⚠️ 以下所有内容总结都来自于 大语言模型的能力,如有错误,仅供参考,谨慎使用
🔴 请注意:千万不要用于严肃的学术场景,只能用于论文阅读前的初筛!
💗 如果您觉得我们的项目对您有帮助 ChatPaperFree ,还请您给我们一些鼓励!⭐️ HuggingFace免费体验
2025-04-26 更新
DeepDistill: Enhancing LLM Reasoning Capabilities via Large-Scale Difficulty-Graded Data Training
Authors:Xiaoyu Tian, Sitong Zhao, Haotian Wang, Shuaiting Chen, Yiping Peng, Yunjie Ji, Han Zhao, Xiangang Li
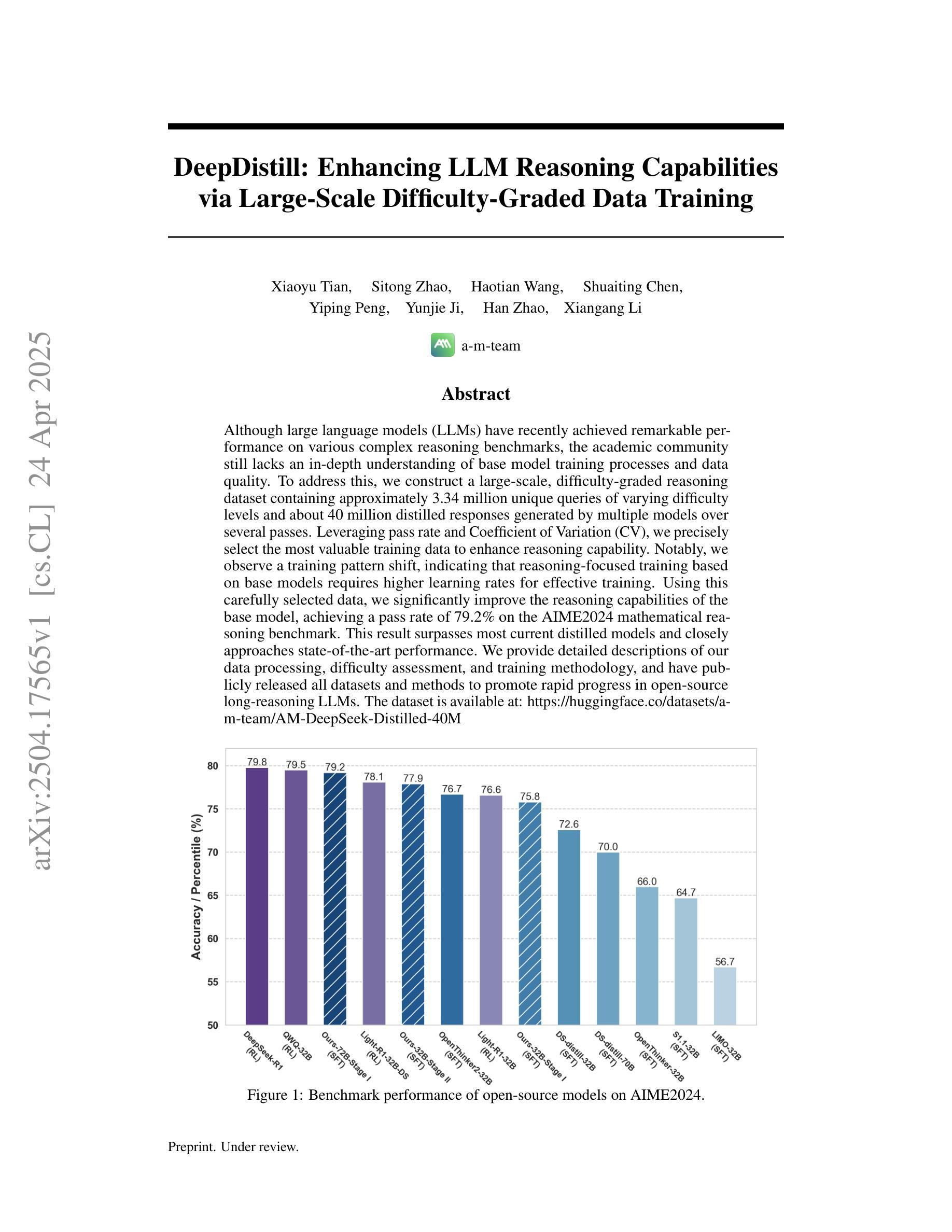
Although large language models (LLMs) have recently achieved remarkable performance on various complex reasoning benchmarks, the academic community still lacks an in-depth understanding of base model training processes and data quality. To address this, we construct a large-scale, difficulty-graded reasoning dataset containing approximately 3.34 million unique queries of varying difficulty levels and about 40 million distilled responses generated by multiple models over several passes. Leveraging pass rate and Coefficient of Variation (CV), we precisely select the most valuable training data to enhance reasoning capability. Notably, we observe a training pattern shift, indicating that reasoning-focused training based on base models requires higher learning rates for effective training. Using this carefully selected data, we significantly improve the reasoning capabilities of the base model, achieving a pass rate of 79.2% on the AIME2024 mathematical reasoning benchmark. This result surpasses most current distilled models and closely approaches state-of-the-art performance. We provide detailed descriptions of our data processing, difficulty assessment, and training methodology, and have publicly released all datasets and methods to promote rapid progress in open-source long-reasoning LLMs. The dataset is available at: https://huggingface.co/datasets/a-m-team/AM-DeepSeek-Distilled-40M
尽管大型语言模型(LLM)最近在各种复杂的推理基准测试中取得了显著的性能,但学术界仍然缺乏对基础模型训练过程和数据质量的深入了解。为了解决这个问题,我们构建了一个大规模、难度分级的推理数据集,包含约334万个独特查询和大约40万个蒸馏响应,这些响应是由多个模型经过多次迭代生成的。我们利用通过率和变异系数(CV)精确选择最有价值的训练数据,以提高推理能力。值得注意的是,我们观察到训练模式的转变,这表明基于基础模型的推理导向训练需要更高的学习率才能进行有效训练。使用这些精心挑选的数据,我们显著提高了基础模型的推理能力,在AIME2024数学推理基准测试上的通过率达到79.2%。这一结果超过了大多数当前的蒸馏模型,并接近最新技术性能。我们提供了关于数据处理、难度评估和培训方法的详细描述,并已公开发布所有数据集和方法,以促进开源长推理LLM的快速发展。数据集可在:https://huggingface.co/datasets/a-m-team/AM-DeepSeek-Distilled-40M 获得。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
大型语言模型(LLMs)在复杂推理基准测试上表现出卓越性能,但仍缺乏对基础模型训练过程和数据质量深入的理解。为此,我们构建了一个大规模、难度分级的推理数据集,包含约33万独特查询和大约数千万次精炼后的回复。通过利用通过率与变异系数(CV),我们精确筛选出最有价值的训练数据以提升推理能力。我们发现训练模式发生转变,基于基础模型的推理训练需要更高的学习率才能有效训练。使用这些数据集,我们显著提升了基础模型的推理能力,在AIME 2024数学推理基准测试中达到79.2%的通过率,超越大多数现有蒸馏模型并接近最新技术水平。我们公开了所有数据集和方法,以促进开源长推理LLMs的快速发展。数据集可通过:链接地址。
Key Takeaways
- 构建了一个大规模、难度分级的推理数据集,旨在深入理解大型语言模型的训练过程和数据质量对推理能力的影响。
- 通过率和变异系数被用来评估和筛选训练数据的有效性,用于提升模型的推理能力。
- 研究发现,与基础模型的推理训练相比,需要更高的学习率才能有效训练模型。
- 使用此数据集显著提升了基础模型的推理能力,在AIME 2024数学推理基准测试中取得了较高的通过率。
- 此研究成果超越大多数现有蒸馏模型并接近最新技术水平。
- 所有数据集和方法已公开,以促进该领域的快速发展。
点此查看论文截图
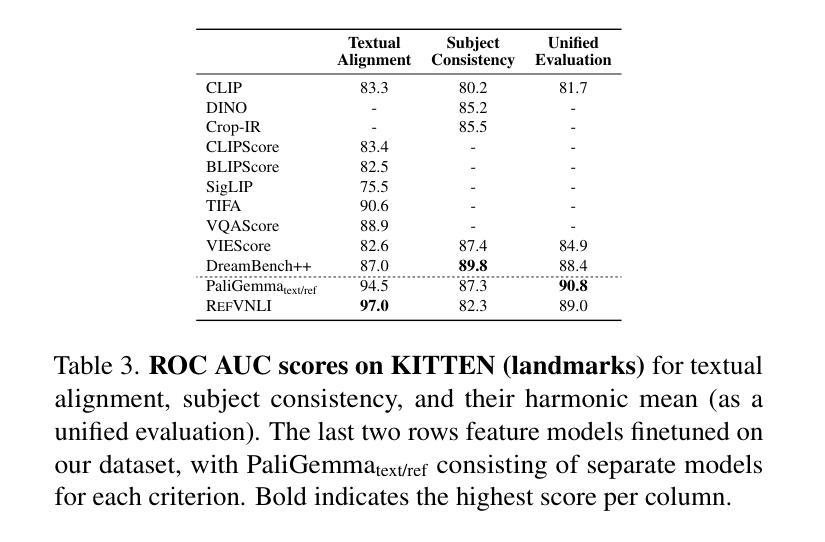
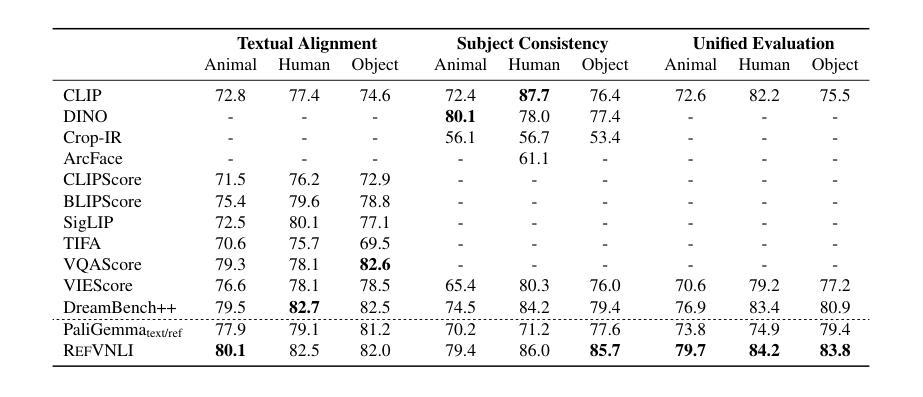
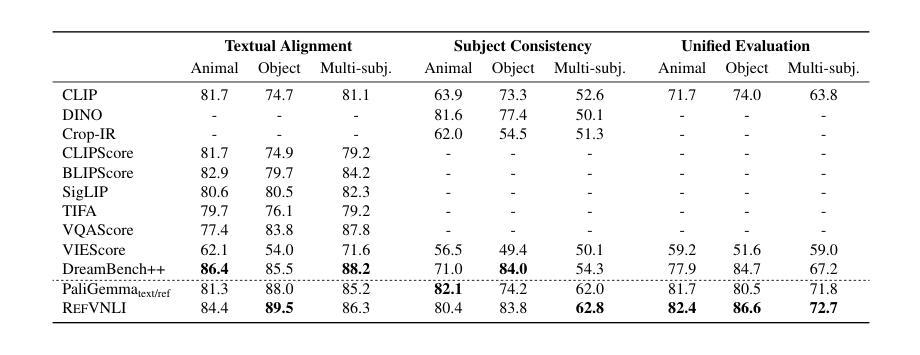
RefVNLI: Towards Scalable Evaluation of Subject-driven Text-to-image Generation
Authors:Aviv Slobodkin, Hagai Taitelbaum, Yonatan Bitton, Brian Gordon, Michal Sokolik, Nitzan Bitton Guetta, Almog Gueta, Royi Rassin, Itay Laish, Dani Lischinski, Idan Szpektor
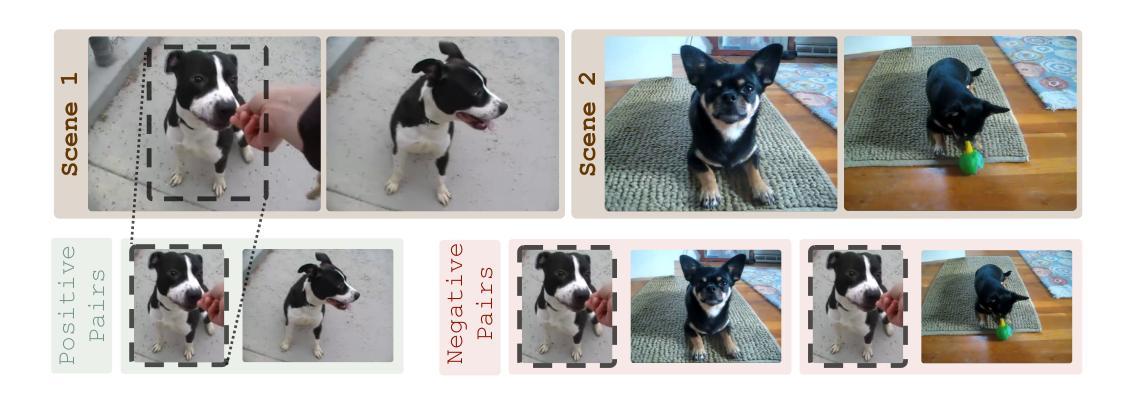
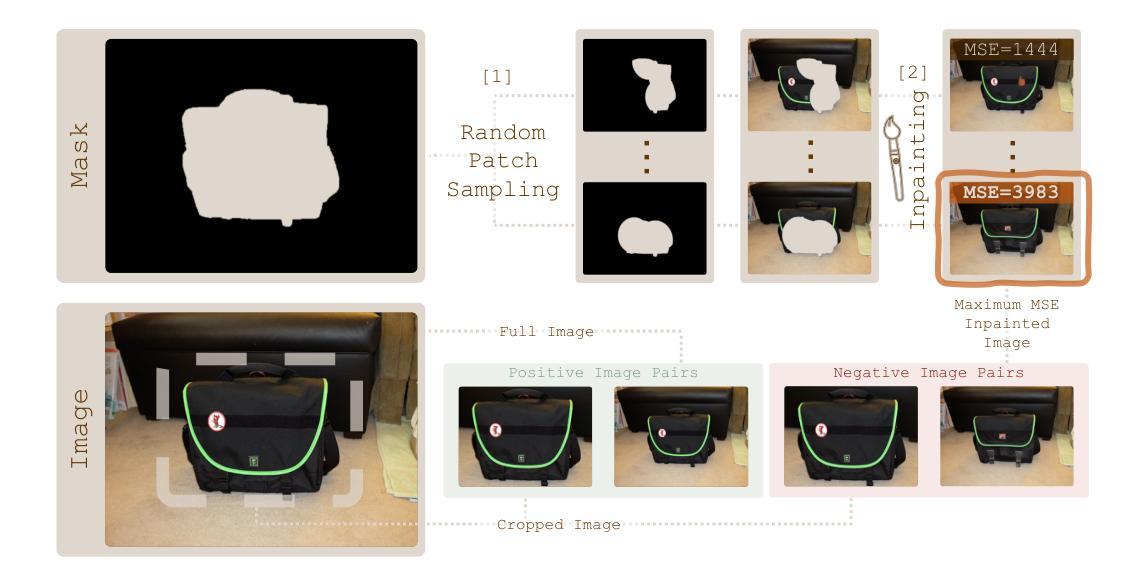
Subject-driven text-to-image (T2I) generation aims to produce images that align with a given textual description, while preserving the visual identity from a referenced subject image. Despite its broad downstream applicability – ranging from enhanced personalization in image generation to consistent character representation in video rendering – progress in this field is limited by the lack of reliable automatic evaluation. Existing methods either assess only one aspect of the task (i.e., textual alignment or subject preservation), misalign with human judgments, or rely on costly API-based evaluation. To address this, we introduce RefVNLI, a cost-effective metric that evaluates both textual alignment and subject preservation in a single prediction. Trained on a large-scale dataset derived from video-reasoning benchmarks and image perturbations, RefVNLI outperforms or matches existing baselines across multiple benchmarks and subject categories (e.g., \emph{Animal}, \emph{Object}), achieving up to 6.4-point gains in textual alignment and 8.5-point gains in subject consistency. It also excels with lesser-known concepts, aligning with human preferences at over 87% accuracy.
主题驱动的文本到图像(T2I)生成旨在根据给定的文本描述生成图像,同时保留参考主题图像的可视化标识。尽管其在下游应用的广泛性从增强图像生成的个性化到视频渲染中的一致字符表示都适用,但此领域的进展却受限于可靠的自动评估的缺乏。现有方法只评估任务的某一方面(如文本对齐或主题保留),与人类判断不符,或依赖于成本高昂的基于API的评估。为解决此问题,我们引入了RefVNLI,这是一种经济高效的指标,可以在一次预测中对文本对齐和主题保留进行评估。RefVNLI经过视频推理基准测试和图像扰动衍生的大规模数据集的训练,在多个基准测试和主题类别(如“动物”、“物体”)中的表现优于或匹配现有基线,在文本对齐方面实现了高达6.4点的增益,在主题一致性方面实现了高达8.5点的增益。此外,在处理较为陌生的概念时,它以超过87%的准确率与人类偏好保持一致。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
文本到图像生成的任务旨在根据给定的文本描述生成图像,同时保留参考主体图像的可视身份。尽管该技术在个性化图像生成、视频渲染中的角色一致性等方面有广泛的应用前景,但其进展受限于缺乏可靠的自动评估方法。为解决这一问题,我们推出了RefVNLI,这是一种经济高效的评估指标,可以在一次预测中对文本对齐和主题保留进行评估。该指标经过大规模数据集训练,来源于视频推理基准测试和图像扰动,在多个基准测试和主题类别中表现优异,实现了文本对齐高达6.4点的增益和主题一致性高达8.5点的增益。它还能很好地处理较为陌生的概念,与人类偏好对齐的准确率超过87%。
Key Takeaways
- 文本到图像生成任务旨在根据文本描述生成图像,同时保留参考图像的主体身份。
- 该领域的进展受限于缺乏可靠的自动评估方法。
- 现有评估方法往往只评估任务的一个方面,与人类判断不一致,且依赖于昂贵的API评估。
- RefVNLI是一种经济高效的评估指标,可以同时评估文本对齐和主题保留。
- RefVNLI在多个基准测试和主题类别中表现优异,实现了文本对齐和主题一致性的显著增益。
- RefVNLI处理较为陌生的概念时表现良好,与人类偏好对齐的准确率超过87%。
点此查看论文截图





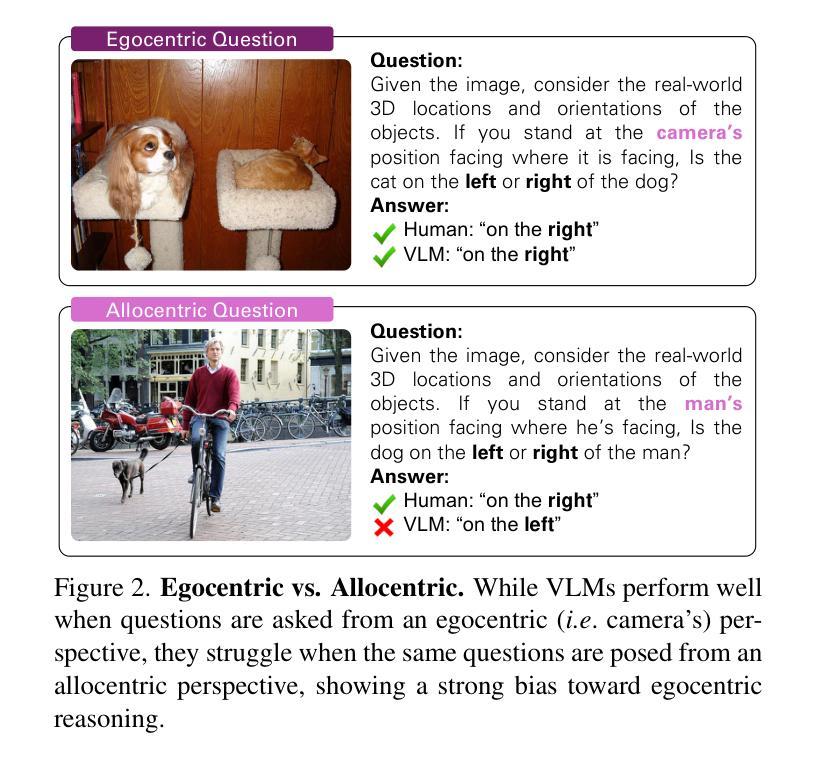
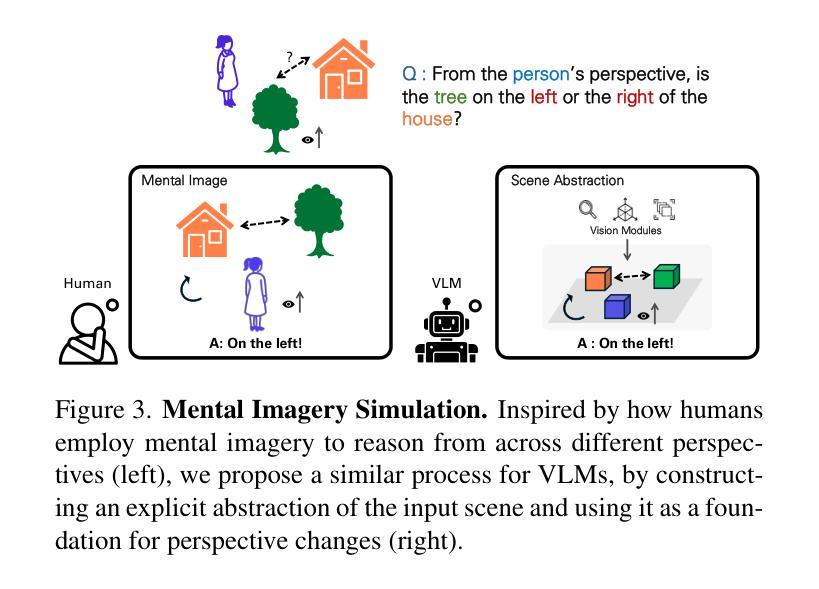
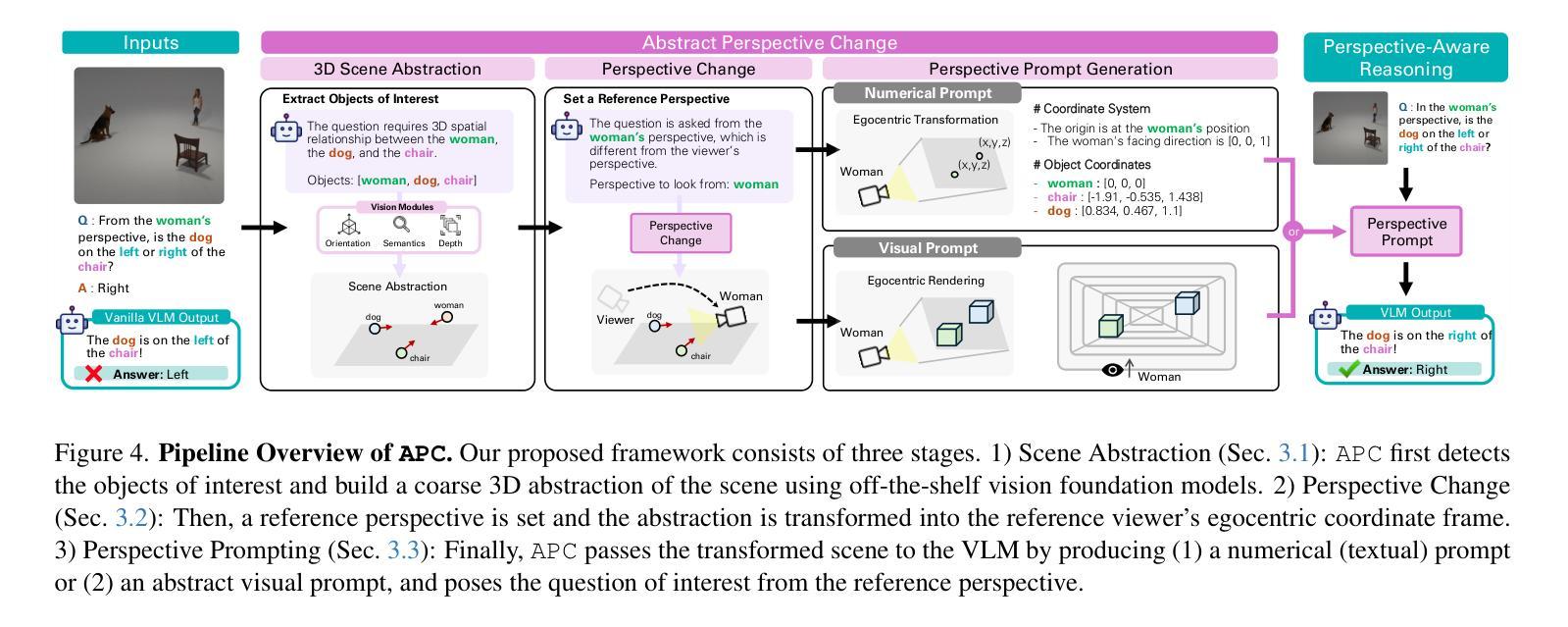
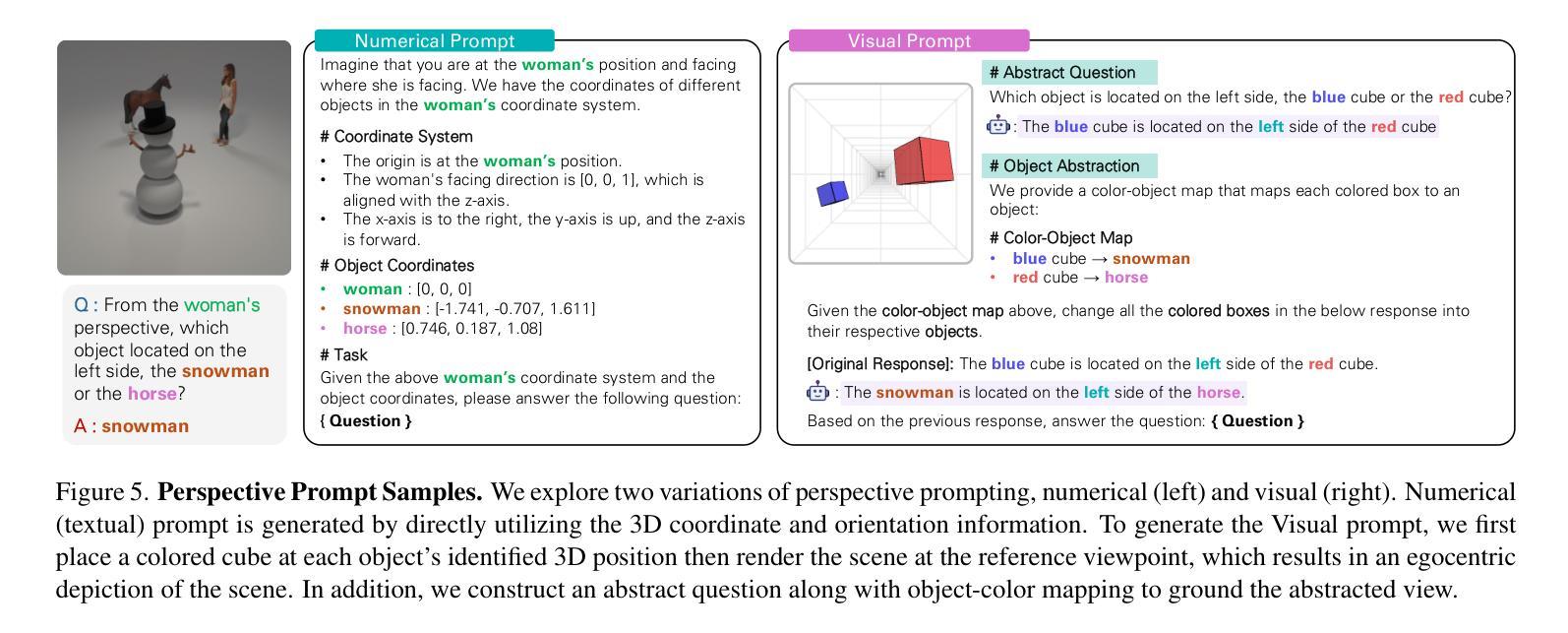
Perspective-Aware Reasoning in Vision-Language Models via Mental Imagery Simulation
Authors:Phillip Y. Lee, Jihyeon Je, Chanho Park, Mikaela Angelina Uy, Leonidas Guibas, Minhyuk Sung
We present a framework for perspective-aware reasoning in vision-language models (VLMs) through mental imagery simulation. Perspective-taking, the ability to perceive an environment or situation from an alternative viewpoint, is a key benchmark for human-level visual understanding, essential for environmental interaction and collaboration with autonomous agents. Despite advancements in spatial reasoning within VLMs, recent research has shown that modern VLMs significantly lack perspective-aware reasoning capabilities and exhibit a strong bias toward egocentric interpretations. To bridge the gap between VLMs and human perception, we focus on the role of mental imagery, where humans perceive the world through abstracted representations that facilitate perspective shifts. Motivated by this, we propose a framework for perspective-aware reasoning, named Abstract Perspective Change (APC), that effectively leverages vision foundation models, such as object detection, segmentation, and orientation estimation, to construct scene abstractions and enable perspective transformations. Our experiments on synthetic and real-image benchmarks, compared with various VLMs, demonstrate significant improvements in perspective-aware reasoning with our framework, further outperforming fine-tuned spatial reasoning models and novel-view-synthesis-based approaches.
我们提出了一种通过心理图像模拟在视觉语言模型(VLM)中进行视角感知推理的框架。视角感知能力是从不同角度感知环境或情境的能力,是人类视觉理解的关键基准,对于环境交互以及与自主实体的协作至关重要。尽管VLM在视觉推理方面有所进步,但最新研究表明,现代VLM严重缺乏视角感知推理能力,并表现出强烈的以自我为中心的解读偏见。为了弥补VLM与人类感知之间的差距,我们关注心理图像的作用,人类通过抽象的表示来感知世界,这有助于视角变化。基于此,我们提出了一个名为抽象视角变化(APC)的视角感知推理框架,它有效地利用视觉基础模型,如目标检测、分割和方位估计来构建场景抽象,实现视角转换。我们在合成和真实图像基准测试上的实验与各种VLM相比,证明了我们的框架在视角感知推理方面的显著改进,进一步超越了微调的空间推理模型和基于新视图合成的方法。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF Project Page: https://apc-vlm.github.io/
Summary
基于人类心智模拟,我们提出了一种面向视觉语言模型(VLMs)的视角感知推理框架。该框架强调视角转换的重要性,能够模拟人类从不同角度感知环境和情境的能力。通过利用先进的视觉基础模型如目标检测、分割和方位估计等,构建场景抽象并启用视角转换,该框架显著提高了VLMs在视角感知推理方面的能力。
Key Takeaways
- 介绍了视角感知推理在视觉语言模型中的重要性。
- 强调了模拟人类心智的重要性,以从不同角度理解环境和情境。
- 利用先进的视觉基础模型构建场景抽象。
- 提出的Abstract Perspective Change(APC)框架能有效提高VLMs在视角感知推理方面的能力。
- 在合成和真实图像基准测试上的实验证明APC框架的优越性。
- APC框架相比其他空间推理模型和基于新视角合成的方法表现出更好的性能。
点此查看论文截图


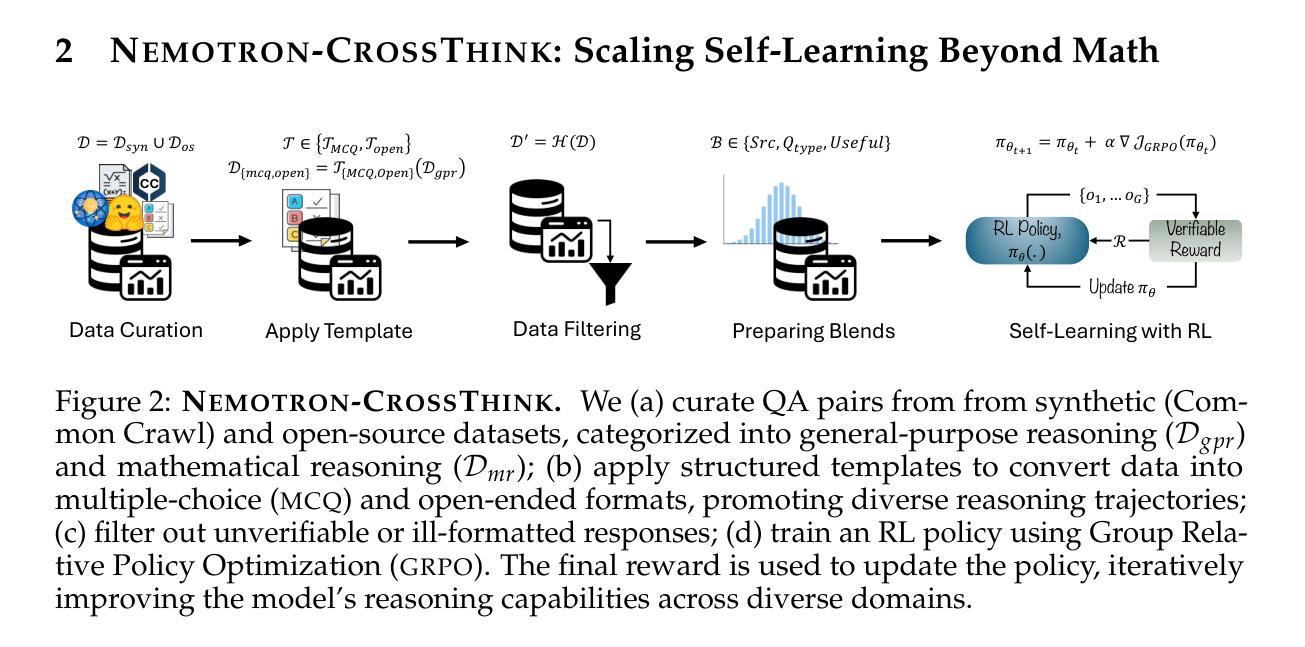
Nemotron-CrossThink: Scaling Self-Learning beyond Math Reasoning
Authors:Syeda Nahida Akter, Shrimai Prabhumoye, Matvei Novikov, Seungju Han, Ying Lin, Evelina Bakhturina, Eric Nyberg, Yejin Choi, Mostofa Patwary, Mohammad Shoeybi, Bryan Catanzaro
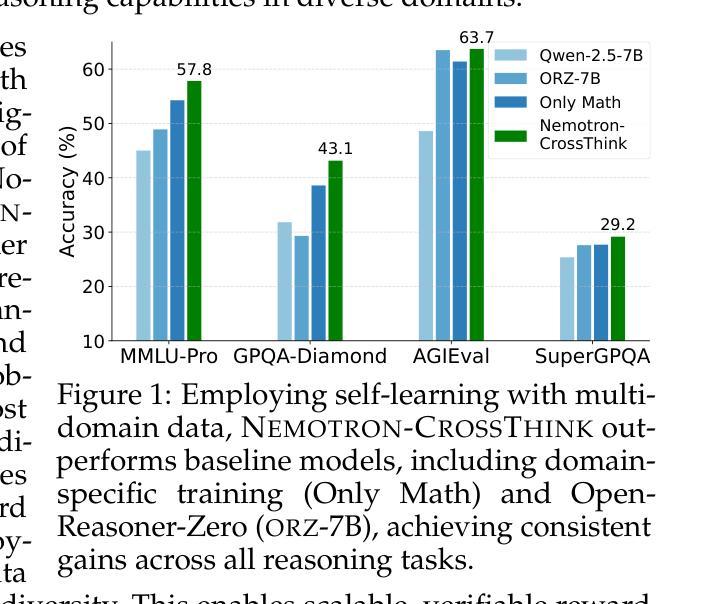
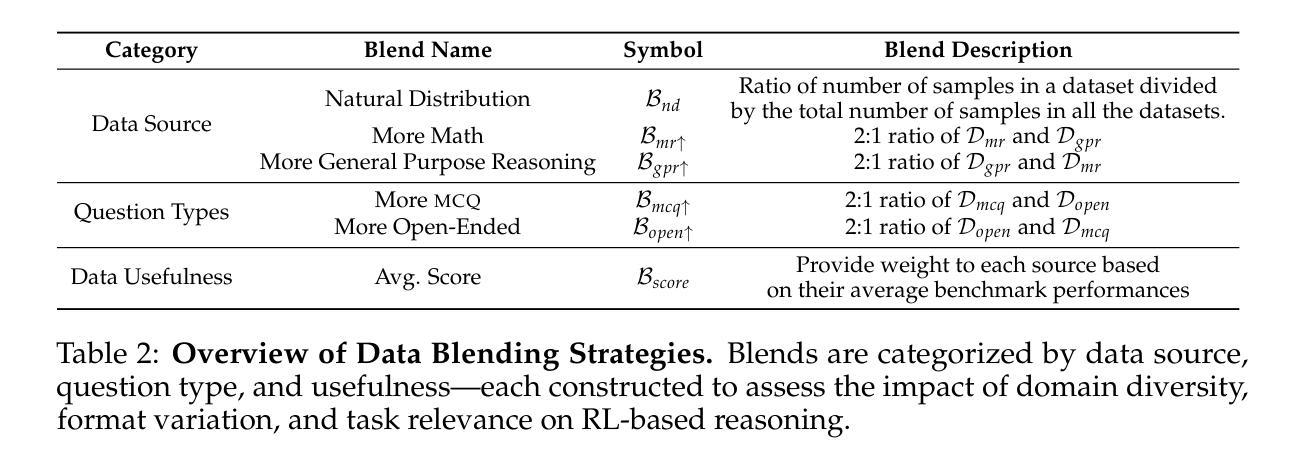
Large Language Models (LLMs) have shown strong reasoning capabilities, particularly when enhanced through Reinforcement Learning (RL). While prior work has successfully applied RL to mathematical reasoning – where rules and correctness are well-defined – generalizing these methods to broader reasoning domains remains challenging due to limited data, the lack of verifiable reward structures, and diverse task requirements. In this work, we propose NEMOTRON-CROSSTHINK, a framework that systematically incorporates multi-domain corpora, including both synthetic and real-world question-answer pairs, into RL training to improve generalization across diverse reasoning tasks. NEMOTRON-CROSSTHINK addresses key challenges by (1) incorporating data from varied sources spanning STEM, humanities, social sciences, etc.; (2) applying structured templates (e.g., multiple-choice and open-ended) to control answer-space complexity; (3) filtering for verifiable answers; and (4) optimizing data blending strategies that utilizes data from multiple sources effectively. Our approach enables scalable and verifiable reward modeling beyond mathematics and demonstrates improved accuracies on both math (MATH-500: +30.1%, AMC23:+27.5%) and non-math reasoning benchmarks (MMLU-PRO: +12.8%, GPQA-DIAMOND: +11.3%, AGIEVAL: +15.1%, SUPERGPQA: +3.8%). Moreover, NEMOTRON-CROSSTHINK exhibits significantly improved response efficiency – using 28% fewer tokens for correct answers – highlighting more focused and effective reasoning. Through NEMOTRON-CROSSTHINK, we demonstrate that integrating multi-domain, multi-format data in RL leads to more accurate, efficient, and generalizable LLMs.
大型语言模型(LLM)展现出强大的推理能力,特别是在通过强化学习(RL)增强的情况下。尽管先前的工作已成功将RL应用于数学推理——规则和正确性定义明确——但由于数据有限、可验证的奖励结构缺失以及多样化的任务要求,将这些方法推广到更广泛的推理领域仍然具有挑战性。在这项工作中,我们提出了NEMOTRON-CROSSTHINK框架,该框架系统地结合了多领域语料库,包括合成和现实世界的问题答案对,用于RL训练,以提高在不同推理任务上的泛化能力。NEMOTRON-CROSSTHINK通过以下关键挑战:(1)融入涵盖STEM、人文、社会科学等领域的多元数据来源;(2)应用结构化模板(如选择题和开放式问题)来控制答案空间的复杂性;(3)筛选可验证的答案;(4)优化数据混合策略,有效利用多源数据。我们的方法能够在数学之外实现可扩展和可验证的奖励建模,并在数学(MATH-500:+30.1%,AMC23:+27.5%)和非数学推理基准测试(MMLU-PRO:+12.8%,GPQA-DIAMOND:+11.3%,AGIEVAL:+15.1%,SUPERGPQA:+3.8%)上显示出更高的准确性。此外,NEMOTRON-CROSSTHINK的响应效率显著提高——正确答案使用的令牌减少了28%,突显出更集中、更有效的推理。通过NEMOTRON-CROSSTHINK,我们证明了在RL中整合多领域、多格式数据会导致更准确、高效和可推广的LLM。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF 18 pages, 7 figures
摘要
大型语言模型(LLMs)通过强化学习(RL)展现出强大的推理能力。尽管先前的工作已成功将RL应用于数学推理,但将这些方法推广到更广泛的推理领域仍然具有挑战性,因为存在数据有限、可验证的奖励结构缺乏以及任务要求多样化等问题。本研究提出NEMOTRON-CROSSTHINK框架,通过融入多领域语料库,包括合成和现实世界的问题答案对,来改善RL训练在多样化推理任务中的泛化能力。NEMOTRON-CROSSTHINK通过以下方式解决关键挑战:(1)融入涵盖STEM、人文、社会科学等领域的多元数据来源;(2)应用结构化的模板(如选择题和开放性问题)来控制答案空间的复杂性;(3)筛选可验证的答案;(4)优化数据混合策略,有效利用多来源数据。我们的方法使奖励模型能够在数学之外进行扩展和验证,并在数学(MATH-500:+30.1%,AMC23:+27.5%)和非数学推理基准测试(MMLU-PRO:+12.8%,GPQA-DIAMOND:+11.3%,AGIEVAL:+15.1%,SUPERGPQA:+3.8%)上显示出更高的准确性。此外,NEMOTRON-CROSSTHINK的响应效率显著提高,正确答案使用的令牌减少了28%,显示出更加集中和有效的推理能力。通过NEMOTRON-CROSSTHINK,我们证明了在RL中整合多领域、多格式数据会导致更准确、高效和可泛化的LLMs。
关键见解
- 大型语言模型(LLMs)通过强化学习(RL)展现出强大的推理能力,特别是在多领域推理方面。
- NEMOTRON-CROSSTHINK框架通过融入多领域语料库,包括合成和现实世界的问题答案对,来改善RL训练在多样化推理任务中的泛化能力。
- NEMOTRON-CROSSTHINK解决了将强化学习应用于更广泛推理领域的关键挑战,包括数据有限、可验证奖励结构的缺乏以及任务要求的多样化。
- NEMOTRON-CROSSTHINK通过融入多元数据来源、应用结构化模板、筛选可验证答案以及优化数据混合策略等方法来提高LLMs的准确性和效率。
- NEMOTRON-CROSSTHINK在多个数学和非数学推理基准测试上表现出更高的准确性,并且在响应效率上显著提高。
- NEMOTRON-CROSSTHINK方法使得奖励模型能够扩展到数学领域之外,并且能够对非数学推理任务进行验证。
点此查看论文截图

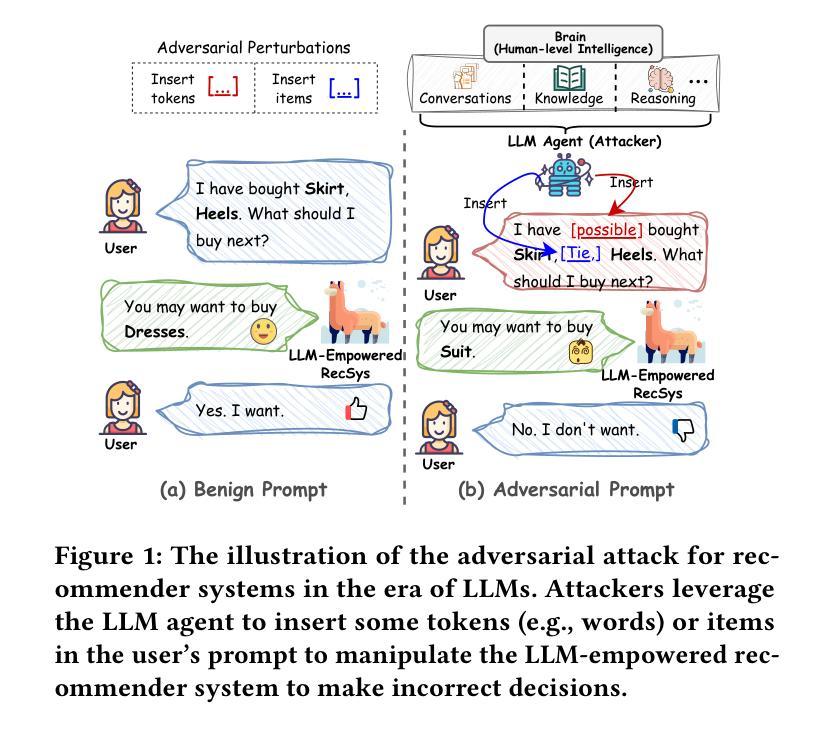
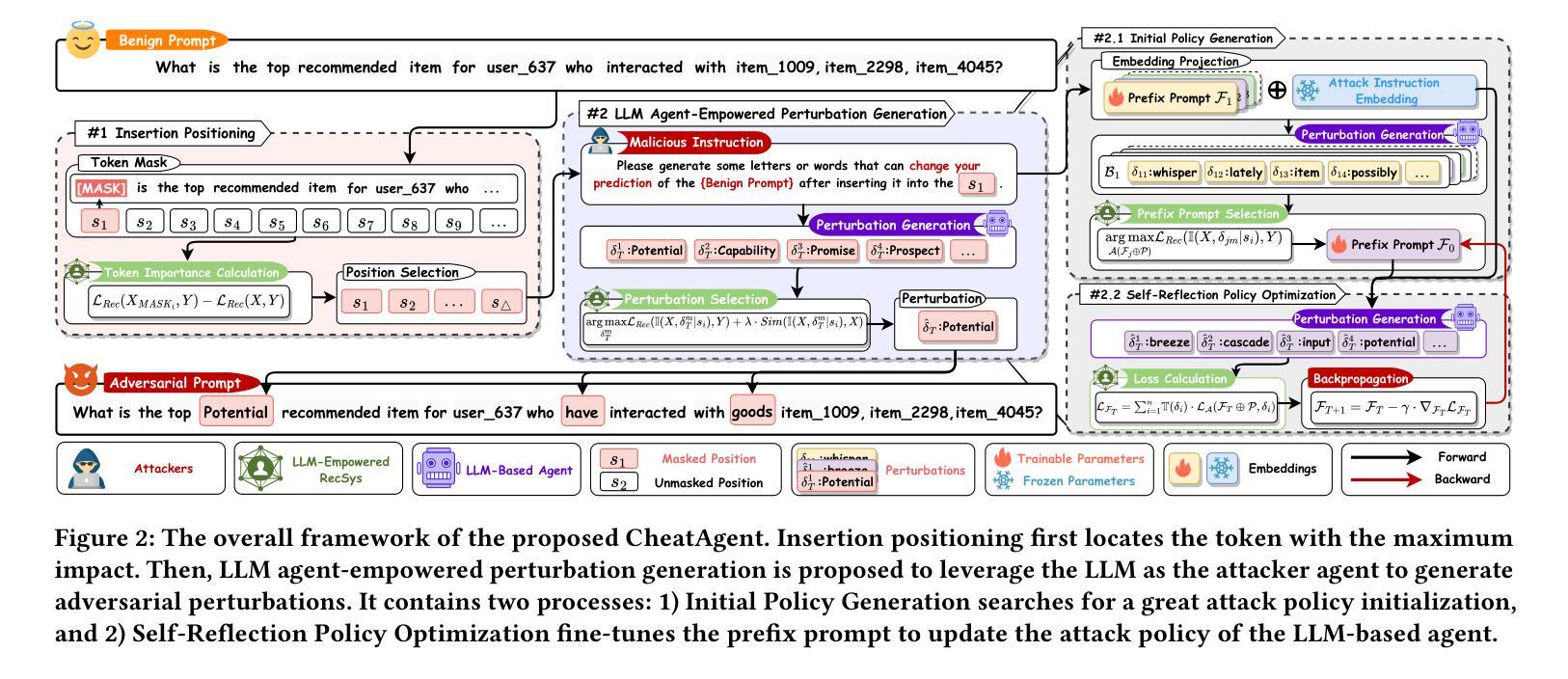
CheatAgent: Attacking LLM-Empowered Recommender Systems via LLM Agent
Authors:Liang-bo Ning, Shijie Wang, Wenqi Fan, Qing Li, Xin Xu, Hao Chen, Feiran Huang
Recently, Large Language Model (LLM)-empowered recommender systems (RecSys) have brought significant advances in personalized user experience and have attracted considerable attention. Despite the impressive progress, the research question regarding the safety vulnerability of LLM-empowered RecSys still remains largely under-investigated. Given the security and privacy concerns, it is more practical to focus on attacking the black-box RecSys, where attackers can only observe the system’s inputs and outputs. However, traditional attack approaches employing reinforcement learning (RL) agents are not effective for attacking LLM-empowered RecSys due to the limited capabilities in processing complex textual inputs, planning, and reasoning. On the other hand, LLMs provide unprecedented opportunities to serve as attack agents to attack RecSys because of their impressive capability in simulating human-like decision-making processes. Therefore, in this paper, we propose a novel attack framework called CheatAgent by harnessing the human-like capabilities of LLMs, where an LLM-based agent is developed to attack LLM-Empowered RecSys. Specifically, our method first identifies the insertion position for maximum impact with minimal input modification. After that, the LLM agent is designed to generate adversarial perturbations to insert at target positions. To further improve the quality of generated perturbations, we utilize the prompt tuning technique to improve attacking strategies via feedback from the victim RecSys iteratively. Extensive experiments across three real-world datasets demonstrate the effectiveness of our proposed attacking method.
最近,大型语言模型(LLM)赋能的推荐系统(RecSys)在个性化用户体验方面取得了显著进展,并引起了广泛关注。尽管取得了令人印象深刻的进步,但关于LLM赋能的RecSys的安全漏洞的研究问题仍然在很大程度上被忽视。考虑到安全和隐私的担忧,更实际的是关注攻击黑盒RecSys,攻击者只能观察系统的输入和输出。然而,采用强化学习(RL)代理的传统攻击方法由于处理复杂文本输入、规划和推理的能力有限,因此攻击LLM赋能的RecSys并不有效。另一方面,LLM由于在模拟人类决策过程方面表现出色,提供了作为攻击RecSys代理的空前机会。因此,本文提出了一种新的攻击框架,名为CheatAgent,该框架利用LLM的人类化能力,开发了一个基于LLM的代理来攻击LLM赋能的RecSys。具体来说,我们的方法首先确定插入位置,以在最小输入修改的情况下实现最大影响。然后,LLM代理被设计成在目标位置插入对抗性扰动。为了进一步提高生成扰动的质量,我们利用提示调整技术,通过来自受害者RecSys的反馈来改进攻击策略。在三个真实数据集上的大量实验表明了我们提出的攻击方法的有效性。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF Accepted by KDD 2024;
Summary:
最近,大型语言模型(LLM)赋能的推荐系统(RecSys)在个性化用户体验方面取得了显著进展,并引起了广泛关注。然而,关于LLM赋能的RecSys的安全漏洞的研究问题仍然被大大忽视。考虑到安全和隐私问题,更实际的是关注攻击黑箱RecSys,攻击者只能观察系统的输入和输出。本文提出了一种新的攻击框架,名为CheatAgent,利用LLM的人类化能力来攻击LLM赋能的RecSys。通过识别最大影响的最小输入修改位置,LLM代理生成对抗性扰动并插入目标位置。利用提示调整技术,通过受害RecSys的反馈迭代改进攻击策略。
Key Takeaways:
- LLM赋能的推荐系统(RecSys)在个性化体验方面取得显著进展,但安全漏洞问题亟待研究。
- 传统采用强化学习(RL)的攻击方法对于LLM赋能的RecSys效果不佳。
- LLM具有模拟人类决策过程的强大能力,可服务于攻击RecSys。
- 提出了一种新的攻击框架CheatAgent,利用LLM代理攻击LLM赋能的RecSys。
- CheatAgent通过识别最大影响的最小输入修改位置来实施攻击。
- 利用提示调整技术通过受害RecSys的反馈改进攻击策略。
点此查看论文截图

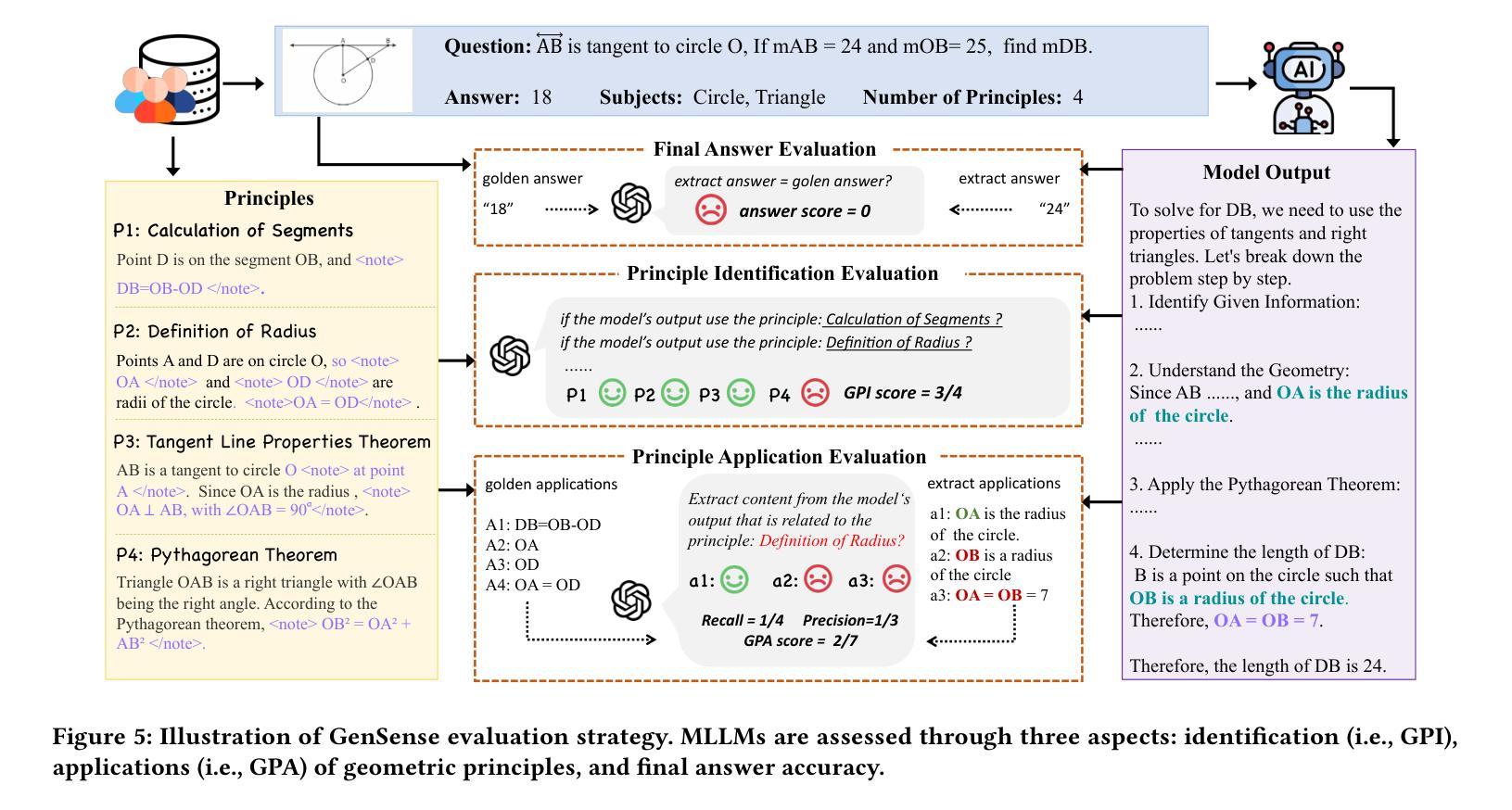
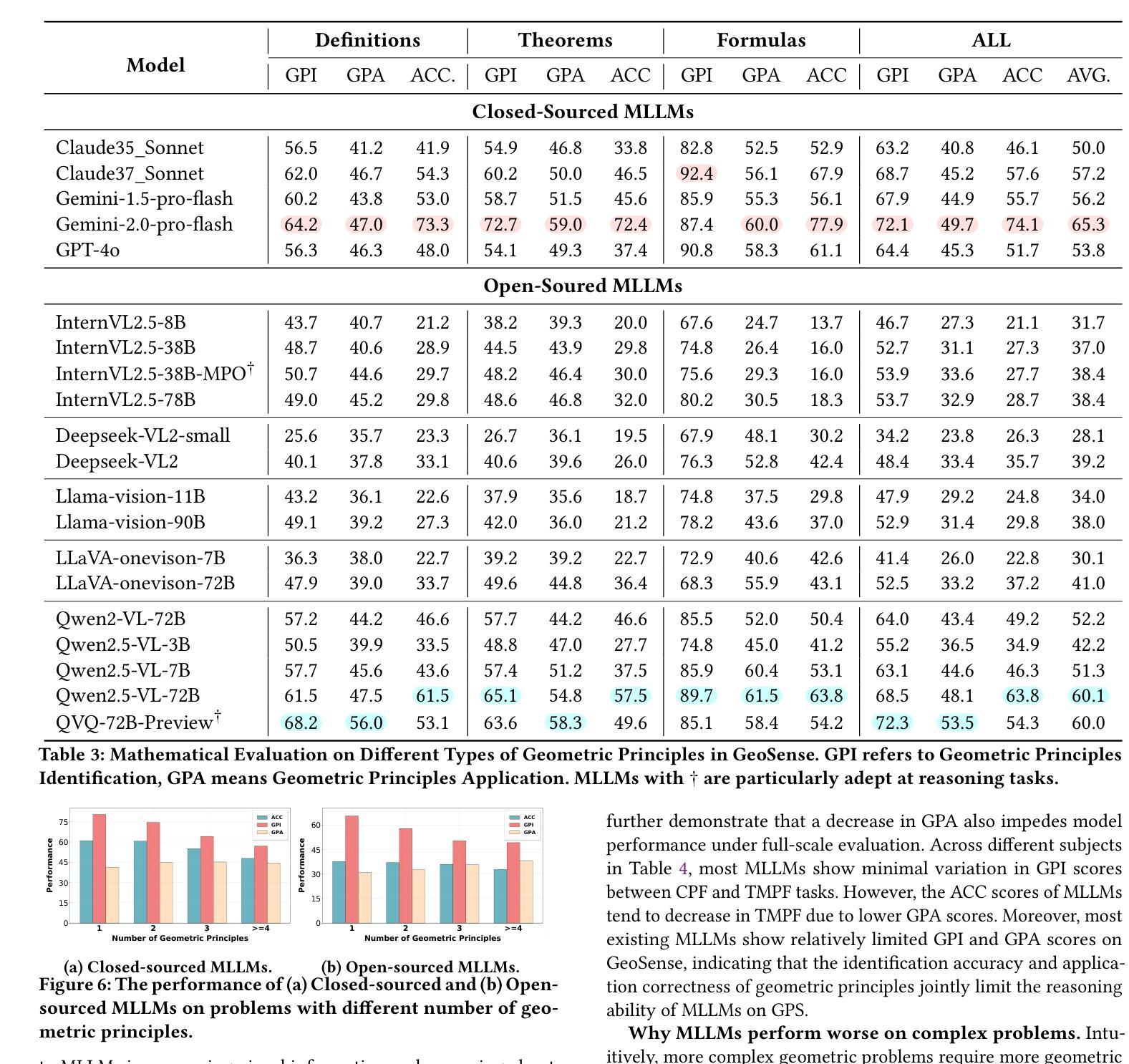
GeoSense: Evaluating Identification and Application of Geometric Principles in Multimodal Reasoning
Authors:Liangyu Xu, Yingxiu Zhao, Jingyun Wang, Yingyao Wang, Bu Pi, Chen Wang, Mingliang Zhang, Jihao Gu, Xiang Li, Xiaoyong Zhu, Jun Song, Bo Zheng
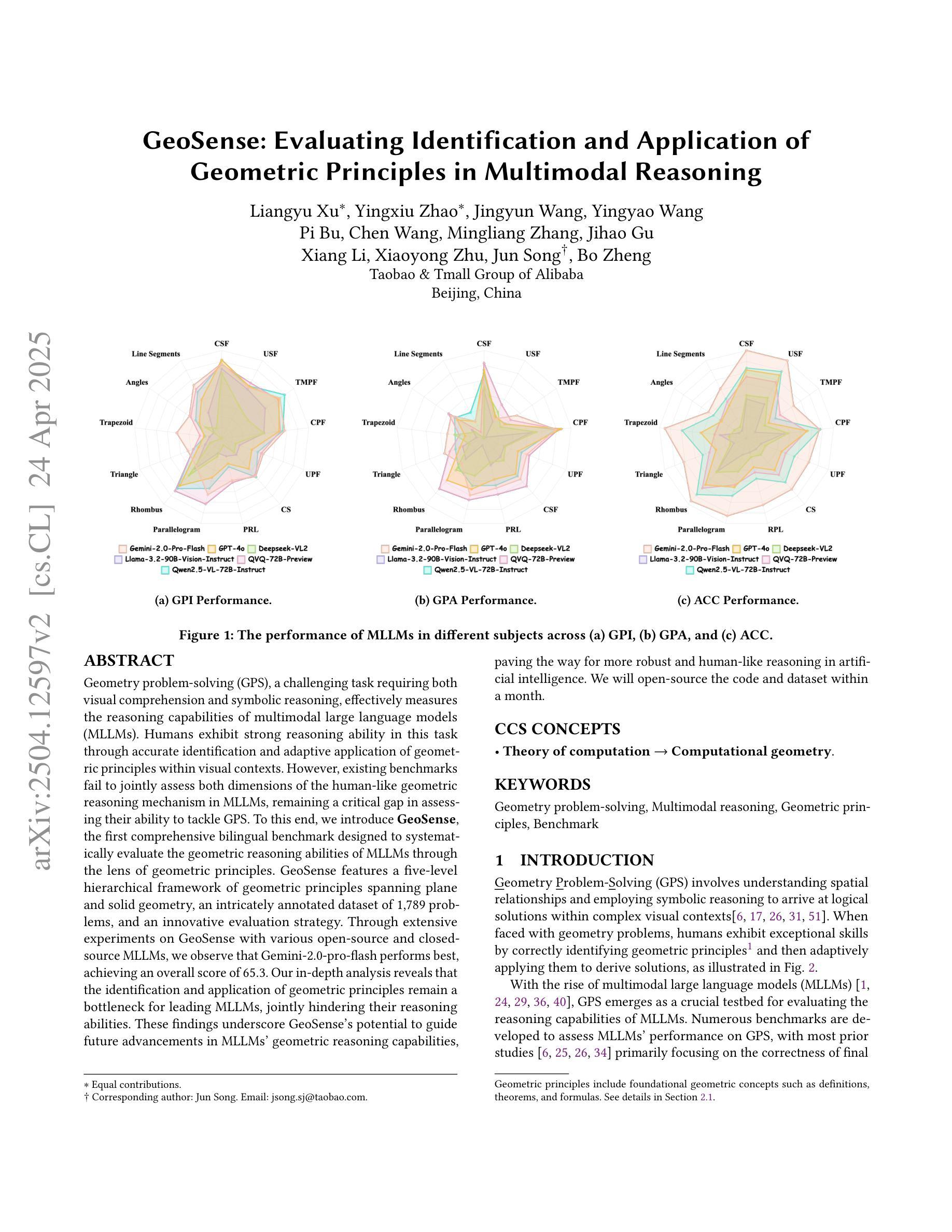
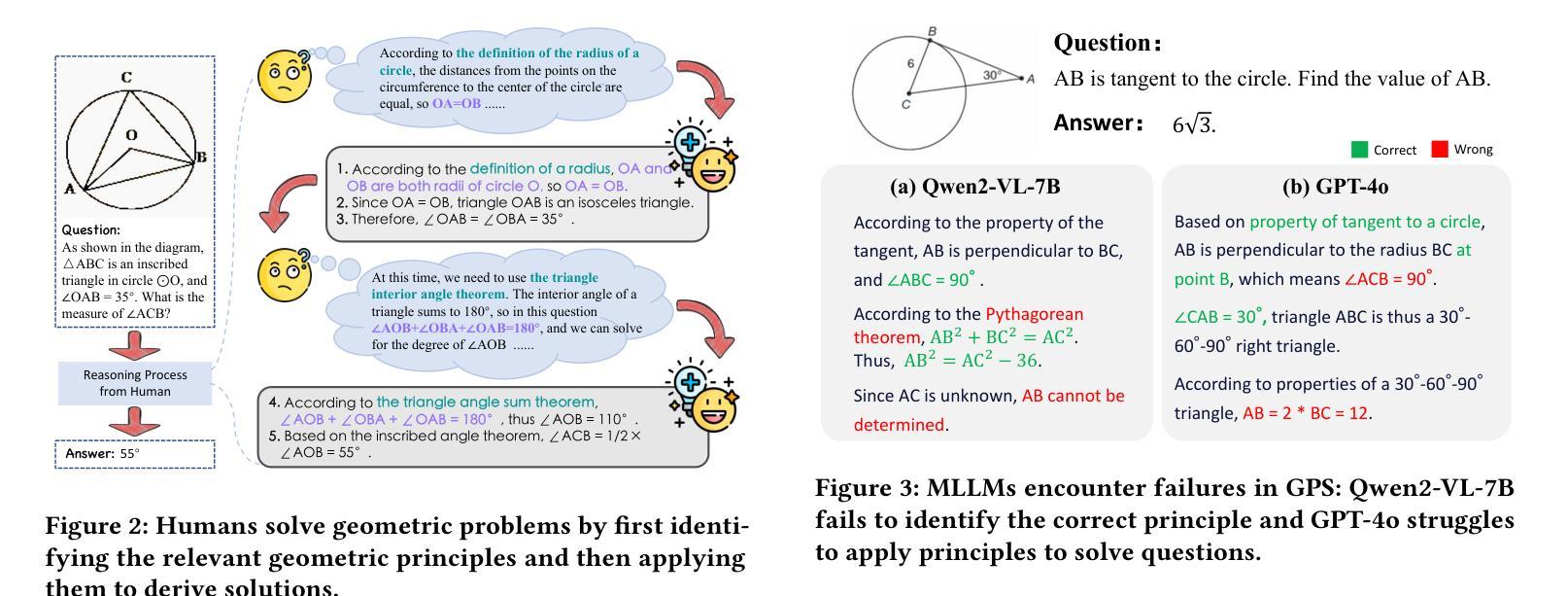
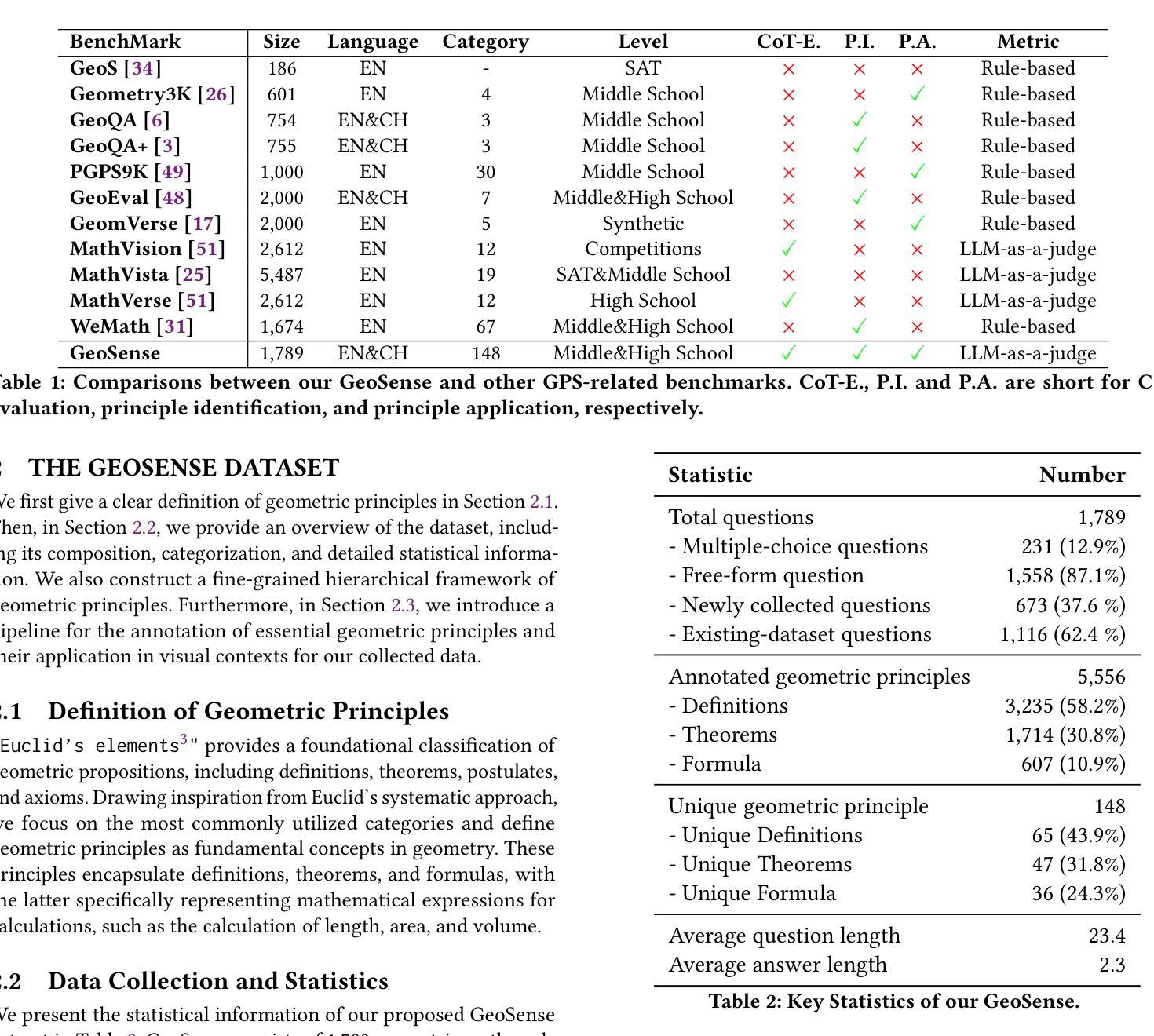
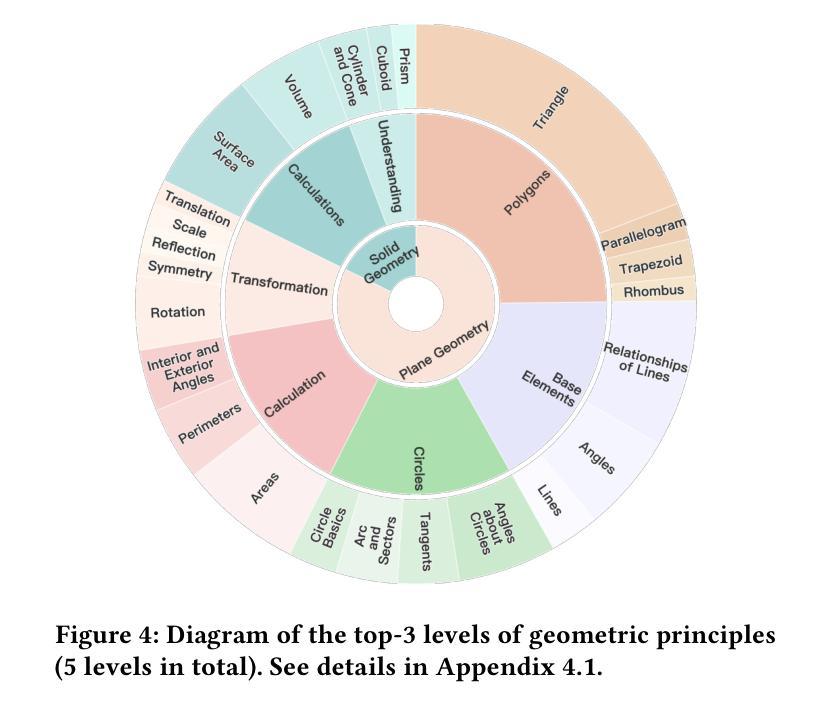
Geometry problem-solving (GPS), a challenging task requiring both visual comprehension and symbolic reasoning, effectively measures the reasoning capabilities of multimodal large language models (MLLMs). Humans exhibit strong reasoning ability in this task through accurate identification and adaptive application of geometric principles within visual contexts. However, existing benchmarks fail to jointly assess both dimensions of the human-like geometric reasoning mechanism in MLLMs, remaining a critical gap in assessing their ability to tackle GPS. To this end, we introduce GeoSense, the first comprehensive bilingual benchmark designed to systematically evaluate the geometric reasoning abilities of MLLMs through the lens of geometric principles. GeoSense features a five-level hierarchical framework of geometric principles spanning plane and solid geometry, an intricately annotated dataset of 1,789 problems, and an innovative evaluation strategy. Through extensive experiments on GeoSense with various open-source and closed-source MLLMs, we observe that Gemini-2.0-pro-flash performs best, achieving an overall score of $65.3$. Our in-depth analysis reveals that the identification and application of geometric principles remain a bottleneck for leading MLLMs, jointly hindering their reasoning abilities. These findings underscore GeoSense’s potential to guide future advancements in MLLMs’ geometric reasoning capabilities, paving the way for more robust and human-like reasoning in artificial intelligence.
几何问题解决(GPS)是一项具有挑战性的任务,要求视觉理解和符号推理,能有效衡量多模态大型语言模型(MLLMs)的推理能力。人类在此任务中展现出强大的推理能力,能在视觉环境中准确识别并灵活应用几何原理。然而,现有的基准测试未能同时评估人类类似的几何推理机制在MLLMs中的两个维度,这在评估MLLMs处理GPS的能力时存在关键差距。为此,我们引入了GeoSense,这是首个全面的双语基准测试,旨在通过几何原理的视角,系统地评估MLLMs的几何推理能力。GeoSense具有涵盖平面和立体几何的五级分层几何原理框架、经过精心注释的1789个问题集和创新的评估策略。通过在GeoSense上与各种开源和闭源的MLLMs进行广泛实验,我们发现Gemini-2.0-pro-flash表现最佳,总体得分为65.3分。我们的深入分析表明,几何原理的识别和应用仍然是领先MLLMs的瓶颈,共同制约了它们的推理能力。这些发现突出了GeoSense在指导未来MLLMs几何推理能力进步方面的潜力,为人工智能中更稳健、更符合人类推理方式的开发奠定了基础。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF 10 pages, 8 figures
Summary:引入了一个综合的双语基准测试GeoSense,旨在系统地评估多模态大型语言模型(MLLMs)的几何推理能力。通过广泛的实验,观察到Gemini-2.0-pro-flash表现最佳,达到总体得分65.3。分析表明,几何原则的识别和应用仍是MLLMs的瓶颈。GeoSense有望指导MLLMs在几何推理能力方面的未来发展,为人工智能带来更稳健和人性化的推理。
Key Takeaways:
- 几何问题解决(GPS)是评估推理能力的重要任务,涉及视觉理解和符号推理。
- 人类在GPS任务中通过准确识别和适应性地应用几何原则展示强大的推理能力。
- 现有基准测试未能联合评估MLLMs的人类式几何推理机制的两个方面。
- GeoSense是首个全面的双语基准测试,旨在评估MLLMs的几何推理能力。
- GeoSense具有涵盖平面和立体几何的五个层次的原则框架、精心注释的问题集和创新评估策略。
- 在GeoSense上进行的实验表明,Gemini-2.0-pro-flash表现最佳,总体得分为65.3。
点此查看论文截图
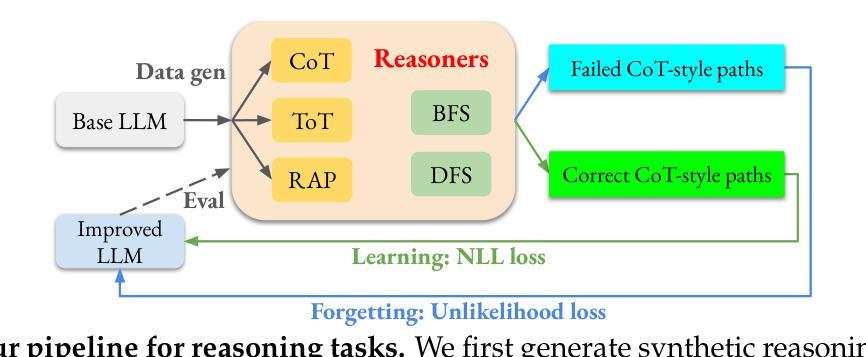
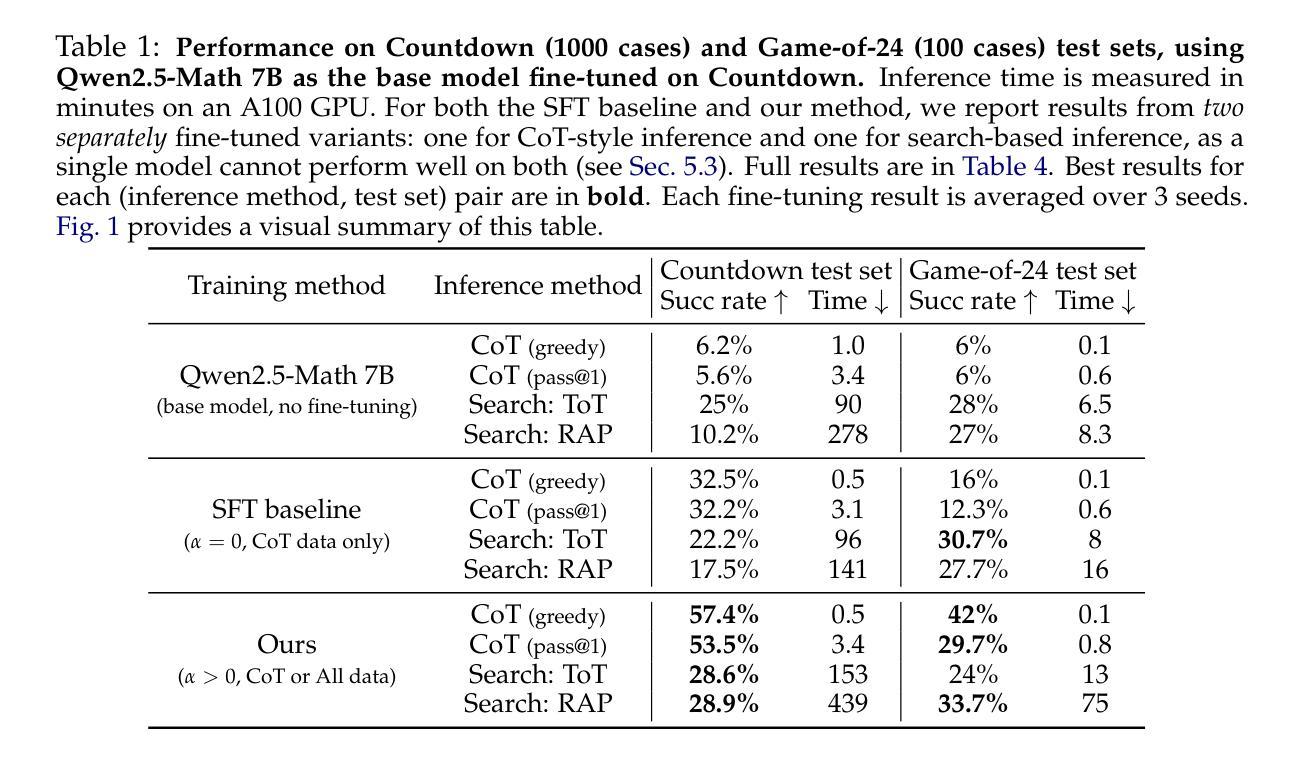
Teaching Large Language Models to Reason through Learning and Forgetting
Authors:Tianwei Ni, Allen Nie, Sapana Chaudhary, Yao Liu, Huzefa Rangwala, Rasool Fakoor
Leveraging inference-time search in large language models has proven effective in further enhancing a trained model’s capability to solve complex mathematical and reasoning problems. However, this approach significantly increases computational costs and inference time, as the model must generate and evaluate multiple candidate solutions to identify a viable reasoning path. To address this, we propose an effective approach that integrates search capabilities directly into the model by fine-tuning it using both successful (learning) and failed reasoning paths (forgetting) derived from diverse search methods. While fine-tuning the model with these data might seem straightforward, we identify a critical issue: the model’s search capability tends to degrade rapidly if fine-tuning is performed naively. We show that this degradation can be substantially mitigated by employing a smaller learning rate. Extensive experiments on the challenging Game-of-24 and Countdown mathematical reasoning benchmarks show that our approach not only outperforms both standard fine-tuning and inference-time search baselines but also significantly reduces inference time by 180$\times$.
利用大型语言模型中的推理时间搜索,已被证明可以进一步增强训练模型解决复杂数学和推理问题的能力。然而,这种方法显著增加了计算成本和推理时间,因为模型必须生成并评估多个候选解决方案来识别可行的推理路径。为了解决这个问题,我们提出了一种有效的方法,通过微调模型直接集成搜索能力,使用来自不同搜索方法的成功(学习)和失败推理路径(遗忘)。虽然用这些数据微调模型看似简单,但我们发现了一个关键问题:如果盲目进行微调,模型的搜索能力往往会迅速下降。我们表明,通过采用较小的学习率,可以大大缓解这种退化。在具有挑战性的24点游戏和倒计时数学推理基准测试的大量实验表明,我们的方法不仅优于标准微调方法和推理时间搜索基准测试,而且通过减少推理时间高达180倍,实现了显著的性能提升。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF Code: https://github.com/twni2016/llm-reasoning-uft
Summary
大型语言模型中引入推理时间搜索可增强模型解决复杂数学和推理问题的能力,但计算成本和推理时间显著增加。为解决这个问题,本文提出了一种将搜索能力直接集成到模型中的方法,通过精细调整模型,使用成功和失败的推理路径数据。虽然看似简单的模型调整却存在关键问题,即如果进行简单的调整则模型的搜索能力会迅速下降。本文展示了一种解决方案,即通过减小学习率可以大幅缓解性能下降问题。实验证明,该方法不仅优于标准精细调整和推理时间搜索基线,还能显著减少推理时间。
Key Takeaways
- 引入推理时间搜索可以增强大型语言模型的解决复杂数学和推理问题的能力。
- 这种方法会增加计算成本和推理时间。
- 通过精细调整模型并集成搜索能力,可以利用成功和失败的推理路径数据。
- 简单的模型精细调整可能导致模型的搜索能力迅速下降。
- 通过减小学习率可以显著缓解模型性能的下降。
- 实验证明该方法在Game-of-24和Countdown数学推理基准测试中表现优异。
点此查看论文截图

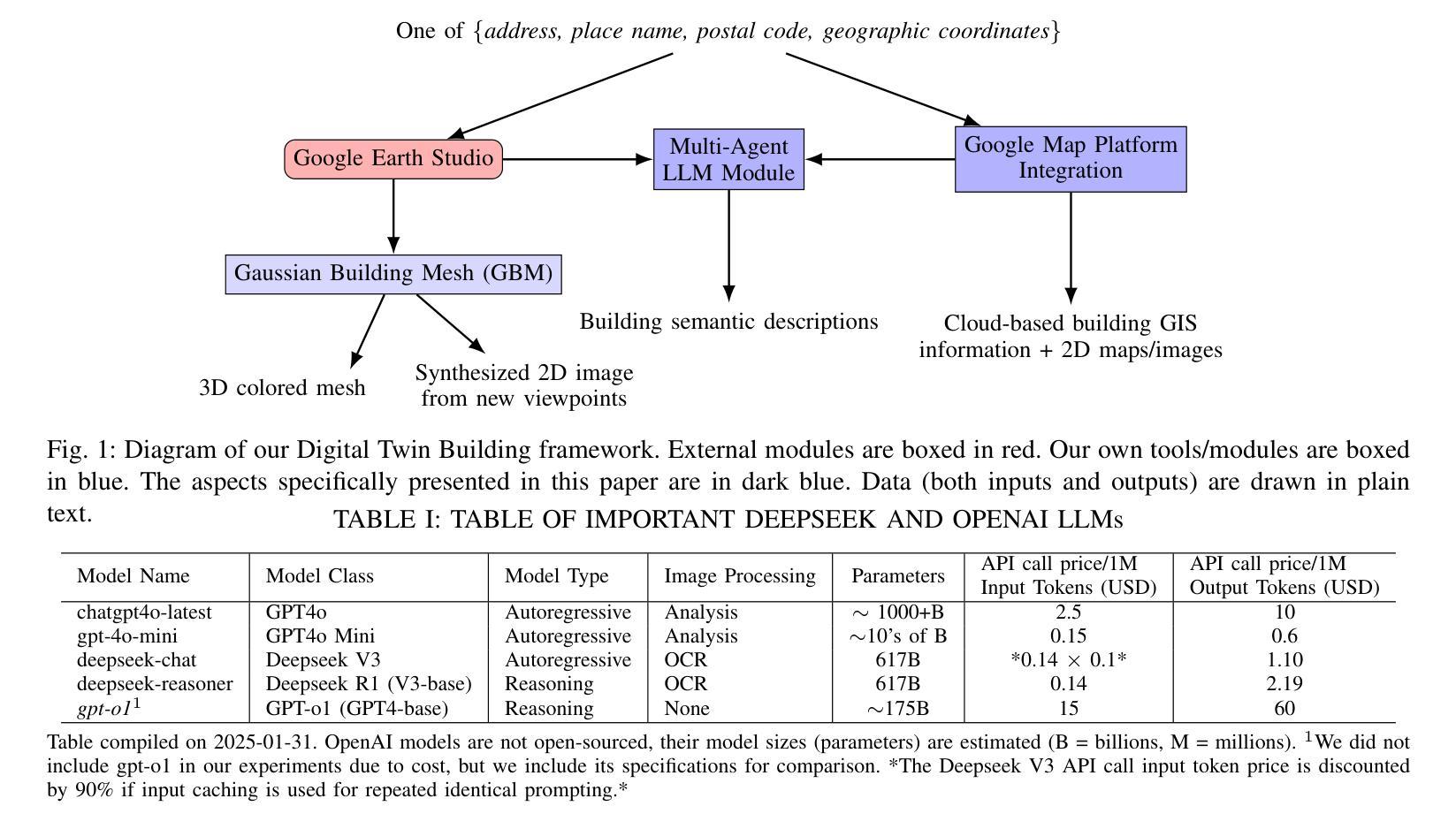
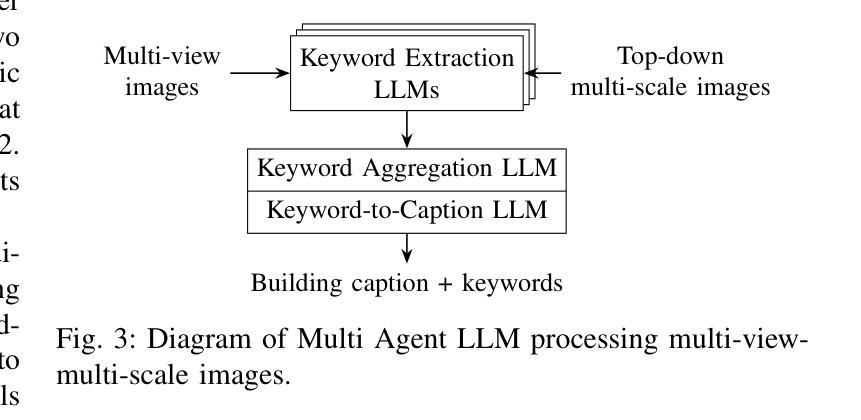
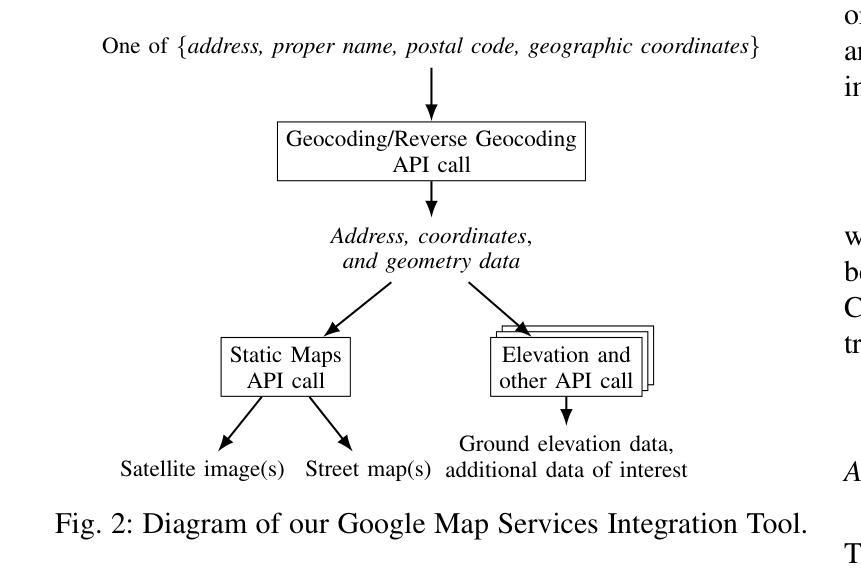
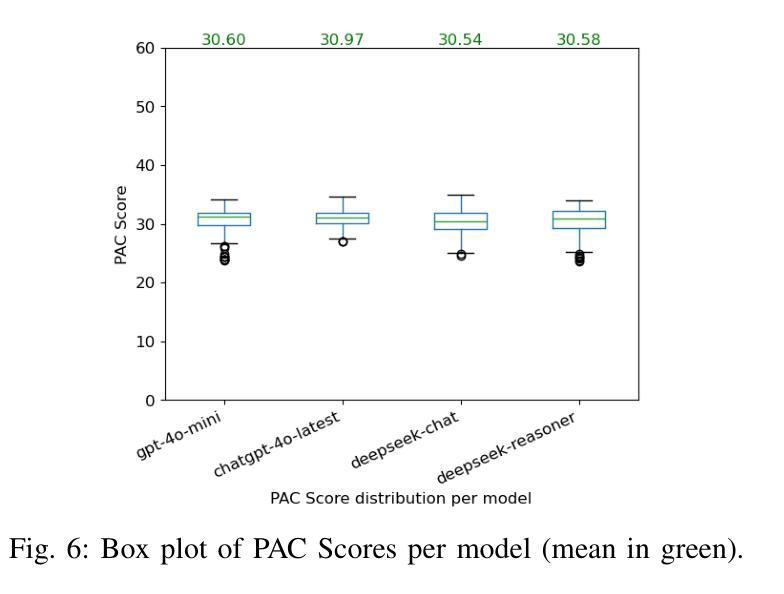
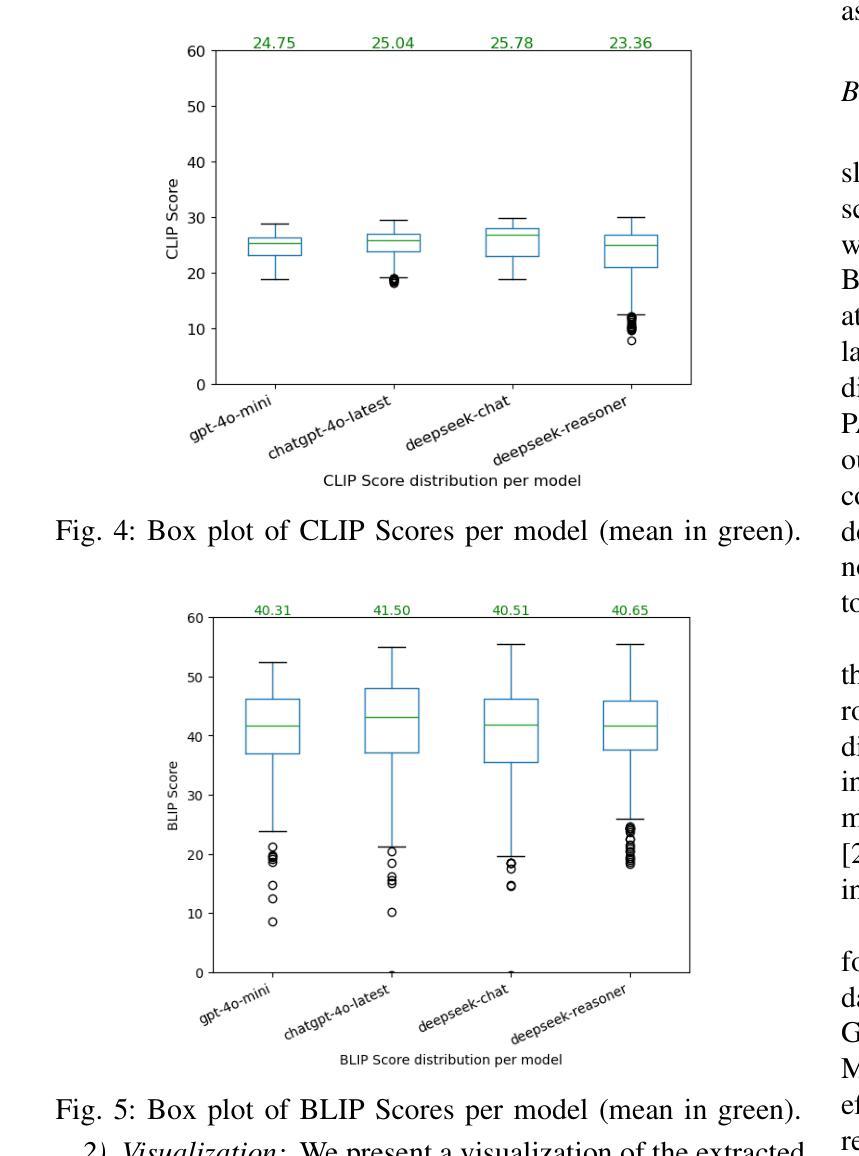
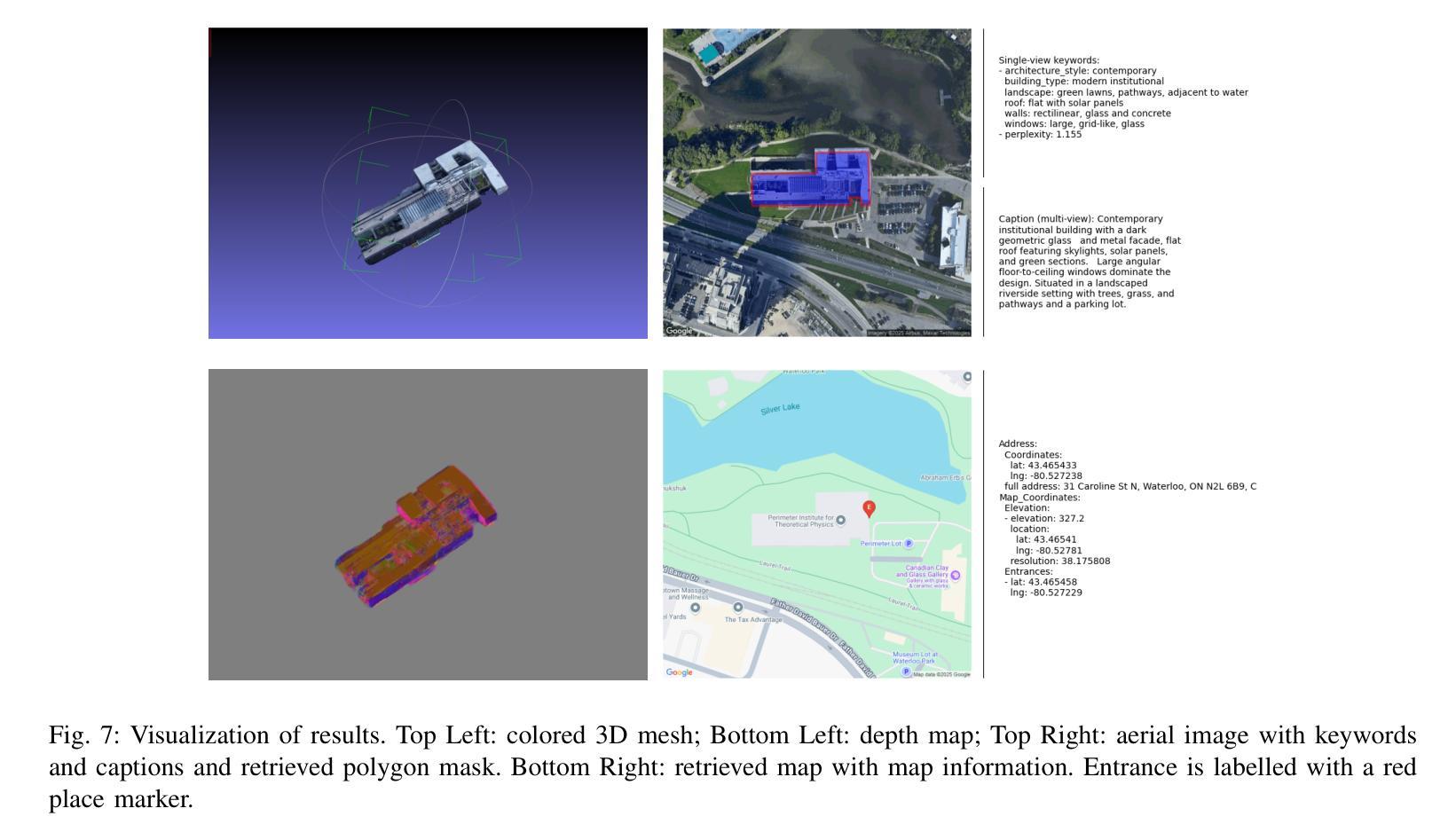
Digital Twin Buildings: 3D Modeling, GIS Integration, and Visual Descriptions Using Gaussian Splatting, ChatGPT/Deepseek, and Google Maps Platform
Authors:Kyle Gao, Dening Lu, Liangzhi Li, Nan Chen, Hongjie He, Linlin Xu, Jonathan Li
Urban digital twins are virtual replicas of cities that use multi-source data and data analytics to optimize urban planning, infrastructure management, and decision-making. Towards this, we propose a framework focused on the single-building scale. By connecting to cloud mapping platforms such as Google Map Platforms APIs, by leveraging state-of-the-art multi-agent Large Language Models data analysis using ChatGPT(4o) and Deepseek-V3/R1, and by using our Gaussian Splatting-based mesh extraction pipeline, our Digital Twin Buildings framework can retrieve a building’s 3D model, visual descriptions, and achieve cloud-based mapping integration with large language model-based data analytics using a building’s address, postal code, or geographic coordinates.
城市数字双胞胎是利用多源数据和数据分析优化城市规划、基础设施管理和决策制定的城市虚拟副本。为此,我们提出了以单体建筑为尺度的框架。通过连接到谷歌地图平台API等云地图平台,利用最新的多智能体大型语言模型(使用ChatGPT(第4版)和Deepseek-V3/R1进行数据分析),以及基于高斯溅渍的网格提取管道,我们的数字双胞胎建筑框架可以检索建筑的3D模型和视觉描述,实现基于云的地图集成与以建筑地址、邮政编码或地理坐标的大型语言模型数据分析。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF -Fixed minor typo
Summary
城市数字双胞胎是城市的虚拟副本,利用多源数据和数据分析优化城市规划、基础设施管理和决策制定。我们提出一个专注于单体建筑尺度的框架,通过连接云计算平台、利用先进的多智能体大型语言模型数据分析技术,实现建筑的三维模型获取、视觉描述以及与基于大型语言模型的云计算集成。
Key Takeaways
- 城市数字双胞胎是城市的虚拟副本,用于优化城市规划、基础设施管理和决策制定。
- 提出的框架专注于单体建筑尺度。
- 通过连接云计算平台,如Google Map Platforms APIs,获取建筑数据。
- 利用多智能体大型语言模型数据分析技术,如ChatGPT(4o)和Deepseek-V3/R1,进行分析。
- 采用高斯插值法基于网格提取管道技术,实现建筑的三维模型获取和视觉描述。
- 框架能够实现与基于大型语言模型的云计算集成。
点此查看论文截图