⚠️ 以下所有内容总结都来自于 大语言模型的能力,如有错误,仅供参考,谨慎使用
🔴 请注意:千万不要用于严肃的学术场景,只能用于论文阅读前的初筛!
💗 如果您觉得我们的项目对您有帮助 ChatPaperFree ,还请您给我们一些鼓励!⭐️ HuggingFace免费体验
2025-04-29 更新
HepatoGEN: Generating Hepatobiliary Phase MRI with Perceptual and Adversarial Models
Authors:Jens Hooge, Gerard Sanroma-Guell, Faidra Stavropoulou, Alexander Ullmann, Gesine Knobloch, Mark Klemens, Carola Schmidt, Sabine Weckbach, Andreas Bolz
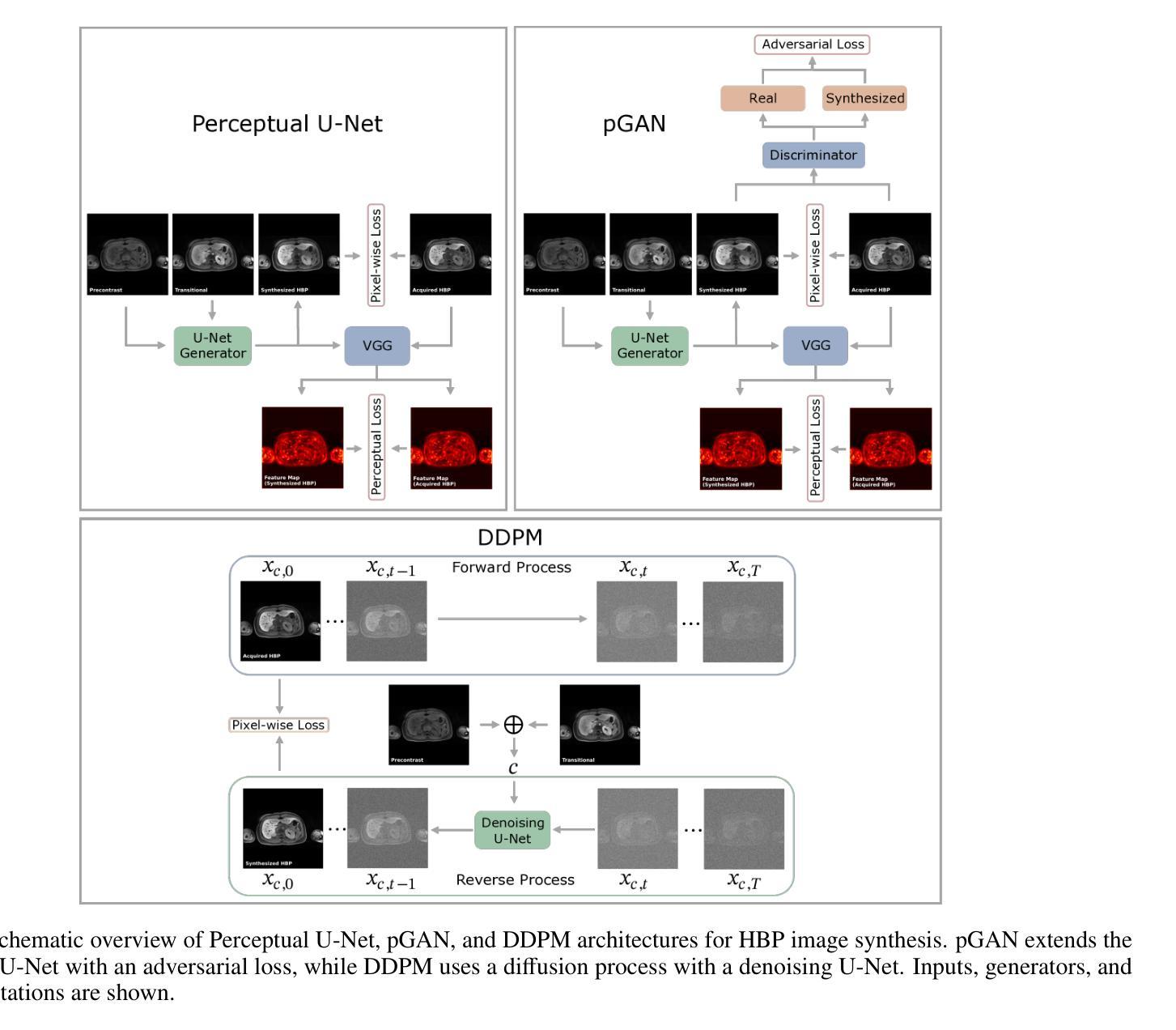
Dynamic contrast-enhanced magnetic resonance imaging (DCE-MRI) plays a crucial role in the detection and characterization of focal liver lesions, with the hepatobiliary phase (HBP) providing essential diagnostic information. However, acquiring HBP images requires prolonged scan times, which may compromise patient comfort and scanner throughput. In this study, we propose a deep learning based approach for synthesizing HBP images from earlier contrast phases (precontrast and transitional) and compare three generative models: a perceptual U-Net, a perceptual GAN (pGAN), and a denoising diffusion probabilistic model (DDPM). We curated a multi-site DCE-MRI dataset from diverse clinical settings and introduced a contrast evolution score (CES) to assess training data quality, enhancing model performance. Quantitative evaluation using pixel-wise and perceptual metrics, combined with qualitative assessment through blinded radiologist reviews, showed that pGAN achieved the best quantitative performance but introduced heterogeneous contrast in out-of-distribution cases. In contrast, the U-Net produced consistent liver enhancement with fewer artifacts, while DDPM underperformed due to limited preservation of fine structural details. These findings demonstrate the feasibility of synthetic HBP image generation as a means to reduce scan time without compromising diagnostic utility, highlighting the clinical potential of deep learning for dynamic contrast enhancement in liver MRI. A project demo is available at: https://jhooge.github.io/hepatogen
动态对比增强磁共振成像(DCE-MRI)在检测及定性肝局灶性病变中起到关键作用,其中肝胆期(HBP)提供了重要的诊断信息。然而,获取HBP图像需要较长的扫描时间,这可能影响患者舒适度并降低扫描仪的扫描效率。本研究中,我们提出了一种基于深度学习的方法,通过合成早期对比阶段的图像来生成HBP图像(包括前期对比和过渡阶段),并比较了三种生成模型:感知U-Net、感知生成对抗网络(pGAN)和去噪扩散概率模型(DDPM)。我们从不同的临床环境中采集了一个多站点DCE-MRI数据集,并引入对比演化得分(CES)来评估训练数据质量,以提高模型性能。通过像素级和感知指标的定量评估,以及通过盲态放射科医生审查的定性评估,结果显示pGAN在定量性能上表现最佳,但在非分布案例中引入了异质对比。相比之下,U-Net产生的肝脏增强效果更稳定,伪影更少,而DDPM由于未能很好地保留精细结构细节而表现不佳。这些发现证明了合成HBP图像生成的可行性,作为一种减少扫描时间而不影响诊断效用的手段,突出了深度学习在肝脏MRI动态对比增强中的临床潜力。项目演示可在:https://jhooge.github.io/hepatogen 查看。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary:本研究探讨了利用深度学习技术合成肝细胞期(HBP)图像的方法,以缩短扫描时间并提高患者舒适度和扫描仪效率。研究中比较了三种生成模型——感知U-Net、感知生成对抗网络(pGAN)和去噪扩散概率模型(DDPM)。研究结果表明,pGAN在定量性能上表现最佳,但在异常情况下引入了异质对比。相比之下,U-Net产生了一致的肝脏增强效果,伪影较少,而DDPM由于细节保护不足而表现不佳。该研究证明了合成HBP图像生成的可行性,可作为减少扫描时间而不影响诊断效用的手段,突显了深度学习在动态对比增强肝脏MRI中的临床潜力。
Key Takeaways:
- DCE-MRI在检测和分析肝脏局部病灶中起关键作用,其中肝细胞期(HBP)提供重要诊断信息。
- 获取HBP图像需要长时间的扫描,可能影响患者舒适度和扫描效率。
- 深度学习被用于合成HBP图像,研究比较了三种生成模型:感知U-Net、感知生成对抗网络(pGAN)和去噪扩散概率模型(DDPM)。
- pGAN在定量评价上表现最佳,但在特定情况下可能引入异质对比。
- U-Net生成了具有一致肝脏增强效果的图像,并且伪影较少。
- DDPM因细节保护不足而表现较差。
- 该研究展示了合成HBP图像生成的潜力,可作为减少扫描时间同时保持诊断效用的方法,突显了深度学习在肝脏MRI中的临床潜力。
点此查看论文截图