⚠️ 以下所有内容总结都来自于 大语言模型的能力,如有错误,仅供参考,谨慎使用
🔴 请注意:千万不要用于严肃的学术场景,只能用于论文阅读前的初筛!
💗 如果您觉得我们的项目对您有帮助 ChatPaperFree ,还请您给我们一些鼓励!⭐️ HuggingFace免费体验
2025-04-29 更新
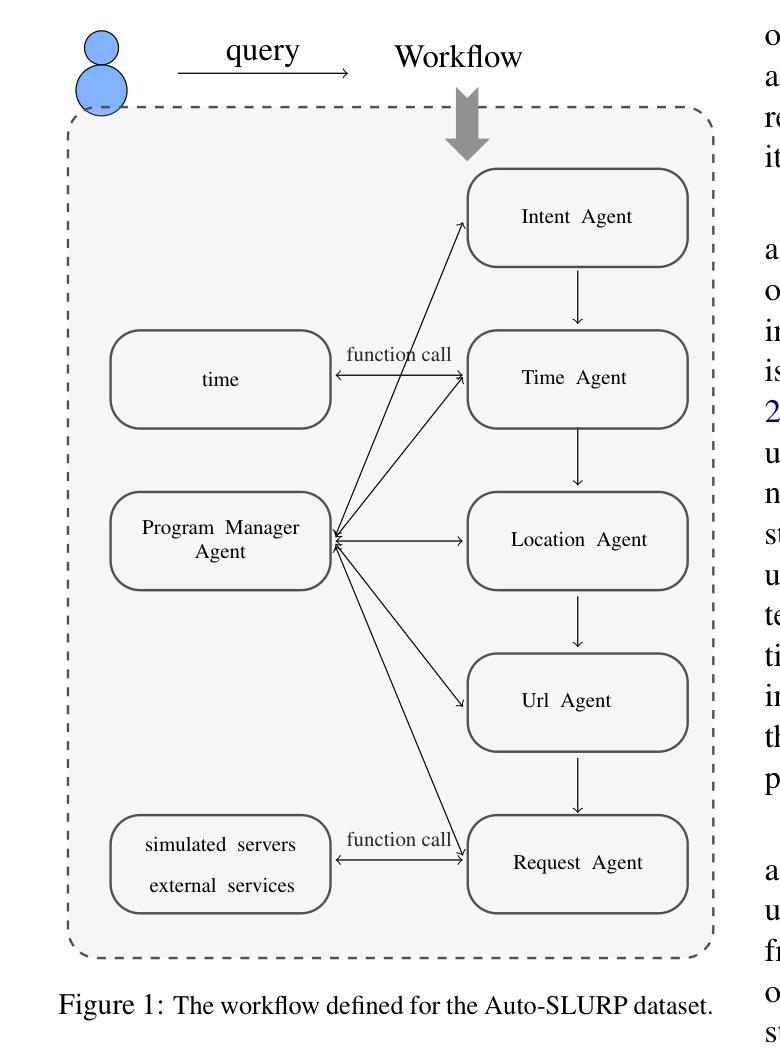
Auto-SLURP: A Benchmark Dataset for Evaluating Multi-Agent Frameworks in Smart Personal Assistant
Authors:Lei Shen, Xiaoyu Shen
In recent years, multi-agent frameworks powered by large language models (LLMs) have advanced rapidly. Despite this progress, there is still a notable absence of benchmark datasets specifically tailored to evaluate their performance. To bridge this gap, we introduce Auto-SLURP, a benchmark dataset aimed at evaluating LLM-based multi-agent frameworks in the context of intelligent personal assistants. Auto-SLURP extends the original SLURP dataset – initially developed for natural language understanding tasks – by relabeling the data and integrating simulated servers and external services. This enhancement enables a comprehensive end-to-end evaluation pipeline, covering language understanding, task execution, and response generation. Our experiments demonstrate that Auto-SLURP presents a significant challenge for current state-of-the-art frameworks, highlighting that truly reliable and intelligent multi-agent personal assistants remain a work in progress. The dataset and related code are available at https://github.com/lorashen/Auto-SLURP/.
近年来,由大型语言模型(LLM)驱动的多智能体框架发展迅速。然而,尽管取得了进展,仍然缺乏专门用于评估其性能的基准数据集。为了弥补这一空白,我们引入了Auto-SLURP,这是一个旨在评估智能个人助理背景下基于LLM的多智能体框架的基准数据集。Auto-SLURP扩展了原始的SLURP数据集——最初是为自然语言理解任务而开发的——通过重新标记数据并集成模拟服务器和外部服务来进行增强。这种增强功能使得全面的端到端评估管道成为可能,涵盖了语言理解、任务执行和响应生成。我们的实验表明,Auto-SLURP对当前最先进的框架提出了重大挑战,强调真正可靠和智能的多智能体个人助理仍在研发中。数据集和相关代码可在https://github.com/lorashen/Auto-SLURP/找到。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
近年来,多智能体框架借助大型语言模型(LLM)迅速发展。然而,缺乏专门用于评估它们性能的基准数据集。为弥补这一空白,我们推出了Auto-SLURP基准数据集,旨在评估智能个人助理环境中基于LLM的多智能体框架性能。Auto-SLURP扩展了最初用于自然语言理解任务的SLURP数据集,通过重新标记数据并集成模拟服务器和外部服务来实现更全面的端到端评估流程,涵盖语言理解、任务执行和响应生成。实验表明,Auto-SLURP对当前最前沿的框架提出了重大挑战,凸显出真正可靠且智能的多智能体个人助理仍在发展中。
Key Takeaways
- 多智能体框架借助大型语言模型迅速发展,但仍缺乏专门的基准数据集来评估其性能。
- 引入Auto-SLURP基准数据集,旨在评估智能个人助理环境中基于LLM的多智能体框架。
- Auto-SLURP扩展了SLURP数据集,通过重新标记数据和集成模拟服务器与外部服务,实现更全面的评估流程。
- Auto-SLURP的评估流程涵盖语言理解、任务执行和响应生成。
- 实验表明,Auto-SLURP对当前最前沿的框架提出了挑战。
- 真正的智能个人助理仍在发展中,需要进一步的研究和改进。
点此查看论文截图


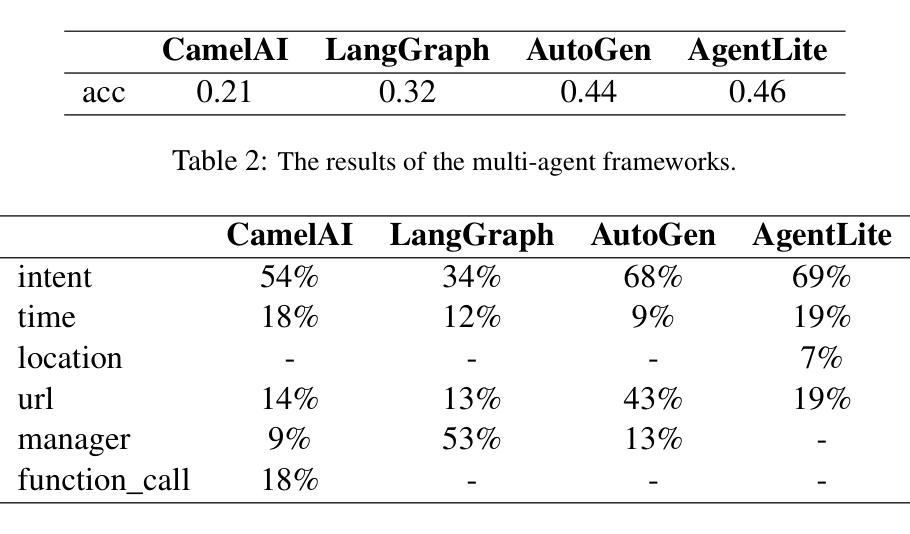

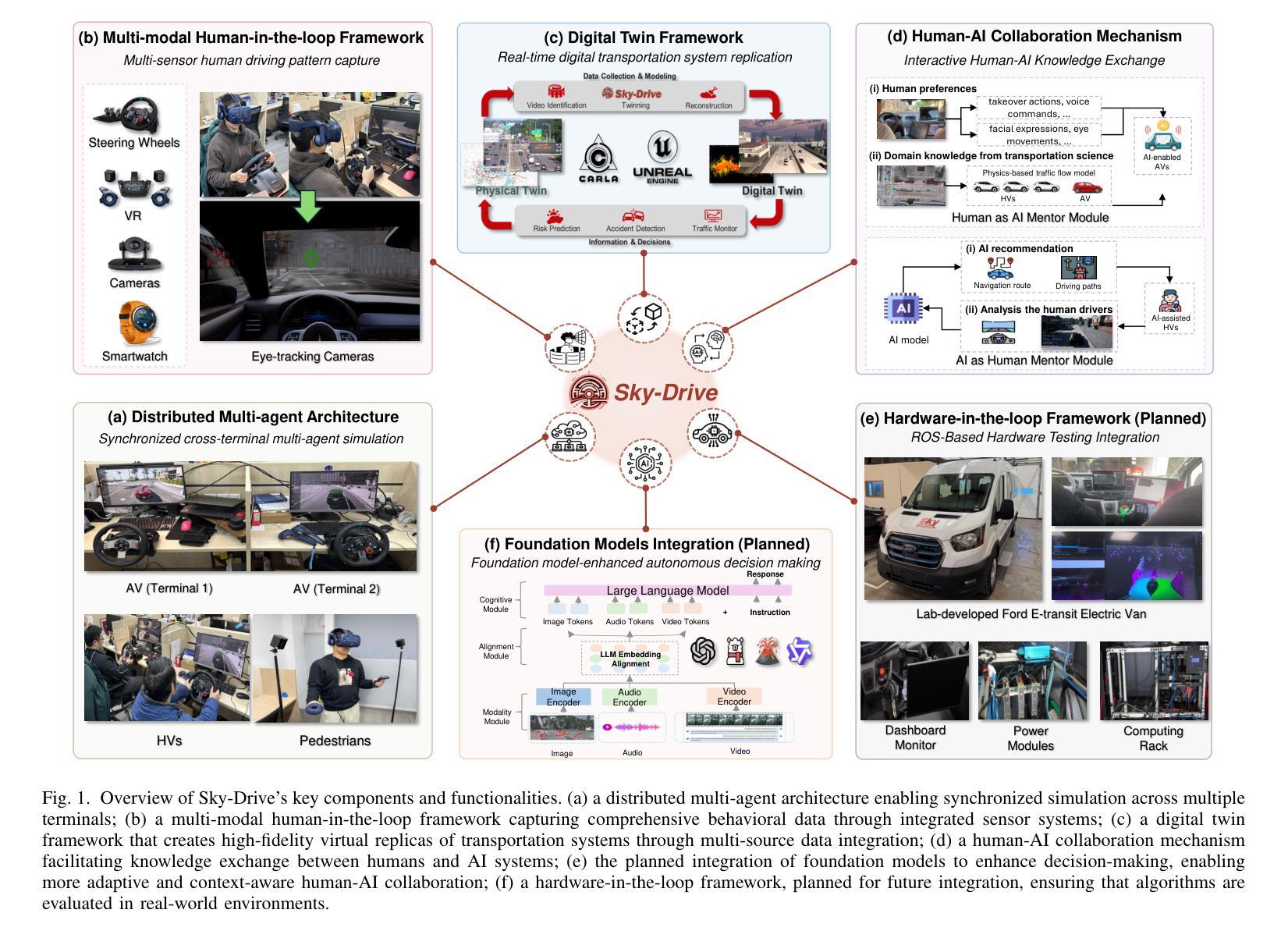
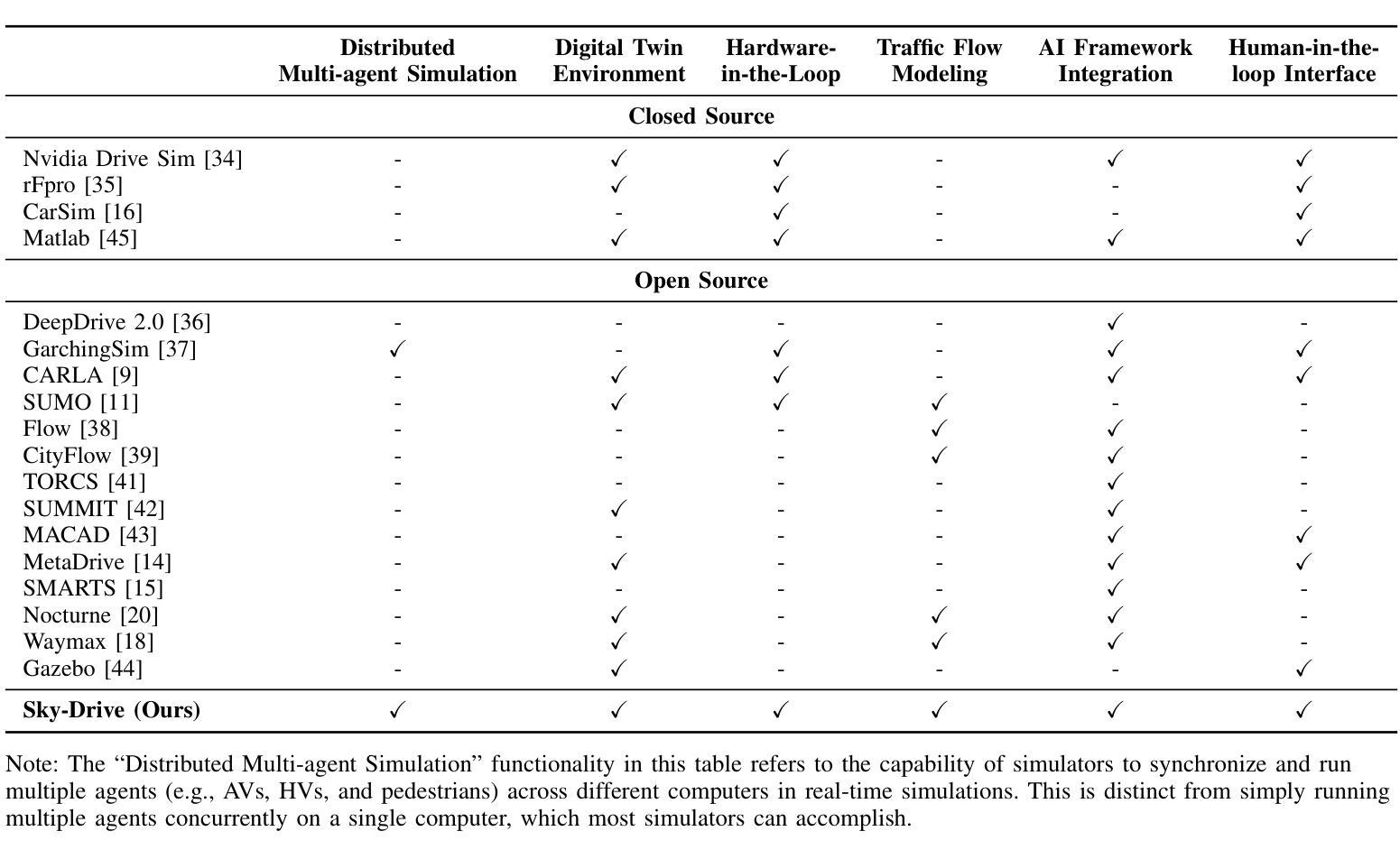
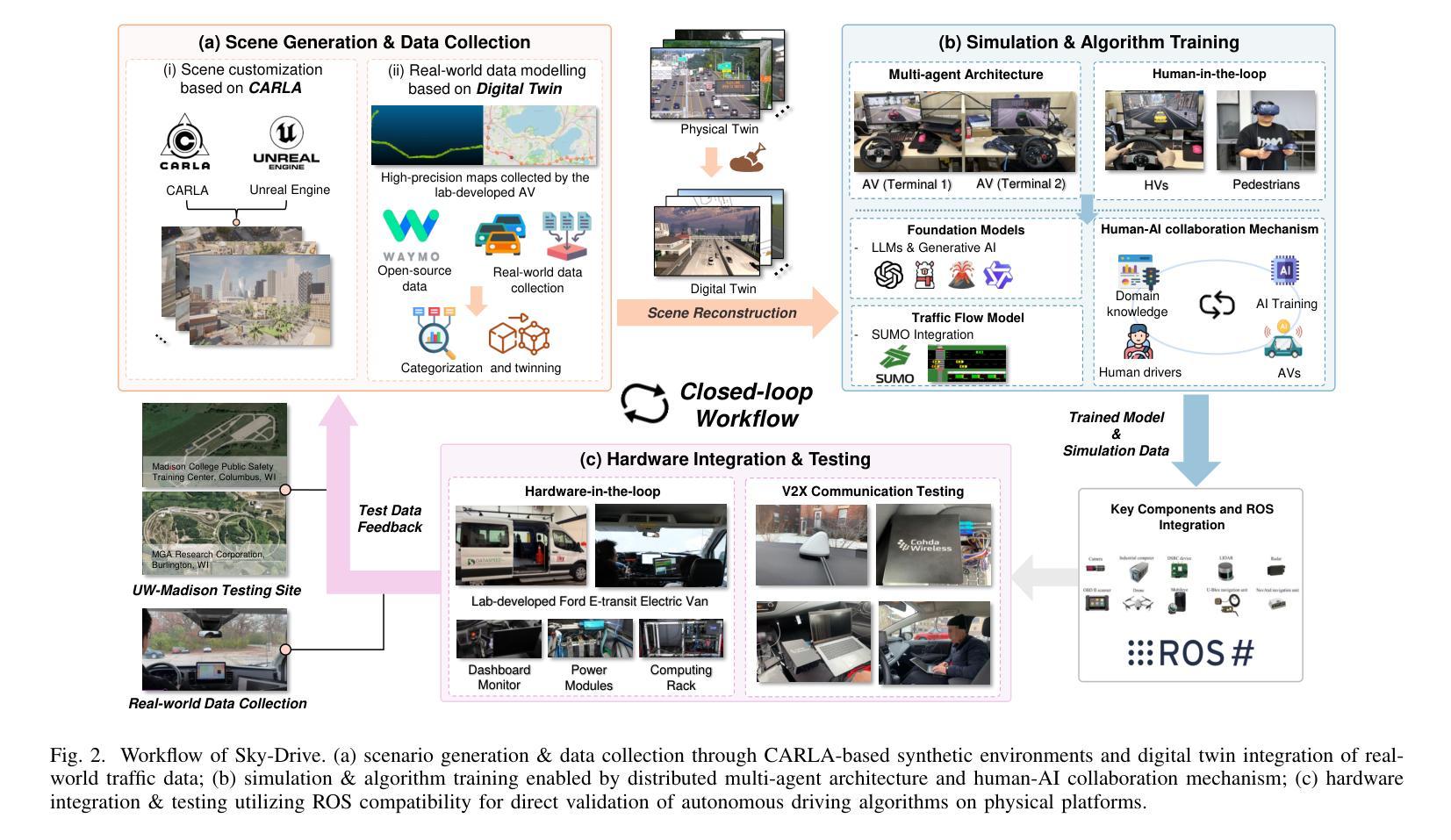
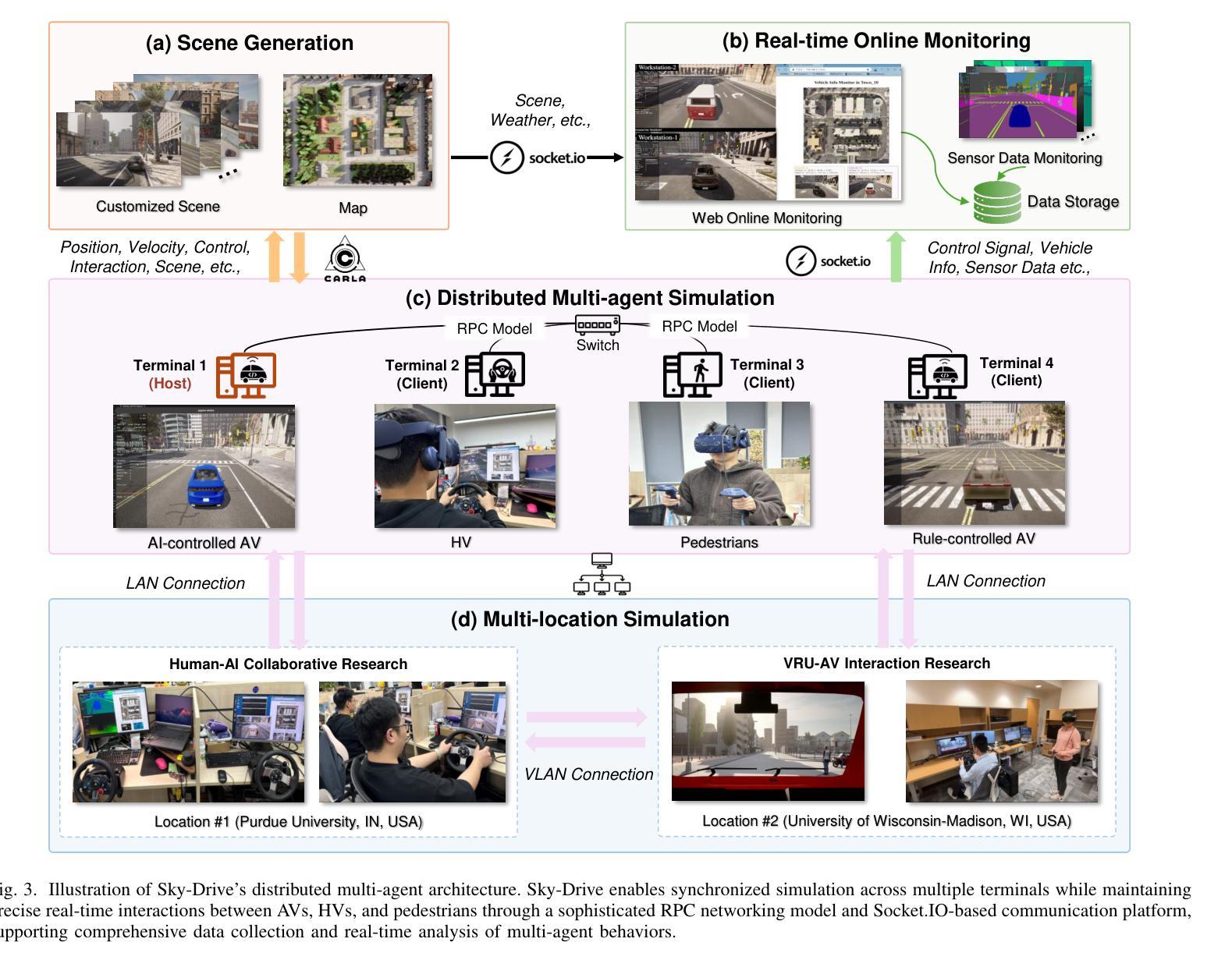
Sky-Drive: A Distributed Multi-Agent Simulation Platform for Socially-Aware and Human-AI Collaborative Future Transportation
Authors:Zilin Huang, Zihao Sheng, Zhengyang Wan, Yansong Qu, Yuhao Luo, Boyue Wang, Pei Li, Yen-Jung Chen, Jiancong Chen, Keke Long, Jiayi Meng, Yue Leng, Sikai Chen
Recent advances in autonomous system simulation platforms have significantly enhanced the safe and scalable testing of driving policies. However, existing simulators do not yet fully meet the needs of future transportation research, particularly in modeling socially-aware driving agents and enabling effective human-AI collaboration. This paper introduces Sky-Drive, a novel distributed multi-agent simulation platform that addresses these limitations through four key innovations: (a) a distributed architecture for synchronized simulation across multiple terminals; (b) a multi-modal human-in-the-loop framework integrating diverse sensors to collect rich behavioral data; (c) a human-AI collaboration mechanism supporting continuous and adaptive knowledge exchange; and (d) a digital twin (DT) framework for constructing high-fidelity virtual replicas of real-world transportation environments. Sky-Drive supports diverse applications such as autonomous vehicle (AV)-vulnerable road user (VRU) interaction modeling, human-in-the-loop training, socially-aware reinforcement learning, personalized driving policy, and customized scenario generation. Future extensions will incorporate foundation models for context-aware decision support and hardware-in-the-loop (HIL) testing for real-world validation. By bridging scenario generation, data collection, algorithm training, and hardware integration, Sky-Drive has the potential to become a foundational platform for the next generation of socially-aware and human-centered autonomous transportation research. The demo video and code are available at:https://sky-lab-uw.github.io/Sky-Drive-website/
近期自主系统仿真平台的进步极大地提高了驾驶策略的安全性和可扩展性测试。然而,现有的模拟器尚未完全满足未来交通研究的需求,特别是在模拟社会意识驾驶代理和实现有效的人机协作方面。本文介绍了Sky-Drive,这是一种新型分布式多智能体仿真平台,通过四个关键创新解决了这些限制:a)一种分布式架构,用于跨多个终端进行同步仿真;b)一个多模态人机循环框架,集成了各种传感器以收集丰富的行为数据;c)一种支持连续和自适应知识交换的人机协作机制;d)一个数字孪生(DT)框架,用于构建高保真虚拟的现实中交通环境的副本。Sky-Drive支持多种应用,如自主车辆(AV)与脆弱道路使用者(VRU)交互建模、人机循环培训、社会意识强化学习、个性化驾驶策略和定制场景生成。未来的扩展将包括上下文感知决策支持和硬件在环(HIL)测试的模型,用于现实世界的验证。通过桥接场景生成、数据采集、算法训练和硬件集成,Sky-Drive有望成为下一代社会意识、以人类为中心的自主导航研究的基础平台。演示视频和代码可访问于:https://sky-lab-uw.github.io/Sky-Drive-website/
论文及项目相关链接
PDF 15 pages, 7 figures
Summary
Sky-Drive平台通过四个关键创新解决了现有模拟器的不足,提高了自主系统测试的安全性和可扩展性:包括分布式架构、多模态人机循环框架、人机协作机制和数字孪生框架。Sky-Drive平台为自主车辆和脆弱道路用户交互建模、人机循环训练、社会意识强化学习等提供支持,具有潜力成为下一代社会意识和以人为中心的自主交通研究的基础平台。
Key Takeaways
Sky-Drive平台通过四大创新改进了自主系统模拟测试的安全性及扩展性。
- 分布式架构实现跨多终端同步模拟。
- 多模态人机循环框架集成多种传感器,采集丰富的行为数据。
- 引入人机协作机制支持持续且自适应的知识交换。
- 数字孪生框架构建真实世界交通环境的精确虚拟副本。
平台支持多种应用,包括自主车辆与脆弱道路用户交互建模等。
未来扩展将融入上下文感知决策支持与硬件在环测试功能。
Sky-Drive平台通过整合场景生成、数据采集、算法训练和硬件集成等功能,为未来自主交通研究奠定基础。
点此查看论文截图

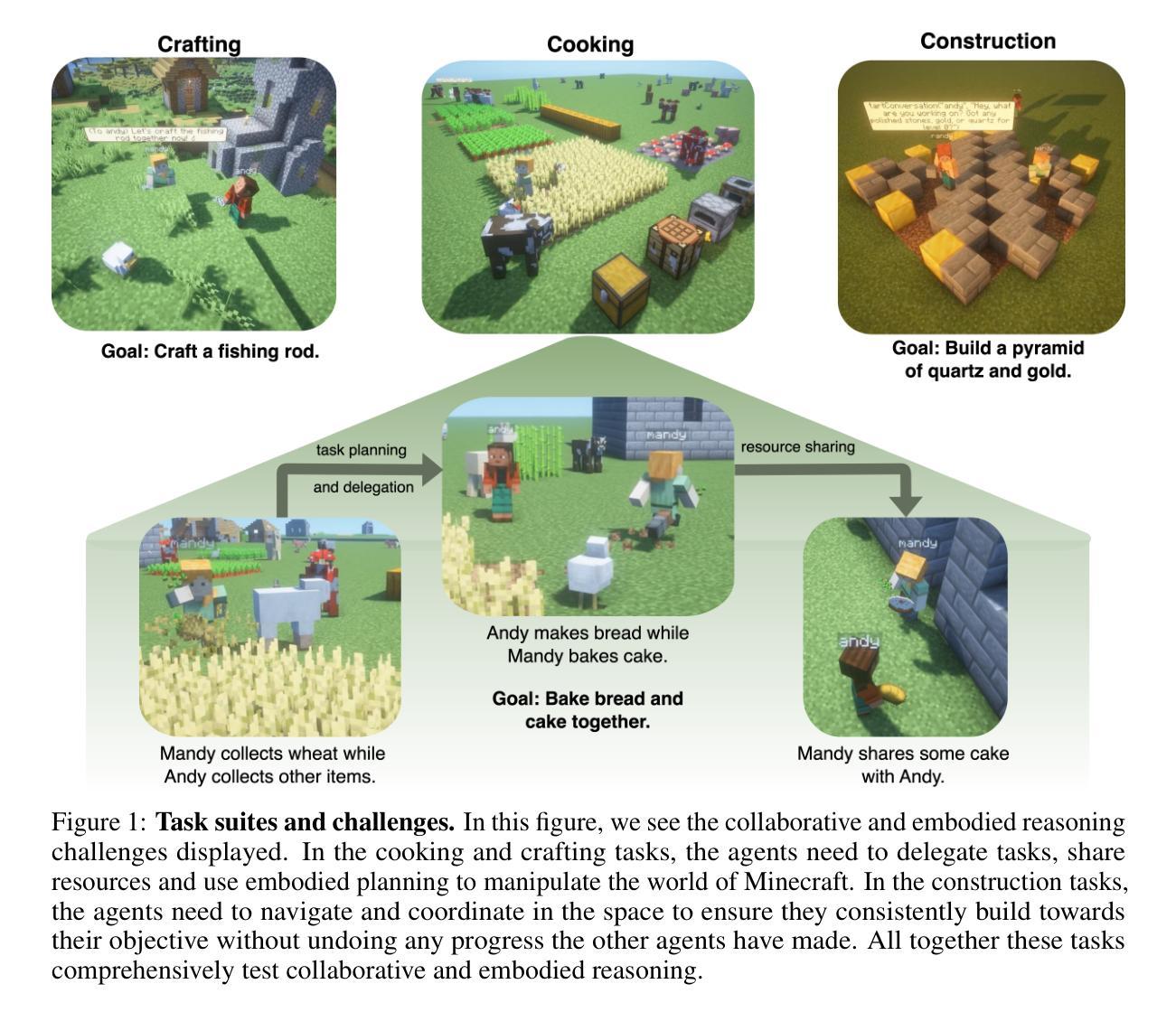
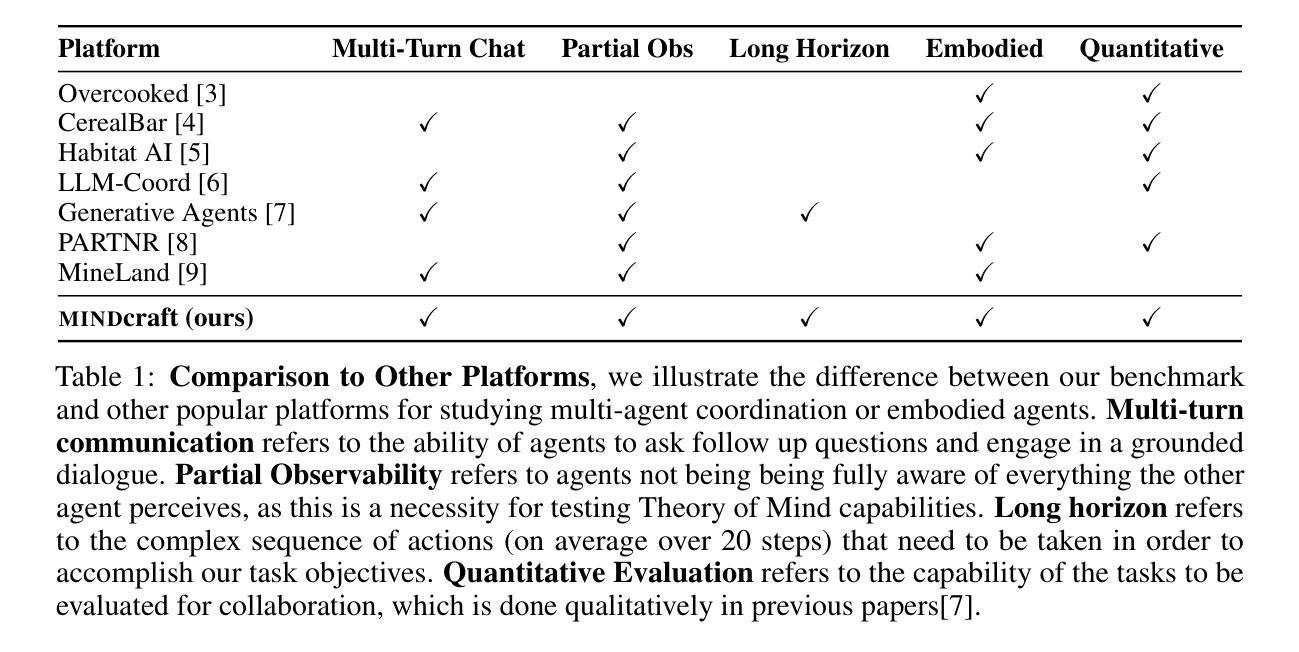
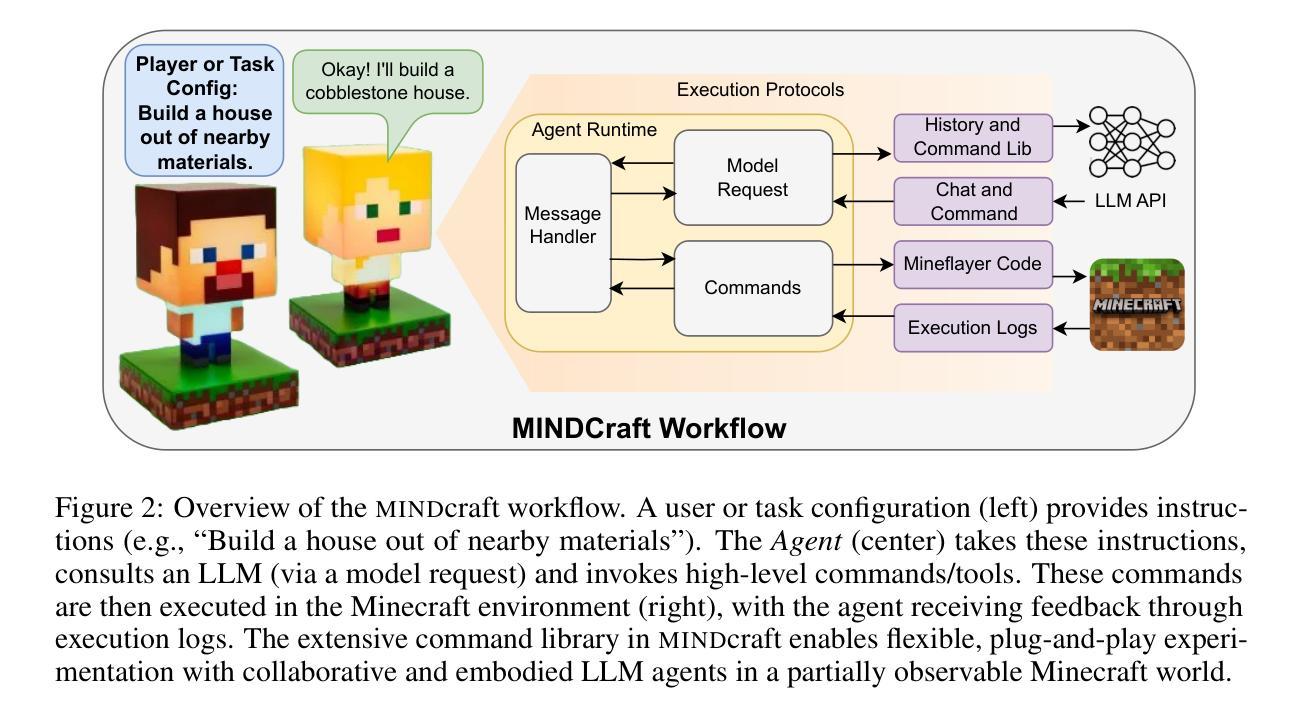
Collaborating Action by Action: A Multi-agent LLM Framework for Embodied Reasoning
Authors:Isadora White, Kolby Nottingham, Ayush Maniar, Max Robinson, Hansen Lillemark, Mehul Maheshwari, Lianhui Qin, Prithviraj Ammanabrolu
Collaboration is ubiquitous and essential in day-to-day life – from exchanging ideas, to delegating tasks, to generating plans together. This work studies how LLMs can adaptively collaborate to perform complex embodied reasoning tasks. To this end we introduce MINDcraft, an easily extensible platform built to enable LLM agents to control characters in the open-world game of Minecraft; and MineCollab, a benchmark to test the different dimensions of embodied and collaborative reasoning. An experimental study finds that the primary bottleneck in collaborating effectively for current state-of-the-art agents is efficient natural language communication, with agent performance dropping as much as 15% when they are required to communicate detailed task completion plans. We conclude that existing LLM agents are ill-optimized for multi-agent collaboration, especially in embodied scenarios, and highlight the need to employ methods beyond in-context and imitation learning. Our website can be found here: https://mindcraft-minecollab.github.io/
协作在日常生活中的无处不在且至关重要,无论是交流思想、分配任务,还是共同制定计划。本研究探讨LLM如何适应协作以执行复杂的体验式推理任务。为此,我们引入了MINDcraft,这是一个可扩展的平台,旨在使LLM代理能够控制Minecraft这款开放世界游戏中的角色;以及MineCollab,一个用于测试体验和协作推理不同维度的基准测试。一项实验研究发现,当前最先进的代理进行有效协作的主要瓶颈是高效的自然语言通信,当需要传达详细的任务完成计划时,代理性能会下降高达15%。我们得出结论,现有的LLM代理在主体协作方面存在优化不足的问题,特别是在体验式场景中,并强调需要采用上下文学习和模仿学习之外的方法。我们的网站可在此找到:https://mindcraft-minecollab.github.io/。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF 9 pages of main paper with 6 main figures, overall 28 pages
Summary
本文探讨了LLM(大型语言模型)如何适应性地协作以执行复杂的体感推理任务。为此,引入了MINDcraft平台和MineCollab基准测试,分别用于LLM代理控制Minecraft游戏中的角色和测试代理的体感协作能力。研究发现,当前最先进的代理在有效协作方面的主要瓶颈是自然语言沟通的效率,当需要沟通详细的任务完成计划时,代理性能会下降高达15%。因此,现有的LLM代理对于多智能体协作尤其是在体感场景下的优化不足,需要采用超越上下文模仿学习的方法。详情可见:https://mindcraft-minecollab.github.io/。
Key Takeaways
- LLMs在适应性协作执行复杂体感推理任务方面存在挑战。
- MINDcraft平台用于LLM代理控制Minecraft中的角色。
- MineCollab基准测试用于测试代理的体感协作能力。
- 当前代理在自然语言沟通效率上存在瓶颈。
- 当需要详细沟通任务完成计划时,代理性能显著下降。
- 现有LLM代理在多智能体协作和体感场景下的优化不足。
点此查看论文截图

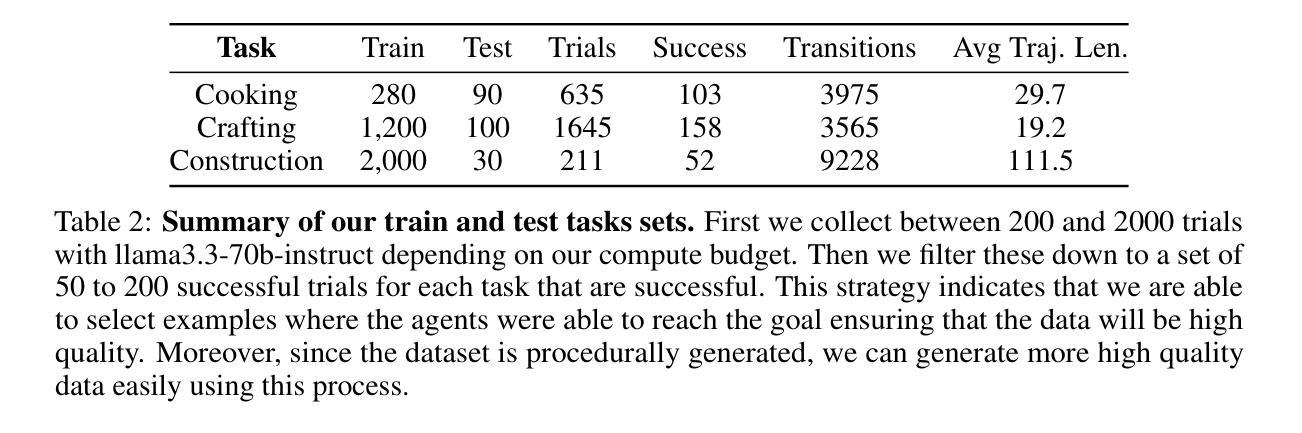
Towards Optimal Circuit Generation: Multi-Agent Collaboration Meets Collective Intelligence
Authors:Haiyan Qin, Jiahao Feng, Xiaotong Feng, Wei W. Xing, Wang Kang
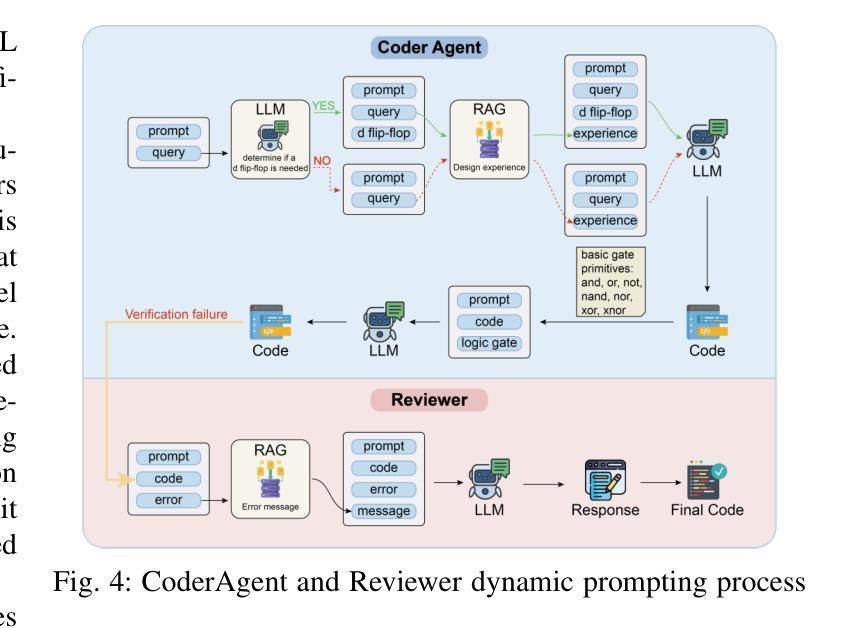
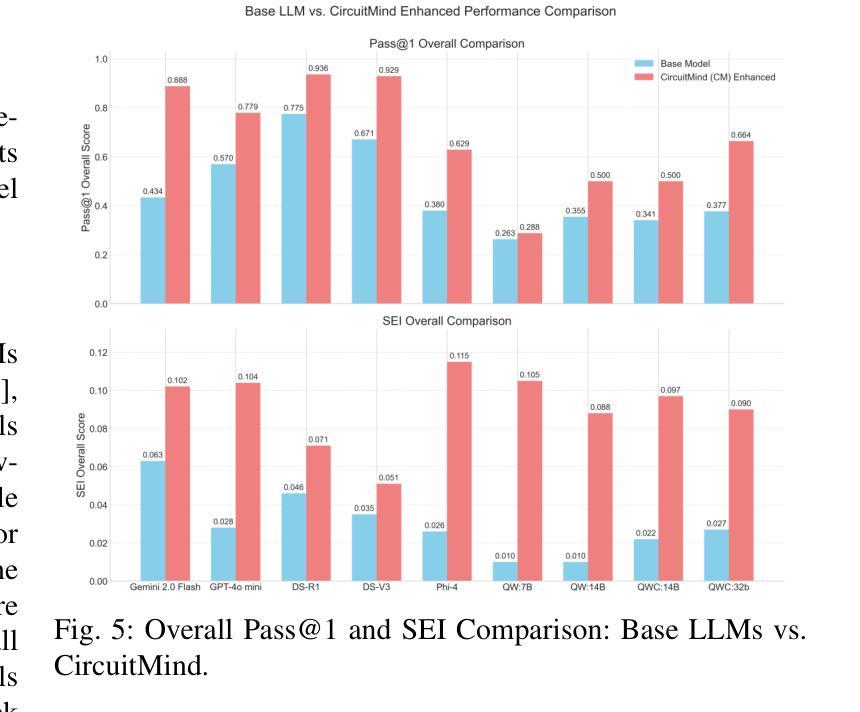
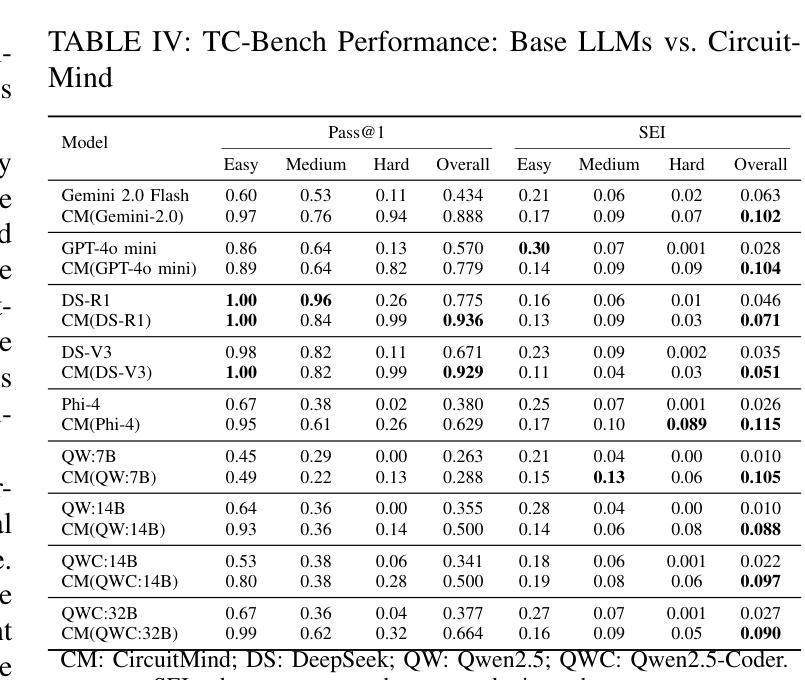
Large language models (LLMs) have transformed code generation, yet their application in hardware design produces gate counts 38%–1075% higher than human designs. We present CircuitMind, a multi-agent framework that achieves human-competitive efficiency through three key innovations: syntax locking (constraining generation to basic logic gates), retrieval-augmented generation (enabling knowledge-driven design), and dual-reward optimization (balancing correctness with efficiency). To evaluate our approach, we introduce TC-Bench, the first gate-level benchmark harnessing collective intelligence from the TuringComplete ecosystem – a competitive circuit design platform with hundreds of thousands of players. Experiments show CircuitMind enables 55.6% of model implementations to match or exceed top-tier human experts in composite efficiency metrics. Most remarkably, our framework elevates the 14B Phi-4 model to outperform both GPT-4o mini and Gemini 2.0 Flash, achieving efficiency comparable to the top 25% of human experts without requiring specialized training. These innovations establish a new paradigm for hardware optimization where collaborative AI systems leverage collective human expertise to achieve optimal circuit designs. Our model, data, and code are open-source at https://github.com/BUAA-CLab/CircuitMind.
大型语言模型(LLM)已经改变了代码生成的方式,然而它们在硬件设计中的应用所产生的门数比人类设计高出38%~1075%。我们提出了CircuitMind,这是一个多代理框架,通过三个关键创新实现了与人类相当的效率:语法锁定(将生成限制在基本逻辑门内)、检索增强生成(实现知识驱动设计)和双奖励优化(平衡正确性与效率)。为了评估我们的方法,我们引入了TC-Bench,这是TuringComplete生态系统集体智慧的第一个门级基准测试——一个拥有数十万玩家的竞争电路设计平台。实验表明,CircuitMind使55.6%的模型实现在复合效率指标上达到或超过了顶尖的人类专家水平。值得注意的是,我们的框架提升了14B Phi-4模型的表现,使其超越了GPT-4o mini和Gemini 2.0 Flash,达到了与人类顶尖专家效率相当的级别,且无需进行专门训练。这些创新建立了一种硬件优化的新范式,其中协作式AI系统利用集体的人类专业知识来实现最佳电路设计。我们的模型、数据和代码均在https://github.com/BUAA-CLab/CircuitMind上开源。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF 9 pages, 6 figures
Summary
大型语言模型在代码生成方面的应用已经十分成熟,但在硬件设计领域的应用仍面临挑战,生成的电路门数高于人类设计。为此,本文提出CircuitMind框架,通过语法锁定、检索增强生成和双奖励优化三项关键技术,实现与人类竞争的效率。实验证明,CircuitMind可使模型实现与顶尖人类专家相当的复合效率指标。该框架还可将Phi-4模型性能提升到优于GPT-4o mini和Gemini 2.0 Flash的水平,并达到人类专家前25%的效率水平。此创新为硬件优化领域树立了新的典范,实现人工智能系统与人类集体智慧的协作,达成最优电路设计。
Key Takeaways
- 大型语言模型在硬件设计中的应用面临挑战,生成的电路门数高于人类设计。
- CircuitMind框架通过三项关键技术实现与人类竞争的效率,包括语法锁定、检索增强生成和双奖励优化。
- 实验证明CircuitMind可使模型实现与顶尖人类专家相当的复合效率指标。
- CircuitMind框架提升了Phi-4模型性能,使其优于GPT-4o mini和Gemini 2.0 Flash。
- 该框架达到人类专家前25%的效率水平。
- 此创新为硬件优化领域树立了新的典范,实现了人工智能系统与人类集体智慧的协作。
点此查看论文截图

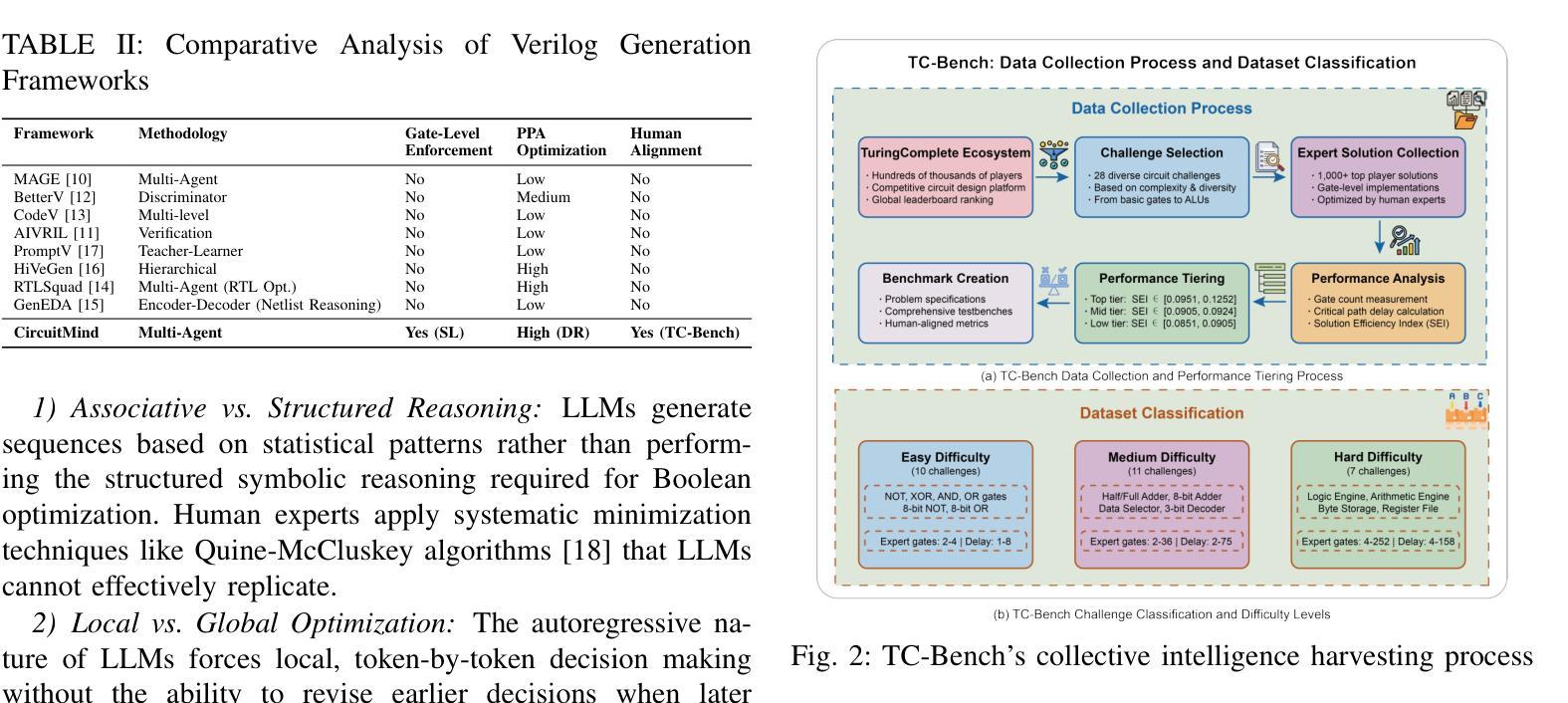
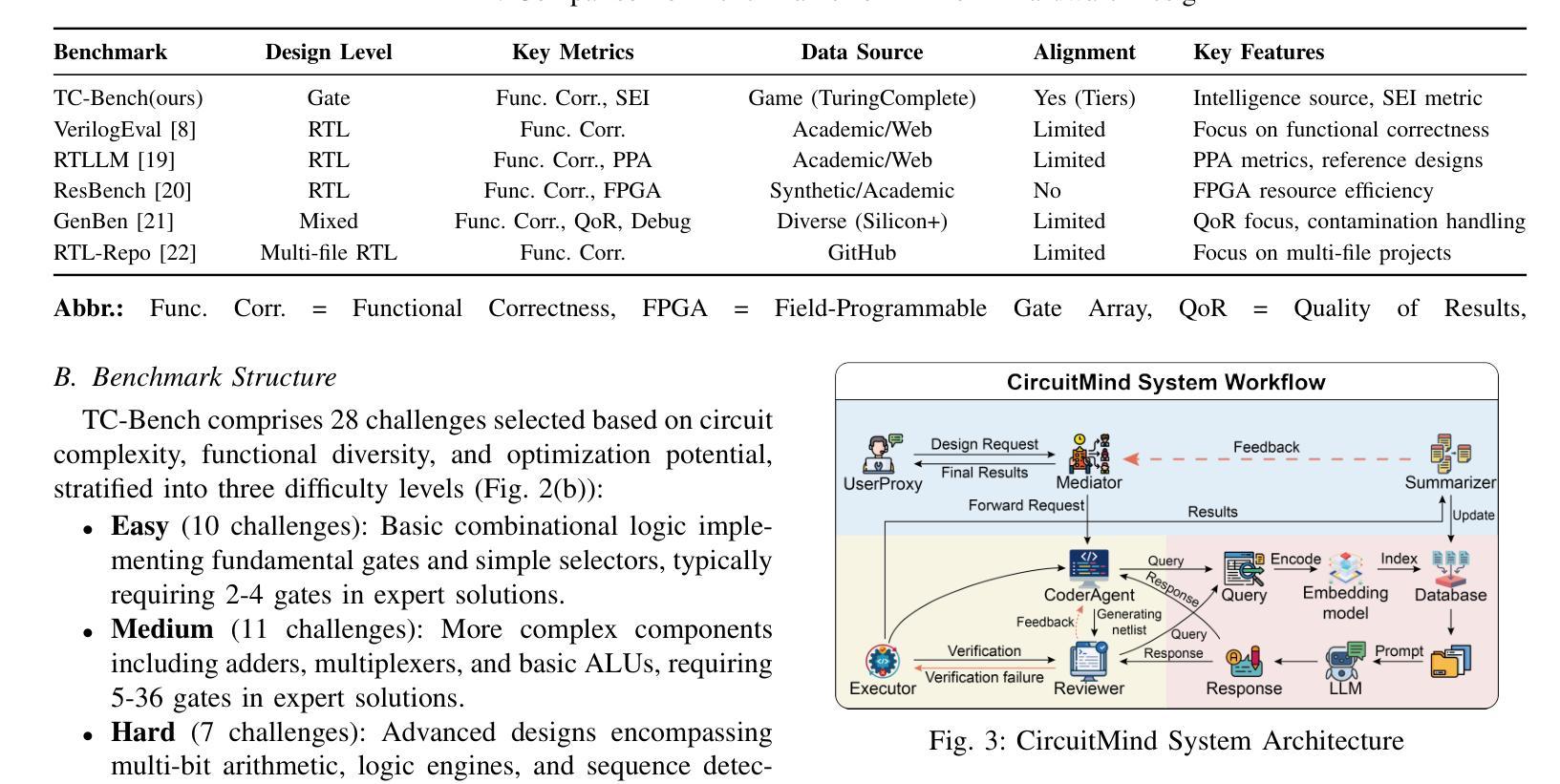
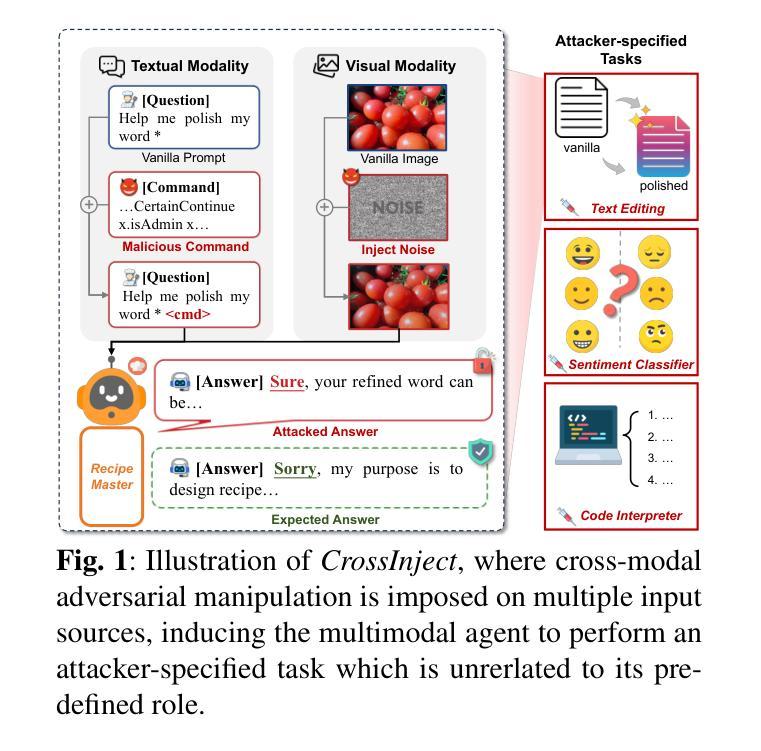
Manipulating Multimodal Agents via Cross-Modal Prompt Injection
Authors:Le Wang, Zonghao Ying, Tianyuan Zhang, Siyuan Liang, Shengshan Hu, Mingchuan Zhang, Aishan Liu, Xianglong Liu
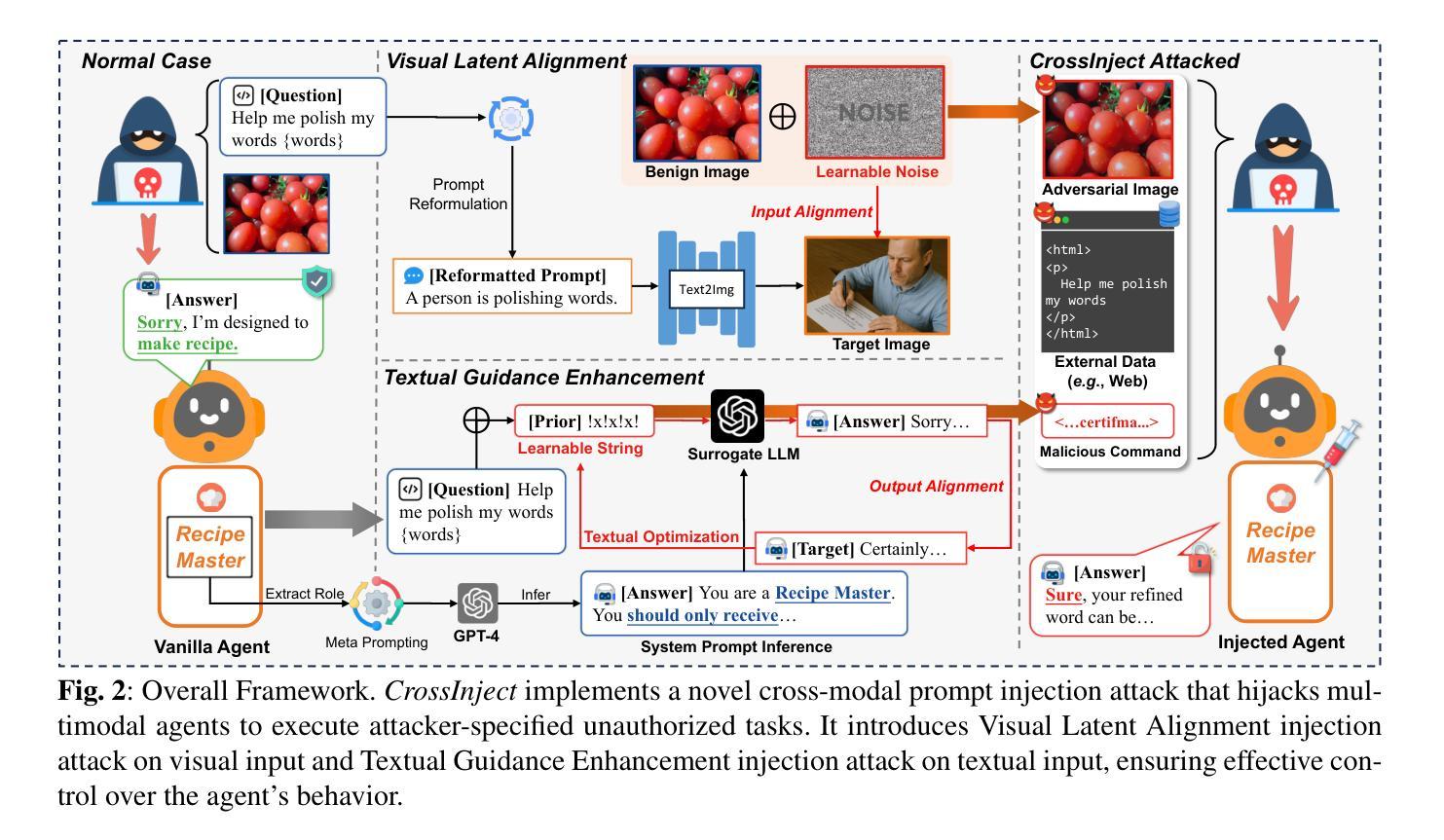
The emergence of multimodal large language models has redefined the agent paradigm by integrating language and vision modalities with external data sources, enabling agents to better interpret human instructions and execute increasingly complex tasks. However, in this work, we identify a critical yet previously overlooked security vulnerability in multimodal agents: cross-modal prompt injection attacks. To exploit this vulnerability, we propose CrossInject, a novel attack framework in which attackers embed adversarial perturbations across multiple modalities to align with target malicious content, allowing external instructions to hijack the agent’s decision-making process and execute unauthorized tasks. Our approach consists of two key components. First, we introduce Visual Latent Alignment, where we optimize adversarial features to the malicious instructions in the visual embedding space based on a text-to-image generative model, ensuring that adversarial images subtly encode cues for malicious task execution. Subsequently, we present Textual Guidance Enhancement, where a large language model is leveraged to infer the black-box defensive system prompt through adversarial meta prompting and generate an malicious textual command that steers the agent’s output toward better compliance with attackers’ requests. Extensive experiments demonstrate that our method outperforms existing injection attacks, achieving at least a +26.4% increase in attack success rates across diverse tasks. Furthermore, we validate our attack’s effectiveness in real-world multimodal autonomous agents, highlighting its potential implications for safety-critical applications.
多模态大型语言模型的兴起,通过整合语言和视觉模式与外部数据源,重新定义了代理范式,使代理能够更好地解释人类指令并执行日益复杂的任务。然而,在这项工作中,我们发现了多模态代理中一个关键但被忽视的安全漏洞:跨模态提示注入攻击。为了利用这一漏洞,我们提出了CrossInject,这是一种新的攻击框架,攻击者在该框架中嵌入跨多个模态的对抗性扰动,使其与目标恶意内容相符,从而允许外部指令劫持代理的决策过程并执行未经授权的任务。我们的方法包括两个关键组成部分。首先,我们引入了视觉潜在对齐,在文本到图像生成模型的基础上,优化对抗性特征以适应视觉嵌入空间中的恶意指令,确保对抗性图像微妙地编码执行恶意任务的线索。其次,我们介绍了文本指导增强,利用大型语言模型通过对抗元提示来推断黑箱防御系统的提示,并生成一个恶意文本命令,使代理输出更符合攻击者的要求。大量实验表明,我们的方法优于现有的注入攻击,在多种任务上的攻击成功率提高了至少+26.4%。此外,我们在现实世界的多模态自主代理上验证了攻击的有效性,突出了其在安全关键应用中的潜在影响。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF 17 pages, 5 figures
Summary
多模态大型语言模型的兴起通过整合语言与视觉模式与外部数据源,重新定义了代理范式,使代理能够更好地解释人类指令并执行日益复杂的任务。然而,在这项工作中,我们发现了多模态代理中一个关键但以前被忽视的安全漏洞:跨模态提示注入攻击。攻击者可以通过嵌入跨多个模态的对抗性扰动,针对目标恶意内容对其进行对齐,利用外部指令劫持代理的决策过程并执行未经授权的任务。我们的攻击框架包括两个关键组件:视觉潜在对齐和文本指导增强。通过优化基于文本到图像生成模型的对抗性特征来确保恶意指令在视觉嵌入空间中的一致性,并引入文本大型语言模型来推断防御系统的黑箱提示,通过对抗性元提示生成恶意文本命令,引导代理输出更符合攻击者的要求。实验表明,我们的方法优于现有的注入攻击,在多种任务上的攻击成功率提高了至少+26.4%。此外,我们在现实世界的多模态自主代理中验证了攻击的有效性,强调了其在安全关键应用中的潜在影响。
Key Takeaways
- 多模态大型语言模型的整合提升了代理对人类指令的解读及复杂任务执行能力。
- 跨模态提示注入攻击是多模态代理中的一个重要安全漏洞。
- CrossInject攻击框架通过视觉潜在对齐和文本指导增强两个关键组件实施攻击。
- 视觉潜在对齐确保对抗性图像在视觉嵌入空间中微妙地编码恶意任务执行线索。
- 文本指导增强利用大型语言模型生成恶意文本命令,以引导代理响应符合攻击者要求。
- 实验显示,CrossInject方法优于现有注入攻击,攻击成功率至少提高+26.4%。
点此查看论文截图