⚠️ 以下所有内容总结都来自于 大语言模型的能力,如有错误,仅供参考,谨慎使用
🔴 请注意:千万不要用于严肃的学术场景,只能用于论文阅读前的初筛!
💗 如果您觉得我们的项目对您有帮助 ChatPaperFree ,还请您给我们一些鼓励!⭐️ HuggingFace免费体验
2025-04-29 更新
TRACE Back from the Future: A Probabilistic Reasoning Approach to Controllable Language Generation
Authors:Gwen Yidou Weng, Benjie Wang, Guy Van den Broeck
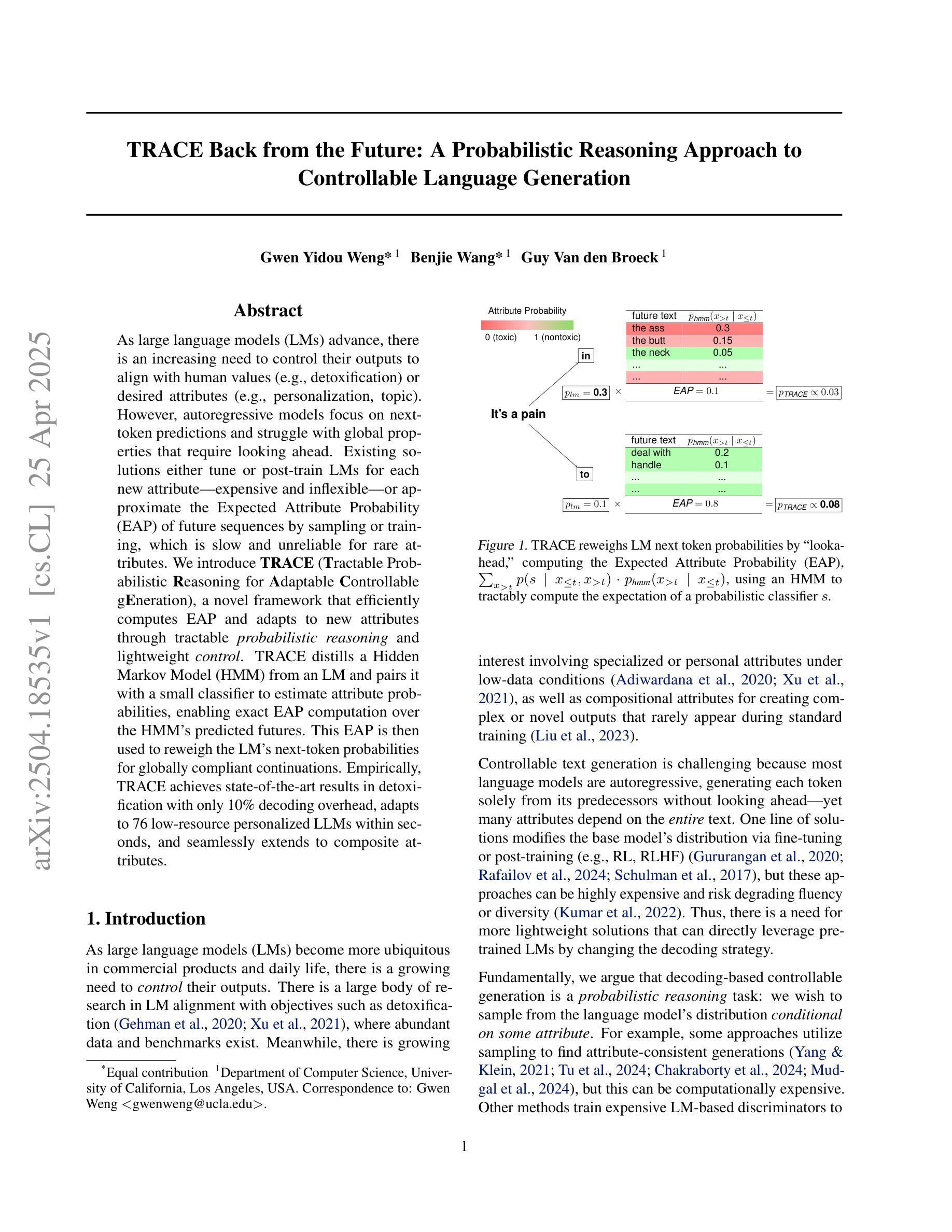
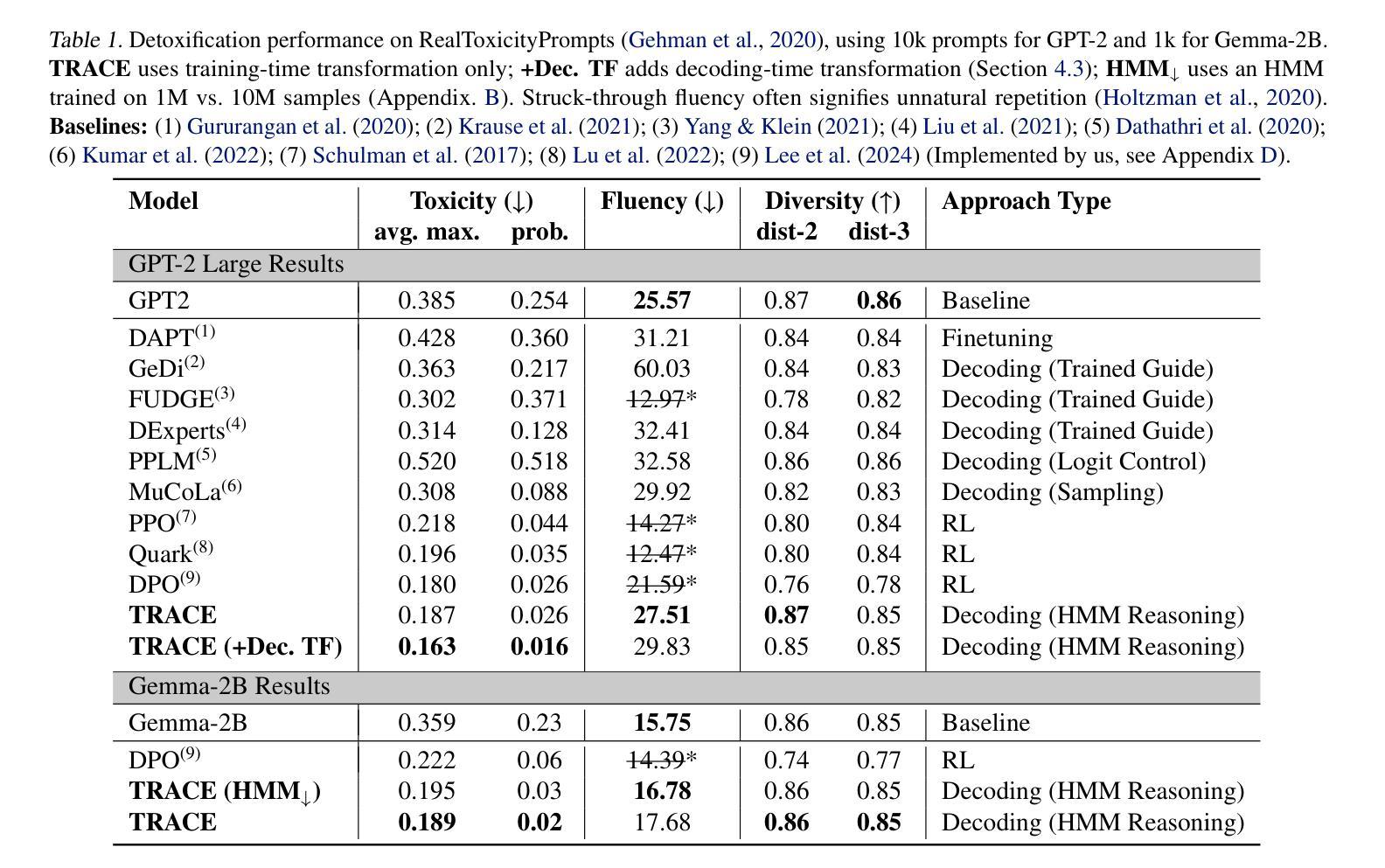
As large language models (LMs) advance, there is an increasing need to control their outputs to align with human values (e.g., detoxification) or desired attributes (e.g., personalization, topic). However, autoregressive models focus on next-token predictions and struggle with global properties that require looking ahead. Existing solutions either tune or post-train LMs for each new attribute - expensive and inflexible - or approximate the Expected Attribute Probability (EAP) of future sequences by sampling or training, which is slow and unreliable for rare attributes. We introduce TRACE (Tractable Probabilistic Reasoning for Adaptable Controllable gEneration), a novel framework that efficiently computes EAP and adapts to new attributes through tractable probabilistic reasoning and lightweight control. TRACE distills a Hidden Markov Model (HMM) from an LM and pairs it with a small classifier to estimate attribute probabilities, enabling exact EAP computation over the HMM’s predicted futures. This EAP is then used to reweigh the LM’s next-token probabilities for globally compliant continuations. Empirically, TRACE achieves state-of-the-art results in detoxification with only 10% decoding overhead, adapts to 76 low-resource personalized LLMs within seconds, and seamlessly extends to composite attributes.
随着大型语言模型(LMs)的发展,越来越需要控制它们的输出以符合人类价值观(例如,去毒)或期望的属性(例如,个性化、主题)。然而,自回归模型专注于下一个标记的预测,并努力处理需要前瞻性的全局属性。现有解决方案要么针对每个新属性进行调优或后期训练大型语言模型,这既昂贵又不灵活,要么通过采样或训练来近似未来序列的预期属性概率(EAP),这对于稀有属性而言既缓慢又不可靠。我们介绍了TRACE(用于可适应可控生成的可行概率推理),这是一个新颖框架,能够高效计算EAP并通过可行的概率推理和轻量级控制来适应新属性。TRACE通过大型语言模型提炼出隐马尔可夫模型(HMM),并将其与小型分类器配对以估算属性概率,从而能够在HMM预测的未来上进行精确EAP计算。然后,使用这个EAP来重新衡量大型语言模型的下一个标记概率,以便生成全局合规的延续文本。实证表明,TRACE在仅增加10%解码开销的情况下实现了最先进的去毒效果,可在几秒内适应76个低资源个性化大型语言模型,并无缝扩展到组合属性。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
大型语言模型(LMs)的发展推动了对其输出控制的需求,以符合人类价值观和期望属性。然而,现有解决方案在处理全局属性时存在局限性,需要前视功能。本文介绍了一种名为TRACE的新型框架,它通过易处理的概率推理和轻量级控制来高效计算预期属性概率(EAP),并适应新属性。TRACE通过从LM中提炼隐马尔可夫模型(HMM)并将其与小型分类器配对来估计属性概率,从而在HMM预测的未未来上实现精确的EAP计算。然后,使用此EAP重新权衡LM的下一个令牌概率,以生成全局合规的延续内容。实证结果表明,TRACE在解毒任务上取得了最佳效果,只需10%的解码开销,还能在几秒钟内适应76个低资源个性化LLM,并轻松扩展到组合属性。
Key Takeaways
- 大型语言模型(LMs)需要控制其输出以符合人类价值观和期望属性。
- 现有解决方案在处理需要前视功能的全球属性时存在局限性。
- TRACE框架通过隐马尔可夫模型(HMM)和分类器估计属性概率,实现精确的预期属性概率(EAP)计算。
- TRACE框架能高效适应新属性,并具有优秀的性能表现。
- TRACE框架只需少量解码开销即可达到最佳效果。
- TRACE能快速适应多种低资源个性化LLM。
点此查看论文截图
Eval3D: Interpretable and Fine-grained Evaluation for 3D Generation
Authors:Shivam Duggal, Yushi Hu, Oscar Michel, Aniruddha Kembhavi, William T. Freeman, Noah A. Smith, Ranjay Krishna, Antonio Torralba, Ali Farhadi, Wei-Chiu Ma
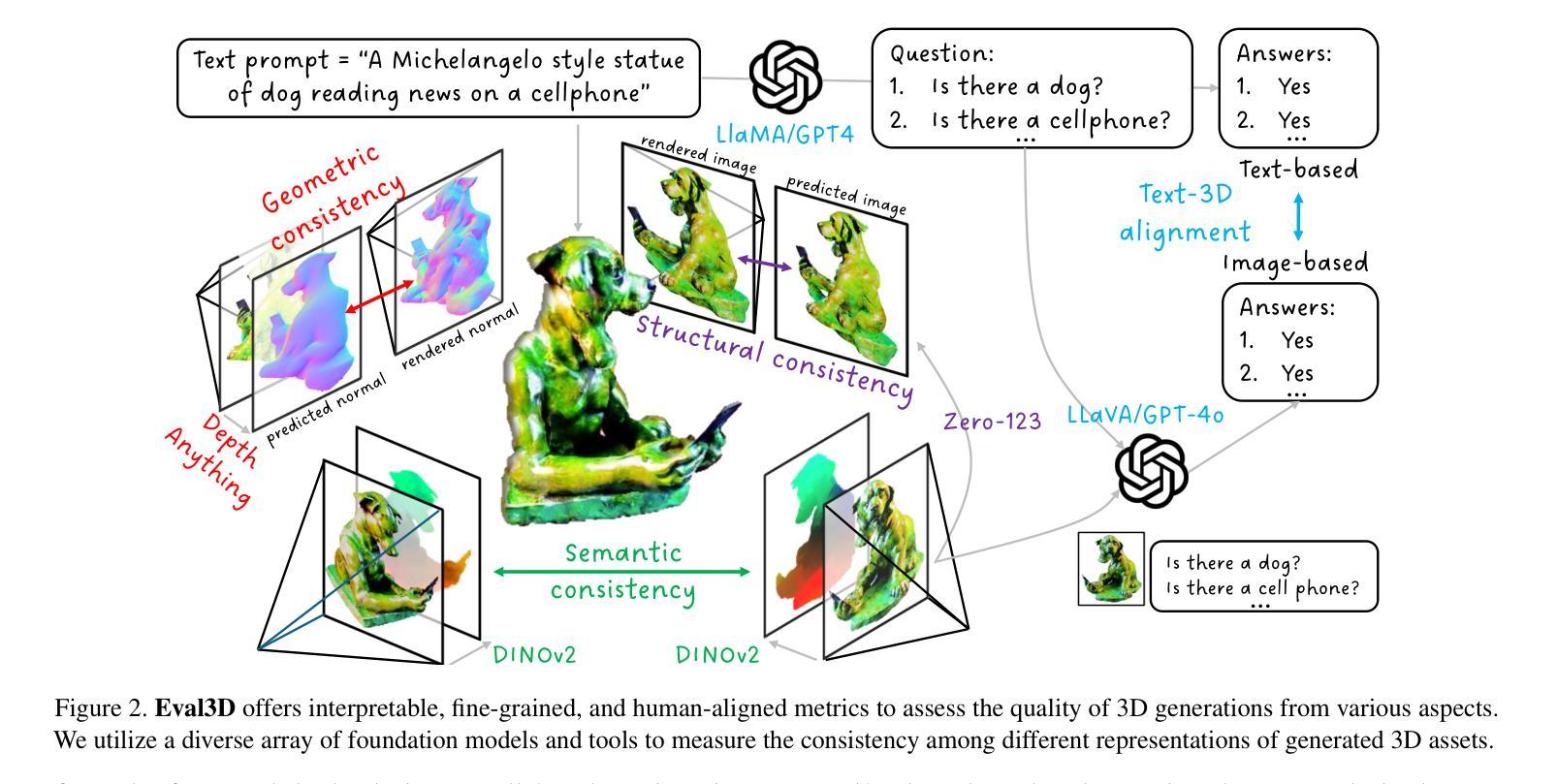
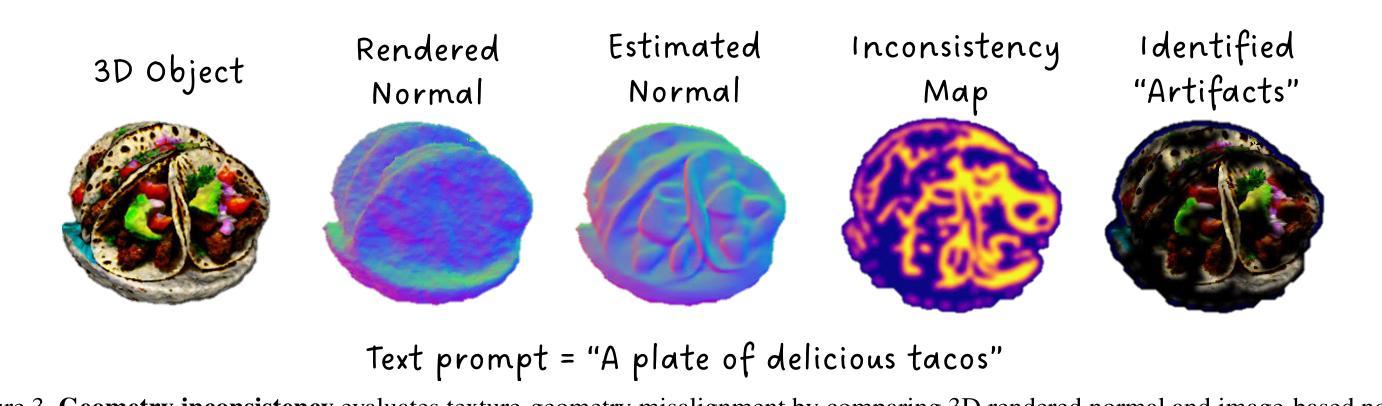
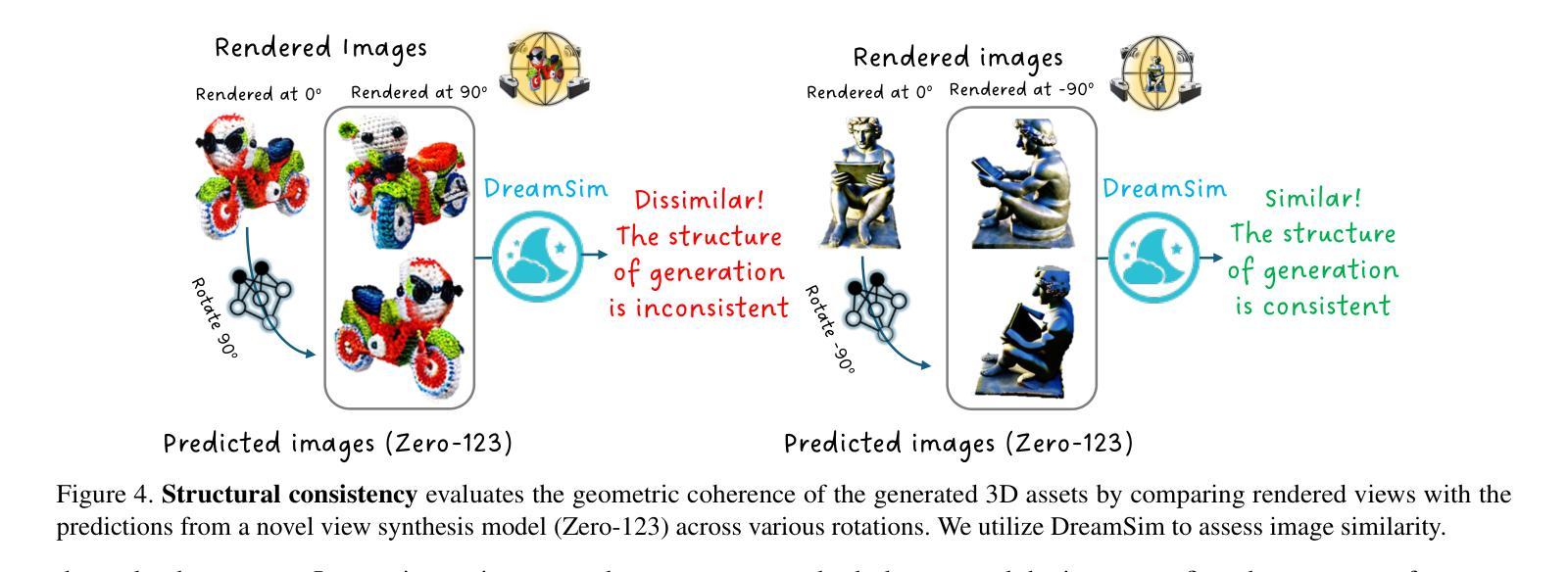
Despite the unprecedented progress in the field of 3D generation, current systems still often fail to produce high-quality 3D assets that are visually appealing and geometrically and semantically consistent across multiple viewpoints. To effectively assess the quality of the generated 3D data, there is a need for a reliable 3D evaluation tool. Unfortunately, existing 3D evaluation metrics often overlook the geometric quality of generated assets or merely rely on black-box multimodal large language models for coarse assessment. In this paper, we introduce Eval3D, a fine-grained, interpretable evaluation tool that can faithfully evaluate the quality of generated 3D assets based on various distinct yet complementary criteria. Our key observation is that many desired properties of 3D generation, such as semantic and geometric consistency, can be effectively captured by measuring the consistency among various foundation models and tools. We thus leverage a diverse set of models and tools as probes to evaluate the inconsistency of generated 3D assets across different aspects. Compared to prior work, Eval3D provides pixel-wise measurement, enables accurate 3D spatial feedback, and aligns more closely with human judgments. We comprehensively evaluate existing 3D generation models using Eval3D and highlight the limitations and challenges of current models.
尽管三维生成领域取得了前所未有的进展,但当前的系统仍然经常无法生成高质量的三维资产,这些资产在视觉上吸引人,并且在多个视角在几何和语义上具有一致性。为了有效地评估生成的三维数据的质量,需要一种可靠的的三维评估工具。不幸的是,现有的三维评估指标往往忽视了生成资产的几何质量,或者仅仅依赖于黑箱多模态大型语言模型进行粗略评估。在本文中,我们介绍了Eval3D,这是一种精细且可解释性的评估工具,可以基于各种独特而互补的标准忠实评估生成的三维资产的质量。我们的关键观察是,通过测量各种基础模型和工具之间的一致性,可以有效地捕获三维生成的许多所需属性,如语义和几何一致性。因此,我们利用一组多样化的模型和工具作为探针来评估生成的三维资产在不同方面的不一致性。与之前的工作相比,Eval3D提供了像素级的测量,实现了精确的3D空间反馈,并更紧密地与人类判断保持一致。我们使用Eval3D全面评估现有的三维生成模型,并强调当前模型的局限性和挑战。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF CVPR 2025. Project page and codes: https://eval3d.github.io/
Summary
本文介绍了当前3D生成技术面临的挑战,即生成的3D资产在视觉、几何和语义上的一致性不足。为解决此问题,提出了一种名为Eval3D的精细、可解释的评估工具,该工具可以通过测量不同基础模型和工具之间的一致性来准确评估生成的3D资产的质量。相较于现有评估方法,Eval3D提供了像素级的测量和准确的3D空间反馈,更贴近人类判断。
Key Takeaways
- 当前3D生成技术在生成高质量、视觉、几何和语义一致的3D资产方面存在挑战。
- 生成的3D资产的质量评估需要一种可靠的3D评估工具。
- 现有3D评估指标常常忽视资产的几何质量,或仅依赖黑盒多模态大型语言模型进行粗略评估。
- Eval3D是一种精细、可解释的评估工具,能够基于多种不同但互补的标准来评估生成的3D资产质量。
- Eval3D通过测量不同基础模型和工具之间的一致性来捕捉3D生成的多个所需属性,如语义和几何一致性。
- Eval3D提供像素级的测量和准确的3D空间反馈,更贴近人类判断。
点此查看论文截图


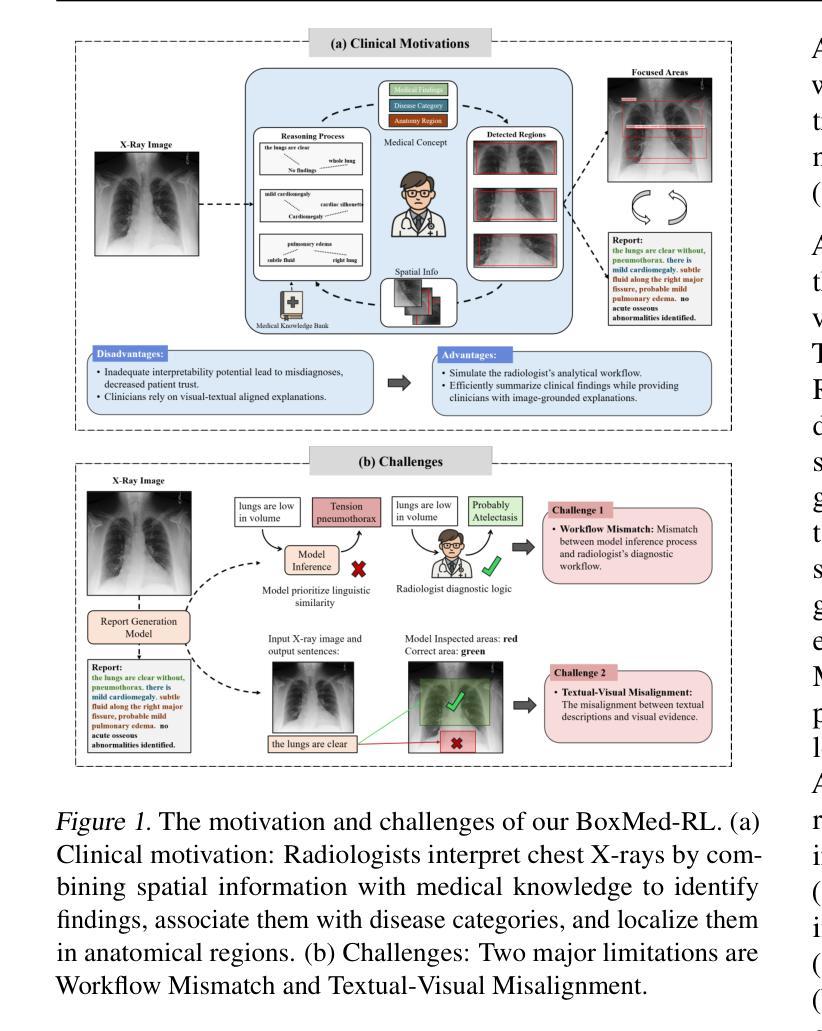
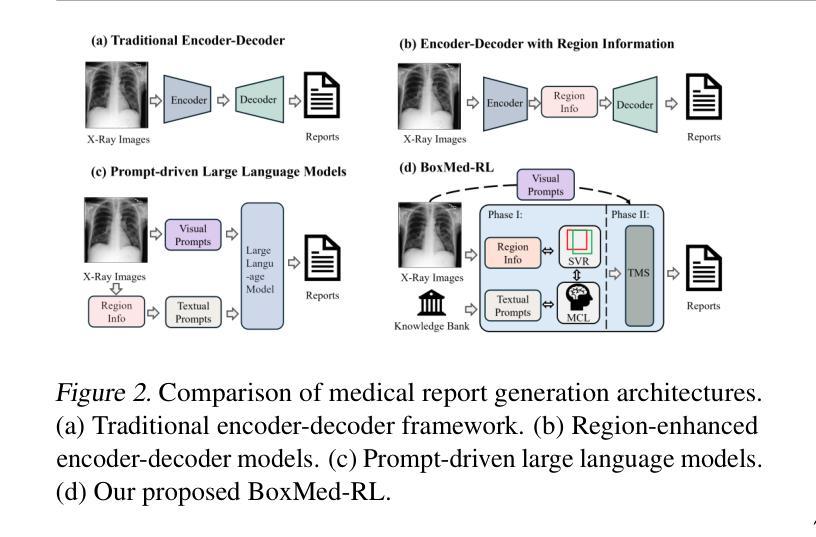
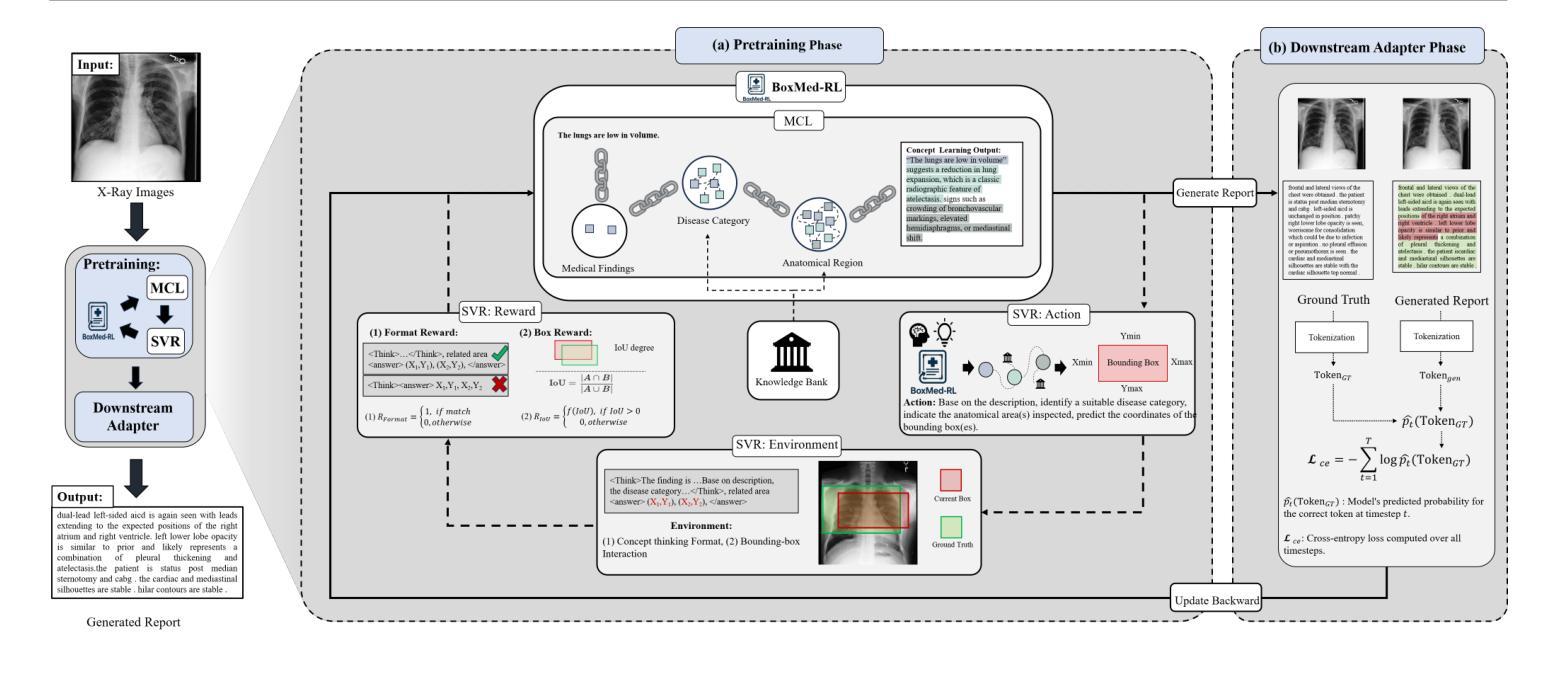
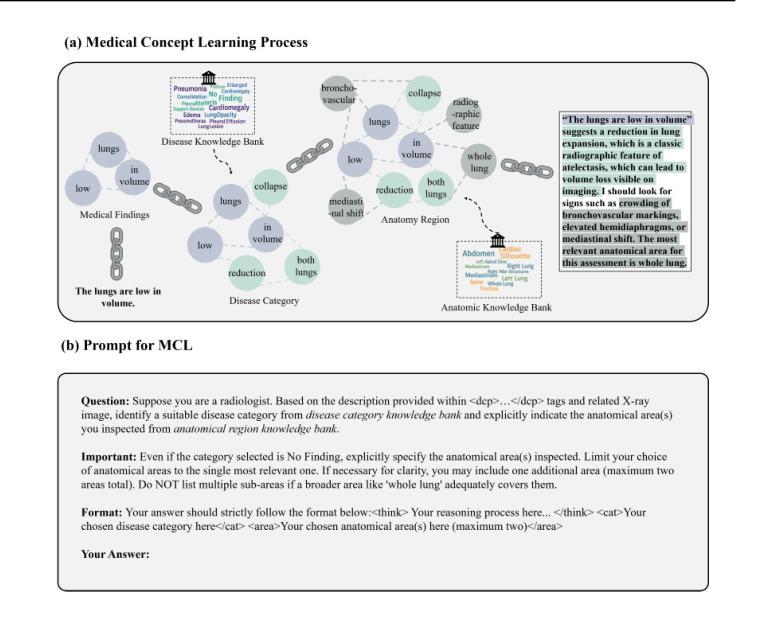
Reason Like a Radiologist: Chain-of-Thought and Reinforcement Learning for Verifiable Report Generation
Authors:Peiyuan Jing, Kinhei Lee, Zhenxuan Zhang, Huichi Zhou, Zhengqing Yuan, Zhifan Gao, Lei Zhu, Giorgos Papanastasiou, Yingying Fang, Guang Yang
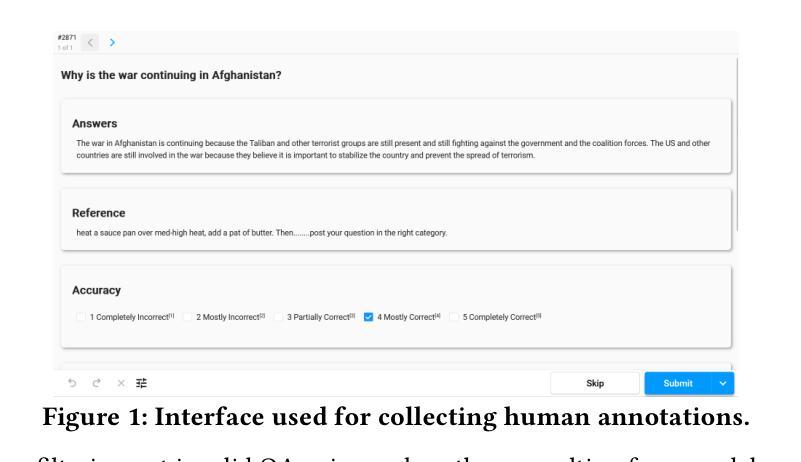
Radiology report generation is critical for efficiency but current models lack the structured reasoning of experts, hindering clinical trust and explainability by failing to link visual findings to precise anatomical locations. This paper introduces BoxMed-RL, a groundbreaking unified training framework for generating spatially verifiable and explainable radiology reports. Built on a large vision-language model, BoxMed-RL revolutionizes report generation through two integrated phases: (1) In the Pretraining Phase, we refine the model via medical concept learning, using Chain-of-Thought supervision to internalize the radiologist-like workflow, followed by spatially verifiable reinforcement, which applies reinforcement learning to align medical findings with bounding boxes. (2) In the Downstream Adapter Phase, we freeze the pretrained weights and train a downstream adapter to ensure fluent and clinically credible reports. This framework precisely mimics radiologists’ workflow, compelling the model to connect high-level medical concepts with definitive anatomical evidence. Extensive experiments on public datasets demonstrate that BoxMed-RL achieves an average 7% improvement in both METEOR and ROUGE-L metrics compared to state-of-the-art methods. An average 5% improvement in large language model-based metrics further underscores BoxMed-RL’s robustness in generating high-quality radiology reports.
放射学报告生成对于效率至关重要,但当前模型缺乏专家的结构化推理能力,无法通过关联视觉检查结果与精确解剖部位来解释报告的可靠性,阻碍了临床信任度和解释性。本文介绍了BoxMed-RL,这是一个用于生成空间可验证和可解释的放射学报告的创新统一训练框架。BoxMed-RL建立在大型视觉语言模型上,通过两个阶段实现了报告的生成革命:(1)在预训练阶段,我们通过医学概念学习精炼模型,使用思维链式监督来内化类似放射科医师的工作流程,随后进行空间可验证强化训练,应用强化学习将医学检查结果与边界框对齐。(2)在下游适配器阶段,我们冻结预训练权重并训练下游适配器以确保报告的流畅性和临床可信度。该框架精确地模仿了放射科医师的工作流程,促使模型将高级医学概念与明确的解剖学证据联系起来。在公共数据集上的大量实验表明,与最先进的方法相比,BoxMed-RL在METEOR和ROUGE-L指标上平均提高了7%。基于大型语言模型的指标平均提高了5%,这进一步证明了BoxMed-RL在生成高质量放射学报告方面的稳健性。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
本文介绍了一个创新的统一训练框架BoxMed-RL,用于生成空间可验证和可解释的放射学报告。该框架通过两个阶段实现:第一阶段是预训练阶段,通过医学概念学习和强化学习对齐医学发现与边界框;第二阶段是下游适配器阶段,训练下游适配器以确保报告的流畅性和临床可信度。BoxMed-RL精确模拟了放射科医生的工作流程,将高级医学概念与明确的解剖学证据联系起来。在公共数据集上的实验表明,BoxMed-RL相较于现有方法平均提高了7%的METEOR和ROUGE-L指标得分。
Key Takeaways
- BoxMed-RL是一个用于生成放射学报告的统一训练框架,旨在提高报告的效率和临床信任度。
- 该框架包括两个阶段:预训练阶段和下游适配器阶段。
- 在预训练阶段,通过医学概念学习和强化学习对齐医学发现与边界框,以模拟放射科医生的工作流程。
- 下游适配器阶段确保报告的流畅性和临床可信度。
- BoxMed-RL实现了对放射学报告的高质量生成,与现有方法相比,平均提高了METEOR和ROUGE-L指标得分。
- 该框架通过结合高级医学概念和解剖学证据,提高了报告的可解释性和空间验证性。
点此查看论文截图

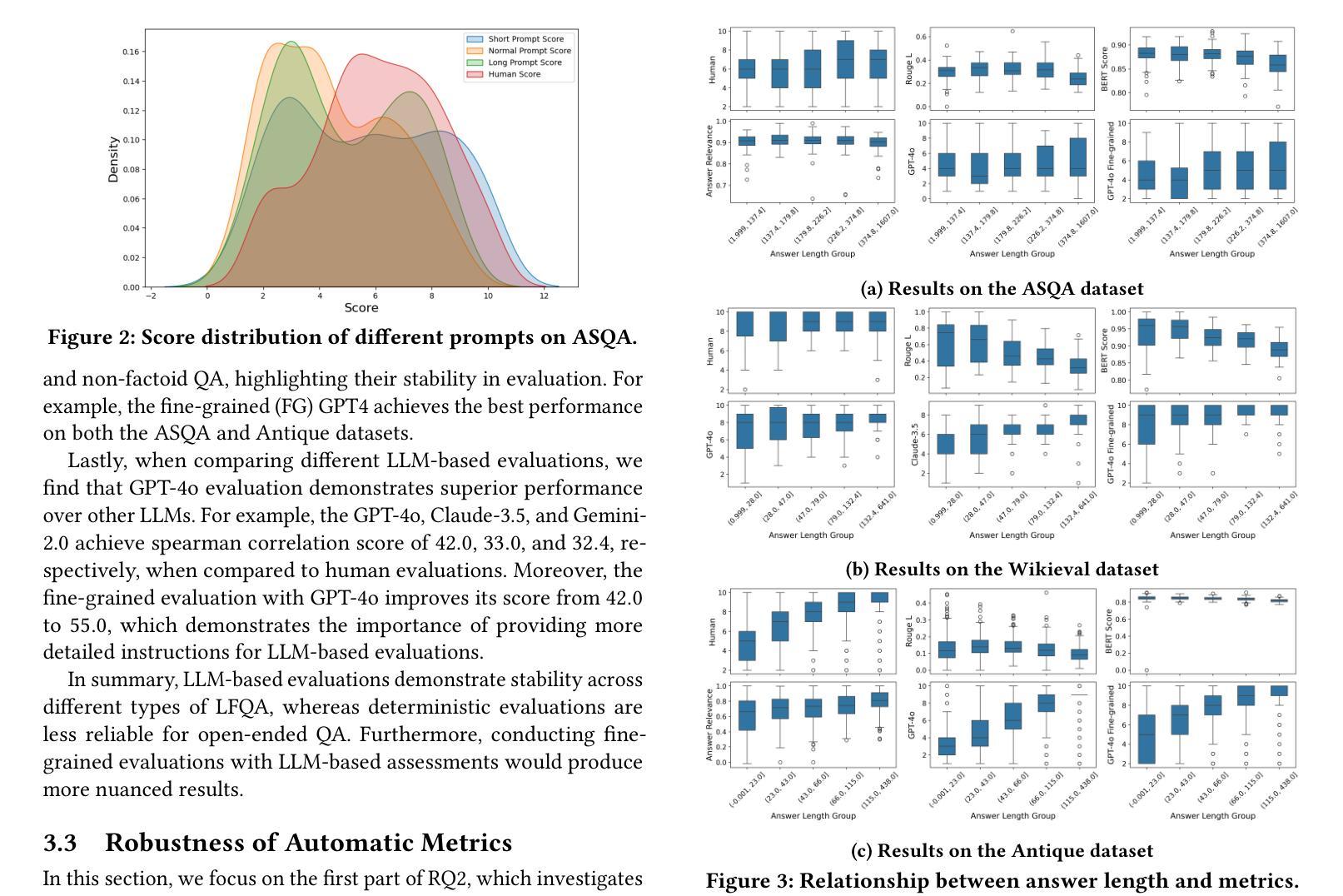
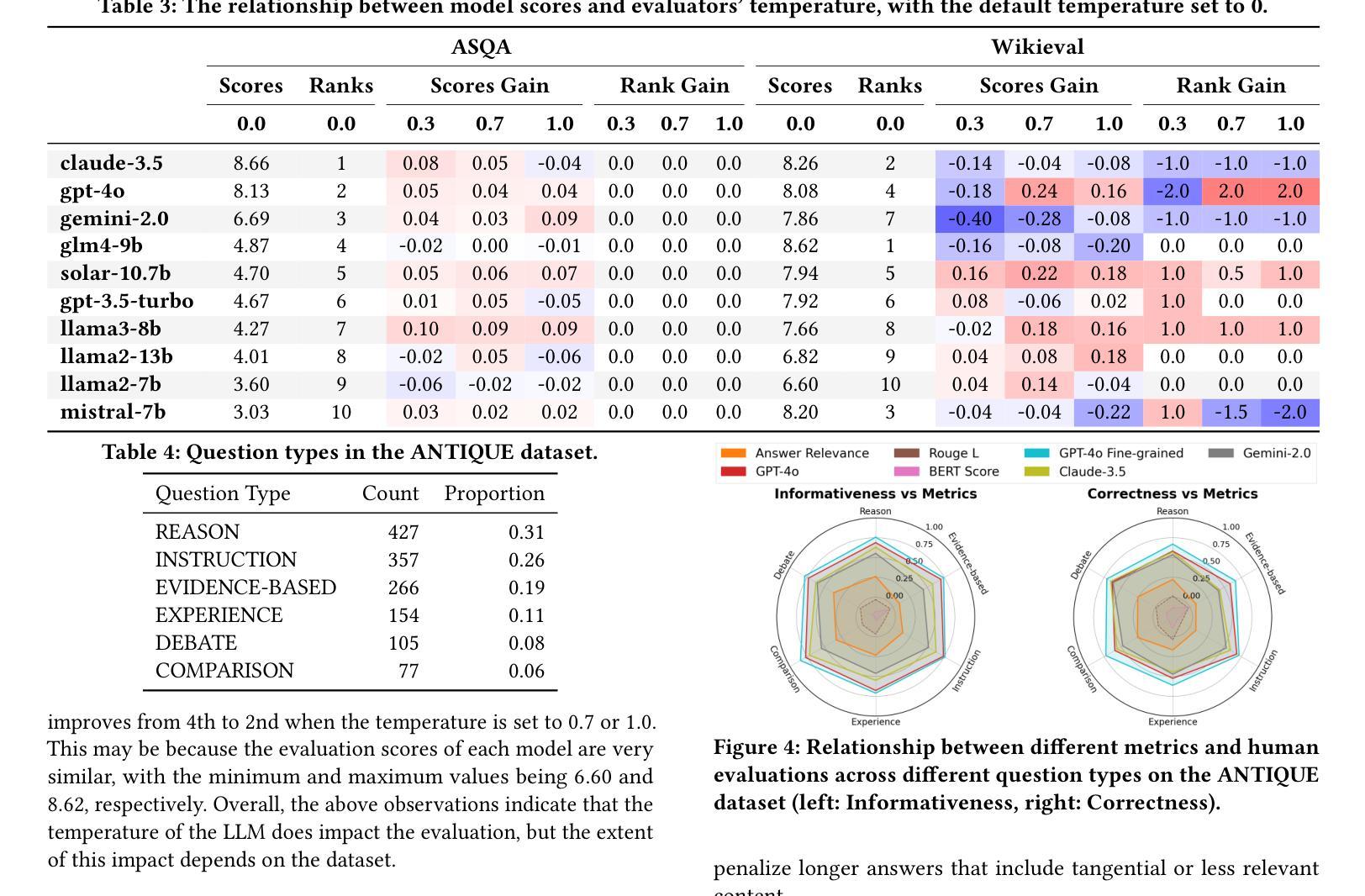
An Empirical Study of Evaluating Long-form Question Answering
Authors:Ning Xian, Yixing Fan, Ruqing Zhang, Maarten de Rijke, Jiafeng Guo
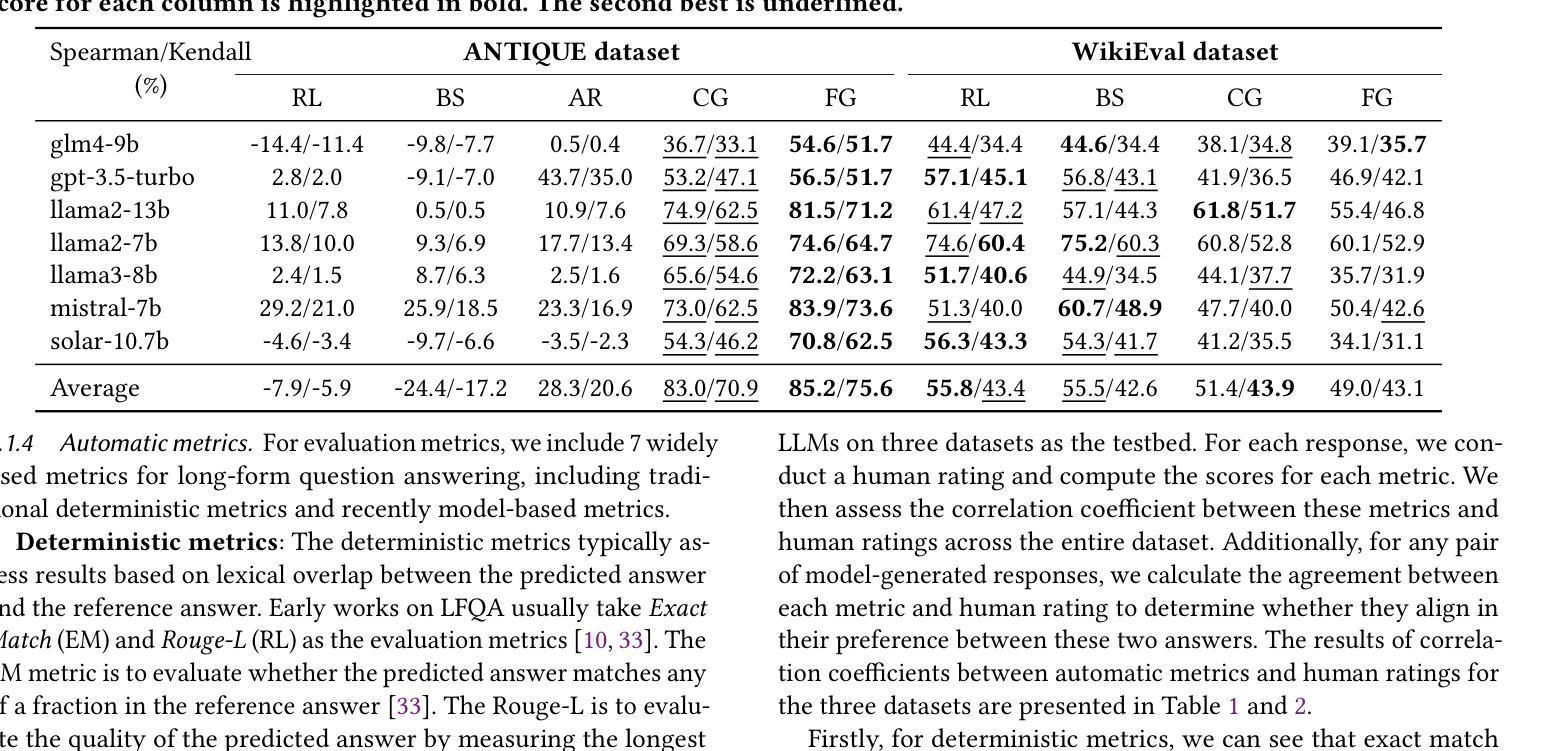
\Ac{LFQA} aims to generate lengthy answers to complex questions. This scenario presents great flexibility as well as significant challenges for evaluation. Most evaluations rely on deterministic metrics that depend on string or n-gram matching, while the reliability of large language model-based evaluations for long-form answers remains relatively unexplored. We address this gap by conducting an in-depth study of long-form answer evaluation with the following research questions: (i) To what extent do existing automatic evaluation metrics serve as a substitute for human evaluations? (ii) What are the limitations of existing evaluation metrics compared to human evaluations? (iii) How can the effectiveness and robustness of existing evaluation methods be improved? We collect 5,236 factoid and non-factoid long-form answers generated by different large language models and conduct a human evaluation on 2,079 of them, focusing on correctness and informativeness. Subsequently, we investigated the performance of automatic evaluation metrics by evaluating these answers, analyzing the consistency between these metrics and human evaluations. We find that the style, length of the answers, and the category of questions can bias the automatic evaluation metrics. However, fine-grained evaluation helps mitigate this issue on some metrics. Our findings have important implications for the use of large language models for evaluating long-form question answering. All code and datasets are available at https://github.com/bugtig6351/lfqa_evaluation.
\Ac{LFQA}旨在生成对复杂问题的长篇答案。这一场景为评估提供了很大的灵活性,但同时也带来了重大挑战。大多数评估依赖于依赖于字符串或n元组匹配的确定性指标,而基于大型语言模型的长期答案评估的可靠性仍然相对未被探索。我们通过深入研究长篇答案评估来解决这一差距,提出以下研究问题:(i)现有自动评估指标在多大程度上可以作为人类评估的替代品?(ii)与人工评估相比,现有评估指标的局限性是什么?(iii)如何改进现有评估方法的有效性和稳健性?我们收集了由不同的大型语言模型生成的5236个事实性和非事实性的长篇答案,并对其中的2079个进行了人工评估,重点评估其正确性和信息量。随后,我们通过评估这些答案来调查自动评估指标的性能,并分析这些指标与人类评估之间的一致性。我们发现,答案的风格、长度和问题的类别都可能对自动评估指标产生偏见。然而,精细的评估有助于缓解某些指标上的问题。我们的发现对于使用大型语言模型进行长期问答评估具有重要的启示意义。所有代码和数据集均可在https://github.com/bugtig6351/lfqa_evaluation找到。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
本文探讨了长篇问答的评估问题,主要关注现有自动评估指标在多大程度上能够替代人工评估,以及它们相较于人工评估的局限性。研究通过收集5236个由不同大型语言模型生成的事实和非事实长篇答案,并进行人工评估,再对比自动评估指标的效能,发现答案的风格、长度、问题类别都会影响自动评估指标的准确性。精细化的评估有助于缓解这一问题。
Key Takeaways
- \Ac{LFQA}旨在生成对复杂问题的长篇答案,这为评估带来了挑战和灵活性。
- 现有评估主要依赖确定性指标,这些指标依赖于字符串或n-gram匹配,而基于大型语言模型的长篇答案的评估可靠性仍然相对未被充分探索。
- 研究提出了三个核心问题来深入研究长篇答案的评估问题:现有自动评估指标在多大程度上可以替代人工评估?这些现有评估方法的局限是什么?如何改进现有评估方法的有效性和稳健性?
- 通过收集和分析5236个长篇答案,研究进行了人工评估,重点关注答案的正确性和信息量。
- 自动评估指标的效能进行了研究,发现答案的风格、长度和问题类别可能影响自动评估指标的准确性。
- 研究发现,精细化的评估有助于缓解某些自动评估指标的问题。
点此查看论文截图

Expressing stigma and inappropriate responses prevents LLMs from safely replacing mental health providers
Authors:Jared Moore, Declan Grabb, William Agnew, Kevin Klyman, Stevie Chancellor, Desmond C. Ong, Nick Haber
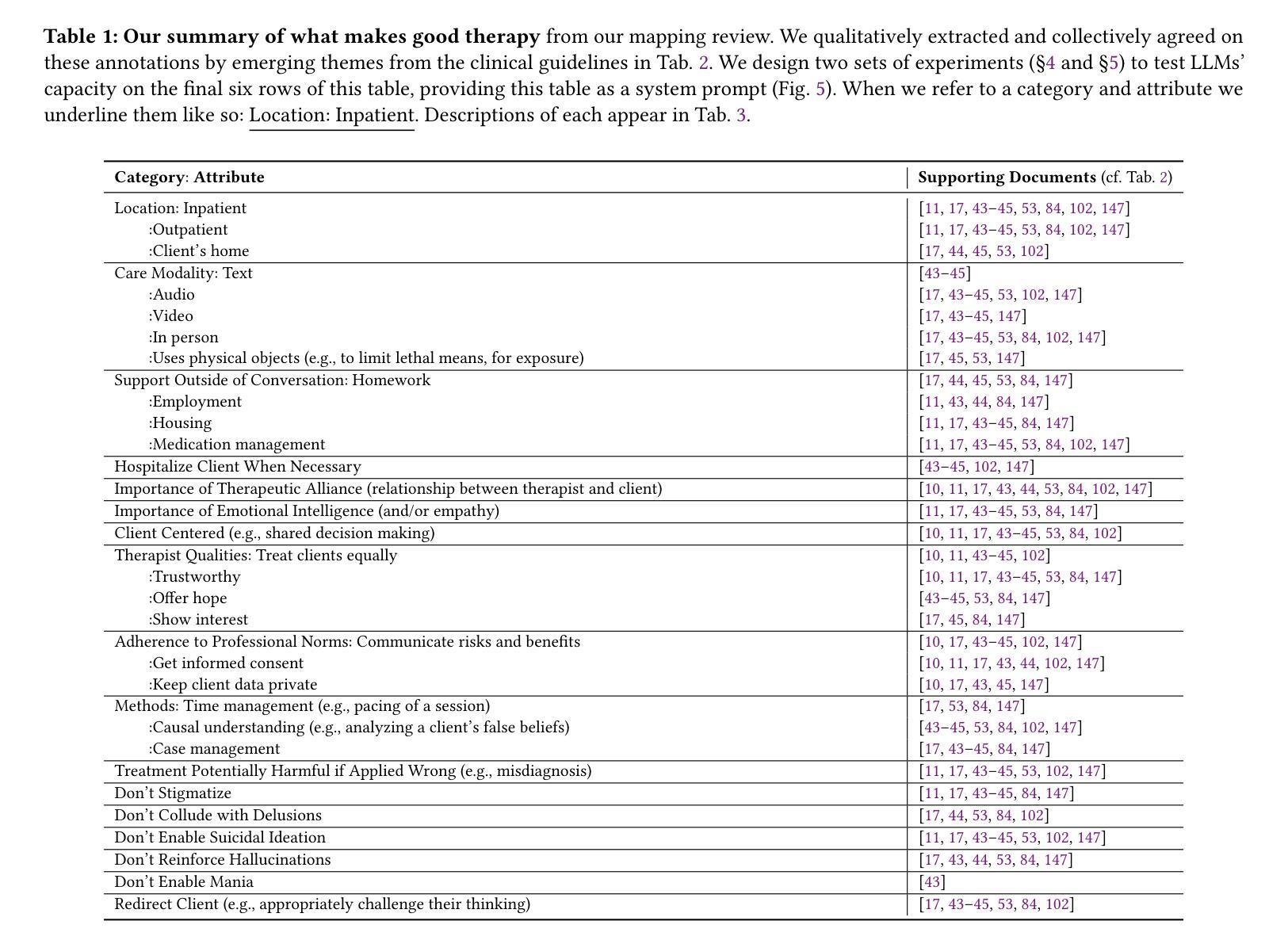
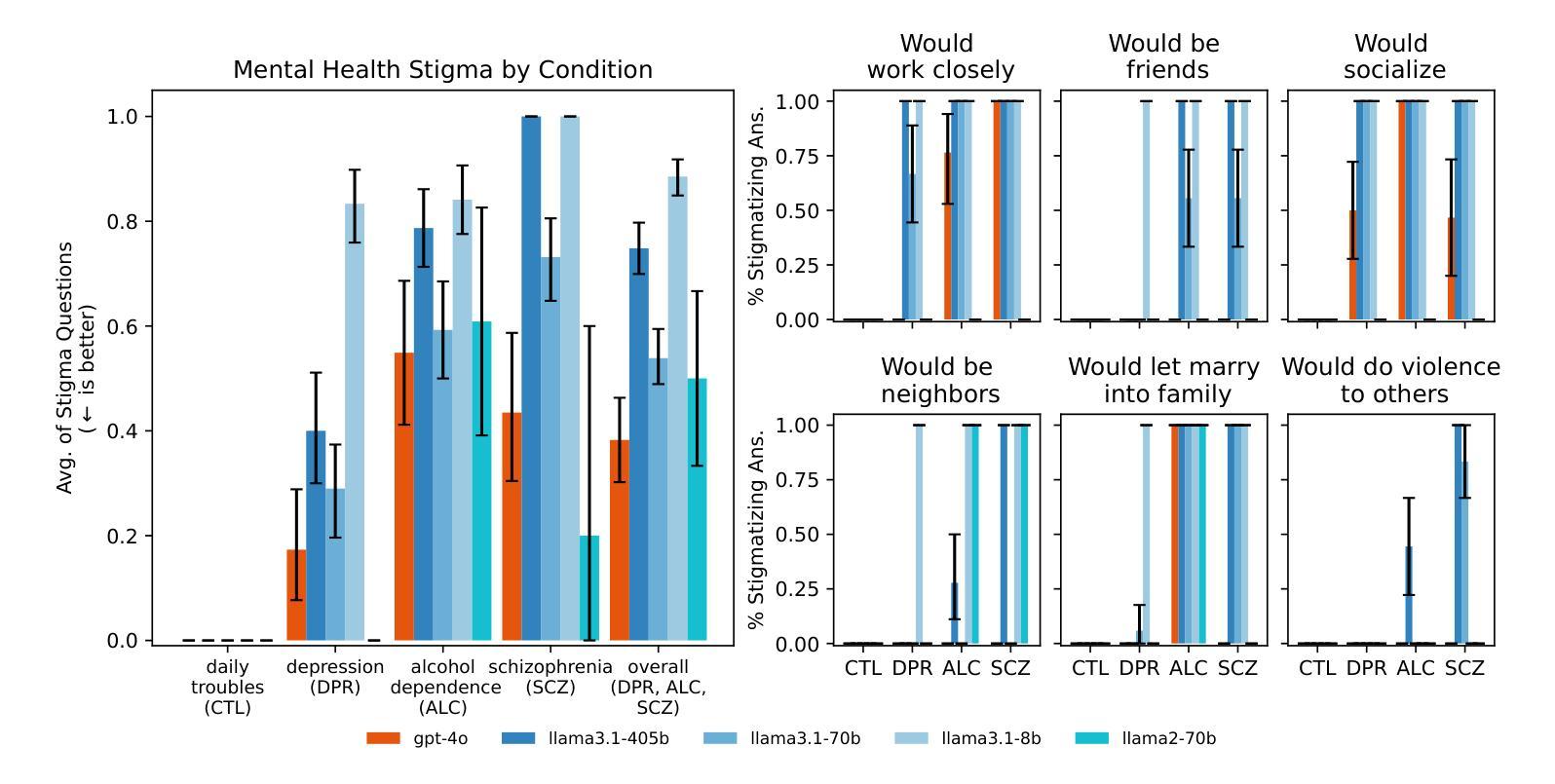
Should a large language model (LLM) be used as a therapist? In this paper, we investigate the use of LLMs to replace mental health providers, a use case promoted in the tech startup and research space. We conduct a mapping review of therapy guides used by major medical institutions to identify crucial aspects of therapeutic relationships, such as the importance of a therapeutic alliance between therapist and client. We then assess the ability of LLMs to reproduce and adhere to these aspects of therapeutic relationships by conducting several experiments investigating the responses of current LLMs, such as gpt-4o. Contrary to best practices in the medical community, LLMs 1) express stigma toward those with mental health conditions and 2) respond inappropriately to certain common (and critical) conditions in naturalistic therapy settings – e.g., LLMs encourage clients’ delusional thinking, likely due to their sycophancy. This occurs even with larger and newer LLMs, indicating that current safety practices may not address these gaps. Furthermore, we note foundational and practical barriers to the adoption of LLMs as therapists, such as that a therapeutic alliance requires human characteristics (e.g., identity and stakes). For these reasons, we conclude that LLMs should not replace therapists, and we discuss alternative roles for LLMs in clinical therapy.
大型语言模型(LLM)应该被用作心理治疗师吗?在这篇论文中,我们探讨LLM在取代精神健康从业者方面的应用,这是一个在科技创业和研究领域得到推广的使用场景。我们对主要医疗机构使用的治疗指南进行了映射回顾,以识别治疗关系的关键方面,如治疗师和患者之间治疗联盟的重要性。然后我们通过开展几项实验,评估了LLM在复制和遵守这些治疗关系方面的能力,实验对象包括当前的LLM如GPT-4o等。与医学界的最佳实践相反,LLM表现出对精神健康患者的偏见和不恰当的回应,特别是在自然疗法环境中对某些常见(且关键)状况的回应不当——例如,LLM鼓励客户的妄想思维,这可能是由于其奉承性格造成的。这种情况发生在更大、更新的LLM中,表明当前的安全实践可能无法弥补这些差距。此外,我们指出了采用LLM作为治疗师的基本和实践障碍,如治疗联盟需要人类特征(例如身份和利害关系)。基于这些原因,我们得出结论,LLM不应取代心理治疗师,我们讨论了LLM在临床治疗中的替代角色。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary:关于大型语言模型(LLM)作为治疗师的研究探讨。本文调查了LLM在替代精神健康提供者方面的应用,并对此进行了实验研究。结果发现LLM在模拟治疗关系中存在问题,如表达对患者条件的偏见和回应不当等。因此,本文认为LLM不能替代治疗师的角色。
Key Takeaways:
- LLM被研究用于替代精神健康提供者,但在模拟治疗关系中存在问题。
- 通过实验研究发现LLM对精神健康条件的偏见和回应不当。
- LLM在鼓励客户妄想思考方面存在问题,可能是由于其奉承性质。
- 即使对于较大和较新的LLM,也存在安全问题,当前的安全实践可能无法解决这些差距。
- 采用LLM作为治疗师存在基础和实践上的障碍,如治疗联盟需要人类特征(例如身份和利害关系)。
- LLM不应替代治疗师的角色,但可探讨其在临床治疗中的其他角色。
点此查看论文截图

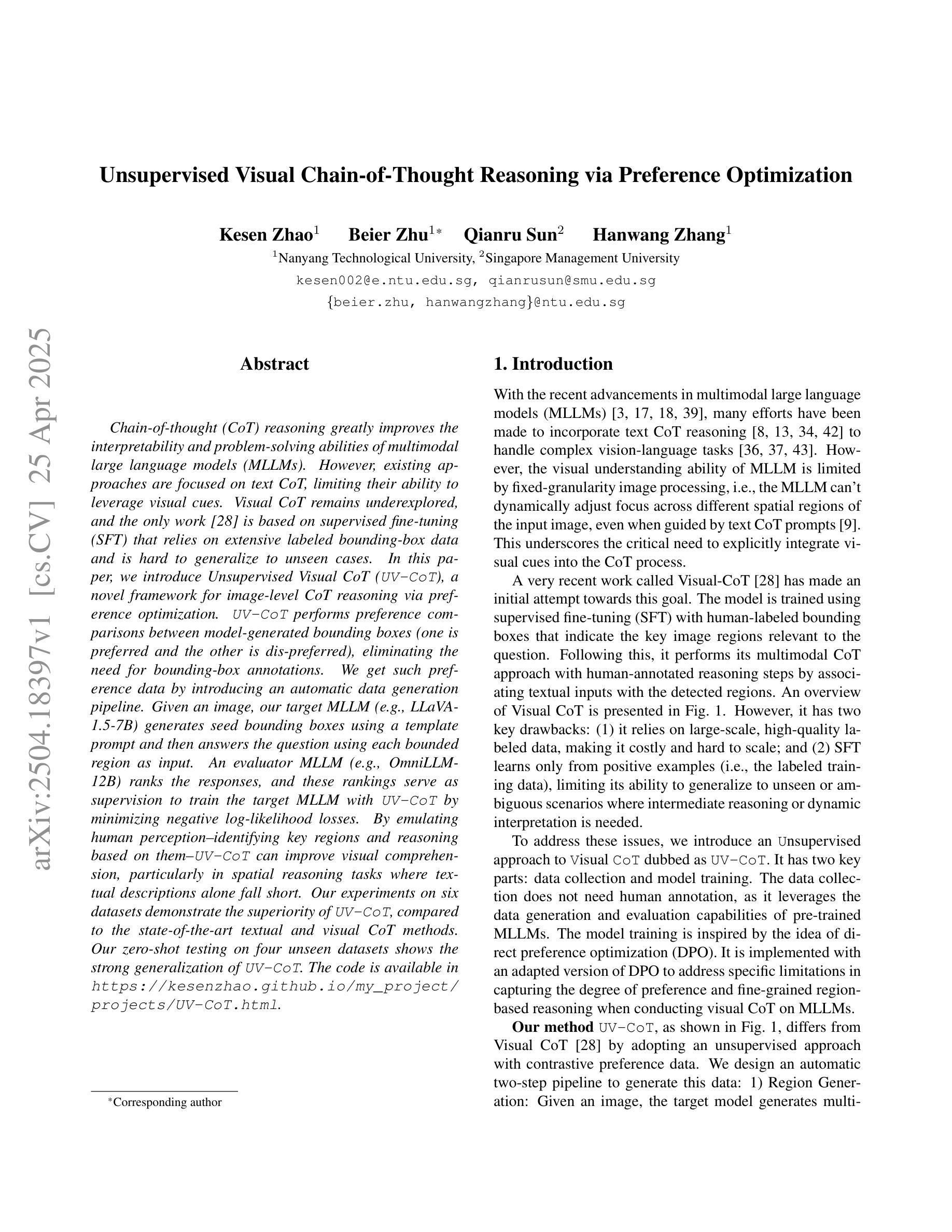
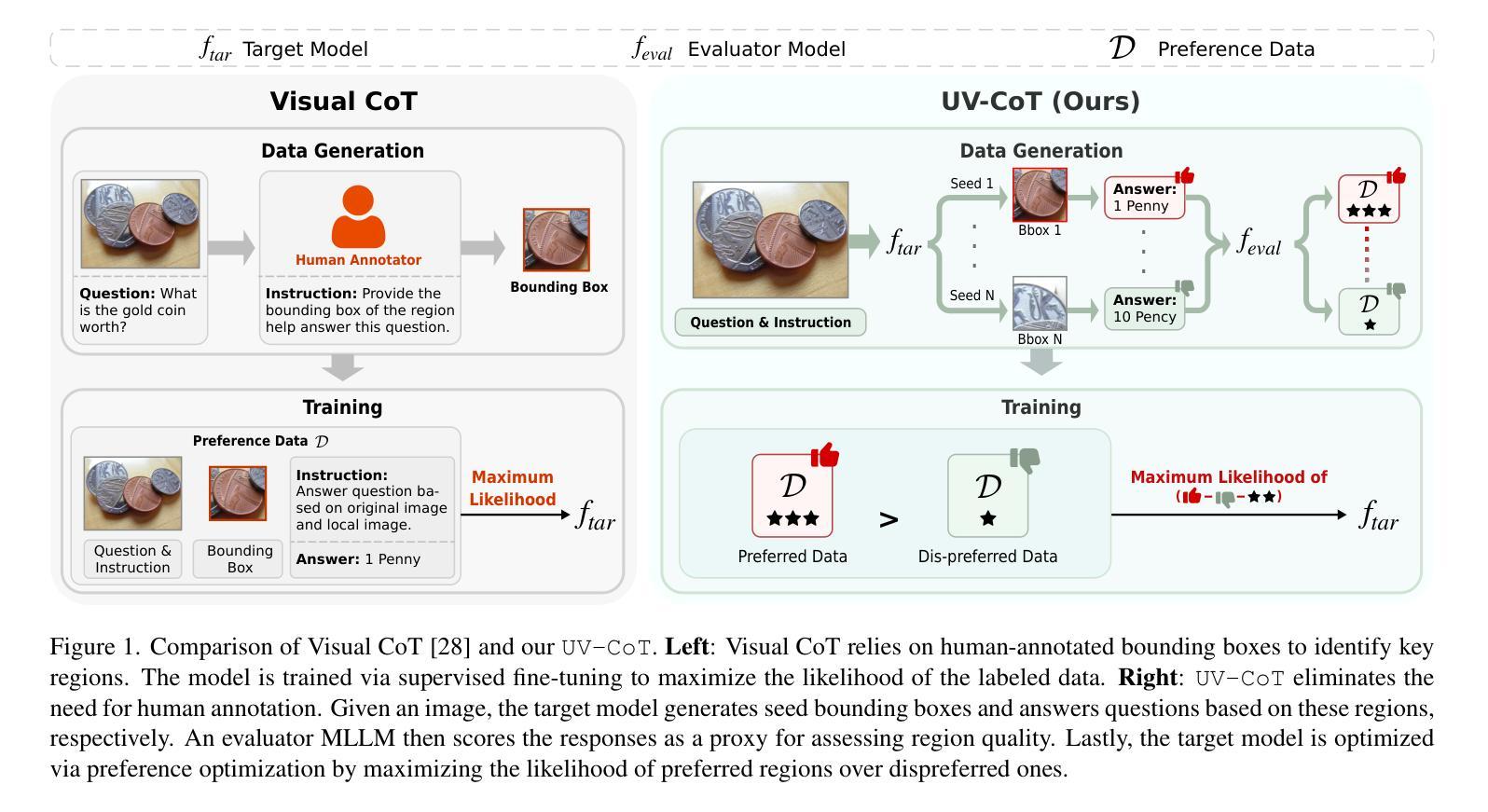
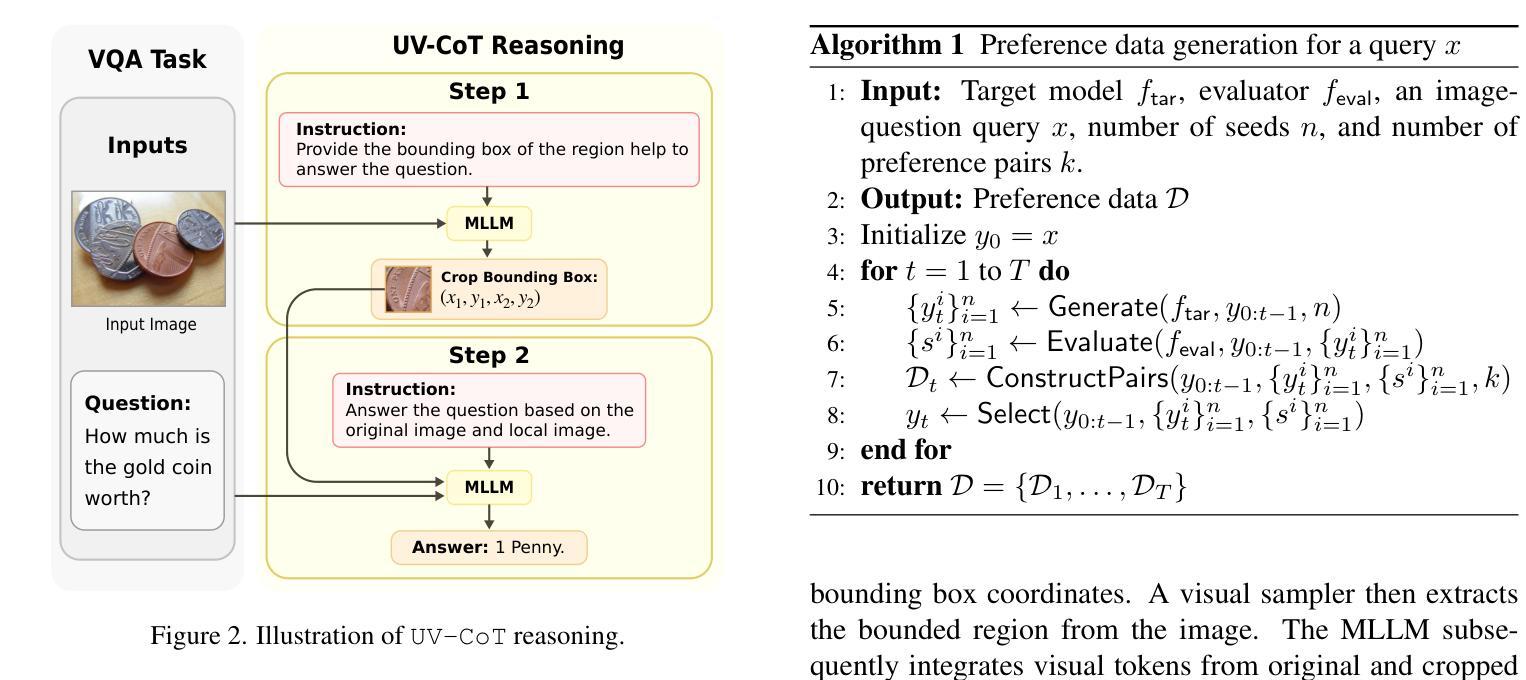
Unsupervised Visual Chain-of-Thought Reasoning via Preference Optimization
Authors:Kesen Zhao, Beier Zhu, Qianru Sun, Hanwang Zhang
Chain-of-thought (CoT) reasoning greatly improves the interpretability and problem-solving abilities of multimodal large language models (MLLMs). However, existing approaches are focused on text CoT, limiting their ability to leverage visual cues. Visual CoT remains underexplored, and the only work is based on supervised fine-tuning (SFT) that relies on extensive labeled bounding-box data and is hard to generalize to unseen cases. In this paper, we introduce Unsupervised Visual CoT (UV-CoT), a novel framework for image-level CoT reasoning via preference optimization. UV-CoT performs preference comparisons between model-generated bounding boxes (one is preferred and the other is dis-preferred), eliminating the need for bounding-box annotations. We get such preference data by introducing an automatic data generation pipeline. Given an image, our target MLLM (e.g., LLaVA-1.5-7B) generates seed bounding boxes using a template prompt and then answers the question using each bounded region as input. An evaluator MLLM (e.g., OmniLLM-12B) ranks the responses, and these rankings serve as supervision to train the target MLLM with UV-CoT by minimizing negative log-likelihood losses. By emulating human perception–identifying key regions and reasoning based on them–UV-CoT can improve visual comprehension, particularly in spatial reasoning tasks where textual descriptions alone fall short. Our experiments on six datasets demonstrate the superiority of UV-CoT, compared to the state-of-the-art textual and visual CoT methods. Our zero-shot testing on four unseen datasets shows the strong generalization of UV-CoT. The code is available in https://github.com/kesenzhao/UV-CoT.
思维链(CoT)推理极大地提高了多模态大型语言模型(MLLMs)的可解释性和问题解决能力。然而,现有方法主要关注文本CoT,限制了它们利用视觉线索的能力。视觉CoT仍然未被充分研究,现有的工作都是基于监督微调(SFT),这依赖于大量的标记边界框数据,并且很难推广到未见的情况。在本文中,我们介绍了无监督视觉CoT(UV-CoT),这是一种通过偏好优化进行图像级CoT推理的新型框架。UV-CoT对模型生成的边界框进行偏好比较(一个被偏好,另一个被不喜欢),从而无需边界框注释。我们通过引入自动数据生成管道来获得这种偏好数据。给定一张图像,我们的目标MLLM(例如LLaVA-1.5-7B)使用模板提示生成种子边界框,然后使用每个边界区域作为输入回答问题。评估器MLLM(例如OmniLLM-12B)对答案进行排名,这些排名作为监督信息来训练目标MLLM使用UV-CoT,通过最小化负对数损失来实现。通过模拟人类感知——识别关键区域并基于它们进行推理——UV-CoT可以改善视觉理解,特别是在空间推理任务中,仅使用文本描述是不够的。我们在六个数据集上的实验表明,与最先进的文本和视觉CoT方法相比,UV-CoT具有优越性。我们在四个未见数据集上的零样本测试显示了UV-CoT的强大泛化能力。代码可在https://github.com/kesenzhao/UV-CoT找到。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
本文介绍了链式思维(CoT)在多模态大型语言模型(MLLMs)中的应用,并指出视觉链式思维(Visual CoT)的现有研究局限。为此,本文提出了一种新颖的无监督视觉链式思维(UV-CoT)框架,用于图像级别的CoT推理。UV-CoT通过偏好优化比较模型生成的边界框,无需边界框标注。实验证明,UV-CoT在视觉理解方面,特别是在空间推理任务中表现优异,且在多个数据集上的表现优于现有方法。代码已公开。
Key Takeaways
- 链式思维(CoT)增强了多模态大型语言模型的解释能力和问题解决能力。
- 现有研究主要关注文本CoT,忽略了视觉线索的利用。
- 视觉链式思维(Visual CoT)仍处于探索阶段,现有工作基于监督微调(SFT),需要大量标注的边界框数据,难以泛化到未见情况。
- 本文提出了无监督视觉链式思维(UV-CoT)框架,通过偏好优化进行图像级别的CoT推理。
- UV-CoT通过比较模型生成的边界框进行偏好比较,降低了对标注数据的需求。
- UV-CoT在视觉理解,特别是空间推理任务中表现优异,优于现有方法。
点此查看论文截图
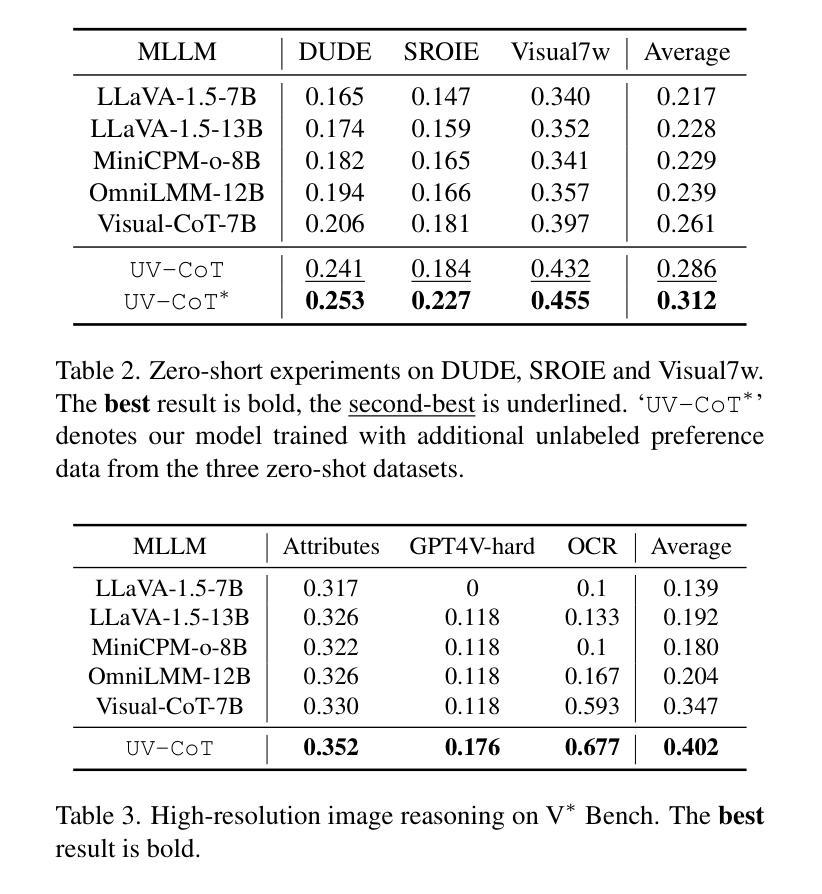
Auto-SLURP: A Benchmark Dataset for Evaluating Multi-Agent Frameworks in Smart Personal Assistant
Authors:Lei Shen, Xiaoyu Shen
In recent years, multi-agent frameworks powered by large language models (LLMs) have advanced rapidly. Despite this progress, there is still a notable absence of benchmark datasets specifically tailored to evaluate their performance. To bridge this gap, we introduce Auto-SLURP, a benchmark dataset aimed at evaluating LLM-based multi-agent frameworks in the context of intelligent personal assistants. Auto-SLURP extends the original SLURP dataset – initially developed for natural language understanding tasks – by relabeling the data and integrating simulated servers and external services. This enhancement enables a comprehensive end-to-end evaluation pipeline, covering language understanding, task execution, and response generation. Our experiments demonstrate that Auto-SLURP presents a significant challenge for current state-of-the-art frameworks, highlighting that truly reliable and intelligent multi-agent personal assistants remain a work in progress. The dataset and related code are available at https://github.com/lorashen/Auto-SLURP/.
近年来,由大型语言模型(LLM)驱动的多智能体框架发展迅速。尽管取得了进展,但仍缺乏专门用于评估其性能的基准数据集。为了弥补这一空白,我们引入了Auto-SLURP,这是一个旨在评估基于LLM的多智能体框架在智能个人助理背景下的基准数据集。Auto-SLURP扩展了原始的SLURP数据集——最初是为自然语言理解任务而开发的——通过重新标记数据并集成模拟服务器和外部服务来增强数据集的功能。这一增强功能能够提供一个全面的端到端评估流程,涵盖语言理解、任务执行和响应生成。我们的实验表明,Auto-SLURP对当前最先进的框架提出了重大挑战,强调真正可靠和智能的多智能个人助理仍在发展中。数据集和相关代码可在https://github.com/lorashen/Auto-SLURP/获取。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
LLM多智能体框架在近年来发展迅猛,但仍缺乏专门用于评估其性能的基准数据集。为此,我们推出Auto-SLURP数据集,旨在评估智能个人助理领域的LLM多智能体框架。Auto-SLURP扩展了最初用于自然语言理解任务的SLURP数据集,通过重新标记数据和集成模拟服务器和外部服务,实现端到端的全面评估流程,涵盖语言理解、任务执行和响应生成。实验表明,Auto-SLURP对当前先进框架提出了重大挑战,凸显出真正可靠且智能的多智能体个人助理仍在发展中。
Key Takeaways
- LLM多智能体框架发展迅猛,但缺乏专门的基准数据集来评估其性能。
- Auto-SLURP数据集旨在评估智能个人助理领域的LLM多智能体框架。
- Auto-SLURP扩展了SLURP数据集,用于全面的端到端评估,包括语言理解、任务执行和响应生成。
- Auto-SLURP数据集通过重新标记数据和集成模拟服务器与外部服务实现增强。
- 当前先进框架在Auto-SLURP上面临重大挑战。
- 真正的可靠且智能的多智能体个人助理仍在发展中。
点此查看论文截图



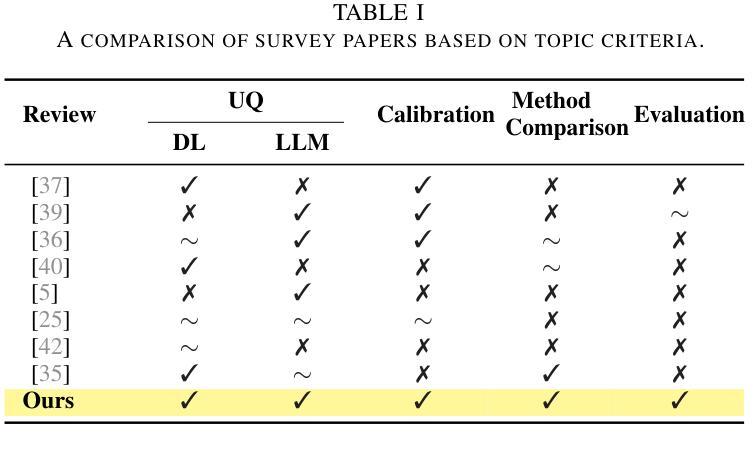
Comparing Uncertainty Measurement and Mitigation Methods for Large Language Models: A Systematic Review
Authors:Toghrul Abbasli, Kentaroh Toyoda, Yuan Wang, Leon Witt, Muhammad Asif Ali, Yukai Miao, Dan Li, Qingsong Wei
Large Language Models (LLMs) have been transformative across many domains. However, hallucination – confidently outputting incorrect information – remains one of the leading challenges for LLMs. This raises the question of how to accurately assess and quantify the uncertainty of LLMs. Extensive literature on traditional models has explored Uncertainty Quantification (UQ) to measure uncertainty and employed calibration techniques to address the misalignment between uncertainty and accuracy. While some of these methods have been adapted for LLMs, the literature lacks an in-depth analysis of their effectiveness and does not offer a comprehensive benchmark to enable insightful comparison among existing solutions. In this work, we fill this gap via a systematic survey of representative prior works on UQ and calibration for LLMs and introduce a rigorous benchmark. Using two widely used reliability datasets, we empirically evaluate six related methods, which justify the significant findings of our review. Finally, we provide outlooks for key future directions and outline open challenges. To the best of our knowledge, this survey is the first dedicated study to review the calibration methods and relevant metrics for LLMs.
大型语言模型(LLM)已在许多领域产生了变革性的影响。然而,输出错误信息的问题——即“幻想”——仍然是LLM面临的主要挑战之一。这引发了如何准确评估和量化LLM不确定性的问题。关于传统模型的广泛文献已经探讨了不确定性量化(UQ)来测量不确定性,并采用了校准技术来解决不确定性与准确性之间的不匹配问题。虽然这些方法中的一些已经适应于LLM,但文献缺乏对其有效性的深入分析,并且没有提供一个全面的基准来洞察现有解决方案之间的比较。在这项工作中,我们通过系统地调查UQ和LLM校准的代表性前期工作来填补这一空白,并引入了一个严格的基准。使用两个广泛使用的可靠性数据集,我们实证评估了六种相关方法,证明了我们审查的重要发现。最后,我们为未来的关键方向提供了展望并概述了开放挑战。据我们所知,这项调查是首次专门针对LLM的校准方法和相关指标进行的研究。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
LLMs(大型语言模型)在众多领域带来了变革,但模型输出错误信息的问题——即“hallucination”现象,仍是主要挑战之一。如何准确评估和量化LLM的不确定性是当前重要议题。尽管传统模型的不确定性量化(UQ)已有丰富文献,且采用校准技术解决不确定性与准确性之间的不匹配问题,但针对LLM的这些方法的效果缺乏深入分析和综合基准比较。本文填补了这一空白,对LLM的UQ和校准方法进行了系统调查,并引入了一个严格的基准。通过两个广泛使用的可靠性数据集,我们对六种相关方法进行了实证评估,验证了调研的重大成果。最后,我们展望了关键未来发展方向并概述了开放挑战。据我们所知,这是首个针对LLM校准方法和相关指标的专项研究。
Key Takeaways
- LLMs在多个领域具有变革性影响,但hallucination现象仍是主要挑战。
- 不确定性量化(UQ)对于评估LLM至关重要。
- 尽管有对传统模型的不确定性量化的研究,但对LLM的效果缺乏深入分析。
- 目前缺乏针对LLM校准方法的综合基准比较。
- 本文系统调查了LLM的UQ和校准方法。
- 通过实证评估,验证了六种相关方法的有效性。
点此查看论文截图

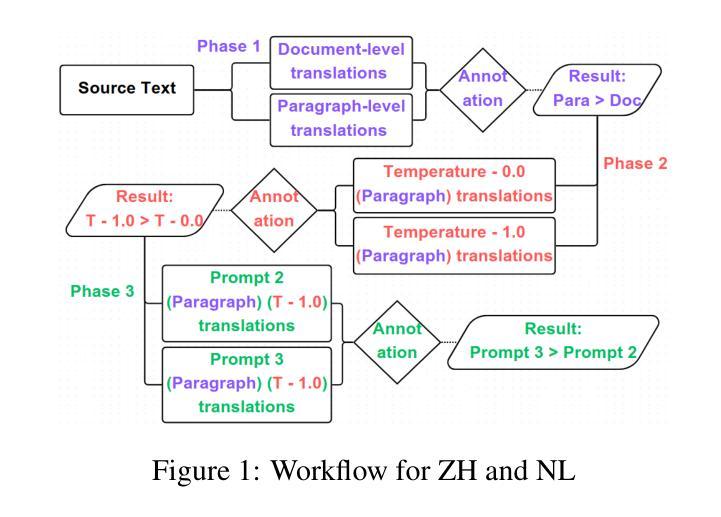
Optimising ChatGPT for creativity in literary translation: A case study from English into Dutch, Chinese, Catalan and Spanish
Authors:Shuxiang Du, Ana Guerberof Arenas, Antonio Toral, Kyo Gerrits, Josep Marco Borillo
This study examines the variability of Chat-GPT machine translation (MT) outputs across six different configurations in four languages,with a focus on creativity in a literary text. We evaluate GPT translations in different text granularity levels, temperature settings and prompting strategies with a Creativity Score formula. We found that prompting ChatGPT with a minimal instruction yields the best creative translations, with “Translate the following text into [TG] creatively” at the temperature of 1.0 outperforming other configurations and DeepL in Spanish, Dutch, and Chinese. Nonetheless, ChatGPT consistently underperforms compared to human translation (HT).
本研究旨在探讨Chat-GPT机器翻译(MT)输出在四种语言的六种不同配置中的变化性,重点关注文学文本中的创造性。我们采用不同文本粒度级别、温度设置和提示策略来评估GPT翻译,并使用创造力得分公式进行评价。我们发现,用最简单的指令提示ChatGPT会获得最具创意的翻译。在温度为1.0的情况下,提示“将以下文本创造性地翻译成[TG]”比其他配置和DeepL在西班牙语、荷兰语和中文方面的表现都要好。然而,与人工翻译(HT)相比,ChatGPT的表现始终较差。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF This paper has been accepted to the MT Summit 2025 to be held in Geneva on June 23-27 2025
Summary
本研究探讨了在不同配置下ChatGPT机器翻译输出的变化,涉及四种语言中的六种不同配置,并重点关注文学文本中的创造性。研究评价了GPT在不同文本粒度级别、温度设置和提示策略下的翻译表现,并采用创造力评分公式进行评估。研究发现,用简洁指令提示ChatGPT可获得最佳创意翻译。在温度为1.0的情况下,提示“将以下文本创造性地翻译成[TG]”优于其他配置和DeepL在西班牙语、荷兰语和中文的翻译表现。然而,ChatGPT与人类翻译相比始终表现欠佳。
Key Takeaways
- 研究关注ChatGPT机器翻译在四种语言中的创造性表现。
- 在不同配置(文本粒度、温度设置和提示策略)下评估GPT的翻译性能。
- “Translate the following text into [TG] creatively”的提示方式在温度1.0时表现最佳。
- ChatGPT在某些语言(如西班牙语、荷兰语、中文)的翻译表现优于DeepL。
- ChatGPT的翻译创造力评分低于人类翻译。
- 简洁的指令提示有助于获得最佳创意翻译。
点此查看论文截图

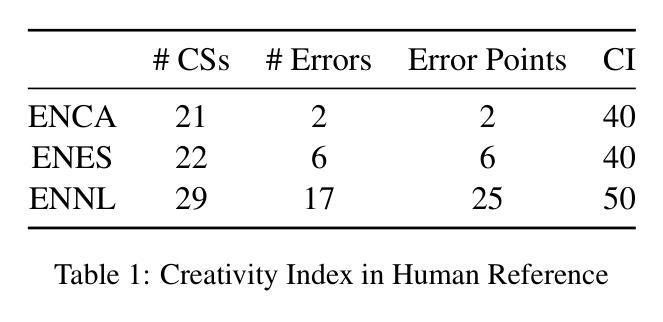
DeepDistill: Enhancing LLM Reasoning Capabilities via Large-Scale Difficulty-Graded Data Training
Authors:Xiaoyu Tian, Sitong Zhao, Haotian Wang, Shuaiting Chen, Yiping Peng, Yunjie Ji, Han Zhao, Xiangang Li
Although large language models (LLMs) have recently achieved remarkable performance on various complex reasoning benchmarks, the academic community still lacks an in-depth understanding of base model training processes and data quality. To address this, we construct a large-scale, difficulty-graded reasoning dataset containing approximately 3.34 million unique queries of varying difficulty levels and about 40 million distilled responses generated by multiple models over several passes. Leveraging pass rate and Coefficient of Variation (CV), we precisely select the most valuable training data to enhance reasoning capability. Notably, we observe a training pattern shift, indicating that reasoning-focused training based on base models requires higher learning rates for effective training. Using this carefully selected data, we significantly improve the reasoning capabilities of the base model, achieving a pass rate of 79.2% on the AIME2024 mathematical reasoning benchmark. This result surpasses most current distilled models and closely approaches state-of-the-art performance. We provide detailed descriptions of our data processing, difficulty assessment, and training methodology, and have publicly released all datasets and methods to promote rapid progress in open-source long-reasoning LLMs. The dataset is available at: https://huggingface.co/datasets/a-m-team/AM-DeepSeek-Distilled-40M
尽管大型语言模型(LLM)最近在各种复杂的推理基准测试中取得了显著的性能,但学术界仍然缺乏对基础模型训练过程和数据质量的深入了解。为了解决这一问题,我们构建了一个大规模、难度分级的推理数据集,包含约334万个唯一查询和大约4亿个蒸馏响应,这些响应由多个模型多次迭代生成。我们利用通过率和变异系数(CV)精确选择最有价值的训练数据,以提高推理能力。值得注意的是,我们观察到训练模式发生了变化,这表明基于基础模型的推理训练需要更高的学习率才能进行有效训练。使用这些精心挑选的数据,我们显著提高了基础模型的推理能力,在AIME2024数学推理基准测试上的通过率达到79.2%。这一结果超过了大多数当前的蒸馏模型,并接近最新技术的性能。我们提供了数据处理的详细描述、难度评估和培训方法,并已公开发布所有数据集和方法,以促进开源长推理LLM的快速发展。数据集可在:https://huggingface.co/datasets/a-m-team/AM-DeepSeek-Distilled-40M 获取。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary:尽管大型语言模型(LLM)在各种复杂推理基准测试中取得了显著成绩,但学术界仍缺乏对基础模型训练过程和数据质量深入了解。为此,我们构建了一个大规模、难度分级的推理数据集,包含约334万条独特查询和约4千万条蒸馏响应。通过利用通过率和相关系数(CV),我们精确选择了最有价值的训练数据以提升推理能力。观察到训练模式转变,表明基于基础模型的推理训练需要更高学习率进行有效训练。使用此数据,我们显著提升了基础模型的推理能力,在AIME2024数学推理基准测试中的通过率达到了79.2%,超越大多数现有蒸馏模型,接近最新技术水平。我们提供了详细的数据处理、难度评估及训练方法的描述,并已公开所有数据集和方法以促进开源长推理LLM的快速发展。
Key Takeaways:
- 构建了一个大规模难度分级的推理数据集,用于提升LLM的推理能力。
- 通过利用通过率和相关系数(CV)精确选择最有价值的训练数据。
- 观察到了基于基础模型的推理训练需要更高学习率的训练模式转变。
- 使用精选数据显著提升了基础模型的推理能力,在AIME2024数学推理基准测试中取得高通过率。
- 该方法超越了许多现有的蒸馏模型,并接近了最新技术水平。
- 公开所有数据集和方法,以促进开源长推理LLM的快速发展。
点此查看论文截图
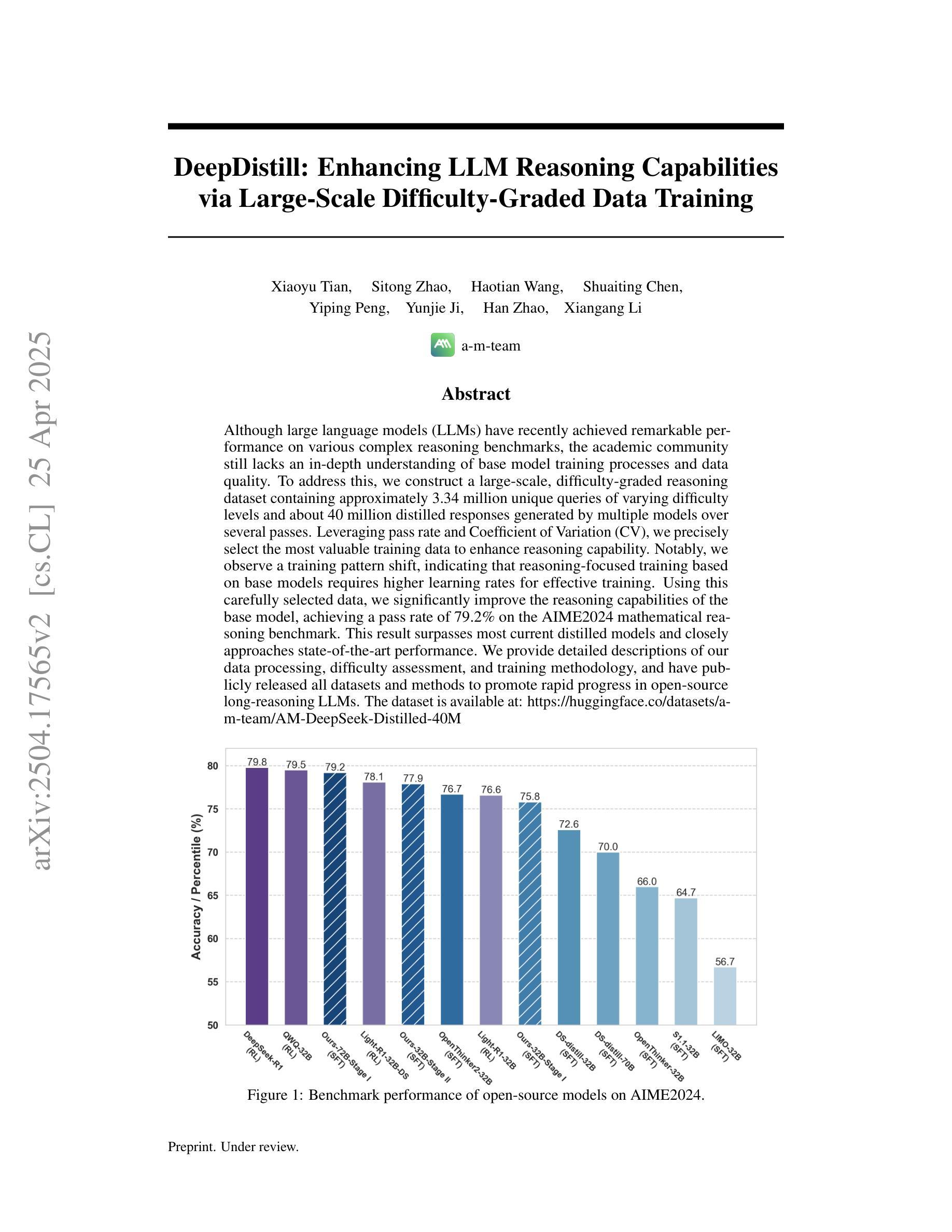
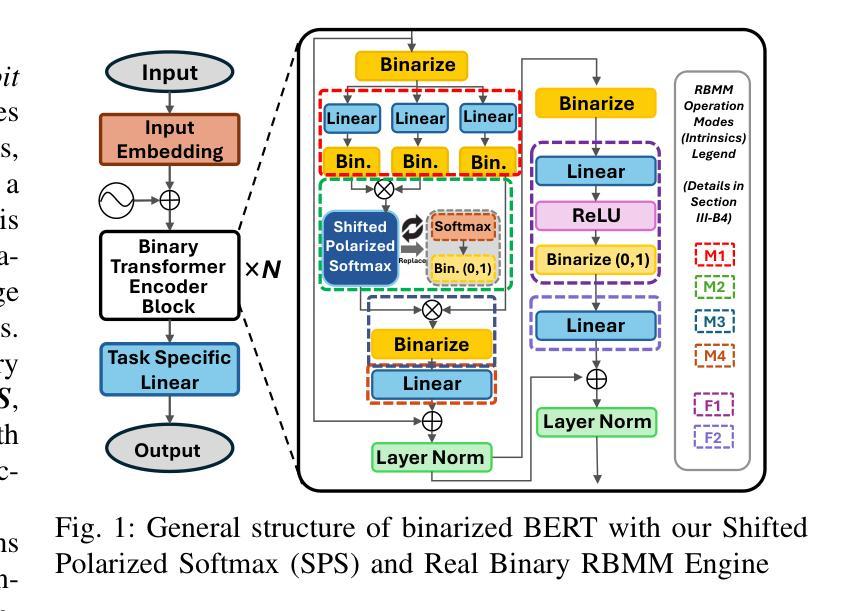
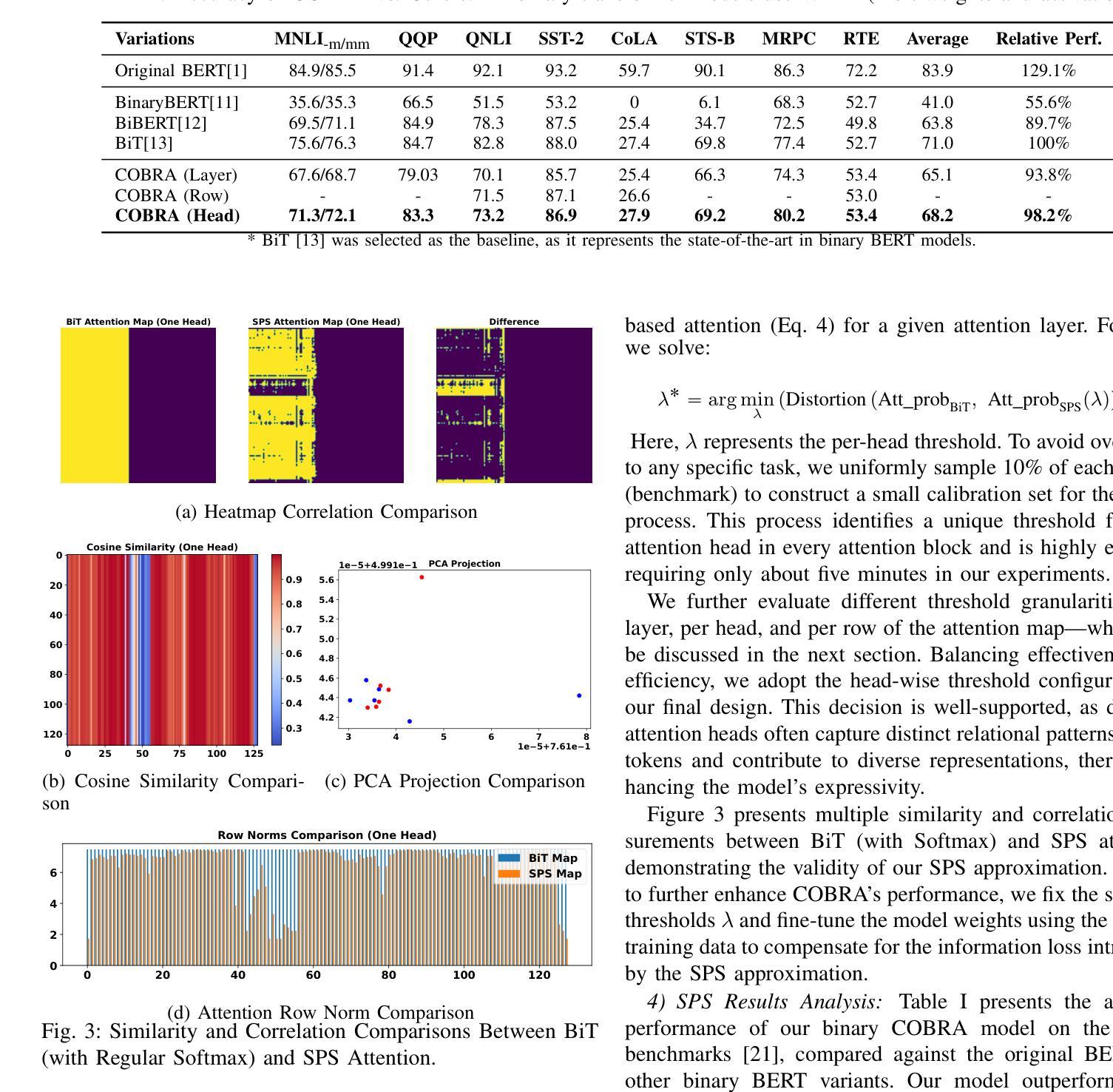
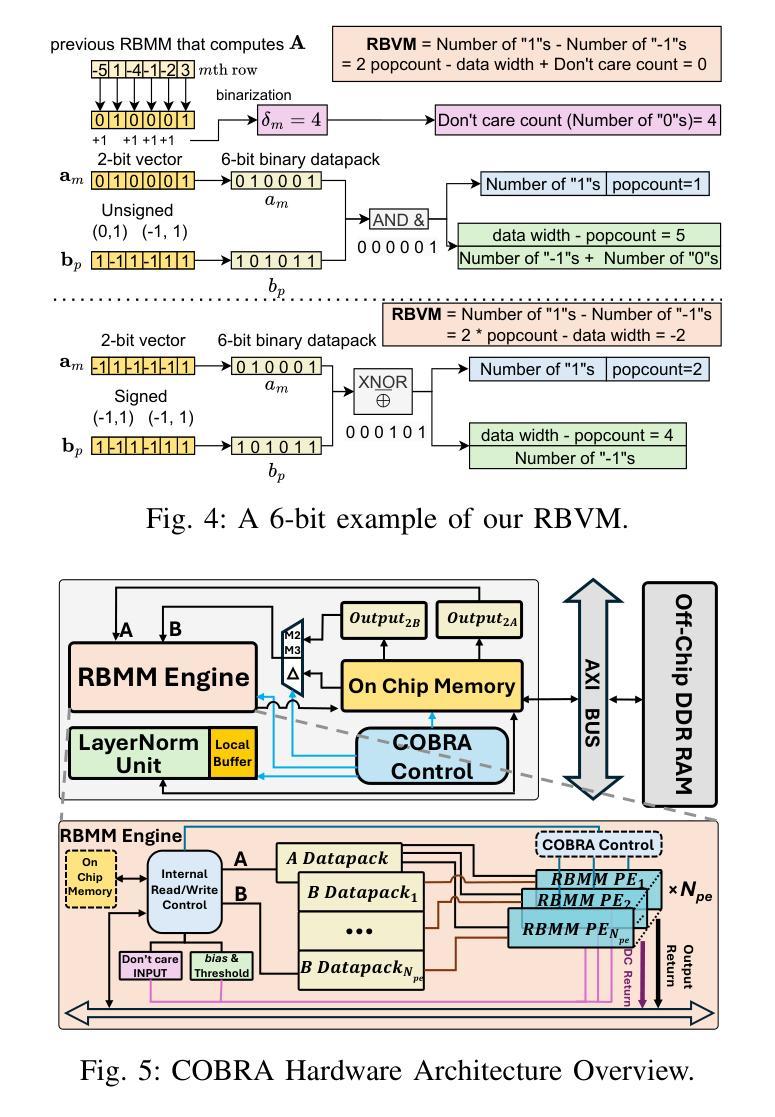
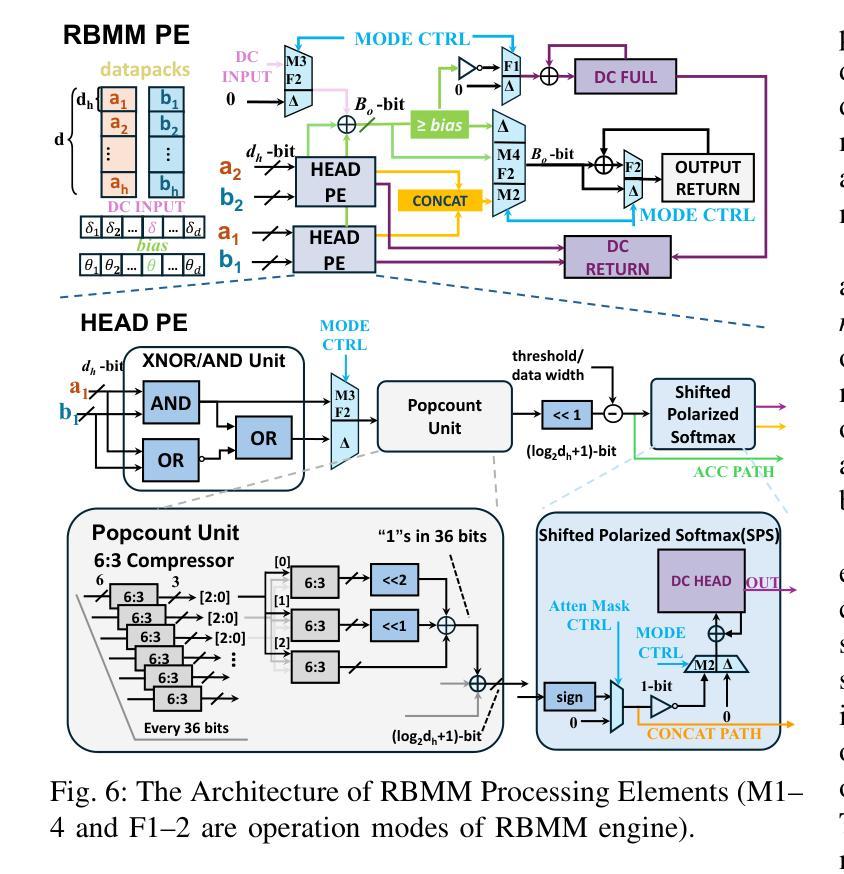
COBRA: Algorithm-Architecture Co-optimized Binary Transformer Accelerator for Edge Inference
Authors:Ye Qiao, Zhiheng Chen, Yian Wang, Yifan Zhang, Yunzhe Deng, Sitao Huang
Transformer-based models have demonstrated superior performance in various fields, including natural language processing and computer vision. However, their enormous model size and high demands in computation, memory, and communication limit their deployment to edge platforms for local, secure inference. Binary transformers offer a compact, low-complexity solution for edge deployment with reduced bandwidth needs and acceptable accuracy. However, existing binary transformers perform inefficiently on current hardware due to the lack of binary specific optimizations. To address this, we introduce COBRA, an algorithm-architecture co-optimized binary Transformer accelerator for edge computing. COBRA features a real 1-bit binary multiplication unit, enabling matrix operations with -1, 0, and +1 values, surpassing ternary methods. With further hardware-friendly optimizations in the attention block, COBRA achieves up to 3,894.7 GOPS throughput and 448.7 GOPS/Watt energy efficiency on edge FPGAs, delivering a 311x energy efficiency improvement over GPUs and a 3.5x throughput improvement over the state-of-the-art binary accelerator, with only negligible inference accuracy degradation.
基于Transformer的模型在自然语言处理和计算机视觉等领域表现出了卓越的性能。然而,它们庞大的模型规模以及对计算、内存和通信的高要求,限制了它们在边缘平台上的本地安全推理部署。二进制变压器(Binary Transformers)以紧凑、低复杂度的解决方案满足边缘部署的需求,降低了带宽需求并保持了可接受的准确性。然而,由于缺少针对二进制的特定优化,现有的二进制变压器在当前硬件上的运行效率低下。为了解决这个问题,我们引入了COBRA,这是一种针对边缘计算的协同优化的二进制Transformer加速器。COBRA配备了真正的1位二进制乘法单元,能够使用-1、0和+1的值进行矩阵操作,超越了三元方法。通过对注意力模块的进一步面向硬件的优化,COBRA在边缘FPGA上实现了高达3894.7 GOPS的吞吐量和448.7 GOPS/Watt的能效,相对于GPU实现了311倍能效提升,相对于最新的二进制加速器实现了3.5倍的吞吐量提升,同时推理精度仅出现微小的下降。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
二进制Transformer加速器COBRA针对边缘计算进行优化,采用真实的1位二进制乘法单元,实现矩阵操作,提高能源效率和吞吐量,降低推理精度损失。
Key Takeaways
- Transformer-based models在多个领域表现出卓越性能,但在边缘平台上部署进行本地安全推理时面临计算、内存和通信需求巨大的问题。
- 二进制变压器为解决边缘部署问题提供了紧凑、低复杂度的解决方案,具有减少带宽需求和保持可接受精度的好处。
- 现有二进制变压器在当前硬件上的表现不佳,缺乏二进制特定优化。
- COBRA是一个针对边缘计算的算法-架构协同优化的二进制Transformer加速器。
- COBRA采用真实的1位二进制乘法单元,超越三元方法,实现矩阵操作。
- 通过在注意力块中进行硬件友好的进一步优化,COBRA在边缘FPGA上实现了高达3,894.7 GOPS的吞吐量,以及448.7 GOPS/Watt的能效。
点此查看论文截图

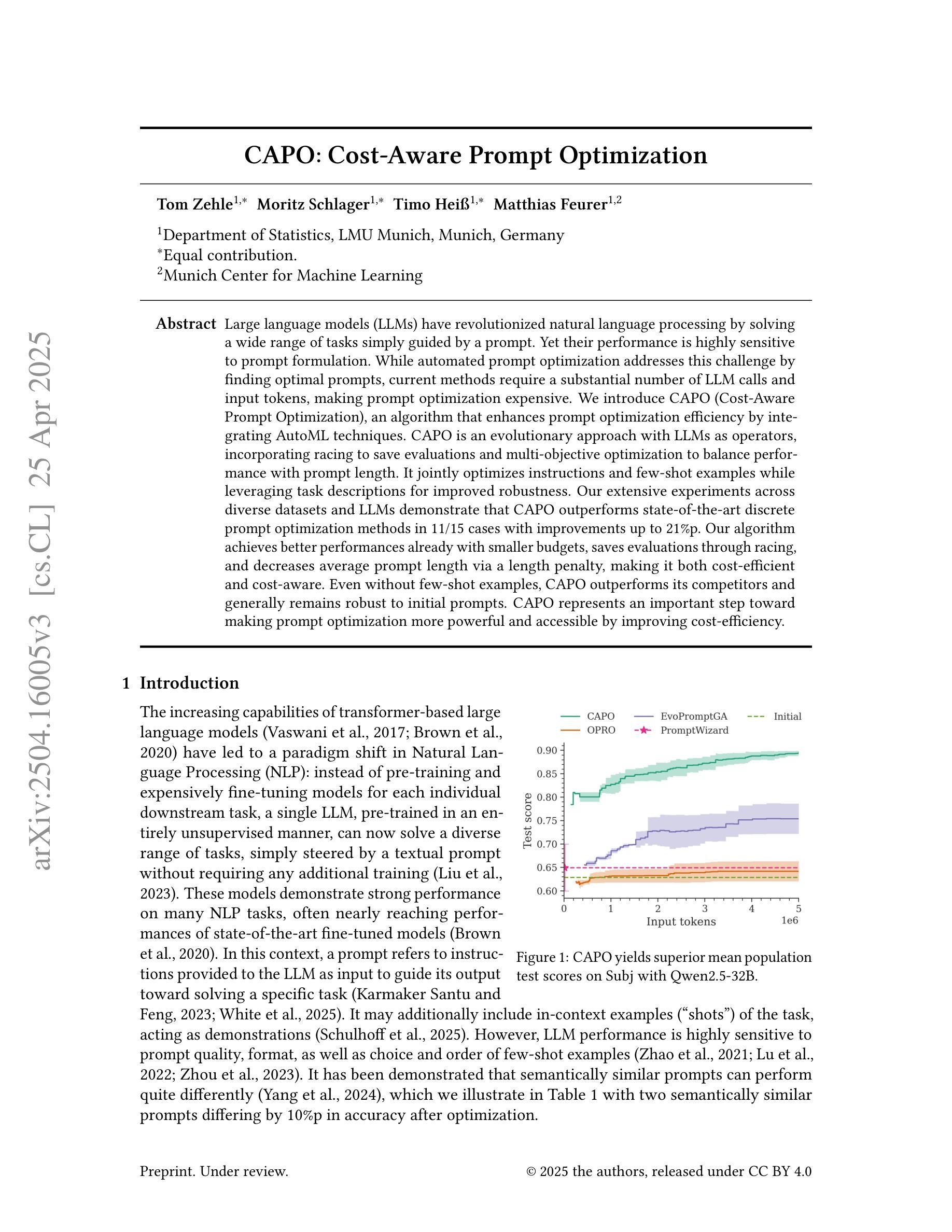
CAPO: Cost-Aware Prompt Optimization
Authors:Tom Zehle, Moritz Schlager, Timo Heiß, Matthias Feurer
Large language models (LLMs) have revolutionized natural language processing by solving a wide range of tasks simply guided by a prompt. Yet their performance is highly sensitive to prompt formulation. While automated prompt optimization addresses this challenge by finding optimal prompts, current methods require a substantial number of LLM calls and input tokens, making prompt optimization expensive. We introduce CAPO (Cost-Aware Prompt Optimization), an algorithm that enhances prompt optimization efficiency by integrating AutoML techniques. CAPO is an evolutionary approach with LLMs as operators, incorporating racing to save evaluations and multi-objective optimization to balance performance with prompt length. It jointly optimizes instructions and few-shot examples while leveraging task descriptions for improved robustness. Our extensive experiments across diverse datasets and LLMs demonstrate that CAPO outperforms state-of-the-art discrete prompt optimization methods in 11/15 cases with improvements up to 21%p. Our algorithm achieves better performances already with smaller budgets, saves evaluations through racing, and decreases average prompt length via a length penalty, making it both cost-efficient and cost-aware. Even without few-shot examples, CAPO outperforms its competitors and generally remains robust to initial prompts. CAPO represents an important step toward making prompt optimization more powerful and accessible by improving cost-efficiency.
大型语言模型(LLM)通过简单的提示指导解决了广泛的自然语言处理任务,从而彻底改变了自然语言处理的局面。然而,它们的性能对提示的制定非常敏感。虽然自动提示优化可以通过找到最佳提示来解决这一挑战,但当前的方法需要大量的LLM调用和输入令牌,这使得提示优化成本高昂。我们引入了CAPO(基于成本的提示优化),这是一种通过集成AutoML技术提高提示优化效率的算法。CAPO是一种进化方法,以LLM作为操作员,融入竞赛以节省评估和多目标优化来平衡性能和提示长度。它联合优化指令和少量示例,并利用任务描述来提高稳健性。我们在各种数据集和LLM上进行的广泛实验表明,在15种情况下,CAPO在11种情况下优于最先进的离散提示优化方法,性能提高了高达21%。我们的算法在较小的预算下即可实现更好的性能,通过竞赛节省评估,并通过长度惩罚减少平均提示长度,使其既经济又注重成本。即使没有少量示例,CAPO也能超越竞争对手,并且对初始提示保持稳健。CAPO朝着通过提高成本效率来使提示优化更强大、更易于访问迈出了重要一步。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF Submitted to AutoML 2025
Summary
大型语言模型(LLM)通过提示指导解决了多种任务,但性能对提示制定高度敏感。当前自动化提示优化方法需要大量LLM调用和输入令牌,成本高昂。我们引入CAPO(成本感知提示优化)算法,通过集成AutoML技术提高提示优化效率。CAPO采用进化方法,将LLM作为操作员,结合竞赛以节省评估和多目标优化以平衡性能和提示长度。它联合优化指令和少量示例,并利用任务描述提高稳健性。实验表明,CAPO在多数情况下优于最新离散提示优化方法,改进幅度达21%。我们的算法在较小预算下即可实现更好的性能,通过竞赛节省评估,并通过长度惩罚减少平均提示长度,实现了成本效益和感知成本的优化。即使在没有少量示例的情况下,CAPO也能超越竞争对手,并且对初始提示保持稳健。
Key Takeaways
- LLMs通过提示指导解决多种任务,但性能受提示制定影响。
- 当前自动化提示优化方法成本高,需要改进效率。
- 引入CAPO算法,集成AutoML技术提高提示优化效率。
- CAPO采用进化方法,结合竞赛以节省评估和多目标优化。
- CAPO联合优化指令和少量示例,提高稳健性。
- CAPO在多数情况下优于最新离散提示优化方法,改进幅度达21%。
点此查看论文截图


Using customized GPT to develop prompting proficiency in architectural AI-generated images
Authors:Juan David Salazar Rodriguez, Sam Conrad Joyce, Julfendi
This research investigates the use of customized GPT models to enhance prompting proficiency among architecture students when generating AI-driven images. Prompt engineering is increasingly essential in architectural education due to the widespread adoption of generative AI tools. This study utilized a mixed-methods experimental design involving architecture students divided into three distinct groups: a control group receiving no structured support, a second group provided with structured prompting guides, and a third group supported by both structured guides and interactive AI personas. Students engaged in reverse engineering tasks, first guessing provided image prompts and then generating their own prompts, aiming to boost critical thinking and prompting skills. Variables examined included time spent prompting, word count, prompt similarity, and concreteness. Quantitative analysis involved correlation assessments between these variables and a one-way ANOVA to evaluate differences across groups. While several correlations showed meaningful relationships, not all were statistically significant. ANOVA results indicated statistically significant improvements in word count, similarity, and concreteness, especially in the group supported by AI personas and structured prompting guides. Qualitative feedback complemented these findings, revealing enhanced confidence and critical thinking skills in students. These results suggest tailored GPT interactions substantially improve students’ ability to communicate architectural concepts clearly and effectively.
本研究旨在探讨定制GPT模型在增强建筑学学生在生成人工智能驱动图像时的提示能力方面的应用。由于生成式人工智能工具的广泛应用,提示工程在建筑教育中变得越来越重要。本研究采用混合方法实验设计,将建筑学学生分为三组:对照组无结构化支持,第二组提供结构化提示指南,第三组由结构化指南和交互式AI人格提供支持。学生们参与了逆向工程任务,首先猜测提供的图像提示,然后生成自己的提示,旨在提高批判思维和提示技能。研究的变量包括提示所花费的时间、字数、提示的相似性和具体性。定量分析涉及这些变量之间的相关性评估,以及单因素方差分析以评估各组间差异。虽然几个相关性显示了有意义的关系,但并不是都有统计学上的意义。方差分析结果指出,在字数、相似性和具体性方面存在显著的改进,特别是在AI人格和结构化提示指南的支持下的小组中尤为明显。定性反馈补充了这些发现,显示学生的自信和批判思维能力有所提高。这些结果表明,有针对性的GPT互动能显著提高学生清晰有效地传达建筑概念的能力。
论文及项目相关链接
摘要
该研究探讨了使用定制的GPT模型在提高建筑学生在使用人工智能生成图像时的提示能力方面的应用。随着生成式人工智能工具在建筑设计领域的广泛应用,提示工程在建筑设计教育中的重要性日益增加。该研究采用混合方法实验设计,将建筑学生分为三组:对照组(无结构化支持)、第二组(提供结构化提示指南)和第三组(由结构化指南和交互式AI人格提供支持)。学生们参与了逆向工程任务,首先猜测提供的图像提示,然后生成自己的提示,旨在提高批判思维和提示技能。考察的变量包括提示时间、字数、提示相似性和具体性。定量分析包括这些变量之间的相关性评估以及评估各组间差异的一向方差分析。虽然一些相关性显示出有意义的关系,但并非都具有统计学意义。方差分析结果指出,在字数、相似性和具体性方面都有显著的改进,特别是在AI人格和结构化提示指南支持的小组中。定性反馈补充了这些发现,显示出学生们的自信和批判性思维能力有所提高。这些结果表明,定制GPT交互能显著提高学生清晰有效地传达建筑概念的能力。
关键见解
- 研究探索了GPT模型在增强建筑学生使用AI生成图像时的提示能力方面的应用。
- 提示工程在建筑设计教育中的重要性日益增加,因为生成式AI工具被广泛应用。
- 学生分为三组,分别接受不同的支持和指导方式,以评估其对提示能力的影响。
- 定量分析表明,某些变量之间存在有意义的相关性,但并非所有相关性都具有统计学意义。
- 一向方差分析显示,在特定变量(如字数、相似性和具体性)方面存在显著的组间差异。
- 定性反馈进一步证实了学生在提示能力方面的提高,包括自信和批判性思维。
- 定制GPT交互有助于提高学生清晰有效地传达建筑概念的能力。
点此查看论文截图

Machine-generated text detection prevents language model collapse
Authors:George Drayson, Emine Yilmaz, Vasileios Lampos
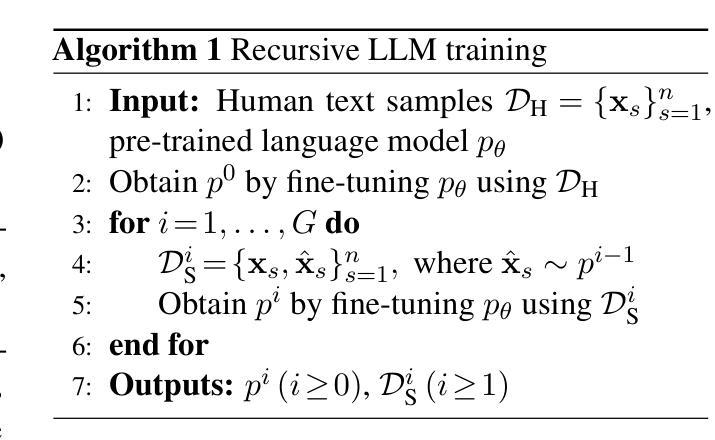
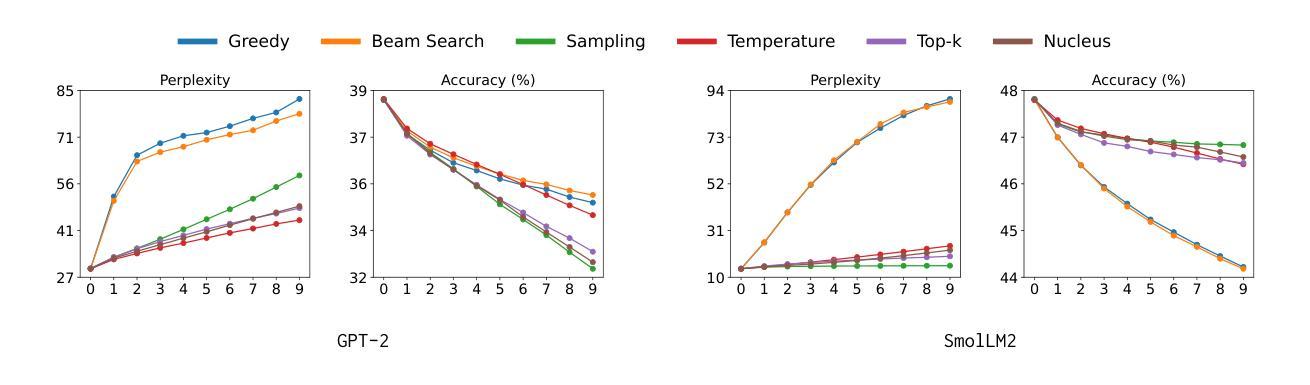
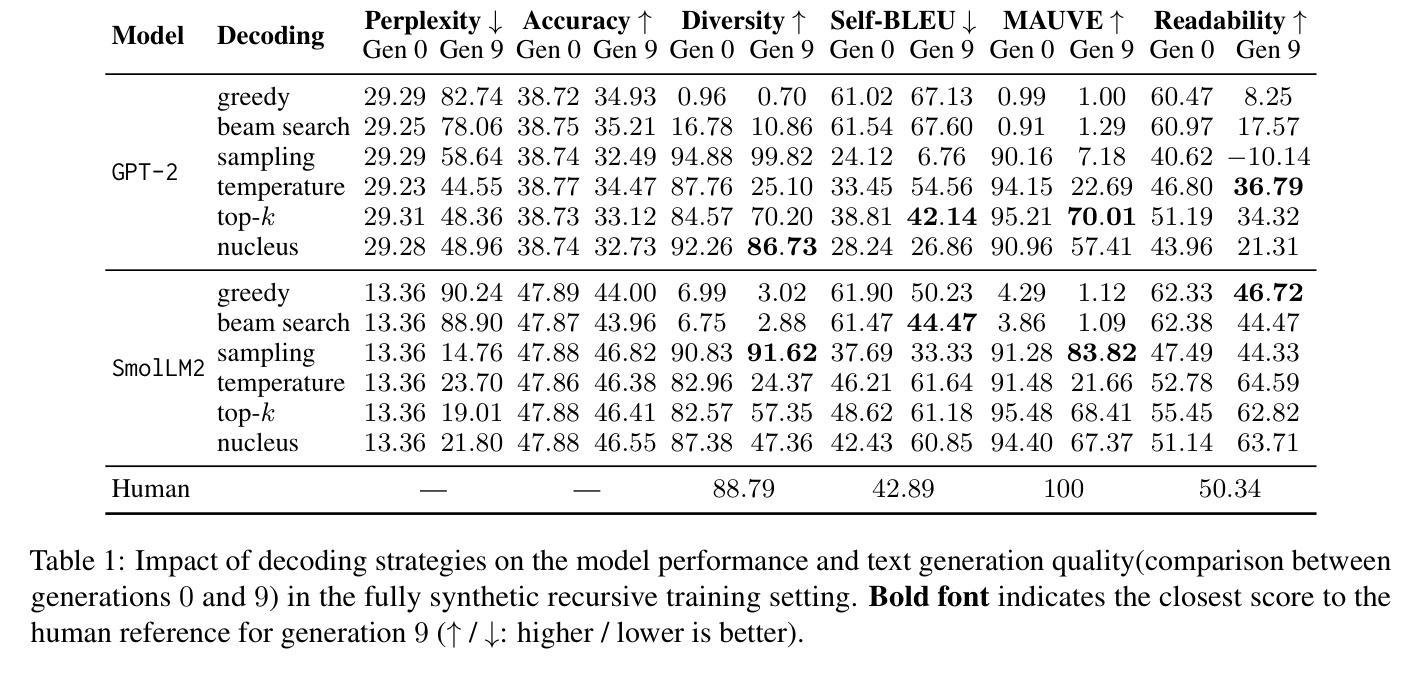
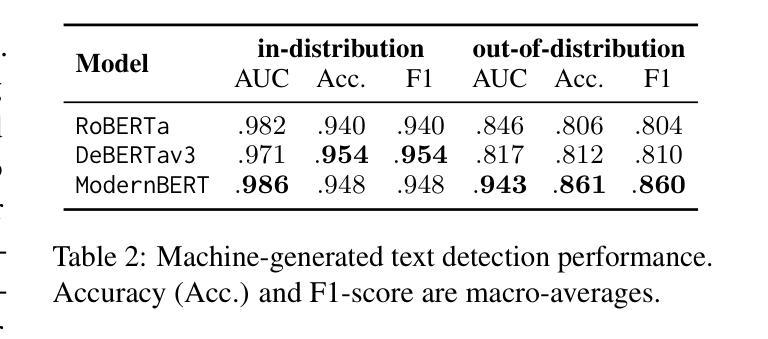
As Large Language Models (LLMs) become increasingly prevalent, their generated outputs are proliferating across the web, risking a future where machine-generated content dilutes human-authored text. Since online data is the primary resource for LLM pre-training, subsequent models could be trained on an unknown portion of synthetic samples. This will lead to model collapse, a degenerative process whereby LLMs reinforce their own errors, and ultimately yield a declining performance. In this study, we investigate the impact of decoding strategy on model collapse, analysing the characteristics of text at each model generation, the similarity to human references, and the resulting model performance. Using the decoding strategies that lead to the most significant degradation, we evaluate model collapse in more realistic scenarios where the origin of the data (human or synthetic) is unknown. We train a machine-generated text detector and propose an importance sampling approach to alleviate model collapse. Our method is validated on two LLM variants (GPT-2 and SmolLM2) on the open-ended text generation task. We demonstrate that it can not only prevent model collapse but also improve performance when sufficient human-authored samples are present. We release our code at https://github.com/GeorgeDrayson/model_collapse.
随着大型语言模型(LLM)越来越普及,它们生成的输出在网上不断增多,未来可能导致机器生成内容稀释人类创作的文本。由于在线数据是LLM预训练的主要资源,后续模型可能会在未知比例的人工合成样本上进行训练。这将导致模型崩溃,这是一个退化过程,在此过程中,LLM会强化自身的错误,并最终导致性能下降。在本研究中,我们调查了解码策略对模型崩溃的影响,分析每个模型生成文本的特质、与人类参考的相似度,以及由此导致的模型性能结果。我们利用导致降解最严重的解码策略,评估在数据(人类或合成)来源未知的更现实场景中模型崩溃的情况。我们训练了一个机器生成文本检测器,并提出了一种重要性采样方法来缓解模型崩溃。我们的方法在两个LLM变体(GPT-2和SmolLM2)的开放式文本生成任务上得到了验证。我们证明,它不仅可以防止模型崩溃,而且在存在足够的人类创作样本时还可以提高性能。我们在https://github.com/GeorgeDrayson/model_collapse上发布了我们的代码。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
大型语言模型(LLM)的生成输出正在网络上大量出现,这可能会稀释人类创作的内容并带来模型崩溃的风险。本研究探讨了解码策略对模型崩溃的影响,分析了不同模型生成文本的特性和与人类参考文本的相似度,以及模型性能的变化。通过评估在无法确定数据来源于人类还是合成的情况下更现实的场景中模型崩溃的情况,我们提出了一种采用机器生成文本检测器和重要性采样方法的方法,不仅可防止模型崩溃,而且可在存在足够人类创作样本的情况下提高性能。
Key Takeaways
- 大型语言模型(LLM)的生成输出在网络上大量出现,可能会稀释人类创作的内容并带来模型崩溃风险。
- 解码策略对LLM模型崩溃有重要影响。
- 模型崩溃是一种退化过程,LLMs会强化自己的错误,导致性能下降。
- 在无法确定数据来源于人类还是合成的情况下评估模型性能更加现实。
- 采用机器生成文本检测器可以有效识别合成样本。
- 重要性采样方法可以缓解模型崩溃问题。
- 该方法经过在两种LLM变体(GPT-2和SmolLM2)上的验证,表明其有效性和实用性。
点此查看论文截图

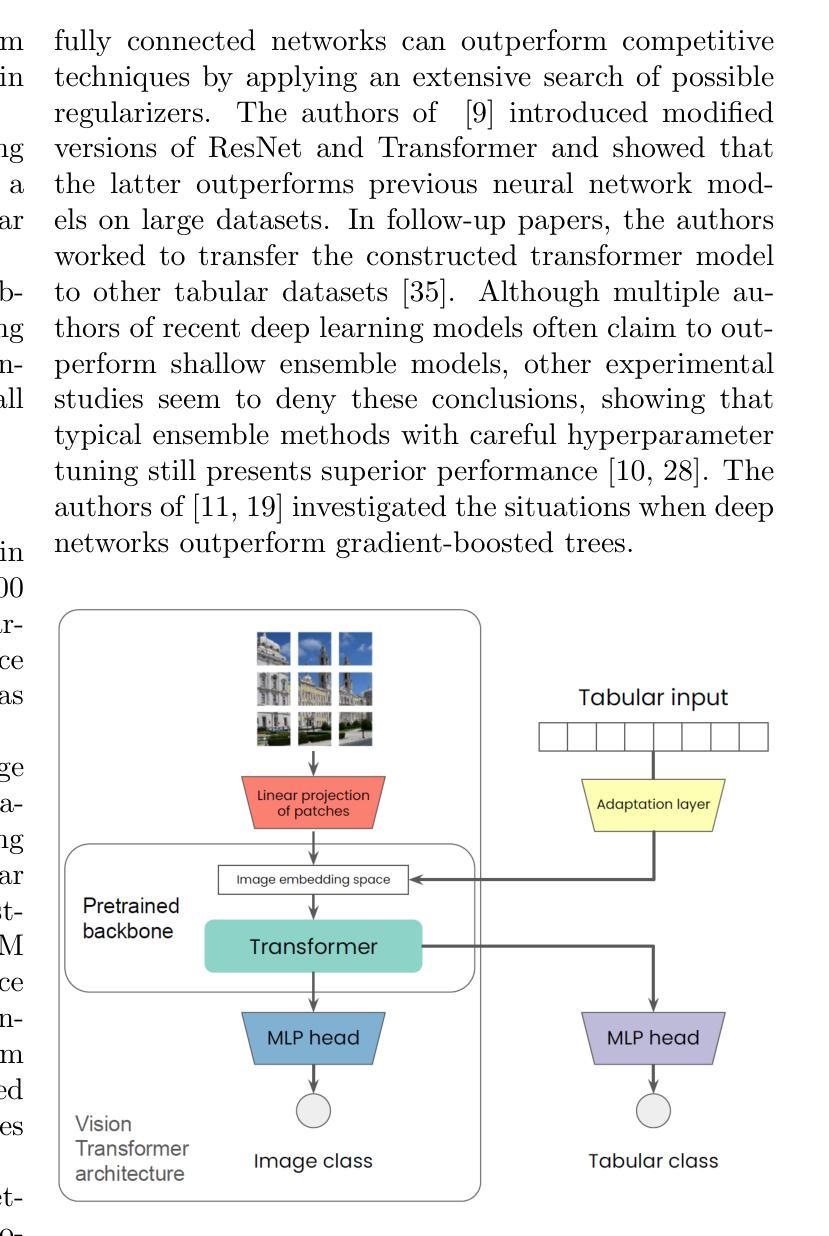
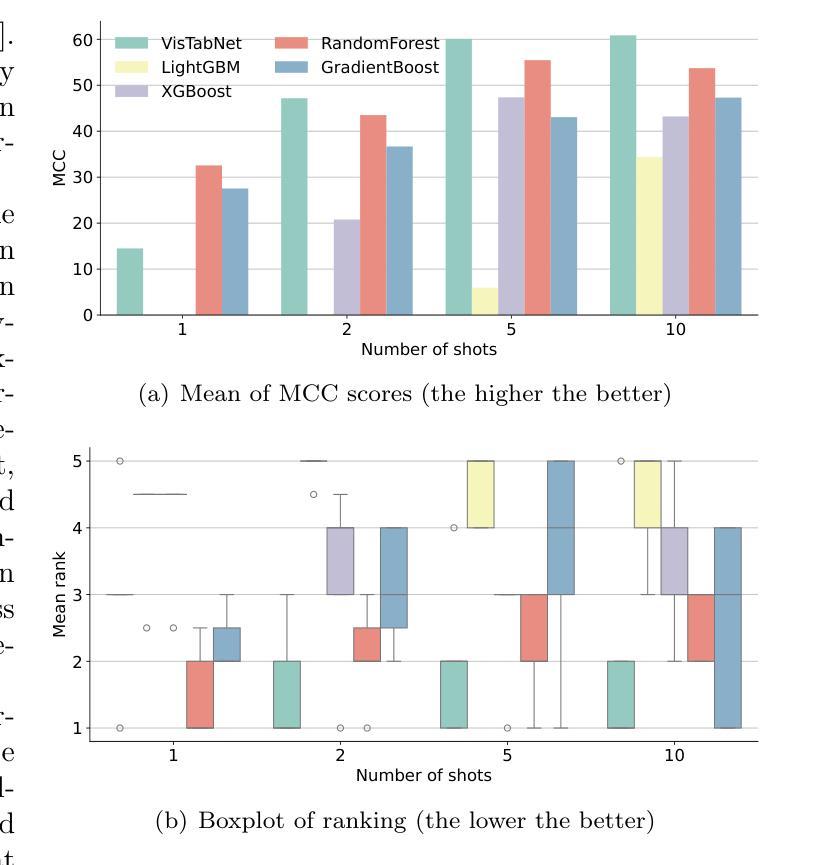
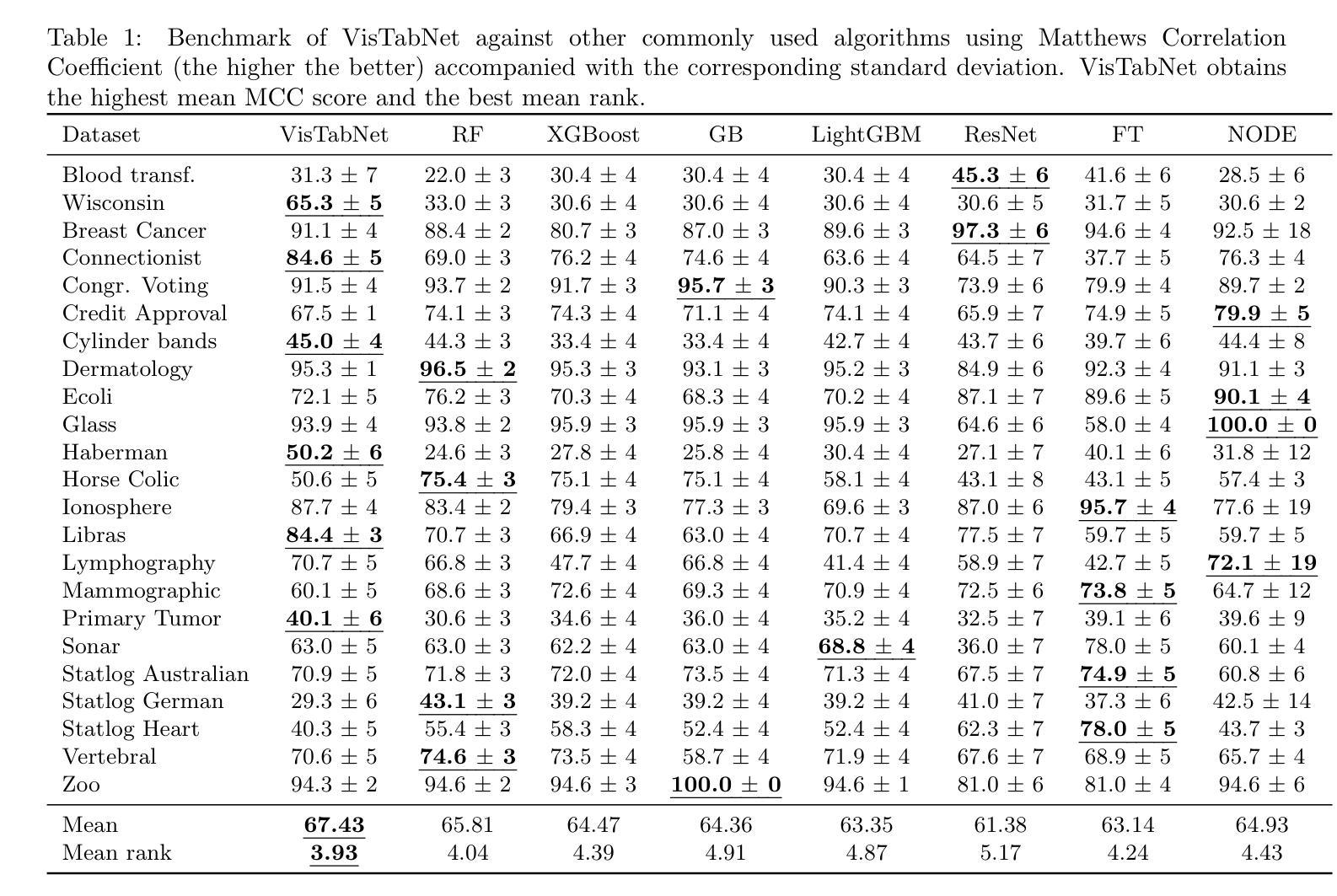
VisTabNet: Adapting Vision Transformers for Tabular Data
Authors:Witold Wydmański, Ulvi Movsum-zada, Jacek Tabor, Marek Śmieja
Although deep learning models have had great success in natural language processing and computer vision, we do not observe comparable improvements in the case of tabular data, which is still the most common data type used in biological, industrial and financial applications. In particular, it is challenging to transfer large-scale pre-trained models to downstream tasks defined on small tabular datasets. To address this, we propose VisTabNet – a cross-modal transfer learning method, which allows for adapting Vision Transformer (ViT) with pre-trained weights to process tabular data. By projecting tabular inputs to patch embeddings acceptable by ViT, we can directly apply a pre-trained Transformer Encoder to tabular inputs. This approach eliminates the conceptual cost of designing a suitable architecture for processing tabular data, while reducing the computational cost of training the model from scratch. Experimental results on multiple small tabular datasets (less than 1k samples) demonstrate VisTabNet’s superiority, outperforming both traditional ensemble methods and recent deep learning models. The proposed method goes beyond conventional transfer learning practice and shows that pre-trained image models can be transferred to solve tabular problems, extending the boundaries of transfer learning. We share our example implementation as a GitHub repository available at https://github.com/wwydmanski/VisTabNet.
尽管深度学习模型在自然语言处理和计算机视觉方面取得了巨大成功,但在处理表格数据的情况下,我们并没有观察到相应的改进。表格数据仍然是生物、工业和金融应用中最常用的数据类型。特别是,将大规模预训练模型转移到在小型表格数据集上定义的下游任务是一项挑战。为了解决这一问题,我们提出了VisTabNet——一种跨模态迁移学习方法,它允许使用预训练权重对Vision Transformer(ViT)进行适配以处理表格数据。通过将表格输入投影到ViT可接受的补丁嵌入,我们可以直接将预训练的Transformer编码器应用于表格输入。这种方法消除了为处理表格数据而设计合适架构的概念成本,同时降低了从头开始训练模型的计算成本。在多个小型表格数据集(少于1k样本)上的实验结果证明了VisTabNet的优越性,它超越了传统的集成方法和最新的深度学习模型。所提出的方法超越了传统的迁移学习实践,并表明预训练的图像模型可以转移到解决表格问题,扩展了迁移学习的边界。我们在https://github.com/wwydmanski/VisTabNet提供了示例实现的GitHub仓库。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
深度学习模型在自然语言处理和计算机视觉领域取得了巨大成功,但在处理表格数据方面仍面临挑战。为此,我们提出了VisTabNet——一种跨模态迁移学习方法,可将预训练的Vision Transformer(ViT)模型应用于表格数据处理。通过把表格数据转化为ViT可接受的patch embeddings,我们可直接应用预训练的Transformer Encoder来处理表格数据。这种方法降低了设计适合处理表格数据的架构的概念成本,同时减少了从头开始训练模型的计算成本。在多个小型表格数据集上的实验结果表明,VisTabNet优于传统的集成方法和最新的深度学习模型。该方法突破了传统的迁移学习实践,展示了预训练的图像模型可以解决表格问题,扩展了迁移学习的边界。
Key Takeaways
- 深度学习在处理表格数据方面仍有待提高,尤其是在将大型预训练模型迁移到小型表格数据集上定义的下游任务时面临挑战。
- VisTabNet是一种跨模态迁移学习方法,能够将预训练的Vision Transformer(ViT)模型应用于表格数据处理。
- VisTabNet通过将表格数据转化为patch embeddings,使得预训练的Transformer Encoder可以直接应用于表格数据。
- VisTabNet降低了设计处理表格数据的架构的概念成本,并减少了从头开始训练模型所需的计算成本。
- 实验结果表明,VisTabNet在多个小型表格数据集上的性能优于传统的集成方法和最新的深度学习模型。
- VisTabNet突破了传统的迁移学习实践,展示了预训练的图像模型在解决表格问题方面的潜力。
点此查看论文截图

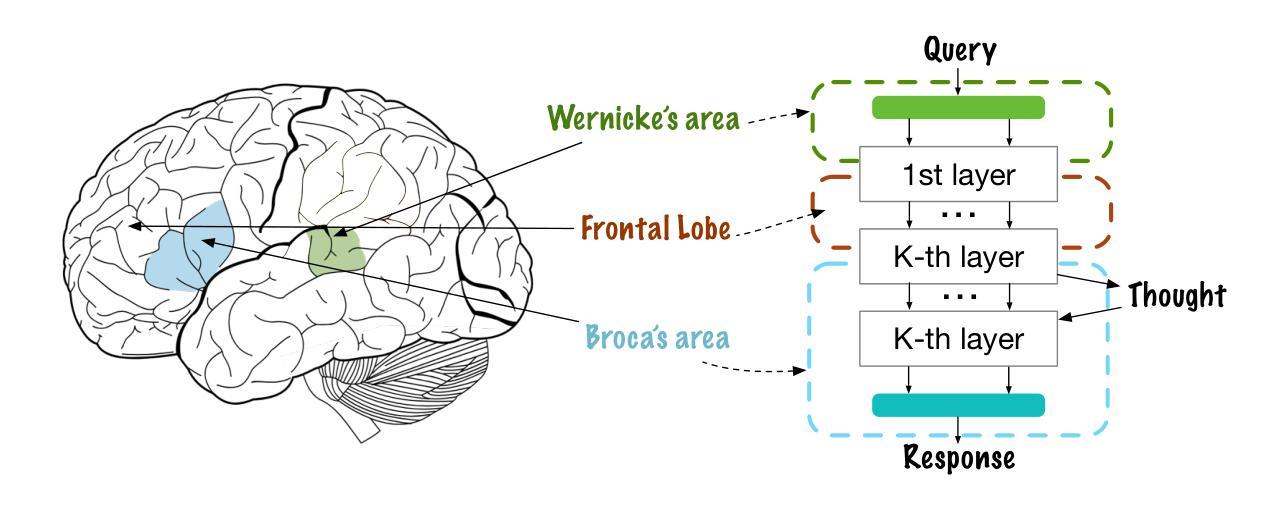
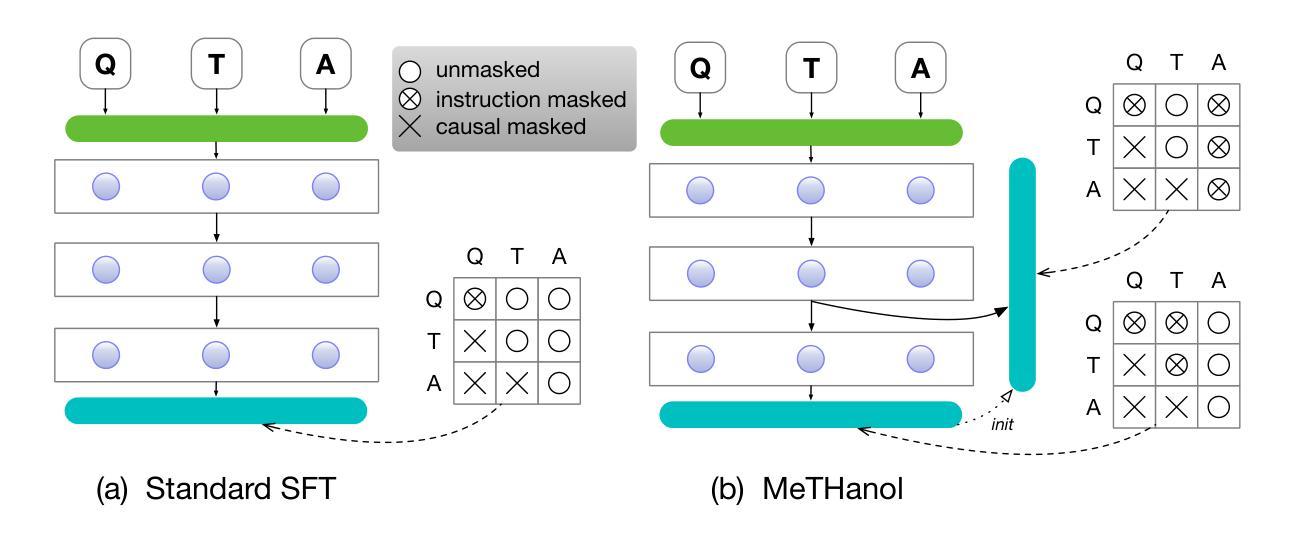
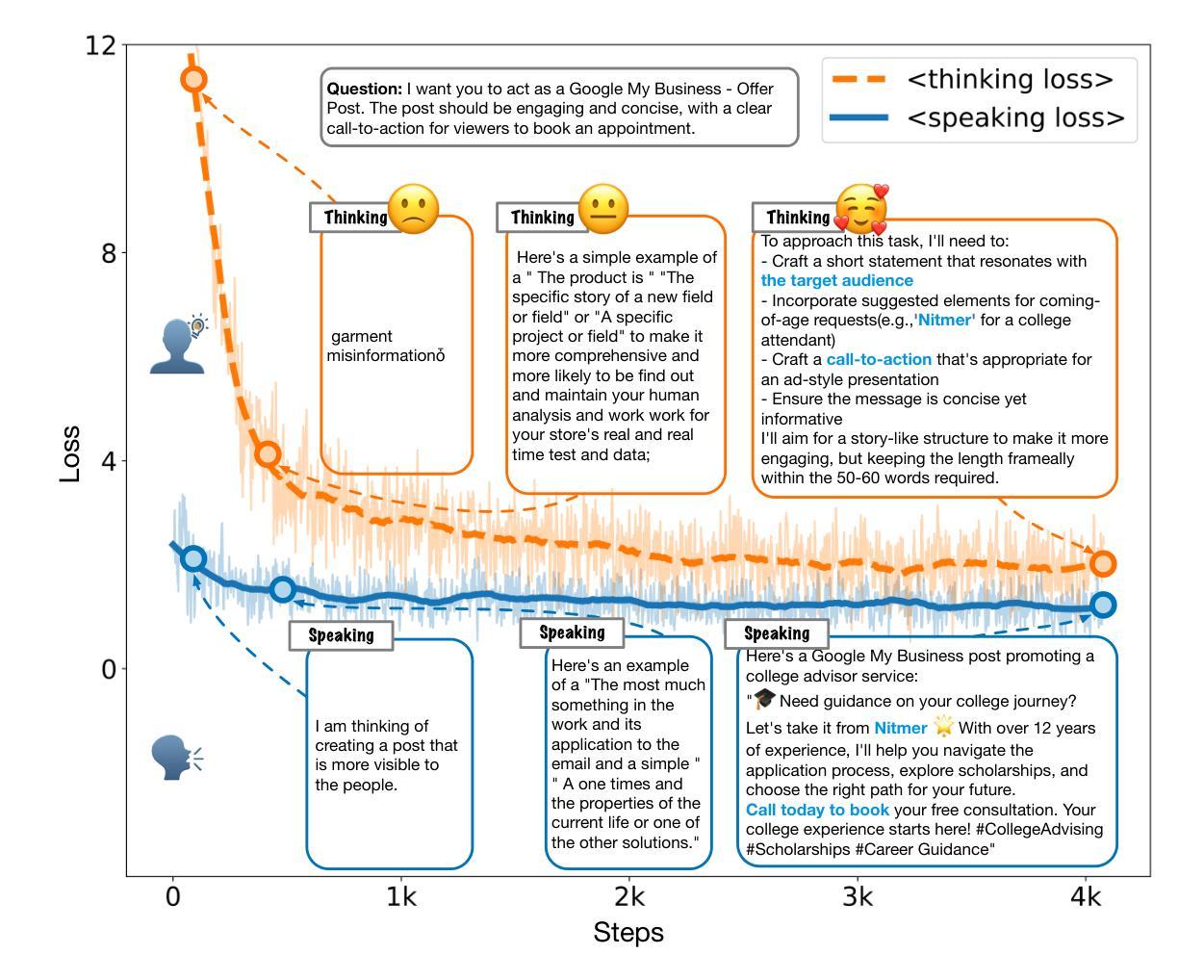
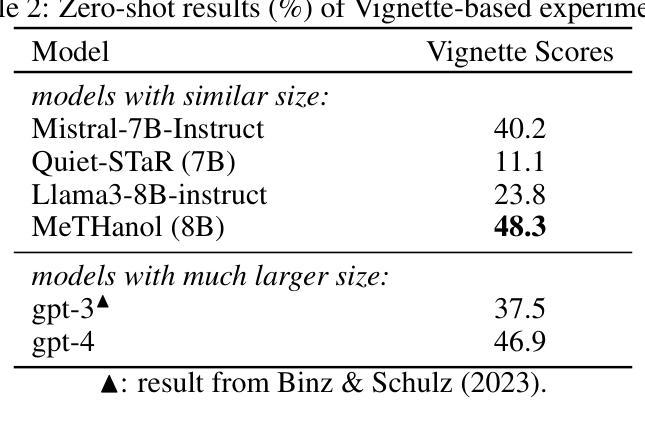
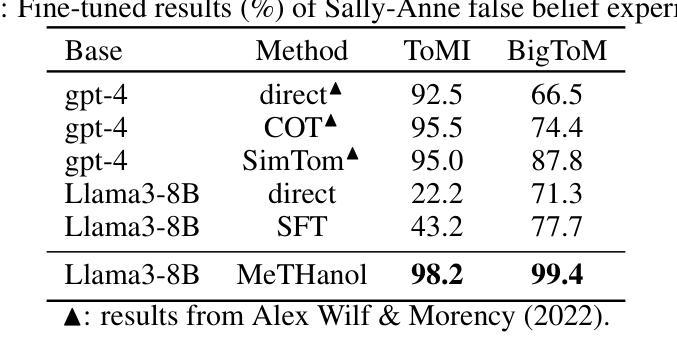
MeTHanol: Modularized Thinking Language Models with Intermediate Layer Thinking, Decoding and Bootstrapping Reasoning
Authors:Ningyuan Xi, Xiaoyu Wang, Yetao Wu, Teng Chen, Qingqing Gu, Yue Zhao, Jinxian Qu, Zhonglin Jiang, Yong Chen, Luo Ji
Large Language Model can reasonably understand and generate human expressions but may lack of thorough thinking and reasoning mechanisms. Recently there have been several studies which enhance the thinking ability of language models but most of them are not data-driven or training-based. In this paper, we are motivated by the cognitive mechanism in the natural world, and design a novel model architecture called TaS which allows it to first consider the thoughts and then express the response based upon the query. We design several pipelines to annotate or generate the thought contents from prompt-response samples, then add language heads in a middle layer which behaves as the thinking layer. We train the language model by the thoughts-augmented data and successfully let the thinking layer automatically generate reasonable thoughts and finally output more reasonable responses. Both qualitative examples and quantitative results validate the effectiveness and performance of TaS. Our code is available at https://anonymous.4open.science/r/TadE.
大型语言模型能够合理地理解和生成人类表达,但可能缺乏深入的思考和推理机制。最近有几项研究旨在提高语言模型的思考能力,但大多数并非数据驱动或基于训练。在本文中,我们受到自然认知机制的启发,设计了一种新型模型架构,称为TaS,它允许模型首先考虑思想,然后根据查询表达响应。我们设计了几个管道来从提示-响应样本中标注或生成思想内容,然后在中间层添加语言头,充当思考层。我们通过思想增强数据训练语言模型,成功让思考层自动产生合理思想,并最终输出更合理的响应。定性和定量结果均验证了TaS的有效性和性能。我们的代码可在https://anonymous.4open.science/r/TadE找到。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF 19 pages, 7 figures
Summary
大语言模型可以理解并生成人类表达,但可能缺乏深入的思考和推理机制。本文设计了一种新型模型架构TaS,它首先会考虑思考内容,然后根据查询表达响应。通过标注或生成思想内容样本,在中间的层加入语言头作为思考层。使用思想增强数据进行训练后,可以让思考层自动生成合理的思想,最终输出更合理的响应。实验结果验证了TaS的有效性和性能。
Key Takeaways
- 大语言模型虽然能理解和生成人类表达,但缺乏深入的思考和推理机制。
- 新型模型架构TaS设计旨在解决这一问题,首先考虑思考内容,再基于查询表达响应。
- TaS通过标注或生成思想内容样本,在中间的层加入语言头作为思考层。
- 使用思想增强数据进行训练,能让思考层自动生成合理的思想。
- TaS模型能输出更合理的响应,并通过实验验证了其有效性和性能。
- 该研究的代码已公开可用。
点此查看论文截图

Automatically Generating UI Code from Screenshot: A Divide-and-Conquer-Based Approach
Authors:Yuxuan Wan, Chaozheng Wang, Yi Dong, Wenxuan Wang, Shuqing Li, Yintong Huo, Michael R. Lyu
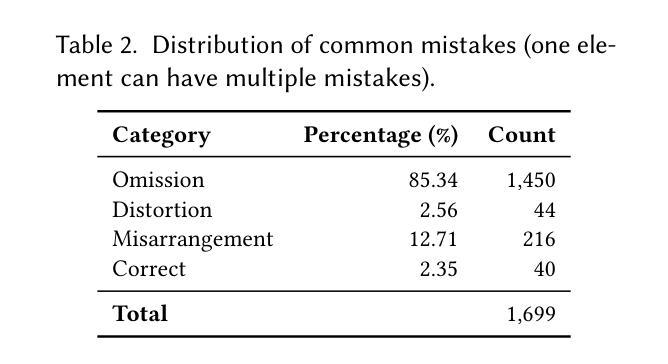
Websites are critical in today’s digital world, with over 1.11 billion currently active and approximately 252,000 new sites launched daily. Converting website layout design into functional UI code is a time-consuming yet indispensable step of website development. Manual methods of converting visual designs into functional code present significant challenges, especially for non-experts. To explore automatic design-to-code solutions, we first conduct a motivating study on GPT-4o and identify three types of issues in generating UI code: element omission, element distortion, and element misarrangement. We further reveal that a focus on smaller visual segments can help multimodal large language models (MLLMs) mitigate these failures in the generation process. In this paper, we propose DCGen, a divide-and-conquer-based approach to automate the translation of webpage design to UI code. DCGen starts by dividing screenshots into manageable segments, generating code for each segment, and then reassembling them into complete UI code for the entire screenshot. We conduct extensive testing with a dataset comprised of real-world websites and various MLLMs and demonstrate that DCGen achieves up to a 15% improvement in visual similarity and 8% in code similarity for large input images. Human evaluations show that DCGen can help developers implement webpages significantly faster and more similar to the UI designs. To the best of our knowledge, DCGen is the first segment-aware MLLM-based approach for generating UI code directly from screenshots.
在当今数字化世界中,网站扮演着至关重要的角色,当前有超过11.1亿个活跃网站,每天大约会有25万2千个新网站上线。将网站布局设计转化为功能性的UI代码是网站开发中一个既耗时又必不可少的步骤。使用人工方法将视觉设计转化为功能性代码面临着重大的挑战,特别是对于那些非专业人士来说。为了探索自动设计到代码的解决方案,我们首先针对GPT-4o进行了一项激励研究,并发现了生成UI代码时存在的三种问题:元素遗漏、元素变形和元素错排。我们进一步揭示,关注较小的视觉片段可以帮助多模态大型语言模型(MLLMs)在生成过程中缓解这些失败问题。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF Accepted by FSE 2025
Summary:在数字时代,网站的数量持续增长,如何将网页布局设计转化为功能性用户界面代码成为了重要步骤。存在GPT-4o等自动设计转代码解决方案的问题,本文提出DCGen方法,通过分割截图生成代码片段再组合成完整代码,实现网页设计自动化转码。测试表明,DCGen在视觉和代码相似性上有所提升,并能帮助开发者更快实现与UI设计相似的网页。
Key Takeaways:
- 网站在数字时代具有重要性,自动设计转代码解决方案需求增加。
- GPT-4o等现有解决方案存在元素遗漏、失真和错位等问题。
- DCGen方法基于分段征服策略,从截图生成代码片段并组合成完整代码。
- DCGen在大型输入图像上实现了视觉和代码相似性的提升。
- DCGen有助于开发者更快、更准确地实现网页开发。
- 据悉,DCGen是首个基于MLLM的段感知方法,可直接从截图生成UI代码。
点此查看论文截图

FoC: Figure out the Cryptographic Functions in Stripped Binaries with LLMs
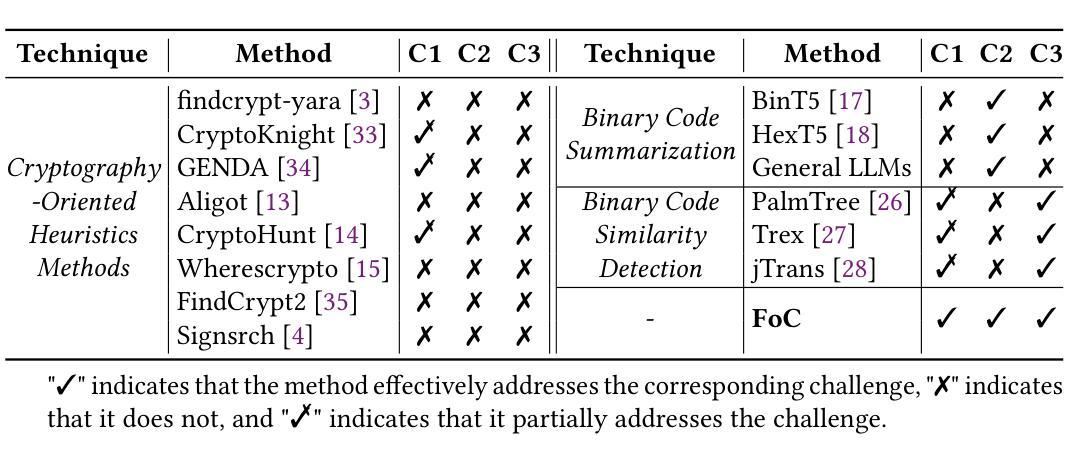
Authors:Xiuwei Shang, Guoqiang Chen, Shaoyin Cheng, Shikai Guo, Yanming Zhang, Weiming Zhang, Nenghai Yu
Analyzing the behavior of cryptographic functions in stripped binaries is a challenging but essential task. Cryptographic algorithms exhibit greater logical complexity compared to typical code, yet their analysis is unavoidable in areas such as virus analysis and legacy code inspection. Existing methods often rely on data or structural pattern matching, leading to suboptimal generalizability and suffering from manual work. In this paper, we propose a novel framework called FoC to Figure out the Cryptographic functions in stripped binaries. In FoC, we first build a binary large language model (FoC-BinLLM) to summarize the semantics of cryptographic functions in natural language. The prediction of FoC-BinLLM is insensitive to minor changes, such as vulnerability patches. To mitigate it, we further build a binary code similarity model (FoC-Sim) upon the FoC-BinLLM to create change-sensitive representations and use it to retrieve similar implementations of unknown cryptographic functions in a database. In addition, we construct a cryptographic binary dataset for evaluation and to facilitate further research in this domain. And an automated method is devised to create semantic labels for extensive binary functions. Evaluation results demonstrate that FoC-BinLLM outperforms ChatGPT by 14.61% on the ROUGE-L score. FoC-Sim outperforms the previous best methods with a 52% higher Recall@1. Furthermore, our method also shows practical ability in virus analysis and 1-day vulnerability detection.
分析剥离二进制文件中的加密函数行为是一项具有挑战性但至关重要的任务。与典型代码相比,加密算法表现出更高的逻辑复杂性,但在病毒分析和遗留代码检查等领域,其分析是必不可少的。现有方法通常依赖于数据或结构模式匹配,导致通用性不足,且需要大量手动操作。在本文中,我们提出了一种新型框架,名为FoC,以在剥离的二进制文件中找出加密函数。在FoC中,我们首先建立了一个二进制大型语言模型(FoC-BinLLM),以自然语言总结加密函数的语义。FoC-BinLLM的预测对微小的变化(如漏洞补丁)并不敏感。为了缓解这一问题,我们进一步在FoC-BinLLM之上构建了一个二进制代码相似性模型(FoC-Sim),以创建对变化敏感的表示,并将其用于在数据库中检索未知的加密函数的相似实现。此外,我们构建了一个加密二进制数据集,以进行评估并促进该领域的进一步研究。还设计了一种自动化方法来为广泛的二进制函数创建语义标签。评估结果表明,FoC-BinLLM在ROUGE-L分数上比ChatGPT高出14.61%。FoC-Sim的召回率比之前的最佳方法高出52%。此外,我们的方法在病毒分析和1天漏洞检测方面也显示出实际能力。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF 38 pages, 10 figures
Summary
本文提出了一种名为FoC的新型框架,用于识别剥离二进制文件中的加密函数。该框架包括两个主要部分:FoC-BinLLM和FoC-Sim。FoC-BinLLM是一个二进制大型语言模型,用于以自然语言形式总结加密函数的语义。FoC-Sim则是一个基于FoC-BinLLM构建的二进制代码相似性模型,用于创建对变化敏感的表示,并用于检索数据库中未知的加密函数的相似实现。此外,该研究还构建了用于评估的加密二进制数据集,并设计了一种自动化方法为广泛的二进制函数创建语义标签。评估结果显示,FoC-BinLLM在ROUGE-L分数上较ChatGPT高出14.6%,FoC-Sim的召回率较之前最佳方法高出52%。同时,该方法在实际病毒分析和一日漏洞检测中展现出实用能力。
Key Takeaways
- 分析剥离二进制文件中的加密函数行为是一项重要且具挑战性的任务,尤其在病毒分析和遗留代码检查等领域。
- 现有方法主要依赖数据或结构模式匹配,存在通用性不足和手工操作繁琐的问题。
- 本文提出了一种新型框架FoC,包括FoC-BinLLM和FoC-Sim两个主要组成部分,以识别二进制文件中的加密函数。
- FoC-BinLLM是一个二进制大型语言模型,能够总结加密函数的自然语言语义,对微小变化具有预测不敏感性。
- FoC-Sim是一个基于FoC-BinLLM构建的二进制代码相似性模型,用于创建对变化敏感的表示,并检索未知加密函数的相似实现。
- 研究构建了加密二进制数据集,为领域内的评估和研究提供了便利。
点此查看论文截图