⚠️ 以下所有内容总结都来自于 大语言模型的能力,如有错误,仅供参考,谨慎使用
🔴 请注意:千万不要用于严肃的学术场景,只能用于论文阅读前的初筛!
💗 如果您觉得我们的项目对您有帮助 ChatPaperFree ,还请您给我们一些鼓励!⭐️ HuggingFace免费体验
2025-04-26 更新
Beyond Whole Dialogue Modeling: Contextual Disentanglement for Conversational Recommendation
Authors:Guojia An, Jie Zou, Jiwei Wei, Chaoning Zhang, Fuming Sun, Yang Yang
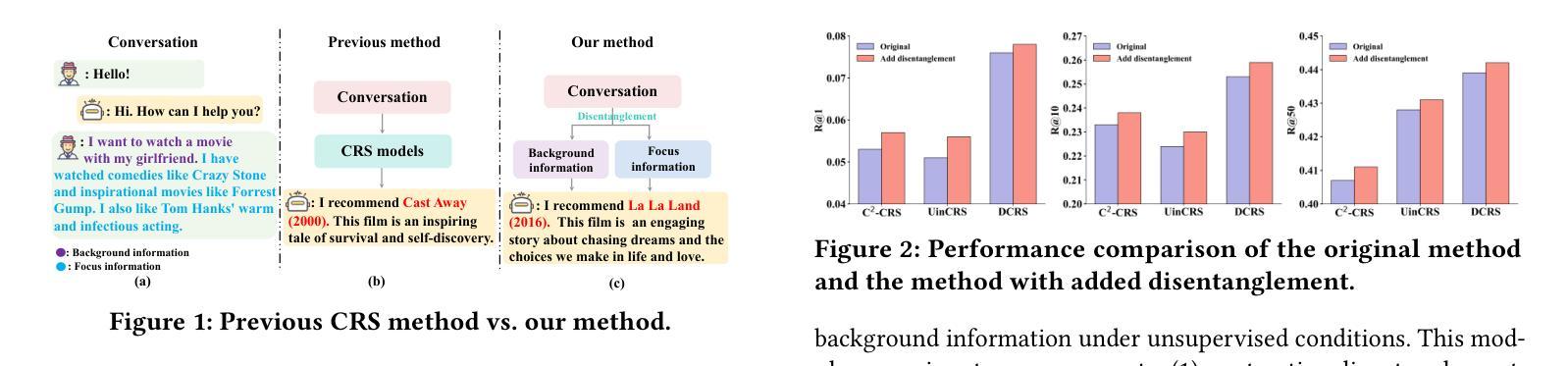
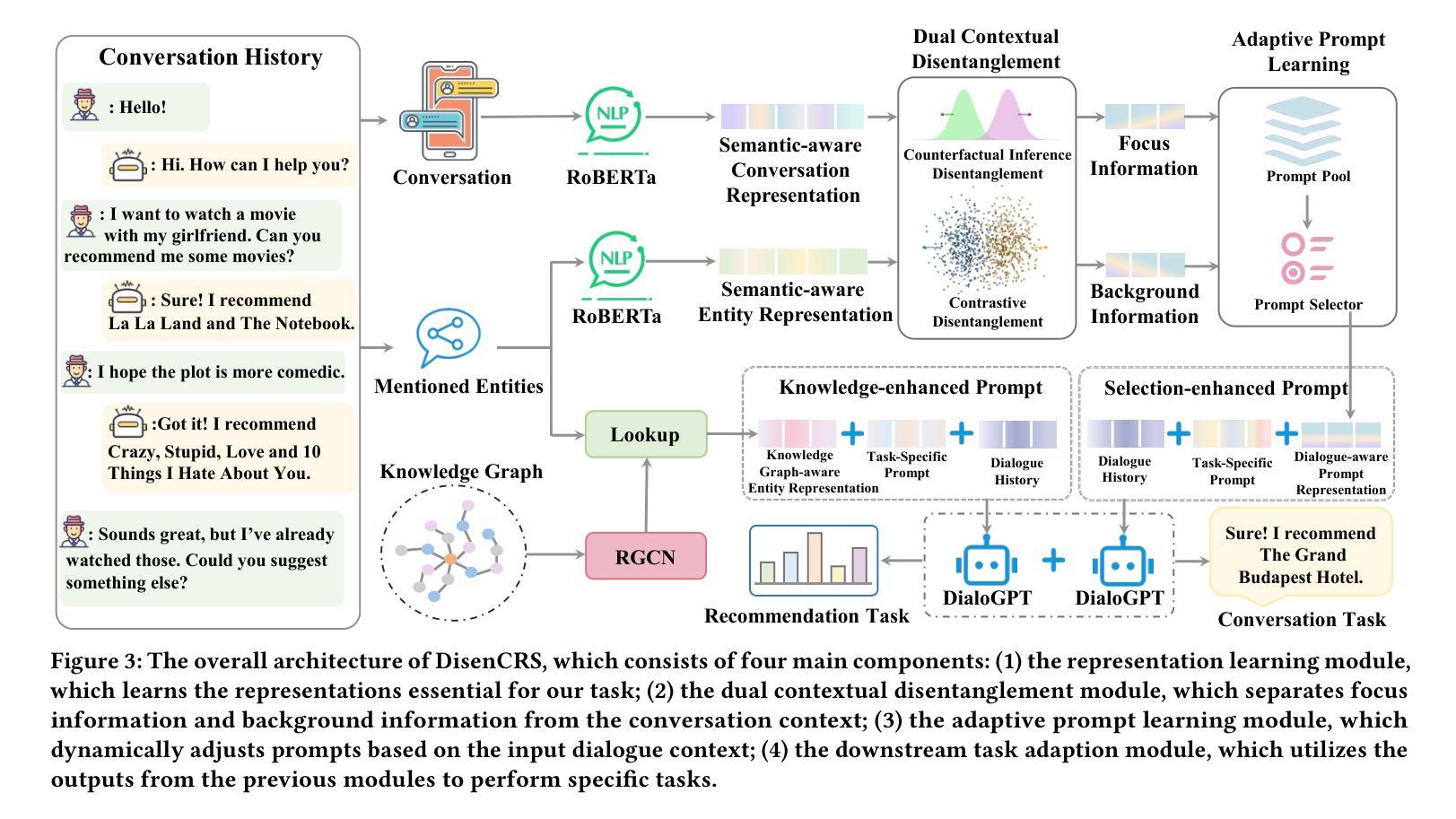
Conversational recommender systems aim to provide personalized recommendations by analyzing and utilizing contextual information related to dialogue. However, existing methods typically model the dialogue context as a whole, neglecting the inherent complexity and entanglement within the dialogue. Specifically, a dialogue comprises both focus information and background information, which mutually influence each other. Current methods tend to model these two types of information mixedly, leading to misinterpretation of users’ actual needs, thereby lowering the accuracy of recommendations. To address this issue, this paper proposes a novel model to introduce contextual disentanglement for improving conversational recommender systems, named DisenCRS. The proposed model DisenCRS employs a dual disentanglement framework, including self-supervised contrastive disentanglement and counterfactual inference disentanglement, to effectively distinguish focus information and background information from the dialogue context under unsupervised conditions. Moreover, we design an adaptive prompt learning module to automatically select the most suitable prompt based on the specific dialogue context, fully leveraging the power of large language models. Experimental results on two widely used public datasets demonstrate that DisenCRS significantly outperforms existing conversational recommendation models, achieving superior performance on both item recommendation and response generation tasks.
对话推荐系统的目标是通过分析和利用与对话相关的上下文信息来提供个性化推荐。然而,现有方法通常将整个对话上下文建模为一个整体,忽略了对话内部固有的复杂性和纠缠关系。具体来说,对话包括焦点信息和背景信息,它们相互影响。当前的方法往往将这两种类型的信息混合建模,导致对用户实际需求的误解,从而降低推荐的准确性。为了解决这一问题,本文提出了一种引入上下文解耦的新模型,以提高对话推荐系统的性能,命名为DisenCRS。所提出的DisenCRS模型采用双解耦框架,包括自监督对比解耦和基于反事实推理的解耦,以在无需监督的情况下有效地从对话上下文中区分出焦点信息和背景信息。此外,我们设计了一个自适应提示学习模块,能够根据特定的对话上下文自动选择最合适的提示,充分利用大型语言模型的潜力。在两个广泛使用的公共数据集上的实验结果表明,DisenCRS显著优于现有的对话推荐模型,在物品推荐和响应生成任务上都取得了优异的表现。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
本文提出了一种名为DisenCRS的新型对话推荐系统改进模型,该模型采用双解纠缠框架,有效区分对话中的焦点信息和背景信息。通过自适应提示学习模块,根据具体对话上下文自动选择最合适的提示,充分利用大型语言模型的威力。在两项广泛使用的公共数据集上的实验结果表明,DisenCRS显著优于现有对话推荐模型,在物品推荐和响应生成任务上都取得了优越的性能。
Key Takeaways
- 对话推荐系统通过分析对话的上下文信息来提供个性化推荐。
- 现存方法往往忽略对话的复杂性和内在纠缠性,误将焦点信息和背景信息混合建模。
- DisenCRS模型采用双解纠缠框架,包括自我监督对比解纠缠和基于反事实推理的解纠缠,以区分对话中的焦点和背景信息。
- DisenCRS通过自适应提示学习模块,根据对话上下文自动选择最合适的提示。
- 该模型在物品推荐和响应生成任务上均表现出卓越性能。
- 实验结果表明,DisenCRS显著优于现有对话推荐模型。
点此查看论文截图

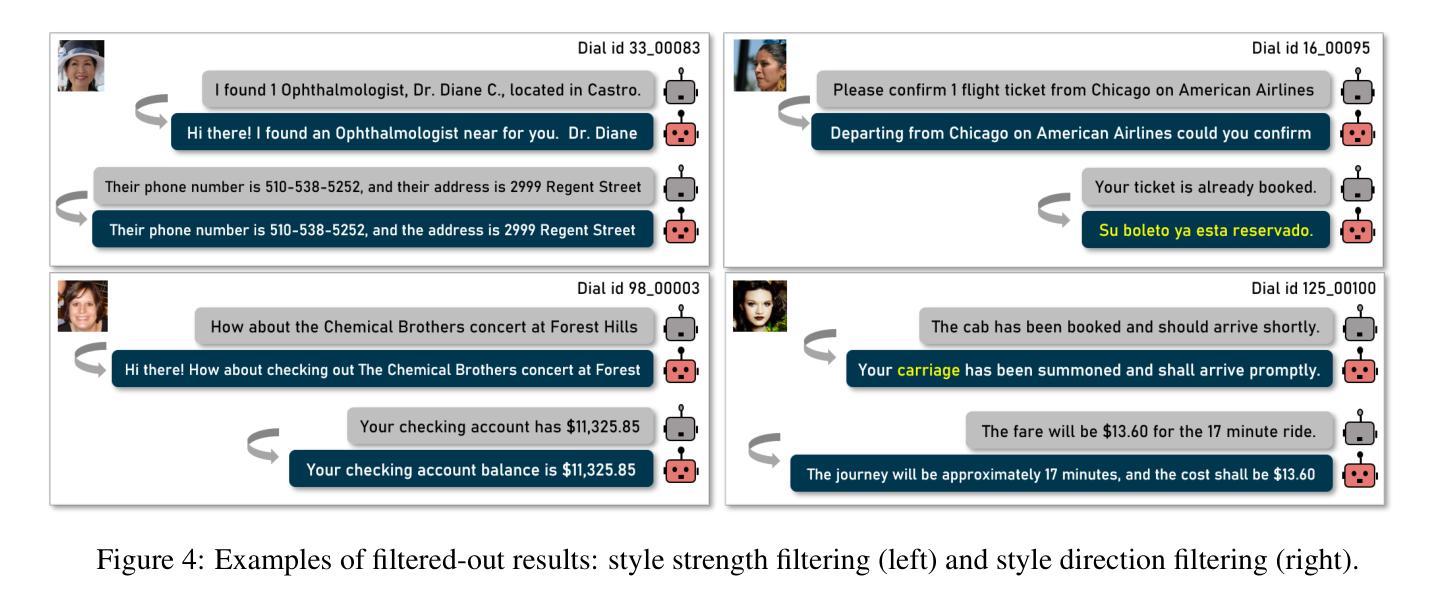
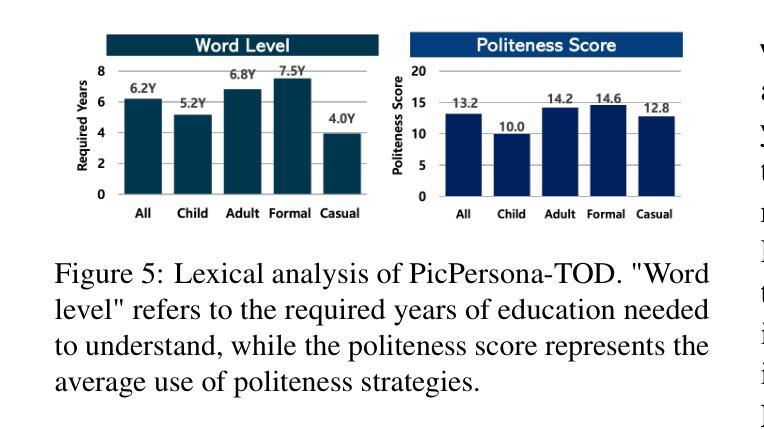
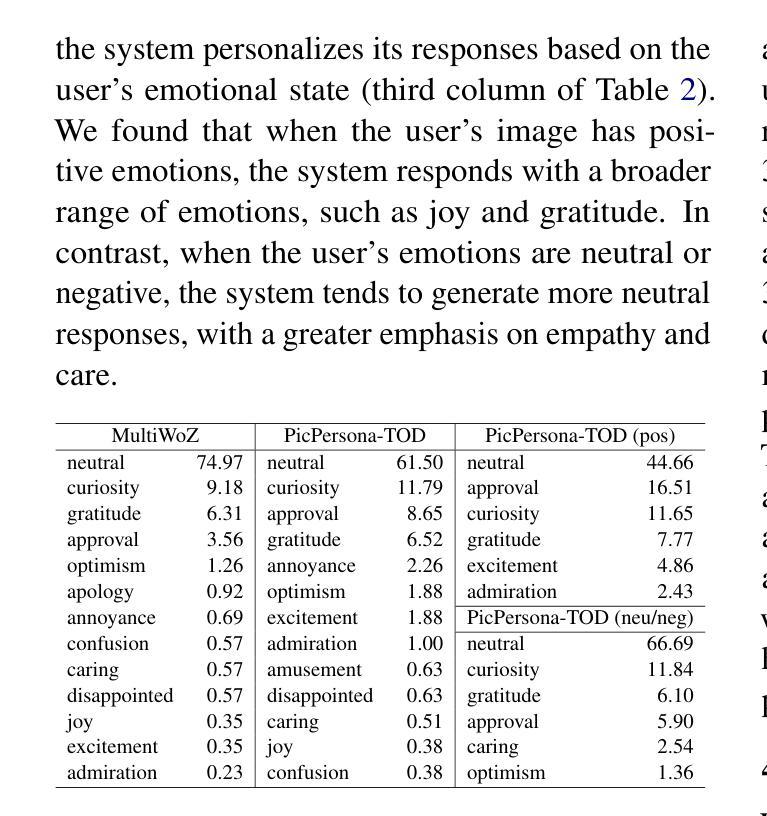
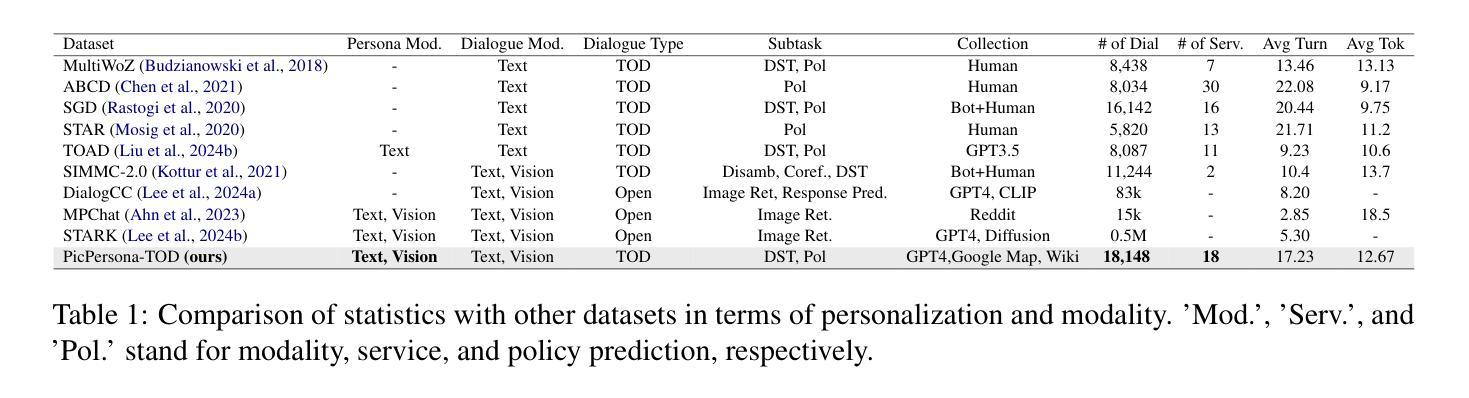
PicPersona-TOD : A Dataset for Personalizing Utterance Style in Task-Oriented Dialogue with Image Persona
Authors:Jihyun Lee, Yejin Jeon, Seungyeon Seo, Gary Geunbae Lee
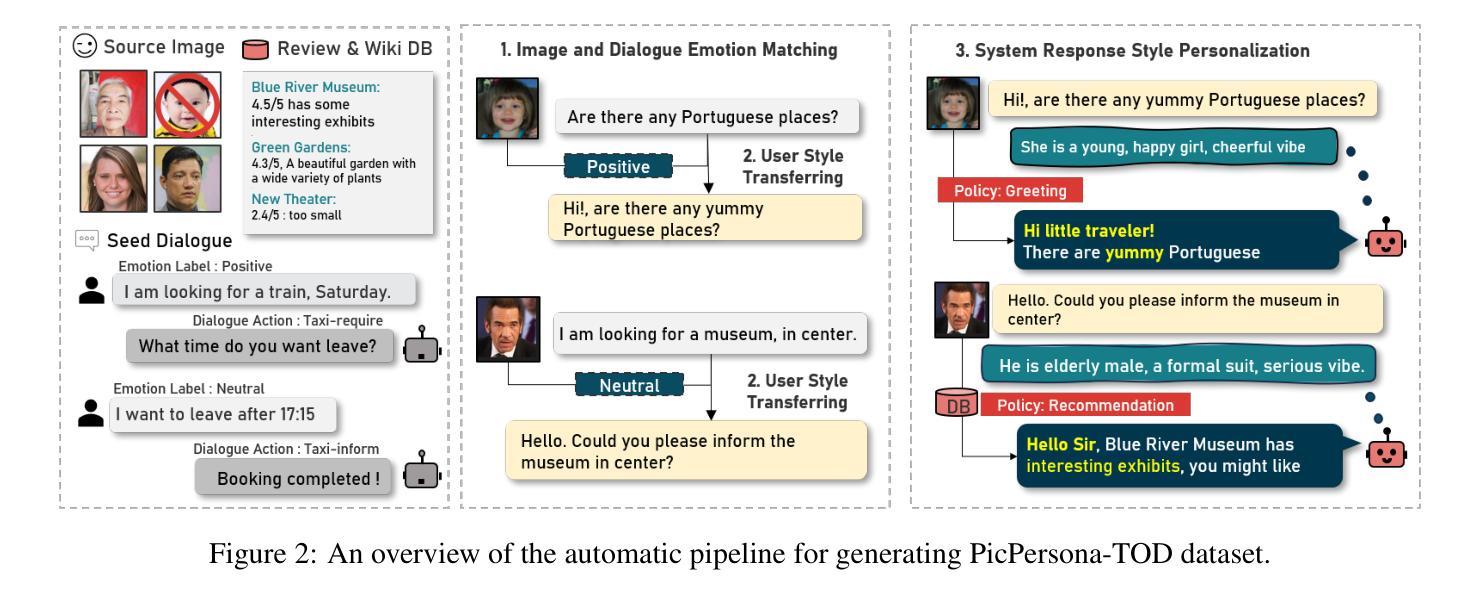
Task-Oriented Dialogue (TOD) systems are designed to fulfill user requests through natural language interactions, yet existing systems often produce generic, monotonic responses that lack individuality and fail to adapt to users’ personal attributes. To address this, we introduce PicPersona-TOD, a novel dataset that incorporates user images as part of the persona, enabling personalized responses tailored to user-specific factors such as age or emotional context. This is facilitated by first impressions, dialogue policy-guided prompting, and the use of external knowledge to reduce hallucinations. Human evaluations confirm that our dataset enhances user experience, with personalized responses contributing to a more engaging interaction. Additionally, we introduce a new NLG model, Pictor, which not only personalizes responses, but also demonstrates robust performance across unseen domains https://github.com/JihyunLee1/PicPersona.
任务导向型对话(TOD)系统旨在通过自然语言交互来达成用户的请求,但现有的系统往往会产生缺乏个性化和无法适应用户个人属性的通用、单调的回应。为了解决这一问题,我们引入了PicPersona-TOD这一新型数据集,它将用户图像作为个性的一部分,能够生成针对用户特定因素(如年龄或情绪背景)的个性化回应。这是通过第一印象、对话策略引导提示以及使用外部知识来减少幻觉来实现的。人类评估证实,我们的数据集增强了用户体验,个性化的回应有助于更吸引人的互动。此外,我们还推出了一个新的自然语言生成模型Pictor,它不仅使回应个性化,而且在看不见的领域中表现出强大的性能:https://github.com/JihyunLee1/PicPersona。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF Accepted in NAACL 2025 main
Summary
任务导向对话(TOD)系统通过自然语言交互实现用户需求,但现有系统通常生成缺乏个性和无法适应用户个人属性的通用、单调的响应。为解决此问题,我们推出PicPersona-TOD数据集,通过融入用户图片构建个性化响应,以适配用户的年龄、情绪背景等个人因素。此过程借助初步印象、对话策略引导提示和外部知识减少虚构内容。人类评估证实,我们的数据集增强了用户体验,个性化的响应使交互更加引人入胜。此外,我们还推出了全新的NLG模型——Pictor,不仅能个性化响应,还能在不同未见领域表现稳健性能。
Key Takeaways
- 任务导向对话(TOD)系统主要目标是满足用户需求,但现有系统响应单调且缺乏个性化。
- PicPersona-TOD数据集通过融入用户图片构建个性化响应,以适配用户的个人属性。
- 该数据集利用初步印象、对话策略引导提示和外部知识来增强个性化响应的质量。
- 人类评估表明,PicPersona-TOD数据集能够增强用户体验和交互的吸引力。
- 新模型Pictor不仅具备个性化响应能力,还在未见领域表现出稳健性能。
- PicPersona-TOD系统和Pictor模型共同促进了对话系统的个性化发展。
点此查看论文截图

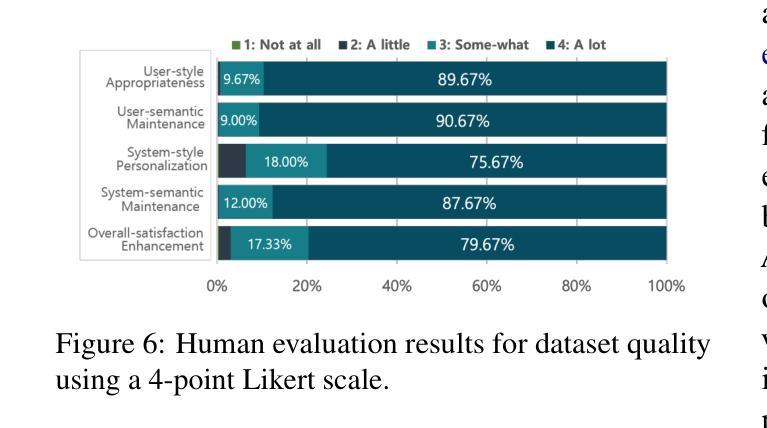
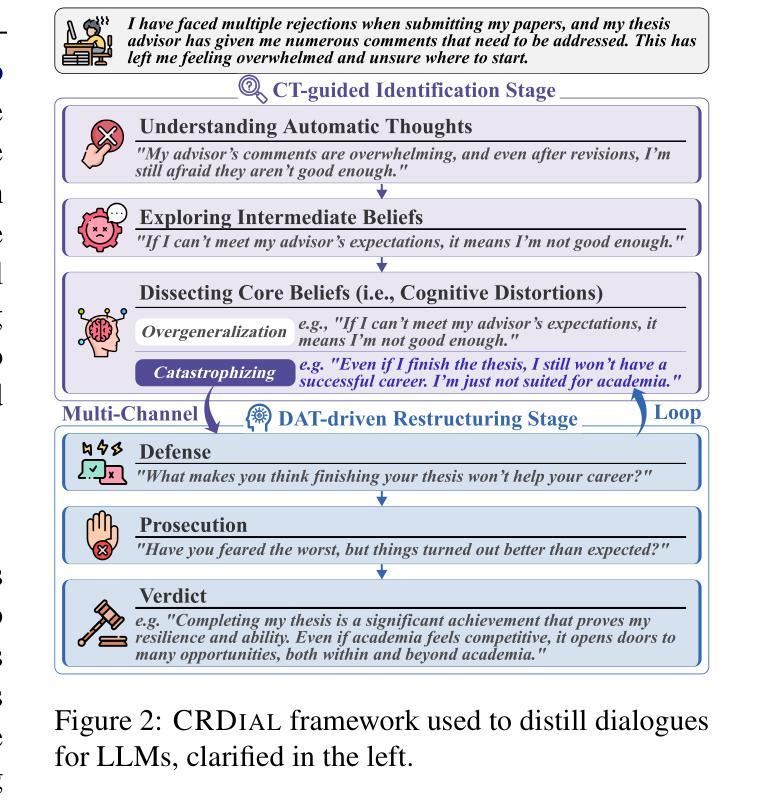
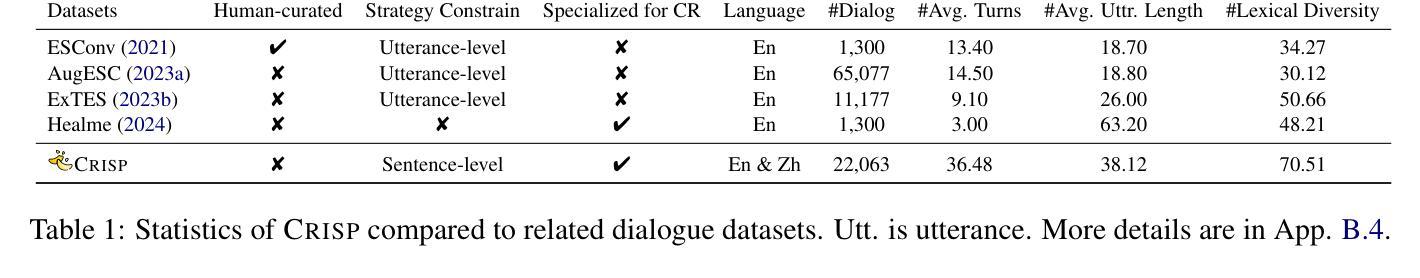
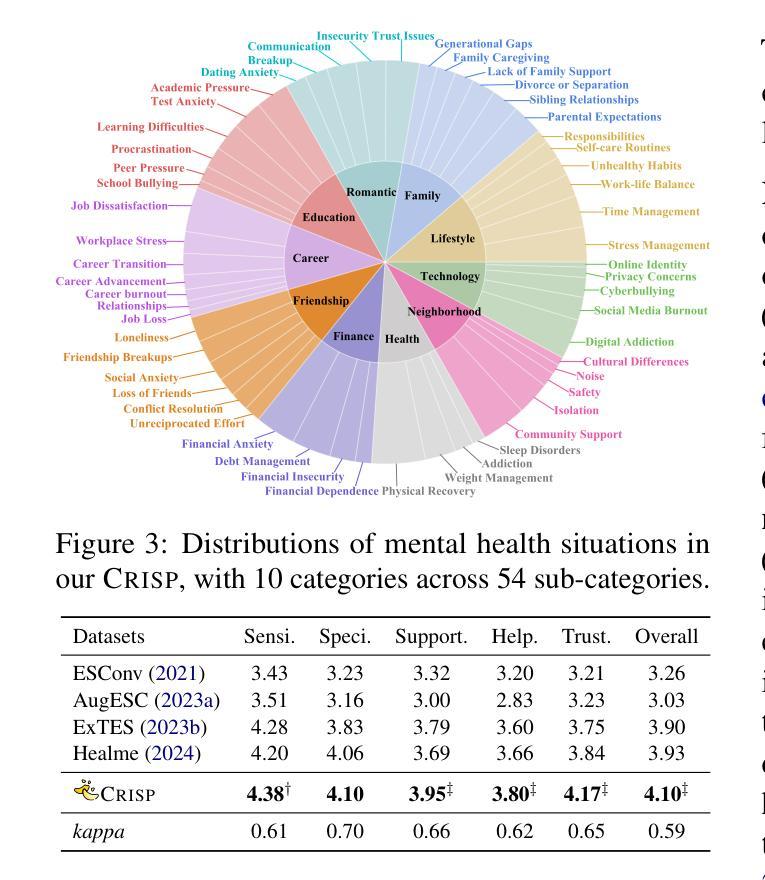
Crisp: Cognitive Restructuring of Negative Thoughts through Multi-turn Supportive Dialogues
Authors:Jinfeng Zhou, Yuxuan Chen, Jianing Yin, Yongkang Huang, Yihan Shi, Xikun Zhang, Libiao Peng, Rongsheng Zhang, Tangjie Lv, Zhipeng Hu, Hongning Wang, Minlie Huang
Cognitive Restructuring (CR) is a psychotherapeutic process aimed at identifying and restructuring an individual’s negative thoughts, arising from mental health challenges, into more helpful and positive ones via multi-turn dialogues. Clinician shortage and stigma urge the development of human-LLM interactive psychotherapy for CR. Yet, existing efforts implement CR via simple text rewriting, fixed-pattern dialogues, or a one-shot CR workflow, failing to align with the psychotherapeutic process for effective CR. To address this gap, we propose CRDial, a novel framework for CR, which creates multi-turn dialogues with specifically designed identification and restructuring stages of negative thoughts, integrates sentence-level supportive conversation strategies, and adopts a multi-channel loop mechanism to enable iterative CR. With CRDial, we distill Crisp, a large-scale and high-quality bilingual dialogue dataset, from LLM. We then train Crispers, Crisp-based conversational LLMs for CR, at 7B and 14B scales. Extensive human studies show the superiority of Crispers in pointwise, pairwise, and intervention evaluations.
认知重构(CR)是一种心理治疗过程,旨在通过多轮对话,识别和重构个人由心理健康挑战产生的负面想法,转化为更有帮助和积极的想法。临床医师短缺和耻感推动了对人类与大型语言模型(LLM)交互心理治疗的开发,用于认知重构。然而,现有的努力往往通过简单的文本重写、固定模式的对话或一次性的认知重构工作流程来实现认知重构,这与有效的认知重构的心理治疗过程并不相符。为了弥补这一差距,我们提出了CRDial,这是一种新型的用于认知重构的框架。它创建了具有专门设计的负面思想识别和重构阶段的多轮对话,集成了句子级的支持性对话策略,并采用了多通道循环机制,以实现迭代的认知重构。通过CRDial,我们从大型语言模型中提炼出Crisp,这是一个大规模、高质量的双语对话数据集。然后,我们在7B和14B的范围内,基于Crisp训练了用于认知重构的聊天LLM,称为Crispers。大量的人类研究表明,Crispers在单点、配对和干预评估中都表现出卓越的性能。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
认知重构(CR)是一种心理疗法过程,旨在通过多回合对话,将个人由心理健康挑战产生的负面想法识别并重构为更积极正面的想法。由于临床医师短缺和偏见,推动了人机互动心理疗法的发展。然而,现有努力往往通过简单的文本重写、固定模式对话或一次性认知重构工作流程来实现,这与有效的认知重构心理疗法过程并不相符。为解决这一差距,我们提出CRDial这一新型认知重构框架,它通过特定设计的负面思想识别和重构阶段,创建多回合对话,并整合句子层面的支持性对话策略,采用多通道循环机制以启用迭代认知重构。基于大型高质量双语对话数据集Crisp,我们从LLM提炼出Crispers,用于认知重构的LLM。大量的人类研究表明,Crispers在单点、配对和干预评估中都表现出卓越的性能。
Key Takeaways
- 认知重构(CR)是一种心理疗法过程,通过多回合对话帮助个体识别并重构负面思想。
- 由于临床医师短缺和偏见,人机互动心理疗法受到关注。
- 现有认知重构方法主要通过简单文本重写、固定模式对话或一次性工作流程实现,与心理疗法过程不符。
- CRDial框架旨在解决这一差距,包括负面思想识别和重构的多回合对话、句子级别的支持性对话策略以及多通道循环机制。
- Crisp是一种大型高质量的双语对话数据集,用于提炼Crispers。
- Crispers是基于LLM的用于认知重构的对话式AI模型。
点此查看论文截图

CADS: A Systematic Literature Review on the Challenges of Abstractive Dialogue Summarization
Authors:Frederic Kirstein, Jan Philip Wahle, Bela Gipp, Terry Ruas
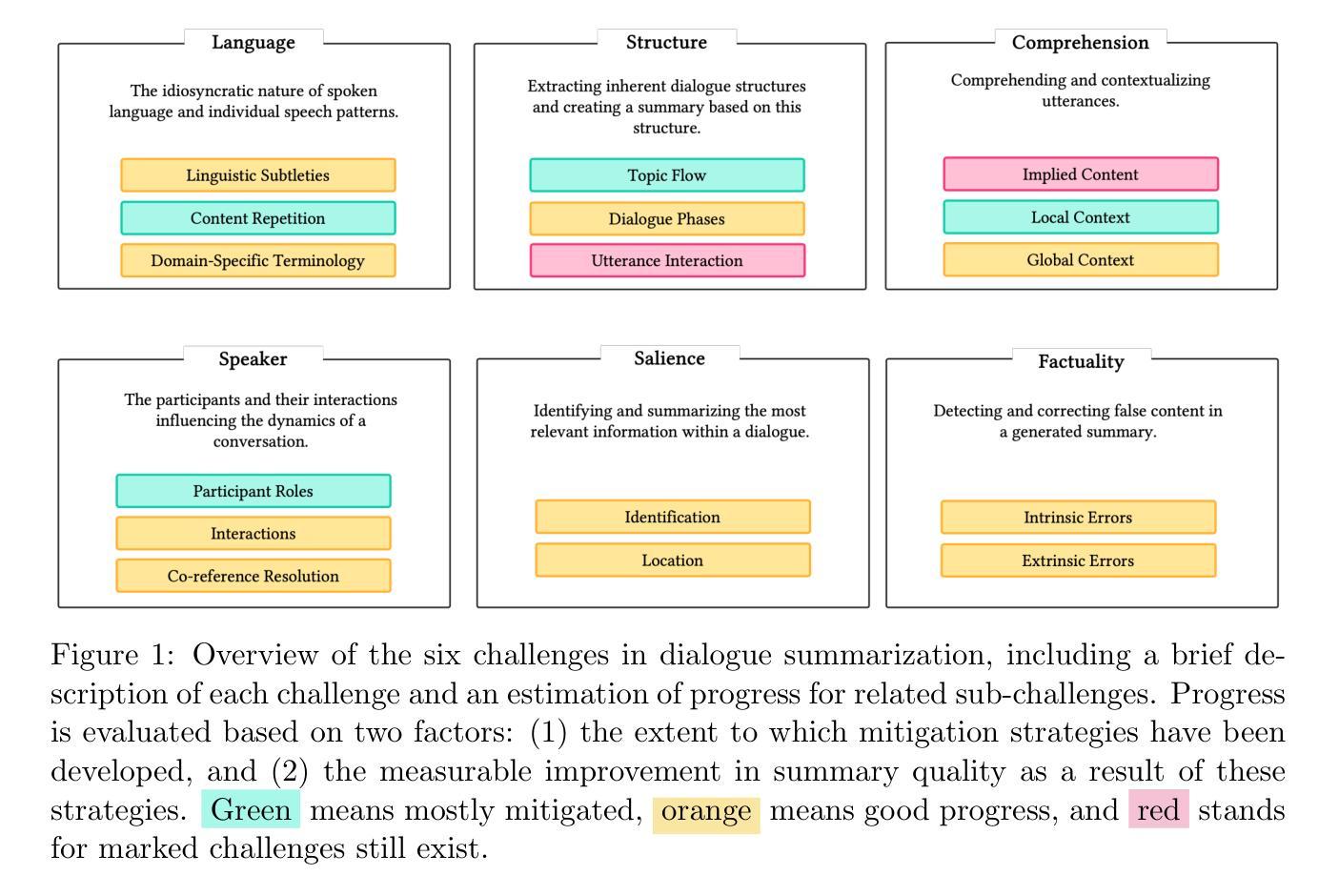
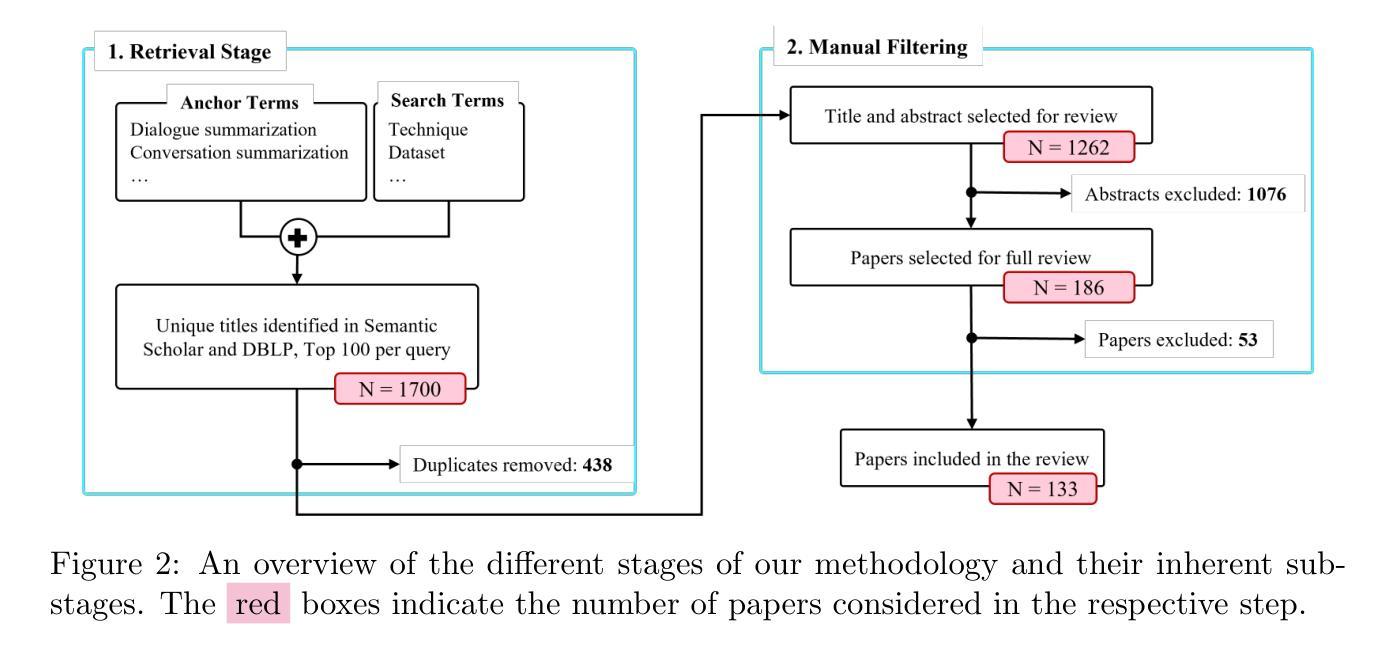
Abstractive dialogue summarization is the task of distilling conversations into informative and concise summaries. Although reviews have been conducted on this topic, there is a lack of comprehensive work detailing the challenges of dialogue summarization, unifying the differing understanding of the task, and aligning proposed techniques, datasets, and evaluation metrics with the challenges. This article summarizes the research on Transformer-based abstractive summarization for English dialogues by systematically reviewing 1262 unique research papers published between 2019 and 2024, relying on the Semantic Scholar and DBLP databases. We cover the main challenges present in dialog summarization (i.e., language, structure, comprehension, speaker, salience, and factuality) and link them to corresponding techniques such as graph-based approaches, additional training tasks, and planning strategies, which typically overly rely on BART-based encoder-decoder models. We find that while some challenges, like language, have seen considerable progress, mainly due to training methods, others, such as comprehension, factuality, and salience, remain difficult and hold significant research opportunities. We investigate how these approaches are typically assessed, covering the datasets for the subdomains of dialogue (e.g., meeting, medical), the established automatic metrics and human evaluation approaches for assessing scores and annotator agreement. We observe that only a few datasets span across all subdomains. The ROUGE metric is the most used, while human evaluation is frequently reported without sufficient detail on inner-annotator agreement and annotation guidelines. Additionally, we discuss the possible implications of the recently explored large language models and conclude that despite a potential shift in relevance and difficulty, our described challenge taxonomy remains relevant.
抽象对话摘要的任务是将对话提炼成信息丰富且简洁的摘要。尽管已经对此主题进行了评论,但缺乏全面工作来详细阐述对话摘要的挑战,统一对此任务的不同理解,以及使所提出的技术、数据集和评估指标与这些挑战相吻合。本文总结了基于Transformer的英语对话抽象摘要的研究,通过系统地回顾2019年至2024年间发表在Semantic Scholar和DBLP数据库上的1262篇独特研究论文。我们介绍了对话摘要中存在的主要挑战(即语言、结构、理解、发言者、显著性和真实性),并将它们与相应的技术(如基于图的方法、额外的训练任务和规划策略)联系起来,这些技术通常过于依赖BART的基于编码器-解码器的模型。我们发现,尽管一些挑战(如语言)由于训练方法而取得了很大进展,但其他挑战(如理解、真实性和显著性)仍然困难重重,并存在重要的研究机会。我们调查了通常如何对这些方法进行评估,涵盖了对话子领域的数据集(例如会议、医疗),用于评估分数和注释者一致性的既定自动指标和人类评估方法。我们发现只有少数数据集涵盖所有子域。ROUGE指标是最常用的指标,而人类评估通常没有详细的内部评估者一致性和注释指南。此外,我们还讨论了最近探索的大型语言模型的可能影响,并得出结论:尽管相关性和难度可能存在潜在变化,但我们描述的挑战分类仍然很重要。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF Published in the Journal of Artificial Intelligence Research (JAIR) (https://www.jair.org/index.php/jair/article/view/16674)
Summary
本文综述了基于Transformer的英语对话摘要研究,通过系统地回顾了2019年至2024年间发表的1262篇独特研究论文,探讨了对话摘要的主要挑战,如语言、结构、理解、说话人、显著性和事实性。文章还介绍了针对这些挑战的技术方法,如基于图的方法、额外的训练任务和规划策略,并发现了一些挑战已经取得了显著进展,而一些挑战仍然存在并提供了重要的研究机会。此外,文章还介绍了相关的数据集评估方法,并讨论了大型语言模型的潜在影响。
Key Takeaways
- 本文综述了基于Transformer的英语对话摘要研究,涉及大量相关论文的系统性回顾。
- 对对话摘要的主要挑战进行了详细分析,包括语言、结构、理解、说话人、显著性和事实性等方面。
- 针对这些挑战的技术方法得到了介绍,如基于图的方法、额外的训练任务和规划策略等。
- 文章发现某些挑战(如语言)已经取得显著进展,而其他挑战(如理解和事实性)仍然存在并需要更多研究。
- 文章讨论了相关的数据集评估方法,指出目前存在的评估工具和方法的优劣。
- 大型语言模型在对话摘要中的应用得到了关注,对其潜在影响进行了讨论。
点此查看论文截图