⚠️ 以下所有内容总结都来自于 大语言模型的能力,如有错误,仅供参考,谨慎使用
🔴 请注意:千万不要用于严肃的学术场景,只能用于论文阅读前的初筛!
💗 如果您觉得我们的项目对您有帮助 ChatPaperFree ,还请您给我们一些鼓励!⭐️ HuggingFace免费体验
2025-04-26 更新
L3: DIMM-PIM Integrated Architecture and Coordination for Scalable Long-Context LLM Inference
Authors:Qingyuan Liu, Liyan Chen, Yanning Yang, Haocheng Wang, Dong Du, Zhigang Mao, Naifeng Jing, Yubin Xia, Haibo Chen
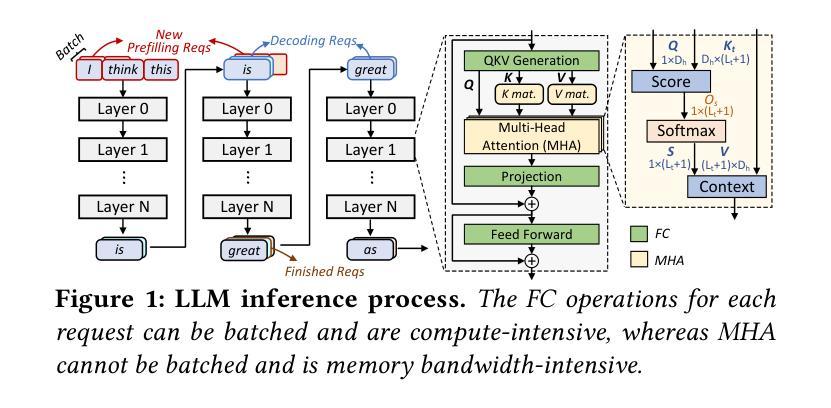
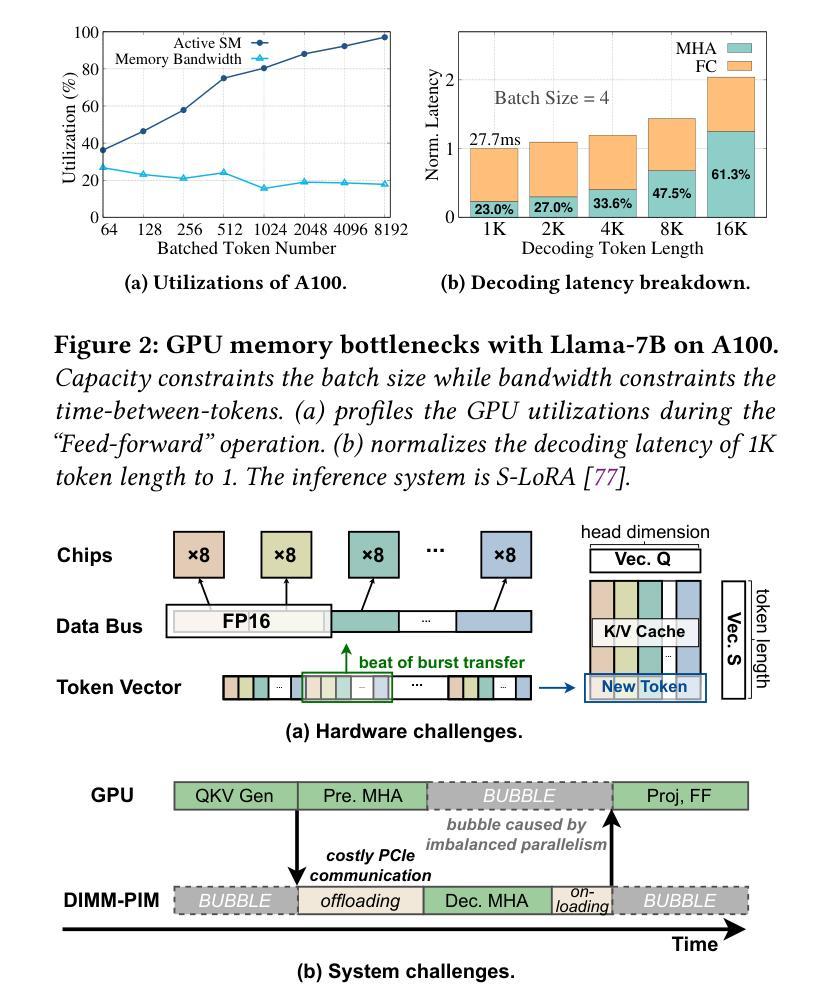
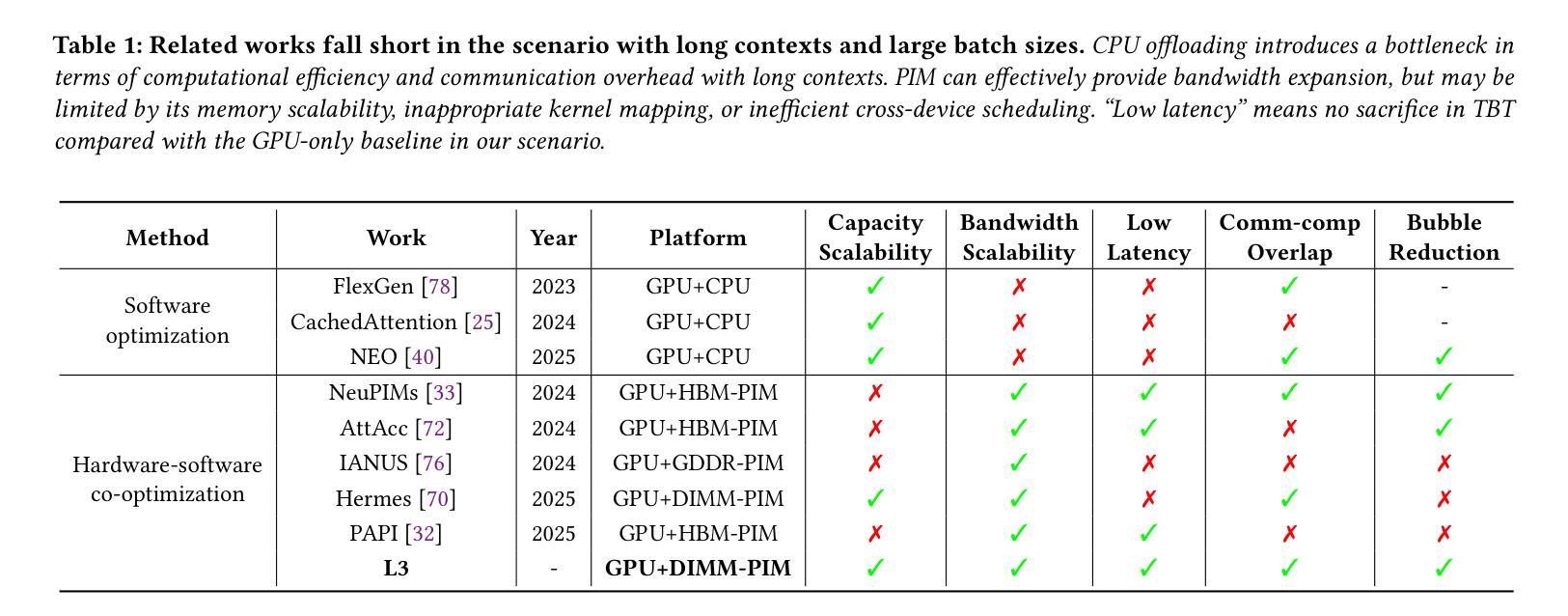
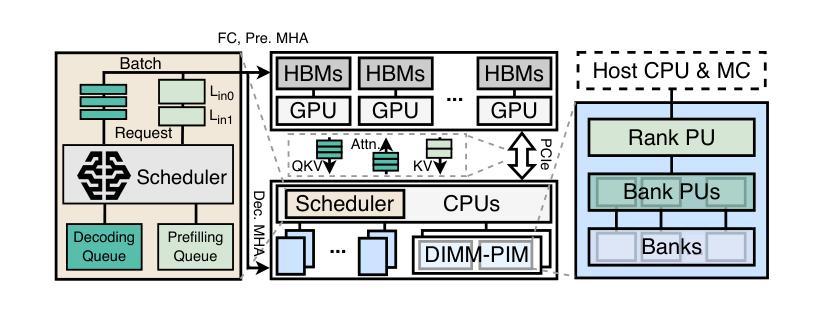
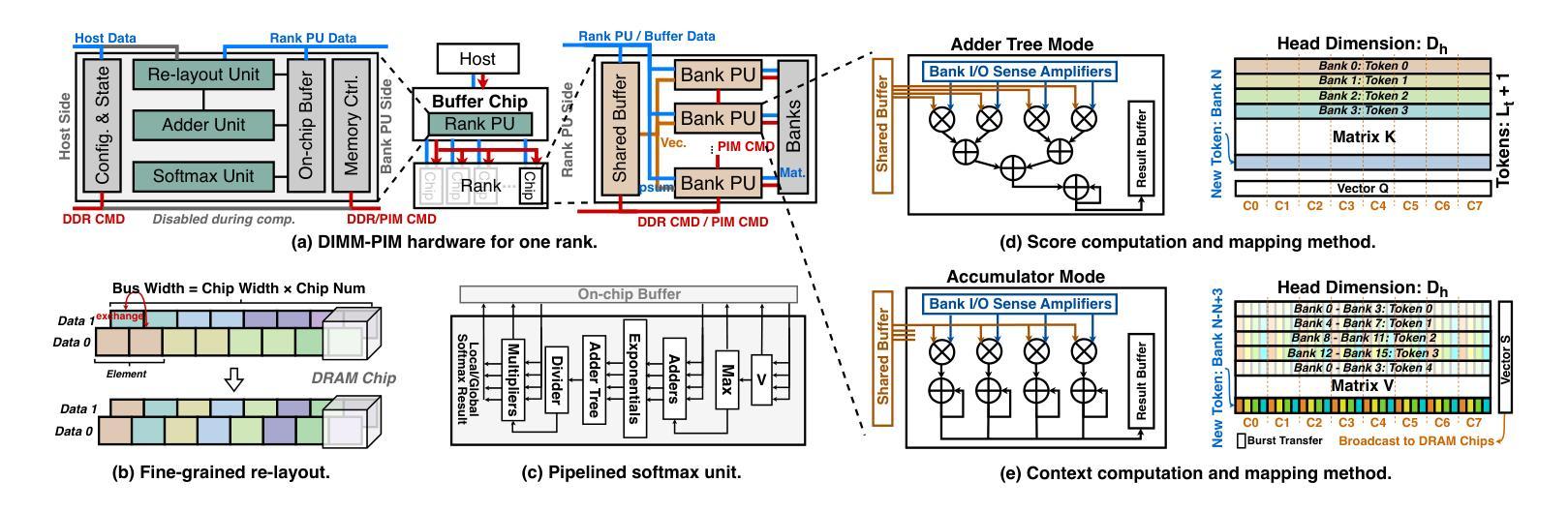
Large Language Models (LLMs) increasingly require processing long text sequences, but GPU memory limitations force difficult trade-offs between memory capacity and bandwidth. While HBM-based acceleration offers high bandwidth, its capacity remains constrained. Offloading data to host-side DIMMs improves capacity but introduces costly data swapping overhead. We identify that the critical memory bottleneck lies in the decoding phase of multi-head attention (MHA) exclusively, which demands substantial capacity for storing KV caches and high bandwidth for attention computation. Our key insight reveals this operation uniquely aligns with modern DIMM-based processing-in-memory (PIM) architectures, which offers scalability of both capacity and bandwidth. Based on this observation and insight, we propose L3, a hardware-software co-designed system integrating DIMM-PIM and GPU devices. L3 introduces three innovations: First, hardware redesigns resolve data layout mismatches and computational element mismatches in DIMM-PIM, enhancing LLM inference utilization. Second, communication optimization enables hiding the data transfer overhead with the computation. Third, an adaptive scheduler coordinates GPU-DIMM-PIM operations to maximize parallelism between devices. Evaluations using real-world traces show L3 achieves up to 6.1$\times$ speedup over state-of-the-art HBM-PIM solutions while significantly improving batch sizes.
大型语言模型(LLMs)需要处理越来越长的文本序列,但GPU内存限制迫使人们在内存容量和带宽之间进行艰难的权衡。虽然基于HBM的加速提供了高带宽,但其容量仍然受限。将数据迁移到主机侧DIMM可以提高容量,但这也引入了昂贵的数据交换开销。我们确定了关键的内存瓶颈仅存在于多头注意力(MHA)的解码阶段,该阶段需要大量存储空间来存储KV缓存和进行注意力计算的高带宽。我们的关键见解表明,这一操作与现代DIMM基于内存处理(PIM)的架构独特地契合,这一架构在容量和带宽方面都提供了可扩展性。基于这一观察和理解,我们提出了L3,这是一个结合了DIMM-PIM和GPU设备的软硬件协同设计系统。L3引入了三项创新:首先,硬件重新设计解决了DIMM-PIM中的数据布局不匹配和计算元素不匹配的问题,提高了LLM推理的利用率;其次,通信优化通过计算隐藏数据传输开销来实现。第三,一个自适应调度器协调GPU-DIMM-PIM操作,以最大限度地提高设备之间的并行性。使用真实世界轨迹的评估表明,L3与最新的HBM-PIM解决方案相比,最高可实现6.1倍的加速,同时显著提高了批次大小。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF 16 pages, 11 figures
Summary
大型语言模型(LLMs)处理长文本序列时面临GPU内存限制的挑战,需要在内存容量和带宽之间进行权衡。本文提出一种基于DIMM的处理内存架构L3,该架构针对多头注意力解码阶段的内存瓶颈进行优化,通过硬件软件协同设计,实现容量和带宽的可扩展性。L3引入三项创新技术:解决DIMM-PIM中的数据布局和计算元素不匹配问题,优化通信隐藏数据传输开销,以及自适应调度器协调GPU-DIMM-PIM操作以最大化设备间的并行性。评估结果显示,L3相较于当前先进的HBM-PIM解决方案,速度提升可达6.1倍,同时显著提高批次大小。
Key Takeaways
- 大型语言模型处理长文本时面临GPU内存限制的挑战,需要在容量和带宽之间做出权衡。
- 问题的关键在于多头注意力解码阶段,需要大量内存缓存和高速计算。
- HBM加速虽提供高带宽,但容量受限;将数据移至主机侧DIMM提高容量但增加数据交换开销。
- 本文提出基于DIMM的处理内存架构L3,针对LLM进行优化,实现容量和带宽的扩展性。
- L3通过硬件软件协同设计,解决DIMM-PIM中的数据布局和计算元素不匹配问题。
- L3引入通信优化和自适应调度技术,隐藏数据传输开销,并最大化设备间的并行性。
点此查看论文截图