⚠️ 以下所有内容总结都来自于 大语言模型的能力,如有错误,仅供参考,谨慎使用
🔴 请注意:千万不要用于严肃的学术场景,只能用于论文阅读前的初筛!
💗 如果您觉得我们的项目对您有帮助 ChatPaperFree ,还请您给我们一些鼓励!⭐️ HuggingFace免费体验
2025-04-30 更新
Breast Cancer Detection from Multi-View Screening Mammograms with Visual Prompt Tuning
Authors:Han Chen, Anne L. Martel
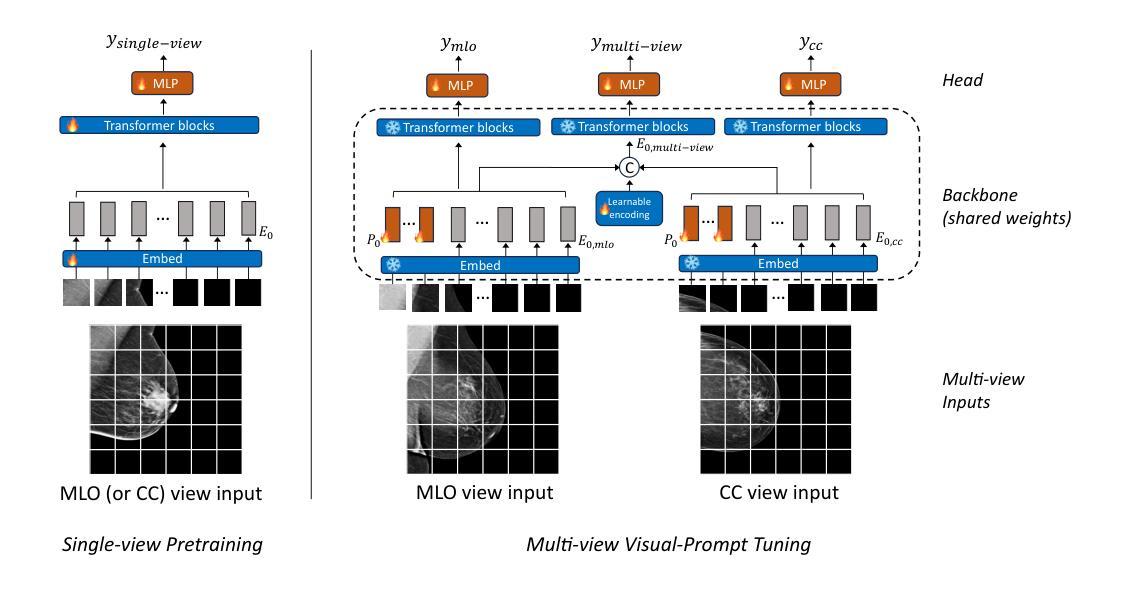
Accurate detection of breast cancer from high-resolution mammograms is crucial for early diagnosis and effective treatment planning. Previous studies have shown the potential of using single-view mammograms for breast cancer detection. However, incorporating multi-view data can provide more comprehensive insights. Multi-view classification, especially in medical imaging, presents unique challenges, particularly when dealing with large-scale, high-resolution data. In this work, we propose a novel Multi-view Visual Prompt Tuning Network (MVPT-NET) for analyzing multiple screening mammograms. We first pretrain a robust single-view classification model on high-resolution mammograms and then innovatively adapt multi-view feature learning into a task-specific prompt tuning process. This technique selectively tunes a minimal set of trainable parameters (7%) while retaining the robustness of the pre-trained single-view model, enabling efficient integration of multi-view data without the need for aggressive downsampling. Our approach offers an efficient alternative to traditional feature fusion methods, providing a more robust, scalable, and efficient solution for high-resolution mammogram analysis. Experimental results on a large multi-institution dataset demonstrate that our method outperforms conventional approaches while maintaining detection efficiency, achieving an AUROC of 0.852 for distinguishing between Benign, DCIS, and Invasive classes. This work highlights the potential of MVPT-NET for medical imaging tasks and provides a scalable solution for integrating multi-view data in breast cancer detection.
乳腺癌的高分辨率钼靶检测对于早期发现和有效治疗计划至关重要。早期研究已经展示了使用单视图钼靶检测乳腺癌的潜力。然而,整合多视图数据可以提供更全面的洞察。多视图分类,特别是在医学影像中,呈现出独特的挑战,尤其是在处理大规模、高分辨率数据时。在这项工作中,我们提出了一种新颖的多视图视觉提示调整网络(MVPT-NET),用于分析多个筛查钼靶图像。我们首先在高分辨率钼靶图像上训练一个稳健的单视图分类模型,然后创新地将多视图特征学习适应为任务特定的提示调整过程。该技术选择性地调整一小部分可训练参数(7%),同时保留预训练单视图模型的稳健性,能够实现多视图数据的有效集成,而无需进行激进的下采样。我们的方法提供了传统特征融合方法的有效替代方案,为钼靶图像的高分辨率分析提供了更稳健、可扩展和高效的解决方案。在大型多机构数据集上的实验结果表明,我们的方法在保持检测效率的同时,优于传统方法,在区分良性、DCIS和侵袭性类别时达到了0.852的AUROC。这项工作突出了MVPT-NET在医学成像任务中的潜力,并为整合多视图数据在乳腺癌检测中提供了可扩展的解决方案。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
本文提出一种新型的多视角视觉提示调整网络(MVPT-NET),用于分析多视角乳腺癌筛查图像。通过预训练单视角分类模型并适应多视角特征学习,该方法能在不牺牲检测效率的前提下,实现多视角数据的有效整合,提高了乳腺癌检测的准确性和效率。实验结果表明,该方法在大型多机构数据集上的表现优于传统方法,达到AUROC 0.852。
Key Takeaways
- MVPT-NET用于分析乳腺癌多视角筛查图像,以提供早期诊断和治疗方案的有效指导。
- 该方法结合了单视角分类模型和多视角特征学习,提高了乳腺癌检测的准确性。
- MVPT-NET采用预训练模型进行微调,提高了模型的鲁棒性和性能。
- 通过创新的提示调整过程实现多视角数据的有效整合,不需要剧烈的降采样操作。
- 该方法优于传统特征融合方法,为医学图像分析提供了更稳健、可扩展和高效的解决方案。
- 实验结果表明,MVPT-NET在大型多机构数据集上的性能优于其他方法,达到了AUROC为0.852的高表现。
点此查看论文截图

Dissipative particle dynamics models of encapsulated microbubbles and gas vesicles for biomedical ultrasound simulations
Authors:Nikolaos Ntarakas, Maša Lah, Daniel Svenšek, Tilen Potisk, Matej Praprotnik
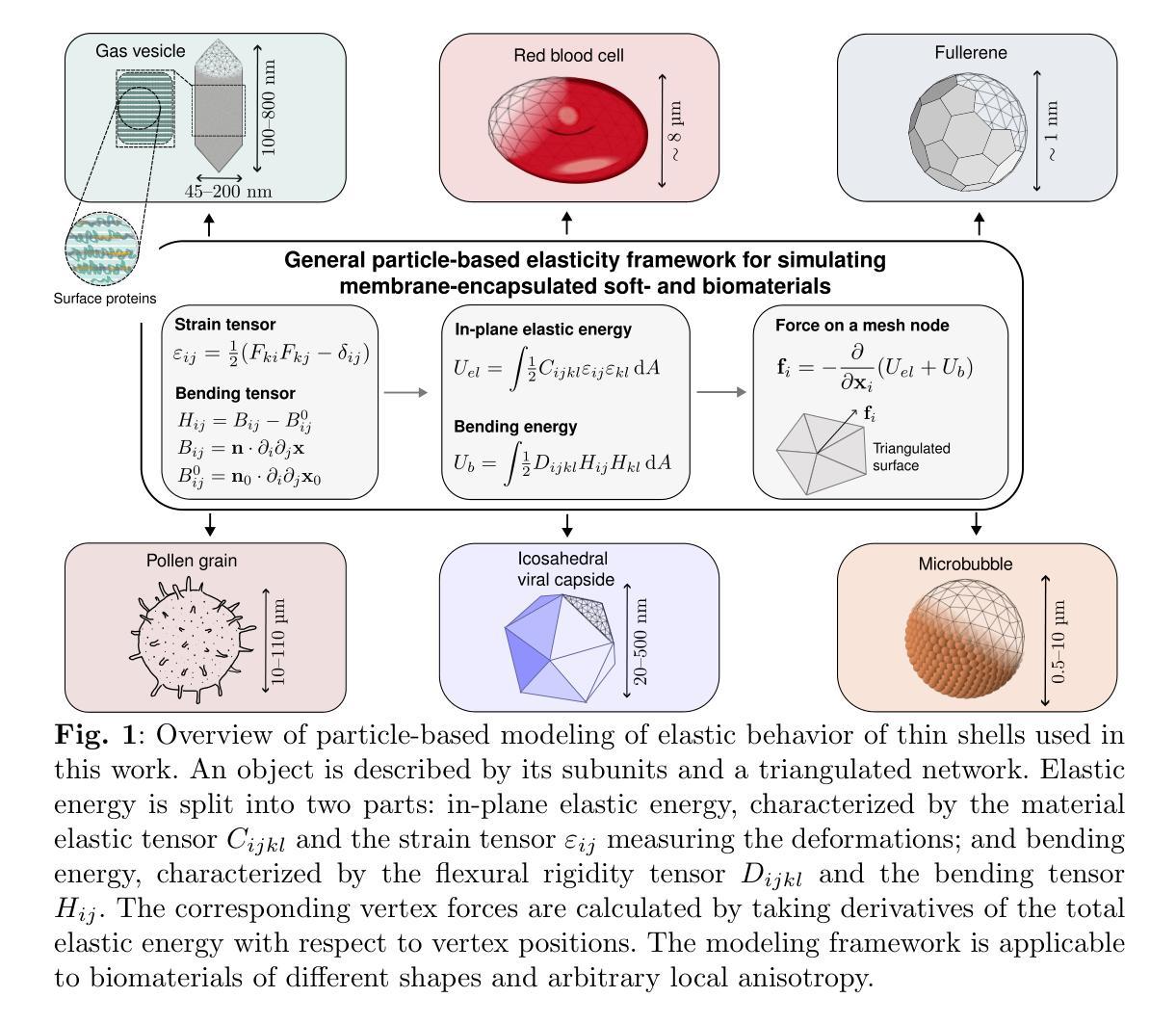
Ultrasound-guided drug and gene delivery (usdg) enables controlled and spatially precise delivery of drugs and macromolecules, encapsulated in microbubbles (embs) and submicron gas vesicles (gvs), to target areas such as cancer tumors. It is a non-invasive, high precision, low toxicity process with drastically reduced drug dosage. Rheological and acoustic properties of gvs and embs critically affect the outcome of usdg and imaging. Detailed understanding and modeling of their physical properties is thus essential for ultrasound-mediated therapeutic applications. State-of-the-art continuuum models of shelled bodies cannot incorporate critical details such as varying thickness of the encapsulating shell or specific interactions between its constituents and interior or exterior solvents. Such modeling approaches also do not allow for detailed modeling of chemical surface functionalizations, which are crucial for tuning the gv-blood interactions. We develop a general particle-based modeling framework for encapsulated bodies that accurately captures elastic and rheological properties of gvs and embs. We use dissipative particle dynamics to model the solvent, the gaseous phase in the capsid, and the triangulated surfaces of immersed objects. Their elastic behavior is studied and validated through stretching and buckling simulations, eigenmode analysis, shear flow simulations, and comparison of predicted gv buckling pressure with experimental data from the literature. The presented modeling approach paves the way for large-scale simulations of encapsulated bodies, capturing their dynamics, interactions, and collective behavior.
超声引导下的药物和基因传递(USDG)技术能够实现药物和大分子在微泡(EMBs)和亚微米气体囊泡(GVs)的封装下,对癌症肿瘤等目标区域的精准空间控制传递。这是一种非侵入性、高精度、低毒性的过程,能大幅度减少药物剂量。GVs和EMBs的流变学和声学特性对USDG和成像的结果具有重要影响。因此,对其物理性质的深入理解和建模对于超声介导的治疗应用至关重要。现有的先进连续体模型无法纳入封装体的重要细节,如封装壳厚度不同或其与内外溶剂之间的特定相互作用。这种建模方法也不允许对表面功能化进行详细的建模,这对于调节GV与血液之间的相互作用至关重要。我们开发了一种用于封装体的通用粒子建模框架,能够准确捕捉GVs和EMBs的弹性和流变性质。我们使用耗散粒子动力学来模拟溶剂、衣壳中的气相和浸没物体的三角形表面。我们研究了他们的弹性行为并通过拉伸和弯曲模拟、特征模态分析、剪切流模拟以及将预测的GV弯曲压力与文献中的实验数据进行比较来验证其有效性。所呈现的建模方法为大规模封装体模拟铺平了道路,能够捕捉其动力学、相互作用和集体行为。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF 55 pages, 18 figures, 4 tables
Summary
本文介绍了超声引导药物和基因传递(usdg)技术,该技术利用微气泡(embs)和亚微米气体囊泡(gvs)封装药物和大分子,实现针对癌症肿瘤等目标区域的精准空间传递。这是一种非侵入性、高精度、低毒性的过程,可大幅度降低药物剂量。文章强调了对gvs和embs流变学和声学特性的深入理解与建模对于超声介导治疗应用的重要性。现有的连续模型无法涵盖关键细节,如封装壳厚度变化或其与内外溶剂间的特定相互作用。因此,开发了一种针对封装体的通用粒子基础建模框架,准确捕捉gvs和embs的弹性和流变特性。该研究为封装体的大规模模拟铺平了道路,能够捕捉其动力学、相互作用和集体行为。
Key Takeaways
- 超声引导药物和基因传递(usdg)能够实现精准的空间药物传递,尤其针对癌症肿瘤等目标区域。
- 该技术利用微气泡(embs)和亚微米气体囊泡(gvs)封装药物和大分子。
- usdg是一种非侵入性、高精度、低毒性的过程,可大幅度降低药物剂量。
- gvs和embs的流变学和声学特性对usdg和成像结果有重要影响。
- 现有连续模型无法充分描述gvs和embs的关键特性,如封装壳的厚度变化和其与溶剂的相互作用。
- 研究开发了一种基于粒子的建模框架来准确捕捉gvs和embs的弹性和流变特性。
点此查看论文截图

SRMF: A Data Augmentation and Multimodal Fusion Approach for Long-Tail UHR Satellite Image Segmentation
Authors:Yulong Guo, Zilun Zhang, Yongheng Shang, Tiancheng Zhao, Shuiguang Deng, Yingchun Yang, Jianwei Yin
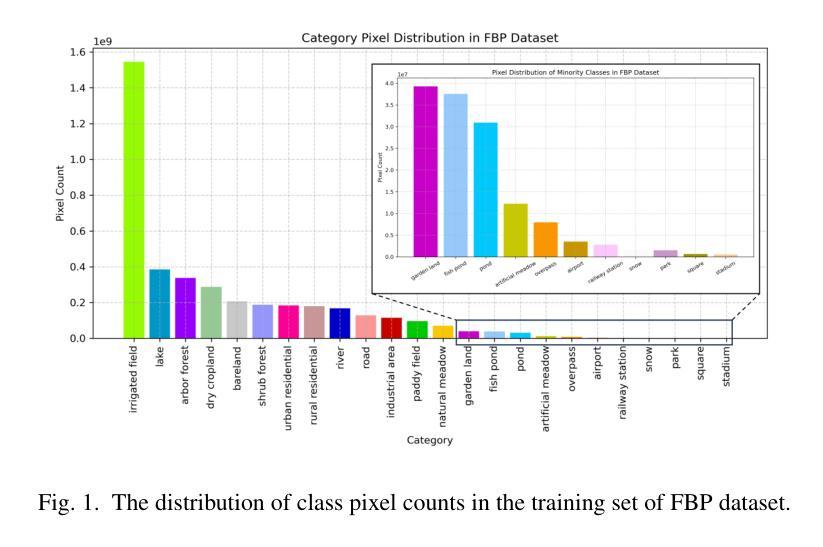
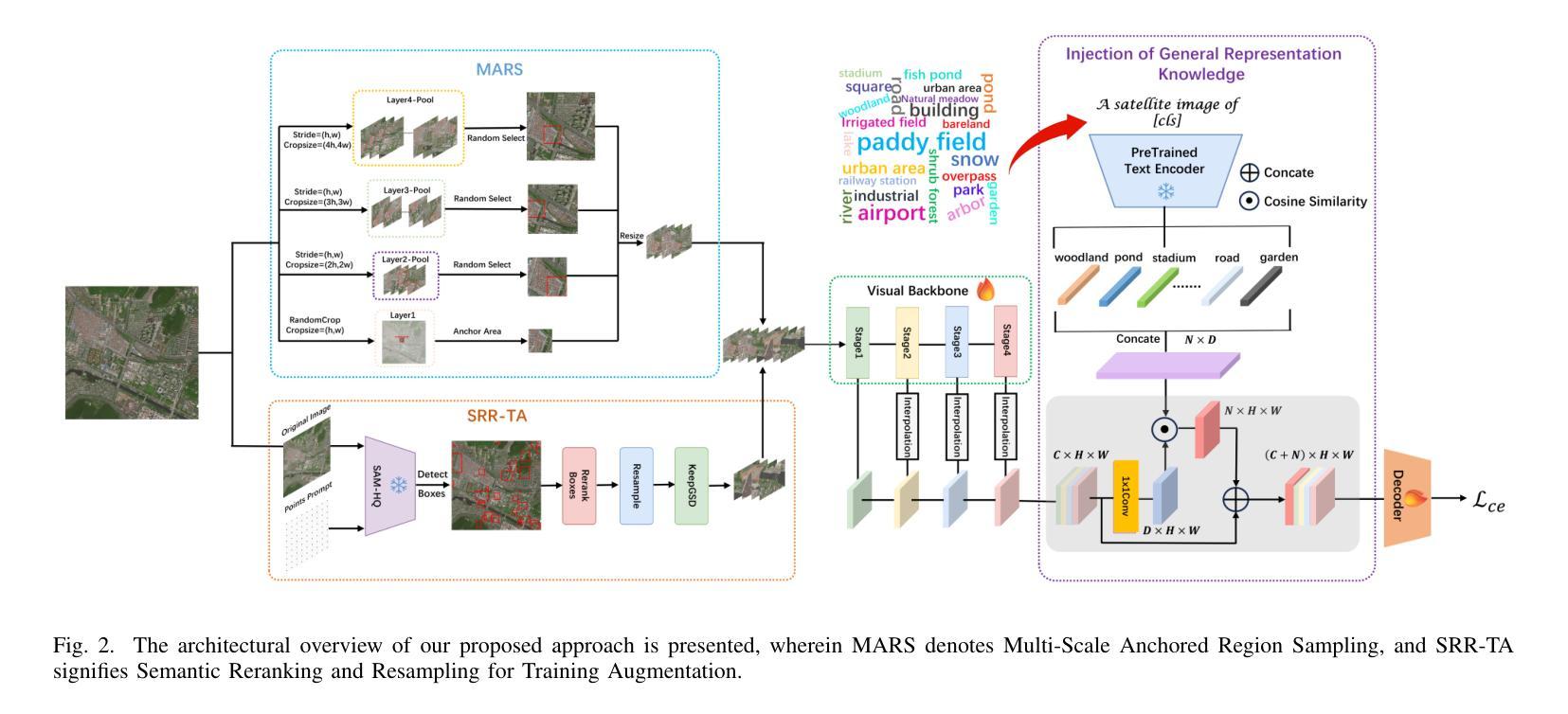
The long-tail problem presents a significant challenge to the advancement of semantic segmentation in ultra-high-resolution (UHR) satellite imagery. While previous efforts in UHR semantic segmentation have largely focused on multi-branch network architectures that emphasize multi-scale feature extraction and fusion, they have often overlooked the importance of addressing the long-tail issue. In contrast to prior UHR methods that focused on independent feature extraction, we emphasize data augmentation and multimodal feature fusion to alleviate the long-tail problem. In this paper, we introduce SRMF, a novel framework for semantic segmentation in UHR satellite imagery. Our approach addresses the long-tail class distribution by incorporating a multi-scale cropping technique alongside a data augmentation strategy based on semantic reordering and resampling. To further enhance model performance, we propose a multimodal fusion-based general representation knowledge injection method, which, for the first time, fuses text and visual features without the need for individual region text descriptions, extracting more robust features. Extensive experiments on the URUR, GID, and FBP datasets demonstrate that our method improves mIoU by 3.33%, 0.66%, and 0.98%, respectively, achieving state-of-the-art performance. Code is available at: https://github.com/BinSpa/SRMF.git.
超长尾问题为超高分辨率(UHR)卫星图像语义分割的进一步发展带来了巨大挑战。以往超高分辨率语义分割的主要努力大多集中在多分支网络架构上,强调多尺度特征提取和融合,往往忽略了解决长尾问题的重要性。与以往侧重于独立特征提取的UHR方法不同,我们强调数据增强和多模态特征融合来缓解长尾问题。在本文中,我们介绍了SRMF,一个用于超高分辨率卫星图像语义分割的新型框架。我们的方法通过结合多尺度裁剪技术,以及基于语义重排和重新采样的数据增强策略,解决了长尾类分布问题。为了进一步提高模型性能,我们提出了一种基于多模态融合的一般表示知识注入方法,该方法首次融合了文本和视觉特征,而无需单独的区域文本描述,从而提取出更稳健的特征。在URUR、GID和FBP数据集上的大量实验表明,我们的方法分别提高了mIoU的3.33%、0.66%和0.98%,达到了最先进的性能。代码可访问:https://github.com/BinSpa/SRMF.git。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF None
Summary
本文介绍了针对超高分辨率卫星图像语义分割的长尾问题,提出了一种新的框架SRMF。该框架通过多尺度裁剪技术和基于语义重排和重采样的数据增强策略来解决长尾类分布问题。同时,引入了一种基于多模态融合的一般表示知识注入方法,融合文本和视觉特征,提取更鲁棒的特征,提高了模型性能。在URUR、GID和FBP数据集上的实验表明,该方法分别提高了mIoU指标3.33%、0.66%和0.98%,达到最新性能水平。
Key Takeaways
- 超高分辨率卫星图像语义分割面临长尾问题挑战。
- 现有方法多关注多分支网络架构,但忽略了解决长尾问题的重要性。
- SRMF框架通过多尺度裁剪和数据增强策略解决长尾类分布问题。
- 引入基于多模态融合的知识注入方法,融合文本和视觉特征,提高模型性能。
- 实验在URUR、GID和FBP数据集上验证了SRMF框架的有效性。
- SRMF框架提高了mIoU指标,达到最新性能水平。
点此查看论文截图

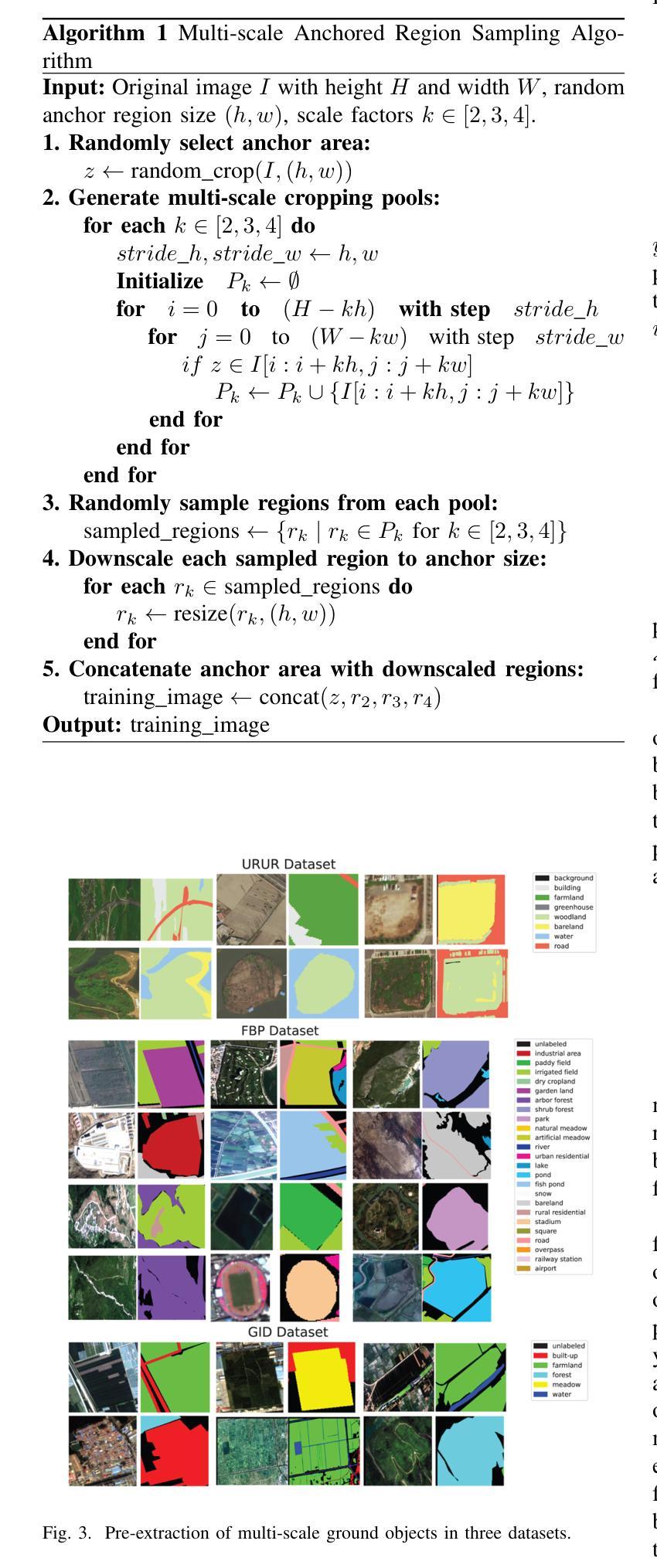
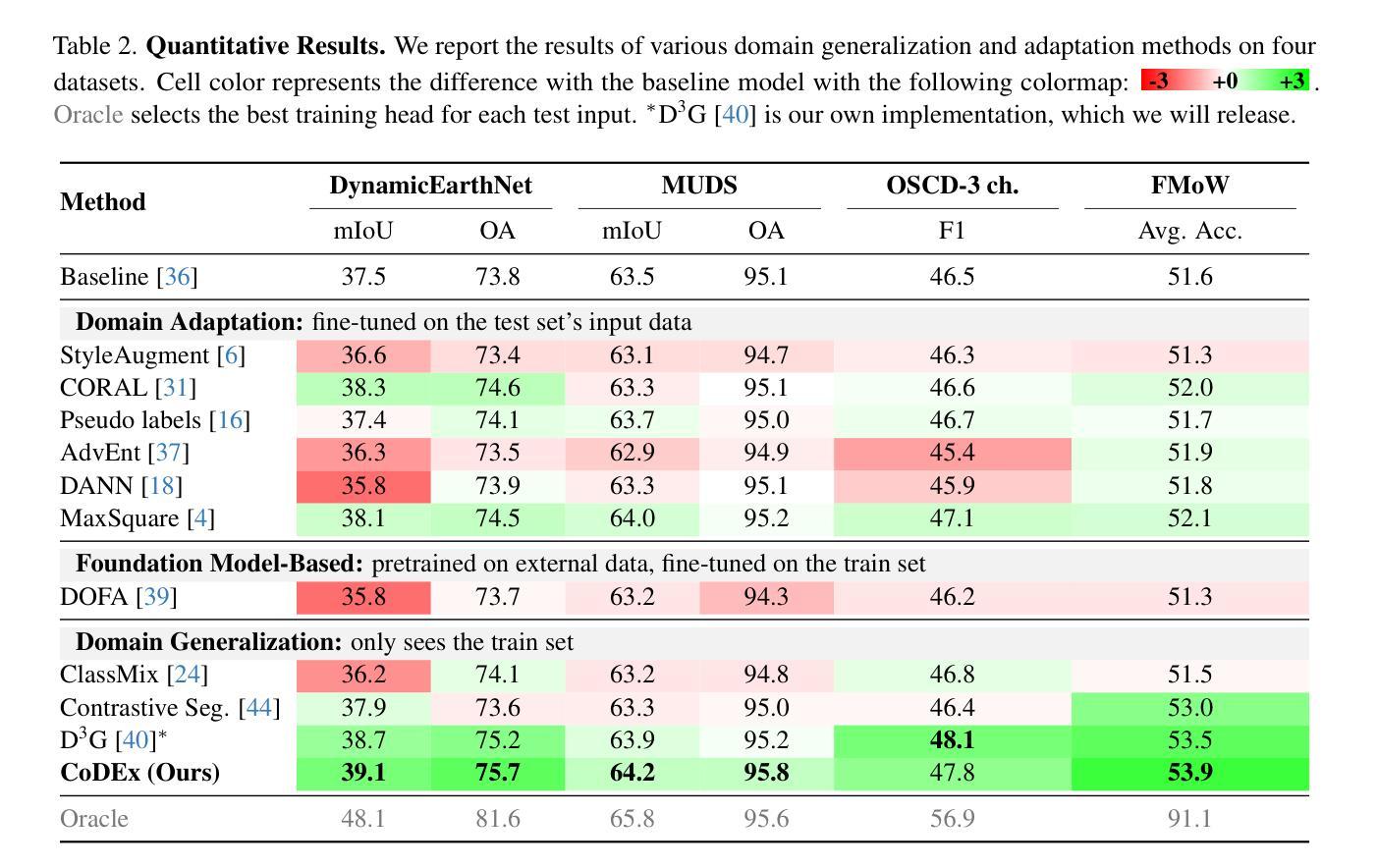
CoDEx: Combining Domain Expertise for Spatial Generalization in Satellite Image Analysis
Authors:Abhishek Kuriyal, Elliot Vincent, Mathieu Aubry, Loic Landrieu
Global variations in terrain appearance raise a major challenge for satellite image analysis, leading to poor model performance when training on locations that differ from those encountered at test time. This remains true even with recent large global datasets. To address this challenge, we propose a novel domain-generalization framework for satellite images. Instead of trying to learn a single generalizable model, we train one expert model per training domain, while learning experts’ similarity and encouraging similar experts to be consistent. A model selection module then identifies the most suitable experts for a given test sample and aggregates their predictions. Experiments on four datasets (DynamicEarthNet, MUDS, OSCD, and FMoW) demonstrate consistent gains over existing domain generalization and adaptation methods. Our code is publicly available at https://github.com/Abhishek19009/CoDEx.
地形外观的全球变化给卫星图像分析带来了重大挑战,尤其是在训练地点与测试地点不同的情况下,模型性能往往较差。即使使用最新的全球大型数据集,情况依然如此。为了应对这一挑战,我们提出了一种新型的卫星图像领域通用化框架。我们并非试图学习单一的通用模型,而是针对每个训练领域训练一个专家模型,同时学习专家之间的相似性并鼓励相似专家保持一致。模型选择模块随后可以确定给定测试样本的最合适专家并对其预测进行汇总。在四个数据集(DynamicEarthNet、MUDS、OSCD和FMoW)上的实验表明,与现有的领域通用化和适应方法相比,该框架具有持续的优势。我们的代码可在https://github.com/Abhishek19009/CoDEx上公开访问。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF CVPR 2025 EarthVision Workshop
Summary
本文主要探讨全球地形变化的卫星图像分析难题。虽然大型全球数据集可以一定程度上解决问题,但针对测试环境与训练环境不一致的问题,文章提出一种新型卫星图像领域泛化框架。不同于单一通用模型学习,该框架训练每个训练领域的专家模型,学习专家模型间的相似性并鼓励相似专家模型保持一致。模型选择模块为给定测试样本选择最合适的专家模型并聚合其预测结果。实验证明该框架在四个数据集上的表现优于现有领域泛化和适应方法。代码已公开在GitHub上。
Key Takeaways
- 全球地形变化给卫星图像分析带来挑战。
- 即使使用大型全球数据集,模型在测试时仍可能表现不佳。
- 提出一种新型卫星图像领域泛化框架,训练针对每个训练领域的专家模型。
- 通过学习专家模型间的相似性并鼓励相似专家保持一致来提高模型性能。
- 模型选择模块能根据测试样本选择最合适的专家模型。
- 在四个数据集上的实验证明该框架表现优于现有方法。
点此查看论文截图

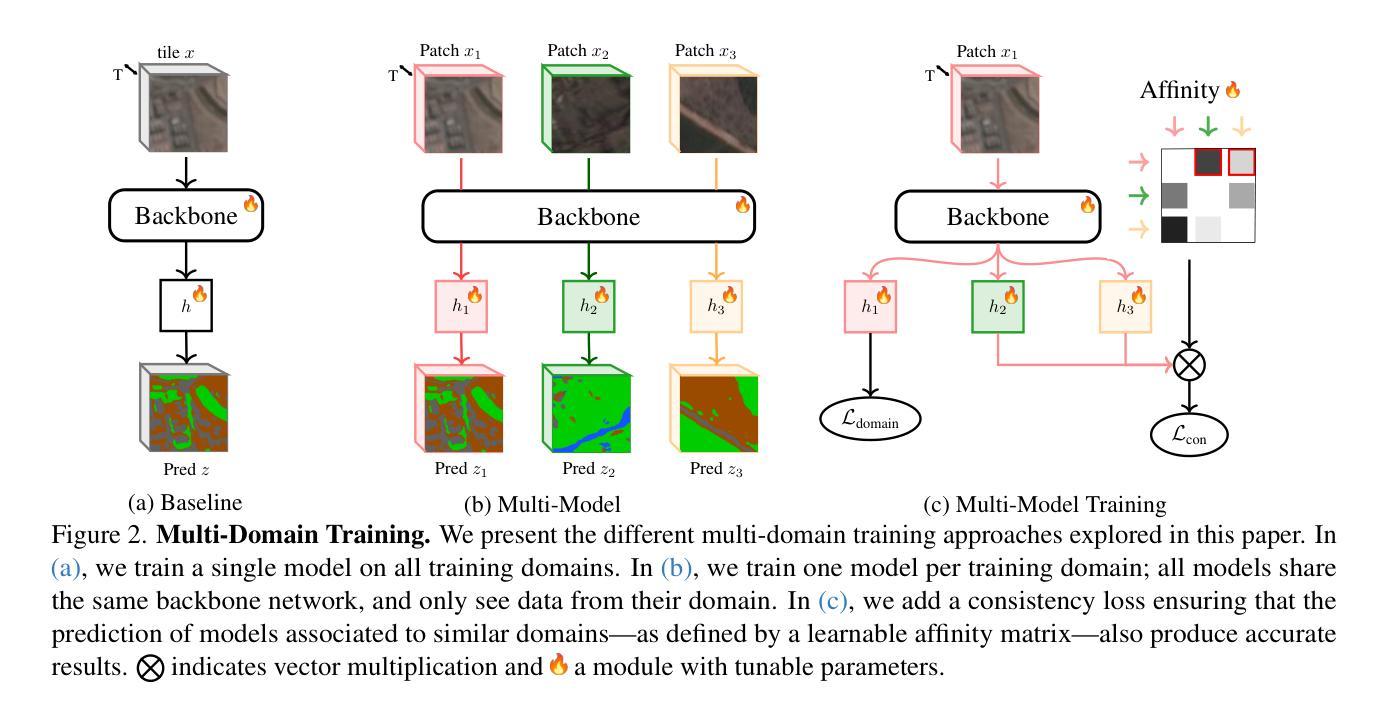
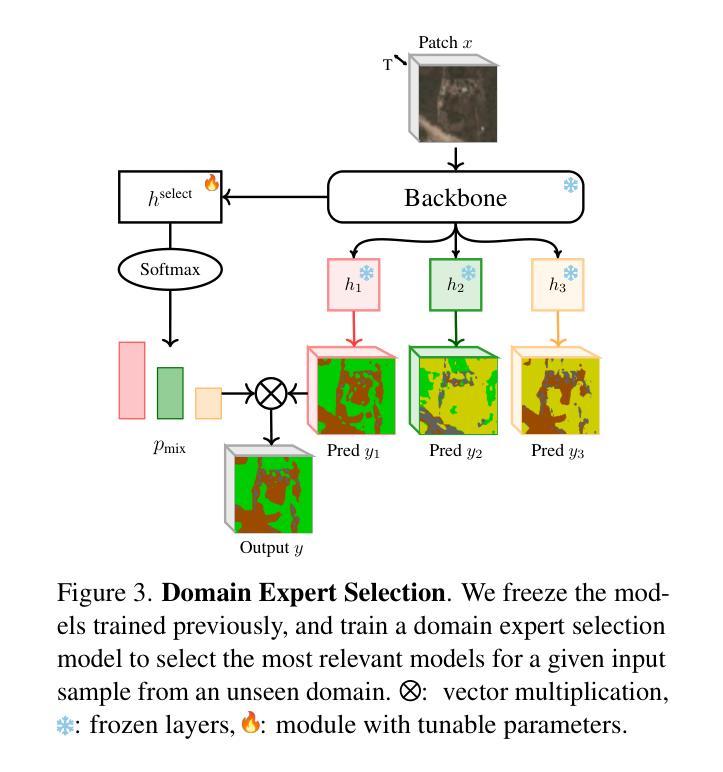
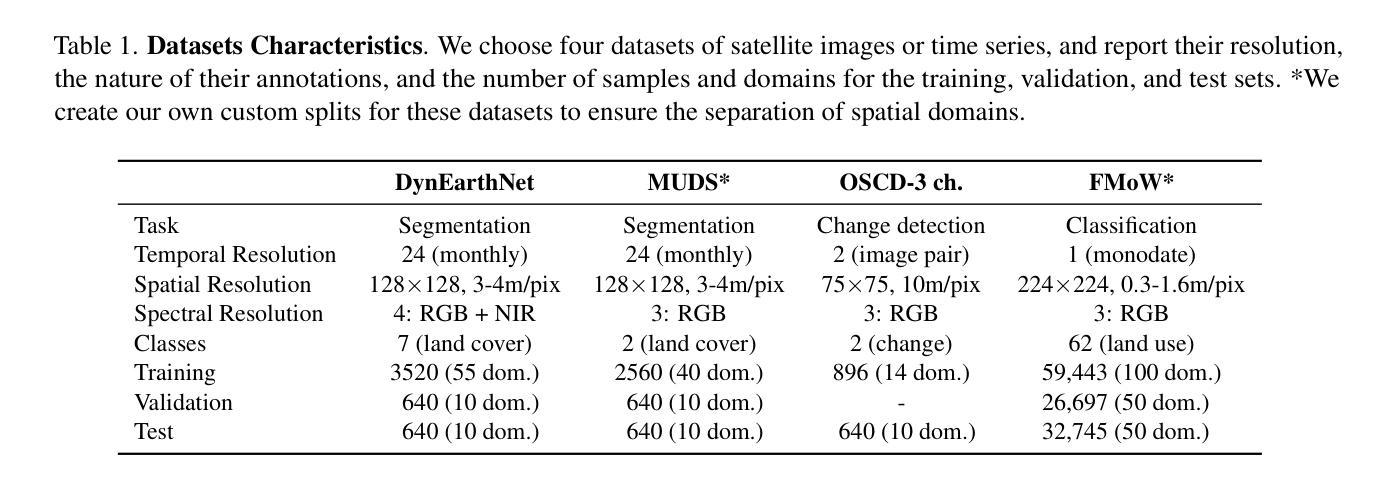
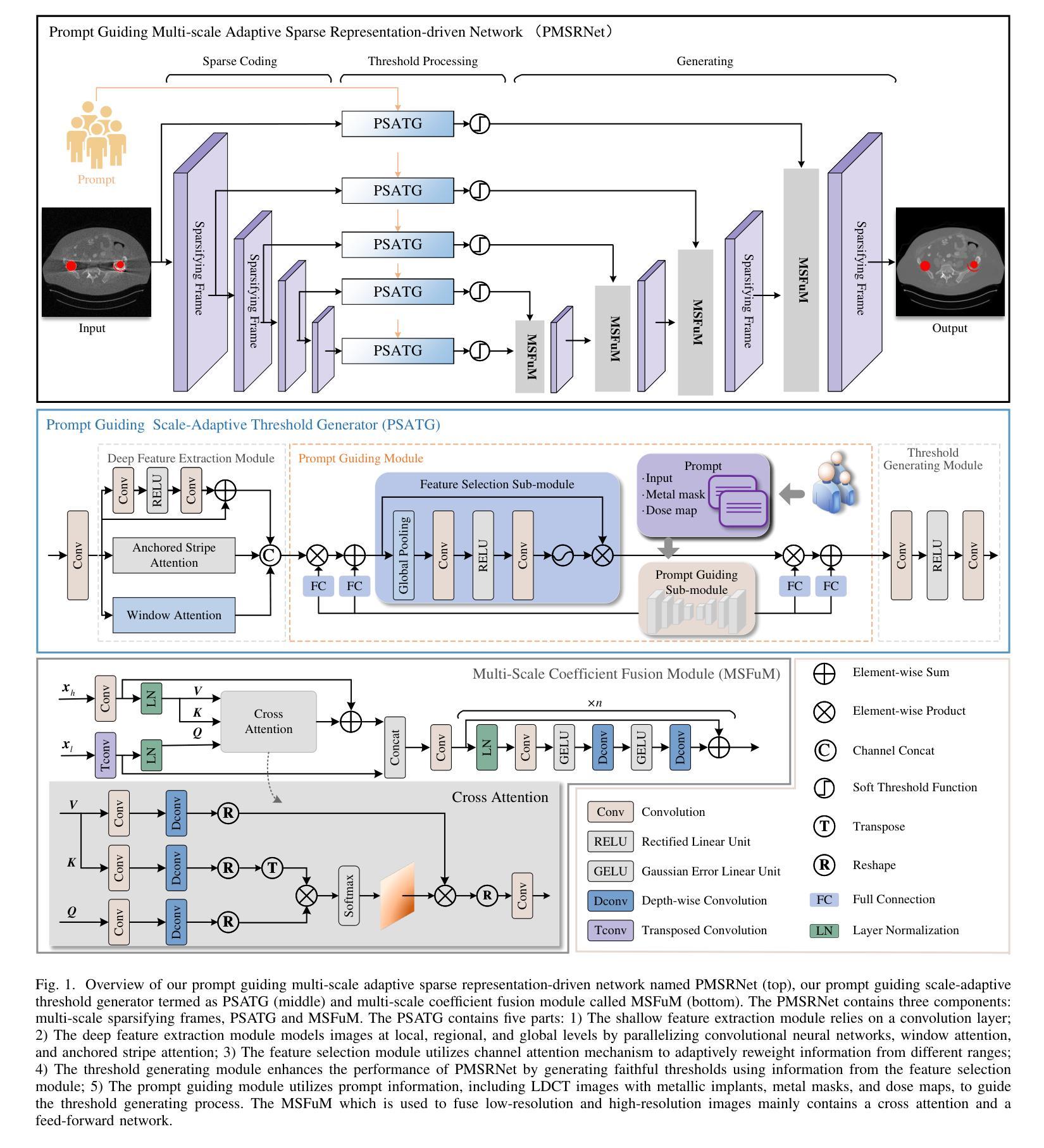
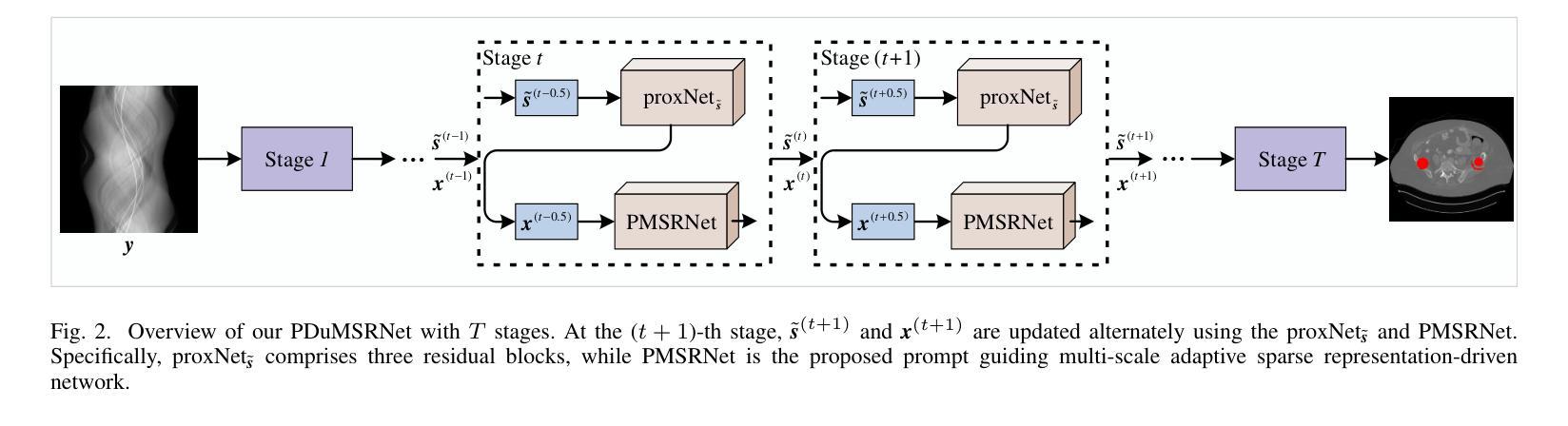
Prompt Guiding Multi-Scale Adaptive Sparse Representation-driven Network for Low-Dose CT MAR
Authors:Baoshun Shi, Bing Chen, Shaolei Zhang, Huazhu Fu, Zhanli Hu
Low-dose CT (LDCT) is capable of reducing X-ray radiation exposure, but it will potentially degrade image quality, even yields metal artifacts at the case of metallic implants. For simultaneous LDCT reconstruction and metal artifact reduction (LDMAR), existing deep learning-based efforts face two main limitations: i) the network design neglects multi-scale and within-scale information; ii) training a distinct model for each dose necessitates significant storage space for multiple doses. To fill these gaps, we propose a prompt guiding multi-scale adaptive sparse representation-driven network, abbreviated as PMSRNet, for LDMAR task. Specifically, we construct PMSRNet inspired from multi-scale sparsifying frames, and it can simultaneously employ within-scale characteristics and cross-scale complementarity owing to an elaborated prompt guiding scale-adaptive threshold generator (PSATG) and a built multi-scale coefficient fusion module (MSFuM). The PSATG can adaptively capture multiple contextual information to generate more faithful thresholds, achieved by fusing features from local, regional, and global levels. Furthermore, we elaborate a model interpretable dual domain LDMAR framework called PDuMSRNet, and train single model with a prompt guiding strategy for multiple dose levels. We build a prompt guiding module, whose input contains dose level, metal mask and input instance, to provide various guiding information, allowing a single model to accommodate various CT dose settings. Extensive experiments at various dose levels demonstrate that the proposed methods outperform the state-of-the-art LDMAR methods.
低剂量CT(LDCT)能够减少X射线辐射暴露,但可能会降低图像质量,甚至在金属植入物的情况下产生金属伪影。对于同时进行的LDCT重建和金属伪影减少(LDMAR),现有的基于深度学习的方法面临两个主要局限性:i)网络设计忽略了多尺度和尺度内的信息;ii)为每个剂量训练一个独特的模型需要大量的存储空间来应对多种剂量。为了填补这些空白,我们提出了一种基于即时引导的多尺度自适应稀疏表示驱动网络(简称PMSRNet),用于LDMAR任务。具体来说,我们受到多尺度稀疏框架的启发构建了PMSRNet,它可以同时利用尺度内的特征和跨尺度的互补性,这得益于精心设计的即时引导尺度自适应阈值生成器(PSATG)和内置的多尺度系数融合模块(MSFuM)。PSATG可以自适应地捕获多种上下文信息来生成更真实的阈值,这是通过融合本地、区域和全局级别的特征来实现的。此外,我们详细阐述了一种模型可解释的双域LDMAR框架,称为PDuMSRNet,并采用即时引导策略为多个剂量水平训练单一模型。我们建立了一个即时引导模块,其输入包括剂量水平、金属掩码和输入实例,以提供多种指导信息,使单一模型能够适应各种CT剂量设置。在不同剂量水平上的大量实验表明,所提出的方法优于现有的最先进的LDMAR方法。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
该文本介绍了一种针对低剂量计算机断层扫描(LDCT)的金属伪影减少技术。文章提出了一个基于深度学习的方法,即提示引导多尺度自适应稀疏表示驱动网络(PMSRNet),用于同时实现LDCT重建和金属伪影减少(LDMAR)。该网络设计灵感来源于多尺度稀疏框架,可以充分利用尺度内特性和跨尺度互补性。此外,文章还介绍了一种模型可解释的跨域LDMAR框架(PDuMSRNet),通过提示引导策略训练单一模型以适应多种剂量水平。该方法的性能在多个剂量水平上进行了广泛实验验证,证明了其优于现有LDMAR方法的效果。
Key Takeaways
- 低剂量计算机断层扫描(LDCT)可以减少X射线辐射暴露,但可能导致图像质量下降,甚至出现金属伪影。
- 现有的基于深度学习的LDMAR方法面临两个主要限制:忽视多尺度和尺度内信息,以及为每个剂量水平训练不同模型需要大量存储空间。
- 提出的PMSRNet网络受到多尺度稀疏框架的启发,可以充分利用尺度内特性和跨尺度互补性,通过精细的提示引导尺度自适应阈值生成器和多尺度系数融合模块实现LDMAR。
- 提示引导模块包含剂量水平、金属掩码和输入实例,为各种剂量设置提供指导信息,使单一模型适应各种CT剂量水平。
- PDuMSRNet框架是一种模型可解释的跨域LDMAR框架,通过提示引导策略训练单一模型,以处理多种剂量水平的LDCT图像。
- 广泛实验表明,所提出的方法在多个剂量水平上优于现有的LDMAR方法。
点此查看论文截图

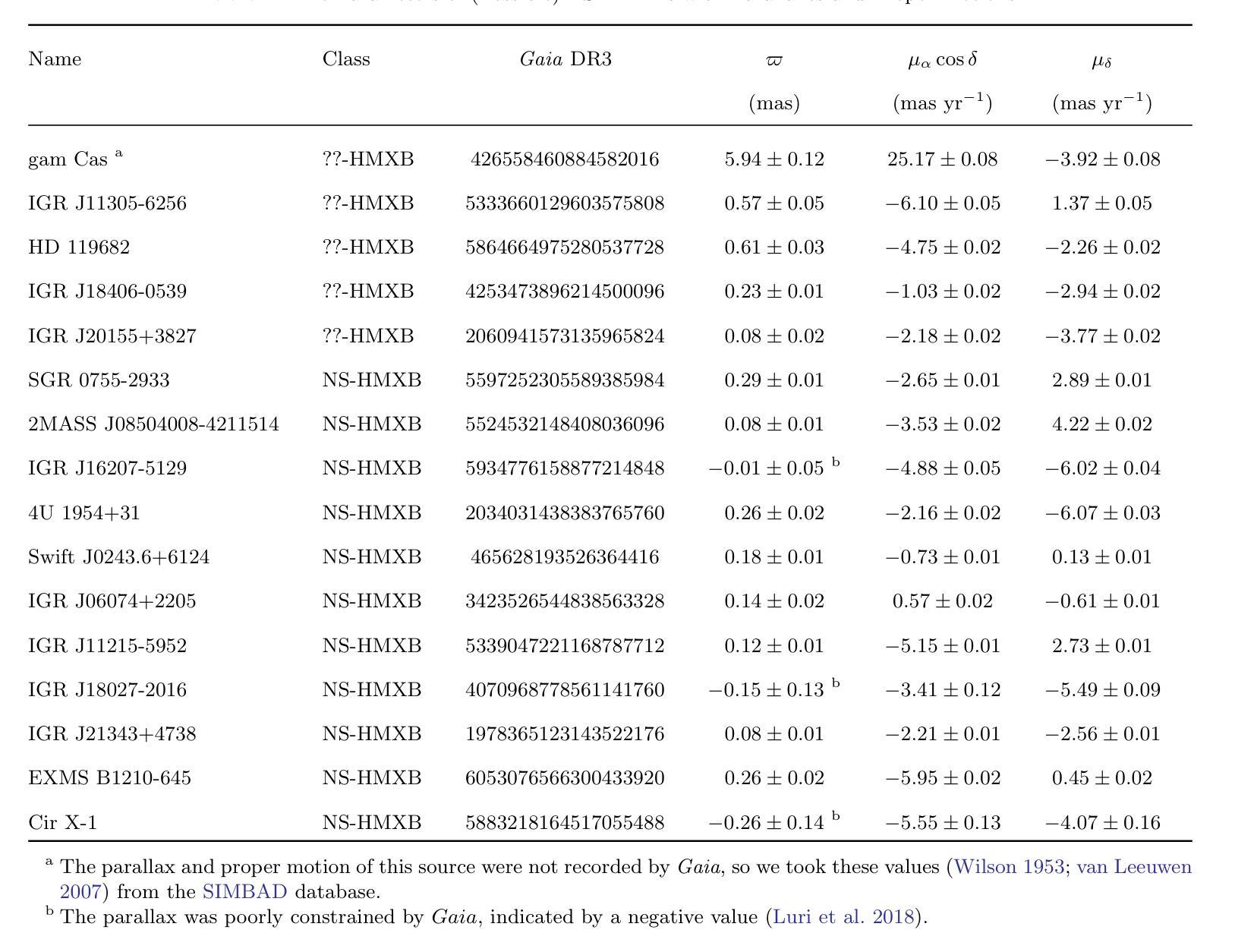
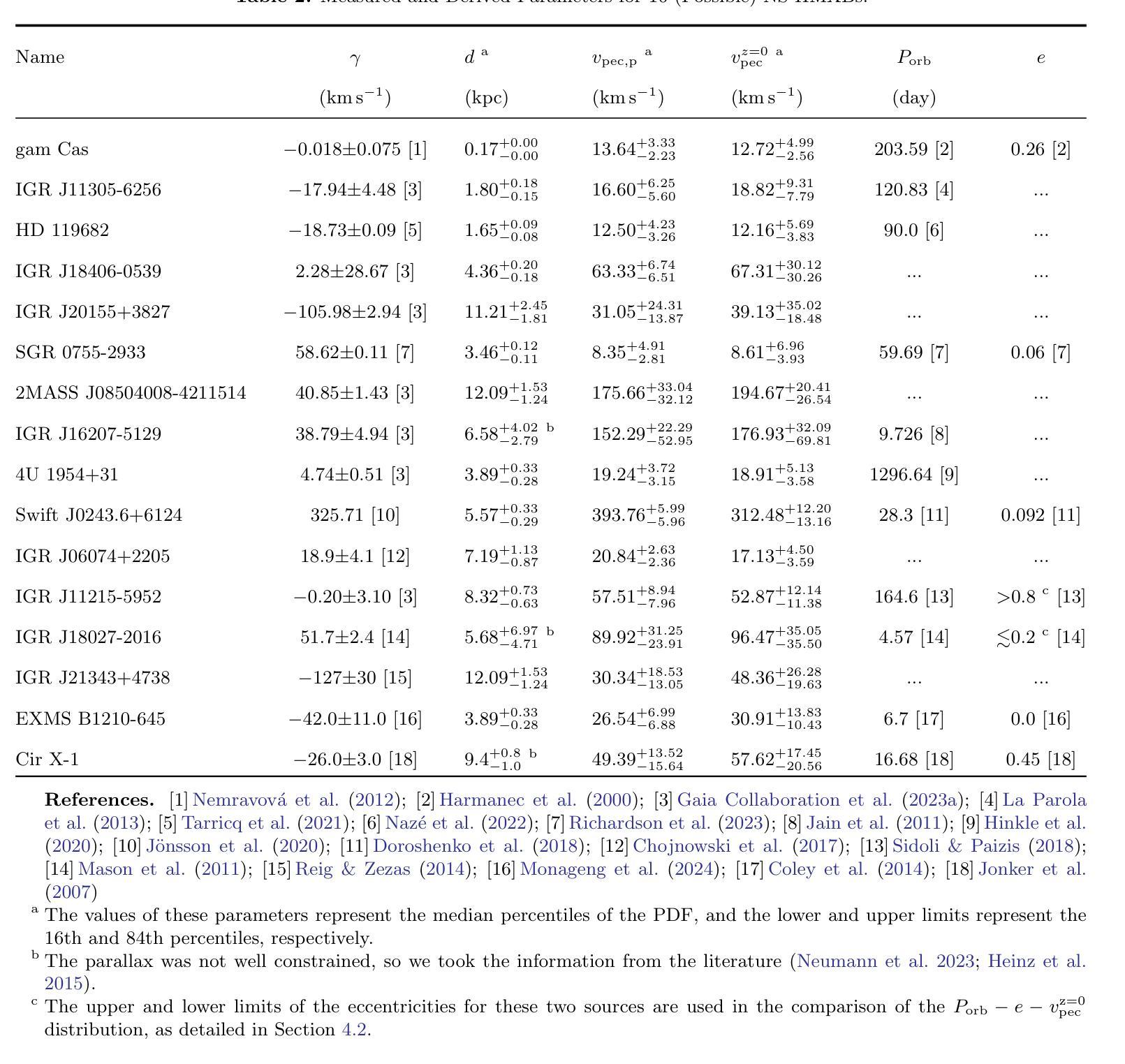
On Neutron Star Natal Kicks in High-Mass X-Ray Binaries: Insights from Population Synthesis
Authors:Xiangyu Ivy Wang, Xiang-Dong Li
The motion of neutron stars (NSs) in the Galaxy is largely dependent on natal kicks received by the NSs during supernova explosions. Thus, the measured peculiar velocities of NS high-mass X-ray binaries (HMXBs) provide valuable clues to natal kicks, which also play an important role in the evolution of HMXBs. In this work, we collect proper motions, radial velocities and parallaxes for 36 NS HMXBs to derive their peculiar velocities at the birth of the NSs. We then use binary population synthesis to simulate the velocities of NS HMXBs with various choices of the kick velocity distribution for both core-collapse and electron-capture supernovae. Comparing the simulated and measured velocities, orbital periods, and eccentricities, we show that the natal kick distribution that can best match the observations is characterized by a bimodal Maxwellian distribution with $\sigma_1$ = 320 km s$^{-1}$ (for core-collapse supernovae) and $\sigma_2$ = 80 km s$^{-1}$ (for electron-capture supernovae) and the He core mass for the latter in the range of $(1.83-2.25)$ $M_{\odot}$. Our findings provide useful insights for further population synthesis and binary evolution studies of NS binaries.
中子星(NSs)在银河系中的运动在很大程度上取决于超新星爆发期间NSs所受到的初生冲击。因此,测量中子星高质量X射线双星(HMXBs)的特定速度提供了关于初生冲击的宝贵线索,这些线索在HMXBs的演化中也起着重要作用。在这项工作中,我们收集了36个中子星HMXB的自行运动、速度和视差距离,以导出中子星诞生时的特殊速度。然后,我们使用二进制人口合成法模拟了各种中子星初生冲击速度分布下的NS HMXB速度,包括核心崩溃型和电子俘获型超新星。通过比较模拟和测量的速度、轨道周期和离心率,我们发现最能与观测相匹配的初生冲击分布特征是具有双峰麦克斯韦分布,其中σ1= 320公里每秒(适用于核心崩溃型超新星)和σ2= 80公里每秒(适用于电子俘获型超新星),后者的氦核质量范围在(1.83-2.25)$M_{\odot}$之间。我们的发现为进一步的人口合成学和NS双星的二元演化研究提供了有益的见解。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF 16 pages, 4 figures, 3 tables, accepted by ApJ
Summary
中子星在银河系中的运动受到其诞生时超新星爆炸所带来的初始速度影响。通过分析中子星高质量X射线双星(HMXBs)的特殊速度,可以了解初始速度的影响,这对理解HMXBs的演化至关重要。本研究收集了36个NS HMXB的天体运动学数据,推算出在诞生时中子星NS的特殊速度。通过二元合成人口模型模拟特殊速度,与多种模型比较核心塌缩型和电子捕获型超新星的中子星速度的分布特性。比较模拟与观测得到的速度、轨道周期和偏心度等结果后显示最佳匹配的初生状态中性流体速度为包含一组峰值为核心塌缩超新星的中均方根速度为$\sigma_1$= 320千米每秒,另一组为电子捕获型超新星中均方根速度为$\sigma_2$= 80千米每秒,后者的He核心质量在$(1.83-2.25)$M☉范围内。我们的研究对于进一步的二元合成人口模型和二元演化研究提供有价值的信息。
Key Takeaways
- 中子星在银河系中的运动受到超新星爆炸带来的初生速度影响。
- 高质量X射线双星(HMXBs)的特殊速度提供了关于初生速度的线索。
- 研究收集了NS HMXBs的天体运动学数据以推算中子星诞生时的特殊速度。
- 使用二元人口合成模型模拟特殊速度并对比多种模型下的中子星速度分布特性。
- 最佳匹配的初生状态中性流体速度分布表现为双峰Maxwellian分布,其中核心塌缩超新星的中均方根速度为320千米每秒,另一组为电子捕获型超新星的中均方根速度为80千米每秒。
- 电子捕获型超新星的He核心质量范围在$(1.83-2.25)$M☉之间。
点此查看论文截图

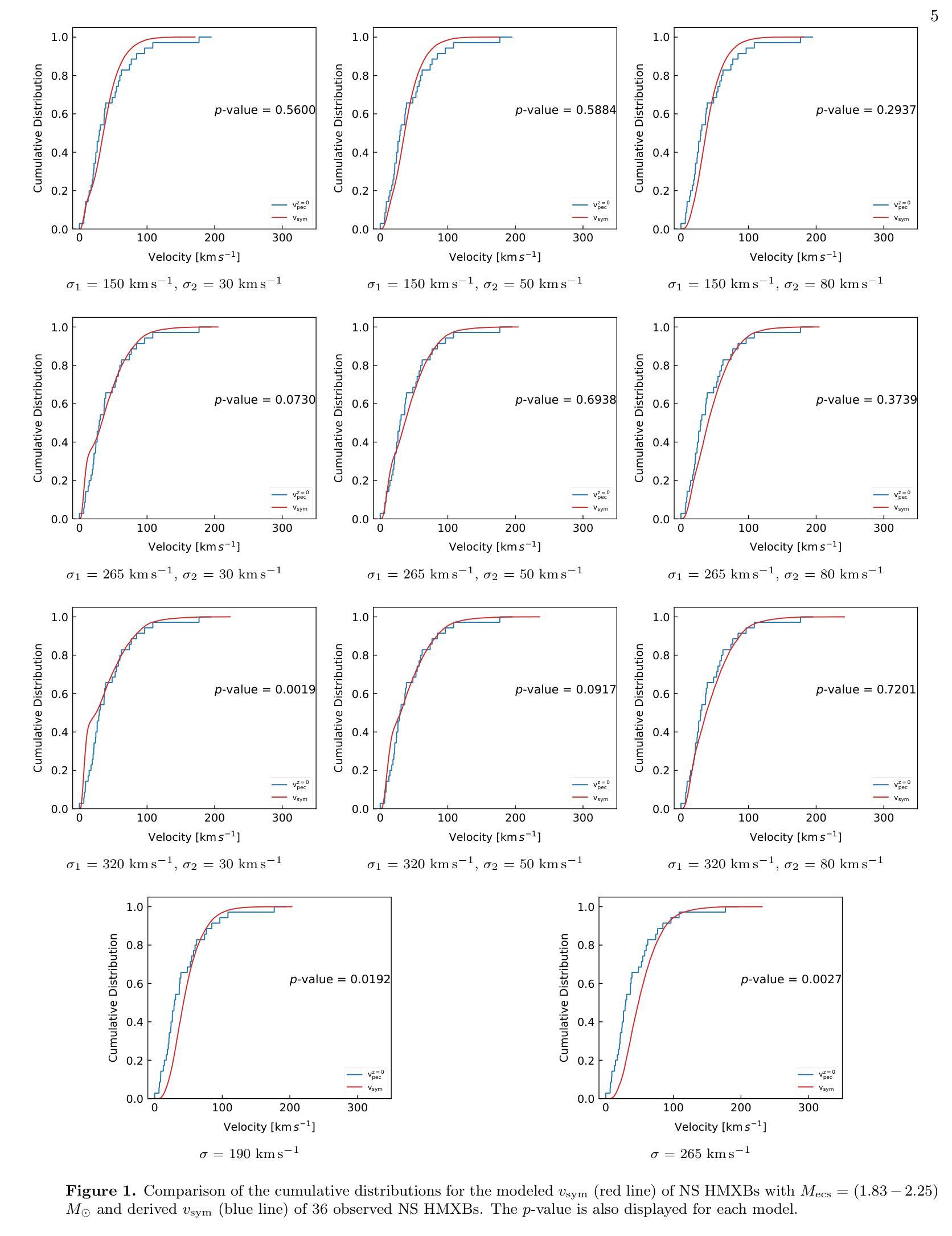
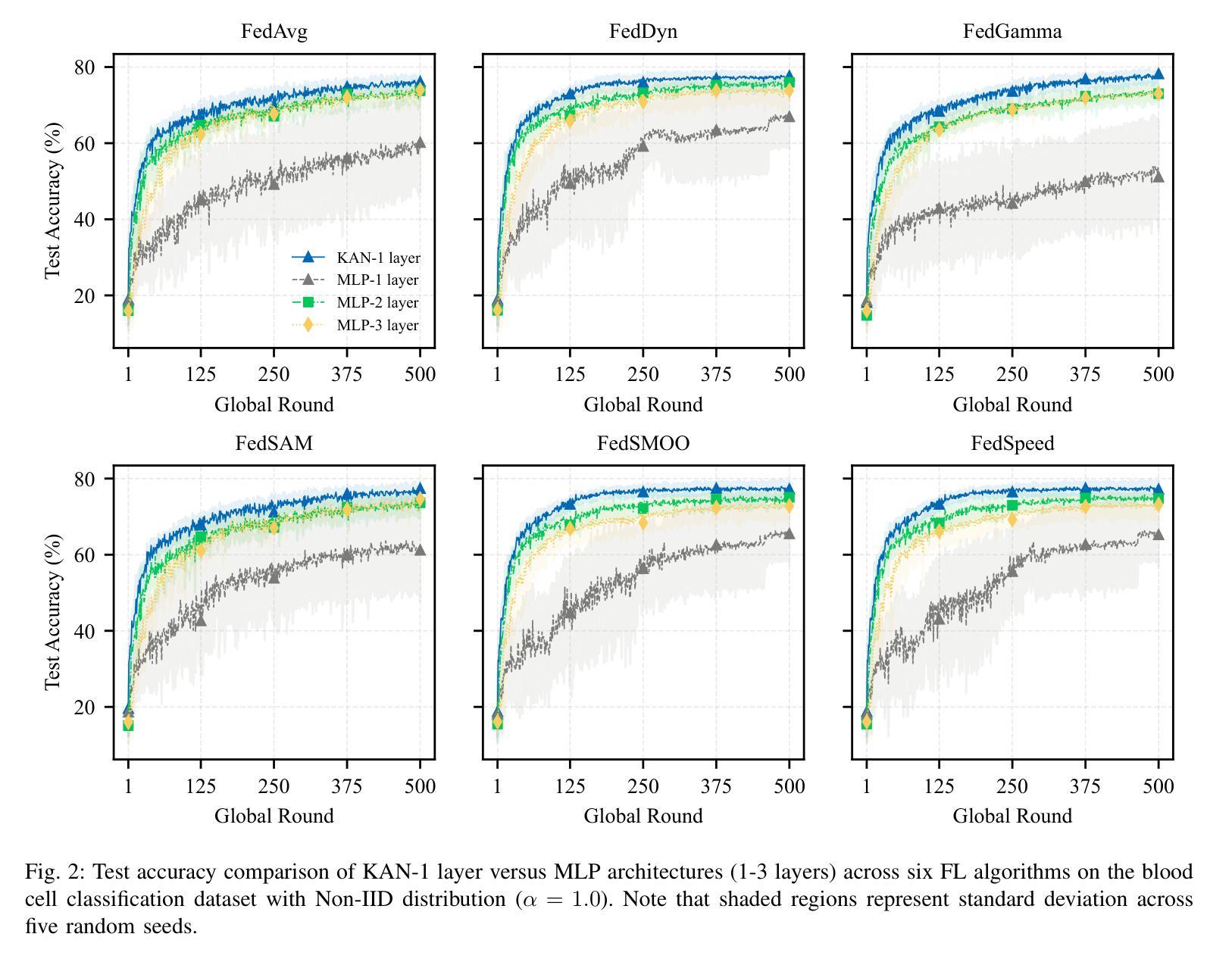
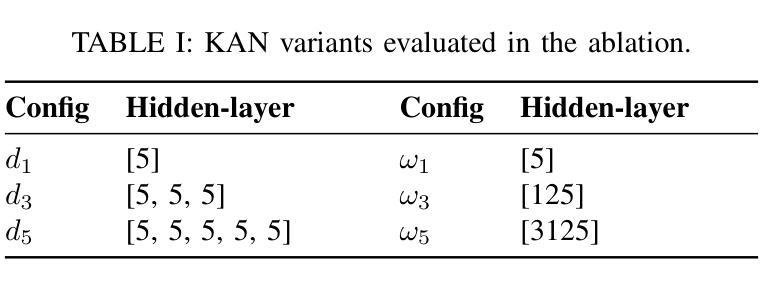
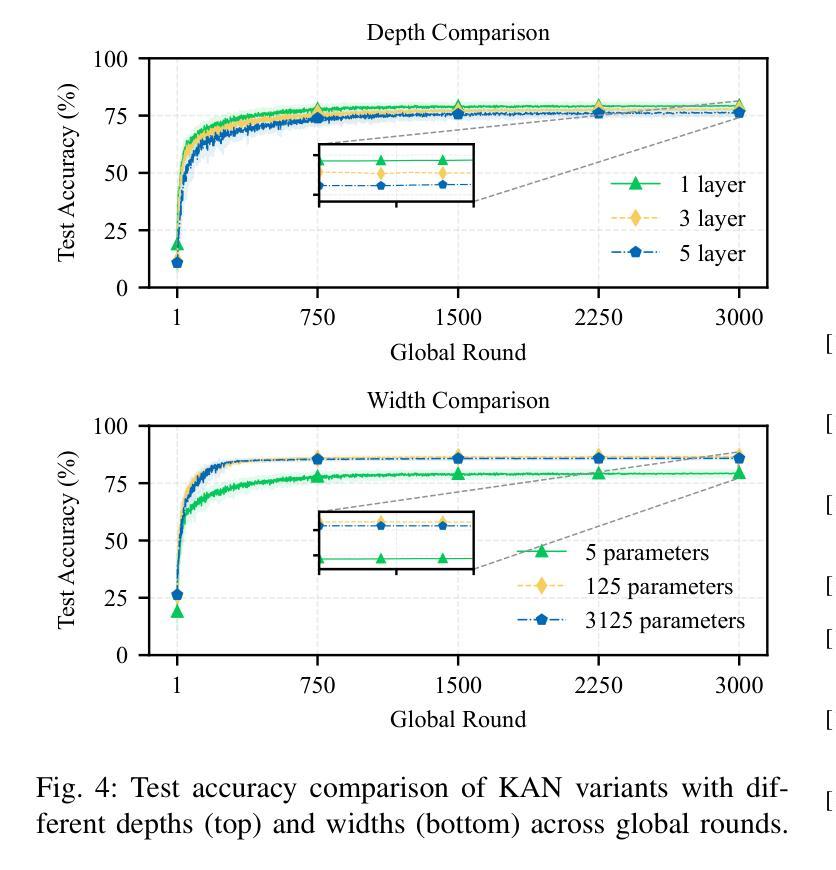
A Unified Benchmark of Federated Learning with Kolmogorov-Arnold Networks for Medical Imaging
Authors:Youngjoon Lee, Jinu Gong, Joonhyuk Kang
Federated Learning (FL) enables model training across decentralized devices without sharing raw data, thereby preserving privacy in sensitive domains like healthcare. In this paper, we evaluate Kolmogorov-Arnold Networks (KAN) architectures against traditional MLP across six state-of-the-art FL algorithms on a blood cell classification dataset. Notably, our experiments demonstrate that KAN can effectively replace MLP in federated environments, achieving superior performance with simpler architectures. Furthermore, we analyze the impact of key hyperparameters-grid size and network architecture-on KAN performance under varying degrees of Non-IID data distribution. Additionally, our ablation studies reveal that optimizing KAN width while maintaining minimal depth yields the best performance in federated settings. As a result, these findings establish KAN as a promising alternative for privacy-preserving medical imaging applications in distributed healthcare. To the best of our knowledge, this is the first comprehensive benchmark of KAN in FL settings for medical imaging task.
联邦学习(FL)能够在分散的设备上进行模型训练,无需共享原始数据,从而在医疗等敏感领域保护隐私。在本文中,我们评估了Kolmogorov-Arnold网络(KAN)架构与传统多层感知机(MLP)在六种最先进联邦学习算法上的表现,这些数据来自于血细胞分类数据集。值得注意的是,我们的实验表明,在联邦环境中,KAN可以有效地替代MLP,以更简单的架构实现卓越的性能。此外,我们分析了关键超参数——网格大小和网络架构在不同程度的非独立同分布(Non-IID)数据分布下对KAN性能的影响。另外,我们的消融研究结果表明,在保持深度最小的情况下优化KAN的宽度,在联邦环境中可以获得最佳性能。因此,这些发现确立了KAN在分布式医疗保健中的隐私保护医学成像应用的潜力。据我们所知,这是首次在联邦学习环境中对KAN进行医学成像任务的全面基准测试。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF 5 pages
Summary
本文探讨了Federated Learning(FL)在医疗图像分类中的表现,评估了Kolmogorov-Arnold Networks(KAN)与传统多层感知机(MLP)在六种先进的FL算法上的性能差异。实验表明,在联邦环境中,KAN能够替代MLP实现更优越的性能,特别是在处理非独立同分布(Non-IID)数据时表现突出。此外,研究还发现优化KAN的宽度并保持较小的深度有助于提高性能。因此,KAN有望成为分布式医疗成像应用中隐私保护的有力替代方案。本文是对医疗图像领域中的KAN在FL环境下的首次全面评估。
Key Takeaways
- Federated Learning (FL) 能够在不共享原始数据的情况下进行模型训练,保护隐私敏感领域如医疗的数据隐私。
- Kolmogorov-Arnold Networks (KAN) 在Federated Learning环境中相较于传统多层感知机(MLP)展现出优越性能。
- KAN在处理非独立同分布(Non-IID)数据时表现良好。
- KAN的性能受到网格大小和网络架构等超参数的影响。
- 在联邦环境中,优化KAN的宽度并维持较小的深度可以获得最佳性能。
- 此研究首次全面评估了KAN在医疗图像领域的Federated Learning环境中的表现。
点此查看论文截图


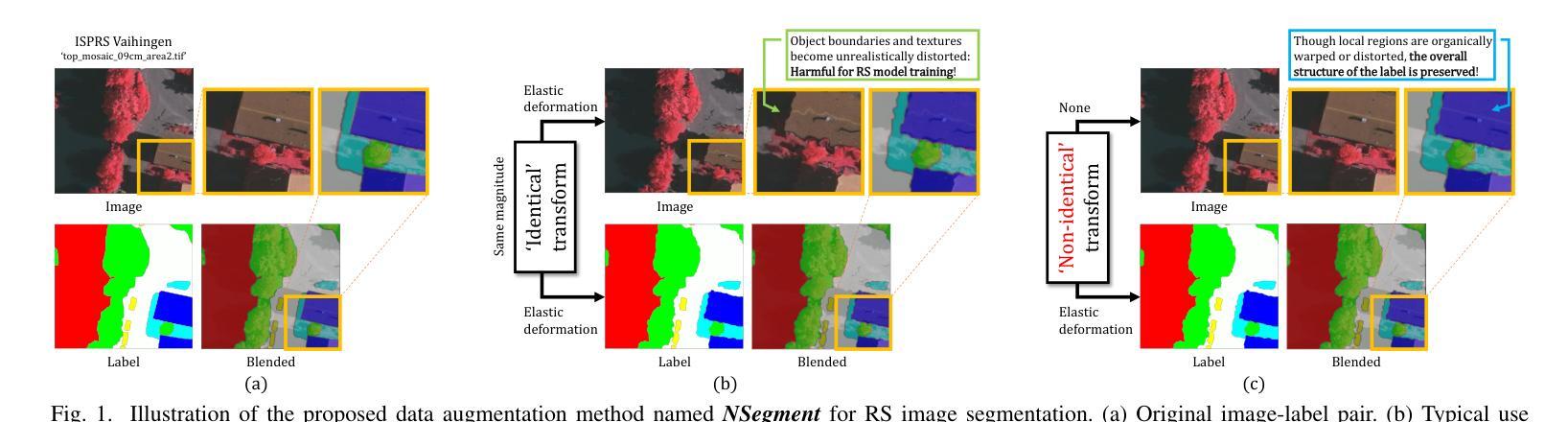
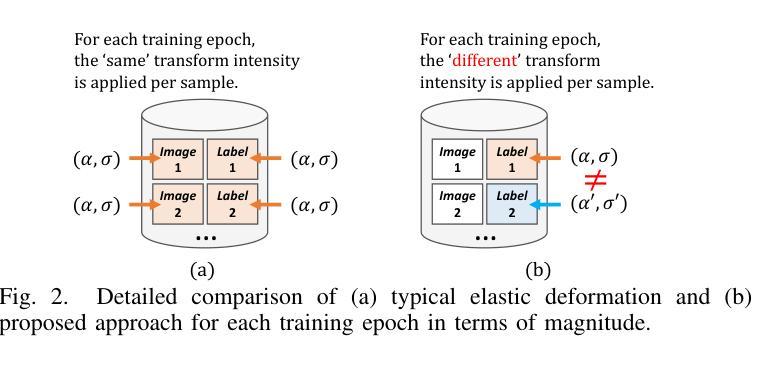
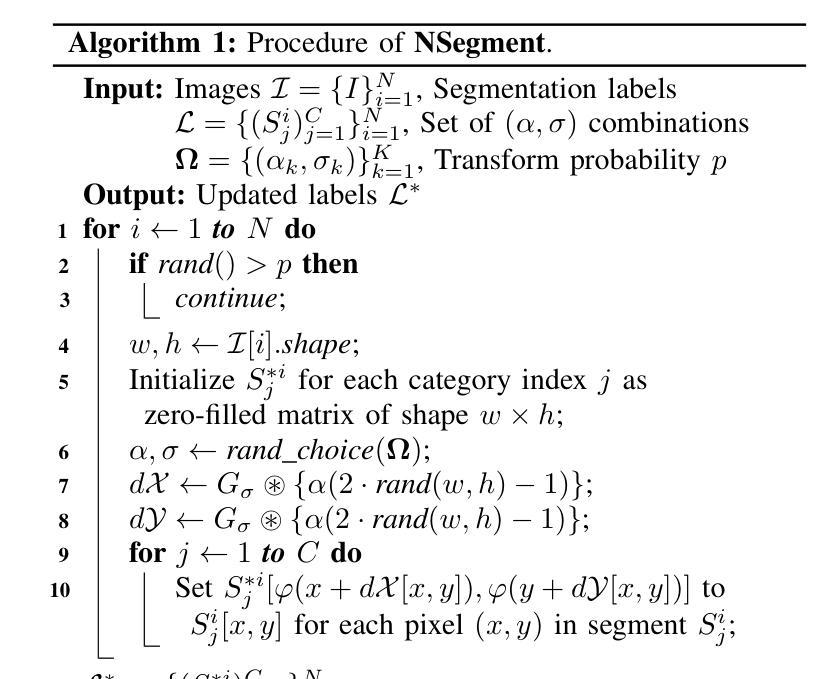
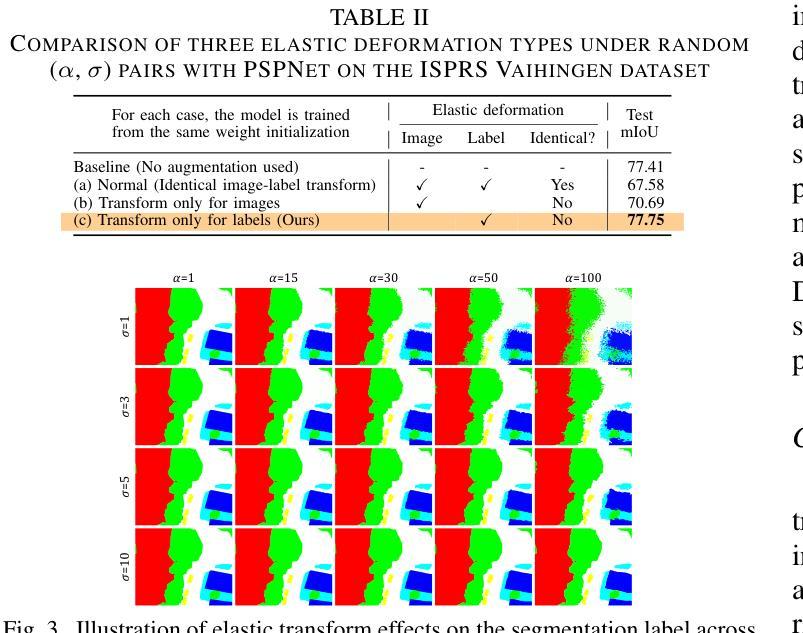
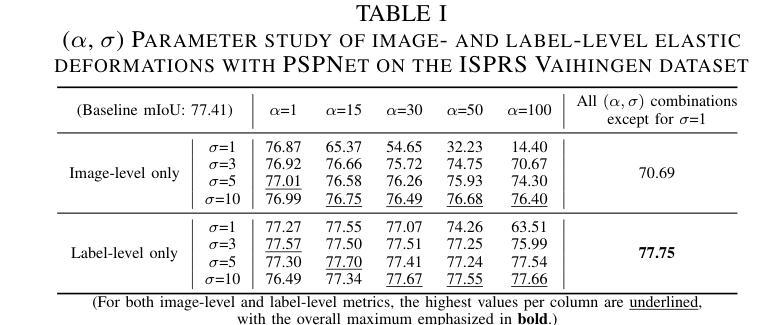
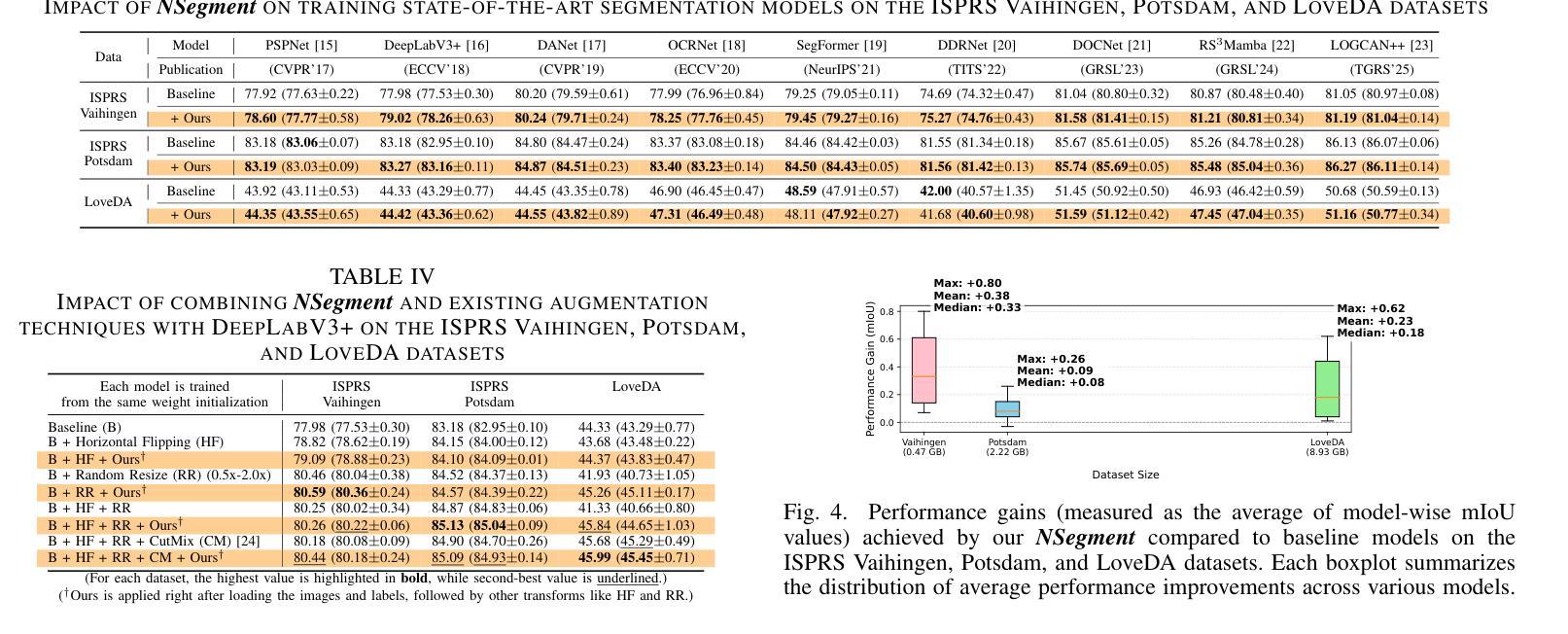
NSegment : Noisy Segment Improves Remote Sensing Image Segmentation
Authors:Yechan Kim, DongHo Yoon, SooYeon Kim, Moongu Jeon
Labeling errors in remote sensing (RS) image segmentation datasets often remain implicit and subtle due to ambiguous class boundaries, mixed pixels, shadows, complex terrain features, and subjective annotator bias. Furthermore, the scarcity of annotated RS data due to high image acquisition and labeling costs complicates training noise-robust models. While sophisticated mechanisms such as label selection or noise correction might address this issue, they tend to increase training time and add implementation complexity. In this letter, we propose NSegment-a simple yet effective data augmentation solution to mitigate this issue. Unlike traditional methods, it applies elastic transformations only to segmentation labels, varying deformation intensity per sample in each training epoch to address annotation inconsistencies. Experimental results demonstrate that our approach improves the performance of RS image segmentation on various state-of-the-art models.
遥感(RS)图像分割数据集标注错误通常由于模糊的类别边界、混合像素、阴影、复杂的地形特征和主观标注者偏见而保持隐蔽和微妙。此外,由于图像采集和标注的高成本,导致标注的遥感数据稀缺,这加剧了训练噪声鲁棒模型的复杂性。虽然标签选择或噪声校正等复杂机制可能解决此问题,但它们往往会增加训练时间并增加实现复杂性。在本信中,我们提出NSegment——一种简单有效的数据增强解决方案,以缓解这个问题。与传统的数据增强方法不同,它仅对分割标签应用弹性变换,并在每个训练周期中对每个样本的变形强度进行变化,以解决标注不一致的问题。实验结果表明,我们的方法提高了各种最先进模型在遥感图像分割方面的性能。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF Preprint
Summary
本文主要讨论了遥感图像分割数据集标注错误的问题,这些错误由于模糊的类别边界、混合像素、阴影、复杂地形特征和主观标注者偏见而隐性存在。由于高图像采集和标注成本,导致标注的遥感数据稀缺,训练噪声鲁棒性模型变得复杂。针对这些问题,本文提出了一种名为NSegment的简单而有效的数据增强解决方案。不同于传统方法,NSegment仅对分割标签应用弹性变换,每个训练周期中对每个样本的变形强度进行变化,以解决标注不一致的问题。实验结果表明,该方法提高了遥感图像分割在各种先进模型上的性能。
Key Takeaways
- 遥感图像分割数据集的标注错误是隐性和微妙的,主要源于模糊的类别边界、混合像素、阴影等问题。
- 标注的遥感数据稀缺,因为图像采集和标注的成本很高。
- 训练噪声鲁棒性模型是必要的,因为标注错误会影响模型的性能。
- 传统数据增强方法可能不适用于遥感图像分割问题。
- NSegment是一种简单而有效的数据增强解决方案,它通过应用弹性变换来解决标注不一致的问题。
- NSegment只在每个训练周期中对分割标签应用变换,以提高模型的性能。
点此查看论文截图

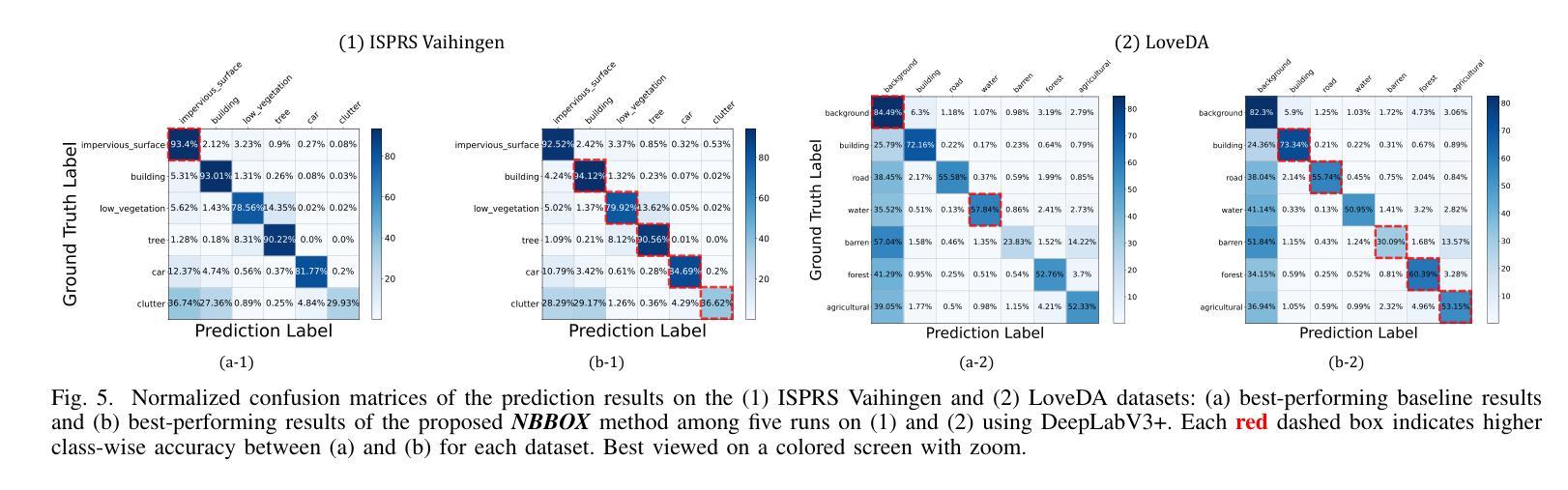
AI Alignment in Medical Imaging: Unveiling Hidden Biases Through Counterfactual Analysis
Authors:Haroui Ma, Francesco Quinzan, Theresa Willem, Stefan Bauer
Machine learning (ML) systems for medical imaging have demonstrated remarkable diagnostic capabilities, but their susceptibility to biases poses significant risks, since biases may negatively impact generalization performance. In this paper, we introduce a novel statistical framework to evaluate the dependency of medical imaging ML models on sensitive attributes, such as demographics. Our method leverages the concept of counterfactual invariance, measuring the extent to which a model’s predictions remain unchanged under hypothetical changes to sensitive attributes. We present a practical algorithm that combines conditional latent diffusion models with statistical hypothesis testing to identify and quantify such biases without requiring direct access to counterfactual data. Through experiments on synthetic datasets and large-scale real-world medical imaging datasets, including \textsc{cheXpert} and MIMIC-CXR, we demonstrate that our approach aligns closely with counterfactual fairness principles and outperforms standard baselines. This work provides a robust tool to ensure that ML diagnostic systems generalize well, e.g., across demographic groups, offering a critical step towards AI safety in healthcare. Code: https://github.com/Neferpitou3871/AI-Alignment-Medical-Imaging.
医学影像机器学习系统展现出了出色的诊断能力,但它们易受偏见影响,这构成了重大风险,因为偏见可能会给泛化性能带来负面影响。在本文中,我们介绍了一种新型统计框架,用于评估医学影像机器学习模型对人口统计学等敏感属性的依赖程度。我们的方法利用反事实不变性的概念,衡量模型预测在敏感属性假设性变化下保持不变的程度。我们提出了一种实用算法,该算法结合了条件潜在扩散模型和统计假设检验,能够在无需访问反事实数据的情况下识别和量化此类偏见。通过在合成数据集和大规模现实世界医学影像数据集(包括\textsc{cheXpert}和MIMIC-CXR)上的实验,我们证明我们的方法与反事实公平原则紧密契合并优于标准基线。这项工作为确保机器学习诊断系统具有良好的泛化能力(例如,跨越不同人口群体)提供了可靠工具,是医疗保健领域人工智能安全性的关键一步。代码:https://github.com/Neferpitou3871/AI-Alignment-Medical-Imaging。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
本文介绍了一种新型的统计框架,用于评估医疗影像机器学习模型对敏感属性(如人口统计学特征)的依赖程度。该框架利用反事实不变性的概念,测量模型预测在敏感属性假设变化下的稳定性。通过结合条件潜在扩散模型和统计假设检验的实用算法,能够在无需反事实数据的情况下识别和量化偏见。在合成数据集和大规模真实医疗影像数据集上的实验表明,该方法与反事实公平性原则相符,并优于标准基线。此工具可确保机器学习诊断系统具有良好的泛化性能,例如跨不同人群,为医疗保健中的AI安全提供了关键步骤。
Key Takeaways
- 医疗影像机器学习模型存在对敏感属性(如人口统计学特征)的偏见,可能影响模型的泛化性能。
- 新型统计框架利用反事实不变性的概念来评估模型预测的稳定性。
- 提出的实用算法结合了条件潜在扩散模型和统计假设检验,以识别和量化偏见。
- 该方法无需反事实数据即可操作,可在真实世界的应用中提供便利。
- 实验结果表明,该方法符合反事实公平性原则,并优于标准基线。
- 此工具有助于提高机器学习诊断系统的泛化性能,特别是在不同人群之间。
点此查看论文截图

Magnifier: A Multi-grained Neural Network-based Architecture for Burned Area Delineation
Authors:Daniele Rege Cambrin, Luca Colomba, Paolo Garza
In crisis management and remote sensing, image segmentation plays a crucial role, enabling tasks like disaster response and emergency planning by analyzing visual data. Neural networks are able to analyze satellite acquisitions and determine which areas were affected by a catastrophic event. The problem in their development in this context is the data scarcity and the lack of extensive benchmark datasets, limiting the capabilities of training large neural network models. In this paper, we propose a novel methodology, namely Magnifier, to improve segmentation performance with limited data availability. The Magnifier methodology is applicable to any existing encoder-decoder architecture, as it extends a model by merging information at different contextual levels through a dual-encoder approach: a local and global encoder. Magnifier analyzes the input data twice using the dual-encoder approach. In particular, the local and global encoders extract information from the same input at different granularities. This allows Magnifier to extract more information than the other approaches given the same set of input images. Magnifier improves the quality of the results of +2.65% on average IoU while leading to a restrained increase in terms of the number of trainable parameters compared to the original model. We evaluated our proposed approach with state-of-the-art burned area segmentation models, demonstrating, on average, comparable or better performances in less than half of the GFLOPs.
在危机管理和遥感领域,图像分割发挥着至关重要的作用,通过分析视觉数据,能够完成灾难响应和应急规划等任务。神经网络能够分析卫星采集的数据,并确定哪些区域受到灾难性事件的影响。然而,在此背景之下,神经网络的发展问题在于数据稀缺,缺乏广泛的基准数据集,这限制了训练大型神经网络模型的能力。在本文中,我们提出了一种新的方法,即Magnifier,以提高在数据有限情况下的分割性能。Magnifier方法适用于任何现有的编码器-解码器架构,因为它通过双编码器方法合并不同上下文级别的信息来扩展模型:本地编码器和全局编码器。Magnifier使用双编码器方法两次分析输入数据。特别是,本地编码器和全局编码器以不同的粒度从同一输入中提取信息。这使得Magnifier能够在给定相同输入图像集的情况下,提取比其他方法更多的信息。Magnifier在提高平均IoU值的基础上提高了结果质量达+2.65%,并且在与原始模型相比的情况下,可训练参数数量方面实现了适度的增长。我们使用先进的燃烧区域分割模型评估了我们提出的方法,结果显示,在不到一半GFLOPs的情况下,我们的方法能够达到平均相当或更好的性能。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF Accepted in IEEE Journal of Selected Topics in Applied Earth Observations and Remote Sensing
Summary
神经网络在分析卫星图像数据、确定受灾区域方面发挥了重要作用。然而,数据稀缺和缺乏广泛的基准数据集限制了大型神经网络模型的发展。本文提出了一种名为Magnifier的新方法,可在有限数据的情况下提高分割性能。Magnifier方法适用于任何现有的编码器-解码器架构,它通过双编码器方法合并不同上下文级别的信息来扩展模型:本地和全局编码器。Magnifier使用双编码器方法两次分析输入数据,使得在相同的输入图像集上,它能提取比其他方法更多的信息。Magnifier提高了平均IoU值达+2.65%,同时与原始模型相比,增加了较少的可训练参数数量。本研究通过先进的燃烧区域分割模型评估了该方法,在GFLOPs不到一半的情况下,表现出平均相当或更好的性能。
Key Takeaways
- 神经网络在分析卫星图像数据方面具有重要作用,可应用于灾难响应和应急规划等任务。
- 数据稀缺和缺乏基准数据集限制了大型神经网络模型在危机管理和遥感图像分割中的发展。
- Magnifier是一种新的方法,旨在解决有限数据下的图像分割问题,适用于各种编码器-解码器架构。
- Magnifier通过双编码器方法(本地和全局编码器)两次分析输入数据,提取不同粒度下的信息。
- Magnifier能提高图像分割的性能,平均IoU值提高了+2.65%。
- 与其他先进的燃烧区域分割模型相比,Magnifier在较少的GFLOPs下表现出相当或更好的性能。
点此查看论文截图



Maximizing Infrared Transmission Contrast Upon Phase Transition of Thermally Grown Vanadium Dioxide Thin Films by Rapid Thermal Processing
Authors:Ken Araki, Vishwa Krishna Rajan, Liping Wang
Pristine vanadium dioxide (VO2), an insulator-to-metal transition (IMT) material, is grown via furnace oxidation followed by rapid thermal annealing with forming gas (5%H2/95%N2) which reduces surface over-oxides such as V2O5 formed during the oxidation. The evolutional IMT behaviors of the thermochromic film and vanadium oxide states over different reduction time are systematically studied with temperature-dependent infrared spectrometry, electrical resistivity, and X-ray diffraction measurements. After optimally reducing surface over-oxides to VO2, infrared transmission contrast upon phase transition is enhanced to 46% (at 9 um wavelength) compared to 23% from fully oxidation without any reduction. Moreover, pristine VO2 thin film obtained from thermal oxidation and optimal reduction processes exhibits sharp phase transition and narrow thermal hysteresis within 2~4{\deg}C in both infrared transmission and electrical resistivity, which are comparable to the VO2 of best quality prepared by other sophisticated fabrication techniques. The thermally grown method presented here would facilitate the scalable fabrication of high-quality VO2 thin films and tunable radiative coatings for high-performance thermal control applications.
纯净的二氧化钒(VO2)是一种绝缘体到金属转变(IMT)材料,通过炉氧化和形成气体(5%H2/95%N2)的快速热退火进行生长,以减少在氧化过程中产生的表面过氧化物,如五氧化二钒(V2O5)。通过温度依赖的红外光谱法、电阻率和X射线衍射测量,系统研究了热变色膜和氧化钒在不同还原时间下的演变IMT行为。通过最优方式还原表面过氧化物至VO2后,与未进行任何还原的完全氧化相比,在相变时红外透射对比度增强至46%(在9微米波长下),增强了近红外波段的光学响应。此外,通过热氧化和最佳还原过程获得的纯净VO2薄膜在红外透射率和电阻率方面表现出锐利的相变和狭窄的热滞回线(在2至4摄氏度内),这与通过其他先进制造技术制备的VO2质量相当。这里展示的热生长方法将有助于实现高质量VO2薄膜和可调辐射涂层的规模化制造,用于高性能热控制应用。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
本文介绍了通过炉氧化和形成气体(5%H2/95%N2)快速热退火制备高纯度二氧化钒(VO2)的过程。系统地研究了其在绝缘体-金属转变(IMT)行为中,热变色膜在不同还原时间下的红外光谱、电阻率和X射线衍射的测量变化。通过优化表面氧化物,红外传输对比度的相变增强至46%(在9微米波长下),相较于完全氧化未经任何还原处理的样品增强了2倍。此外,通过热氧化和最佳还原过程获得的VO2薄膜展现出锐利的相变和狭窄的热滞回线,与通过其他先进制造技术制备的VO2薄膜质量相当。所提出的热生长方法将有助于实现高性能热控制应用中高质量VO2薄膜和可调辐射涂层的规模化制造。
Key Takeaways
- 通过炉氧化和形成气体快速热退火制备了VO2材料。
- 系统研究了VO2材料在不同还原时间的绝缘体-金属转变行为。
- 优化表面氧化物后,红外传输对比度的相变增强至46%。
- 高质量VO2薄膜展现了锐利的相变和狭窄的热滞回线。
- 热生长方法有助于实现高质量VO2薄膜的大规模制造。
- 这种技术可应用于高性能热控制应用中。
点此查看论文截图

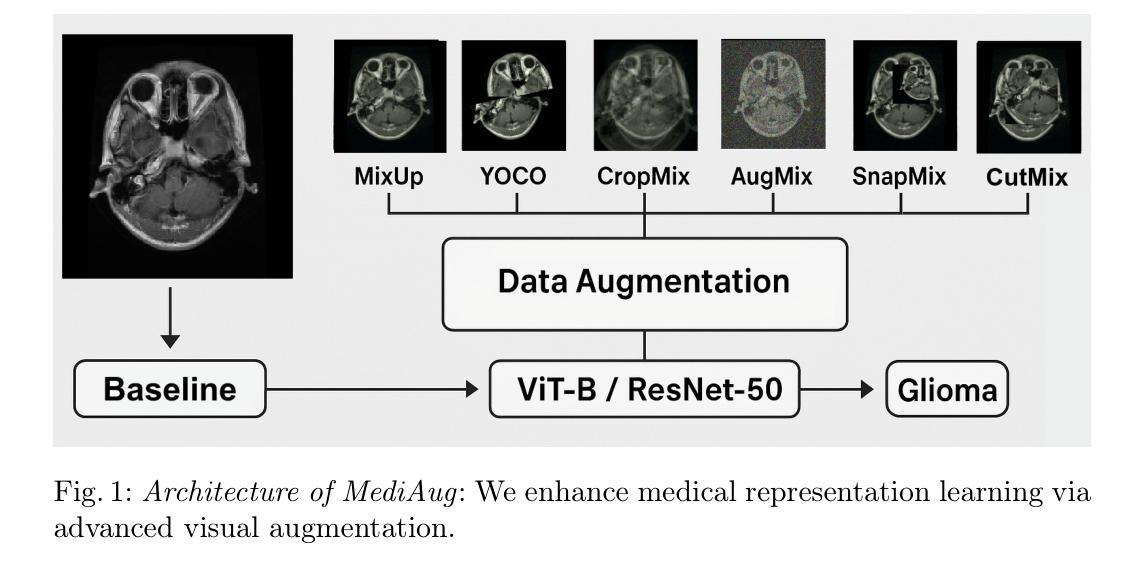
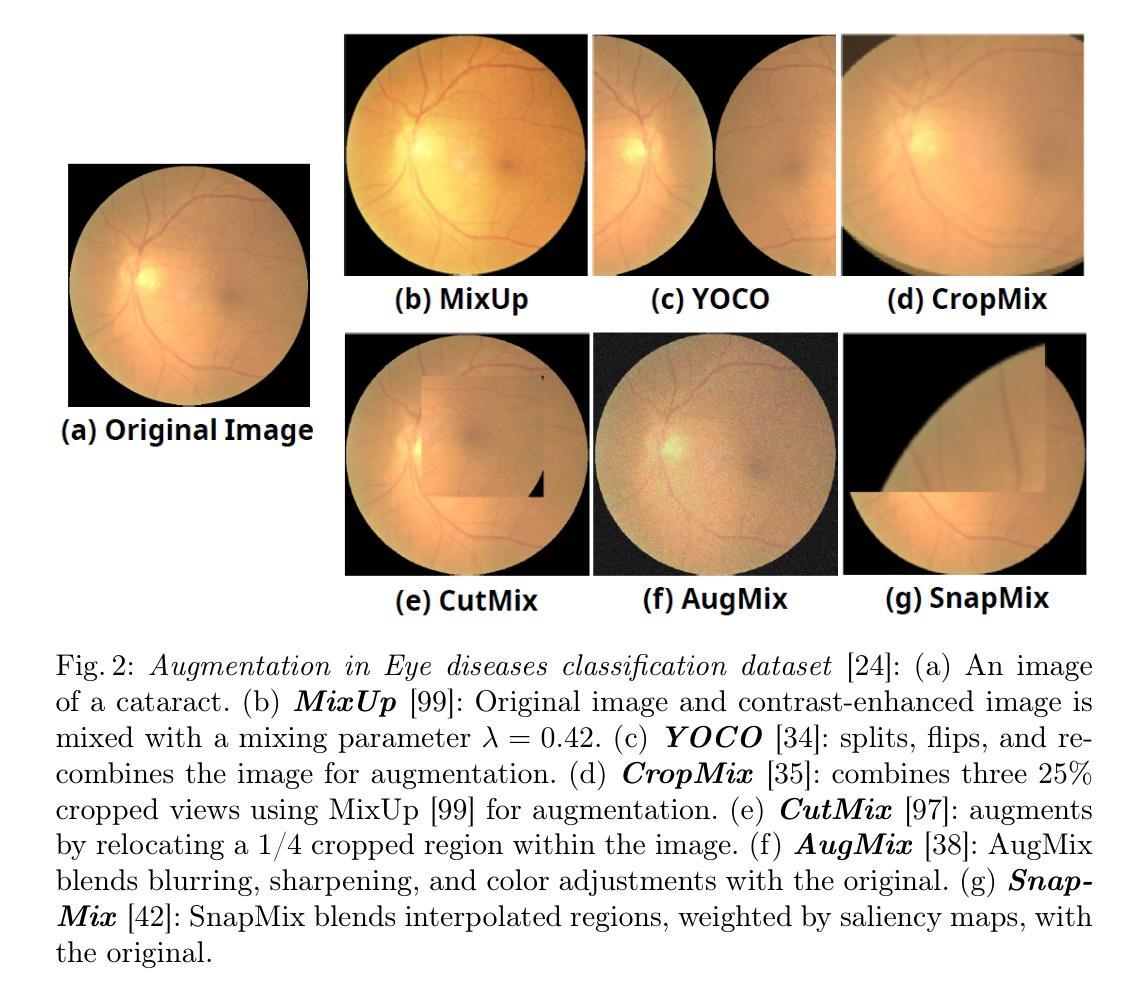
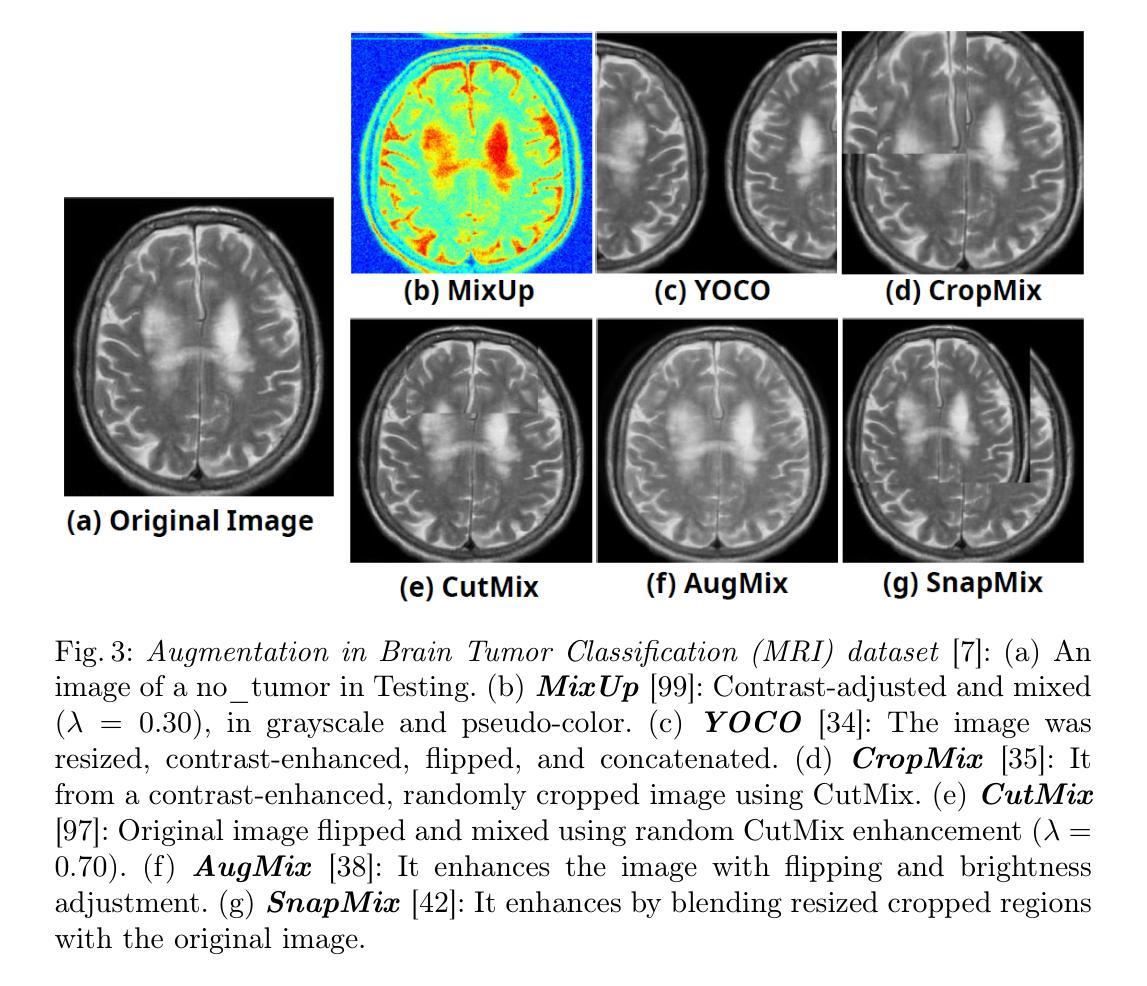
MediAug: Exploring Visual Augmentation in Medical Imaging
Authors:Xuyin Qi, Zeyu Zhang, Canxuan Gang, Hao Zhang, Lei Zhang, Zhiwei Zhang, Yang Zhao
Data augmentation is essential in medical imaging for improving classification accuracy, lesion detection, and organ segmentation under limited data conditions. However, two significant challenges remain. First, a pronounced domain gap between natural photographs and medical images can distort critical disease features. Second, augmentation studies in medical imaging are fragmented and limited to single tasks or architectures, leaving the benefits of advanced mix-based strategies unclear. To address these challenges, we propose a unified evaluation framework with six mix-based augmentation methods integrated with both convolutional and transformer backbones on brain tumour MRI and eye disease fundus datasets. Our contributions are threefold. (1) We introduce MediAug, a comprehensive and reproducible benchmark for advanced data augmentation in medical imaging. (2) We systematically evaluate MixUp, YOCO, CropMix, CutMix, AugMix, and SnapMix with ResNet-50 and ViT-B backbones. (3) We demonstrate through extensive experiments that MixUp yields the greatest improvement on the brain tumor classification task for ResNet-50 with 79.19% accuracy and SnapMix yields the greatest improvement for ViT-B with 99.44% accuracy, and that YOCO yields the greatest improvement on the eye disease classification task for ResNet-50 with 91.60% accuracy and CutMix yields the greatest improvement for ViT-B with 97.94% accuracy. Code will be available at https://github.com/AIGeeksGroup/MediAug.
数据增强在医学成像中至关重要,对于在有限数据条件下提高分类精度、病变检测以及器官分割都至关重要。然而,仍存在两个重大挑战。首先,自然照片和医学图像之间明显的领域差距可能会扭曲关键疾病特征。其次,医学成像中的增强研究是分散的,仅限于单一任务或架构,使得先进的混合策略的优势尚不清楚。为了应对这些挑战,我们提出了一个统一的评估框架,该框架集成了六种基于混合的方法,并结合卷积和transformer骨干网在脑肿瘤MRI和眼底疾病数据集上进行数据增强。我们的贡献主要体现在三个方面。(1)我们引入了MediAug,这是医学成像中高级数据增强的综合和可重现的基准。 (2)我们系统地评估了MixUp、YOCO、CropMix、CutMix、AugMix和SnapMix使用ResNet-50和ViT-B骨干网的效果。(3)我们通过大量实验证明,对于ResNet-50,MixUp在脑肿瘤分类任务上取得了最大的改进,准确率为79.19%;对于ViT-B,SnapMix取得了最大的改进,准确率为99.44%;YOCO在ResNet-50的眼病分类任务上取得了最大改进,准确率为91.60%;而CutMix在ViT-B上取得了最大的改进,准确率为97.94%。代码将在https://github.com/AIGeeksGroup/MediAug上提供。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
本文介绍了数据增强在医学成像中的重要性,针对医学图像分类、病灶检测和器官分割等任务,提出了一个统一评估框架。该框架集成了六种基于混合的数据增强方法,对卷积和transformer架构进行了评估。研究发现,MixUp在脑肿瘤分类任务上表现最佳,SnapMix在ViT-B上表现最佳,YOCO在眼疾分类任务上表现最佳。
Key Takeaways
- 数据增强在医学成像中非常重要,尤其对于任务如分类、病灶检测和器官分割。
- 医学图像数据增强面临两大挑战:与自然照片之间的域差距以及缺乏统一的评估框架。
- 提出了一个统一的评估框架,该框架集成了六种基于混合的数据增强方法。
- 研究表明MixUp在脑肿瘤分类任务上表现最佳,SnapMix在ViT-B架构上表现最佳。
- YOCO在眼疾分类任务上取得了最好的结果。
- 该研究提供了一个全面的医学图像数据增强基准测试平台MediAug。
点此查看论文截图

Theoretical Framework for Tempered Fractional Gradient Descent: Application to Breast Cancer Classification
Authors:Omar Naifar
This paper introduces Tempered Fractional Gradient Descent (TFGD), a novel optimization framework that synergizes fractional calculus with exponential tempering to enhance gradient-based learning. Traditional gradient descent methods often suffer from oscillatory updates and slow convergence in high-dimensional, noisy landscapes. TFGD addresses these limitations by incorporating a tempered memory mechanism, where historical gradients are weighted by fractional coefficients $|w_j| = \binom{\alpha}{j}$ and exponentially decayed via a tempering parameter $\lambda$. Theoretical analysis establishes TFGD’s convergence guarantees: in convex settings, it achieves an $\mathcal{O}(1/K)$ rate with alignment coefficient $d_{\alpha,\lambda} = (1 - e^{-\lambda})^{-\alpha}$, while stochastic variants attain $\mathcal{O}(1/k^\alpha)$ error decay. The algorithm maintains $\mathcal{O}(n)$ time complexity equivalent to SGD, with memory overhead scaling as $\mathcal{O}(d/\lambda)$ for parameter dimension $d$. Empirical validation on the Breast Cancer Wisconsin dataset demonstrates TFGD’s superiority, achieving 98.25% test accuracy (vs. 92.11% for SGD) and 2$\times$ faster convergence. The tempered memory mechanism proves particularly effective in medical classification tasks, where feature correlations benefit from stable gradient averaging. These results position TFGD as a robust alternative to conventional optimizers in both theoretical and applied machine learning.
本文介绍了温度化分数梯度下降法(Tempered Fractional Gradient Descent,简称TFGD)这一新型优化框架。该框架将分数微积分与指数温度化相结合,以提升基于梯度的学习能力。传统的梯度下降法在高维、有噪声的地形上常遭遇振荡更新和收敛缓慢的问题。TFGD通过引入温度化记忆机制来解决这些问题,其中历史梯度通过分数系数$|w_j| = \binom{\alpha}{j}$进行加权,并通过温度参数$\lambda$进行指数衰减。理论分析证明了TFGD的收敛性保证:在凸设置中,它实现了与对齐系数$d_{\alpha,\lambda} = (1 - e^{-\lambda})^{-\alpha}$相关的$\mathcal{O}(1/K)$速率;而随机变量则达到$\mathcal{O}(1/k^\alpha)$误差衰减。该算法的时间复杂度与SGD相当,为$\mathcal{O}(n)$,而内存开销随着参数维度$d$和温度参数$\lambda$之比的增加而增加。在威斯康辛乳腺癌数据集上的实证验证表明TFGD的优越性,其测试准确率达到98.25%(相比之下,SGD为92.11%),并且收敛速度是SGD的2倍。温度化记忆机制在医疗分类任务中表现尤其出色,其中特征相关性受益于稳定的梯度平均。这些结果使TFGD成为理论和应用机器学习领域中常规优化器的稳健替代品。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
TFGD是一种结合分数微积分和指数衰减机制的新型优化框架,旨在提高基于梯度的学习效率并解决传统梯度下降方法在解决高维噪声景观时的局限性。TFGD采用一种加权分数系数的温度记忆机制,实现理论上的收敛保证,并在实证测试中展现了出色的性能,特别是在医学分类任务中表现突出。相较于传统优化器,TFGD提供了稳健的替代方案。
Key Takeaways
- TFGD是一种新型优化框架,融合了分数微积分与指数衰减机制,增强了梯度学习的性能。
- 传统梯度下降方法在处理高维噪声景观时面临震荡更新和缓慢收敛的问题,而TFGD则针对这些局限进行了改进。
- TFGD采用温度记忆机制,通过加权分数系数和指数衰减参数来实现优化。
- 在凸设置下,TFGD实现了特定的收敛率,并且其随机变体还实现了误差衰减。
- TFGD的时间复杂度与SGD相当,但其记忆开销随参数维度的增加而增加。
- 在乳腺癌威斯康星数据集上的实证验证表明,TFGD相较于SGD具有更高的测试准确性和更快的收敛速度。
点此查看论文截图

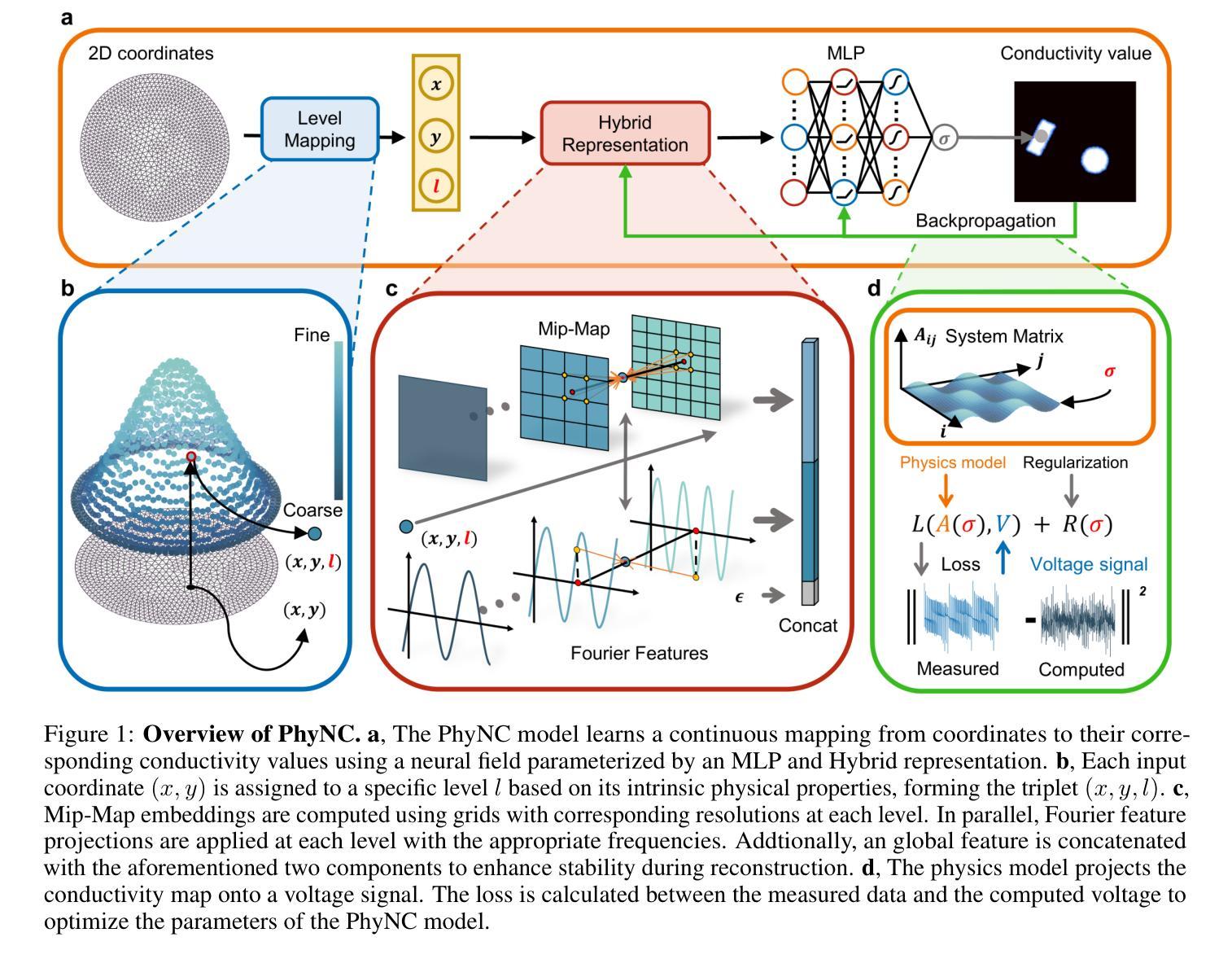
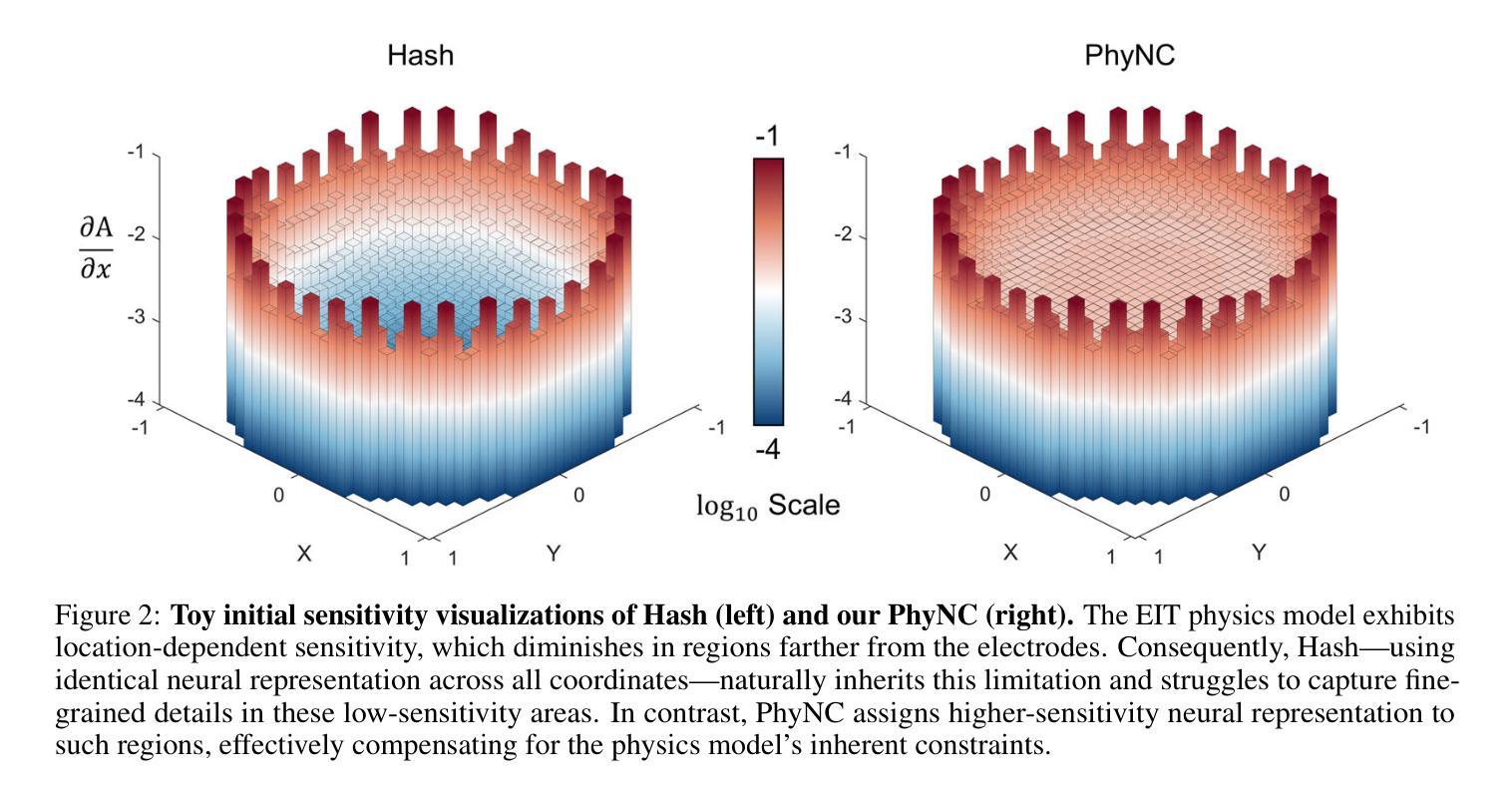
Physics-Driven Neural Compensation For Electrical Impedance Tomography
Authors:Chuyu Wang, Huiting Deng, Dong Liu
Electrical Impedance Tomography (EIT) provides a non-invasive, portable imaging modality with significant potential in medical and industrial applications. Despite its advantages, EIT encounters two primary challenges: the ill-posed nature of its inverse problem and the spatially variable, location-dependent sensitivity distribution. Traditional model-based methods mitigate ill-posedness through regularization but overlook sensitivity variability, while supervised deep learning approaches require extensive training data and lack generalization. Recent developments in neural fields have introduced implicit regularization techniques for image reconstruction, but these methods typically neglect the physical principles underlying EIT, thus limiting their effectiveness. In this study, we propose PhyNC (Physics-driven Neural Compensation), an unsupervised deep learning framework that incorporates the physical principles of EIT. PhyNC addresses both the ill-posed inverse problem and the sensitivity distribution by dynamically allocating neural representational capacity to regions with lower sensitivity, ensuring accurate and balanced conductivity reconstructions. Extensive evaluations on both simulated and experimental data demonstrate that PhyNC outperforms existing methods in terms of detail preservation and artifact resistance, particularly in low-sensitivity regions. Our approach enhances the robustness of EIT reconstructions and provides a flexible framework that can be adapted to other imaging modalities with similar challenges.
电阻抗断层扫描(EIT)提供了一种非侵入性、便携式的成像方式,在医疗和工业应用中具有巨大的潜力。尽管EIT具有优势,但它面临两个主要挑战:其反问题的病态性质和空间变化、位置依赖的灵敏度分布。基于传统模型的方法通过正则化来缓解病态性,但忽略了灵敏度的变化,而监督深度学习的方法需要大量的训练数据且缺乏泛化能力。神经网络领域的最新发展已经引入了隐式正则化技术进行图像重建,但这些方法通常忽略了EIT的物理原理,从而限制了其有效性。本研究中,我们提出了PhyNC(物理驱动神经网络补偿),这是一个结合了EIT物理原理的无监督深度学习框架。PhyNC通过动态分配神经表征容量到灵敏度较低的区域,解决了不适定的反问题和灵敏度分布问题,确保准确且平衡的导电率重建。对模拟和实验数据的广泛评估表明,PhyNC在细节保留和抗伪影方面优于现有方法,特别是在低灵敏度区域。我们的方法提高了EIT重建的稳健性,并提供了一个灵活的框架,可以适应具有类似挑战的其他成像方式。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
本文介绍了电气阻抗成像技术(EIT)的优势及面临的挑战,包括其反问题的病态性和灵敏度分布的空间变化性。提出了一种结合物理原理和深度学习的无监督学习框架PhyNC,通过动态分配神经网络表征容量来解决这些问题,确保导电率重建的准确性和平衡性。在模拟和实验数据上的评估表明,PhyNC在细节保留和抗伪影方面优于现有方法,特别是在低灵敏度区域。
Key Takeaways
- EIT是一种具有医疗和工业应用潜力的非侵入性、可携带的成像模式。
- EIT面临的主要挑战包括其反问题的病态性和灵敏度分布的空间变化性。
- 传统方法通过正则化解决反问题的病态性,但忽略了灵敏度的变化。
- 监督深度学习方法需要大量训练数据,并缺乏泛化能力。
- 最近的神经营略引入了隐式正则化技术用于图像重建,但忽略了EIT的物理原理。
- PhyNC框架结合了EIT的物理原理和深度学习,通过动态分配神经网络表征容量来解决反问题。
点此查看论文截图

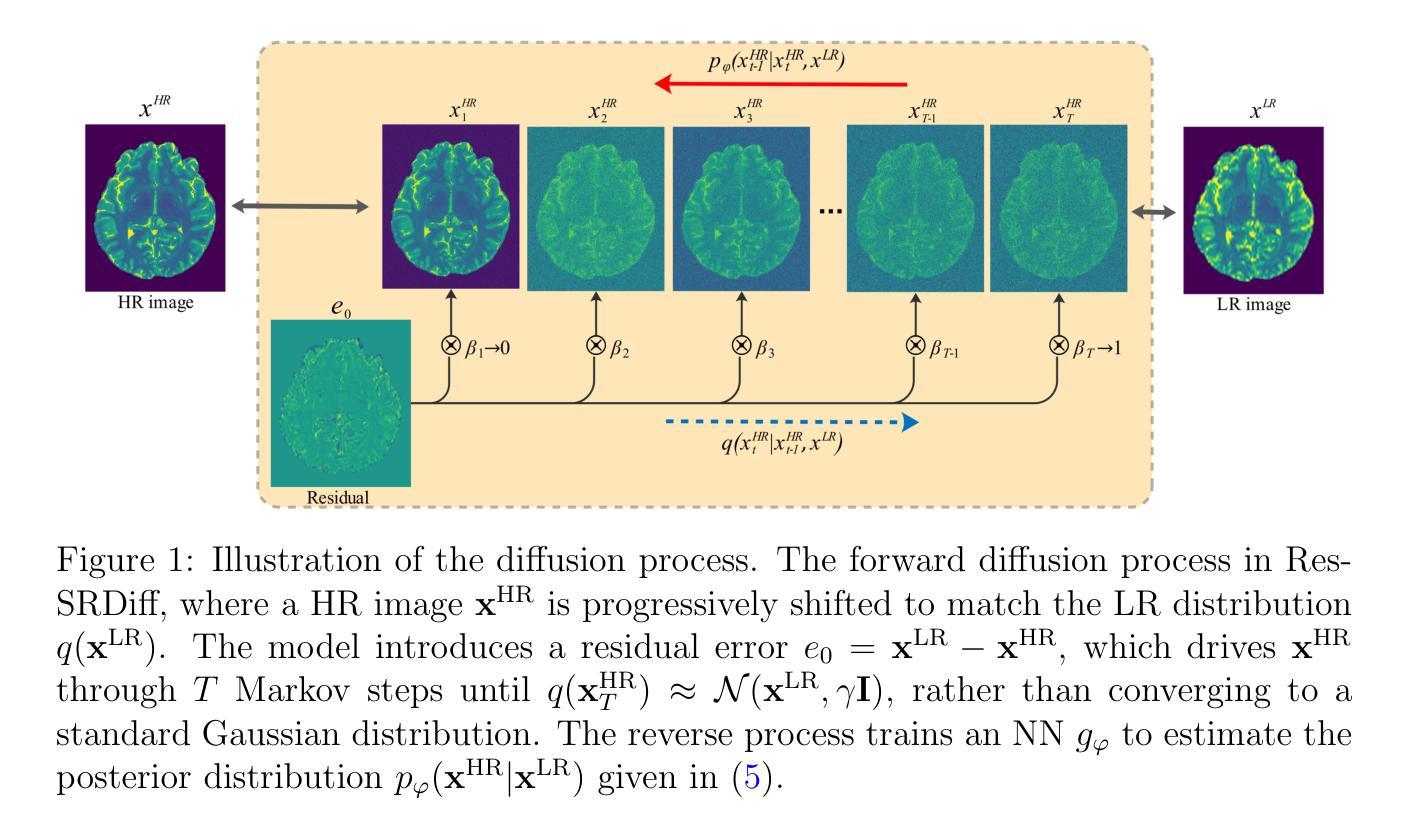
MRI super-resolution reconstruction using efficient diffusion probabilistic model with residual shifting
Authors:Mojtaba Safari, Shansong Wang, Zach Eidex, Qiang Li, Erik H. Middlebrooks, David S. Yu, Xiaofeng Yang
Objective:This study introduces a residual error-shifting mechanism that drastically reduces sampling steps while preserving critical anatomical details, thus accelerating MRI reconstruction. Approach:We propose a novel diffusion-based SR framework called Res-SRDiff, which integrates residual error shifting into the forward diffusion process. This enables efficient HR image reconstruction by aligning the degraded HR and LR distributions.We evaluated Res-SRDiff on ultra-high-field brain T1 MP2RAGE maps and T2-weighted prostate images, comparing it with Bicubic, Pix2pix, CycleGAN, and a conventional denoising diffusion probabilistic model with vision transformer backbone (TM-DDPM), using quantitative metrics such as peak signal-to-noise ratio (PSNR), structural similarity index (SSIM), gradient magnitude similarity deviation (GMSD), and learned perceptual image patch similarity (LPIPS). Main results: Res-SRDiff significantly outperformed all comparative methods in terms of PSNR, SSIM, and GMSD across both datasets, with statistically significant improvements (p-values<<0.05). The model achieved high-fidelity image restoration with only four sampling steps, drastically reducing computational time to under one second per slice, which is substantially faster than conventional TM-DDPM with around 20 seconds per slice. Qualitative analyses further demonstrated that Res-SRDiff effectively preserved fine anatomical details and lesion morphology in both brain and pelvic MRI images. Significance: Our findings show that Res-SRDiff is an efficient and accurate MRI SR method, markedly improving computational efficiency and image quality. Integrating residual error shifting into the diffusion process allows for rapid and robust HR image reconstruction, enhancing clinical MRI workflows and advancing medical imaging research. The source at:https://github.com/mosaf/Res-SRDiff
目标:本研究介绍了一种残差误差偏移机制,该机制能在保持关键解剖细节的同时,大大减少采样步骤,从而加速MRI重建。方法:我们提出了一种基于扩散的超分辨率重建框架Res-SRDiff,它将残差误差偏移集成到正向扩散过程中。这通过对齐退化的高分辨率和低分辨率分布,实现了高效的高分辨率图像重建。我们对超高场脑T1 MP2RAGE图和T2加权前列腺图像进行了Res-SRDiff评估,将其与Bicubic、Pix2pix、CycleGAN以及带有视觉转换器主干(TM-DDPM)的传统去噪扩散概率模型进行了比较,使用了峰值信噪比(PSNR)、结构相似性指数(SSIM)、梯度幅度相似性偏差(GMSD)和学习的感知图像块相似性(LPIPS)等定量指标。主要结果:在的两个数据集中,Res-SRDiff在PSNR、SSIM和GMSD方面显著优于所有比较方法,具有统计学上的显著差异(p值<<0.05)。该模型仅在四个采样步骤内就实现了高保真图像恢复,计算时间缩短至每片不到一秒,这远远快于常规TM-DDPM的约20秒每片。定性分析进一步表明,Res-SRDiff在脑部和盆腔MRI图像中有效地保留了精细的解剖细节和病灶形态。意义:我们的研究结果表明,Res-SRDiff是一种高效且准确的MRI超分辨率重建方法,显著提高了计算效率和图像质量。将残差误差偏移集成到扩散过程中,可实现快速稳健的高分辨率图像重建,增强临床MRI工作流程,推动医学成像研究的发展。更多信息请访问:https://github.com/mosaf/Res-SRDiff
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
该研究引入了一种残差误差移位机制,该机制能在减少采样步骤的同时保留关键解剖细节,从而加速MRI重建。研究团队提出了一种新型的基于扩散的超分辨率(SR)框架——Res-SRDiff,它将残差误差移位整合到前向扩散过程中,使得重建高分辨率(HR)图像时效率更高。该模型在两个不同的数据集上的表现均显著优于其他对比方法,实现了高保真度的图像恢复,且采样步骤仅需四次,计算时间缩短至每片不到一秒,大大快于传统的TM-DDPM模型。该研究显著提高了MRI图像的计算效率和图像质量。
Key Takeaways
- 研究提出了一种新型的MRI超分辨率重建方法——Res-SRDiff框架。
- Res-SRDiff整合了残差误差移位机制到前向扩散过程中。
- Res-SRDiff在超高温场脑T1 MP2RAGE地图和T2加权前列腺图像上的表现均显著优于其他对比方法。
- Res-SRDiff实现了高保真度的图像恢复,并且只需四次采样步骤。
- Res-SRDiff的计算时间大大缩短,每片图像不到一秒。
- Res-SRDiff提高了MRI图像的计算效率和图像质量。
点此查看论文截图

VerteNet – A Multi-Context Hybrid CNN Transformer for Accurate Vertebral Landmark Localization in Lateral Spine DXA Images
Authors:Zaid Ilyas, Arooba Maqsood, Afsah Saleem, Erchuan Zhang, David Suter, Parminder Raina, Jonathan M. Hodgson, John T. Schousboe, William D. Leslie, Joshua R. Lewis, Syed Zulqarnain Gilani
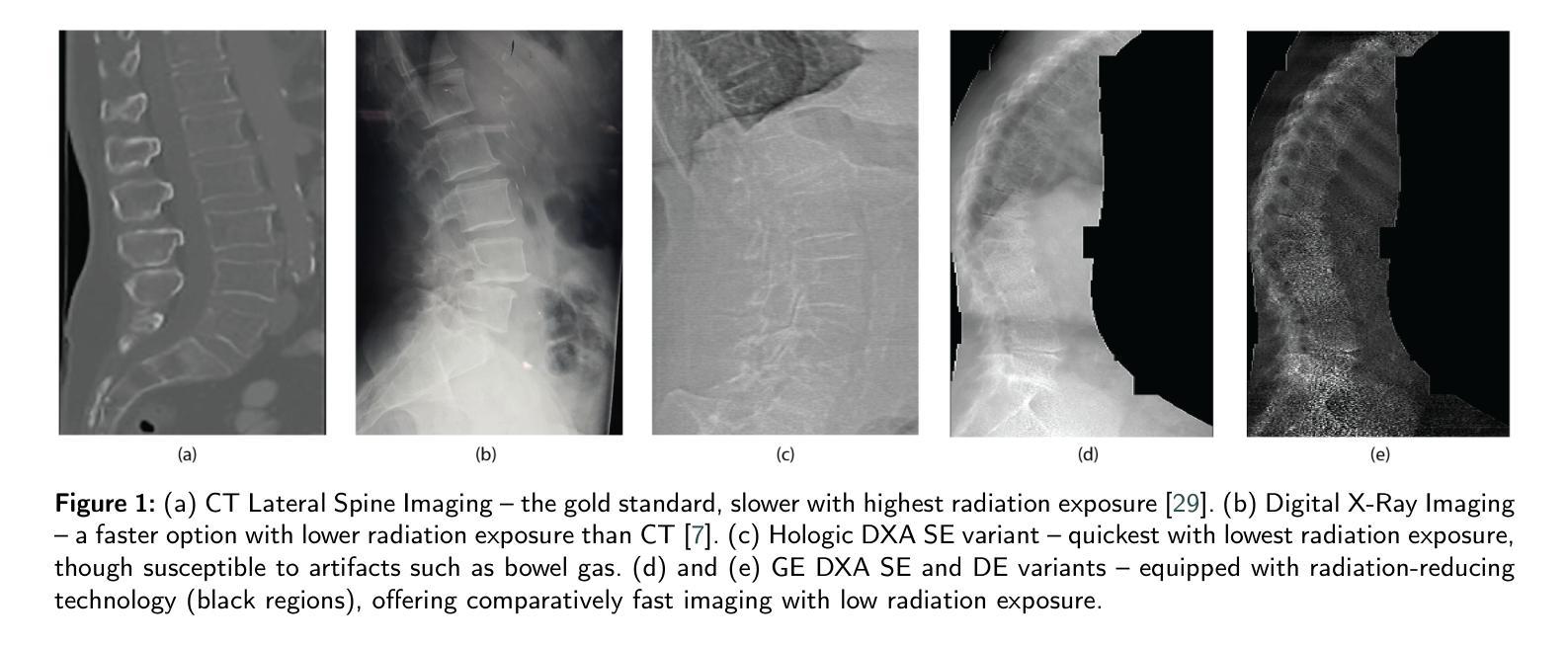
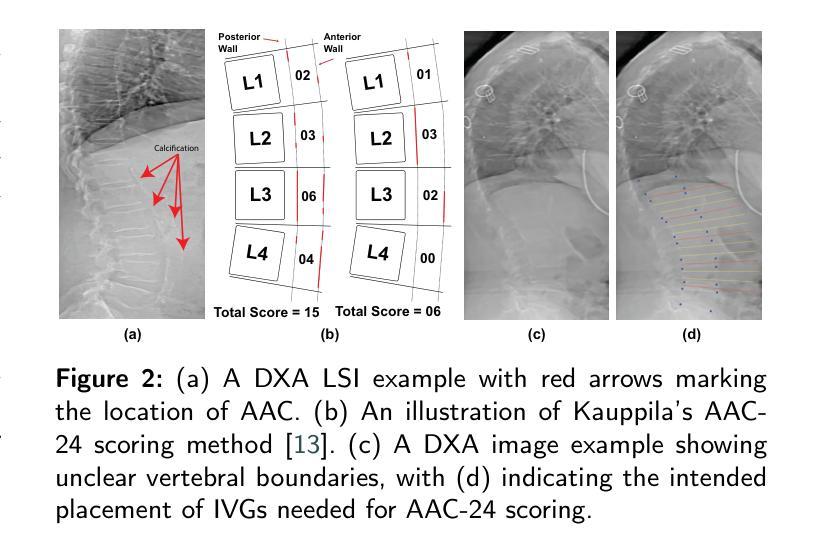
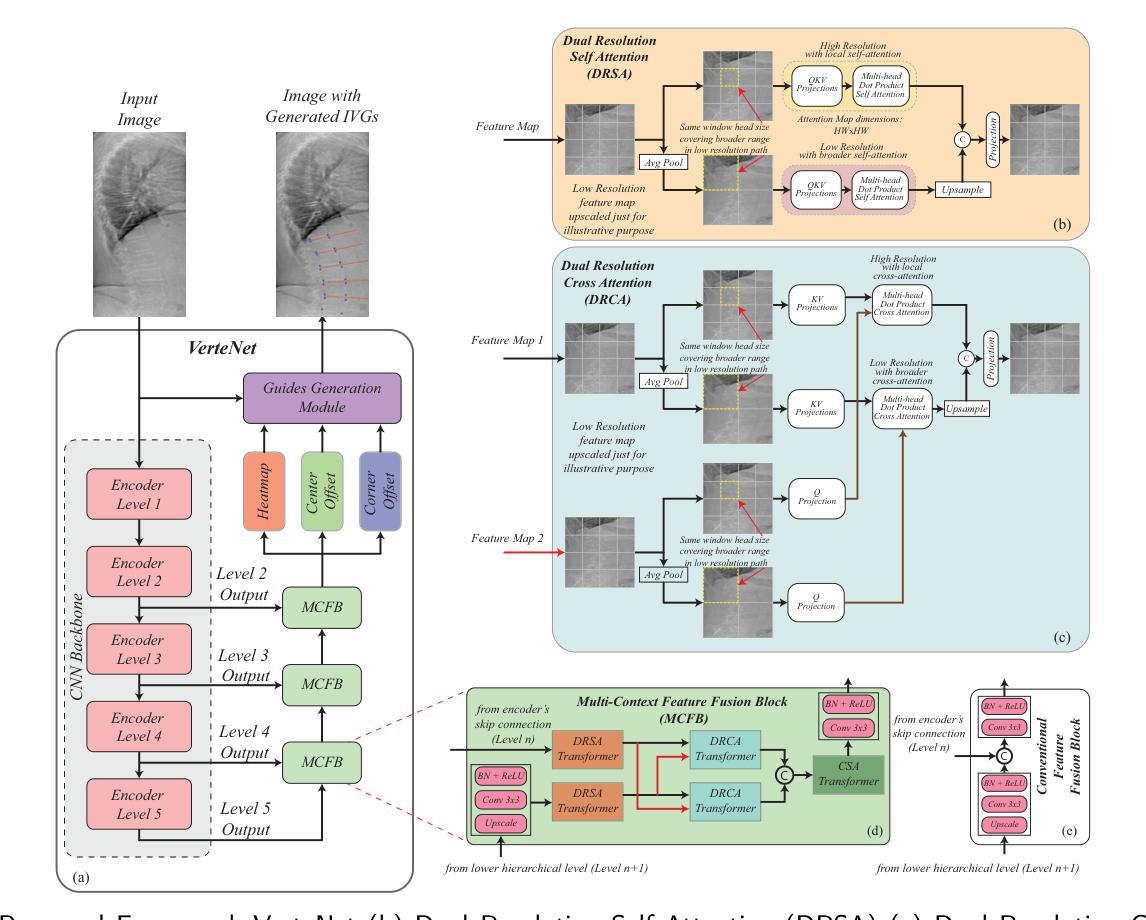
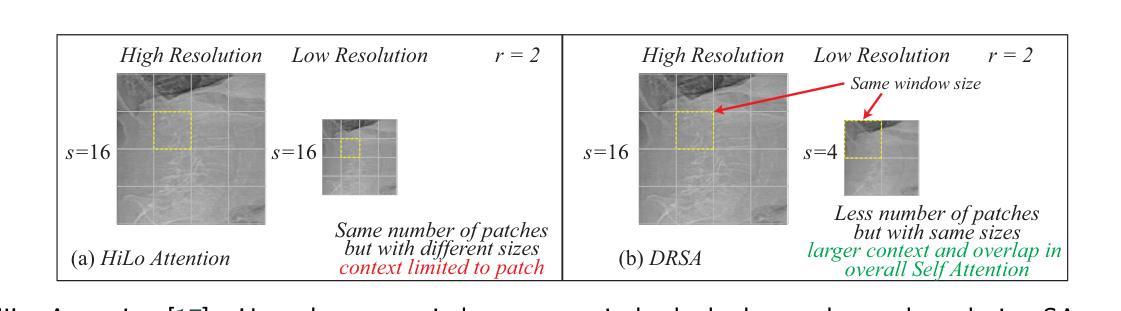
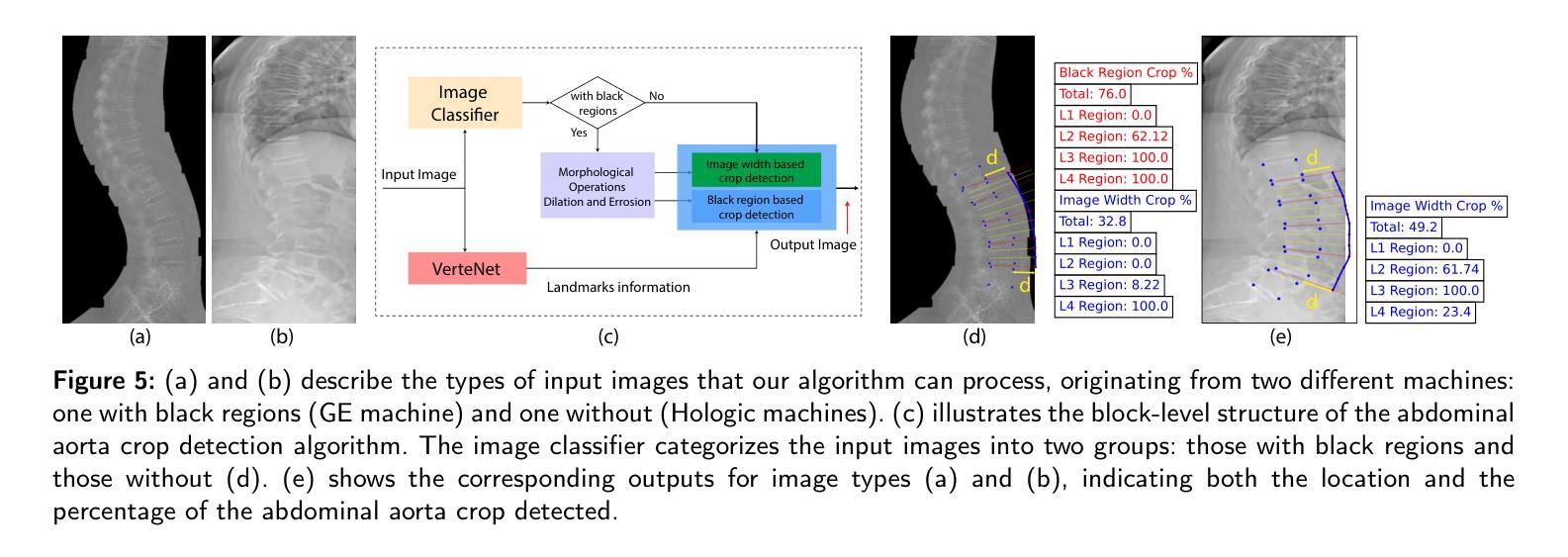
Lateral Spine Image (LSI) analysis is important for medical diagnosis, treatment planning, and detailed spinal health assessments. Although modalities like Computed Tomography and Digital X-ray Imaging are commonly used, Dual Energy X-ray Absorptiometry (DXA) is often preferred due to lower radiation exposure, seamless capture, and cost-effectiveness. Accurate Vertebral Landmark Localization (VLL) on LSIs is important to detect spinal conditions like kyphosis and lordosis, as well as assessing Abdominal Aortic Calcification (AAC) using Inter-Vertebral Guides (IVGs). Nonetheless, few automated VLL methodologies have concentrated on DXA LSIs. We present VerteNet, a hybrid CNN-Transformer model featuring a novel dual-resolution attention mechanism in self and cross-attention domains, referred to as Dual Resolution Self-Attention (DRSA) and Dual Resolution Cross-Attention (DRCA). These mechanisms capture the diverse frequencies in DXA images by operating at two different feature map resolutions. Additionally, we design a Multi-Context Feature Fusion Block (MCFB) that efficiently integrates the features using DRSA and DRCA. We train VerteNet on 620 DXA LSIs from various machines and achieve superior results compared to existing methods. We also design an algorithm that utilizes VerteNet’s predictions in estimating the Region of Interest (ROI) to detect potential abdominal aorta cropping, where inadequate soft tissue hinders calcification assessment. Additionally, we present a small proof-of-concept study to show that IVGs generated from VLL information can improve inter-reader correlation in AAC scoring, addressing two key areas of disagreement in expert AAC-24 scoring: IVG placement and quality control for full abdominal aorta assessment. The code for this work can be found at https://github.com/zaidilyas89/VerteNet.
侧位脊柱图像(LSI)分析在医学诊断、治疗计划和详细的脊柱健康评估中具有重要意义。尽管计算机断层扫描和数字X射线成像等模式常用,但由于较低的辐射暴露、无缝捕获和成本效益,双能X射线吸收法(DXA)往往更受欢迎。在LSIs上进行准确的椎体地标定位(VLL)对于检测脊柱疾病如驼背和腰椎前凸很重要,同时还需使用椎间指南(IVGs)评估腹部主动脉钙化(AAC)。然而,很少有自动化VLL方法专注于DXA LSIs。我们提出了VerteNet,这是一个混合CNN-Transformer模型,具有一种新型的双分辨率注意力机制,在自我和交叉注意力域中被称为双分辨率自注意力(DRSA)和双分辨率交叉注意力(DRCA)。这些机制通过在两种不同特征图分辨率上操作来捕捉DXA图像中的不同频率。此外,我们设计了一个多上下文特征融合块(MCFB),它有效地结合了使用DRSA和DRCA的特征。我们对来自各种机器的620个DXA LSI进行了VerteNet训练,并取得了比现有方法更优越的结果。我们还设计了一种算法,利用VerteNet的预测来估计感兴趣区域(ROI),以检测可能的腹部主动脉裁剪区域,其中软组织不足会阻碍钙化评估。此外,我们还进行了一项小型概念验证研究,以证明由VLL信息生成的IVG可以提高AAC评分的读者间相关性,解决专家AAC-24评分中的两个主要分歧领域:IVG放置和全长腹部主动脉评估的质量控制。该工作的代码可在https://github.com/zaidilyas89/VerteNet找到。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF 10 pages with 7 figures
Summary
医学图像中的侧位脊柱图像(LSI)分析对于医学诊断、治疗计划和详细的脊柱健康评估至关重要。虽然计算机断层扫描和数字X射线成像等模态是常用的,但由于较低的辐射暴露、无缝捕获和成本效益,双能X射线吸收仪(DXA)往往更受欢迎。准确的椎骨地标定位(VLL)对检测脊柱状况如驼背和隆突非常重要。本文提出了一种混合CNN-Transformer模型VerteNet,具有新型的双分辨率注意力机制,用于DXA LSIs的VLL。此外,还设计了一种算法来估计感兴趣区域(ROI),以检测因软组织不足导致的腹部主动脉裁剪评估问题。同时,通过VLL信息生成的IVG能提高AAC评分的读片间相关性。
Key Takeaways
- Lateral Spine Image (LSI)分析在医学诊断、治疗计划和脊柱健康评估中具有重要作用。
- 虽然有多种成像技术可用,但Dual Energy X-ray Absorptiometry (DXA)因低辐射暴露、无缝捕获和成本效益而受到青睐。
- 准确的Vertebral Landmark Localization (VLL)对于检测脊柱疾病至关重要,如驼背和隆突。
- 提出的VerteNet模型具有双分辨率注意力机制,旨在捕捉DXA图像中的不同频率成分。
- VerteNet在多种机器采集的620张DXA LSI图像上进行了训练,并取得了优于现有方法的结果。
- 开发了利用VerteNet预测结果估计感兴趣区域(ROI)的算法,以检测因软组织不足导致的腹部主动脉裁剪问题。
点此查看论文截图

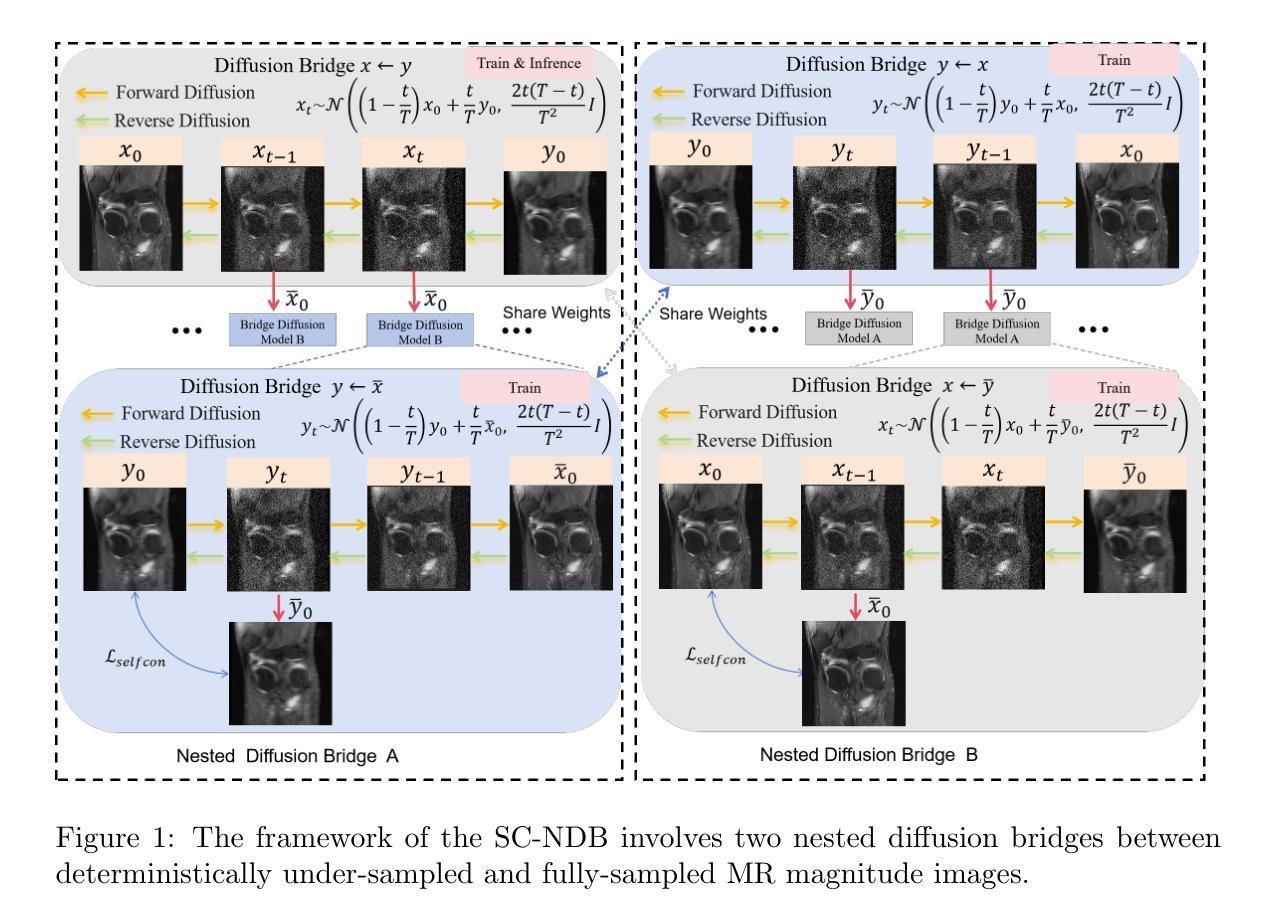
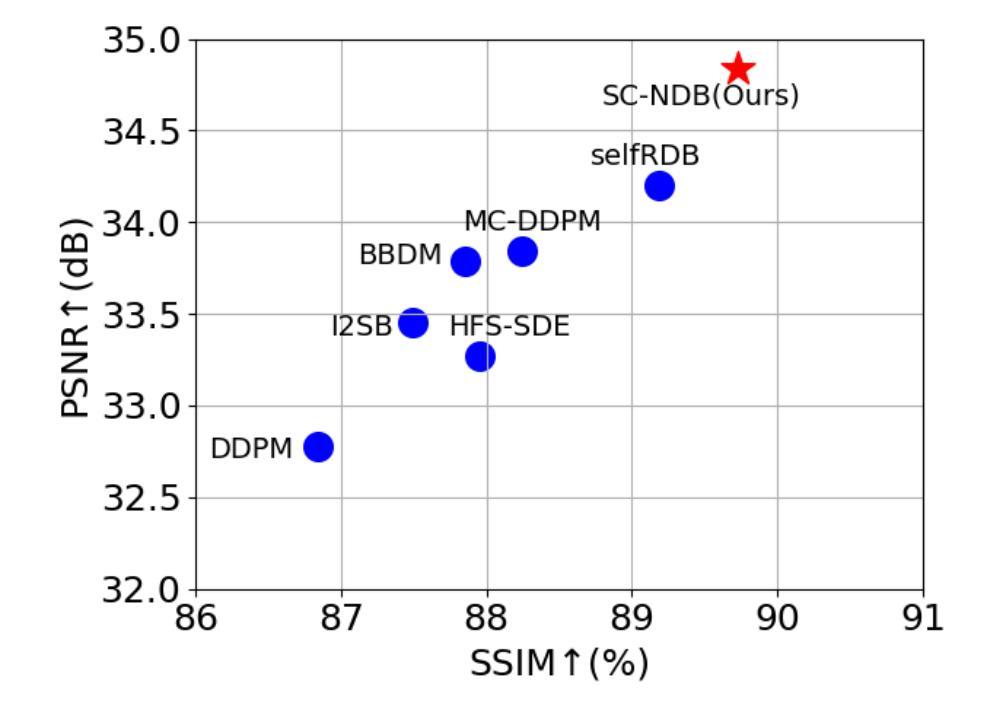
Self-Consistent Nested Diffusion Bridge for Accelerated MRI Reconstruction
Authors:Tao Song, Yicheng Wu, Minhao Hu, Xiangde Luo, Guoting Luo, Guotai Wang, Yi Guo, Feng Xu, Shaoting Zhang
Accelerated MRI reconstruction plays a vital role in reducing scan time while preserving image quality. While most existing methods rely on complex-valued image-space or k-space data, these formats are often inaccessible in clinical practice due to proprietary reconstruction pipelines, leaving only magnitude images stored in DICOM files. To address this gap, we focus on the underexplored task of magnitude-image-based MRI reconstruction. Recent advancements in diffusion models, particularly denoising diffusion probabilistic models (DDPMs), have demonstrated strong capabilities in modeling image priors. However, their task-agnostic denoising nature limits performance in source-to-target image translation tasks, such as MRI reconstruction. In this work, we propose a novel Self-Consistent Nested Diffusion Bridge (SC-NDB) framework that models accelerated MRI reconstruction as a bi-directional image translation process between under-sampled and fully-sampled magnitude MRI images. SC-NDB introduces a nested diffusion architecture with a self-consistency constraint and reverse bridge diffusion pathways to improve intermediate prediction fidelity and better capture the explicit priors of source images. Furthermore, we incorporate a Contour Decomposition Embedding Module (CDEM) to inject structural and textural knowledge by leveraging Laplacian pyramids and directional filter banks. Extensive experiments on the fastMRI and IXI datasets demonstrate that our method achieves state-of-the-art performance compared to both magnitude-based and non-magnitude-based diffusion models, confirming the effectiveness and clinical relevance of SC-NDB.
加速MRI重建在减少扫描时间的同时保持图像质量方面起着至关重要的作用。虽然大多数现有方法依赖于复数值图像空间或k空间数据,但由于专有重建管道,这些格式在临床实践中通常无法访问,只剩下以DICOM文件格式存储的幅度图像。为了解决这一差距,我们专注于基于幅度图像的MRI重建这一尚未得到充分研究的任务。扩散模型的最新进展,特别是去噪扩散概率模型(DDPMs),在建模图像先验方面表现出了强大的能力。然而,其任务无关的去噪性质限制了其在源到目标图像翻译任务(例如MRI重建)中的性能。在这项工作中,我们提出了一种新型的自我一致嵌套扩散桥(SC-NDB)框架,将加速MRI重建建模为欠采样和完全采样幅度MRI图像之间的双向图像翻译过程。SC-NDB引入了一个嵌套扩散架构,具有自我一致性约束和反向桥扩散路径,以提高中间预测保真度并更好地捕获源图像的显式先验。此外,我们结合了轮廓分解嵌入模块(CDEM),通过利用拉普拉斯金字塔和方向滤波银行来注入结构和纹理知识。在fastMRI和IXI数据集上的广泛实验表明,我们的方法达到了最先进的性能,与基于幅度和非基于幅度的扩散模型相比都表现出色,证实了SC-NDB的有效性和临床相关性。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
本文探讨了加速MRI重建的重要性,指出其在减少扫描时间的同时保持图像质量的关键作用。针对现有方法主要依赖复杂值图像空间或k空间数据,而临床实践中往往无法获取这些问题,研究集中在基于幅度图像的MRI重建上。利用扩散模型,特别是去噪扩散概率模型(DDPMs)的图像先验建模能力,提出一种新型的自洽嵌套扩散桥(SC-NDB)框架,将加速MRI重建建模为欠采样和完全采样幅度MRI图像之间的双向图像翻译过程。SC-NDB引入嵌套扩散架构、自洽性约束和反向桥扩散路径,提高中间预测保真度,更好地捕捉源图像的显式先验。结合轮廓分解嵌入模块(CDEM),通过利用拉普拉斯金字塔和方向滤波器库注入结构和纹理知识。在fastMRI和IXI数据集上的广泛实验表明,该方法在幅度和非幅度扩散模型上均达到最新性能水平,验证了SC-NDB的有效性和临床相关性。
Key Takeaways
- 加速MRI重建对于减少扫描时间同时保持图像质量至关重要。
- 现有方法主要依赖复杂值图像空间或k空间数据,但在临床实践中往往无法获取。
- 研究集中在基于幅度图像的MRI重建上。
- 扩散模型,特别是去噪扩散概率模型(DDPMs),具有强大的图像先验建模能力。
- 提出自洽嵌套扩散桥(SC-NDB)框架,将加速MRI重建建模为欠采样和完全采样幅度MRI图像之间的双向翻译过程。
- SC-NDB结合嵌套扩散架构、自洽性约束和反向桥扩散路径,提高预测中间结果的准确性。
点此查看论文截图

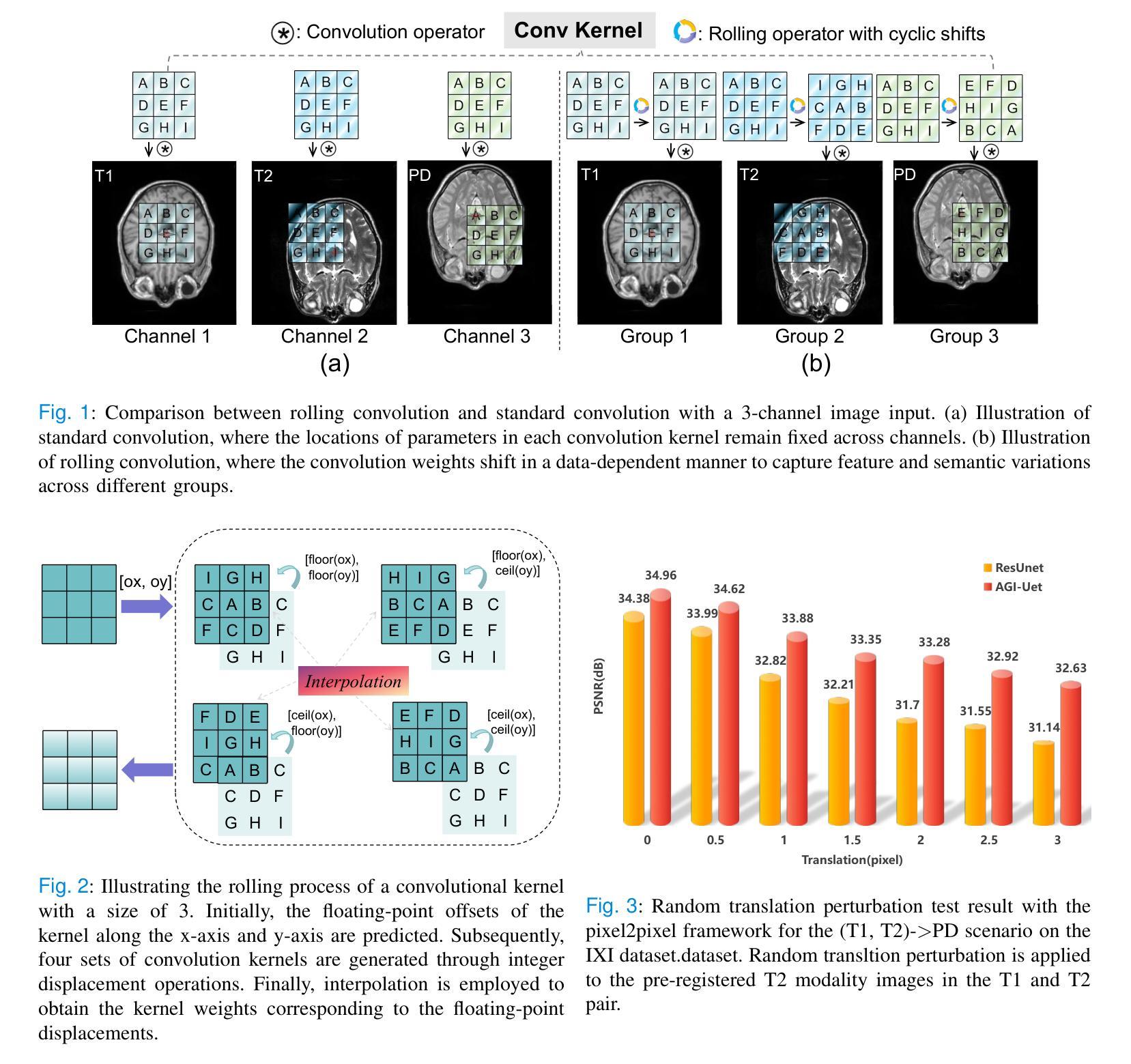
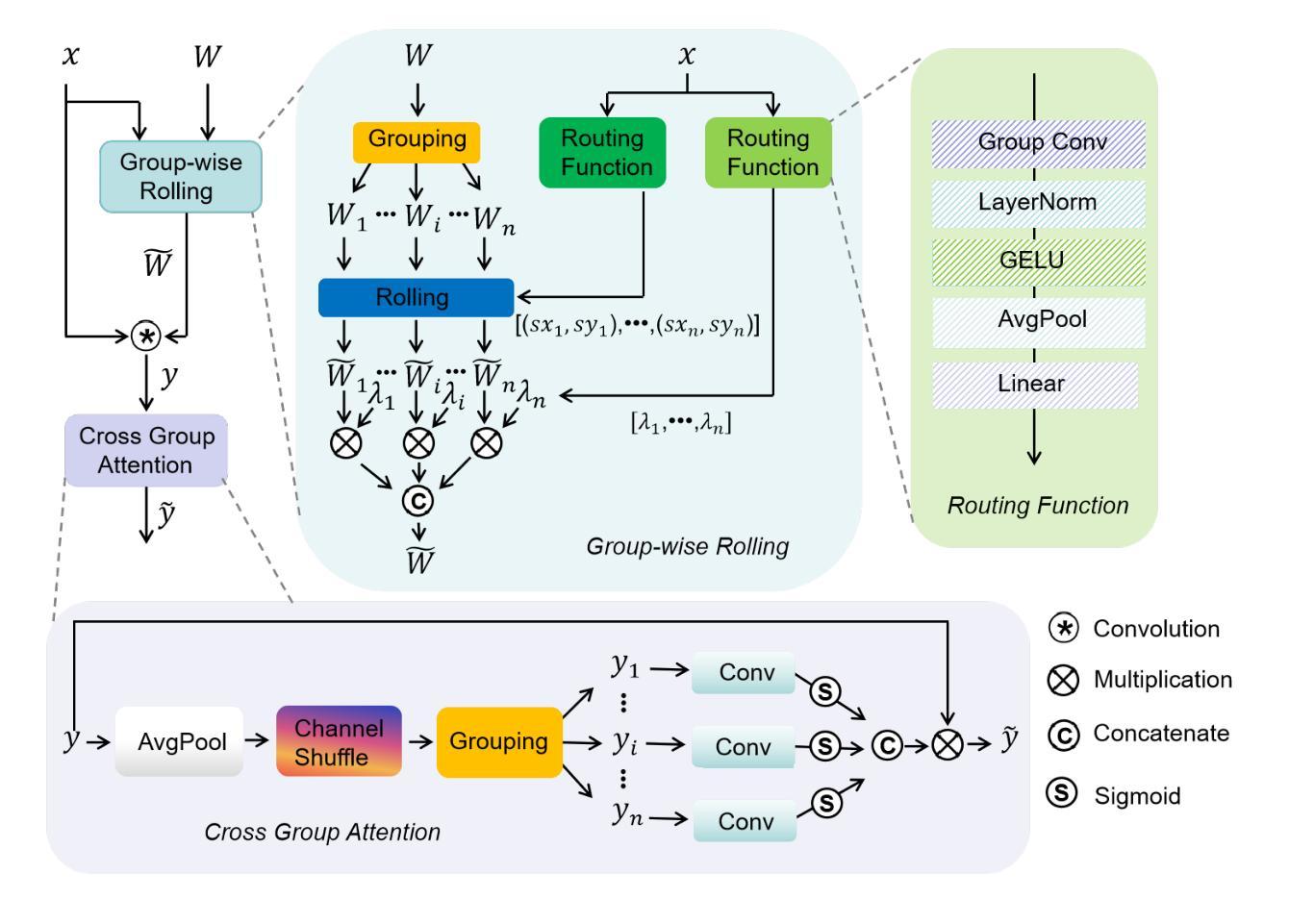
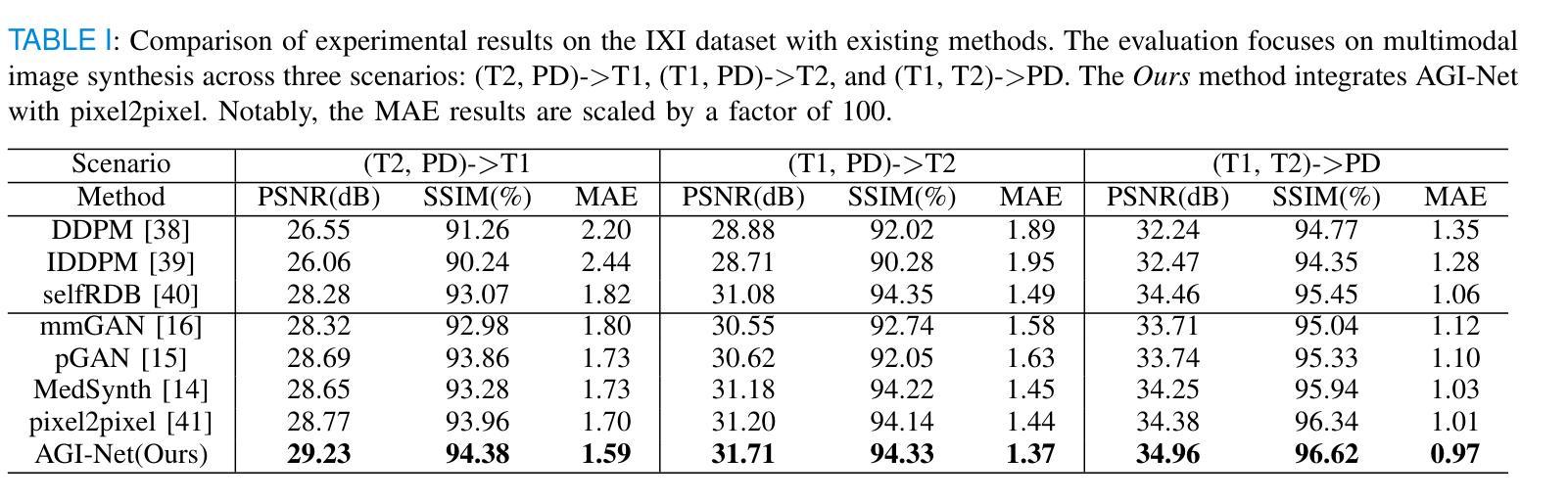
Learning Modality-Aware Representations: Adaptive Group-wise Interaction Network for Multimodal MRI Synthesis
Authors:Tao Song, Yicheng Wu, Minhao Hu, Xiangde Luo, Linda Wei, Guotai Wang, Yi Guo, Feng Xu, Shaoting Zhang
Multimodal MR image synthesis aims to generate missing modality images by effectively fusing and mapping from a subset of available MRI modalities. Most existing methods adopt an image-to-image translation paradigm, treating multiple modalities as input channels. However, these approaches often yield sub-optimal results due to the inherent difficulty in achieving precise feature- or semantic-level alignment across modalities. To address these challenges, we propose an Adaptive Group-wise Interaction Network (AGI-Net) that explicitly models both inter-modality and intra-modality relationships for multimodal MR image synthesis. Specifically, feature channels are first partitioned into predefined groups, after which an adaptive rolling mechanism is applied to conventional convolutional kernels to better capture feature and semantic correspondences between different modalities. In parallel, a cross-group attention module is introduced to enable effective feature fusion across groups, thereby enhancing the network’s representational capacity. We validate the proposed AGI-Net on the publicly available IXI and BraTS2023 datasets. Experimental results demonstrate that AGI-Net achieves state-of-the-art performance in multimodal MR image synthesis tasks, confirming the effectiveness of its modality-aware interaction design. We release the relevant code at: https://github.com/zunzhumu/Adaptive-Group-wise-Interaction-Network-for-Multimodal-MRI-Synthesis.git.
多模态MR图像合成旨在通过有效融合和映射从可用MRI模态的子集来生成缺失的模态图像。大多数现有方法采用图像到图像的翻译模式,将多个模态视为输入通道。然而,由于在不同模态之间实现精确的特征或语义级对齐的固有困难,这些方法通常会产生次优结果。为了应对这些挑战,我们提出了一种自适应组交互网络(AGI-Net),该网络对多模态MR图像合成进行显式建模,建立模态间和模态内的关系。具体来说,特征通道首先被划分为预定义的组,然后对传统卷积核应用自适应滚动机制,以更好地捕获不同模态之间的特征和语义对应关系。同时,引入跨组注意力模块,实现跨组的有效特征融合,从而增强网络的表示能力。我们在公开可用的IXI和BraTS2023数据集上验证了所提出的AGI-Net。实验结果表明,AGI-Net在多模态MR图像合成任务上达到了最先进的性能,证明了其模态感知交互设计的有效性。我们已在https://github.com/zunzhumu/Adaptive-Group-wise-Interaction-Network-for-Multimodal-MRI-Synthesis.git上发布了相关代码。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
本文提出一种自适应组交互网络(AGI-Net),用于多模态MR图像合成。该网络通过建模模态间和模态内关系,改进了图像到图像翻译范式,实现了更精确的特征或语义级对齐。采用分组卷积核自适应滚动机制,并引入跨组注意力模块,提高了网络在多模态特征融合方面的表现。在公开数据集IXI和BraTS2023上的实验结果表明,AGI-Net在多模态MR图像合成任务上达到最佳性能。
Key Takeaways
- 本文旨在通过有效融合和映射部分可用的MRI模态,生成缺失模态的图像。
- 提出一种自适应组交互网络(AGI-Net),以改进多模态MR图像合成的效果。
- AGI-Net通过建模模态间和模态内关系,实现更精确的特征或语义级对齐。
- 采用分组卷积核的自适应滚动机制,以更好地捕捉不同模态之间的特征和语义对应关系。
- 引入跨组注意力模块,提高网络在多模态特征融合方面的能力。
- 在IXI和BraTS2023公开数据集上的实验验证了AGI-Net的有效性。
- 相关代码已发布在https://github.com/zunzhumu/Adaptive-Group-wise-Interaction-Network-for-Multimodal-MRI-Synthesis.git上。
点此查看论文截图

Real-Time Image Segmentation via Hybrid Convolutional-Transformer Architecture Search
Authors:Hongyuan Yu, Cheng Wan, Xiyang Dai, Mengchen Liu, Dongdong Chen, Bin Xiao, Yan Huang, Yuan Lu, Liang Wang
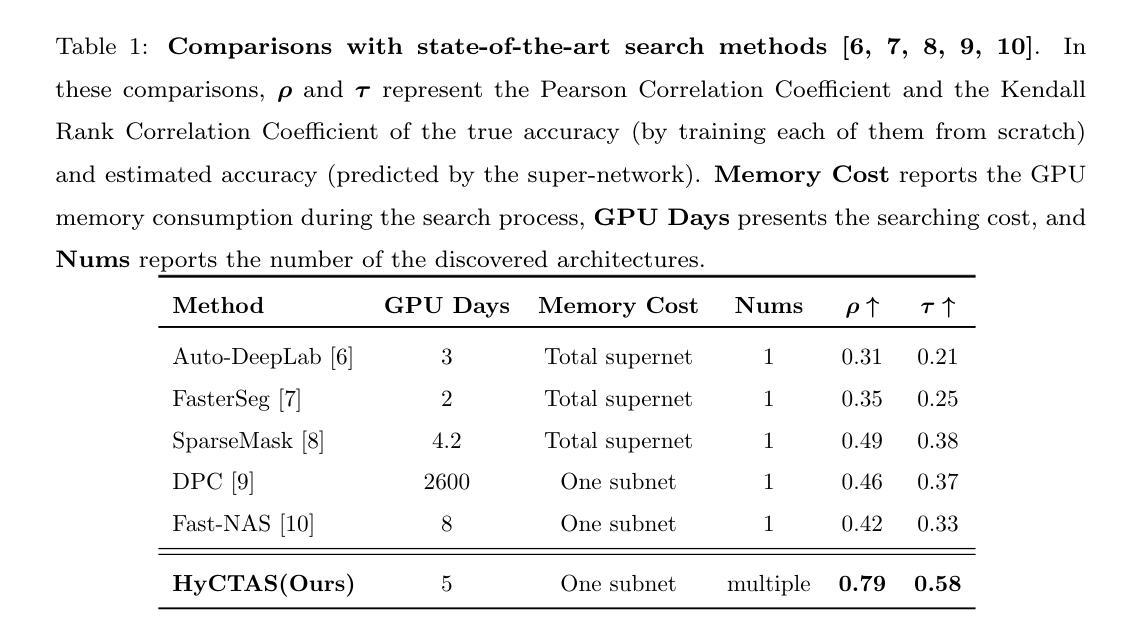
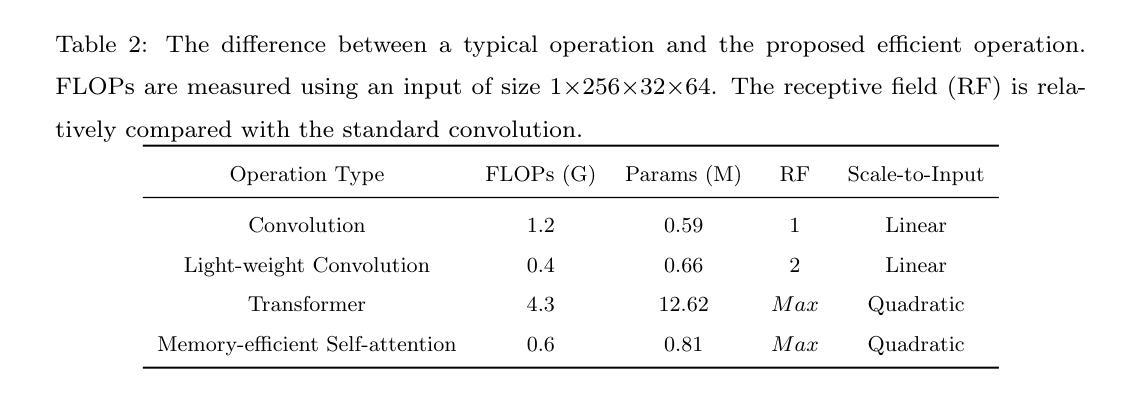
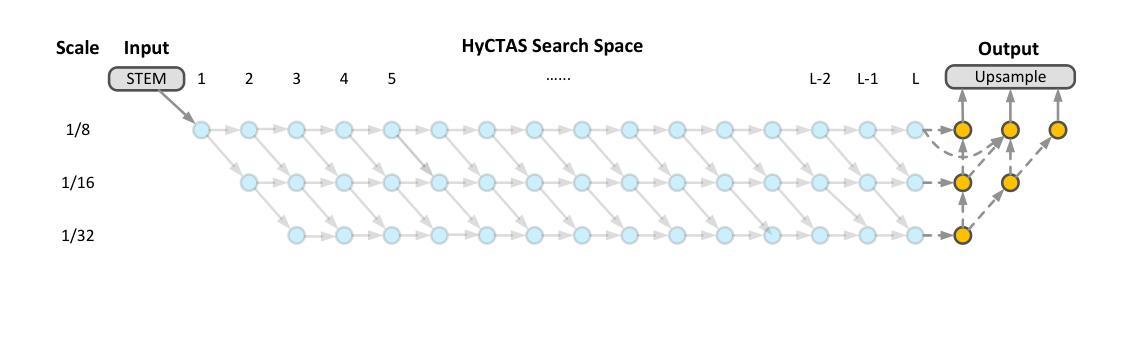
Image segmentation is one of the most fundamental problems in computer vision and has drawn a lot of attention due to its vast applications in image understanding and autonomous driving. However, designing effective and efficient segmentation neural architectures is a labor-intensive process that may require numerous trials by human experts. In this paper, we address the challenge of integrating multi-head self-attention into high-resolution representation CNNs efficiently by leveraging architecture search. Manually replacing convolution layers with multi-head self-attention is non-trivial due to the costly overhead in memory to maintain high resolution. By contrast, we develop a multi-target multi-branch supernet method, which not only fully utilizes the advantages of high-resolution features but also finds the proper location for placing the multi-head self-attention module. Our search algorithm is optimized towards multiple objectives (e.g., latency and mIoU) and is capable of finding architectures on the Pareto frontier with an arbitrary number of branches in a single search. We further present a series of models via the Hybrid Convolutional-Transformer Architecture Search (HyCTAS) method that searches for the best hybrid combination of light-weight convolution layers and memory-efficient self-attention layers between branches from different resolutions and fuses them to high resolution for both efficiency and effectiveness. Extensive experiments demonstrate that HyCTAS outperforms previous methods in both semantic segmentation and panoptic segmentation tasks. Code and models are available at https://github.com/MarvinYu1995/HyCTAS.
图像分割是计算机视觉中最基本的问题之一,由于其在图像理解和自动驾驶等方面的广泛应用而备受关注。然而,设计和开发有效且高效的分割神经网络是一个劳动密集型过程,可能需要人类专家进行多次试验。在本文中,我们通过利用架构搜索来解决将多头自注意力高效集成到高分辨率表示CNN中的挑战。手动将卷积层替换为多头自注意力是非平凡的,因为维持高分辨率需要消耗大量内存资源。相比之下,我们开发了一种多目标多分支超网方法,它不仅充分利用了高分辨率特征的优势,还找到了放置多头自注意力模块的正确位置。我们的搜索算法针对多个目标(例如延迟时间和mIoU)进行了优化,能够在单次搜索中找到具有任意数量的分支的帕累托前沿的架构。我们进一步通过混合卷积-转换器架构搜索(HyCTAS)方法提出了一系列模型,该方法搜索最佳轻量级卷积层和内存高效自注意力层之间的最佳混合组合,这些层来自不同分辨率的分支,并以高分辨率为核心进行融合,以实现高效和有效的分割。大量实验表明,HyCTAS在语义分割和全景分割任务上的性能优于以前的方法。相关代码和模型可访问https://github.com/MarvinYu1995/HyCTAS获取。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF 29 pages, 5 figures, submitted to Knowledge-Baed Systems
摘要
本文将多头自注意力高效集成到高分辨率表示CNN中,解决图像分割领域中的核心问题。通过利用架构搜索,避免了手动替换卷积层与多头自注意力的繁琐过程。开发的多目标多分支超网方法既充分利用了高分辨率特征的优势,又找到了放置多头自注意力模块的最佳位置。搜索算法针对多个目标(如延迟和mIoU)进行优化,能够在单次搜索中找到任意数量的分支的帕累托前沿架构。通过Hybrid Convolutional-Transformer Architecture Search(HyCTAS)方法,搜索最佳轻量级卷积层和内存高效自注意力层的混合组合,从不同分辨率的分支融合到高分辨率,以实现效率和效果的平衡。实验证明,HyCTAS在语义分割和全景分割任务上均优于以前的方法。
关键见解
- 图像分割是计算机视觉中最基本的问题之一,具有广泛的应用于图像理解和自动驾驶等领域。
- 手动将卷积层替换为多头自注意力是一个繁琐且成本高昂的过程。
- 提出的多目标多分支超网方法既利用高分辨率特征,又找到放置多头自注意力模块的最佳位置。
- 搜索算法针对多个目标(如延迟和mIoU)进行优化,能在单次搜索中找到多种优秀架构。
- HyCTAS方法能搜索最佳混合组合,结合轻量级卷积层和内存高效自注意力层。
- 实验证明HyCTAS在语义分割和全景分割任务上的性能超越之前的方法。
点此查看论文截图