⚠️ 以下所有内容总结都来自于 大语言模型的能力,如有错误,仅供参考,谨慎使用
🔴 请注意:千万不要用于严肃的学术场景,只能用于论文阅读前的初筛!
💗 如果您觉得我们的项目对您有帮助 ChatPaperFree ,还请您给我们一些鼓励!⭐️ HuggingFace免费体验
2025-04-29 更新
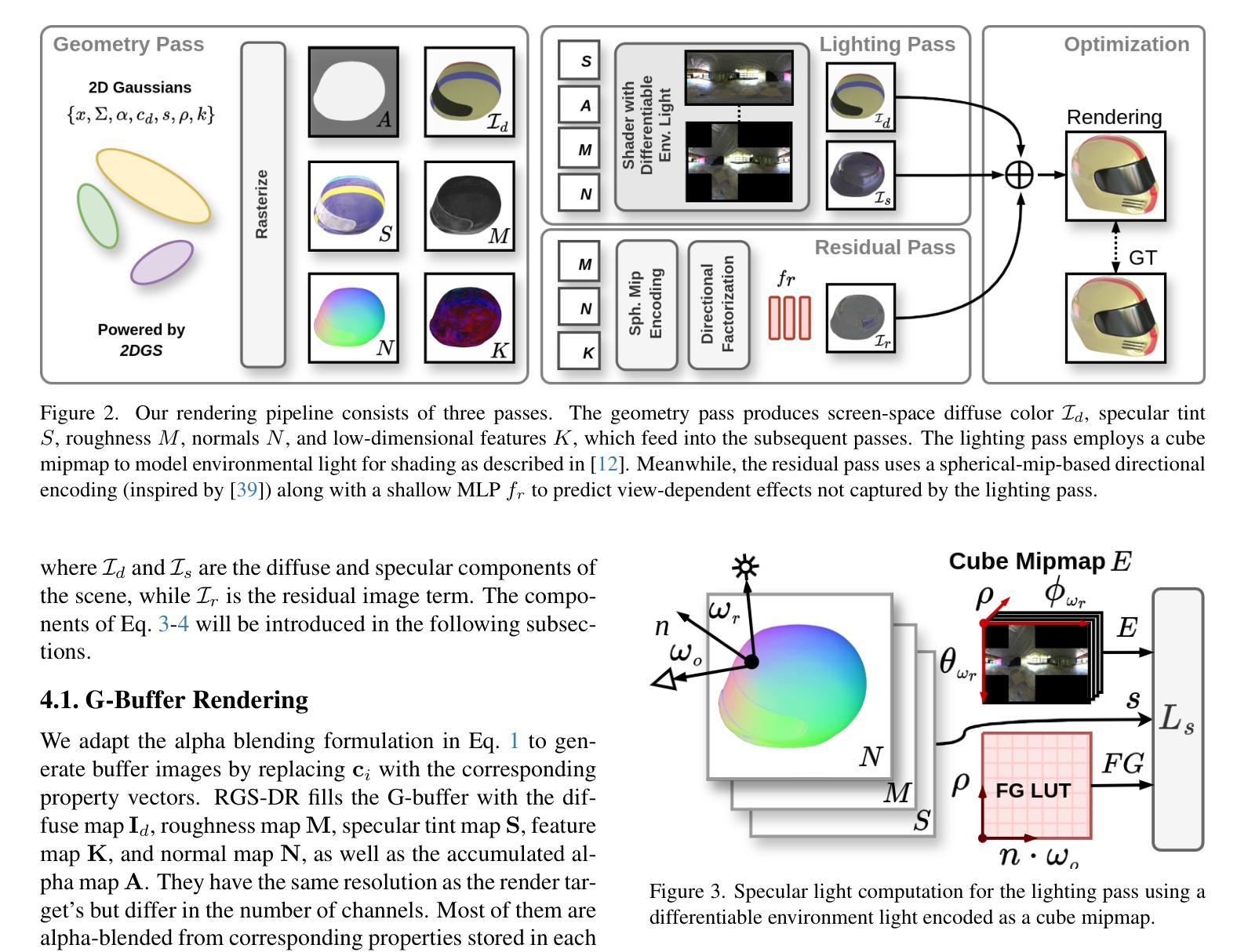
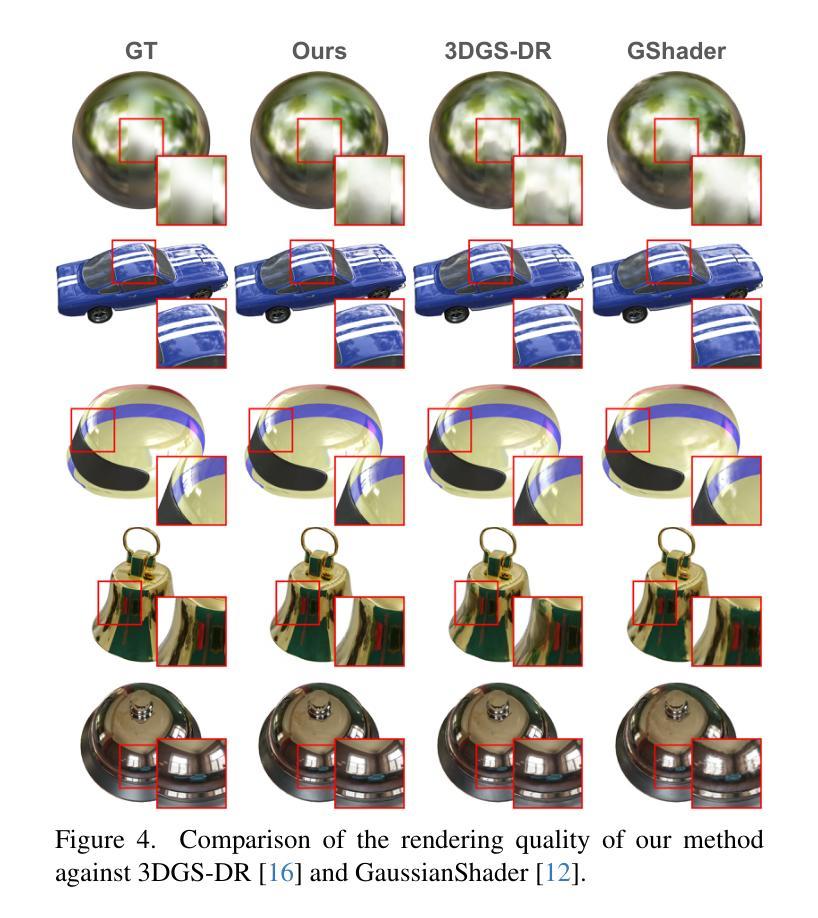
RGS-DR: Reflective Gaussian Surfels with Deferred Rendering for Shiny Objects
Authors:Georgios Kouros, Minye Wu, Tinne Tuytelaars
We introduce RGS-DR, a novel inverse rendering method for reconstructing and rendering glossy and reflective objects with support for flexible relighting and scene editing. Unlike existing methods (e.g., NeRF and 3D Gaussian Splatting), which struggle with view-dependent effects, RGS-DR utilizes a 2D Gaussian surfel representation to accurately estimate geometry and surface normals, an essential property for high-quality inverse rendering. Our approach explicitly models geometric and material properties through learnable primitives rasterized into a deferred shading pipeline, effectively reducing rendering artifacts and preserving sharp reflections. By employing a multi-level cube mipmap, RGS-DR accurately approximates environment lighting integrals, facilitating high-quality reconstruction and relighting. A residual pass with spherical-mipmap-based directional encoding further refines the appearance modeling. Experiments demonstrate that RGS-DR achieves high-quality reconstruction and rendering quality for shiny objects, often outperforming reconstruction-exclusive state-of-the-art methods incapable of relighting.
我们介绍了RGS-DR,这是一种新型逆向渲染方法,用于重建和渲染具有光泽和反射特性的物体,支持灵活的重新打光和场景编辑。与现有方法(例如NeRF和3D高斯拼贴)相比,它们在处理与视图相关的效果时遇到困难,而RGS-DR使用2D高斯surfel表示法来准确估计几何形状和表面法线,这是高质量逆向渲染的基本属性。我们的方法通过可学习的原始模型显式地模拟几何和材质属性,并将其渲染到延迟着色管道中,从而有效地减少渲染伪影并保持锐利的反射。通过采用多级立方体mipmap,RGS-DR能够准确地近似环境光照积分,从而实现高质量的重建和重新打光。基于球形mipmap的方向编码的残差传递进一步改进了外观建模。实验表明,RGS-DR在重建和渲染光泽物体方面达到了高质量,通常优于那些无法进行重新打光的仅用于重建的最先进的方法。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
RGS-DR是一种新型逆向渲染方法,可重建和渲染具有光泽和反射特性的物体,支持灵活的重新照明和场景编辑。它采用2D高斯surfel表示法准确估计几何和表面法线,通过可学习的原始元素显式建模几何和材质属性,并进入一个延迟着色管道。利用多层立方体mipmap近似环境光照积分,实现高质量重建和重新照明。使用基于球形mipmap的方向编码的残差传递进一步改进外观建模。实验表明,RGS-DR在光泽物体的重建和渲染质量方面达到高水平,经常超越只能重建而不能重新照明的最新技术方法。
Key Takeaways
- RGS-DR是一种用于重建和渲染具有光泽和反射特性的物体的新型逆向渲染方法。
- 它采用2D高斯surfel表示法来估计几何和表面法线,这对于高质量逆向渲染至关重要。
- RGS-DR通过可学习的原始元素显式建模几何和材质属性,以减少渲染伪影并保留锐反射。
- 利用多层立方体mipmap,RGS-DR能准确近似环境光照积分,实现高质量重建和重新照明。
- 残差传递与基于球形mipmap的方向编码相结合,进一步改进了外观建模。
- 实验表明,RGS-DR在光泽物体的重建和渲染质量方面表现出卓越性能。
点此查看论文截图

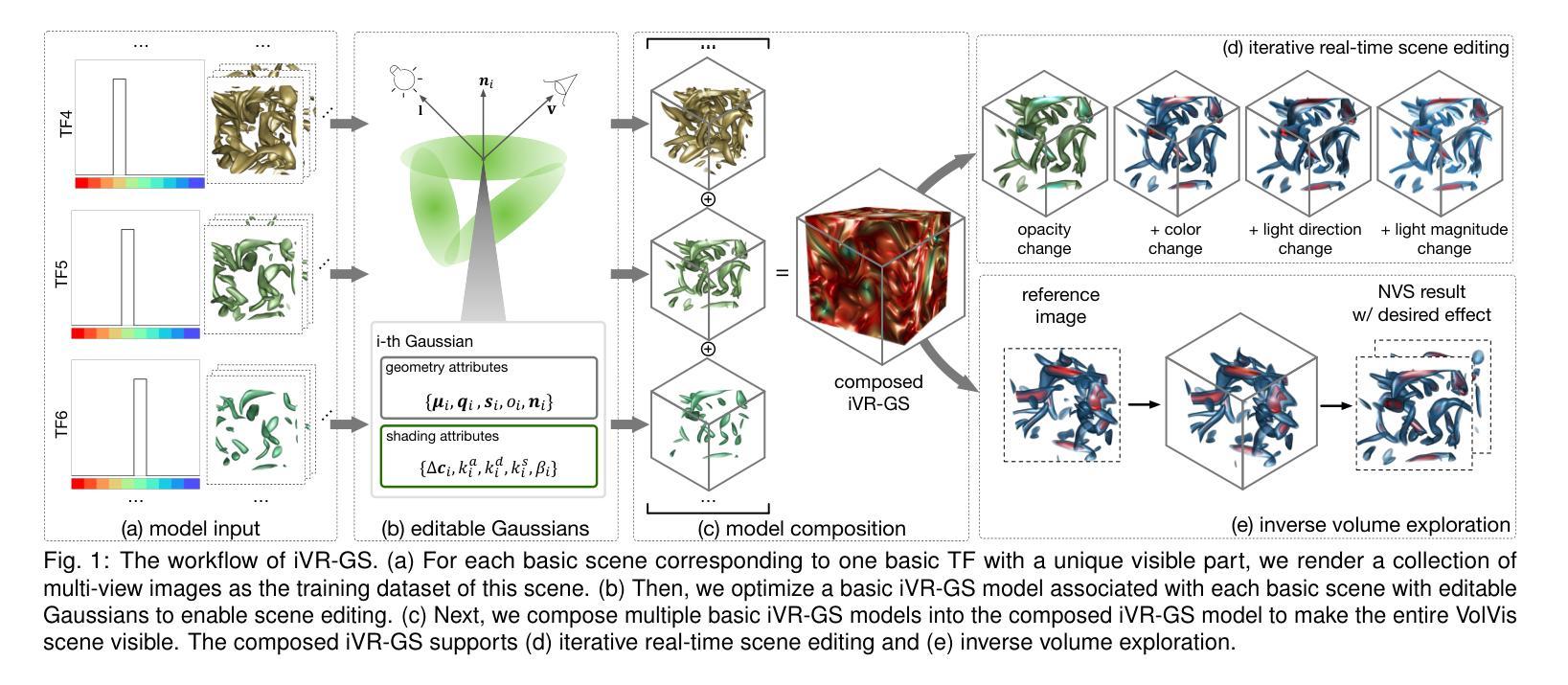
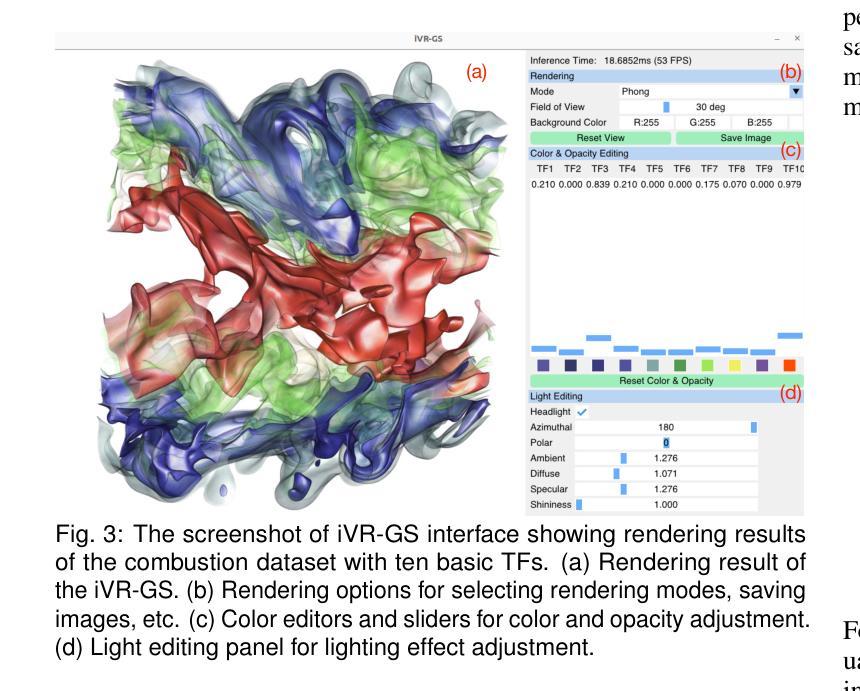
iVR-GS: Inverse Volume Rendering for Explorable Visualization via Editable 3D Gaussian Splatting
Authors:Kaiyuan Tang, Siyuan Yao, Chaoli Wang
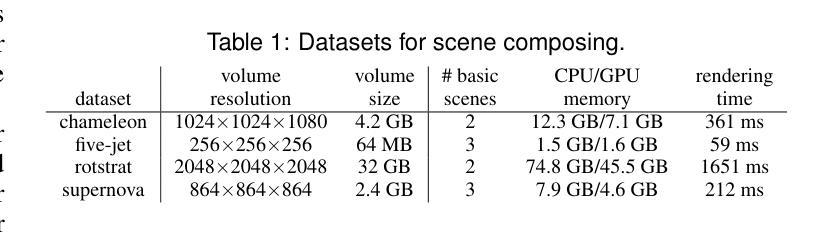
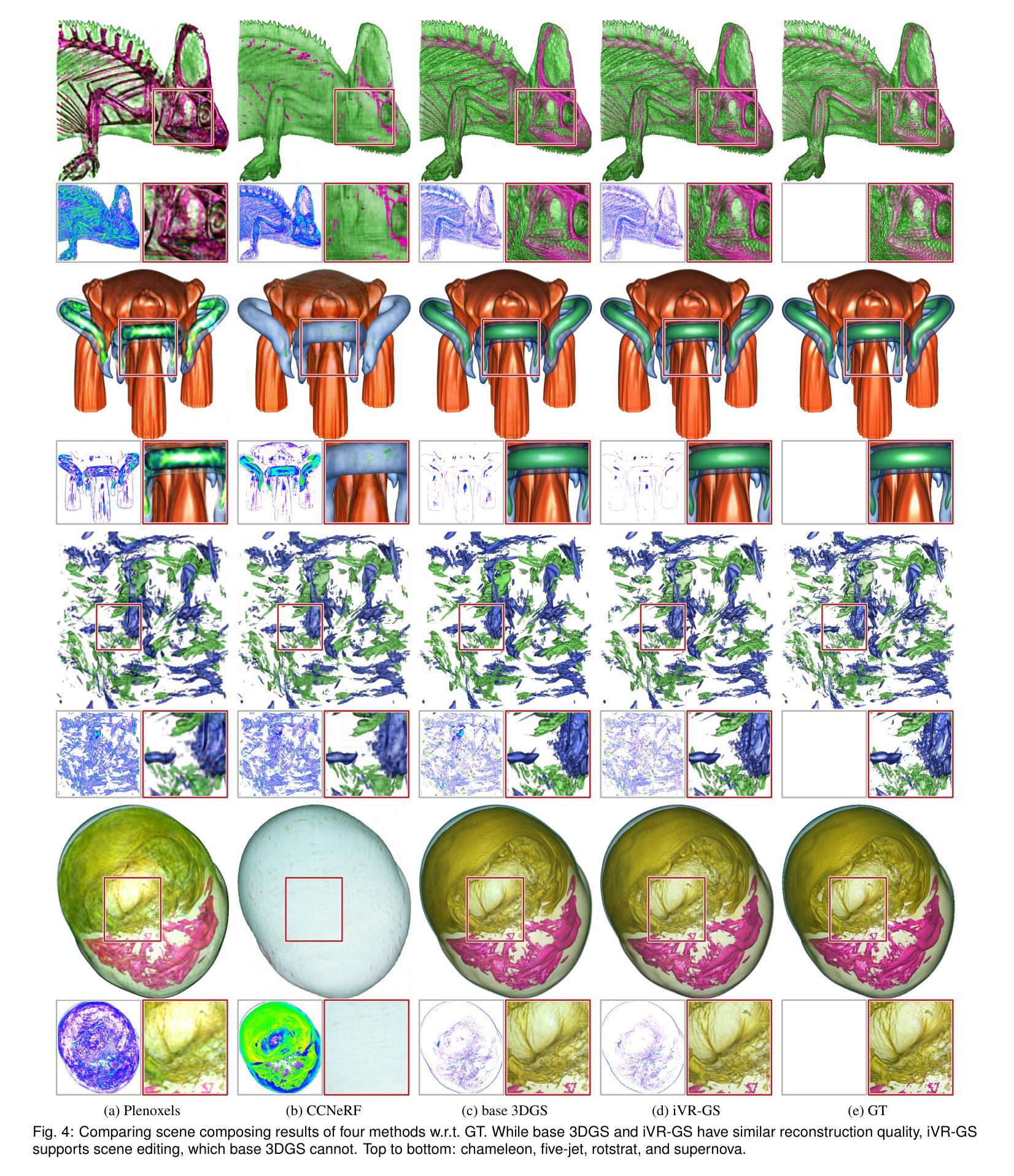
In volume visualization, users can interactively explore the three-dimensional data by specifying color and opacity mappings in the transfer function (TF) or adjusting lighting parameters, facilitating meaningful interpretation of the underlying structure. However, rendering large-scale volumes demands powerful GPUs and high-speed memory access for real-time performance. While existing novel view synthesis (NVS) methods offer faster rendering speeds with lower hardware requirements, the visible parts of a reconstructed scene are fixed and constrained by preset TF settings, significantly limiting user exploration. This paper introduces inverse volume rendering via Gaussian splatting (iVR-GS), an innovative NVS method that reduces the rendering cost while enabling scene editing for interactive volume exploration. Specifically, we compose multiple iVR-GS models associated with basic TFs covering disjoint visible parts to make the entire volumetric scene visible. Each basic model contains a collection of 3D editable Gaussians, where each Gaussian is a 3D spatial point that supports real-time scene rendering and editing. We demonstrate the superior reconstruction quality and composability of iVR-GS against other NVS solutions (Plenoxels, CCNeRF, and base 3DGS) on various volume datasets. The code is available at https://github.com/TouKaienn/iVR-GS.
在体积可视化中,用户可以通过在传输函数(TF)中指定颜色和透明度映射或调整光照参数来交互式地探索三维数据,从而促进对底层结构的有意义解释。然而,呈现大规模体积需要高性能的GPU和高速内存访问以实现实时性能。尽管现有的新型视图合成(NVS)方法提供了更快的渲染速度和较低的硬件要求,但重建场景的可见部分是由预设的TF设置固定和约束的,从而显著限制了用户的探索。本文介绍了通过高斯拼贴进行逆向体积渲染(iVR-GS),这是一种创新的NVS方法,可以降低渲染成本,同时实现场景编辑,用于交互式体积探索。具体来说,我们组合了与基本TF相关联的多个iVR-GS模型,覆盖不连续的可见部分,使整个体积场景可见。每个基本模型都包含一组可编辑的3D高斯,每个高斯都是一个支持实时场景渲染和编辑的3D空间点。我们在各种体积数据集上展示了iVR-GS相对于其他NVS解决方案(Plenoxels、CCNeRF和基础3DGS)的优越重建质量和可组合性。代码可在https://github.com/TouKaienn/iVR-GS上找到。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF Accepted by IEEE Transactions on Visualization and Computer Graphics (TVCG)
Summary
大规模数据体可视化领域存在诸多挑战,用户对于真实三维数据互动探索的需求迫切。现有的新型视图合成方法虽能提高渲染速度并降低硬件要求,但在预设传输函数设置下,重建场景的可见部分受限,用户探索自由度受限。本文提出一种基于高斯散斑的逆向体积渲染(iVR-GS)新型视图合成方法,旨在降低渲染成本并提升场景编辑能力,以实现交互式体积探索。该方法通过组合多个与基本传输函数相关联的iVR-GS模型,使整体体积场景可见。每个模型包含一系列支持实时场景渲染和编辑的三维可编辑高斯。实验证明,与其他新型视图合成解决方案相比,iVR-GS在多种体积数据集上表现出更好的重建质量和可组合性。
Key Takeaways
- 用户可通过指定颜色和不透明度映射在传输函数中进行互动,以探索三维数据,这有助于对底层结构的解读。
- 大规模数据体的渲染需要高性能GPU和高速内存来支持实时性能。
- 现有新型视图合成方法虽然提高了渲染速度并降低了硬件要求,但用户探索受限。
- iVR-GS是一种新型视图合成方法,旨在解决上述问题,它通过组合多个模型实现整个体积场景的可见性。
- 每个iVR-GS模型包含支持实时场景渲染和编辑的三维可编辑高斯。
- iVR-GS在多种体积数据集上展示了优秀的重建质量和可组合性,相较于其他新型视图合成解决方案(如Plenoxels、CCNeRF和基础3DGS)。
点此查看论文截图


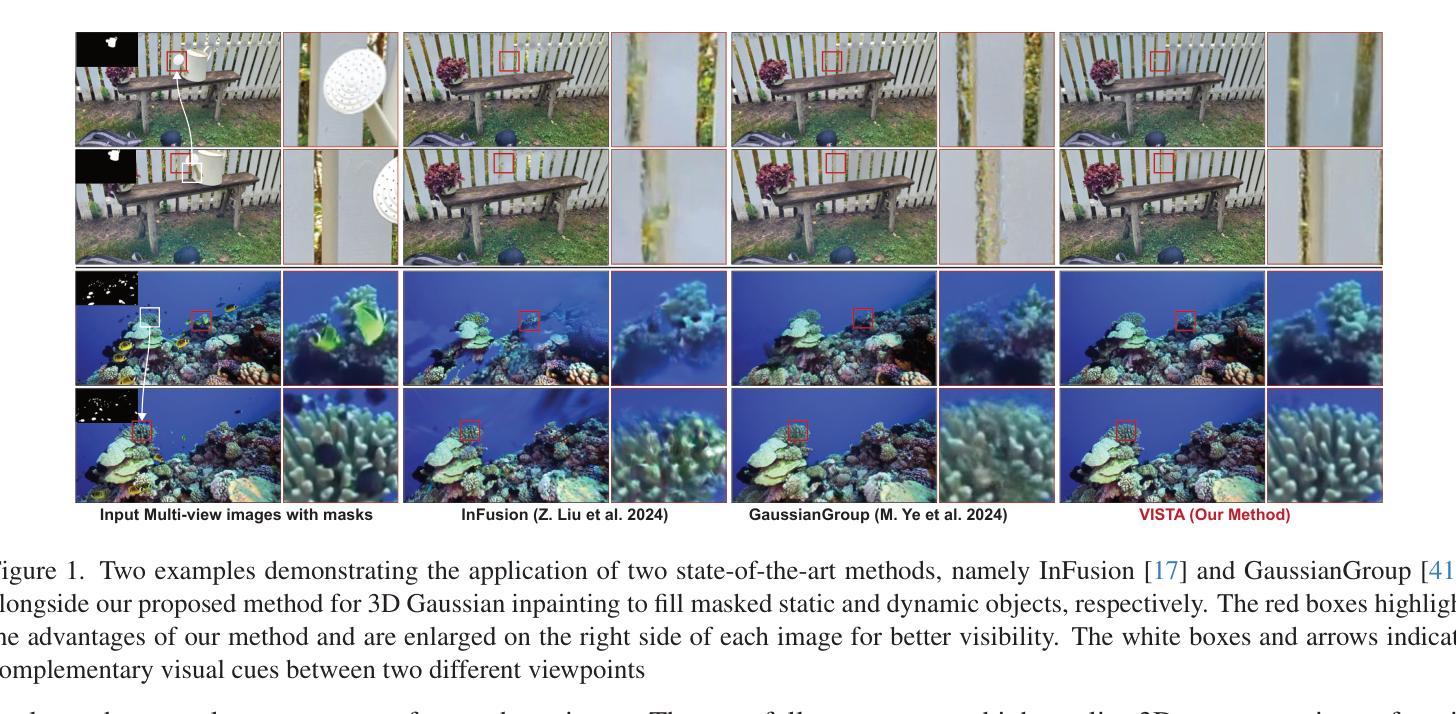
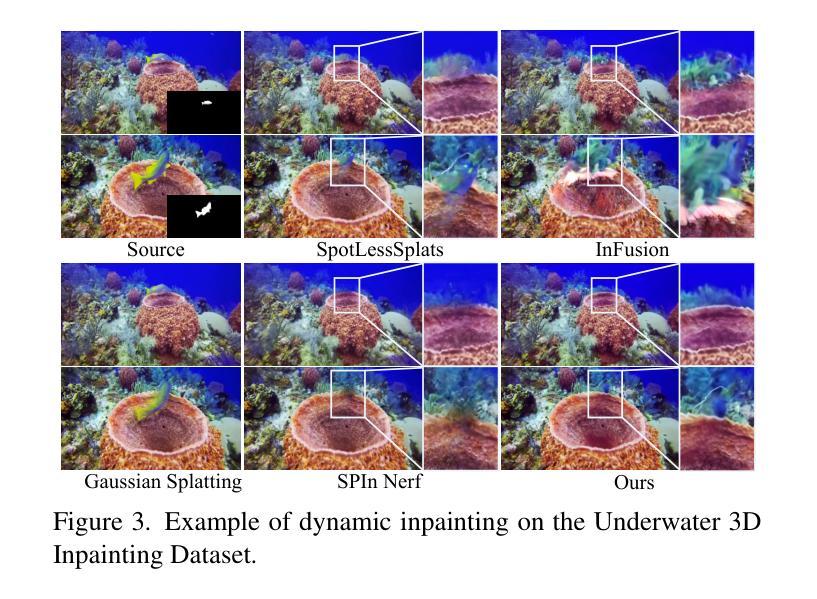
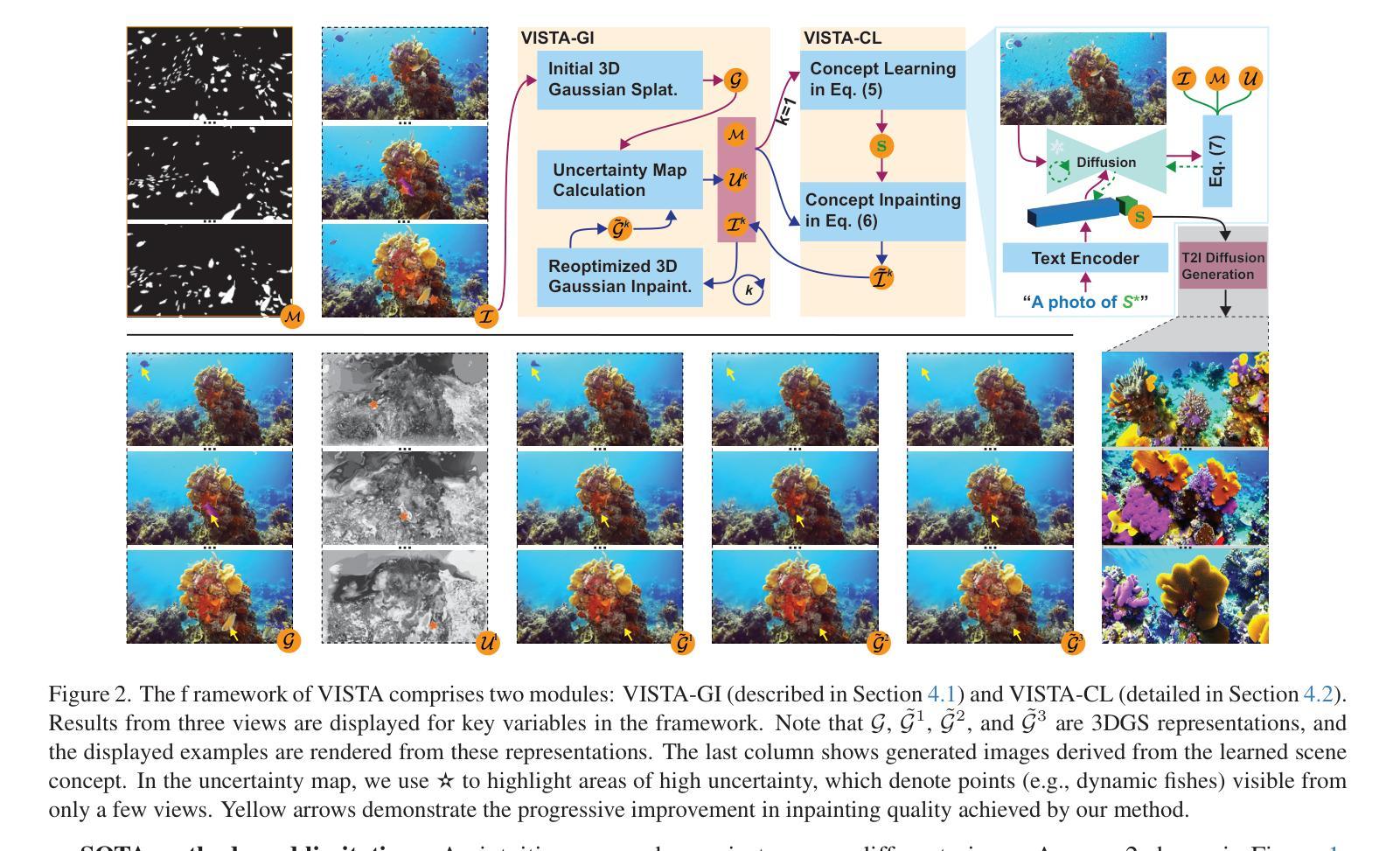
Visibility-Uncertainty-guided 3D Gaussian Inpainting via Scene Conceptional Learning
Authors:Mingxuan Cui, Qing Guo, Yuyi Wang, Hongkai Yu, Di Lin, Qin Zou, Ming-Ming Cheng, Xi Li
3D Gaussian Splatting (3DGS) has emerged as a powerful and efficient 3D representation for novel view synthesis. This paper extends 3DGS capabilities to inpainting, where masked objects in a scene are replaced with new contents that blend seamlessly with the surroundings. Unlike 2D image inpainting, 3D Gaussian inpainting (3DGI) is challenging in effectively leveraging complementary visual and semantic cues from multiple input views, as occluded areas in one view may be visible in others. To address this, we propose a method that measures the visibility uncertainties of 3D points across different input views and uses them to guide 3DGI in utilizing complementary visual cues. We also employ uncertainties to learn a semantic concept of scene without the masked object and use a diffusion model to fill masked objects in input images based on the learned concept. Finally, we build a novel 3DGI framework, VISTA, by integrating VISibility-uncerTainty-guided 3DGI with scene conceptuAl learning. VISTA generates high-quality 3DGS models capable of synthesizing artifact-free and naturally inpainted novel views. Furthermore, our approach extends to handling dynamic distractors arising from temporal object changes, enhancing its versatility in diverse scene reconstruction scenarios. We demonstrate the superior performance of our method over state-of-the-art techniques using two challenging datasets: the SPIn-NeRF dataset, featuring 10 diverse static 3D inpainting scenes, and an underwater 3D inpainting dataset derived from UTB180, including fast-moving fish as inpainting targets.
三维高斯溅落技术(3DGS)已成为一种强大的新型三维视图合成方法。本文扩展了3DGS在图像修复方面的应用,其中场景中的遮挡对象被新的内容所替换,这些新内容无缝地融入了周围环境。不同于二维图像修复,三维高斯图像修复(3DGI)在有效利用来自多个输入视图的辅助视觉和语义线索方面更具挑战性,因为一个视图中的遮挡区域可能在其他视图中是可见的。为解决这一问题,我们提出了一种方法,该方法可以测量不同输入视图中三维点的可见性不确定性,并利用这些不确定性来指导三维高斯图像修复利用辅助视觉线索。我们还利用不确定性来学习场景中不带遮挡对象的语义概念,并使用扩散模型基于学习到的概念来填充输入图像中的遮挡对象。最后,我们构建了一个名为VISTA的新型三维高斯图像修复框架,通过整合可见性不确定性指导的三维高斯图像修复与场景概念学习。VISTA可以生成高质量的三维溅落模型,能够合成无伪影的自然修复新视图。此外,我们的方法还扩展到处理由于临时对象变化而产生的动态干扰因素,增强了在各种场景重建场景中的通用性。我们使用两个具有挑战性的数据集:包含10个多样静态三维修复场景的SPIn-NeRF数据集和从UTB180派生的水下三维修复数据集,其中包括快速移动的鱼类作为修复目标,展示了我们的方法在性能上的优越性。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF 14 pages, 12 figures, ICCV
Summary
3DGS被扩展应用于三维场景中的遮罩对象替换(inpainting)任务,提出了一个可见性不确定性引导的三维高斯填充(VISTA)框架。该框架能够利用多视角的视觉和语义线索,生成高质量的无遮挡的三维场景表示,并可在动态干扰物场景下应用。
Key Takeaways
- 3DGS被应用于三维场景的遮罩对象替换任务。
- VISTA框架利用可见性不确定性来指导三维高斯填充过程。
- VISTA框架能够利用多视角的视觉和语义线索。
- VISTA生成的模型能够合成无瑕疵的新视角图像。
- 该方法可应用于动态干扰物场景下的重建。
- 使用了扩散模型进行遮挡对象的填充。
点此查看论文截图



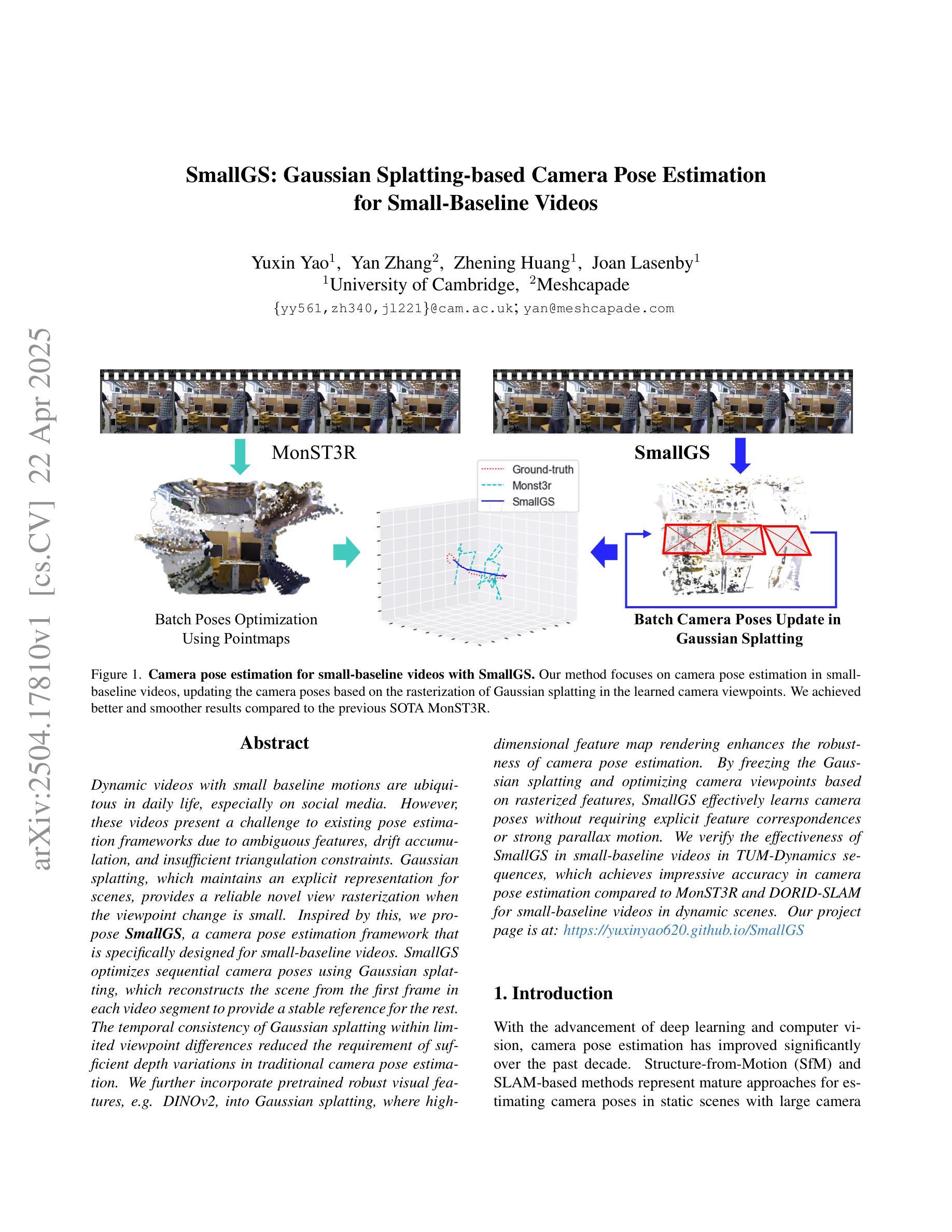
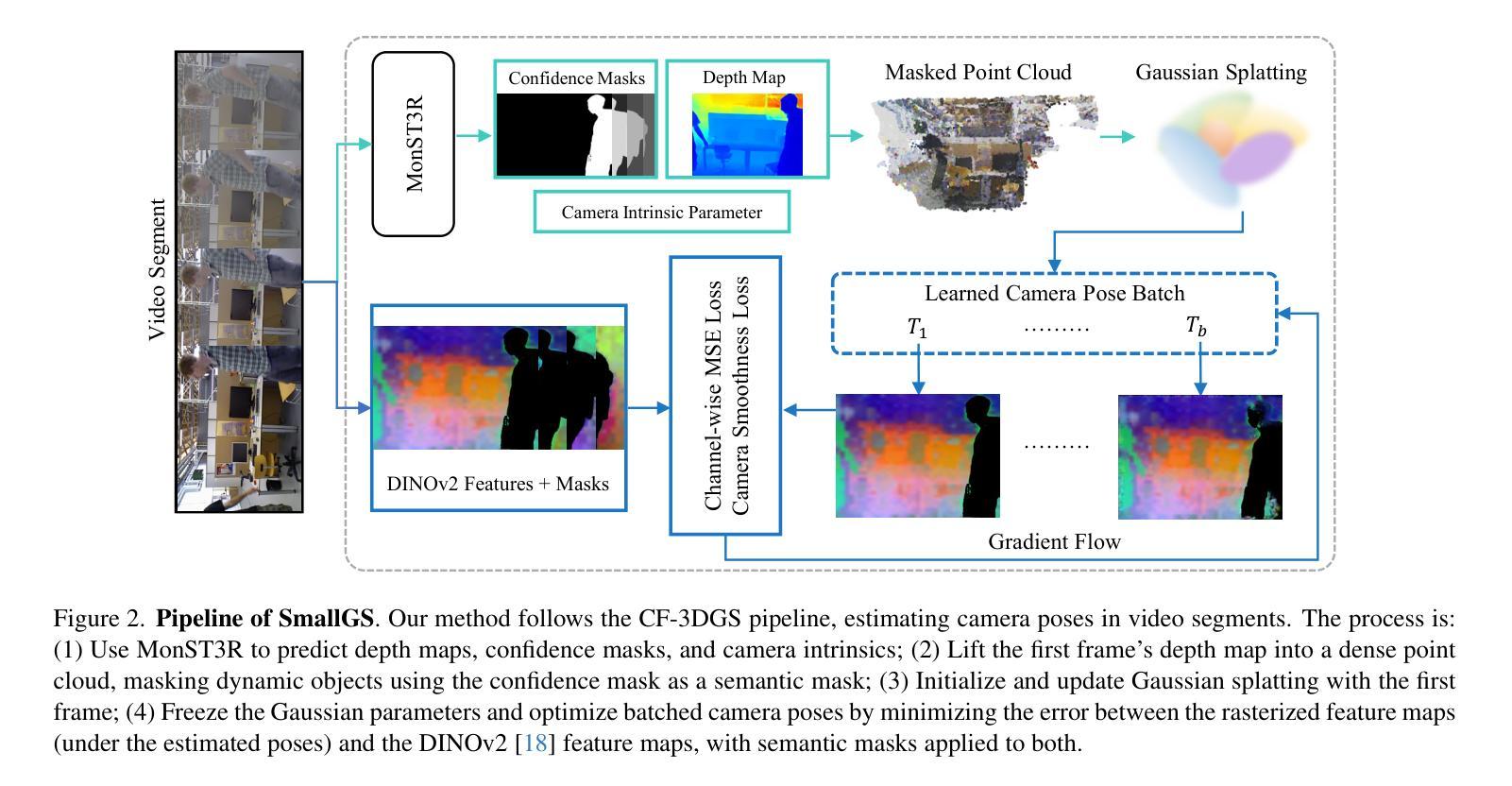
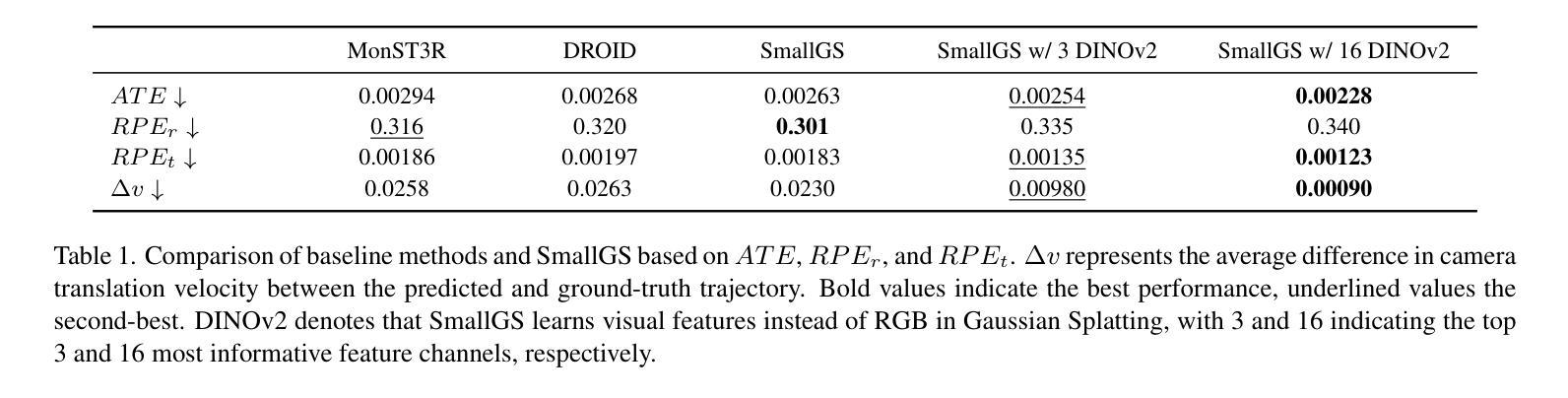
SmallGS: Gaussian Splatting-based Camera Pose Estimation for Small-Baseline Videos
Authors:Yuxin Yao, Yan Zhang, Zhening Huang, Joan Lasenby
Dynamic videos with small baseline motions are ubiquitous in daily life, especially on social media. However, these videos present a challenge to existing pose estimation frameworks due to ambiguous features, drift accumulation, and insufficient triangulation constraints. Gaussian splatting, which maintains an explicit representation for scenes, provides a reliable novel view rasterization when the viewpoint change is small. Inspired by this, we propose SmallGS, a camera pose estimation framework that is specifically designed for small-baseline videos. SmallGS optimizes sequential camera poses using Gaussian splatting, which reconstructs the scene from the first frame in each video segment to provide a stable reference for the rest. The temporal consistency of Gaussian splatting within limited viewpoint differences reduced the requirement of sufficient depth variations in traditional camera pose estimation. We further incorporate pretrained robust visual features, e.g. DINOv2, into Gaussian splatting, where high-dimensional feature map rendering enhances the robustness of camera pose estimation. By freezing the Gaussian splatting and optimizing camera viewpoints based on rasterized features, SmallGS effectively learns camera poses without requiring explicit feature correspondences or strong parallax motion. We verify the effectiveness of SmallGS in small-baseline videos in TUM-Dynamics sequences, which achieves impressive accuracy in camera pose estimation compared to MonST3R and DORID-SLAM for small-baseline videos in dynamic scenes. Our project page is at: https://yuxinyao620.github.io/SmallGS
动态视频带有小基线运动在日常生活中无处不在,特别是在社交媒体上。然而,这些视频对现有姿态估计框架构成挑战,原因包括特征模糊、漂移累积和三角约束不足。高斯平铺技术能够保持场景明确表述,当视点变化较小时,它提供了一种可靠的新视图栅格化方法。受其启发,我们提出了专为小基线视频设计的相机姿态估计框架——SmallGS。SmallGS使用高斯平铺技术优化序列相机姿态,从每个视频片段的第一帧重建场景,为其余部分提供一个稳定的参考。高斯平铺的时空一致性在有限的视点差异内降低了传统相机姿态估计中对足够深度变化的要求。我们还将预训练的稳健视觉特征(例如DINOv2)融入高斯平铺技术中,其中高维特征图渲染提高了相机姿态估计的稳健性。通过冻结高斯平铺技术并基于栅格化特征优化相机视角,SmallGS可以有效地学习相机姿态,而无需明确的特征对应关系或强烈的视差运动。我们在TUM-Dynamics序列中的小基线视频上验证了SmallGS的有效性,与MonST3R和DORID-SLAM相比,它在动态场景的小基线视频相机姿态估计中达到了令人印象深刻的准确性。我们的项目页面是:https://yuxinyao620.github.io/SmallGS
论文及项目相关链接
PDF 10 pages, 4 figures, Accepted by CVPR workshop
Summary
针对动态场景中具有小基线运动特征的动态视频(尤其是社交媒体中的常见类型),本文提出了一种新的相机姿态估计框架,名为SmallGS。它利用高斯敷彩(Gaussian splatting)技术,从视频每段的初始帧重建场景,为后续帧提供稳定的参考。结合预训练的稳健视觉特征(如DINOv2),在高斯敷彩中进行高维特征映射渲染,提高相机姿态估计的稳健性。SmallGS在TUM-Dynamics序列中的小基线视频上表现出优异的相机姿态估计准确性,相较于MonST3R和DORID-SLAM在处理动态场景的小基线视频时更具优势。
Key Takeaways
- SmallGS框架专门针对具有小基线运动的视频设计,适用于日常动态场景中的相机姿态估计。
- 利用高斯敷彩技术,SmallGS通过重建每段视频的初始场景,为后续帧提供稳定参考。
- 高维特征映射渲染结合预训练视觉特征提升了相机姿态估计的稳健性。
- SmallGS在有限视角差异内保持高斯敷彩的时空一致性,减少对深度变化传统的相机姿态估计的依赖。
- 该方法无需明确特征对应或强烈的并行运动即可学习相机姿态。
- 在TUM-Dynamics序列中,SmallGS对小基线视频的相机姿态估计表现出极高准确性。
点此查看论文截图
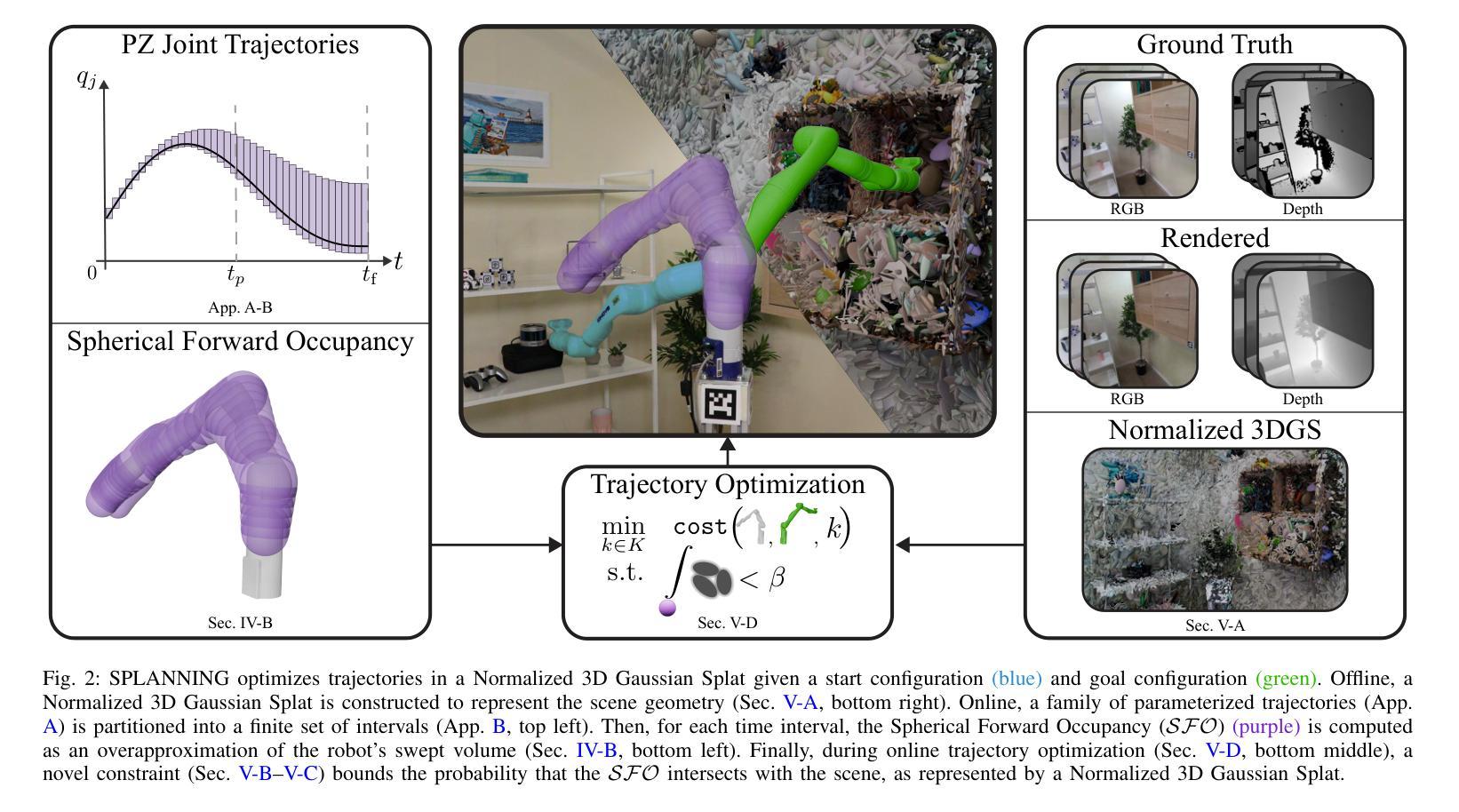
Let’s Make a Splan: Risk-Aware Trajectory Optimization in a Normalized Gaussian Splat
Authors:Jonathan Michaux, Seth Isaacson, Challen Enninful Adu, Adam Li, Rahul Kashyap Swayampakula, Parker Ewen, Sean Rice, Katherine A. Skinner, Ram Vasudevan
Neural Radiance Fields and Gaussian Splatting have recently transformed computer vision by enabling photo-realistic representations of complex scenes. However, they have seen limited application in real-world robotics tasks such as trajectory optimization. This is due to the difficulty in reasoning about collisions in radiance models and the computational complexity associated with operating in dense models. This paper addresses these challenges by proposing SPLANNING, a risk-aware trajectory optimizer operating in a Gaussian Splatting model. This paper first derives a method to rigorously upper-bound the probability of collision between a robot and a radiance field. Then, this paper introduces a normalized reformulation of Gaussian Splatting that enables efficient computation of this collision bound. Finally, this paper presents a method to optimize trajectories that avoid collisions in a Gaussian Splat. Experiments show that SPLANNING outperforms state-of-the-art methods in generating collision-free trajectories in cluttered environments. The proposed system is also tested on a real-world robot manipulator. A project page is available at https://roahmlab.github.io/splanning.
神经辐射场和高斯拼贴技术最近通过实现复杂场景的照片级真实表示,从而转变了计算机视觉领域。然而,它们在现实世界中的机器人任务(如轨迹优化)中的应用仍然有限。这是由于在辐射模型中推理碰撞的困难以及与在密集模型中进行操作相关的计算复杂性。本文针对这些挑战,提出了SPLANNING这一风险感知的轨迹优化器,它在高斯拼贴模型中进行操作。本文首先推导了一种方法,可以严格地上限机器人与辐射场之间发生碰撞的概率。然后,本文介绍了高斯拼贴的归一化重新表述,这能够高效地计算此碰撞上限。最后,本文提出了一种在高斯拼贴中避免碰撞的轨迹优化方法。实验表明,SPLANNING在杂乱环境中生成无碰撞轨迹方面优于最先进的方法。所提出系统在真实世界的机器人操纵器上也经过了测试。项目页面位于 https://roahmlab.github.io/splanning 。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF First two authors contributed equally. Project Page: https://roahmlab.github.io/splanning
Summary
神经网络辐射场和高斯涂抹技术已重塑计算机视觉,可实现复杂场景的光照现实表示。然而,它们在现实世界机器人任务中的应用有限,如轨迹优化。本文提出SPLANNING,一种在Gaussian Splatting模型中的风险意识轨迹优化器,解决这些挑战。本文首先推导了一种方法,严格地上界机器人与辐射场碰撞的概率。然后,本文介绍了Gaussian Splatting的归一化改革,使碰撞边界的有效计算成为可能。最后,本文提出了一种在高斯Splat中避免碰撞的轨迹优化方法。实验表明,SPLANNING在拥挤环境中生成无碰撞轨迹的方法优于现有技术,并在真实世界机器人操纵器上进行了测试。
Key Takeaways
- 神经网络辐射场和高斯涂抹技术能够生成复杂场景的光照现实表示。
- 这些技术在机器人轨迹优化等现实世界任务中的应用受到限制,主要由于碰撞推理的困难和在密集模型中的计算复杂性。
- SPLANNING是一种在Gaussian Splatting模型中的风险意识轨迹优化器,旨在解决这些挑战。
- 本文提供了一种方法,严格地上界机器人与辐射场碰撞的概率。
- 通过归一化改革Gaussian Splatting,实现了碰撞边界的有效计算。
- SPLANNING能优化轨迹,避免在高斯Splat中的碰撞。
点此查看论文截图