⚠️ 以下所有内容总结都来自于 大语言模型的能力,如有错误,仅供参考,谨慎使用
🔴 请注意:千万不要用于严肃的学术场景,只能用于论文阅读前的初筛!
💗 如果您觉得我们的项目对您有帮助 ChatPaperFree ,还请您给我们一些鼓励!⭐️ HuggingFace免费体验
2025-04-29 更新
POET: Prompt Offset Tuning for Continual Human Action Adaptation
Authors:Prachi Garg, Joseph K J, Vineeth N Balasubramanian, Necati Cihan Camgoz, Chengde Wan, Kenrick Kin, Weiguang Si, Shugao Ma, Fernando De La Torre
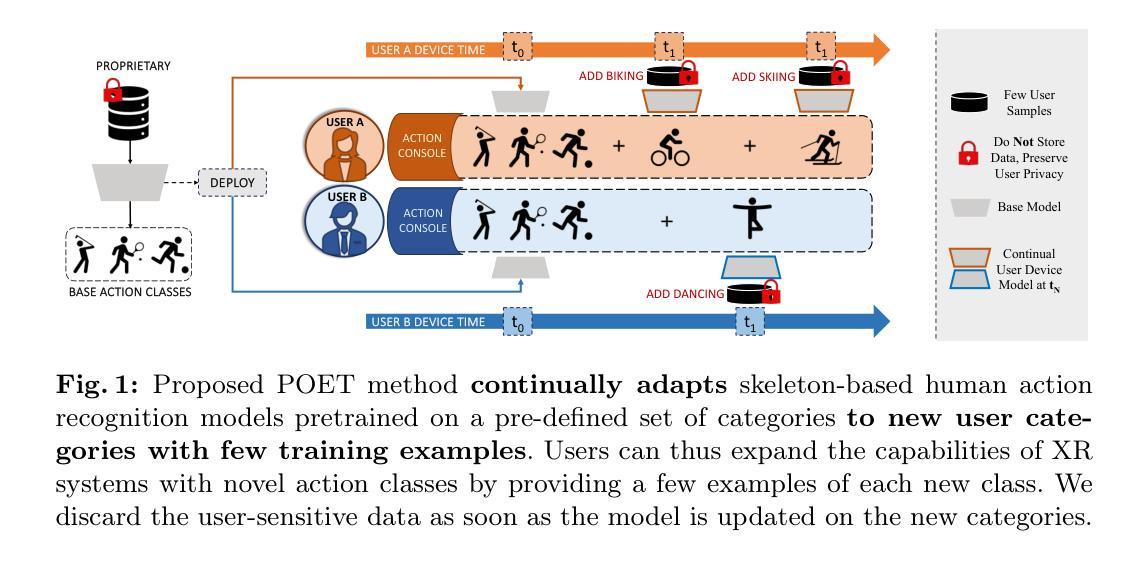
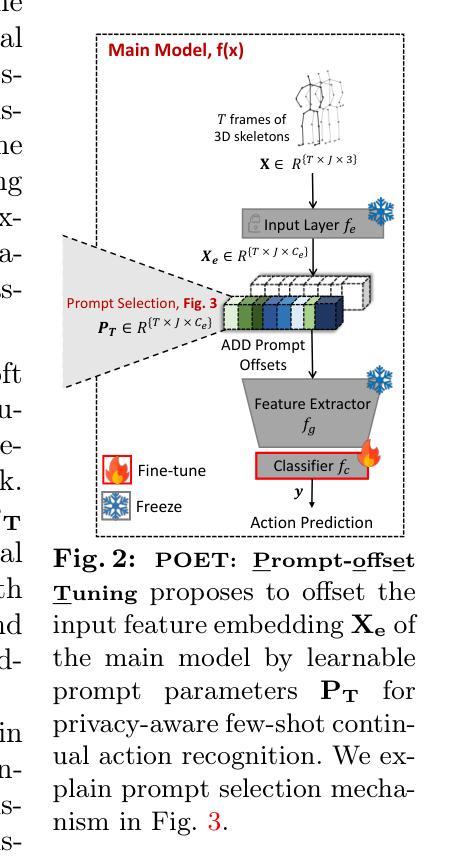
As extended reality (XR) is redefining how users interact with computing devices, research in human action recognition is gaining prominence. Typically, models deployed on immersive computing devices are static and limited to their default set of classes. The goal of our research is to provide users and developers with the capability to personalize their experience by adding new action classes to their device models continually. Importantly, a user should be able to add new classes in a low-shot and efficient manner, while this process should not require storing or replaying any of user’s sensitive training data. We formalize this problem as privacy-aware few-shot continual action recognition. Towards this end, we propose POET: Prompt-Offset Tuning. While existing prompt tuning approaches have shown great promise for continual learning of image, text, and video modalities; they demand access to extensively pretrained transformers. Breaking away from this assumption, POET demonstrates the efficacy of prompt tuning a significantly lightweight backbone, pretrained exclusively on the base class data. We propose a novel spatio-temporal learnable prompt offset tuning approach, and are the first to apply such prompt tuning to Graph Neural Networks. We contribute two new benchmarks for our new problem setting in human action recognition: (i) NTU RGB+D dataset for activity recognition, and (ii) SHREC-2017 dataset for hand gesture recognition. We find that POET consistently outperforms comprehensive benchmarks. Source code at https://github.com/humansensinglab/POET-continual-action-recognition.
随着扩展现实(XR)重新定义了用户与计算设备的交互方式,人类动作识别研究越来越突出。通常,部署在沉浸式计算设备上的模型是静态的,并且仅限于其默认类别集。我们研究的目标是为用户和开发人员提供能力,通过持续向其设备模型添加新的动作类别来个性化他们的体验。重要的是,用户应该能够以低样本量且高效的方式添加新类别,同时此过程不应需要存储或重新播放用户的任何敏感训练数据。我们将此问题正式定为隐私感知的少样本持续动作识别。为此,我们提出POE模型(Prompt-Offset Tuning)。虽然现有的提示微调方法已显示出对图像、文本和视频模态的持续学习的巨大潜力,但它们需要访问经过广泛预训练的转换器。打破了这一假设,POE模型展示了在仅对基本类别数据进行预训练的显著轻量级主干上进行提示微调的有效性。我们提出了一种新型的时空可学习提示偏移微调方法,并且是首次将这种提示微调应用于图神经网络。我们为人类动作识别问题设置了两个新基准测试:(i)用于动作识别的NTU RGB+D数据集,(ii)用于手势识别的SHREC-2017数据集。我们发现POE模型在全面的基准测试中表现一直出色。源代码可访问:[链接地址](https://github.com/humansensinglab/POET-continual-action-recognition)。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF ECCV 2024 (Oral), webpage https://humansensinglab.github.io/POET-continual-action-recognition/
Summary
本文研究了扩展现实(XR)环境下人机交互的新趋势,特别是在持续动作识别领域。研究目标是使用户和开发者能够持续地为设备模型添加新的动作类别,以实现个性化体验。为实现这一目标,提出了一种基于提示偏移调节(Prompt-Offset Tuning)的方法POET,用于在少量样本下实现隐私保护式的持续动作识别。该研究创新性地应用于图神经网络,并在两个新建立的人类动作识别数据集上取得了显著效果。
Key Takeaways
- 扩展现实(XR)正改变用户与计算设备的交互方式,人类动作识别的研究因此受到重视。
- 研究目标是为用户和开发者提供持续为设备模型添加新动作类别的能力,实现个性化体验。
- 提出了一种基于提示偏移调节(Prompt-Offset Tuning)的方法POET,适用于少量样本下的持续动作识别。
- POET方法不依赖大规模预训练模型,可以在仅基于基础类别数据预训练的轻量级模型上有效工作。
- 研究首次将提示调节应用于图神经网络,为相关领域提供了新的视角。
- 建立了两个新的人类动作识别数据集,分别是NTU RGB+D数据集用于动作识别,SHREC-2017数据集用于手势识别。
点此查看论文截图

CAPO: Cost-Aware Prompt Optimization
Authors:Tom Zehle, Moritz Schlager, Timo Heiß, Matthias Feurer
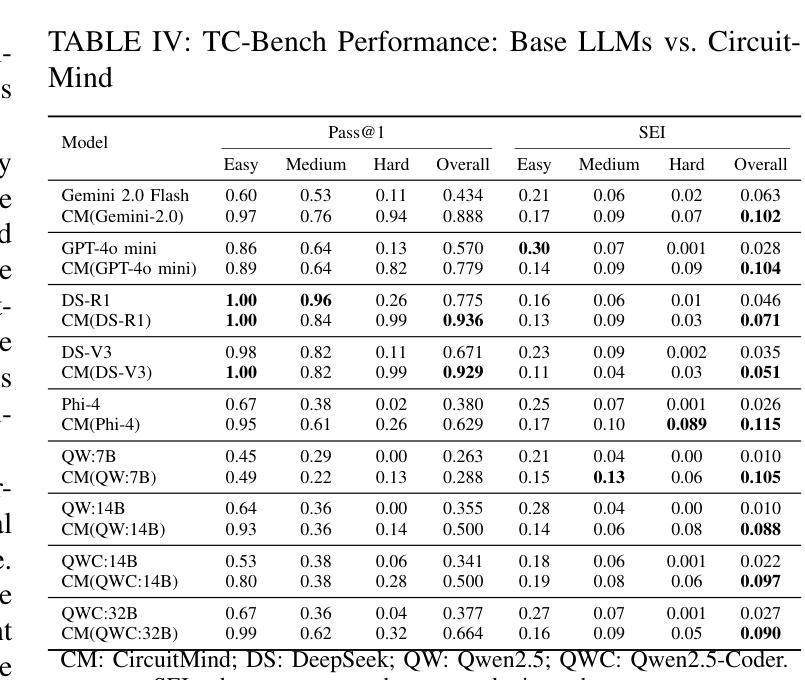
Large language models (LLMs) have revolutionized natural language processing by solving a wide range of tasks simply guided by a prompt. Yet their performance is highly sensitive to prompt formulation. While automated prompt optimization addresses this challenge by finding optimal prompts, current methods require a substantial number of LLM calls and input tokens, making prompt optimization expensive. We introduce CAPO (Cost-Aware Prompt Optimization), an algorithm that enhances prompt optimization efficiency by integrating AutoML techniques. CAPO is an evolutionary approach with LLMs as operators, incorporating racing to save evaluations and multi-objective optimization to balance performance with prompt length. It jointly optimizes instructions and few-shot examples while leveraging task descriptions for improved robustness. Our extensive experiments across diverse datasets and LLMs demonstrate that CAPO outperforms state-of-the-art discrete prompt optimization methods in 11/15 cases with improvements up to 21%p. Our algorithm achieves better performances already with smaller budgets, saves evaluations through racing, and decreases average prompt length via a length penalty, making it both cost-efficient and cost-aware. Even without few-shot examples, CAPO outperforms its competitors and generally remains robust to initial prompts. CAPO represents an important step toward making prompt optimization more powerful and accessible by improving cost-efficiency.
大型语言模型(LLM)通过简单的提示指导解决了多种任务,从而彻底改变了自然语言处理的格局。然而,它们的性能对提示的构思非常敏感。虽然自动提示优化可以通过找到最佳提示来解决这一挑战,但当前的方法需要大量的LLM调用和输入令牌,这使得提示优化成本高昂。我们引入了CAPO(基于成本的提示优化),这是一种通过集成AutoML技术提高提示优化效率的算法。CAPO是一种进化方法,以LLM作为操作员,结合比赛来节省评估和多目标优化来平衡性能和提示长度。它联合优化指令和少量示例,并利用任务描述来提高稳健性。我们在多个数据集和LLM上进行的广泛实验表明,在15种情况下,CAPO在11种情况下优于最先进的离散提示优化方法,性能提高了高达21%。我们的算法在较小的预算下就已经实现了更好的性能,通过比赛节省评估,并通过长度惩罚减少平均提示长度,这使得它既经济又注重成本。即使没有少量示例,CAPO也能超越竞争对手,并且对初始提示保持稳健。CAPO朝着提高提示优化的成本效益方向迈出了重要一步,使其更具威力且易于访问。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF Submitted to AutoML 2025
Summary
大型语言模型(LLM)通过提示引导解决多种任务,但性能对提示制定非常敏感。当前自动化提示优化方法需要大量LLM调用和输入令牌,使得提示优化成本高昂。我们引入了CAPO(成本感知提示优化),通过集成AutoML技术提高提示优化效率。CAPO采用进化方法,以LLM作为操作员,结合竞赛以节省评估和多重目标优化来平衡性能和提示长度。它联合优化指令和少量示例,并利用任务描述提高稳健性。实验表明,CAPO在多数情况下优于最新离散提示优化方法,并在预算较小的情况下实现更好的性能,通过竞赛节省评估,并通过长度惩罚减少平均提示长度,既节约成本又高效。即使不依赖少量示例,CAPO也能保持稳健性并优于竞争对手。这为更强大和可访问的提示优化迈出了重要一步。
Key Takeaways
- 大型语言模型(LLM)可以通过简单的提示引导解决多种任务,但提示制定对其性能有显著影响。
- 当前自动化提示优化方法成本高,需要大量的LLM调用和输入令牌。
- 引入CAPO算法,结合AutoML技术提高提示优化效率。
- CAPO采用进化方法,以LLM作为操作员,结合竞赛节省评估,并通过多目标优化平衡性能和提示长度。
- CAPO联合优化指令和少量示例,利用任务描述提高稳健性。
- 实验表明,CAPO在多数情况下优于现有方法,并在预算有限的情况下实现更好的性能。
点此查看论文截图


Rethinking Few-Shot Image Fusion: Granular Ball Priors Enable General-Purpose Deep Fusion
Authors:Minjie Deng, Yan Wei, Hao Zhai, An Wu, Yuncan Ouyang, Qianyao Peng
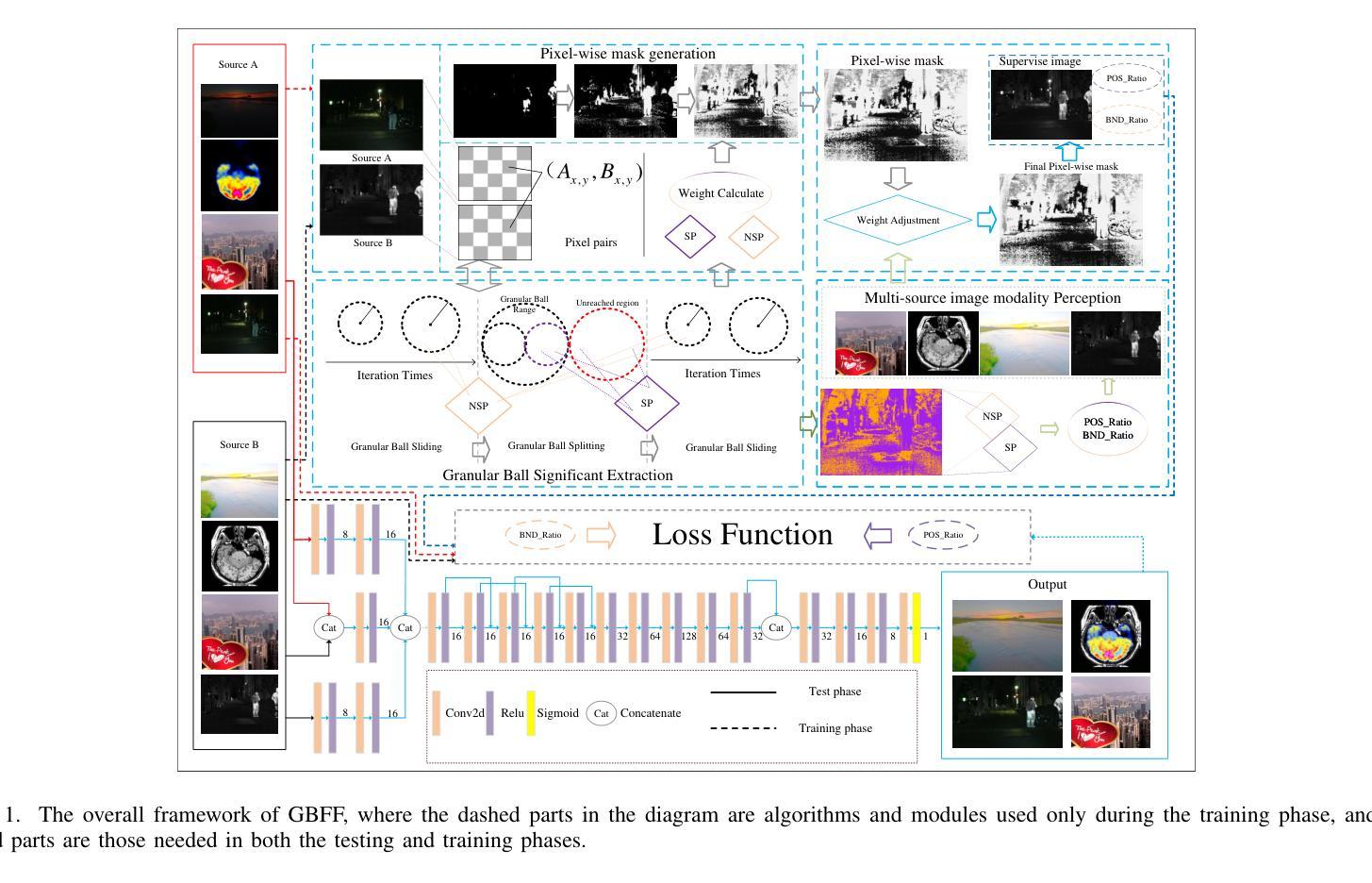
In image fusion tasks, the absence of real fused images as priors presents a fundamental challenge. Most deep learning-based fusion methods rely on large-scale paired datasets to extract global weighting features from raw images, thereby generating fused outputs that approximate real fused images. In contrast to previous studies, this paper explores few-shot training of neural networks under the condition of having prior knowledge. We propose a novel fusion framework named GBFF, and a Granular Ball Significant Extraction algorithm specifically designed for the few-shot prior setting. All pixel pairs involved in the fusion process are initially modeled as a Coarse-Grained Granular Ball. At the local level, Fine-Grained Granular Balls are used to slide through the brightness space to extract Non-Salient Pixel Pairs, and perform splitting operations to obtain Salient Pixel Pairs. Pixel-wise weights are then computed to generate a pseudo-supervised image. At the global level, pixel pairs with significant contributions to the fusion process are categorized into the Positive Region, while those whose contributions cannot be accurately determined are assigned to the Boundary Region. The Granular Ball performs modality-aware adaptation based on the proportion of the positive region, thereby adjusting the neural network’s loss function and enabling it to complement the information of the boundary region. Extensive experiments demonstrate the effectiveness of both the proposed algorithm and the underlying theory. Compared with state-of-the-art (SOTA) methods, our approach shows strong competitiveness in terms of both fusion time and image expressiveness. Our code is publicly available at:
在图像融合任务中,缺乏真实融合图像作为先验信息是一个基本挑战。大多数基于深度学习的融合方法依赖于大规模配对数据集,从原始图像中提取全局加权特征,从而生成近似真实融合图像的融合输出。与以前的研究相比,本文探讨了具备先验知识条件下的神经网络少样本训练。我们提出了一种新的融合框架GBFF和一种专为少样本先验设置设计的Granular Ball显著提取算法。所有参与融合过程的像素对最初都被建模为粗粒度粒球。在局部层面,我们使用细粒度粒球在亮度空间中进行滑动以提取非显著像素对,并执行分割操作以获得显著像素对。然后计算像素级权重以生成伪监督图像。在全局层面,对融合过程有显著贡献的像素对被分类为正区域,而无法准确确定贡献的像素对被分配给边界区域。粒球根据正区域的比例进行模态感知适应,从而调整神经网络的损失函数并使其能够补充边界区域的信息。大量实验证明了所提出算法和底层理论的有效性。与最先进的方法相比,我们的方法在融合时间和图像表现力方面都表现出强大的竞争力。我们的代码公开可用在:
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
本文提出了一种基于少样本训练的神经网络图像融合框架GBFF,以及专为少样本先验设置设计的Granular Ball Significant Extraction算法。该算法通过构建粗粒度和细粒度Granular Balls来处理和提取图像中的非显著和显著像素对,进而计算像素级权重生成伪监督图像。同时,根据正区域的占比进行模态感知适应,调整神经网络的损失函数,补充边界区域的信息。实验表明,该方法在融合时间和图像表现力方面表现出较强的竞争力。
Key Takeaways
- 提出了基于少样本训练的神经网络图像融合框架GBFF。
- 使用了Granular Ball Significant Extraction算法来处理少样本先验条件下的图像融合。
- 通过构建粗粒度和细粒度Granular Balls来提取非显著和显著像素对。
- 计算像素级权重生成伪监督图像。
- 根据正区域的占比进行模态感知适应,调整神经网络的损失函数。
- 方法在融合时间和图像表现力方面表现出较强的竞争力。
点此查看论文截图


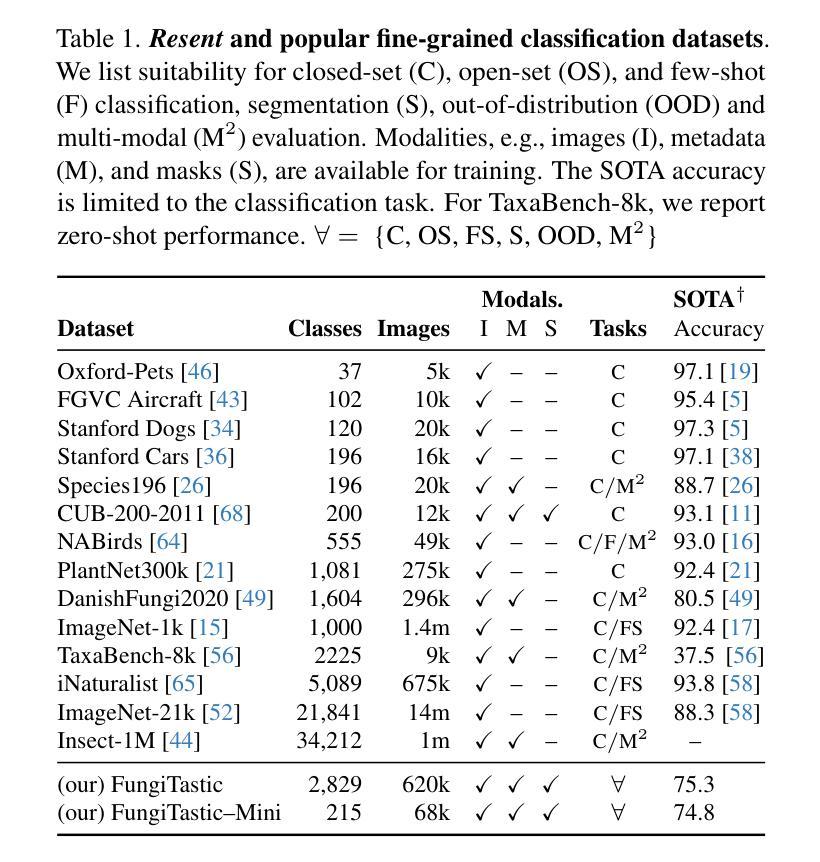
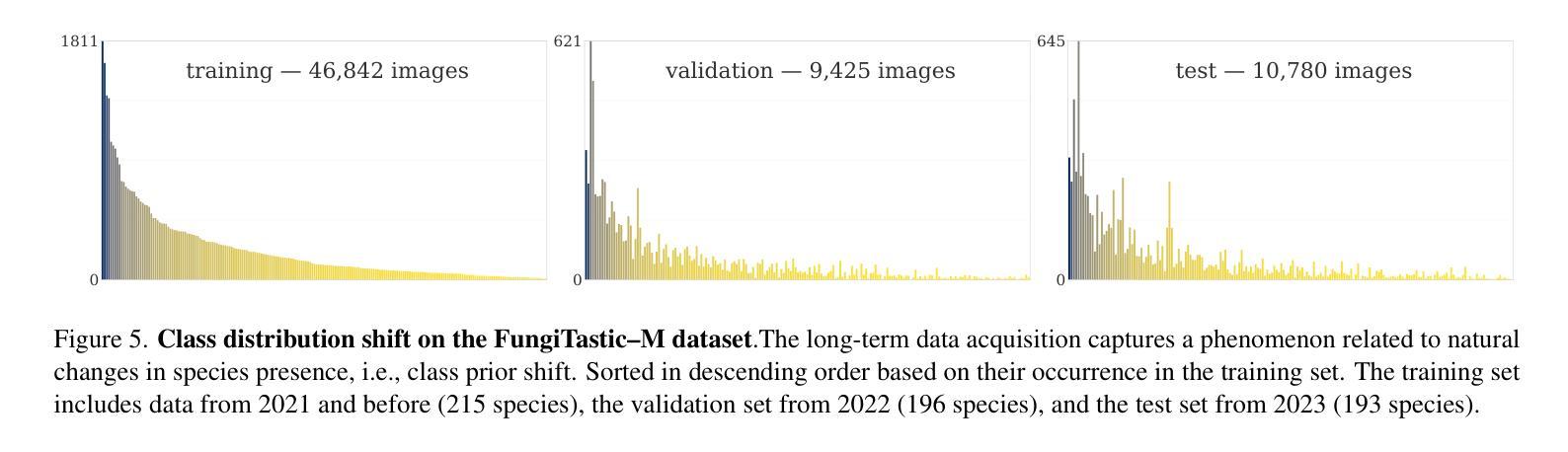
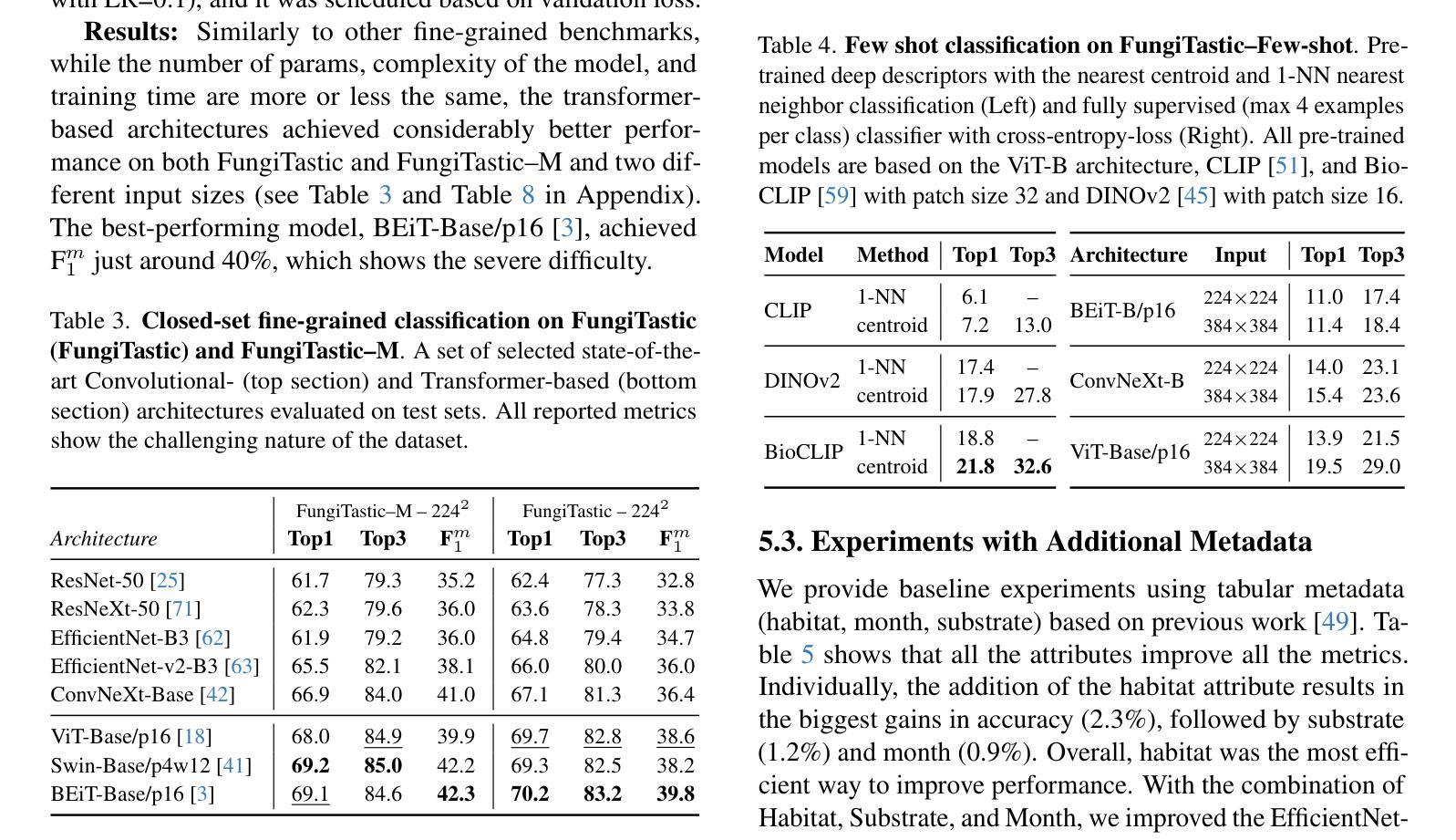
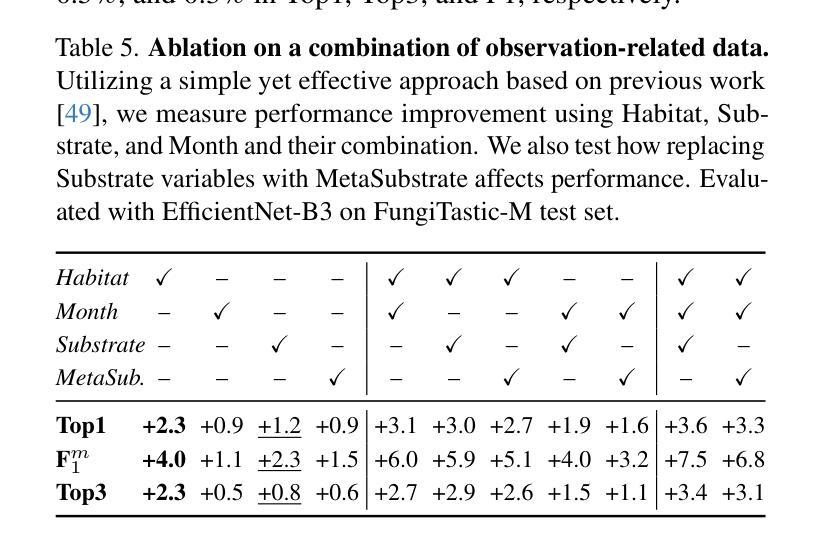
FungiTastic: A multi-modal dataset and benchmark for image categorization
Authors:Lukas Picek, Klara Janouskova, Vojtech Cermak, Jiri Matas
We introduce a new, challenging benchmark and a dataset, FungiTastic, based on fungal records continuously collected over a twenty-year span. The dataset is labelled and curated by experts and consists of about 350k multimodal observations of 6k fine-grained categories (species). The fungi observations include photographs and additional data, e.g., meteorological and climatic data, satellite images, and body part segmentation masks. FungiTastic is one of the few benchmarks that include a test set with DNA-sequenced ground truth of unprecedented label reliability. The benchmark is designed to support (i) standard closed-set classification, (ii) open-set classification, (iii) multi-modal classification, (iv) few-shot learning, (v) domain shift, and many more. We provide tailored baselines for many use cases, a multitude of ready-to-use pre-trained models on https://huggingface.co/collections/BVRA/fungitastic-66a227ce0520be533dc6403b, and a framework for model training. The documentation and the baselines are available at https://github.com/BohemianVRA/FungiTastic/ and https://www.kaggle.com/datasets/picekl/fungitastic.
我们基于连续采集的二十年真菌记录数据,推出了一个新的具有挑战性的基准测试集和数据集——FungiTastic。该数据集由专家进行标注和整理,包含大约35万条对6千种精细类别(物种)的多模式观察数据。真菌观察数据包括照片和其他数据,例如气象和气候数据、卫星图像和部位分割掩模。FungiTastic是少数包含具有前所未有的标签可靠性的测试集的基准测试集之一。该基准测试集旨在支持(i)标准封闭集分类、(ii)开放集分类、(iii)多模式分类、(iv)小样本学习、(v)域迁移等多种任务,以及其他更多任务。我们为多种用例提供了专门的基准测试,在多个即用型预训练模型上提供了培训框架,相关文档和基准测试集可通过以下链接获取:https://huggingface.co/collections/BVRA/fungitastic-66a227ce0520be533dc6403b 以及 https://github.com/BohemianVRA/FungiTastic/ 和 https://www.kaggle.com/datasets/picekl/fungitastic。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF FGVC workshop, CVPR 2025
Summary:
介绍了一个新的基于真菌记录的挑战基准测试数据集FungiTastic,包含约35万多种模态观察数据和6千种精细分类(物种)。数据集由专家标记和整理,包含照片、气象和气候数据、卫星图像和部位分割掩膜等多种数据。FungiTastic支持多种任务,如标准封闭集分类、开放集分类、多模态分类、少样本学习和领域迁移等。同时提供了多个用例的定制基准、预训练模型和训练框架。文档和基准测试可在相关网站找到。
Key Takeaways:
- 介绍了新的真菌记录基准测试数据集FungiTastic,包含多模态数据和多种任务。
- 数据集由专家标记和整理,包含约350k多模态观察数据和6k精细分类。
- FungiTastic包括照片、气象和气候数据、卫星图像等多种数据。
- 该基准测试支持多种任务,包括封闭集分类、开放集分类等。
- 提供了定制基准、预训练模型和训练框架。
- 文档和基准测试可在相关网站找到。
点此查看论文截图