⚠️ 以下所有内容总结都来自于 大语言模型的能力,如有错误,仅供参考,谨慎使用
🔴 请注意:千万不要用于严肃的学术场景,只能用于论文阅读前的初筛!
💗 如果您觉得我们的项目对您有帮助 ChatPaperFree ,还请您给我们一些鼓励!⭐️ HuggingFace免费体验
2025-04-29 更新
VEU-Bench: Towards Comprehensive Understanding of Video Editing
Authors:Bozheng Li, Yongliang Wu, Yi Lu, Jiashuo Yu, Licheng Tang, Jiawang Cao, Wenqing Zhu, Yuyang Sun, Jay Wu, Wenbo Zhu
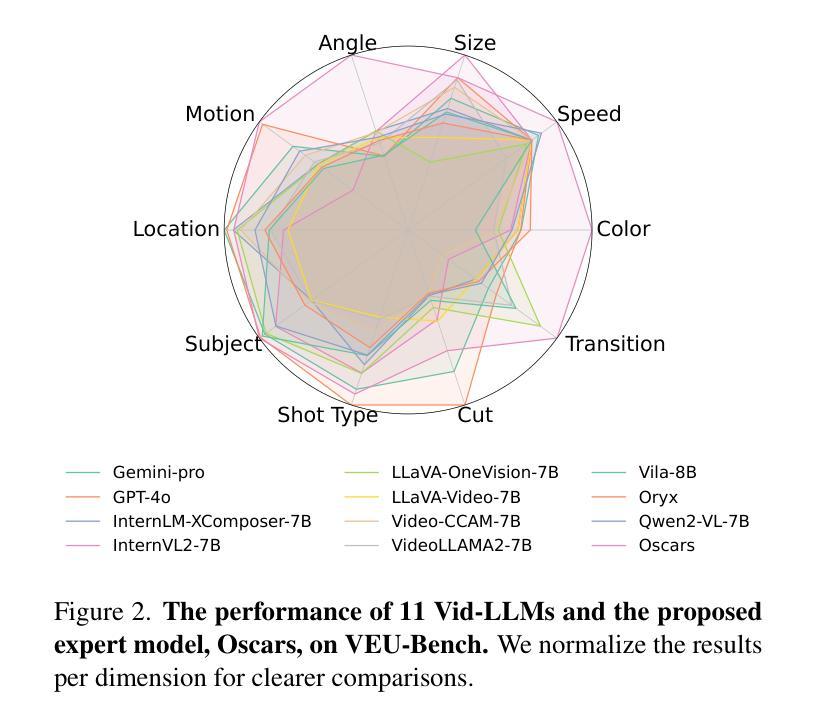
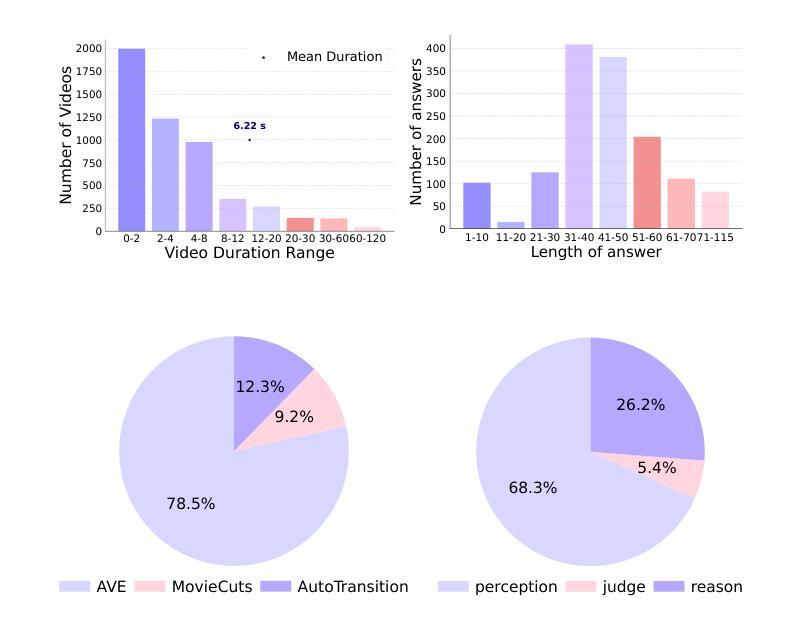
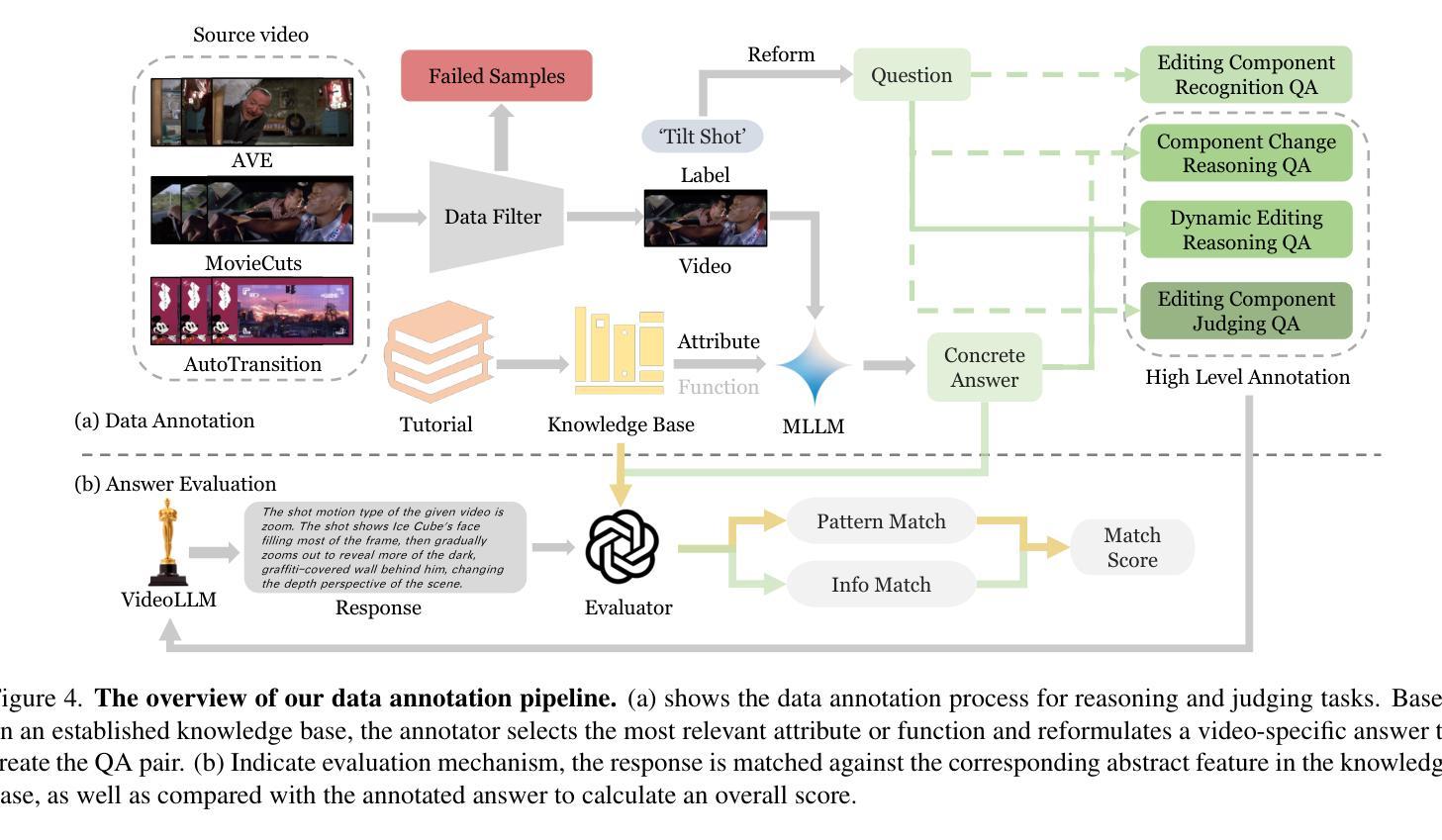
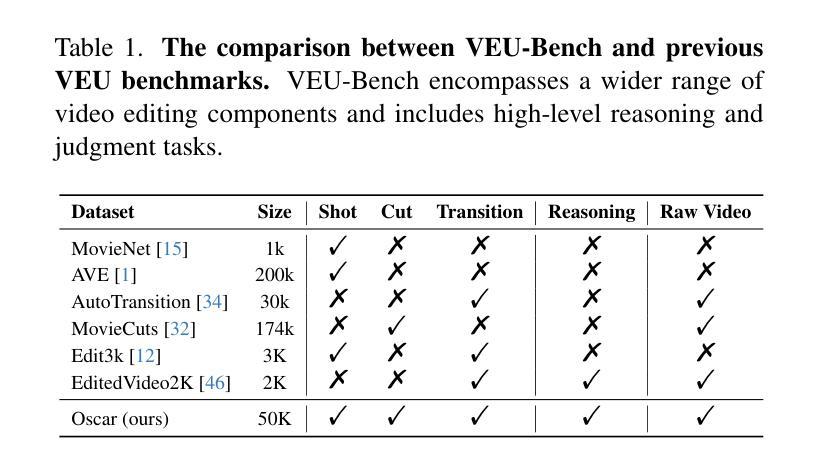
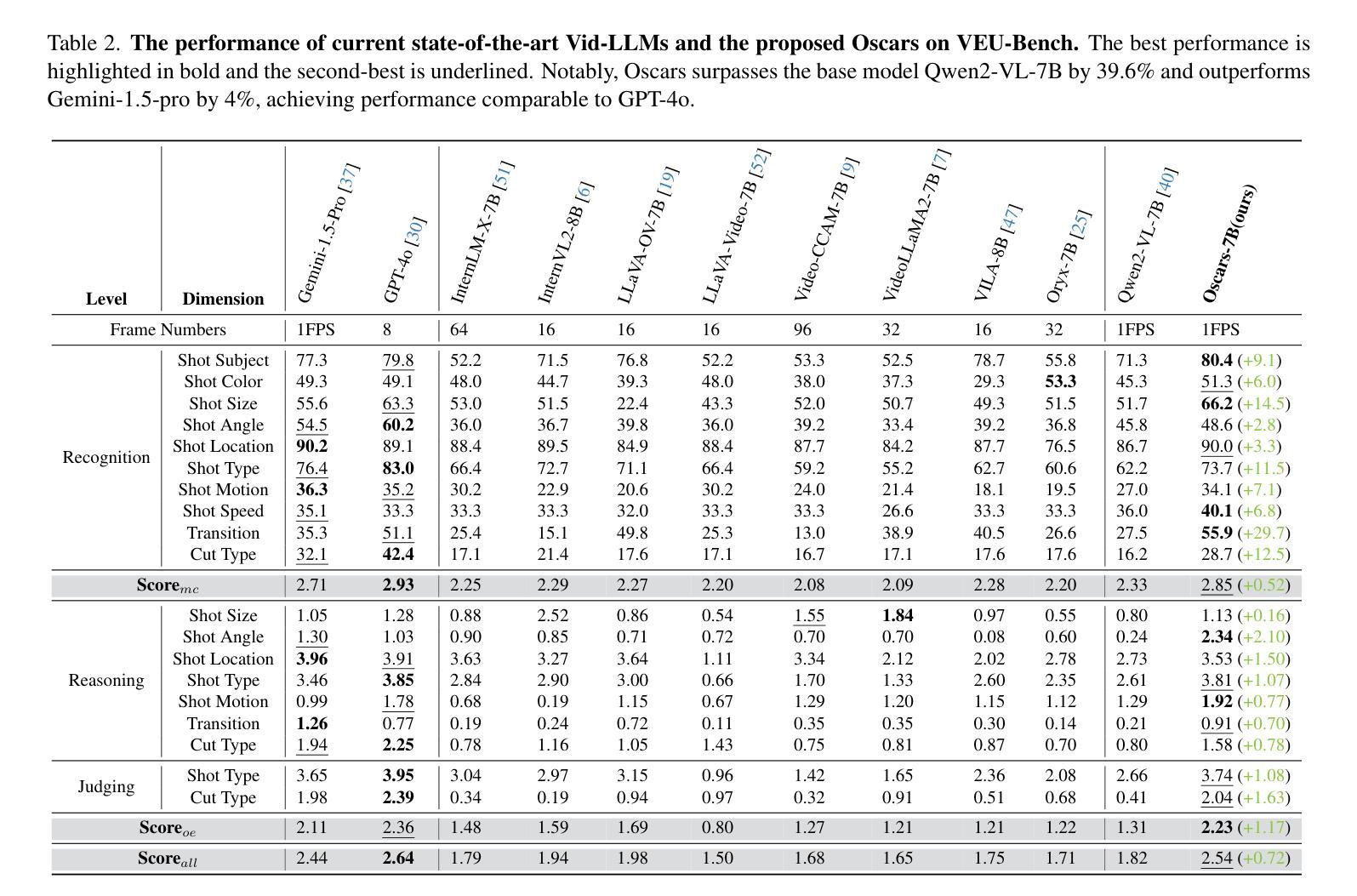
Widely shared videos on the internet are often edited. Recently, although Video Large Language Models (Vid-LLMs) have made great progress in general video understanding tasks, their capabilities in video editing understanding (VEU) tasks remain unexplored. To address this gap, in this paper, we introduce VEU-Bench (Video Editing Understanding Benchmark), a comprehensive benchmark that categorizes video editing components across various dimensions, from intra-frame features like shot size to inter-shot attributes such as cut types and transitions. Unlike previous video editing understanding benchmarks that focus mainly on editing element classification, VEU-Bench encompasses 19 fine-grained tasks across three stages: recognition, reasoning, and judging. To enhance the annotation of VEU automatically, we built an annotation pipeline integrated with an ontology-based knowledge base. Through extensive experiments with 11 state-of-the-art Vid-LLMs, our findings reveal that current Vid-LLMs face significant challenges in VEU tasks, with some performing worse than random choice. To alleviate this issue, we develop Oscars, a VEU expert model fine-tuned on the curated VEU-Bench dataset. It outperforms existing open-source Vid-LLMs on VEU-Bench by over 28.3% in accuracy and achieves performance comparable to commercial models like GPT-4o. We also demonstrate that incorporating VEU data significantly enhances the performance of Vid-LLMs on general video understanding benchmarks, with an average improvement of 8.3% across nine reasoning tasks.
互联网上广泛分享的视频经常经过编辑。尽管视频大语言模型(Vid-LLMs)在一般的视频理解任务中取得了巨大的进步,但它们在视频编辑理解(VEU)任务中的能力仍然未被探索。为了弥补这一空白,本文介绍了VEU-Bench(视频编辑理解基准测试),这是一个全面的基准测试,它根据各种维度对视频编辑组件进行分类,包括帧内特征(如镜头大小)和镜头间属性(如剪辑类型和过渡)。与以前主要关注编辑元素分类的视频编辑理解基准测试不同,VEU-Bench包含三个阶段共19个精细任务:识别、推理和判断。为了提高VEU的自动标注,我们建立了一个与基于本体知识库相结合的标注管道。通过对11款最先进的Vid-LLMs进行的大量实验,我们发现当前Vid-LLMs在VEU任务中面临巨大挑战,部分模型的表现甚至不如随机选择。为了缓解这个问题,我们开发了一种名为Oscars的视频编辑理解专家模型,该模型在精选的VEU-Bench数据集上进行微调。它在VEU-Bench上的准确率超过了现有开源Vid-LLMs超过28.3%,并且性能与商业模型如GPT-4o相当。我们还证明,纳入VEU数据可以显著提高Vid-LLMs在一般视频理解基准测试上的表现,九个推理任务的平均改进率为8.3%。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF Accepted to CVPR2025
摘要
本文介绍了视频编辑理解(VEU)任务的重要性及其在当前研究中的空白。为填补这一空白,提出了VEU-Bench基准测试平台,该平台全面涵盖了视频编辑的各个组成部分,包括镜头大小等帧内特征和剪辑类型等镜头间属性。不同于以往主要关注编辑元素分类的视频编辑理解基准测试,VEU-Bench包含了识别、推理和判断三个阶段的19个精细任务。为了自动标注VEU,建立了一个基于本体知识的标注管道。通过对11款最先进的视频大型语言模型(Vid-LLMs)的广泛实验,发现当前模型在VEU任务上面临巨大挑战,某些模型的表现甚至不及随机选择。为解决这一问题,开发了一款名为Oscars的VEU专家模型,该模型在精选的VEU-Bench数据集上进行微调,在VEU-Bench上的准确率较现有开源Vid-LLMs提高了28.3%,与商业模型如GPT-4o的表现相当。此外,研究还显示,纳入VEU数据能显著提高Vid-LLMs在一般视频理解基准测试上的表现,九个推理任务的平均提高了8.3%。
关键见解
- 视频在互联网上广泛传播时经常经过编辑。
- 当前Video Large Language Models(Vid-LLMs)在视频编辑理解(VEU)任务上的能力尚未被探索。
- 引入VEU-Bench基准测试平台,全面涵盖视频编辑的多个方面。
- 不同于其他主要关注编辑元素分类的基准测试,VEU-Bench包含识别、推理和判断三个阶段的多种任务。
- 当前Vid-LLMs在VEU任务上表现不佳,某些模型表现甚至随机性更高。
- 开发Oscars模型,针对VEU-Bench数据集进行微调,显著提高性能。
点此查看论文截图