⚠️ 以下所有内容总结都来自于 大语言模型的能力,如有错误,仅供参考,谨慎使用
🔴 请注意:千万不要用于严肃的学术场景,只能用于论文阅读前的初筛!
💗 如果您觉得我们的项目对您有帮助 ChatPaperFree ,还请您给我们一些鼓励!⭐️ HuggingFace免费体验
2025-04-30 更新
Can AI Agents Design and Implement Drug Discovery Pipelines?
Authors:Khachik Smbatyan, Tsolak Ghukasyan, Tigran Aghajanyan, Hovhannes Dabaghyan, Sergey Adamyan, Aram Bughdaryan, Vahagn Altunyan, Gagik Navasardyan, Aram Davtyan, Anush Hakobyan, Aram Gharibyan, Arman Fahradyan, Artur Hakobyan, Hasmik Mnatsakanyan, Narek Ginoyan, Garik Petrosyan
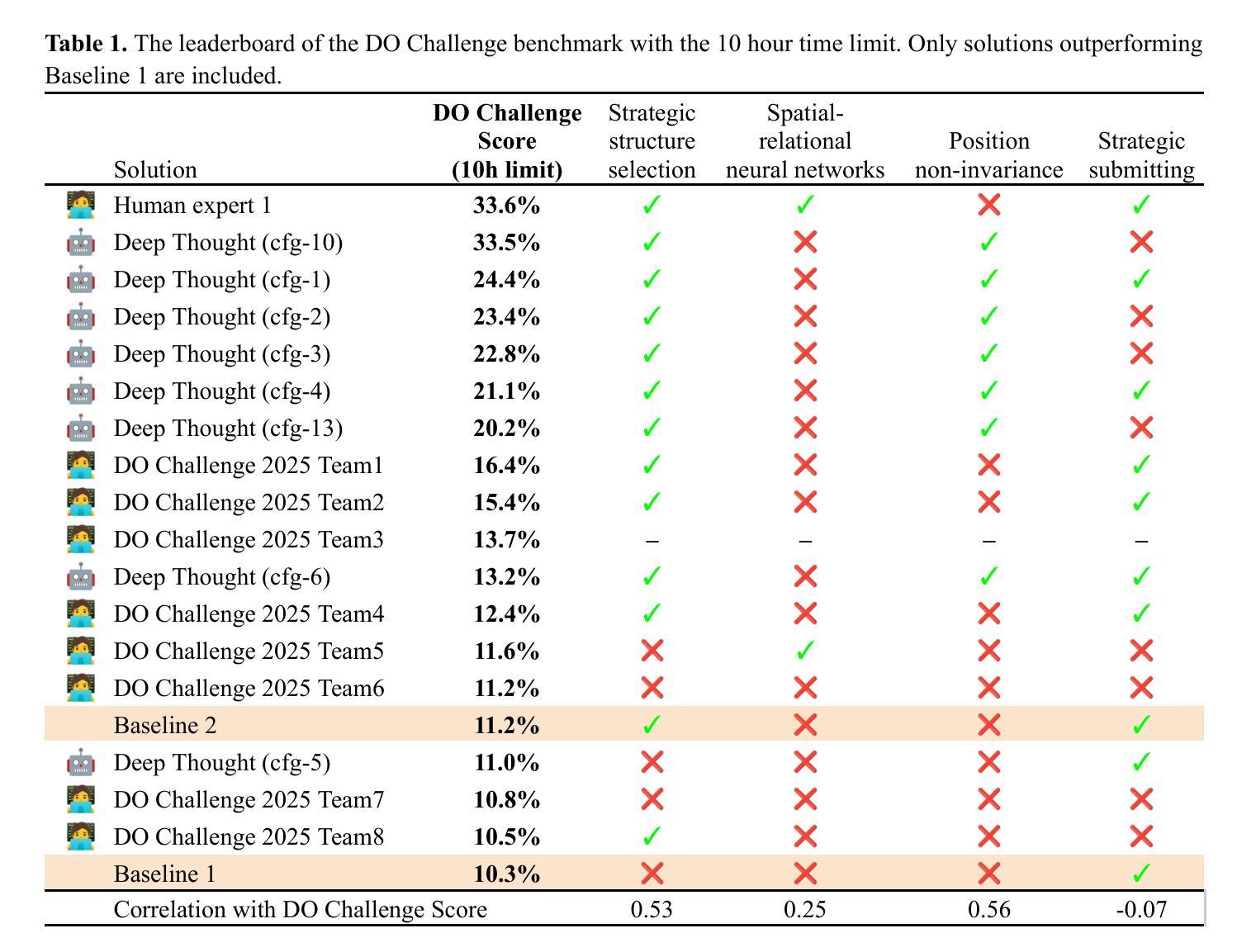
The rapid advancement of artificial intelligence, particularly autonomous agentic systems based on Large Language Models (LLMs), presents new opportunities to accelerate drug discovery by improving in-silico modeling and reducing dependence on costly experimental trials. Current AI agent-based systems demonstrate proficiency in solving programming challenges and conducting research, indicating an emerging potential to develop software capable of addressing complex problems such as pharmaceutical design and drug discovery. This paper introduces DO Challenge, a benchmark designed to evaluate the decision-making abilities of AI agents in a single, complex problem resembling virtual screening scenarios. The benchmark challenges systems to independently develop, implement, and execute efficient strategies for identifying promising molecular structures from extensive datasets, while navigating chemical space, selecting models, and managing limited resources in a multi-objective context. We also discuss insights from the DO Challenge 2025, a competition based on the proposed benchmark, which showcased diverse strategies explored by human participants. Furthermore, we present the Deep Thought multi-agent system, which demonstrated strong performance on the benchmark, outperforming most human teams. Among the language models tested, Claude 3.7 Sonnet, Gemini 2.5 Pro and o3 performed best in primary agent roles, and GPT-4o, Gemini 2.0 Flash were effective in auxiliary roles. While promising, the system’s performance still fell short of expert-designed solutions and showed high instability, highlighting both the potential and current limitations of AI-driven methodologies in transforming drug discovery and broader scientific research.
人工智能的快速发展,尤其是基于大型语言模型(LLM)的自主代理系统,为通过改进计算机模拟建模和减少对昂贵实验试点的依赖来加速药物发现提供了新的机遇。当前的基于人工智能代理的系统在解决编程挑战和研究方面表现出色,这表明有潜力开发能够解决诸如药物设计和药物发现等复杂问题的软件。本文介绍了DO Challenge,这是一个基准测试,旨在评估人工智能代理在类似于虚拟筛选场景的单个复杂问题中的决策能力。该基准测试挑战系统独立开发、实施并执行有效的策略,从大量数据集中识别出有前景的分子结构,同时导航化学空间、选择模型并在多目标背景下管理有限资源。我们还讨论了基于该基准测试的DO Challenge 2025竞赛的见解,展示了人类参与者探索的各种策略。此外,我们还介绍了在基准测试中表现强劲的深度思维多智能体系统,它在大多数人类团队中表现出色。在测试的语言模型中,Claude 3.7 Sonnet、Gemini 2.5 Pro和o3在主要代理角色中表现最佳,GPT-4o和Gemini 2.0 Flash在辅助角色中效果显著。虽然很有前途,但该系统的性能仍然落后于专家设计的解决方案,并表现出高度的不稳定,这突出了人工智能驱动方法在药物发现和更广泛的科学研究中的潜力和当前局限性。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
本文介绍了人工智能在药物发现领域的新机遇。特别是基于大型语言模型(LLM)的自主代理系统,通过改善硅基建模并减少对昂贵实验试点的依赖,来加速药物发现的进程。文章提出了一个名为DO Challenge的基准测试,用于评估AI代理在类似于虚拟筛选场景中的决策能力。此外,还讨论了基于该基准测试的DO Challenge 2025竞赛的见解,并展示了一个在多目标环境中表现出色的多代理系统——Deep Thought。虽然Deep Thought系统的性能仍低于专家设计的解决方案并显示出高不稳定性,但它突显了人工智能在药物发现和更广泛科学研究中的潜力和当前局限。
Key Takeaways
- 人工智能,特别是基于大型语言模型的自主代理系统,为药物发现带来了新的机遇。
- 通过改善硅基建模和减少对昂贵实验试点的依赖,AI加速了药物发现的进程。
- DO Challenge基准测试用于评估AI代理在虚拟筛选场景中的决策能力。
- Deep Thought多代理系统在多目标环境中表现出色,但仍存在性能不稳定的问题。
- AI代理系统在药物发现和更广泛科学研究领域具有潜力,但仍存在局限性。
- 在DO Challenge 2025竞赛中,人类参与者的策略多样性得到了展示。
点此查看论文截图

m-KAILIN: Knowledge-Driven Agentic Scientific Corpus Distillation Framework for Biomedical Large Language Models Training
Authors:Meng Xiao, Xunxin Cai, Chengrui Wang, Yuanchun Zhou
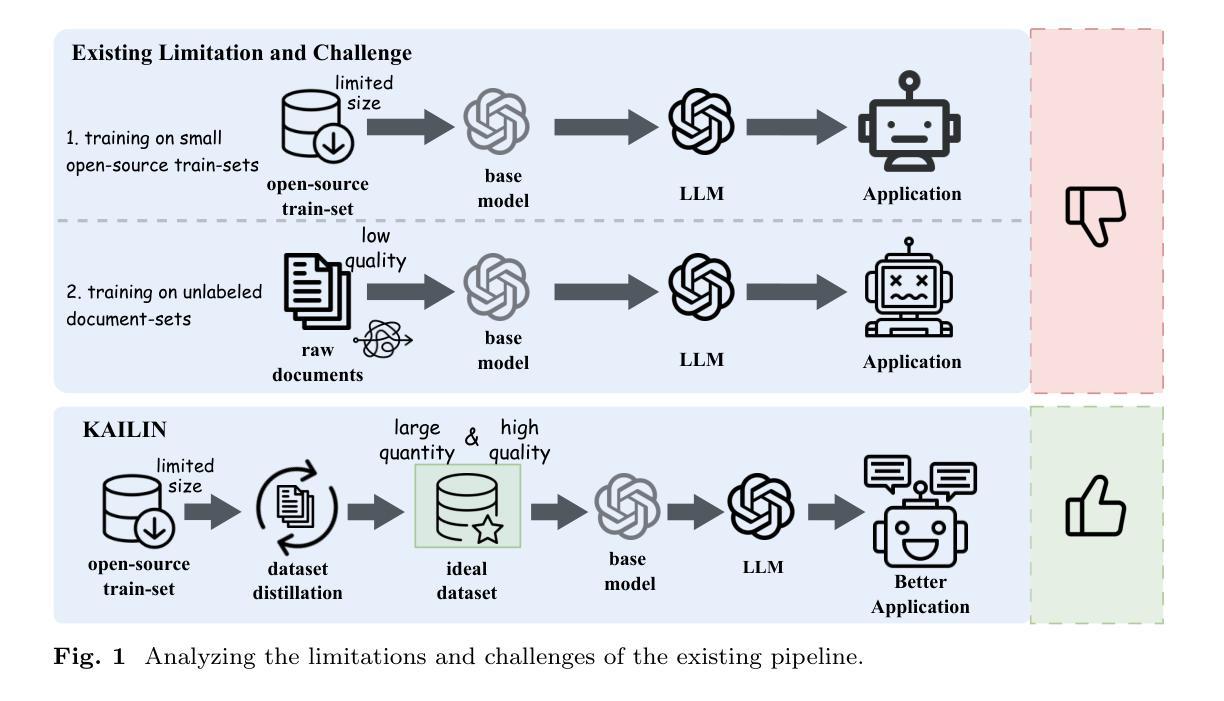
The rapid progress of large language models (LLMs) in biomedical research has underscored the limitations of existing open-source annotated scientific corpora, which are often insufficient in quantity and quality. Addressing the challenge posed by the complex hierarchy of biomedical knowledge, we propose a knowledge-driven, multi-agent framework for scientific corpus distillation tailored for LLM training in the biomedical domain. Central to our approach is a collaborative multi-agent architecture, where specialized agents, each guided by the Medical Subject Headings (MeSH) hierarchy, work in concert to autonomously extract, synthesize, and self-evaluate high-quality textual data from vast scientific literature. These agents collectively generate and refine domain-specific question-answer pairs, ensuring comprehensive coverage and consistency with biomedical ontologies while minimizing manual involvement. Extensive experimental results show that language models trained on our multi-agent distilled datasets achieve notable improvements in biomedical question-answering tasks, outperforming both strong life sciences LLM baselines and advanced proprietary models. Notably, our AI-Ready dataset enables Llama3-70B to surpass GPT-4 with MedPrompt and Med-PaLM-2, despite their larger scale. Detailed ablation studies and case analyses further validate the effectiveness and synergy of each agent within the framework, highlighting the potential of multi-agent collaboration in biomedical LLM training.
大型语言模型(LLM)在生物医学研究中的快速进步凸显了现有开源注释科学语料库的局限性,这些语料库在数量和质量上通常都不足。针对生物医学知识复杂层次结构所带来的挑战,我们提出了一种面向LLM训练的生物医学领域科学语料库提炼的知识驱动多智能体框架。我们的方法的核心是一个协作的多智能体架构,其中每个智能体由医学主题标题(MeSH)层次结构指导,协同工作,自主提取、合成和自我评估来自大量科学文献的高质量文本数据。这些智能体共同生成和精炼特定领域的问答对,确保全面覆盖并与生物医学本体论保持一致,同时最大限度地减少人工参与。广泛的实验结果表明,在我们多智能体提炼的数据集上训练的语言模型在生物医学问答任务中取得了显著的改进,超过了强大的生命科学LLM基准测试和先进的专有模型。值得注意的是,我们的AI就绪数据集使Llama3-70B能够超越GPT-4的MedPrompt和Med-PaLM-2,尽管它们的规模更大。详细的消融研究和案例分析进一步验证了框架中每个智能体的有效性及其协同作用,突出了多智能体协作在生物医学LLM训练中的潜力。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF 22 pages, Large Language Model, Agentic AI, Dataset Distillation, Multi-agent Collaboration
Summary:针对大型语言模型在生物医学研究中的快速进步,现有开源注释科学语料库的局限性日益凸显,其数量和质量均不足。为此,我们提出了一种面向生物医学领域大型语言模型训练的知识驱动多智能体框架,用于科学语料库提炼。该框架的核心是协作式多智能体架构,各智能体以医学主题标题(MeSH)层次结构为指导,协同工作,自主提取、合成和自我评价高质量文本数据。实验结果表明,使用该框架提炼的数据集训练的模型在生物医学问答任务中有显著提升,优于生命科学大型语言模型基准模型和高级专有模型。尤其是我们的AI就绪数据集使Llama3-70B超越了GPT-4。
Key Takeaways:
- 大型语言模型在生物医学研究中的应用凸显出现有开源注释科学语料库的不足。
- 提出了一种知识驱动的多智能体框架,用于生物医学领域的大型语言模型训练。
- 框架中的智能体以医学主题标题(MeSH)层次结构为指导,协同工作。
- 智能体能自主提取、合成和自我评价高质量文本数据,生成精炼的域特定问答对。
- 实验结果表明,使用该框架的数据集训练的模型在生物医学问答任务中表现优异。
- 与其他强大的模型和基准进行比较,验证了该框架的有效性。
点此查看论文截图

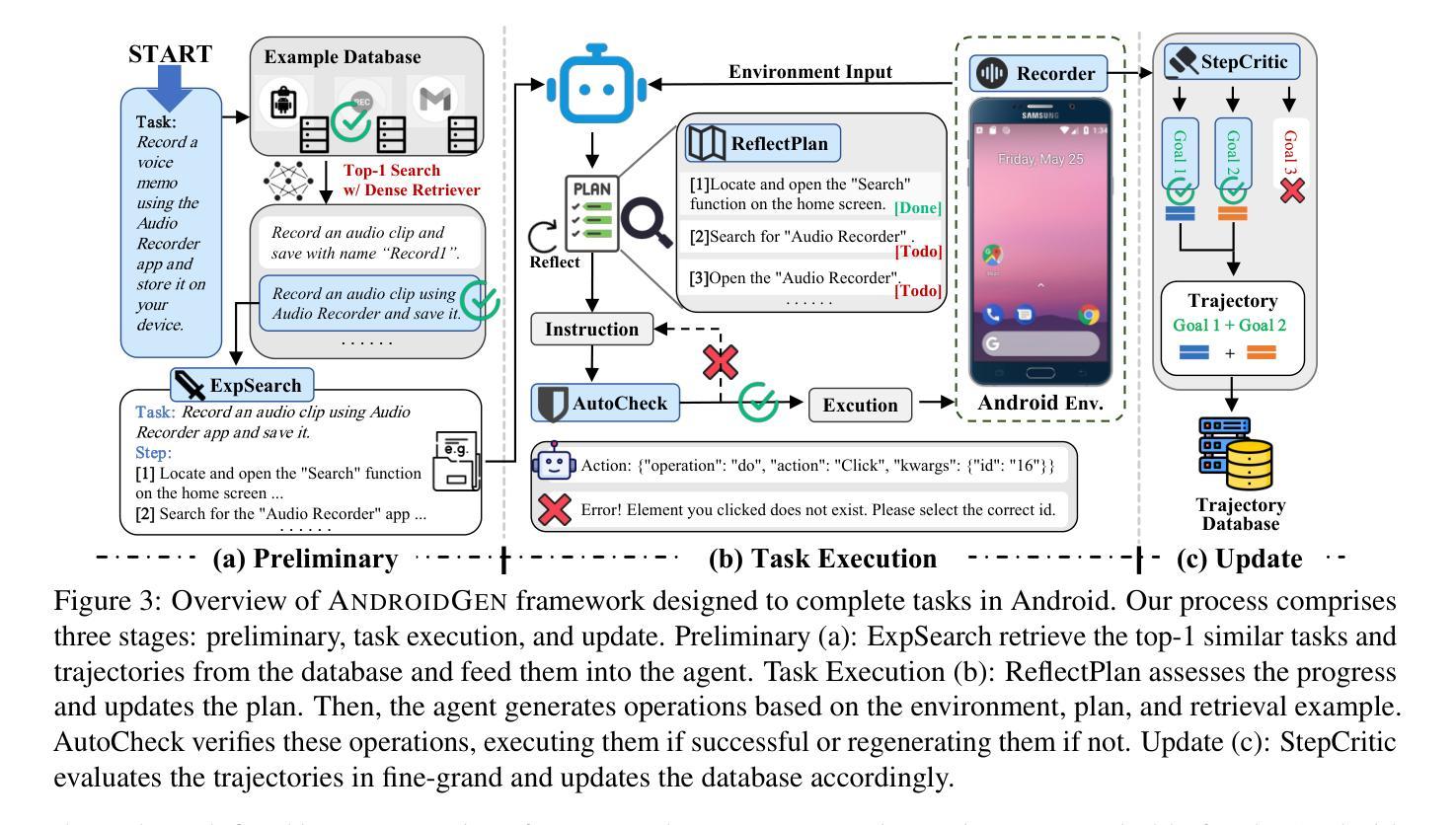
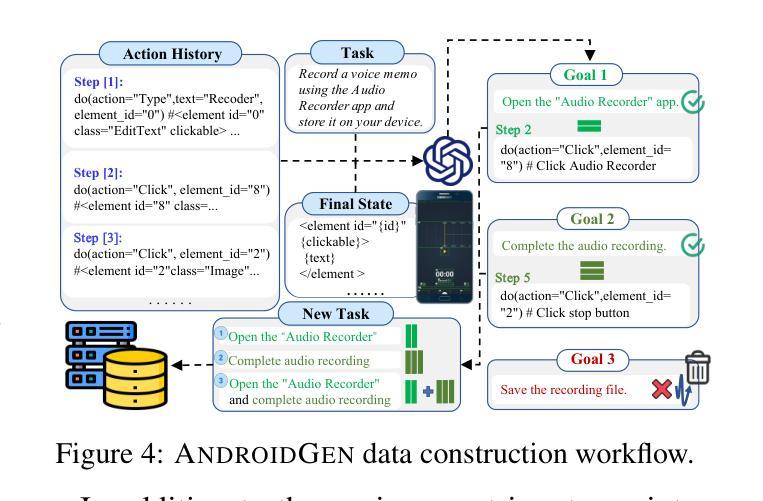
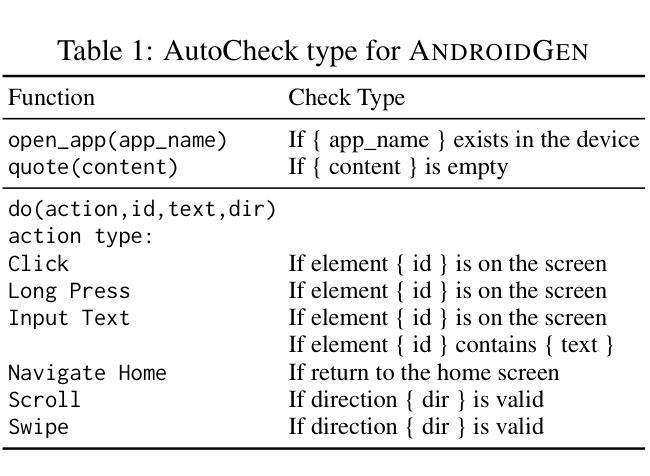
AndroidGen: Building an Android Language Agent under Data Scarcity
Authors:Hanyu Lai, Junjie Gao, Xiao Liu, Yifan Xu, Shudan Zhang, Yuxiao Dong, Jie Tang
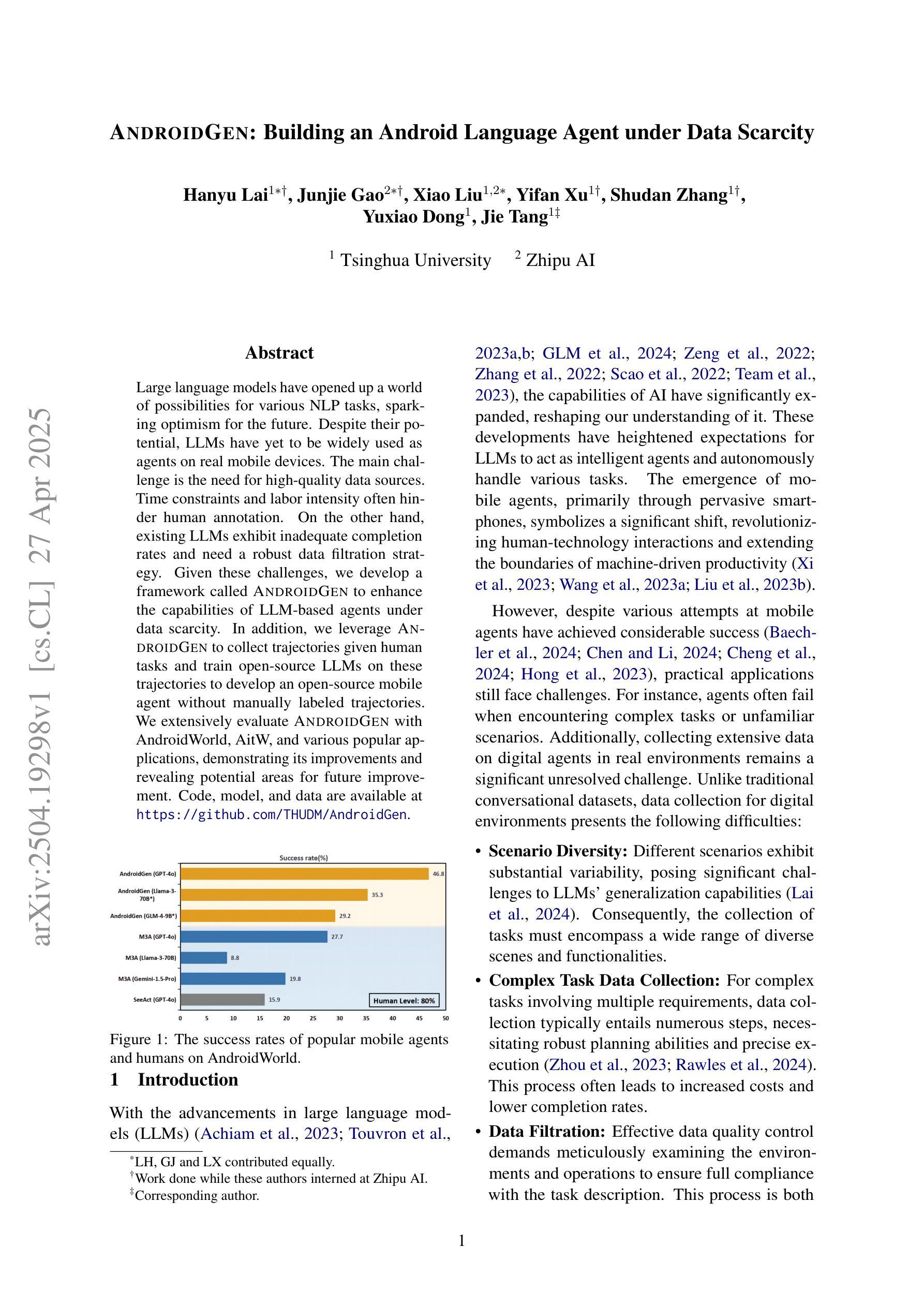
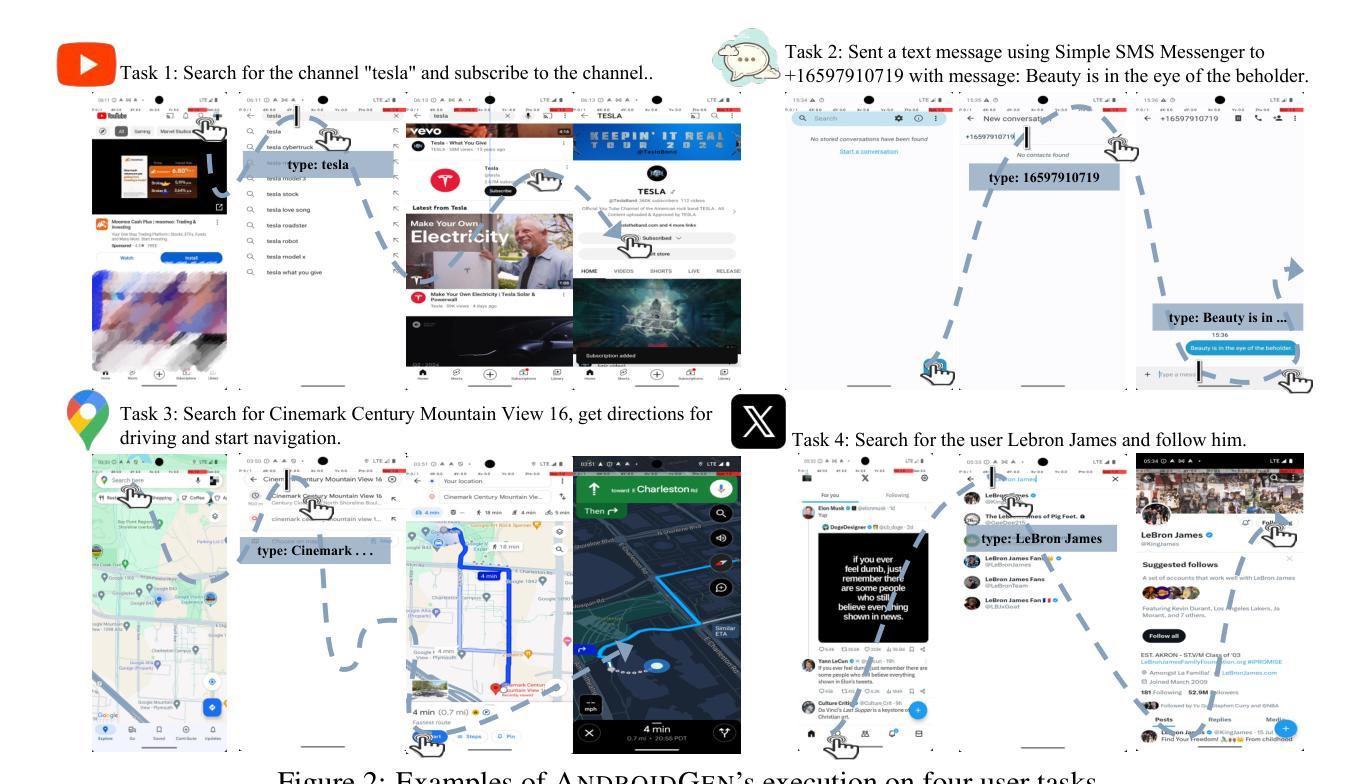
Large language models have opened up a world of possibilities for various NLP tasks, sparking optimism for the future. Despite their potential, LLMs have yet to be widely used as agents on real mobile devices. The main challenge is the need for high-quality data sources. Time constraints and labor intensity often hinder human annotation. On the other hand, existing LLMs exhibit inadequate completion rates and need a robust data filtration strategy. Given these challenges, we develop a framework called AndroidGen to enhance the capabilities of LLM-based agents under data scarcity. In addition, we leverage AndroidGen to collect trajectories given human tasks and train open-source LLMs on these trajectories to develop an open-source mobile agent without manually labeled trajectories. We extensively evaluate AndroidGen with AndroidWorld, AitW, and various popular applications, demonstrating its improvements and revealing potential areas for future improvement. Code, model, and data are available at https://github.com/THUDM/AndroidGen.
大型语言模型为各种NLP任务打开了可能性的大门,为未来带来了希望。尽管具有潜力,但大型语言模型尚未被广泛应用为真实移动设备上的代理。主要挑战在于需要高质量的数据源。时间限制和劳动强度经常阻碍人工标注。另一方面,现有的大型语言模型表现出较低的完成率,需要强大的数据过滤策略。针对这些挑战,我们开发了一个名为AndroidGen的框架,以提高在数据稀缺情况下基于大型语言模型的代理的能力。此外,我们利用AndroidGen收集人类任务的轨迹,并在这些轨迹上训练开源的大型语言模型,从而开发出无需手动标注轨迹的开源移动代理。我们在AndroidWorld、AitW和各种流行应用程序上全面评估了AndroidGen,展示了其改进之处并揭示了未来改进的领域。代码、模型和数据可在https://github.com/THUDM/AndroidGen找到。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
大型语言模型为各种自然语言处理任务开启了新的可能,但对未来充满期待的同时,也存在诸多挑战。特别是在真实移动设备上的使用,由于高质量数据源的需求以及时间约束和人工标注的劳动强度,大型语言模型的完成率尚不理想。针对这些挑战,我们开发了一个名为AndroidGen的框架,旨在提高基于大型语言模型的代理在数据稀缺环境下的能力。此外,我们还利用AndroidGen收集人类任务轨迹,并在这些轨迹上训练开源大型语言模型,开发出无需手动标注轨迹的开源移动代理。经过AndroidWorld、AitW和各种流行应用的广泛评估,证明了其改进效果并揭示了未来改进方向。相关代码、模型和数据可通过https://github.com/THUDM/AndroidGen获取。
Key Takeaways
- 大型语言模型为NLP任务带来新机遇,但对在真实移动设备上的应用存在挑战。
- 高质量数据源的需求以及时间约束和人工标注的劳动强度是主要挑战。
- 现有大型语言模型的完成率有待提高,需要更完善的数据过滤策略。
- 开发了一个名为AndroidGen的框架,旨在提高大型语言模型在移动设备上的性能。
- 利用AndroidGen收集人类任务轨迹,训练出无需手动标注轨迹的开源移动代理。
- AndroidGen经过广泛评估,包括在AndroidWorld、AitW和各种流行应用上的测试。
点此查看论文截图
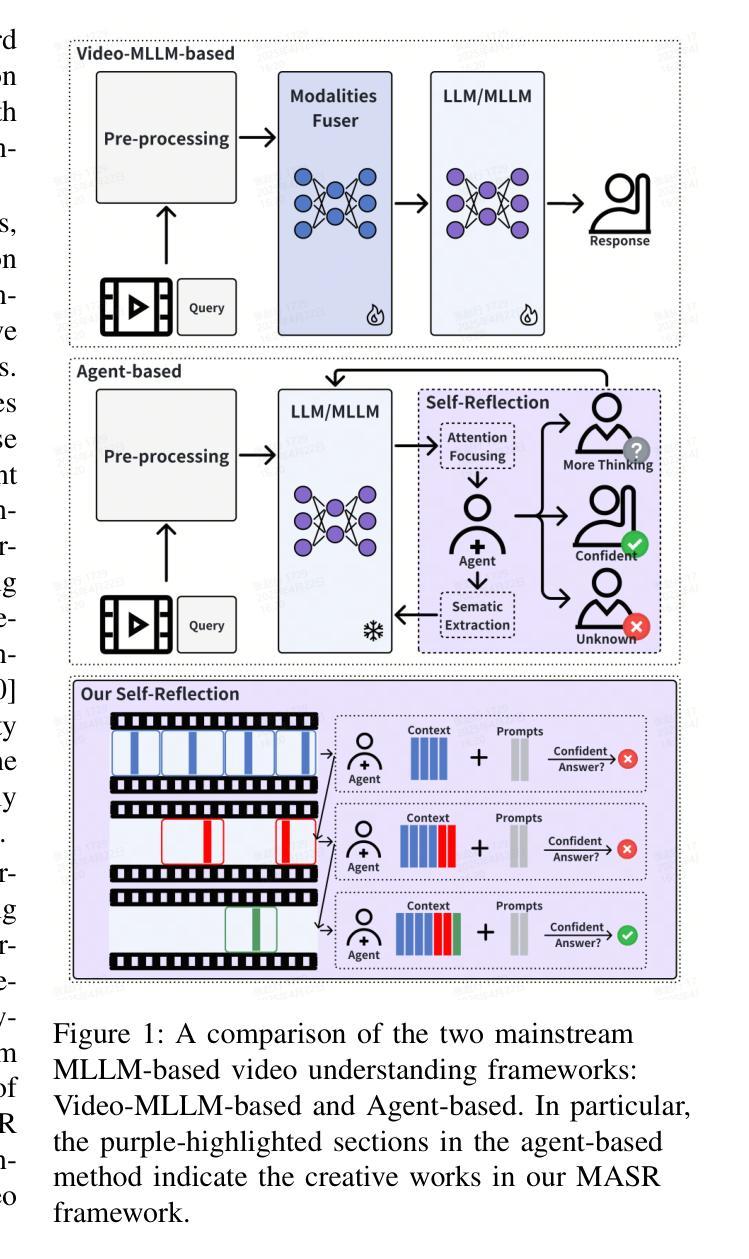
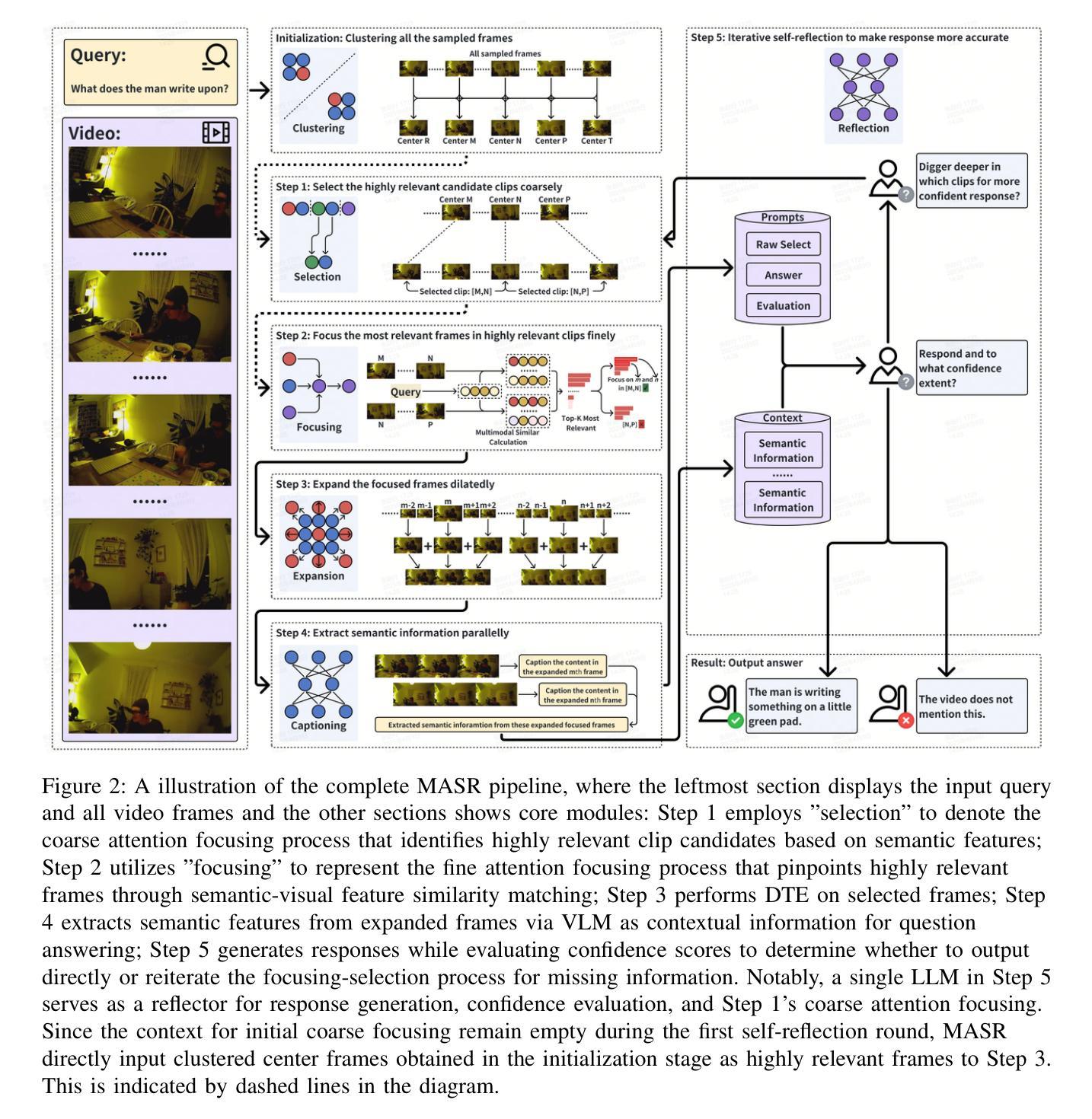
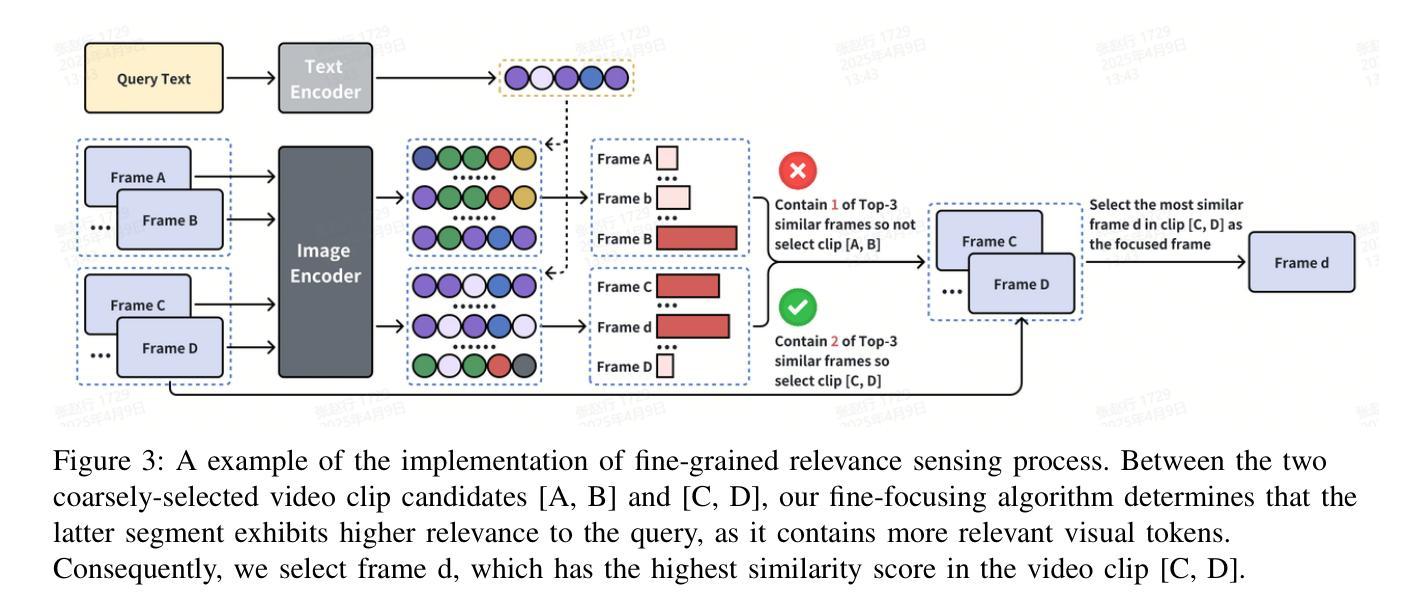
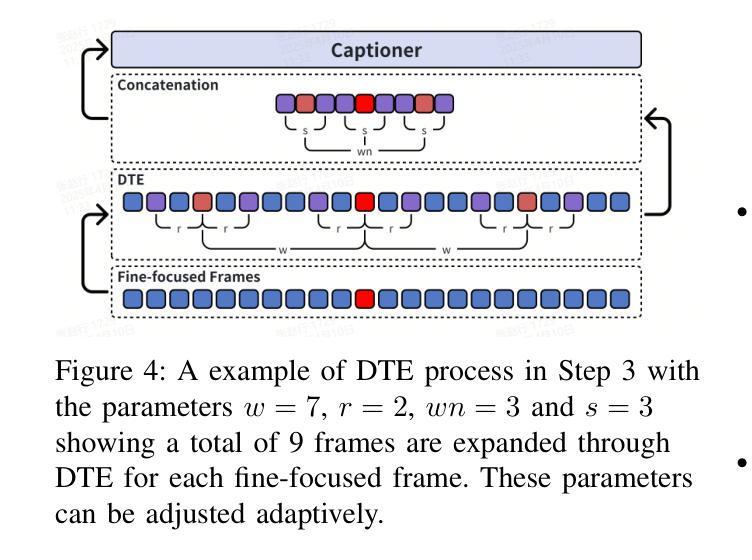
MASR: Self-Reflective Reasoning through Multimodal Hierarchical Attention Focusing for Agent-based Video Understanding
Authors:Shiwen Cao, Zhaoxing Zhang, Junming Jiao, Juyi Qiao, Guowen Song, Rong Shen, Xiangbing Meng
Even in the era of rapid advances in large models, video understanding remains a highly challenging task. Compared to texts or images, videos commonly contain more information with redundancy, requiring large models to properly allocate attention at a global level for comprehensive and accurate understanding. To address this, we propose a Multimodal hierarchical Attention focusing Self-reflective Reasoning (MASR) framework for agent-based video understanding. The key innovation lies in its ability to detect and prioritize segments of videos that are highly relevant to the query. Firstly, MASR realizes Multimodal Coarse-to-fine Relevance Sensing (MCRS) which enhances the correlation between the acquired contextual information and the query. Secondly, MASR employs Dilated Temporal Expansion (DTE) to mitigate the risk of missing crucial details when extracting semantic information from the focused frames selected through MCRS. By iteratively applying MCRS and DTE in the self-reflective reasoning process, MASR is able to adaptively adjust the attention to extract highly query-relevant context and therefore improve the response accuracy. In the EgoSchema dataset, MASR achieves a remarkable 5% performance gain over previous leading approaches. In the Next-QA and IntentQA datasets, it outperforms the state-of-the-art standards by 0.2% and 0.3% respectively. In the Video-MME dataset that contains long-term videos, MASR also performs better than other agent-based methods.
即使在大型模型飞速发展的时代,视频理解仍然是一项极具挑战性的任务。相比于文本或图像,视频通常包含更多冗余信息,需要大型模型在全局范围内适当地分配注意力,以实现全面而准确的视频理解。为了解决这一问题,我们提出了基于多模态层次化注意力的自我反思推理(MASR)框架,用于基于主体的视频理解。其主要创新之处在于能够检测和优先处理与查询高度相关的视频片段。首先,MASR实现了多模态粗到细的相关性感知(MCRS),增强了获取上下文信息与查询之间的相关性。其次,MASR采用膨胀时间扩展(DTE)策略,以缓解在通过MCRS选择的关键帧中提取语义信息时遗漏重要细节的风险。通过自我反思推理过程中迭代应用MCRS和DTE,MASR能够自适应地调整注意力以提取高度相关的上下文信息,从而提高响应准确性。在EgoSchema数据集上,MASR相较于之前领先的方法取得了5%的性能提升。在Next-QA和IntentQA数据集上,其性能超过了最新标准分别为0.2%和0.3%。对于包含长期视频的视频MME数据集,MASR在基于主体的方法中表现也更好。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
本文介绍了在视频理解领域的一个挑战,即视频信息冗余度高,需要全局注意力分配。为此,提出了一种基于多模态层次注意力的自反思推理(MASR)框架,用于基于代理的视频理解。MASR通过实现多模态粗到细的相关性感知(MCRS)和膨胀时间扩展(DTE)来优化视频段的选择和语义信息的提取,从而提高了查询响应的准确性。在多个数据集上的实验结果表明,MASR在视频理解方面取得了显著的性能提升。
Key Takeaways
- 视频理解面临信息冗余度高的问题,需要大模型进行全局注意力分配。
- 提出了一种基于多模态层次注意力的自反思推理(MASR)框架,用于解决该问题。
- MASR通过实现多模态粗到细的相关性感知(MCRS),增强获取上下文信息与查询之间的相关性。
- MASR采用膨胀时间扩展(DTE)方法,减少在提取关键语义信息时遗漏重要细节的风险。
- 自反思推理过程中迭代应用MCRS和DTE,使MASR能够自适应调整注意力以提取与查询高度相关的上下文。
- 在EgoSchema数据集上,MASR较之前的方法实现了5%的性能提升。
点此查看论文截图

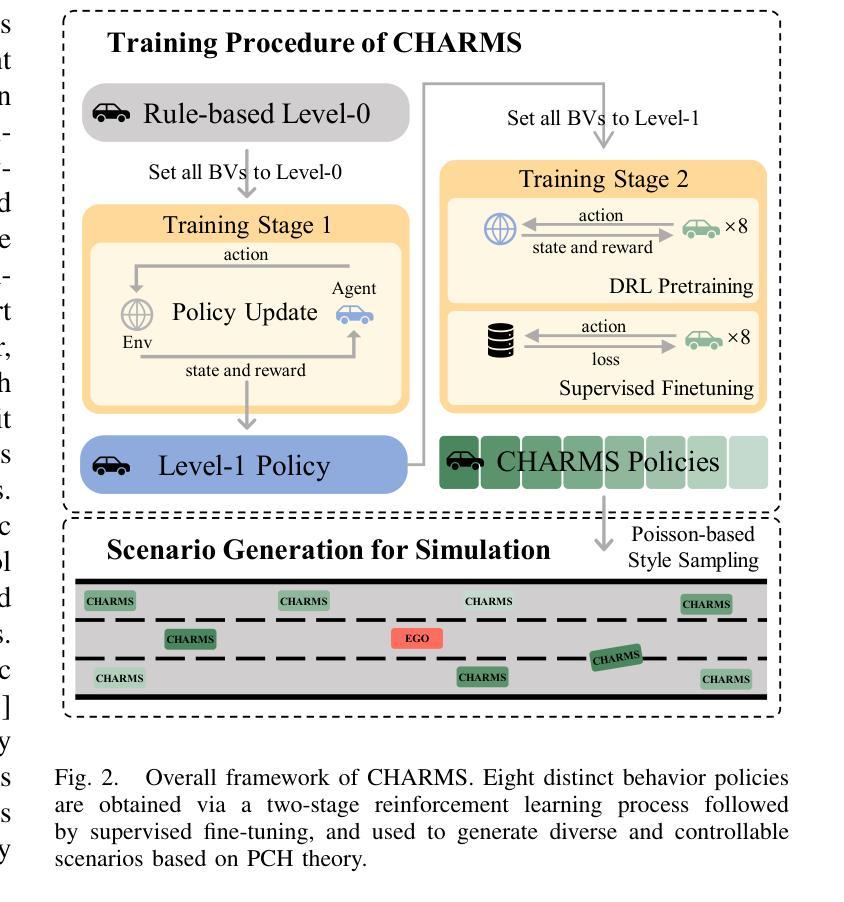
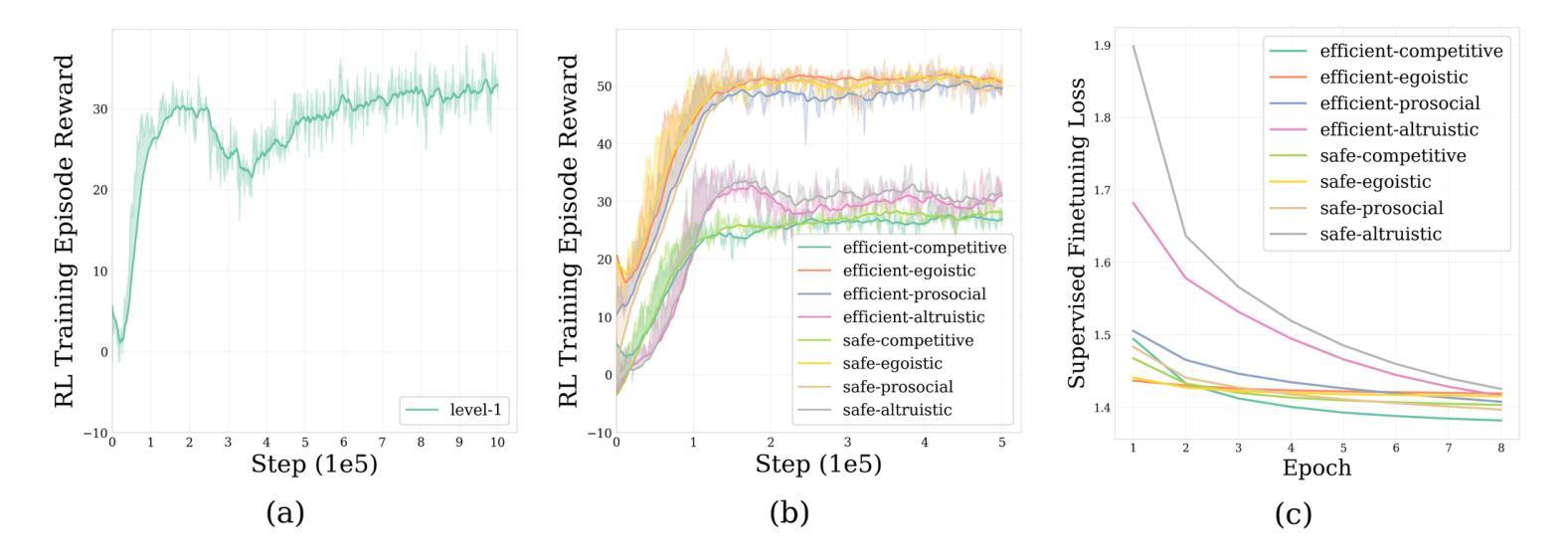
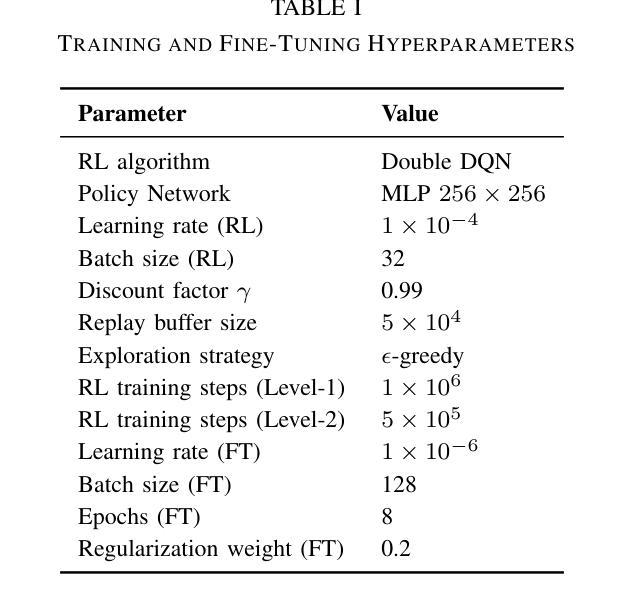
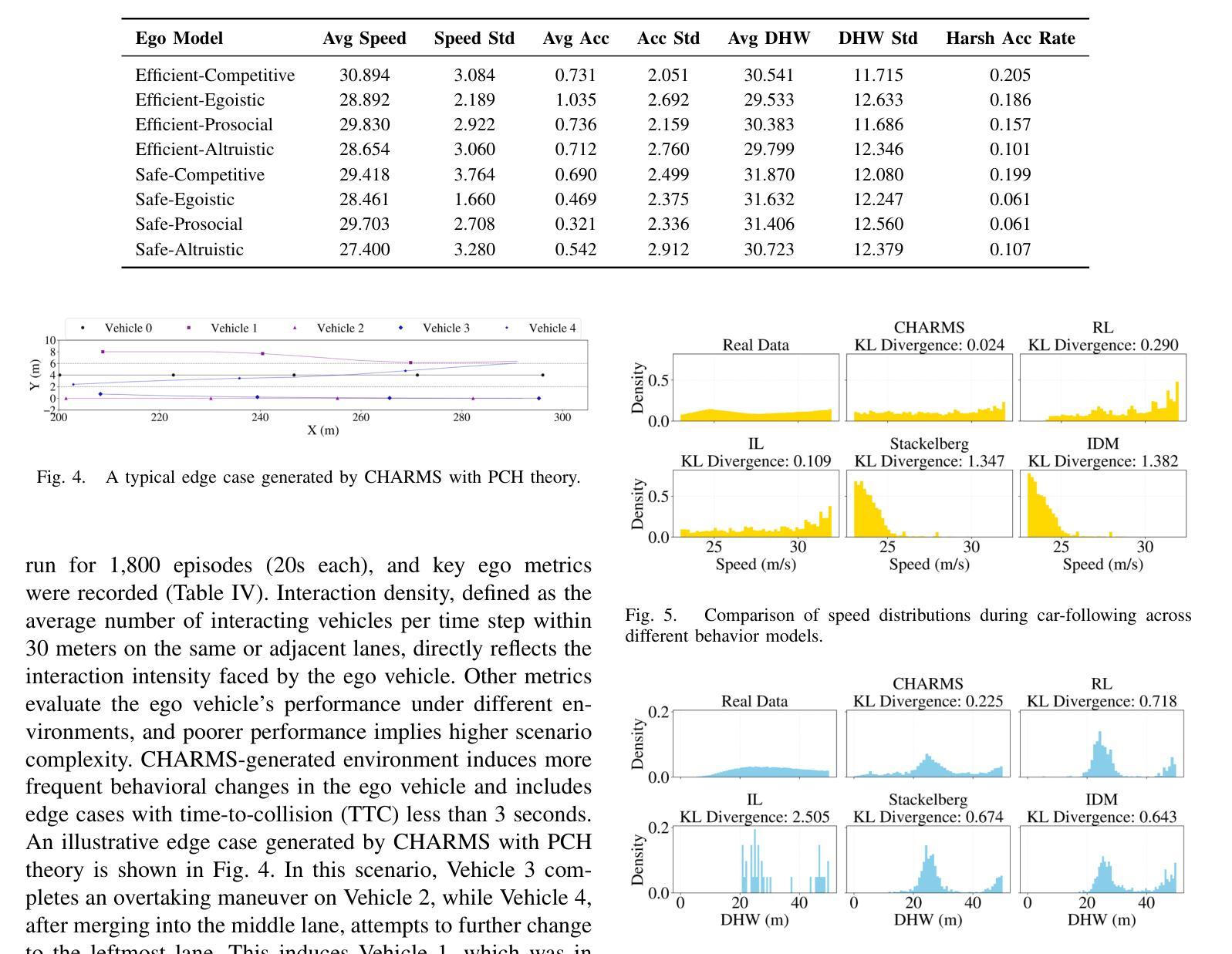
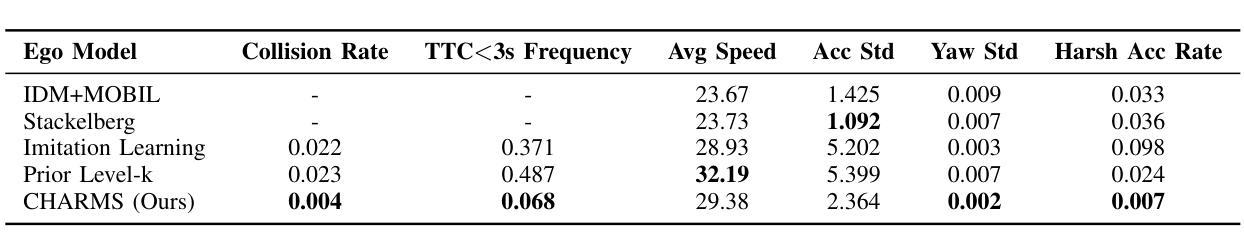
CHARMS: A Cognitive Hierarchical Agent for Reasoning and Motion Stylization in Autonomous Driving
Authors:Jingyi Wang, Duanfeng Chu, Zejian Deng, Liping Lu, Jinxiang Wang, Chen Sun
To address the challenge of insufficient interactivity and behavioral diversity in autonomous driving decision-making, this paper proposes a Cognitive Hierarchical Agent for Reasoning and Motion Stylization (CHARMS). By leveraging Level-k game theory, CHARMS captures human-like reasoning patterns through a two-stage training pipeline comprising reinforcement learning pretraining and supervised fine-tuning. This enables the resulting models to exhibit diverse and human-like behaviors, enhancing their decision-making capacity and interaction fidelity in complex traffic environments. Building upon this capability, we further develop a scenario generation framework that utilizes the Poisson cognitive hierarchy theory to control the distribution of vehicles with different driving styles through Poisson and binomial sampling. Experimental results demonstrate that CHARMS is capable of both making intelligent driving decisions as an ego vehicle and generating diverse, realistic driving scenarios as environment vehicles. The code for CHARMS is released at https://github.com/chuduanfeng/CHARMS.
本文提出了一个用于推理和运动风格化的认知层次代理(CHARMS),以解决自动驾驶决策中交互性和行为多样性不足的挑战。CHARMS通过利用Level-k博弈理论,通过强化学习预训练和监督精细调整的两阶段训练管道,捕捉人类类似的推理模式。这使得模型能够表现出多样化和人类类似的行为,提高其在复杂交通环境中的决策能力和交互真实性。在此基础上,我们进一步开发了一个情景生成框架,该框架利用Poisson认知层次理论,通过Poisson和二项抽样来控制不同驾驶风格的车辆分布。实验结果表明,CHARMS既能够作为自我车辆做出智能驾驶决策,又能够生成多样、现实的驾驶场景作为环境车辆。CHARMS的代码已发布在https://github.com/chuduanfeng/CHARMS。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
本文提出一种名为CHARMS的认知分层代理推理与运动风格化方法,用于解决自动驾驶决策制定中交互性和行为多样性不足的问题。利用Level-k博弈理论,CHARMS通过包括强化学习预训练和监督微调的两阶段训练流程,模拟人类推理模式。这使得模型能够展现出多样化和人类化的行为,提升其决策能力和在复杂交通环境中的交互真实性。此外,研究还开发了一个基于Poisson认知层次理论的场景生成框架,通过Poisson和二项采样控制不同驾驶风格的车辆分布。实验结果表明,CHARMS不仅能作为自主车辆做出智能驾驶决策,还能生成多样且现实的驾驶场景。
Key Takeaways
- CHARMS利用Level-k游戏理论模拟人类推理模式,提升自动驾驶模型的决策能力。
- 通过强化学习预训练和监督微调的两阶段训练流程,CHARMS模型展现出多样化和人类化的行为。
- CHARMS提高了模型在复杂交通环境中的交互真实性。
- 基于Poisson认知层次理论开发的场景生成框架能控制不同驾驶风格的车辆分布。
- CHARMS能够作为自主车辆做出智能决策。
- CHARMS生成的驾驶场景具有多样性和现实性。
点此查看论文截图

VideoGen-Eval: Agent-based System for Video Generation Evaluation
Authors:Yuhang Yang, Ke Fan, Shangkun Sun, Hongxiang Li, Ailing Zeng, FeiLin Han, Wei Zhai, Wei Liu, Yang Cao, Zheng-Jun Zha
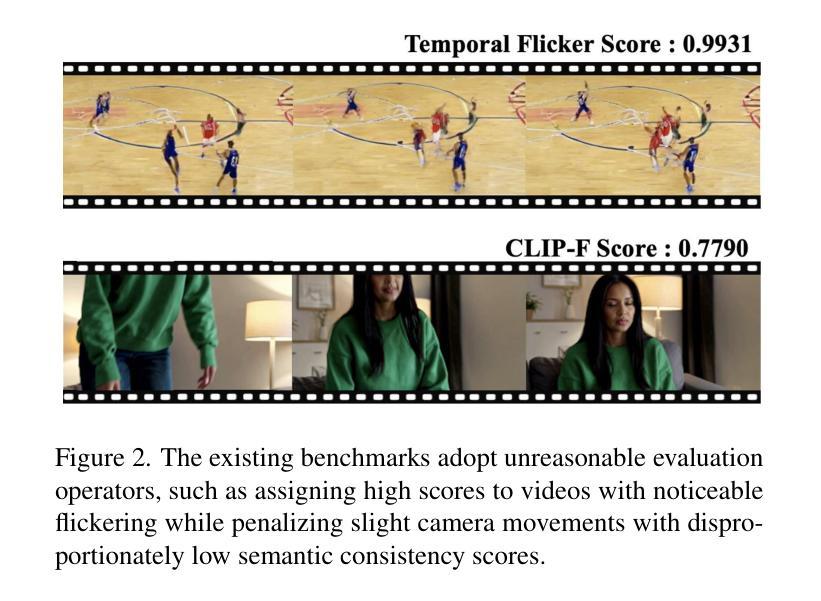
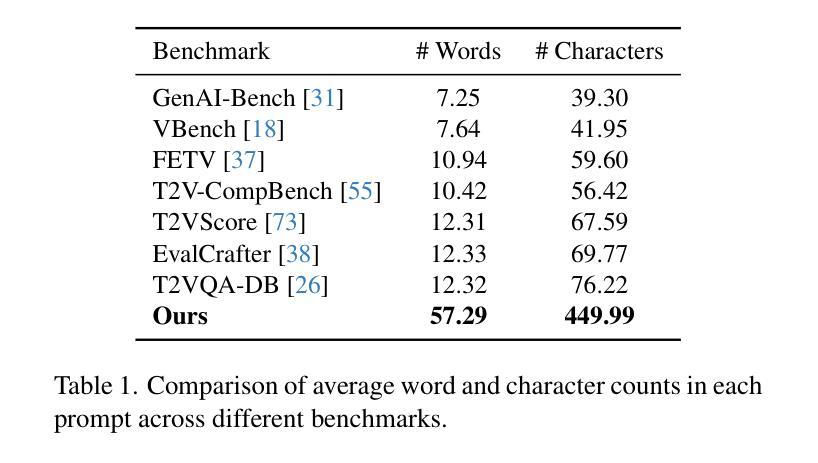
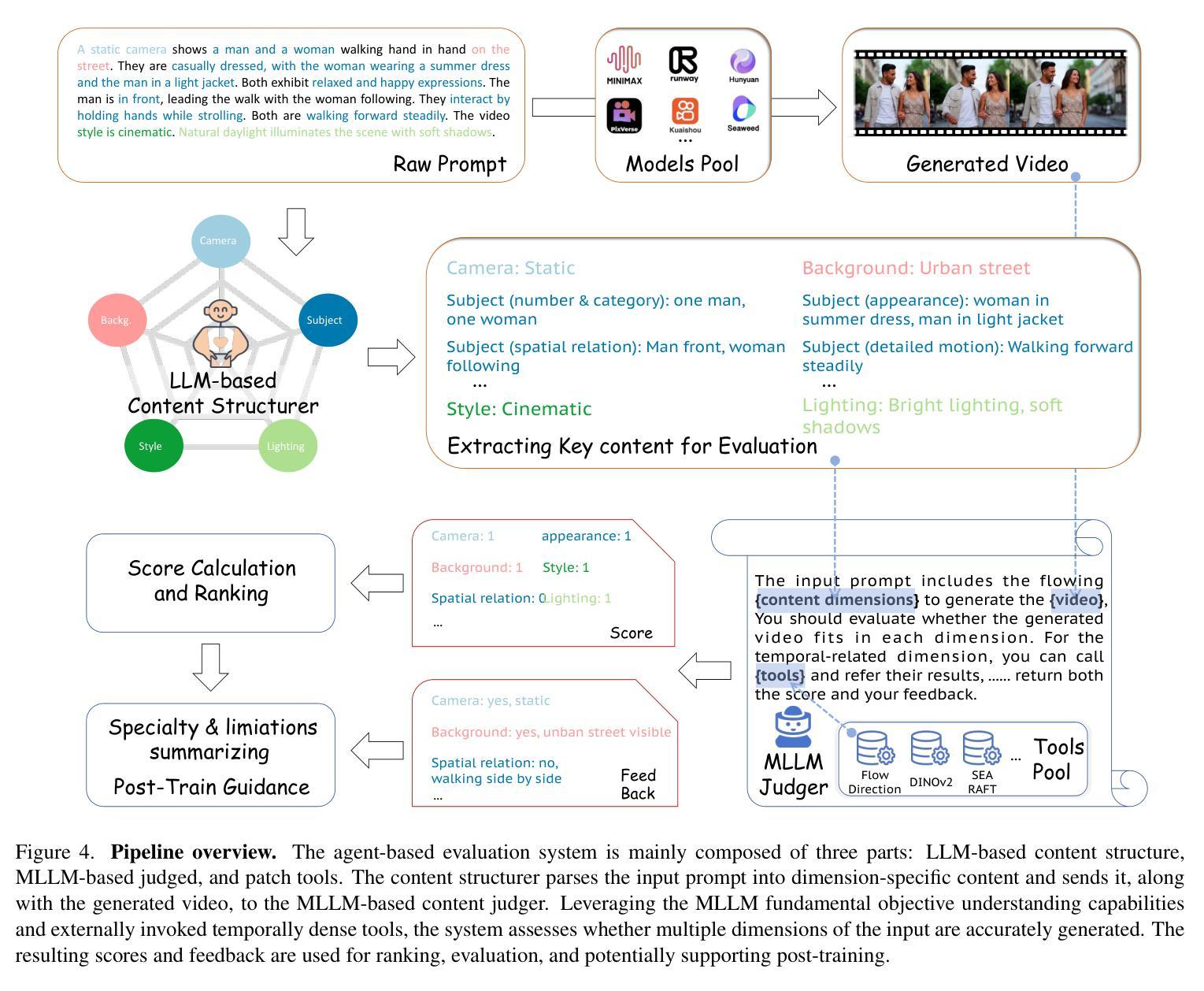
The rapid advancement of video generation has rendered existing evaluation systems inadequate for assessing state-of-the-art models, primarily due to simple prompts that cannot showcase the model’s capabilities, fixed evaluation operators struggling with Out-of-Distribution (OOD) cases, and misalignment between computed metrics and human preferences. To bridge the gap, we propose VideoGen-Eval, an agent evaluation system that integrates LLM-based content structuring, MLLM-based content judgment, and patch tools designed for temporal-dense dimensions, to achieve a dynamic, flexible, and expandable video generation evaluation. Additionally, we introduce a video generation benchmark to evaluate existing cutting-edge models and verify the effectiveness of our evaluation system. It comprises 700 structured, content-rich prompts (both T2V and I2V) and over 12,000 videos generated by 20+ models, among them, 8 cutting-edge models are selected as quantitative evaluation for the agent and human. Extensive experiments validate that our proposed agent-based evaluation system demonstrates strong alignment with human preferences and reliably completes the evaluation, as well as the diversity and richness of the benchmark.
视频生成的快速发展使得现有评估系统无法评估最前沿模型的状态,这主要是由于无法展示模型能力的简单提示、处理离群值(OOD)案例时的固定评估操作以及计算指标与人类偏好之间的不一致。为了缩小这一差距,我们提出了VideoGen-Eval评估系统,该系统集成了基于LLM的内容结构、基于MLLM的内容判断以及针对时间密集维度的专用工具,以实现动态、灵活和可扩展的视频生成评估。此外,我们还引入了一个视频生成基准测试,以评估现有的顶尖模型并验证我们的评估系统的有效性。该基准测试包含700个结构清晰、内容丰富的提示(包括T2V和I2V),以及由20多个模型生成的超过12000个视频,其中选择了8个顶尖模型进行定量评估。大量实验验证,我们提出的基于代理的评估系统与人类偏好高度一致,并能可靠地完成评估,同时基准测试具有丰富的多样性和丰富性。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF project:https://github.com/AILab-CVC/VideoGen-Eval
Summary
视频生成技术的快速发展使得现有的评估系统无法对先进技术模型进行有效的评估,主要表现在无法展示模型能力、难以处理离群值以及计算指标与人类偏好之间的不匹配。为此,我们提出了VideoGen-Eval评估系统,该系统融合了基于大型语言模型的内容结构、基于多模态语言模型的内容判断以及针对时序密集维度的工具设计,实现了动态、灵活和可扩展的视频生成评估。此外,我们还推出了视频生成基准测试,以评估现有尖端模型并验证我们的评估系统的有效性。
Key Takeaways
- 视频生成技术的快速发展导致现有评估系统不足。
- 现有评估系统无法充分展示模型能力、难以处理离群值,且计算指标与人类偏好存在不匹配。
- VideoGen-Eval评估系统融合了大型语言模型和多模态语言模型技术。
- VideoGen-Eval系统设计了针对时序密集维度的工具,以实现动态、灵活和可扩展的视频生成评估。
- 推出了视频生成基准测试,包括结构化、内容丰富的提示和大量生成视频,以评估现有模型。
- VideoGen-Eval系统与人类偏好强相关,并能可靠地完成评估。
点此查看论文截图



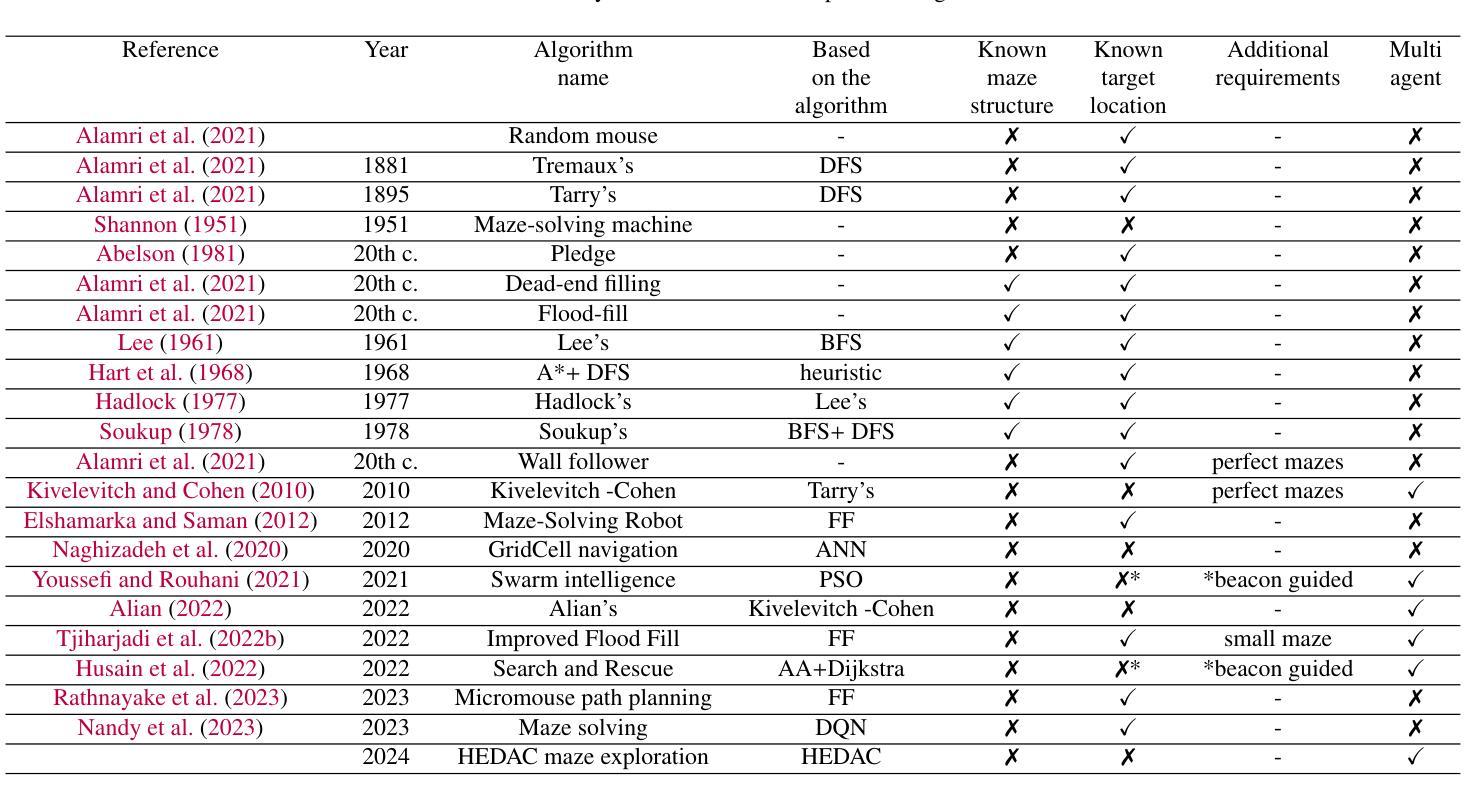
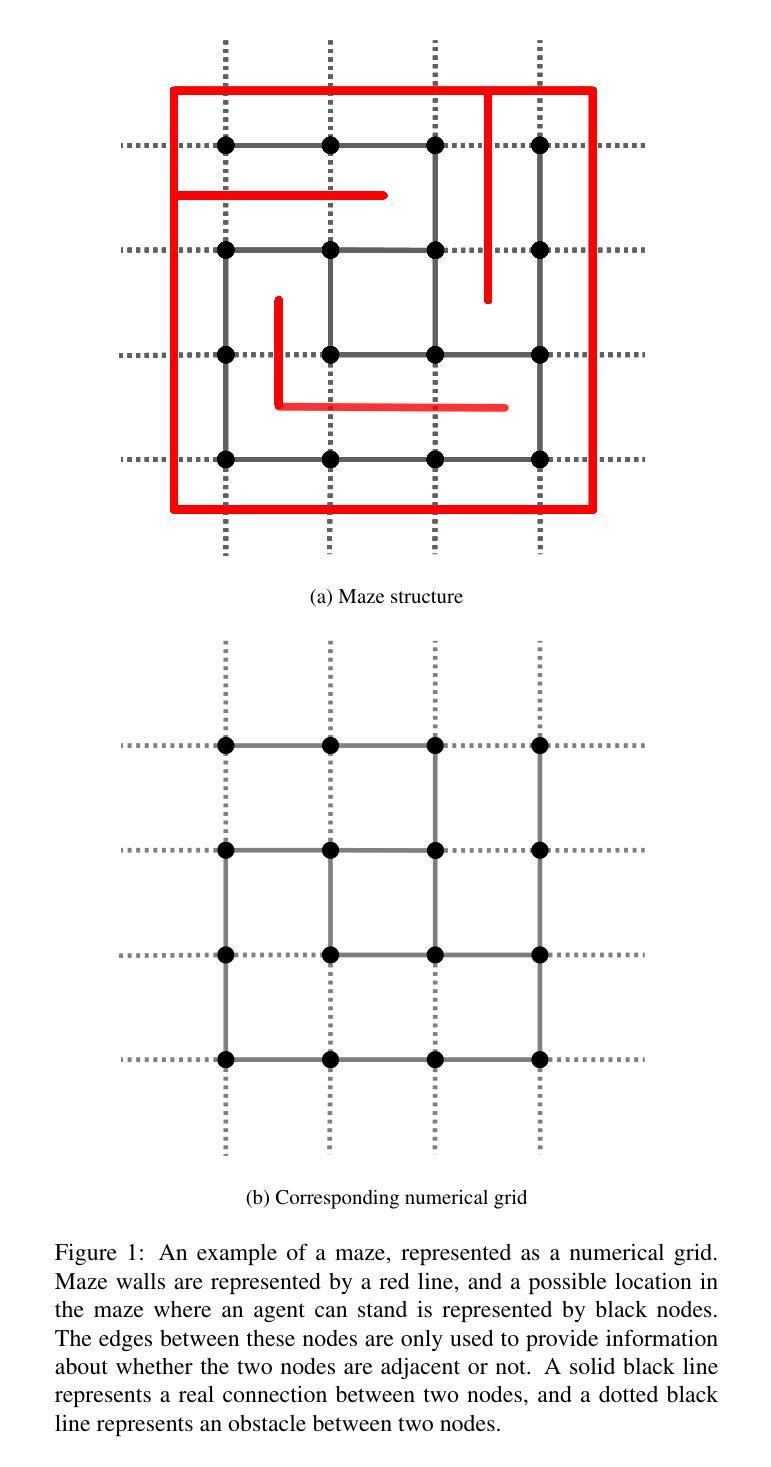
Fast algorithm for centralized multi-agent maze exploration
Authors:Bojan Crnković, Stefan Ivić, Mila Zovko
Recent advances in robotics have paved the way for robots to replace humans in perilous situations, such as searching for victims in burning buildings, in earthquake-damaged structures, in uncharted caves, traversing minefields or patrolling crime-ridden streets. These challenges can be generalized as problems where agents have to explore unknown mazes. We propose a cooperative multi-agent system of automated mobile agents for exploring unknown mazes and localizing stationary targets. The Heat Equation-Driven Area Coverage (HEDAC) algorithm for maze exploration employs a potential field to guide the exploration of the maze and integrates cooperative behaviors of the agents such as collision avoidance, coverage coordination, and path planning. In contrast to previous applications for continuous static domains, we adapt the HEDAC method for mazes on expanding rectilinear grids. The proposed algorithm guarantees the exploration of the entire maze and can ensure the avoidance of collisions and deadlocks. Moreover, this is the first application of the HEDAC algorithm to domains that expand over time. To cope with the dynamically changing domain, succesive over-relaxation (SOR) iterative linear solver has been adapted and implemented, which significantly reduced the computational complexity of the presented algorithm when compared to standard direct and iterative linear solvers. The results highlight significant improvements and show the applicability of the algorithm in different mazes. They confirm its robustness, adaptability, scalability and simplicity, which enables centralized parallel computation to control multiple agents/robots in the maze.
近年来,机器人技术的进展为机器人在危险情况下替代人类提供了可能,例如在燃烧的建筑物、地震受损的结构、未知的洞穴、穿越地雷区或巡逻犯罪多发街道中寻找受害者。这些挑战可以概括为代理需要在未知迷宫中寻找的问题。我们提出了一种用于探索未知迷宫并定位静止目标的自动化移动代理的合作多代理系统。迷宫探索的热方程驱动区域覆盖(HEDAC)算法利用潜在领域来引导迷宫的探索,并整合了代理的合作行为,如避碰、覆盖协调和路径规划。与之前连续静态领域的应用不同,我们适应了扩展直线网格迷宫的HEDAC方法。所提出的算法可以保证整个迷宫的探索,并确保避免碰撞和死锁。此外,这是HEDAC算法首次应用于随时间扩展的领域。为了应对动态变化的领域,相继松弛(SOR)迭代线性求解器被适应和实施,与标准直接和迭代线性求解器相比,这大大降低了所提出算法的计算复杂性。结果突出了显著的改进,并显示了该算法在不同迷宫中的应用性。它们证实了其稳健性、适应性、可扩展性和简单性,这能够实现集中式并行计算以控制迷宫中的多个代理/机器人。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF Improved manuscript
Summary
近期机器人技术的进步使得机器人在危险场景如火灾搜救、地震救援、洞穴探索、穿越雷区及巡逻犯罪多发街区等方面替代人类成为可能。本文提出一种用于探索未知迷宫并定位静止目标的合作多智能体系统,采用热方程驱动区域覆盖算法进行迷宫探索,通过势能场引导探索,集成智能体间的合作行为如防撞、覆盖协调及路径规划等。文章将该算法扩展到动态扩展的直线网格迷宫上,确保了迷宫的全覆盖并避免碰撞和死锁问题。该方法首次应用于随时间变化的领域,采用连续过度松弛迭代线性求解器降低了算法的计算复杂度。结果证明了该算法的稳健性、适应性、可扩展性和简单性,可实现多智能体/机器人在迷宫中的集中并行计算控制。
Key Takeaways
- 机器人技术已发展到可替代人类在危险场景中进行任务,如迷宫探索等。
- 提出一种合作多智能体系统用于探索未知迷宫并定位静止目标。
- 采用热方程驱动区域覆盖算法进行迷宫探索,包含势能场引导和智能体间的合作行为。
- 将算法扩展到动态扩展的直线网格迷宫上,确保全覆盖并避免碰撞和死锁。
- 该方法是首次应用于随时间变化的领域。
- 采用连续过度松弛迭代线性求解器降低了算法的计算复杂度。
点此查看论文截图