⚠️ 以下所有内容总结都来自于 大语言模型的能力,如有错误,仅供参考,谨慎使用
🔴 请注意:千万不要用于严肃的学术场景,只能用于论文阅读前的初筛!
💗 如果您觉得我们的项目对您有帮助 ChatPaperFree ,还请您给我们一些鼓励!⭐️ HuggingFace免费体验
2025-04-29 更新
RSFR: A Coarse-to-Fine Reconstruction Framework for Diffusion Tensor Cardiac MRI with Semantic-Aware Refinement
Authors:Jiahao Huang, Fanwen Wang, Pedro F. Ferreira, Haosen Zhang, Yinzhe Wu, Zhifan Gao, Lei Zhu, Angelica I. Aviles-Rivero, Carola-Bibiane Schonlieb, Andrew D. Scott, Zohya Khalique, Maria Dwornik, Ramyah Rajakulasingam, Ranil De Silva, Dudley J. Pennell, Guang Yang, Sonia Nielles-Vallespin
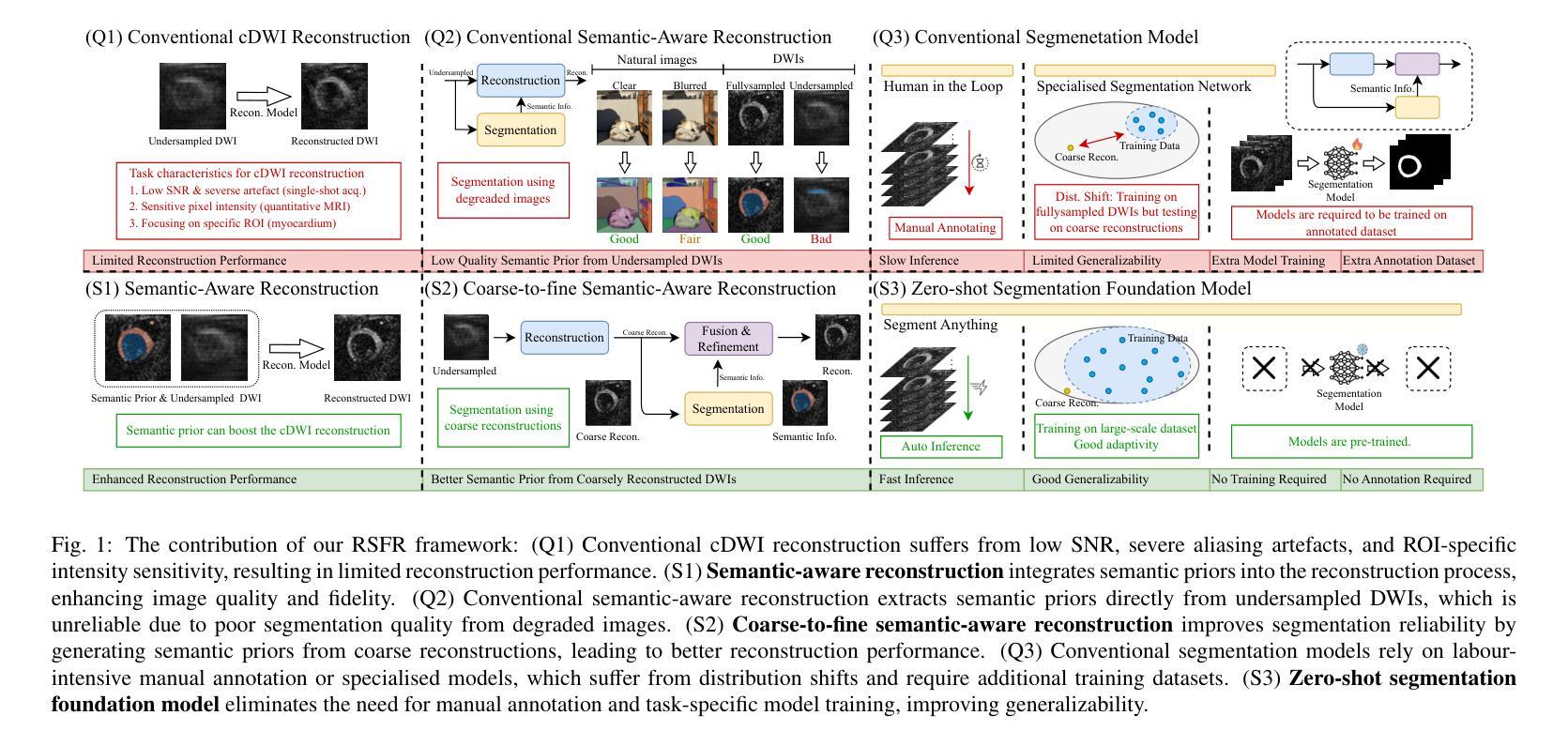
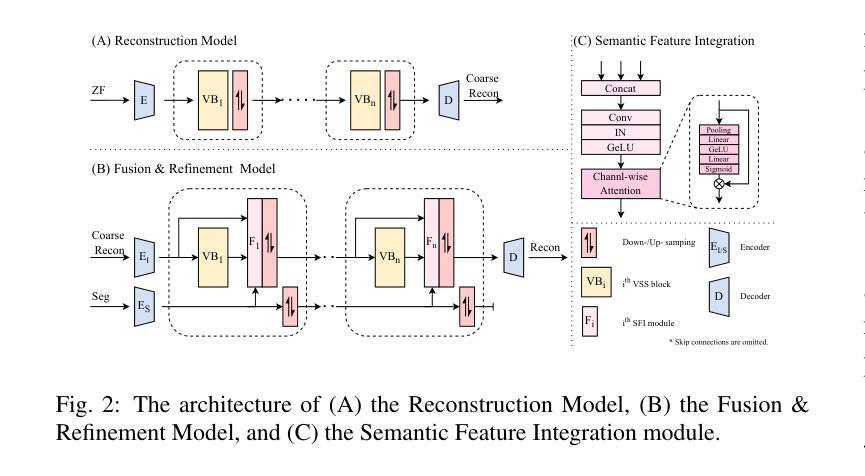
Cardiac diffusion tensor imaging (DTI) offers unique insights into cardiomyocyte arrangements, bridging the gap between microscopic and macroscopic cardiac function. However, its clinical utility is limited by technical challenges, including a low signal-to-noise ratio, aliasing artefacts, and the need for accurate quantitative fidelity. To address these limitations, we introduce RSFR (Reconstruction, Segmentation, Fusion & Refinement), a novel framework for cardiac diffusion-weighted image reconstruction. RSFR employs a coarse-to-fine strategy, leveraging zero-shot semantic priors via the Segment Anything Model and a robust Vision Mamba-based reconstruction backbone. Our framework integrates semantic features effectively to mitigate artefacts and enhance fidelity, achieving state-of-the-art reconstruction quality and accurate DT parameter estimation under high undersampling rates. Extensive experiments and ablation studies demonstrate the superior performance of RSFR compared to existing methods, highlighting its robustness, scalability, and potential for clinical translation in quantitative cardiac DTI.
心脏扩散张量成像(DTI)为心肌细胞排列提供了独特的见解,架起了微观和宏观心脏功能之间的桥梁。然而,由于其信号噪声比低、存在混叠伪影和需要准确的定量保真等技术挑战,其临床应用受到限制。为了解决这些局限性,我们引入了RSFR(重建、分割、融合与细化)——一种用于心脏扩散加权图像重建的新型框架。RSFR采用由粗到细的策略,通过分割任何事物模型和基于稳健的愿景妈妈(Vision Mamba)的重建主干,利用零射击语义先验。我们的框架有效地集成了语义特征,以减轻伪影并提高保真度,实现了高欠采样率下的最先进的重建质量和准确的DT参数估计。大量实验和消融研究证明了RSFR相较于现有方法的优越性能,突出了其稳健性、可扩展性和在定量心脏DTI中临床转化的潜力。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary:心脏扩散张量成像(DTI)可从微观到宏观的角度洞察心肌细胞排列,填补功能间隙。为克服低信噪比、混叠效应等技术挑战,我们提出RSFR(重建、分割、融合与细化)这一全新心脏扩散加权图像重建框架。RSFR利用零射击语义先验,结合分段任何模型与稳健的愿景曼巴重建后盾,实现优质重建与准确的DT参数估算。实验证明RSFR性能卓越,具有鲁棒性、可扩展性和临床转化的潜力。
Key Takeaways:
- 心脏扩散张量成像(DTI)可从微观到宏观角度揭示心肌细胞排列的独特洞察信息。
- 心脏DTI的临床应用受限于技术挑战,如低信噪比和混叠效应。
- RSFR框架旨在解决这些问题,实现心脏扩散加权图像的高质量重建。
- RSFR采用粗到细的策略,利用零射击语义先验和分段任何模型来提高图像质量。
- 实验证明RSFR性能优于现有方法,展现出其鲁棒性和可扩展性。
- RSFR框架能够实现准确的DT参数估算,为临床转化提供了潜力。
点此查看论文截图

Spatial Reasoner: A 3D Inference Pipeline for XR Applications
Authors:Steven Häsler, Philipp Ackermann
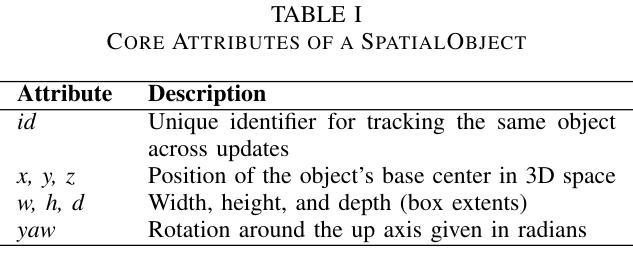
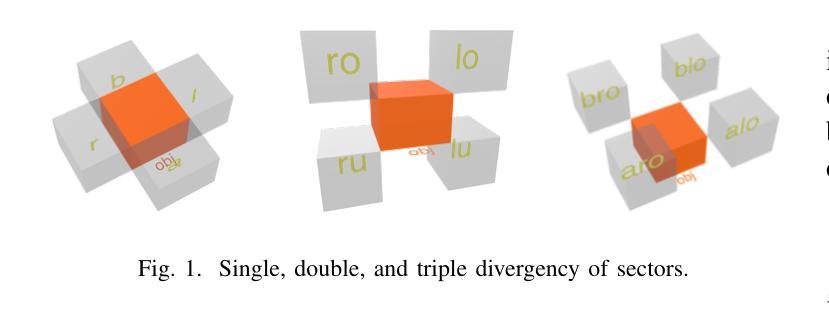
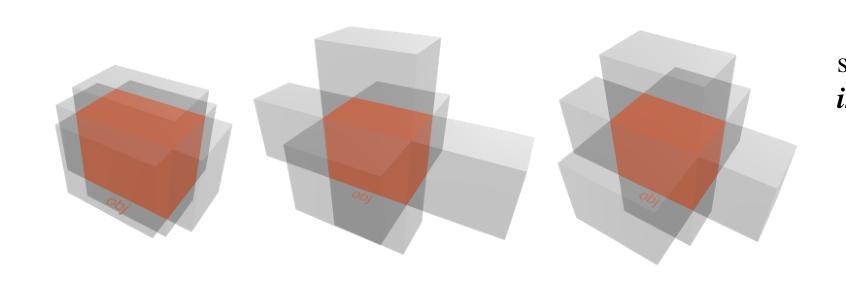
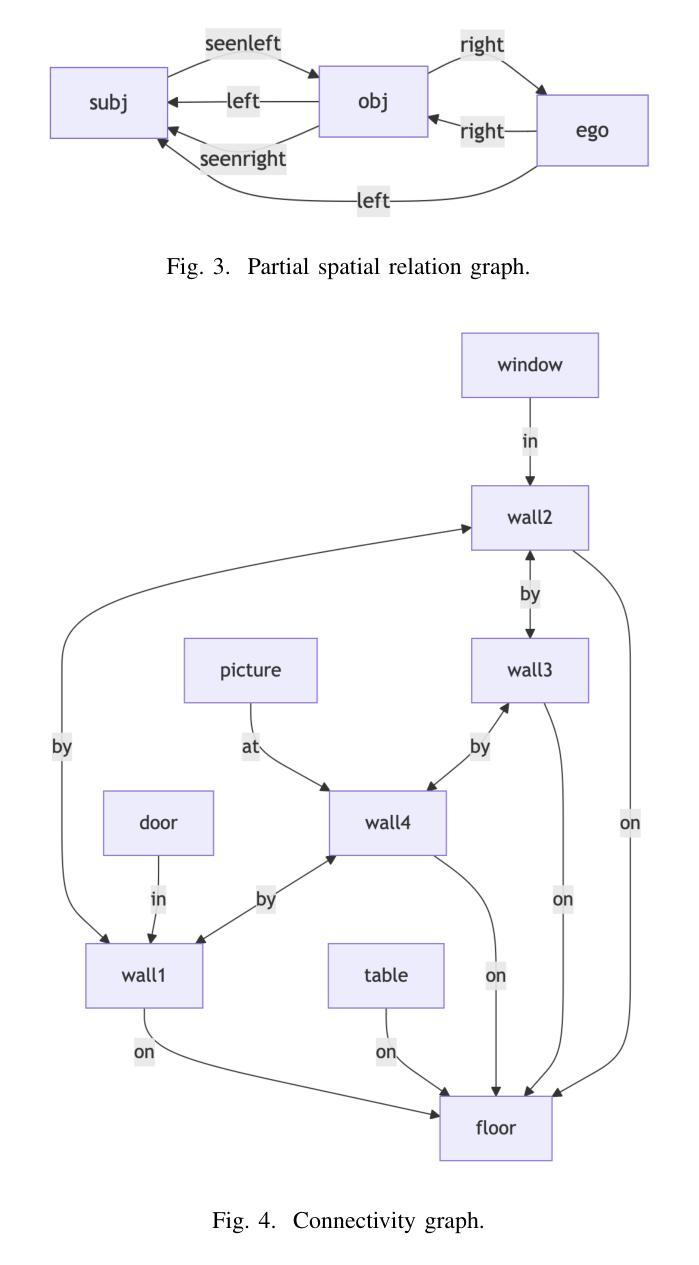
Modern extended reality XR systems provide rich analysis of image data and fusion of sensor input and demand AR/VR applications that can reason about 3D scenes in a semantic manner. We present a spatial reasoning framework that bridges geometric facts with symbolic predicates and relations to handle key tasks such as determining how 3D objects are arranged among each other (‘on’, ‘behind’, ‘near’, etc.). Its foundation relies on oriented 3D bounding box representations, enhanced by a comprehensive set of spatial predicates, ranging from topology and connectivity to directionality and orientation, expressed in a formalism related to natural language. The derived predicates form a spatial knowledge graph and, in combination with a pipeline-based inference model, enable spatial queries and dynamic rule evaluation. Implementations for client- and server-side processing demonstrate the framework’s capability to efficiently translate geometric data into actionable knowledge, ensuring scalable and technology-independent spatial reasoning in complex 3D environments. The Spatial Reasoner framework is fostering the creation of spatial ontologies, and seamlessly integrates with and therefore enriches machine learning, natural language processing, and rule systems in XR applications.
现代扩展现实XR系统提供了丰富的图像数据分析以及传感器输入的融合,并需要AR/VR应用程序能够以语义方式理解3D场景。我们提出一个空间推理框架,该框架能够结合几何事实与符号谓词和关系来处理主要任务,比如确定3D对象是如何相互排列的(如“在……上面”,“在……后面”,“靠近”等)。它的基础依赖于定向的三维边界框表示,通过一系列空间谓词增强,这些谓词涵盖了拓扑和连接性到方向性和方位,并以与自然语言相关的形式化语言来表达。所得到的谓词形成空间知识图谱,结合基于管道推理模型,能够实现空间查询和动态规则评估。客户端和服务器端处理的实现证明了该框架能够高效地将几何数据转化为可操作知识,确保在复杂的3D环境中进行可伸缩和技术独立的空间推理。空间推理框架正在促进空间本体论的产生,并可与机器学习、自然语言处理和XR应用程序的规则系统无缝集成,从而丰富其内容。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF 11 pages, preprint of ICVARS 2025 paper
Summary
现代扩展现实XR系统需要能够理解和推理三维场景语义的AR/VR应用。我们提出了一种空间推理框架,该框架将几何事实与符号谓词和关系相结合,处理关键任务如确定三维对象之间的排列关系(如“在”、“后面”、“附近”等)。该框架基于定向三维边界框表示,通过一套全面的空间谓词增强,包括拓扑、连接性、方向性和方位等,以与自然语言相关的形式化表达。派生出的谓词形成空间知识图谱,结合基于管道的推理模型,实现空间查询和动态规则评估。客户端和服务器端处理的实现证明了该框架将几何数据高效翻译成可操作知识的能力,确保在复杂的三维环境中进行可伸缩和技术独立的空间推理。空间推理框架正促进空间本体论的创建,并与机器学习、自然语言处理和规则系统无缝集成,从而丰富XR应用。
Key Takeaways
- 现代XR系统需要能够理解和推理三维场景语义的AR/VR应用。
- 提出了一个空间推理框架,结合几何事实与符号谓词和关系。
- 框架基于定向三维边界框表示,通过全面的空间谓词增强。
- 框架支持空间查询和动态规则评估。
- 框架能将几何数据高效转化为可操作知识。
- 框架具有在复杂三维环境中进行可伸缩和技术独立的空间推理能力。
点此查看论文截图

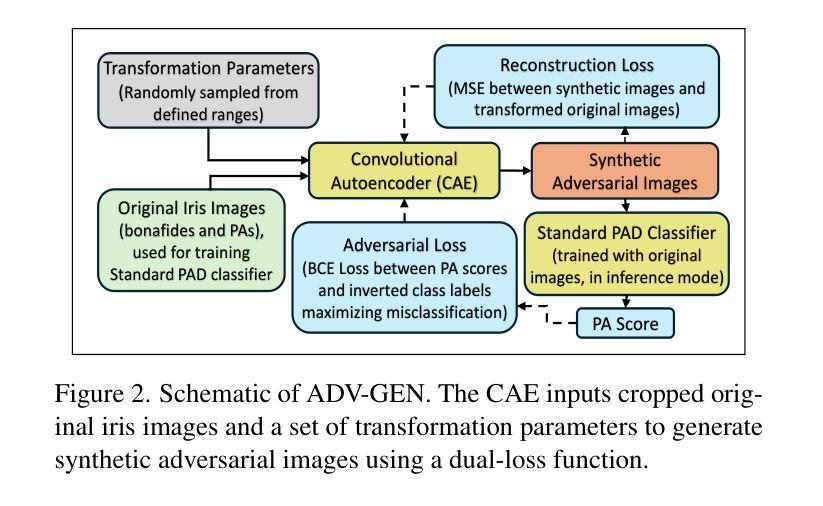
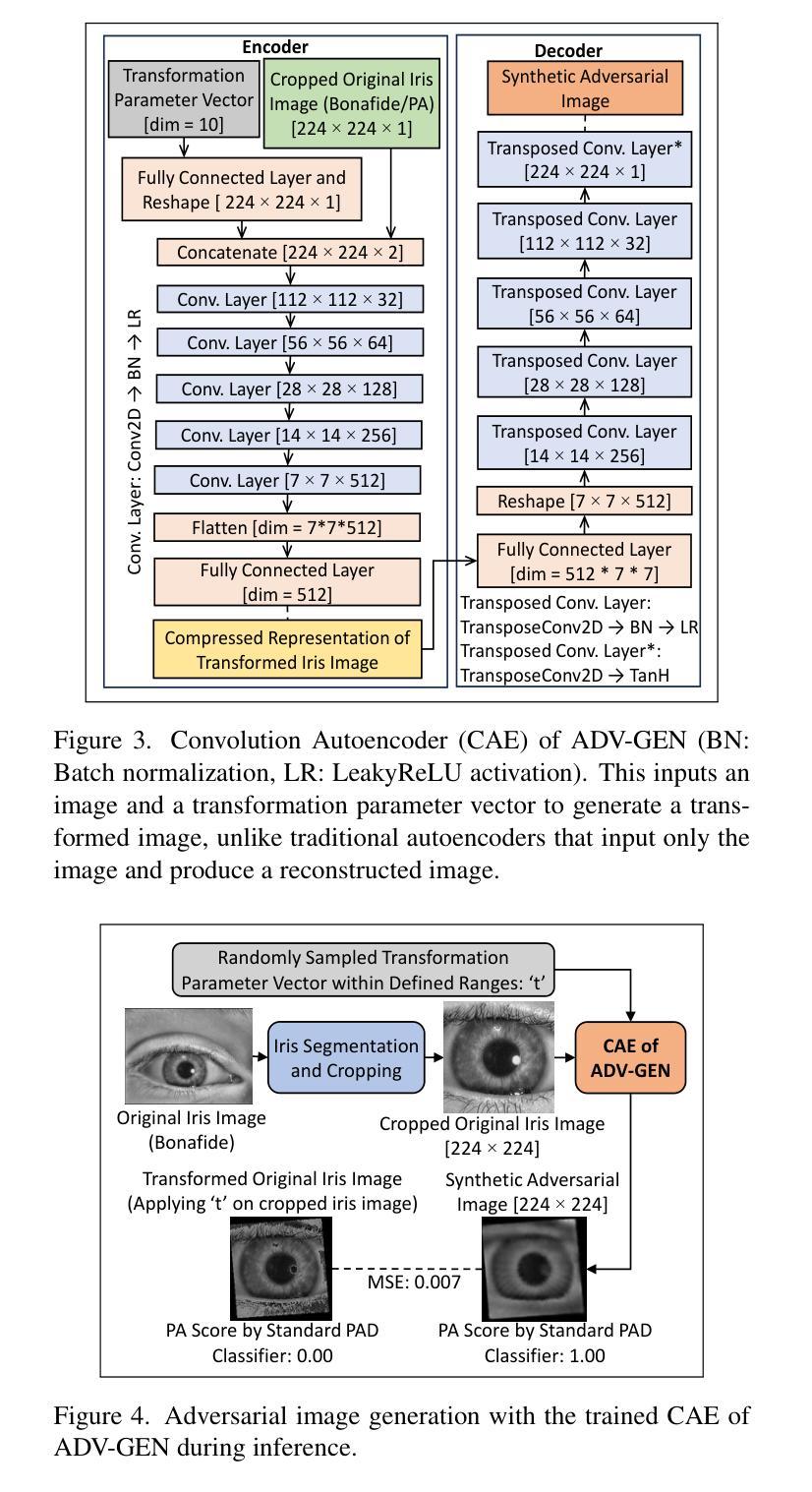
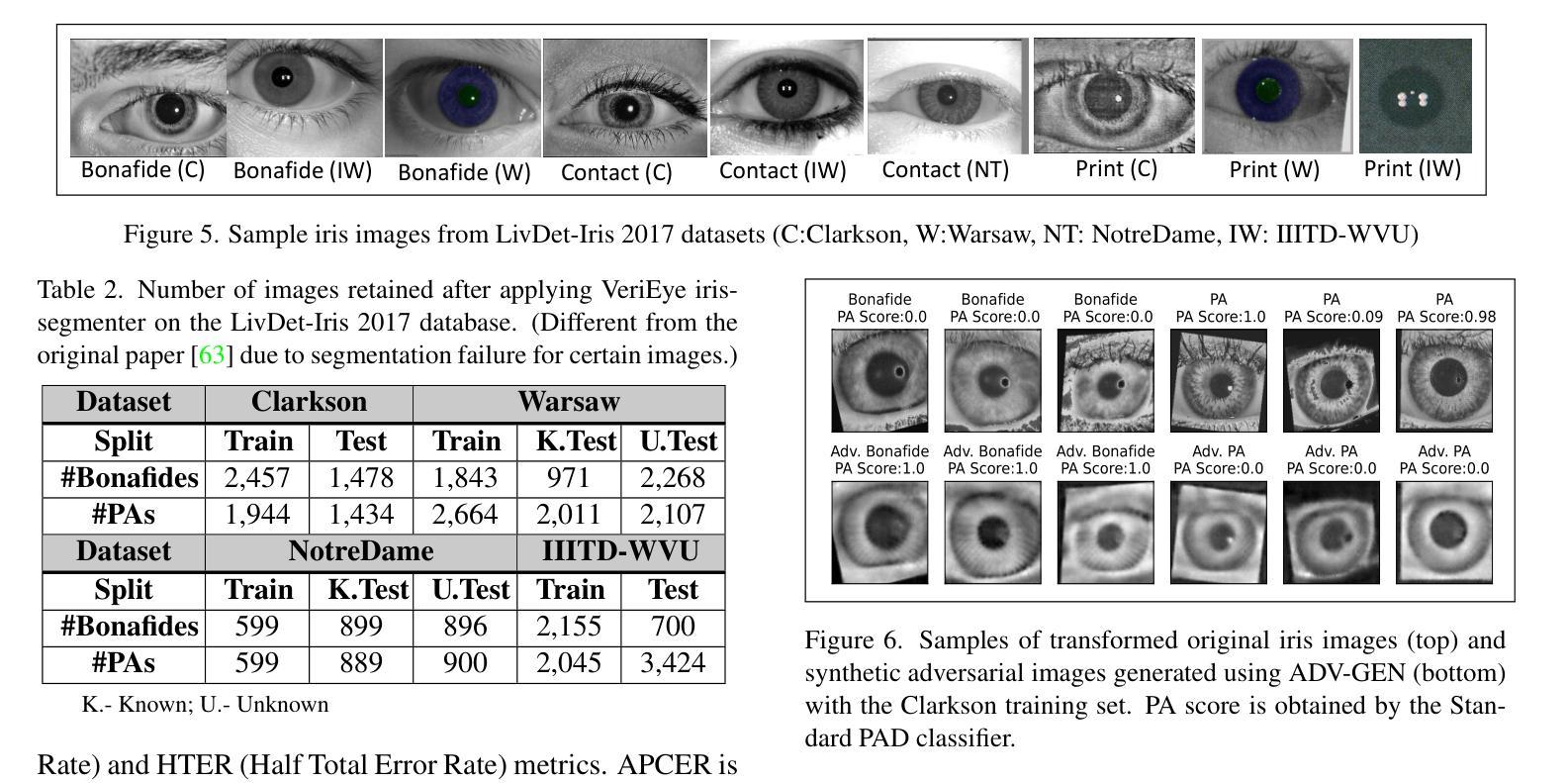
A Parametric Approach to Adversarial Augmentation for Cross-Domain Iris Presentation Attack Detection
Authors:Debasmita Pal, Redwan Sony, Arun Ross
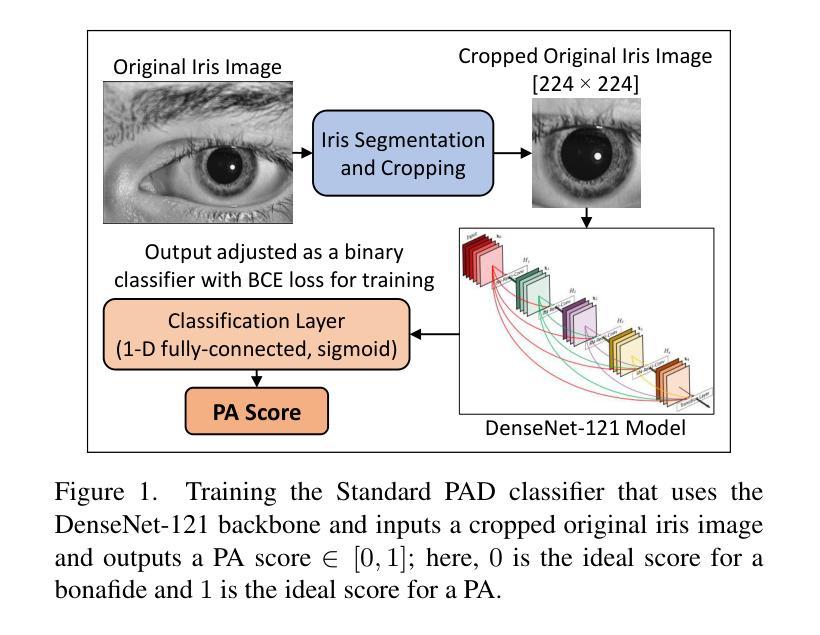
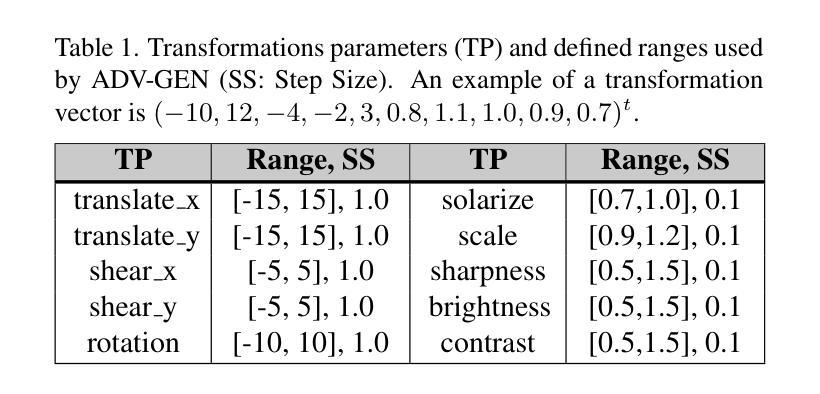
Iris-based biometric systems are vulnerable to presentation attacks (PAs), where adversaries present physical artifacts (e.g., printed iris images, textured contact lenses) to defeat the system. This has led to the development of various presentation attack detection (PAD) algorithms, which typically perform well in intra-domain settings. However, they often struggle to generalize effectively in cross-domain scenarios, where training and testing employ different sensors, PA instruments, and datasets. In this work, we use adversarial training samples of both bonafide irides and PAs to improve the cross-domain performance of a PAD classifier. The novelty of our approach lies in leveraging transformation parameters from classical data augmentation schemes (e.g., translation, rotation) to generate adversarial samples. We achieve this through a convolutional autoencoder, ADV-GEN, that inputs original training samples along with a set of geometric and photometric transformations. The transformation parameters act as regularization variables, guiding ADV-GEN to generate adversarial samples in a constrained search space. Experiments conducted on the LivDet-Iris 2017 database, comprising four datasets, and the LivDet-Iris 2020 dataset, demonstrate the efficacy of our proposed method. The code is available at https://github.com/iPRoBe-lab/ADV-GEN-IrisPAD.
基于虹膜的生物识别系统容易受到伪装攻击(Presentation Attacks,简称PA)的威胁,攻击者会使用物理伪制品(如打印的虹膜图像、纹理隐形眼镜)来欺骗系统。这促使了多种伪装攻击检测(Presentation Attack Detection,简称PAD)算法的发展,这些算法通常在单一领域内表现良好。然而,当面临跨域场景时,这些算法往往难以有效推广,其中训练和测试使用的是不同的传感器、攻击仪器和数据集。在这项工作中,我们利用真实的虹膜和伪装攻击的对抗训练样本,以提高PAD分类器在跨域场景下的性能。我们的方法新颖之处在于借鉴经典数据增强方案的转换参数(如平移、旋转等)来生成对抗样本。我们通过卷积自编码器ADV-GEN实现这一点,它输入原始训练样本以及一组几何和光度转换。转换参数作为正则化变量,指导ADV-GEN在约束的搜索空间内生成对抗样本。在LivDet-Iris 2017数据库(包含四个数据集)和LivDet-Iris 2020数据集上进行的实验证明了我们的方法的有效性。相关代码可通过https://github.com/iPRoBe-lab/ADV-GEN-IrisPAD获取。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF IEEE/CVF Winter Conference on Applications of Computer Vision (WACV), 2025
Summary
本文介绍了基于虹膜的生物识别系统易受到呈现攻击(PAs)的问题,研究者们为此开发了多种呈现攻击检测(PAD)算法。然而,这些算法在跨域场景下往往表现不佳。本文采用对抗性训练样本,结合真实虹膜和呈现攻击样本,以提高PAD分类器在跨域场景下的性能。通过利用经典数据增强方案中的转换参数来生成对抗性样本,实现了一种新的方法。实验结果表明,该方法在LivDet-Iris 2017和LivDet-Iris 2020数据集上表现出良好的性能。
Key Takeaways
- 虹膜生物识别系统面临呈现攻击(PAs)的问题。
- 现有的呈现攻击检测(PAD)算法在跨域场景下表现不佳。
- 对抗性训练样本用于提高PAD分类器的跨域性能。
- 利用经典数据增强方案的转换参数生成对抗性样本。
- 引入了一种名为ADV-GEN的卷积自编码器来生成对抗性样本。
- 在LivDet-Iris 2017和LivDet-Iris 2020数据集上的实验验证了该方法的有效性。
点此查看论文截图

Automatically Generating UI Code from Screenshot: A Divide-and-Conquer-Based Approach
Authors:Yuxuan Wan, Chaozheng Wang, Yi Dong, Wenxuan Wang, Shuqing Li, Yintong Huo, Michael R. Lyu
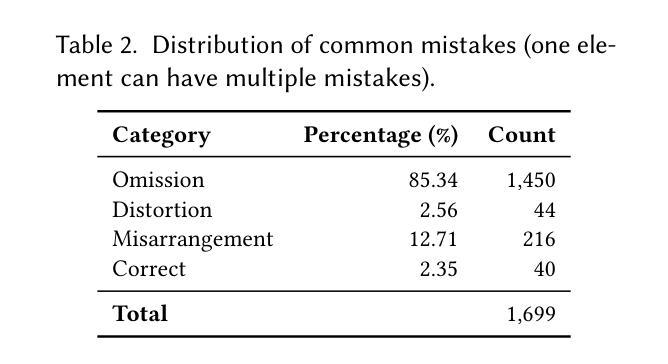
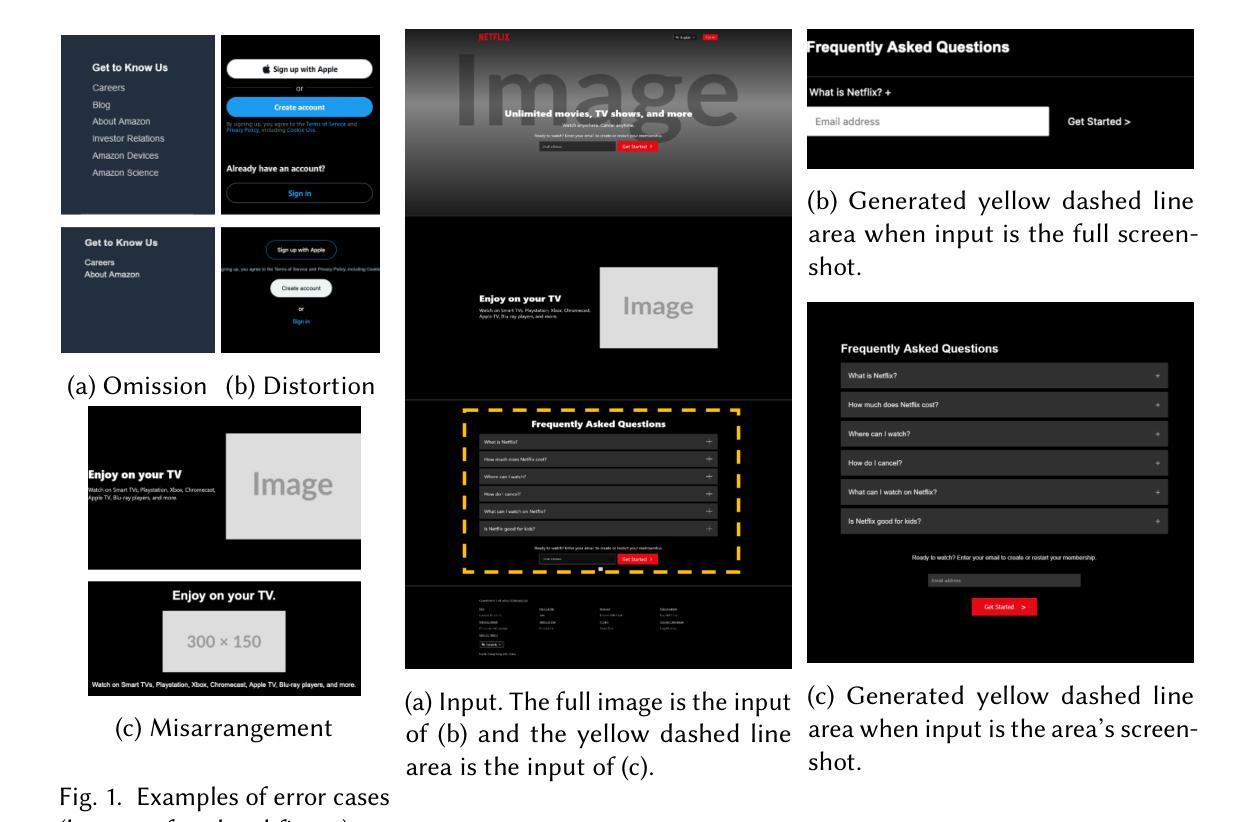
Websites are critical in today’s digital world, with over 1.11 billion currently active and approximately 252,000 new sites launched daily. Converting website layout design into functional UI code is a time-consuming yet indispensable step of website development. Manual methods of converting visual designs into functional code present significant challenges, especially for non-experts. To explore automatic design-to-code solutions, we first conduct a motivating study on GPT-4o and identify three types of issues in generating UI code: element omission, element distortion, and element misarrangement. We further reveal that a focus on smaller visual segments can help multimodal large language models (MLLMs) mitigate these failures in the generation process. In this paper, we propose DCGen, a divide-and-conquer-based approach to automate the translation of webpage design to UI code. DCGen starts by dividing screenshots into manageable segments, generating code for each segment, and then reassembling them into complete UI code for the entire screenshot. We conduct extensive testing with a dataset comprised of real-world websites and various MLLMs and demonstrate that DCGen achieves up to a 15% improvement in visual similarity and 8% in code similarity for large input images. Human evaluations show that DCGen can help developers implement webpages significantly faster and more similar to the UI designs. To the best of our knowledge, DCGen is the first segment-aware MLLM-based approach for generating UI code directly from screenshots.
在当今数字化世界中,网站扮演着至关重要的角色,当前有超过11.1亿活跃网站,大约每天新推出252,000个网站。将网站布局设计转化为功能性的UI代码是网站建设过程中既耗时又不可或缺的一步。手动将视觉设计转化为功能性代码面临巨大挑战,尤其是非专业人士面临的挑战更大。为了探索自动设计转代码的解决方案,我们首先对GPT-4o进行了激励研究,并确定了在生成UI代码时存在的三类问题:元素遗漏、元素变形和元素错序。我们进一步揭示,关注较小的视觉片段有助于多模态大型语言模型(MLLMs)减轻生成过程中的这些失败。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF Accepted by FSE 2025
Summary
网页设计自动转换为功能性的UI代码是网站开发中的重要环节,存在诸多挑战。本文提出DCGen方法,通过截图分割成可管理片段,生成每段代码后再重新组合成完整的UI代码,提高了生成代码的准确性和效率。
Key Takeaways
- 网站开发过程中,将网页布局设计转换为功能性UI代码是一个重要且耗时的步骤。
- 手动转换视觉设计到功能性代码对非专家来说具有挑战。
- GPT-4o在生成UI代码时存在三种主要问题:元素遗漏、元素变形和元素错排。
- 多模态大型语言模型(MLLMs)关注较小的视觉片段有助于减轻生成过程中的失败问题。
- DCGen方法采用基于分割和合并的策略,将网页截图分割成可管理片段,生成每段代码后再组合成完整的UI代码。
- DCGen在真实网站数据集上的测试表明,其在视觉相似性和代码相似性方面实现了显著提升。
- DCGen可帮助开发者更快、更准确地实现网页设计。
点此查看论文截图