⚠️ 以下所有内容总结都来自于 大语言模型的能力,如有错误,仅供参考,谨慎使用
🔴 请注意:千万不要用于严肃的学术场景,只能用于论文阅读前的初筛!
💗 如果您觉得我们的项目对您有帮助 ChatPaperFree ,还请您给我们一些鼓励!⭐️ HuggingFace免费体验
2025-04-29 更新
RSFR: A Coarse-to-Fine Reconstruction Framework for Diffusion Tensor Cardiac MRI with Semantic-Aware Refinement
Authors:Jiahao Huang, Fanwen Wang, Pedro F. Ferreira, Haosen Zhang, Yinzhe Wu, Zhifan Gao, Lei Zhu, Angelica I. Aviles-Rivero, Carola-Bibiane Schonlieb, Andrew D. Scott, Zohya Khalique, Maria Dwornik, Ramyah Rajakulasingam, Ranil De Silva, Dudley J. Pennell, Guang Yang, Sonia Nielles-Vallespin
Cardiac diffusion tensor imaging (DTI) offers unique insights into cardiomyocyte arrangements, bridging the gap between microscopic and macroscopic cardiac function. However, its clinical utility is limited by technical challenges, including a low signal-to-noise ratio, aliasing artefacts, and the need for accurate quantitative fidelity. To address these limitations, we introduce RSFR (Reconstruction, Segmentation, Fusion & Refinement), a novel framework for cardiac diffusion-weighted image reconstruction. RSFR employs a coarse-to-fine strategy, leveraging zero-shot semantic priors via the Segment Anything Model and a robust Vision Mamba-based reconstruction backbone. Our framework integrates semantic features effectively to mitigate artefacts and enhance fidelity, achieving state-of-the-art reconstruction quality and accurate DT parameter estimation under high undersampling rates. Extensive experiments and ablation studies demonstrate the superior performance of RSFR compared to existing methods, highlighting its robustness, scalability, and potential for clinical translation in quantitative cardiac DTI.
心脏扩散张量成像(DTI)为心肌细胞排列提供了独特的见解,架起了微观和宏观心脏功能之间的桥梁。然而,由于其信号噪声比较低、存在混叠伪影以及需要准确的定量保真等技术挑战,其临床应用受到限制。为了克服这些局限性,我们引入了RSFR(重建、分割、融合与细化)——一种用于心脏扩散加权图像重建的新型框架。RSFR采用由粗到细的策略,利用基于Segment Anything模型的零样本语义先验和基于Vision Mamba的稳健重建主干。我们的框架有效地集成了语义特征,以减轻伪影并提高保真度,实现了在高欠采样率下的最先进的重建质量和准确的DT参数估计。广泛的实验和消融研究证明了RSFR相较于现有方法的卓越性能,凸显了其稳健性、可扩展性以及定量心脏DTI临床转化的潜力。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
心脏扩散张量成像(DTI)能够深入了解心肌组织排列,为微观和宏观心脏功能之间的联系提供桥梁。然而,其临床应用受限于技术挑战,如低信噪比、混叠伪影和定量准确性需求。为解决这些问题,我们提出了RSFR(重建、分割、融合与细化)这一新型心脏扩散加权图像重建框架。RSFR采用由粗到细的策略,通过Segment Anything模型和基于Vision Mamba的稳健重建后盾,有效利用语义特征来减少伪影并增强准确性。该框架实现了最先进的重建质量和准确的DT参数估计,在高欠采样率下表现优异。广泛实验和消融研究证明了RSFR相较于现有方法的优越性,凸显了其稳健性、可扩展性和在定量心脏DTI中临床转化的潜力。
Key Takeaways
- 心脏扩散张量成像(DTI)可揭示心肌组织排列,为微观与宏观心脏功能研究提供桥梁。
- 当前临床应用受限于技术挑战,如低信噪比和混叠伪影。
- RSFR框架旨在解决这些技术挑战,通过重建、分割、融合与细化过程优化图像质量。
- RSFR利用语义特征减少伪影,增强图像准确性。
- RSFR框架实现了先进的重建质量和DT参数估计。
- 大量实验和消融研究证明了RSFR的优越性,凸显其临床转化的潜力。
点此查看论文截图

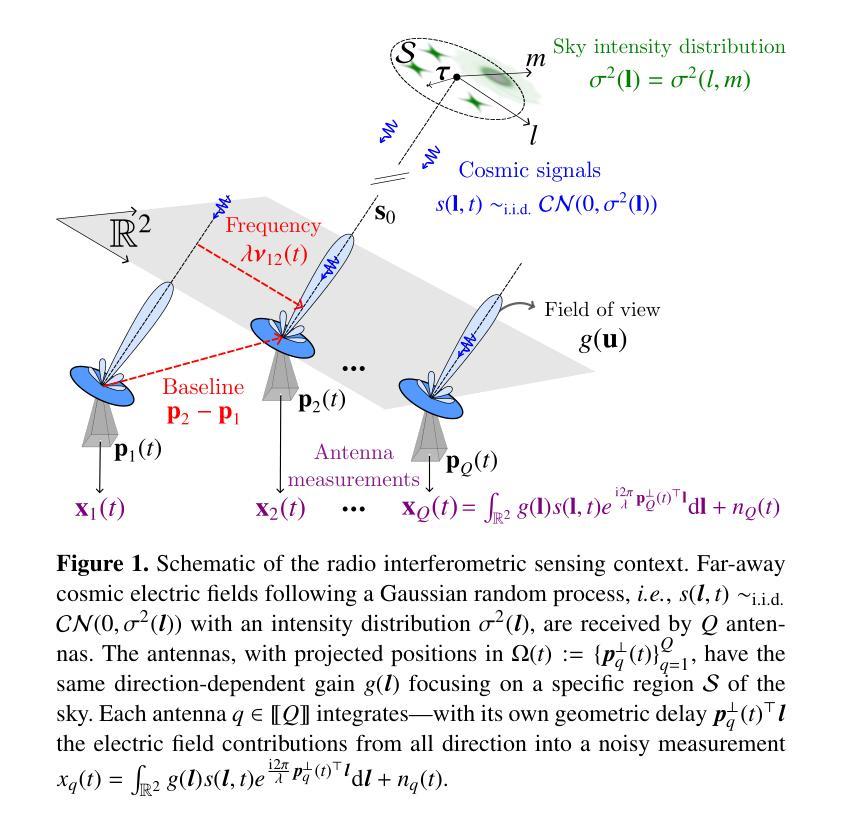
MROP: Modulated Rank-One Projections for compressive radio interferometric imaging
Authors:Olivier Leblanc, Chung San Chu, Laurent Jacques, Yves Wiaux
The emerging generation of radio-interferometric (RI) arrays are set to form images of the sky with a new regime of sensitivity and resolution. This implies a significant increase in visibility data volumes, scaling as $\mathcal{O}(Q^{2}B)$ for $Q$ antennas and $B$ short-time integration intervals (or batches), calling for efficient data dimensionality reduction techniques. This paper proposes a new approach to data compression during acquisition, coined modulated rank-one projection (MROP). MROP compresses the $Q\times Q$ batchwise covariance matrix into a smaller number $P$ of random rank-one projections and compresses across time by trading $B$ for a smaller number $M$ of random modulations of the ROP measurement vectors. Firstly, we introduce a dual perspective on the MROP acquisition, which can either be understood as random beamforming, or as a post-correlation compression. Secondly, we analyse the noise statistics of MROPs and demonstrate that the random projections induce a uniform noise level across measurements independently of the visibility-weighting scheme used. Thirdly, we propose a detailed analysis of the memory and computational cost requirements across the data acquisition and image reconstruction stages, with comparison to state-of-the-art dimensionality reduction approaches. Finally, the MROP model is validated in simulation for monochromatic intensity imaging, with comparison to the classical and baseline-dependent averaging (BDA) models, and using the uSARA optimisation algorithm for image formation. An extensive experimental setup is considered, with ground-truth images containing diffuse and faint emission and spanning a wide variety of dynamic ranges, and for a range of $uv$-coverages corresponding to VLA and MeerKAT observation.
新一代射电干涉测量(RI)阵列将以新的灵敏度和分辨率机制形成天空图像。这意味着可见数据量大幅增加,随着天线数量Q和短时间积分间隔(或批次)B的增加,数据量的增长量级为$\mathcal{O}(Q^{2}B)$,因此需要高效的数据降维技术。本文提出了一种新的数据压缩采集方法,称为调制秩一投影(MROP)。MROP将$Q\times Q$批处理协方差矩阵压缩成较小数量的随机秩一投影P,并通过用较小的调制数M代替时间压缩,对随机调制的ROP测量向量进行压缩。首先,我们对MROP采集进行了双重角度的介绍,可以将其理解为随机波束形成,也可以理解为后关联压缩。其次,我们分析了MROP的噪声统计,并证明随机投影会在测量中引起均匀噪声水平,与使用可见性加权方案无关。再次,我们详细分析了数据采集和图像重建阶段所需的内存和计算成本要求,并与最新的降维方法进行了比较。最后,通过模拟对MROP模型进行了单色强度成像的验证,并与经典模型和基线依赖平均(BDA)模型进行了比较,使用uSARA优化算法进行成像。实验考虑了广泛的设置,包括包含漫射和微弱发射的真实图像以及各种各样的动态范围,以及对应于VLA和MeerKAT观测的一系列uv覆盖。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
新一代射电干涉测量阵列(RI arrays)将形成天空图像,具有新的敏感性和分辨率。随着数据量的增长,需要高效的数据降维技术。本文提出了一种新的数据压缩采集方法——调制秩一投影(MROP)。MROP将QQ批处理协方差矩阵压缩成较小的随机秩一投影,并通过时间交换压缩。本文介绍了MROP采集的双重视角,分析了MROP的噪声统计,并与其他降维方法比较了内存和计算成本要求。最后,通过模拟验证了MROP模型在单色强度成像中的表现。
Key Takeaways
- 新一代RI arrays将提高图像敏感性和分辨率,导致数据量大幅增加。
- 数据降维技术对于处理大规模数据至关重要。
- MROP是一种新的数据压缩采集方法,通过随机秩一投影和调制来压缩数据。
- MROP采集具有双重视角:随机波束形成或后关联压缩。
- MROP的噪声统计特性被分析,表明随机投影在所有测量中产生均匀噪声水平。
- 相较于其他降维方法,MROP在内存和计算成本方面具有优势。
点此查看论文截图

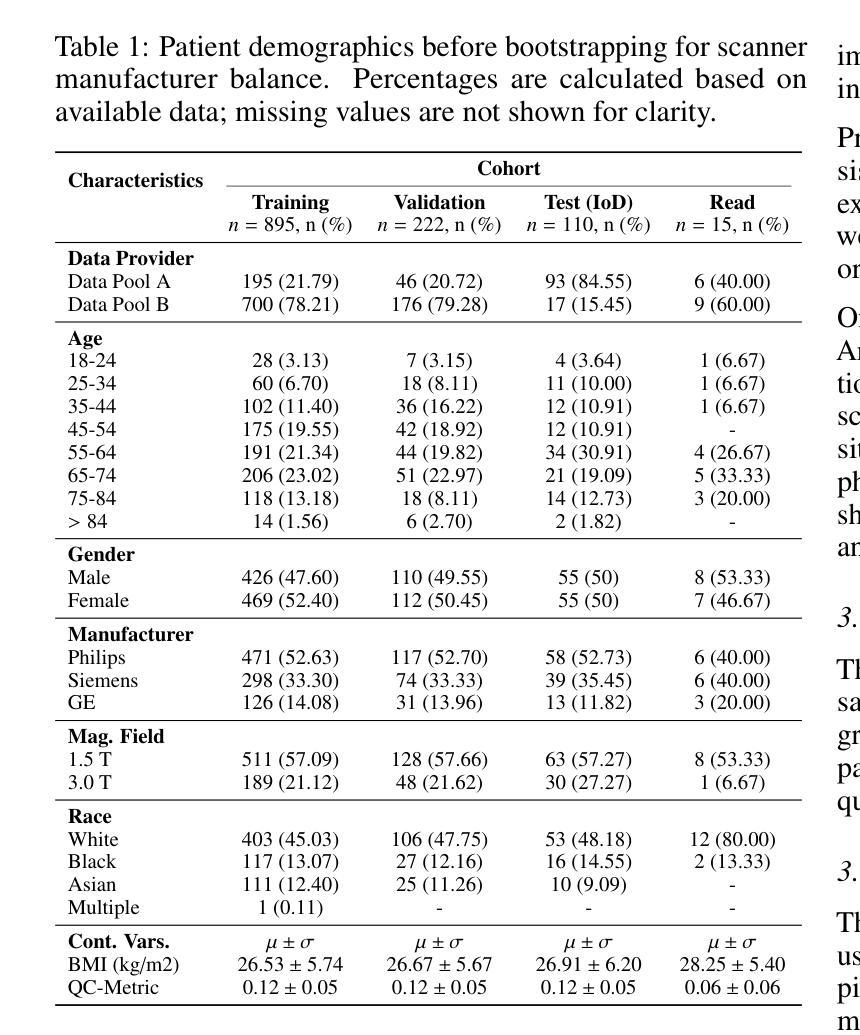
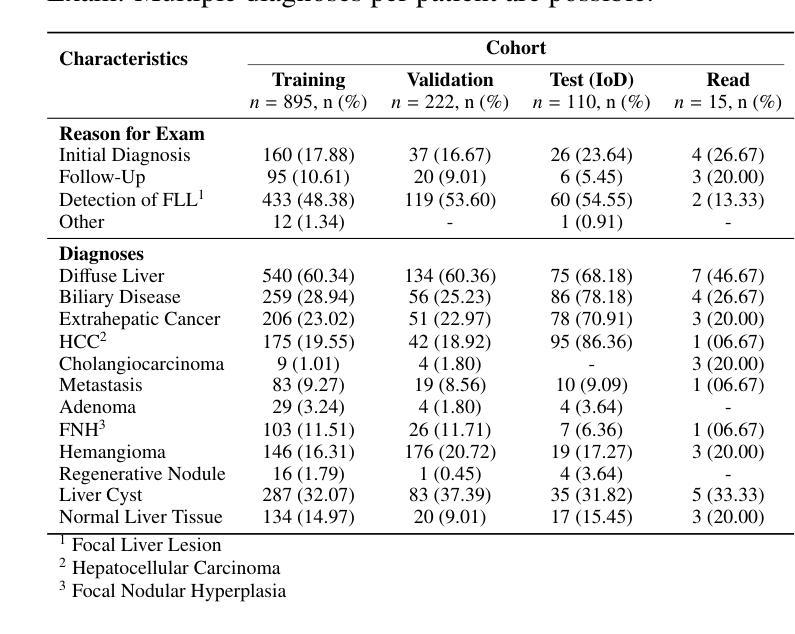
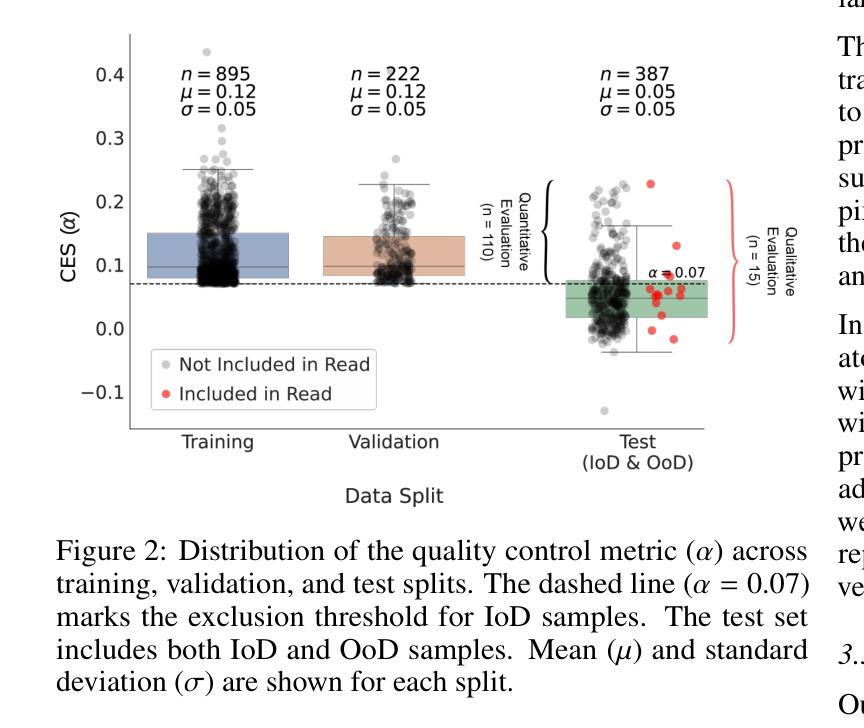
HepatoGEN: Generating Hepatobiliary Phase MRI with Perceptual and Adversarial Models
Authors:Jens Hooge, Gerard Sanroma-Guell, Faidra Stavropoulou, Alexander Ullmann, Gesine Knobloch, Mark Klemens, Carola Schmidt, Sabine Weckbach, Andreas Bolz
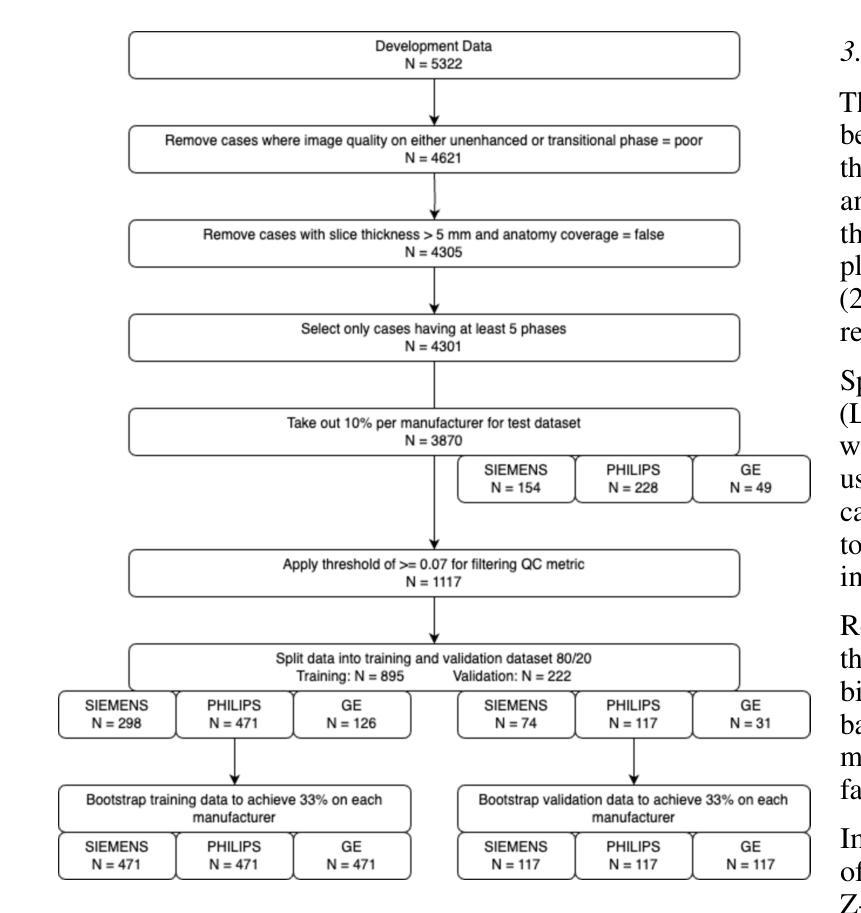
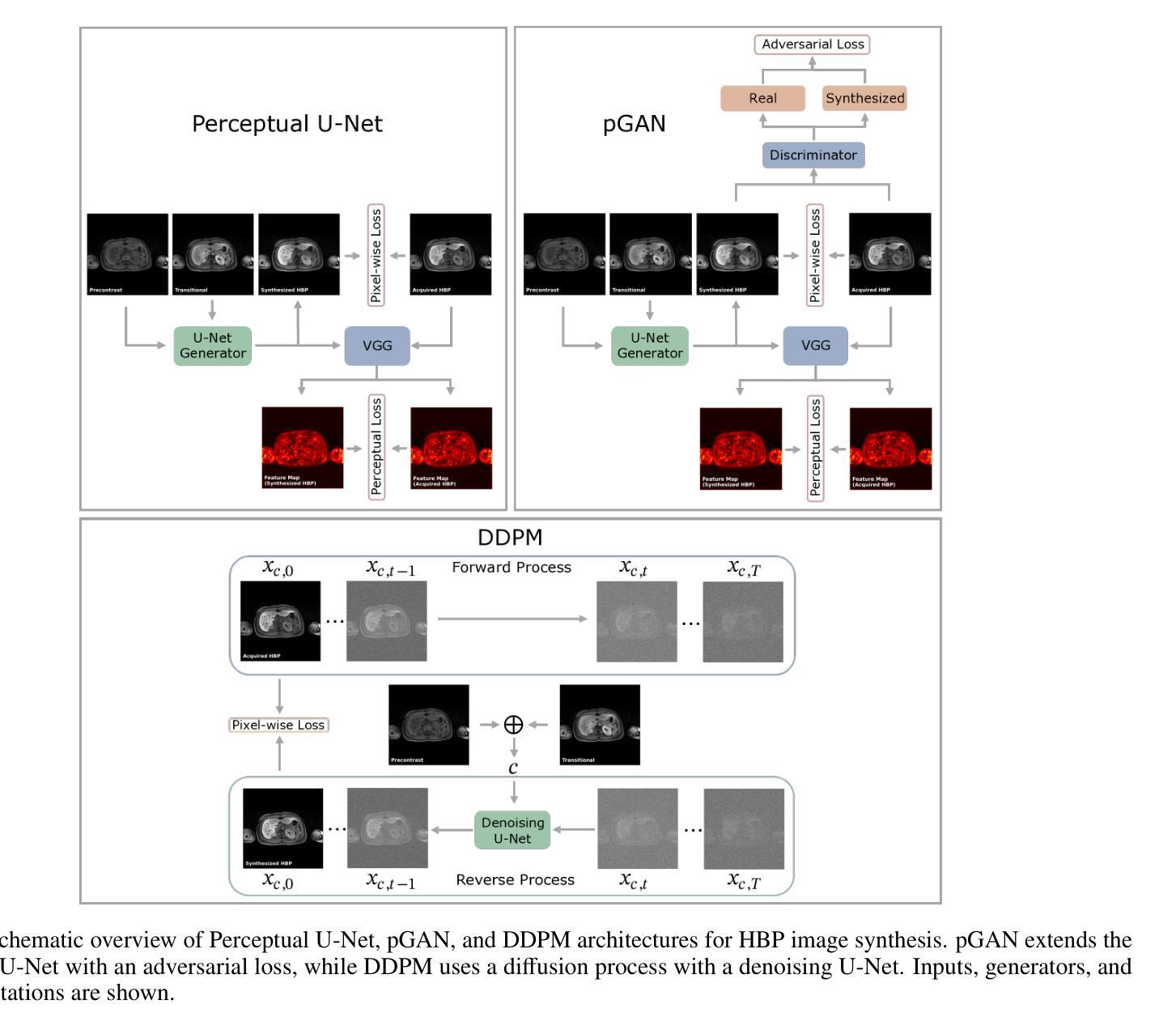
Dynamic contrast-enhanced magnetic resonance imaging (DCE-MRI) plays a crucial role in the detection and characterization of focal liver lesions, with the hepatobiliary phase (HBP) providing essential diagnostic information. However, acquiring HBP images requires prolonged scan times, which may compromise patient comfort and scanner throughput. In this study, we propose a deep learning based approach for synthesizing HBP images from earlier contrast phases (precontrast and transitional) and compare three generative models: a perceptual U-Net, a perceptual GAN (pGAN), and a denoising diffusion probabilistic model (DDPM). We curated a multi-site DCE-MRI dataset from diverse clinical settings and introduced a contrast evolution score (CES) to assess training data quality, enhancing model performance. Quantitative evaluation using pixel-wise and perceptual metrics, combined with qualitative assessment through blinded radiologist reviews, showed that pGAN achieved the best quantitative performance but introduced heterogeneous contrast in out-of-distribution cases. In contrast, the U-Net produced consistent liver enhancement with fewer artifacts, while DDPM underperformed due to limited preservation of fine structural details. These findings demonstrate the feasibility of synthetic HBP image generation as a means to reduce scan time without compromising diagnostic utility, highlighting the clinical potential of deep learning for dynamic contrast enhancement in liver MRI. A project demo is available at: https://jhooge.github.io/hepatogen
动态增强磁共振成像(DCE-MRI)在检测和识别局部肝脏病变中起着关键作用,其中肝胆相(HBP)提供了关键的诊断信息。然而,获取HBP图像需要长时间的扫描,可能会影响患者的舒适度和扫描器的通过率。本研究提出了一种基于深度学习的方法,用于从早期的对比阶段(预对比和过渡阶段)合成HBP图像,并比较了三种生成模型:感知U-Net、感知GAN(pGAN)和去噪扩散概率模型(DDPM)。我们从不同的临床环境中整理了一个多站点DCE-MRI数据集,并引入了一个对比演化分数(CES)来评估训练数据的质量,以提高模型的性能。利用像素级和感知指标的定量评估,结合通过盲放射科医生审查的定性评估,结果显示pGAN在定量性能上表现最佳,但在非分布案例中引入了异质对比。相比之下,U-Net产生的肝脏增强效果一致且伪影较少,而DDPM由于精细结构细节保存有限而表现不佳。这些发现证明了合成HBP图像生成的可行性,作为一种减少扫描时间而不影响诊断效用的手段,突出了深度学习在肝脏MRI动态对比增强中的临床潜力。项目演示可在:[https://jhooge.github.io/hepatogen] 处查看。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
本文研究了动态对比增强磁共振成像(DCE-MRI)中肝胆相(HBP)图像合成的新方法,利用深度学习技术从早期对比相合成HBP图像。研究中比较了三种生成模型:感知U-Net、感知GAN(pGAN)和去噪扩散概率模型(DDPM)。通过对比定量评估和放射科医生盲审结果,发现pGAN在定量性能上表现最佳,但在异常情况下引入了异质对比。U-Net在保持肝脏增强一致性方面表现出优势,DDPM则因细节保留不足而表现较差。研究结果表明,合成HBP图像是减少扫描时间而不损失诊断价值的有效手段,突显深度学习在肝脏MRI动态对比增强中的临床潜力。
Key Takeaways
- DCE-MRI中HBP图像对焦点肝病变的检测和特征表征至关重要。
- HBP图像的获取需要长时间扫描,可能影响患者舒适度和扫描效率。
- 深度学习可用于从早期对比阶段合成HBP图像,减少扫描时间。
- 对比了三种生成模型:感知U-Net、感知GAN(pGAN)和DDPM。
- pGAN在定量性能上表现最佳,但在异常情况下引入异质对比。
- U-Net在保持肝脏增强一致性方面表现出优势,且较少出现伪影。
点此查看论文截图

A Multimodal Deep Learning Approach for White Matter Shape Prediction in Diffusion MRI Tractography
Authors:Yui Lo, Yuqian Chen, Dongnan Liu, Leo Zekelman, Jarrett Rushmore, Yogesh Rathi, Nikos Makris, Alexandra J. Golby, Fan Zhang, Weidong Cai, Lauren J. O’Donnell
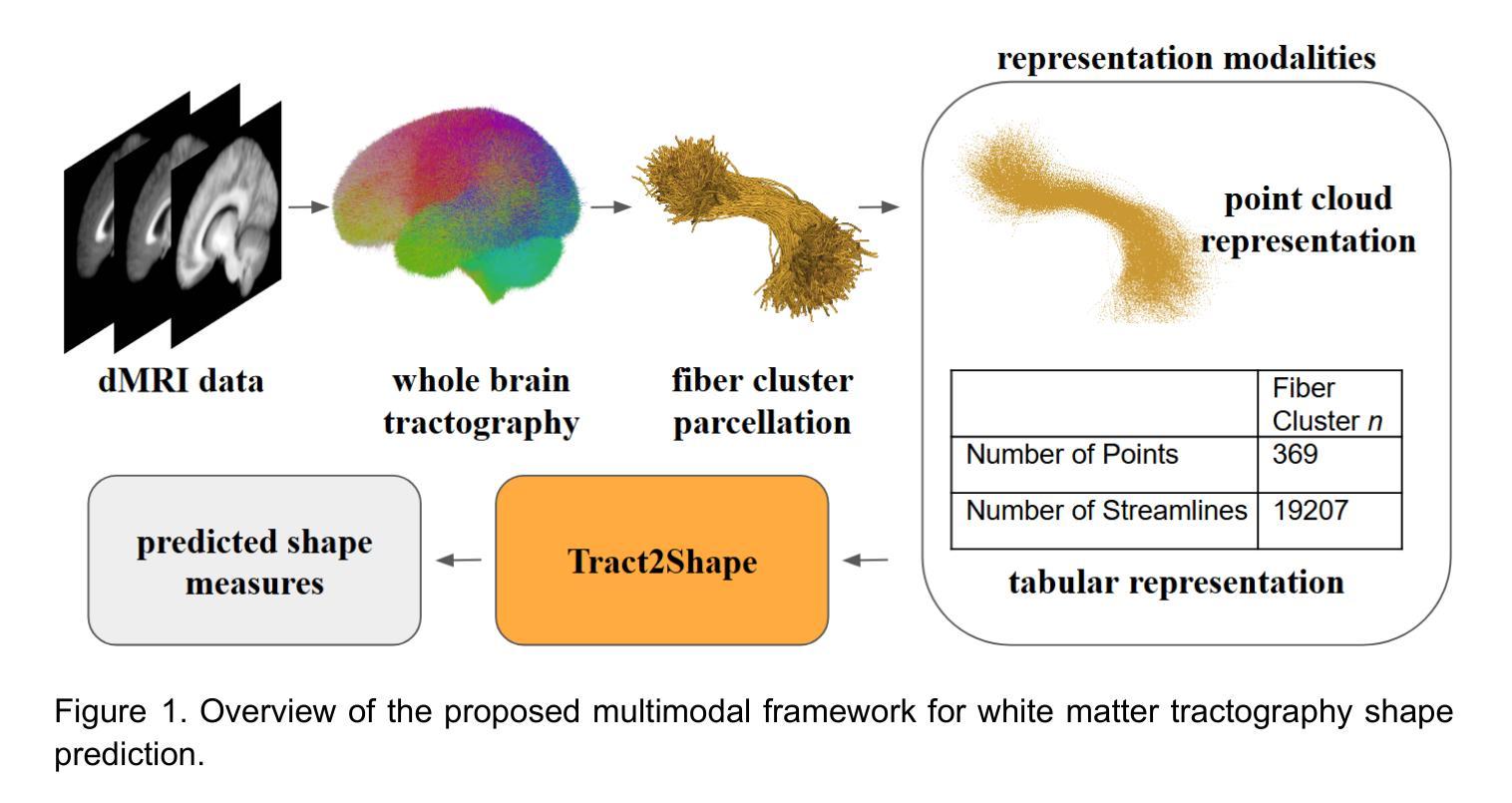
Shape measures have emerged as promising descriptors of white matter tractography, offering complementary insights into anatomical variability and associations with cognitive and clinical phenotypes. However, conventional methods for computing shape measures are computationally expensive and time-consuming for large-scale datasets due to reliance on voxel-based representations. We propose Tract2Shape, a novel multimodal deep learning framework that leverages geometric (point cloud) and scalar (tabular) features to predict ten white matter tractography shape measures. To enhance model efficiency, we utilize a dimensionality reduction algorithm for the model to predict five primary shape components. The model is trained and evaluated on two independently acquired datasets, the HCP-YA dataset, and the PPMI dataset. We evaluate the performance of Tract2Shape by training and testing it on the HCP-YA dataset and comparing the results with state-of-the-art models. To further assess its robustness and generalization ability, we also test Tract2Shape on the unseen PPMI dataset. Tract2Shape outperforms SOTA deep learning models across all ten shape measures, achieving the highest average Pearson’s r and the lowest nMSE on the HCP-YA dataset. The ablation study shows that both multimodal input and PCA contribute to performance gains. On the unseen testing PPMI dataset, Tract2Shape maintains a high Pearson’s r and low nMSE, demonstrating strong generalizability in cross-dataset evaluation. Tract2Shape enables fast, accurate, and generalizable prediction of white matter shape measures from tractography data, supporting scalable analysis across datasets. This framework lays a promising foundation for future large-scale white matter shape analysis.
形态测量已作为有前途的白质轨迹描述方法出现,为解剖变异性提供了补充见解,并与认知和临床表型相关联。然而,由于传统计算形态测量的方法依赖于基于体素(voxel-based)的表示,因此在大规模数据集上计算成本高昂且耗时。我们提出了Tract2Shape,这是一种新型的多模式深度学习框架,它利用几何(点云)和标量(表格)特征来预测十个白质轨迹形态测量方法。为了提高模型效率,我们使用降维算法来预测五个主要形态成分。该模型在两个独立获取的数据集上进行训练和评估,即HCP-YA数据集和PPMI数据集。我们通过训练Tract2Shape并在HCP-YA数据集上测试它,并与最先进的模型比较结果来评估其性能。为了进一步评估其稳健性和泛化能力,我们还对未见过的PPMI数据集进行了Tract2Shape测试。Tract2Shape在所有十个形态测量指标上均优于SOTA深度学习模型,在HCP-YA数据集上取得了最高的平均Pearson r值和最低的平均平方误差(nMSE)。消融研究表明,多模式输入和主成分分析(PCA)都有助于性能提升。在未见的测试数据集PPMI上,Tract2Shape保持了较高的Pearson r值和较低的nMSE值,表现出良好的跨数据集评估泛化能力。Tract2Shape能够从轨迹数据快速、准确、通用地预测白质形态测量指标,支持跨数据集的可扩展性分析。这一框架为未来大规模白质形态分析奠定了有前途的基础。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF 21 pages, 3 figures, 6 tables
Summary
提出一种名为Tract2Shape的多模态深度学习框架,利用几何点云和标量特征预测白质轨迹图形状指标。通过降低维度的方法提升模型效率并预测主要形状成分。该模型在两个独立数据集上的训练和评估表现优异,且在未见数据集上具有良好的泛化能力。Tract2Shape为快速、准确和通用的白质形状指标预测提供了支持,为大规模数据集的白质形状分析提供了前景。
Key Takeaways
- 白质轨迹图形状指标作为认知和临床现象的重要补充信息。
- 常规计算形状指标的方法对于大规模数据集存在计算昂贵和时间消耗的问题。
- 提出Tract2Shape多模态深度学习框架,利用点云和标量特征预测白质轨迹图形状指标。
- 通过降低维度提高模型效率,预测主要形状成分。
- 在两个独立数据集上的训练和评估表现优异。
- Tract2Shape在未见数据集上具有良好的泛化能力。
点此查看论文截图

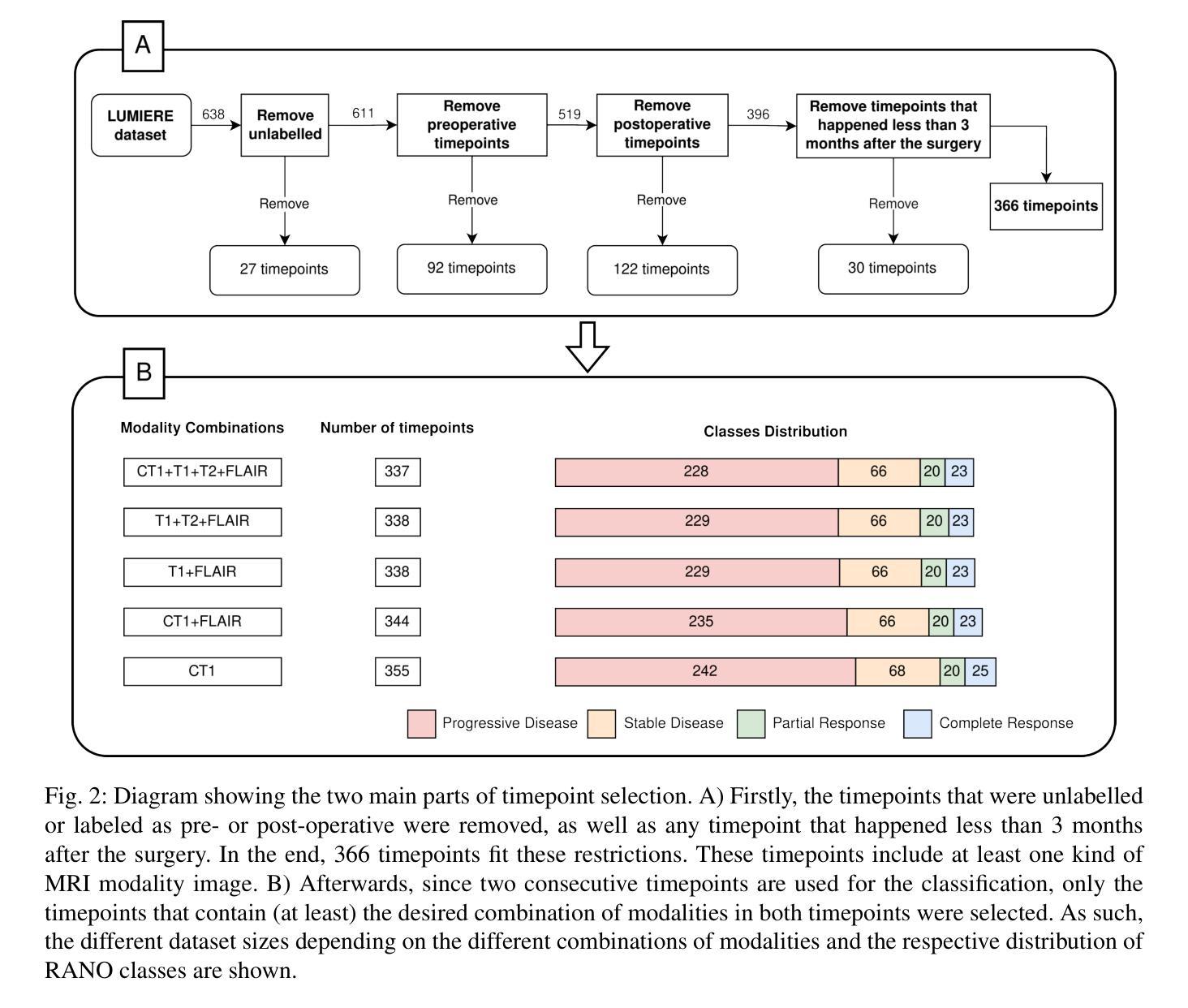
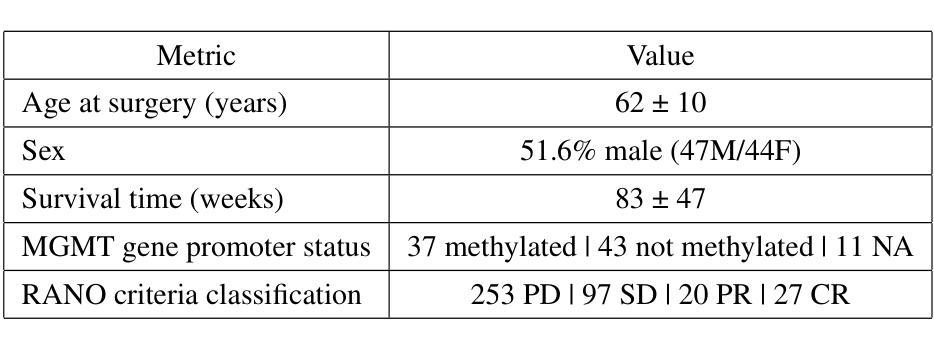
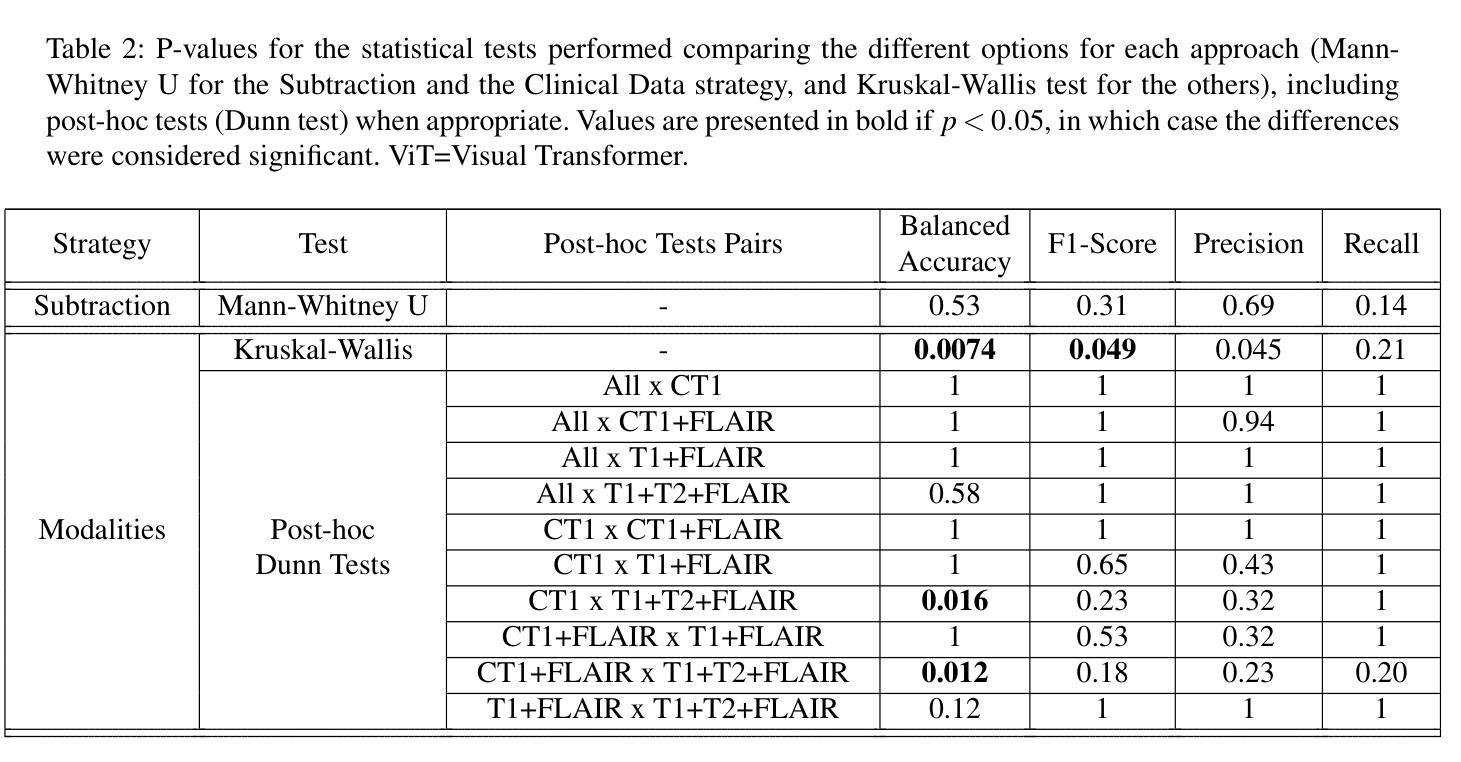
Towards a deep learning approach for classifying treatment response in glioblastomas
Authors:Ana Matoso, Catarina Passarinho, Marta P. Loureiro, José Maria Moreira, Patrícia Figueiredo, Rita G. Nunes
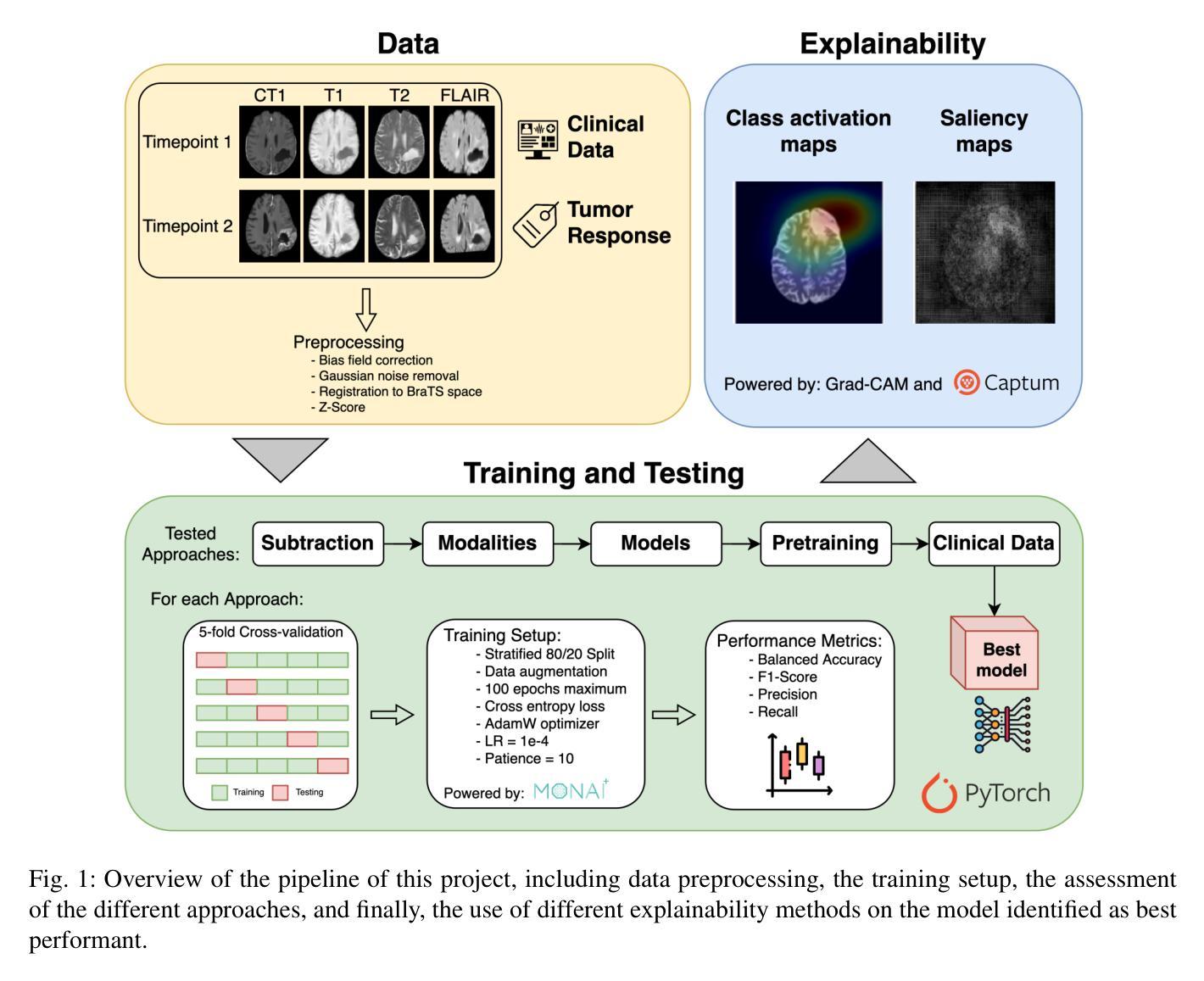
Glioblastomas are the most aggressive type of glioma, having a 5-year survival rate of 6.9%. Treatment typically involves surgery, followed by radiotherapy and chemotherapy, and frequent magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) scans to monitor disease progression. To assess treatment response, radiologists use the Response Assessment in Neuro-Oncology (RANO) criteria to categorize the tumor into one of four labels based on imaging and clinical features: complete response, partial response, stable disease, and progressive disease. This assessment is very complex and time-consuming. Since deep learning (DL) has been widely used to tackle classification problems, this work aimed to implement the first DL pipeline for the classification of RANO criteria based on two consecutive MRI acquisitions. The models were trained and tested on the open dataset LUMIERE. Five approaches were tested: 1) subtraction of input images, 2) different combinations of modalities, 3) different model architectures, 4) different pretraining tasks, and 5) adding clinical data. The pipeline that achieved the best performance used a Densenet264 considering only T1-weighted, T2-weighted, and Fluid Attenuated Inversion Recovery (FLAIR) images as input without any pretraining. A median Balanced Accuracy of 50.96% was achieved. Additionally, explainability methods were applied. Using Saliency Maps, the tumor region was often successfully highlighted. In contrast, Grad-CAM typically failed to highlight the tumor region, with some exceptions observed in the Complete Response and Progressive Disease classes, where it effectively identified the tumor region. These results set a benchmark for future studies on glioblastoma treatment response assessment based on the RANO criteria while emphasizing the heterogeneity of factors that might play a role when assessing the tumor’s response to treatment.
胶质母细胞瘤是最具侵袭性的胶质瘤类型,5年存活率为6.9%。治疗通常包括手术,然后是放疗和化疗,以及经常进行磁共振成像(MRI)扫描以监测疾病进展。为了评估治疗反应,放射科医生使用神经肿瘤学反应评估(RANO)标准,根据影像学和临床特征将肿瘤分为四种标签:完全反应、部分反应、稳定性疾病和进展性疾病。这种评估非常复杂且耗时。由于深度学习(DL)已广泛应用于解决分类问题,因此,这项工作旨在实施基于两次连续MRI采集的RANO标准分类的第一个DL管道。模型在公开数据集LUMIERE上进行训练和测试。测试了五种方法:1)输入图像的减法,2)不同模态的组合,3)不同的模型架构,4)不同的预训练任务,以及5)添加临床数据。表现最佳的管道仅使用Densenet264,仅考虑T1加权、T2加权和液体衰减反转恢复(FLAIR)图像作为输入,无需任何预训练。取得了50.96%的中位数平衡精度。此外,还应用了可解释性方法。使用显著性图(Saliency Maps),肿瘤区域通常被成功突出显示。相反,Grad-CAM通常未能突出显示肿瘤区域,但在完全反应和进展性疾病类别中观察到一些例外,在这些类别中,它有效地识别了肿瘤区域。这些结果为基于RANO标准的胶质母细胞瘤治疗反应评估的未来研究设定了基准,同时强调了评估肿瘤对治疗反应时可能起作用的因素的异质性。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
本文介绍了胶质母细胞瘤的治疗反应评估。传统评估方法复杂耗时,现采用深度学习技术建立分类模型。最佳模型基于Densenet264架构,使用T1加权、T2加权和FLAIR图像为输入,无需预训练,达到平衡精度为50.96%。利用解释性方法,如显著性图(Saliency Maps),成功突出肿瘤区域。不过,Grad-CAM在多数情况下未能有效标识肿瘤区域,但在完全反应和疾病进展类别中有较好表现。这为基于RANO标准的胶质母细胞瘤治疗反应评估提供了基准,并强调了评估肿瘤反应时可能存在的因素异质性。
Key Takeaways
- 胶质母细胞瘤是胶质瘤中最具侵袭性的类型,其五年存活率为6.9%。
- 治疗通常包括手术、放疗和化疗,以及通过MRI扫描监测疾病进展。
- 使用RANO标准评估治疗反应涉及复杂的分类问题。
- 研究采用深度学习技术建立模型,以MRI图像为基础进行RANO标准的分类。
- 最佳模型使用Densenet264架构,仅考虑T1、T2加权和FLAIR图像作为输入,无需预训练,达到平衡精度为50.96%。
- 通过解释性方法,如显著性图(Saliency Maps),能够突出肿瘤区域。
点此查看论文截图

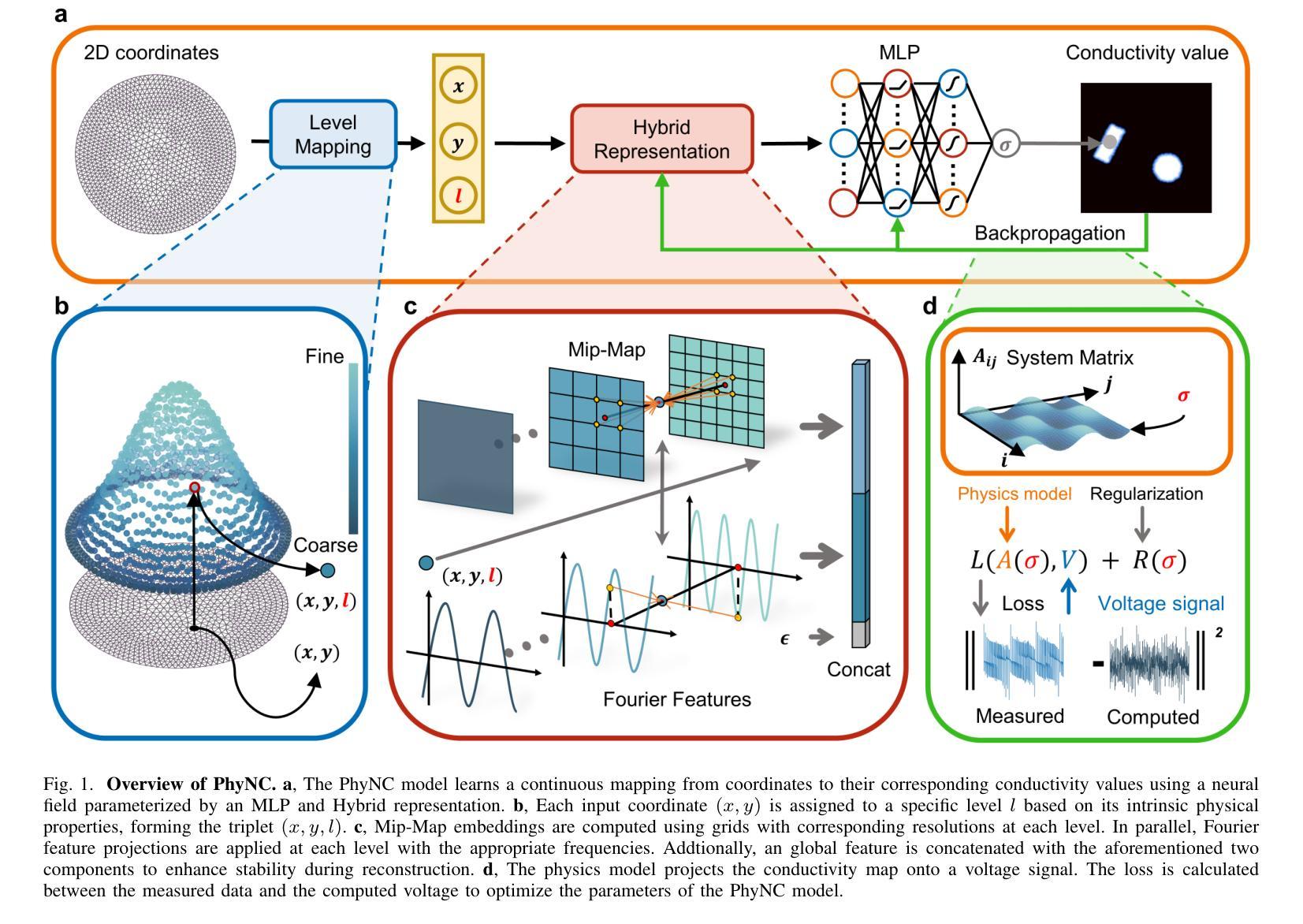
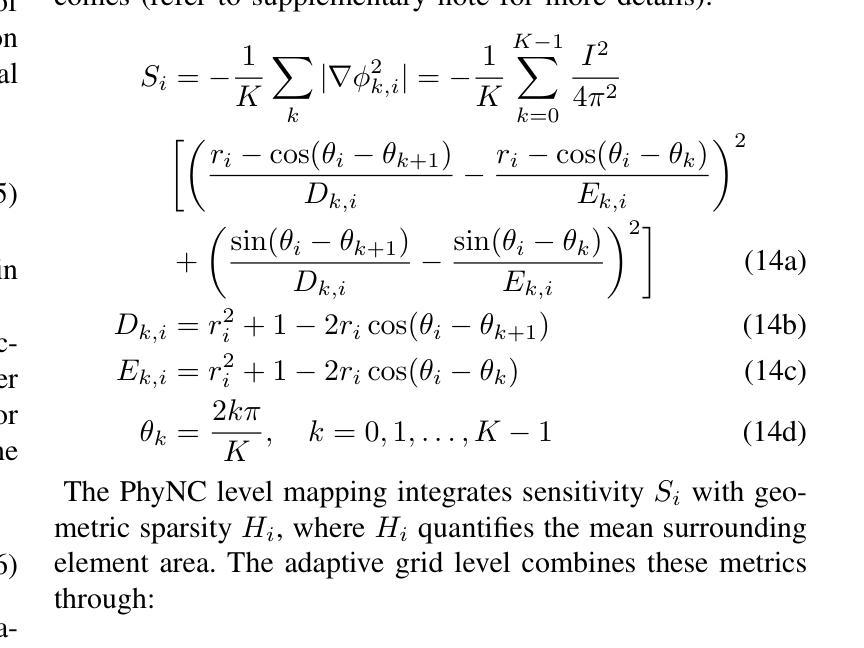
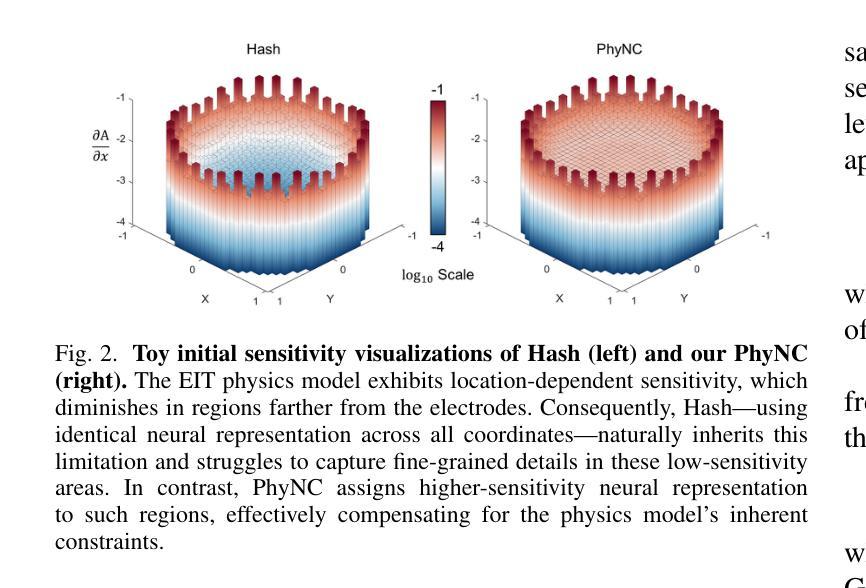
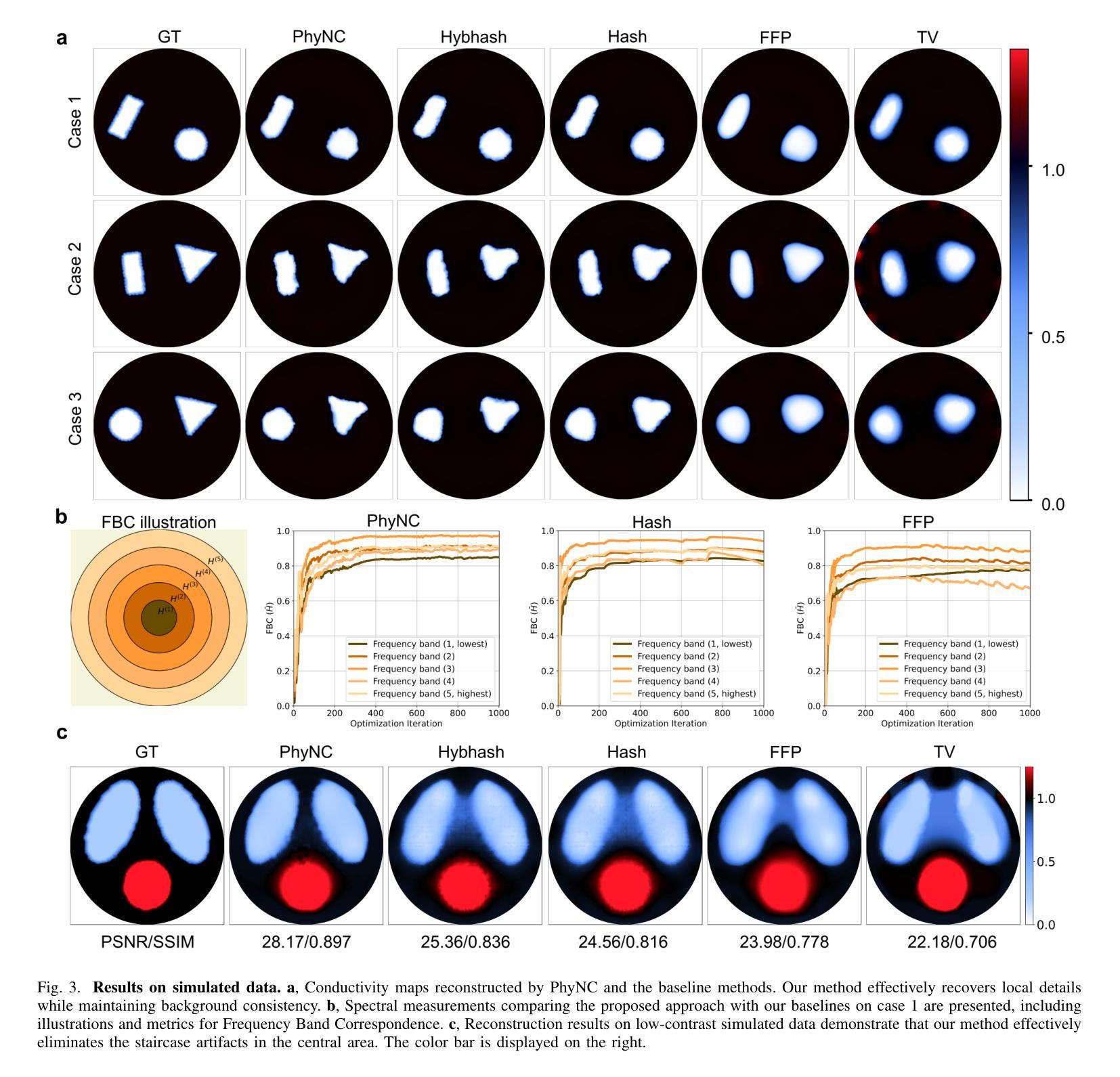
Physics-Driven Neural Compensation For Electrical Impedance Tomography
Authors:Chuyu Wang, Huiting Deng, Dong Liu
Electrical Impedance Tomography (EIT) provides a non-invasive, portable imaging modality with significant potential in medical and industrial applications. Despite its advantages, EIT encounters two primary challenges: the ill-posed nature of its inverse problem and the spatially variable, location-dependent sensitivity distribution. Traditional model-based methods mitigate ill-posedness through regularization but overlook sensitivity variability, while supervised deep learning approaches require extensive training data and lack generalization. Recent developments in neural fields have introduced implicit regularization techniques for image reconstruction, but these methods typically neglect the physical principles underlying EIT, thus limiting their effectiveness. In this study, we propose PhyNC (Physics-driven Neural Compensation), an unsupervised deep learning framework that incorporates the physical principles of EIT. PhyNC addresses both the ill-posed inverse problem and the sensitivity distribution by dynamically allocating neural representational capacity to regions with lower sensitivity, ensuring accurate and balanced conductivity reconstructions. Extensive evaluations on both simulated and experimental data demonstrate that PhyNC outperforms existing methods in terms of detail preservation and artifact resistance, particularly in low-sensitivity regions. Our approach enhances the robustness of EIT reconstructions and provides a flexible framework that can be adapted to other imaging modalities with similar challenges.
电阻抗断层扫描(EIT)提供了一种非侵入性、便携式的成像方式,在医疗和工业应用中具有巨大潜力。尽管具有优势,但EIT面临两个主要挑战:其反问题的病态性质和空间变化、位置依赖的灵敏度分布。传统基于模型的方法通过正则化来缓解不适定性,但忽略了灵敏度的变化,而监督深度学习的方法需要大量的训练数据且缺乏泛化能力。最近神经网络领域的发展引入了隐式正则化技术用于图像重建,但这些方法通常忽略了EIT背后的物理原理,从而限制了其有效性。本研究中,我们提出了PhyNC(物理驱动神经网络补偿),这是一个结合了EIT物理原理的无监督深度学习框架。PhyNC通过动态分配神经表征容量到灵敏度较低的区域,解决了不适定的反问题和灵敏度分布问题,确保了精确且平衡的导电率重建。对模拟和实验数据的广泛评估表明,PhyNC在细节保留和抗伪影方面优于现有方法,特别是在低灵敏度区域。我们的方法提高了EIT重建的稳健性,并提供了一个灵活的框架,可以适应具有类似挑战的其他成像模式。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
EIT面临两大挑战:其反问题的病态性和灵敏度分布的空间变化性。本研究提出一种融合物理原理的无监督深度学习框架PhyNC,解决EIT的这两个问题。PhyNC通过动态分配神经网络表征容量来应对低灵敏度区域的需求,确保导电率重建的准确性和平衡性。评估和实验数据表明,PhyNC在细节保留和抗伪影方面优于现有方法,特别是在低灵敏度区域。
Key Takeaways
- EIT面临两大挑战:反问题的病态性和灵敏度分布的空间变化性。
- 传统方法通过正则化解决病态性问题,但忽略灵敏度变化。
- 深度学习方法需要大量训练数据,并缺乏泛化能力。
- 最近神经场的发展引入了隐式正则化技术,但忽略了EIT的物理原理。
- PhyNC是一种无监督深度学习框架,结合EIT的物理原理。
- PhyNC通过动态分配神经网络表征容量,应对低灵敏度区域,确保导电率重建的准确性和平衡性。
点此查看论文截图

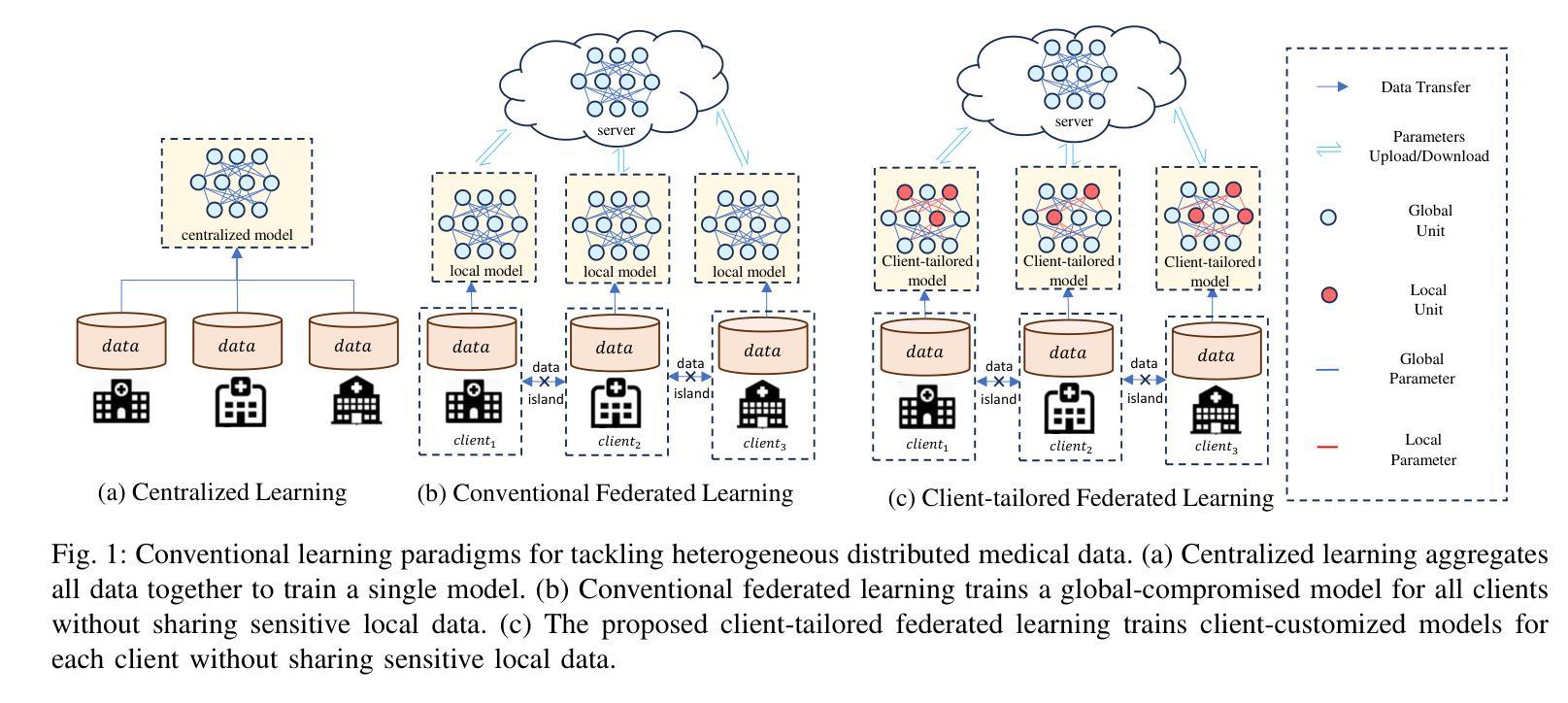
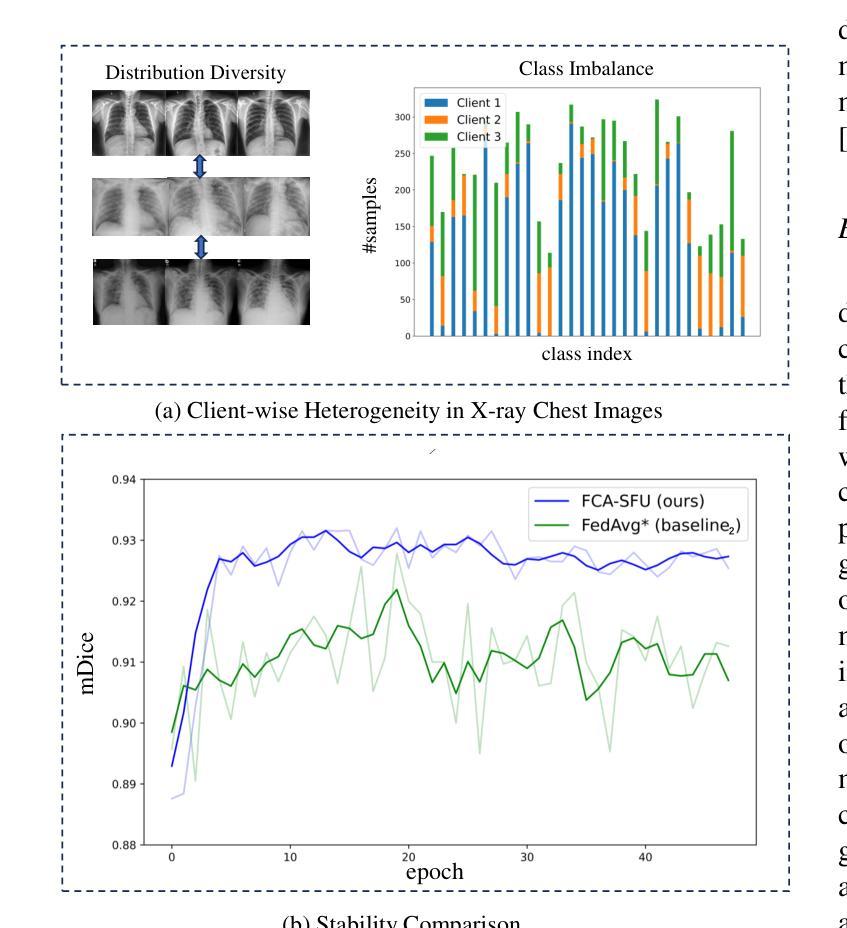
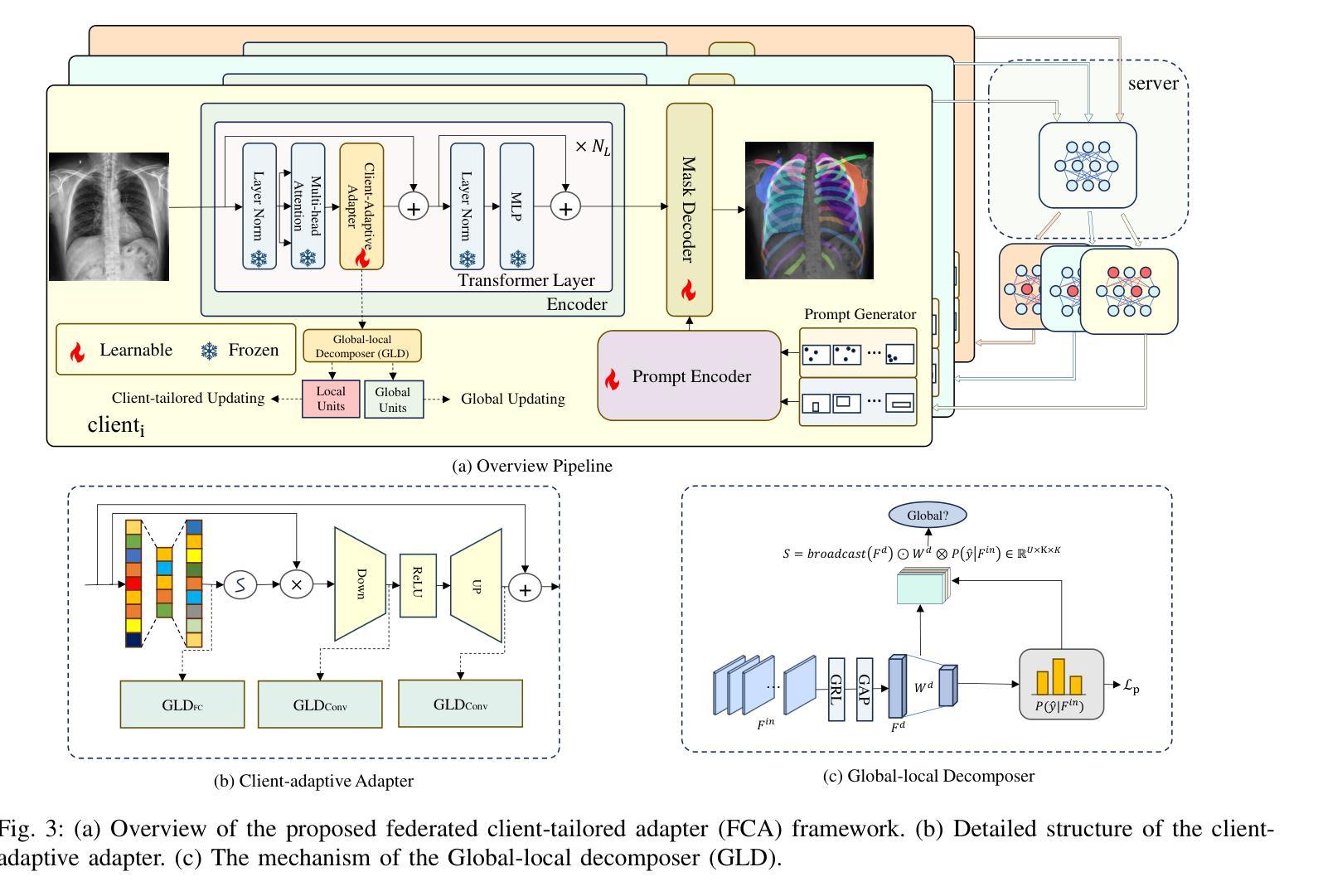
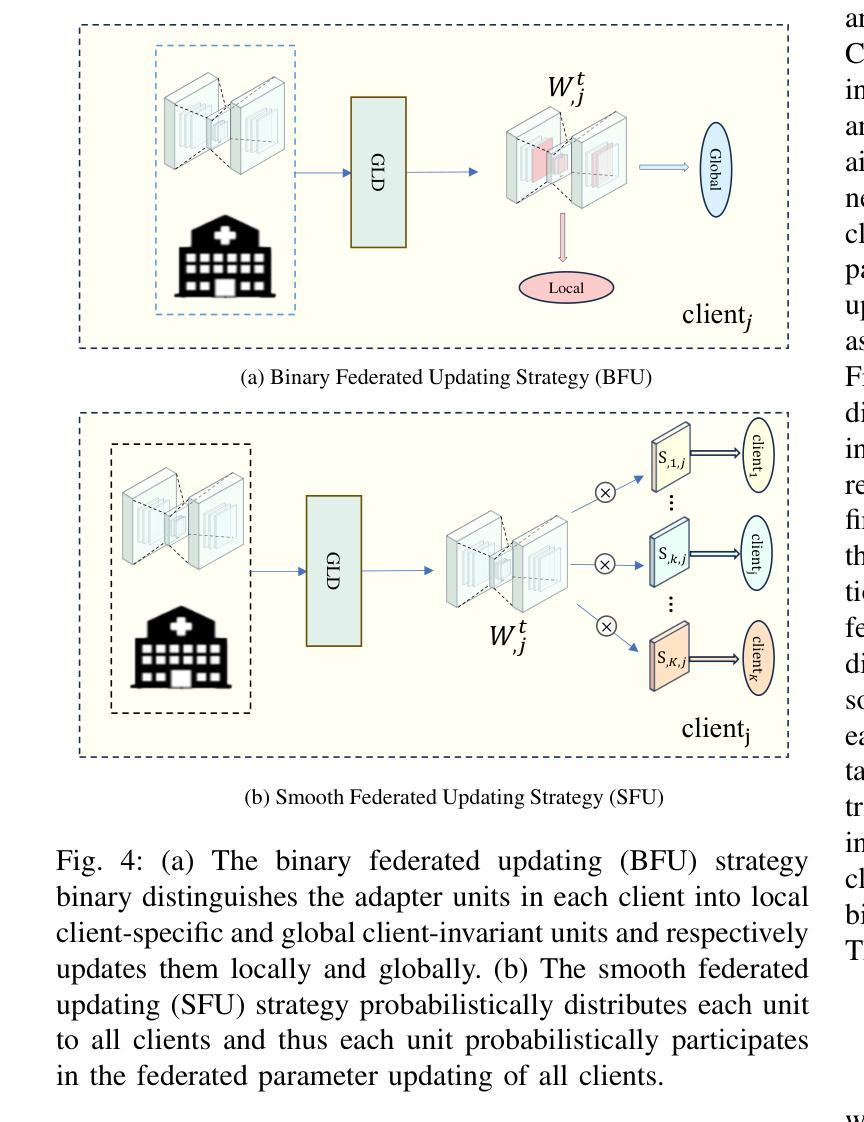
Federated Client-tailored Adapter for Medical Image Segmentation
Authors:Guyue Hu, Siyuan Song, Yukun Kang, Zhu Yin, Gangming Zhao, Chenglong Li, Jin Tang
Medical image segmentation in X-ray images is beneficial for computer-aided diagnosis and lesion localization. Existing methods mainly fall into a centralized learning paradigm, which is inapplicable in the practical medical scenario that only has access to distributed data islands. Federated Learning has the potential to offer a distributed solution but struggles with heavy training instability due to client-wise domain heterogeneity (including distribution diversity and class imbalance). In this paper, we propose a novel Federated Client-tailored Adapter (FCA) framework for medical image segmentation, which achieves stable and client-tailored adaptive segmentation without sharing sensitive local data. Specifically, the federated adapter stirs universal knowledge in off-the-shelf medical foundation models to stabilize the federated training process. In addition, we develop two client-tailored federated updating strategies that adaptively decompose the adapter into common and individual components, then globally and independently update the parameter groups associated with common client-invariant and individual client-specific units, respectively. They further stabilize the heterogeneous federated learning process and realize optimal client-tailored instead of sub-optimal global-compromised segmentation models. Extensive experiments on three large-scale datasets demonstrate the effectiveness and superiority of the proposed FCA framework for federated medical segmentation.
医学图像中的X光图像分割对于计算机辅助诊断和病灶定位非常有益。现有的方法主要遵循集中式学习模式,这在只能访问分布式数据孤岛的实际医疗场景中并不适用。联邦学习(Federated Learning)有潜力提供分布式解决方案,但由于客户端域异构性(包括分布多样性和类别不平衡)而面临训练不稳定的挑战。在本文中,我们提出了一种新型的针对医疗图像分割的联邦客户端定制适配器(FCA)框架,实现了在不共享敏感本地数据的情况下稳定和适应客户端的定制化分割。具体来说,联邦适配器将现成的医学基础模型中的通用知识混合在一起,以稳定联邦训练过程。此外,我们开发了两项针对客户端定制的联邦更新策略,自适应地将适配器分解为通用和个性化组件,然后分别全局和独立地更新与通用客户端不变和个性化客户端相关的参数组。它们进一步稳定了异构的联邦学习过程,实现了针对客户端的最优而非次优全局妥协分割模型。在三个大规模数据集上的广泛实验证明了所提出的FCA框架在医学图像联邦分割中的有效性和优越性。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
医学图像分割在X光图像中有助于计算机辅助诊断和病灶定位。现有方法主要采用集中式学习范式,不适用于仅访问分布式数据岛的实际医学场景。联邦学习有潜力提供分布式解决方案,但由于客户端领域异质性(包括分布多样性和类别不平衡)而面临训练不稳定的挑战。本文提出一种用于医学图像分割的新型联邦客户端定制适配器(FCA)框架,可在不共享敏感本地数据的情况下实现稳定且客户定制的适应性分割。具体来说,联邦适配器搅拌现成的医学基础模型中的通用知识以稳定联邦训练过程。此外,我们开发了两种客户定制的联邦更新策略,自适应地将适配器分解为通用和个体组件,然后全局和独立地更新与通用客户端不变和个体客户端特定单元相关的参数组,进一步稳定了异构联邦学习过程,实现了优化的客户定制而非次优的全局妥协分割模型。
Key Takeaways
- 医学图像分割在X光图像中有助于计算机辅助诊断和病灶定位。
- 现有方法主要采用集中式学习范式,不适用于分布式数据环境。
- 联邦学习面临因客户端领域异质性导致的训练不稳定问题。
- 提出了联邦客户端定制适配器(FCA)框架,实现稳定且客户定制的适应性分割。
- 联邦适配器利用通用知识稳定联邦训练过程。
- 开发两种客户定制的联邦更新策略,自适应分解适配器并更新参数。
点此查看论文截图


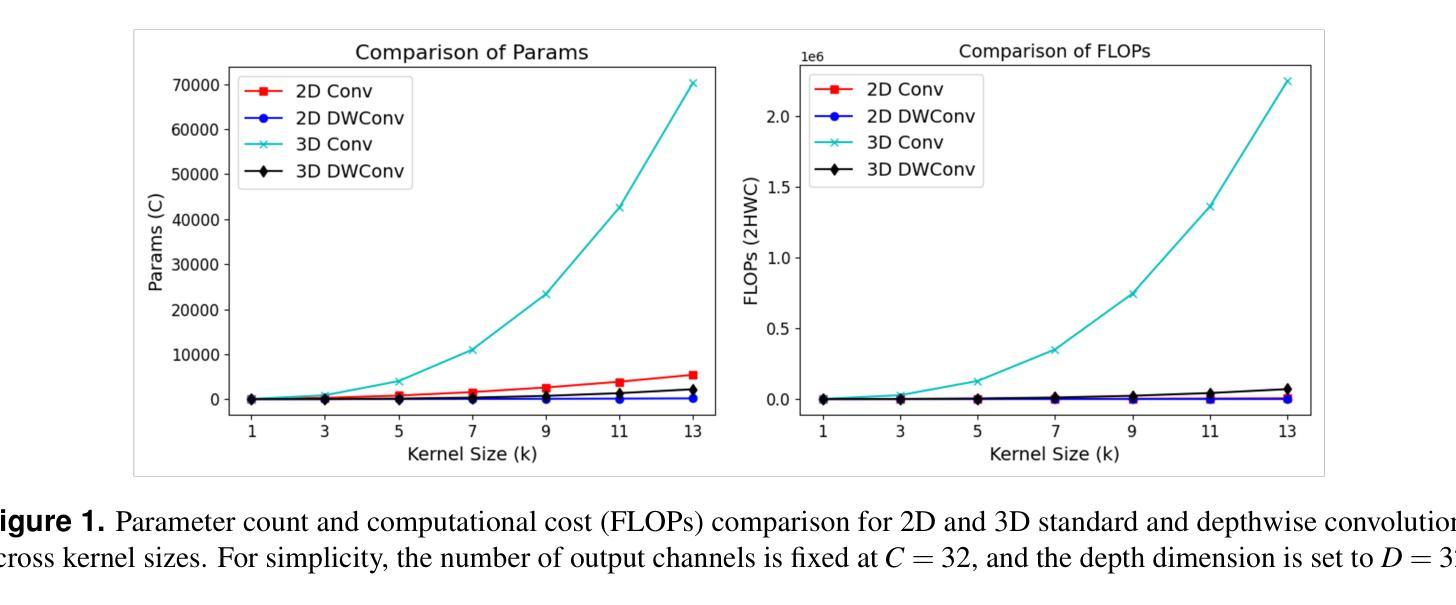
DCFormer: Efficient 3D Vision-Language Modeling with Decomposed Convolutions
Authors:Gorkem Can Ates, Yu Xin, Kuang Gong, Wei Shao
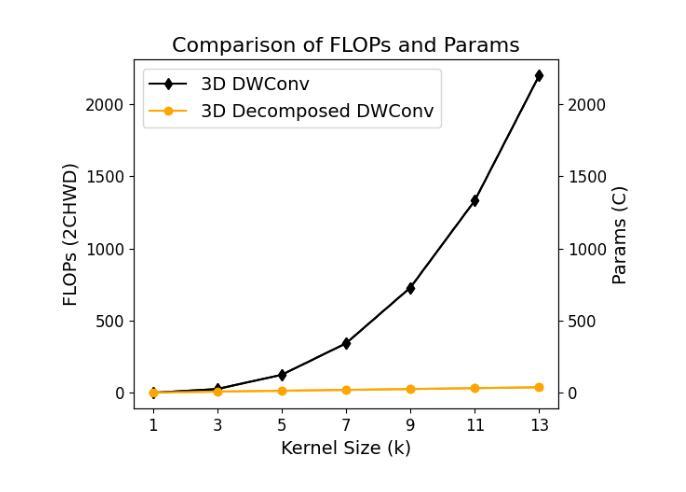
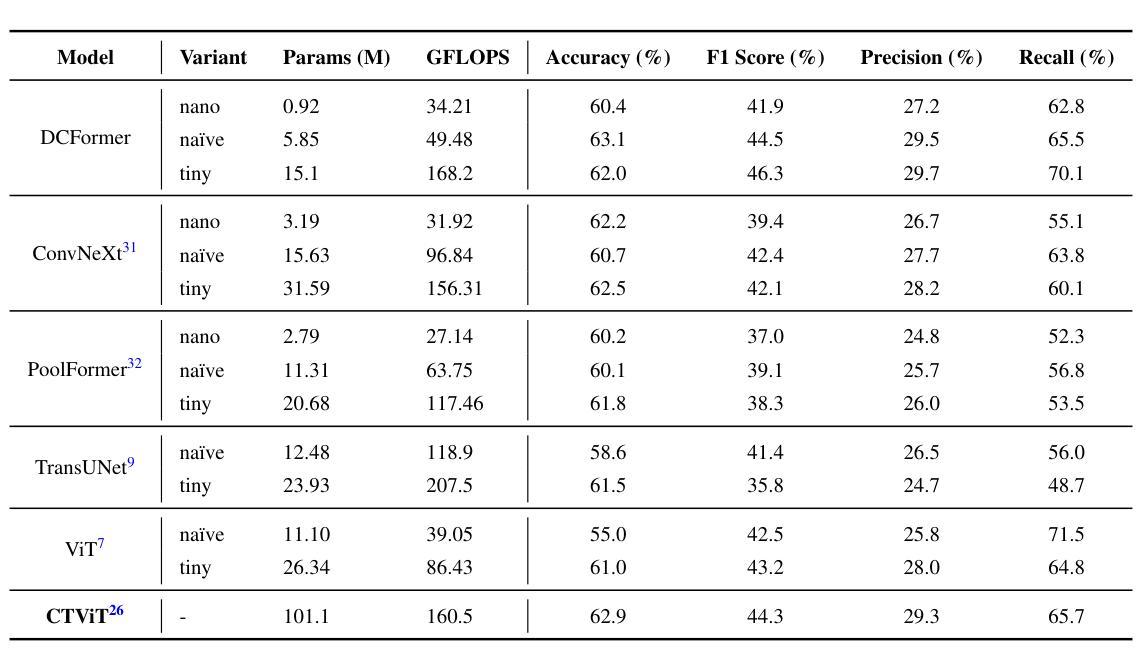
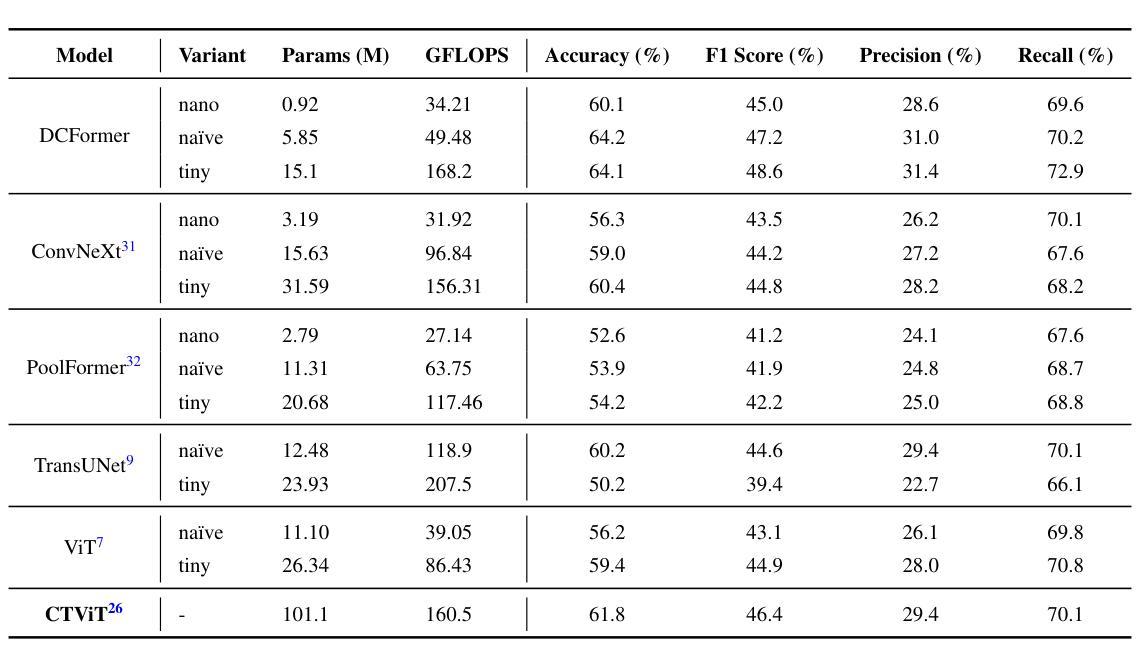
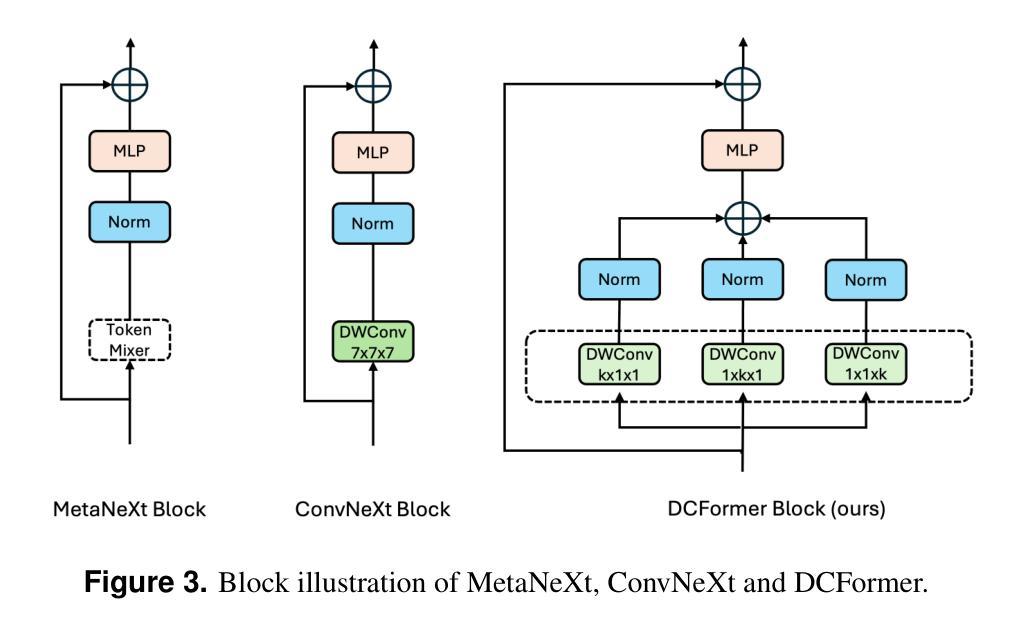
Vision-language models (VLMs) have been widely applied to 2D medical image analysis due to their ability to align visual and textual representations. However, extending VLMs to 3D imaging remains computationally challenging. Existing 3D VLMs often rely on Vision Transformers (ViTs), which are computationally expensive due to the quadratic complexity of self-attention, or on 3D convolutions, which require large numbers of parameters and FLOPs as kernel size increases. We introduce DCFormer, an efficient 3D image encoder that factorizes 3D convolutions into three parallel 1D convolutions along the depth, height, and width dimensions. This design preserves spatial information while significantly reducing computational cost. Integrated into a CLIP-based vision-language framework, DCFormer is trained and evaluated on CT-RATE, a dataset of 50,188 paired 3D chest CT volumes and radiology reports. In zero-shot and fine-tuned detection of 18 pathologies, as well as in image-text retrieval tasks, DCFormer consistently outperforms state-of-the-art 3D vision encoders, including CT-ViT, ViT, ConvNeXt, PoolFormer, and TransUNet. These results highlight DCFormer’s potential for scalable, clinically deployable 3D medical VLMs. Our code is available at: https://github.com/mirthAI/DCFormer.
视觉语言模型(VLMs)由于其视觉和文本表示对齐的能力,已广泛应用于二维医学图像分析。然而,将VLMs扩展到三维成像在计算上仍然具有挑战性。现有的三维VLMs通常依赖于视觉转换器(ViTs),由于自注意力的二次复杂性,其计算成本高昂,或者依赖于三维卷积,随着内核大小的增加,需要大量的参数和浮点运算(FLOPs)。我们引入了DCFormer,这是一种高效的三维图像编码器,它将三维卷积分解为沿深度、高度和宽度方向的三个并行一维卷积。这种设计保留了空间信息,同时大大降低了计算成本。DCFormer被集成到一个基于CLIP的视觉语言框架中,并在CT-RATE数据集上进行训练和评估,该数据集包含50,188对三维胸部CT体积和放射学报告。在零样本和微调检测18种病理情况以及图像文本检索任务中,DCFormer持续优于最新的三维视觉编码器,包括CT-ViT、ViT、ConvNeXt、PoolFormer和TransUNet。这些结果突出了DCFormer在可扩展、可部署的临床三维医学VLMs中的潜力。我们的代码位于:https://github.com/mirthAI/DCFormer。
论文及项目相关链接
摘要
基于视觉-语言模型(VLMs)对二维医学影像分析的广泛应用及其强大的视觉与文本对齐能力,人们正试图将其扩展到三维成像领域。然而,由于计算上的挑战,现有三维VLMs通常采用视觉转换器(ViTs),其自注意力的二次复杂性导致计算量大;或是采用三维卷积,随着内核大小增加,其所需的参数和浮点运算量也急剧增长。本文提出DCFormer,一种高效的三维图像编码器,将三维卷积分解为沿深度、高度和宽度方向的三个并行一维卷积。这种设计在保留空间信息的同时显著降低了计算成本。DCFormer被集成到一个基于CLIP的视野语言框架中,并在CT-RATE数据集(包含50,188对三维胸部CT体积和放射学报告)上进行训练和评估。在零样本和微调检测18种病理情况以及图像文本检索任务中,DCFormer始终优于最新的三维视觉编码器,包括CT-ViT、ViT、ConvNeXt、PoolFormer和TransUNet。这些结果突显了DCFormer在可扩展的临床部署三维医学VLMs方面的潜力。
关键见解
- VLMs已广泛应用于二维医学影像分析,但扩展到三维成像仍存在计算挑战。
- 现有三维VLMs多采用ViTs或三维卷积,前者自注意力机制计算量大,后者参数和计算量大。
- DCFormer是一种高效的三维图像编码器,通过分解三维卷积以降低计算成本并保留空间信息。
- DCFormer在CLIP基础上被集成到视野语言框架中,并在大规模CT-RATE数据集上进行训练和评估。
- 在零样本学习和微调检测病理情况,以及图像文本检索任务中,DCFormer表现优于其他先进的三维视觉编码器。
- DCFormer具有潜力成为可扩展的、可临床部署的三维医学VLMs解决方案。
点此查看论文截图

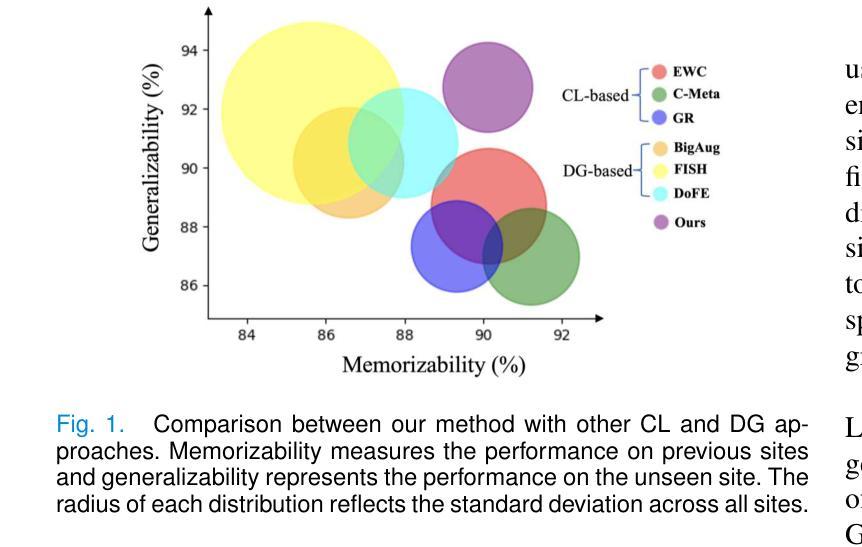
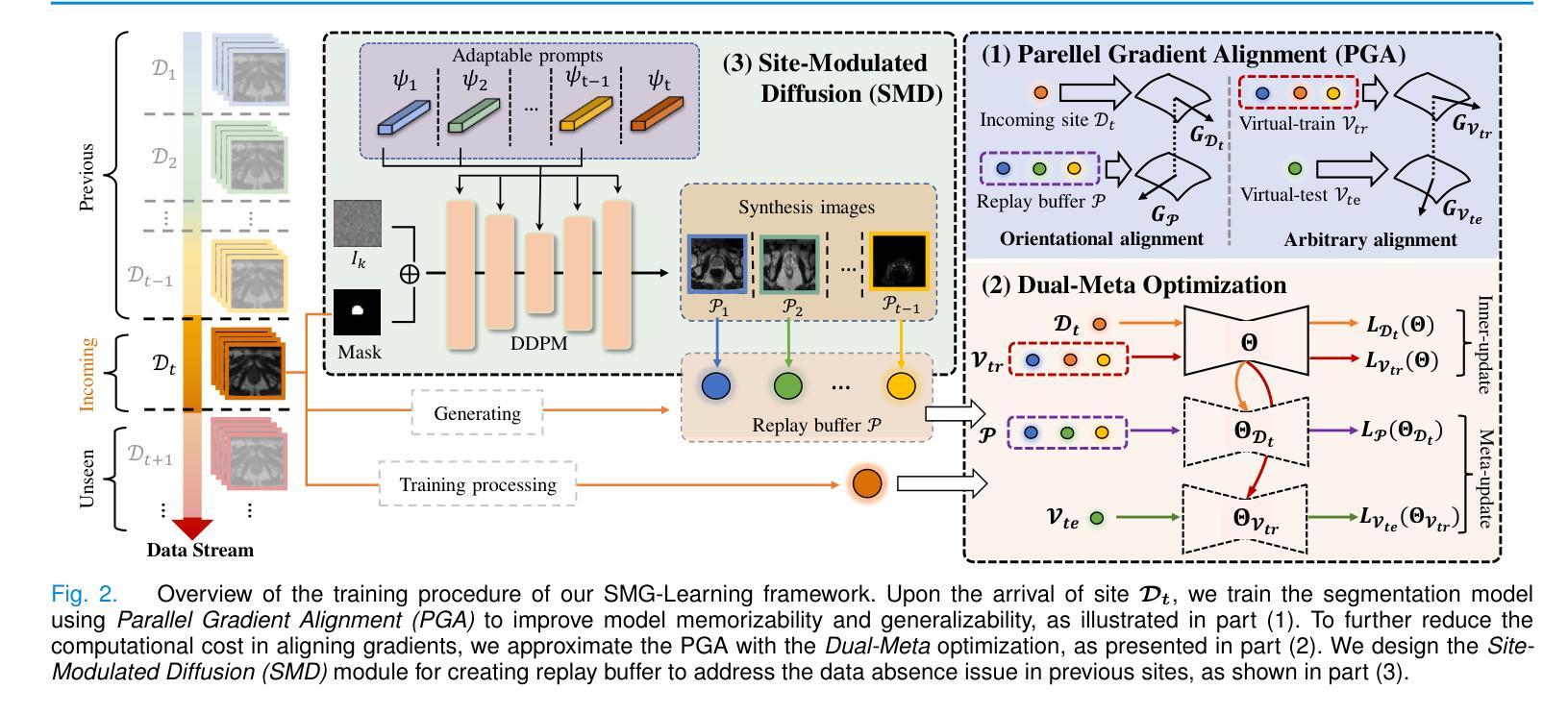
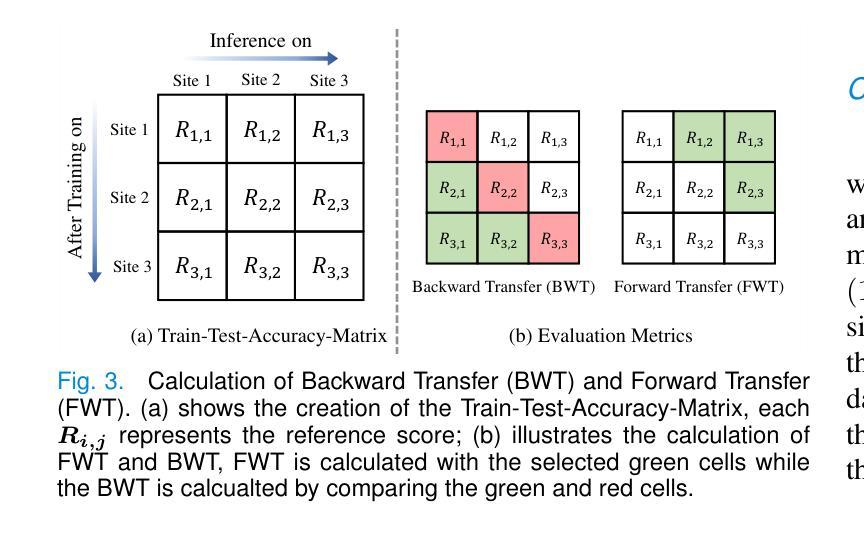
Towards Synchronous Memorizability and Generalizability with Site-Modulated Diffusion Replay for Cross-Site Continual Segmentation
Authors:Dunyuan Xu, Xi Wang, Jingyang Zhang, Pheng-Ann Heng
The ability to learn sequentially from different data sites is crucial for a deep network in solving practical medical image diagnosis problems due to privacy restrictions and storage limitations. However, adapting on incoming site leads to catastrophic forgetting on past sites and decreases generalizablity on unseen sites. Existing Continual Learning (CL) and Domain Generalization (DG) methods have been proposed to solve these two challenges respectively, but none of them can address both simultaneously. Recognizing this limitation, this paper proposes a novel training paradigm, learning towards Synchronous Memorizability and Generalizability (SMG-Learning). To achieve this, we create the orientational gradient alignment to ensure memorizability on previous sites, and arbitrary gradient alignment to enhance generalizability on unseen sites. This approach is named as Parallel Gradient Alignment (PGA). Furthermore, we approximate the PGA as dual meta-objectives using the first-order Taylor expansion to reduce computational cost of aligning gradients. Considering that performing gradient alignments, especially for previous sites, is not feasible due to the privacy constraints, we design a Site-Modulated Diffusion (SMD) model to generate images with site-specific learnable prompts, replaying images have similar data distributions as previous sites. We evaluate our method on two medical image segmentation tasks, where data from different sites arrive sequentially. Experimental results show that our method efficiently enhances both memorizability and generalizablity better than other state-of-the-art methods, delivering satisfactory performance across all sites. Our code will be available at: https://github.com/dyxu-cuhkcse/SMG-Learning.
能够从不同的数据站点进行顺序学习对于深度网络解决实际的医学图像诊断问题至关重要,因为存在隐私限制和存储限制。然而,适应新站点会导致对过去站点的灾难性遗忘,并降低对未见站点的泛化能力。现有的持续学习(CL)和域泛化(DG)方法分别被提出来解决这两个挑战,但没有任何一种方法可以同时解决这两个问题。本文认识到了这一局限性,提出了一种新的训练范式,即学习面向同步记忆能力和泛化能力(SMG-Learning)。为实现这一目标,我们创建方向梯度对齐以确保对过去站点的记忆能力,并创建任意梯度对齐以增强对未见站点的泛化能力。这种方法被称为并行梯度对齐(PGA)。此外,我们将PGA近似为双元目标使用一阶泰勒展开,以减少梯度对齐的计算成本。考虑到进行梯度对齐,尤其是对以前的站点,由于隐私约束而不可行,我们设计了一个站点调制扩散(SMD)模型,以生成具有站点特定可学习提示的图像,回放图像的 数据分布与以前的站点相似。我们在两个医学图像分割任务上评估了我们的方法,其中来自不同站点的数据会顺序到达。实验结果表明,我们的方法有效地增强了记忆能力和泛化能力,比其他最先进的方法表现更好,并在所有站点上表现出令人满意的性能。我们的代码将在https://github.com/dyxu-cuhkcse/SMG-Learning上提供。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF This paper is not proper to be published on arXiv, since we think some method are quite similar with one other paper
摘要
这篇论文针对因隐私限制和存储限制导致的医学图像诊断问题,提出了一种新的训练范式——同步记忆性和泛化性学习(SMG-Learning)。为解决这个问题,创建了方向梯度对齐以确保对之前站点的记忆能力,任意梯度对齐以增强对未见站点的泛化能力。这种方法被称为并行梯度对齐(PGA)。此外,通过将PGA近似为双重元目标使用一阶泰勒展开,减少了梯度对齐的计算成本。考虑到梯度对齐特别是针对之前站点不可行是由于隐私约束,设计了一种名为Site-Modulated Diffusion(SMD)的模型来生成具有特定学习提示的图像回放,这些图像具有与之前站点相似的数据分布。在两项医学图像分割任务上评估了该方法,不同站点的数据按顺序到达。实验结果表明,该方法在记忆性和泛化性方面均优于其他最新方法,在所有站点上均表现出令人满意的性能。
关键见解
- 论文强调了从多个数据站点顺序学习对于解决因隐私和存储限制导致的医学图像诊断问题的深度网络的重要性。
- 存在持续学习(CL)和域泛化(DG)方法分别应对顺序学习和泛化挑战,但没有一种方法可以同时解决这两个问题。
- 论文提出了一种新的训练范式——同步记忆性和泛化性学习(SMG-Learning)来解决上述问题。
- 通过创建方向梯度对齐和任意梯度对齐来提升记忆性和泛化性,提出了并行梯度对齐(PGA)方法。
- 使用一阶泰勒展开将PGA近似为双重元目标以降低计算成本。
- 考虑隐私约束,设计了一种名为Site-Modulated Diffusion(SMD)的模型来生成具有特定学习提示的图像回放。
- 在医学图像分割任务上的实验结果表明,该方法在记忆性和泛化性方面表现出卓越性能。
点此查看论文截图