⚠️ 以下所有内容总结都来自于 大语言模型的能力,如有错误,仅供参考,谨慎使用
🔴 请注意:千万不要用于严肃的学术场景,只能用于论文阅读前的初筛!
💗 如果您觉得我们的项目对您有帮助 ChatPaperFree ,还请您给我们一些鼓励!⭐️ HuggingFace免费体验
2025-04-30 更新
DeeCLIP: A Robust and Generalizable Transformer-Based Framework for Detecting AI-Generated Images
Authors:Mamadou Keita, Wassim Hamidouche, Hessen Bougueffa Eutamene, Abdelmalik Taleb-Ahmed, Abdenour Hadid
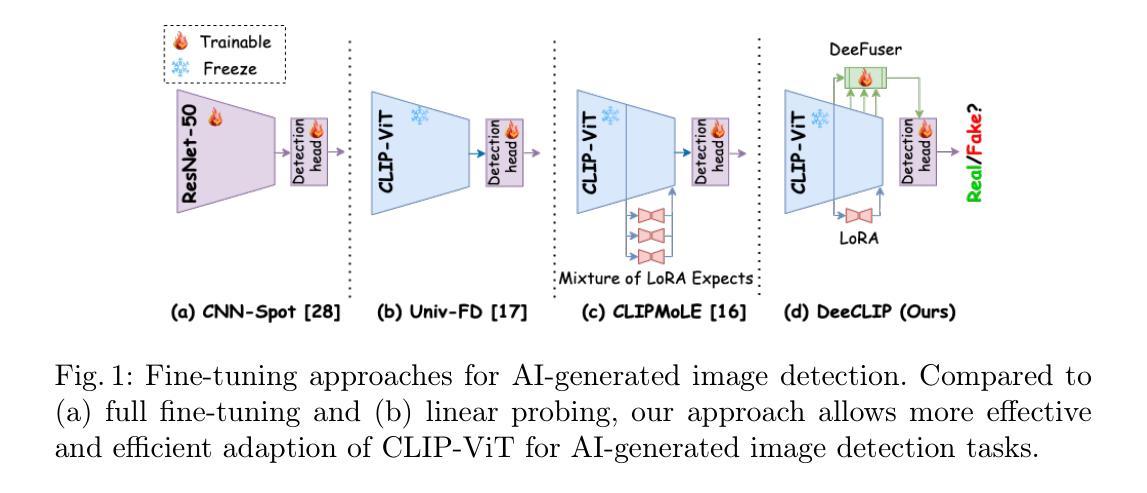
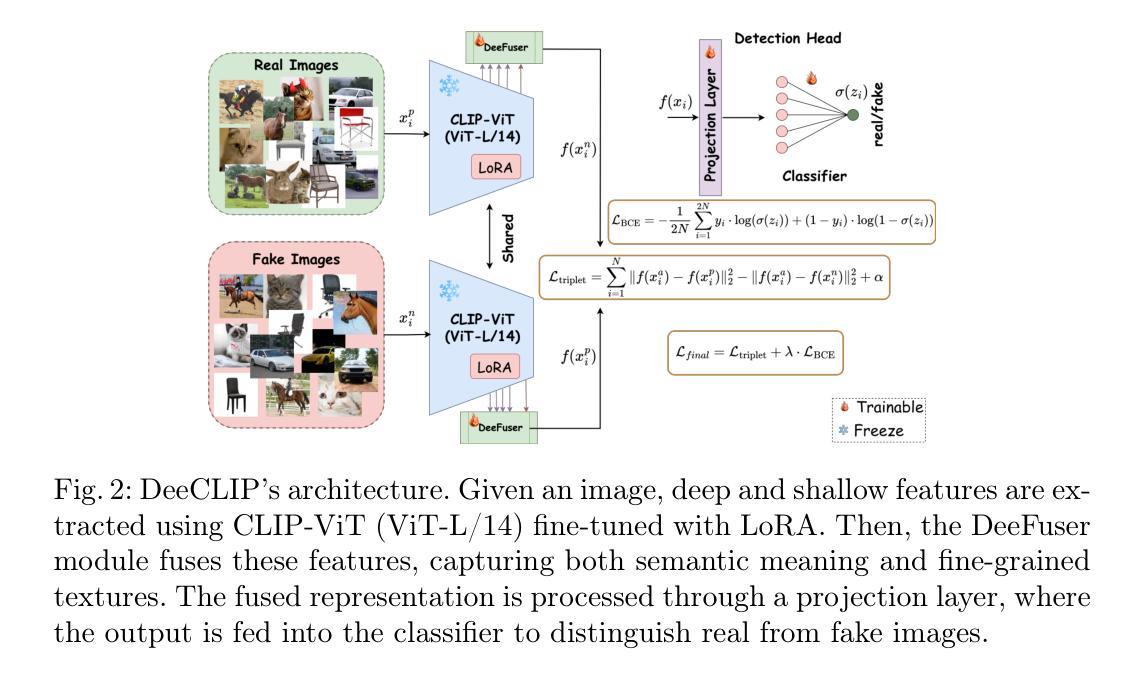
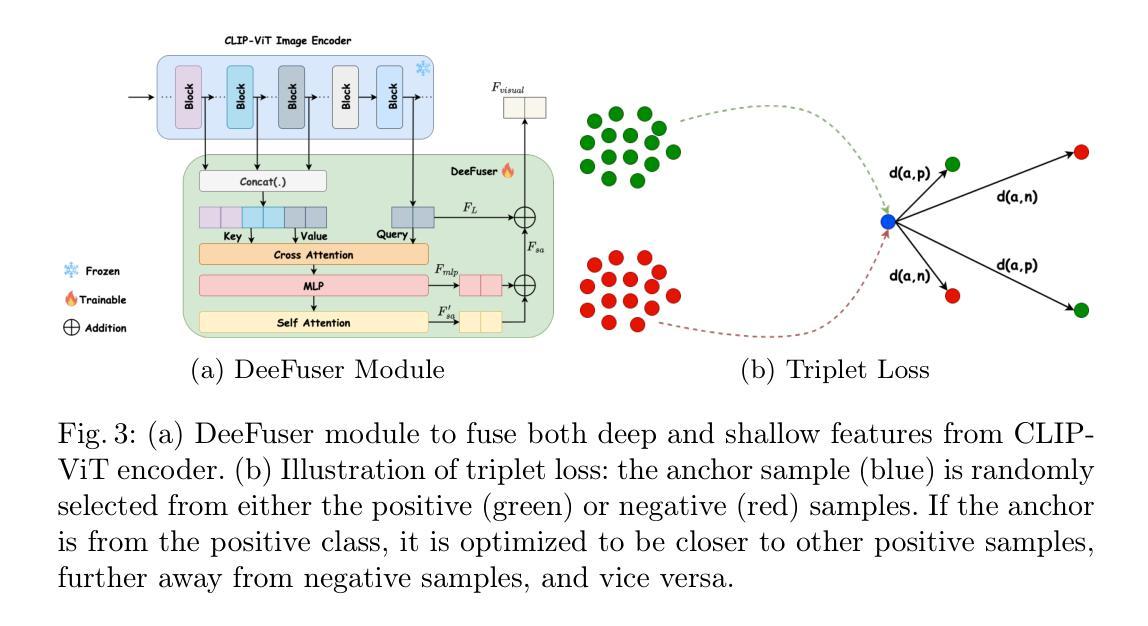
This paper introduces DeeCLIP, a novel framework for detecting AI-generated images using CLIP-ViT and fusion learning. Despite significant advancements in generative models capable of creating highly photorealistic images, existing detection methods often struggle to generalize across different models and are highly sensitive to minor perturbations. To address these challenges, DeeCLIP incorporates DeeFuser, a fusion module that combines high-level and low-level features, improving robustness against degradations such as compression and blurring. Additionally, we apply triplet loss to refine the embedding space, enhancing the model’s ability to distinguish between real and synthetic content. To further enable lightweight adaptation while preserving pre-trained knowledge, we adopt parameter-efficient fine-tuning using low-rank adaptation (LoRA) within the CLIP-ViT backbone. This approach supports effective zero-shot learning without sacrificing generalization. Trained exclusively on 4-class ProGAN data, DeeCLIP achieves an average accuracy of 89.00% on 19 test subsets composed of generative adversarial network (GAN) and diffusion models. Despite having fewer trainable parameters, DeeCLIP outperforms existing methods, demonstrating superior robustness against various generative models and real-world distortions. The code is publicly available at https://github.com/Mamadou-Keita/DeeCLIP for research purposes.
本文介绍了DeeCLIP,这是一个使用CLIP-ViT和融合学习检测AI生成图像的新型框架。尽管生成模型在创造高度逼真的图像方面取得了显著进展,但现有的检测方法在跨不同模型推广时经常遇到困难,并且对微小的扰动非常敏感。为了应对这些挑战,DeeCLIP结合了DeeFuser,一个融合模块,它结合了高级和低级特征,提高了对压缩、模糊等降质的稳健性。此外,我们应用了三元组损失来优化嵌入空间,提高模型区分真实和合成内容的能力。为了进一步实现在保持预训练知识的同时进行轻量级适应,我们在CLIP-ViT主干中采用低秩适应(LoRA)进行参数高效微调。这种方法支持有效的零样本学习,而不会牺牲泛化能力。DeeCLIP仅对ProGAN的四大类数据进行训练,在对由生成对抗网络(GAN)和扩散模型组成的19个测试子集上取得了平均89.00%的准确率。尽管拥有较少的可训练参数,但DeeCLIP在针对各种生成模型和现实世界畸变的测试中表现出卓越的稳健性。该代码已公开发布在https://github.com/Mamadou-Keita/DeeCLIP上供研究使用。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
DeeCLIP框架利用CLIP-ViT和融合学习技术检测AI生成的图像。它通过结合高级和低级特征提高检测模型的稳健性,并采用三重损失优化嵌入空间。通过采用低秩适应(LoRA)进行微调,支持零样本学习且不影响泛化能力。在特定数据集上训练的DeeCLIP对多种生成对抗网络(GAN)和扩散模型表现出强大的性能。
Key Takeaways
- DeeCLIP是一个用于检测AI生成图像的新框架,结合CLIP-ViT和融合学习技术。
- DeeCLIP解决了现有检测方法的两大挑战:难以跨不同模型泛化和对微小扰动的敏感性。
- DeeCLIP引入DeeFuser模块,结合高低级特征以提高稳健性,对抗图像压缩、模糊等降解。
- 采用三重损失来优化嵌入空间,提高模型区分真实和合成内容的能力。
- 通过采用低秩适应(LoRA)进行微调,DeeCLIP实现了有效的零样本学习,同时保持泛化能力。
- DeeCLIP在特定数据集上训练,对多种生成对抗网络(GAN)和扩散模型表现出强大的检测性能。
点此查看论文截图

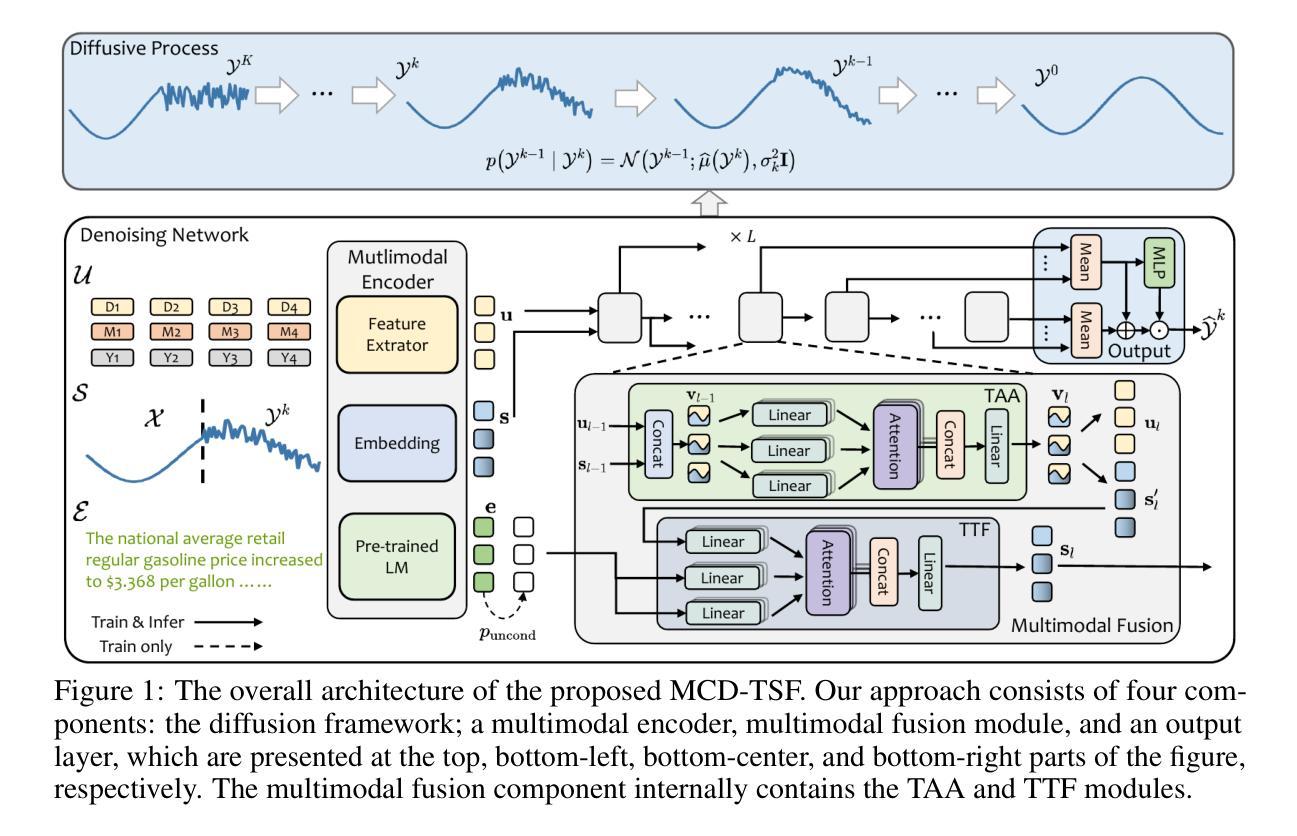
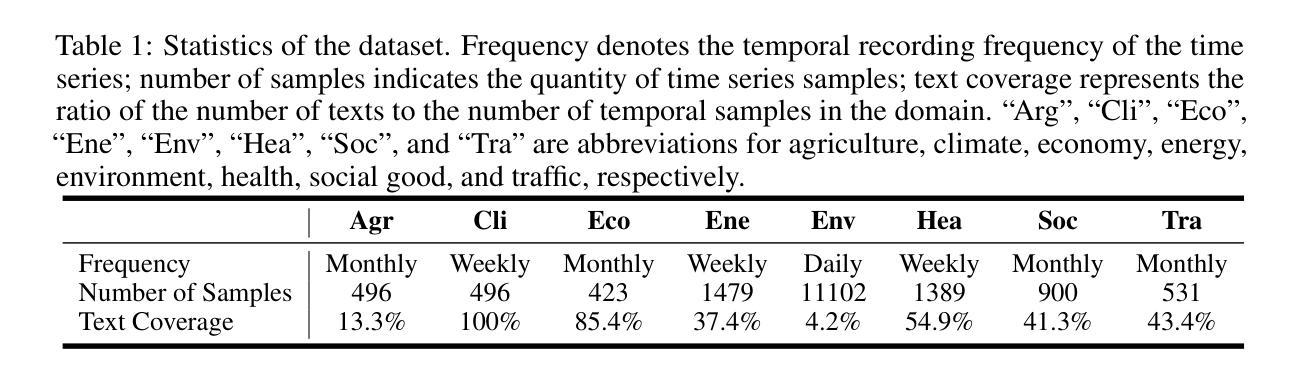
Multimodal Conditioned Diffusive Time Series Forecasting
Authors:Chen Su, Yuanhe Tian, Yan Song
Diffusion models achieve remarkable success in processing images and text, and have been extended to special domains such as time series forecasting (TSF). Existing diffusion-based approaches for TSF primarily focus on modeling single-modality numerical sequences, overlooking the rich multimodal information in time series data. To effectively leverage such information for prediction, we propose a multimodal conditioned diffusion model for TSF, namely, MCD-TSF, to jointly utilize timestamps and texts as extra guidance for time series modeling, especially for forecasting. Specifically, Timestamps are combined with time series to establish temporal and semantic correlations among different data points when aggregating information along the temporal dimension. Texts serve as supplementary descriptions of time series’ history, and adaptively aligned with data points as well as dynamically controlled in a classifier-free manner. Extensive experiments on real-world benchmark datasets across eight domains demonstrate that the proposed MCD-TSF model achieves state-of-the-art performance.
扩散模型在处理图像和文本方面取得了显著的成功,并已扩展到时间序列预测(TSF)等特殊领域。现有的基于扩散的TSF方法主要专注于对单模态数值序列进行建模,忽视了时间序列数据中的丰富多模态信息。为了有效利用这些信息来进行预测,我们提出了一种用于TSF的多模态条件扩散模型,即MCD-TSF,以联合使用时间戳和文本作为时间序列建模的额外指导,尤其是进行预测。具体来说,时间戳与时间序列相结合,在沿时间维度聚合信息时建立不同数据点之间的时态和语义关联。文本作为时间序列历史的补充描述,与数据点自适应对齐,并以无分类器的方式动态控制。在八个领域的真实世界基准数据集上进行的大量实验表明,所提出的MCD-TSF模型达到了最先进的性能。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
扩散模型在图像和文本处理方面取得了显著的成功,并已扩展到时间序列预测等特殊领域。针对现有基于扩散的时间序列预测方法主要关注单模态数值序列建模,忽视时间序列数据中丰富的多模态信息的问题,我们提出了一种多模态条件扩散模型MCD-TSF,该模型能够联合利用时间戳和文本作为时间序列建模的额外指导,尤其是进行预测。通过结合时间戳和时间序列,建立不同数据点之间的时间和语义关联,同时利用文本作为时间序列历史的补充描述,自适应地与目标数据点对齐,并以无分类器的方式动态控制。在八个领域的真实世界基准数据集上进行的广泛实验表明,所提出的MCD-TSF模型达到了最新技术水平。
Key Takeaways
- 扩散模型已成功应用于图像和文本处理,并扩展至时间序列预测领域。
- 现有时序预测模型主要关注单模态数值序列建模,忽视了多模态信息的重要性。
- 提出了一种新的多模态条件扩散模型MCD-TSF,联合利用时间戳和文本信息。
- MCD-TSF模型通过结合时间戳和时间序列信息,建立数据点间的时空语义关联。
- 文本信息作为时间序列历史的补充描述,与数据点自适应对齐。
- MCD-TSF模型以无分类器的方式动态控制文本信息的利用。
点此查看论文截图

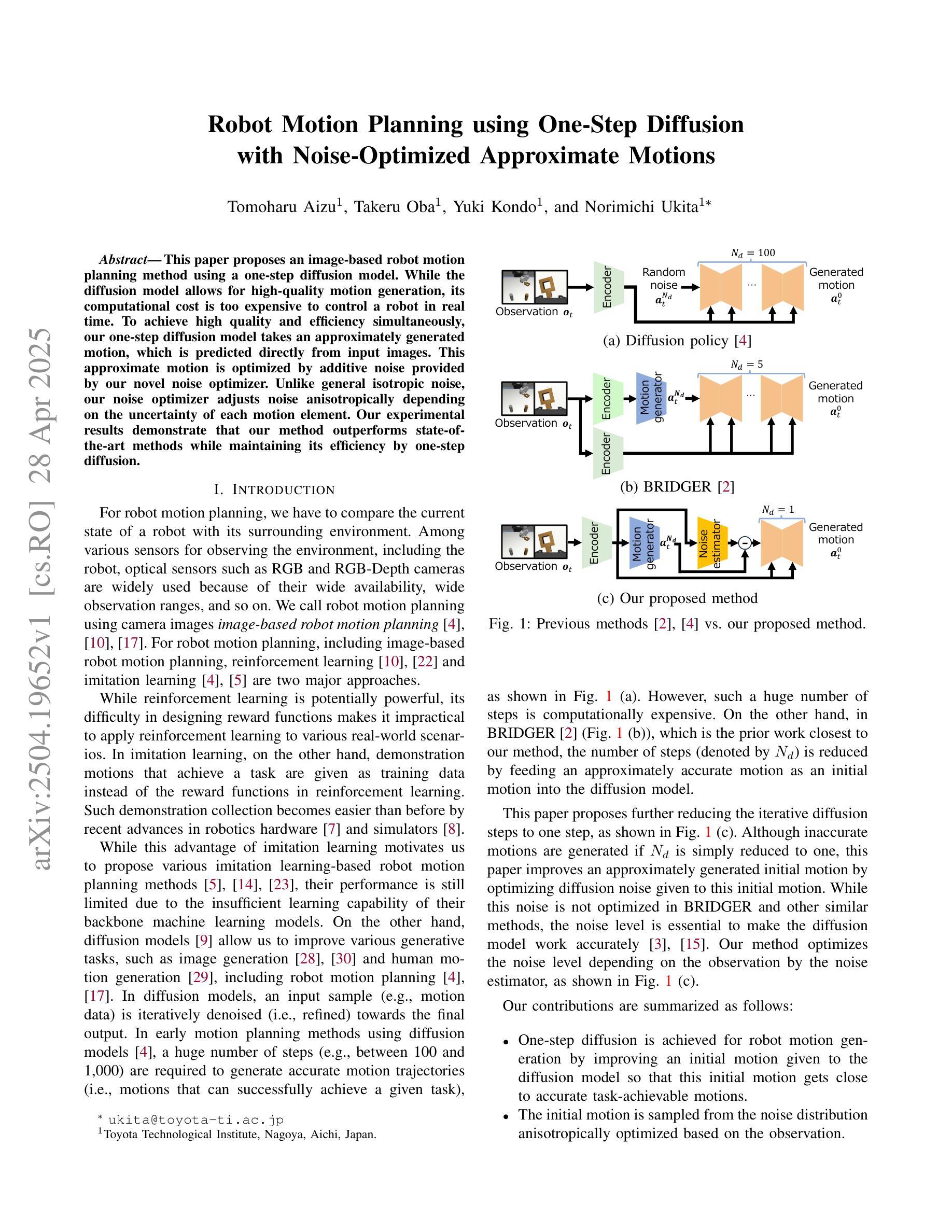
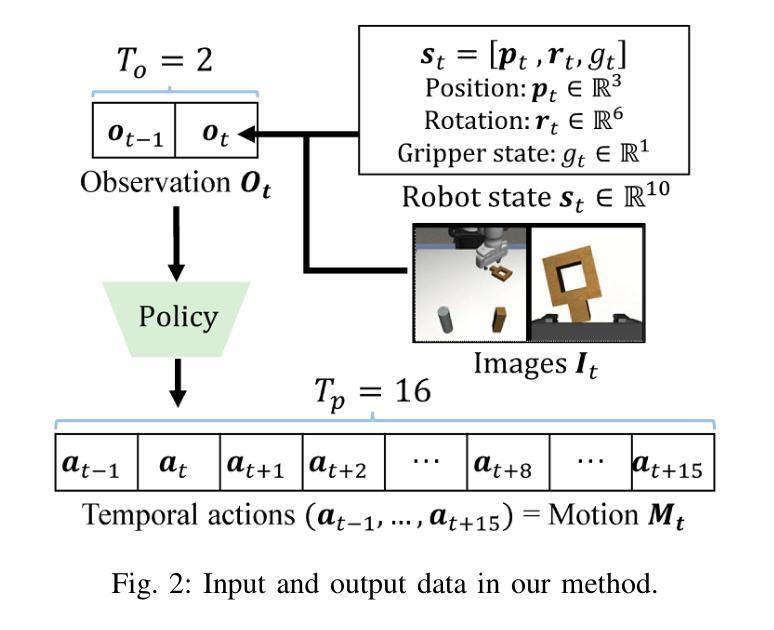
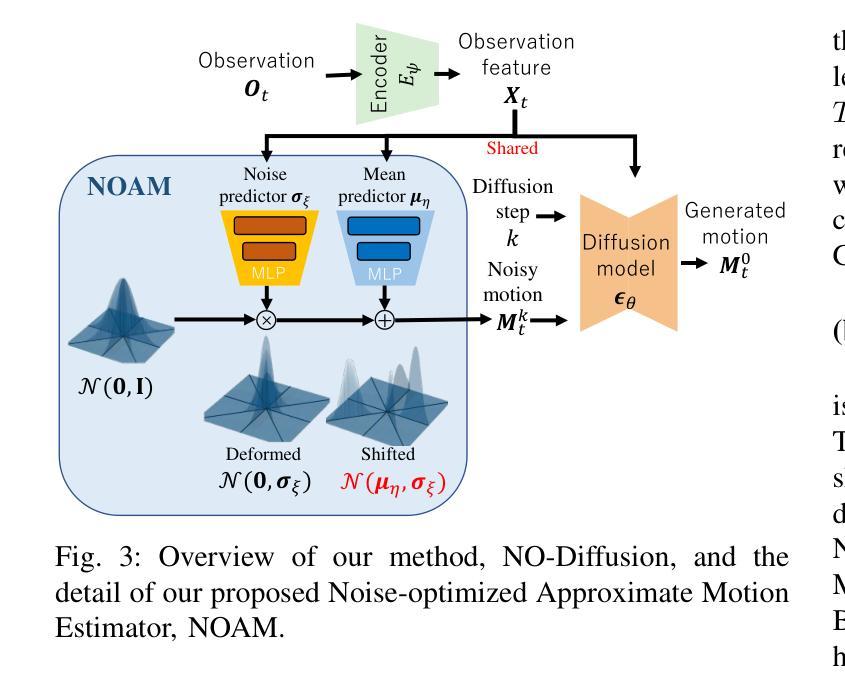
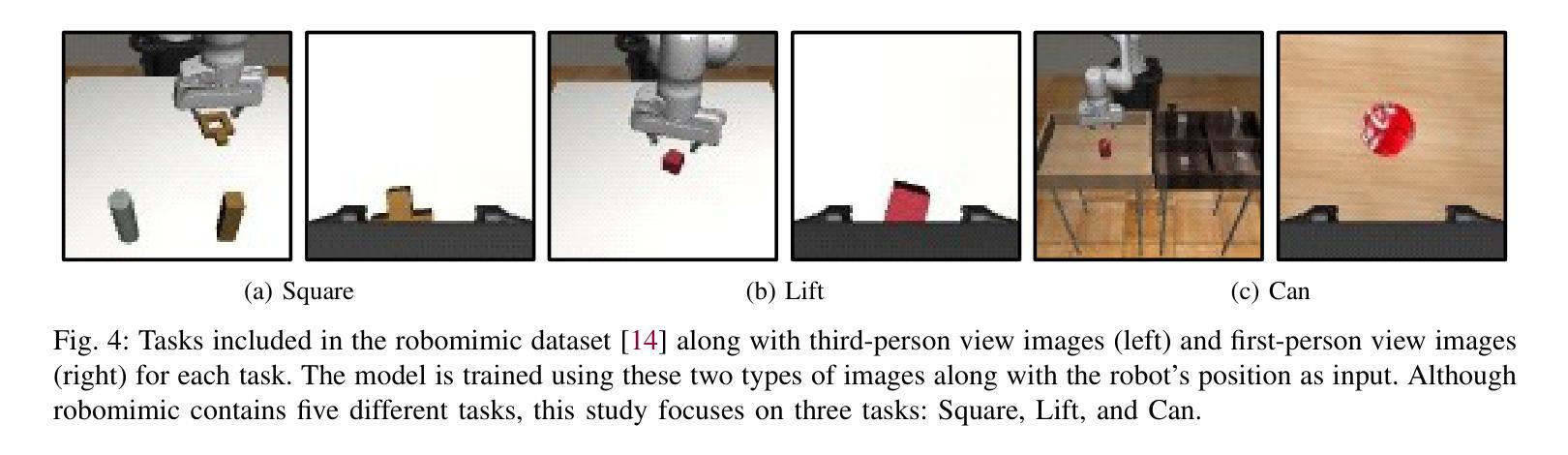
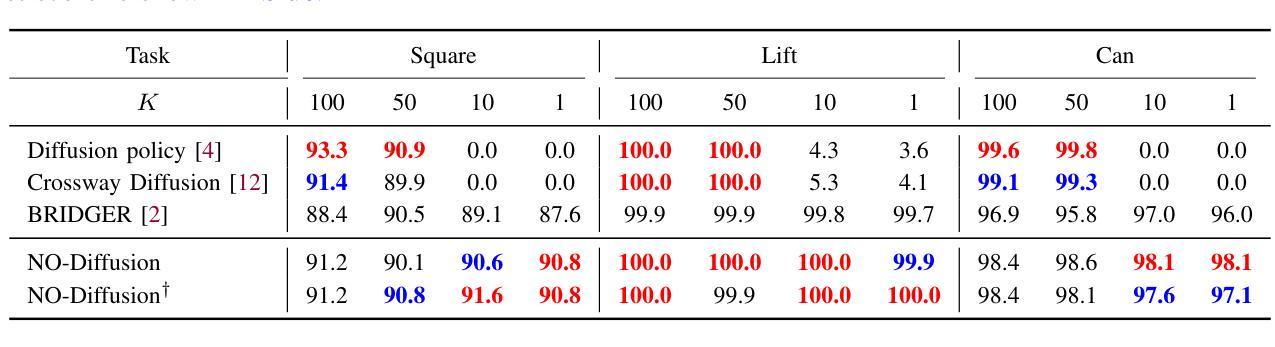
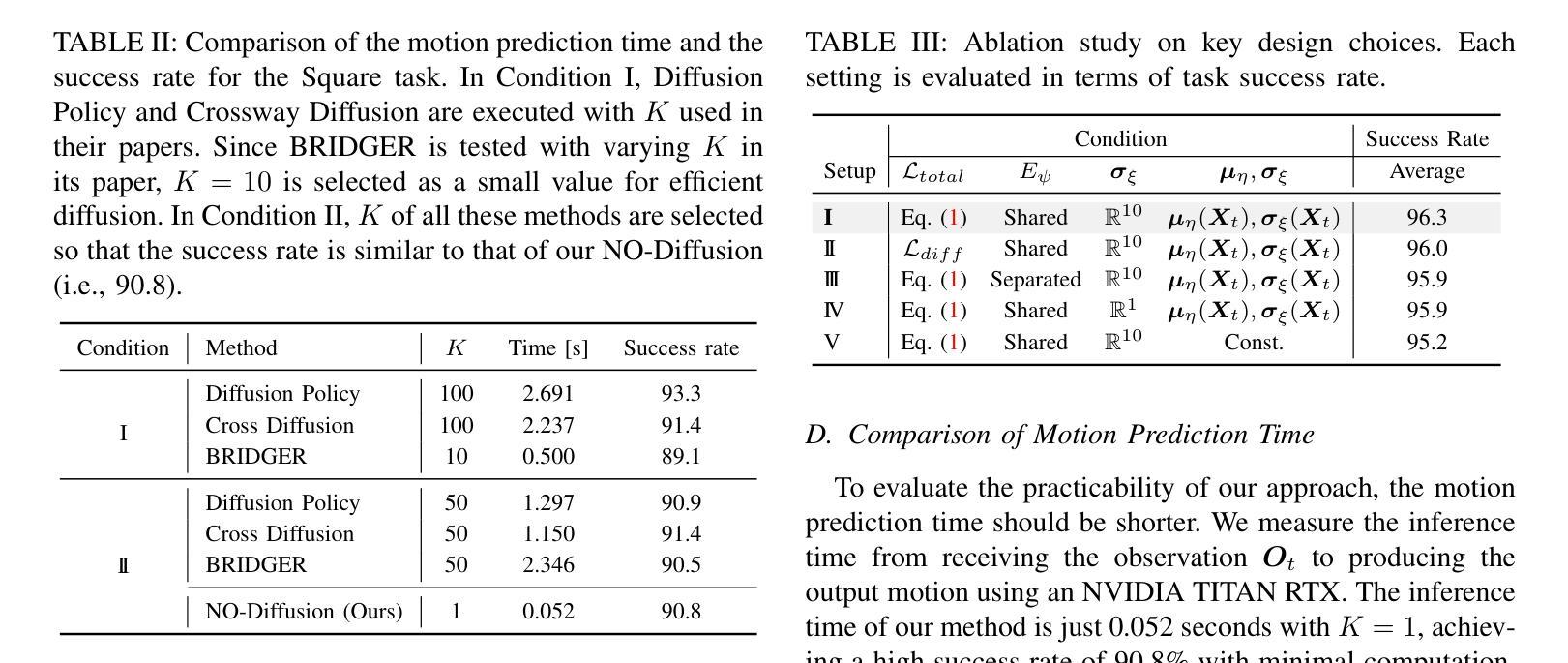
Robot Motion Planning using One-Step Diffusion with Noise-Optimized Approximate Motions
Authors:Tomoharu Aizu, Takeru Oba, Yuki Kondo, Norimichi Ukita
This paper proposes an image-based robot motion planning method using a one-step diffusion model. While the diffusion model allows for high-quality motion generation, its computational cost is too expensive to control a robot in real time. To achieve high quality and efficiency simultaneously, our one-step diffusion model takes an approximately generated motion, which is predicted directly from input images. This approximate motion is optimized by additive noise provided by our novel noise optimizer. Unlike general isotropic noise, our noise optimizer adjusts noise anisotropically depending on the uncertainty of each motion element. Our experimental results demonstrate that our method outperforms state-of-the-art methods while maintaining its efficiency by one-step diffusion.
本文提出了一种基于图像的机器人运动规划方法,使用一步扩散模型。虽然扩散模型可以生成高质量的运动,但其计算成本过高,无法实时控制机器人。为了同时实现高质量和高效率,我们的一步扩散模型直接从输入图像预测近似生成的运动。这种近似运动通过我们新型噪声优化器提供的附加噪声进行优化。不同于一般的同向噪声,我们的噪声优化器会根据每个运动元素的不确定性来调整异向噪声。实验结果表明,我们的方法在保持一步扩散效率的同时,优于最先进的方法。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF 7 pages, 5 figures. Under peer review
Summary
该论文提出了一种基于扩散模型的图像机器人运动规划方法。通过扩散模型实现高质量运动生成,但其计算成本高昂无法实现实时控制机器人。为解决这一难题,采用一步扩散模型对基于图像预测的近似运动进行优化,并通过新型噪声优化器添加噪声。该噪声优化器能够根据不同运动元素的不确定性调整噪声的异向性。实验结果表明,该方法在保持效率的同时,优于现有技术。
Key Takeaways
- 论文提出了一种基于扩散模型的图像机器人运动规划方法。
- 扩散模型可实现高质量运动生成,但计算成本高昂。
- 为提高效率,采用一步扩散模型对基于图像预测的近似运动进行优化。
- 新型噪声优化器能够根据不同运动元素的不确定性调整噪声的异向性。
- 论文通过实验结果验证了该方法在保持效率的同时,优于现有技术。
- 该方法实现了图像信息到机器人运动的转化,提高了机器人的自主性和适应性。
点此查看论文截图
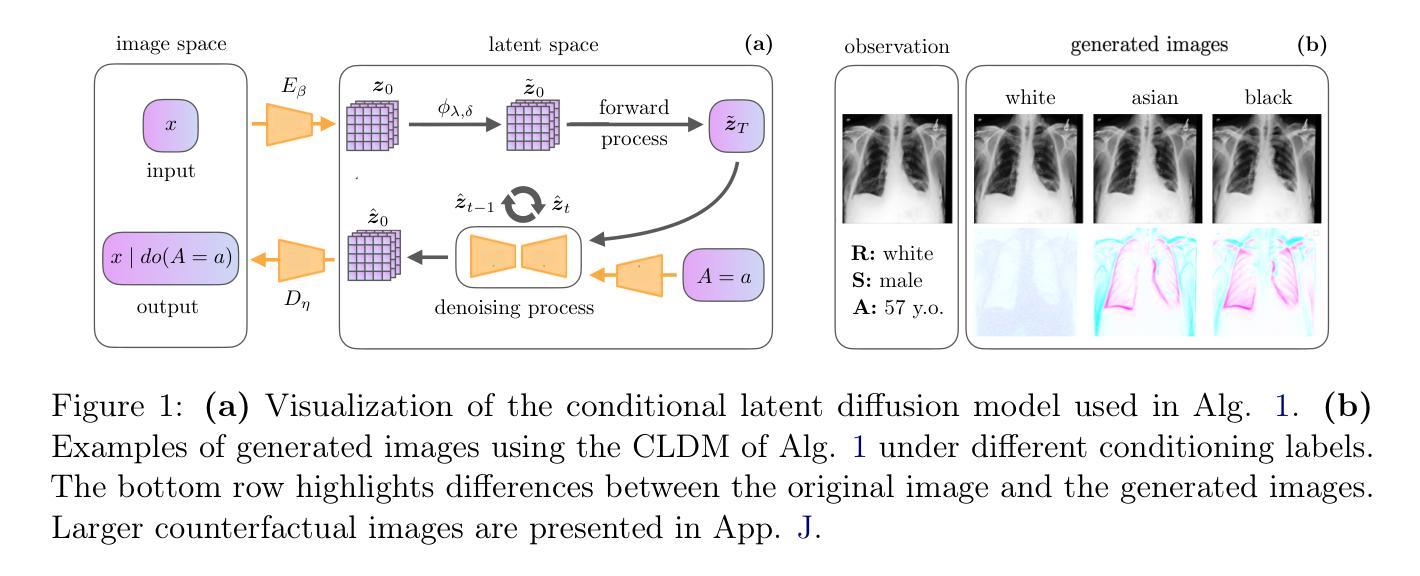
AI Alignment in Medical Imaging: Unveiling Hidden Biases Through Counterfactual Analysis
Authors:Haroui Ma, Francesco Quinzan, Theresa Willem, Stefan Bauer
Machine learning (ML) systems for medical imaging have demonstrated remarkable diagnostic capabilities, but their susceptibility to biases poses significant risks, since biases may negatively impact generalization performance. In this paper, we introduce a novel statistical framework to evaluate the dependency of medical imaging ML models on sensitive attributes, such as demographics. Our method leverages the concept of counterfactual invariance, measuring the extent to which a model’s predictions remain unchanged under hypothetical changes to sensitive attributes. We present a practical algorithm that combines conditional latent diffusion models with statistical hypothesis testing to identify and quantify such biases without requiring direct access to counterfactual data. Through experiments on synthetic datasets and large-scale real-world medical imaging datasets, including \textsc{cheXpert} and MIMIC-CXR, we demonstrate that our approach aligns closely with counterfactual fairness principles and outperforms standard baselines. This work provides a robust tool to ensure that ML diagnostic systems generalize well, e.g., across demographic groups, offering a critical step towards AI safety in healthcare. Code: https://github.com/Neferpitou3871/AI-Alignment-Medical-Imaging.
医学影像机器学习系统展现出了出色的诊断能力,但它们容易受到偏见的影响,从而带来重大风险,因为偏见可能会损害其泛化性能。在本文中,我们介绍了一种新型统计框架,用于评估医学影像机器学习模型对敏感属性的依赖程度,例如人口统计学特征。我们的方法利用反事实不变性的概念,衡量模型预测在敏感属性假设性变化下保持不变的程度。我们提出了一种实用算法,它将条件潜在扩散模型与统计假设检验相结合,无需直接访问反事实数据即可识别和量化这种偏见。通过对合成数据集和大规模现实世界医学影像数据集(包括 CheXpert 和 MIMIC-CXR)的实验,我们证明了我们的方法与反事实公平原则高度吻合,并优于标准基线。这项工作提供了一个强大的工具,可以确保机器学习诊断系统在诸如人口统计学特征等方面具有良好的泛化性能,为医疗保健领域的人工智能安全迈出了关键一步。代码:https://github.com/Neferpitou3871/AI-Alignment-Medical-Imaging。
论文及项目相关链接
摘要
针对机器学习在医疗影像诊断中存在的偏见问题,本文提出一种新型统计框架用于评估医疗影像机器学习模型对敏感属性(如人口统计学特征)的依赖程度。该框架利用反事实不变性概念,衡量模型预测在敏感属性假设变化下的一致性。结合条件潜在扩散模型和统计假设检验的实用算法,可在无需反事实数据的情况下识别和量化偏见。在合成数据集和大规模真实医疗影像数据集(包括CheXpert和MIMIC-CXR)上的实验表明,该方法与反事实公平原则紧密契合并优于标准基线。本研究为确保机器学习诊断系统在诸如跨不同人群等情况下具有良好的泛化能力提供了强有力的工具,是医疗保健领域人工智能安全的关键一步。
关键见解
- 机器学习在医疗影像诊断中存在偏见风险,可能影响模型的泛化性能。
- 本文提出一种新型统计框架,用于评估医疗影像ML模型对敏感属性的依赖程度。
- 利用反事实不变性概念,衡量模型预测在敏感属性假设变化下的一致性。
- 提出结合条件潜在扩散模型和统计假设检验的实用算法,识别并量化偏见。
- 无需反事实数据即可进行偏见识别和量化是一种创新方法。
- 在合成和真实医疗影像数据集上的实验验证了该方法的有效性和优越性。
- 该方法为确保机器学习诊断系统的泛化能力和在医疗保健领域的人工智能安全提供了重要工具。
点此查看论文截图

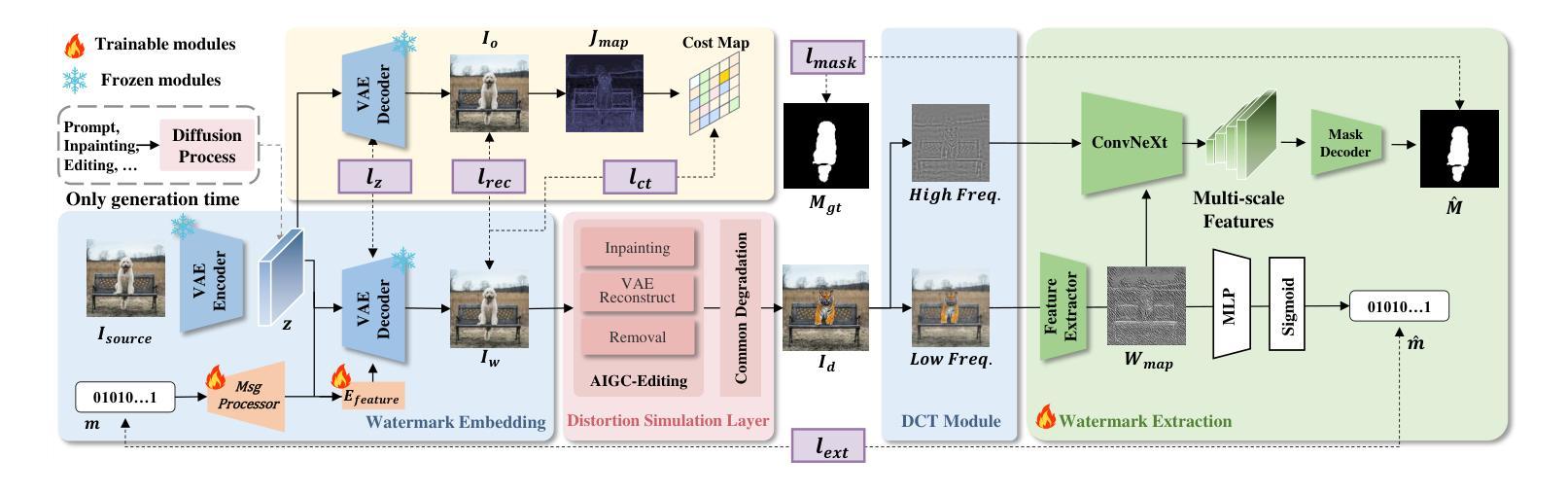
GenPTW: In-Generation Image Watermarking for Provenance Tracing and Tamper Localization
Authors:Zhenliang Gan, Chunya Liu, Yichao Tang, Binghao Wang, Weiqiang Wang, Xinpeng Zhang
The rapid development of generative image models has brought tremendous opportunities to AI-generated content (AIGC) creation, while also introducing critical challenges in ensuring content authenticity and copyright ownership. Existing image watermarking methods, though partially effective, often rely on post-processing or reference images, and struggle to balance fidelity, robustness, and tamper localization. To address these limitations, we propose GenPTW, an In-Generation image watermarking framework for latent diffusion models (LDMs), which integrates Provenance Tracing and Tamper Localization into a unified Watermark-based design. It embeds structured watermark signals during the image generation phase, enabling unified provenance tracing and tamper localization. For extraction, we construct a frequency-coordinated decoder to improve robustness and localization precision in complex editing scenarios. Additionally, a distortion layer that simulates AIGC editing is introduced to enhance robustness. Extensive experiments demonstrate that GenPTW outperforms existing methods in image fidelity, watermark extraction accuracy, and tamper localization performance, offering an efficient and practical solution for trustworthy AIGC image generation.
生成式图像模型的快速发展为人工智能生成内容(AIGC)创作带来了巨大的机遇,同时也带来了确保内容真实性和版权归属的关键挑战。现有的图像水印方法虽然部分有效,但通常依赖于后处理或参考图像,并且在平衡保真度、鲁棒性和篡改定位方面存在困难。为了解决这些限制,我们提出了GenPTW,这是一种针对潜在扩散模型(LDM)的在生成图像水印框架,它将来源追踪和篡改定位集成到一个统一的水印设计之中。它在图像生成阶段嵌入结构化水印信号,以实现统一的来源追踪和篡改定位。对于提取,我们构建了一个频率协调解码器,以提高复杂编辑场景下的鲁棒性和定位精度。此外,还引入了一个模拟AIGC编辑的失真层,以提高鲁棒性。大量实验表明,GenPTW在图像保真度、水印提取准确性和篡改定位性能等方面优于现有方法,为可信的AIGC图像生成提供了高效实用的解决方案。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
生成式图像模型的快速发展为人工智能生成内容(AIGC)创作带来了巨大机遇,同时也对确保内容真实性和版权所有权提出了严峻挑战。针对现有图像水印方法在保真度、稳健性和篡改定位方面的不足,我们提出了GenPTW,一个基于潜在扩散模型(LDM)的生成式图像水印框架。它通过嵌入结构化水印信号,实现了溯源追踪和篡改定位的统一设计。实验表明,GenPTW在图像保真度、水印提取准确性和篡改定位性能上优于现有方法,为可信的AIGC图像生成提供了高效实用的解决方案。
Key Takeaways
- 生成式图像模型的发展促进了AIGC内容的创作,同时也带来了内容真实性和版权保护的挑战。
- 现有图像水印方法存在局限性,难以平衡保真度、稳健性和篡改定位。
- GenPTW是一个针对潜在扩散模型(LDM)的生成式图像水印框架,实现了溯源追踪和篡改定位的统一设计。
- GenPTW通过嵌入结构化水印信号,在图像生成阶段保护版权。
- GenPTW使用频率协调解码器提高水印提取的稳健性和定位精度。
- 引入模拟AIGC编辑的失真层,增强了GenPTW的稳健性。
点此查看论文截图



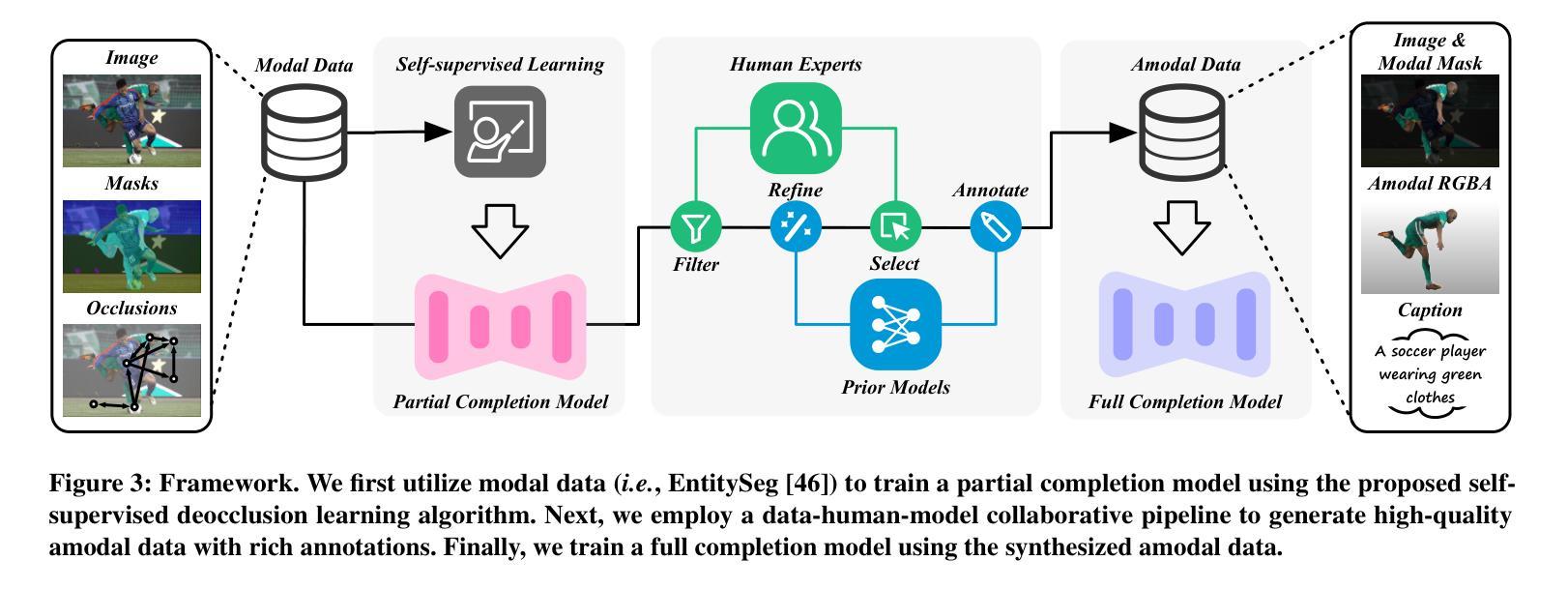
SynergyAmodal: Deocclude Anything with Text Control
Authors:Xinyang Li, Chengjie Yi, Jiawei Lai, Mingbao Lin, Yansong Qu, Shengchuan Zhang, Liujuan Cao
Image deocclusion (or amodal completion) aims to recover the invisible regions (\ie, shape and appearance) of occluded instances in images. Despite recent advances, the scarcity of high-quality data that balances diversity, plausibility, and fidelity remains a major obstacle. To address this challenge, we identify three critical elements: leveraging in-the-wild image data for diversity, incorporating human expertise for plausibility, and utilizing generative priors for fidelity. We propose SynergyAmodal, a novel framework for co-synthesizing in-the-wild amodal datasets with comprehensive shape and appearance annotations, which integrates these elements through a tripartite data-human-model collaboration. First, we design an occlusion-grounded self-supervised learning algorithm to harness the diversity of in-the-wild image data, fine-tuning an inpainting diffusion model into a partial completion diffusion model. Second, we establish a co-synthesis pipeline to iteratively filter, refine, select, and annotate the initial deocclusion results of the partial completion diffusion model, ensuring plausibility and fidelity through human expert guidance and prior model constraints. This pipeline generates a high-quality paired amodal dataset with extensive category and scale diversity, comprising approximately 16K pairs. Finally, we train a full completion diffusion model on the synthesized dataset, incorporating text prompts as conditioning signals. Extensive experiments demonstrate the effectiveness of our framework in achieving zero-shot generalization and textual controllability. Our code, dataset, and models will be made publicly available at https://github.com/imlixinyang/SynergyAmodal.
图像去遮挡(或模态完成)旨在恢复图像中遮挡实例的不可见区域(即形状和外观)。尽管最近取得了进展,但缺乏高质量数据仍然是一个主要障碍,这些高质量数据需要平衡多样性、可行性和保真度。为了应对这一挑战,我们确定了三个关键要素:利用野生图像数据增加多样性,结合人类专家知识增加可行性,利用生成先验增加保真度。我们提出了SynergyAmodal,这是一个新型框架,用于合成带有全面形状和外观注释的野生无模态数据集,通过三方数据-人类-模型协作整合这些要素。首先,我们设计了一种基于遮挡的自监督学习算法,以利用野生图像数据的多样性,对填充扩散模型进行微调,使其适应部分完成扩散模型。其次,我们建立了一个合成管道,通过人类专家的指导和先验模型约束来迭代过滤、细化、选择和注释部分完成扩散模型的初始去遮挡结果,确保可行性和保真度。该管道生成了一个高质量配对的无模态数据集,具有广泛的类别和规模多样性,包含大约16K对数据。最后,我们在合成数据集上训练了一个完整的完成扩散模型,将文本提示作为条件信号。大量实验证明了我们框架在零样本泛化和文本可控性方面的有效性。我们的代码、数据集和模型将在https://github.com/imlixinyang/SynergyAmodal上公开可用。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF 17 pages
Summary
本文旨在解决图像去遮挡(或模态完成)中高质量数据稀缺的问题,通过结合野外图像数据、人类专家和生成先验,提出SynergyAmodal框架,该框架通过三方数据-人类-模型合作,共同合成野外模态数据集,并带有全面的形状和外观注释。该框架设计了一种基于遮挡的自监督学习算法,利用野外图像数据的多样性,将扩散模型微调为部分完成扩散模型。建立合成管道,通过人类专家指导和先验模型约束,对初始去遮挡结果进行过滤、细化、选择和注释,生成高质量配对模态数据集。在合成数据集上训练完整的完成扩散模型,结合文本提示作为条件信号,实现零样本泛化和文本可控性。
Key Takeaways
- 图像去遮挡旨在恢复被遮挡实例的隐形区域(形状和外观)。
- 高质量数据的稀缺性是主要挑战,需要平衡多样性、可行性和保真度。
- 提出SynergyAmodal框架,结合野外图像数据、人类专家和生成先验。
- 通过三方数据-人类-模型合作,共同合成带有全面注释的模态数据集。
- 利用基于遮挡的自监督学习算法,将扩散模型微调为部分完成扩散模型。
- 建立合成管道,确保去遮挡结果的可行性和保真度。
点此查看论文截图


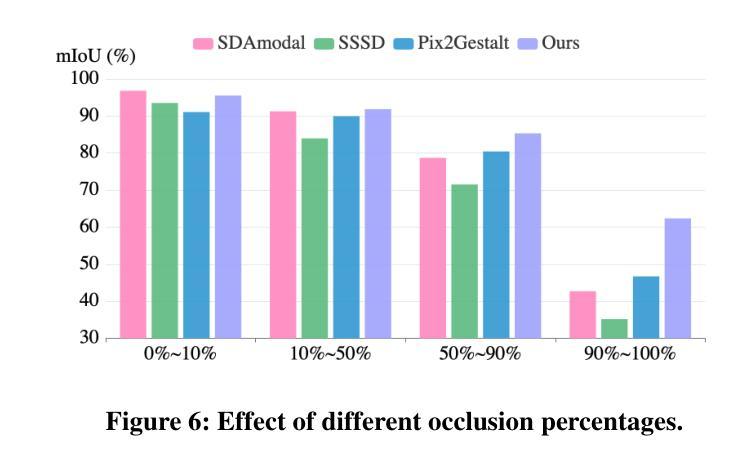
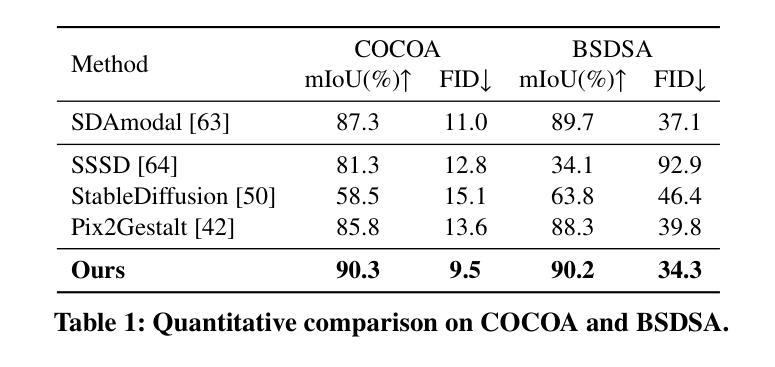
Generative AI for Character Animation: A Comprehensive Survey of Techniques, Applications, and Future Directions
Authors:Mohammad Mahdi Abootorabi, Omid Ghahroodi, Pardis Sadat Zahraei, Hossein Behzadasl, Alireza Mirrokni, Mobina Salimipanah, Arash Rasouli, Bahar Behzadipour, Sara Azarnoush, Benyamin Maleki, Erfan Sadraiye, Kiarash Kiani Feriz, Mahdi Teymouri Nahad, Ali Moghadasi, Abolfazl Eshagh Abianeh, Nizi Nazar, Hamid R. Rabiee, Mahdieh Soleymani Baghshah, Meisam Ahmadi, Ehsaneddin Asgari
Generative AI is reshaping art, gaming, and most notably animation. Recent breakthroughs in foundation and diffusion models have reduced the time and cost of producing animated content. Characters are central animation components, involving motion, emotions, gestures, and facial expressions. The pace and breadth of advances in recent months make it difficult to maintain a coherent view of the field, motivating the need for an integrative review. Unlike earlier overviews that treat avatars, gestures, or facial animation in isolation, this survey offers a single, comprehensive perspective on all the main generative AI applications for character animation. We begin by examining the state-of-the-art in facial animation, expression rendering, image synthesis, avatar creation, gesture modeling, motion synthesis, object generation, and texture synthesis. We highlight leading research, practical deployments, commonly used datasets, and emerging trends for each area. To support newcomers, we also provide a comprehensive background section that introduces foundational models and evaluation metrics, equipping readers with the knowledge needed to enter the field. We discuss open challenges and map future research directions, providing a roadmap to advance AI-driven character-animation technologies. This survey is intended as a resource for researchers and developers entering the field of generative AI animation or adjacent fields. Resources are available at: https://github.com/llm-lab-org/Generative-AI-for-Character-Animation-Survey.
生成式人工智能正在重塑艺术、游戏,尤其是动画产业。近期在基础和扩散模型方面的突破减少了动画内容制作的时间和成本。角色是动画的核心组成部分,涉及动作、情感、手势和面部表情。近几个月来,技术的进步速度之快、范围之广,使得很难对该领域保持连贯的视野,这激发了需要进行综合性回顾的需要。不同于以前只针对化身、手势或面部动画的概述,这篇综述提供了关于角色动画所有主要生成式人工智能应用的单一、全面的视角。我们首先考察面部动画、表情渲染、图像合成、化身创建、手势建模、动作合成、对象生成和纹理合成的最新状态。我们强调了各领域的主要研究、实际部署、常用数据集和新兴趋势。为了支持新手,我们还提供了一个全面的背景部分,介绍基础模型和评估指标,为读者提供进入该领域所需的知识。我们讨论了开放挑战并绘制了未来研究的方向图,为推进人工智能驱动的角色动画技术提供路线图。本综述旨在为进入生成式人工智能动画或其相关领域的研究者和开发者提供参考。相关资源可访问:链接地址。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF 50 main pages, 30 pages appendix, 21 figures, 8 tables, GitHub Repository: https://github.com/llm-lab-org/Generative-AI-for-Character-Animation-Survey
Summary
生成式人工智能正在重塑艺术、游戏和动画领域。近期在基础模型和扩散模型方面的突破,减少了动画内容制作的时间和成本。角色动画涉及动作、情感、手势和面部表情等核心要素。本文综述了面部动画、表情渲染、图像合成、角色创建、手势建模、动作合成、对象生成和纹理合成等领域的最新进展,强调了前沿研究、实际应用部署、常用数据集和未来趋势。本文旨在为进入生成式动画或相关领域的研究者和开发者提供资源。
Key Takeaways
- 生成式人工智能正在改变艺术、游戏和动画领域。
- 突破性的基础模型和扩散模型减少了动画制作的时间和成本。
- 角色动画包括动作、情感、手势和面部表情等核心要素。
- 综述全面涵盖了面部动画、表情渲染等多个主要生成式AI应用领域。
- 综述强调了前沿研究、实际应用部署和常用数据集。
- 综述提供了开放挑战和未来研究方向的探讨。
点此查看论文截图

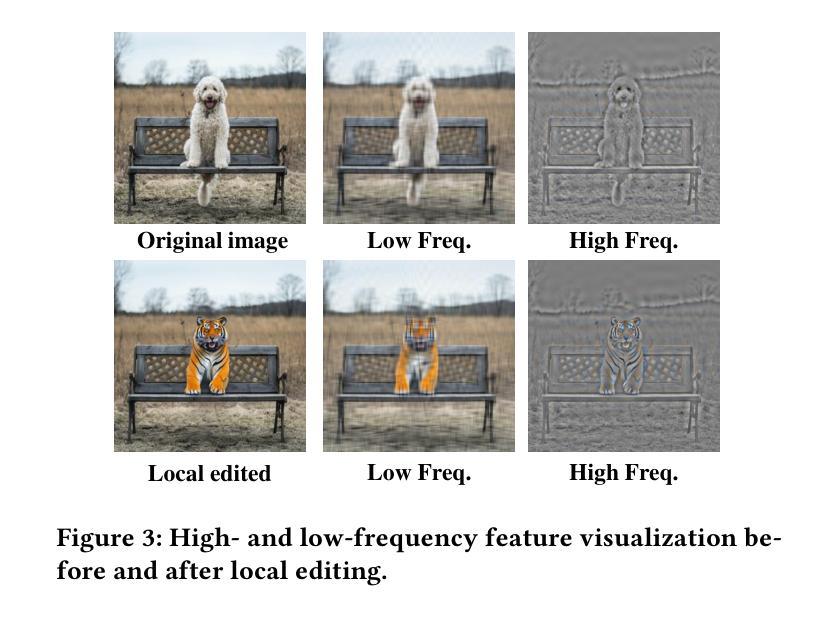
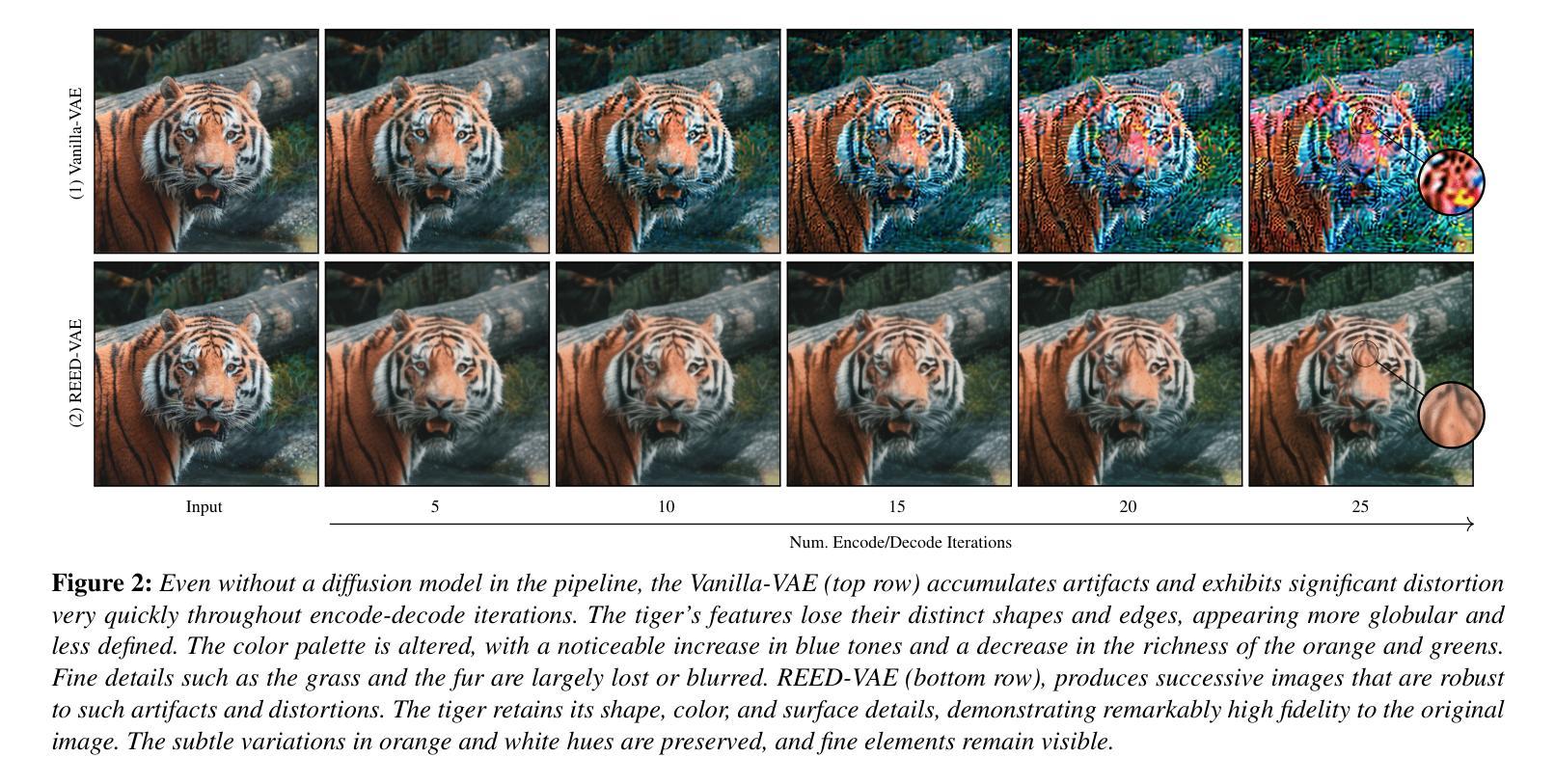
REED-VAE: RE-Encode Decode Training for Iterative Image Editing with Diffusion Models
Authors:Gal Almog, Ariel Shamir, Ohad Fried
While latent diffusion models achieve impressive image editing results, their application to iterative editing of the same image is severely restricted. When trying to apply consecutive edit operations using current models, they accumulate artifacts and noise due to repeated transitions between pixel and latent spaces. Some methods have attempted to address this limitation by performing the entire edit chain within the latent space, sacrificing flexibility by supporting only a limited, predetermined set of diffusion editing operations. We present a RE-encode decode (REED) training scheme for variational autoencoders (VAEs), which promotes image quality preservation even after many iterations. Our work enables multi-method iterative image editing: users can perform a variety of iterative edit operations, with each operation building on the output of the previous one using both diffusion-based operations and conventional editing techniques. We demonstrate the advantage of REED-VAE across a range of image editing scenarios, including text-based and mask-based editing frameworks. In addition, we show how REED-VAE enhances the overall editability of images, increasing the likelihood of successful and precise edit operations. We hope that this work will serve as a benchmark for the newly introduced task of multi-method image editing. Our code and models will be available at https://github.com/galmog/REED-VAE
潜在扩散模型在图像编辑方面取得了令人印象深刻的成果,但它们在相同图像的迭代编辑应用上受到严重限制。当尝试使用当前模型进行连续编辑操作时,由于像素和潜在空间之间的重复转换,它们会积累伪影和噪声。一些方法试图通过仅在潜在空间内执行整个编辑链来解决这一局限性,但只支持有限、预先确定的扩散编辑操作,牺牲了灵活性。我们提出了一种针对变分自编码器(VAE)的RE-encode decode(REED)训练方案,即使在多次迭代后也能促进图像质量保留。我们的工作实现了多方法迭代图像编辑:用户可以进行多种迭代编辑操作,每个操作都以前一个操作的输出为基础,使用基于扩散的操作和常规编辑技术。我们展示了REED-VAE在各种图像编辑场景中的优势,包括基于文本和基于掩码的编辑框架。此外,我们还展示了REED-VAE如何增强图像的整体可编辑性,提高成功和精确编辑操作的可能性。我们希望这项工作能为新引入的多方法图像编辑任务提供基准。我们的代码和模型将在https://github.com/galmog/REED-VAE上提供。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF Accepted to Eurographics 2025. Project page: https://reed-vae.github.io/
Summary:
潜在扩散模型在图像编辑中表现卓越,但在同一图像的迭代编辑方面存在局限。当前模型在连续编辑操作时会产生伪影和噪声。我们提出一种针对变分自动编码器(VAE)的RE-encode decode(REED)训练方案,促进图像质量在多次迭代后的保留,实现多方法迭代图像编辑。此方案使用户可运用多种迭代编辑操作,每次操作基于前一次输出,支持扩散操作和传统编辑技术。REED-VAE在多种图像编辑场景中表现优越,如文本和遮罩编辑框架。它提高了图像的整体可编辑性,增加精确编辑操作的成功率。
Key Takeaways:
- 潜在扩散模型在图像编辑中表现优秀,但迭代编辑存在局限。
- 当前模型在连续编辑操作时会产生伪影和噪声。
- 提出RE-encode decode(REED)训练方案,适用于变分自动编码器(VAE)。
- REED方案促进图像质量在多次迭代后的保留。
- 实现多方法迭代图像编辑,支持扩散操作和传统编辑技术。
- REED-VAE在多种图像编辑场景中表现优越。
- REED-VAE提高了图像的整体可编辑性,增加精确编辑操作的成功率。
点此查看论文截图




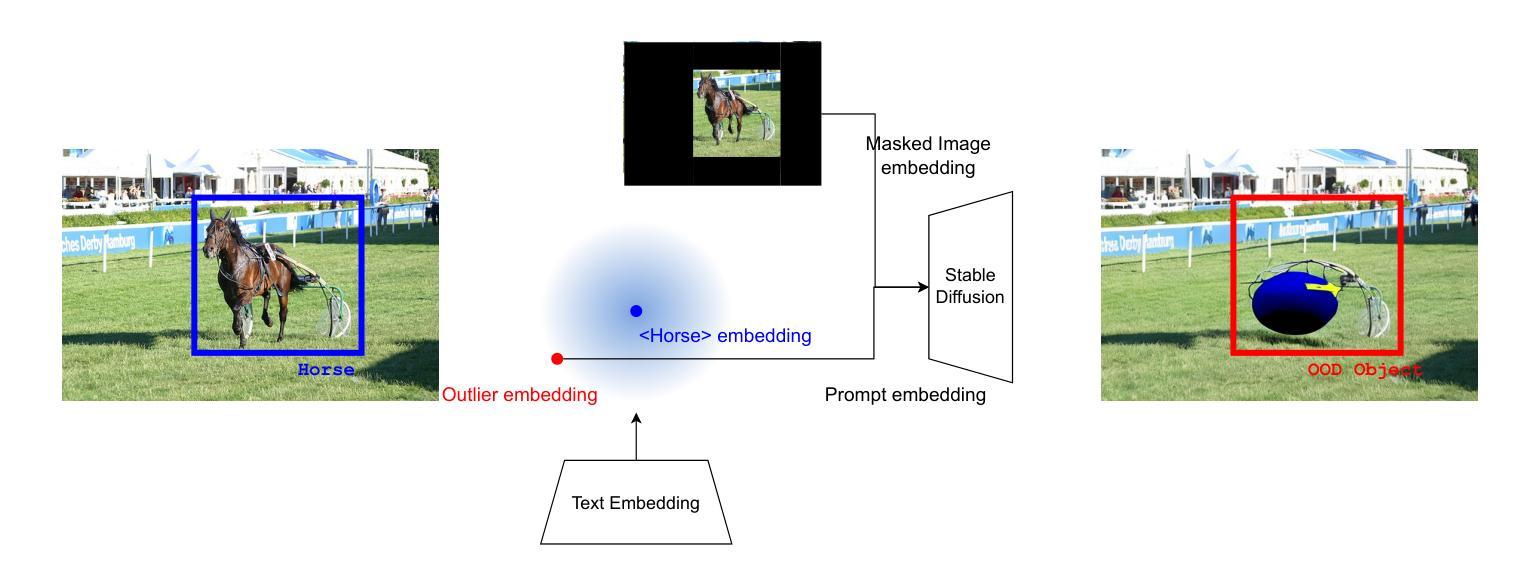
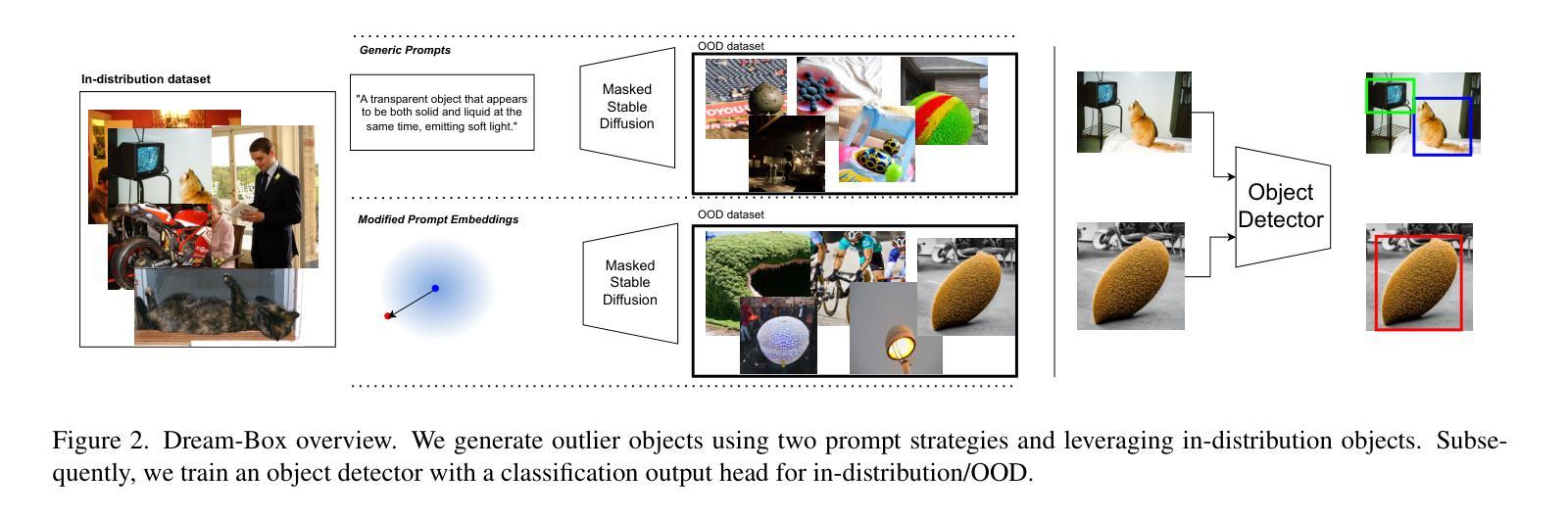
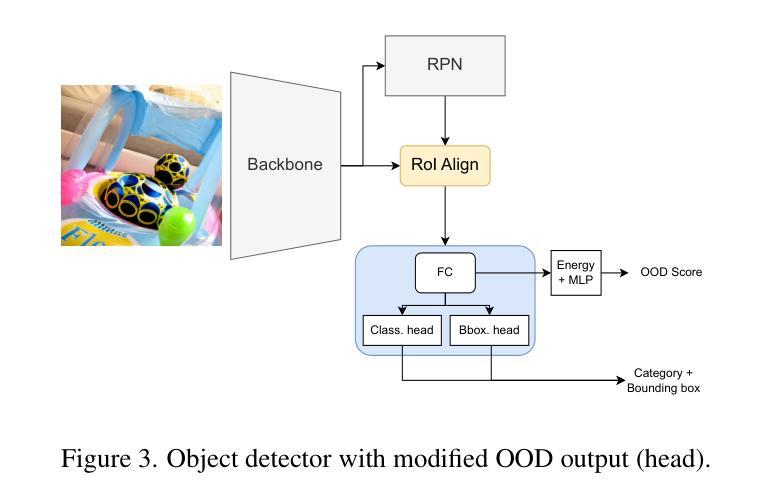
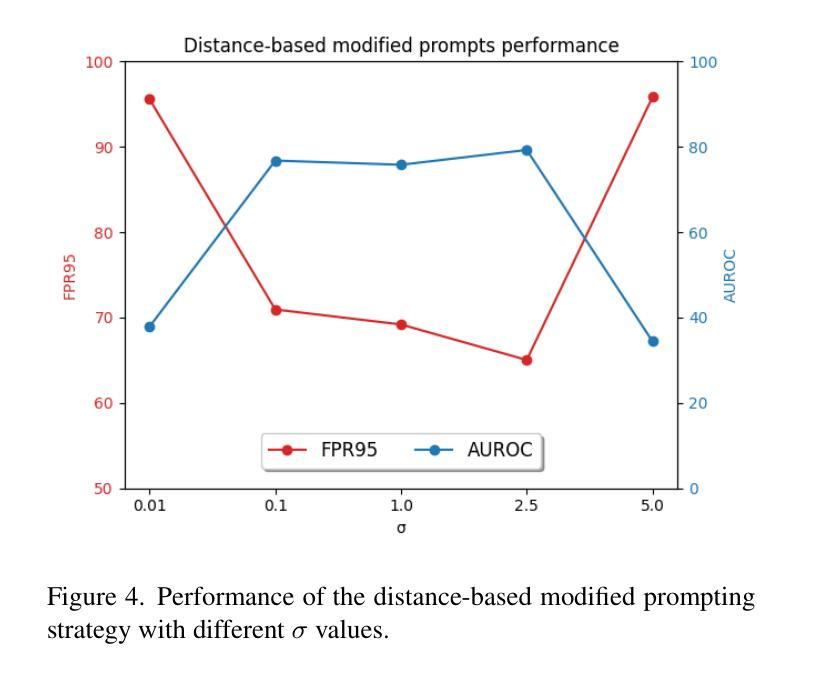
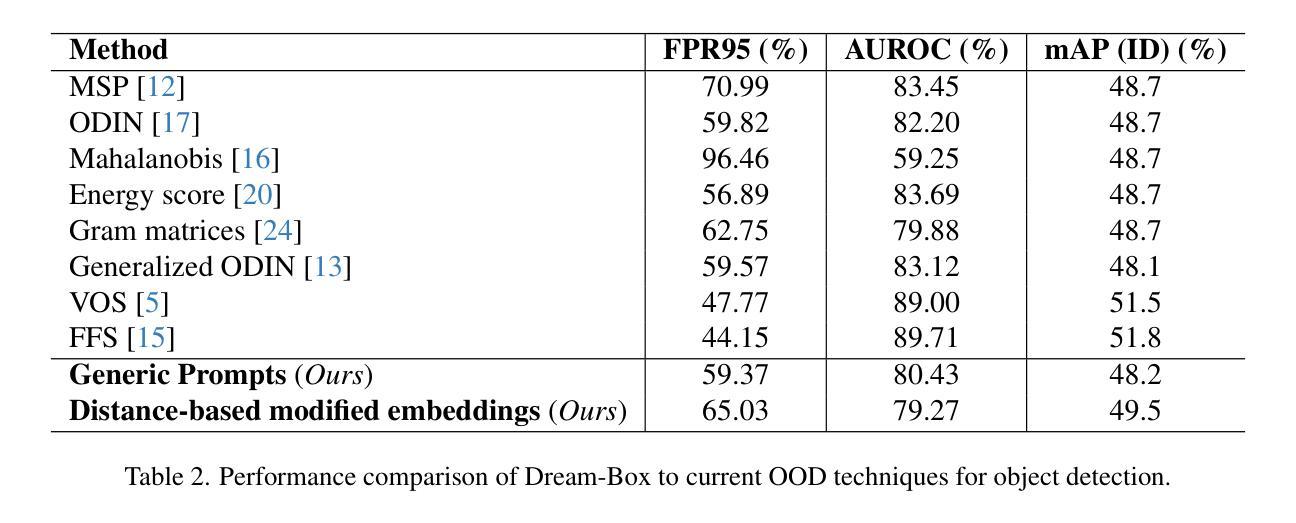
Dream-Box: Object-wise Outlier Generation for Out-of-Distribution Detection
Authors:Brian K. S. Isaac-Medina, Toby P. Breckon
Deep neural networks have demonstrated great generalization capabilities for tasks whose training and test sets are drawn from the same distribution. Nevertheless, out-of-distribution (OOD) detection remains a challenging task that has received significant attention in recent years. Specifically, OOD detection refers to the detection of instances that do not belong to the training distribution, while still having good performance on the in-distribution task (e.g., classification or object detection). Recent work has focused on generating synthetic outliers and using them to train an outlier detector, generally achieving improved OOD detection than traditional OOD methods. In this regard, outliers can be generated either in feature or pixel space. Feature space driven methods have shown strong performance on both the classification and object detection tasks, at the expense that the visualization of training outliers remains unknown, making further analysis on OOD failure modes challenging. On the other hand, pixel space outlier generation techniques enabled by diffusion models have been used for image classification using, providing improved OOD detection performance and outlier visualization, although their adaption to the object detection task is as yet unexplored. We therefore introduce Dream-Box, a method that provides a link to object-wise outlier generation in the pixel space for OOD detection. Specifically, we use diffusion models to generate object-wise outliers that are used to train an object detector for an in-distribution task and OOD detection. Our method achieves comparable performance to previous traditional methods while being the first technique to provide concrete visualization of generated OOD objects.
深度神经网络对于训练和测试集来自同一分布的任务表现出了很强的泛化能力。然而,离群点检测仍然是一个具有挑战性的任务,近年来备受关注。具体来说,离群点检测是指检测不属于训练分布但属于同一分布任务(例如分类或对象检测)的实例,近年来许多研究开始集中在生成合成异常值和使用它们来训练异常检测器,通常比在常规离群点检测方面传统方法达到更好的效果。在这方面,异常值可以在特征空间或像素空间中生成。特征空间驱动的方法在分类和对象检测任务中都显示出强大性能,但以无法可视化训练异常值为代价,这使得对离群点失效模式的进一步分析具有挑战性。另一方面,由扩散模型支持的像素空间异常值生成技术已用于图像分类中,提供改进的异常值检测性能和异常值可视化,尽管它们在对象检测任务上的适应性尚未探索。因此,我们引入了Dream-Box方法,该方法为离群点检测在像素空间中提供了目标相关的异常值生成联系。具体来说,我们使用扩散模型生成目标相关的异常值,用于训练用于内部分布任务和离群点检测的对象检测器。我们的方法与先前的方法相比达到了相当的性能水平,并首次提供了生成对象外统计的具体可视化工具。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF 9 pages, 6 figures, 2 tables, LatinX in AI CVPR 2025 Workshop
Summary
本文介绍了深度神经网络在任务中的优异表现,尤其是在训练和测试集来自同一分布时。然而,对于不属于训练分布但仍在分布内的任务中表现良好的实例(即离群值检测)仍然是一个挑战。近期研究通过生成合成异常值来训练异常检测器,并实现了比传统异常检测方法更好的离群值检测性能。针对特征空间和像素空间生成离群值的方法,特征空间驱动的方法在分类和对象检测任务上表现出强大的性能,但无法可视化训练中的异常值,使得对离群值检测失败模式的进一步分析变得困难。而扩散模型生成的像素空间异常检测技术已经用于图像分类,为对象检测任务的离群值检测提供了新的可能。本研究介绍了一种名为Dream-Box的方法,该方法使用扩散模型生成对象级异常值,用于训练对象检测器进行分布内任务和离群值检测。该方法实现了与传统方法相当的性能,并且是首个提供生成离群对象的可视化技术。
Key Takeaways
- 深度神经网络在训练和测试集来自同一分布的任务中表现出强大的泛化能力。
- 离群值检测(OOD)是一个挑战性问题,指的是检测不属于训练分布但仍属于特定任务分布实例的检测问题。
- 生成合成异常值的近期方法在分类和对象检测任务中表现出优于传统OOD方法的效果。这些方法在特征空间和像素空间中生成异常值,为这些异常值的可视化提供了新的途径。然而特征空间方法的可视化效果有待进一步验证,像素空间方法则具有可视化优势。
- 扩散模型在图像分类中用于生成像素空间的异常值检测取得了显著进展,但对对象检测任务的适应仍是一个新的挑战。为此提出了一种名为Dream-Box的方法,该方法使用扩散模型生成对象级异常值用于训练对象检测器进行OOD检测。
点此查看论文截图


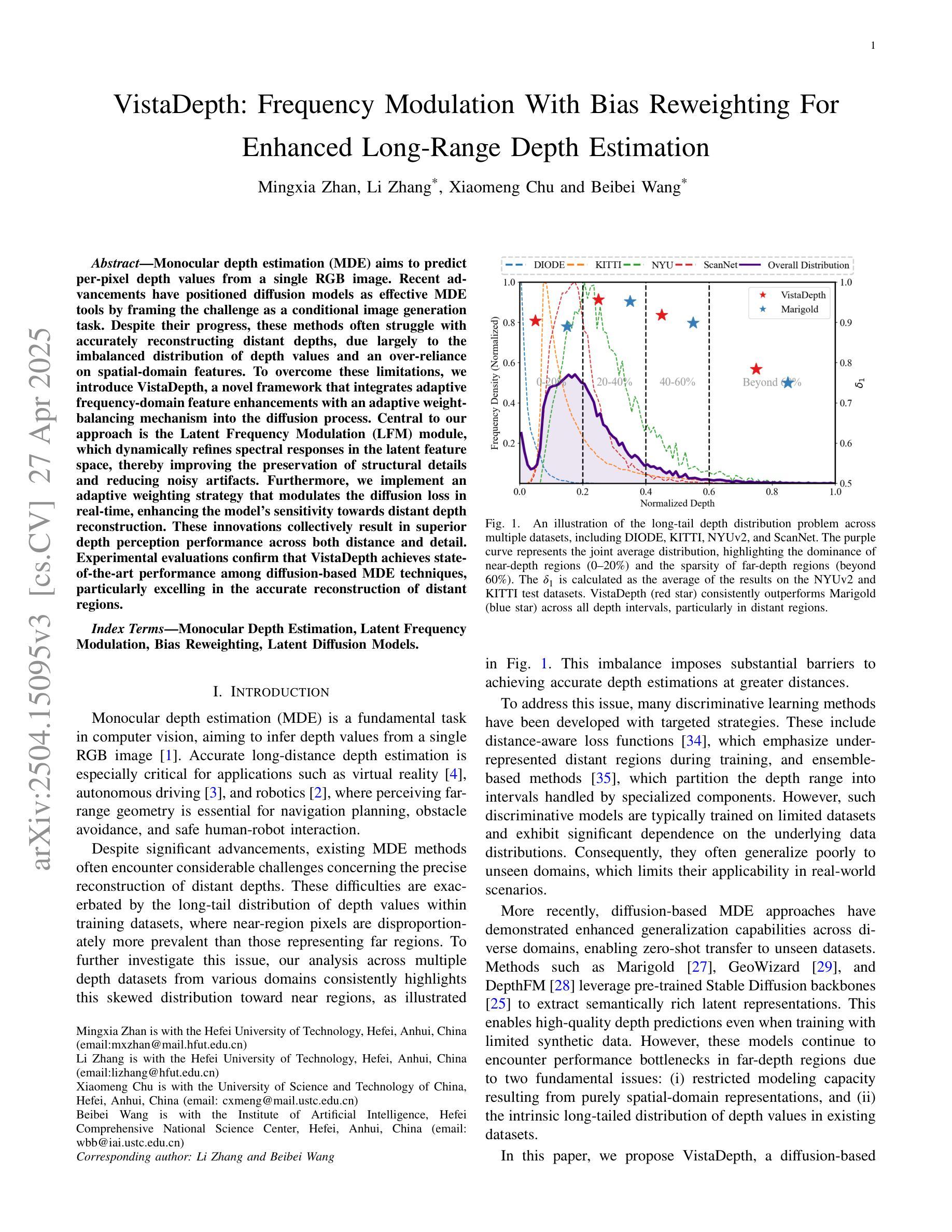
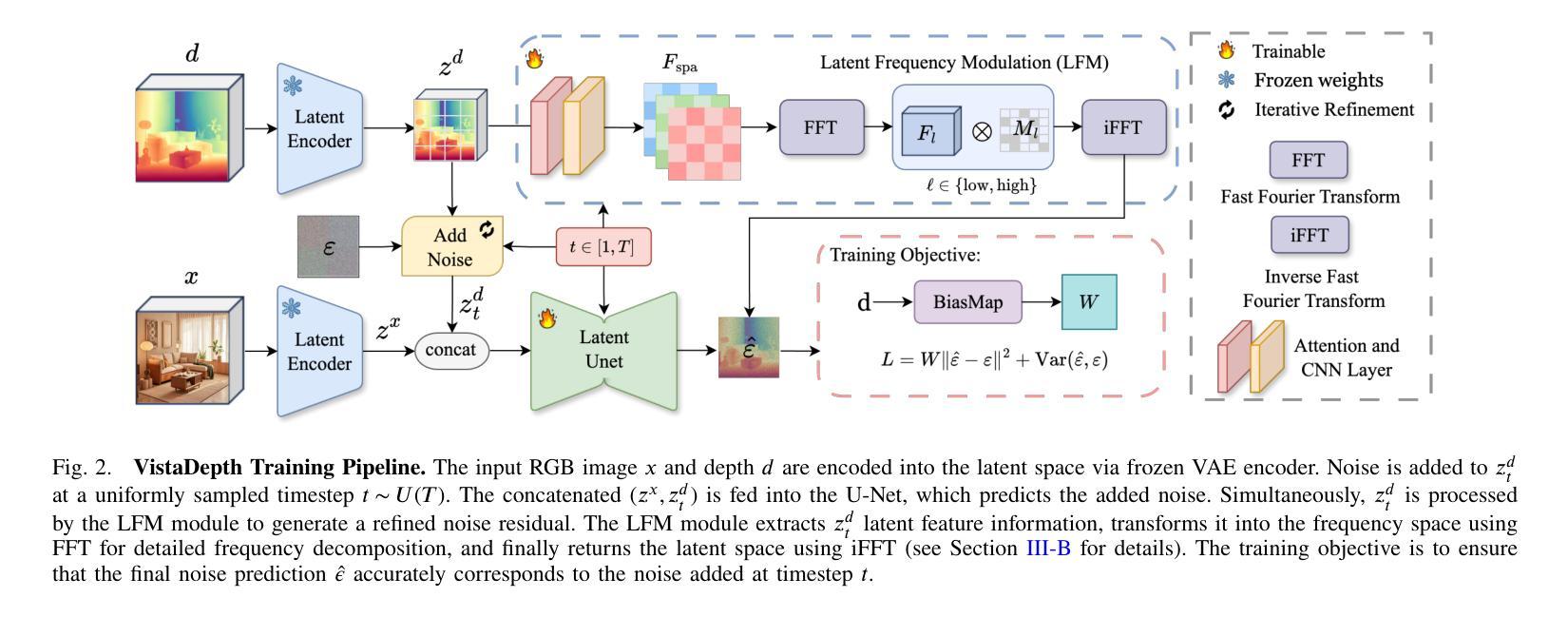
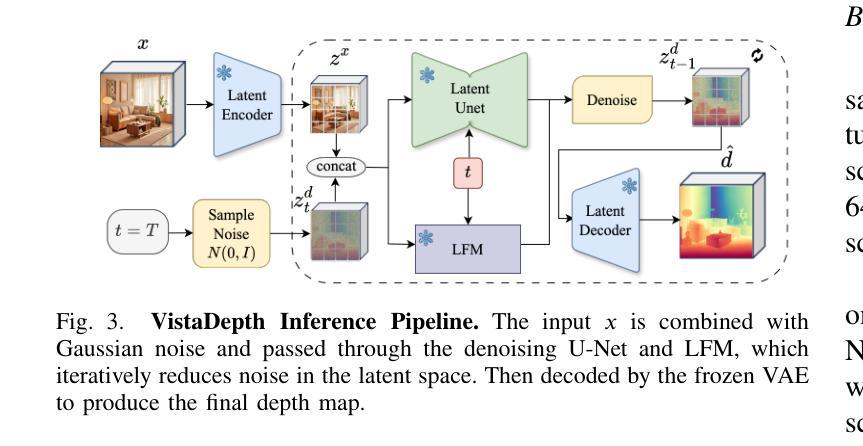
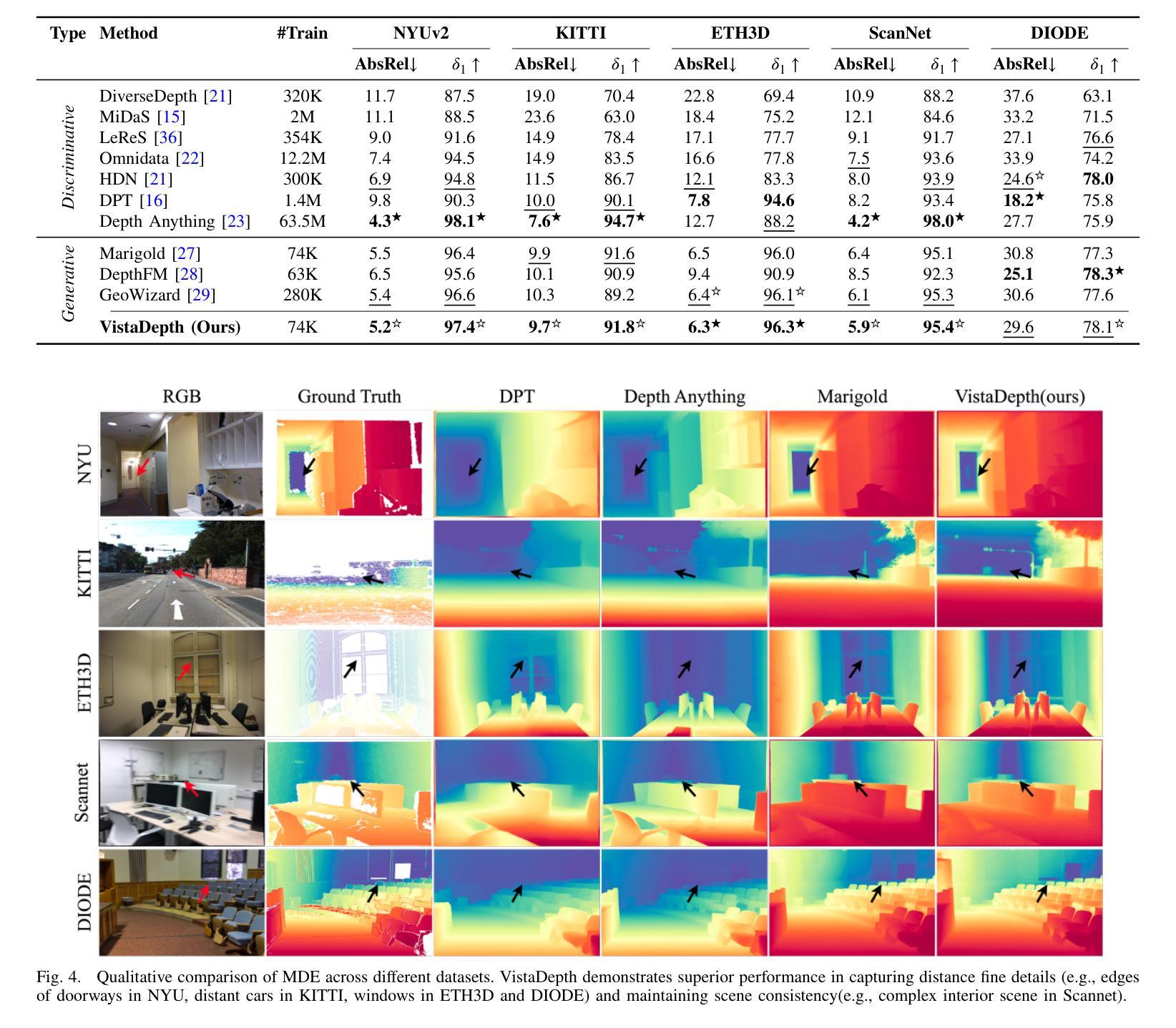
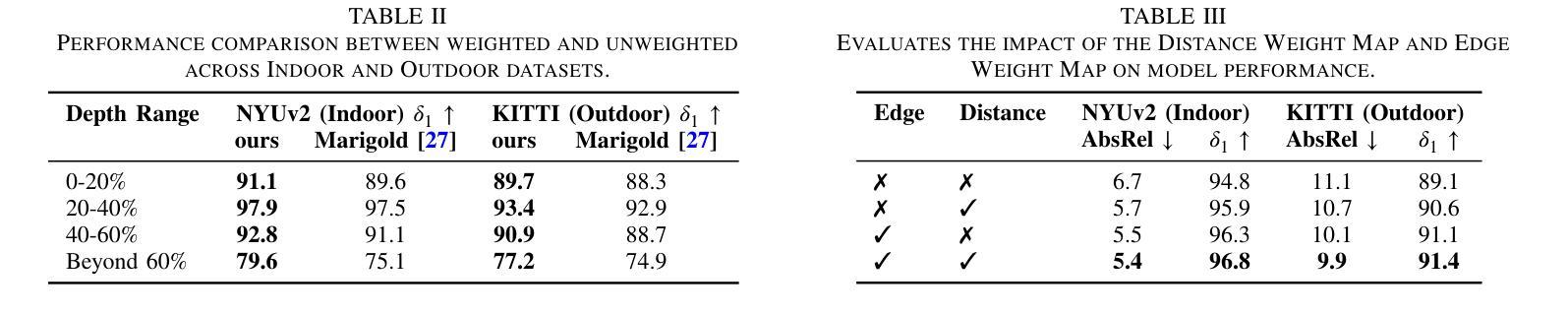
VistaDepth: Frequency Modulation With Bias Reweighting For Enhanced Long-Range Depth Estimation
Authors:Mingxia Zhan, Li Zhang, Xiaomeng Chu, Beibei Wang
Monocular depth estimation (MDE) aims to predict per-pixel depth values from a single RGB image. Recent advancements have positioned diffusion models as effective MDE tools by framing the challenge as a conditional image generation task. Despite their progress, these methods often struggle with accurately reconstructing distant depths, due largely to the imbalanced distribution of depth values and an over-reliance on spatial-domain features. To overcome these limitations, we introduce VistaDepth, a novel framework that integrates adaptive frequency-domain feature enhancements with an adaptive weight-balancing mechanism into the diffusion process. Central to our approach is the Latent Frequency Modulation (LFM) module, which dynamically refines spectral responses in the latent feature space, thereby improving the preservation of structural details and reducing noisy artifacts. Furthermore, we implement an adaptive weighting strategy that modulates the diffusion loss in real-time, enhancing the model’s sensitivity towards distant depth reconstruction. These innovations collectively result in superior depth perception performance across both distance and detail. Experimental evaluations confirm that VistaDepth achieves state-of-the-art performance among diffusion-based MDE techniques, particularly excelling in the accurate reconstruction of distant regions.
单眼深度估计(MDE)旨在从单一RGB图像预测每个像素的深度值。最近的进展将扩散模型定位为有效的MDE工具,将挑战视为条件图像生成任务。尽管有所进展,这些方法在准确重建远距离深度方面往往遇到困难,这主要是因为深度值分布不平衡以及过于依赖空间域特征。为了克服这些局限性,我们引入了VistaDepth,这是一个新型框架,将自适应频域特征增强和自适应权重平衡机制集成到扩散过程中。我们的方法的核心是潜在频率调制(LFM)模块,它动态地优化潜在特征空间中的光谱响应,从而提高结构细节的保留,减少噪声伪影。此外,我们实现了自适应权重策略,以实时调整扩散损失,提高模型对远距离深度重建的敏感性。这些创新共同带来了在距离和细节方面的卓越深度感知性能。实验评估证实,VistaDepth在基于扩散的MDE技术中达到了最先进的性能,特别是在准确重建远距离区域方面表现出色。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF 8 pages, 6 figures, 4 tables
Summary
扩散模型在单目深度估计(MDE)领域展现出强大的潜力,通过将挑战转化为条件图像生成任务。然而,现有方法常面临重建远距离深度不准确的问题。为解决此,VistaDepth框架引入自适应频域特征增强和自适应权重平衡机制。其核心模块——潜在频率调制(LFM)能动态优化潜在特征空间的频谱响应,提升结构细节保留并减少噪声。同时,实施自适应权重策略,实时调整扩散损失,增强模型对远距离深度的敏感性。这些创新共同提升了深度感知性能,在距离和细节上均表现优越。实验评估显示,VistaDepth在基于扩散的MDE技术中达到领先水平,尤其在重建远距离区域方面表现突出。
Key Takeaways
- 扩散模型在单目深度估计中表现出色,通过条件图像生成任务框架应对挑战。
- 现有方法面临重建远距离深度不准确的问题,主要是由于深度值分布不均衡以及过于依赖空间域特征。
- VistaDepth框架通过整合自适应频域特征增强和自适应权重平衡机制来解决这些问题。
- 潜在频率调制(LFM)模块能动态优化潜在特征空间的频谱响应,改善结构细节保留,减少噪声。
- 自适应权重策略实时调整扩散损失,增强模型对远距离深度的敏感性。
- 这些创新共同提升了深度感知性能,在距离和细节上均有所突破。
点此查看论文截图
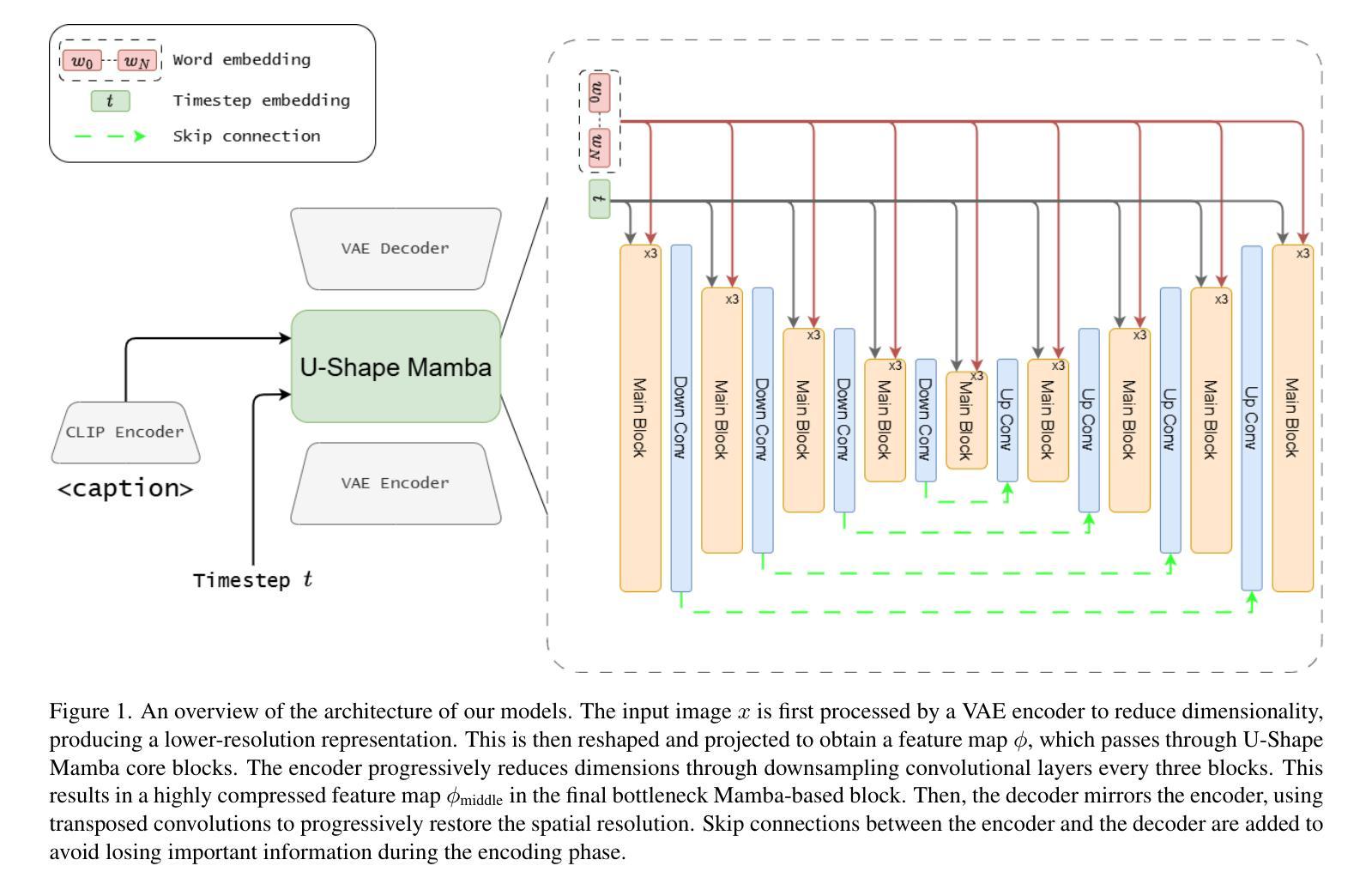
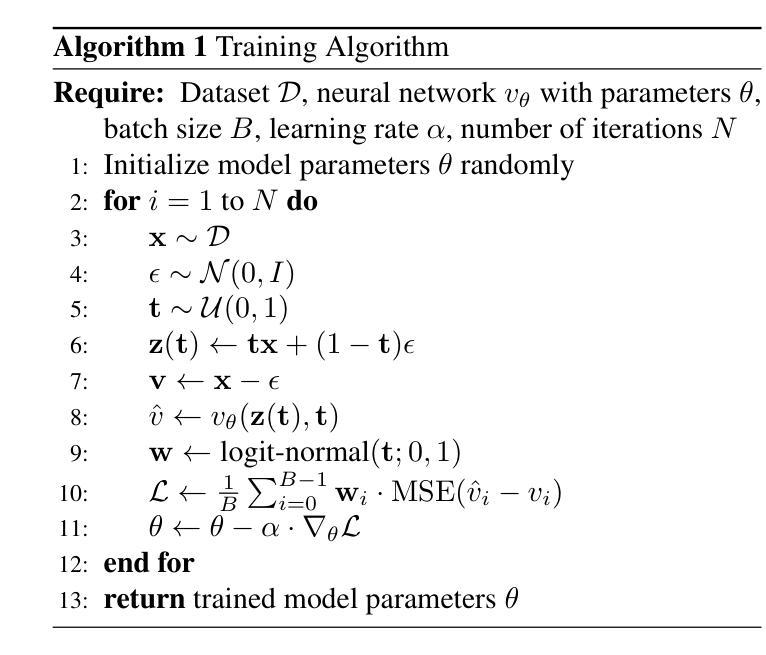
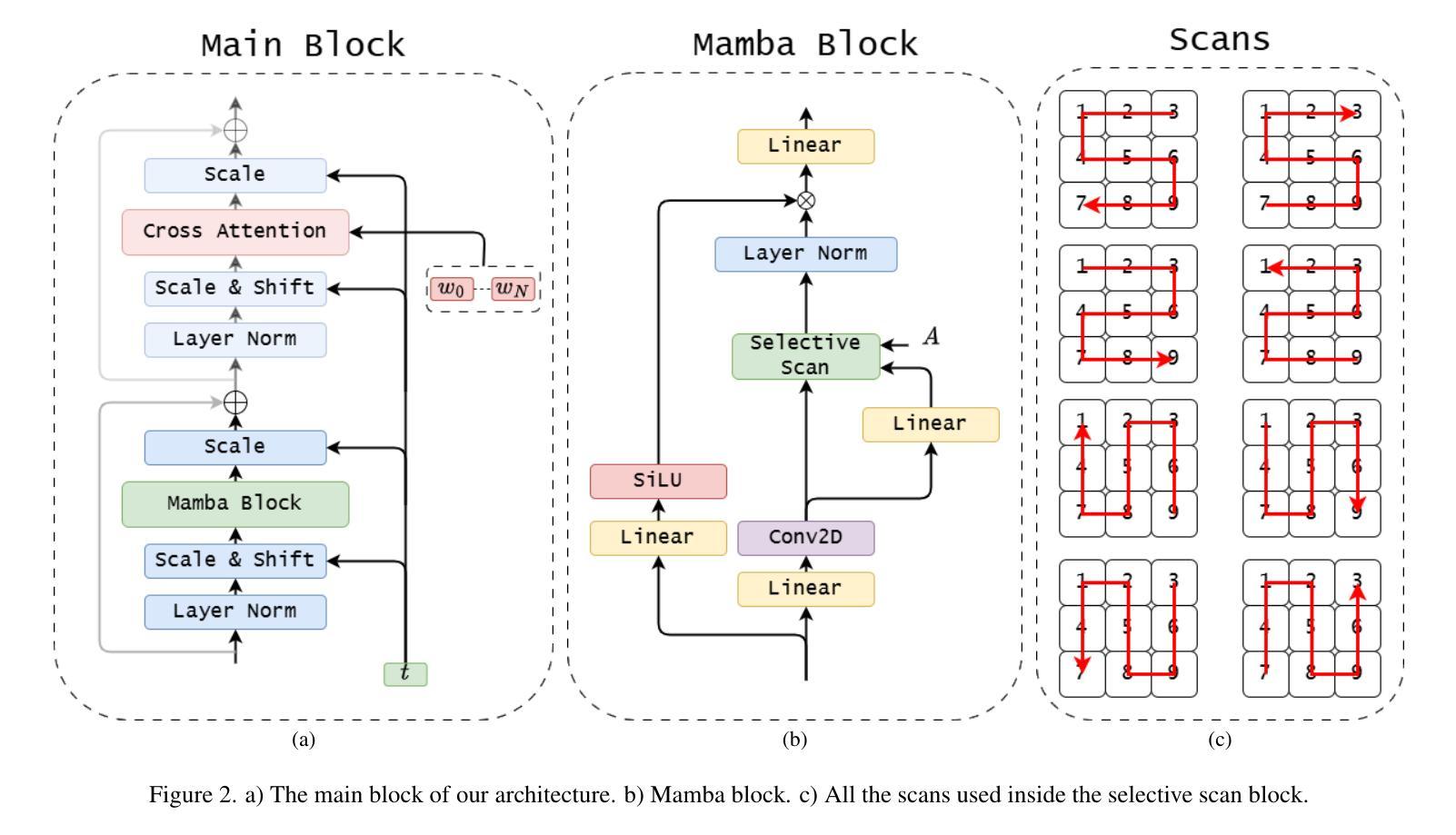
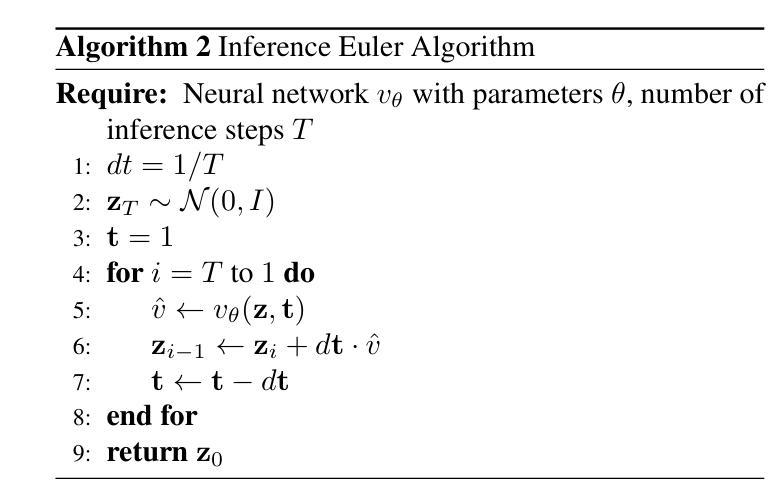
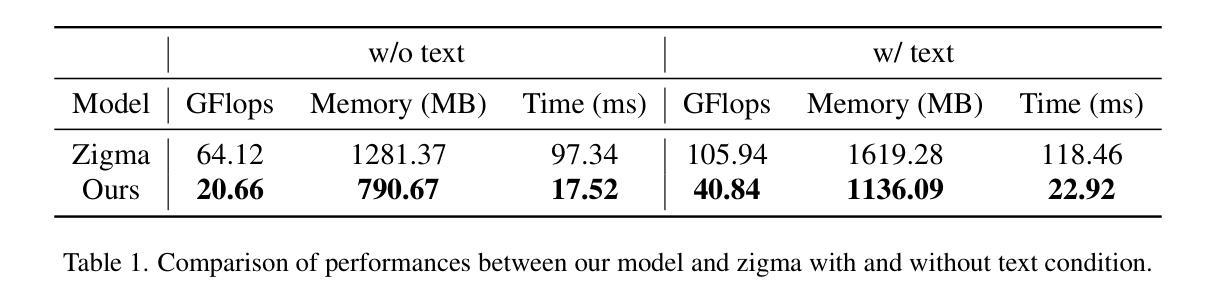
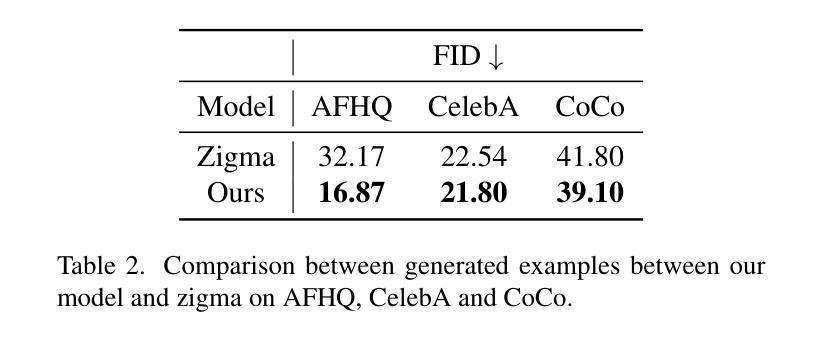
U-Shape Mamba: State Space Model for faster diffusion
Authors:Alex Ergasti, Filippo Botti, Tomaso Fontanini, Claudio Ferrari, Massimo Bertozzi, Andrea Prati
Diffusion models have become the most popular approach for high-quality image generation, but their high computational cost still remains a significant challenge. To address this problem, we propose U-Shape Mamba (USM), a novel diffusion model that leverages Mamba-based layers within a U-Net-like hierarchical structure. By progressively reducing sequence length in the encoder and restoring it in the decoder through Mamba blocks, USM significantly lowers computational overhead while maintaining strong generative capabilities. Experimental results against Zigma, which is currently the most efficient Mamba-based diffusion model, demonstrate that USM achieves one-third the GFlops, requires less memory and is faster, while outperforming Zigma in image quality. Frechet Inception Distance (FID) is improved by 15.3, 0.84 and 2.7 points on AFHQ, CelebAHQ and COCO datasets, respectively. These findings highlight USM as a highly efficient and scalable solution for diffusion-based generative models, making high-quality image synthesis more accessible to the research community while reducing computational costs.
扩散模型已成为高质量图像生成的最流行方法,但其高计算成本仍然是一个巨大的挑战。为了解决这个问题,我们提出了U形Mamba(USM),这是一种新型的扩散模型,它利用基于Mamba的层次结构内的U-Net结构。通过逐步减少编码器中的序列长度并在解码器通过Mamba块进行恢复,USM在保持强大的生成能力的同时显著降低了计算开销。与目前基于Mamba的最有效的Zigma模型的实验对比表明,USM实现了三分之一GFLOPS,内存需求更少且速度更快,同时在图像质量上优于Zigma。在AFHQ、CelebAHQ和COCO数据集上,Frechet Inception Distance(FID)分别提高了15.3、0.84和2.7点。这些发现突出了USM作为基于扩散的生成模型的高效且可扩展的解决方案,使高质量图像合成更容易为研究领域所获取,同时降低了计算成本。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF Accepted at CVPR 2025 eLVM workshop. The code is here: https://github.com/ErgastiAlex/U-Shape-Mamba
Summary
扩散模型在高质量图像生成中备受欢迎,但其高计算成本仍是重大挑战。为解决此问题,我们提出了U-Shape Mamba(USM),这是一种新型的扩散模型,它利用基于Mamba的层次结构内的U-Net样结构。通过逐步减少编码器中的序列长度并在解码器中恢复,USM在降低计算开销的同时保持了强大的生成能力。与当前最有效的基于Mamba的扩散模型Zigma相比,实验结果表明,USM实现了三分之一GFLOPS,内存需求更少,速度更快,同时在图像质量上优于Zigma。在AFHQ、CelebAHQ和COCO数据集上,Frechet Inception Distance(FID)分别提高了15.3、0.84和2.7点。这些发现突显了USM作为扩散生成模型的高效可伸缩解决方案,使高质量图像合成更容易为研究领域所接受,同时降低了计算成本。
Key Takeaways
- 扩散模型在图像生成中受到欢迎,但计算成本高昂仍是挑战。
- 提出U-Shape Mamba(USM)模型,结合Mamba-based层和U-Net结构以降低成本。
- USM通过减少编码器中的序列长度并增加解码器中的恢复来降低计算开销。
- 与现有模型Zigma相比,USM在计算效率、内存使用和速度方面表现更优秀。
- USM在维持低计算成本的同时,提高了图像质量,优于Zigma。
- 在多个数据集上的Frechet Inception Distance(FID)指标显示USM性能显著提高。
点此查看论文截图


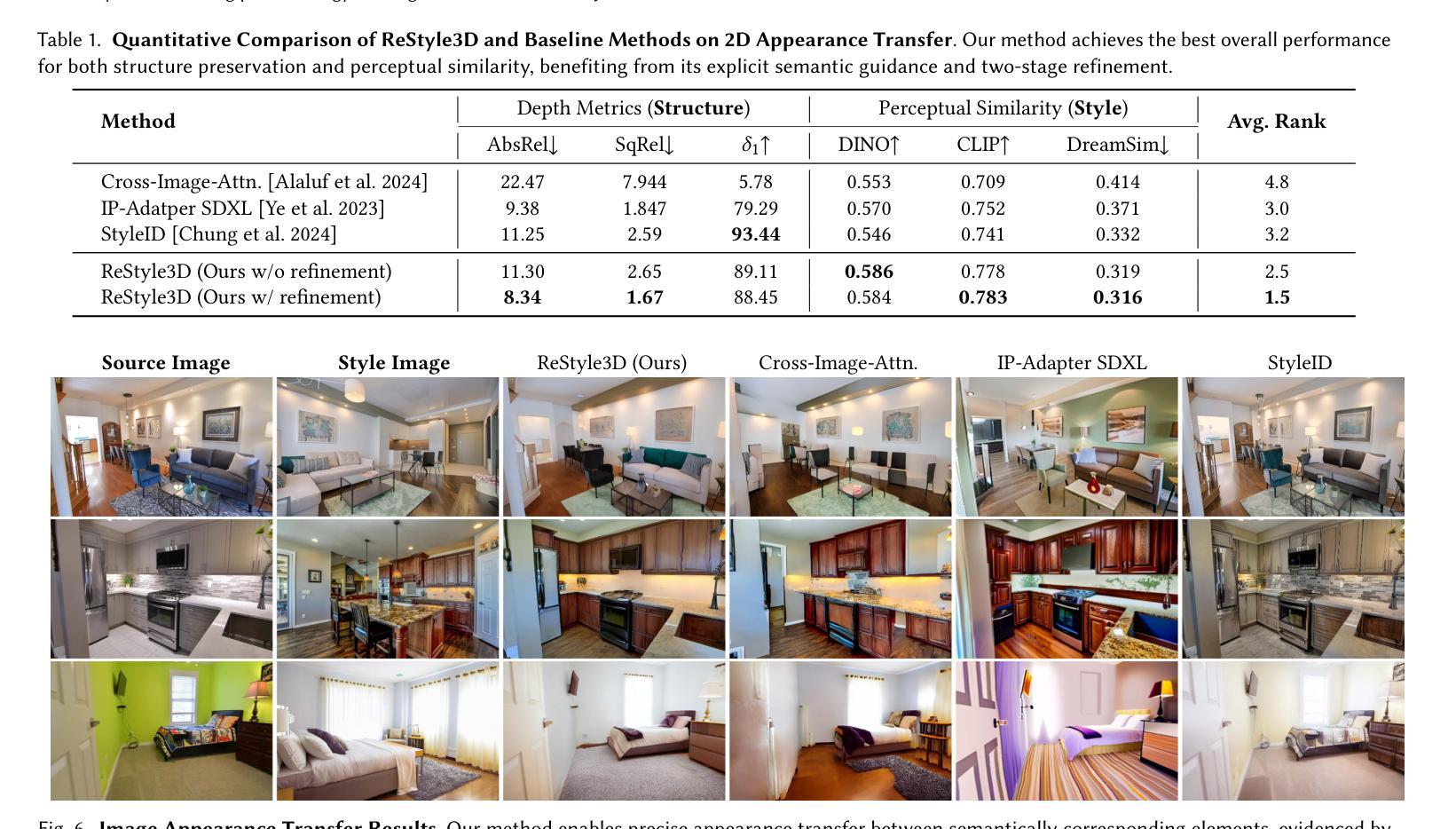
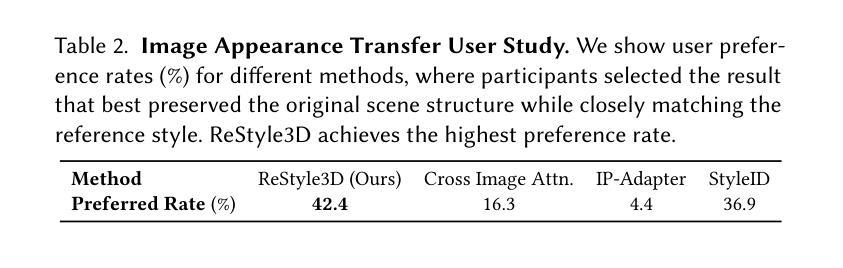
ReStyle3D: Scene-Level Appearance Transfer with Semantic Correspondences
Authors:Liyuan Zhu, Shengqu Cai, Shengyu Huang, Gordon Wetzstein, Naji Khosravan, Iro Armeni
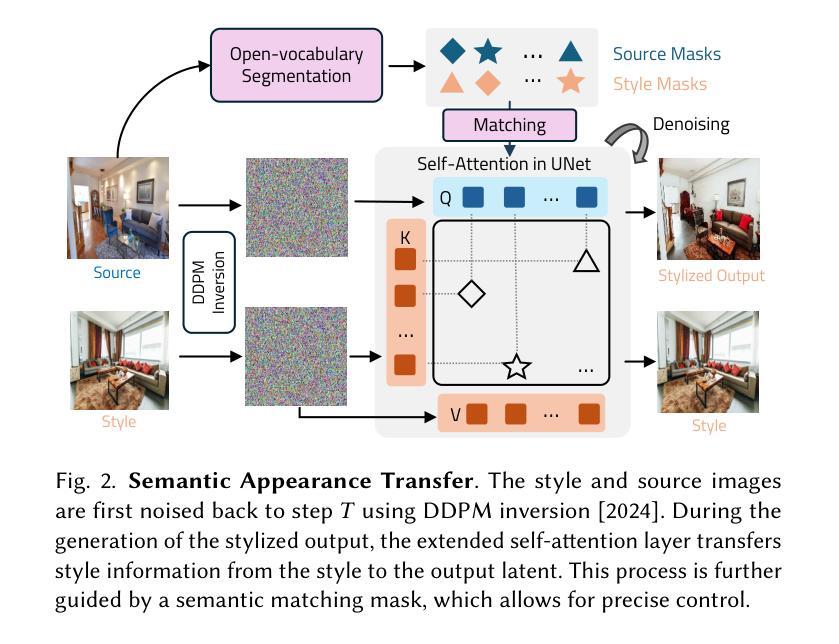
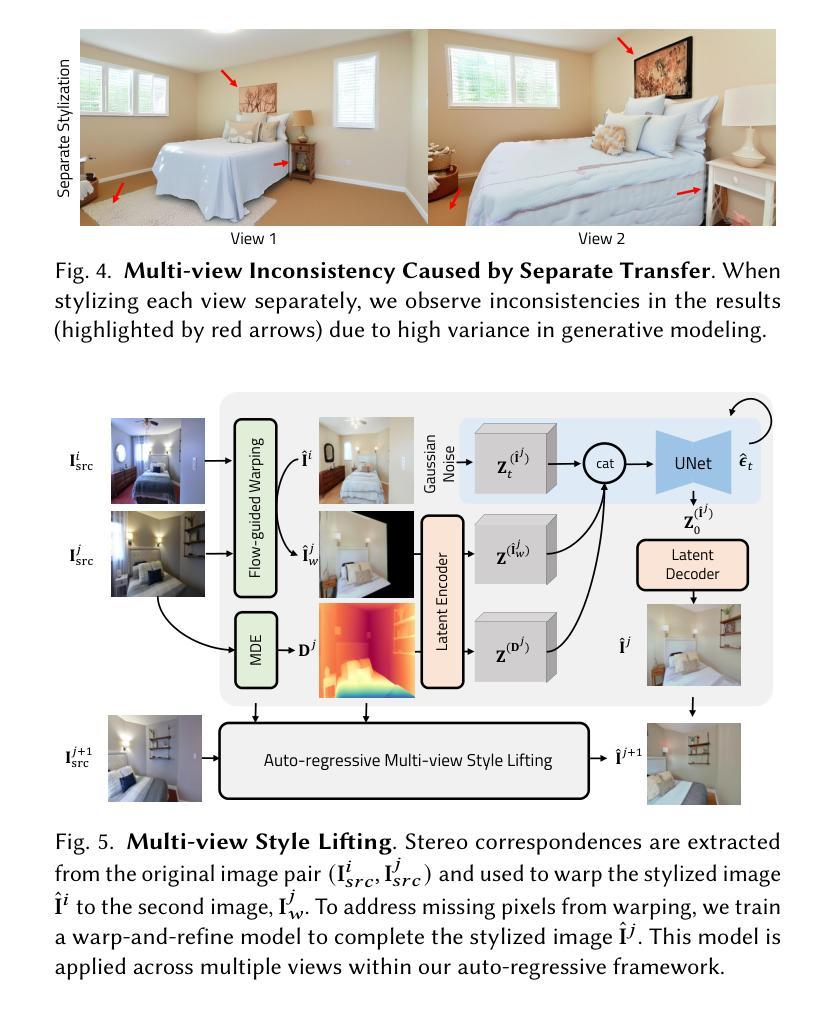
We introduce ReStyle3D, a novel framework for scene-level appearance transfer from a single style image to a real-world scene represented by multiple views. The method combines explicit semantic correspondences with multi-view consistency to achieve precise and coherent stylization. Unlike conventional stylization methods that apply a reference style globally, ReStyle3D uses open-vocabulary segmentation to establish dense, instance-level correspondences between the style and real-world images. This ensures that each object is stylized with semantically matched textures. It first transfers the style to a single view using a training-free semantic-attention mechanism in a diffusion model. It then lifts the stylization to additional views via a learned warp-and-refine network guided by monocular depth and pixel-wise correspondences. Experiments show that ReStyle3D consistently outperforms prior methods in structure preservation, perceptual style similarity, and multi-view coherence. User studies further validate its ability to produce photo-realistic, semantically faithful results. Our code, pretrained models, and dataset will be publicly released, to support new applications in interior design, virtual staging, and 3D-consistent stylization.
我们介绍了ReStyle3D,这是一个新的场景级外观转换框架,它可以从单个风格图像将风格应用到现实世界场景,该场景由多个视图表示。该方法结合了明确的语义对应和多视图一致性,以实现精确和连贯的风格化。与传统的全局应用参考风格的方法不同,ReStyle3D使用开放词汇分割来在风格图像和真实世界图像之间建立密集、实例级的对应。这确保每个对象都用语义匹配的纹理进行风格化。它首先使用扩散模型中的无训练语义注意力机制将风格转移到单个视图。然后,通过由单眼深度和像素级对应引导的学习warp-and-refine网络,将风格化提升到其他视图。实验表明,ReStyle3D在结构保持、感知风格相似性和多视图一致性方面均优于以前的方法。用户研究进一步验证了其生成具有真实感和语义忠实结果的能力。我们的代码、预训练模型和数据集将公开发布,以支持室内设计、虚拟舞台和3D一致风格化的新应用。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF SIGGRAPH 2025. Project page: https://restyle3d.github.io/
Summary
ReStyle3D是一种新颖的场景级风格转换框架,可从单个风格图像对现实世界场景进行风格转换,该场景由多个视图表示。结合显式语义对应和多视图一致性,实现精确和连贯的风格化。不同于传统全局应用参考风格的方法,ReStyle3D使用开放词汇分割在风格图像和真实世界图像之间建立密集、实例级的对应,确保每个对象都用语义匹配的纹理进行风格化。首先,通过扩散模型中的无训练语义注意力机制将风格转移到单个视图上,然后通过以单目深度和像素级对应为指导的学习warp-and-refine网络将风格化提升到其他视图。实验表明,ReStyle3D在结构保持、感知风格相似性和多视图一致性方面均优于先前的方法。用户研究进一步验证了其在生成逼真、语义忠实结果方面的能力。
Key Takeaways
- ReStyle3D是一个场景级风格转换框架,能够实现从单个风格图像到多视图现实场景的转换。
- 该方法结合显式语义对应和多视图一致性,实现精确和连贯的风格化。
- ReStyle3D使用开放词汇分割建立密集、实例级的风格图像和真实世界图像之间的对应。
- 通过扩散模型中的无训练语义注意力机制,ReStyle3D首先将风格转移到单个视图上。
- 通过学习warp-and-refine网络,ReStyle3D能够将风格化扩展到其他视图。
- 实验表明,ReStyle3D在结构保持、感知风格相似性和多视图一致性方面表现优异。
点此查看论文截图


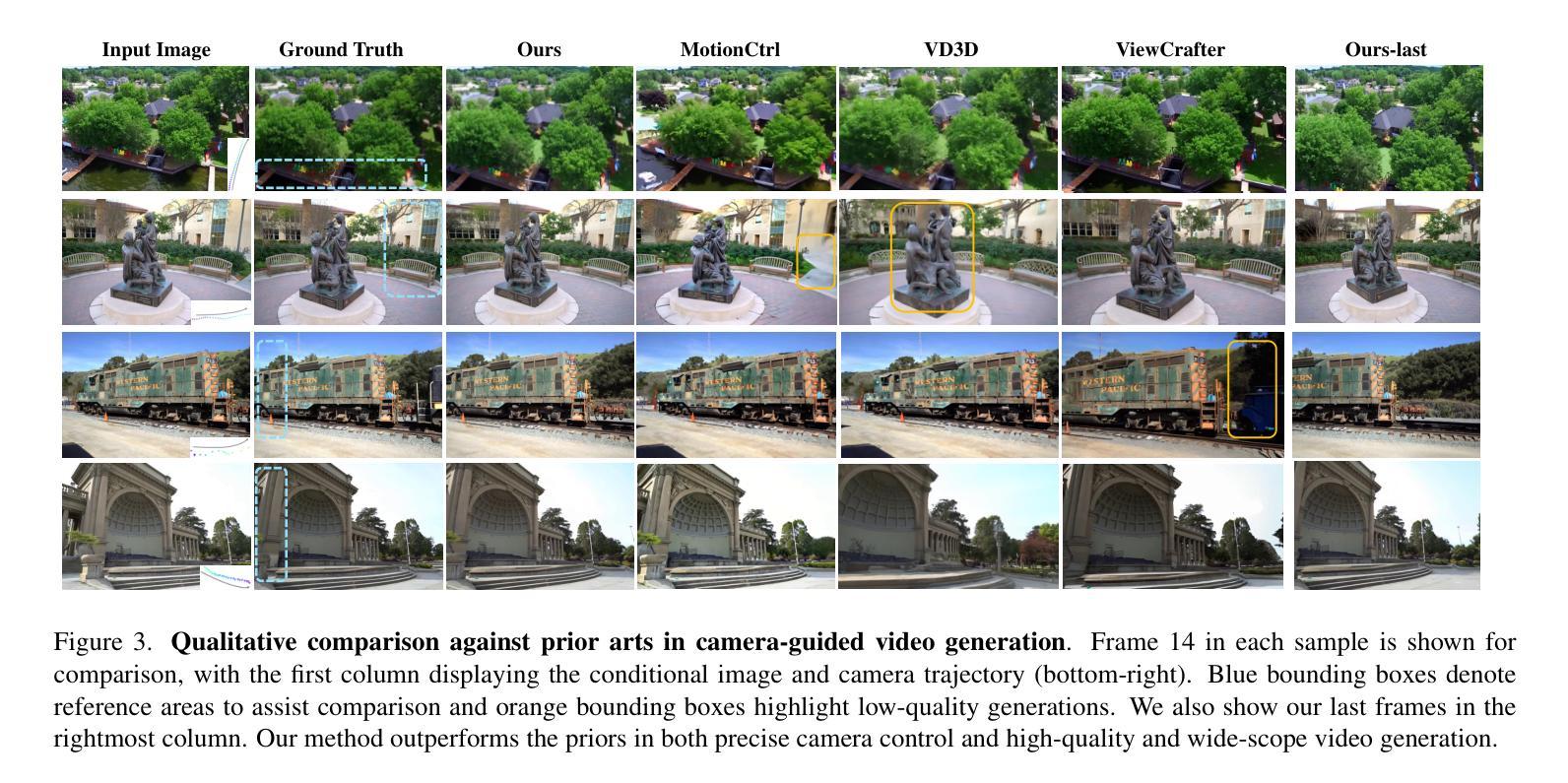
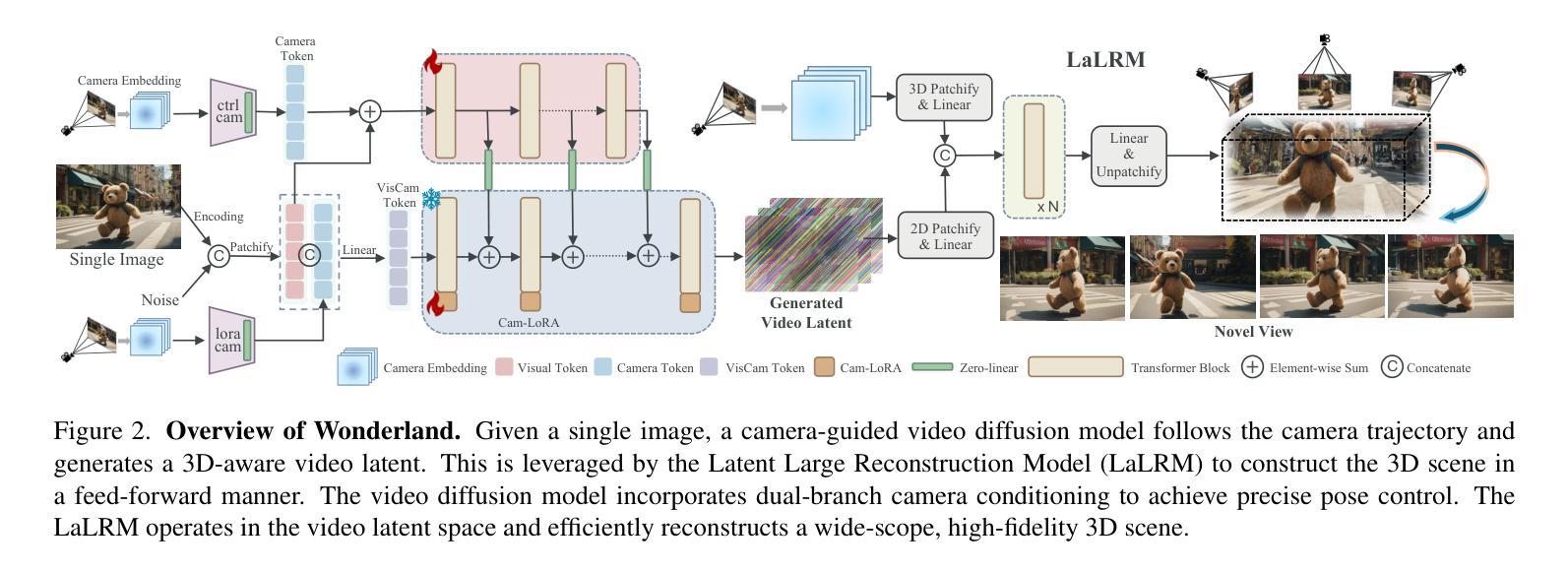
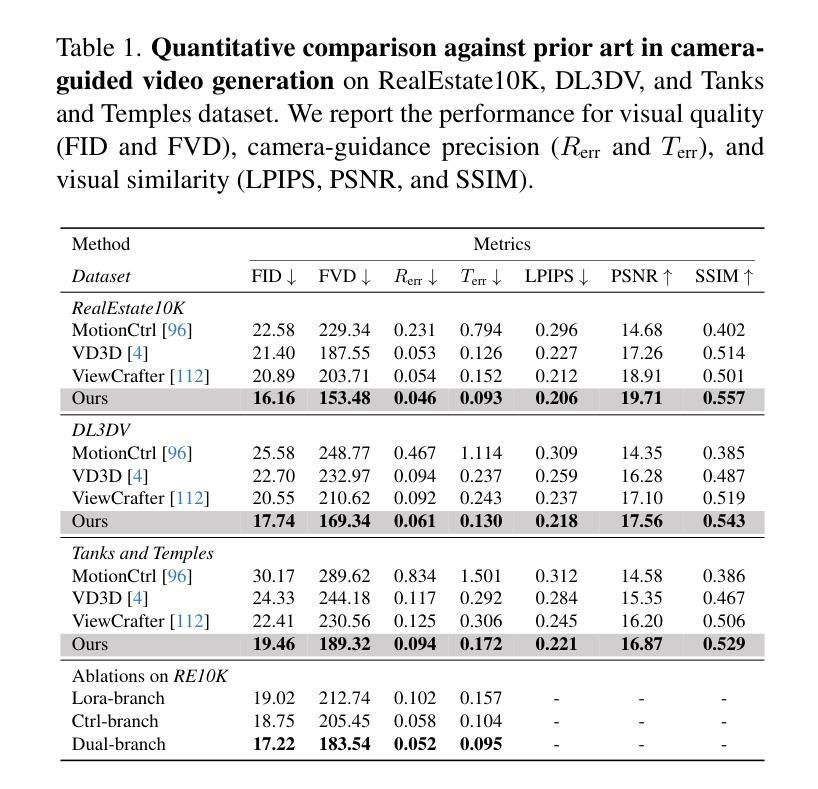
Wonderland: Navigating 3D Scenes from a Single Image
Authors:Hanwen Liang, Junli Cao, Vidit Goel, Guocheng Qian, Sergei Korolev, Demetri Terzopoulos, Konstantinos N. Plataniotis, Sergey Tulyakov, Jian Ren
How can one efficiently generate high-quality, wide-scope 3D scenes from arbitrary single images? Existing methods suffer several drawbacks, such as requiring multi-view data, time-consuming per-scene optimization, distorted geometry in occluded areas, and low visual quality in backgrounds. Our novel 3D scene reconstruction pipeline overcomes these limitations to tackle the aforesaid challenge. Specifically, we introduce a large-scale reconstruction model that leverages latents from a video diffusion model to predict 3D Gaussian Splattings of scenes in a feed-forward manner. The video diffusion model is designed to create videos precisely following specified camera trajectories, allowing it to generate compressed video latents that encode multi-view information while maintaining 3D consistency. We train the 3D reconstruction model to operate on the video latent space with a progressive learning strategy, enabling the efficient generation of high-quality, wide-scope, and generic 3D scenes. Extensive evaluations across various datasets affirm that our model significantly outperforms existing single-view 3D scene generation methods, especially with out-of-domain images. Thus, we demonstrate for the first time that a 3D reconstruction model can effectively be built upon the latent space of a diffusion model in order to realize efficient 3D scene generation.
如何从任意单张图像高效生成高质量、大范围的三维场景?现有方法存在诸多缺点,例如需要多视角数据、耗时的场景优化、遮挡区域的失真几何以及背景的低视觉质量。我们的新型三维场景重建流程克服了这些限制,以应对上述挑战。具体来说,我们引入了一种大规模重建模型,该模型以视频扩散模型的潜在特征为基础,以前馈方式预测场景的三维高斯Splattings。视频扩散模型的设计旨在精确遵循指定的相机轨迹创建视频,使其能够生成压缩的视频潜在特征,在编码多视角信息的同时保持三维一致性。我们采用渐进学习策略对三维重建模型进行训练,使其能够在视频潜在空间上运行,从而能够高效生成高质量、大范围且通用的三维场景。在多个数据集上的广泛评估证实,我们的模型在单视图三维场景生成方面显著优于现有方法,特别是在域外图像上。因此,我们首次证明,可以在扩散模型的潜在空间上建立三维重建模型,以实现高效的三维场景生成。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF Project page: https://snap-research.github.io/wonderland/
Summary
本文介绍了一种基于视频扩散模型的3D场景重建方法,解决了从任意单图像高效生成高质量、大范围3D场景的问题。该方法利用视频扩散模型的潜在特征预测场景的3D高斯Splattings,以生成具有多视角信息的压缩视频潜在特征并保持3D一致性。采用渐进学习策略训练3D重建模型,使其能在视频潜在空间上操作,实现高效、高质量、通用性强的大范围3D场景生成。实验表明,该模型显著优于现有单视角3D场景生成方法,尤其是处理非域图像时表现更佳。首次展示了在扩散模型的潜在空间上构建有效的3D重建模型,可实现高效的3D场景生成。
Key Takeaways
- 介绍了一种基于视频扩散模型的3D场景重建方法,旨在从任意单图像生成高质量、大范围3D场景。
- 利用视频扩散模型的潜在特征预测场景的3D高斯Splattings,实现多视角信息的压缩视频潜在特征并保持3D一致性。
- 采用渐进学习策略训练的3D重建模型能够在视频潜在空间上操作,提高了生成效率和质量。
- 该模型显著优于现有单视角3D场景生成方法,特别是在处理非域图像时表现更佳。
- 首次展示了结合扩散模型的潜在空间构建有效的3D重建模型,为高效生成高质量3D场景提供了新的途径。
- 该方法具有广泛的应用前景,可应用于虚拟现实、增强现实、游戏开发等领域。
点此查看论文截图


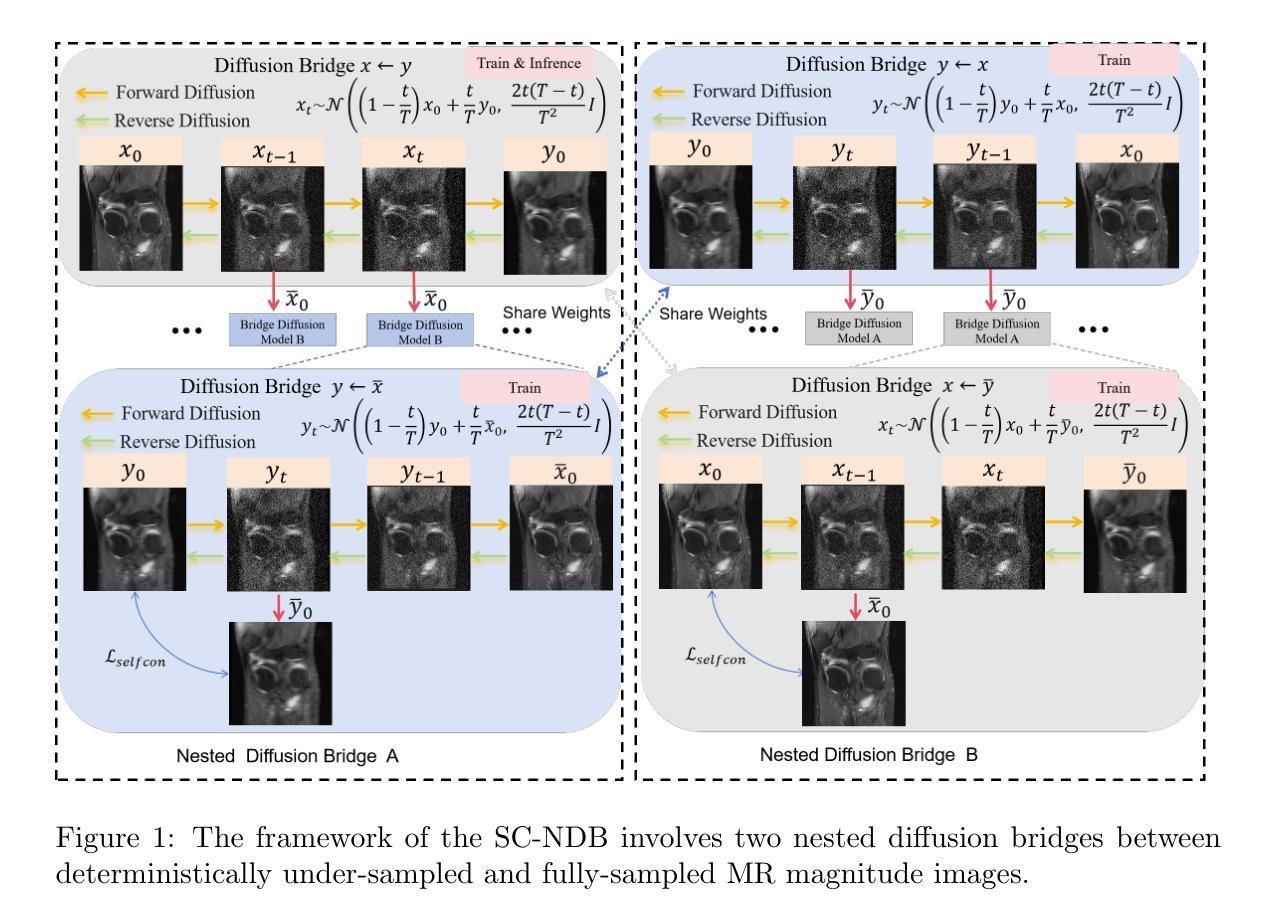
Self-Consistent Nested Diffusion Bridge for Accelerated MRI Reconstruction
Authors:Tao Song, Yicheng Wu, Minhao Hu, Xiangde Luo, Guoting Luo, Guotai Wang, Yi Guo, Feng Xu, Shaoting Zhang
Accelerated MRI reconstruction plays a vital role in reducing scan time while preserving image quality. While most existing methods rely on complex-valued image-space or k-space data, these formats are often inaccessible in clinical practice due to proprietary reconstruction pipelines, leaving only magnitude images stored in DICOM files. To address this gap, we focus on the underexplored task of magnitude-image-based MRI reconstruction. Recent advancements in diffusion models, particularly denoising diffusion probabilistic models (DDPMs), have demonstrated strong capabilities in modeling image priors. However, their task-agnostic denoising nature limits performance in source-to-target image translation tasks, such as MRI reconstruction. In this work, we propose a novel Self-Consistent Nested Diffusion Bridge (SC-NDB) framework that models accelerated MRI reconstruction as a bi-directional image translation process between under-sampled and fully-sampled magnitude MRI images. SC-NDB introduces a nested diffusion architecture with a self-consistency constraint and reverse bridge diffusion pathways to improve intermediate prediction fidelity and better capture the explicit priors of source images. Furthermore, we incorporate a Contour Decomposition Embedding Module (CDEM) to inject structural and textural knowledge by leveraging Laplacian pyramids and directional filter banks. Extensive experiments on the fastMRI and IXI datasets demonstrate that our method achieves state-of-the-art performance compared to both magnitude-based and non-magnitude-based diffusion models, confirming the effectiveness and clinical relevance of SC-NDB.
加速MRI重建在减少扫描时间的同时保持图像质量方面起着至关重要的作用。虽然现有的大多数方法都依赖于复数值图像空间或k空间数据,但这些格式由于专有重建管道而在临床实践中往往无法访问,只留下以DICOM文件存储的幅度图像。为了弥补这一空白,我们专注于基于幅度图像的MRI重建这一尚未得到充分研究的任务。扩散模型的最新进展,特别是去噪扩散概率模型(DDPMs),在建模图像先验方面表现出强大的能力。然而,其任务无关的去噪性质限制了其在源到目标图像翻译任务(例如MRI重建)中的性能。在这项工作中,我们提出了一种新型的Self-Consistent Nested Diffusion Bridge(SC-NDB)框架,将加速MRI重建建模为欠采样幅度MRI图像与全采样幅度MRI图像之间的双向图像翻译过程。SC-NDB引入了一种带有自一致性约束和反向桥扩散路径的嵌套扩散架构,以提高中间预测保真度并更好地捕获源图像的显式先验。此外,我们结合了一个轮廓分解嵌入模块(CDEM),通过利用拉普拉斯金字塔和方向滤波器库来注入结构和纹理知识。在fastMRI和IXI数据集上的广泛实验表明,我们的方法相较于基于幅度和非基于幅度的扩散模型达到了最先进的性能,证实了SC-NDB的有效性和临床相关性。
论文及项目相关链接
摘要
本研究针对加速MRI重建问题,提出了一种基于扩散模型的新方法。考虑到现有方法主要依赖复杂值图像空间或k空间数据,而临床实践中常因专有重建流程只能获取到DICOM文件中的幅度图像,本研究专注于基于幅度图像的MRI重建这一未充分研究的问题。采用自洽嵌套扩散桥(SC-NDB)框架,将加速MRI重建建模为欠采样与全采样幅度MRI图像之间的双向图像翻译过程。SC-NDB引入嵌套扩散架构,通过自我一致性约束和反向桥梁扩散路径提高中间预测保真度,更好地捕捉源图像的显式先验信息。结合轮廓分解嵌入模块(CDEM),通过利用拉普拉斯金字塔和方向滤波器库注入结构和纹理知识。在fastMRI和IXI数据集上的广泛实验表明,该方法较基于幅度和非基于幅度的扩散模型均取得最新性能,证明了SC-NDB的有效性和临床相关性。
要点掌握
- 加速MRI重建对于缩短扫描时间同时保持图像质量至关重要。
- 现有方法大多依赖于复杂值图像空间或k空间数据,但在临床实践中由于专有重建流程,只能获取到DICOM文件中的幅度图像。
- 本研究专注于基于幅度图像的MRI重建方法,利用扩散模型解决这一问题。
- 提出了一种名为自洽嵌套扩散桥(SC-NDB)的新框架,将MRI重建建模为欠采样与全采样幅度图像之间的双向翻译过程。
- SC-NDB通过嵌套扩散架构和自我一致性约束提高预测中间结果的准确性,更好地捕捉源图像的显式先验信息。
- 结合轮廓分解嵌入模块(CDEM)以增强图像的结构和纹理信息。
点此查看论文截图

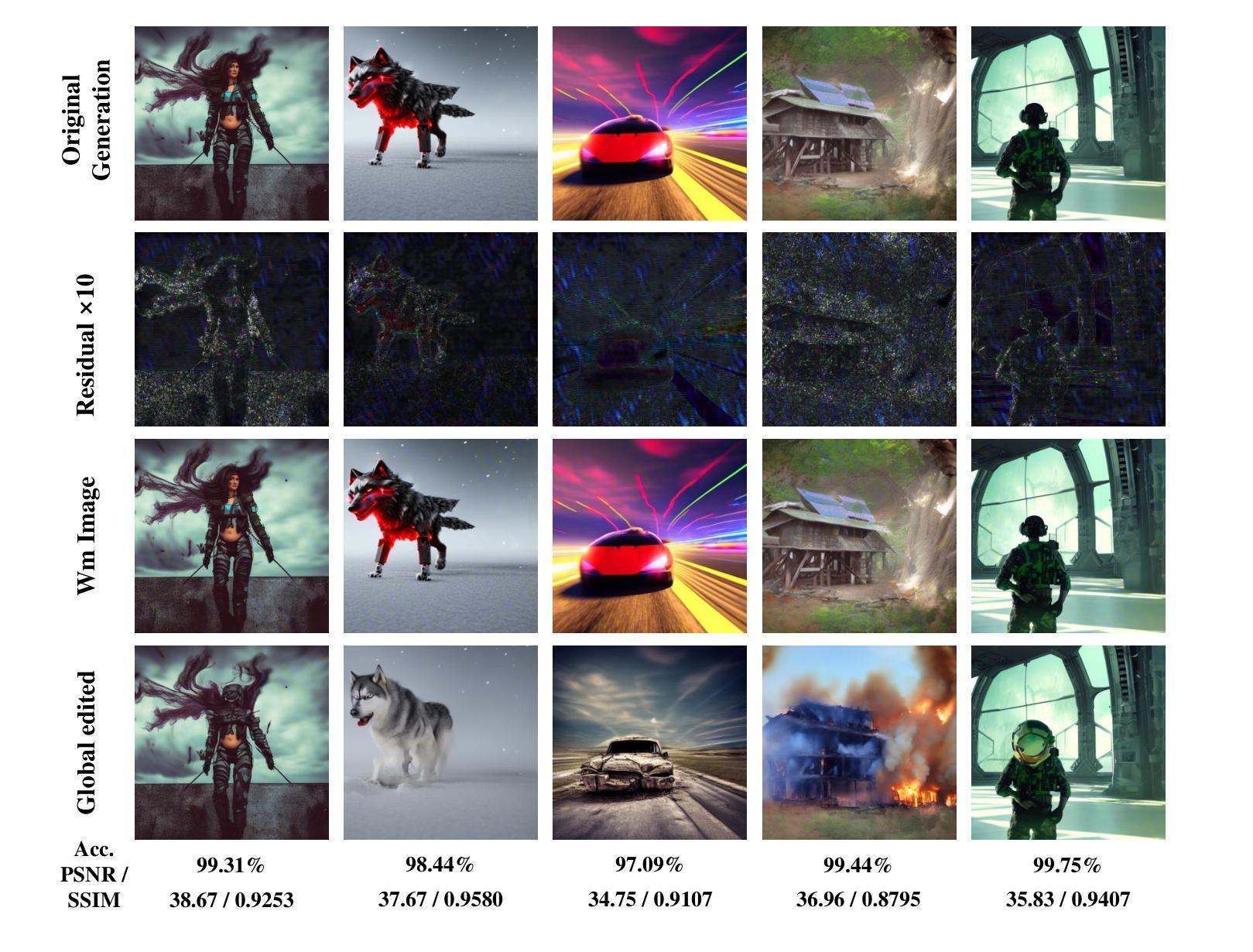
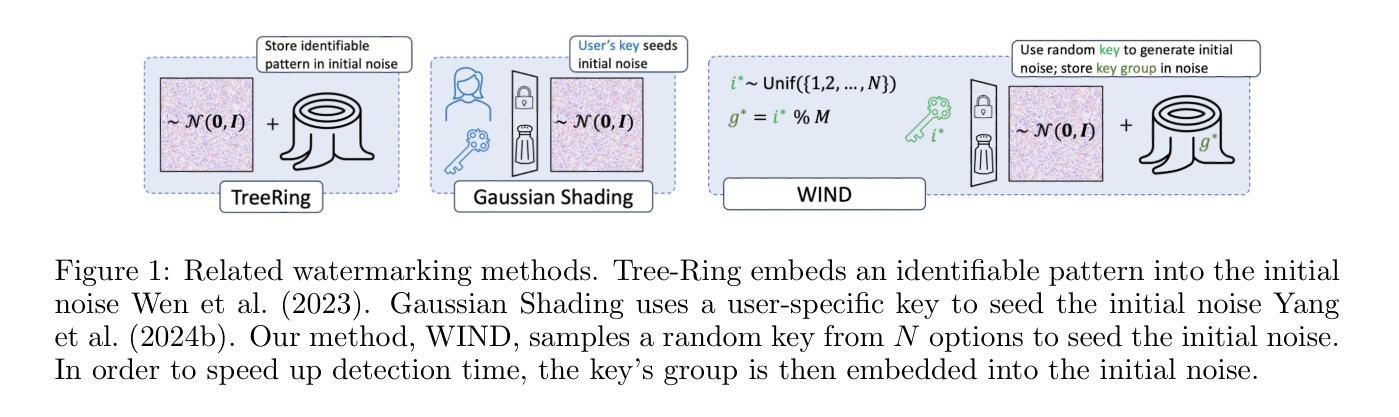
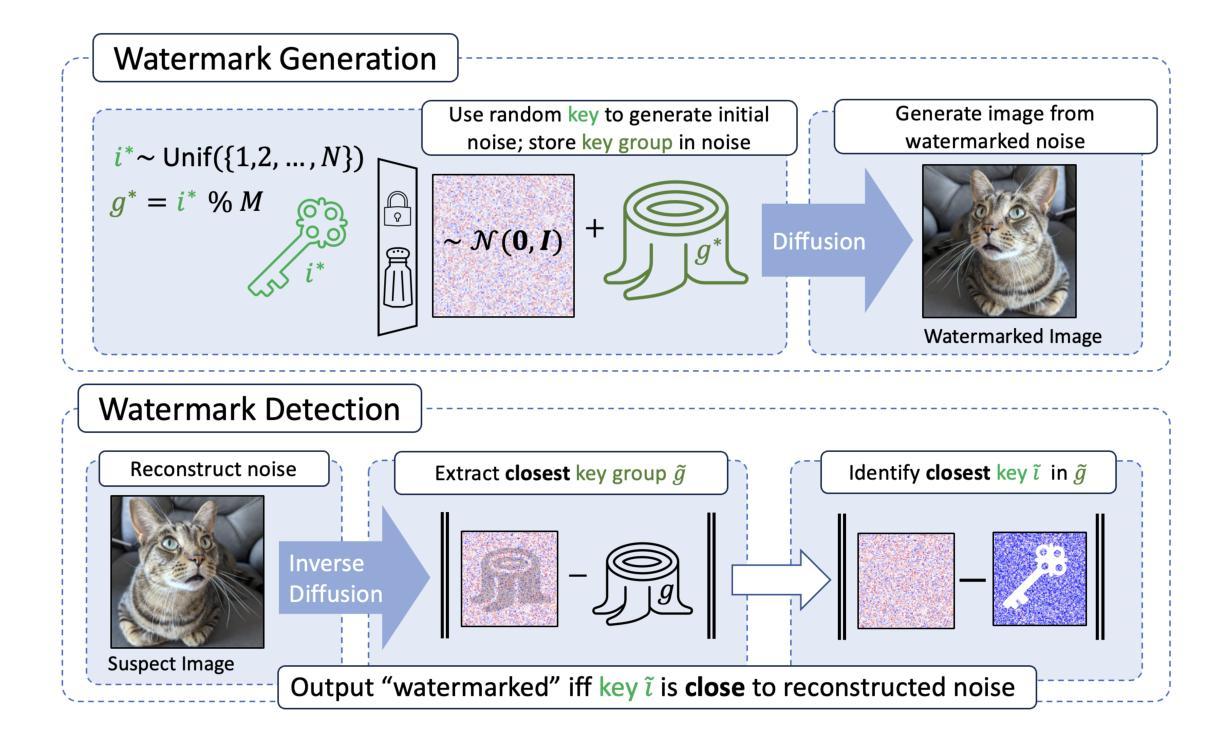
Hidden in the Noise: Two-Stage Robust Watermarking for Images
Authors:Kasra Arabi, Benjamin Feuer, R. Teal Witter, Chinmay Hegde, Niv Cohen
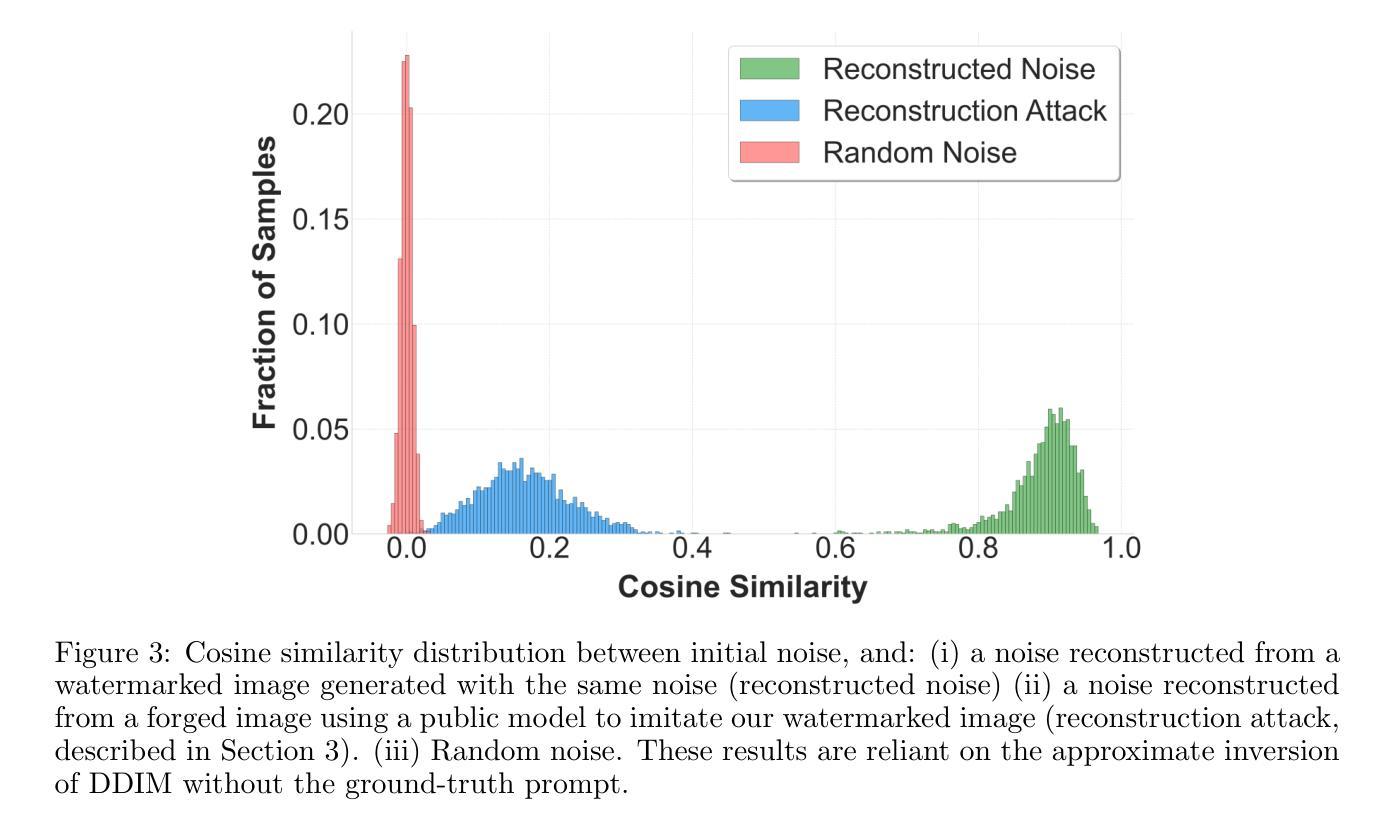
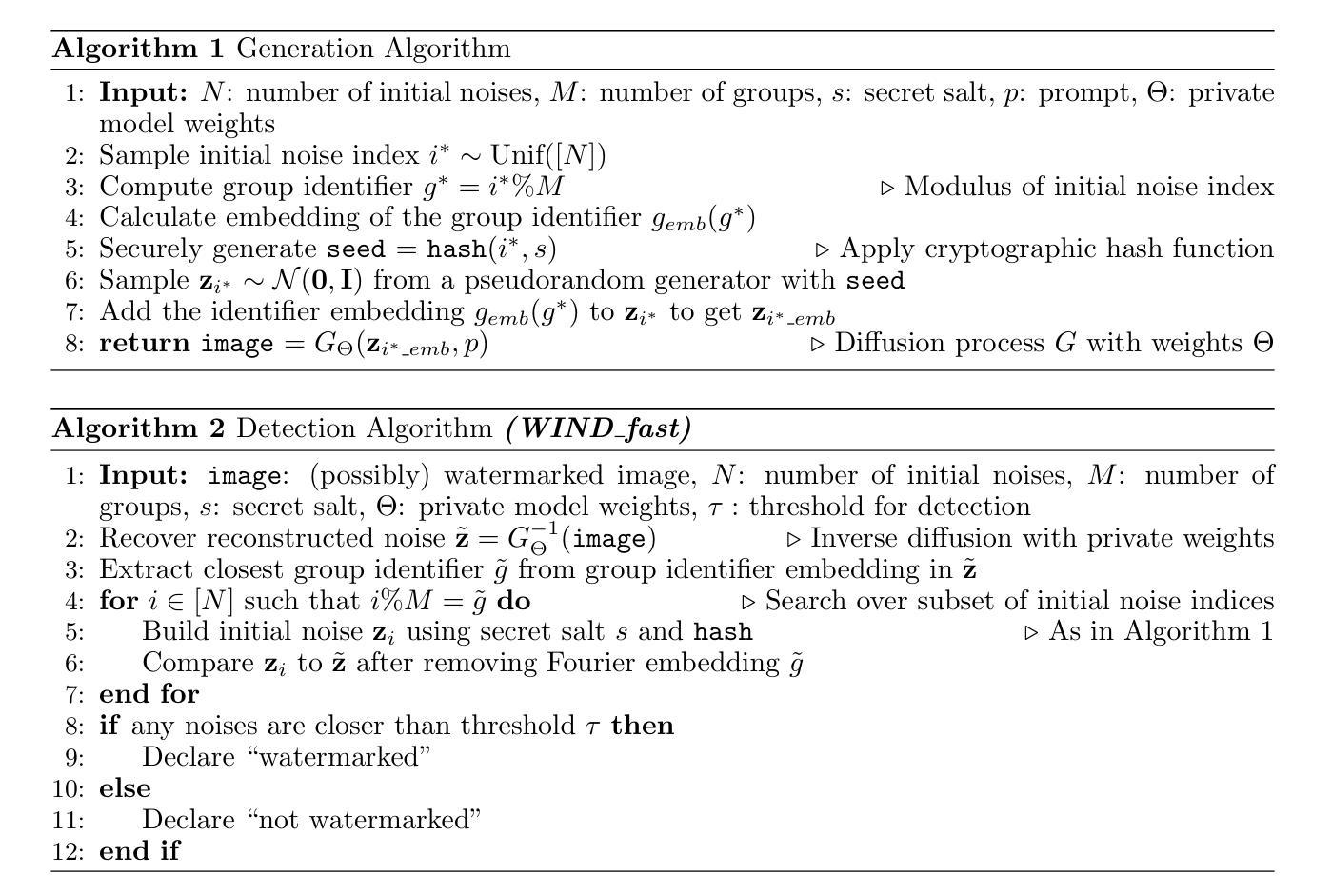
As the quality of image generators continues to improve, deepfakes become a topic of considerable societal debate. Image watermarking allows responsible model owners to detect and label their AI-generated content, which can mitigate the harm. Yet, current state-of-the-art methods in image watermarking remain vulnerable to forgery and removal attacks. This vulnerability occurs in part because watermarks distort the distribution of generated images, unintentionally revealing information about the watermarking techniques. In this work, we first demonstrate a distortion-free watermarking method for images, based on a diffusion model’s initial noise. However, detecting the watermark requires comparing the initial noise reconstructed for an image to all previously used initial noises. To mitigate these issues, we propose a two-stage watermarking framework for efficient detection. During generation, we augment the initial noise with generated Fourier patterns to embed information about the group of initial noises we used. For detection, we (i) retrieve the relevant group of noises, and (ii) search within the given group for an initial noise that might match our image. This watermarking approach achieves state-of-the-art robustness to forgery and removal against a large battery of attacks.
随着图像生成器的质量不断提高,深度伪造技术成为社会热议的话题。图像水印允许模型所有者对其生成的AI内容进行检测和标记,从而减轻潜在的伤害。然而,当前最先进的水印嵌入技术仍容易受到伪造和移除攻击的影响。这种脆弱性部分是因为水印会扭曲生成的图像分布,从而无意中泄露有关水印技术的信息。在这项工作中,我们首先展示了一种基于扩散模型的初始噪声的无失真水印嵌入方法。然而,检测水印需要对比图像重建的初始噪声与所有之前使用的初始噪声。为了解决这些问题,我们提出了一种用于高效检测的两阶段水印框架。在生成阶段,我们通过将生成的傅里叶模式添加到初始噪声中来嵌入有关我们使用的初始噪声组的信息。对于检测阶段,我们(i)检索相关的噪声组,(ii)在给定的噪声组内搜索可能与我们的图像匹配的初始噪声。这种水印方法达到了对抗一系列攻击的卓越抗伪造和移除性能。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
新一代图像生成器质量不断提升,深伪技术成为社会热议的话题。图像水印技术能让模型所有者对其AI生成的内容进行检测和标注,减轻潜在危害。然而,当前先进的水印方法仍然容易受到伪造和移除攻击。本文首次展示了一种基于扩散模型初始噪声的无失真图像水印方法。为了解决检测问题,我们提出了一种两阶段的水印检测框架。生成阶段,我们通过将生成的傅里叶模式与初始噪声相结合,嵌入关于所用初始噪声组的信息。检测阶段分为两步:首先找出相关的噪声组,然后在该组内搜索可能与图像匹配的初始噪声。此水印方法在对抗一系列攻击时,实现了卓越的防伪和防移除效果。
Key Takeaways
- 图像生成器质量的提升引发了深伪技术的社会讨论。
- 图像水印技术允许模型所有者检测和标注其AI生成的内容。
- 当前先进的水印方法容易受到伪造和移除攻击,存在缺陷。
- 提出了一种基于扩散模型初始噪声的无失真图像水印方法。
- 为了解决检测问题,采用两阶段水印检测框架。
- 在生成阶段,结合傅里叶模式与初始噪声嵌入信息。
- 此水印方法在对抗一系列攻击时表现出卓越性能。
点此查看论文截图

OmniEdit: Building Image Editing Generalist Models Through Specialist Supervision
Authors:Cong Wei, Zheyang Xiong, Weiming Ren, Xinrun Du, Ge Zhang, Wenhu Chen
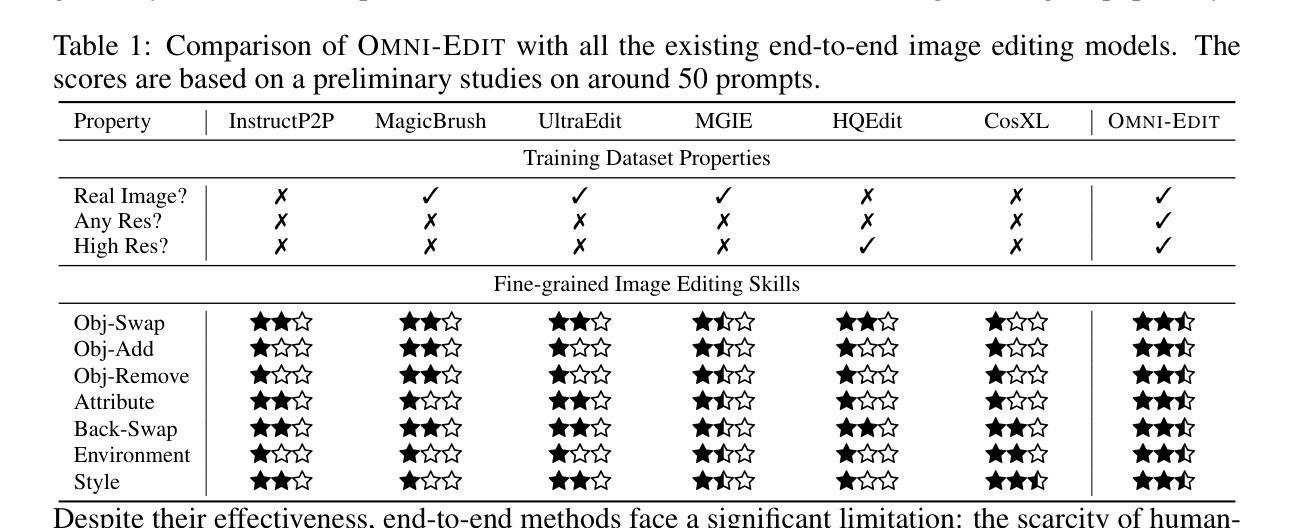
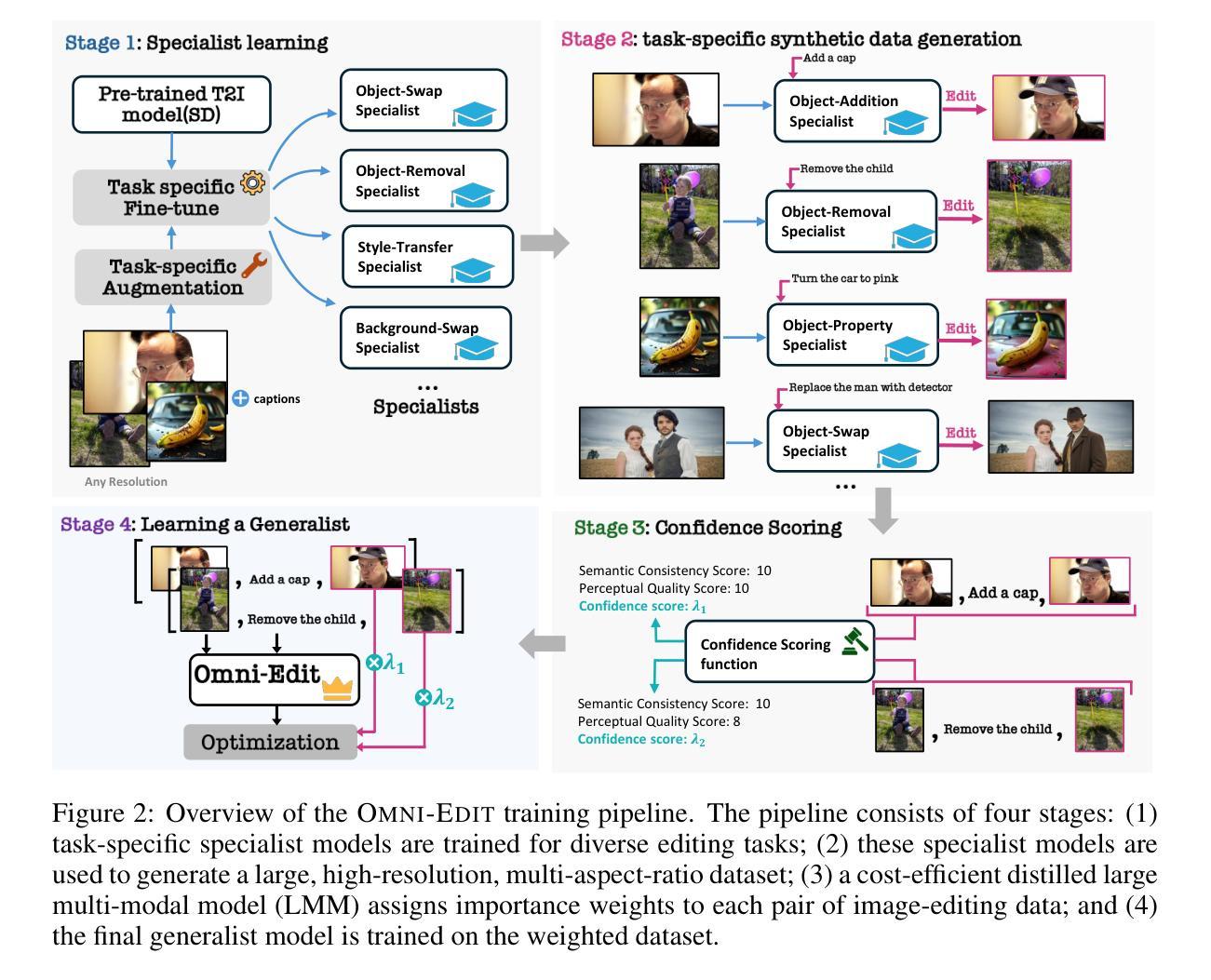
Instruction-guided image editing methods have demonstrated significant potential by training diffusion models on automatically synthesized or manually annotated image editing pairs. However, these methods remain far from practical, real-life applications. We identify three primary challenges contributing to this gap. Firstly, existing models have limited editing skills due to the biased synthesis process. Secondly, these methods are trained with datasets with a high volume of noise and artifacts. This is due to the application of simple filtering methods like CLIP-score. Thirdly, all these datasets are restricted to a single low resolution and fixed aspect ratio, limiting the versatility to handle real-world use cases. In this paper, we present \omniedit, which is an omnipotent editor to handle seven different image editing tasks with any aspect ratio seamlessly. Our contribution is in four folds: (1) \omniedit is trained by utilizing the supervision from seven different specialist models to ensure task coverage. (2) we utilize importance sampling based on the scores provided by large multimodal models (like GPT-4o) instead of CLIP-score to improve the data quality. (3) we propose a new editing architecture called EditNet to greatly boost the editing success rate, (4) we provide images with different aspect ratios to ensure that our model can handle any image in the wild. We have curated a test set containing images of different aspect ratios, accompanied by diverse instructions to cover different tasks. Both automatic evaluation and human evaluations demonstrate that \omniedit can significantly outperform all the existing models. Our code, dataset and model will be available at https://tiger-ai-lab.github.io/OmniEdit/
基于指令的图像编辑方法通过在自动合成或手动标注的图像编辑对上训练扩散模型,已经展现出显著潜力。然而,这些方法距离实际、现实生活应用仍然相去甚远。我们确定了导致这一差距的三个主要挑战。首先,现有模型的编辑能力有限,这是由于合成过程存在偏见。其次,这些方法使用大量噪声和伪影的数据集进行训练,这是由于应用了简单的过滤方法,如CLIP评分。第三,所有这些数据集都局限于单一的低分辨率和固定的比例,限制了其处理真实世界用例的通用性。在本文中,我们提出了全能编辑器\omniedit,它能够无缝地处理七种不同的图像编辑任务,且适用于任何比例。我们的贡献在于四个方面:(1)\omniedit通过利用七种不同专业模型的监督来保证任务覆盖。我们利用大型多模态模型(如GPT-4o)提供的分数进行重要性采样,而不是使用CLIP评分来提高数据质量。(3)我们提出了一种新的编辑架构——EditNet,以提高编辑成功率。(4)我们提供了不同比例的图片,以确保我们的模型能够处理任何野生图像。我们精心准备了一个测试集,其中包含不同比例的图片和多样化的指令来涵盖不同的任务。自动评估和人为评估均表明,\omniedit可以显著优于所有现有模型。我们的代码、数据集和模型将在https://tiger-ai-lab.github.io/OmniEdit/上提供。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF 21 pages
Summary
本文指出了当前指令引导的图像编辑方法在实践中存在的三大挑战,并为此提出了一种全新的图像编辑方法——OmniEdit。OmniEdit通过利用来自七个不同专业模型的监督,实现多种任务覆盖;利用大型多模态模型(如GPT-4o)提供的分数进行重要性采样以提高数据质量;推出新的编辑架构EditNet,极大地提高了编辑成功率;能处理不同比例尺的图像,确保模型适应任何野生图像。实验证明,OmniEdit在自动评估和人工评估中都显著优于现有模型。
Key Takeaways
- 当前指令引导的图像编辑方法存在三大挑战:模型编辑技能有限、数据集噪声和伪影多、以及数据集分辨率和比例固定,难以应对真实世界应用。
- OmniEdit通过结合七个不同专业模型的监督,实现了多种图像编辑任务的覆盖。
- OmniEdit利用大型多模态模型提供的分数进行重要性采样,提高了数据质量和编辑效果。
- OmniEdit引入了新的编辑架构EditNet,显著提高了编辑成功率。
- OmniEdit能够处理不同比例尺的图像,增强了模型在实际应用中的通用性。
- 实验结果显示,OmniEdit在自动和人工评估中都优于现有模型。
点此查看论文截图


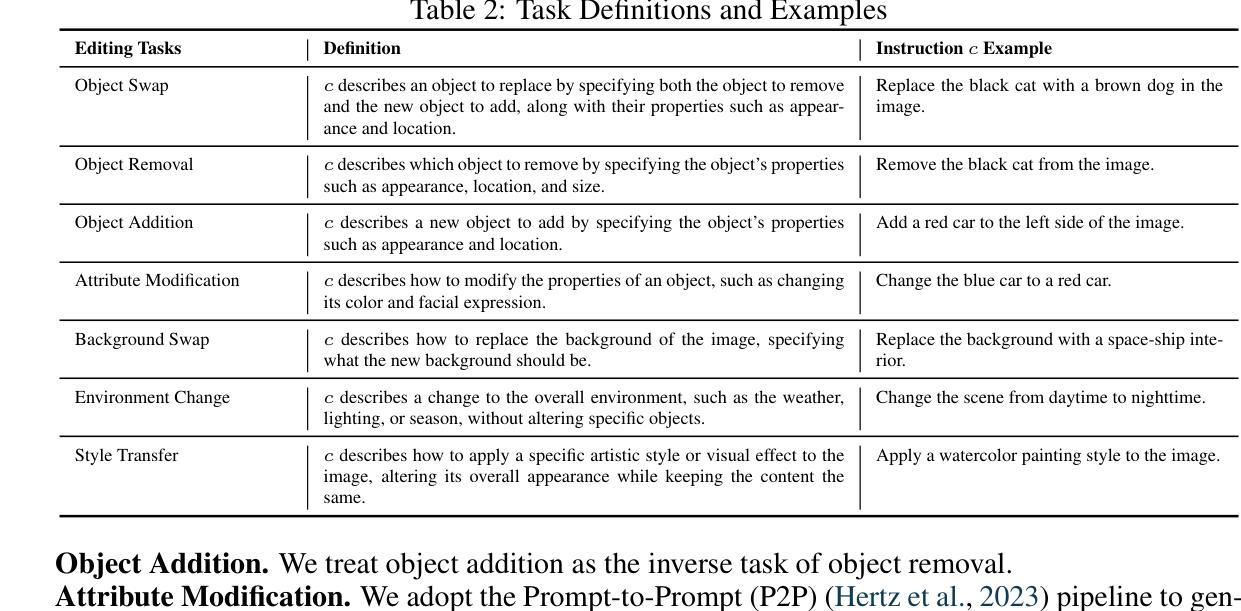
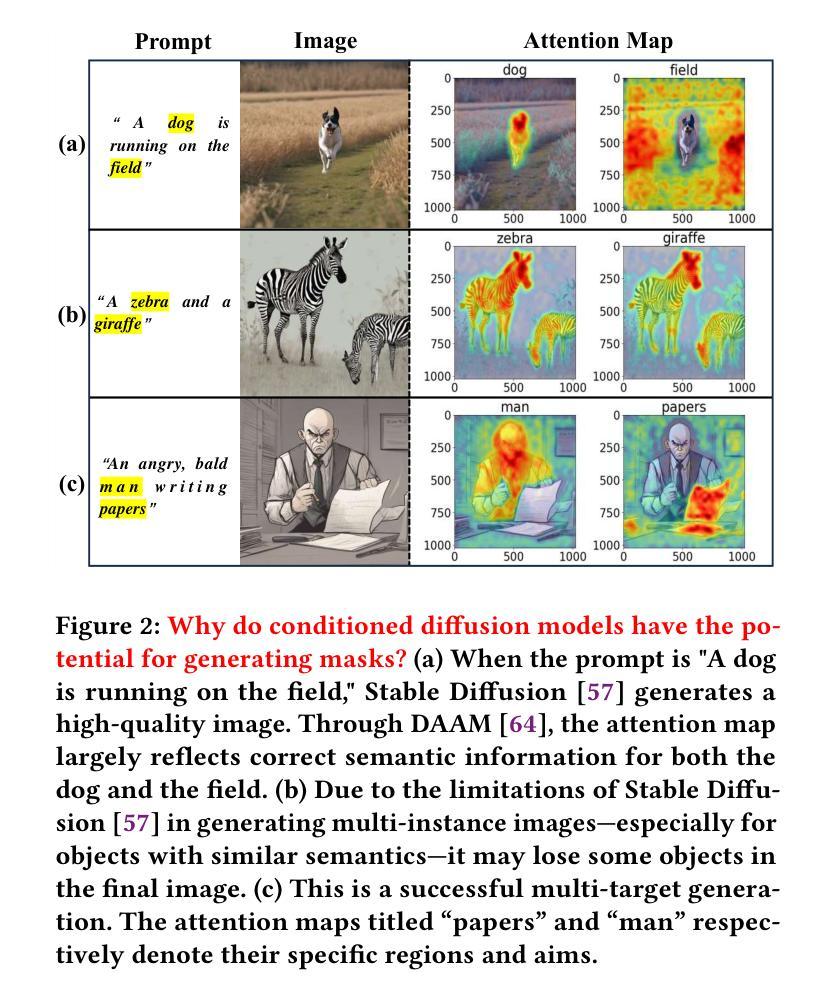
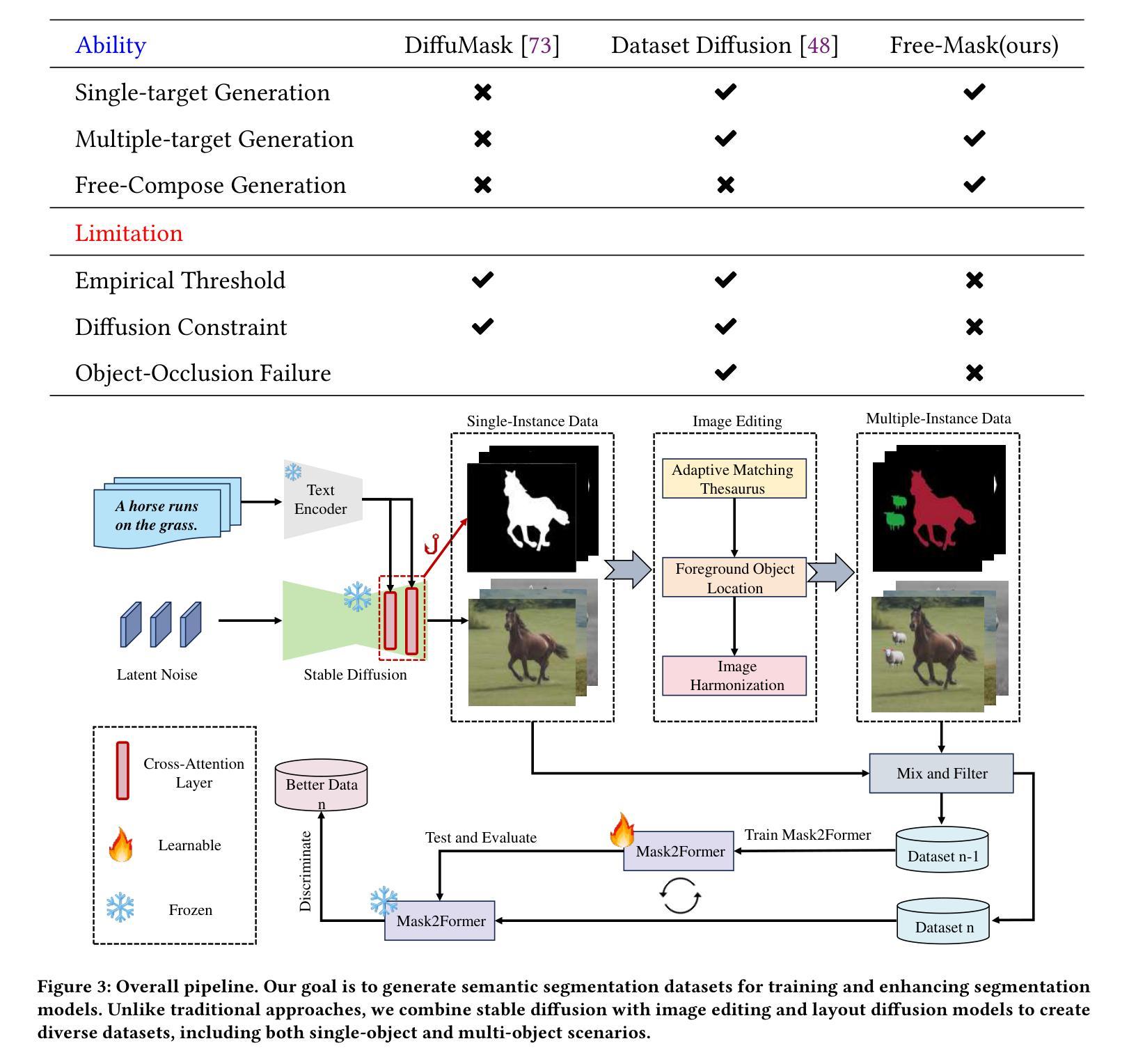
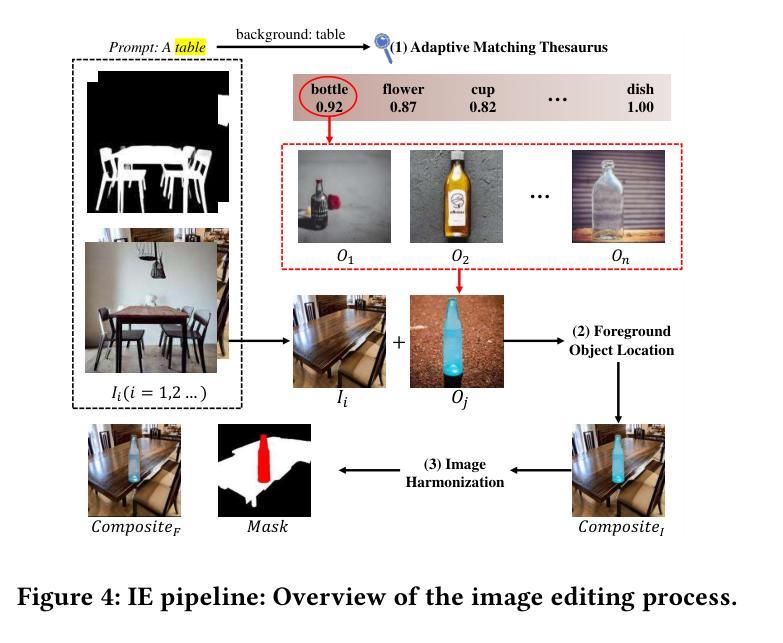
Free-Mask: A Novel Paradigm of Integration Between the Segmentation Diffusion Model and Image Editing
Authors:Bo Gao, Jianhui Wang, Xinyuan Song, Yangfan He, Fangxu Xing, Tianyu Shi
Current semantic segmentation models typically require a substantial amount of manually annotated data, a process that is both time-consuming and resource-intensive. Alternatively, leveraging advanced text-to-image models such as Midjourney and Stable Diffusion has emerged as an efficient strategy, enabling the automatic generation of synthetic data in place of manual annotations. However, previous methods have been limited to generating single-instance images, as the generation of multiple instances with Stable Diffusion has proven unstable. To address this limitation and expand the scope and diversity of synthetic datasets, we propose a framework \textbf{Free-Mask} that combines a Diffusion Model for segmentation with advanced image editing capabilities, allowing for the integration of multiple objects into images via text-to-image models. Our method facilitates the creation of highly realistic datasets that closely emulate open-world environments while generating accurate segmentation masks. It reduces the labor associated with manual annotation and also ensures precise mask generation. Experimental results demonstrate that synthetic data generated by \textbf{Free-Mask} enables segmentation models to outperform those trained on real data, especially in zero-shot settings. Notably, \textbf{Free-Mask} achieves new state-of-the-art results on previously unseen classes in the VOC 2012 benchmark.
当前语义分割模型通常需要大量手动标注的数据,这一过程既耗时又耗资源。相比之下,利用先进的文本到图像模型,如Midjourney和Stable Diffusion,已成为一种有效策略,能够在不需要手动注释的情况下自动生成合成数据。然而,以前的方法仅限于生成单一实例图像,因为使用Stable Diffusion生成多个实例被证明是不稳定的。为了解决这一限制并扩大合成数据集的范围和多样性,我们提出了一个名为Free-Mask的框架,它将扩散模型用于分割,并结合先进的图像编辑功能,允许通过文本到图像的模型将多个对象集成到图像中。我们的方法能够创建高度逼真的数据集,紧密模拟开放世界环境,同时生成精确的分割掩膜。它减少了与手动注释相关的劳动力,并确保精确生成掩膜。实验结果表明,使用Free-Mask生成的合成数据训练的分割模型在零样本设置下表现优于在真实数据上训练的模型。值得注意的是,Free-Mask在VOC 2012基准测试中的未见类别上取得了最新最先进的成果。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF 19 pages,11 figures,5 tables
Summary
文本描述了一种利用先进的文本到图像模型(如Midjourney和Stable Diffusion)自动生成合成数据以替代手动标注的方法。然而,现有方法仅限于生成单一实例图像,且不稳定。为解决这一问题并扩大合成数据集的范围和多样性,提出了一种结合扩散模型分割和高级图像编辑功能的框架Free-Mask。该方法能够整合文本到图像模型,将多个对象融入图像中,创建高度逼真的数据集,模拟开放世界环境,同时生成精确的分割掩膜。实验结果表明,Free-Mask生成的合成数据使分割模型在零样本设置中的性能超越了真实数据训练的模型,并在VOC 2012基准测试中实现了前所未有的新最佳结果。
Key Takeaways
- 当前语义分割模型需要大量手动标注数据,这一过程既耗时又耗资源。
- 利用先进的文本到图像模型(如Midjourney和Stable Diffusion)可以自动生成合成数据,作为手动标注的替代方案。
- 现有方法主要限于生成单一实例图像,且不稳定。
- 提出的Free-Mask框架结合了扩散模型分割和高级图像编辑功能。
- Free-Mask能够整合多个对象到图像中,创建高度逼真的数据集,模拟开放世界环境。
- Free-Mask可以生成精确的分割掩膜,减少手动标注的劳动力。
点此查看论文截图

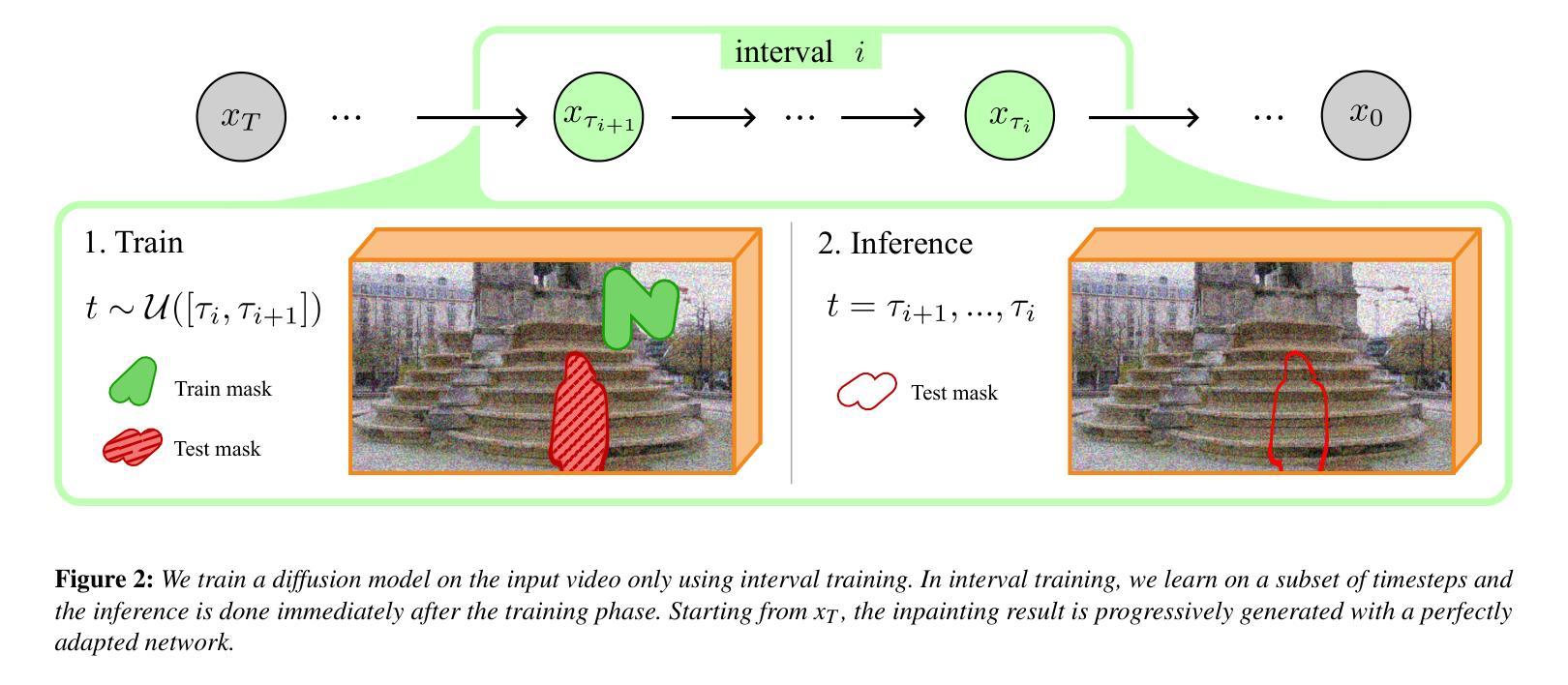
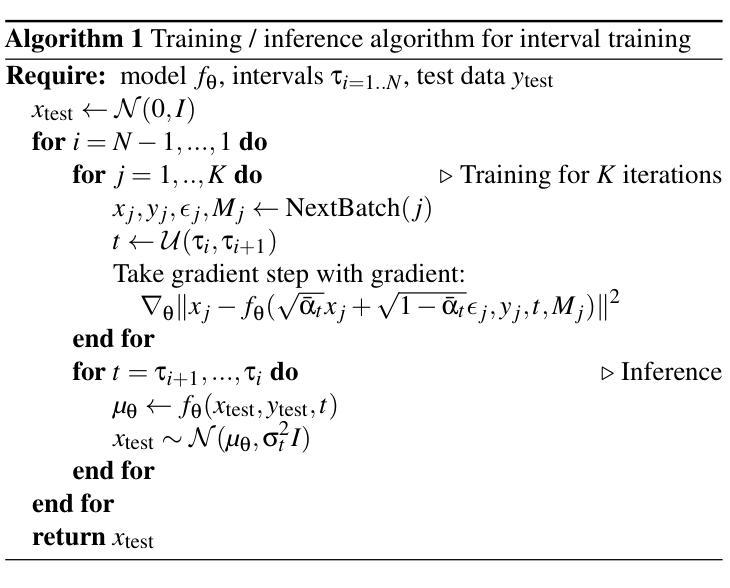
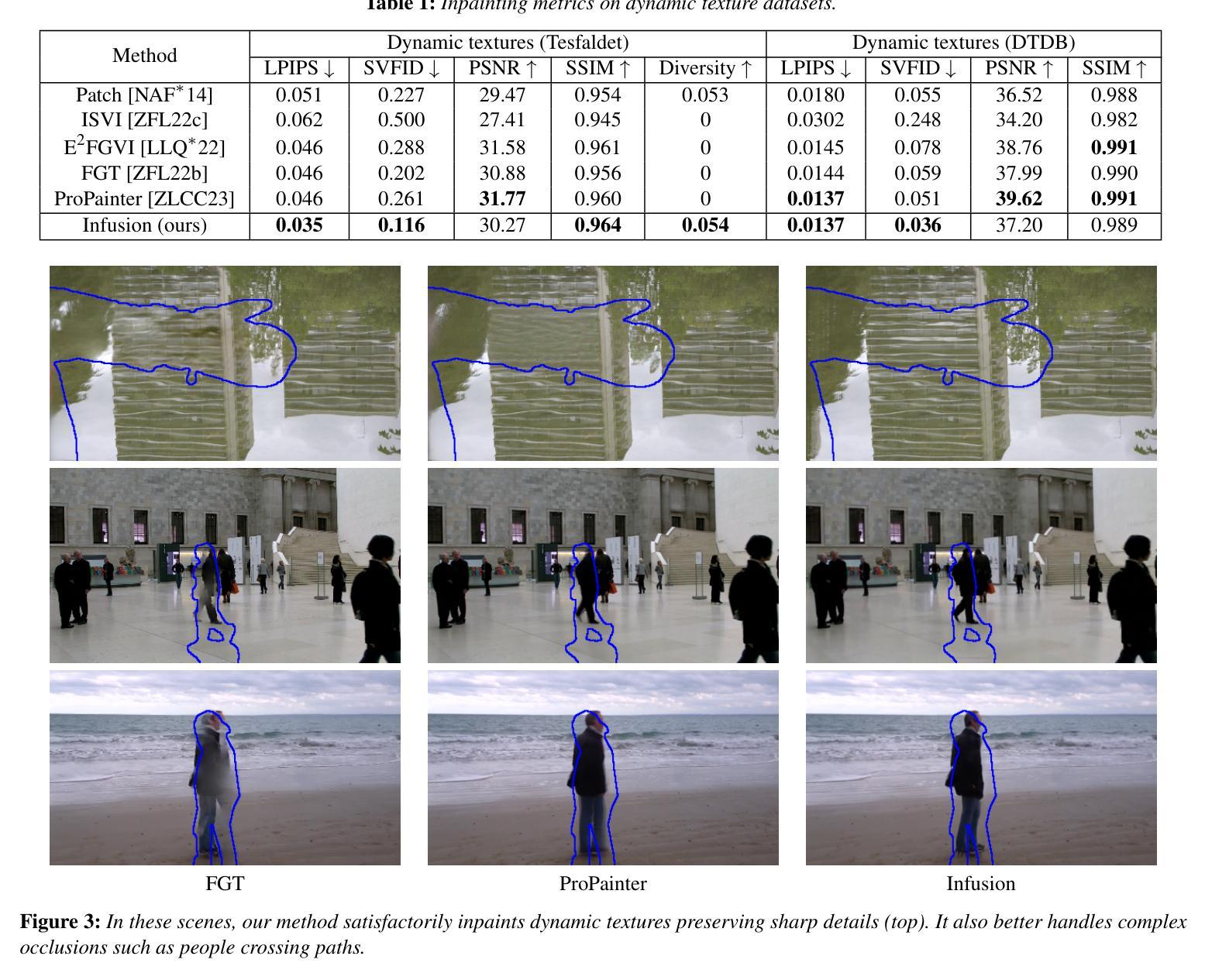
Infusion: internal diffusion for inpainting of dynamic textures and complex motion
Authors:Nicolas Cherel, Andrés Almansa, Yann Gousseau, Alasdair Newson
Video inpainting is the task of filling a region in a video in a visually convincing manner. It is very challenging due to the high dimensionality of the data and the temporal consistency required for obtaining convincing results. Recently, diffusion models have shown impressive results in modeling complex data distributions, including images and videos. Such models remain nonetheless very expensive to train and to perform inference with, which strongly reduce their applicability to videos, and yields unreasonable computational loads. We show that in the case of video inpainting, thanks to the highly auto-similar nature of videos, the training data of a diffusion model can be restricted to the input video and still produce very satisfying results. With this internal learning approach, where the training data is limited to a single video, our lightweight models perform very well with only half a million parameters, in contrast to the very large networks with billions of parameters typically found in the literature. We also introduce a new method for efficient training and inference of diffusion models in the context of internal learning, by splitting the diffusion process into different learning intervals corresponding to different noise levels of the diffusion process. We show qualitative and quantitative results, demonstrating that our method reaches or exceeds state of the art performance in the case of dynamic textures and complex dynamic backgrounds
视频补全的任务是以视觉说服力的方式填充视频中的区域。由于数据的高维度和获得令人信服结果所需的时序一致性,这使得该任务非常具有挑战性。最近,扩散模型在建模复杂数据分布方面取得了令人印象深刻的结果,包括图像和视频。然而,这样的模型在训练和进行推理时仍然非常昂贵,大大降低了它们对视频的适用性,并产生了不合理的计算负载。我们表明,在视频补全的情况下,由于视频的固有高度自相似性,扩散模型的训练数据可以局限于输入视频,但仍能产生非常令人满意的结果。采用这种内部学习方法,训练数据仅限于单个视频,我们的轻量级模型表现良好,仅使用五百万个参数,与文献中通常发现的使用数十亿参数的庞大网络形成鲜明对比。我们还介绍了一种新的高效训练和推理扩散模型的方法,它是在内部学习的背景下,通过将扩散过程分割成对应于扩散过程不同噪声水平的不同学习间隔来进行。我们展示了定性和定量的结果,证明我们的方法在动态纹理和复杂动态背景的案例中达到了或超过了最新技术的性能。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF 14 pages, 11 figures. Published in Eurographics 2025
Summary
视频补全任务旨在以视觉说服力的方式填充视频中的区域。由于数据的高维度性和获得令人信服结果所需的时序一致性,这使得任务非常具有挑战性。最近,扩散模型在建模复杂数据分布(包括图像和视频)方面显示出令人印象深刻的结果。然而,扩散模型在训练和进行推理时仍然非常昂贵,大大降低了其应用于视频的实用性,并产生了不合理的计算负载。针对视频补全任务,我们利用视频的高度自相似性质,展示了扩散模型可以通过仅使用输入视频作为训练数据来产生令人满意的结果。通过内部学习方法,我们的轻量级模型在只有五百万参数的情况下表现良好,这与文献中通常发现的大规模网络形成鲜明对比。我们还介绍了一种在内部学习的背景下对扩散模型进行高效训练和推理的新方法,通过将扩散过程分成对应于扩散过程不同噪声水平的学习间隔。我们展示了定性和定量的结果,证明我们的方法在动态纹理和复杂动态背景的情况下达到了或超过了最新技术的性能。
Key Takeaways
- 视频补全任务具有挑战性,因为需要处理高维度数据和保证时序一致性。
- 扩散模型在建模复杂数据分布(如图像和视频)方面表现出色。
- 扩散模型的训练和推理成本高昂,限制了其在实际视频应用中的使用。
- 视频的自我相似性使得仅使用输入视频作为训练数据成为可能。
- 通过内部学习方法,轻量级扩散模型在只有少量参数的情况下表现良好。
- 介绍了一种通过分割扩散过程来高效训练和推理扩散模型的新方法,对应不同的噪声水平。
点此查看论文截图