⚠️ 以下所有内容总结都来自于 大语言模型的能力,如有错误,仅供参考,谨慎使用
🔴 请注意:千万不要用于严肃的学术场景,只能用于论文阅读前的初筛!
💗 如果您觉得我们的项目对您有帮助 ChatPaperFree ,还请您给我们一些鼓励!⭐️ HuggingFace免费体验
2025-04-29 更新
Generative Induction of Dialogue Task Schemas with Streaming Refinement and Simulated Interactions
Authors:James D. Finch, Yasasvi Josyula, Jinho D. Choi
In task-oriented dialogue (TOD) systems, Slot Schema Induction (SSI) is essential for automatically identifying key information slots from dialogue data without manual intervention. This paper presents a novel state-of-the-art (SoTA) approach that formulates SSI as a text generation task, where a language model incrementally constructs and refines a slot schema over a stream of dialogue data. To develop this approach, we present a fully automatic LLM-based TOD simulation method that creates data with high-quality state labels for novel task domains. Furthermore, we identify issues in SSI evaluation due to data leakage and poor metric alignment with human judgment. We resolve these by creating new evaluation data using our simulation method with human guidance and correction, as well as designing improved evaluation metrics. These contributions establish a foundation for future SSI research and advance the SoTA in dialogue understanding and system development.
在面向任务的对话(TOD)系统中,插槽模式归纳(SSI)对于从对话数据中自动识别关键信息插槽而无需人工干预至关重要。本文提出了一种最新(SoTA)的方法,将SSI表述为文本生成任务,其中语言模型会在对话数据流上逐步构建和完善插槽模式。为了开发这种方法,我们提出了一种基于LLM的全自动TOD仿真方法,该方法为新型任务领域创建了具有高质量状态标签的数据。此外,我们确定了SSI评估中由于数据泄露和与人类判断对齐不佳的指标所产生的问题。我们通过使用模拟方法创建新的评估数据并辅以人类指导和校正来解决这些问题,同时设计改进的评价指标。这些贡献为未来SSI研究奠定了基础,并推动了对话理解和系统开发的最新进展。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF Accepted (B) to TACL 2025
Summary:
本文介绍了任务导向对话系统中的槽位模式归纳技术,该技术对于自动从对话数据中识别关键信息槽位至关重要。该文提出了一种新型的最新方法,将槽位模式归纳视为文本生成任务,利用语言模型逐步构建并改进在对话数据流中的槽位模式。为了开发这种方法,本文提出了一种完全自动化的基于LLM的任务导向对话仿真方法,为新型任务领域创建高质量状态标签的数据。此外,本文解决了因数据泄露以及指标与人类判断不对齐所带来的SSI评估问题,通过模拟方法实现有人工指导和校正的新评估数据创建,并设计改进评估指标。这些贡献为未来SSI研究奠定了基础,并推动了对话理解和系统开发的最新进展。
Key Takeaways:
- 介绍了任务导向对话系统中槽位模式归纳技术的重要性及其在自动识别关键信息槽位中的应用。
- 提出了一种新型的最新方法,将槽位模式归纳视为文本生成任务,并利用语言模型逐步构建和改进槽位模式。
- 介绍了一种基于LLM的任务导向对话仿真方法,能够创建高质量状态标签数据以用于开发和研究。
- 识别了当前SSI评估存在的问题,包括数据泄露和评估指标与人类判断的不对齐问题。
- 通过新的评估数据创建和更优化的评估指标设计来解决上述问题,其中新评估数据包括人工指导和校正。
- 这些成果为未来SSI研究奠定了基础,推动了对话理解和系统开发的进展。
点此查看论文截图


The impact of new ($α$, n) reaction rates on the weak s-process in metal-poor massive stars
Authors:Wenyu Xin, Chun-Ming Yip, Ken’ichi Nomoto, Xianfei Zhang, Shaolan Bi
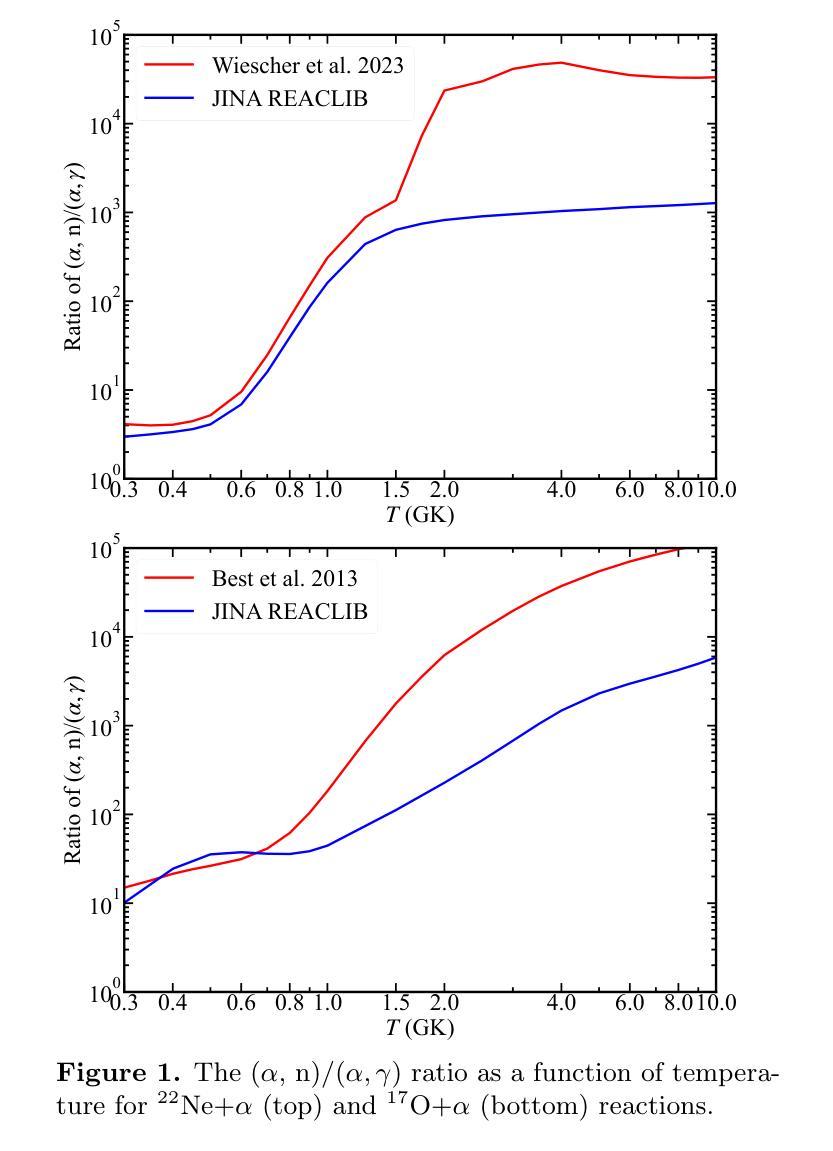
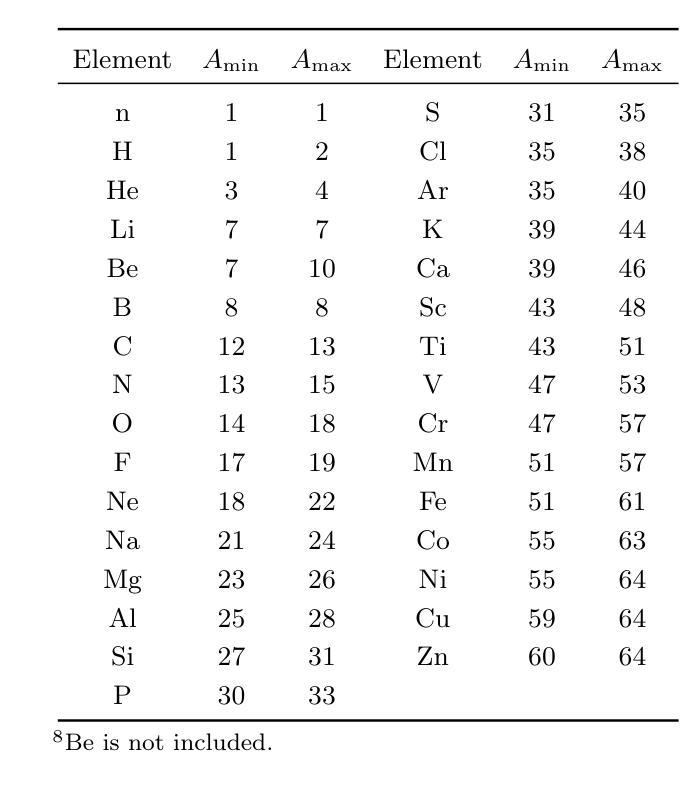
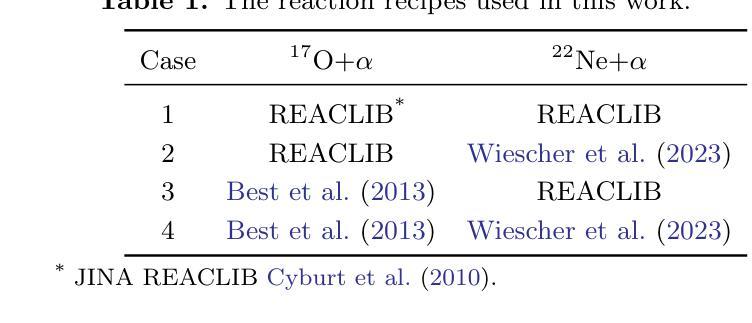
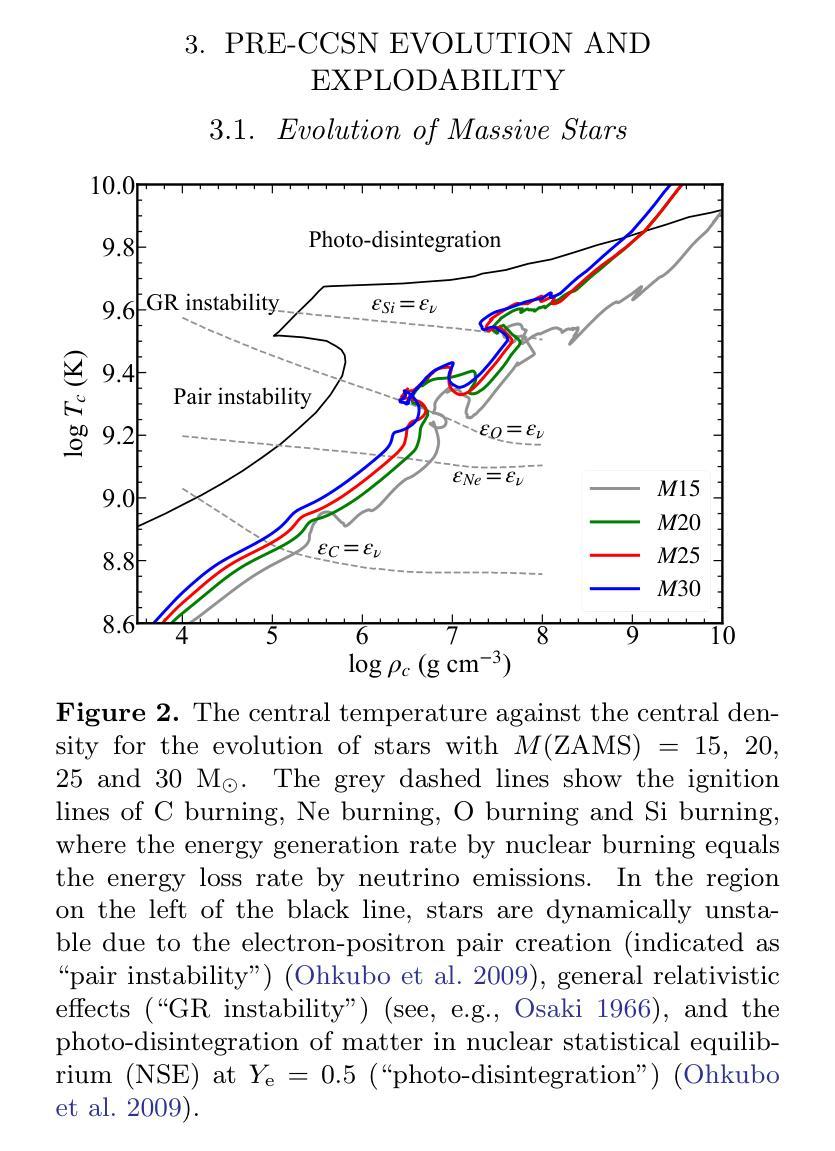
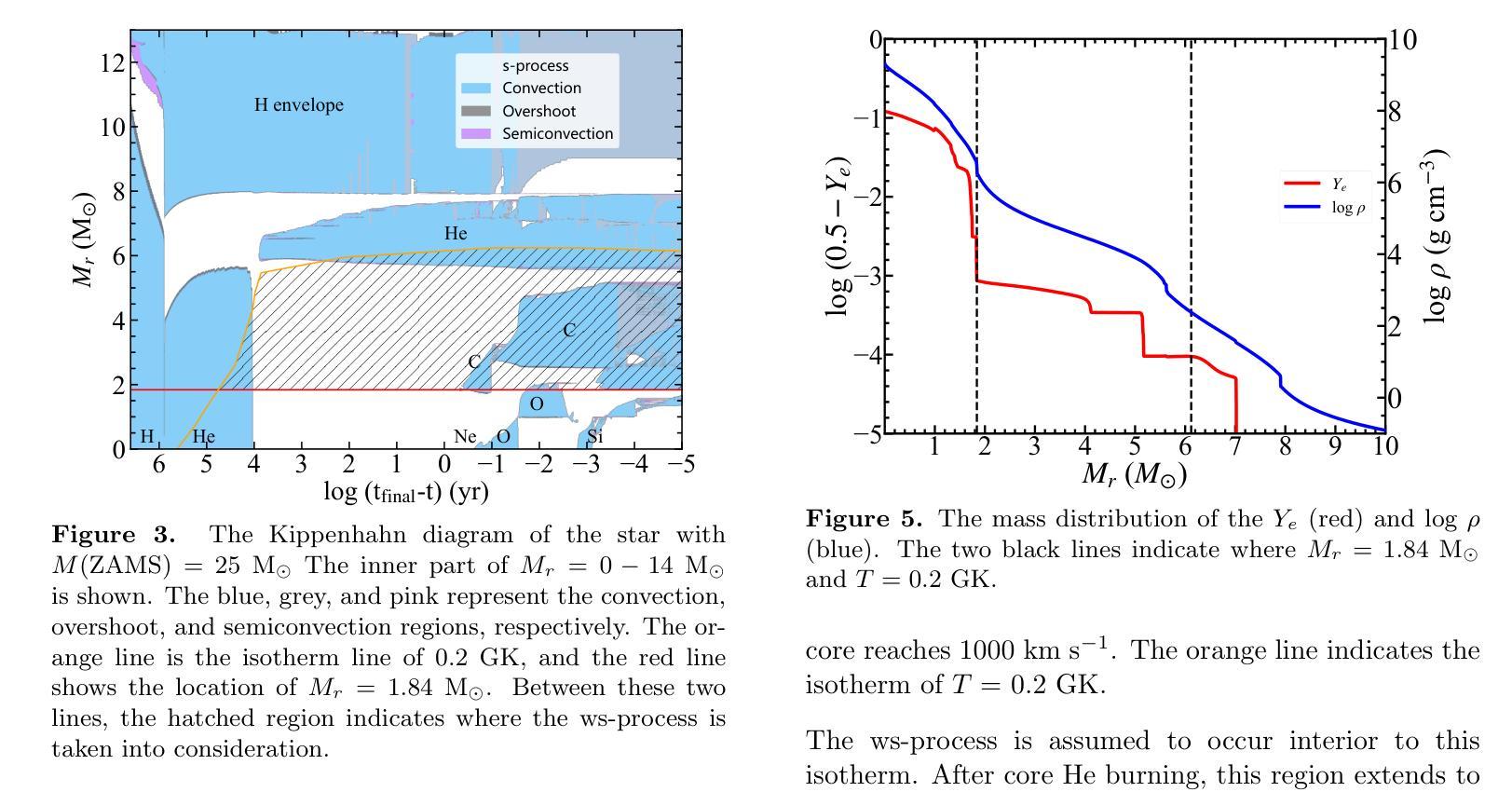
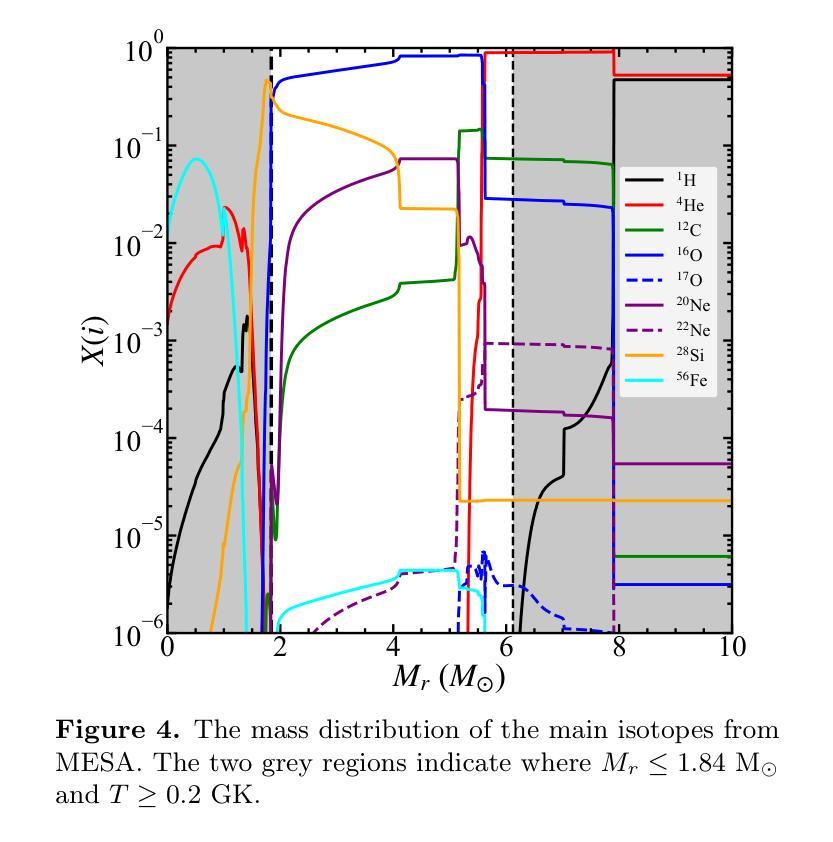
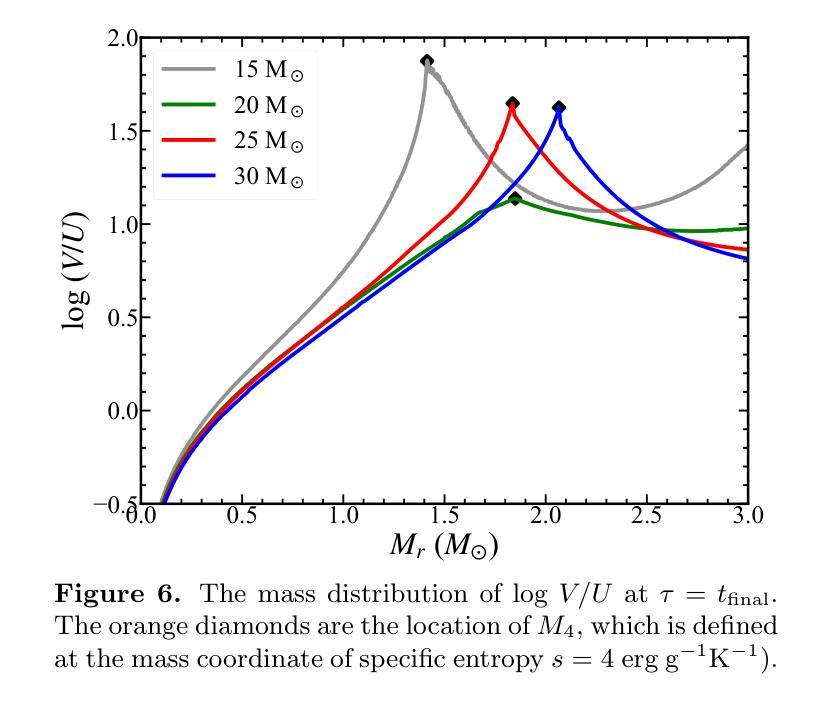
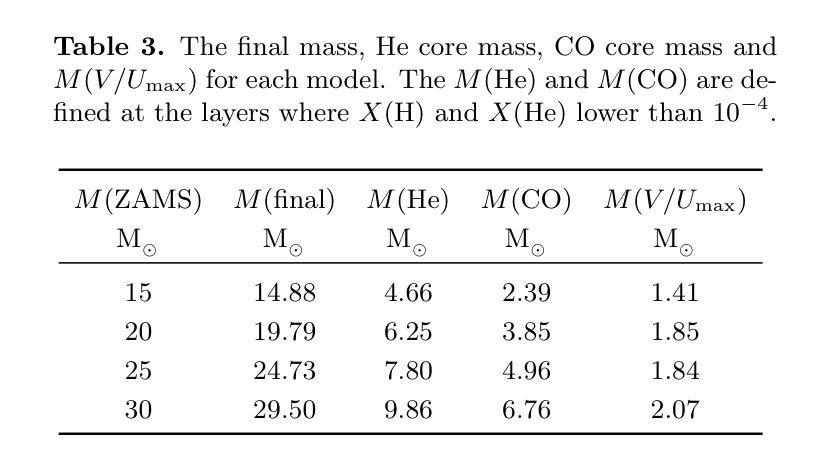
Massive stars are significant sites for the weak s-process (ws-process). $^{22}$Ne and $^{16}$O are, respectively, the main neutron source and poison for the ws-process. In the metal-poor stars, the abundance of $^{22}$Ne is limited by the metallicity, so that the contribution of $^{22}$Ne($\alpha$, n)$^{25}$Mg reaction on the s-process is weaker. Conversely, the $^{17}$O($\alpha$, n)$^{20}$Ne reaction is more evident in more metal-poor stars due to the most abundant $^{16}$O in all metallicities. In this work, we calculate the evolution of four metal-poor models ($Z=10^{-3}$) for the Zero-Age Main-Sequence (ZAMS) masses of $M ({\rm ZAMS})=$ 15, 20, 25, and 30 M$_{\odot}$ to investigate the effect of reaction rates on the ws-process. We adopt the new $^{17}$O($\alpha$, n)$^{20}$Ne and $^{17}$O($\alpha, \gamma$)$^{21}$Ne reaction rates suggested by Wiescher et al. (2023) and $^{22}$Ne($\alpha$, n)$^{25}$Mg and $^{22}$Ne($\alpha, \gamma$)$^{26}$Mg from Best et al. (2013). The yields of the s-process isotope with updated reaction rates are compared with the results using default reaction rates from JINA REACLIB. We find that the new $^{17}$O+$\alpha$ reaction rates increase the ws-process mainly in all the stages, while the new $^{22}$Ne+$\alpha$ reaction rates only increase the ws-process in C and Ne burning stages. Updating these new reaction rates would increase the production of ws-process isotopes by tens of times. We also note that for more massive stars, the enhancement by new $^{17}$O+$\alpha$ reaction rates become more significant.
大规模恒星对于弱s过程(ws过程)具有重要意义。$^{22}$Ne和$^{16}$O分别是ws过程的主要中子来源和毒药。在贫金属恒星中,$^{22}$Ne的丰度受到金属丰度的影响,因此$^{22}$Ne($\alpha$, n)$^{25}$Mg反应对s过程的贡献较弱。相反,由于所有金属性的$^{16}$O最丰富,因此在金属含量较低的恒星中,$^{17}$O($\alpha$, n)$^{20}$Ne反应更加明显。在这项工作中,我们计算了四个贫金属模型($Z=10^{-3}$)的演化过程,初始主序(Zero-Age Main-Sequence,ZAMS)质量为$M ({\rm ZAMS})= 15、 20、 25和 30 M_{\odot}$,以研究反应速率对ws过程的影响。我们采用了Wiescher等人(2023年)提出的新反应速率,包括$^{17}$O($\alpha$, n)$^{20}$Ne和$^{17}$O($\alpha, \gamma$)$^{21}$Ne反应速率,以及Best等人(Best et al., 2013)给出的$^{22}$Ne($\alpha$, n)$^{25}$Mg和$^{22}$Ne($\alpha, \gamma$)$^{26}$Mg反应速率。将更新后的反应速率的s过程同位素产量与采用JINA REACLIB默认反应速率的结果进行比较。我们发现新的$^{17}$O+$\alpha$反应速率在所有阶段都提高了ws过程,而新的$^{22}$Ne+$\alpha$反应速率仅在C和Ne燃烧阶段提高了ws过程。更新这些新的反应速率将提高ws过程同位素的产量数十倍。我们还注意到,对于质量更大的恒星,新的$^{17}$O+$\alpha$反应速率的增强效果变得更加显著。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF 16 pages, 15 figures
Summary
大型恒星是弱s过程(ws-process)的重要场所。在贫金属恒星中,^{22}Ne是主要的中子源,而其在金属丰度中的贡献受到限制。通过采用新的反应率,本研究发现新的^{17}O+α反应率对ws过程的增强作用显著,特别是在质量较大的恒星中。更新这些新反应率将增加ws过程同位素的产量数十倍。
Key Takeaways
- 大型恒星是弱s过程(ws-process)的重要场所,其中^{22}Ne和^{16}O分别作为主要的中子源和毒素。
- 在贫金属恒星中,由于金属丰度的限制,^{22}Ne对s过程的贡献受到限制。
- 新采用的^{17}O+α和^{22}Ne+α的反应率对ws过程有显著影响。
- 新反应率导致ws过程同位素产量大幅增加,最高达数十倍。
- ^{17}O+α的新反应率在质量较大的恒星中作用更为显著。
- 本研究通过计算四个贫金属模型(Z=10^{-3})的演化,探讨了反应率对ws过程的影响。
点此查看论文截图