⚠️ 以下所有内容总结都来自于 大语言模型的能力,如有错误,仅供参考,谨慎使用
🔴 请注意:千万不要用于严肃的学术场景,只能用于论文阅读前的初筛!
💗 如果您觉得我们的项目对您有帮助 ChatPaperFree ,还请您给我们一些鼓励!⭐️ HuggingFace免费体验
2025-04-30 更新
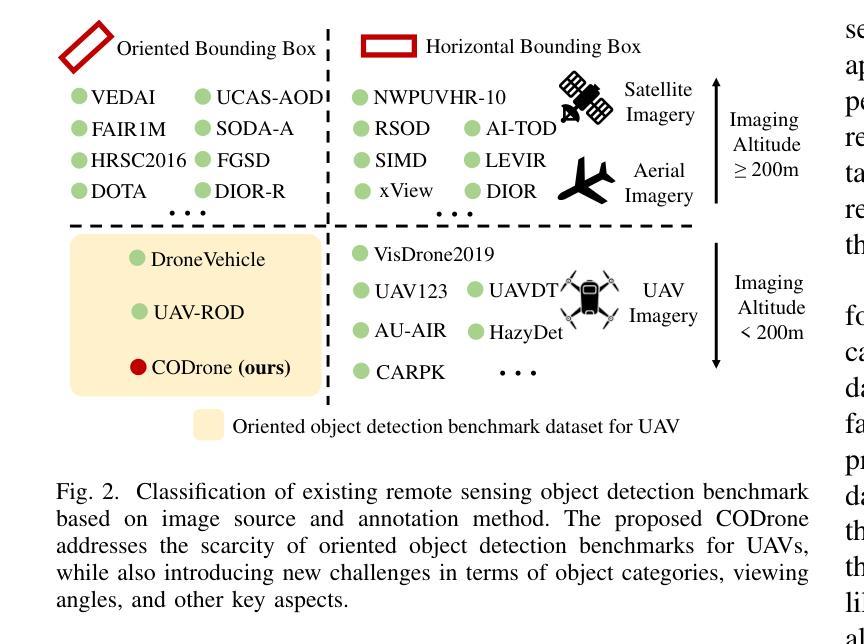
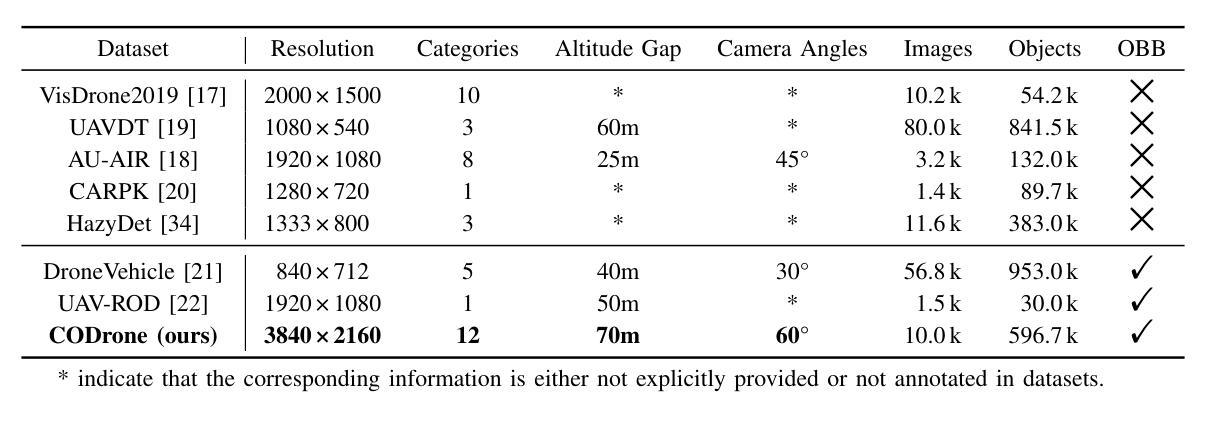
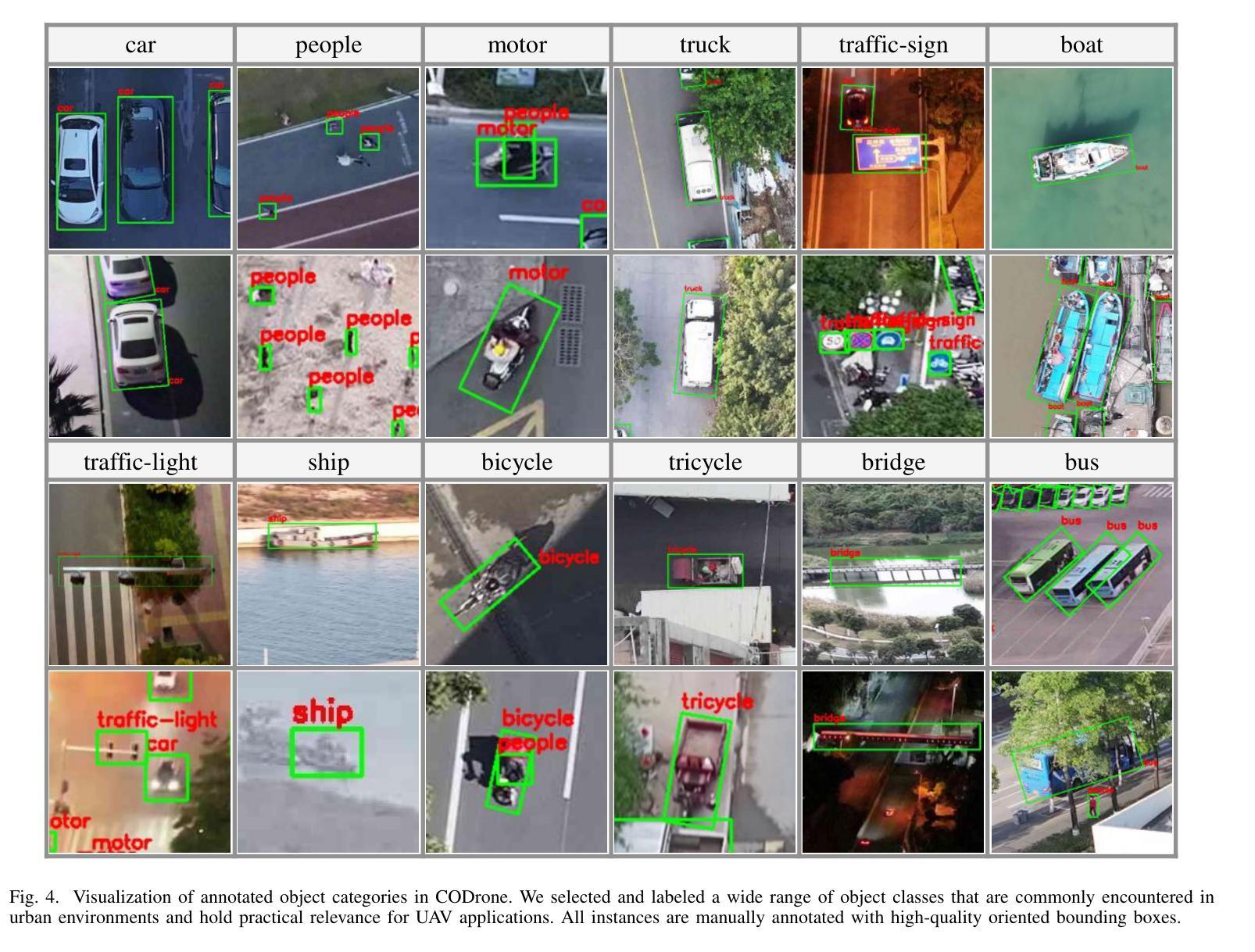
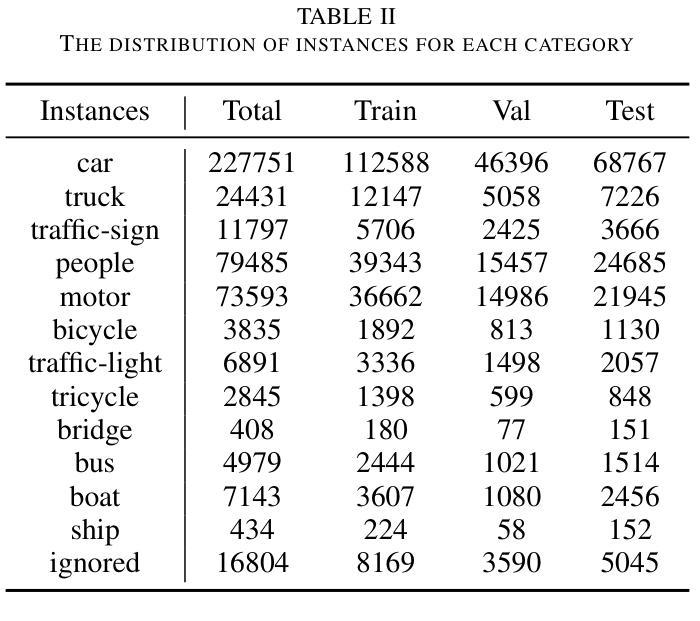
More Clear, More Flexible, More Precise: A Comprehensive Oriented Object Detection benchmark for UAV
Authors:Kai Ye, Haidi Tang, Bowen Liu, Pingyang Dai, Liujuan Cao, Rongrong Ji
Applications of unmanned aerial vehicle (UAV) in logistics, agricultural automation, urban management, and emergency response are highly dependent on oriented object detection (OOD) to enhance visual perception. Although existing datasets for OOD in UAV provide valuable resources, they are often designed for specific downstream tasks.Consequently, they exhibit limited generalization performance in real flight scenarios and fail to thoroughly demonstrate algorithm effectiveness in practical environments. To bridge this critical gap, we introduce CODrone, a comprehensive oriented object detection dataset for UAVs that accurately reflects real-world conditions. It also serves as a new benchmark designed to align with downstream task requirements, ensuring greater applicability and robustness in UAV-based OOD.Based on application requirements, we identify four key limitations in current UAV OOD datasets-low image resolution, limited object categories, single-view imaging, and restricted flight altitudes-and propose corresponding improvements to enhance their applicability and robustness.Furthermore, CODrone contains a broad spectrum of annotated images collected from multiple cities under various lighting conditions, enhancing the realism of the benchmark. To rigorously evaluate CODrone as a new benchmark and gain deeper insights into the novel challenges it presents, we conduct a series of experiments based on 22 classical or SOTA methods.Our evaluation not only assesses the effectiveness of CODrone in real-world scenarios but also highlights key bottlenecks and opportunities to advance OOD in UAV applications.Overall, CODrone fills the data gap in OOD from UAV perspective and provides a benchmark with enhanced generalization capability, better aligning with practical applications and future algorithm development.
无人机(UAV)在物流、农业自动化、城市管理和应急响应中的应用高度依赖于定向对象检测(OOD)以增强视觉感知。尽管现有的无人机OOD数据集提供了有价值的资源,但它们通常是为特定的下游任务而设计的。因此,它们在真实飞行场景中的泛化性能有限,无法彻底证明算法在实际环境中的有效性。为了弥补这一关键差距,我们引入了CODrone,这是一个全面的无人机定向对象检测数据集,准确反映了真实世界的情况。它还作为一个新基准,旨在符合下游任务的要求,确保在无人机基于OOD的应用中具有更大的适用性和稳健性。基于应用要求,我们确定了当前无人机OOD数据集的四个关键局限性:图像分辨率低、对象类别有限、单视图成像和飞行高度受限,并提出了相应的改进措施来提高其适用性和稳健性。此外,CODrone包含从多个城市在各种光照条件下收集的广泛注释的图像,增强了基准测试的真实性。为了严格评估CODrone作为一个新基准的挑战性并深入了解其呈现的新挑战,我们基于22种经典或最新方法进行了一系列实验。我们的评估不仅评估了CODrone在真实场景中的有效性,而且还强调了推进无人机应用中OOD的关键瓶颈和机会。总体而言,CODrone填补了从无人机角度进行OOD的数据空白,并提供了一个具有增强泛化能力的基准测试,更好地符合实际应用和未来的算法开发。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
无人机在物流、农业自动化、城市管理和应急响应等领域的应用中,面向对象的检测(OOD)技术对于提升视觉感知至关重要。现有的无人机OOD数据集存在局限性,难以满足真实飞行场景的需求。为解决这一问题,CODrone数据集应运而生,它真实反映了现实世界的复杂环境,增强了无人机面向对象的检测能力。该数据集具有图像分辨率高、对象类别丰富、多视角成像等特点,能够适用于各种应用场景的需求。通过对不同方法的评估,验证了CODrone数据集的有效性,并揭示了面向对象的无人机检测中的关键瓶颈和未来发展方向。
Key Takeaways
- 无人机在多个领域的应用中,依赖于面向对象的检测(OOD)技术提升视觉感知。
- 当前无人机OOD数据集存在局限性,难以满足真实飞行场景的需求。
- CODrone数据集具备真实反映现实世界的复杂环境的能力,增强了无人机面向对象的检测能力。
- CODrone数据集具有图像分辨率高、对象类别丰富等特点,适用于多种应用场景。
- 通过实验评估,验证了CODrone数据集的有效性。
点此查看论文截图


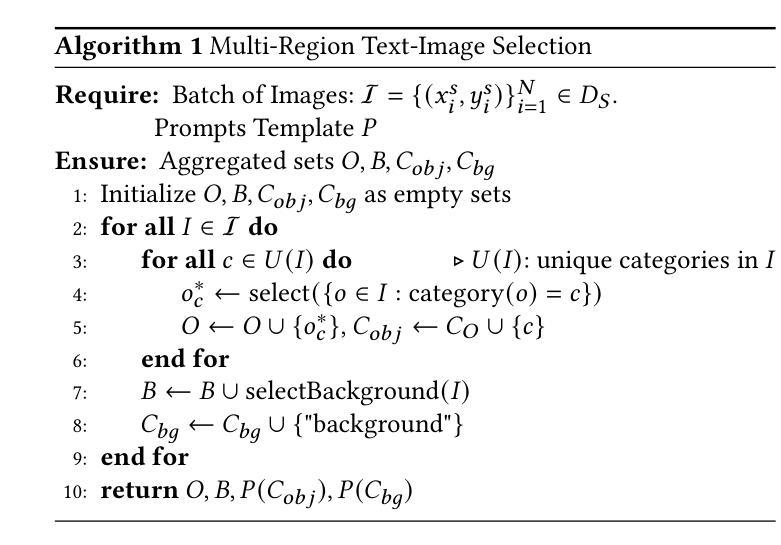
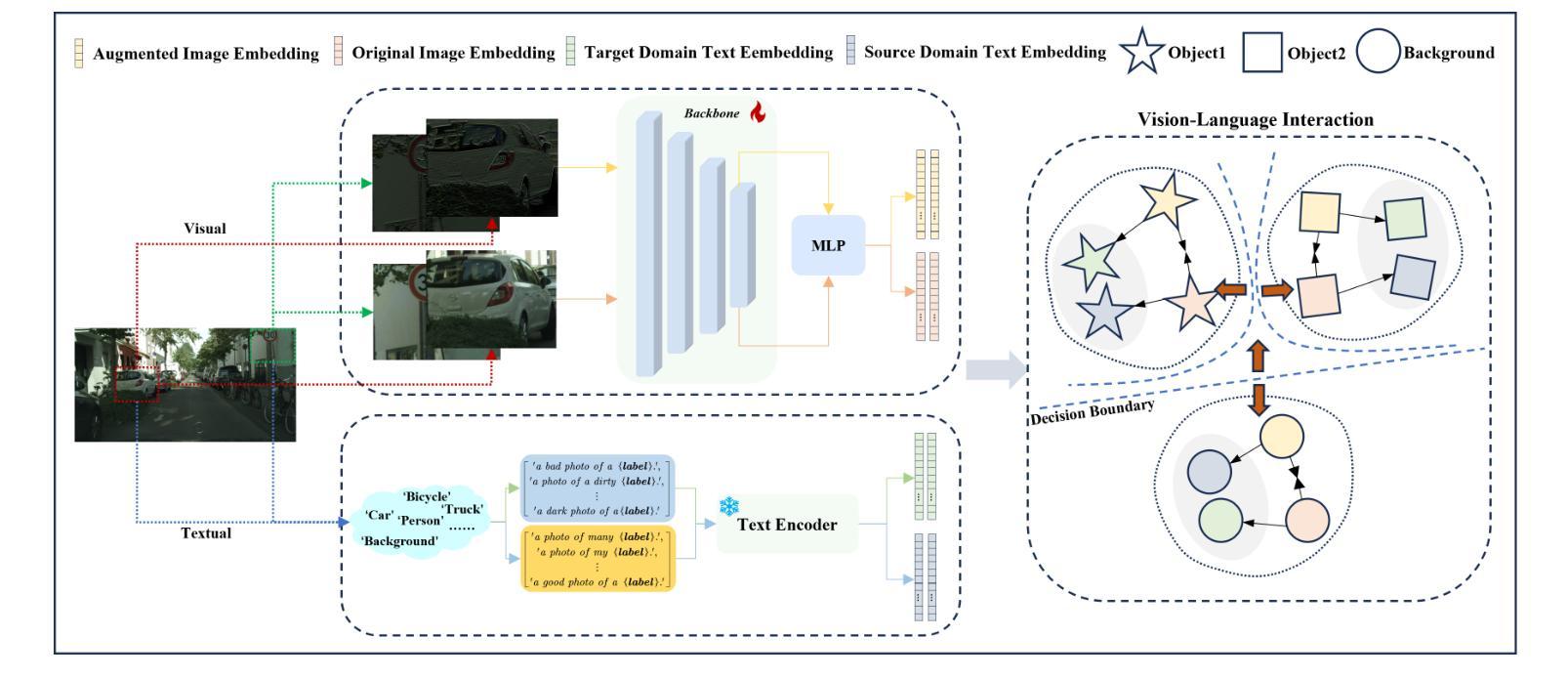
Boosting Single-domain Generalized Object Detection via Vision-Language Knowledge Interaction
Authors:Xiaoran Xu, Jiangang Yang, Wenyue Chong, Wenhui Shi, Shichu Sun, Jing Xing, Jian Liu
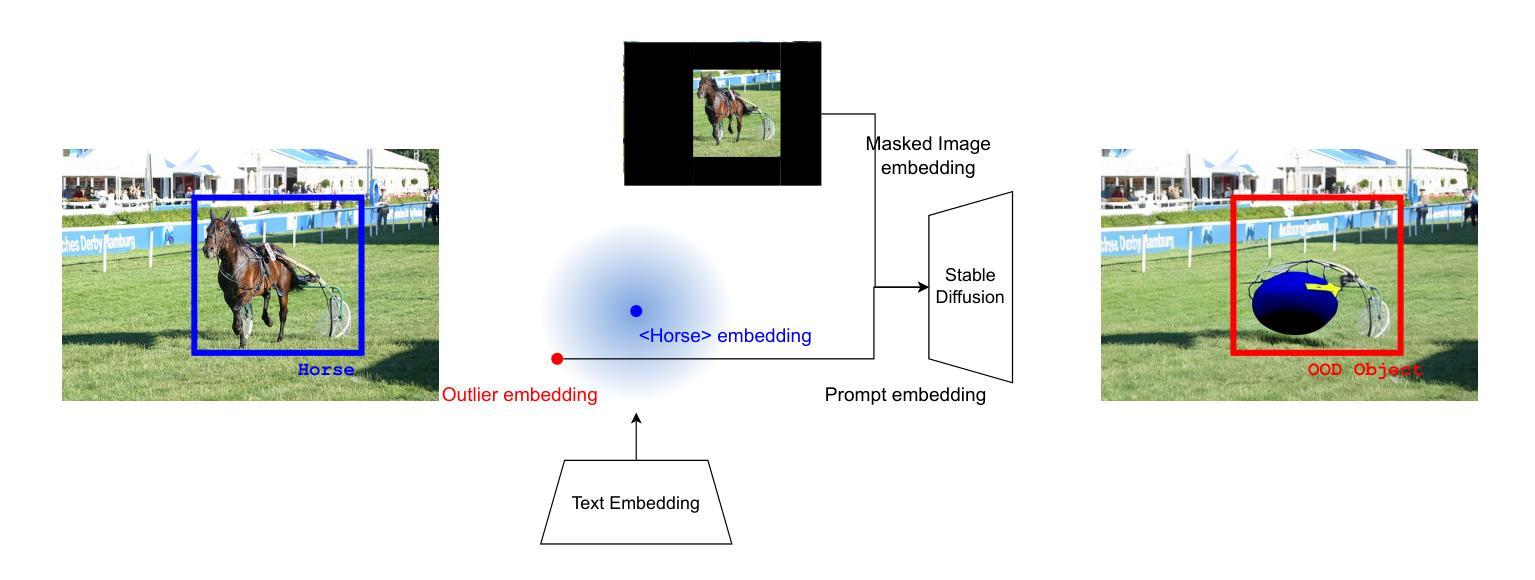
Single-Domain Generalized Object Detection(S-DGOD) aims to train an object detector on a single source domain while generalizing well to diverse unseen target domains, making it suitable for multimedia applications that involve various domain shifts, such as intelligent video surveillance and VR/AR technologies. With the success of large-scale Vision-Language Models, recent S-DGOD approaches exploit pre-trained vision-language knowledge to guide invariant feature learning across visual domains. However, the utilized knowledge remains at a coarse-grained level(e.g., the textual description of adverse weather paired with the image) and serves as an implicit regularization for guidance, struggling to learn accurate region- and object-level features in varying domains. In this work, we propose a new cross-modal feature learning method, which can capture generalized and discriminative regional features for S-DGOD tasks. The core of our method is the mechanism of Cross-modal and Region-aware Feature Interaction, which simultaneously learns both inter-modal and intra-modal regional invariance through dynamic interactions between fine-grained textual and visual features. Moreover, we design a simple but effective strategy called Cross-domain Proposal Refining and Mixing, which aligns the position of region proposals across multiple domains and diversifies them, enhancing the localization ability of detectors in unseen scenarios. Our method achieves new state-of-the-art results on S-DGOD benchmark datasets, with improvements of +8.8%mPC on Cityscapes-C and +7.9%mPC on DWD over baselines, demonstrating its efficacy.
单域广义目标检测(S-DGOD)旨在针对单一源域训练目标检测器,并在多样化的未见目标域上实现良好的泛化性能,使其成为适用于涉及各种域偏移的多媒体应用(如智能视频监控和虚拟现实/增强现实技术)的理想选择。随着大规模视觉语言模型的成功,最近的S-DGOD方法利用预训练的视觉语言知识来指导跨视觉域的鲁棒特征学习。然而,所利用的知识仍处于较粗的粒度级别(例如,不利天气的文本描述与图像配对),作为隐式正则化指导,难以在多个域中学习准确的区域和对象级特征。在这项工作中,我们提出了一种新的跨模态特征学习方法,可以为S-DGOD任务捕获通用和区分性的区域特征。我们方法的核心是跨模态和区域感知特征交互机制,它通过细粒度文本和视觉特征之间的动态交互,同时学习跨模态和跨模态的区域不变性。此外,我们设计了一种简单有效的策略,称为跨域提案精炼和混合(Cross-domain Proposal Refining and Mixing),它调整了多个域的区域提案的位置并使其多样化,增强了检测器在未见场景中的定位能力。我们的方法在S-DGOD基准数据集上取得了最新的最佳结果,在Cityscapes-C上较基线提高了8.8% mPC,在DWD上较基线提高了7.9% mPC,证明了其有效性。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary:本文提出一种新型的跨模态特征学习方法,用于单域广义目标检测(S-DGOD)。该方法通过跨模态和区域感知特征交互机制,学习跨不同域内模态间和模态内的区域性不变性特征,实现了良好的泛化性能。同时,采用了一种简单有效的跨域提议精炼和混合策略,提高了检测器在未见场景中的定位能力。该方法在S-DGOD基准数据集上取得了最新成果。
Key Takeaways:
- S-DGOD旨在训练一个目标检测器,使其能够在单一源域上表现良好,同时泛化到多样化的未见目标域。
- 该方法利用大规模视觉语言模型的知识进行跨域不变特征学习。
- 传统方法使用粗粒度知识作为隐式正则化指导,难以学习准确的区域和对象级别特征。
- 本文提出一种新型跨模态特征学习方法,包括跨模态和区域感知特征交互机制。
- 该方法通过动态交互精细粒度文本和视觉特征,同时学习跨模态和模态内的区域性不变性。
- 采用跨域提议精炼和混合策略,提高了检测器在未见场景中的定位能力。
点此查看论文截图


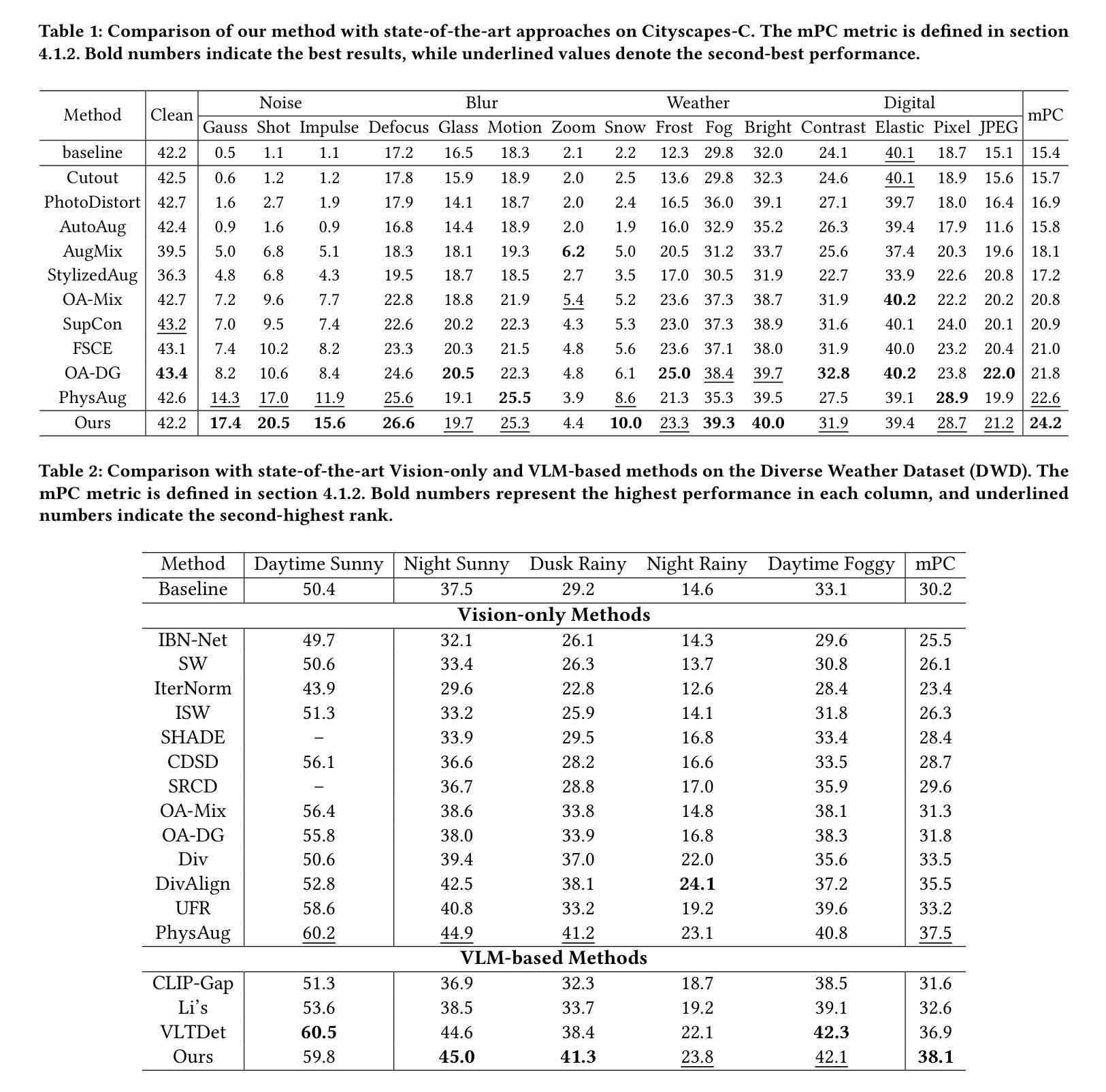
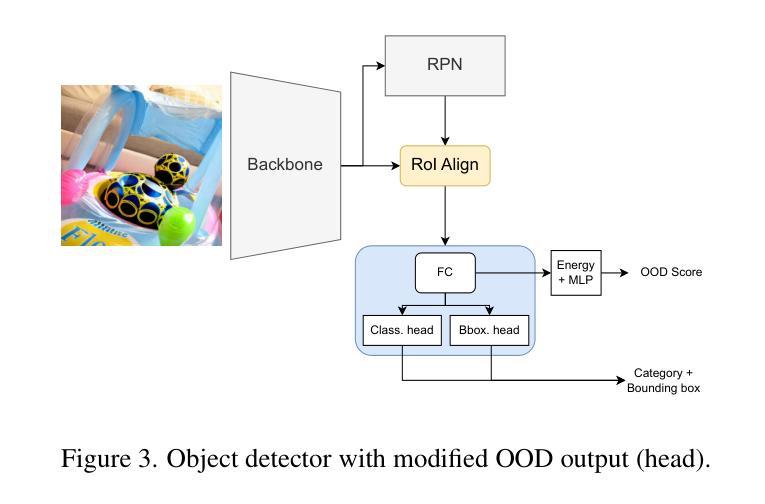
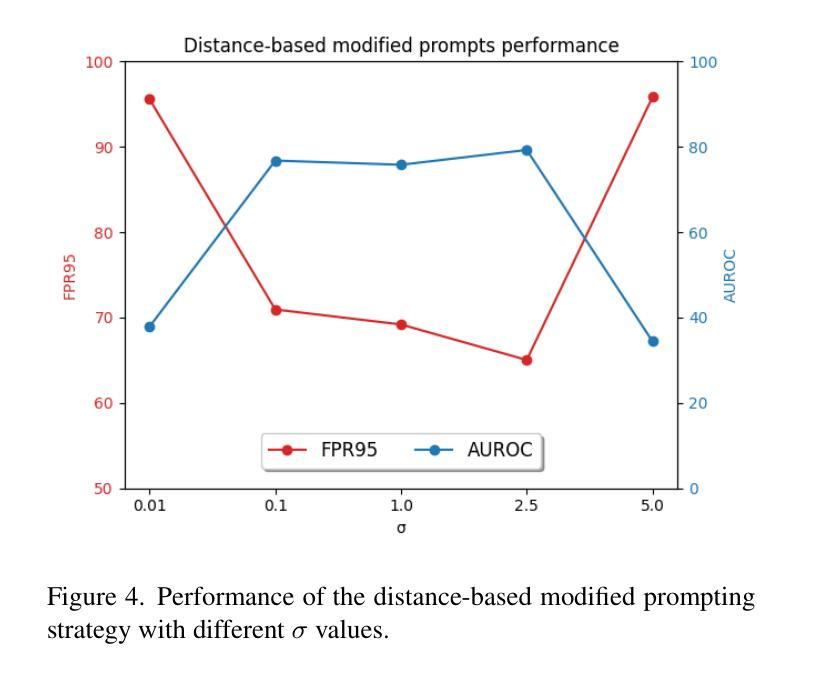
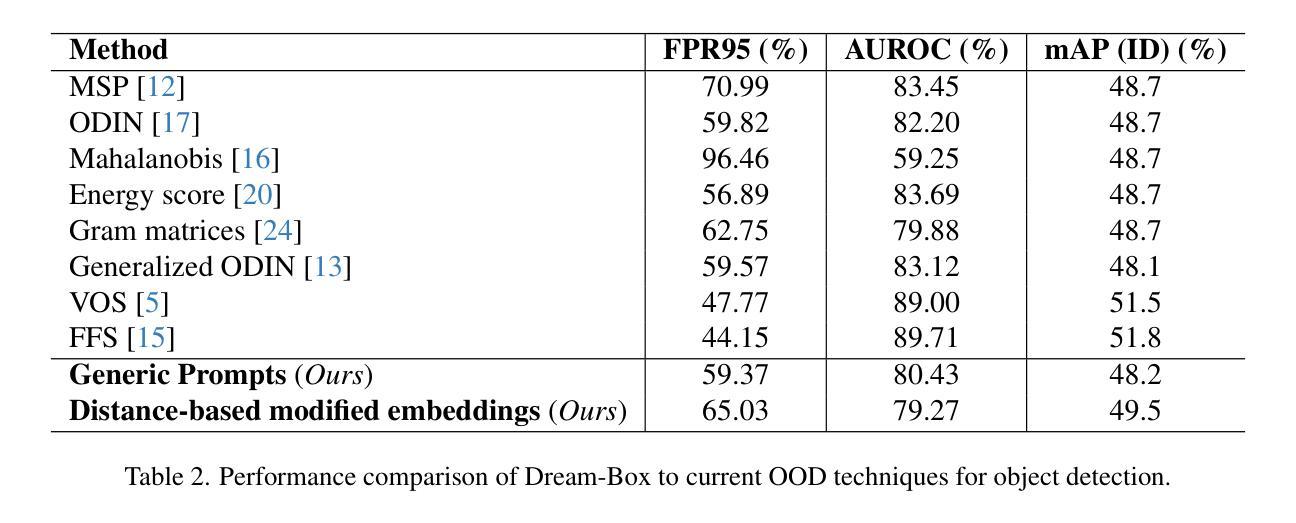
Dream-Box: Object-wise Outlier Generation for Out-of-Distribution Detection
Authors:Brian K. S. Isaac-Medina, Toby P. Breckon
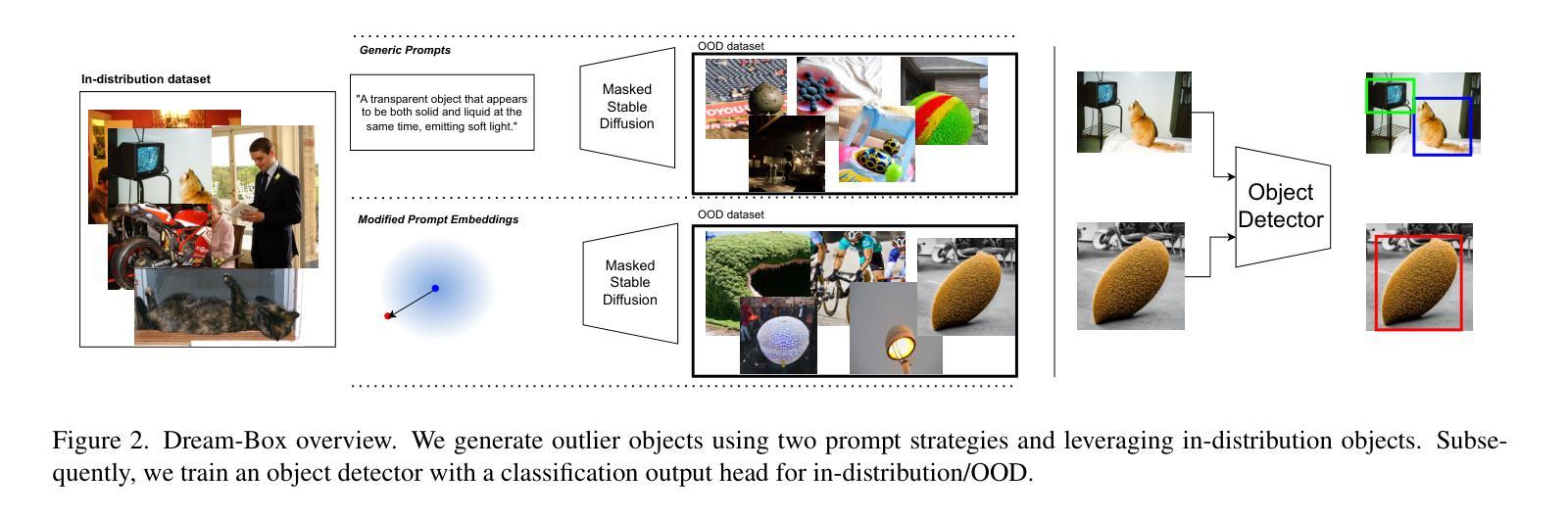
Deep neural networks have demonstrated great generalization capabilities for tasks whose training and test sets are drawn from the same distribution. Nevertheless, out-of-distribution (OOD) detection remains a challenging task that has received significant attention in recent years. Specifically, OOD detection refers to the detection of instances that do not belong to the training distribution, while still having good performance on the in-distribution task (e.g., classification or object detection). Recent work has focused on generating synthetic outliers and using them to train an outlier detector, generally achieving improved OOD detection than traditional OOD methods. In this regard, outliers can be generated either in feature or pixel space. Feature space driven methods have shown strong performance on both the classification and object detection tasks, at the expense that the visualization of training outliers remains unknown, making further analysis on OOD failure modes challenging. On the other hand, pixel space outlier generation techniques enabled by diffusion models have been used for image classification using, providing improved OOD detection performance and outlier visualization, although their adaption to the object detection task is as yet unexplored. We therefore introduce Dream-Box, a method that provides a link to object-wise outlier generation in the pixel space for OOD detection. Specifically, we use diffusion models to generate object-wise outliers that are used to train an object detector for an in-distribution task and OOD detection. Our method achieves comparable performance to previous traditional methods while being the first technique to provide concrete visualization of generated OOD objects.
深度神经网络在从同一分布中提取的训练集和测试集上执行的任务中表现出了强大的泛化能力。然而,异常值检测(Out-of-Distribution,OOD)仍然是一个具有挑战性的任务,近年来受到了广泛关注。具体来说,OOD检测是指检测那些不属于训练分布但仍在分布内任务(例如分类或对象检测)上表现良好的实例。近期的研究主要集中在生成合成异常值并使用它们来训练异常检测器,通常比传统OOD方法实现了更好的OOD检测性能。在这方面,异常值可以在特征空间或像素空间生成。特征空间驱动的方法在分类和对象检测任务上都表现出了强大的性能,但训练异常值的可视化仍然未知,使得对OOD失败模式的进一步分析具有挑战性。另一方面,由扩散模型驱动的像素空间异常值生成技术已被用于图像分类,提供了改进的OOD检测性能和异常值可视化,但它们对对象检测任务的适应尚未被探索。因此,我们引入了Dream-Box方法,该方法为OOD检测的像素空间中的对象级异常值生成提供了联系。具体来说,我们使用扩散模型生成对象级异常值,这些异常值用于训练用于分布内任务和OOD检测的对象检测器。我们的方法与之前的方法相比取得了相当的性能,并且是第一个提供生成的OOD对象具体可视化的技术。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF 9 pages, 6 figures, 2 tables, LatinX in AI CVPR 2025 Workshop
Summary
深神经网络在同分布任务中表现出良好的泛化能力,但对于跨分布检测(OOD)仍然是一个挑战。近期研究集中在生成合成异常值并训练异常检测器,特征空间驱动的方法和像素空间技术均有尝试。特征空间方法在分类和对象检测任务上表现优异,但训练异常值的可视化未知,使得进一步分析OOD失败模式具有挑战性。像素空间技术通过扩散模型用于图像分类,但对象检测任务的适应仍是未知。本研究介绍Dream-Box方法,结合扩散模型进行像素级的对象异常值生成,以支持OOD检测。此方法可实现与传统方法相当的性能,并提供具象化的生成OOD对象可视化。
Key Takeaways
- 深神经网络在同分布任务中泛化能力强,但在跨分布检测(OOD)上仍面临挑战。
- 特征空间方法在分类和对象检测任务上表现良好,但训练异常值的可视化未知。
- 像素空间技术通过扩散模型在图像分类中用于OOD检测,但尚未适应对象检测任务。
- Dream-Box方法结合扩散模型进行像素级的对象异常值生成,支持OOD检测。
- Dream-Box方法可实现与传统方法相当的性能。
- Dream-Box方法提供具象化的生成OOD对象可视化。
点此查看论文截图


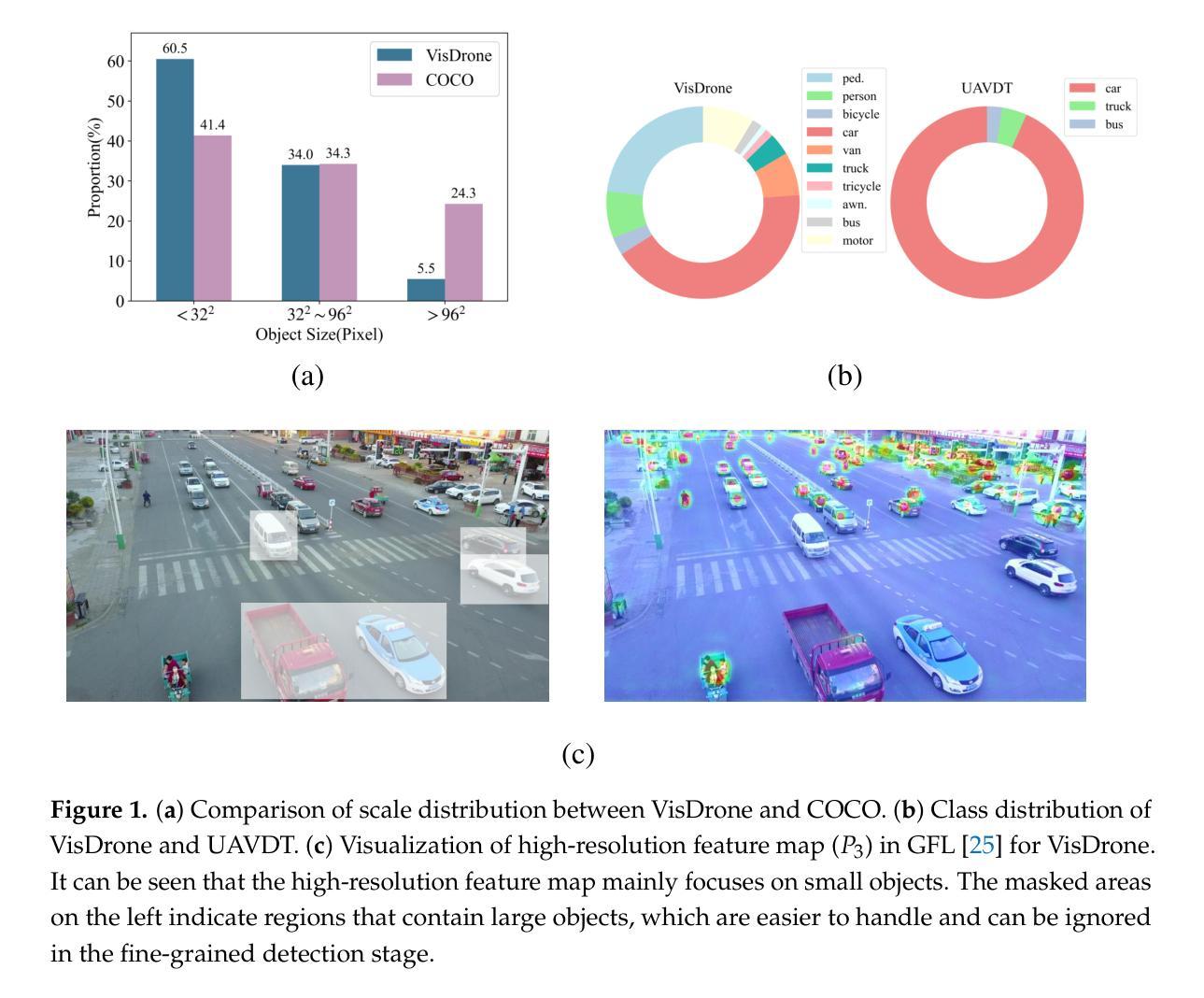
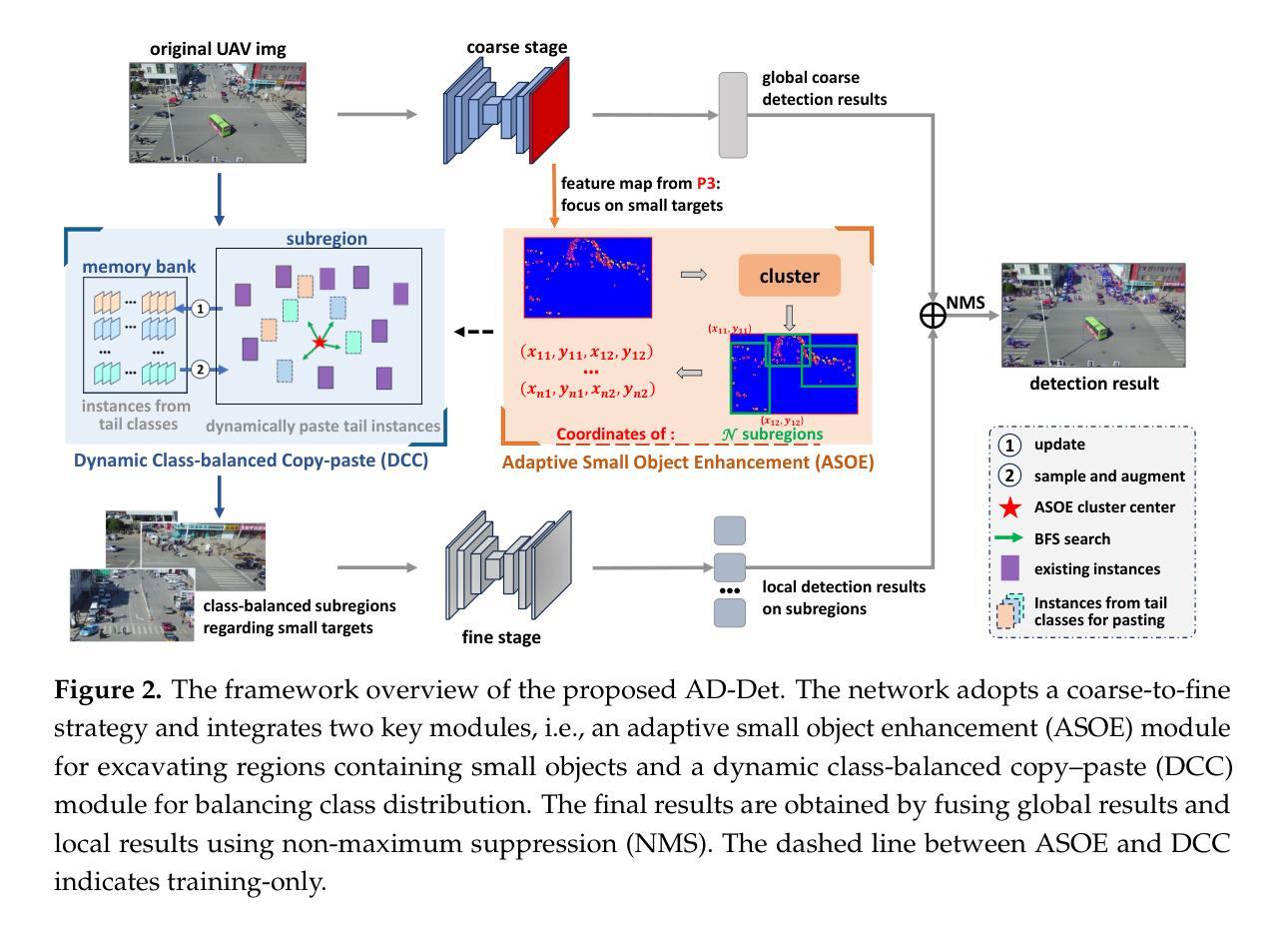
AD-Det: Boosting Object Detection in UAV Images with Focused Small Objects and Balanced Tail Classes
Authors:Zhenteng Li, Sheng Lian, Dengfeng Pan, Youlin Wang, Wei Liu
Object detection in Unmanned Aerial Vehicle (UAV) images poses significant challenges due to complex scale variations and class imbalance among objects. Existing methods often address these challenges separately, overlooking the intricate nature of UAV images and the potential synergy between them. In response, this paper proposes AD-Det, a novel framework employing a coherent coarse-to-fine strategy that seamlessly integrates two pivotal components: Adaptive Small Object Enhancement (ASOE) and Dynamic Class-balanced Copy-paste (DCC). ASOE utilizes a high-resolution feature map to identify and cluster regions containing small objects. These regions are subsequently enlarged and processed by a fine-grained detector. On the other hand, DCC conducts object-level resampling by dynamically pasting tail classes around the cluster centers obtained by ASOE, main-taining a dynamic memory bank for each tail class. This approach enables AD-Det to not only extract regions with small objects for precise detection but also dynamically perform reasonable resampling for tail-class objects. Consequently, AD-Det enhances the overall detection performance by addressing the challenges of scale variations and class imbalance in UAV images through a synergistic and adaptive framework. We extensively evaluate our approach on two public datasets, i.e., VisDrone and UAVDT, and demonstrate that AD-Det significantly outperforms existing competitive alternatives. Notably, AD-Det achieves a 37.5% Average Precision (AP) on the VisDrone dataset, surpassing its counterparts by at least 3.1%.
无人机图像中的目标检测面临着尺度变化复杂和各类目标类别不平衡的重大挑战。现有方法往往分别应对这些挑战,忽略了无人机图像的复杂性和它们之间的潜在协同作用。针对这些问题,本文提出了AD-Det,一个采用连贯的由粗到细策略的新型框架,无缝集成了两个关键组件:自适应小目标增强(ASOE)和动态类别平衡复制粘贴(DCC)。ASOE利用高分辨率特征图来识别和聚类包含小目标的区域。随后,这些区域会被放大并由精细检测器进行处理。另一方面,DCC通过动态粘贴尾类,围绕ASOE获得的聚类中心进行对象级重采样,并为每个尾类维护一个动态内存库。这种方法使AD-Det不仅能够精确检测小目标区域,还能为尾类目标进行动态合理的重采样。因此,AD-Det通过一个协同自适应的框架,解决了无人机图像中尺度变化和类别不平衡的挑战,从而提高了整体检测性能。我们在两个公共数据集VisDrone和UAVDT上广泛评估了我们的方法,证明AD-Det显著优于现有的竞争方法。值得注意的是,AD-Det在VisDrone数据集上的平均精度(AP)达到37.5%,超过同类产品至少3.1%。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF Published in Remote Sensing
Summary:
该文本介绍了在无人机图像中进行目标检测所面临的挑战,并提出了一个新的框架AD-Det来解决这些问题。AD-Det通过自适应精细到粗糙的策略无缝集成了两个关键组件:自适应小目标增强(ASOE)和动态类平衡复制粘贴(DCC)。ASOE利用高分辨率特征图识别并聚类包含小目标的区域,对其进行精细检测。而DCC则通过动态复制尾类对象并粘贴到由ASOE获得的聚类中心周围,实现尾类的动态记忆管理。因此,AD-Det不仅可以精确地检测小目标区域,还可以动态地解决尾类对象的问题,从而提高了无人机图像的整体检测性能。在VisDrone和UAVDT两个公开数据集上的评估表明,AD-Det显著优于现有竞争对手。
Key Takeaways:
- 在无人机图像的目标检测中面临尺度变化和类别不平衡两大挑战。
- AD-Det框架通过自适应精细到粗糙的策略来解决这些问题。
- ASOE组件利用高分辨率特征图识别并聚类小目标区域进行精细检测。
- DCC组件通过动态复制粘贴尾类对象来解决类别不平衡问题。
- AD-Det结合两个组件实现了对无人机图像中的小目标和尾类对象的精确检测。
- 在VisDrone和UAVDT数据集上的评估显示,AD-Det显著优于现有方法,特别是在VisDrone数据集上实现了较高的平均精度(AP)。
点此查看论文截图

Statistical Management of the False Discovery Rate in Medical Instance Segmentation Based on Conformal Risk Control
Authors:Mengxia Dai, Wenqian Luo, Tianyang Li
Instance segmentation plays a pivotal role in medical image analysis by enabling precise localization and delineation of lesions, tumors, and anatomical structures. Although deep learning models such as Mask R-CNN and BlendMask have achieved remarkable progress, their application in high-risk medical scenarios remains constrained by confidence calibration issues, which may lead to misdiagnosis. To address this challenge, we propose a robust quality control framework based on conformal prediction theory. This framework innovatively constructs a risk-aware dynamic threshold mechanism that adaptively adjusts segmentation decision boundaries according to clinical requirements.Specifically, we design a \textbf{calibration-aware loss function} that dynamically tunes the segmentation threshold based on a user-defined risk level $\alpha$. Utilizing exchangeable calibration data, this method ensures that the expected FNR or FDR on test data remains below $\alpha$ with high probability. The framework maintains compatibility with mainstream segmentation models (e.g., Mask R-CNN, BlendMask+ResNet-50-FPN) and datasets (PASCAL VOC format) without requiring architectural modifications. Empirical results demonstrate that we rigorously bound the FDR metric marginally over the test set via our developed calibration framework.
实例分割在医学图像分析中扮演着至关重要的角色,因为它能够实现对病变、肿瘤和解剖结构的精确定位和划分。尽管Mask R-CNN和BlendMask等深度学习模型已经取得了显著进展,但它们在高风险医疗场景中的应用仍然受到置信度校准问题的制约,可能导致误诊。为了应对这一挑战,我们提出了一种基于顺应性预测理论的稳健的质量控制框架。该框架创新地构建了一种风险感知动态阈值机制,该机制能够根据临床需求自适应地调整分割决策边界。具体来说,我们设计了一种校准感知损失函数,它根据用户定义的风险水平α动态调整分割阈值。利用可交换的校准数据,该方法确保测试数据的预期FNR或FDR在大概率下保持在α以下。该框架与主流分割模型(例如Mask R-CNN、BlendMask+ResNet-50-FPN)和数据集(PASCAL VOC格式)兼容,无需进行架构修改。实证结果表明,通过我们开发的校准框架,我们严格地将FDR指标控制在测试集之上。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF Accepted by 2025 IEEE 3rd International Conference on Image Processing and Computer Applications (ICIPCA 2025)
Summary
本文介绍了实例分割在医学图像分析中的重要性,它能够精确地定位和区分病变、肿瘤和解剖结构。尽管深度学习模型如Mask R-CNN和BlendMask取得了显著进展,但在高风险医疗场景中,由于置信度校准问题,可能导致误诊。为解决此挑战,本文提出基于置信度预测的稳健质量控制框架。该框架创新地构建了一个风险感知动态阈值机制,根据临床需求自适应调整分割决策边界。设计了一种校准感知损失函数,根据用户定义的风险水平α动态调整分割阈值。利用可交换的校准数据,确保测试数据的预期假负率(FNR)或假阳性率(FDR)保持在高概率低于α的水平。该框架与主流分割模型和数据集兼容,无需进行架构修改。实验结果表明,通过开发的校准框架,FDR指标在测试集上略有控制。
Key Takeaways
- 实例分割在医学图像分析中起到关键作用,能精确识别和区分病变、肿瘤和解剖结构。
- 深度学习模型(如Mask R-CNN和BlendMask)虽有所进展,但在高风险医疗场景中仍面临置信度校准问题。
- 置信度校准问题可能导致误诊,因此需要解决。
- 提出了一种基于置信度预测的质量控制框架,该框架具有风险感知能力并能动态调整分割决策边界。
- 引入了校准感知损失函数,能够根据用户定义的风险水平动态调整分割阈值。
- 利用可交换的校准数据确保测试数据的预期假负率(FNR)或假阳性率(FDR)低于设定的风险水平α。
点此查看论文截图

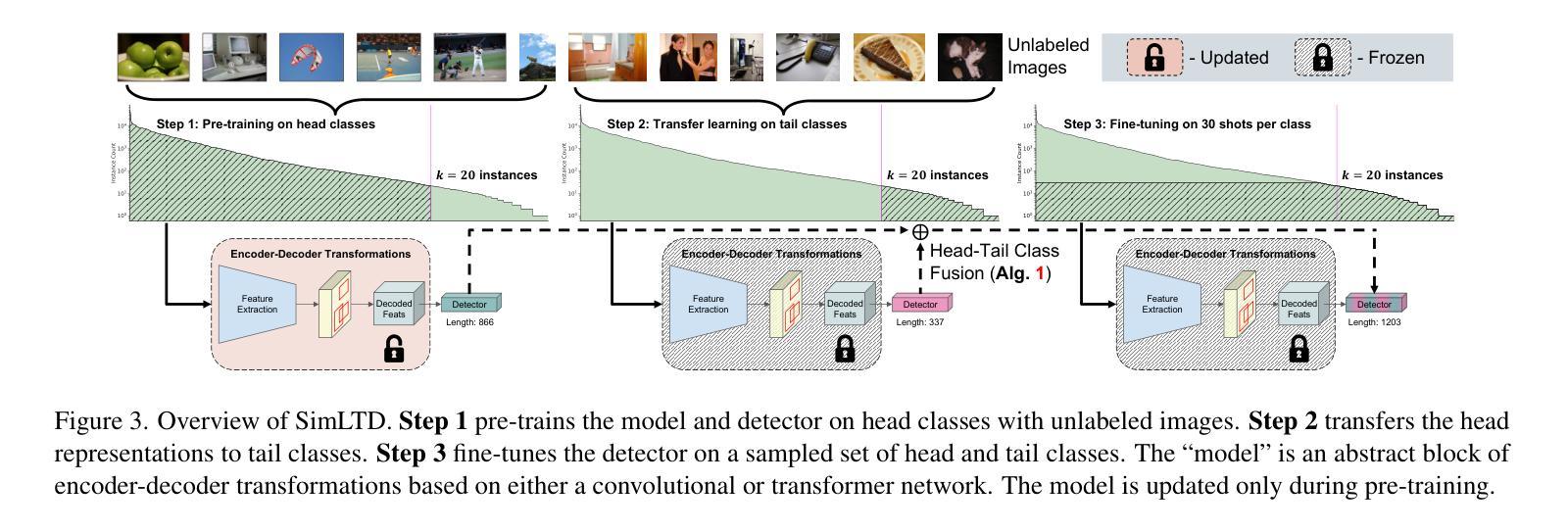
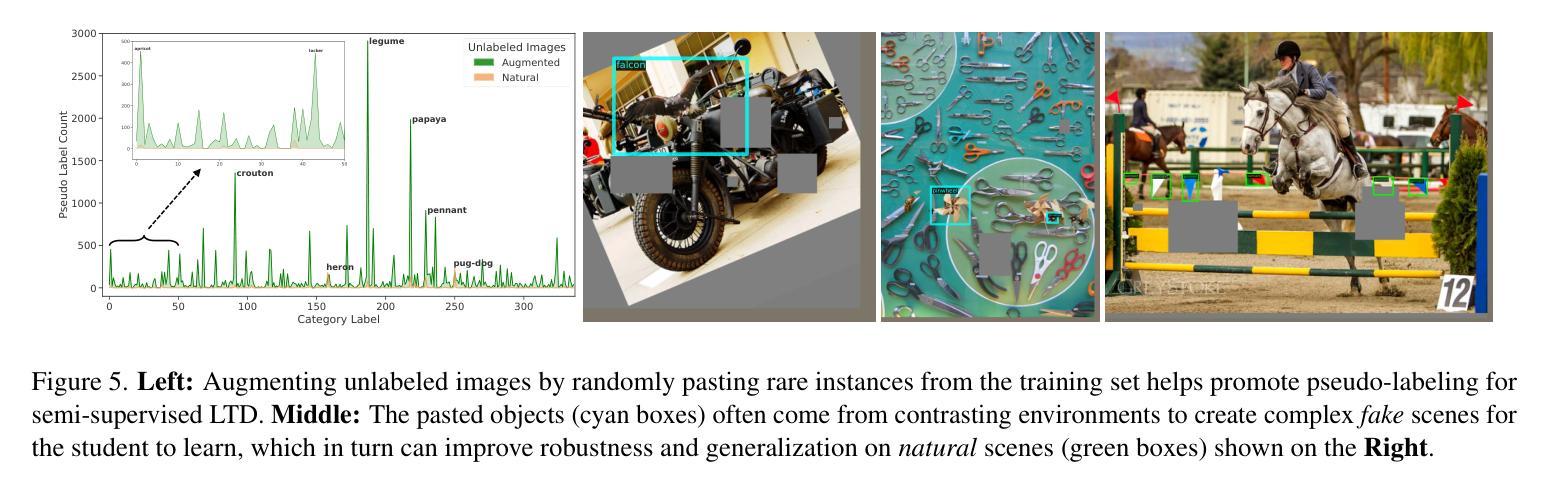
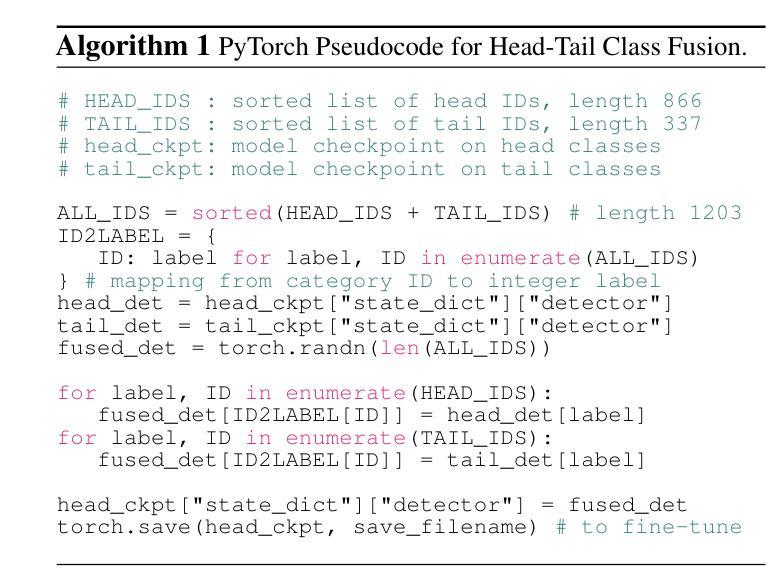
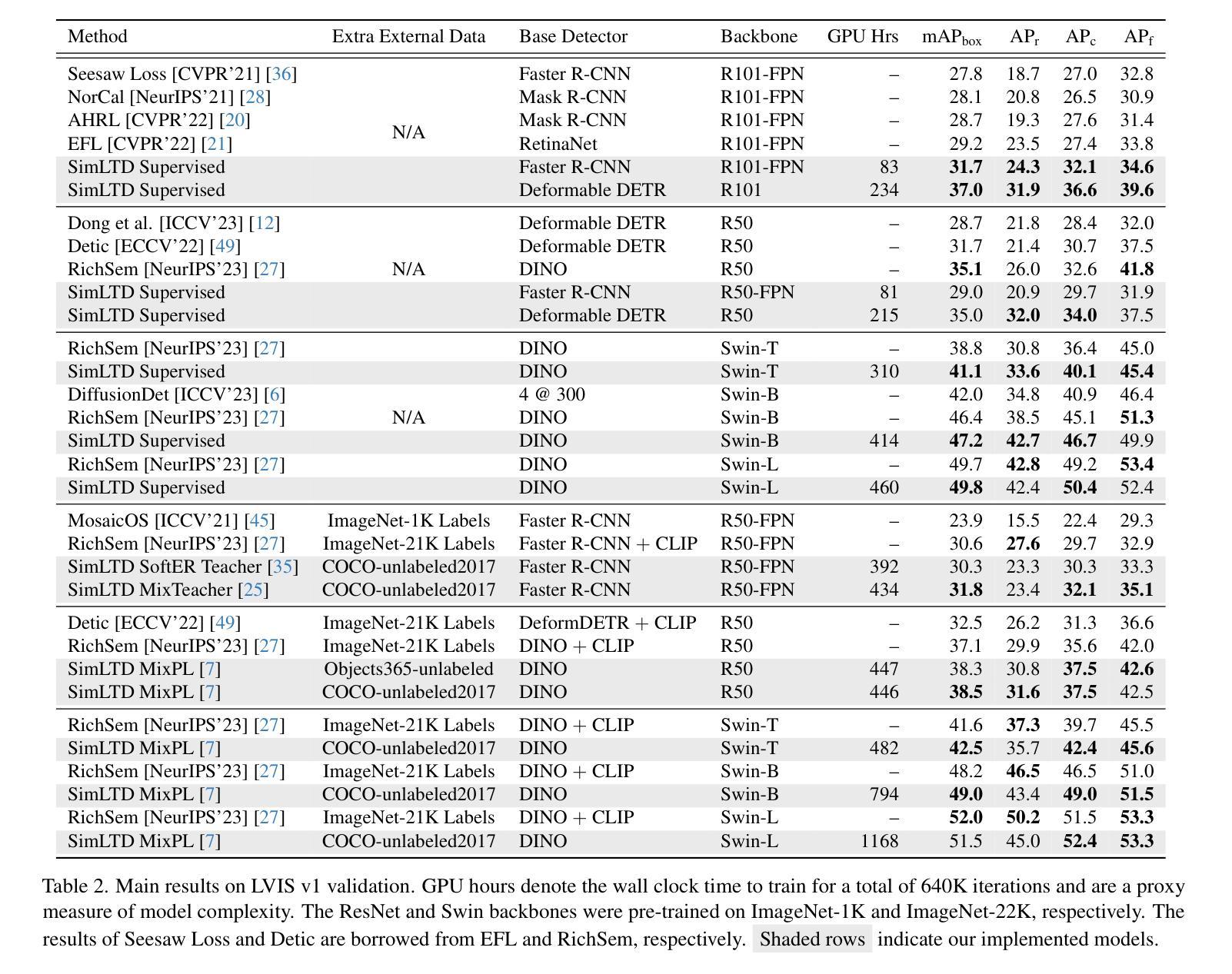
SimLTD: Simple Supervised and Semi-Supervised Long-Tailed Object Detection
Authors:Phi Vu Tran
While modern visual recognition systems have made significant advancements, many continue to struggle with the open problem of learning from few exemplars. This paper focuses on the task of object detection in the setting where object classes follow a natural long-tailed distribution. Existing methods for long-tailed detection resort to external ImageNet labels to augment the low-shot training instances. However, such dependency on a large labeled database has limited utility in practical scenarios. We propose a versatile and scalable approach to leverage optional unlabeled images, which are easy to collect without the burden of human annotations. Our SimLTD framework is straightforward and intuitive, and consists of three simple steps: (1) pre-training on abundant head classes; (2) transfer learning on scarce tail classes; and (3) fine-tuning on a sampled set of both head and tail classes. Our approach can be viewed as an improved head-to-tail model transfer paradigm without the added complexities of meta-learning or knowledge distillation, as was required in past research. By harnessing supplementary unlabeled images, without extra image labels, SimLTD establishes new record results on the challenging LVIS v1 benchmark across both supervised and semi-supervised settings.
虽然现代视觉识别系统已经取得了重大进展,但许多系统仍面临着从少量样本中学习的开放性问题。本文关注在物体类别遵循自然长尾分布的情境下目标检测任务。现有的长尾检测方法是依赖外部ImageNet标签来增加低样本训练实例。然而,在实际场景中,对大量有标签数据库的依赖限制了其效用。我们提出了一种通用且可扩展的方法,利用可选的无标签图像,这些图像无需人工标注即可轻松收集。我们的SimLTD框架简单直观,包括三个步骤:(1)在丰富的头部类别上进行预训练;(2)在稀缺的尾部类别上进行迁移学习;(3)在头部和尾部类别的采样集上进行微调。我们的方法可以被视为一种改进的头到尾模型迁移范式,无需引入元学习或知识蒸馏等过去研究所需的复杂性。通过利用额外的无标签图像,无需额外的图像标签,SimLTD在具有挑战性的LVIS v1基准测试中建立了有监督和半监督环境下的新纪录结果。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF CVPR 2025. The reference code is available at https://github.com/lexisnexis-risk-open-source/simltd
Summary
本文解决现代视觉识别系统从少量样本中学习的问题,特别是在目标类遵循自然长尾分布的情境下。不同于依赖ImageNet标签扩充低样本训练实例的方法,本文提出一种灵活且可扩展的策略,利用可选的无标签图像,无需大量人工标注即可收集。SimLTD框架简单直观,分为三个步骤:在丰富的头部类别上进行预训练,在稀缺的尾部类别上进行迁移学习,并在头部和尾部类别的采样集上进行微调。该方法可视为改进的头到尾模型迁移范式,无需引入元学习或知识蒸馏等额外复杂性。通过利用额外的无标签图像,无需额外的图像标签,SimLTD在具有挑战性的LVIS v1基准测试中实现了监督学习和半监督环境下的新纪录结果。
Key Takeaways
- 现代视觉识别系统仍面临从少量样本中学习的问题,特别是在目标类别长尾分布情境下。
- 现有方法常依赖ImageNet标签来扩充低样本训练实例,但在实际场景中效用有限。
- 本文提出SimLTD框架,利用无标签图像,无需大量人工标注,为解决此问题提供新的策略。
- SimLTD框架包括三个简单步骤:预训练、迁移学习和微调。
- SimLTD框架是一种改进的头到尾模型迁移范式,无需引入元学习或知识蒸馏等额外复杂性。
- 通过利用无标签图像,SimLTD在LVIS v1基准测试中实现了新纪录结果。
点此查看论文截图

Multi-Scale Grouped Prototypes for Interpretable Semantic Segmentation
Authors:Hugo Porta, Emanuele Dalsasso, Diego Marcos, Devis Tuia
Prototypical part learning is emerging as a promising approach for making semantic segmentation interpretable. The model selects real patches seen during training as prototypes and constructs the dense prediction map based on the similarity between parts of the test image and the prototypes. This improves interpretability since the user can inspect the link between the predicted output and the patterns learned by the model in terms of prototypical information. In this paper, we propose a method for interpretable semantic segmentation that leverages multi-scale image representation for prototypical part learning. First, we introduce a prototype layer that explicitly learns diverse prototypical parts at several scales, leading to multi-scale representations in the prototype activation output. Then, we propose a sparse grouping mechanism that produces multi-scale sparse groups of these scale-specific prototypical parts. This provides a deeper understanding of the interactions between multi-scale object representations while enhancing the interpretability of the segmentation model. The experiments conducted on Pascal VOC, Cityscapes, and ADE20K demonstrate that the proposed method increases model sparsity, improves interpretability over existing prototype-based methods, and narrows the performance gap with the non-interpretable counterpart models. Code is available at github.com/eceo-epfl/ScaleProtoSeg.
原型部分学习正在成为一种有前景的方法,使语义分割具有可解释性。该模型选择训练过程中出现的真实补丁作为原型,并根据测试图像部分与原型之间的相似性构建密集预测图。这提高了可解释性,因为用户可以根据原型信息检查预测输出与模型学习模式之间的联系。在本文中,我们提出了一种利用多尺度图像表示进行原型部分学习的可解释语义分割方法。首先,我们引入了一个原型层,该层在多个尺度上显式地学习各种原型部分,导致原型激活输出中的多尺度表示。然后,我们提出了一种稀疏分组机制,这些尺度特定的原型部分产生多尺度稀疏组。这提供了对多尺度对象表示之间交互的深刻理解,同时提高了分割模型的可解释性。在Pascal VOC、Cityscapes和ADE20K上进行的实验表明,该方法提高了模型的稀疏性,在现有基于原型的方法中提高了可解释性,并缩小了与非可解释的对应模型之间的性能差距。代码可在github.com/eceo-epfl/ScaleProtoSeg找到。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF Accepted at WACV 2025
Summary
原型部分学习正在成为一种有前景的方法,用于使语义分割具有可解释性。该模型通过选择训练过程中出现的真实补丁作为原型,并根据测试图像的部分与原型之间的相似性构建密集预测图。通过引入多尺度图像表示法,该方法能更好地用于原型部分学习并实现可解释的语义分割。它通过引入原型层,在不同尺度上显式地学习多样化的原型部分,并在原型激活输出中产生多尺度表示。此外,提出的稀疏分组机制能产生这些尺度特定原型部分的多尺度稀疏组,增强了模型对多尺度对象表示的交互理解,提高了分割模型的解释性。实验表明,该方法提高了模型的稀疏性,在现有的基于原型的方法中增强了可解释性,并缩小了与非解释性模型的性能差距。
Key Takeaways
- 原型部分学习有助于提高语义分割的可解释性。
- 模型通过选择训练中的真实补丁作为原型,并基于测试图像与这些原型的相似性构建预测图。
- 引入多尺度图像表示法以增强原型部分学习的效果。
- 通过原型层和稀疏分组机制,模型能在不同尺度上学习并表示原型部分。
- 该方法能提高模型的稀疏性,增强模型的可解释性。
- 与现有基于原型的方法相比,该方法在可解释性方面有所提高。
点此查看论文截图