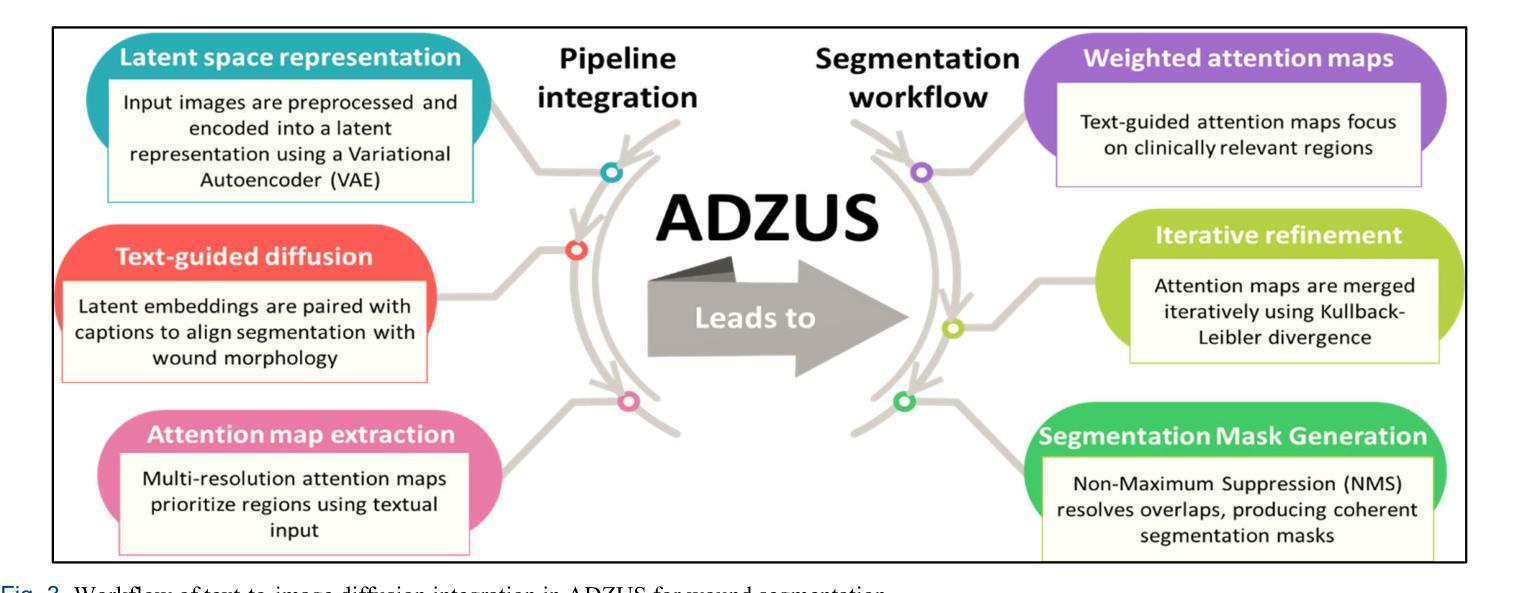
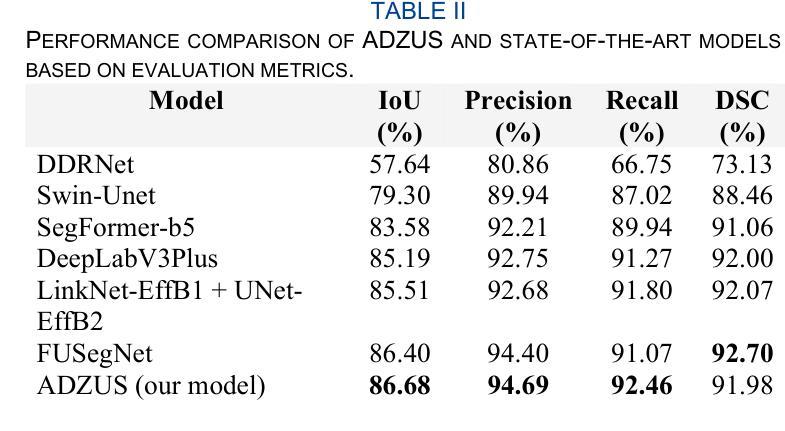
Diabetic foot ulcers (DFUs) pose a significant challenge in healthcare, requiring precise and efficient wound assessment to enhance patient outcomes. This study introduces the Attention Diffusion Zero-shot Unsupervised System (ADZUS), a novel text-guided diffusion model that performs wound segmentation without relying on labeled training data. Unlike conventional deep learning models, which require extensive annotation, ADZUS leverages zero-shot learning to dynamically adapt segmentation based on descriptive prompts, offering enhanced flexibility and adaptability in clinical applications. Experimental evaluations demonstrate that ADZUS surpasses traditional and state-of-the-art segmentation models, achieving an IoU of 86.68% and the highest precision of 94.69% on the chronic wound dataset, outperforming supervised approaches such as FUSegNet. Further validation on a custom-curated DFU dataset reinforces its robustness, with ADZUS achieving a median DSC of 75%, significantly surpassing FUSegNet’s 45%. The model’s text-guided segmentation capability enables real-time customization of segmentation outputs, allowing targeted analysis of wound characteristics based on clinical descriptions. Despite its competitive performance, the computational cost of diffusion-based inference and the need for potential fine-tuning remain areas for future improvement. ADZUS represents a transformative step in wound segmentation, providing a scalable, efficient, and adaptable AI-driven solution for medical imaging.
糖尿病足溃疡(DFUs)在医疗保健中构成重大挑战,需要进行精确高效的伤口评估以提高患者治疗效果。本研究介绍了注意力扩散零样本无监督系统(ADZUS),这是一种新型文本引导扩散模型,可在无需标注训练数据的情况下进行伤口分割。不同于需要大量标注的传统深度学习模型,ADZUS采用零样本学习,根据描述性提示动态适应分割,在临床应用中提供了更高的灵活性和适应性。实验评估表明,ADZUS超越了传统和最先进的分割模型,在慢性伤口数据集上达到86.68%的交并比(IoU)和最高94.69%的精确度,超越了如FUSegNet等监督方法。在自定义的DFU数据集上进一步验证,ADZUS的中位DSC达到75%,显著超越了FUSegNet的45%。该模型的文本引导分割能力能够实时定制分割输出,允许根据临床描述进行有针对性的伤口特征分析。尽管其性能具有竞争力,但扩散推理的计算成本和潜在精细调整的需求仍是未来改进的领域。ADZUS是伤口分割中的一项变革性进步,提供可规模化、高效、适应性强的AI驱动解决方案,用于医学成像。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF 12 pages, 8 figures, journal article
摘要
本研究引入了一种名为Attention Diffusion Zero-shot Unsupervised System(ADZUS)的新型文本引导扩散模型,用于糖尿病足溃疡(DFU)的伤口分割,且无需标注训练数据。ADZUS采用零样本学习方式,可根据描述性提示动态适应分割,提高了在临床应用中的灵活性和适应性。实验评估表明,ADZUS在慢性伤口数据集上的表现超越了传统和最新分割模型,交并比(IoU)达到86.68%,精度最高达94.69%,甚至超越了FUSegNet等监督方法。在定制的DFU数据集上的验证也证明了其稳健性,ADZUS的中位DSC达到75%,远超FUSegNet的45%。该模型的文本引导分割能力可实现分割输出的实时定制,根据临床描述进行有针对性的伤口特性分析。虽然扩散推理的计算成本较高且可能需要进行微调,但ADZUS仍为伤口分割提供了可规模化、高效和适应性强的AI驱动解决方案。
关键见解
- ADZUS是一种新型的文本引导扩散模型,用于糖尿病足溃疡的伤口分割,无需标注训练数据。
- ADZUS采用零样本学习,可动态适应分割,提高了临床应用的灵活性和适应性。
- 实验评估显示,ADZUS在慢性伤口数据集上的表现超越了传统和最新的分割模型。
- ADZUS在定制的DFU数据集上表现出稳健性,中位DSC达到75%。
- ADZUS具备文本引导分割能力,可实现分割输出的实时定制。
- 扩散推理的计算成本较高,可能需要进行微调。
- ADZUS为伤口分割提供了可规模化、高效和适应性强的AI驱动解决方案。
点此查看论文截图

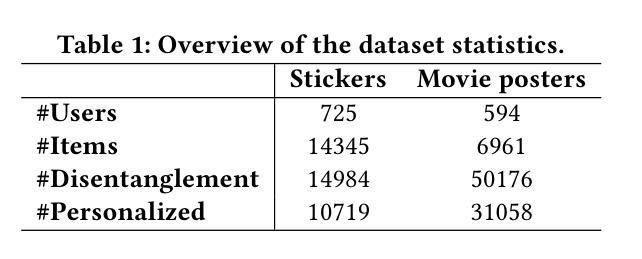
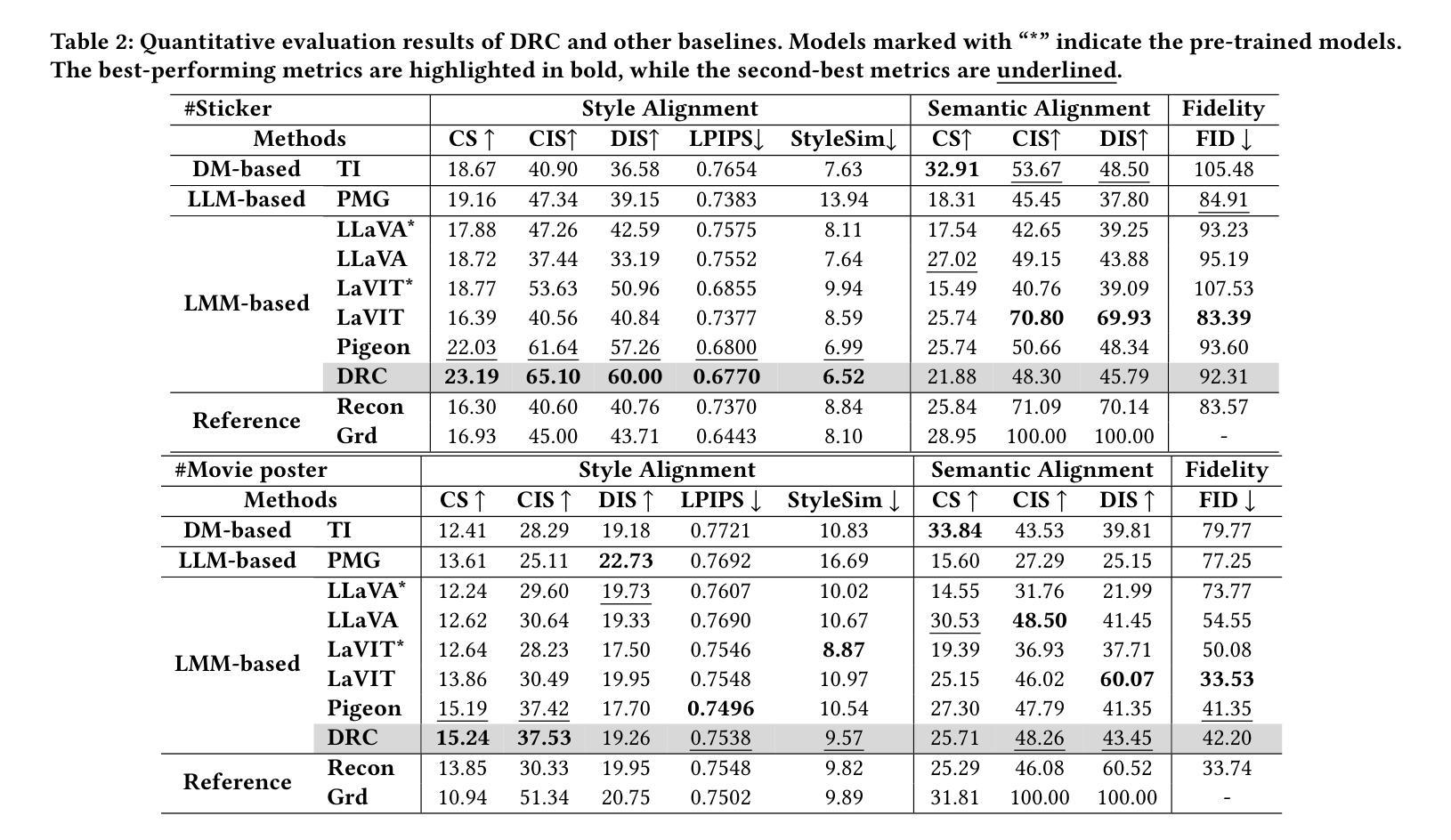
DRC: Enhancing Personalized Image Generation via Disentangled Representation Composition
Authors:Yiyan Xu, Wuqiang Zheng, Wenjie Wang, Fengbin Zhu, Xinting Hu, Yang Zhang, Fuli Feng, Tat-Seng Chua
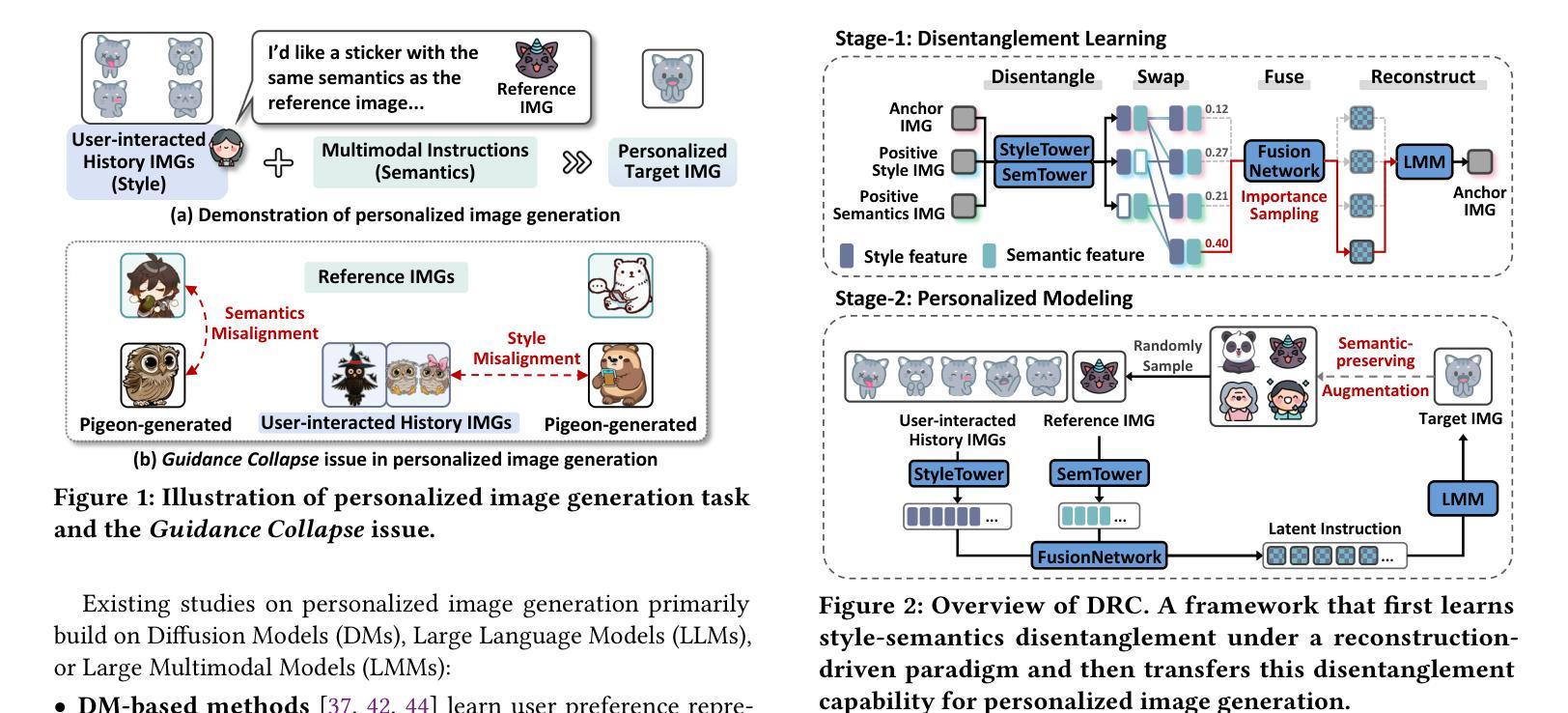
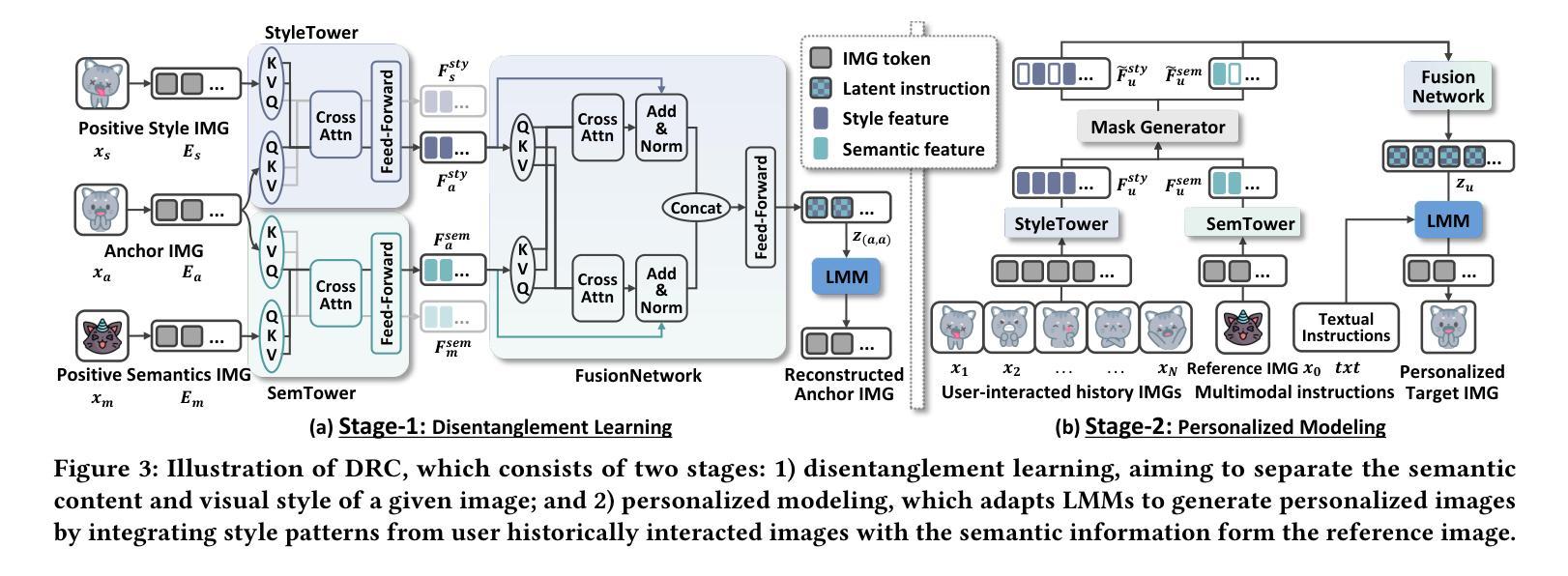
Personalized image generation has emerged as a promising direction in multimodal content creation. It aims to synthesize images tailored to individual style preferences (e.g., color schemes, character appearances, layout) and semantic intentions (e.g., emotion, action, scene contexts) by leveraging user-interacted history images and multimodal instructions. Despite notable progress, existing methods – whether based on diffusion models, large language models, or Large Multimodal Models (LMMs) – struggle to accurately capture and fuse user style preferences and semantic intentions. In particular, the state-of-the-art LMM-based method suffers from the entanglement of visual features, leading to Guidance Collapse, where the generated images fail to preserve user-preferred styles or reflect the specified semantics. To address these limitations, we introduce DRC, a novel personalized image generation framework that enhances LMMs through Disentangled Representation Composition. DRC explicitly extracts user style preferences and semantic intentions from history images and the reference image, respectively, to form user-specific latent instructions that guide image generation within LMMs. Specifically, it involves two critical learning stages: 1) Disentanglement learning, which employs a dual-tower disentangler to explicitly separate style and semantic features, optimized via a reconstruction-driven paradigm with difficulty-aware importance sampling; and 2) Personalized modeling, which applies semantic-preserving augmentations to effectively adapt the disentangled representations for robust personalized generation. Extensive experiments on two benchmarks demonstrate that DRC shows competitive performance while effectively mitigating the guidance collapse issue, underscoring the importance of disentangled representation learning for controllable and effective personalized image generation.
个性化图像生成已成为多媒体内容创建的一个具有前景的方向。它旨在通过利用用户交互的历史图像和多模态指令,合成符合个人风格偏好(如色彩方案、角色外观、布局)和语义意图(如情绪、动作、场景上下文)的图像。尽管取得了显著的进展,但现有方法——无论是基于扩散模型、大型语言模型还是大型多媒体模型(LMM)——在准确捕捉和融合用户风格偏好和语义意图方面都存在困难。特别是最先进的基于LMM的方法受到视觉特征纠缠的影响,导致出现“指导崩溃”的问题,生成的图像无法保持用户偏好的风格或反映指定的语义。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
个性化图像生成是一个充满前景的多模态内容创建方向。它旨在通过利用用户交互的历史图像和多模态指令,合成符合个人风格偏好和语义意图的图像。尽管已有显著进展,但现有方法,无论是基于扩散模型、大型语言模型还是大型多模态模型(LMMs),在准确捕捉和融合用户风格偏好和语义意图方面仍存在困难。针对当前先进LMMs的缺陷,我们引入了DRC框架,通过解耦表示组合增强LMMs。DRC从用户历史图像中提取用户风格偏好和语义意图,形成用户特定的潜在指令,在LMMs内部指导图像生成。实验证明,DRC在竞争性能的同时有效缓解了指导崩溃问题,凸显了解耦表示学习对于可控、高效个性化图像生成的重要性。
Key Takeaways
- 个人化图像生成已成为多模态内容创建的一个前景方向,旨在根据用户的风格偏好和语义意图合成图像。
- 当前方法(基于扩散模型、大型语言模型或大型多模态模型)在捕捉和融合用户风格偏好和语义意图方面存在困难。
- 引入DRC框架以增强大型多模态模型(LMMs),通过解耦表示组合解决现有问题。
- DRC从用户历史图像中提取用户风格偏好和语义意图,形成特定的潜在指令来指导图像生成。
- DRC包含两个关键学习阶段:解耦学习和个性化建模。
- 解耦学习阶段采用双塔分离器来明确区分风格和语义特征,通过重建驱动方法和难度感知重要性采样进行优化。
- 实验证明,DRC在竞争性能的同时有效缓解了指导崩溃问题,凸显解耦表示学习的重要性。
点此查看论文截图

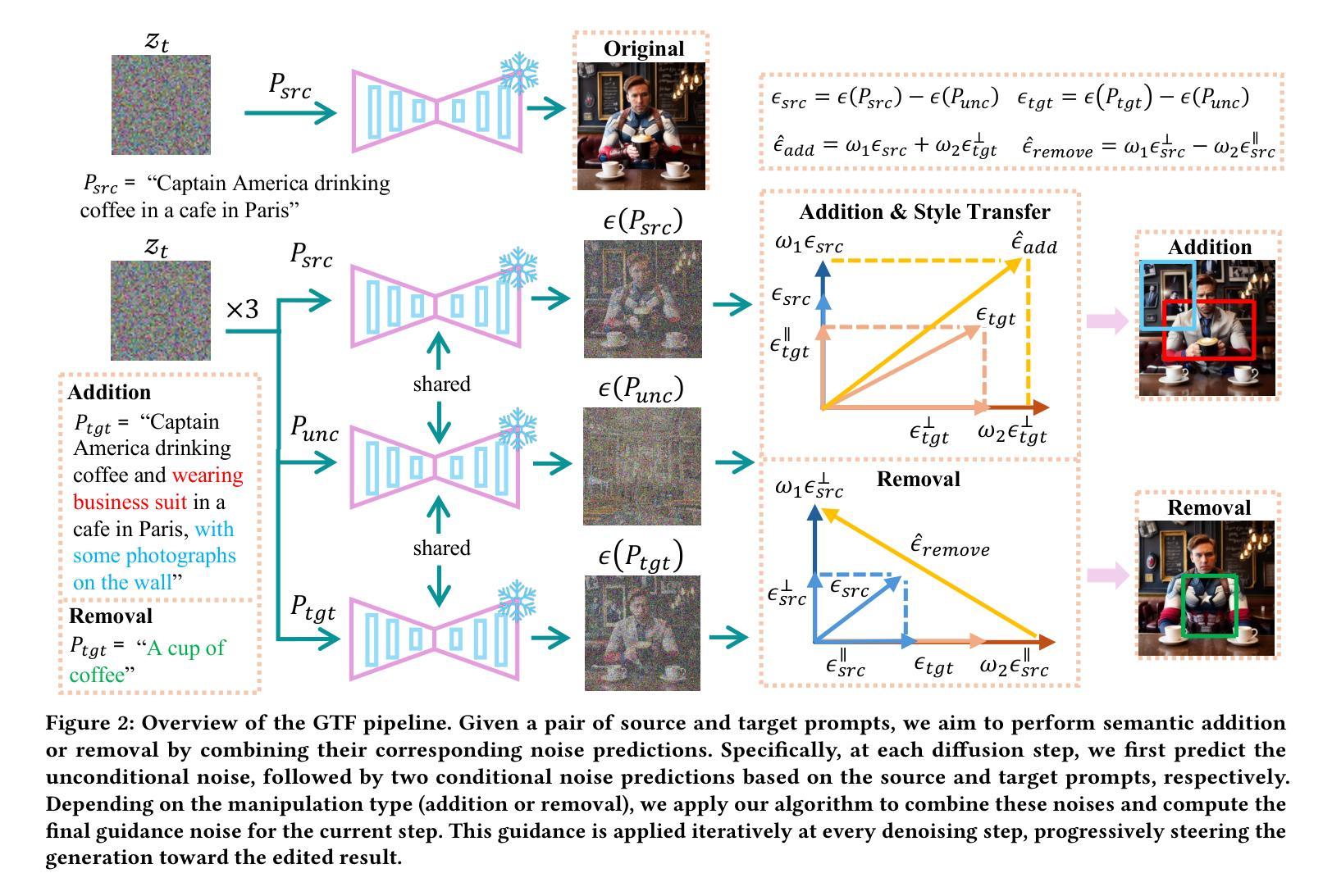
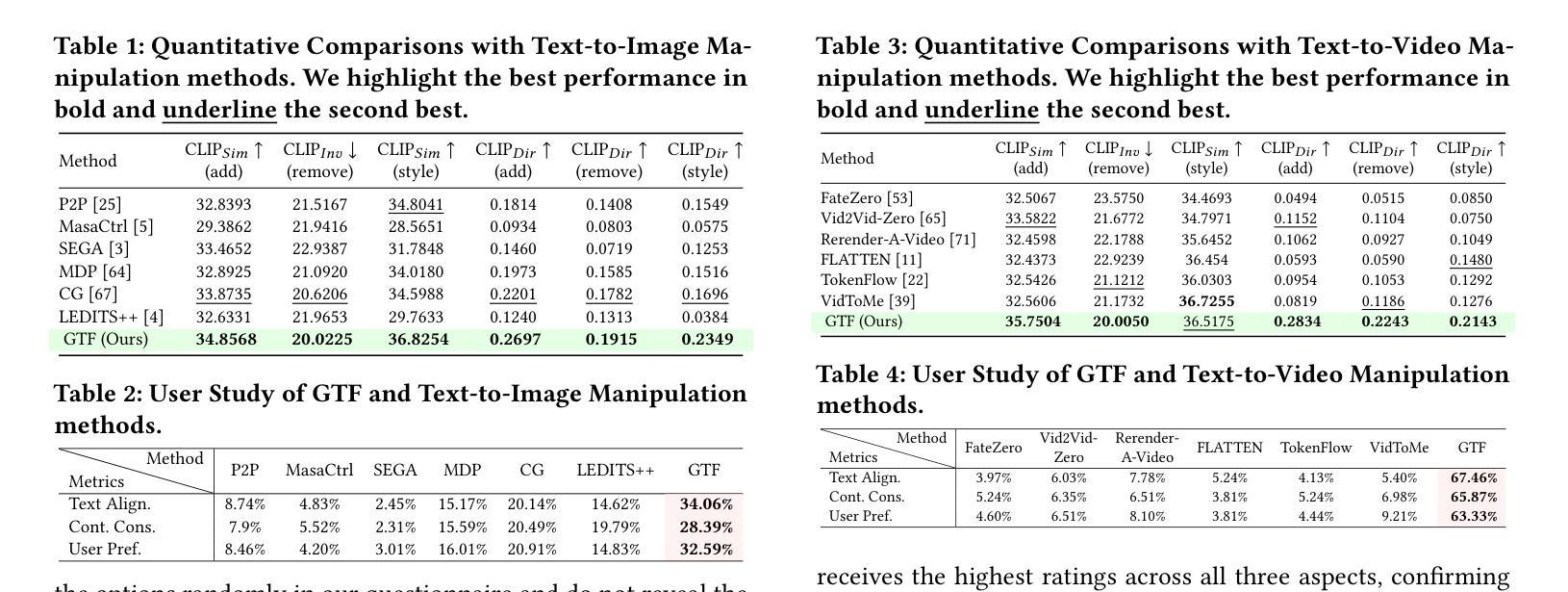
Towards Generalized and Training-Free Text-Guided Semantic Manipulation
Authors:Yu Hong, Xiao Cai, Pengpeng Zeng, Shuai Zhang, Jingkuan Song, Lianli Gao, Heng Tao Shen
Text-guided semantic manipulation refers to semantically editing an image generated from a source prompt to match a target prompt, enabling the desired semantic changes (e.g., addition, removal, and style transfer) while preserving irrelevant contents. With the powerful generative capabilities of the diffusion model, the task has shown the potential to generate high-fidelity visual content. Nevertheless, existing methods either typically require time-consuming fine-tuning (inefficient), fail to accomplish multiple semantic manipulations (poorly extensible), and/or lack support for different modality tasks (limited generalizability). Upon further investigation, we find that the geometric properties of noises in the diffusion model are strongly correlated with the semantic changes. Motivated by this, we propose a novel $\textit{GTF}$ for text-guided semantic manipulation, which has the following attractive capabilities: 1) $\textbf{Generalized}$: our $\textit{GTF}$ supports multiple semantic manipulations (e.g., addition, removal, and style transfer) and can be seamlessly integrated into all diffusion-based methods (i.e., Plug-and-play) across different modalities (i.e., modality-agnostic); and 2) $\textbf{Training-free}$: $\textit{GTF}$ produces high-fidelity results via simply controlling the geometric relationship between noises without tuning or optimization. Our extensive experiments demonstrate the efficacy of our approach, highlighting its potential to advance the state-of-the-art in semantics manipulation.
文本引导语义操纵是指对由源提示生成的图像进行语义编辑,使其与目标提示相匹配,从而实现期望的语义变化(例如添加、删除和风格转换),同时保留无关内容。扩散模型的强大生成能力使该任务有潜力生成高保真视觉内容。然而,现有方法通常需要耗时的微调(效率低下)、无法完成多次语义操纵(扩展性差),并且/或缺乏对不同模态任务的支持(泛化能力有限)。通过进一步调查,我们发现扩散模型中的噪声几何属性与语义变化具有很强的相关性。受此启发,我们提出了一种用于文本引导语义操纵的新型GTF方法,它具有以下吸引人的能力:1)通用性:我们的GTF支持多种语义操纵(例如添加、删除和风格转换),可以无缝集成到所有基于扩散的方法中(即插即用),适用于不同模态(即模态无关);2)无训练:GTF通过简单控制噪声之间的几何关系即可产生高保真结果,无需调整或优化。我们的大量实验证明了我们的方法的有效性,突出了其在语义操纵方面领先技术的潜力。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
文本引导语义操纵指的是对由源提示生成的图像进行语义编辑,使其匹配目标提示,从而实现期望的语义变化(例如添加、删除和风格转换),同时保留无关内容。借助扩散模型的强大生成能力,该任务有潜力生成高保真视觉内容。然而,现有方法通常需要耗时且效率低下的微调,难以完成多种语义操纵,且缺乏对不同模态任务的支持。我们发现扩散模型中的噪声几何属性与语义变化之间存在强烈相关性。因此,我们提出了一种新型的GTF文本引导语义操纵方法,具有支持多种语义操纵、可无缝集成到所有扩散基方法、无需训练即可产生高保真结果等吸引力人的能力。
Key Takeaways
- 文本引导语义操纵能够编辑图像以匹配目标提示,实现语义变化,同时保留无关内容。
- 扩散模型具有强大的生成能力,在语义操纵任务中表现出潜力。
- 现有方法存在效率低下、难以完成多种语义操纵、缺乏对不同模态任务支持的问题。
- 噪声的几何属性与语义变化之间存在强烈相关性。
- 提出的GTF方法支持多种语义操纵,并能无缝集成到所有扩散基方法中。
- GTF方法无需训练即可产生高保真结果。
点此查看论文截图


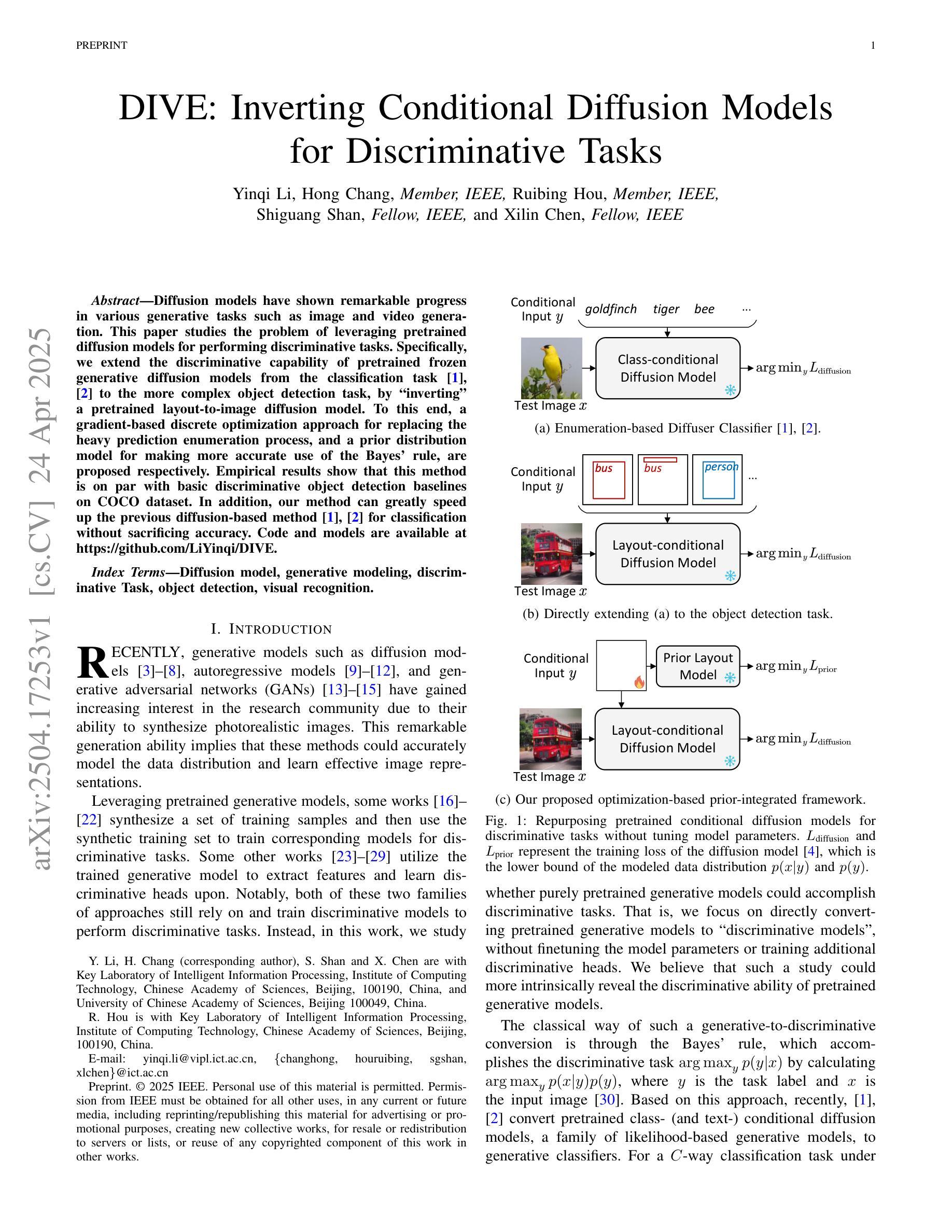
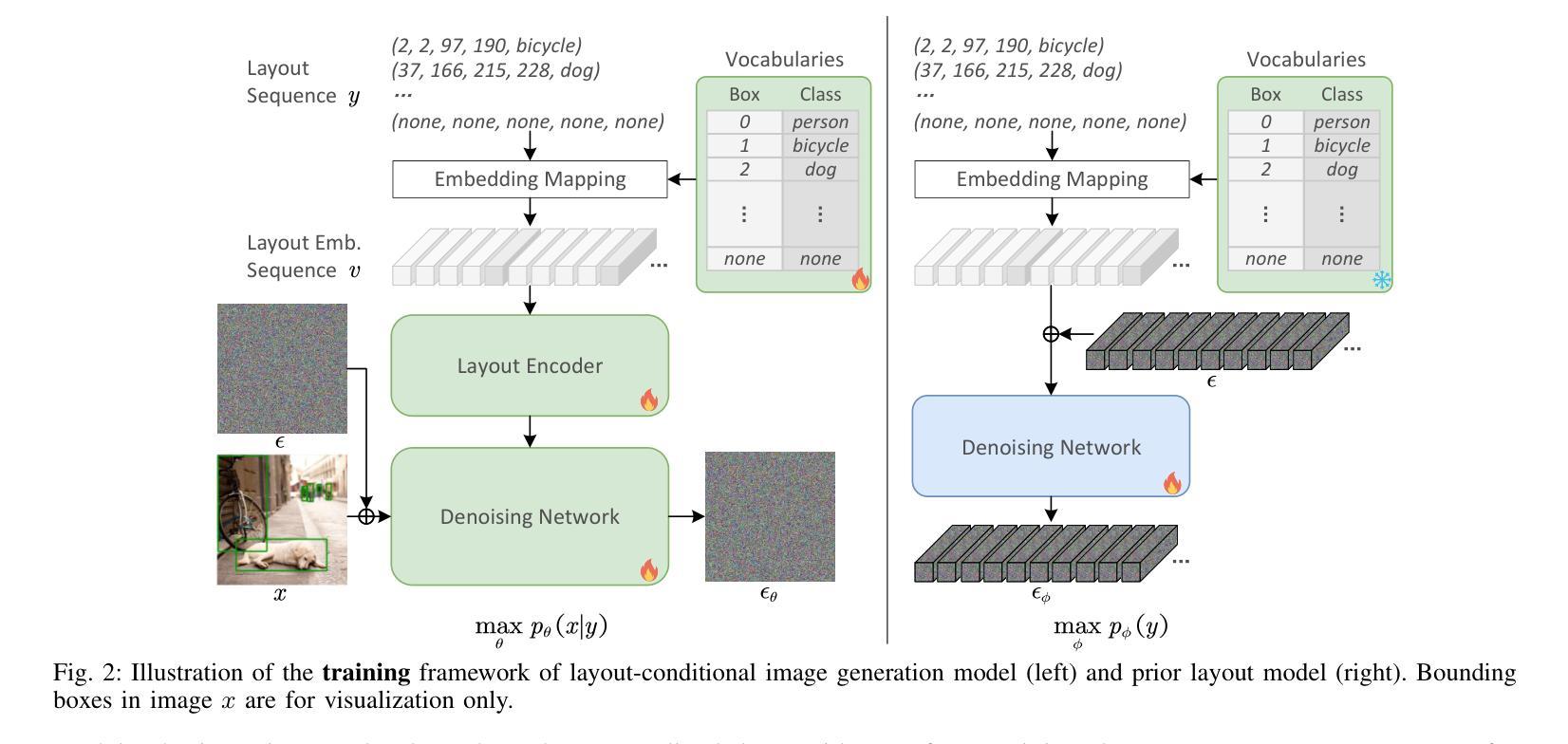
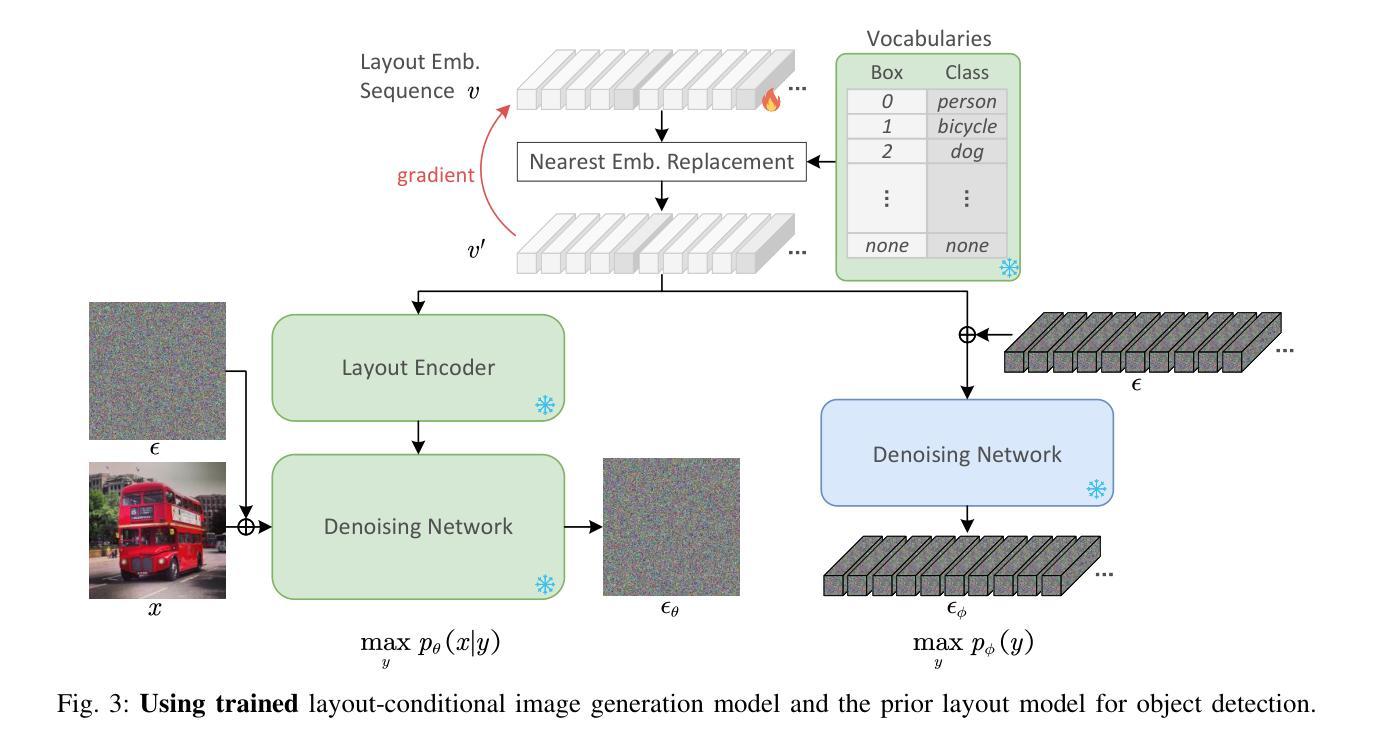
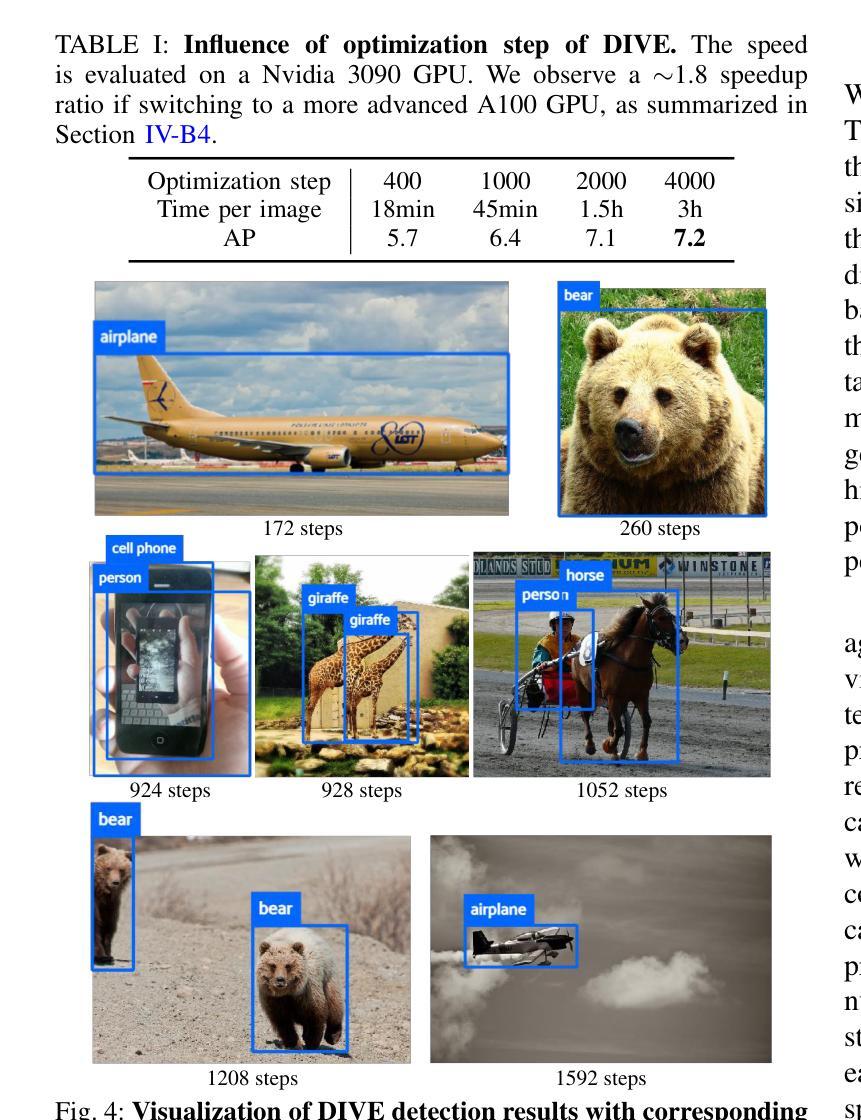
DIVE: Inverting Conditional Diffusion Models for Discriminative Tasks
Authors:Yinqi Li, Hong Chang, Ruibing Hou, Shiguang Shan, Xilin Chen
Diffusion models have shown remarkable progress in various generative tasks such as image and video generation. This paper studies the problem of leveraging pretrained diffusion models for performing discriminative tasks. Specifically, we extend the discriminative capability of pretrained frozen generative diffusion models from the classification task to the more complex object detection task, by “inverting” a pretrained layout-to-image diffusion model. To this end, a gradient-based discrete optimization approach for replacing the heavy prediction enumeration process, and a prior distribution model for making more accurate use of the Bayes’ rule, are proposed respectively. Empirical results show that this method is on par with basic discriminative object detection baselines on COCO dataset. In addition, our method can greatly speed up the previous diffusion-based method for classification without sacrificing accuracy. Code and models are available at https://github.com/LiYinqi/DIVE .
扩散模型在图像和视频生成等各种生成任务中取得了显著的进步。本文研究了利用预训练的扩散模型执行判别任务的问题。具体来说,我们通过“反转”预训练的布局到图像的扩散模型,将预冻结生成扩散模型的判别能力从分类任务扩展到更复杂的对象检测任务。为此,分别提出了基于梯度的离散优化方法,以替代繁重的预测枚举过程,以及先验分布模型,以更准确地应用贝叶斯法则。经验结果表明,该方法在COCO数据集上的表现与基本的判别对象检测基线相当。此外,我们的方法可以大大提高之前用于分类的扩散方法的速度,而不会牺牲准确性。代码和模型可在https://github.com/LiYinqi/DIVE中找到。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF Accepted by IEEE Transactions on Multimedia
Summary
本文研究了如何利用预训练的扩散模型执行判别任务,特别是将预训练的冷冻生成扩散模型的判别能力从分类任务扩展到更复杂的对象检测任务。通过采用梯度基础上的离散优化方法和先验分布模型,实现了对预训练布局到图像扩散模型的“反转”。在COCO数据集上,该方法与基本的判别对象检测基线表现相当,并且能显著加快之前的扩散分类方法的速度,同时不损失准确性。
Key Takeaways
- 本文探索了预训练扩散模型在判别任务中的应用,特别是将分类任务的判别能力扩展到对象检测任务。
- 通过“反转”预训练的布局到图像扩散模型,实现了这一扩展。
- 采用了梯度基础上的离散优化方法,以替代繁重的预测枚举过程。
- 引入了先验分布模型,更准确地应用贝叶斯规则。
- 在COCO数据集上,该方法与判别对象检测的基线方法表现相当。
- 与之前的扩散分类方法相比,该方法显著加速了过程,同时保持了准确性。
点此查看论文截图
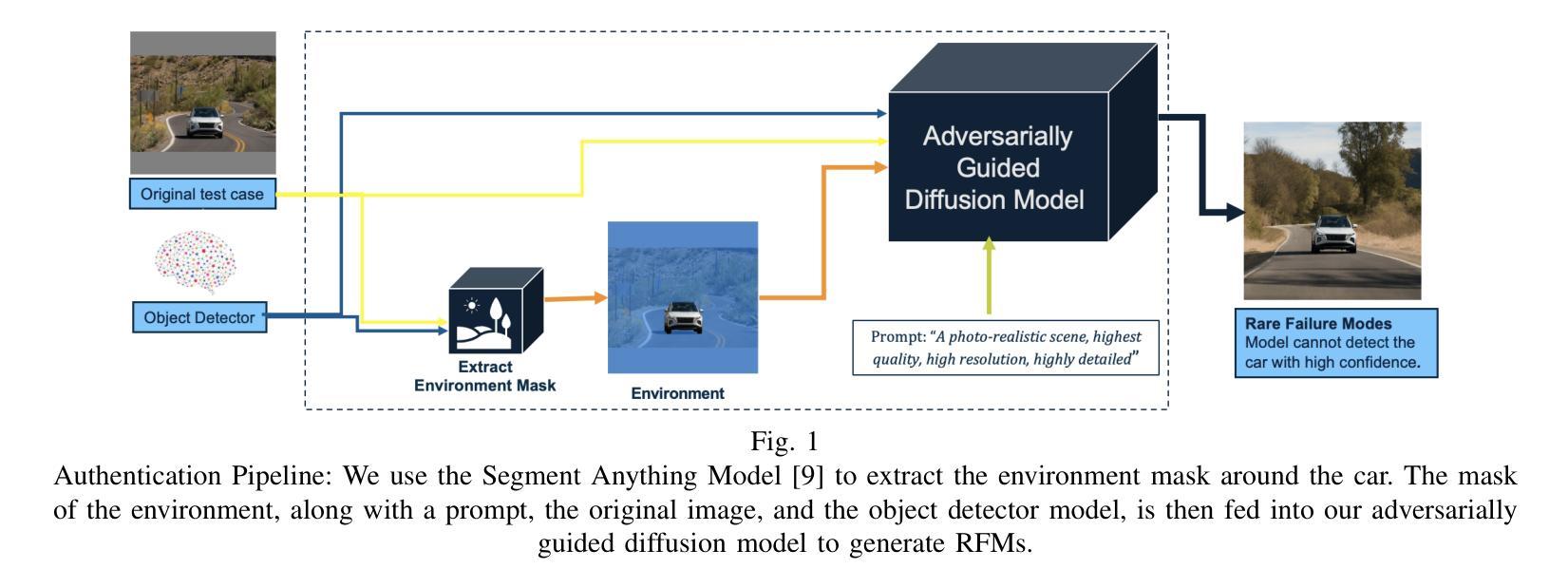
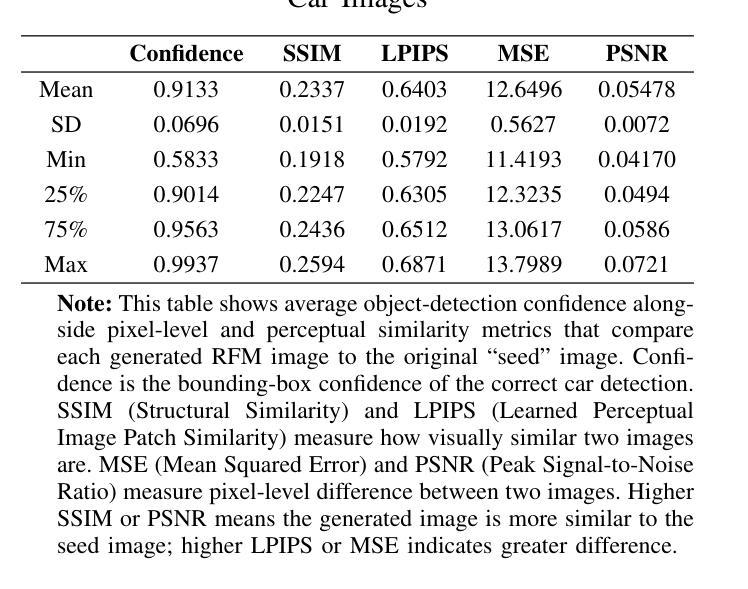
AUTHENTICATION: Identifying Rare Failure Modes in Autonomous Vehicle Perception Systems using Adversarially Guided Diffusion Models
Authors:Mohammad Zarei, Melanie A Jutras, Eliana Evans, Mike Tan, Omid Aaramoon
Autonomous Vehicles (AVs) rely on artificial intelligence (AI) to accurately detect objects and interpret their surroundings. However, even when trained using millions of miles of real-world data, AVs are often unable to detect rare failure modes (RFMs). The problem of RFMs is commonly referred to as the “long-tail challenge”, due to the distribution of data including many instances that are very rarely seen. In this paper, we present a novel approach that utilizes advanced generative and explainable AI techniques to aid in understanding RFMs. Our methods can be used to enhance the robustness and reliability of AVs when combined with both downstream model training and testing. We extract segmentation masks for objects of interest (e.g., cars) and invert them to create environmental masks. These masks, combined with carefully crafted text prompts, are fed into a custom diffusion model. We leverage the Stable Diffusion inpainting model guided by adversarial noise optimization to generate images containing diverse environments designed to evade object detection models and expose vulnerabilities in AI systems. Finally, we produce natural language descriptions of the generated RFMs that can guide developers and policymakers to improve the safety and reliability of AV systems.
自动驾驶车辆(AVs)依赖于人工智能(AI)来准确检测物体并解读周围环境。然而,即使使用数百万英里的真实世界数据进行训练,AVs通常也无法检测到罕见的失败模式(RFMs)。由于数据分布包含许多很少见到的实例,RFM的问题通常被称为“长尾挑战”。在本文中,我们提出了一种利用先进的生成式和可解释的人工智能技术来帮助理解RFMs的新方法。当与下游模型训练和测试相结合时,我们的方法可用于提高AVs的鲁棒性和可靠性。我们提取感兴趣对象(例如汽车)的分割掩膜并将其反转以创建环境掩膜。这些掩膜与精心设计的文本提示相结合,输入到自定义的扩散模型中。我们利用由对抗性噪声优化引导的Stable Diffusion补全模型,生成包含各种环境的图像,这些图像旨在避开物体检测模型并暴露AI系统的漏洞。最后,我们生成对生成的RFMs的自然语言描述,可以指导开发者和政策制定者提高AV系统的安全性和可靠性。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF 8 pages, 10 figures. Accepted to IEEE Conference on Artificial Intelligence (CAI), 2025
Summary
本文提出一种利用先进的生成式和可解释的人工智能技术来理解自动驾驶车辆的罕见故障模式(RFMs)的新方法。通过结合下游模型训练和测试,增强自动驾驶车辆的稳健性和可靠性。通过提取感兴趣对象的分割掩膜并反转创建环境掩膜,结合精心设计的文本提示,输入到自定义的扩散模型中。利用对抗性噪声优化引导的Stable Diffusion inpainting模型生成包含多样环境的图像,以避开物体检测模型并暴露AI系统的漏洞。最后,生成对RFMs的自然语言描述,可指导开发者和政策制定者提高自动驾驶系统的安全性和可靠性。
Key Takeaways
- 自动驾驶车辆(AVs)依赖人工智能(AI)来检测物体和解读周围环境,但面临罕见故障模式(RFMs)的挑战。
- RFMs问题被称为“长尾挑战”,因为数据分布包含许多很少见到的实例。
- 本文提出一种利用生成式和可解释的人工智能技术理解RFMs的新方法。
- 通过提取感兴趣对象的分割掩膜并创建环境掩膜,结合文本提示输入到自定义扩散模型中。
- 利用Stable Diffusion inpainting模型生成多样环境图像,以检测物体并暴露AI系统的漏洞。
- 生成的自然语言描述可以帮助开发者和政策制定者了解RFMs,提高自动驾驶系统的安全性和可靠性。
点此查看论文截图




Physics-guided and fabrication-aware inverse design of photonic devices using diffusion models
Authors:Dongjin Seo, Soobin Um, Sangbin Lee, Jong Chul Ye, Haejun Chung
Designing free-form photonic devices is fundamentally challenging due to the vast number of possible geometries and the complex requirements of fabrication constraints. Traditional inverse-design approaches–whether driven by human intuition, global optimization, or adjoint-based gradient methods–often involve intricate binarization and filtering steps, while recent deep learning strategies demand prohibitively large numbers of simulations (10^5 to 10^6). To overcome these limitations, we present AdjointDiffusion, a physics-guided framework that integrates adjoint sensitivity gradients into the sampling process of diffusion models. AdjointDiffusion begins by training a diffusion network on a synthetic, fabrication-aware dataset of binary masks. During inference, we compute the adjoint gradient of a candidate structure and inject this physics-based guidance at each denoising step, steering the generative process toward high figure-of-merit (FoM) solutions without additional post-processing. We demonstrate our method on two canonical photonic design problems–a bent waveguide and a CMOS image sensor color router–and show that our method consistently outperforms state-of-the-art nonlinear optimizers (such as MMA and SLSQP) in both efficiency and manufacturability, while using orders of magnitude fewer simulations (approximately 2 x 10^2) than pure deep learning approaches (approximately 10^5 to 10^6). By eliminating complex binarization schedules and minimizing simulation overhead, AdjointDiffusion offers a streamlined, simulation-efficient, and fabrication-aware pipeline for next-generation photonic device design. Our open-source implementation is available at https://github.com/dongjin-seo2020/AdjointDiffusion.
设计自由形式的光子器件具有根本挑战性,原因在于存在大量可能的几何结构以及复杂的制造约束要求。传统的逆向设计方法——无论是基于人类直觉、全局优化还是基于伴随的梯度方法——通常涉及复杂的二值化和过滤步骤,而最近的深度学习策略则需要进行大量模拟(从10万到一百万)。为了克服这些局限性,我们提出了AdjointDiffusion,这是一个物理引导框架,它将伴随敏感性梯度整合到扩散模型的采样过程中。AdjointDiffusion首先在一个合成且了解制造过程的二进制掩膜数据集上训练扩散网络。在推理过程中,我们计算候选结构的伴随梯度,并在每个去噪步骤中注入基于物理的指导,引导生成过程朝着高品质因数(FoM)解决方案发展,无需额外的后处理。我们在两个典型的光子设计问题上展示了我们的方法——弯曲波导和CMOS图像传感器颜色路由器——并证明我们的方法在效率和制造性方面始终优于最先进的非线性优化器(如MMA和SLSQP),同时使用的模拟次数比纯深度学习方法少几个数量级(大约为2 x 10² vs. 大约介于一百万以上)。通过消除复杂的二值化时间表并最大限度地减少模拟开销,AdjointDiffusion为下一代光子器件设计提供了简化、模拟高效且了解制造过程的管道。我们的开源实现可在https://github.com/dongjin-seo2020/AdjointDiffusion找到。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF 25 pages, 7 Figures
Summary
光子器件设计面临巨大的几何可能性和复杂的制造约束挑战。传统逆向设计方法和最新的深度学习策略都存在局限性。AdjointDiffusion框架结合逆向敏感性梯度与扩散模型的采样过程,以物理指导生成设计。该框架在合成、具有制造意识的二进制掩膜数据集上训练扩散网络,并在推理过程中计算候选结构的逆向梯度,在每个去噪步骤中注入物理指导,引导生成过程向高图梅尔性能解决方案发展。该方法在光子设计问题上表现优异,使用较少的模拟次数,提高了效率和制造性。
Key Takeaways
- 光子器件设计面临巨大的几何和制造约束挑战。
- 传统逆向设计方法和深度学习策略都有局限性。
- AdjointDiffusion框架通过结合逆向敏感性梯度和扩散模型的采样过程来进行物理指导生成设计。
- 该框架使用合成、具有制造意识的二进制掩膜数据集进行训练。
- 在推理过程中,计算候选结构的逆向梯度并注入物理指导。
- AdjointDiffusion在光子设计问题上表现优异,提高了效率和制造性。
点此查看论文截图

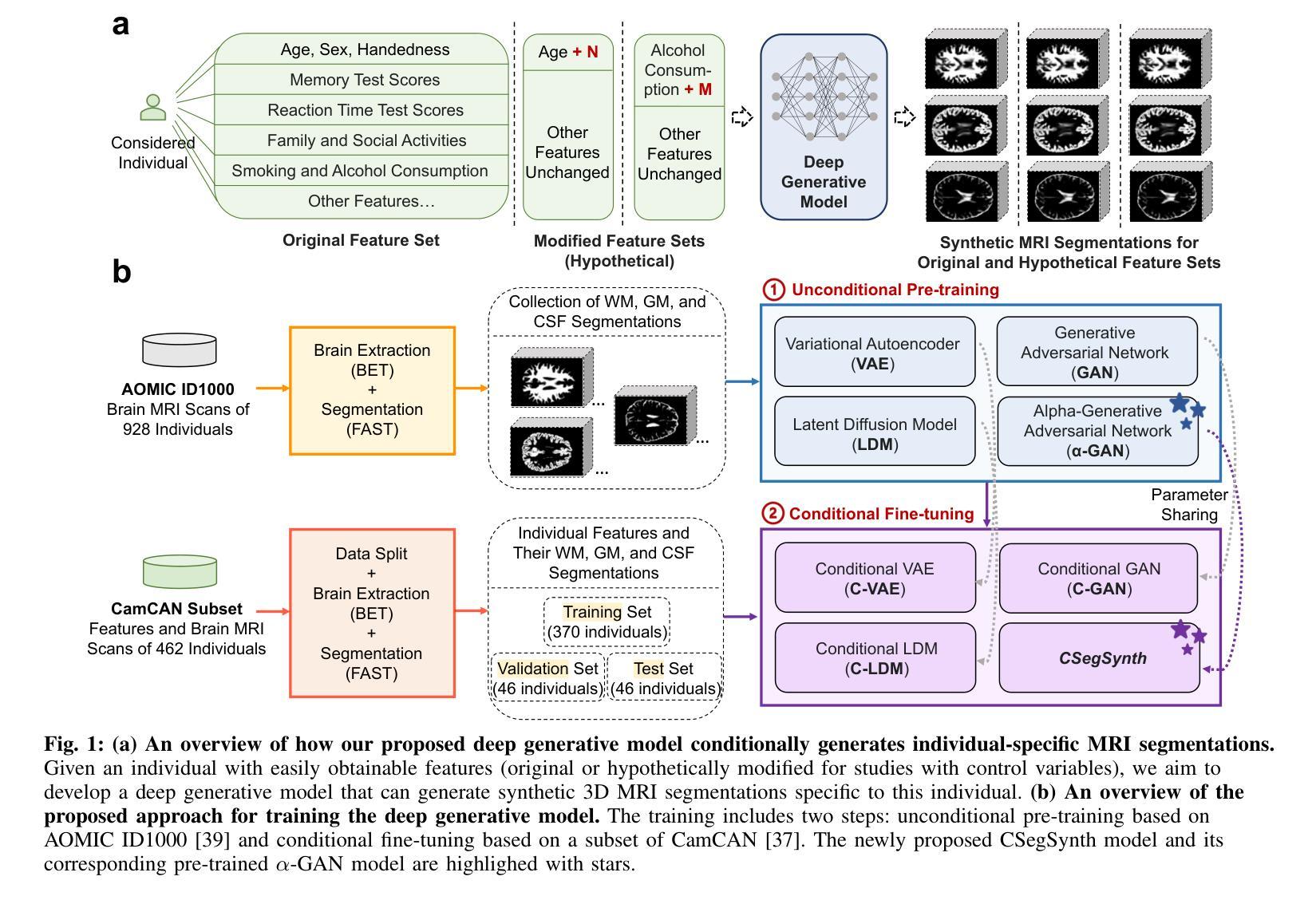
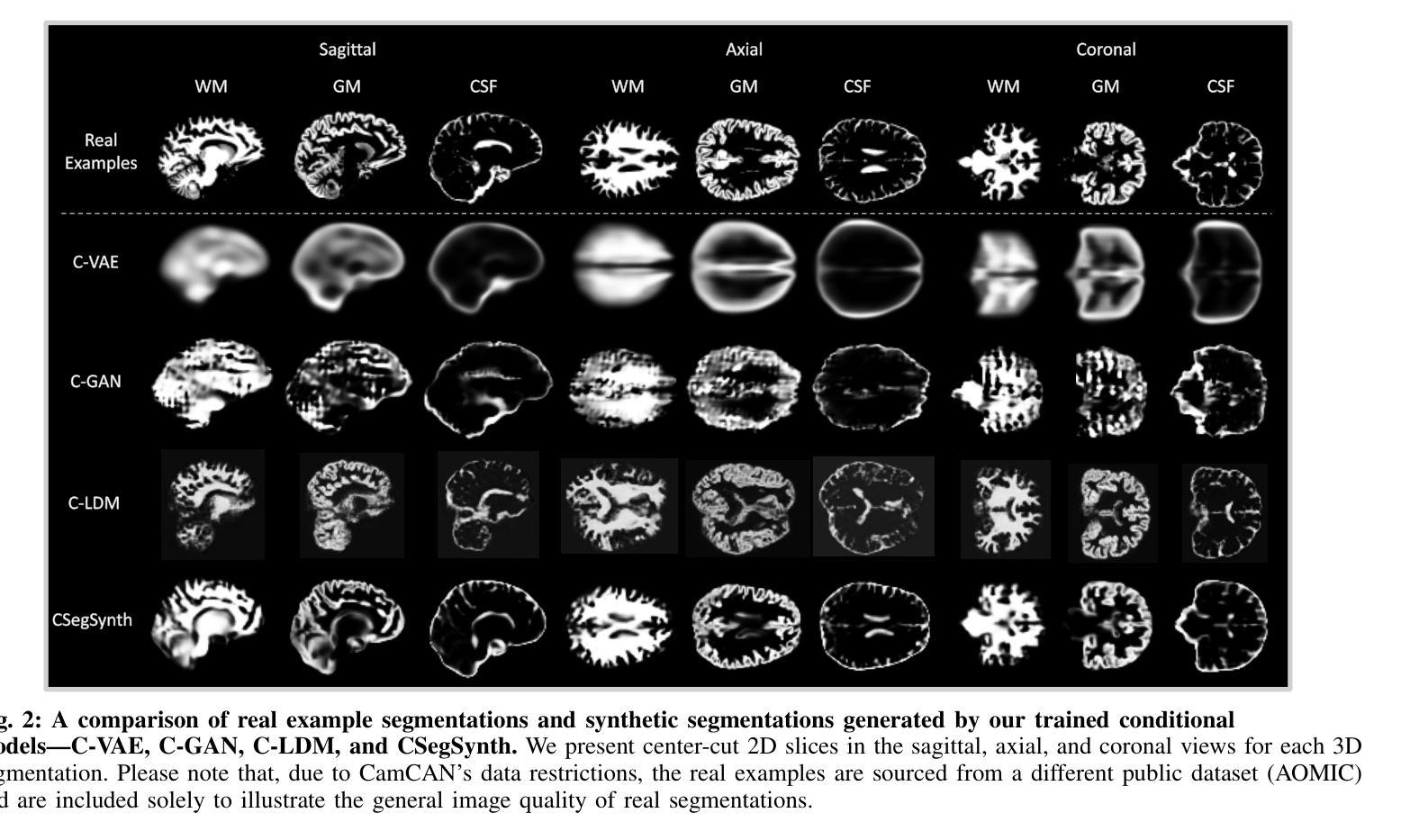
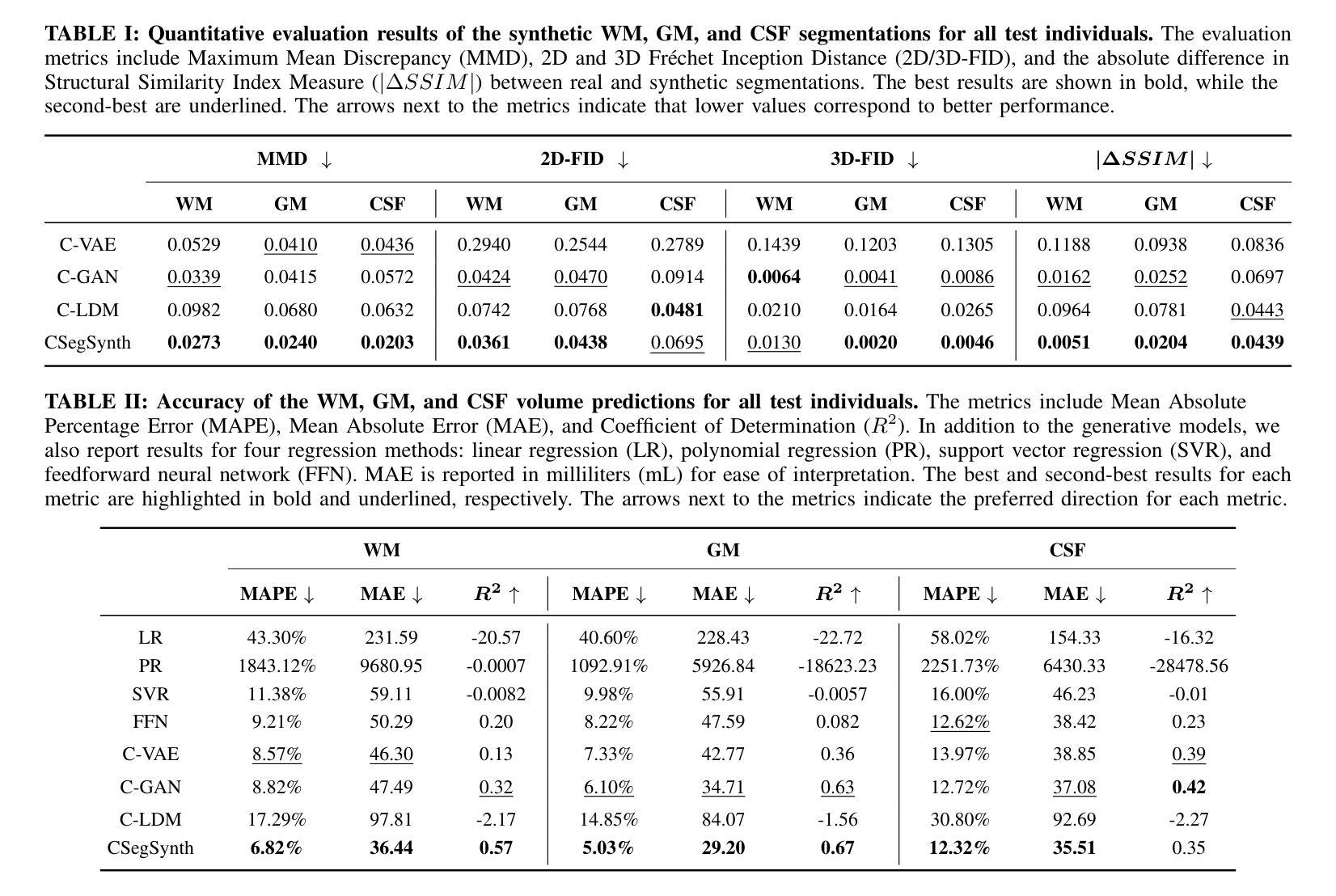
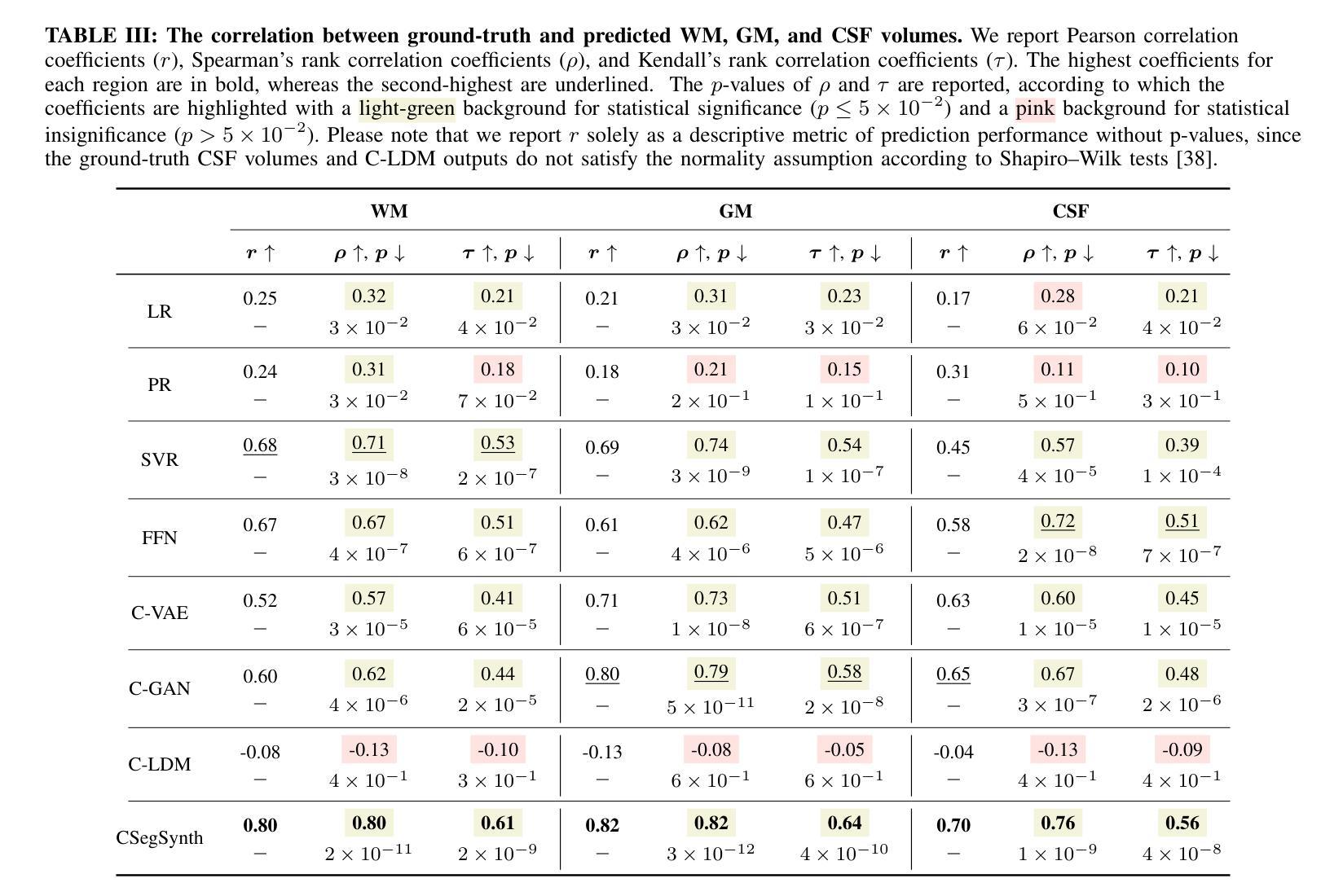
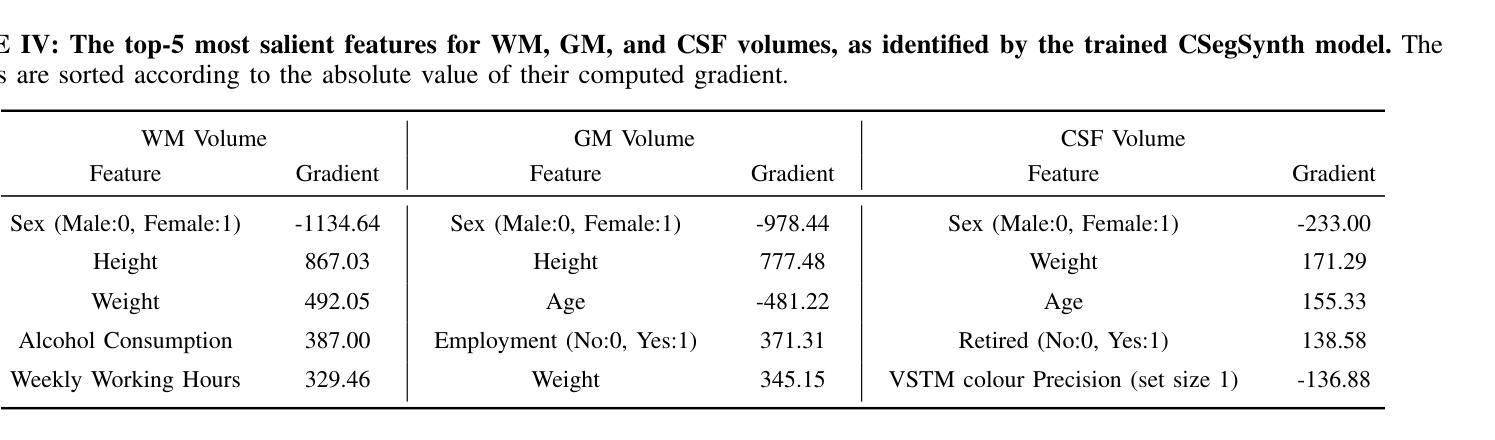
Deep Generative Model-Based Generation of Synthetic Individual-Specific Brain MRI Segmentations
Authors:Ruijie Wang, Luca Rossetto, Susan Mérillat, Christina Röcke, Mike Martin, Abraham Bernstein
To the best of our knowledge, all existing methods that can generate synthetic brain magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) scans for a specific individual require detailed structural or volumetric information about the individual’s brain. However, such brain information is often scarce, expensive, and difficult to obtain. In this paper, we propose the first approach capable of generating synthetic brain MRI segmentations – specifically, 3D white matter (WM), gray matter (GM), and cerebrospinal fluid (CSF) segmentations – for individuals using their easily obtainable and often readily available demographic, interview, and cognitive test information. Our approach features a novel deep generative model, CSegSynth, which outperforms existing prominent generative models, including conditional variational autoencoder (C-VAE), conditional generative adversarial network (C-GAN), and conditional latent diffusion model (C-LDM). We demonstrate the high quality of our synthetic segmentations through extensive evaluations. Also, in assessing the effectiveness of the individual-specific generation, we achieve superior volume prediction, with mean absolute errors of only 36.44mL, 29.20mL, and 35.51mL between the ground-truth WM, GM, and CSF volumes of test individuals and those volumes predicted based on generated individual-specific segmentations, respectively.
据我们所知,所有目前能够针对特定个人生成合成的大脑磁共振成像(MRI)扫描方法都需要关于个人大脑的详细结构或体积信息。然而,此类大脑信息通常稀缺、昂贵且难以获取。在本文中,我们提出了第一种能够生成合成大脑MRI分割的方法——具体来说,是生成三维白质(WM)、灰质(GM)和脑脊液(CSF)的分割——使用个人易于获取且经常容易获得的人口统计、面试和认知测试信息。我们的方法采用了一种新型深度生成模型CSegSynth,它在现有突出的生成模型中表现出色,包括条件变分自动编码器(C-VAE)、条件生成对抗网络(C-GAN)和条件潜在扩散模型(C-LDM)。我们通过广泛评估证明了合成分割的高质量。同时,在评估特定个人的生成效果时,我们实现了出色的体积预测,测试个体真实WM、GM和CSF体积与基于生成个体特定分割所预测的相应体积之间的平均绝对误差分别为仅36.44mL、29.20mL和35.51mL。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
本文提出了一种全新的方法,通过个体易于获取且经常可得的诸如人口统计信息、访谈和认知测试信息,生成合成的大脑MRI扫描图像分割结果。该方法采用创新的深度生成模型CSegSynth,相较于现有的主流生成模型如条件变分自编码器(C-VAE)、条件生成对抗网络(C-GAN)和条件潜在扩散模型(C-LDM)有更好的表现。通过广泛的评估和体积预测,验证了该方法的优越性和准确性。
Key Takeaways
- 现有生成大脑MRI扫描图像的方法需要详细的个体结构或体积信息,这些信息通常稀缺、昂贵且难以获取。
- 本文提出了使用个体易于获取的信息(如人口统计信息、访谈和认知测试信息)生成合成大脑MRI分割结果的方法。
- 采用创新的深度生成模型CSegSynth,能生成特定个体的3D白质、灰质和脑脊液分割图像。
- CSegSynth模型在性能上超越了现有的主流生成模型,如条件变分自编码器、条件生成对抗网络和条件潜在扩散模型。
- 本文通过广泛的评估验证了合成分割图像的高质量。
- 在评估个体特定生成的有效性方面,该方法实现了优异的体积预测,与真实MRI体积相比,预测误差非常小。
点此查看论文截图
Improved implicit diffusion model with knowledge distillation to estimate the spatial distribution density of carbon stock in remote sensing imagery
Authors:Zhenyu Yu, Jinnian Wang, Mohd Yamani Idna Idris
The forest serves as the most significant terrestrial carbon stock mechanism, effectively reducing atmospheric CO2 concentrations and mitigating climate change. Remote sensing provides high data accuracy and enables large-scale observations. Optical images facilitate long-term monitoring, which is crucial for future carbon stock estimation studies. This study focuses on Huize County, Qujing City, Yunnan Province, China, utilizing GF-1 WFV satellite imagery. The KD-VGG and KD-UNet modules were introduced for initial feature extraction, and the improved implicit diffusion model (IIDM) was proposed. The results showed: (1) The VGG module improved initial feature extraction, improving accuracy, and reducing inference time with optimized model parameters. (2) The Cross-attention + MLPs module enabled effective feature fusion, establishing critical relationships between global and local features, achieving high-accuracy estimation. (3) The IIDM model, a novel contribution, demonstrated the highest estimation accuracy with an RMSE of 12.17%, significantly improving by 41.69% to 42.33% compared to the regression model. In carbon stock estimation, the generative model excelled in extracting deeper features, significantly outperforming other models, demonstrating the feasibility of AI-generated content in quantitative remote sensing. The 16-meter resolution estimates provide a robust basis for tailoring forest carbon sink regulations, enhancing regional carbon stock management.
森林作为最重要的陆地碳储存机制,有效地降低了大气中二氧化碳的浓度,缓解了气候变化。遥感技术提供了高精度的数据,并实现了大规模观测。光学图像有助于长期监测,对未来碳储量估算研究至关重要。本研究以位于中国云南省曲靖市会泽县为例,利用GF-1卫星WFV影像数据,引入了KD-VGG和KD-UNet模块进行初步特征提取,并提出了改进型隐式扩散模型(IIDM)。研究结果表明:(1)VGG模块改进了初始特征提取,提高了精度,并优化了模型参数,减少了推理时间。(2)Cross-attention+MLPs模块实现了有效的特征融合,建立了全局和局部特征之间的关键关系,实现了高精度估算。(3)新型贡献的IIDM模型表现出最高的估算精度,均方根误差为12.17%,与回归模型相比,改进了41.69%至42.33%。在碳储量估算方面,生成模型在提取深层特征方面表现出色,显著优于其他模型,证明了人工智能生成内容在定量遥感中的可行性。16米分辨率的估计为定制森林碳汇法规、增强区域碳储量管理提供了坚实的基础。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
该研究利用光学图像和遥感技术,对云南省曲靖市会泽县的森林碳储量进行了估算。研究引入了KD-VGG和KD-UNet模块进行初步特征提取,并提出了改进型隐式扩散模型(IIDM)。结果显示,该模型在森林碳储量估算中具有较高准确性,为制定森林碳汇政策提供了坚实基础。
Key Takeaways
- 森林是减少大气中二氧化碳浓度和缓解气候变化的重要机制。
- 遥感技术为大规模观察提供了高度准确的数据。
- 光学图像对于长期森林碳储量监测至关重要。
- KD-VGG和KD-UNet模块的引入改进了初步特征提取,提高了估算精度并缩短了推理时间。
- Cross-attention + MLPs模块实现了有效的特征融合,建立了全局和局部特征之间的关键关系。
- 改进型隐式扩散模型(IIDM)在森林碳储量估算中表现出最高精度。
点此查看论文截图

Convergence of Diffusion Models Under the Manifold Hypothesis in High-Dimensions
Authors:Iskander Azangulov, George Deligiannidis, Judith Rousseau
Denoising Diffusion Probabilistic Models (DDPM) are powerful state-of-the-art methods used to generate synthetic data from high-dimensional data distributions and are widely used for image, audio, and video generation as well as many more applications in science and beyond. The \textit{manifold hypothesis} states that high-dimensional data often lie on lower-dimensional manifolds within the ambient space, and is widely believed to hold in provided examples. While recent results have provided invaluable insight into how diffusion models adapt to the manifold hypothesis, they do not capture the great empirical success of these models, making this a very fruitful research direction. In this work, we study DDPMs under the manifold hypothesis and prove that they achieve rates independent of the ambient dimension in terms of score learning. In terms of sampling complexity, we obtain rates independent of the ambient dimension w.r.t. the Kullback-Leibler divergence, and $O(\sqrt{D})$ w.r.t. the Wasserstein distance. We do this by developing a new framework connecting diffusion models to the well-studied theory of extrema of Gaussian Processes.
去噪扩散概率模型(DDPM)是目前用于从高维数据分布生成合成数据的最先进方法之一,广泛用于图像、音频和视频生成以及科学和其他更多领域。流形假设指出,高维数据通常位于环境空间中的低维流形上,并且在提供的示例中普遍认为存在。虽然最近的研究结果提供了关于扩散模型如何适应流形假设的宝贵见解,但它们并没有捕捉到这些模型的巨大经验成就,这使得这成为一个非常有成果的研究方向。在本研究中,我们在流形假设下研究DDPM,并证明其在得分学习方面实现了独立于环境维度的速率。在采样复杂度方面,我们获得了独立于环境维度的速率,关于Kullback-Leibler散度以及关于Wasserstein距离的$O(\sqrt{D})$。我们通过开发将扩散模型与广受欢迎的Gaussian Processes极值理论相联系的新框架来实现这一点。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
基于去噪扩散概率模型(DDPM)的强大能力,它已成为生成高维数据分布合成数据的最先进方法之一,广泛应用于图像、音频和视频生成以及科学和其他领域。本研究在流形假设下研究DDPM,证明其在评分学习方面实现了与环境维度无关的比率。在采样复杂性方面,我们获得了与环境维度无关的关于Kullback-Leibler散度的比率,以及关于Wasserstein距离的O(√D)比率。我们通过开发将扩散模型与高斯过程极值理论研究相连的新框架来实现这一点。
Key Takeaways
- DDPM是生成高维数据分布合成数据的先进方法之一,广泛应用于多个领域。
- 流形假设指出高维数据经常位于环境空间中的低维流形上,DDPM在此假设下进行了研究。
- DDPM在评分学习方面实现了与环境维度无关的比率。
- 在采样复杂性方面,DDPM获得了与环境维度无关的关于Kullback-Leibler散度的比率。
- 关于Wasserstein距离,DDPM的比率是O(√D)。
- 本研究通过开发新的框架将扩散模型与高斯过程极值理论相连。
点此查看论文截图

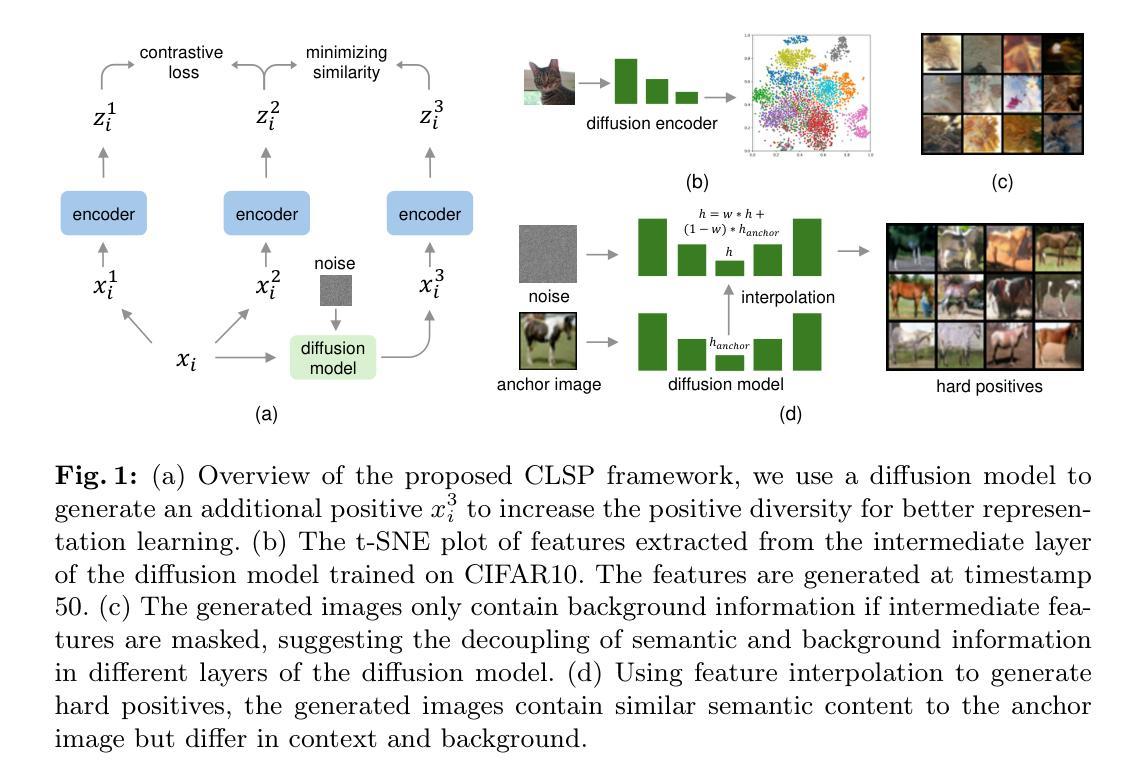
Contrastive Learning with Synthetic Positives
Authors:Dewen Zeng, Yawen Wu, Xinrong Hu, Xiaowei Xu, Yiyu Shi
Contrastive learning with the nearest neighbor has proved to be one of the most efficient self-supervised learning (SSL) techniques by utilizing the similarity of multiple instances within the same class. However, its efficacy is constrained as the nearest neighbor algorithm primarily identifies “easy” positive pairs, where the representations are already closely located in the embedding space. In this paper, we introduce a novel approach called Contrastive Learning with Synthetic Positives (CLSP) that utilizes synthetic images, generated by an unconditional diffusion model, as the additional positives to help the model learn from diverse positives. Through feature interpolation in the diffusion model sampling process, we generate images with distinct backgrounds yet similar semantic content to the anchor image. These images are considered “hard” positives for the anchor image, and when included as supplementary positives in the contrastive loss, they contribute to a performance improvement of over 2% and 1% in linear evaluation compared to the previous NNCLR and All4One methods across multiple benchmark datasets such as CIFAR10, achieving state-of-the-art methods. On transfer learning benchmarks, CLSP outperforms existing SSL frameworks on 6 out of 8 downstream datasets. We believe CLSP establishes a valuable baseline for future SSL studies incorporating synthetic data in the training process.
对比学习结合最近邻已被证明是一种非常有效的自监督学习(SSL)技术,它利用同一类别内多个实例的相似性。然而,其效果受到限制,因为最近邻算法主要识别的是“容易”的正对,这些正对的表示在嵌入空间中已经位于相近位置。在本文中,我们介绍了一种称为合成阳性对比学习(CLSP)的新方法,它利用无条件扩散模型生成的合成图像作为额外的正样本,帮助模型从多样化的正样本中学习。在扩散模型采样过程中的特征插值中,我们生成了具有不同背景但语义内容与锚图像相似的图像。这些图像被认为是锚图像的“硬”正样本,当它们作为对比损失中的附加正样本时,与之前的NNCLR和All4One方法相比,在CIFAR10等多个基准数据集上实现了超过2%和1%的线性评估性能提升,达到了最先进的水平。在迁移学习基准测试中,CLSP在8个下游数据集中的6个上超越了现有的SSL框架。我们相信CLSP为未来的SSL研究在训练过程中融入合成数据建立了有价值的基准线。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF 8 pages, conference
Summary
对比学习通过最近邻方法在自我监督学习中展现了出色的效率,其主要利用同一类别实例间的相似性。然而,由于最近邻算法主要识别“容易”的正样本对,其有效性受到限制。本文提出了一种名为“对比学习与合成正样本(CLSP)”的新方法,利用由无条件扩散模型生成的合成图像作为额外的正样本,帮助模型从多样化的正样本中学习。通过扩散模型采样过程中的特征插值,我们生成了具有不同背景但语义内容与锚图像相似的图像。这些图像被视为锚图像的“硬”正样本,并作为对比损失中的补充正样本包含在内,从而提高了性能。相较于先前的NNCLR和All4One方法,CLSP在多个基准数据集(如CIFAR10)上的线性评估性能提高了超过2%和1%,并且在迁移学习基准测试中,CLSP在六个下游数据集中的表现优于现有SSL框架。我们相信CLSP为未来的自我监督学习中融入合成数据的研究建立了有价值的基准。
Key Takeaways
- 对比学习通过最近邻方法是一种有效的自我监督学习方法,但受限于识别“容易”正样本的能力。
- 本文提出CLSP方法,利用合成图像作为额外的正样本,以增强模型的泛化能力。
- 通过扩散模型的特征插值生成合成图像,这些图像具有不同的背景但相似的语义内容。
- 合成图像被视为“硬”正样本,有助于模型在对比学习中更有效地学习。
- CLSP在多个基准数据集上的性能超过之前的NNCLR和All4One方法。
- 在迁移学习测试中,CLSP在多个下游数据集上的表现优于现有的SSL框架。
点此查看论文截图

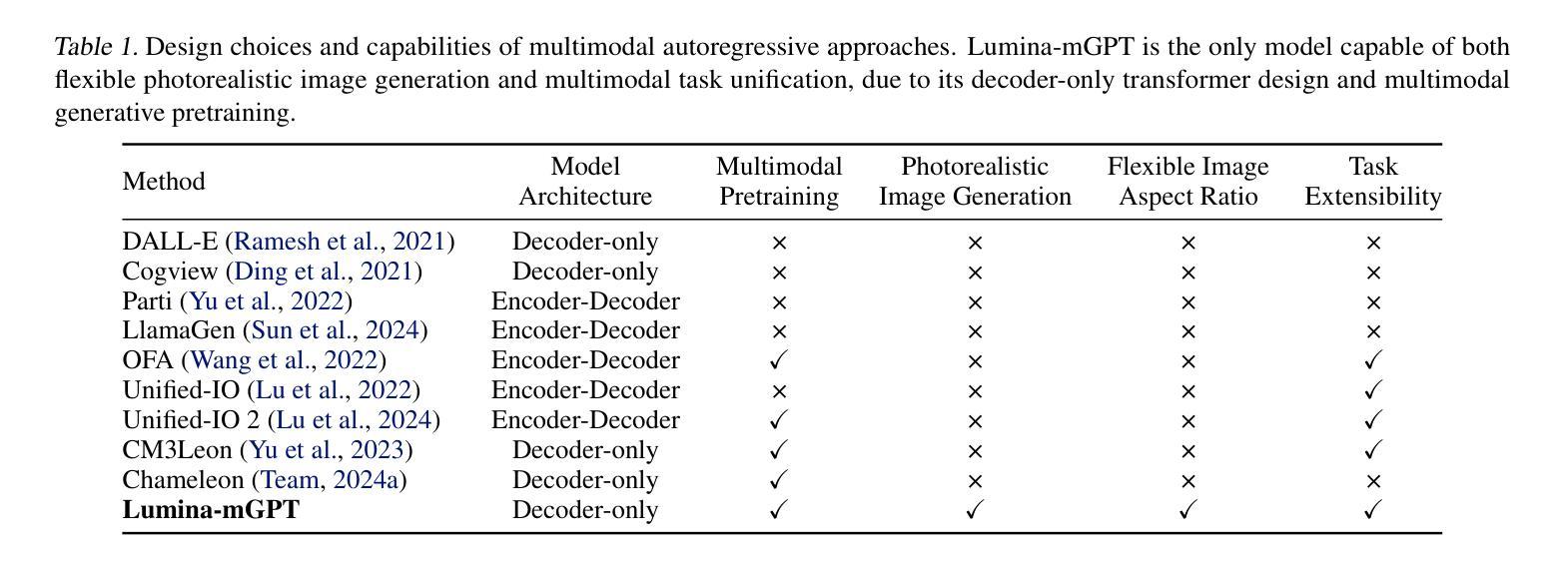
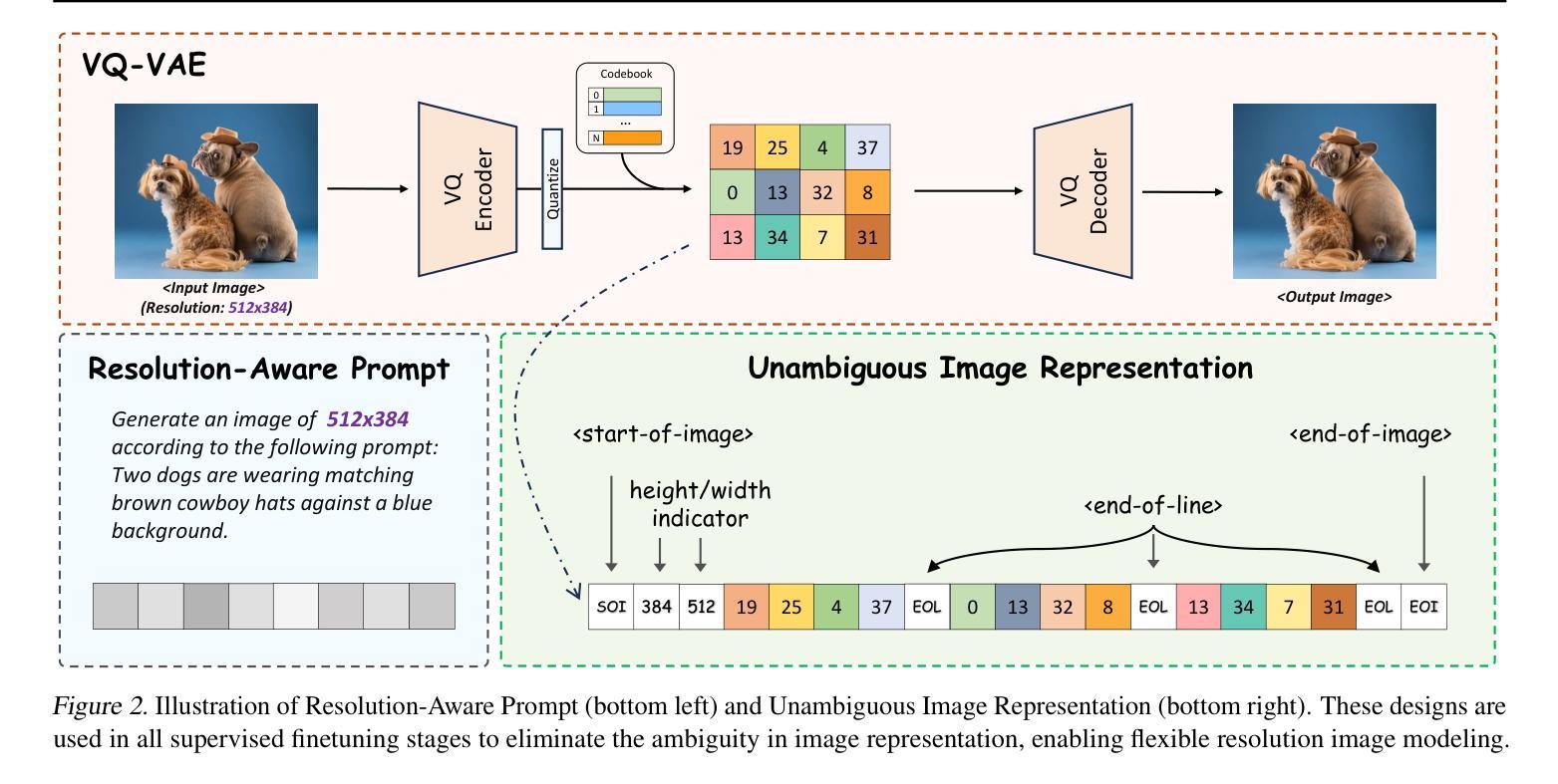
Lumina-mGPT: Illuminate Flexible Photorealistic Text-to-Image Generation with Multimodal Generative Pretraining
Authors:Dongyang Liu, Shitian Zhao, Le Zhuo, Weifeng Lin, Yi Xin, Xinyue Li, Qi Qin, Yu Qiao, Hongsheng Li, Peng Gao
We present Lumina-mGPT, a family of multimodal autoregressive models capable of various vision and language tasks, particularly excelling in generating flexible photorealistic images from text descriptions. By initializing from multimodal Generative PreTraining (mGPT), we demonstrate that decoder-only Autoregressive (AR) model can achieve image generation performance comparable to modern diffusion models with high efficiency through Flexible Progressive Supervised Fine-tuning (FP-SFT). Equipped with our proposed Unambiguous image Representation (UniRep), Lumina-mGPT can flexibly generate high-quality images of varying aspect ratios. Building on the strong image generation capabilities, we further explore Ominiponent Supervised Fine-tuning (Omni-SFT), an initial attempt to elevate Lumina-mGPT into a unified multi-modal generalist. The resulting model demonstrates versatile multimodal capabilities, including visual generation tasks like text-to-image/multiview generation and controllable generation, visual recognition tasks like segmentation and depth estimation, and vision-language tasks like multi-turn visual question answering, showing the rosy potential of the technical direction. Codes and checkpoints are available at https://github.com/Alpha-VLLM/Lumina-mGPT.
我们推出了Lumina-mGPT,这是一系列多模态自回归模型,能够执行各种视觉和语言任务,特别是在根据文本描述生成灵活的光栅图像方面表现出色。通过采用多模态生成预训练(mGPT)进行初始化,我们证明了解码器仅有的自回归(AR)模型可以通过灵活的渐进式监督微调(FP-SFT)实现与现代扩散模型相当的高效图像生成性能。配备了我们提出的明确图像表示(UniRep),Lumina-mGPT可以灵活地生成各种纵横比的高质量图像。在强大的图像生成能力的基础上,我们进一步探索了全能监督微调(Omni-SFT),这是首次尝试将Lumina-mGPT提升为统一的多模态通才。结果证明该模型具有多功能的多模态能力,包括视觉生成任务(如文本到图像/多视图生成和可控生成)、视觉识别任务(如分割和深度估计)以及视觉语言任务(如多轮视觉问答),展示了该技术方向的广阔潜力。相关代码和检查点可访问https://github.com/Alpha-VLLM/Lumina-mGPT获取。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF Code available at: https://github.com/Alpha-VLLM/Lumina-mGPT
Summary
Lumina-mGPT是一个多模态自回归模型家族,擅长根据文本描述生成灵活逼真的图像。通过多模态生成预训练(mGPT)初始化,并借助灵活渐进监督微调(FP-SFT)和高效率的无歧义图像表示(UniRep),Lumina-mGPT能够灵活生成高质量、不同比例尺的图像。该模型还能执行多种视觉和语言任务,包括文本到图像/多视图生成、可控生成、分割、深度估计和多轮视觉问答等。相关代码和检查点已发布在GitHub上。
Key Takeaways
- Lumina-mGPT是一个多模态自回归模型,能处理多种视觉和语言任务。
- 模型能从文本描述中生成灵活的逼真图像。
- 通过多模态生成预训练(mGPT)初始化,实现了高效的图像生成性能。
- 借助灵活渐进监督微调(FP-SFT),模型的性能与现代扩散模型相当。
- 无歧义图像表示(UniRep)使模型能够生成高质量、不同比例尺的图像。
- 模型具备多种视觉生成任务能力,如文本到图像生成、可控生成等。
点此查看论文截图